Page 1

Zebra
Radio Frequency Identification (RFID)
Programming Guide
®
58978L-008
Page 2

© 2008 ZIH Corp. The copyrights in this manual and the software and/or firmware in the printer described
therein are owned by ZIH Corp. Unauthorized reproduction of this manual or the software and/or firmware in the
printer may result in imprisonment of up to one year and fines of up to $10,000 (17 U.S.C.506). Copyright violators
may be subject to civil liability.
This product may contain ZPL
Monotype Imaging fonts. Software © ZIH Corp. All rights reserved worldwide.
®
, ZPL II®, and ZebraLink™ programs; Element Energy Equalizer® Circuit; E3®; and
ZebraLink and all product names and numbers are trademarks, and Zebra, the Zebra logo, ZPL, ZPL II, Element
Energy Equalizer Circuit, and E
All other brand names, product names, or trademarks belong to their respective holders. For additional trademark
information, please see “Trademarks” on the product CD.
This RFID product is manufactured under one or more licenses, which contain certain exclusions. This product may
not be sold, used, leased, offered for sale, or otherwise transferred, exported, and im ported in the Transpor tation
Market. The Transportation Market means (i) Electronic Toll and Traffic Management (ETTM), (ii) Public Sector
Vehicle Registration, Inspection and Licensing Programs, (iii) Railroad Locomotive and Wagon tracking,
(iv) airport-based ground transportation management systems (GTMS) and taxi dispatch, (v) revenue-based parking,
and (vi) vehicle-initiated mobile payment applications, where the RFID tag is initially attached to the vehicle but not
incorporated at the point of vehicle manufacture.
3
Circuit are registered trademarks of ZIH Corp. All rights reserved worldwide.
Proprietary Statement This manual contains proprietary information of Zebra Technologies Corporation and its
subsidiaries (“Zebra Technologies”). It is intended solely for the information and use of parties operating and
maintaining the equipment described herein. Such proprietary information may not be used, reproduced, or disclosed
to any other parties for any other purpose without the express, written permission of Zebra Technologies Corporation.
Product Improvements Continuous improvement of products is a policy of Zebra Technologies Corporation.
All specifications and designs are subject to change without notice.
Liability Disclaimer Zebra Technologies Corporation takes steps to ensure that its published Engineering
specifications and manuals are correct; however, errors do occur. Zebra Technologies Corporation reserves the right
to correct any such errors and disclaims liability resulting therefrom.
Limitation of Liability In no event shall Zebra Technologies Corporation or anyone else involved in the creation,
production, or delivery of the accompanying product (including hard ware and software) be liab le for any damages
whatsoever (including, without limitation, consequential damages including loss of busin ess profi ts, business
interruption, or loss of business information) arising out of the use of, the results of use of, or inability to use such
product, even if Zebra Technologies Corporation has been advised of the possibility of such damages. Some
jurisdictions do not allow the exclusion or limitation of incidental or consequential damages, so the above limitation
or exclusion may not apply to you.
Part Number: 58978L-008 Rev. A
Page 3

Contents
About This Document . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
Who Should Use This Document . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
How This Document Is Organized . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
Contacts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
Document Conventions. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .11
1 • Introduction to RFID . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
RFID Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
RFID Label Selection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Considering RFID Transponder (Tag) Types . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Accounting for Transponder Inlay Placement. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Selecting and Purchasing RFID Labels . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Performing Label Placement Tests. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Storing RFID Labels . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Radio Frequency Interference . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
ZPL Commands for RFID Applications. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
SGD Commands for RFID Applications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
2 • RFID Printer Setup and Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
Set Tag Type. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
Set RF Power Levels . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
Perform RFID Transponder Calibration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
Download Latest Firmware. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
3 • RFID Control Panel Parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
11/14/2008 RFID Programming Guide 58978L-008 Rev. A
Page 4

Contents
4
4 • Creating Basic RFID Label Formats . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
Create and Send an RFID Label Format . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
Sample RFID Label Formats . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
RFID Label Format 1—Encode a Gen 2 Tag in Hexadecimal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
RFID Label Format 2—Encode a Gen 2 Tag in ASCII . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
RFID Label Format 3—Read Data from Tag and Print Data on Label . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
RFID Label Format 4—Encode Tag, Read Tag, and Print Data on Label . . . . . . . . . 34
RFID Label Format 5—Encode a Class 1 64-bit Tag in Hexadecimal . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
RFID Label Format 6—Encode Tag, Read Tag, and Return Results to Host. . . . . . . 37
5 • RFID Antenna Location . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
RXi and RXi HF. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
RZ400 and RZ600 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
R110PAX4. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
RP4T. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
R4Mplus . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
6 • Transponder Characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
Basic Transponder Characteristics. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
Electronic Product Code (EPC) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
EPC Fields . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
EPC Structure in RFID Labels . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
EPC Class 1, Generation 2 (Gen 2) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
Data Content. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
Data and Tag Security . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
Gen 2 Memory Map . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
7 • Troubleshooting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
RFID Problems . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 50
RFID Error Codes and Messages . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 53
Error and Status Messages . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 53
Error Codes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 66
8 • ZPL II Commands for RFID . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 79
ZPL Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 81
Printer and Firmware Compatibility. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 82
^HL or ~HL Return RFID Data Log to Host . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 84
^HR Calibrate RFID Transponder Position . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 85
^HV Host Verification . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 88
^MM Print Mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 89
^RA Read AFI or DSFID Byte . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 91
^RB Define EPC Data Structure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 93
^RE Enable/Disable E.A.S. Bit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 95
^RF Read or Write RFID Format . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 96
58978L-008 Rev. A RFID Programming Guide 11/14/2008
Page 5

Contents
^RI Get RFID Tag ID . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 100
^RM Enable RFID Motion . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 101
^RN Detect Multiple RFID Tags in Encoding Field . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 102
~RO Reset Advanced Counters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 103
^RQ Quick Write EPC Data and Passwords . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 105
^RR Specify RFID Retries for a Block . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 107
^RS Set Up RFID Parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 108
^RT Read RFID Tag . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .115
~RV Report RFID Encoding Results . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .117
^RW Set RF Power Levels for Read and Write . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .118
^RZ Set RFID Tag Password and Lock Tag . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 120
^WF Encode AFI or DSFID Byte . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 123
^WT Write (Encode) RFID Tag . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 125
^WV Verify RFID Encoding Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 127
9 • SGD Commands for RFID . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 129
Printer and Firmware Compatibility. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 130
odometer.rfid.valid_resettable . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 132
odometer.rfid.void_resettable . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 133
rfid.error.response . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 134
rfid.position.program . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 135
rfid.reader_1.antenna_port . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 136
rfid.reader_1.power.read . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 137
rfid.reader_1.power.single_power . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 138
rfid.reader_1.power.write . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 139
rfid.tag.calibrate . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 141
rfid.tag.data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 142
rfid.tag.test . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 143
rfid.tag.type . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 144
5
10 • RFID Applicator Signals . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 149
Timing Diagrams for RFID . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 150
Single Signal Mode. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 150
Double Signal Mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 152
Applicator Interface Connector Pin Configuration. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 153
Jumper Configurations and Pinouts for +5 V I/O Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 156
Pinouts for +24-28 V I/O Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 157
Index . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 159
11/14/2008 RFID Programming Guide 58978L-008 Rev. A
Page 6
Contents
Notes • ___________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________
6
58978L-008 Rev. A RFID Programming Guide 11/14/2008
Page 7

About This Document
This section provides you with contact information, documen t struc ture and organization, and
additional reference documents.
Contents
Who Should Use This Document. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
How This Document Is Organized . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
Contacts. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
Document Conventions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
11/14/2008 RFID Programming Guide 58978L-008 Rev. A
Page 8
About This Document
8
Who Should Use This Document
Who Should Use This Document
This Programming Guide is intended for use by the label format developer o r printer integrator
to create label formats that will encode RFID tags. The following printers/print engines are
supported by this Programming Guide:
• R110Xi, R170Xi, and R110Xi HF
• RZ400 and RZ600
•R110PAX4
• R4Mplus
• R2844-Z
•RP4T
How This Document Is Organized
The RFID Programming Guide is set up as follows:
Section Description
About This Document on page 7 This section provides you with contact information, document
structure and organization, and additional reference documents.
Introduction to RFID on page 13 This section describes the basic concepts of Radio Frequency
Identification (RFID) and how RFID works with your printer.
RFID Printer Setup and Operation
on page 17
RFID Control Panel Parameters
on page 21
Creating Basic RFID Label Formats
on page 29
Troubleshooting on page 49 This section provides information about RFID operational errors
ZPL II Commands for RFID
on page 79
SGD Commands for RFID
on page 129
How you set up your printer for RFID applications is de termined in
part by the transponder that you select. This section guides you
through some tasks that you may need to perform on your printer to
make RFID reading and encoding possible. When you have
completed this section, you will be ready to program your RFID
label formats.
This section shows the control panel para meters that appear on most
Zebra RFID printers that have a graphic display.
After you have selected a transponder type and set your printer
appropriately, use the ZPL samples in this section as a base for
programming your own RFID label formats.
that you might need to troubleshoot. For other types of pr oblems,
consult the user guide for your printer.
This section contains the ZPL II commands for RFID-specific
applications.
This section contains the Set/Get/Do (SGD) commands for RFIDspecific applications.
RFID Antenna Location on page 39 Operations to test the RFID functions and display RFID tag data
require you to place an RFID label over the RFID antenna area.
This section shows the location of the RFID antenna in the various
Zebra RFID printers.
58978L-008 Rev. A RFID Programming Guide 11/14/2008
Page 9
Section Description
About This Document
How This Document Is Organized
9
Transponder Characteristics
on page 43
This section describes the dif ferent characteristi cs of some common
transponder types.
RFID Applicator Signals on page 149 This section applies to printers that have applicator ports and that
are being used in a print and apply system. Included are timing
diagrams for good and bad RFID tags and the pin configuration for
the applicator port. For basic timing diagrams, see the User Guide
for your printer.
11/14/2008 RFID Programming Guide 58978L-008 Rev. A
Page 10
About This Document
10
Contacts
Contacts
Technical Support via the Internet is available 24 hours per day, 365 days per year.
Web Site: www.zebra.com
E-mail Back Technical Library:
E-mail address: emb@zebra.com
Subject line: Emaillist
Self Service Knowledge Base: www.zebra.com/knowledgebase
Online Case Registration: www.zebra.com/techrequest
Which Department
Do You Need?
Regional Headquarters
Technical Support
For questions on the
operation of Zebra
equipment and software,
please call your distributor.
For additional assistance,
contact us.
Please have your model and
serial numbers available.
Repair Service
Department
For back-to-base service and
repair.
Technical Tr aining
Department
For Zebra product training
courses.
Inquiry Department
For product literature and
distributor and dealer
information.
Customer Service
Department (US)
Internal Sales
Department (UK)
For printers, parts, media,
and ribbon, please call your
distributor or contact us.
Key:
T: Telephone
F: Facsimile
E: E-mail
The Americas
Zebra Technologies In ternational, LLC
333 Corporate W oods Parkway
Vernon Hills, IL 60061-3109
U.S.A.
T: +1 847 793 2600
Toll-free +1 800 423 0422
F: +1 847 913 8766
T: +1 877 ASK ZEBRA (275 9327)
F: +1 847 913 2578
Hardware: ts1@zebra.com
Software: ts3@zebra.com
Kiosk printers:
T: +1 866 322 5202
E: kiosksupport@zebra.com
T: +1 877 ASK ZEBRA (275 9327)
F: +1 847 821 1797
E: repair@zebra.com
To request a repair in the U.S.,
go to www.zebra.com/repair
T: +1 847 793 6868
T: +1 847 793 6864
F: +1 847 913 2578
E: ttamerica@zebra.com
T: +1 877 ASK ZEBRA (275 9327)
E: inquiry4@zebra.com
T: +1 877 ASK ZEBRA (275 9327)
E: clientcare@zebra.com
.
Europe, Africa,
Middle East, India
Zebra Technologies Europe Limited
Dukes Meadow
Millboard Road
Bourne End
Buckinghamshire, SL8 5XF
United Kingdom
T: +44 (0) 1628 556000
F: +44 (0) 1628 556001
T: +44 (0) 1628 556039
F: +44 (0) 1628 556003
E: Tseurope@zebra.com
T: +44 (0) 1772 693069
F: +44 (0) 1772 693046
New requests: ukrma@zebra.com
Status updates:
repairupdate@zebra.com
T: +44 (0) 1628 556000
F: +44 (0) 1628 556001
E: Eurtraining@zebra.com
T: +44 (0) 1628 556037
F: +44 (0) 1628 556005
E: mseurope@zebra.com
T: +44 (0) 1628 556032
F: +44 (0) 1628 556001
E: cseurope@zebra.com
Asia Pacific
Zebra Technologies Asia
Pacific Pte. Ltd.
120 Robinson Road
#06-01 Parakou Building
Singapore 068913
T: + 65 6858 0722
F: +65 6885 0838
T: +65 6858 0722
F: +65 6885 0838
E: China: tschina@zebra.com
All other areas:
tsasiapacific@zebra.com
T: +65 6858 0722
F: +65 6885 0838
E: China: tschina@zebra.com
All other areas:
tsasiapacific@zebra.com
T: + 65 6858 0722
F: +65 6885 0838
E: China: tschina@zebra.com
All other areas:
tsasiapacific@zebra.com
E: China: GCmarketing@zebra.com
All other areas:
AP ACChannelmarketing@zebra.com
T: +65 6858 0722
F: +65 6885 0836
E: China: order-csr@zebra.com
All other areas:
csasiapacific@zebra.com
58978L-008 RFID Programming Guide 11/14/08
Page 11
Document Conventions
PAUSE
21
The following conventions are used throughout this document to convey certain information.
Alternate Color (online only) Cross-references contain hot links to other sections in this
guide. If you are viewing this guide online in .p df format, you can click the cross-reference
(blue text) to jump directly to its location.
LCD Display Examples Text from a printer’s Liquid Crystal Display (LCD) appears in
Bubbledot ICG font.
Command Line Examples Command line examples appear in Courier New font. For
example, type
Files and Directories File names and directories appear in Courier New font. For
example, the
Icons Used
ZTools to get to the Post-Install scripts in the bin directory.
Zebra<version number>.tar file and the /root directory.
About This Document
Document Conventions
11
Important • Advises you of informatio n that is essential to complete a task.
Note • Indicates neutral or positive information that emphasizes or supplements important
points of the main text.
Example • Provides an example, often a scenario, to better clarify a section of text.
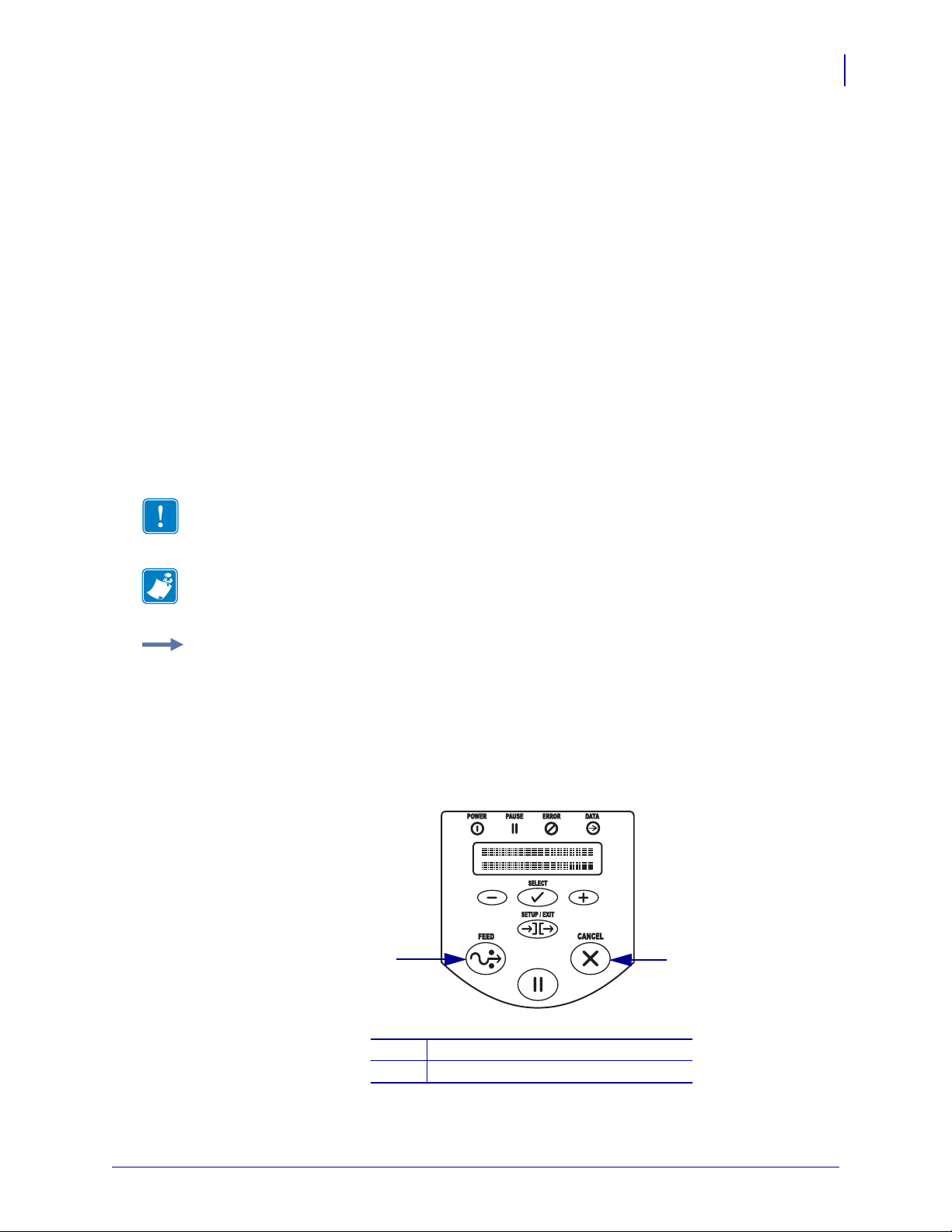
Illustration Callouts Callouts are used when an illustration contains information that needs
to be labeled and described. A table that contains the labels and descriptions follows the
graphic. Figure 1 provides an example.
Figure 1 • Sample Figure with Callouts
FEED button
1
CANCEL button
2
11/14/2008 RFID Programming Guide 58978L-008 Rev. A
Page 12
About This Document
Notes • ___________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________
12
Document Conventions
58978L-008 Rev. A RFID Programming Guide 11/14/2008
Page 13

