YAMAHA YMU757 Datasheet
#
#
#
YMU757
MA-1
#
#
#
YAMAHA CORPORATION
#
YMU757 CATALOG
CATALOG No.:LSI-4MU757A2
2000.2
Outline
The Y M U 757 is a high quality melody LSI for cel lul ar phone ha nds e ts, supporting the data for mat for var ious a pplicat ions
inc luding ringing and holding melody s ounds . The built-in Yamaha's or iginal FM synthesi zer can cr eat e va r ious timbres,
and its built-in s e que nc er can pr oduc e up to 4 different sounds with 4 different timbres simultaneousl y without placi ng a
load to the control ler.
The serial por t controller interface enabl es real time reproduc tion of the melody data vi a FIFO, without the limitat ion of
the data capaci ty.
With a built-in am pl ifier to drive the dynam ic type speaker , it is possible to connect the speaker direct ly.
This LSI al so has an anal og- ou tput terminal for the phone jack. In the stand- by m ode , the pow er cons um ption
can be reduced to 1
µ
A or less while waiting.
A por tabl e terminal m achi ne .
Features
YAM AHA's or igi na l FM s ound gene r at or function
Built-in se que nc er
Capa ble of pr oduc ing up to 4 differ ent s ounds simultaneousl y (4 indepe nde nt timbres avai labl e)
Built-in output 400m W speaker am pl ifier
Built-in ci rcui t for s ound quality correct ing equalizer
Built-in serial interface
2.688, 8.4, 12.6, 14.4, 19.2, 19.68, 19.8 and 27.82 MHz serial cl ock inputs suppor t
Analog output for ear phone.
Power dow n m ode (Typ 1µA or less)
Power s upply vol tage (Digital and Analog) : 3.0V ±10 %
20-pin TSSO P

YMU757
#
#
-2-
Contents
• G ene r al des c ription of Y M U 757…
………………………………………………………………3
• Bl oc k des c ription……..
…………………………………………………………………………4
• Pin configur at ion… ..
……………………………………………………………………………5
• Pin description… .
………………………………………………………………………………6
• Bl oc k diagram … . .
………………………………………………………………………………7
• Register map…….
………………………………………………………………………………8
• Explanat ion of regi ster s… .
………………………………………………………………………9-19
Musical score da ta. ..
……………………………………………………………………9-13
Timbre da ta……….
……………………………………………………………………14-17
Other control data………
………………………………………………………………17-19
• Pow er-dow n control divi si on di agr am … …
………………………………………………………20
• Explanat ion of each bit..…...
……………………………………………………………………20-22
• Res etting………………………………………..….
………………………………………………23
• Settings & pr oc e dure required to gener at e melody………………
…………………………………23
• I nterrupt s e quenc e ...…..……
……………………………………………………………………23-24
• St at e transi tion des c ription..……...
………………………………………………………………25-26
• O perat ion in FIFO em pt y stat e...
…………………………………………………………………27
• Repr oduc tion method assum ing occur rence of em pt y stat e…
………………………………………27
• Exam pl e of system connect ion...
…………………………………………………………………28
• O ne sound and vol um e level adj us tment in 4 s ound pr onunc iat ion.…
………………………………29-30
• Sound quality cor rect ion ci rcui t.
…………………………………………………………………31-32
• Ser ial inter face speci ficat ions .…
…………………………………………………………………33
• Elect rical char act eristics… . …
……………………………………………………………………34-39
• G ene r al des c ription of FM s ound gene r at or.…
……………………………………………………40
• Externa l di mensions … … ..
