Enterprise Wireless LAN Antenna
Specification Guide
Version 2.0 Rev A April 2012

© 2012 Motorola Solutions, Inc. All rights reserved.
MOTOROLA and the Stylized M Logo are registered in the US Patent & Trademark Office. .

Chapter 1. Antenna Selection and Description
1.1 Antenna Selection. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-1
1.2 Antenna Selection Criteria . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-6
1.3 Antenna Accessories for Enterprise WLANs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-7
Chapter 2. Product Compatibility
2.1 FCC Compliance. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-1
2.2 FCC Approval Statement . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-3
2.3 FCC USA Compaibility Matrix . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-6
Chapter 3. 2.4 GHz Single Band Antenna Suite
3.1 Supported 802.11b/g/n Antenna Suite. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-1
Chapter 4. 5.2 Ghz Single Band Antenna Suite
4.1 Supported 802.11a/n Antenna Suite . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-1
Chapter 5. 2.4GHz - 5.2GHz Dual Band Antenna Suite
5.1 Supported 802.11a/b/g/n Dual Band Antennas . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-1
Contents
Chapter 6. Antenna Cables
6.1 Supported Antenna Cables . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-1
Chapter 7. Supported Antenna Adapters
7.1 Supported Adapters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-1
Chapter 8. Supported Lightning Arrestors
8.1 Lightning Arrestors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8-1
Chapter 9. Mounting Kits
9.1 Mounting Kit Support . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-1
Chapter 10. AP-5131 Antenna Connections
10.1 2.4 GHz AP-5131 Antenna Connections . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10-2
10.2 5 GHz AP-5131 Antenna Connections. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10-9

TOC-2 Enterprise Wireless LAN Antenna Specification Guide
Chapter 11. AP300 Antenna Connections
11.1 2.4 GHz AP300 Antenna Connections . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11-1
11.2 5 GHz AP300 Antenna Connections . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11-8
Chapter 12. AP7131 Transmit Power
12.1 Configuring the AP7131 Series Transmit Power. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12-1
12.2 US Regulatory Domain 2.4 GHz Band . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12-8
12.3 US Regulatory Domain 5.2 GHz Band . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12-13
12.4 Japanese TELEC Regulatory Domain 2.4 GHz Band . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12-23
12.5 Japan TELEC Regulatory Domain 5.2 GHz Band . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12-27
Chapter 13. AP650 Regulatory Domains
13.1 US Regulatory Domain 2.4 GHz Band . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13-1
13.2 US Regulatory Domain 5 GHz Band. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13-6
13.3 Japan TELEC Regulatory Domain 2.4 GHz Band . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13-16
13.4 Japan TELEC Regulatory Domain 5 GHz Band . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13-22
13.5 EU Regulatory Domain 2.4 GHz Band . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13-34
13.6 EU Regulatory Domain 5 GHz Band. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13-39
Chapter 14. RFS4011 Regulatory Domains
14.1 US Regulatory Domain 2.4 GHz Band . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14-1
14.2 US Regulatory Domain 5 GHz Band. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14-5
14.3 Canada Regulatory Domain 2.4 GHz Band . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14-13
14.4 Canada Regulatory Domain 5 GHz Band . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14-17
14.5 EU Regulatory Domain 2.4 GHz Band . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14-25
14.6 EU Regulatory Domain 5 GHz Band. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14-29
14.7 Japan Regulatory Domain 2.4 GHz Band . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14-37
14.8 Japan Regulatory Domain 5 GHz Band . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14-41
Chapter 15. AP-6511 Regulatory Domains
15.1 US Regulatory Domain 2.4 GHz Band . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15-1
15.2 US Regulatory Domain 5 GHz Band. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15-2
15.3 EU Regulatory Domain 2.4 GHz Band . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15-3
15.4 EU Regulatory Domain 5 GHz Band. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15-4
15.5 Japan Regulatory Domain 2.4 GHz Band . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15-6
15.6 Japan Regulatory Domain 5 GHz Band . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15-7
Chapter 16. AP-621 and AP-6521 Regulatory Domains
16.1 AP-621 (Standard Power) US Regulatory Domain 2.4GHz Band. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16-1
16.2 AP-621 (Standard Power) US Regulatory Domain 5GHz Band . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16-5
16.3 AP-6521 (High Power) US Regulatory Domain 2.4GHz Band . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16-13
16.4 AP-6521 (High Power) US Regulatory Domain 5GHz Band . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16-17
16.5 AP-621 (Standard Power) EU Regulatory Domain 2.4GHz Band . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16-25
16.6 AP-621 (Standard Power) EU Regulatory Domain 5GHz Band . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16-29
16.7 AP6521 (High Power) EU Regulatory Domain 2.4GHz Band . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16-37
16.8 AP-6521 (High Power) EU Regulatory Domain 5GHz Band . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16-41
Appendix A.Technical Support

Introduction
This guide provides a Professional RF engineer a catalog of antennas, parts, and accessories to complete a
customized RF instillation of Motorola Solutions Enterprise Access Points. This guide specifically addresses
the antennas used for 2.4 GHz, 5.2 GHz and dual band antenna implementations for Wireless Local Area
Networks (WLANs).
It’s important to understand that antenna and accessory selection should be qualified by on-site verification
with the actual components used. Signal attenuation is cumulative with each connection and component
added between the antenna and the radio, so careful study and planning should be used to verify the given
arrangement ensures a compliant installation.
NOTE: Illustrations displayed in this guide are samples and can differ from the actual
antenna.
Document Conventions
The following conventions are used in this document to draw your attention to important information:
NOTE: Indicate tips or special requirements.
About This Guide
CAUTION: Indicates conditions that can cause equipment damage or data loss.
!
WARNING! Indicates a condition or procedure that could result in
personal injury or equipment damage.

viii Enterprise Wireless LAN Antenna Specification Guide
Notational Conventions
The following additional notational conventions are used in this document:
• Italics are used to highlight the following:
• Chapters and sections in this and related documents
• Dialog box, window and screen names
• Drop-down list and list box names
• Check box and radio button names
• Icons on a screen.
• GUI text is used to highlight the following:
• Screen names
• Menu items
• Button names on a screen.
• bullets (•) indicate:
• Action items
• Lists of alternatives
• Lists of required steps that are not necessarily sequential
• Sequential lists (those that describe step-by-step procedures) appear as numbered lists.
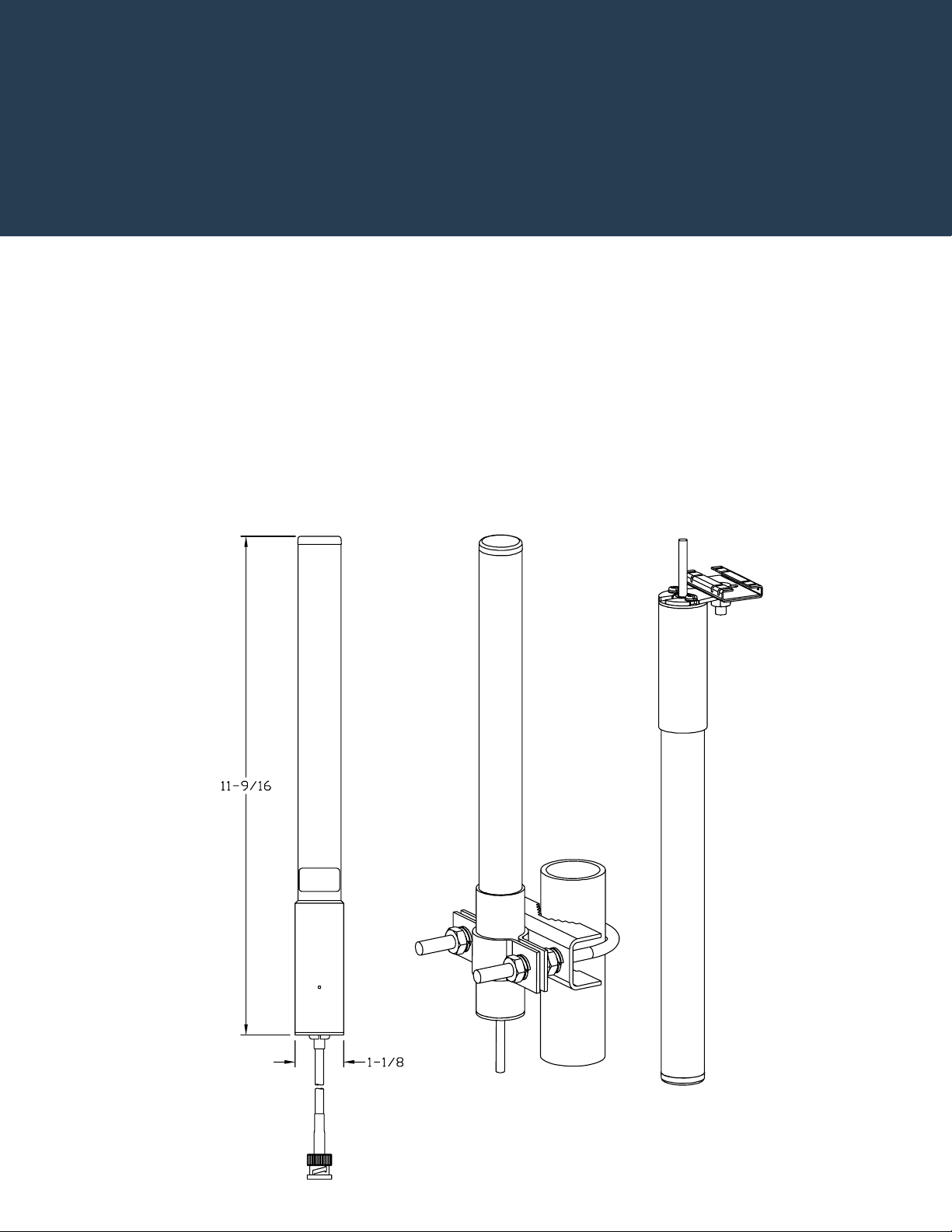
Antenna Selection and Description
1.1 Antenna Selection
While several antennas may work in a given environment, some will provide better coverage than others.
Using the right antenna in the right location will maximize both the performance and coverage of your
network. Understanding the key characteristics that describe how an antenna sends and receives radio
frequency signals is critical to finding the ideal antenna for your deployment. This guide supports the
antennas used for AP-5131, AP-5181, AP-7131, AP-6511, AP621, AP622 and AP-6521 model access points,
AP650 and AP300 (non-integrated antenna) model access port and the RFS4011 Integrated Services
Controller.
Motorola Solutions Enterprise Wireless LAN products operate in the 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz ISM bands allocated
for unlicensed use. Access point and access port products available today support either the 802.11b/g/n or
the 802.11a/n standard, or both. Wireless devices conforming to the 802.11b/g standard operate in the 2.4
GHz ISM band, while 802.11a devices operate in the 5 GHz band. The antennas in this guide are grouped
according to the frequency band they support. Some antennas are designed to operate within either band.
These antennas (described as "Dual-band") may be connected to radios operating in either the 2.4 or 5 GHz
bands, although a single antenna may not be connected to two radios at the same time.

1-2 Enterprise Wireless LAN Antenna Specification Guide
1.1.1 Connector Types and Definitions
There are combinations of antenna types and cables required to provide a satisfactory connection to the AP.
One confusing factor is “reverse polarity”. Reverse polarity is the FCC's requirement for each WLAN
manufacturer to have unique access point connectors. Motorola Solutions had previously standardized our
offerings for access points/ports:
• 2.4 GHz is Reverse polarity BNC female (RP-BNC-F)
• 5 GHz is reverse polarity SMA female (RP-SMA-F)
• Dual Band is reverse polarity SMA female (for AP-5131), and N-Female (for AP-5181).
NOTE: Reverse polarity presents confusion because of a lack of a standardized definition
from connector manufactures. Reverse polarity provides a center element, which should
not be confused with a male connector. A male connector is defined by the outer jacket of
the connector rather than the center element.
The following are the connectors used within this guide:
Figure 1.1 RP-BNC-F
Figure 1.2 RP-BNC-M

Antenna Selection and Description 1-3
Figure 1.3 RP-SMA-F
Figure 1.4 RP-SMA-M

1-4 Enterprise Wireless LAN Antenna Specification Guide
Additionally, antennas deployed outdoors and industry standard accessories (like lightening arrestors) use
Type-N connectors (as displayed below). Therefore, with the combinations devices required
(access points/ports, antennas, cable extensions, and lightening arrestors), various adapter cables are
required to connect an antenna to an access point/port.
Figure 1.5 Type N-F
Figure 1.6 Type N-M

1.1.2 Indoor and Outdoor Antennas
One important aspect of an antenna is whether it is weather sealed to protect it from the environment
Because of this extra protection, outdoor antennas are typically more expensive than those rated for indoor
use. Outdoor antennas can be used for indoor applications, such as freezers and cooler where moisture is
common. Outdoor antennas can be used for indoor applications, but indoor applications should not be used
in outdoor applications.
One common distinction of outdoor antennas is the connector. Since lightning protection is always advised
for outdoor antennas, these antennas typically have Type N Male to directly attach the lightning arrestor.
This is true of 2.4 GHz, 5 GHz, and dual-band outdoor antennas.
1.1.3 Spectrum and Part Number Designations
The antennas listed in this document are ultimately referenced by part number. A numerical sequence is used
within each antenna’s part number to identify the spectrum supported by the antennas.
• The antenna part numbers with a 2499 indicates a 2.4 GHz antenna. For more information on the 2.4 GHz
antenna suite, see 2.4 GHz Single Band Antenna Suite on page 3-1.
• The antenna part numbers with a 5299 indicates a 5 GHz antenna. For more information on the 2.4 GHz
antenna suite, see 5.2 Ghz Single Band Antenna Suite on page 4-1.
Antenna Selection and Description 1-5
• The antenna part numbers with a 2452 indicates a dual band antenna (2.4GHz and 5 GHz). For more
information on the 2.4 GHz antenna suite, see 2.4GHz - 5.2GHz Dual Band Antenna Suite on page 5-1.
1.1.4 Extended AP to Antenna Cable Lengths
Most indoor antennas are intended to be mounted directly to the AP's connectors. Some mounting
arrangements call for positioning the AP a significant distance away from the antenna due to serviceability
or other reason. In these situations, various adapters and cable extensions are required.
In these situations be mindful of:
• The connector on the AP
• The connector on the antenna
• The spectrum being implemented
• Signal loss due to multiple connectors and long cable lengths
Combinations of these attributes present different parts required to complete the connection. The Product
Compatibility matrix addresses the parts required to make a proper connection. For more information, see
FCC Compliance on page 2-1.

