
Operation & Options
This section helps you get the most from your printer.
You must use programming to control many of the printer’s functions. A
few examples:
■
The
~JL
command controls label length.
■
The
^XA^MTD^XZ
thermal; the
thermal transfer.
■
The
^XA^JUS^XZ
For detailed information about creating labels using ZPL II, refer to the ZPL
II Programming Guide or visit our web site at www.zebra.com.
To improve print quality, changing both print speed and density may be
required to achieve the desired results. Your application’s printer driver
provides control of the speed and heat (density).
command changes the printing mode to direct
^XA^MTT^XZ
command saves the new settings to flash memory.
command changes the printing mode to
Thermal Printing
The print head becomes hot while printing. To protect from damaging the
print head and risk of personal injury, avoid touching the print head. Use
only the cleaning pen to perform maintenance.
The discharge of electrostatic energy that accumulates on the surface of the
human body or other surfaces can damage or destroy the print head or
electronic components used in this device. You must observe static-safe
procedures when working with the print head or the electronic components
under the top cover.
You must use the correct media for the type of printing you require. When
printing without a ribbon, you must use direct thermal media. When using
ribbon, you must use thermal transfer media. The printer’s ribbon sensor
detects motion of the supply spindle.
980476-001A 21

Replacing Supplies
If labels or ribbon run out while printing, leave the printer power on while
reloading (data loss results if you turn off the printer). After you load a new
label or ribbon roll, press the Feed button to restart .
Always use high quality, approved labels, tags and ribbons. If adhesive
backed labels are used that don’t lay flat on the backing liner, the exposed
edges may stick to the label guides and rollers inside the printer, causing the