1
Introduction to RFID
This section describes the basic concepts of Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) and how
RFID works with your printer.
Contents
RFID Overview. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
RFID Label Selection. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Considering RFID Transponder (Tag) Types. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Accounting for Transponder Inlay Placement . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Selecting and Purchasing RFID Labels. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Performing Label Placement Tests . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Storing RFID Labels. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Radio Frequency Interference . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
ZPL Commands for RFID Applications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
SGD Commands for RFID Applications. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
11/14/2008 RFID Programming Guide 58978L-008 Rev. A
Page 14

Introduction to RFID
14
RFID Overview
RFID Overview
An RFID printer encodes (writes) information on ultra-thin HF or UHF RFID transponders
that are embedded in “smart” labels, tickets, and tags. The printer encodes the information;
verifies proper encoding; and prints bar codes, graphics, and/or text on the label’s surface.
The RFID transponder is sometimes called the RFID tag or an inlay. The transponder is
usually made of an antenna that is bonded to an integrated cir cu it (IC) chip. The IC chip
contains the RF circuit, coders, decoders, and memory. If you hold an RFID label up to the
light, you can see the transponder’s antenna, and you can fe el a bump in the label whe re the IC
chip is located.
Encoding and printing of an RFID label usually are completed on the first try, but some
failures may occur. If you experience consistent failures, it may signal a problem with the
RFID tags, with your label formats, or with the transponder placement.
RFID Label Selection
To select RFID labels for your printer, consider the type of RFID transponder and where the
transponder is placed on the label.
Considering RFID Transponder (Tag) Types
When selecting RFID labels, consider both your RFID printer and your application. Use tag
types that have been specifically approved for use in your printer. Failure to do so may result
in the inability to read or write to (encode) the embedded RFID tags. To ensure that an
approved tag type will perform up to your expectations, evaluate the transponder’s data
transmission rates, memory, antenna design, and write capabilities.
As new transponders become commercially available, Zebra will evaluate them for
compatibility with your printer. For more information about which tag types can be used with
your printer, see Table 9, Supported Tag Types and Default Values, on page 111, or contact
your authorized Zebra reseller.
Note • RFID transponders operate on different frequencies. You must use a frequency that
complies with local regulations in your country.
For different transponder types, the following characteristics vary:
• The amount of programmable memory, which can include a tag ID (TID), Electronic
Product Code (EPC) data, and user memory.
• The way that data is segmented.
• Whether the tag can be locked.
Before you purchase RFID labels, determine what type of RFID transponder to use. Different
transponder types can have different attributes. Some transponders can only be read while
others can be read and written to repeatedly. Transponders also have different amounts of
available memory, which corresponds to the amount of data that can be encoded in it. Select
the combination that best suits your needs. For more information on different transponder
types, see Transponder Characteristics on page 43.
58978L-008 Rev. A RFID Programming Guide 11/14/2008
Page 15

Accounting for Transponder Inlay Placement
Communication between the RFID label and the printer is established when the label’s
transponder inlay lines up with the printer’s antenna. The optimal transponder programming
position varies with the transponder size, its configuration, and the type of RFID IC chip used.
For transponder inlay placement information, go to http://www.zebra.com/rfid_transponders.
Print quality may be affected by pri nting directly ove r the transponder. In particular, there is an
area on each label immediately around the location of the IC chip where the printer may print
with low quality. Design your printed label around the location of the chip in the type of
approved RFID label that you select.
Selecting and Purchasing RFID Labels
Before you purchase a large quantity of the RFID labels you selected, test a small batch of the
labels to make sure they function as you need them to. You may need to adjust the transponder
location or switch to a different tag type if the RFID labels do not work in your application.
To order labels with transponders that are approved for your specific RFID printer, contact
your authorized Zebra reseller, or go to http://www.zebra.com/smart_labels for more
information.
Introduction to RFID
RFID Label Selection
15
Performing Label Placement Tests
After an RFID label is encoded, how well it functions depends on several things:
• where the label is placed on an item
• the contents of the item (such as metals or liquids)
• the location of the RFID readers.
Perform label placement tests with your readers to identify where labels should be placed on
an item to ensure high read rates. Contact the supplier of your RFID transponders for
assistance with these types of issues.
Storing RFID Labels
Store RFID labels at temperatures ranging from 60 to 203 °F (15.5 to 95 °C) in
environmentally stable conditions. Limit RFID label exposure to electrostatic discharge
(ESD). Low-humidity environments may require th e use of anti stat ic ma ts, straps, or clothing
to help counter ESD.
11/14/2008 RFID Programming Guide 58978L-008 Rev. A
Page 16

Introduction to RFID
16
Radio Frequency Interference
Radio Frequency Interference
Radio Frequency (RF) interference can be caused by many sources. This interference can
affect RFID performance by limiting the ra nge of the RFID tag s or prev enting readin g/writin g
to the tags.
• Foil and metal-based media should not be used for RFID applications. Metal reflects radio
frequency signals and is a leading source of RF interference.
• Water and other liquids can absorb RF signals. Some media adhesives and label materials
can be unexpected sources of liquids that cause performance problems.
• Other RF equipment can cause interference if the equipment is positioned too close
together. Allow sufficient physical space between the RFID printer and other RF products
that share the same bandwidth (such as antennas, readers, wireless LANs, or other RFID
printer/encoders).
ZPL Commands for RFID Applications
Each RFID label has memory that can be read and most have memory that can be written to
through Zebra Programming Language (ZPL) commands. Use ZPL to read and write to
(encode) RFID labels just as you would use ZPL to print data on the labels. You can use
serialized fields, field variables, and any other ZPL features (such as the command ^HV
on page 88 to return the results to a host computer).
RFID-specific ZPL commands are described in ZPL II Commands for RFID on page 79. For
examples of how to use the ZPL commands, see Create and Send an RFID Label Format
on page 30.
For more information about non-RFID ZPL commands and how to use them, refer to the
ZPL II Programming Guide. A copy is available online at http://www.zebra.com/manuals.
SGD Commands for RFID Applications
Your RFID printer is able to use Set/Get/Do (SGD) commands just as it does ZPL commands.
Many ZPL commands have equivalent SGD commands. Usually, you will need to run one
SGD command for each parameter in the corresponding ZPL command . RFID-specific SGD
commands are described in SGD Commands for RFID on page 129.
For more information about non-RFID SGD commands and how to use them, refer to the
ZPL II Programming Guide. A copy is available online at http://www.zebra.com/manuals.
58978L-008 Rev. A RFID Programming Guide 11/14/2008
Page 17

2
RFID Printer Setup
and Operation
How you set up your printer for RFID applications is determined in part by the transponder
that you select. This section guides you through some tasks that you may need to perform on
your printer to make RFID reading and encoding possible. When you have completed this
section, you will be ready to program your RFID label formats.
Contents
Set Tag Type . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
Set RF Power Levels . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
Perform RFID Transponder Calibration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
Download Latest Firmware . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
11/14/2008 RFID Programming Guide 58978L-008 Rev. A
Page 18

RFID Printer Setup and Operation
18
Set Tag Type
Set Tag Type
After you select a transponder type and purchase labels, set the transponder (tag) type on the
printer. Do this through the control panel menu (see Specify RFID Tag Type on page 27) or
through the
Set RF Power Levels
Each transponder has specific radio frequency (RF) power setting requirements for read and
write operations, which define how much power is necessary to “energize” the transponder in
its targeted encoding field. The tag type that you are using must match the RFID power
settings of the printer. If necessary, you can change the power settings:
• through the control panel (see View or Change RFID Read Power on page 24 or View or
Change RFID Write Power on page 25)
• through the
• through SGD commands (see
• rfid.reader_1.power.read on page 137
• rfid.reader_1.power.single_power on page 138
• rfid.reader_1.power.write on page 139)
^RS ZPL command (see ^RS on page 108).
^RW ZPL command (see ^RW on page 118)
Perform RFID Transponder Calibration
If you are using RFID labels that were desi gned to meet the specifications of your printer, you
do not need to perform RFID transponder calibration. The printer will automatically place the
labels in the optimal programming position. For transponder placement specifications, go to
http://www.zebra.com/rfid_transponders.
If you are using RFID labels that were n ot desi gned for your printer, you may need to perform
an RFID transponder calibration to determine the optimal programming position for your
media. You can perform this calibration through the
parameter (see Calibrate RFID Tag on page 23) or through the
or ~HL on page 84). To return to the default programming position at any time, use the
RESTORE option in the
Tag on page 23).
RFID TAG CALIB control panel parameter (see Calibrate RFID
RFID TAG CALIB control panel
^HR ZPL command (see ^HL
58978L-008 Rev. A RFID Programming Guide 11/14/2008
Page 19

Download Latest Firmware
Zebra may update printer and reader firmware periodically to add new functionality or to fix
any known issues with older firmware. At any time, you may download th e most recent
firmware for your RFID printer. For the firmware files and the downloading instructions, go to
http://www.zebra.com/firmware.
Important • Download only the firmware designed for your printer and for your region or
country. Downloading inappropriate firmware may disable your printer or some or all of the
RFID functionality.
Before downloading new firmware, p rint a printe r configuration label and verify that the ne w
printer firmware version is appropriate for your printer. The underlined part of the firmware
version shown in Table 1 must match exactly with what was originally installed on your
printer.
Table 1 • RFID Printer Firmware Versions
RFID Printer Setup and Operation
Download Latest Firmware
19
Printer
Firmware Version
R110Xi/R170Xi (UHF) R60.X.X
R110Xi HF R65.X.X
R110PAX4R62
.X.X
R63.X.X
R4Mplus SP994X
SP999
X
SP1027X
SP1056X
SP1082
X
RZ400/RZ600 R53.X.X
11/14/2008 RFID Programming Guide 58978L-008 Rev. A
Page 20
RFID Printer Setup and Operation
Notes • ___________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________
20
Download Latest Firmware
58978L-008 Rev. A RFID Programming Guide 11/14/2008
Page 21

3
RFID Control Panel
Parameters
This section shows the control panel parameters that appear on most Zebra RFID printers that
have a graphic display.
Note • The RP4T does not display these parameters.
The parameters shown in Table 2 on page 22 display only if you have an RFID reader and
antenna installed. Depending on whi ch type of printer you have an d which version of firmware
that you are using, not all parameters or options for the parameters may display.
Note • When you enter Setup mode, press PREVIOUS or MINUS (-) (depending on the
printer) to access the RFID parameters without scrolling through all of the other printer
parameters. Refer to the user guide for your printer for specific instruc tions on how to use the
control panel.
11/14/2008 RFID Programming Guide 58978L-008 Rev. A
Page 22
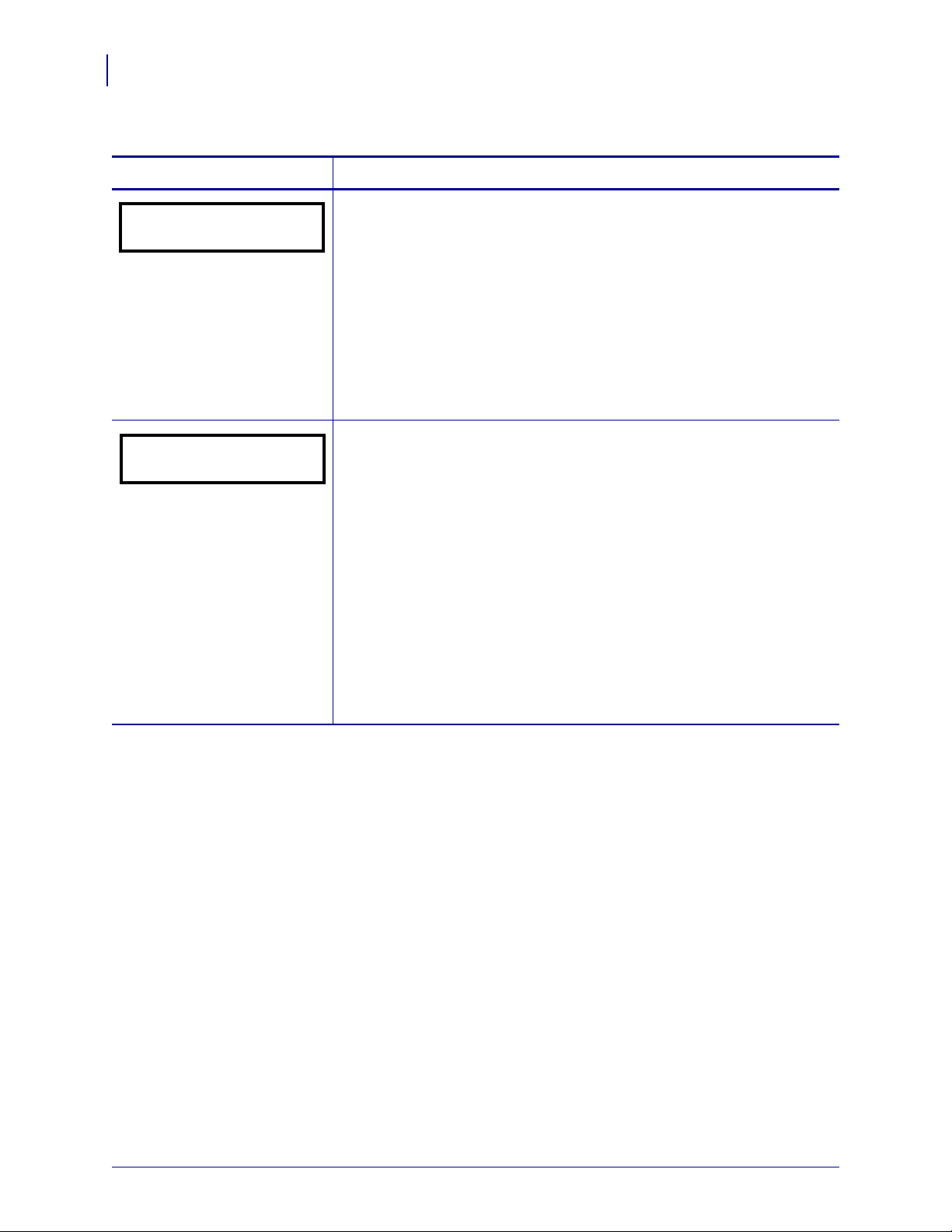
RFID Control Panel Parameters
PRINT MODE
- RFID +
RFID TEST
QUICK SLOW
22
Table 2 • RFID Parameters (Page 1 of 7)
Parameter Action/Explanation
Select Print Mode
Print mode settings tell the printer the method of media delivery to use.
Make sure that your printer can support the selected optio n. Use RFID
mode when printing batches of RFID labels to increase throughput time.
Default: (R110PAX4) APPLICATOR
Default: (all other RFID printers) RFID
Selections: vary by printer
To change the value shown:
1. Press the left oval/MINUS (-) or the right oval/PLUS (+) to scroll
through the options.
Perform RFID Test
In the RFID test, the printer attempts to read and write to a transponder. In
the slow version, the printer first displays the hardware version, the reader
firmware version, and the program position. If the printer fails the test, the
control panel displays READ ERROR. No printer movement occurs with
this test.
To perform the RFID test:
1. Position an RFID label with its transponder over an RFID antenna
location. For the location of the RFID antenna on your printer, see
RFID Antenna Location on page 39.
2. Press the left oval/
MINUS (-) to select QUICK.
OR
Press the right oval/
PLUS (+) to select SLOW.
3. If necessary, press the right oval/PLUS (+) to select CONTINUE.
58978L-008 Rev. A RFID Programming Guide 11/14/2008
Page 23
Table 2 • RFID Parameters (Page 2 of 7)
RFID TAG CALIB
RESTORE RUN
Parameter Action/Explanation
Calibrate RFID Tag
This parameter sets the RFID programming position through a tag
calibration, or it restores the programming position back to the printer
default.
RESTORE Selecting this option resets the RFID programming position
to the printer default.
Note • With some printers and firmware versions, no label
movement or changes to the control panel occur. W ith others, the
printer displays PROGRAM POSITION RESTORED.
• For the R110PAX4, the RFID programming po sition is zero (the
printer programs the tag without moving the label). By default, the
print engine has backfeed set to After, which places the transponder in
the optimal place for encoding for Zebra-specified media. If you are
using a backfeed setting other than After, do not use the RESTORE
function unless the position of the transponder in your media accounts
for this change.
• For other RFID printers, the RFID programming position is the label
length minus 1 mm (0.04 in.).
RFID Control Panel Parameters
23
RUN If the media being used does not conform to transponder placement
requirements for your printer, use the
RUN option to have the printer
determine the optimum programming position for the non-standard labels.
Important • Do not perform transponder calibration for RFID
media that meets the transponder placement specifications for your
printer. RFID tag calibration is necessary only if the transponder is
not in the ideal location for programming at the printer’s default
position.
The printer feeds an RFID label one millimeter at a time while taking
readings (via the READ TAG command and the WRITE TAG commands)
to profile the RFID transponder. Based on the results, the printer
determines the optimum programming position for the me dia and saves th e
position to nonvolatile memory (the value is saved even if the power is
turned off). The calibrated value is used as the programming position for
^RS command unless the command specifies a different value.
the
Tag calibration takes into account the print mode, backfeed mode, and tear
off position. The
^HR ZPL command performs the same calibration and
returns a results table to the host (see ^HL or ~HL on page 84). An auto-
calibration occurs after the tag calibration. This realigns the media to its
proper rest position and updates the media tracking values in the printer.
To restore the programming position to the default:
1. Press the left oval/MINUS (-) to select RESTORE.
11/14/2008 RFID Programming Guide 58978L-008 Rev. A
To calibrate an RFID tag:
1. Loa d the printer with RFID media.
2. Close the printhead.
3. Press the right oval/
PLUS (+) to select RUN.
Page 24
RFID Control Panel Parameters
RFID VALID CTR
956 RESET
RFID VOID CTR
23 RESET
RFID READ PWR
16
Printer Firmware Version
Selections
Default
H, M, L 0–30
RXi R60.15.8Z and earlier X — L
R60.16.4Z X X L
R60.16.5Z and later (M4xxx…x reader) X X L
R60.16.5Z and later (M5xxx…x reader) — X 16
R4Mplus SP994P, SP999F, SP1027F, SP1056E, SP1082F,
and earlier
X—L
SP994Q, SP999G, SP1027G , SP1056F, SP1082G,
and later
XXL
R110PAX4 R62.15.8Z and earlier X — L
R62.16.4Z and later X X L
R63.15.8Z and earlier X — L
R63.16.4Z and later X X L
RZx00 all versions — X 16
RP4T all versions — X 16
24
Table 2 • RFID Parameters (Page 3 of 7)
Parameter Action/Explanation
View Valid RFID Label Counter
This parameter displays the total number of valid RFID labels that have
been printed/encoded. You can use this parameter or
odometer.rfid.valid_resettable on page 132 to reset the counter to zero.
To reset the counter to zero:
1. Press the right oval/PLUS (+) to select RESET.
View Void RFID Label Counter
This parameter displays the total number of RFID labels that have been
voided. You can use this parameter or odometer.rfid.void_resettable
on page 133 to reset the counter to zero.
To reset the counter to zero:
1. Press the right oval/PLUS (+) to select RESET.
View or Change RFID Read Power
This parameter displays the current value for RFID read power.
Note •
· This parameter does not appear on the R110Xi HF printer.
· On some printers, the options vary based on the reader. Check
the printer configuration label for the RFID_HW_VER line or
perform the RFID SLOW test (see Perform RFID Test
on page 22) to determine the reader type.
58978L-008 Rev. A RFID Programming Guide 11/14/2008
To change the value shown:
1. Press the left oval/MINUS (-) or the right oval/PLUS (+) to scroll
through the options.
Page 25
Table 2 • RFID Parameters (Page 4 of 7)
RFID WRITE PWR
16
Printer Firmware Version
Selections
Default
H, M, L 0–30
RXi R60.15.8Z and earlier X — L
R60.16.4Z X X L
R60.16.5Z and later (M4xxx…x reader) X X L
R60.16.5Z and later (M5xxx…x reader) — X 16
R4Mplus SP994P, SP999F, SP1027F, SP1056E, SP1082F,
and earlier
X—L
SP994Q, SP999G, SP1027G , SP1056F, SP1082G,
and later
XXL
R110PAX4 R62.15.8Z and earlier X — L
R62.16.4Z and later X X L
R63.15.8Z and earlier X — L
R63.16.4Z and later X X L
RZx00 all versions — X 16
RP4T all versions — X 16
RFID POWER
LOW
Parameter Action/Explanation
View or Change RFID Write Power
This parameter displays the current value for RFID write power.
Note •
· This parameter does not appear on the R110Xi HF printer.
· On some printers, the options vary based on the reader. Check
the printer configuration label for the RFID_HW_VER line or
perform the RFID SLOW test (see Perform RFID Test
on page 22) to determine the reader type.
RFID Control Panel Parameters
25
To change the value shown:
1. Press the left oval/MINUS (-) or the right oval/PLUS (+) to scroll
through the options.
View or Change RFID Read/Write Power
Note • This parameter appears only for the R110Xi HF printer,
which uses identical RF power settings for read and write
operations.
This parameter displays the current value for RFID power.
Default: LOW
Selections: HIGH, MEDIUM, LOW
11/14/2008 RFID Programming Guide 58978L-008 Rev. A
To change the value shown:
1. Press the left oval/MINUS (-) or the right oval/PLUS (+) to scroll
through the options.
Page 26
RFID Control Panel Parameters
RFID ANTENNA
ANTENNA PORT 1
RFID ERR STATUS
26
Table 2 • RFID Parameters (Page 5 of 7)
Parameter Action/Explanation
Select the RFID Antenna Port
This parameter displays the current antenna port.
Default: ANTENNA PORT 1
Selections: ANTENNA PORT 1, ANTENNA PORT 2
To change the value shown:
1. Press the left oval/MINUS (-) or the right oval/PLUS (+) to scroll
through the options.
RFID Error Status
During an error condition, an error message show s on the second li ne of the
display. See Table 6 on page 53 in the RFID Troubleshooting section for
descriptions of the error messages. This field cannot be modified.
Note • This parameter appears only for the R110Xi HF printer.
58978L-008 Rev. A RFID Programming Guide 11/14/2008
Page 27
Table 2 • RFID Parameters (Page 6 of 7)
RFID TAG TYPE
CLASS 1 96-BIT
Parameter Action/Explanation
Specify RFID Tag Type
Select the RFID tag type that you are using. See Table 9, Supported Tag
Types and Default V a lu es on page 111 for tag types that your printer
supports. If a tag type is supported but does not appear on your printer’s
control panel, you may need to upgrade the printer’s firmware (see
http://www.zebra.com/firmware).
UHF Tag Type Selections
• NONE
• CLASS 0 (EPC Class 0)
• CLASS 0+ (EPC Class 0 Plus)
• CLASS 1 64-BIT (EPC Class 1 64-bit)
• CLASS 1 96-BIT (EPC Class 1 96-bit)
•UCODE EPC 1.19
• CLASS 0+ IMPINJ (Impinj Class 0 Plus)
• ISO18000A (ISO 18000-06A)
• GEN2 (EPC Class 1, Gen 2)
• ISO18000B (ISO 18000-06B)
HF Tag Type Selections
• NONE
• AUTO DETECT (query tag to determine)
• TAG-IT (Texas Instruments Tagit tags)
• ICODE (Phillips Icode tags)
• PICO (Pico Tag Inside Technology’s)
• ISO15693
• EPC (13.56 MHz)
•UID
• MIFARE ULTRALT (Mifare UltraLight)
RFID Control Panel Parameters
27
11/14/2008 RFID Programming Guide 58978L-008 Rev. A
To change the value shown:
1. Press the left oval/MINUS (-) or the right oval/PLUS (+) to scroll
through the options.
Page 28
RFID Control Panel Parameters
RFID TAG DATA
28
Table 2 • RFID Parameters (Page 7 of 7)
Parameter Action/Explanation
Read and Display RFID Tag Data
When this option is selected, the reader attempts to read a tag over the
RFID antenna, even if the printhead is open. Results are displayed in
hexadecimal format. The printer rereads the tag every 2 seconds, so if the
tag changes, data is displayed for the current tag over the antenna. No
printer movement occurs while tag data is read.
• If no tag data can be read, the text
line of the LCD display.
• If a tag is present, the data for that tag appears on the b ottom line of the
display in hexadecimal format. If there is more data than can fit on th e
bottom line (such as for 96-bit tags), the bottom line will cycle from
the first 8 bytes (most significant) to the next 4 byt es (least sig nificant)
approximately every 2 seconds. The hexadecimal data that can fit on
two screens is displayed and cycled through.
For example, if the tag contains the data
0x112233445566778899001122, when this option is selected,
the bottom line of the display shows:
seconds followed by
through these indefinitely.
NO DATA appears on the bottom
1122334455667788 for 2
99001122 for 2 seconds. The printer cycles
To read RFID tag data:
1. Position an RFID label with its transponder over an RFID antenna
location. For the location of the RFID antenna on your printer, see
RFID Antenna Location on page 39.
58978L-008 Rev. A RFID Programming Guide 11/14/2008
Page 29