1-6 Enterprise Wireless LAN Antenna Specification Guide
1.2 Antenna Selection Criteria
In addition to antenna frequency, there is other criteria to consider when selecting an antenna.
1.2.1 Antenna Pattern
1.2.1.1 Omni-Directional
Signal radiates from the antenna in all directions on the horizontal plane.
1.2.1.2 Directional
Signal radiates in a specific direction, typically described as a beam of given width, expressed in degrees in
the horizontal and vertical plane. For more information, see Azimuth 3dB Beamwidth on page 1-7 and
Elevation 3dB Beamwidth on page 1-7.
1.2.2 Antenna Type
1.2.2.1 Panel
A panel antenna is a flat antenna mounted to a wall or other vertical surface and radiates RF energy (radio
waves) directionally away from the wall. They usually have gain greater than 5 dBi and are not suitable for
omni-directional situations. Ideally suited for long hallways.
1.2.2.2 Patch
A patch antenna is a flat antenna mounted on the ceiling but whose pattern is omni-directional. Most of the
energy goes out horizontally to the sides of the antenna and equal in all directions.
1.2.2.3 Dipole
A dipole antenna is a tubular antenna that can be either a pipe shape, a straight flexible rod or a paddle. This
antenna has an omni-directional pattern when placed in a vertical position. It usually has 2 dBi of gain.
1.2.2.4 Dipole Array
Essentially a dipole, a dipole array is two or more dipoles that are placed one on top of the other, requiring
a longer tube to hold them. The advantage of a dipole array is that it has higher gain.
1.2.2.5 Parabolic Grid
A parabolic grid antenna is a very directional, dish-like antenna. Its parabolic reflector focuses the RF energy
like a flashlight. Most of the time the radiating element is a dipole, but when combined with the dish, it
becomes very directional with gain up to 24 dBi. Usually used in long point-to-point systems.
1.2.2.6 Yagi
A yagi antenna is a antenna that has an internal structure resembling that of typical antennas used for TV
reception (a series of rods perpendicular to a main rod, making a triangular shape). This is a directional
antenna with less gain than the PGA, typically around 13 dBi. It may be used in either point-to-point
situations, or to cover a very long, narrow area in point-to-multi-point situations.

1.2.3 Antenna Performance Characteristics
1.2.3.1 Frequency
The frequency band within which the antenna performs at the stated specifications
1.2.3.2 Gain (dBi)
The relative amplification of the antenna with respect to an equivalent isotropic antenna, expressed on the
decibel logarithmic scale.
1.2.3.3 Cable loss (dB)
The signal strength loss introduced by the cable connected to the antenna expressed on the decibel
logarithmic scale.
1.2.3.4 Net gain (dBi)
The resulting amplification of the antenna paired with its cable.
1.2.3.5 Polarization
The orientation of the electrical field which the antenna is optimized to receive. If the transmitting and
receiving antennas are both linear polarized, then turning one 90° so that they are cross polarized will reduce
the range significantly.
Antenna Selection and Description 1-7
1.2.3.6 VSWR
Voltage Standing Wave Ratio (VSWR) is the ratio of maximum voltage to minimum voltage along the line.
Expresses the degree of match between the transmission line and the terminating element (antenna). When
VSWR is 1:1 the match is perfect, a VSWR of 1.5:1 corresponds to 96% power efficiency.
1.2.3.7 Azimuth 3dB Beamwidth
Width of the antenna beam on the horizontal plane expressed in degrees.
1.2.3.8 Elevation 3dB Beamwidth
Height of the antenna beam on the vertical plane expressed in degrees.
1.3 Antenna Accessories for Enterprise WLANs
Motorola Solutions offers a complete selection of antennas and accessories to ensure optimal coverage and
performance for wireless LANs. Regardless of the size or layout of your environment, from a small office or
storefront to campus-wide, multiple-site, indoor and outdoor deployments, Motorola Solutions offers the
antennas, cables and accessories designed to fit your needs.
By combining this portfolio with a broad line of wireless switches, access ports, access points, client
connectivity cards, ruggedized mobile voice/data devices and network management software, as well as
wireless mobility planning and deployment services, Motorola Solutions offers comprehensive end-to-end
wireless enterprise LAN solutions, giving you secure, reliable access to your critical business data and
applications at the point of activity. For more information on Motorola Solutions's wireless products, visit
www.motorolasolutions.com.

1-8 Enterprise Wireless LAN Antenna Specification Guide
1.3.1 Choosing the Right Antenna and accessories for your WLAN
It is important to consider a number of factors when choosing an antenna and accessories for your Motorola
Solutions enterprise WLAN. To choose the right components, you'll need to know:
• Where is the antenna to be installed, and what type of coverage is required. Knowing the intended radio
band is central. Determine if the intended radio coverage area supports dual 2.4/5.2 band traffic. Has the
antenuation of the coverage been discerned in respect to known barriers.
• The band (802.11b/g/n or 802.11a/n) your network supports
• Which Motorola Solutions AP to use
• Whether you will be deploying the network indoors or outdoors
• The distance between AP and antenna, to determine extender cable length, if any
• The serviceablity requirement for each AP and antenna deployment
Review the chart to determine which antennas suit your needs. Using the part numbers provided, determine
which of the antennas will work with your hardware in your environment.

Product Compatibility
To find the right antenna and accessories for your deployment:
• Find your access point or access port model at the top of the chart (refer to the chart on the following
page). Follow that column down to find the antennas, cables and lightning arrestors compatible with
that model access port or access point. Write those part numbers down.
• Follow the row antenna across the table to the columns for the lightning arrestors and cables you wrote
down to confirm that they compatible with the antenna you've chosen and determine if an adaptor is
required to connect the two selected parts.
2.1 FCC Compliance
Motorola Solutions enterprise Access Points are approved by the FCC with the understanding that these
devices are Professionally Installed. Under FCC regulations, this allows the Professional Installers the
flexibility to configure the Access Points for each specific customers needs and insure a compliant
installation. The antennas offered in our portfolio have different coverage patterns and antenna gains to
meet the needs of different installation requirements and require careful planning. The Access Point
transmitter power must be adjusted by the professional installer based on the specific antenna and other
installation components used in the installation to ensure compliant operation.
A professional installer must:
• Have a good understanding of RF theory
• Be able to calculate a link budget for a given transmitter configuration. For example, Conducted Output
Power + Cabling Losses + Mechanical Connection Losses + Antenna Gain = Output Power (This output
power should be equal or lower than the Maximum Power as listed on the FCC Grant for a transmitter)
• Be familiar with both the mechanical and software tools required to configure and adjust the transmitter
being installed
• Understand basic FCC regulations for the site specific location and installation requirements of the
various radio products being installed
• Understand basic antenna operational theory and standard industry antenna installation practices
• Be certified by local authorities to install electrical devices.

2-2 Enterprise Wireless LAN Antenna Specification Guide
WARNING! OPERATING A TRANSMITTER THAT IS CONFIGURED FOR
INDOOR USE IN AN OUTDOOR ENVIORNMENT IS AGAINST FCC
REGULATIONS AND SUBJECT TO FCC ENFORCEMENT ACTIONS
AGAINST BOTH THE INSTALLER AND THE OPERATOR.
2.1.1 Outdoor Access Point Installations
The FCC regulations for the indoor and outdoor installation are different; the professional installer must
configure the Access Point transmitters accordingly. Products that are specifically intended to be placed
outdoors are configured at the factory for compliant outdoor operation. Motorola Solutions recommends
professional installers review the following to assess the legality of outdoor deplyments:
• If a transmitter is placed indoors but the antenna is placed outdoors, the FCC interprets this as an outdoor
installation
• If a transmitter is placed indoors and the antenna is oriented to intentionally radiate outdoors, the FCC
interprets this as an outdoor installation
• If the transmitter is placed on a loading dock or inside a covered stadium with a retractable cover, the FCC
views this as an outdoor installation
The Federal Communications Commission (FCC), the National Telecommunications and Information
Administration (NTIA) and the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) have an ongoing investigation of
interference caused to Terminal Doppler Weather Radar (TDWR) systems operating in the 5600-5650 MHz band.
TDWRs are used to detect wind shear and other weather conditions near airports.
The interference at most locations was attributed to fixed wireless transmitters operating outdoors in the
vicinity of airports at high elevations that are line-of-sight to the TDWR installations (5 GHz network equipment).
In some instances, the interference was caused by equipment that was not properly certified or configured. In
other instances, equipment was FCC certified nonetheless caused interference. The FCC has taken appropriate
enforcement action in each of these cases.
If everything is determined to be compliant - the FCC orders the interfering transmitter turned off or adjustments
be made such that there is no more interference; any non-compliance determined is resolved with an
enforcement action.
On 14 OCTOBER 2010 the FCC published the following notice that requests that devices operating in the 5.4 GHz
band located near the appended list of airports register these devices. A voluntary WISPA sponsored database
has been developed that allows operators and installers to register the location information of the UNII devices
operating outdoors in the 5470 - 5725 MHz band within 35 km of any TDWR location.
NOTE: Motorola Solutions strongly encourages the voluntary registration of all outdoor
installations at http://www.spectrumbridge.com/udia/home.aspx
.