label to peel off from the liner and jam the printer. Permanent damage to the
print head may result if a non-approved ribbon is used as it may be wound
incorrectly for the printer or contain chemicals corrosive to the print head.
Approved supplies can be ordered from your dealer.
Adding a New Transfer Ribbon
If ribbon runs out in the middle of a print job, the indicator lights red and
the printer waits for you to add a fresh roll.
1. Keep the power on as you change ribbon.
2. Open the top cover, then cut the used ribbon so you can remove the
cores.
3. Load a new ribbon roll. If necessary, review the Ribbon Loading steps.
4. Close the top cover.
5. Press the Feed button to restart printing.
Replacing a Partially Used Transfer Ribbon
To remove used transfer ribbon, perform the following steps.
1. Cut the ribbon from the take-up roll.
2. Remove the take-up roll and discard used ribbon.
3. Remove the supply roll and tape the end of any fresh ribbon to prevent
it from unwrapping.
When reinstalling a partially used supply roll, tape the cut end onto the
empty take-up roll.
22 980476-001A
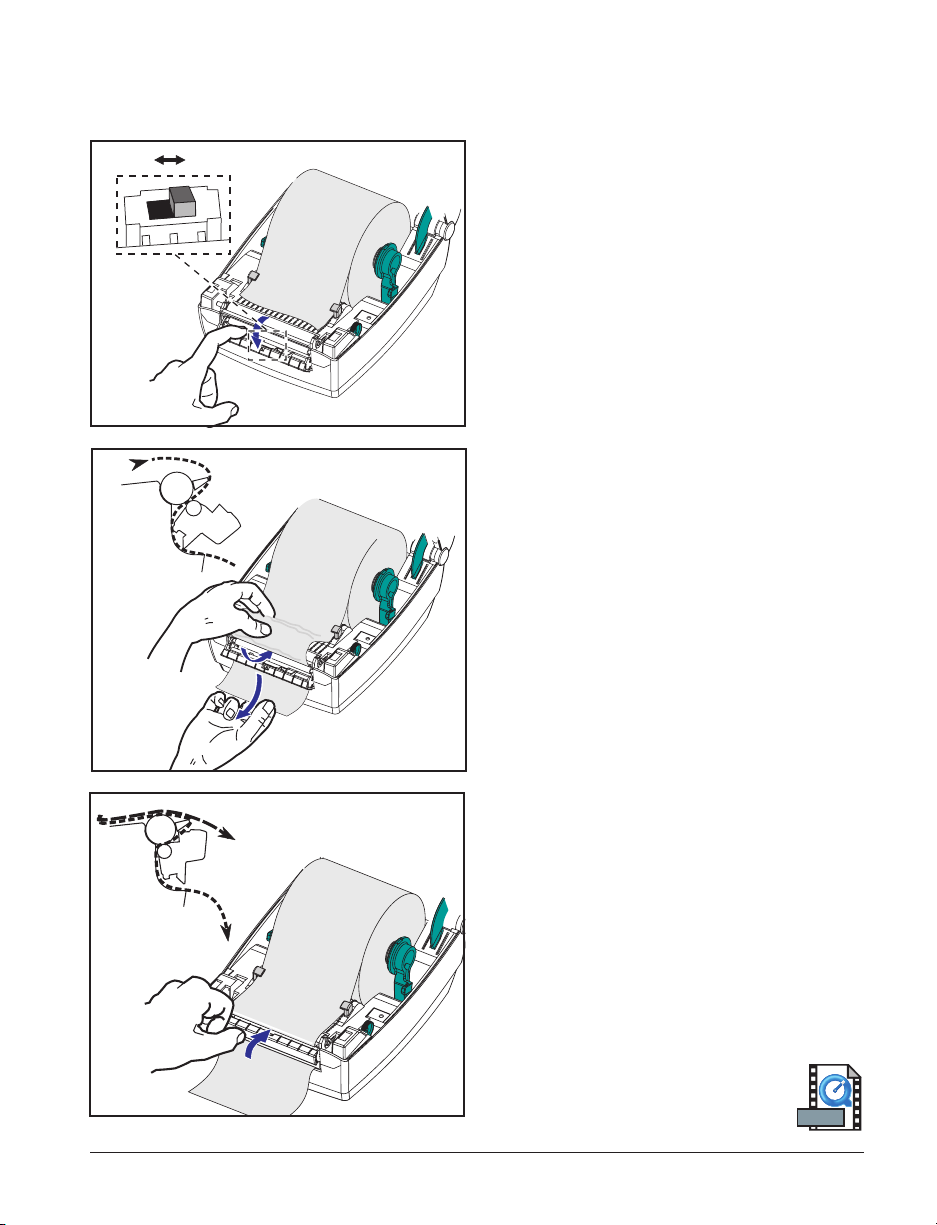
Printing in Peel-Mode
ON OFF
The optional dispenser allows you
to print in “peel-mode” where the
label backing follows a different path and
the labels are presented one at a time for
subsequent placement.
Before using peel-mode, you must send
the programming commands
^XA ^MMP ^XZ
^XA ^JUS ^XZ
to the printer. Refer to your ZPL II
Programmer’s Manual.
1. Remove several labels from the
backing material.
2. Open the top cover.
3. Open the dispenser door.
4. Switch on the label-taken sensor.
5. Insert the backing in front of the peel
bar and behind the peel roller.
6. Close the dispenser door.
7. Close the top cover.
8. Press the Feed button to advance the
label.
During the print job, the printer will peel
off the backing and present a single label.
Take the label from the printer so it will
print the next label.