4
Creating Basic RFID
Label Formats
After you have selected a transponder type and set your printer appropriately, use the ZPL
samples in this section as a base for programming your own RFID label formats.
For specific information about individual ZPL commands, see ZPL II Commands for RFID
on page 79.
Contents
Create and Send an RFID Label Format . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
Sample RFID Label Formats . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
RFID Label Format 1—Encode a Gen 2 Tag in Hexadecimal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
RFID Label Format 2—Encode a Gen 2 Tag in ASCII. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
RFID Label Format 3—Read Data from Tag and Print Data on Label. . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
RFID Label Format 4—Encode Tag, Read Tag, and Print Data on Label . . . . . . . . . . 34
RFID Label Format 5—Encode a Class 1 64-bit Tag in Hexadecimal . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
RFID Label Format 6—Encode Tag, Read Tag, and Return Results to Host . . . . . . . 37
11/14/2008 RFID Programming Guide 58978L-008 Rev. A
Page 30

Creating Basic RFID Label Formats
30
Create and Send an RFID Label Format
Create and Send an RFID Label Format
The following pages contain sample RFID label formats that you can modify to create your
own RFID label formats.
To create an RFID label based on a sample label, complete these steps:
1. Using any word processor or text editor that is capable of creating ASCII-only files (for
example, use Microsoft
®
Word and save as a .txt file), type in the label format exactly as
shown in the desired sample.
2. Save the file to your computer.
When naming the file, use
choose to name a file
3. Set up the printer, and turn the power On (I).
4. Copy the file to the printer.
.zpl as the extension for the file (for example, you may
format1.zpl).
If you are connected to the printer via the parallel port, from the DOS command window,
use the “COPY” command to send a file to the printer. For example, if your file name is
format1.zpl, type:
COPY FORMAT1.ZPL XXXX
XXXX is the port to which your printer is connected (such as LPT1).
where
5. Compare you r lab el re sults with t hose sh own in the samp le. If yo ur print out d oes not look
like the one shown, confirm that t he fil e yo u crea ted is identica l to the format sh own, t hen
repeat the printing procedure.
6. Check the RFID data on your label.
a. Open the printhead, and place the label above the antenna in the printer.
b. Use the control panel to view the transponder data (see Read and Display RFID Tag
Data on page 28).
c. Co mpare your RFID data with that shown i n the samp le. If yo ur control pa nel displ ay
does not look like what is shown, confirm that the file you created is id entical to the
format shown, then repeat the printing procedure.
7. When you are certain that the file you created is correct, substitute your data in the label
format where necessary.
58978L-008 Rev. A RFID Programming Guide 11/14/2008
Page 31

Creating Basic RFID Label Formats
Simple write example
RFID TAG DATA
1122334455667788
RFID TAG DATA
99001122
Sample RFID Label Formats
Sample RFID Label Formats
Use the formats in this section to assist you in creating your own RFID label formats.
RFID Label Format 1—Encode a Gen 2 Tag in Hexadecimal
31
Line
Number
1
2
3
4
5
Type This ZPL Code Function of ZPL Code
^XA
^RS8
^FO50,50
^A0N,65
Indicates start of label format.
Sets tag type to Gen 2
Prints “Simple write example” on the label
at location 50,50.
^FDSimple write example
^FS
^RFW,H
^FD112233445566778899001122
^FS
^XZ
W,H = write he x
Encodes the 12 bytes of data (96 bits) to the
tag. The data written is:
112233445566778899001122
Indicates end of label format.
Resulting Label
11/14/2008 RFID Programming Guide 58978L-008 Rev. A
Programmed to Transponder
112233445566778899001122
Control Panel Display (toggles between these two)
Page 32

Creating Basic RFID Label Formats
Simple write example
RFID TAG DATA
3030207266696420
RFID TAG DATA
64617461
32
Sample RFID Label Formats
RFID Label Format 2—Encode a Gen 2 Tag in ASCII
This label format is different in what shows on the control panel. The control panel always
displays RFID data in hexadecimal.
Line
Number
1
2
3
4
5
Type This ZPL Code Function of ZPL Code
^XA
^RS8
^FO50,50
^A0N,65
Indicates start of label format.
Sets tag type to Gen 2
Prints “Simple write example” on the label at
location 50,50.
^FDSimple write example
^FS
^RFW,A
^FD00 rfid data
^FS
^XZ
W,A = write ASCII
Encodes the 12 bytes of data (96 bits) to the tag. The
data written is: 00 rfid data
Indicates end of label format.
Resulting Label
58978L-008 Rev. A RFID Programming Guide 11/14/2008
Programmed to Transponder
00 rfid data
Control Panel Display (toggles between these two)
Page 33

Creating Basic RFID Label Formats
112233445566778899001122
RFID TAG DATA
1122334455667788
RFID TAG DATA
99001122
Sample RFID Label Formats
RFID Label Format 3—Read Data from Tag and Print Data on Label
This example assumes that the tag created using RFID Label Format 1—Encode a Gen 2 Tag
in Hexadecimal on page 31 is being read.
33
Line
Number
1
2
3
4
5
Type This ZPL Code Function of ZPL Code
^XA
^RS8
^FO50,50
^A0N,40
^FN0
^FS
^FN0
^RFR,H
^FS
^XZ
Indicates start of label format.
Sets tag type to Gen 2
is a placeholder field variable for the tag data
^FN0
that will be read in the following line. When the l abel
prints, the data read from the tag will be printed at
location 50,50.
R,H = read hexadecimal
The read results are put into field variable 0 (
At this point, the printer substitutes previous
instances of
from this field. The data read from the tag will be
padded with zeroes to the maximum bit size.
Indicates end of label format.
^FN0 in the label format with the data
Read from Transpon der
112233445566778899001122
Resulting Label
^FN0).
11/14/2008 RFID Programming Guide 58978L-008 Rev. A
Control Panel Display (toggles between these two)
Page 34

Creating Basic RFID Label Formats
0data
34
Sample RFID Label Formats
RFID Label Format 4—Encode Tag, Read Tag, and Print Data on Label
Line
Number
1
2
3
4
5
6
Type This ZPL Code Function of ZPL Code
^XA
^RS8
^FO60,60
^A0N,40
^FN7
^FS
^RFW,A
^FD0data
^FS
^FN7
^RFR,A
^FS
^XZ
Indicates start of label format.
Sets tag type to Gen 2
When the label prints, the data read from the tag at
field variable 7 (
60,60.
W,A = write ASCII
Encodes “0data” into the block padded with 8 bytes
of zeroes to make the data 12 bytes. The data written
is: 306461746100000000000000 (“0data” in ASCII)
R,A = read ASCII
Reads the tag data into field variable 7 (
After this occurs, any fields in this label format that
^FN7 will be replaced with this read data.
have
Indicates end of label format.
^FN7) will be printed at location
Programmed to Transponder
306461746100000000000000
^FN7).
Read from Transpon der
306461746100000000000000
Resulting Label
58978L-008 Rev. A RFID Programming Guide 11/14/2008
Page 35

Control Panel Display (toggles between these two)
RFID TAG DATA
3064617461000000
RFID TAG DATA
00000000
Creating Basic RFID Label Formats
Sample RFID Label Formats
35
11/14/2008 RFID Programming Guide 58978L-008 Rev. A
Page 36

Creating Basic RFID Label Formats
Simple write example
RFID TAG DATA
1122334455667788
36
Sample RFID Label Formats
RFID Label Format 5—Encode a Class 1 64-bit Tag in Hexadecimal
Line
Number
1
2
3
4
5
Type This ZPL Code Function of ZPL Code
^XA
^RS3
^FO50,50
^A0N,65
Indicates start of label format.
Sets tag type to EPC Class 1 64-bit.
Prints “Simple write example” on the label at
location 50,50.
^FDSimple write example
^FS
^RFW,H
^FD1122334455667788
^FS
^XZ
W,H = write he x
Encodes the 8 bytes of data (64 bits) to the tag. The
data written is: 1122334455667788
Indicates end of label format.
Resulting Label
Programmed to Transponder
1122334455667788
Control Panel Display
58978L-008 Rev. A RFID Programming Guide 11/14/2008
Page 37

Creating Basic RFID Label Formats
010203040500000000000000
Sample RFID Label Formats
RFID Label Format 6—Encode Tag, Read Tag, and Return Results to Host
37
Line
Number
1
2
3
4
5
6
Type This ZPL Code Function of ZPL Code
^XA
^RS8
^FO50,50
^A0N,65
^FN3
^FS
^RFW,H
^FD0102030405
^FS
^FN3
^RFR,H
^FS
^HV3
Indicates start of label format.
Sets tag type to Gen 2
When the label prints, the data read from the tag at
field variable 3 (
50,50.
W,H = write he x
Encodes 12 bytes of data (96 bits) to the tag with
7 bytes of zeroes as padding. The data written is:
010203040500000000000000
R,H = read hexadecimal
Reads the tag data into field variable 3 (
After this occurs, any fields in this label format that
^FN3 will be replaced with this read data.
have
Returns the value in ^FN3 to the host computer.
Data is sent over whichever communication channel
is established with the host (such as parallel, serial,
USB, Ethernet). In this example,
010203040500000000000000 would be returned to
the host.
^FN3) will be printed at location
^FN3).
7
^XZ
Programmed to Transponder
010203040500000000000000
Read from Transpon der
010203040500000000000000
Resulting Label
Indicates end of label format.
11/14/2008 RFID Programming Guide 58978L-008 Rev. A
Page 38

Creating Basic RFID Label Formats
RFID TAG DATA
0102030405000000
RFID TAG DATA
00000000
38
Sample RFID Label Formats
Control Panel Display (toggles between these two)
Sent to Host Computer
010203040500000000000000
58978L-008 Rev. A RFID Programming Guide 11/14/2008
Page 39

5
RFID Antenna Location
Operations to test the RFID functions and display RFID tag data require you to place an RFID
label over the RFID antenna area. This section shows the location of the RFID antenna in the
various Zebra RFID printers.
Contents
RXi and RXi HF . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
RZ400 and RZ600 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
R110PAX4 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
RP4T . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
R4Mplus. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
11/14/2008 RFID Programming Guide 58978L-008 Rev. A
Page 40

RFID Antenna Location
1
1
40
RXi and RXi HF
RXi and RXi HF
Figure 2 • RXi and RXi HF Antenna Location
RZ400 and RZ600
Figure 3 • RZ400 and RZ600 Antenna Location
58978L-008 Rev. A RFID Programming Guide 11/14/2008
Page 41

R110PAX4
1
1
Figure 4 • R110PAX4 Antenna Location
RFID Antenna Location
R110PAX4
41
RP4T
Figure 5 • RP4T Antenna Location
11/14/2008 RFID Programming Guide 58978L-008 Rev. A
Page 42

RFID Antenna Location
1
42
R4Mplus
R4Mplus
Figure 6 • R4Mplus Antenna Location
58978L-008 Rev. A RFID Programming Guide 11/14/2008
Page 43