Product Compatibility 2-3
2.2 FCC Approval Statement
Federal Communications Commission
Office of Engineering and Technology
Laboratory Division
Interim Plans to Approve UNII Devices Operating in the 5470 - 5725 MHz Band with Radar
Detection and DFS Capabilities
The FCC, NTIA, FAA and industry are working to resolve interference to Terminal Doppler Weather Radar
(TDWR) systems used near airports that has occurred from some outdoor wireless systems operating in the
5470 MHz – 5725 MHz band. These wireless devices are subject to Section 15.407 of our rules and when
operating as a master device they are required to implement radar detection and DFS functions. We are
continuing our work to develop long-term equipment authorization test procedures that will ensure that the
devices comply with our rules that include protecting the TDWR operations. In the interim, the Commission
will now allow certification of wireless master devices with radar detection function and with DFS capability,
if they meet the following conditions:
• Devices will not transmit on channels which overlap the 5600 – 5650 MHz band.
1
• Devices intended for outdoor use will be further restricted, as follows:
• Devices must be professionally installed when operating in the 5470 – 5725 MHz band.
• Grantees must provide owners, operators and all such installers with specific instructions in their
user’s manual on requirements to avoid interference to TDWRs and information that meets the
following instructions:
2
• Any installation of either a master or a client device within 35 km of a TDWR location shall be
separated by at least 30 MHz (center-to-center) from the TDWR operating frequency (as shown in
the attached table)
1
The devices subject to the requirements in this KDB can select the initial channel for operation to avoid
3, 4
, and 5.
TDWRs and apply the Uniform Channel Spreading requirements (see FCC 06-96 in ET Docket 03-122 released
June 30, 2006) on the remaining available frequency band of operation. All the other test procedures
including the test radar patterns remain the same at the present time. A revision to the measurement
procedure with modification to the Uniform Channel Spreading requirement and other changes will be
released in the future. The Commission will also address the issue of any field upgrade option at that time.
2
The grantee must identify the specific expertise and the training required by the installers for installing
these types of devices.
3
In some instances it is possible that a device may be within 35 km of multiple TDWRs. In this case the
device must ensure that it avoids operation within 30 MHz for each of the TDWRs. This requirement applies
even if the master is outside the 35 km radius but communicates with outdoor clients which may be within
the 35 km radius of the TDWRs.
4
The requirement for ensuring 30 MHz frequency separation is based on the best information available to
date. If interference is not eliminated, a distance limitation based on line-of-sight from TDWR will need to
be used. In addition, devices with bandwidths greater than 20 MHz may require greater frequency
separation.
• Procedures for the installers and the operators on how to register the devices in the industry-sponsored
database with the appropriate information regarding the location and operation of the device and
installer information is included.
6
• Devices must meet all of the other requirements specified in Section 15.407, and it is prohibited to
include configuration controls (e.g. country code settings or other options to modify DFS functions) to
change the frequency of operations to any frequency other than those specified on the grant of
certification for US operation.
7
2-4 Enterprise Wireless LAN Antenna Specification Guide
• All applications for equipment authorization must clearly show compliance with all of the technical
requirements under worst case parameters, under user or operator control, based on frame rates,
listen/talk ratios and user data transfer conditions.
All the devices subject to the DFS requirements must be submitted to the Commission’s Laboratory Division
for pre-grant testing and equipment authorization.
8
The applicant must ensure that all equipment
authorization applications subject to this interim procedure include appropriate attestations that the device
has no option to change the DFS parameters and that transmissions are disabled at least in the 5600 – 5650
MHz band. The application must include the user’s manual with the appropriate installation and operations
requirements for the installers and operators.
We are continuing to evaluate additional measures that may need to be taken to further ensure against
interference caused by 5 GHz outdoor wireless systems located near airports. While manufacturers have an
obligation to ensure that their equipment complies with FCC rules, and must take steps to ensure their
devices are unlikely to cause harmful interference, Section 15.5 of the Commission’s rules also places an
obligation on users of devices to avoid causing interference and to correct any interference that may occur.
We encourage the manufacturers to include information for the users, including the operators and installers,
to ensure that they understand that it is incumbent on them to cooperate with manufacturers to implement
any changes necessary to facilitate compliance.
5
Devices may be optionally designed not to transmit on channels which overlap 5570 – 5680 MHz instead
of requiring installers to perform site-by-site adjustments. In that case it is still required that the devices
should be installed professionally and the procedures for registering the device in the industry database
should be included in the Users Manual.
6
A voluntary WISPA sponsored database has been developed that allows operators and installers to register
the location information of the UNII devices operating outdoors in the 5470 – 5725 MHz band within 35 km
of any TDWR location (see http://www.spectrumbridge.com/udia/home.aspx). This database may be used
by government agencies in order to expedite resolution of any interference to TDWRs.
7
For example, device software must not have any country code options or software configuration settings
which allow an end user to modify the DFS operation or impact the performance of DFS. See KDB 594280.
8
The TCBs are not permitted to approve transmitters with radar detection capabilities. See KDB 628591.
9 The manufacturers may consider taking steps providing clear instructions to operators and installers of
devices as to the need to comply with rules for use of the band, guidance on registration of devices and any
other processes that are designed to avoid interference. They may use methods that include, but are not
limited to, instructions in manuals, notification on product web pages and service bulletins issued for
products in the field.
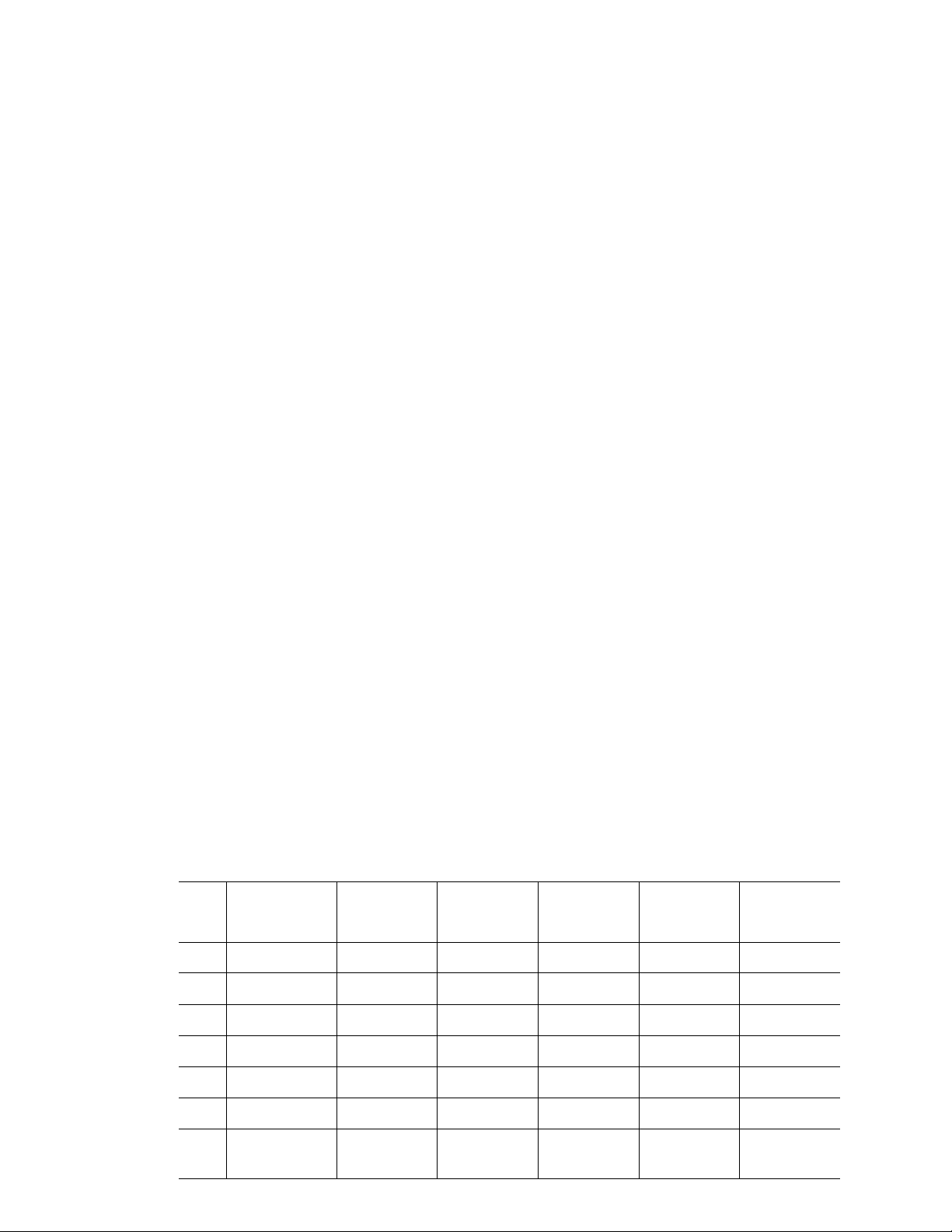