MOVIE
980476-001A 23
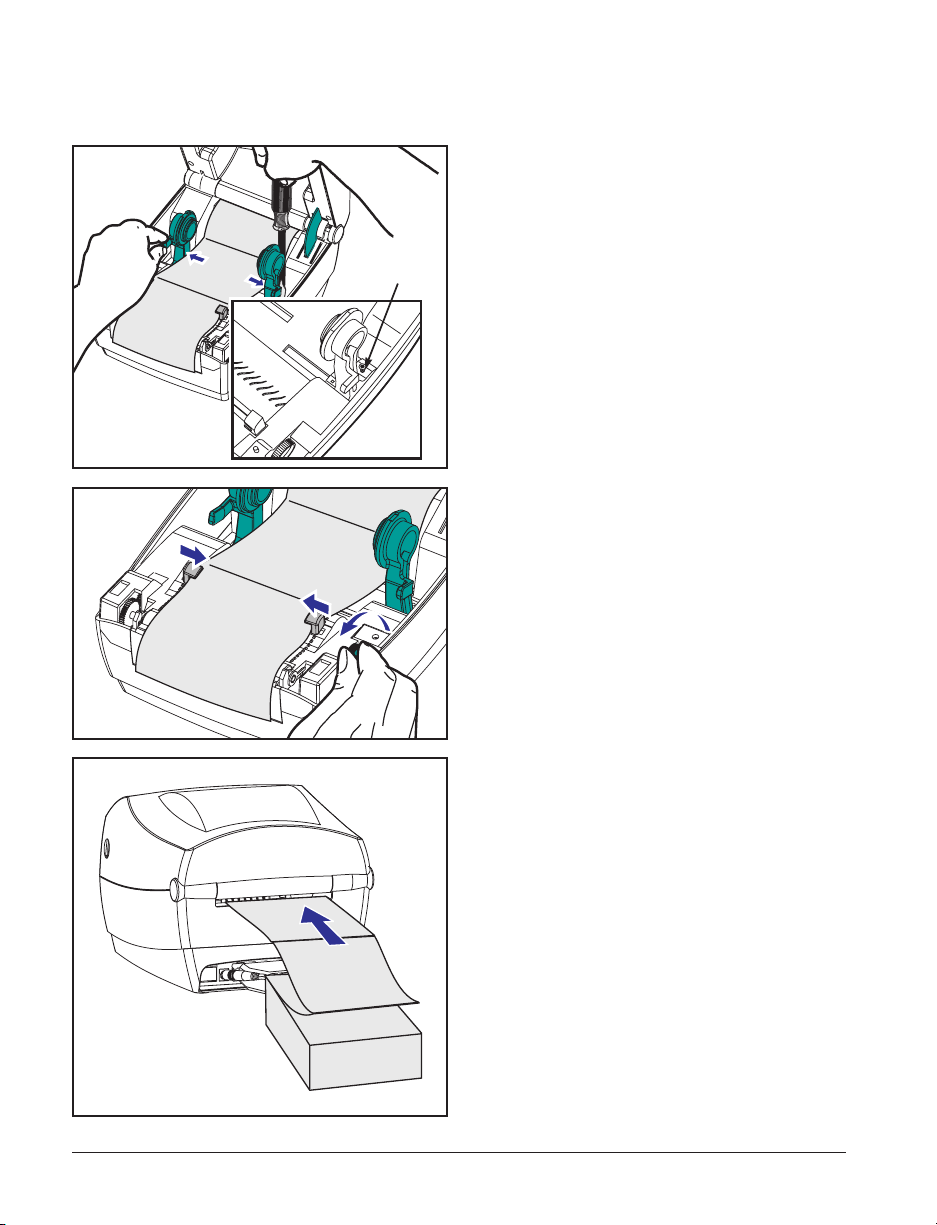
Printing on Fan-Fold Media
Printing on fan-fold media requires you to
set both the media hangers and the media
guides in position.
Lock-down
Screw
1. Open the top cover.
2. With a sample of your media, adjust
the media hangers to the width of the
media. The hangers should just touch,
but not restrict, the edges of the
media.
3. Tighten the screw using a small
Phillips driver #1.
4. With a sample of your media, adjust
the guides to the width of the media.
The guides should just touch, but not
restrict, the edges of the media.
5. Insert the media through the slot at the
rear of the printer.
6. Run the media between the hangers
and guides.