………………………………………………………………………41
YMU757
#
#
-3-
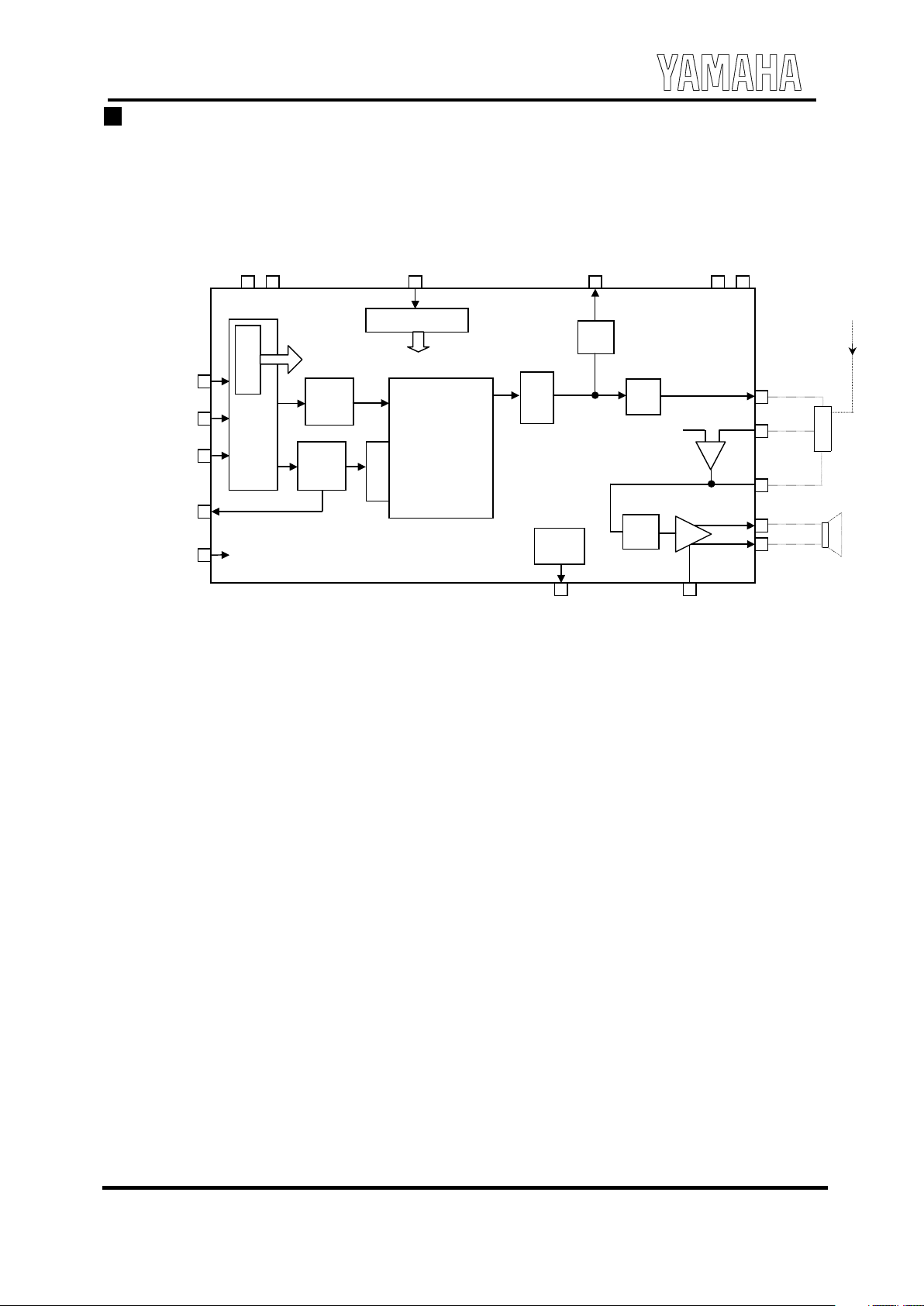
General description of YMU757
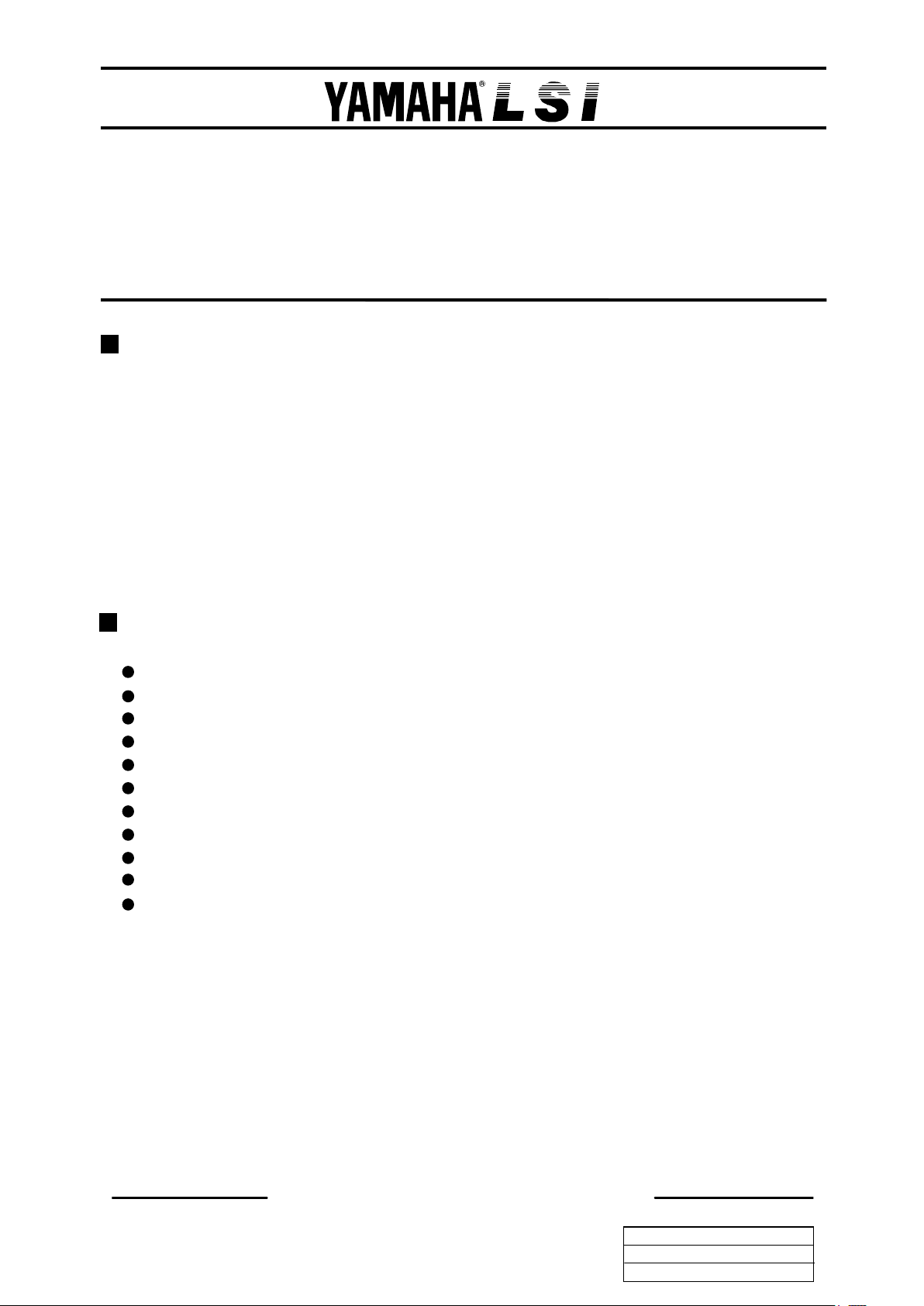
The Y M U 757 is control led by way of the serial interface.
Show n below is its interna l configur at ion.
W hen t he dat a i s i nputted i nto t he ser ial i nterface, i t i s c onver ted i nto t he par al lel data and t ransm i tted t o each
function block accor ding to the index address.
The musical score da ta is stor ed in the 32- word FIFO first and then transm i tted to the se que nc er where it is interpr et ed
and signals to control sound generat ion of the FM synthes izer is output.
The timbre regi ster is where up to 8 timber data can be stored.
Also, as the se que nc er controlling param et er s, the star t/stop and tem po signa ls ar e provided.
In or de r to hav e s ound gener at ed, the follow ing pr ocesses must be perfor med for this LSI.
1) Initial stat us setting (cancel lat ion of pow er-dow n function, cl ock select ion, et c. )
2) Timbre da ta setting
3) Writing the musical score da ta in FIFO before starting the s eque nc e
4) Writing t he next mu sical score dat a befor e FIF O becom es em pty upon r eceipt of the i nt errupt signa l from
FIFO during repr oduction.
(For the detai ls, ref er to "S ettings & pr oc e dure required to gene r at e melody".)
Se rial
int er face
FIFO
32w or d
/IRQ
Seque nce r
FM
Syn thes izer
D/A +
Volum e
AM P
Timbre
regist er
Musical score
data
Tem po
STA RT/STO P
Timbre allotment
Timbre Data
Volum e, pow er management, et c.
SDIN