TDWR Location Information*
TERRAIN
ELEVATION
STATE CITY LONGITUDE LATITUDE FREQUENCY
AZ PHOENIX W 112 09 46 N 33 25 14 5610 MHz 1024 64
CO DENVER W 104 31 35 N 39 43 39 5615 MHz 5643 64
FL FT LAUDERDALE W 080 20 39 N 26 08 36 5645 MHz 7 113
FL MIAMI W 080 29 28 N 25 45 27 5605 MHz 10 113
FL ORLANDO W 081 19 33 N 28 20 37 5640 MHz 72 97
FL TAMPA W 082 31 04 N 27 51 35 5620 MHz 14 80
FL WEST PALM
BEACH
W 080 16 23 N 26 41 17 5615 MHz 20 113
(MSL) [ft]
ANTENNA
HEIGHT ABOVE
TERRAIN [ft]
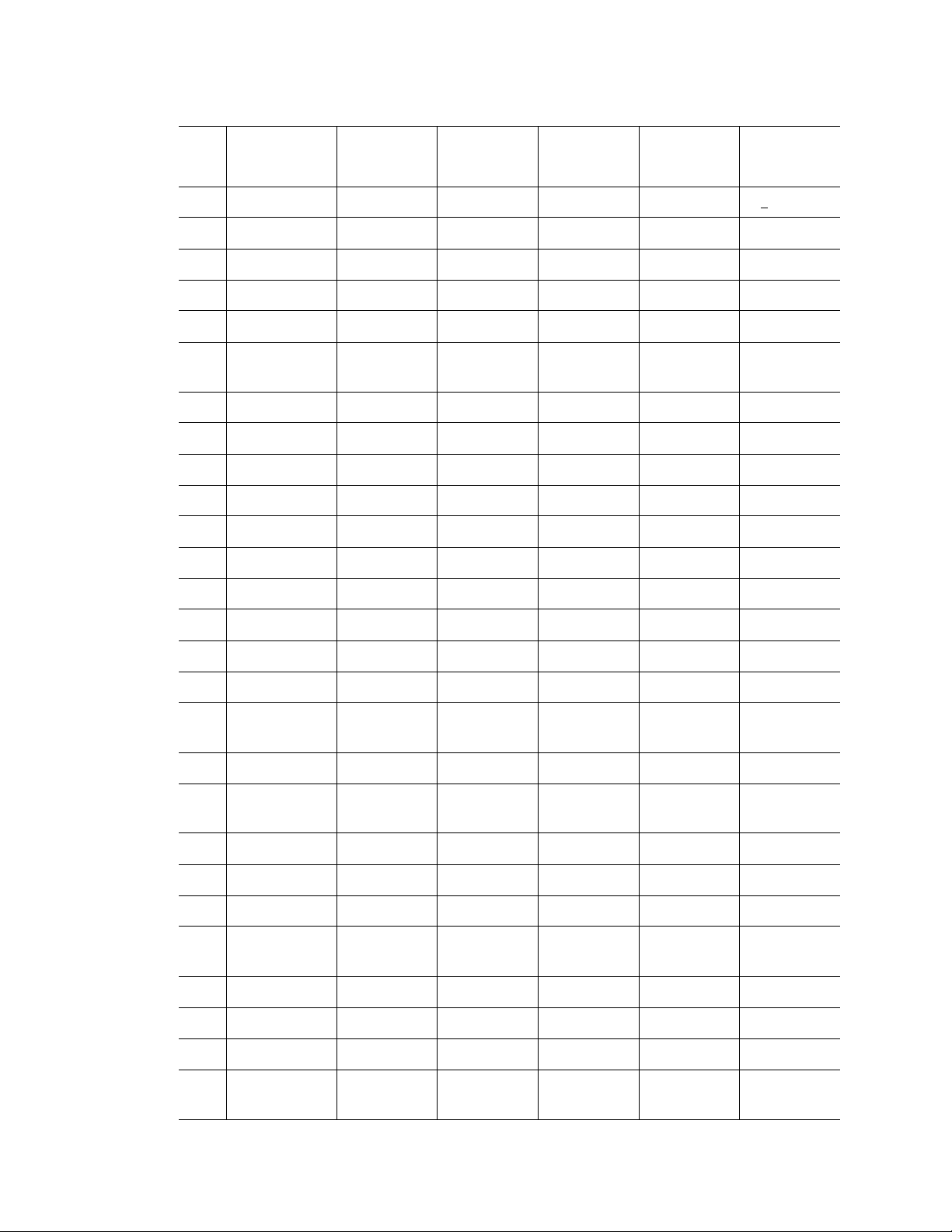
Product Compatibility 2-5
STATE CITY LONGITUDE LATITUDE FREQUENCY
TERRAIN
ELEVATION
(MSL) [ft]
ANTENNA
HEIGHT ABOVE
TERRAIN [ft]
GS ATLANTA W 084 15 44 N 33 38 48 5615 MHz 962 113
IL MCCOOK W 087 51 31 N 41 47 50 5615 MHz 646 97
IL CRESTWOOD W 087 43 47 N 41 39 05 5645 MHz 663 113
IN INDIANAPOLIS W 086 26 08 N 39 38 14 5605 MHz 751 97
KS WICHITA W 097 26 13 N 37 30 26 5603 MHz 1270 80
KY COVINGTON
W 084 34 48 N 38 53 53 5610 MHz 942 97
CINNCINNATI
KY LOUISVILLE W 085 36 38 N 38 02 45 5646 MHz 617 113
LA NEW ORLEANS W 090 24 11 N 30 01 18 5645 MHz 2 97
MA BOSTON W 070 56 01 N 42 09 30 5610 MHz 151 113
MD BRANYWINE W 076 50 42 N 38 41 43 5635 MHz 233 113
MD BENFIELD W 076 37 48 N 39 05 23 5645 MHz 184 113
MD CLINTON W 076 57 43 N 38 45 32 5615 MHz 249 97
MI DETROIT W 083 30 54 N 42 06 40 5615 MHz 656 113
MN MINNEAPOLIS W 092 55 58 N 44 52 17 5610 MHz 1040 80
MO KANSAS CITY W 094 44 31 N 39 29 55 5605 MHz 1040 64
MO SAINT LOUIS W 090 29 21 N 38 48 20 5610 MHz 551 97
MS DESOTO
W 089 59 33 N 34 53 45 5610 MHz 371 113
COUNTY
NC CHARLOTTE W 080 53 06 N 35 20 14 5608 MHz 757 113
NC RALEIGH
W 078 41 50 N 36 00 07 5647 MHz 400 113
DURHAM
NJ WOODBRIDGE W 074 16 13 N 40 35 37 5620 MHz 19 113
NJ PENNSAUKEN W 075 04 12 N 39 56 57 5610 MHz 39 113
NV LAS VEGAS W 115 00 26 N 36 08 37 5645 MHz 1995 64
NY FLOYD BENNETT
W 073 52 49 N 40 35 20 5647 MHz 8 97
FIELD
OH DAYTON W 084 07 23 N 40 01 19 5640 MHz 922 97
OH CLEVELAND W 082 00 28 N 41 17 23 5645 MHz 817 113
OH COLUMBUS W 082 42 55 N 40 00 20 5605 MHz 1037 113
OK AERO. CTR
W 097 37 31 N 35 24 19 5610 MHz 1285 80
TDWR #1
2-6 Enterprise Wireless LAN Antenna Specification Guide
TERRAIN
ELEVATION
STATE CITY LONGITUDE LATITUDE FREQUENCY
OK AERO. CTR
TDWR #2
OK TULSA W 095 49 34 N 36 04 14 5605 MHz 712 113
OK OKLAHOMA
CITY
PA HANOVER W 080 29 10 N 40 30 05 5615 MHz 1266 113
PR SAN JUAN W 066 10 46 N 18 28 26 5610 MHz 59 113
TN NASHVILLE W 086 39 42 N 35 58 47 5605 MHz 722 97
TX HOUSTON
INTERCONTL
TX PEARLAND W 095 14 30 N 29 30 59 5645 MHz 36 80
TX DALLAS LOVE
FIELD
TX LEWISVILLE
DFW
W 097 37 43 N 35 23 34 5620 MHz 1293 97
W 097 30 36 N 35 16 34 5603 MHz 1195 64
W 095 34 01 N 30 03 54 5605 MHz 154 97
W 096 58 06 N 32 55 33 5608 MHz 541 80
W 096 55 05 N 33 03 53 5640 MHz 554 31
(MSL) [ft]
ANTENNA
HEIGHT ABOVE
TERRAIN [ft]
UT SALT LAKE CITY W 111 55 47 N 40 58 02 5610 MHz 4219 80
VA LEESBURG W 077 31 46 N 39 05 02 5605 MHz 361 113
WI MILWAUKEE W 088 02 47 N 42 49 10 5603 MHz 820 113
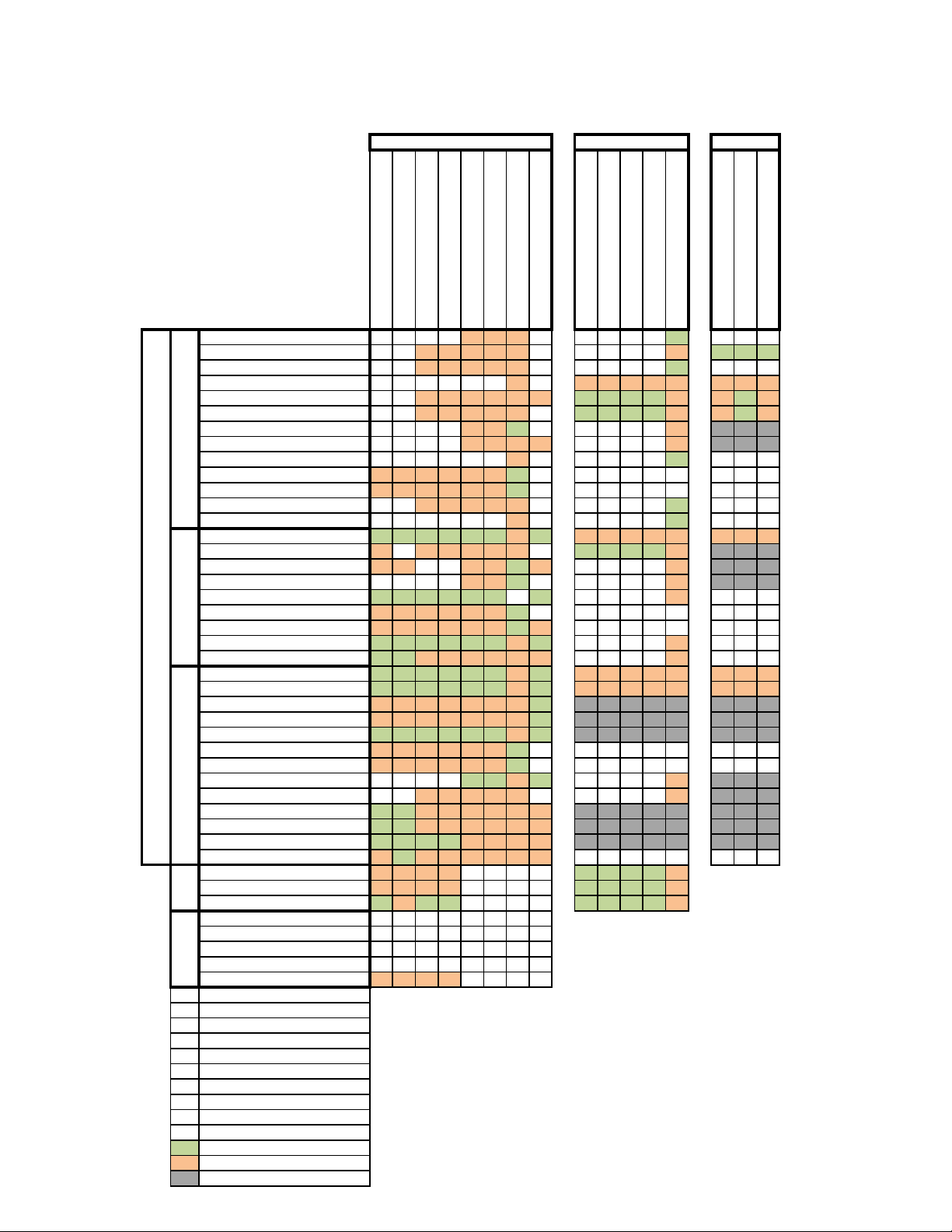
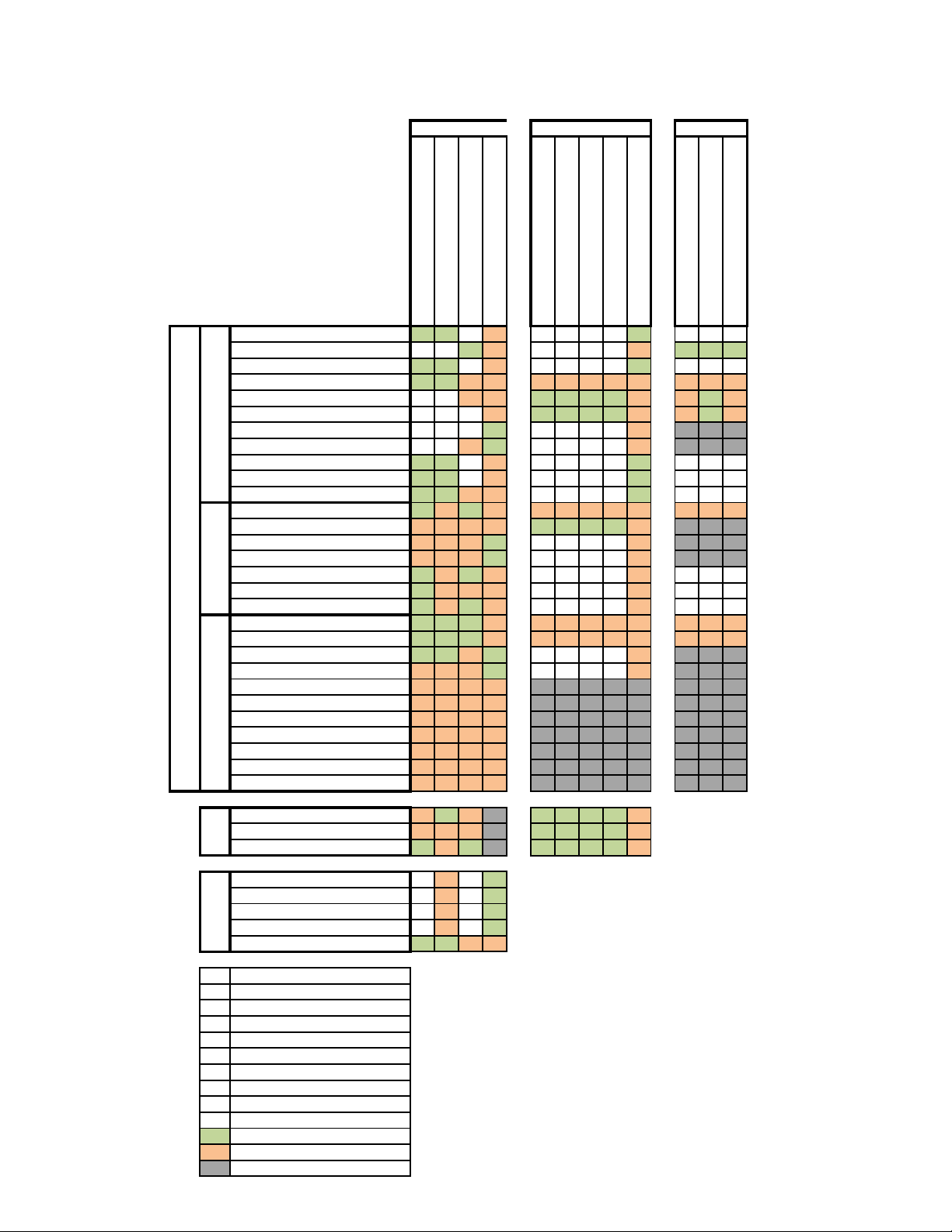
2.3 FCC USA Compaibility Matrix
The following (on the next two pages) displays Motorola Solutions FCC approved AP radio, antenna, cable
and accessory combinations for use in the United States for both current and legacy access points:
Product Compatibility 2-7
p
p
q
Cables LAsAP Radios
AP-7131 ABGN (US7AP7131)
AP-7131N AGBN (UZ7AP7131NAP-650 AGBN (UZ7MB82)
AP-6532 AGBN (UZ7MB82)
AP-621 ABGN (UZ7AP6)
AP-6521 ABGN (UZ7AP6)
AP-7161 ABGN (QJEAP716101)
AP-622 ABGN (UZ7AP0622)
ML-1499-100JK-01R
ML-1499-10JK-01R
ML-1499-25JK-01R
ML-1499-50JK-01R
ML-1499-72PJ-01R
ML-1499-LAK1-01R
ML-1499-LAK2-01R
ML-2452-LAK1-01R
ML-2499-11PNA2-01R 3333XXX3 1111* 222
ML-2499-5PNL-72-N 77XXXXX7 AAAA X ***
ML-2499-7PNA2-01R 33XXXXX3 1111* 222
ML-2499-APA2-01 333333X3 XXXXX XXX
ML-2499-BPNA3-01R 77XXXXXX ****XX* X
ML-2499-BYGA2-01R 7 7XXXXX7 ****XX* X
ML-2499-FHPA5-01R 7777XX* 7 AAAAX
ML-2499-FHPA9-01R 7777XXXX AAAAX
2.4 GHz5 GHzDual-Band
ML-2499-HPA3-01R 333333X3 1111* 222
ML-2499-HPA4-01 XXXXXX * 7
ML-2499-HPA8-01 XXXXXX * 7
ML-2499-PNAHD-01R 33XXXXX3 1111* 222
ML-2499-SD3-01R 333333X3 1111* 222
ML-5299-APA1-01R ******X * XXXXX XXX
ML-5299-BYGA15-012 X7XXXXX7 ****X
ML-5299-FHPA10-01R XX77 XX* X AAAAX
ML-5299-FHPA6-01R 7777XX* 7 AAAAX
ML-5299-HPA1-01R ******5 * 4444X 555
ML-5299-HPA5-01 XXXXXX * 7
Antennas
ML-5299-HPA10-01 XXXXXX* X
ML-5299-PTA1-01R ******X * 4444X 555
ML-5299-WPNA1-01R * * XXXXXX 4444X 555
ML-2452-APA2-01 ******X * XXXXX XXX
ML-2452-APA2-02
******X * XXXXX
XXX
ML-2452-APAG2A1-01 XXXXXXX*
ML-2452-APAG2A1-02 XXXXXXX*
ML-2452-HPA5-036 ******X *
ML-2452-HPAG4A6-01 XXXXXX* 7
ML-2452-HPAG5A8-01 XXXXXX* 7
ML-2452-PNA5-01R 7777**X * AAAAX
ML-2452-PNA7-01R 77XXXXX7 AAAA X
ML-2452-PNL9M3-036 * * XXXXXX
ML-2452-PTA2M3X3-1 * * XXXXXX
ML-2452-PTA3M3-036 ****XXXX
ML-2452-PTA6X6-036 X * XXXXXX
ML-1499-LAK1-01R XXXX ****X
ML-1499-LAK2-01R XXXX ****X
LAsCables
ML-2452-LAK1-01R * X ** ****X
ML-1499-100JK-01R 7777
ML-1499-10JK-01R 7777
ML-1499-25JK-01R 7777
ML-1499-50JK-01R 7777
ML-1499-72PJ-01R XXXX
1 ML-1499-RBNCA1-01R
2 ML-1499-RBNCA2-01R
3 25-72178-01
4 25-90262-01R
5 25-90263-01R
6 25-85391-01R
7 25-85392-01R
must use ML-1499-LAK1-01R
8
9 25-97261-01R
A 25-99175-01R
Not re
atible
atible
uired
*Com
X Not com
2-8 Enterprise Wireless LAN Antenna Specification Guide
p
p
q
AP Radios
AP300 (H9PWSAP5100)
AP300 B/G (H9PWSAP5200bg)
AP-5131 (H9PA5131)
AP-5181 (H9PA5181)
Cables LAs
ML-1499-100JK-01R
ML-1499-10JK-01R
ML-1499-25JK-01R
ML-1499-50JK-01R
ML-1499-72PJ-01R
ML-2499-11PNA2-01R * * 3X 1111* 222
ML-2499-5PNL-72-N 88* X AAAAX ***
ML-2499-7PNA2-01R * * 3X 1111* 222
ML-2499-APA2-01 * * XX XXXXX XXX
ML-2499-BPNA3-01R 99XX ****XX* X
ML-2499-BYGA2-01R 996X ****XX* X
ML-2499-FHPA5-01R 889* AAAAX
2.4 GHz5 GHzDual
ML-2499-FHPA9-01R 88X* AAAAX
ML-2499-HPA3-01R * * 3X 1111* 222
ML-2499-PNAHD-01R * * 3X 1111* 222
ML-2499-SD3-01R * * XX 1111* 222
ML-5299-APA1-01R * X * X XXXXX XXX
ML-5299-BYGA15-012 XXXX ****X
ML-5299-FHPA10-01R XXX* AAAAX
ML-5299-FHPA6-01R XXX* AAAAX
ML-5299-HPA1-01R * X * X 4444X 555
Antennas
ML-5299-PTA1-01R * XXX 4444X 555
ML-5299-WPNA1-01R * X * X 4444X 555
ML-2452-APA2-01 * * * X XXXXX XXX
ML-2452-APA2-02 * * * X XXXXX XXX
ML-2452-PNA5-01R * * X * AAAAX
ML-2452-PNA7-01R XXX* AAAA X
ML-2452-PTA2M3X3-1 XXXX
ML-2452-PTA3M3-036 XXXX
ML-2452-HPA5-036 XXXX
ML-2452-PNL9M3-036 XXXX
ML-2452-APA6J-01 XXXX
ML-2452-APAG2A1-01 XXXX
ML-2452-APAG2A1-02 XXXX
ML-1499-LAK1-01R
ML-1499-LAK2-01R
ML-2452-LAK1-01R
ML-1499-LAK1-01R X * X ****X
L-1499-LAK2-01R XXX ****X
M
LAsCables
ML-2452-LAK1-01R * X * ****X
ML-1499-100JK-01R 7X7*
ML-1499-10JK-01R 7X7*
ML-1499-25JK-01R 7X7*
ML-1499-50JK-01R 7X7*
ML-1499-72PJ-01R * * XX
1 ML-1499-RBNCA1-01R
2 ML-1499-RBNCA2-01R
3 25-72178-01
4 25-90262-01R
5 25-90263-01R
6 25-85391-01R
7 25-85392-01R
must use ML-1499-LAK1-01R
8
9 25-97261-01R
A 25-99175-01R
Not re
atible
atible
uired
*Com
X Not com