7. Close the top cover.
24 980476-001A
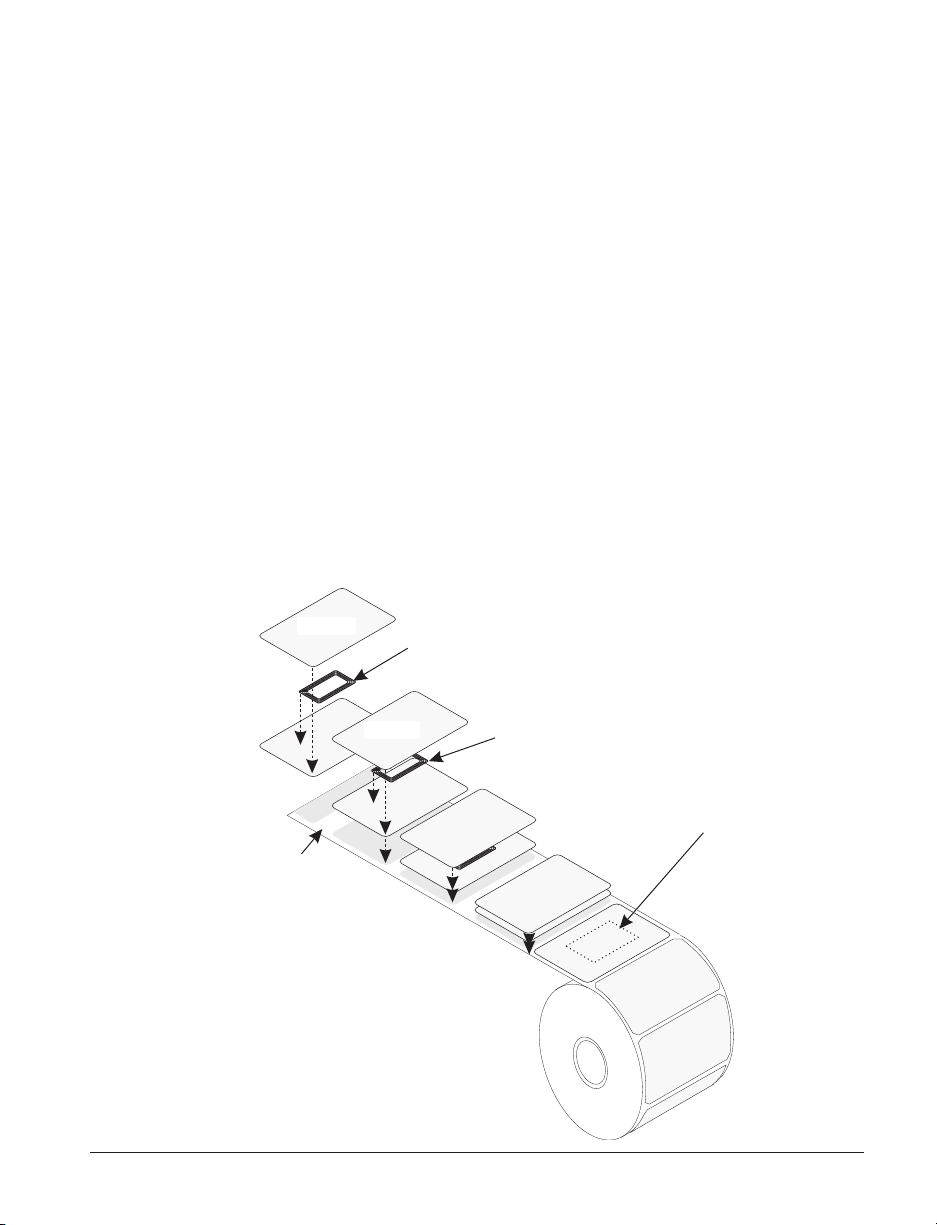
RFID Guidelines
The Zebra R2844-Z Smart Label Printer and Encoder serves as dynamic
tool for both printing and programming smart labels and tags. These labels
and tags are usually made from two components, media and an RFID (radio
frequency identification) transponder.
■
The media is comprised of synthetic- or paper-based material that can be
printed upon using direct thermal or thermal transfer printing techniques.
The media is typically made from the same materials and adhesives used
by a standard barcode printer.