SYNC
SCLK
SPOUT
HPOUT

YMU757
#
#
-4-
Block description
1) Serial inter face
When the serial interface recei ves the serial data, it identifies the index da ta and transm i ts the control data to each
function block.
2) FIFO
The musical sco re data are stor ed tem porar ily in FIFO which can contai n up to 32 musical score da ta. The musical
score data ar e pr ocessed ar e pr ocessed in the s eque nc er when they are ge ner at ed as s ounds and those that have been
processed ar e de let ed one after another. When the rem ai ning data am ount in FIFO reaches the regi ster setting (IRQ
point) or less, it outputs an int er rupt signa l to ask for the continuing musical sco re da ta to be fed.
3) Seque nc er
When the s e quenc e r recei ves the START command, it star ts to read the musical score data which ha ve been stored in
FIFO . The pr ocessed musical score da ta are delet ed.
4) Timbre regi ster
The timbre data are stor ed in this regi ster which can c ontai n up to 8 timbres. Se ttings for this regi ster must be made
before s ound generat ion. It is initial ized when the hardw are or the software is reset but the values are ret ai ned while
in the pow er-dow n m ode and al so after it is cancel led.
5) FM synthe s izer
The timbres ar e synthe s ized a nd gene r at ed according to settings . Four sounds can be gene r at ed at the sam e time.
6) D/A, volum e and am pl ifier
The out put s f rom t he synt hes i zer are D /A conver ted and vol um e pr ocessed. After t ha t, t hey a r e output f rom t he
speaker or the earphone out termina l.