2.4 GHz Single Band Antenna Suite
3.1 Supported 802.11b/g/n Antenna Suite
Motorola Solutions supports numerous single-band 2.4 GHz 802.11b/g/n antennas to suit the requirements of your
unique access point or access port deployment. Check the Motorola Solutions Web site periodically, as newly
supported 802.11b/g/n antennas will be added to this document as they are released. For more information, go to
http://supportcentral.motorola.com/support/product/manuals.do
For detailed information on supported 802.11b/g/n antenna models, refer to:
.
• ML-2499-5PNL-72-N Outdoor 135° Panel Antenna: Male Connector
• ML-2499-7PNA2-01R Indoor 60° Diversity Panel: RP-BNC Male
• ML-2499-11PNA2-01R 97°Sector Panel: RP-BNC Male
• ML-2499-APA2-01R Indoor Rubber Flex, Elbow Joint Dipole: RP-BNC Male
• ML-2499-BPNA3-01R Outdoor 35° High-Gain Directional Panel: Type N - Female
• ML-2499-BYGA2-01R Outdoor 35° High-Gain Directional Yagi: N Female
• ML-2499-HPA3-01R High Performance Omni-Directional "Pipe" Antenna: RP-BNC Male
• ML-2499-PNAHD-01R Indoor 55°Directional Panel: RP-BNC Male
• ML-2499-SD3-01R Low Profile Ceiling/Surface Mount Omni-Directional Patch: RP-BNC Male
• ML-2499-FHPA5-01R Omni-Directional "Pipe" Antenna: N Male Connector
• ML-2499-FHPA9-01R High Performance Fixed Point Dipole: Male Connector
• ML-2499-HPA4-01 Outdoor Dipole Omni Antenna: N Male Connector
• ML-2499-HPA8-01 Outdoor Dipole Omni Antenna: N Male Connector
• ML-2499-7PNA2-02R Outdoor 60° Diversity Panel: RP-SMA Male
• ML-2499-HPA3-02R 11BGN, DP, 3dBi, LP, CBL 48, RP-SMA-Male
• ML-2499-PNAHD-02R 11BGN, 65° Patch, 7.5 dBI, LP, CBL 48, RP-SMA-M
• ML-2499-SD3-02R 11BGN, 50° Patch Omni, 4 dBI, LP, CBL 48, RP-SMA-M
NOTE: For examples on how various antenna and connectors are deployed in a 2.4 GHz
AP-5131 installation, see 2.4 GHz AP-5131 Antenna Connections.
3-2 Enterprise Wireless LAN Antenna Specification Guide
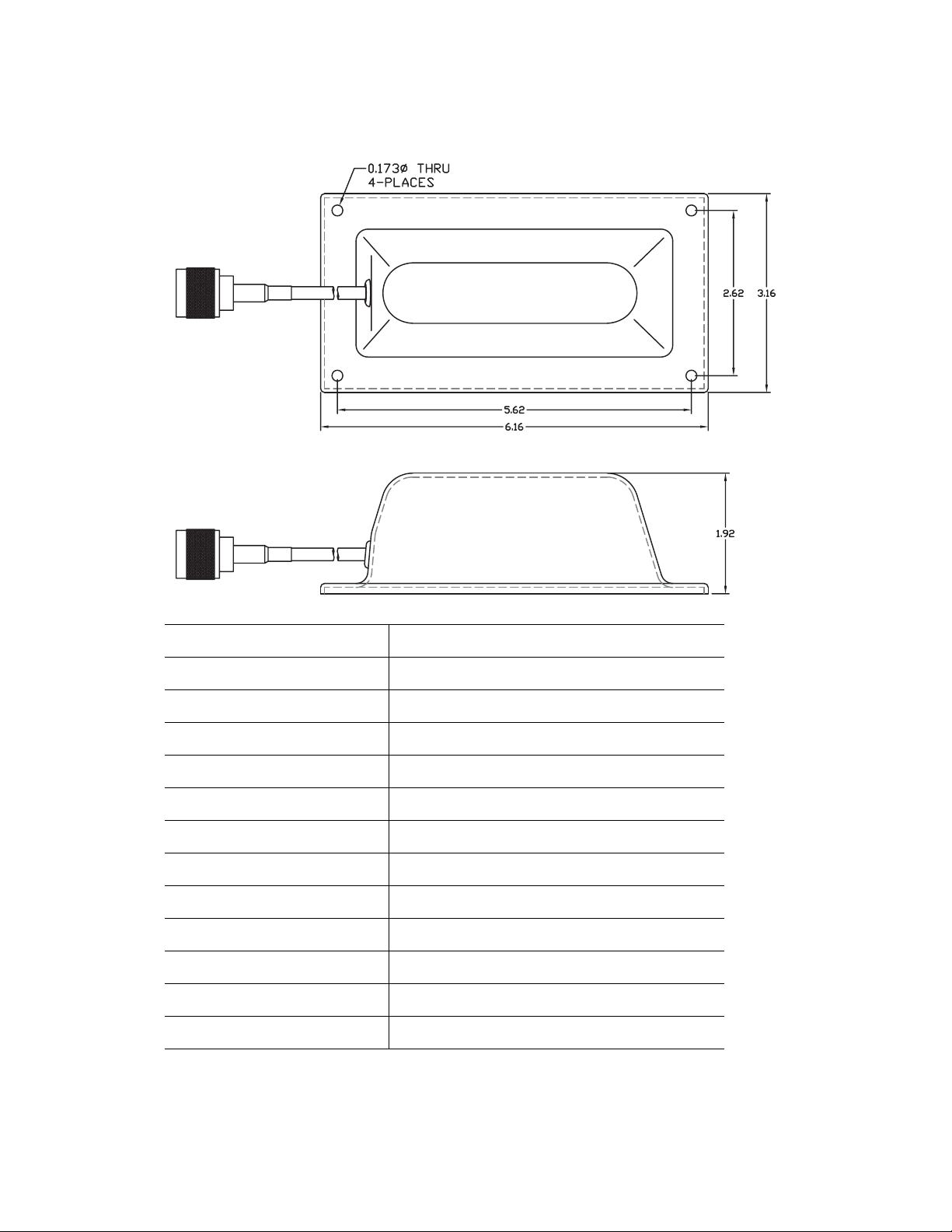
3.1.1 ML-2499-5PNL-72-N Outdoor 135° Panel Antenna: Male Connector
Type Panel
Frequency 2400-2500 MHz
Gain (dBi) 5
Polarization Linear, Vertical
Azimuth 3dB Beamwidth: 135°
Elevation 3dB Beamwidth: 56°
Cable Length (in.) 72
Cable Type RG-58 Ultralink
Connector Type Type N Male
Weight 0.5 lb
Plenum Antenna No
Plenum Cable Yes
Outdoor Rated Yes
2.4 GHz Single Band Antenna Suite 3-3
V
y
(°)
y
(
)
0.7342
MP 10:02:21 5002/31/9
081
09
)zHM( tF
tretiraloP
0.010.01
0.5
0.0
0.5-
0.01-
0.51-
0.02-
0.52-
0.03-
iBd
htdiwmaeB
072
1.431
17.5
)iBd( evA htdiwmaeB
nrettaP htumizA
0.7342
MP 22:70:21 5002/31/9
081
09
072
)zHM( tF
htdiwmaeB
zroHtiraloP
0.010.01
0.5
0.0
0.5-
0.01-
0.51-
0.02-
0.52-
0.03-
iBd
6.27
°
23.6
)iBd( evA htdiwmaeB
nrettaP noitavelE
3-4 Enterprise Wireless LAN Antenna Specification Guide
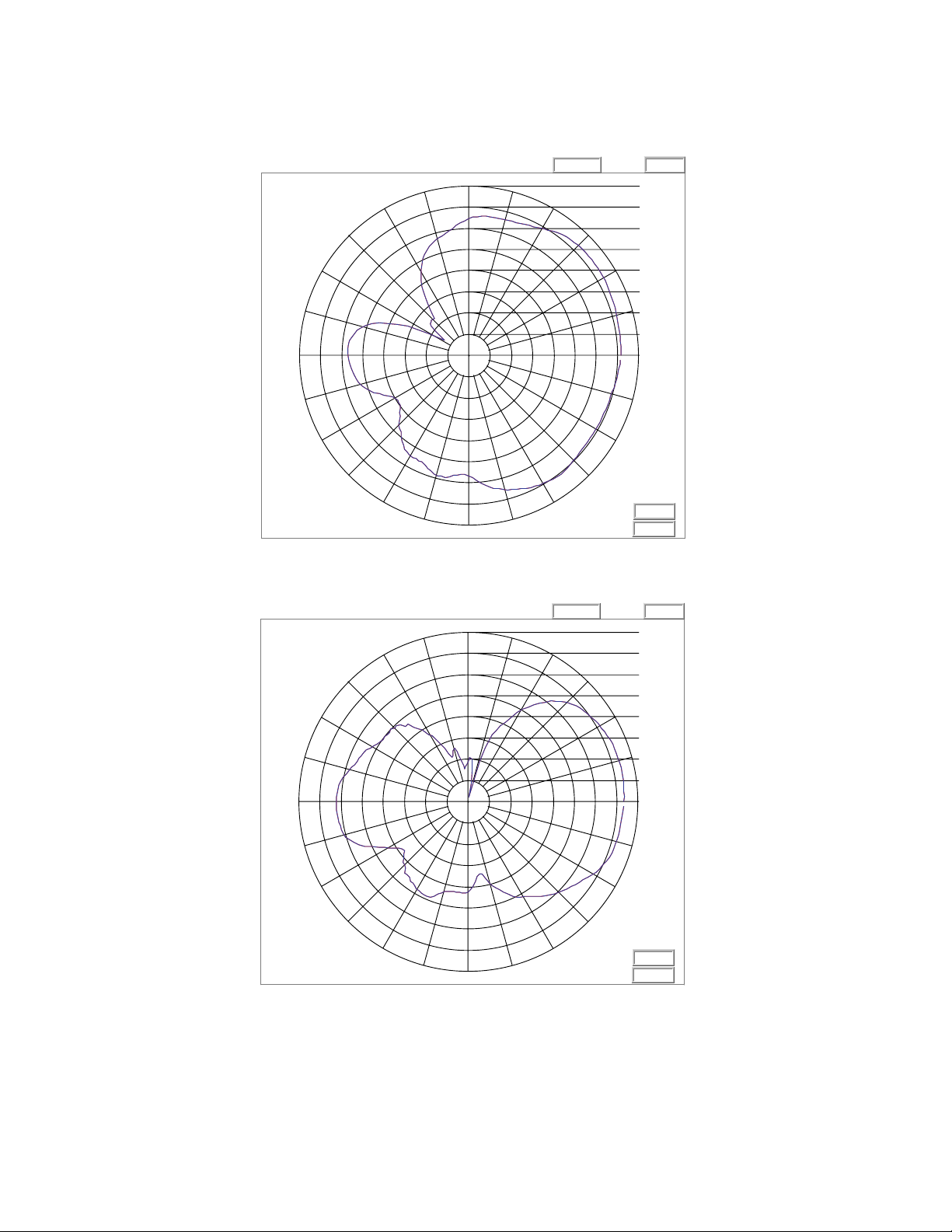
3.1.2 ML-2499-7PNA2-01R Indoor 60° Diversity Panel: RP-BNC Male
Type Panel x 2 (Diversity)
Frequency 2400-2500 MHz
Gain (dBi) 6.5
Polarization Linear, Vertical
Azimuth 3dB Beamwidth: 80°
Elevation 3dB Beamwidth: 55°
Cable Length (in.) 48
Cable Type RG-58 Ultralink
Connector Type RP-BNC Male x 2
Weight 0.6 lbs
Plenum Antenna No
Plenum Cable Yes
Outdoor Rated No
2.4 GHz Single Band Antenna Suite 3-5
(
)
V
y
(°)
(
)
V
y
(°)
tuC zA 10-2ANP7-9942-LMledoM
09
081
zHM
0.0542tF
tretiraloP
0.010.01
0.5
0.0
0.5-
0.01-
0.51-
0.02-
0.52-
0.03-
iBd
7.95
072
MP 92:05:2 3002/21/11
htdiw maeB
tuC htumizA
tuC lE 10-2ANP7-9942-LMledoM
09
081
0.0542tF
zHM
tretiraloP
0.010.01
0.5
0.0
0.5-
0.01-
0.51-
0.02-
0.52-
0.03-
iBd
1.75
072
MP 62:35:2 3002/21/11
htdiw maeB
tuC noitavelE
3-6 Enterprise Wireless LAN Antenna Specification Guide
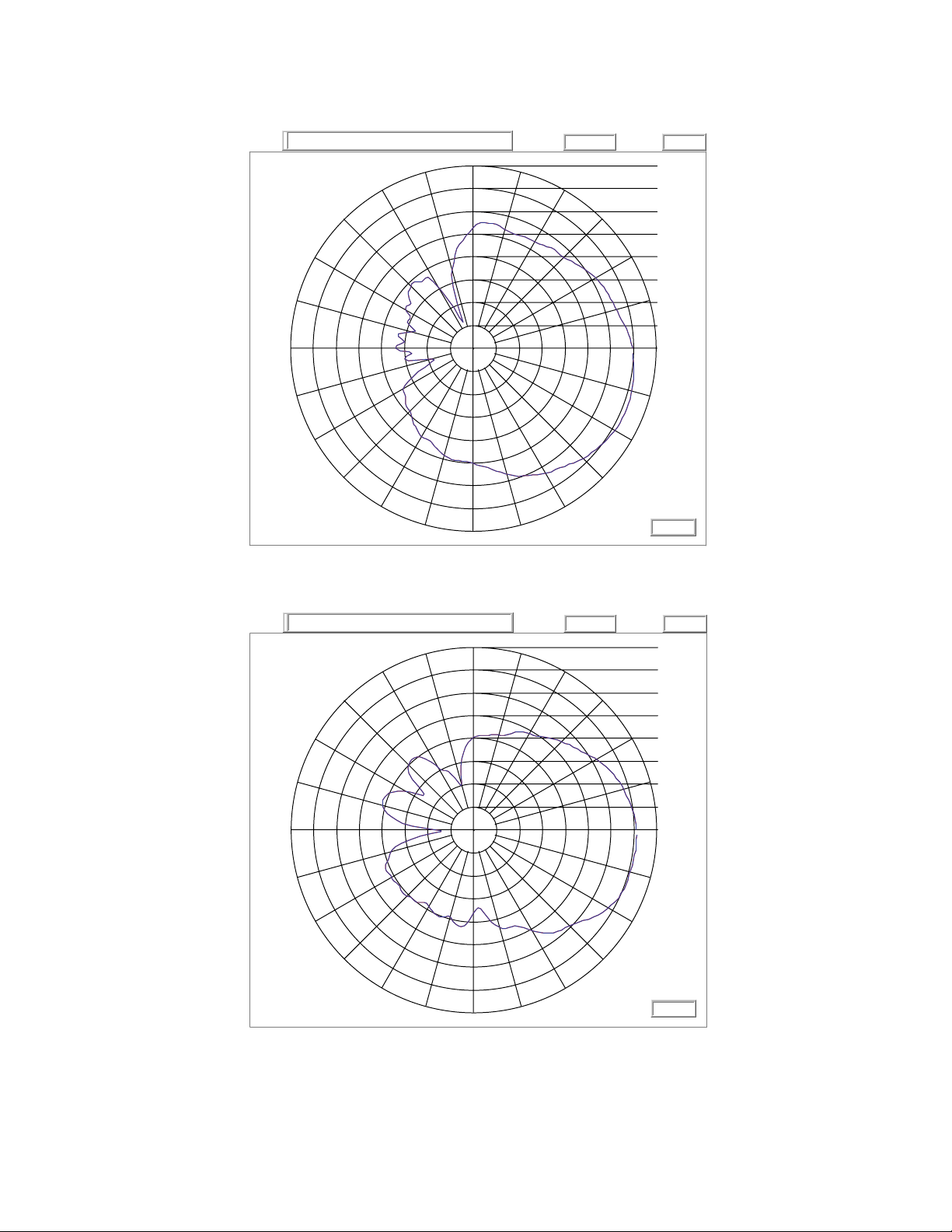
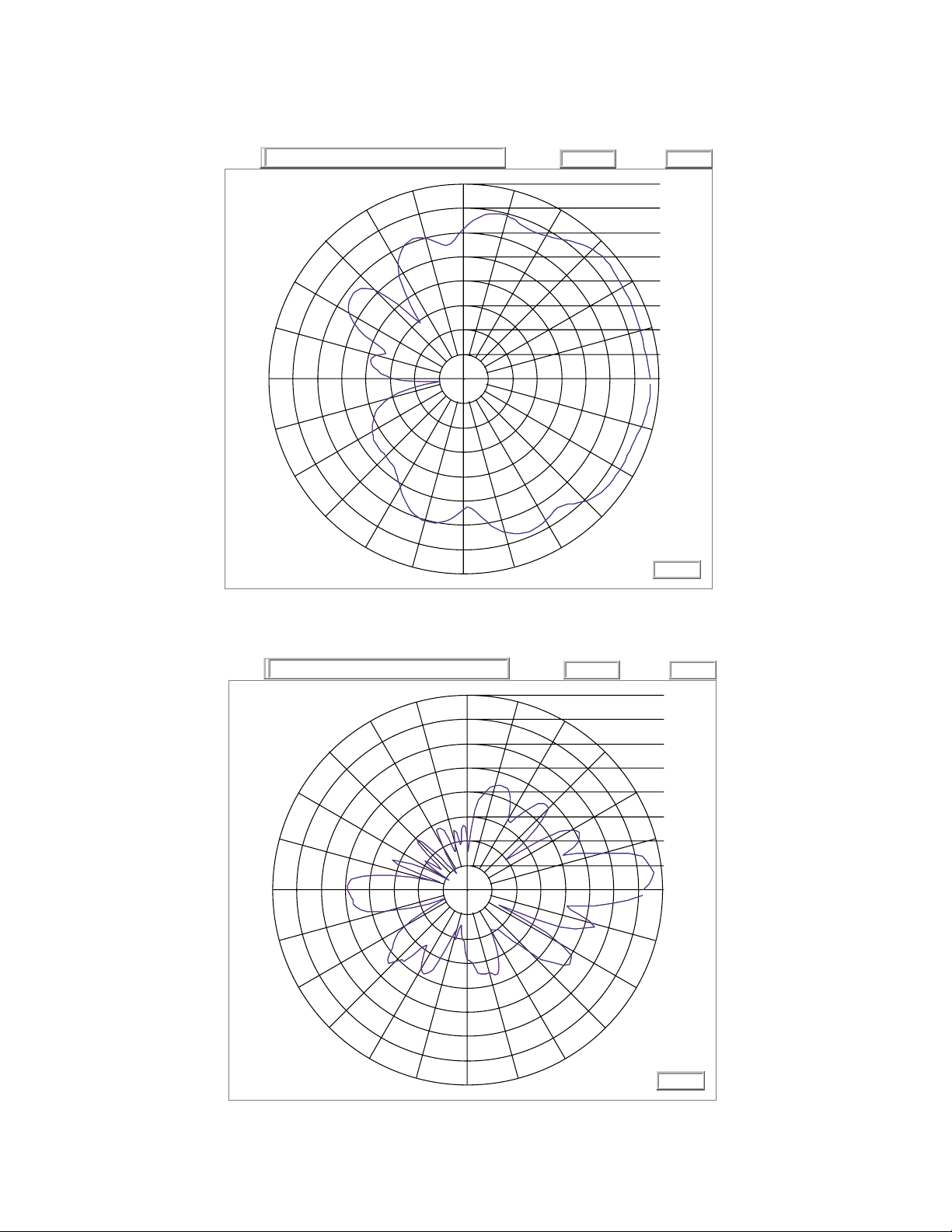
3.1.3 ML-2499-11PNA2-01R 97°Sector Panel: RP-BNC Male
Type Panel
Frequency 2400-1500 MHz
Gain (dBi) 11
Polarization Linear, Vertical
Azimuth 3dB Beamwidth: 120°
Elevation 3dB Beamwidth: 13°
Cable Length (in.) 96
Cable Type RG-58 Ultralink
Connector Type RP-BNC Male
Weight 1.5 lb
Plenum Antenna No
Plenum Cable Yes
Outdoor Rated Yes
2.4 GHz Single Band Antenna Suite 3-7
(
)
V
y
(°)
(
)
V
y
(°)
tuC zA 10-2ANP11-9942-LMledoMtuC zA 10-2ANP11-9942-LMledoMtuC zA 10-2ANP11-9942-LMledoM
09
09
09
081
081
081
0.0542tF 0.0542tF
zHM
tretiraloPtretiraloPtretiraloP
0.010.01
0.5
0.0
0.5-
0.01-
0.51-
0.02-
0.52-
0.03-
iBd
6.89
htdiw maeB
072
072
072
MP 84:74:7 3002/21/11
htdiw maeB
6.89
nrettaP htumizA
tuC lE 10-2ANP11-9942-LMledoMtuC lE 10-2ANP11-9942-LMledoMtuC lE 10-2ANP11-9942-LMledoM
09
09
09
081
081
081
072
072
072
MP 40:55:7 3002/21/11
zHM
0.0542tF0.0542tF
tretiraloPtretiraloPtretiraloP
0.010.01
0.5
0.0
0.5-
0.01-
0.51-
0.02-
0.52-
0.03-
iBd
7.31
htdiw maeB
htdiw maeB
7.31
nrettaP noitavelE
3-8 Enterprise Wireless LAN Antenna Specification Guide
3.1.4 ML-2499-APA2-01R Indoor Rubber Flex, Elbow Joint Dipole: RP-BNC Male
Type Dipole
Frequency 2400-2500 MHz
Gain (dBi) 2
Polarization Linear, Vertical
Azimuth 3dB Beamwidth: 360°
Elevation 3dB Beamwidth: 60°
Cable Length (in.) 0
Cable Type N/A
Connector Type RP-BNC Male
Weight 0.075 lbs
Plenum Antenna No
Plenum Cable N/A
Outdoor Rated No