6
Transponder
Characteristics
This section describes the different characteristics of some common transponder types.
Contents
Basic Transponder Characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
Electronic Product Code (EPC) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
EPC Fields. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
EPC Structure in RFID Labels. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
EPC Class 1, Generation 2 (Gen 2). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
Data Content . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
Data and Tag Security . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
Gen 2 Memory Map. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
11/14/2008 RFID Programming Guide 58978L-008 Rev. A
Page 44

Transponder Characteristics
44
Basic Transponder Characteristics
Basic Transponder Characteristics
Table 3 shows some of the basic characteristics of common transponder types.
Table 3 • Characteristics of Transponder Types
Transponder Type
Class 0 Yes No 96 bits
Class 0+ Yes Yes 96 bit (TID)
Class 1 64 bits Yes Yes 64 bits
Class 1 96 bits Yes Yes 96 bits
ISO18000-6A Yes Yes Varies
ISO18000-6B Yes Yes Varies
Gen 2 Yes Yes Varies by manufacturer and tag. See
Depending on which printer you have and which firmware you are using, you may or may not
be able to use the tag types shown in this section. Go to Table 9, Supported Tag Types and
Default Values, on page 111 for more information about which tag types work with which
printers.
Read Write Size (in bits)
104 bit (USER)
Gen 2 Memory Map on page 46 for
additional memory information.
58978L-008 Rev. A RFID Programming Guide 11/14/2008
Page 45

Electronic Product Code (EPC)
EPC is a product numbering standard that can be used to identify a variety of items by using
RFID technology. The 96-bit EPC code links to an online database, prov id in g a secure way of
sharing product-specific information along the supply chain.
Note • The information in this section is provided for your convenience only and is subject to
change. Go to http://www.epcglobalinc.org for the latest EPC information.
EPC Fields
As with bar codes, EPC is divided into numbers that identify the manufacturer and product
type. However, EPC contains the following additional information:
• Header—identifies the length, type, structure, version, and generation of EPC
• Manager Number—identifies the company or company entity
• Object Class—similar to a stock keeping unit (SKU)
• Serial Number—the specific instance of the Object Class being tagged
Additional fields may be used as part of the EPC code to encode and decode information from
different numbering systems into human-readable form. For more information ab ou t EPC
specifications, refer to the EPC Global web site.
Transponder Characteristics
Electronic Product Code (EPC)
45
EPC Structure in RFID Labels
In the printer, you can subdivide transponder data into unique fields. You can customize these
fields to create “smart” labels that meet your needs or that meet the standards necessary in
EPC programming.
^RB ZPL command is used to define EPC structure. EPC field data ca n be deli mited with
The
any of the following characters:
, ~ ! @ # $ % ^ & * | . < > / \ : ;
See ^RB on page 93 for more information about and examples for defining EPC structure.
11/14/2008 RFID Programming Guide 58978L-008 Rev. A
Page 46

Transponder Characteristics
46
EPC Class 1, Generation 2 (Gen 2)
EPC Class 1, Generation 2 (Gen 2)
EPC Gen 2 tags offer advantages over other tag types. The tag identification (TID) memory in
a Gen 2 tag includes the chip manufacturer and model number in formation, which can be us ed
to identify which optional featu res are present on the tag. These optional features include those
for data content and security.
See Table 9, Supported Tag Types and Default Values, on page 111 for the UHF printers and
firmware versions that can use Gen 2 tags.
Data Content
Gen 2 tags typically have a 96-bit EPC identifier, which is different from the 64-bit identifiers
common in early EPC tags. Gen 2 tags also support much larger data structures. The size of
user memory available (if any) varies by the model and manufacturer of the tag.
Data and Tag Security
Tag Passwords You can set op tio nal 32-bit passwords that allow you to access tag data, to
lock tag data, or to permanently disable (kill) a tag. Use the ZPL comma nd ^RZ on page 120 to
set the passwords (if desired) and ^RF on page 96 to re ad the passwords.
Data Locking Options User-allocated memory can be safeguarded with flexible locking
options using ^RZ on page 120. For example, you can lock a tag’s blank memory to prevent it
from being encoded accidentally and later unlock it for writing. A permanent locking feature
prevents rewriting of tag data.
Gen 2 Memory Map
Table 4 shows how information is stored on a Gen 2 tag.
Bank Memory Bank
3User
2TID
1EPCEPC (15:0)
Table 4 • Gen 2 Tag Logical Memory Map
Memory Contents
…
…
TID (15:0)
TID (31:16)
…
EPC (N:N-15)
PC (15:0)
CRC-16 (15:0)
58978L-008 Rev. A RFID Programming Guide 11/14/2008
Page 47

Transponder Characteristics
EPC Class 1, Generation 2 (Gen 2)
Table 4 • Gen 2 Tag Logical Memory Map (Continued)
47
Bank Memory Bank
0 Reserved
Memory Contents
…
access password (15:0)
access password (31:16)
kill password (15:0)
kill password (31:16)
11/14/2008 RFID Programming Guide 58978L-008 Rev. A
Page 48

Transponder Characteristics
Notes • ___________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________
48
EPC Class 1, Generation 2 (Gen 2)
58978L-008 Rev. A RFID Programming Guide 11/14/2008
Page 49

7
Troubleshooting
This section provides information about RFID operati onal errors that you might need to
troubleshoot. For other types of problems, consult the user guide for your printer.
Contents
RFID Problems. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 50
RFID Error Codes and Messages . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 53
Error and Status Messages . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 53
Error Codes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 66
11/14/2008 RFID Programming Guide 58978L-008 Rev. A
Page 50

Troubleshooting
50
RFID Problems
RFID Problems
Table 5 identifies problems that may occur with RFID printers, the possible causes, and the
recommended solutions.
Table 5 • RFID Problems
Problem Possible Cause Recommended Solution
The RFID-enabled
printer voids every
label.
The printer is not calibrated for
the RFID label being used.
The printer is set for the wrong
tag type.
The printer is unable to
communicate with the RFID
reader.
The settings are incorrect in
your label designer software.
You are using an incorrect
programming position,
particularly if the tags being
used are within printer
specifications.
Refer to the User Guide for your printer for
instructions.
Set the correct tag type using Specify RFID Tag
Type on page 27. If the tag type is not listed, you
may not be able to use the labels with your
printer.
1. Turn off (
2. Wait 10 seconds.
3. Turn on (
4. If the problem persists, you may have a bad
RFID reader or a loose connection between
the RFID reader and the printer. Contact
Technical Support or an authorized Zebra
RFID service technician for assistance.
The software settings override the printer
settings. Make sure that the software and printer
settings match.
Do one or more of the following as necessary:
• Check the programming position being used
with the ^RS command, or the program
position setting in your label designer
software. If the position is incorrect, change
the setting.
• Select RESTORE for the
CALIB
on page 23).
O) the printer.
I) the printer.
RFID TAG
parameter (see Calibrate RFID Tag
You are sending RFID ZPL
commands that are incorrect.
Radio frequency (RF)
interference from another RF
source.
58978L-008 Rev. A RFID Programming Guide 11/14/2008
See ZPL II Commands for RFID on page 79.
Do one or more of the following as necessary:
• Move the printer away from fixed RFID
readers or other RF sources.
• Make sure that the media door is closed at all
times during RFID programming.
Page 51

Ta ble 5 • RFID Problems (Continued)
Problem Possible Cause Recommended Solution
Troubleshooting
RFID Problems
51
Low yields. T oo many
RFID tags per roll
are voided.
The RFID labels are not within
specifications for the printer,
which means that the
transponder is not in an area
that can be programmed
consistently.
Some RFID tags are more
sensitive than others and may
require special printer settings.
Incorrect read and write power
levels for the RFID tag type.
Make sure that the labels meet transponder
placement specifications for your printer. See
http://www.zebra.com/id/zebra/na/en/index/
products/supplies/rfid_supplies/
rfid_transponder_inlay.html for transponder
placement information.
Contact an authorized Zebra RFID reseller for
more information.
1. Verify that the printer is set for the correct
write power. See
http://www.zebra.com/id/zebra/na/en/index/
products/supplies/rfid_supplies/
rfid_transponder_inlay.html for the
recommended power setting for each tag
type.
2. If necessary, run the ^HR command to
manually calibrate the transponder position.
3. If the problem persist s, con side r using a
different tag type.
Contact an authorized Zebra RFID reseller for
more information.
Change the RFID read and write power levels
(see View or Change RFID Read Power
on page 24 or View or Change RFID Write
Power on page 25).
With a Gen 2 tag, no
data is written to the
tag even though the
printer says that the
write operation
succeeded.
Radio frequency (RF)
interference from another RF
source.
The printer is using outdated
printer firmware and reader
firmware versions.
The RFID reader/encoder is not
enabled for Gen 2.
Do one or more of the following as necessary:
• Move the printer away from fixed RFID
readers.
• Make sure that the media door is closed at all
times during RFID programming.
Go to http://www.zebra.com/firmware for
updated firmware.
Check Table 9, Supported Tag Types and D efault
Values, on page 111 to see if your printer
supports Gen 2 tags.
• If your printer supports Gen 2 tags, make sure
that you are using the appropriate firmware
version. Download printer and reader
firmware, if necessary.
• If your printer does not support Gen 2 tags,
you will not be able to use these tags wi th your
printer.
11/14/2008 RFID Programming Guide 58978L-008 Rev. A
Page 52

Troubleshooting
52
RFID Problems
Ta ble 5 • RFID Problems (Continued)
Problem Possible Cause Recommended Solution
The printer stops at
the RFID inlay.
The DATA light
flashes indefinitely
after you attempt to
download printer or
reader firmware.
RFID parameters do
not appear in Setup
mode, and RFID
information does not
appear on the printer
configuration label.
The printer calibrated the label
length only to the RFID inlay
instead of to the interlabel gap.
The download was not
successful. For best results,
cycle power on the printer
before downloading any
firmware.
The printer was powered
O) and then back on (I) too
off (
quickly for the RFID reader to
initialize properly.
An incorrect version of printer
or reader firmware was loaded
on the printer.
1.
2. Refer to the User Guide for your printer for
instructions.
1. Turn off (
O) the printer.
2. Wait 10 seconds.
3. Turn on (
I) the printer.
4. Attempt to download the firmware again.
5. If the problem persists, contact Technical
Support.
Wait at least 10 seconds after turning the printer
power off before turning it back on.
1. Turn off (
O) the printer.
2. Wait 10 seconds.
3. Turn on (
I) the printer.
4. Check for the RFID parameters in Setup
mode or for RFID information on a new
configuration label.
1. C ompare the fi rmw are versio n on you r
printer to those listed in Table 1, RFID
Printer Firmware Versions, on page 19.
2. Download the correct printer or reader
firmware if necessary.
3. If the problem persists, contact Technical
Support.
The printer is unable to
communicate with the RFID
reader.
1. Turn off (
2. Wait 10 seconds.
3. Turn on (
O) the printer.
I) the printer.
4. If the problem persists, you may have a bad
RFID reader or a loose connection between
the RFID reader and the printer. Contact
Technical Support or an authorized service
technician for assistance.
58978L-008 Rev. A RFID Programming Guide 11/14/2008
Page 53

RFID Error Codes and Messages
In the event of an RFID error, the printer does the following:
Troubleshooting
RFID Error Codes and Messages
53
• displays an RFID error or status message on the second line of the
control panel parameter
• returns RFID error codes to the RFID data log (see ^HL or ~HL on page 84 for more
information about the RFID data log)
Table 6 provid es the po ssible problems sorted by the error message, while Table 7 on page 66
provides these problems sorted by the error code.
Error and Status Messages
Table 6 shows the possible error and status messages, the corresponding error codes, and the
action required (if any).
Table 6 • RFID Error and Status Message Definitions
Error
Code
8104
0405
0033
RFID Error or
Status Message
ACTIVATE TAG ERR If the problem persists, contact Technical Support.
AFE NOT ON Internal problem with the reader. The Analog Front End is turned
ANT FAILURE Antenna failure. Contact Technical Support.
RFID ERR STATUS
Description/Action Required
off. Contact T echnical Support.
0025
900F
F003
9401
8201
0026
0201
000A
ANT. BAD/GONE The RFID reader cannot detect the RFID antenna (coupler), or the
antenna (coupler) does not work. Contact Technical Support.
ANT. BAD/GONE The RFID reader cannot detect the RFID antenna (coupler), or the
antenna (coupler) does not work. Contact Technical Support.
ANTENNA SEL ERR The printer firmware could not verify that the selected RFID
antenna (coupler) is properly connected.
If selecting the antenna through ZPL, ensure that your printer
supports this feature and that your parameters are correct. If the
problem persists, contact Technical Support.
AUTHEN RDR ERR If the problem persists, contact Technical Support.
AUTHEN TAG ERR Tag not authenticated.
BAD ANT.MUX Internal problem with the reader. Contact Technical Support.
BAD APP END ADD The RFID reader received a command to erase some part of the
flash memory. This typically would happen during a reader
firmware upgrade. Make sure that you download the appropriate
version of reader firmware. If the problem persists, contact
Technical Support.
BAD COMMAND The reader received a bad command from the printer. If the
problem persists, contact Technical Support.
11/14/2008 RFID Programming Guide 58978L-008 Rev. A
Page 54

Troubleshooting
54
RFID Error Codes and Messages
Table 6 • RFID Error and Status Message Definitions (Continued)
Error
Code
0004
0005
0200
0001
0008
0009
0052
000B
RFID Error or
Status Message
BAD CRC The last valid message string had a bad Cyc lic Redundancy Check
BAD DATA The reader received bad data from the printer. If the problem
BAD IMAGE CRC The RFID reader received a command to erase some part of the
BAD MESSAGE Internal communications problem with the reader. If the problem
BAD MSG HEAD Internal communications problem with the reader. If the problem
BAD MSG TAIL Internal communications problem with the reader. If the problem
BAD PASSCODE Bad passcode for kill tag function.
BAD SUBCMD Internal communications problem with the reader. If the problem
Description/Action Required
(CRC). An integrity check of the reader firmware failed. If the
problem persists, contact Technical Support.
persists, contact Technical Support.
flash memory. This typically would happen during a reader
firmware upgrade. Make sure that you download the appropriate
version of reader firmware. If the problem persists, contact
Technical Support.
persists, contact Technical Support.
persists, contact Technical Support.
persists, contact Technical Support.
persists, contact Technical Support.
0053
8005
9103
8409
0054
0010
8003
8303
8403
8508
BAUD ERR Internal problem with the reader. If the problem persists, contact
Technical Support.
BLOCK(S) LOCKED A write operation could not be performed because a block was
locked.
BOOTLOADER ERR The reader failed to enter bootloader mode, which is necessary to
upgrade firmware. If the problem persists, contact Technical
Support.
CLEAR FILE ERR Internal problem with the reader. If the problem persists, contact
Technical Support.
CMD FAIL Internal communications problem with the reader. If the problem
persists, contact Technical Support.
CMD INHIBITED Internal communications problem with the reader. If the problem
persists, contact Technical Support.
COLLISION ERR Multiple tags in the field have the same tag ID.
CREATE APPLI ERR Internal problem with the reader. If the problem persists, contact
Technical Support.
CREATE FILE ERR Internal problem with the reader. If the problem persists, contact
Technical Support.
CREDIT VALUE ERR If the problem persists, contact Technical Support.
58978L-008 Rev. A RFID Programming Guide 11/14/2008
Page 55

RFID Error Codes and Messages
Table 6 • RFID Error and Status Message Definitions (Continued)
Troubleshooting
55
Error
Code
0100
0037
040B
8105
8509
840B
800D
8408
RFID Error or
Status Message
DATA AMOUNT ERR Two situations can result in this error:
DATA CRC An integrity check of the reader firmware failed. If the problem
DATA TOO LARGE Internal problem with the reader. If the problem persists, contact
DEACTIV. TAG ERR If the problem persists, contact Technical Support.
DEBIT VALUE ERR If the problem persists, contact Technical Support.
DEC VAL FILE ERR Internal problem with the reader. If the problem persists, contact
DECRYPT TAG ERR The data read from the tag was not decrypted properly or was
DELETE FILE ERR Internal problem with the reader. If the problem persists, contact
Description/Action Required
• The data length in a message to the RFID reader from the
printer is less than the number of arguments in the message.
• The data length is greater than the number of arguments. The
reader will wait indefinitely until it receives all of the data
specified in the data length field.
If the problem persists, contact Technical Support.
persists, contact Technical Support.
Technical Support.
Technical Support.
corrupted.
Technical Support.
8502
9403
8501
9402
800C
810B
8ACA
8011
0300
0301
0302
0303
0304
0305
0306
DISABLE EAS ERR There was an error while clearing the EAS bit.
Verify that the tag that you are using supports this feature.
DISABLE_DEBG ERR If the problem persists, contact Technical Support.
ENABLE EAS ERR There was an error while setting the EAS bit.
Verify that the tag that you are using supports this feature.
ENABLE_DEBUG ERR If the problem persists, contact Technical Support.
ENCRYPT TAG ERR The data to be written to the tag was not encrypted properly.
ERASE TAG ERR If the problem persists, contact Technical Support.
EXIT TAGLOOP ERR Internal problem with the reader. If the problem persists, contact
Technical Support.
FILE NOT FOUND The specified file was not found on the application.
FLASH ERROR An error occurred reading or writing from the reader’s Flash
memory. If the problem persists, contact Technical Support.
810C
11/14/2008 RFID Programming Guide 58978L-008 Rev. A
FORMAT TAG ERR If the problem persists, contact Technical Support.
Page 56