YMU757
#
#
-5-
Pin configuration
20 Pin TSSO P Top View
DVDD
SDIN
SYNC
SCLK
AV SS
VREF
HPOUT
EQ1
EQ2
EQ3
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
20
19
18
17
16
15
14
13
12
11
CLK_I
/IRQ
TESTO
/RST
/TESTI
DV SS
SPVSS
SPOUT2
SPOUT1
AVDD
YMU757
#
#
-6-
Pin description
No. Pin I/O Function
1 DVDD -
Digital power supply (+3.0V)
Connect 0.1µF and 4.7µF capacitors between this terminal and the
digital ground terminal.
2 SDIN I
Serial I/F data input
3 SYNC I
Serial I/F synchronous signal input
4 SCLK Ish
Serial I/F bit clock input
5 AVSS -
Analog ground
6 VREF A
Analog reference voltage termi nal Connect 0.1µF capacitor between this
terminal and the analog ground terminal.
7 HPOUT AO
Analog output terminal for ear phone
8 EQ1 AO
Equalizer terminal 1
9 EQ2 AI
Equalizer terminal 2
10 EQ3 AO
Equalizer terminal 3
11 AVDD -
Analog power supply (+3.0V)
Connect 0.1
µ
F and 4.7µF capacitors between this terminal and the analog
ground terminal
12 SPOUT1 A0
Speaker output terminal 1
13 SPOUT2 AO
Speaker output terminal 2
14 SPVSS -
Analog ground exclusively used for speaker
15 DVSS -
Digital ground
16 /TESTI I
LSI test input t erm inal (Always connect with DVDD.)
17 /RST I
Hardware reset terminal
18 TESTO O
LSI TEST output termi nal (di sconnected)
19 /IRQ O
Interrupt signal output
20 CLK_I Ish
Clock input terminal (8 t y pes of frequency are supported.)
Note : I sh = Sc hm itt input termina l A I = Analog input terminal A 0 = Analog output ter mina l
YMU757
#
#
-7-
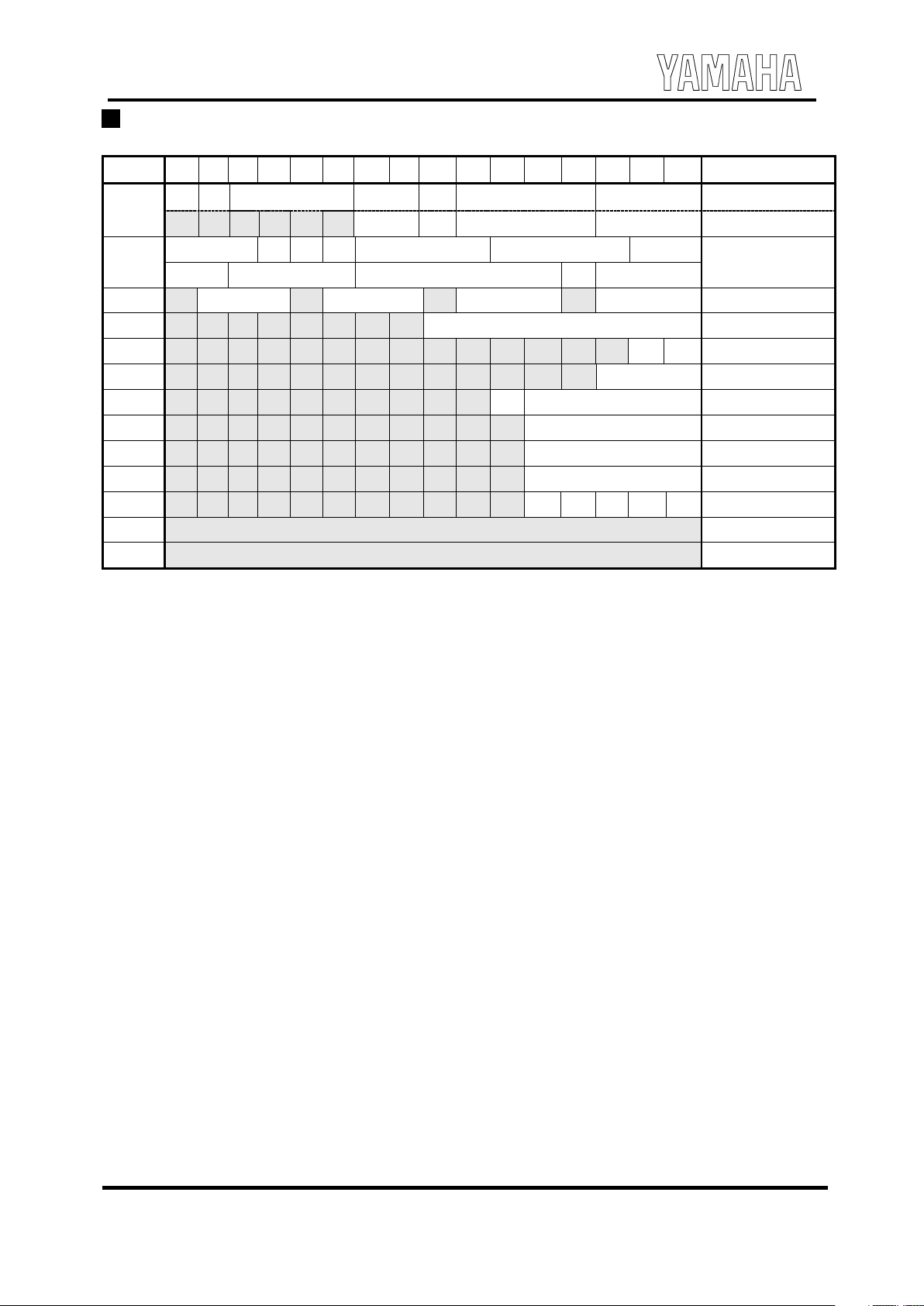
Block diagram
C oncerning AIN signal inputted int o equa lizer ci rcui t
As this design pres upposes the us e of this LSI for the " hands-free", it is possible to pr ocess the FM sound and cal l sound by
anal og mixing in the equa lizer ci rcui t and output the resul ting s ound through the speaker.