2.4 GHz Single Band Antenna Suite 3-9
(
)
V
y
(°)
(
)
V
y
(°)
tuC zA 10-2APA-9942-LMledoM
09
081
zHM
0.0542tF
tretiraloP
0.5 0.5
0.0
0.5-
0.01-
0.51-
0.02-
0.52-
0.03-
0.53-
iBd
072
MP 14:31:4 3002/21/11
htdiw maeB
6.282
A nrettaP htumiz
tuC lE 10-2APA-9942-LMledoM
09
081
0.0542tF
zHM
tretiraloP
0.5 0.5
0.0
0.5-
0.01-
0.51-
0.02-
0.52-
0.03-
0.53-
iBd
072
MP 42:80:4 3002/21/11
htdiw maeB
6.61
nrettaP noitavelE

3-10 Enterprise Wireless LAN Antenna Specification Guide
3.1.5 ML-2499-BPNA3-01R Outdoor 35° High-Gain Directional Panel: Type N - Female
10.13 ± .04”
1.58 ± .04”
5.14”
10.13 ± .04”
Type Panel (Outdoor)
Frequency 2400-2500 MHz
Gain (dBi) 13.9
Net Gain (dBi) 10.9 (minimum cable configuration)
Cable Loss (dB) 3 (minimum cable configuration)
Polarization Linear, Vertical
Azimuth 3dB Beamwidth: 35°
Elevation 3dB Beamwidth: 28°
Cable Length (in.) Use minimum configuration (or more)
Cable Type Varies per cable configuration
Connector Type Type N Female
Weight 1.5 lb
Plenum Antenna N/A
Plenum Cable N/A
Outdoor Rated Yes

2.4 GHz Single Band Antenna Suite 3-11
(
)
V
y
(°)
)
V
y
(°)
tuC zA 10-3ANPB-9942-LMledoM
09
081
zHM
0.0542tF
tretiraloP
0.510.51
0.01
0.5
0.0
0.5-
0.01-
0.51-
0.02-
0.52-
0.03-
iBd
3.13
072
MP 00:94:4 3002/21/11
htdiw maeB
nrettaP htumizA
tuC lE 10-3ANPB-9942-LMledoM
09
081
0.0542tF(zHM
tretiraloP
0.510.51
0.01
0.5
0.0
0.5-
0.01-
0.51-
0.02-
0.52-
0.03-
iBd
1.82
072
MP 04:44:4 3002/21/11
htdiw maeB
nrettaP noitavelE

3-12 Enterprise Wireless LAN Antenna Specification Guide
3.1.6 ML-2499-BYGA2-01R Outdoor 35° High-Gain Directional Yagi: N Female
26.44”
1.40”
3.73”
Type Yagi (Outdoor)
Frequency 2400-2500 MHz
Gain (dBi) 14.1
Net Gain (dBi) 11.1 (minimum cable configuration)
Cable Loss (dB) 3 (minimum cable configuration)
Polarization Linear, Vertical
Azimuth 3dB Beamwidth: 35°
Elevation 3dB Beamwidth: 30°
Cable Length (in.) 12
Cable Type Varies per the cable configuration used
Connector Type Type N - Female
Power 50 W
Weight 1.25 lbs

2.4 GHz Single Band Antenna Suite 3-13
(
)
V
y
(°)
)
V
y
(°)
tuC zA 10-2AGYB-9942-LMledoM
09
081
zHM
0.0542tF
tretiraloP
0.510.51
0.01
0.5
0.0
0.5-
0.01-
0.51-
0.02-
0.52-
0.03-
iBd
8.72
072
MP 01:85:5 3002/21/11
htdiw maeB
nrettaP htumizA
tuC lE 10-2AGYB-9942-LMledoM
09
081
0.0542tF(zHM
tretiraloP
0.510.51
0.01
0.5
0.0
0.5-
0.01-
0.51-
0.02-
0.52-
0.03-
iBd
2.72
072
MP 20:00:6 3002/21/11
htdiw maeB
nrettaP noitavelE

3-14 Enterprise Wireless LAN Antenna Specification Guide
3.1.7 ML-2499-HPA3-01R High Performance Omni-Directional "Pipe" Antenna:
RP-BNC Male
Type Dipole Array
Frequency 2400-2500 MHz
Gain (dBi) 4.7
Polarization Linear, Vertical
Azimuth 3dB Beamwidth: 360°
Elevation 3dB Beamwidth: 31°
Cable Length (in.) 48
Cable Type RG-58 Ultralink
Connector Type RP-BNC Male
Weight 0.3 lbs
Plenum Antenna No
Plenum Cable Yes
Outdoor Rated Yes (in a cable down orientation)

2.4 GHz Single Band Antenna Suite 3-15
(
)
V
y
)
V
y
(°)
tuC zA 10-3APH-9942-LMledoM
09
081
zHM
0.0542tF
tretiraloP
0.50.5
0.0
0.5-
0.01-
0.51-
0.02-
0.52-
0.03-
0.53-
iBd
306
072
MP 31:22:6 3002/21/11
htdiw maeB(°)
nrettaP htumizA
tuC lE 10-3APH-9942-LMledoM
09
081
0.0542tF(zHM
tretiraloP
0.5 0.5
0.0
0.5-
0.01-
0.51-
0.02-
0.52-
0.03-
0.53-
iBd
3.41
072
MP 01:91:6 3002/21/11
htdiw maeB
nrettaP noitavelE

3-16 Enterprise Wireless LAN Antenna Specification Guide
3.1.8 ML-2499-PNAHD-01R Indoor 55°Directional Panel: RP-BNC Male
Type Panel
Frequency 2400-2500 Mhz
Gain (dBi) 7.5
Polarization Linear, Vertical
Azimuth 3dB Beamwidth: 65°
Elevation 3dB Beamwidth: 50 °
Cable Length (in.) 48
Cable Type RG-58 Ultralink
Connector Type RP-BNC Male
Weight 0.5 lbs
Plenum Antenna No
Plenum Cable Yes
Outdoor Rated No