Troubleshooting
56
RFID Error Codes and Messages
Table 6 • RFID Error and Status Message Definitions (Continued)
Error
Code
0048
0423
042F
042B
0424
0420
0430
8301
RFID Error or
Status Message
FPGA OLD The FPGA code is out of date. This would typically happen during
GEN2 BAD PC Internal problem with the reader. If the problem persists, contact
GEN2 ERROR Internal problem with the reader. If the problem persists, contact
GEN2 LOW PWR Internal problem with the reader. If the problem persists, contact
GEN2 MEM LOCKED Internal problem with the reader. If the problem persists, contact
GEN2 PROT OTHER Internal problem with the reader. If the problem persists, contact
GEN2 UNKNWN ERR Internal problem with the reader. If the problem persists, contact
GET APPLI ID ERR Internal problem with the reader. If the problem persists, contact
Description/Action Required
a reader firmware upgrade. Make sure you download the
appropriate version of reader firmware. If the problem persists,
contact Technical Support.
Technical Support.
Technical Support.
Technical Support.
Technical Support.
Technical Support.
Technical Support.
Technical Support.
9302
8401
8404
8108
8107
0046
0601
840A
800E
0409
GET DEFAULT ERR There was a problem reading a parameter from the non-volatile
memory of the reader. If the problem persists, contact Technical
Support.
GET FILE IDs ERR Internal problem with the reader. If the problem persists, contact
Technical Support.
GET FILE SET ERR Internal problem with the reader. If the problem persists, contact
Technical Support.
GET LOCK STA ERR The reader was unable to acquire the lock status from the tag.
GET TAG INFO ERR The reader was unable to acquire the information from the tag.
The reader may not contain information for the selected tag.
HARDWARE ERR If the problem persists, contact Technical Support.
ID BUFFER FULL The tag ID buf fer is full. If th e problem persists, contact Technical
Support.
INC VAL FILE ERR Internal problem with the reader. If the problem persists, contact
Technical Support.
INVALD SIGNATURE The HMAC written to the tag did not match the data and the key.
INVALID ADDR The RFID reader received a command to write to an invalid
address in the tag data address space. Make sure that the address
specified is within the scope of the tag data address space.
9005
58978L-008 Rev. A RFID Programming Guide 11/14/2008
INVALID ADDRESS The address specified for the command was invalid. If the
problem persists, contact Technical Support.
Page 57

RFID Error Codes and Messages
Table 6 • RFID Error and Status Message Definitions (Continued)
Troubleshooting
57
Error
Code
800F
010A
0109
9002
9003
9009
9006
0104
RFID Error or
Status Message
INVALID AUTH KEY The key number does not exist or is invalid for authentication with
INVALID BAUD Internal problem with the reader. If the problem persists, cont act
INVALID CMD The command does not exist or is invalid for the reader.
INVALID CMD The command does not exist or is invalid for the reader.
INVALID CRC Invalid CRC sent in the request to the reader. If the problem
INVALID DATA LEN The length of the data specified in the request was invalid for the
INVALID FLAGS The flags specified were invalid for the command specified. If the
INVALID FREQ The RFID reader received a command to set the frequency outside
Description/Action Required
a specific reader or tag.
Technical Support.
Internal problem with the reader. If the problem persists, cont act
Technical Support.
Internal problem with the reader. If the problem persists, cont act
Technical Support.
persists, contact Technical Support.
command specified. If the problem persists, contact Technical
Support.
problem persists, contact Technical Support.
of the supported range. If the problem persists, contact Technical
Support.
0500
8014
8013
9004
0101
OOOC
OOOD
0105
INVALID FREQ The RFID reader received a command to set the frequency outside
of the supported range. If the problem persists, contact Technical
Support.
INVALID KEY LEN The key length is not valid for the tag type, the command, or the
reader.
INVALID KEY NO. The key number does not exis t or is ou t of th e ran ge o f v ali d k eys.
INVALID MESS LEN The number of bytes sent to the reader was invalid for the
command or for the message length passed in. If the problem
persists, contact Technical Support.
INVALID OPCODE The opCode received by the RFID reader is invalid or not
supported with the current version of reader firmware. Make sure
you download the appropriate version of reader firmware. If the
problem persists, contact Technical Support.
INVALID PARAM The RFID reader received a valid command with an unsupported
or invalid value for one of the parameters. If the problem persists,
contact Technical Support.
INVALID PARAM The RFID reader received a valid command with an unsupported
or invalid value for one of the parameters. If the problem persists,
contact Technical Support.
11/14/2008 RFID Programming Guide 58978L-008 Rev. A
Page 58

Troubleshooting
58
RFID Error Codes and Messages
Table 6 • RFID Error and Status Message Definitions (Continued)
Error
Code
0402
8001
0045
0408
810F
9007
RFID Error or
Status Message
INVALID PROTOC The RFID reader received a command for a protocol value that is
INVALID TAG TYPE The tag type was not valid for the command specified.
INVALID VAR. Invalid configuration variable. Internal problem with the re ader . If
INVALID WR DATA In EPC 0+, the first two bits determine the tag ID length. If the
INVENTORY DONE Status message indicating that the reader exited the Inventory
INVLD ASCII BYTE A non-ASCII byte value was sent in an ASCII mode command. If
Description/Action Required
not supported with the current version of reader firmware. Make
sure you have the right tag type selected and that you are using a
tag that is supported by your printer.
Make sure that you are using the right tag type for your operation.
If the problem persists, contact Technical Support.
the problem persists, contact Technical Support.
first two bits are 0b00, then the tag ID must be 96 bits. Otherwise,
the tag ID is 64 bits.
Make sure that the first two bits have the correct values,
depending on the tag ID length.
mode. No action required.
the problem persists, contact Technical Support.
9008
8109
0029
9101
8602
0403
0039
003A
INVLD NO. BLOCKS The number of blocks field in the request was invalid for the
command specified. If the problem persists, contact Technical
Support.
KILL TAG ERR If the problem persists, contact Technical Support.
LISTEN BUSY Listen before transmit; all frequencies occupied. Internal problem
with the reader. If the problem persists, contact T ec hnical Su pport.
LOAD DEFAULT ERR The reader was unable to successfully load its default parameters.
If the problem persists, contact Technical Support.
LOAD KEY ERR If the problem persists, contact Technical Support.
LOCK ERROR The lock process failed during a write tag data for an ISO 18 000-
6B tag. The write tag command passed, but the lock did not. This
could indicate a bad tag.
Repeat the process with another RFID tag. Make sure that the tag
is placed within the RF field.
LOCKED BLOCK Attempt to write to a read-only tag or to a locked bloc k. Make sure
you have the right tag type selected and that you are u sing a tag
that is supported by your printer. Ensure that the block that you are
trying to write to is not already locked.
LOST LOCK UHF synthesizer error. Internal problem with the reader. If the
problem persists, contact Technical Support.
0042
58978L-008 Rev. A RFID Programming Guide 11/14/2008
MEMORY ERR Non-volatile memory data element does not exist or was not found
when requesting a read of a specific element in non-volatile
memory. If the problem persists, contact Technical Support.
Page 59

RFID Error Codes and Messages
Table 6 • RFID Error and Status Message Definitions (Continued)
Troubleshooting
59
Error
Code
0003
8405
1237
8010
0404
8012
0044
RFID Error or
Status Message
MESSAGE SYNCH Point-to-point only. Current message head or “}” character
MOD FILE SET ERR Internal problem with the reader. If the problem persists, contact
MULTIPLE TAGS More than one RFID tag was detected in the RF field.
NO APPLI PRESENT The application specified could not be found.
NO DATA READ The RFID tag used failed or does not have the correct CRC.
NO FILE SELECTED The command requires a file, but none was selected.
NO NVM PRESENT Internal problem with the reader. If the problem persists, contact
Description/Action Required
interrupted a previous message.
Turn the printer power off (
printer power on (
Support.
Technical Support.
Make sure only one label is in the RF field and that another tag is
not elsewhere in the field. Make sure that the labels meet
transponder placement specifications.
Try to read a few other tags. If the problem persists, contact
Technical Support.
Technical Support.
I). If the problem persists, contact Technical
O). W ait ten seconds, and then turn the
0401
0035
0036
NO PROTOCOL The RFID reader received a command to perform a protocol
command, but no protocol was initially set. The reader powers up
with no protocols set.
Make sure you have the right tag type selected and that you are
using a tag that is supported by your printer.
NO RF FIELD Internal problem with the reader. If the problem persists, contact
Technical Support.
NO TAG
NO TAG FOUND
No RFID tag was detected in the RF field. Several things can
cause this error:
• No acceptable RFID tag is in the RF field. This can happen if an
• The read/write power being used is too low.
• The RFID tag is weak or dead.
Retry with another RFID tag. Make sure you have the right tag
type selected and that you are using a tag that is supported by yo ur
printer. If the problem persists, contact Technical Support.
Note • This error message varies by reader type.
RFID label is present but the transponder is not placed correctly
within the label or if the wrong tag type is used.
11/14/2008 RFID Programming Guide 58978L-008 Rev. A
Page 60

Troubleshooting
60
RFID Error Codes and Messages
Table 6 • RFID Error and Status Message Definitions (Continued)
Error
Code
0400
8002
RFID Error or
Status Message
NO TAG
NO TAG FOUND
NO TAG
NO TAG FOUND
Description/Action Required
Note • This error message varies by reader type.
No RFID tag was detected in the RF field. Several things can
cause this error:
• No acceptable RFID tag is in the RF field. This can happen if an
RFID label is present but the transponder is not placed correctly
within the label or if the wrong tag type is used.
• The read/write power being used is too low.
• The RFID tag is weak or dead.
Retry with another RFID tag. Make sure you have the right tag
type selected and that you are using a tag that is supported by yo ur
printer. If the problem persists, contact Technical Support.
Note • This error message varies by reader type.
No RFID tag was detected in the RF field. Several things can
cause this error:
• No acceptable RFID tag is in the RF field. This can happen if an
RFID label is present but the transponder is not placed correctly
within the label or if the wrong tag type is used.
• The read/write power being used is too low.
• The RFID tag is weak or dead.
Retry with another RFID tag. Make sure you have the right tag
type selected and that you are using a tag that is supported by yo ur
printer. If the problem persists, contact Technical Support.
0407
NOT IMPLEMENTED The reader received a command that is not supported by the tag
type.
Make sure that you have the latest reader firmware, that you have
the right tag type selected, and that you are using a tag that is
supported by your printer. If the problem persists, contact
Technical Support.
0603
NUM IDS TOO LG Internal problem with the reader. If the problem persists, contact
Technical Support.
0043
NVM FULL Internal problem with the reader. If you are upgrading reader
firmware, try resending the file. If the problem persists, contact
Technical Support.
58978L-008 Rev. A RFID Programming Guide 11/14/2008
Page 61

RFID Error Codes and Messages
Table 6 • RFID Error and Status Message Definitions (Continued)
Troubleshooting
61
Error
Code
0102
0055
F004
0103
0106
RFID Error or
Status Message
OPCODE UNAVAIL The opCode received by the RFID reader is invalid or not
OVERWRITE EPC Error trying to overwrite a valid EPC code.
POWER SELECT ERR The printer could not verify that the intended power setting has
POWER TOO HI The RFID reader received a command to set the read or write
POWER TOO LOW The RFID reader received a command to set the read or write
Description/Action Required
supported with the current version of reader firmware.
1. Make sure you download the appropriate version of reader
firmware.
2. Turn the printer power off (
turn the printer power on (
If the problem persists, contact Technical Support.
Internal problem with the reader. If the problem persists, cont act
Technical Support.
been set successfully. If the problem persists, contact Technical
Support.
power to a level that is higher than the RFID reader supports.
Check the versions of the reader firmware and printer firmware.
You may need to download different versions.
power to a level that is lower than the RFID reader supports.
Check the versions of the reader firmware and printer firmware.
You may need to download different versions.
O). Wait ten seconds, and then
I).
0022
1234
F002
— RDR ERR
8505
8102
8507
8406
RAM ERROR Internal problem with the reader. If the problem persists, contact
RDR COM TIMEOUT The printer was not able to communicate with the reader. If the
RDR COM TIMEOUT The printer was not able to communicate with the reader. If the
READ AFI ERR There was an error reading the AFI byte.
READ DATA ERR This can occur when one of a number of RFID operations fails.
READ DSFID ERR There was an error reading the DSFID byte.
READ FILE ERR Internal problem with the reade r. If the problem persists, cont act
xxxx
Technical Support.
problem persists, contact Technical Support.
problem persists, contact Technical Support.
Internal problem with the reader. If the problem persists, cont act
Technical Support.
Verify that the tag that you are using supports this feature. If the
problem persists, contact Technical Support.
Check that the tag is good, and repeat the process with another
RFID label. If the problem persists, contact Technical Support.
Verify that the tag that you are using supports this feature. If the
problem persists, contact Technical Support.
Technical Support.
11/14/2008 RFID Programming Guide 58978L-008 Rev. A
Page 62

Troubleshooting
62
RFID Error Codes and Messages
Table 6 • RFID Error and Status Message Definitions (Continued)
Error
Code
9201
0602
9102
810A
0031
0000
0023
800C
RFID Error or
Status Message
READ SYS ERR There was a problem reading a parameter from the non-volatile
REPEATED ID One of the protocols is trying to add an existing tag ID to the
RESET DEVICE ERR The reader was unable to successfully reset the reader. If the
REVIVE TAG ERR If the problem persists, contact Technical Support.
RF SECTION ERR Radio controller does not respond or general RF section failure.
RFID OK Normal operation.
ROM ERROR Internal problem with the reader. If the problem persists, contact
R-T DATARATE ERR The reader to tag data bit rate is not supported by the reader, the
Description/Action Required
memory of the reader. If the problem persists, contact Technical
Support.
buffer.
Internal problem with the reader. If the problem persists, cont act
Technical Support.
problem persists, contact Technical Support.
Internal problem with the reader. If the problem persists, cont act
Technical Support.
Technical Support.
tag, or both.
0051
0050
0027
002A
0028
8503
8302
RX R/T FAIL Receiver tuning runtime failure.
Internal problem with the reader. If the problem persists, cont act
Technical Support.
RX TUNE FAIL Receiver tuning training failure.
Internal problem with the reader. If the problem persists, cont act
Technical Support.
RXD POWER HI RXD reflective power too high.
Check antenna or cable connection. If the problem persists,
contact Technical Support.
RXD POWER MAX RXD reflective power max fault.
Internal problem with the reader. If the problem persists, cont act
Technical Support.
RXD WARNING RXD reflective power warning level. Occurs at –10 dBm.
Internal problem with the reader. If the problem persists, cont act
Technical Support.
SCAN EAS ERR The reader did not detect an EAS code in the field.
Verify that the tag that you are using supports this fea ture and that
the EAS bit is enabled.
SELECT APPLI ERR Internal problem with the reader. If the problem persists, contact
Technical Support.
8402
58978L-008 Rev. A RFID Programming Guide 11/14/2008
SELECT FILE ERR Internal problem with the reader. If the problem persists, contact
Technical Support.
Page 63

RFID Error Codes and Messages
Table 6 • RFID Error and Status Message Definitions (Continued)
Troubleshooting
63
Error
Code
8101
002F
8202
0024
000E
000F
RFID Error or
Status Message
SELECT TAG ERR The reader failed to select a specified tag in the RF field.
SELF TST ERR Self-test error.
SEND PASSWRD ERR Internal problem with the reader. If the problem persists, contact
SERIAL # ERR Serial number chip error.
SERIAL ERROR 1 High level serial error 1.
SERIAL ERROR 2 High level serial error 2.
Description/Action Required
Verify that a tag is within the field and that the current tag type is
valid with the printer firmware (see Table 9, Supported Tag Types
and Default Values, on page 111).
Internal problem with the reader. If the problem persists, cont act
Technical Support.
Technical Support.
Internal problem with the reader. If the problem persists, cont act
Technical Support.
Internal problem with the reader. If the problem persists, cont act
Technical Support.
Internal problem with the reader. If the problem persists, cont act
Technical Support.
0011
9301
810D
8106
8601
7F00
0041
040A
SERIAL OVERFLW Serial overflow error.
Internal problem with the reader. If the problem persists, cont act
Technical Support.
SET DEFAULT ERR There was a problem writing a parameter to the non-volatile
memory of the reader. If the problem persists, contact Technical
Support.
SET RDR DAT RATE Internal problem with the reader. If the problem persists, contact
Technical Support.
SET TAG DAT RATE If the problem persists, contact Technical Support.
STORE KEY ERR If the problem persists, contact Technical Support.
SYS UNKNWN ERR Internal problem with the reader. If the problem persists, contact
Technical Support.
TAG DATA LOST In serial polled or RF continuous mode, incoming new tag data
overwrote old tag data between polls.
Internal problem with the reader. If the problem persists, cont act
Technical Support.
TAG ERROR Internal problem with the reader. If the problem persists, contact
Technical Support.
11/14/2008 RFID Programming Guide 58978L-008 Rev. A
Page 64

Troubleshooting
64
RFID Error Codes and Messages
Table 6 • RFID Error and Status Message Definitions (Continued)
Error
Code
0600
8004
8006
0038
8007
0021
0107
RFID Error or
Status Message
TAG ID FAULT The reader received a command to get a certain number of tag IDs
TAG INTEGRITY ERR Response from the tag failed the CRC check.
TAG NOT AUTHENTC An operation could not be performed on the tag because the tag
TAG NOT FOUND Good tag data is available, but the tag specifically requested was
TAG NOT IN FIELD The tag specified was not in the RFID field.
TEMP ERROR Temperature sensor error.
TIMEOUT TO LONG Internal problem with the reader. If the problem persists, contact
Description/Action Required
from the tag ID buffer . The re ader contains less tag IDs stored in
its tag ID buffer than the number the host sent.
Internal problem with the reader. If the problem persists, cont act
Technical Support.
was not authenticated.
not found (^RT, ^WT commands).
Repeat the process with another RFID label. If the problem
persists, contact Technical Support.
Internal problem with the reader. If the problem persists, cont act
Technical Support.
Technical Support.
7F01
800B
9001
1236
003B
8504
8103
TM ASSERT FAIL Internal problem with the reader. If the problem persists, contact
Technical Support.
T-R DATARATE ERR The tag to reader data bit rate is not supported by the reader, the
tag, or both.
UNKNOWN ERR An unidentified error occurred.
If the problem persists, contact Technical Support.
VERIFY FAIL In ternal problem with the reader. If the problem persists, contact
Technical Support.
VERIFY FAILED The write operation could not be verified because the tag data
could not be read.
Check that the tag is good, and repeat the process with another
RFID label. If the problem persists, contact Technical Support.
WRITE AFI ERR There was an error writing to the AFI byte.
Verify that the tag that you are using supports this fea ture and that
they byte is unlocked. If the problem persists, contact Technical
Support.
WRITE DATA ERR This can occur when one of a number of RFID operations fails.
Check that the tag is good, and repeat the process with another
RFID label. If the problem persists, contact Technical Support.
58978L-008 Rev. A RFID Programming Guide 11/14/2008
Page 65