6<1&#
6',1#
6&/.#
&/.B,#
2567#
2,54#
(44#
95()#
6HULDO#
,2)#
#
'9''#
'966#
)092/#
65VWHS#
3RZHU#GRZQ
#
&RQWURO
#
5HJLVWHU
#
)0#
6\QWKHVL]HU#
76RXQG#VLJQDOV#JHQHUDWHG#
VLPXOWDQHRXVO\
#
##'$&#
$03#
$9''#
$966#
7LPLQJ#*HQHUDWRU#
+328
+392/#
65VWHS#
),)2#
49E#[#65Z#
(45#
(46#
63287
63287
# 95()#
CR ci rcui t EQ
63966#
6392/#
65VWHS#
$,1#-
#
6HTXHQFHU#
.#
95()#
YMU757
#
#
-8-
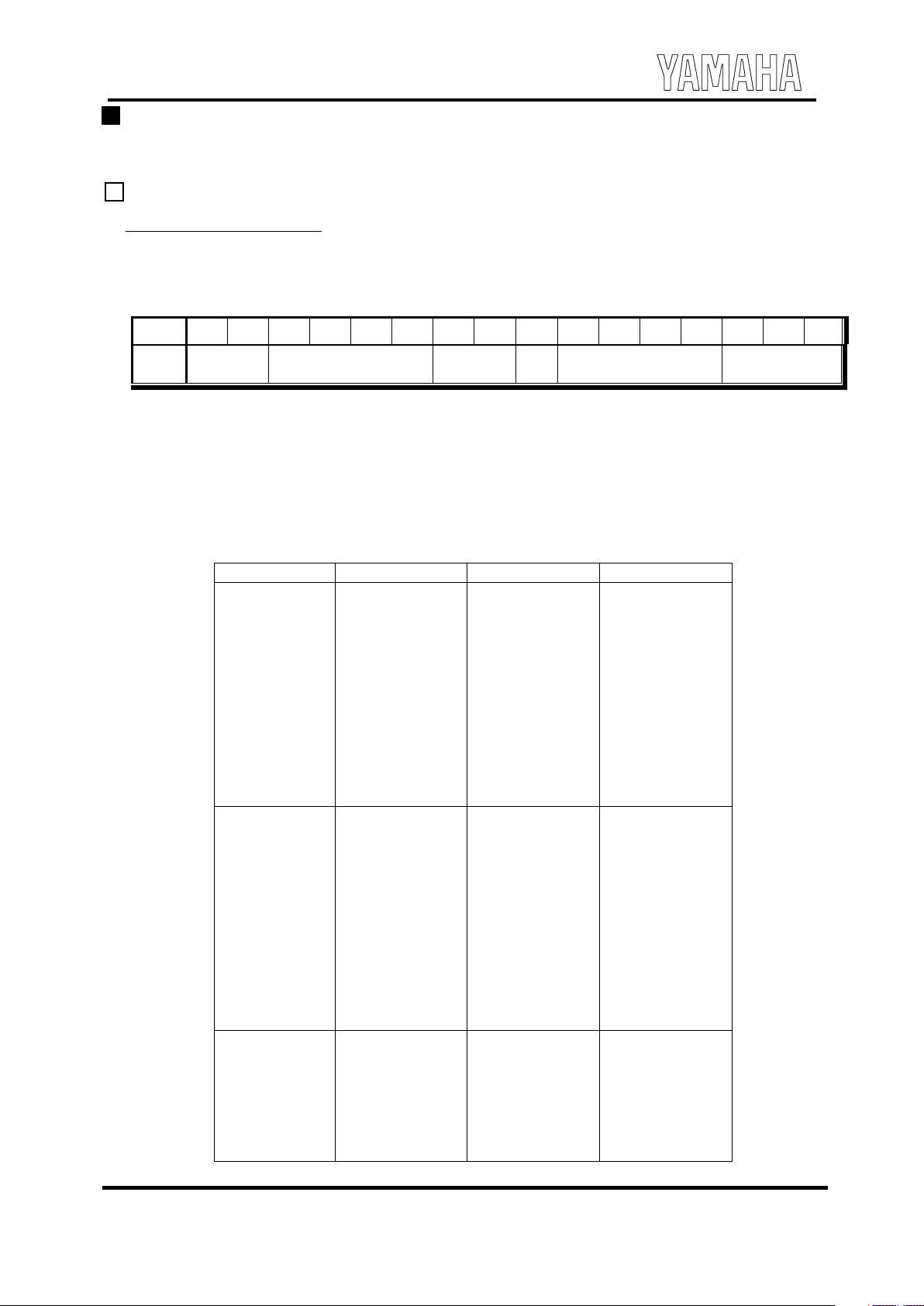
Register map
Index
b15 b14 b13 b12 b11 b10 b9 b8 b7 b6 b5 b4 b3 b2 b1 b0
Description
BL1 B L0 N T3 N T2 N T1 N T 0 C H 1 CH 0 V I B TI3 T I 2 TI1 TI 0 TK 2 TK1 TK 0
Note data
$00h
0 0 1 1 0 0 C H 1 CH 0 V C H E T I 3 TI2 TI 1 TI0 V C H 2 V C H 1 V C H 0
Rest data
M L2 M L 1 M L0 V IB EG T SU S RR3 R R 2 RR1 R R 0 DR3 D R2 D R 1 D R 0 A R 3 A R2
$10-2Fh
A R1 A R0 SL 3 SL2 SL1 SL0 TL 5 TL 4 TL3 TL2 T L1 T L0 W A V FL 2 FL 1 FL0
Timbre data (Left data
for 1 timbre)
$30h
0 V 32 V 31 V 30 0 V 22 V 21 V 20 0 V 12 V 11 V 10 0 V 02 V 01 V 00
Timbre allotment data
$31h
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 T 7 T6 T5 T 4 T3 T 2 T 1 T0
Tempo data
$32h
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 CLR ST
FM Control
$33h
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 C LK SEL
CLK_I select
$34h
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 IRQ E IRQ Point
IRQ Control
$35h
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 V 4 V 3 V 2 V 1 V0
Speaker Volume
$36h
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 V 4 V 3 V 2 V 1 V0
FM Volume
$37h
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 V4 V3 V 2 V 1 V 0