■
The transponder is usually comprised of an antenna coil that is bonded
to an integrated circuit (IC) chip. The IC contains the drivers, coders,
decoders and memory. At a minimum, the transponder has memory that
can be read, while the vast majority also have memory that can be
programmed by the user as well.
Media
Liner
Transponder
Media
Transponder
Outline of
transponder
(
shape varies
by manufacturer
Media
Supply
)
980476-001A 25
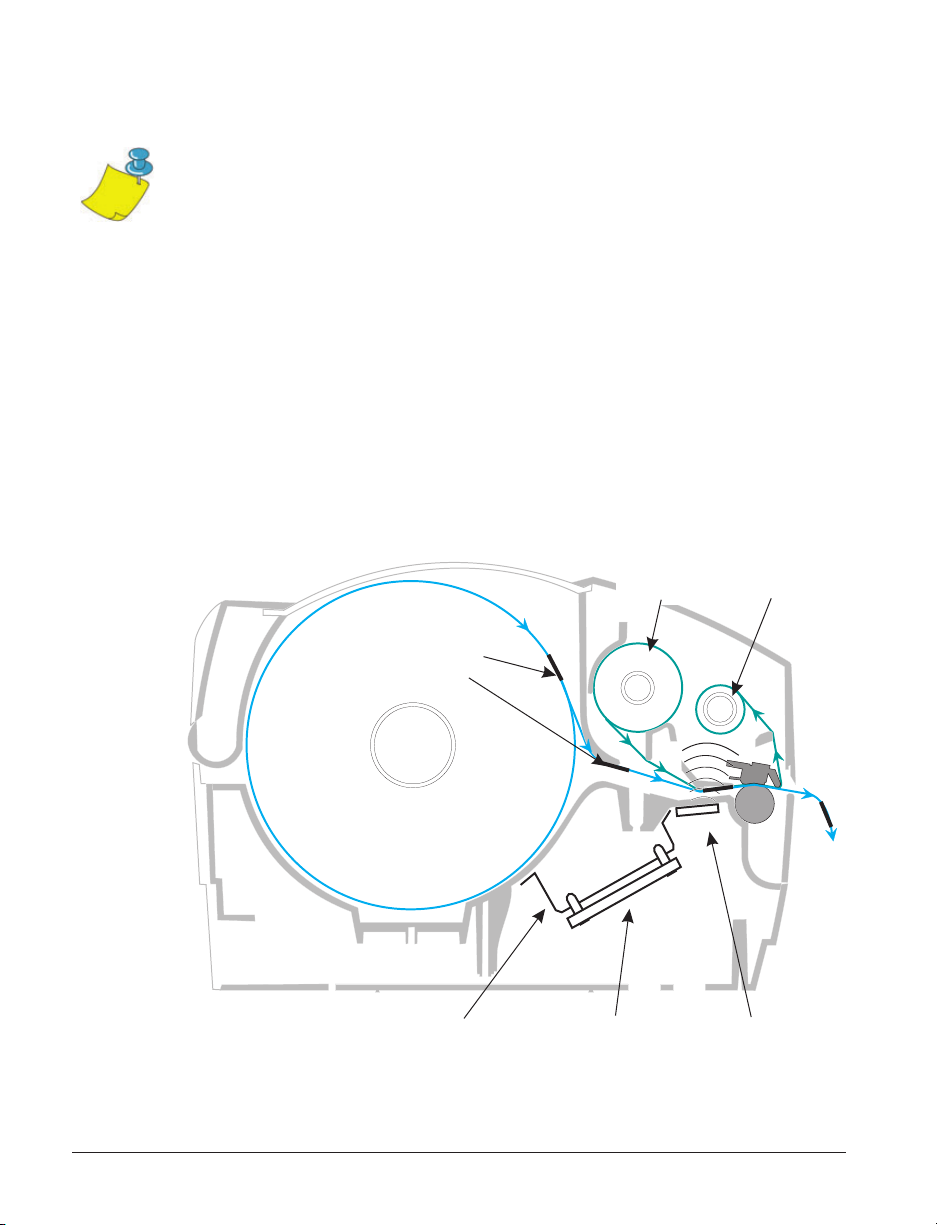
The communication between the RFID tag and the printer is established
when the transponder lines up with the printer’s antenna.