RFID Error Codes and Messages
Table 6 • RFID Error and Status Message Definitions (Continued)
Troubleshooting
65
Error
Code
8506
0406
8407
9202
RFID Error or
Status Message
Description/Action Required
WRITE DSFID ERR There was an error writing to the DSFID byte.
Verify that the tag that you are using supports this fea ture and that
they byte is unlocked. If the problem persists, contact Technical
Support.
WRITE FAILED This can occur when one of a number of RFID operations fails.
Check that the tag is good, and repeat the process with another
RFID label. If the problem persists, contact Technical Support.
WRITE FILE ERR Internal problem with the reader. If the problem persists, contact
Technical Support.
WRITE SYS ERR There was a problem writing a parameter to the non-volatile
memory of the reader. If the problem persists, contact Technical
Support.
11/14/2008 RFID Programming Guide 58978L-008 Rev. A
Page 66

Troubleshooting
66
RFID Error Codes and Messages
Error Codes
Table 7 shows the possib le error codes, the corresponding error or status message, and the
action required (if any).
Table 7 • RFID Error Code Definitions
Error
Code
— RDR ERR
0000
0001
0003
0004
0005
0008
0009
Status Message
RFID OK Normal operation.
BAD MESSAGE Internal communications problem with the reader. If the problem
MESSAGE SYNCH Point-to-point only. Current message head or “}” character
BAD CRC The last valid message string had a bad Cyc lic Redundancy Check
BAD DATA The reader received bad data from the printer. If the problem
BAD MSG HEAD Internal communications problem with the reader. If the problem
BAD MSG TAIL Internal communications problem with the reader. If the problem
RFID Error or
xxxx
Description/Action Required
Internal problem with the reader. If the problem persists, cont act
Technical Support.
persists, contact Technical Support.
interrupted a previous message.
Turn the printer power off (
printer power on (
Support.
(CRC). An integrity check of the reader firmware failed. If the
problem persists, contact Technical Support.
persists, contact Technical Support.
persists, contact Technical Support.
persists, contact Technical Support.
I). If the problem persists, contact Technical
O). W ait ten seconds, and then turn the
0010
0011
000A
000B
OOOC
OOOD
000E
58978L-008 Rev. A RFID Programming Guide 11/14/2008
CMD INHIBITED Internal communications problem with the reader. If the problem
persists, contact Technical Support.
SERIAL OVERFLW Serial overflow error.
Internal problem with the reader. If the problem persists, cont act
Technical Support.
BAD COMMAND The reader received a bad command from the printer. If the
problem persists, contact Technical Support.
BAD SUBCMD Internal communications problem with the reader. If the problem
persists, contact Technical Support.
INVALID PARAM The RFID reader received a valid command with an unsupported
or invalid value for one of the parameters. If the problem persists,
contact Technical Support.
SERIAL ERROR 1 High level serial error 1.
Internal problem with the reader. If the problem persists, cont act
Technical Support.
Page 67

RFID Error Codes and Messages
Table 7 • RFID Error Code Definitions (Continued)
Troubleshooting
67
Error
Code
000F
0021
0022
0023
0024
0025
0026
0027
RFID Error or
Status Message
SERIAL ERROR 2 High level serial error 2.
TEMP ERROR Temperature sensor error.
RAM ERROR Internal problem with the reader. If the problem persists, contact
ROM ERROR Internal problem with the reader. If the problem persists, contact
SERIAL # ERR Serial number chip error.
ANT. BAD/GONE The RFID reader cannot detect the RFID antenna (coupler), or the
BAD ANT.MUX Internal problem with the reader. Contact Technical Support.
RXD POWER HI RXD reflective power too high.
Description/Action Required
Internal problem with the reader. If the problem persists, cont act
Technical Support.
Internal problem with the reader. If the problem persists, cont act
Technical Support.
Technical Support.
Technical Support.
Internal problem with the reader. If the problem persists, cont act
Technical Support.
antenna (coupler) does not work. Contact Technical Support.
Check antenna or cable connection. If the problem persists,
contact Technical Support.
0028
0029
002A
002F
0031
0033
0035
RXD WARNING RXD reflective power warning level. Occurs at –10 dBm.
Internal problem with the reader. If the problem persists, cont act
Technical Support.
LISTEN BUSY Listen before transmit; all frequencies occupied. Internal problem
with the reader. If the problem persists, contact T ec hnical Su pport.
RXD POWER MAX RXD reflective power max fault.
Internal problem with the reader. If the problem persists, cont act
Technical Support.
SELF TST ERR Self-test error.
Internal problem with the reader. If the problem persists, cont act
Technical Support.
RF SECTION ERR Radio controller does not respond or general RF section failure.
Internal problem with the reader. If the problem persists, cont act
Technical Support.
ANT FAILURE Antenna failure. Contact Technical Support.
NO RF FIELD Internal problem with the reader. If the problem persists, contact
Technical Support.
11/14/2008 RFID Programming Guide 58978L-008 Rev. A
Page 68

Troubleshooting
68
RFID Error Codes and Messages
Table 7 • RFID Error Code Definitions (Continued)
Error
Code
0036
0037
0038
RFID Error or
Status Message
NO TAG
NO TAG FOUND
DATA CRC An integrity check of the reader firmware failed. If the problem
TAG NOT FOUND Good tag data is available, but the tag specifically requested was
Description/Action Required
Note • This error message varies by reader type.
No RFID tag was detected in the RF field. Several things can
cause this error:
• No acceptable RFID tag is in the RF field. This can happen if an
RFID label is present but the transponder is not placed correctly
within the label or if the wrong tag type is used.
• The read/write power being used is too low.
• The RFID tag is weak or dead.
Retry with another RFID tag. Make sure you have the right tag
type selected and that you are using a tag that is supported by yo ur
printer. If the problem persists, contact Technical Support.
persists, contact Technical Support.
not found (^RT, ^WT commands).
Repeat the process with another RFID label. If the problem
persists, contact Technical Support.
0039
003A
003B
0041
0042
0043
0044
LOCKED BLOCK Attempt to write to a read-only tag or to a locked bloc k. Make sure
you have the right tag type selected and that you are u sing a tag
that is supported by your printer. Ensure that the block that you are
trying to write to is not already locked.
LOST LOCK UHF synthesizer error. Internal problem with the reader. If the
problem persists, contact Technical Support.
VERIFY FAILED The write operation could not be verified because the tag data
could not be read.
Check that the tag is good, and repeat the process with another
RFID label. If the problem persists, contact Technical Support.
TAG DATA LOST In serial polled or RF continuous mode, incoming new tag data
overwrote old tag data between polls.
Internal problem with the reader. If the problem persists, cont act
Technical Support.
MEMORY ERR Non-volatile memory data element does not exist or was not found
when requesting a read of a specific element in non-volatile
memory. If the problem persists, contact Technical Support.
NVM FULL Internal problem with the reader. If you are upgrading reader
firmware, try resending the file. If the problem persists, contact
Technical Support.
NO NVM PRESENT Internal problem with the reader. If the problem persists, contact
Technical Support.
58978L-008 Rev. A RFID Programming Guide 11/14/2008
Page 69

RFID Error Codes and Messages
Table 7 • RFID Error Code Definitions (Continued)
Troubleshooting
69
Error
Code
0045
0046
0048
0050
0051
0052
0053
0054
RFID Error or
Status Message
INVALID VAR. Invalid configuration variable. Internal problem with the re ader . If
HARDWARE ERR If the problem persists, contact Technical Support.
FPGA OLD The FPGA code is out of date. This would typically happen during
RX TUNE FAIL Receiver tuning training failure.
RX R/T FAIL Receiver tuning runtime failure.
BAD PASSCODE Bad passcode for kill tag function.
BAUD ERR Internal problem with the reader. If the problem persists, contact
CMD FAIL Internal communications problem with the reader. If the problem
Description/Action Required
the problem persists, contact Technical Support.
a reader firmware upgrade. Make sure you download the
appropriate version of reader firmware. If the problem persists,
contact Technical Support.
Internal problem with the reader. If the problem persists, cont act
Technical Support.
Internal problem with the reader. If the problem persists, cont act
Technical Support.
Technical Support.
persists, contact Technical Support.
0055
0100
0101
0102
OVERWRITE EPC Error trying to overwrite a valid EPC code.
Internal problem with the reader. If the problem persists, cont act
Technical Support.
DATA AMOUNT ERR Two situations can result in this error:
• The data length in a message to the RFID reader from the
printer is less than the number of arguments in the message.
• The data length is greater than the number of arguments. The
reader will wait indefinitely until it receives all of the data
specified in the data length field.
If the problem persists, contact Technical Support.
INVALID OPCODE The opCode received by the RFID reader is invalid or not
supported with the current version of reader firmware. Make sure
you download the appropriate version of reader firmware. If the
problem persists, contact Technical Support.
OPCODE UNAVAIL The opCode received by the RFID reader is invalid or not
supported with the current version of reader firmware.
1. Make sure you download the appropriate version of reader
firmware.
2. Turn the printer power off (
turn the printer power on (
If the problem persists, contact Technical Support.
O). Wait ten seconds, and then
I).
11/14/2008 RFID Programming Guide 58978L-008 Rev. A
Page 70

Troubleshooting
70
RFID Error Codes and Messages
Table 7 • RFID Error Code Definitions (Continued)
Error
Code
0103
0104
0105
0106
0107
0109
RFID Error or
Status Message
POWER TOO HI The RFID reader received a command to set the read or write
INVALID FREQ The RFID reader received a command to set the frequency outside
INVALID PARAM The RFID reader received a valid command with an unsupported
POWER TOO LOW The RFID reader received a command to set the read or write
TIMEOUT TO LONG Internal problem with the reader. If the problem persists, contact
INVALID CMD The command does not exist or is invalid for the reader.
Description/Action Required
power to a level that is higher than the RFID reader supports.
Check the versions of the reader firmware and printer firmware.
You may need to download different versions.
of the supported range. If the problem persists, contact Technical
Support.
or invalid value for one of the parameters. If the problem persists,
contact Technical Support.
power to a level that is lower than the RFID reader supports.
Check the versions of the reader firmware and printer firmware.
You may need to download different versions.
Technical Support.
Internal problem with the reader. If the problem persists, cont act
Technical Support.
010A
0200
0201
0300
0301
0302
0303
0304
0305
0306
INVALID BAUD Internal problem with the reader. If the problem persists, cont act
Technical Support.
BAD IMAGE CRC The RFID reader received a command to erase some part of the
flash memory. This typically would happen during a reader
firmware upgrade. Make sure that you download the appropriate
version of reader firmware. If the problem persists, contact
Technical Support.
BAD APP END ADD The RFID reader received a command to erase some part of the
flash memory. This typically would happen during a reader
firmware upgrade. Make sure that you download the appropriate
version of reader firmware. If the problem persists, contact
Technical Support.
FLASH ERROR An error occurred reading or writing from the reader’s Flash
memory. If the problem persists, contact Technical Support.
58978L-008 Rev. A RFID Programming Guide 11/14/2008
Page 71

RFID Error Codes and Messages
Table 7 • RFID Error Code Definitions (Continued)
Troubleshooting
71
Error
Code
0400
0401
0402
RFID Error or
Status Message
NO TAG
NO TAG FOUND
NO PROTOCOL The RFID reader received a command to perform a protocol
INVALID PROTOC The RFID reader received a command for a protocol value that is
Description/Action Required
Note • This error message varies by reader type.
No RFID tag was detected in the RF field. Several things can
cause this error:
• No acceptable RFID tag is in the RF field. This can happen if an
RFID label is present but the transponder is not placed correctly
within the label or if the wrong tag type is used.
• The read/write power being used is too low.
• The RFID tag is weak or dead.
Retry with another RFID tag. Make sure you have the right tag
type selected and that you are using a tag that is supported by yo ur
printer. If the problem persists, contact Technical Support.
command, but no protocol was initially set. The reader powers up
with no protocols set.
Make sure you have the right tag type selected and that you are
using a tag that is supported by your printer.
not supported with the current version of reader firmware. Make
sure you have the right tag type selected and that you are using a
tag that is supported by your printer.
0403
0404
0405
0406
0407
LOCK ERROR The lock process failed during a write tag data for an ISO 18 000-
6B tag. The write tag command passed, but the lock did not. This
could indicate a bad tag.
Repeat the process with another RFID tag. Make sure that the tag
is placed within the RF field.
NO DATA READ The RFID tag used failed or does not have the correct CRC.
Try to read a few other tags. If the problem persists, contact
Technical Support.
AFE NOT ON Internal problem with the reader. The Analog Front End is turned
off. Contact T echnical Support.
WRITE FAILED This can occur when one of a number of RFID operations fails.
Check that the tag is good, and repeat the process with another
RFID label. If the problem persists, contact Technical Support.
NOT IMPLEMENTED The reader received a command that is not supported by the tag
type.
Make sure that you have the latest reader firmware, that you have
the right tag type selected, and that you are using a tag that is
supported by your printer. If the problem persists, contact
Technical Support.
11/14/2008 RFID Programming Guide 58978L-008 Rev. A
Page 72

Troubleshooting
72
RFID Error Codes and Messages
Table 7 • RFID Error Code Definitions (Continued)
Error
Code
0408
0409
040A
040B
0420
0423
0424
RFID Error or
Status Message
INVALID WR DATA In EPC 0+, the first two bits determine the tag ID length. If the
INVALID ADDR The RFID reader received a command to write to an invalid
TAG ERROR Internal problem with the reader. If the problem persists, contact
DATA TOO LARGE Internal problem with the reader. If the problem persists, contact
GEN2 PROT OTHER Internal problem with the reader. If the problem persists, contact
GEN2 BAD PC Internal problem with the reader. If the problem persists, contact
GEN2 MEM LOCKED Internal problem with the reader. If the problem persists, contact
Description/Action Required
first two bits are 0b00, then the tag ID must be 96 bits. Otherwise,
the tag ID is 64 bits.
Make sure that the first two bits have the correct values,
depending on the tag ID length.
address in the tag data address space. Make sure that the address
specified is within the scope of the tag data address space.
Technical Support.
Technical Support.
Technical Support.
Technical Support.
Technical Support.
042B
042F
0430
0500
0600
0601
0602
GEN2 LOW PWR Internal problem with the reader. If the problem persists, contact
Technical Support.
GEN2 ERROR Internal problem with the reader. If the problem persists, contact
Technical Support.
GEN2 UNKNWN ERR Internal problem with the reader. If the problem persists, contact
Technical Support.
INVALID FREQ The RFID reader received a command to set the frequency outside
of the supported range. If the problem persists, contact Technical
Support.
TAG ID FAULT The reader received a command to get a certain number of tag IDs
from the tag ID buffer . The re ader contains less tag IDs stored in
its tag ID buffer than the number the host sent.
Internal problem with the reader. If the problem persists, cont act
Technical Support.
ID BUFFER FULL The tag ID buf fer is full. If th e problem persists, contact Technical
Support.
REPEATED ID One of the protocols is trying to add an existing tag ID to the
buffer.
Internal problem with the reader. If the problem persists, cont act
Technical Support.
0603
58978L-008 Rev. A RFID Programming Guide 11/14/2008
NUM IDS TOO LG Internal problem with the reader. If the problem persists, contact
Technical Support.
Page 73

RFID Error Codes and Messages
Table 7 • RFID Error Code Definitions (Continued)
Troubleshooting
73
Error
Code
1234
1236
1237
7F00
7F01
8001
8002
RFID Error or
Status Message
RDR COM TIMEOUT The printer was not able to communicate with the reader. If the
VERIFY FAIL In ternal problem with the reader. If the problem persists, contact
MULTIPLE TAGS More than one RFID tag was detected in the RF field.
SYS UNKNWN ERR Internal problem with the reader. If the problem persists, contact
TM ASSERT FAIL Internal problem with the reader. If the problem persists, contact
INVALID TAG TYPE The tag type was not valid for the command specified.
NO TAG
NO TAG FOUND
Description/Action Required
problem persists, contact Technical Support.
Technical Support.
Make sure only one label is in the RF field and that another tag is
not elsewhere in the field. Make sure that the labels meet
transponder placement specifications.
Technical Support.
Technical Support.
Make sure that you are using the right tag type for your operation.
If the problem persists, contact Technical Support.
Note • This error message varies by reader type.
No RFID tag was detected in the RF field. Several things can
cause this error:
• No acceptable RFID tag is in the RF field. This can happen if an
RFID label is present but the transponder is not placed correctly
within the label or if the wrong tag type is used.
• The read/write power being used is too low.
• The RFID tag is weak or dead.
Retry with another RFID tag. Make sure you have the right tag
type selected and that you are using a tag that is supported by yo ur
printer. If the problem persists, contact Technical Support.
8003
8004
8005
8006
8007
800B
800C
800C
11/14/2008 RFID Programming Guide 58978L-008 Rev. A
COLLISION ERR Multiple tags in the field have the same tag ID.
TAG INTEGRITY ERR Response from the tag failed the CRC check.
BLOCK(S) LOCKED A write operation could not be performed because a block was
locked.
TAG NOT AUTHENTC An operation could not be performed on the tag because the tag
was not authenticated.
TAG NOT IN FIELD The tag specified was not in the RFID field.
T-R DATARATE ERR The tag to reader data bit rate is not supported by the reader, the
tag, or both.
ENCRYPT TAG ERR The data to be written to the tag was not encrypted properly.
R-T DATARATE ERR The reader to tag data bit rate is not supported by the reader, the
tag, or both.
Page 74