HPOUT Volume
$38h
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 AP4 A P3 A P2 A P1 DP
Power Management
$39 - $EFh
R es erved ( acces s prohi bited)
Reserved
$F0 - FFh
For LSI TEST (access prohibited)
LSI TEST
Note : Making an access to the spaces marked "R eser ved" and "F or LSI TEST" in the above tabl e is pr ohibited.
Be sure to write "0" for the em pt y bit, al though writing "1" there will not affect the LSI operat ion.
YMU757
#
#
-9-
Explanation of registers
The Y M U 757 has three types of control regi ster s. They are musical score da ta, timbre data and other control data.
Musical score data
$00h Musical score data
Th e mu sical score dat a ar e w r itten i n FIF O w hose capaci ty is 32 wor ds . There ar e t wo types of musical score
data; note dat a and r est data.
Note dat a
Default: 0000h
Index
B15 b14 b13 b12 b11 b10 b9 b8 b7 b6 b5 b4 b3 b2 b1 b0
$00h
BL1 BL0 NT3 NT2 NT1 NT0 CH1 CH0 VIB TI3 TI2 TI1 TI 0 TK2 TK1 TK0
BL1 – BL0 : Octave block setting
Three octave blocks ar e avai labl e for s ound range setting. The setting range is 1 to 3. Do not us e "0 " for setting.
The s ound generat ion range involves the coef fici ent nam ed "M ultiple (multipl ying fact or for sound freque ncy ).
By com bi ning the octave block and Multipl e settings , s ounds can be generat ed in the ranges as listed in the tabl e blow .
Since the set ting ranges of "M ultiple" coeffici ent is 0 to 7, actually, s ounds can be generated in a wi der ranges t han
thos e given in the tabl e below .