Note • The transponder position, prior to encode/decode, is critical. The optimal
transponder position varies with antenna coil size and type of RFID IC used. It is
important to use media and tags that have been specifically designed for use in this
printer. Failure to do so may result in the inability to read or program the embedded
RFID tags.
Printing and programming of smart labels is handled through the use of
Zebra's printer programming language, ZPL. The printer segments the
received ZPL's RFID-specific and printing-related commands. The printer
will execute the RFID commands first, followed by those for printing
barcodes and text. Each transponder has blocks of addressable memory that
are written to and read from through ZPL commands. Many transponders
also contain a pre-programmed unique ID/serial number. The ZPL
commands also provide for exception handling, such as setting the number
of read/write retries before declaring the transponder defective.
Transponders
imbedded
in media
Media
Supply
Bracket
Ribbon
Supply
Reader/Writer
Board
Ribbon
Take-up
Antenna
26 980476-001A
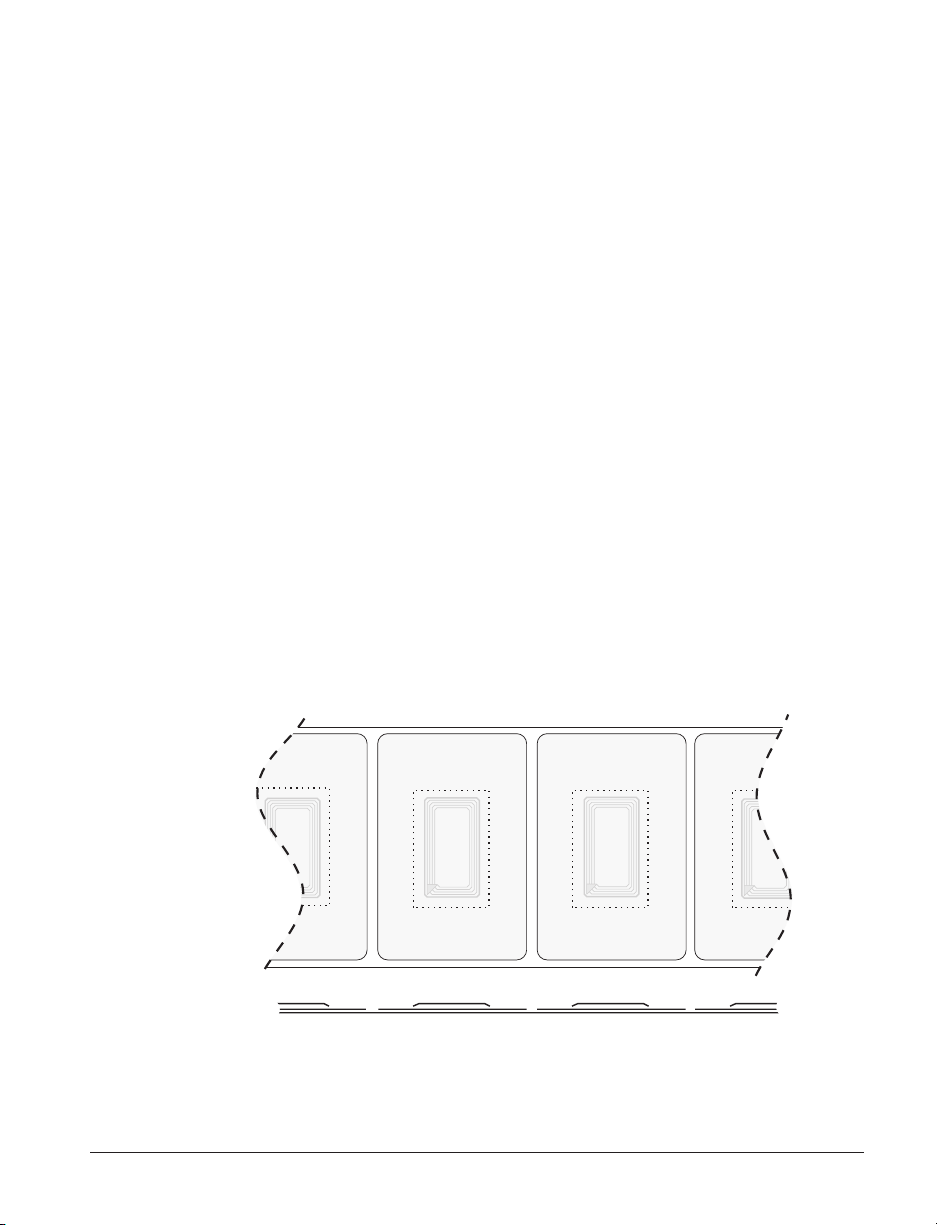
If an RFID tag is declared defective (fails to program correctly or cannot be
detected) the printer ejects it and prints the word "void" across the entire
label (see samples on page 45). If problems persist, this process—using the
same data and format—will continue from one to ten tags; you set the
retries using a parameter in the RFID Setup command (^RS). After the last
tag is ejected the printer removes the customer format from the print queue,
and proceeds with the next format (if one exists in the buffer).
Print Quality Over the Transponder
There is a raised area on each label immediately around the location of the
IC chip where the printer may print with low quality.
Design your printed label around the location of the chip in the type of
approved smart label you select. For best results, do not print barcodes
directly over the transponder. If in doubt, check the print quality and adjust
the label format, or obtain smart labels with an alternate transponder
placement.
Top View
Profile
980476-001A 27

Supported Transponders
Use transponders specifically approved for use in the R2844-Z printer.
Failure to do so may result in the inability to read or write to imbedded