Troubleshooting
74
RFID Error Codes and Messages
Table 7 • RFID Error Code Definitions (Continued)
Error
Code
800D
800E
800F
8010
8011
8012
8013
8014
8101
8102
RFID Error or
Status Message
DECRYPT TAG ERR The data read from the tag was not decrypted properly or was
INVALD SIGNATURE The HMAC written to the tag did not match the data and the key.
INVALID AUTH KEY The key number does not exist or is invalid for authentication with
NO APPLI PRESENT The application specified could not be found.
FILE NOT FOUND The specified file was not found on the application.
NO FILE SELECTED The command requires a file, but none was selected.
INVALID KEY NO. The key number does not exis t or is ou t of th e ran ge o f v ali d k eys.
INVALID KEY LEN The key length is not valid for the tag type, the command, or the
SELECT TAG ERR The reader failed to select a specified tag in the RF field.
READ DATA ERR This can occur when one of a number of RFID operations fails.
Description/Action Required
corrupted.
a specific reader or tag.
reader.
Verify that a tag is within the field and that the current tag type is
valid with the printer firmware (see Table 9, Supported Tag Types
and Default Values, on page 111).
Check that the tag is good, and repeat the process with another
RFID label. If the problem persists, contact Technical Support.
8103
8104
8105
8106
8107
8108
8109
810A
810B
810C
810D
810F
8201
WRITE DATA ERR This can occur when one of a number of RFID operations fails.
Check that the tag is good, and repeat the process with another
RFID label. If the problem persists, contact Technical Support.
ACTIVATE TAG ERR If the problem persists, contact Technical Support.
DEACTIV. TAG ERR If the problem persists, contact Technical Support.
SET TAG DAT RATE If the problem persists, contact Technical Support.
GET TAG INFO ERR The reader was unable to acquire the information from the tag.
The reader may not contain information for the selected tag.
GET LOCK STA ERR The reader was unable to acquire the lock status from the tag.
KILL TAG ERR If the problem persists, contact Technical Support.
REVIVE TAG ERR If the problem persists, contact Technical Support.
ERASE TAG ERR If the problem persists, contact Technical Support.
FORMAT TAG ERR If the problem persists, contact Technical Support.
SET RDR DAT RATE Internal problem with the reader. If the problem persists, contact
Technical Support.
INVENTORY DONE Status message indicating that the reader exited the Inventory
mode. No action required.
AUTHEN TAG ERR Tag not authenticated.
58978L-008 Rev. A RFID Programming Guide 11/14/2008
Page 75

RFID Error Codes and Messages
Table 7 • RFID Error Code Definitions (Continued)
Troubleshooting
75
Error
Code
8202
8301
8302
8303
8401
8402
8403
8404
8405
RFID Error or
Status Message
SEND PASSWRD ERR Internal problem with the reader. If the problem persists, contact
GET APPLI ID ERR Internal problem with the reader. If the problem persists, contact
SELECT APPLI ERR Internal problem with the reader. If the problem persists, contact
CREATE APPLI ERR Internal problem with the reader. If the problem persists, contact
GET FILE IDs ERR Internal problem with the reader. If the problem persists, contact
SELECT FILE ERR Internal problem with the reader. If the problem persists, contact
CREATE FILE ERR Internal problem with the reader. If the problem persists, contact
GET FILE SET ERR Internal problem with the reader. If the problem persists, contact
MOD FILE SET ERR Internal problem with the reader. If the problem persists, contact
Description/Action Required
Technical Support.
Technical Support.
Technical Support.
Technical Support.
Technical Support.
Technical Support.
Technical Support.
Technical Support.
Technical Support.
8406
8407
8408
8409
840A
840B
8501
8502
8503
READ FILE ERR Internal problem with the reade r. If the problem persists, cont act
Technical Support.
WRITE FILE ERR Internal problem with the reader. If the problem persists, contact
Technical Support.
DELETE FILE ERR Internal problem with the reader. If the problem persists, contact
Technical Support.
CLEAR FILE ERR Internal problem with the reader. If the problem persists, contact
Technical Support.
INC VAL FILE ERR Internal problem with the reader. If the problem persists, contact
Technical Support.
DEC VAL FILE ERR Internal problem with the reader. If the problem persists, contact
Technical Support.
ENABLE EAS ERR There was an error while setting the EAS bit.
Verify that the tag that you are using supports this feature.
DISABLE EAS ERR There was an error while clearing the EAS bit.
Verify that the tag that you are using supports this feature.
SCAN EAS ERR The reader did not detect an EAS code in the field.
Verify that the tag that you are using supports this fea ture and that
the EAS bit is enabled.
11/14/2008 RFID Programming Guide 58978L-008 Rev. A
Page 76

Troubleshooting
76
RFID Error Codes and Messages
Table 7 • RFID Error Code Definitions (Continued)
Error
Code
8504
8505
8506
8507
8508
8509
8601
RFID Error or
Status Message
WRITE AFI ERR There was an error writing to the AFI byte.
READ AFI ERR There was an error reading the AFI byte.
WRITE DSFID ERR There was an error writing to the DSFID byte.
READ DSFID ERR There was an error reading the DSFID byte.
CREDIT VALUE ERR If the problem persists, contact Technical Support.
DEBIT VALUE ERR If the problem persists, contact Technical Support.
STORE KEY ERR If the problem persists, contact Technical Support.
Description/Action Required
Verify that the tag that you are using supports this fea ture and that
they byte is unlocked. If the problem persists, contact Technical
Support.
Verify that the tag that you are using supports this feature. If the
problem persists, contact Technical Support.
Verify that the tag that you are using supports this fea ture and that
they byte is unlocked. If the problem persists, contact Technical
Support.
Verify that the tag that you are using supports this feature. If the
problem persists, contact Technical Support.
8602
8ACA
9001
9002
9003
9004
9005
9006
9007
9008
LOAD KEY ERR If the problem persists, contact Technical Support.
EXIT TAGLOOP ERR Internal problem with the reader. If the problem persists, contact
Technical Support.
UNKNOWN ERR An unidentified error occurred.
If the problem persists, contact Technical Support.
INVALID CMD The command does not exist or is invalid for the reader.
Internal problem with the reader. If the problem persists, cont act
Technical Support.
INVALID CRC Invalid CRC sent in the request to the reader. If the problem
persists, contact Technical Support.
INVALID MESS LEN The number of bytes sent to the reader was invalid for the
command or for the message length passed in. If the problem
persists, contact Technical Support.
INVALID ADDRESS The address specified for the command was invalid. If the
problem persists, contact Technical Support.
INVALID FLAGS The flags specified were invalid for the command specified. If the
problem persists, contact Technical Support.
INVLD ASCII BYTE A non-ASCII byte value was sent in an ASCII mode command. If
the problem persists, contact Technical Support.
INVLD NO. BLOCKS The number of blocks field in the request was invalid for the
command specified. If the problem persists, contact Technical
Support.
58978L-008 Rev. A RFID Programming Guide 11/14/2008
Page 77

RFID Error Codes and Messages
Table 7 • RFID Error Code Definitions (Continued)
Troubleshooting
77
Error
Code
9009
9101
9102
9103
9201
9202
9301
RFID Error or
Status Message
INVALID DATA LEN The length of the data specified in the request was invalid for the
LOAD DEFAULT ERR The reader was unable to successfully load its default parameters.
RESET DEVICE ERR The reader was unable to successfully reset the reader. If the
BOOTLOADER ERR The reader failed to enter bootloader mode, which is necessary to
READ SYS ERR There was a problem reading a parameter from the non-volatile
WRITE SYS ERR There was a problem writing a parameter to the non-volatile
SET DEFAULT ERR There was a problem writing a parameter to the non-volatile
Description/Action Required
command specified. If the problem persists, contact Technical
Support.
If the problem persists, contact Technical Support.
problem persists, contact Technical Support.
upgrade firmware. If the problem persists, contact Technical
Support.
memory of the reader. If the problem persists, contact Technical
Support.
memory of the reader. If the problem persists, contact Technical
Support.
memory of the reader. If the problem persists, contact Technical
Support.
9302
9401
9402
9403
900F
F002
F003
F004
GET DEFAULT ERR There was a problem reading a parameter from the non-volatile
memory of the reader. If the problem persists, contact Technical
Support.
AUTHEN RDR ERR If the problem persists, contact Technical Support.
ENABLE_DEBUG ERR If the problem persists, contact Technical Support.
DISABLE_DEBG ERR If the problem persists, contact Technical Support.
ANT. BAD/GONE The RFID reader cannot detect the RFID antenna (coupler), or the
antenna (coupler) does not work. Contact Technical Support.
RDR COM TIMEOUT The printer was not able to communicate with the reader. If the
problem persists, contact Technical Support.
ANTENNA SEL ERR The printer firmware could not verify that the selected RFID
antenna (coupler) is properly connected.
If selecting the antenna through ZPL, ensure that your printer
supports this feature and that your parameters are correct. If the
problem persists, contact Technical Support.
POWER SELECT ERR The printer could not verify that the intended power setting has
been set successfully. If the problem persists, contact Technical
Support.
11/14/2008 RFID Programming Guide 58978L-008 Rev. A
Page 78

Troubleshooting
Notes • ___________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________
78
RFID Error Codes and Messages
58978L-008 Rev. A RFID Programming Guide 11/14/2008
Page 79

8
ZPL II Commands for RFID
This section contains the ZPL II commands for RFID-specific applications.
For non-RFID ZPL commands, refer to the ZPL II Programming Guide. A copy is available
on the User CD provided with your printer and online at http://www.zebra.com/manuals.
Contents
ZPL Overview. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 81
Printer and Firmware Compatibility . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 82
^HL or ~HL Return RFID Data Log to Host . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 84
^HR Calibrate RFID Transponder Position . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 85
^HV Host Verification. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 88
^MM Print Mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 89
^RA Read AFI or DSFID Byte . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 91
^RB Define EPC Data Structure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 93
^RE Enable/Disable E.A.S. Bit. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 95
^RF Read or Write RFID Format. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 96
^RI Get RFID Tag ID. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 100
^RM Enable RFID Motion. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 101
^RN Detect Multiple RFID Tags in Encoding Field. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 102
~RO Reset Advanced Counters. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 103
^RQ Quick Write EPC Data and Passwords . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 105
^RR Specify RFID Retries for a Block . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 107
^RS Set Up RFID Parameters. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 108
^RT Read RFID Tag . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 115
~RV Report RFID Encoding Results . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 117
^RW Set RF Power Levels for Read and Write . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 118
^RZ Set RFID Tag Password and Lock Tag . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 120
^WF Encode AFI or DSFID Byte . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 123
11/14/2008 RFID Programming Guide 58978L-008 Rev. A
Page 80

ZPL II Commands for RFID
80
Contents (Continued)
^WT Write (Encode) RFID Tag. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 125
^WV Verify RFID Encoding Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 127
58978L-008 Rev. A RFID Programming Guide 11/14/2008
Page 81

ZPL Overview
In addition to reading or encoding RFID tags, the RFID ZPL commands also provi de for RFID
exception handling, such as setting the number of read/write retries befo re declaring a
transponder defective (set with
be attempted if an error occurs (set with
For example, if an RFID label fails to program correctly or if the transponder cannot be
detected, the printer ejects the label and prints VOID across it. The printer will try to print
another label with the same data and format for the number of RFID labels specified by the
^RS command. If the problem persists, the printer follows the error handling instructions
specified by the
queue and proceed with the next format (if one exists in the buffer), or it may place the print er
in Pause or Error mode.
Important • Consider the following before using any command in this section:
• Before using a particular command, verify that it is compatible with your printer and
firmware version. See Table 8 on page 82.
• If a parameter in the following tables is designated as not applicable for a particular
printer, any value entered for the parameter will be ignored, but the place holder for the
field is required.
ZPL II Commands for RFID
ZPL Overview
^RR, ^RT, and ^WT) or setting the number of labels that will
^RS).
^RS command: the printer may remove the problematic format from the print
81
11/14/2008 RFID Programming Guide 58978L-008 Rev. A
Page 82

ZPL II Commands for RFID
Printer and Firmware Compatibility
82
R2844-Z
R110Xi HF
RP4T
R4Mplus
Firmware
UHF Printers HF Printers
R110PAX4
RZ400 and RZ600
all
all
all
SP1082X
SP1056X
SP1027X
SP999X
SP994X
R63.X.X
R62.X.X
R53.16.X
* * * * ****
*
or later)
(R63.13.0.11Z
or later)
(R62.13.0.13ZC
**
** — — — — — —* *—
Table 8 shows which RFID ZPL commands you can use with different printers and firmware versions.
Printer and Firmware Compatibility
Ta ble 8 • Supported Commands Based on Printer and Firmware
and R170Xi
R110Xi
all
* ** * * * * * ***—
* ** * * * * * ***—
* ** * * * * * ***—
— —— — — — — — —— *—
— —— — — — — — —— **
* ** * * * * * ***—
*
or later)
(R60.13.0.13ZD
* ** * * * * * ***—
*
or later)
(R60.13.0.3
* ** * * * * * ***—
Return RFID Data Log to Host
Command Function
^HL or ~HL
on page 84
^HR on page 85 Calibrate RFID Transponder Position
^RA on page 91 Read AFI or DSFID Byte
^HV on page 88 Host Verification * ** * * * * * **a **
^RB on page 93 Define EPC Data Structure
^RE on page 95 Enable/Disable E.A.S. Bit
^RF on page 96 Read or Write RFID Format
^RI on page 100 Get RFID Tag ID
^RM on page 101 Enable RFID Motion
^RN on page 102 Detect Multiple RFID Tags in Encoding Field
~RO on page 103 Reset Advanced Counters
* = Supported — = Not supported
a. Not ^FH capable. Also, parameters t and a do not apply. b. For parameter e, the only accepted value is N for No Action.
c. Use the ^RF, ^RM, and ^RR commands rather than the ^RT command. d. Use the ^RF, ^RM, ^RR, and ^WV commands rather than the ^WT command.
11/14/2008 RFID Programming Guide 58978L-008 Rev. A
Page 83

ZPL II Commands for RFID
83
Printer and Firmware Compatibility
R2844-Z
R110Xi HF
RP4T
R4Mplus
Firmware
UHF Printers HF Printers
R110PAX4
all
all
all
SP1082X
SP1056X
SP1027X
SP999X
SP994X
R63.X.X
——————*——
R62.X.X
or later)
(R62.15.7Z
*——
***
*
or later)
(SP999C
or later)
(SP994J
RZ400 and RZ600
and R170Xi
R110Xi
Table 8 • Supported Commands Based on Printer and Firmware (Continued)
R53.16.X
* *
all
*
(R60.15.7Z or
* * * ********—
* * * ******* b * *
later)
* * * **
* * * ********—
* c * c * c * c * c * c * c * c * c * c * c *
* * * *******——
* * * *******——
— — — ———————*—
* d * d * d * d * d * d * d * d * d * d * d *
Command Function
^RQ on page 105 Quick Write EPC Data and Passwords
^RR on page 107 Specify RFID Retries for a Block
^RS on page 108 Set Up RFID Paramete rs
^RT on page 115 Read RFID Tag
~RV on page 117 Report RFID Encoding Results
^RW on page 118 Set RF Power Levels for Read and Write
^RZ on page 120 Set RFID Tag Password and Lock Tag
^WF on page 123 Encode AFI or DSFID Byte
^WT on page 125 Write (Encode) RFID Tag
^WV on page 127 Verify RFID Encoding Operation
* = Supported — = Not supported
a. Not ^FH capable. Also, parameters t and a do not apply. b. For parameter e, the only accepted value is N for No Action.
c. Use the ^RF, ^RM, and ^RR commands rather than the ^RT command. d. Use the ^RF, ^RM, ^RR, and ^WV commands rather than the ^WT command.
58978L-008 Rev. A RFID Programming Guide 11/14/2008
Page 84

ZPL II Commands for RFID
84
^HL or ~HL
^HL or ~HL
Return RFID Data Log to Host
Description The printer continually logs RFID data a nd stores it in the print er’s RAM. Use
this command to request that the RFID data log be returned to the host computer, to clear the
current data log, and to restart data recording. The data returned show the status of the RFID
read, write, and lock commands and show any resulting error codes.
Format ^HL or ~HL
Comments
• Data is shown in the format sent by the ^RFW command (ASCII, Hex, or EPC).
• In the log, the data displays in this manner:
C,EEEE,DDDDDDDDDDDDDDDDDDDDDDDD
where
C = the RFID operation
UHF:
R = Read
W=Write
L=Lock
Q = Quick Write EPC Data and Passwords
Z = Set RFID Tag Password and Lock Tag
A = Read Password
I = Read RFID Tag ID
HF:
R = read (^RF)
W= write (^RF)
r=read (^RT)
w=write (^WT)
l=Lock
TIDR = Read RFID Tag ID
EASS = Enable/Disable E.A.S. Bit
AFIR = Read AFI Byte
DSFIDR = Read DSFID Byte
AFIW = Encode AFI Byte
DSFIDW = Encode DSFID Byte
EEEE = the RFID error code (see RFID Error Codes and Messages on page 53)
DDDDDDDDDDDDDDDDDDDDDDDD = data read or written
• If the log exceeds 64K (approximately 2000 operations), the data log is cleared
automatically , and data recordi ng restarts. When this happens, the following app ears in the
log:
Logfile automatically reset
• If the printer loses power , the log is lost. If the log re sults are important to you, retrieve the
log frequently.
58978L-008 Rev. A RFID Programming Guide 11/14/08
Page 85

^HR
Calibrate RFID Transponder Position
Important • Consider the following before using this command:
• This command is not supported by all printers or firmware. See Printer and Firmware
Compatibility on page 82 for the list of printers and firmware with which you can use this
command.
• Do not perform transponder calibration for RFID media that meets the transponder
placement specifications for your printer. Doing so will slow the printer’s throughput
unnecessarily. To order media that is designed for use with your RFID printer, cont act
your authorized Zebra reseller.
Description Use this command to initiate an RFID transponder calibration for a specific
RFID label. Results are returned to the host computer. This calibration is used to determine the
optimal programming position for RFID media that may not meet the transponder placement
specifications for the printer.
During transponder calibration, the printe r feeds the RFID labe l one millimete r at a time wh ile
taking readings (via the READ T AG command and the WRITE TAG commands) to profile the
RFID transponder. Based on the results, the printer determines the optimal programming
position for the label and returns a results table to the host. The calibrated value is used as the
programming position for the
saved to nonvolatile memory (the value is saved even if the power is turned off).
^RS command, can be overwritten by the ^RS command, and is
ZPL II Commands for RFID
^HR
85
This calibration takes into account the print mode, backfeed mode, and tear off position. The
RUN option in the RFID TAG CALIB control panel parameter performs the same
calibration but does not create a results table.
Important • If a label format specifies a value for parameter p (read/write position of the
transponder) in the
all RFID labels until a new posi tion i s specifi ed or u ntil the printer i s turned Of f (
back On (
Format ^HRa,b
This table identifies the parameters for this format.
Parameters Details
I).
a = start string
b
=end string
^RS command, that value will be used for the programming position for
O) and then
User text to appear before the results table.
Accepted values: any string less than 65 characters
Default value:
User text to appear after the results table.
Accepted values: any string less than 65 characters
Default value:
start
end
11/14/2008 RFID Programming Guide 58978L-008 Rev. A
Page 86