Multiple = 1 (x1) Multiple = 2 (x2) Multiple = 4 (x4)
BL[1:0] = 01b
C#3 (139Hz)
D3 (147Hz)
D#3 (156Hz)
E3 (165Hz)
F3 (175Hz)
F#3 (185Hz)
G3 (196Hz)
G#3 (208Hz)
A3 (220Hz)
A#3 (233Hz)
B3 (247Hz)
C4 (262Hz)
C#4 (277Hz)
D4 (294Hz)
D#4 (311Hz)
E4 (330Hz)
F4 (349Hz)
F#4 (370Hz)
G4 (392Hz)
G#4 (415Hz)
A4 (440Hz)
A#4 (466Hz)
B4 (494Hz)
C5 (523Hz)
C#5 (554Hz)
D5 (587Hz)
D#5 (622Hz)
E5 (659Hz)
F5 (698Hz)
F#5 (740Hz)
G5 (784Hz)
G#5 (831Hz)
A5 (880Hz)
A#5 (932Hz)
B5 (988Hz)
C6 (1046Hz)
BL[1:0] = 10b
C#4 (277Hz)
D4 (294Hz)
D#4 (311Hz)
E4 (330Hz)
F4 (349Hz)
F#4 (370Hz)
G4 (392Hz)
G#4 (415Hz)
A4 (440Hz)
A#4 (466Hz)
B4 (494Hz)
C5 (523Hz)
C#5 (554Hz)
D5 (587Hz)
D#5 (622Hz)
E5 (659Hz)
F5 (698Hz)
F#5 (740Hz)
G5 (784Hz)
G#5 (831Hz)
A5 (880Hz)
A#5 (932Hz)
B5 (988Hz)
C6 (1046Hz)
C#6 (1109Hz)
D6 (1175Hz)
D#6 (1245Hz)
E6 (1319Hz)
F6 (1397Hz)
F#6 (1480Hz)
G6 (1568Hz)
G#6 (1661Hz)
A6 (1760Hz)
A#6 (1865Hz)
B6 (1976Hz)
C7 (2093Hz)
BL[1:0] = 11b
C#5 (554Hz)
D5 (587Hz)
D#5 (622Hz)
E5 (659Hz)
F5 (698Hz)
F#5 (740Hz)
G5 (784Hz)
C#6 (1109Hz)
D6 (1175Hz)
D#6 (1245Hz)
E6 (1319Hz)
F6 (1397Hz)
F#6 (1480Hz)
G6 (1568Hz)
C#7 (2217Hz)
D7 (2349Hz)
D#7 (2489Hz)
E7 (2637Hz)
F7 (2794Hz)
F#7 (2960Hz)
G7 (3136Hz)
YMU757
#
#
-10-
G#5 (831Hz)
A5 (880Hz)
A#5 (932Hz)
B5 (988Hz)
C6 (1046Hz)
G#6 (1661Hz)
A6 (1760Hz)
A#6 (1865Hz)
B6 (1976Hz)
C7 (2093Hz)
G#7 (3322Hz)
A7 (3520Hz)
A#7 (3729Hz)
B7 (3951Hz)
C8 (4186Hz)
NT3 - NT0 : Pitch setting
Four bits from NT3 to 0 ar e us ed to speci fy the pi tch. The bit assignm ent is as s hown below .
N T[ 3:0] Pi tch
0h not pr onounce
1h C #
2h D
3h D #
4h Inhibi t
5h E
6h F
7h F#
8h Inhibi t
9h G
A h G #
B h A
C h Inhi bit
D h A #
Eh B
Fh C
If “0h” is set to NT[3:0] , movement of LSI is as follow s .
•The problem that LSI hangs up does n't occur.
•The part speci fied with CH [1:0] isn ' t pr onounc ed in spite of the est abl ish m ent value of pr onunc iat ion head TK[2:0] to
expl ai n in the rest .
•The interva l time when it is set with TI[3:0] to expl ai n in the rest is ef fect ive.
When inter val time passes, it deal s with the next music data.