RFID tags. For a current list of approved transponders, contact Zebra
Technologies Corporation or visit the website (http://www.rfid.zebra.com).
As new transponders become commercially available, Zebra will evaluate
them for compatibility with the R2844-Z printer.
Important • Function of an encoded smart label in an application depends on factors
such as where the label is placed on an item (such as a carton or a pallet) as well as
on the contents of the items (such as metals or liquids). Contact the supplier of your
external RFID reader for assistance with these types of issues. Zebra can only
support issues regarding printing and encoding smart labels.
28 980476-001A

Transmission and Identification Standards
ISO-15693
ISO-15693 is an international standard for 13.56 MHz RFID devices. As
this is a public standard, tags and integrated circuits may be produced by a
wide variety of manufacturers. The current standard stipulates that
manufacturers may configure memory in various ways (up to 256 blocks
comprising a block size up to 256 bits (32 bytes)). The standard also
stipulates that a manufacturer may, or may not, use the recommended
methods of reading and writing to the tag as stipulated in the standard. For
these reasons, the printer may not be compatible with every manufacturer's
ISO-15693 transponders. Contact your technical support representative for
the latest list of supported ISO-15693 transponders.
For more information, see the International Standards Organization web
site at:
http://www.iso.org
Electronic Product Code™ (EPC™)
The Electronic Product Code™ (EPC™) is a product numbering standard
that can be used to identify a variety of items using RFID technology. The
EPC format contains 12-bytes (96-bits) of data defining the manufacturer,
product, and serial number. The EPC can link to an online database,
providing a secure way of sharing product-specific information along the
supply chain.
For more information, see the EPCglobal web site at:
http://www.epcglobalinc.org
980476-001A 29

Manufacturers and Brands
In your printer, you can use these brands of transponders:
■
Texas Instruments® Tag-it™
■
Philips® I•Code
■
Inside Technologies Picotag® 2K
■
Infineon Technologies® my-d vicinity
30 980476-001A
 Loading...
Loading...