ZPL II Commands for RFID
86
^HR
Comments
• Based on the recommended transponder placement position for most RFID labels, the
printer’s default RFID programming position is zero for the R110PAX4. For other RFID
printers, the default programming position is the label length minus 1 mm (0.04 in.).
T o return to the default programming position at any time, use the RESTORE option in the
RFID TAG CALIB control panel parameter (see Calibrate RFID Tag on page 23).
• To see the current programming position (shown in dot rows), refer to the printer
configuration label:
or use the SGD command rfid.position.program on page 135.
• At the end of calibration, a results table is returned to the host. Each line in the results
table appears as:
Row, Read Result, Write Result
where
Row = the millimeter where calibration occurred
Read Result = results of calibration (R = read, " " = unable to read)
Write Result = results of calibration (W = write, " " = unable to write)
The programming position is indicated in dot rows.
58978L-008 Rev. A RFID Programming Guide 11/14/2008
Page 87

ZPL II Commands for RFID
^HR
Example • If the following command is sent to the printer:
^XA^HR^XZ
The printer starts the transponder calibration and return s a results table such as the followi ng:
start
position=480
82, ,
80, ,
79, ,
.
.
.
56,R,
55,R,W
54,R,W
53,R,W
52,R,W
51,R,W
50,R,W
49,R,W
48,R,W
47,R,W
46,R,W
45,R,W
44,R,W
43,R,W
42,R,W
41,R,W
40,R,W <---**** 480 dots
39,R,W
38,R,W
37,R,W
36,R,W
35,R,W
34,R,W
33,R,W
32,R,W
31,R,W
30,R,W
29,R,W
28,R,W
27,R,W
26,R,W
25,R,W
24,R,W
23,R,
22, ,
21, ,
.
.
.
end
In this example, performed on a 300 dpi printer, the optimal programming position is at
40 mm or 480 dot rows. This is identified at the top of the table (
an the arrow (
<---****) in the table.
position=480) and with
87
11/14/2008 RFID Programming Guide 58978L-008 Rev. A
Page 88

ZPL II Commands for RFID
88
^HV
^HV
Host Verification
Description Use this command to return data from specified fields, along with an optional
ASCII header, to the host computer. You can use this command with any field that has been
assigned a number with the
Format ^HV#,n,h,t,a
This table identifies the parameters for this format:
Parameters Details
^RT command or the ^FN and ^RF commands.
# = field number
specified with
another command
n = number of bytes to be
returned
h = header to be returned
with the data
t = termination
a = command applies to
Example • The following code:
The value assigned to this parameter should be the same as
the one used in another command.
Accepted Values:
Default Value: 0
Accepted Values: 1 to 256
Default Value: 64
Delimiter characters terminate the string. This field is Field
Hex (^FH) capable.
Accepted Values:
Default Value: no header
This field is Field Hex (^FH) capable.
Accepted Values: 0 to 3072 characters
When ^PQ is greater than 1, send one response for a label
format or one for every label printed.
Accepted Values:
F =Format
L = Label
Default Value: F
0 to 9999
0 to 3072 bytes
^XA
.
.
.
^FH_^HV0,8,EPC[,]_0D_0A,L^FS
^PQ2
^XZ
Would return data such as this:
EPC[12345678]
EPC[55554444]
58978L-008 Rev. A RFID Programming Guide 11/14/2008
Page 89

^MM
Print Mode
ZPL II Commands for RFID
Description The ^MM command determines the action the printer takes after a label or
group of labels has printed.
Format ^MMa,b
This table identifies the parameters for this format:
Parameters Details
^MM
89
a = desired mode
Accepted Values:
T = Tear-off
P = Peel-off (not available on S-300)
R = Rewind (depends on printer model)
A = Applicator (depends on printer model)
C = Cutter (depends on printer model)
D = Delayed cutter (depends on printer model)
F = RFID (not valid on the RP4T)
Default Value:
The values available for parameter
printer being used and whether it supports the option.
For supported RFID printers, the defaults are as follows:
A = R110PAX4 print engines
F = other RFID printers
b = prepeel select Accepted Values:
N = no
Y = yes
Default Value:
The command is ignored if parameters are missing or
invalid. The current value of the command remains
unchanged.
N
a depend on the
This list identifies the different modes of operation:
• Tear-off — after printing, the label advances so the web is over the tear bar. The label,
with liner attached, can be torn off manually.
11/14/2008 RFID Programming Guide 58978L-008 Rev. A
Page 90

ZPL II Commands for RFID
90
^MM
• Peel-off — after printing, t he label moves forward and ac tivates a Label Available Sensor .
Printing stops until the label is manually removed from the printer.
Power Peel – liner automatically rewinds using an optional internal rewind spindle.
Value Peel – liner feeds down the front of the printer and is manually removed.
Prepeel – after eac h labe l is manually removed, t he printer feeds th e next label forward to
prepeel a small portion of th e label away from the liner material. The printer then
backfeeds and prints the label. The prepeel feature assists in the proper peel operation of
some media types.
• Rewind — the label and backing are rewound on an (optional) external rewind device.
The next label is positioned under the printhead (no backfeed motion).
• Applicator — when used with an application device, the label move far enough forward to
be removed by the applicator and applied to an item.
• Cutter — after printing, the media feed s forward and is automatically cut into
predetermined lengths.
• Delayed cutter — When the printer is in the Delayed Cut PRINT MODE, it will cut the
label when it receives the ~JK (Delayed Cut) command. To activate the ~JK command,
the printer's PRINT MODE must be set to Delayed Cut and there must be a label waiting
to be cut. When the printer is not in the Delayed Cut PRINT MODE, the printer will not
cut the label when it receives the ~JK command.
The Delayed Cut feature can be activated:
• through PRINT MODE on the printer’s control panel
•with a ^MMD command
• RFID — increases throughput time when printing batches of RFID labels by eliminating
backfeed between labels.
Comments Be sure to select the appropriate value for the print mode being used to avoid
unexpected results.
58978L-008 Rev. A RFID Programming Guide 11/14/2008
Page 91

^RA
Read AFI or DSFID Byte
Important • This command is not supported by all printers or firmware. See Printer and
Firmware Compatibility on page 82 for the list of printers and firmware with which you can
use this command.
Description Use this command to read the AFI or DSFID byte. The data can be returned to
the host via the
Format ^RA#,f,r,m,b
This table identifies the parameters for this format.
Parameters Details
^HV command.
ZPL II Commands for RFID
^RA
91
# =field number
specified with
another command
f = format
r = number of retries
m = motion
b = type of byte to read
The value assigned to this parameter should be the same as
the one used in the
Accepted values: 0 to 9999
Default value: 0
Accepted values:
^RT command.
0 = ASCII
1 = Hexadecimal
Default value: 0
Accepted values: 0 to 10
Default value: 0
Accepted values:
0 = Feed label after writing.
1 = No Feed after writing. Other ZPL may cause a feed.
Default value: 0
Accepted values:
A = AFI byte
D = DSFID byte
Default value: A
Example 1 •This example reads the AFI byte in ASCII format and returns AFI Byte:x
to the host. The printer will retry the command five times if necessary. A voided label is
generated if the read is unsuccessful after these retries. The data read will go into the
location of the recalled format.
^FN1
^XA
^FO20,120^A0N,60^FN1^FS
^RA1,0,5,0^FS
^HV1,,AFI Byte:^FS
^XZ
11/14/2008 RFID Programming Guide 58978L-008 Rev. A
Page 92

ZPL II Commands for RFID
92
^RA
Example 2 •This example reads the DSFID byte in ASCII format and returns
DSFID Byte:x to the host. The printer will retry the command three times if necessary. A
voided label is generated if the read is unsuccessful after these retries. The data read will go
into the
^FN1 location of the recalled format.
^XA
^FO20,120^A0N,60^FN1^FS
^RA1,0,3,0,D^FS
^HV1,,DSFID Byte:^FS
^XZ
58978L-008 Rev. A RFID Programming Guide 11/14/2008
Page 93

^RB
Define EPC Data Structure
Important • This command is not supported by all printers or firmware. See Printer and
Firmware Compatibility on page 82 for the list of printers and firmware with which you can
use this command.
Description Use this command to define the structure of EPC data, which can be read from
or written to an RFID transponder. For more in formation about EPC specifications, refer to the
EPC Global web site. All parameters in this command are persistent and will be used in
subsequent formats if not provided. The values are initially set to the default values.
RFID transponders can have different partitions defined. This command specifies the number
of partitions and how many bits are in each partition.
Format ^RBn,p0,p1,p2, ..., p15
This table identifies the parameters for this format.
ZPL II Commands for RFID
^RB
93
Parameters Details
n = total bit size of the
partitions
p0 ... p15
partition sizes
Example 1 •The following command specifies that there are 96 bits used with three fields.
Fields 0, 1, and 2 contain 10, 26, and 60 bits, respectively.
=
Specify the number of bits to include in the partitions.
Accepted values: 1 to n, where n is the bit size of the tag.
Default value:
Specify the number of bits to include in the individual
partitions. The partition sizes must add up to the bit size
specified for the previous parameter. The largest individual
partition size is 64 bits.
Accepted values: 1 to 64
Default value:
96
1
^RB96,10,26,60
The ZPL code to encode a tag with this format would look like this:
^RFW,E^FD1000.67108000.1122921504606846976^FS
When the tag is being encoded, the tag stores the data in the following way:
• Field 0 contains
1000. This value is stored in the first 10 bits
• Field 1 contains 67108000. This value is stored in the next 26 bits.
• Field 2 contains 1122921504606846976. This value is stored in the remaining
60 bits.
11/14/2008 RFID Programming Guide 58978L-008 Rev. A
Page 94

ZPL II Commands for RFID
Header Filter Value
Company
Prefix Index
Item Reference Serial Numb er
SGTIN-64 2 bits 3 bits 14 bits 20 bits 25 bits
10
(binary value)
8
(decimal
capacity)
16,383
(decimal
capacity)
9 to 1,048,575
(decimal
capacity*)
33,554,431
(decimal
capacity)
* Capacity of Item Reference field varies with the length of the company prefix.
0.3.12345.544332.22335221
94
^RB
Example 2 •The following command specifies that there are 64 bits used with eight 8-bit
fields.
^RB64,8,8,8,8,8,8,8,8^FS
The ZPL code to encode a tag with this format would look like this:
^RFW,E^FD1.123.160.200.249.6.1.0^FS
When writing to the tag, each set of data is written in its respective 8-bit field.
Example 3 •This example uses the SGTIN-64 standard, which defines 64-bit structure in the
following way:
The ZPL code to encode a tag with this format would look like this:
^XA
^RB64,2,3,14,20,25
^RFW,E^FD0,3,12345,544332,22335221^FS
^XZ
These commands would put
• 0 in the header
• 3 as the filter value
• 12345 as the company prefix
• 544332 as the item reference
• 22335221 as the serial number
To read this EPC data and print the results on the label, you woul d use the following code:
^XA
^RB64,2,3,14,20,25
^FO50,50^A0N,40^FN0^FS
^FN0^RFR,E^FS
^XZ
The resulting label would look like this:
58978L-008 Rev. A RFID Programming Guide 11/14/2008
Page 95

^RE
Enable/Disable E.A.S. Bit
Important • This command is not supported by all printers or firmware. See Printer and
Firmware Compatibility on page 82 for the list of printers and firmware with which you can
use this command.
Description Use this command to enable or disable the Electronic Article Surveillance
(E.A.S.) bit that is available in some ISO15693 tags (such as Philips). This command works
only on those ISO15693 transponders and will be ignored if the tag does not support E.A.S.
Format ^REt,r
The following table identifies the parameters for this format.
Parameters Details
ZPL II Commands for RFID
^RE
95
t = Enable/disable the
E.A.S. bit in the
ISO15693
transponder
r = number of retries
Example • This example enables the E.A.S. bit in the transponder. It will retry the command
five times if necessary.
Accepted values:
N = Disable E.A.S.
Y = Enable E.A.S.
Default value: N
Accepted values: 0 to 10
Default value: 0
^XA
^REy,5
^XZ
11/14/2008 RFID Programming Guide 58978L-008 Rev. A
Page 96

ZPL II Commands for RFID
96
^RF
^RF
Read or Write RFID Format
Important • This command is not supported by all printers or firmware. See Printer and
Firmware Compatibility on page 82 for the list of printers and firmware with which you can
use this command.
Description Use this command to read or write to (encode) an RFID tag. When using this
command to read a tag, you may use a field variable to print the tag data on the label or to
return the data to the host. See Create and Send an RFID Label Format on page 30 for
examples that use a field variable.
Format ^RFo,f,b,n,m
This table identifies the parameters for this format.
Parameters Details
o = operation
f =format
Specifies the action to be performed.
Accepted Values:
W=write to (encode) the tag
L=write with LOCK (if supported by tag type; Gen 2
tag type does not use this locking function)
R=read the tag
P = read password (Gen 2 tag type only)
Default Value: W
Accepted Values:
A = ASCII
H = Hexadecimal
E = EPC (ensure proper setup with the ^RB command)
Default Value: H
58978L-008 Rev. A RFID Programming Guide 11/14/2008
Page 97

Parameters Details
ZPL II Commands for RFID
^RF
97
b = s tarting block
number
n = number of bytes to
read or write
For tag types other Gen 2:
Specifies the starting block number.
Accepted Values: 0 to n, where n is the maximum number of
blocks for the tag.
Default Value: 0
For Gen 2 tag type only:
What you specify for this parameter depends on what you
entered for the operation parameter.
• When W, L, or R are specified for the operation parameter,
this parameter specifies a 16-bit word block number.
Accepted Values: 0 to n, where n is the maximum number
of blocks for the bank specified in the memory bank
parameter
Default Value: 0
• When P is specified for the operation parameter, this
parameter specifies which password to read.
Accepted Values:
K=kill password
A=access password
Default Value: K
Specifies the number of bytes to read or write.
For high-frequency (HF) printers:
Accepted Values: 1 to n, where n is the maximum number of
bytes for the tag.
Default Value: 1
For Gen 2 tag type only:
When E is specified for the memory bank parameter, this
value is not required.
Accepted Values: 1 to n, where n is the maximum number of
bytes for the tag.
Default Value: 1
For all other printers and tag types:
This parameter applies only when the starting block number
is 1.
Accepted Values: 1 to n, where n is the maximum number of
bytes for the tag. For UCODE EPC 1.19, n is 32.
Default Value: 1
11/14/2008 RFID Programming Guide 58978L-008 Rev. A
Page 98

ZPL II Commands for RFID
98
^RF
Parameters Details
m = memory bank
Note • This parameter applies to Gen 2 tags only.
Specifies the Gen 2 memory bank. See Gen 2 Memory Map
on page 46 for more information about Gen 2 memory.
Accepted Values:
E = EPC 96-bit (command automatically performs
operation on Gen 2 bit address 20
12 bytes of the EPC memory bank)
0 = Reserved
1 = EPC
2 = TID (Tag ID)
3 = User
Default Value: E
Example 1 •This example encodes 96-bit data in ASCII format.
^XA
^RS4
^RFw,a^FD00 my data^FS
^XZ
and accesses
h
Example 2 •This example encodes 64-bit data in hexadecimal format.
^XA
^RS3
^RFW,H^FD1122334455667788^FS
^XZ
Example 3 •This example encodes 96-bit EPC data, as specified by the ^RB command.
^XA
^RB96,8,3,3,20,24,38
^RFw,e^FD16.3.5.78742.146165.1234567891^FS
^XZ
Example 4 •This example encodes 4 bytes of hexadecimal formatted data, starting in
block 3 of Gen 2 EPC bank 1.
^XA
^RS8
^RFW,H,3,4,1^FD11112222^FS
^XZ
58978L-008 Rev. A RFID Programming Guide 11/14/2008
Page 99

ZPL II Commands for RFID
^RF
Example 5 •This example reads the extended Gen 2 tag ID (TID), which is not read by the
^RI command, and returns the results to the host computer. The results are labeled with the
header “8-byte Tag ID Data.”
^XA
^RS8
^RFR,H,0,8,2^FN1^FS^HV1,,8-byte Tag ID Data:^FS
^XZ
99
11/14/2008 RFID Programming Guide 58978L-008 Rev. A
Page 100

100
ZPL II Commands for RFID
^RI
^RI
Get RFID Tag ID
Important • This command is not supported by all printers or firmware. See Printer and
Firmware Compatibility on page 82 for the list of printers and firmware with which you can
use this command.
Description Use this command to get the unique serial number of the tag and return it in
hexadecimal format. The data can be sent back to the host via the
For Gen 2 tag types, this command will return the 32-bit tag ID (TID) for the tag. If your
Gen 2 tag supports TID data beyond 32 bits, see ^RF on page 96 to access the TID memory
bank.
Format ^RI#,s,r,m
This table identifies the parameters for this format.
Parameters Details
^HV command.
# = number to be
assigned to the field
s = specify data order
Accepted values: 0 to 9999
Default value: 0
Note • This parameter applies only to the R110Xi HF
and R2844-Z printers.
Accepted values: Accepted Values:
0=Most significant byte first for Tag*It and PicoTag.
Least significant byte first for I*code and
ISO15693.
1=Reverse the data order
Default value: 0
r = number of retries
m = motion
Accepted values: 0 to 10
Default value: 0
Accepted values:
0 = Feed label after writing
1 = No Feed after writing (other ZPL commands may
cause a feed)
Default value: 0
Example • This example reads a tag ID, prints it on a label, and sends string
Tag ID:xxxxxxxx to the host. The data read will go into the ^FN0 location of the
format. The printer will retry the command five times, if necessary.
^XA
^FO20,120^A0N,60^FN0^FS
^RI0,,5^FS
^HV0,,Tag ID:^FS
^XZ
58978L-008 Rev. A RFID Programming Guide 11/14/2008
 Loading...
Loading...