2.4 GHz Single Band Antenna Suite 3-17
(
)
V
y
(°)
(
)
V
y
(°)
tuC zA 10-DHANP-9942-LMledoM
09
081
zHM
0.0542tF
tretiraloP
0.010.01
0.5
0.0
0.5-
0.01-
0.51-
0.02-
0.52-
0.03-
0.53-
iBd
3.55
072
MP 71:14:6 3002/21/11
htdiw maeB
nrettaP htumizA
tuC lE 10-DHANP-9942-LMledoM
09
081
0.0542tF
zHM
tretiraloP
0.010.01
0.5
0.0
0.5-
0.01-
0.51-
0.02-
0.52-
0.03-
0.53-
iBd
2.65
072
MP 73:44:6 3002/21/11
htdiw maeB
nrettaP noitavelE

3-18 Enterprise Wireless LAN Antenna Specification Guide
3.1.9 ML-2499-SD3-01R Low Profile Ceiling/Surface Mount Omni-Directional
Patch: RP-BNC Male
Type Patch (ceiling mount)
Frequency 2400-2500 MHz
Gain (dBi) 3.5
Polarization Linear, Vertical
Azimuth 3dB Beamwidth: 360°
Elevation 3dB Beamwidth: 45°
Cable Length (in.) 48
Cable Type RG-58 Ultralink
Connector Type RP-BNC Male
Weight 0.21 lbs
Plenum Antenna No
Plenum Cable Yes
Outdoor Rated No

2.4 GHz Single Band Antenna Suite 3-19
(
)
V
y
)
V
y
(°)
tuC zA 10-3DS-9942-LMledoM
09
081
zHM
0.0542tF
tretiraloP
0.5 0.5
0.0
0.5-
0.01-
0.51-
0.02-
0.52-
0.03-
0.53-
iBd
063
072
MP 72:41:4 3002/42/11
htdiw maeB(°)
nrettaP htumizA
tuC lE 10-3DS-9942-LMledoM
09
081
0.0542tF(zHM
tretiraloP
0.50.5
0.0
0.5-
0.01-
0.51-
0.02-
0.52-
0.03-
0.53-
iBd
7.15
072
MP 03:45:6 3002/21/11
htdiw maeB
nrettaP noitavelE

3-20 Enterprise Wireless LAN Antenna Specification Guide
3.1.10 ML-2499-FHPA5-01R Omni-Directional "Pipe" Antenna: N Male Connector
ML-2499-FHPA5-01R
Type Dipole Array
Frequency 2400-2500 MHz
Gain (dBi) 5
Polarization Linear, Vertical
Azimuth 3dB Beamwidth: 360°
Elevation 3dB Beamwidth: 25°
Cable Length (in.) N/A
Cable Type N/A
Connector Type Type N Male
Weight 0.7 lbs
Plenum Antenna No
Plenum Cable N/A
Outdoor Rated Yes

2.4 GHz Single Band Antenna Suite 3-21

3-22 Enterprise Wireless LAN Antenna Specification Guide
3.1.11 ML-2499-FHPA9-01R High Performance Fixed Point Dipole: Male Connector
ML-2499-FHPA9-01R
Type Dipole Array
Frequency 2400-2500 MHz
Gain (dBi) 9
Polarization Linear, Vertical
Azimuth 3dB Beamwidth: 360°
Elevation 3dB Beamwidth: 14°
Cable Length (in.) N/A
Cable Type N/A
Connector Type Type N Male
Weight 1.1 lbs
Plenum Antenna No
Plenum Cable N/A
Outdoor Rated Yes

2.4 GHz Single Band Antenna Suite 3-23

3-24 Enterprise Wireless LAN Antenna Specification Guide
3.1.12 ML-2499-HPA4-01 Outdoor Dipole Omni Antenna: N Male Connector
Type Dipole
Frequency 2400-2500 MHz
Gain (dBi) 4.5
Polarization Linear, Vertical
Azimuth 3dB Beamwidth: 360°
Elevation 3dB Beamwidth: 42°
Cable Length (in.) n/a
Cable Type n/a
Connector Type N-Type Male
Weight 118 grams
Plenum Antenna No
Plenum Cable n/a
Outdoor Rated Yes

2.4 GHz Single Band Antenna Suite 3-25

3-26 Enterprise Wireless LAN Antenna Specification Guide
3.1.13 ML-2499-HPA8-01 Outdoor Dipole Omni Antenna: N Male Connector
Type Dipole, Omni
Frequency 2400-2500 MHz
Gain (dBi) 8
Polarization Linear, Vertical
Azimuth 3dB Beamwidth: 360°
Elevation 3dB Beamwidth: 14°
Cable Length (in.) n/a
Cable Type n/a
Connector Type N-Type Male
Weight 0.45 lbs
Plenum Antenna No

2.4 GHz Single Band Antenna Suite 3-27
Plenum Cable n/a
Outdoor Rated Yes

3-28 Enterprise Wireless LAN Antenna Specification Guide
3.1.14 ML-2499-7PNA2-02R Outdoor 60° Diversity Panel: RP-SMA Male
Type Panel x 2 (Diversity)
Frequency 2400-2500 MHz
Gain (dBi) 7.5
Polarization Linear, Vertical
Azimuth 3dB Beamwidth: 80°
Elevation 3dB Beamwidth: 55°
Cable Length (in.) 121.9 +/- 13 (x2)
Cable Type RG-58
Connector Type RP SMA Male (x2)
Weight 0.50 lbs
Plenum Antenna Yes
Plenum Cable N/A
Outdoor Rated Yes

2.4 GHz Single Band Antenna Suite 3-29

3-30 Enterprise Wireless LAN Antenna Specification Guide
3.1.15 ML-2499-HPA3-02R 11BGN, DP, 3dBi, LP, CBL 48, RP-SMA-Male
Type Dipole Omni
Frequency 2400-2500 MHz
Gain (dBi) 5
Polarization Linear, Vertical
Azimuth 3dB Beamwidth: 360°
Elevation 3dB Beamwidth: 32°
Cable Length (in.) 121.9 cm +/- 13 mm
Cable Type RG-58
Connector Type RP-SMA-Male
Weight 0.3 lbs.
Plenum Antenna Yes

2.4 GHz Single Band Antenna Suite 3-31
Plenum Cable N/A
Outdoor Rated Yes

3-32 Enterprise Wireless LAN Antenna Specification Guide
3.1.16 ML-2499-PNAHD-02R 11BGN, 65° Patch, 7.5 dBI, LP, CBL 48, RP-SMA-M
Type Patch
Frequency 2400-2500 Mhz
Gain (dBi) 7.5
Polarization Linear, Vertical
Azimuth 3dB Beamwidth: 65°
Elevation 3dB Beamwidth: 55 °
Cable Length (cm.) 121.9 +/- 1.3
Cable Type RG-58
Connector Type RP-SMA Male
Weight 0.5 lbs
Plenum Antenna N/A
Plenum Cable Yes
Outdoor Rated Yes

2.4 GHz Single Band Antenna Suite 3-33

3-34 Enterprise Wireless LAN Antenna Specification Guide
3.1.17 ML-2499-SD3-02R 11BGN, 50° Patch Omni, 4 dBI, LP, CBL 48, RP-SMA-M
Type Patch Omni
Frequency 2400-2500 MHz
Gain (dBi) 4.0
Polarization Linear, Vertical
Azimuth 3dB Beamwidth: 360°
Elevation 3dB Beamwidth: 50°
Cable Length (cm.) 121.9 +/- 1.3
Cable Type RG-58
Connector Type RP-SMA Male
Weight 0.52 lbs
Plenum Antenna N/A
Plenum Cable Yes
Outdoor Rated No

2.4 GHz Single Band Antenna Suite 3-35

3-36 Enterprise Wireless LAN Antenna Specification Guide

5.2 Ghz Single Band Antenna Suite
4.1 Supported 802.11a/n Antenna Suite
Motorola Solutions supports numerous 802.11a/n antennas to suit the requirements of your unique access
point or access port deployment. Check the Motorola Solutions Web site periodically, as newly supported
802.11a/n antennas will be added to this document as they are released. For more information, go to
http://supportcentral.motorola.com/support/product/manuals.do
For detailed information on supported 802.11a/n antenna models, refer to:
.
• ML-5299-APA1-01R Indoor Rubber Flex Jointed Dipole: RP-SMA Male Connector
• ML-5299-HPA1-01R High Performance Omni-Directional Dipole Antenna: RP-SMA Male Connector
• ML-5299-PTA1-01R Low Profile Ceiling-Tile Mount Patch: RP-SMA Male Connector
• ML-5299-WPNA1-01R Wall Mount Panel Antenna w/Articulating Mount: RP-SMA Male
• ML-5299-FHPA10-01R Omni-Directional "Pipe" Antenna: N-Male Connector
• ML-5299-FHPA6-01R Omni-Directional "Pipe" Antenna: N-Male Connector
• ML-5299-BYGA15-012 Yagi Antenna: N-Female
• ML-5299-HPA5-01 Outdoor Dipole Omni N-Male
• ML-5299-HPA10-01 Outdoor Dipole Omni N-Male
NOTE: For examples on how various antenna and connectors are deployed in a 5 GHz
AP-5131 installation, see 5 GHz AP-5131 Antenna Connections.

4-2 Enterprise Wireless LAN Antenna Specification Guide
4.1.1 ML-5299-APA1-01R Indoor Rubber Flex Jointed Dipole: RP-SMA Male Connector
Type Dipole
Frequency 4900-5875 MHz
Gain (dBi) 2
Polarization Linear, Vertical
Azimuth 3dB Beamwidth: 360°
Elevation 3dB Beamwidth: 75°
Cable Length (in.) N/A
Cable Type N/A
Connector Type RP-SMA Male
Weight 0.063 lb
Plenum Antenna No
Plenum Cable N/A
Outdoor Rated No

5.2 Ghz Single Band Antenna Suite 4-3
)
V
y
(°)
(
)
V
y
ledoM
081
tuC zA 10-1APA-9925-LM
09
072
MP 62:24:8 4002/7/1
tF(zHM
0.0525
htdiw maeB
tretiraloP
0.50.5
0.0
0.5-
0.01-
0.51-
0.02-
0.52-
0.03-
0.53-
iBd
4.203
nrettaP htumizA
ledoM
081
tuC lE 10-1APA-9925-LM
09
072
MP 75:74:8 4002/7/1
tF
0.0525
zHM
htdiw maeB (°)
tretiraloP
0.5 0.5
0.0
0.5-
0.01-
0.51-
0.02-
0.52-
0.03-
0.53-
iBd
75
nrettaP noitavelE

4-4 Enterprise Wireless LAN Antenna Specification Guide
4.1.2 ML-5299-HPA1-01R High Performance Omni-Directional Dipole Antenna: RP-SMA
Male Connector
Type Dipole Array
Frequency 4900-5875 MHz
Gain (dBi) 5
Polarization Linear, Vertical
Azimuth 3dB Beamwidth: 360°
Elevation 3dB Beamwidth: 17°
Cable Length (in.) 36
Cable Type LMR195
Connector Type RP-SMA Male
Weight 0.3 lb.
Plenum Antenna No
Plenum Cable Yes
Outdoor Rated Yes (cable down orientation only)

5.2 Ghz Single Band Antenna Suite 4-5
(
)
V
y
(°)
(
)
V
y
ledoM
081
APH-9925-LM1tuC zA 10-
tF
09
0.0525
zHM
tretiraloP
0.50.5
0.0
0.5-
0.01-
0.51-
0.02-
0.52-
0.03-
0.53-
iBd
6.09
072
MA 20:84:11 3002/51/21
htdiw maeB
nrettaP htumizA
ledoM
081
APH-9925-LM1tuC lE 10-
0.0525
zHM
tF
09
tretiraloP
0.50.5
0.0
0.5-
0.01-
0.51-
0.02-
0.52-
0.03-
0.53-
iBd
1 0.7
072
MA 03:04:11 3002/51/21
htdiw maeB (°)
nrettaP noitavelE

4-6 Enterprise Wireless LAN Antenna Specification Guide
4.1.3 ML-5299-PTA1-01R Low Profile Ceiling-Tile Mount Patch: RP-SMA
Male Connector
Type Patch
Frequency 5150-5875 MHz
Gain (dBi) 4.6
Polarization Linear, Vertical
Azimuth 3dB Beamwidth: 360°
Elevation 3dB Beamwidth: 45°
Cable Length (in.) 36
Cable Type RG-58
Connector Type RP-SMA Male
Weight 0.15 lb.
Plenum Antenna No
Plenum Cable Yes
Outdoor Rated No

5.2 Ghz Single Band Antenna Suite 4-7
V
y
(
)
V
y
(
)
ledoM
noisreV
081
tniuqS a11.208
nacS zA tnuoM .zroH
09
)zHM( tF
0.5775
tretiraloP
0.50.5
0.0
0.5-
0.01-
0.51-
0.02-
0.52-
0.03-
0.53-
iBd
072
MA 60:64:01 4002/41/7
kaeP
34.1
htdiw maeB
naem
30.0
5.813
°
%
σ
001
571.0
nrettaP htumizA
ledoM
noisreV
081
tniuqS a11.208
nacS lE tnuoM .zroH
09
0.5475
)zHM( tF
tretiraloP
0.50.5
0.0
0.5-
0.01-
0.51-
0.02-
0.52-
0.03-
0.53-
iBd
6.44
htdiw maeB
072
MA 52:72:11 4002/41/7
kaeP
16.4
°
%
naem
40.1-
σ
37
745.0
nrettaP noitavelE

4-8 Enterprise Wireless LAN Antenna Specification Guide
4.1.4 ML-5299-WPNA1-01R Wall Mount Panel Antenna w/Articulating Mount:
RP-SMA Male
Type Panel
Frequency 5150-5875 MHz
Gain (dBi) 12.5
Polarization Linear, Vertical
Azimuth 3dB Beamwidth: 31°
Elevation 3dB Beamwidth: 27°
Cable Length (in.) 36
Cable Type RG-303
Connector Type RP-SMA Male
Weight 0.7 lb.
Plenum Antenna No
Plenum Cable Yes
Outdoor Rated Yes

5.2 Ghz Single Band Antenna Suite 4-9
(
)
V
y
(°)
(
)
V
y
(°)
ledoM
081
MP 33:90:3 4002/5/1
tuC zA 10-1ANPW-9925-LM
09
tF
0.0525
zHM
tretiraloP
0.020.02
0.51
0.01
0.5
0.0
0.5-
0.01-
0.51-
0.02-
0.52-
0.03-
iBd
9.72
072
htdiw maeB
nrettaP htumizA
ledoM
081
tuC lE 10-1ANPW-9925-LM
09
tF
0.0525
zHM
tretiraloP
0.020.02
0.51
0.01
0.5
0.0
0.5-
0.01-
0.51-
0.02-
0.52-
0.03-
iBd
3.32
072
MP 12:61:3 4002/5/1
htdiw maeB
nrettaP noitavelE

4-10 Enterprise Wireless LAN Antenna Specification Guide
4.1.5 ML-5299-FHPA10-01R Omni-Directional "Pipe" Antenna: N-Male Connector
ML-5299-FHPA10-01R
Type Dipole Array
Frequency 4900-5850 MHz
Gain (dBi) 10
Polarization Linear, Vertical
Azimuth 3dB Beamwidth: 360°
Elevation 3dB Beamwidth: 13
Cable Length (in.) N/A
Cable Type N/A
Connector Type Type N Male
Weight 0.37 lb
Plenum Antenna No
Plenum Cable N/A
Outdoor Rated Yes

5.2 Ghz Single Band Antenna Suite 4-11

4-12 Enterprise Wireless LAN Antenna Specification Guide
4.1.6 ML-5299-FHPA6-01R Omni-Directional "Pipe" Antenna: N-Male Connector
Type Dipole Array
Frequency 4900-5875
Gain (dBi) 7.5
Polarization Linear, Vertical
Azimuth 3dB Beamwidth: 360°
Elevation 3dB Beamwidth: 16°
Cable Length (in.) N/A
Cable Type N/A
Connector Type Type N Male
Weight 0.37 lb
Plenum Antenna No
Plenum Cable N/A
Outdoor Rated Yes

5.2 Ghz Single Band Antenna Suite 4-13

4-14 Enterprise Wireless LAN Antenna Specification Guide
4.1.7 ML-5299-BYGA15-012 Yagi Antenna: N-Female
Type Yagi
Frequency 4900-5800
Gain (dBi) 12.0
Polarization Linear, Vertical
Azimuth 3dB Beamwidth: 31°
Elevation 3dB Beamwidth: 33°
Cable Length (in.) N/A
Cable Type ATX195
Connector Type N Female
Weight 1.2 lbs
Plenum Antenna No
Plenum Cable No
Outdoor Rated Yes

5.2 Ghz Single Band Antenna Suite 4-15

4-16 Enterprise Wireless LAN Antenna Specification Guide
4.1.8 ML-5299-HPA5-01 Outdoor Dipole Omni N-Male
Type Dipole Omni
Frequency 4900-5800
Gain (dBi) 5.6
Polarization Linear, Vertical
Azimuth 3dB Beamwidth: 360°
Elevation 3dB Beamwidth: 22°
Cable Length (in.) n/a
Cable Type n/a
Connector Type N-Type Male
Weight 73.8 grams
Plenum Antenna No
Plenum Cable n/a
Outdoor Rated Yes

5.2 Ghz Single Band Antenna Suite 4-17

4-18 Enterprise Wireless LAN Antenna Specification Guide
4.1.9 ML-5299-HPA10-01 Outdoor Dipole Omni N-Male
Type Dipole Omni
Frequency 4900-5800
Gain (dBi) 10.5
Polarization Linear, Vertical
Azimuth 3dB Beamwidth: 360°
Elevation 3dB Beamwidth: 8°
Cable Length (in.) n/a
Cable Type n/a
Connector Type N-Type Male
Weight 0.4 lbs
Plenum Antenna No
Plenum Cable n/a
Outdoor Rated Yes

5.2 Ghz Single Band Antenna Suite 4-19

4-20 Enterprise Wireless LAN Antenna Specification Guide

2.4GHz - 5.2GHz Dual Band Antenna Suite
5.1 Supported 802.11a/b/g/n Dual Band Antennas
Motorola Solutions supports several 2.4GHz - 5.2GHz Dual Band antennas to suit the requirements of your
unique access point or access port deployment. Check the Motorola Solutions Web site periodically, as
newly supported 2.4GHz - 5.2GHz Dual Band antennas will be added to this document as they are released.
For more information, go to http://supportcentral.motorola.com/support/product/manuals.do
For detailed information on supported 2.4GHz - 5.2GHz Dual Band antenna models, refer to:
.
• ML-2452-APA2-01 Indoor Dual Band Elbow Jointed Dipole: RP-SMA Male (Black) ML-2452-APA2-02
Indoor Dual Band Elbow Jointed Dipole: RP-SMA Male (White)
• ML-2452-PNA5-01R Dual Band Panel: Connector Type N-Male
• ML-2452-PNA7-01R Dual Band Panel: Connector Type N-Male
• ML-2452-PTA2M3X3-1 AP-7131 MIMO Facade: 1 IN, RPSMA
• ML-2452-PTA3M3-036 Ceiling Mount, Dual Band, MIMO Patch: RPSMA
• ML-2452-HPA5-036 Dipole, RP-SMA-Male
• ML-2452-PNL9M3-036 MIMO Dual Band Selector, RP-SMA Male
• ML-2452-APAG2A1-01 Dipole, RP-SMA Male (Black) ML-2452-APAG2A1-02 Dipole, RP-SMA Male
(White)
• ML-2452-HPAG4A6-01 Outdoor Dipole Omni N-Male
• ML-2452-HPAG5A8-01 Outdoor Dipole Omni N-Male
• ML-2452-PTA6X6-036 Indoor dual-band MIMO Omni Array, RP-SMA Male
• ML-2452-PTA2M2-036 Two Port, Dual Band Omni Patch Array, RP-SMA-M
• ML-2452-HPA6X6-036 11ABGN, 6P SB Omni , 4/6 dBi, LP, CBL 48, N-M

5-2 Enterprise Wireless LAN Antenna Specification Guide
5.1.1 ML-2452-APA2-01 Indoor Dual Band Elbow Jointed Dipole: RP-SMA Male (Black)
ML-2452-APA2-02 Indoor Dual Band Elbow Jointed Dipole: RP-SMA Male (White)
Type Dipole
Frequency 2400-2500/5150-5850 MHz
Gain (dBi) 3.0 / 5.0
Polarization Linear, Vertical
Azimuth 3dB Beamwidth: 360°
Elevation 3dB Beamwidth: 35°
Cable Length (in.) N/A
Cable Type N/A
Connector Type RP-SMA Male
Weight 0.7 oz
Plenum Antenna No
Plenum Cable N/A
Outdoor Rated No

2.4GHz - 5.2GHz Dual Band Antenna Suite
V
,
V
y
(°)
V
,
y
(
)
V
,
V
y
)
V
y
(
)
ledo
M
noisreV
081
ledo
M
reV snoi
081
10-2APA-2542-LM
tnuoM tre
tuC zA
MP 64:05:21 5002/81/2
10-2APA-2542-LM
oM tre tnu
tuC zA
P 24:20:2 5002/81/2M
0.6342
09
072
09
)zHM( tF
0.0525
)zHM( tF
tretiraloP
0.010.01
0.5
0.0
0.5-
0.01-
0.51-
0.02-
0.52-
0.03-
iBd
8.19
htdiw maeB
tretiraloP
0.010.01
0.5
0.0
0.5-
0.01-
0.51-
0.02-
0.52-
0.03-
iBd
ledoM
noisreV
081
dnaB b11.208
ledoM
reV snoi
081
10-2APA-2542-LM
tuC lE
tnuoM tre
MA 03:95:01 5002/7/3
10-2APA-2542-LM
oM tretnu,uC lE t
MA 53:00:11 5002/7/3
0.7342
09
)zHM( tF
072
zroHtiraloP
0.010.01
0.5
0.0
0.5-
0.01-
0.51-
0.02-
0.52-
0.03-
iBd
6.54
htdiw maeB
°
nrettaP noitavelE nrettaP htumizA
0.0525
09
)zHM( tF
zroHtiraloP
0.010.01
0.5
0.0
0.5-
0.01-
0.51-
0.02-
0.52-
0.03-
iBd
072
aeBm tdiw h(°
4.533
072
dnaB a11.208
aeB mtdiw h
nrettaP noitavelE nrettaP htumizA
.623
°

5-4 Enterprise Wireless LAN Antenna Specification Guide
5.1.2 ML-2452-PNA5-01R Dual Band Panel: Connector Type N-Male
2.10”
5.12”
Type Panel
Frequency 2400-2500/4900-5900 MHz
Gain (dBi) 4.5 (2400-2500); 5.0 (4900-5250); 4.0 (5250-5900)
Polarization Linear, Vertical
Azimuth 3dB Beamwidth: 120°
Elevation 3dB Beamwidth: 65°
Cable Length (in.) 12
Cable Type RG-58 Ultralink
Connector Type Type N Male
Weight 0.2 lb
Plenum Antenna No
Plenum Cable Yes
Outdoor Rated Yes

2.4GHz - 5.2GHz Dual Band Antenna Suite

5-6 Enterprise Wireless LAN Antenna Specification Guide

2.4GHz - 5.2GHz Dual Band Antenna Suite
5.1.3 ML-2452-PNA7-01R Dual Band Panel: Connector Type N-Male
4.1”
4.1”
Type Panel
Frequency 2400-2500/4900-5900 MHz
Gain (dBi) 7 (2400-2500); 6.3 (4900-5250); 9 (5250-5900)
Polarization Linear, Vertical
Azimuth 3dB Beamwidth: 68°/ 52°
Elevation 3dB Beamwidth: 66°/ 60°
Cable Length (in.) 12
Cable Type RG-58 Ultralink
Connector Type Type N Male
Weight 0.5 lb
Plenum Antenna No
Plenum Cable Yes
Outdoor Rated Yes

5-8 Enterprise Wireless LAN Antenna Specification Guide

2.4GHz - 5.2GHz Dual Band Antenna Suite

5-10 Enterprise Wireless LAN Antenna Specification Guide
5.1.4 ML-2452-PTA2M3X3-1 AP-7131 MIMO Facade: 1 IN, RPSMA
NOTE: ML-2452-PTA2M3x3-1 was formally released as Motorola Solutions part number
ML-2452-APA2-FAC.
Type Patch x 6 in snap-on facade
Frequency 2400-2500/4900-5990 MHz
Gain (dBi) 3.0 / 5.0
Polarization Linear, Vertical
Azimuth 3dB Beamwidth: 360°
Elevation 3dB Beamwidth: 90° (southern hemisphere pattern)
Cable Length (in.) Integrated into snap-on facade
Cable Type 1.20 mm coax
Connector Type RP-SMA Male
Antenna Plenum Rated No
Cable Plenum Rated No
Outdoor Rated No
Weight 0.79 lb

2.4GHz - 5.2GHz Dual Band Antenna Suite

5-12 Enterprise Wireless LAN Antenna Specification Guide

2.4GHz - 5.2GHz Dual Band Antenna Suite
5.1.5 ML-2452-PTA3M3-036 Ceiling Mount, Dual Band, MIMO Patch: RPSMA
12”
Type Patch x 3
Frequency 2400-2500/4900-5990 MHz
Gain (dBi) 3.0 / 4.0
Polarization Linear, Vertical
Azimuth 3dB Beamwidth: 360°
Elevation 3dB Beamwidth: 60° (southern hemisphere pattern)
Cable Length (in.) 60
Cable Type RG-58 50 Ohm coax
Connector Type RP-SMA Male
Antenna Plenum Rated No
Cable Plenum Rated Yes
Outdoor Rated No
Weight 0.7 lb

5-14 Enterprise Wireless LAN Antenna Specification Guide

2.4GHz - 5.2GHz Dual Band Antenna Suite

5-16 Enterprise Wireless LAN Antenna Specification Guide
5.1.6 ML-2452-HPA5-036 Dipole, RP-SMA-Male
Type Dipole
Frequency 2450-2500/5150-5875 MHz
Gain (dBi) 3.0 / 5.0
Polarization Linear, Vertical
Azimuth 3dB Beamwidth: 360°
Elevation 3dB Beamwidth: 50°, 18°
Cable Length (in.) 36
Cable Type RG-58 Plenum
Connector Type RP-SMA Male
Antenna Plenum Rated N/A

2.4GHz - 5.2GHz Dual Band Antenna Suite
Cable Plenum Rated N/A
Outdoor Rated N/A
Weight 0.3 lbs

5-18 Enterprise Wireless LAN Antenna Specification Guide

2.4GHz - 5.2GHz Dual Band Antenna Suite

5-20 Enterprise Wireless LAN Antenna Specification Guide
5.1.7 ML-2452-PNL9M3-036 MIMO Dual Band Selector, RP-SMA Male
NOTE: The dimensions for the ML-2452-PNL9M3-036 model antenna are displayed in
millimeters (mm) within the illustration above.

2.4GHz - 5.2GHz Dual Band Antenna Suite
Type MIMO Dual Band Selector
Frequency 2450-2500/5150-5875 MHz
Gain (dBi) 8.0 / 10.7
Polarization Linear, Vertical
Azimuth 3dB Beamwidth: 75° / 55°
Elevation 3dB Beamwidth: 70° / 60°
Cable Length (in.) 36
Cable Type Low Temperature Plenum
Connector Type RP-SMA Male
Antenna Plenum Rated N/A
Cable Plenum Rated No
Outdoor Rated Yes
Weight 1.81 lbs

5-22 Enterprise Wireless LAN Antenna Specification Guide
 Loading...
Loading...