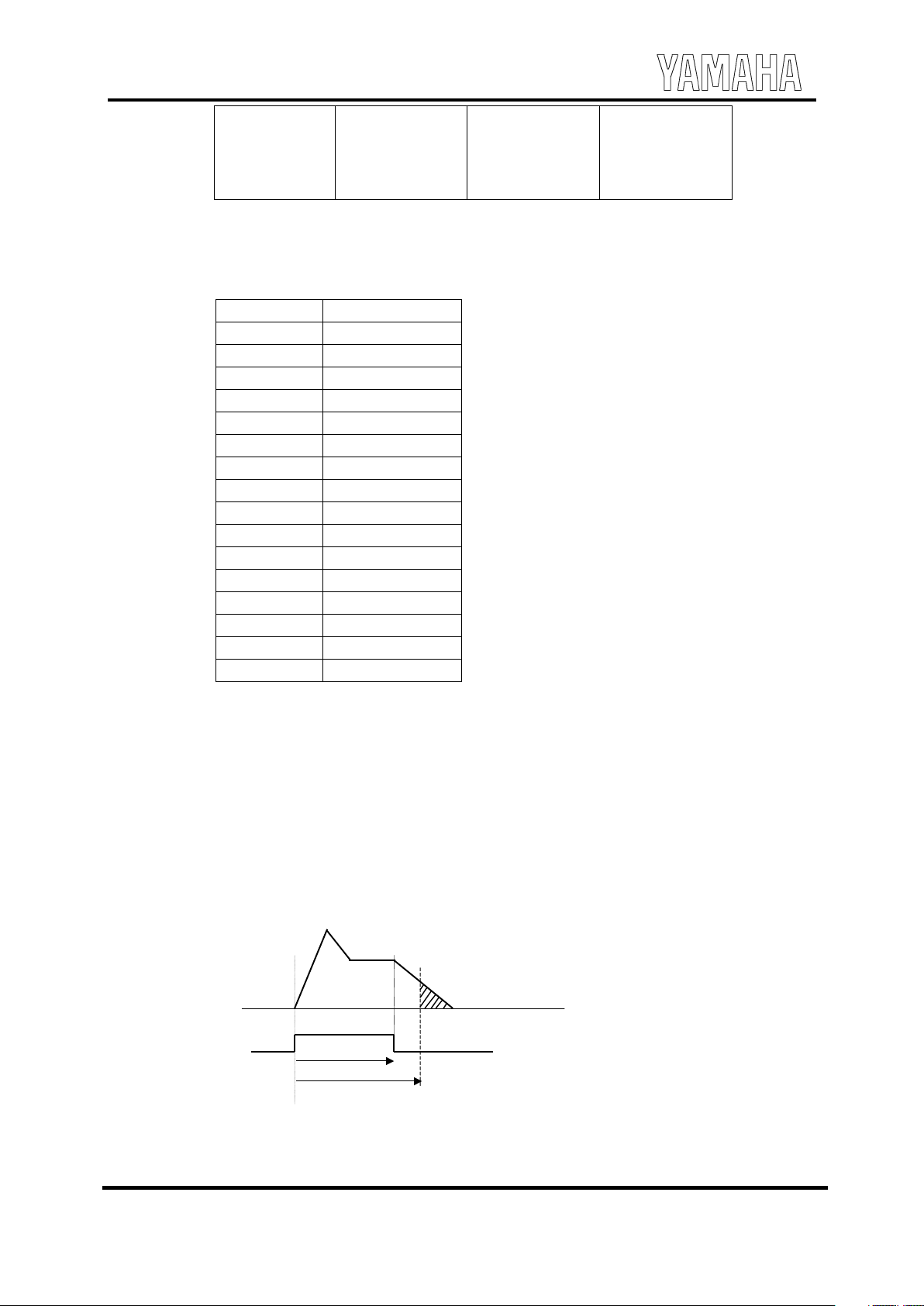
• Though it looks like a "rest ", there is a difference in behav ior with the follow ing case as a movement.
7.#
7,#
The treat ment of the next music data begins at the
time of A.
When rest dat a w ere speci fied, as f or the r eleas
e
time is goes on.
When the data N T i s “ 0h” i n the s a m e pa r t,
a
rel ease of the slant line part is not pr onounc e d.
(QYHORSH#ZDYH#VKDSH#RI#FDUULHU#
YMU757
#
#
-11-
CH1 - CH 0 : Part setting
As the s ound generat or can gene r at e s ounds in 4 pa rts si multaneousl y, set the part for each note by us ing CH 1 and 0
bits.
C H [ 1:0] Pa rt
00b 0
01b 1
10b 2
11b 3
VIB : Vibr at o setting
This bit is us ed to set Vibrat o function on or off for each note : "0" to set it off and "1" to set it on.
The vibr at o frequenc y is 6.4H z and the m odul at ion rat e is ±13.47 cent .
When VIB bit of timbre data($10-2Fh) is "0", Vibrat o function of f.
TI3 - TI0 : Interval setting
These bits are us e d to set the inter val period be for e the note and rest ar e pr ocessed ne xt. The interva l "48" repr esent s
the time for the w hole note.
TI [3:0] Interval
0h 0
1h 2
2h 3
3h 4
4h 6
5h 8
6h 9
7h 12
8h 18
9h 24
Ah 48
Bh 0
Ch 16
Dh 24
Eh 36
Fh 48
TK2 - 0 : Note (s ound lengt h) desi gna tion
These 3 bits ar e us ed to de s ignate the note (s ound lengt h) . D epe nding on the values of inter val setting (TI3 - 0) , the
lengt h varies as show n in the follow ing tabl e. The interva l " 48" repr esent s the time for the w hole note.
TI [3:0] = 0-Ah TI [3:0] = B-Fh
TK[2:0] 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7
Sound length
1 2 3 5 7 8 11 17 15 23 29 32 35 41 47 Tie, Slur
YMU757
#
#
-12-
Precaut ion
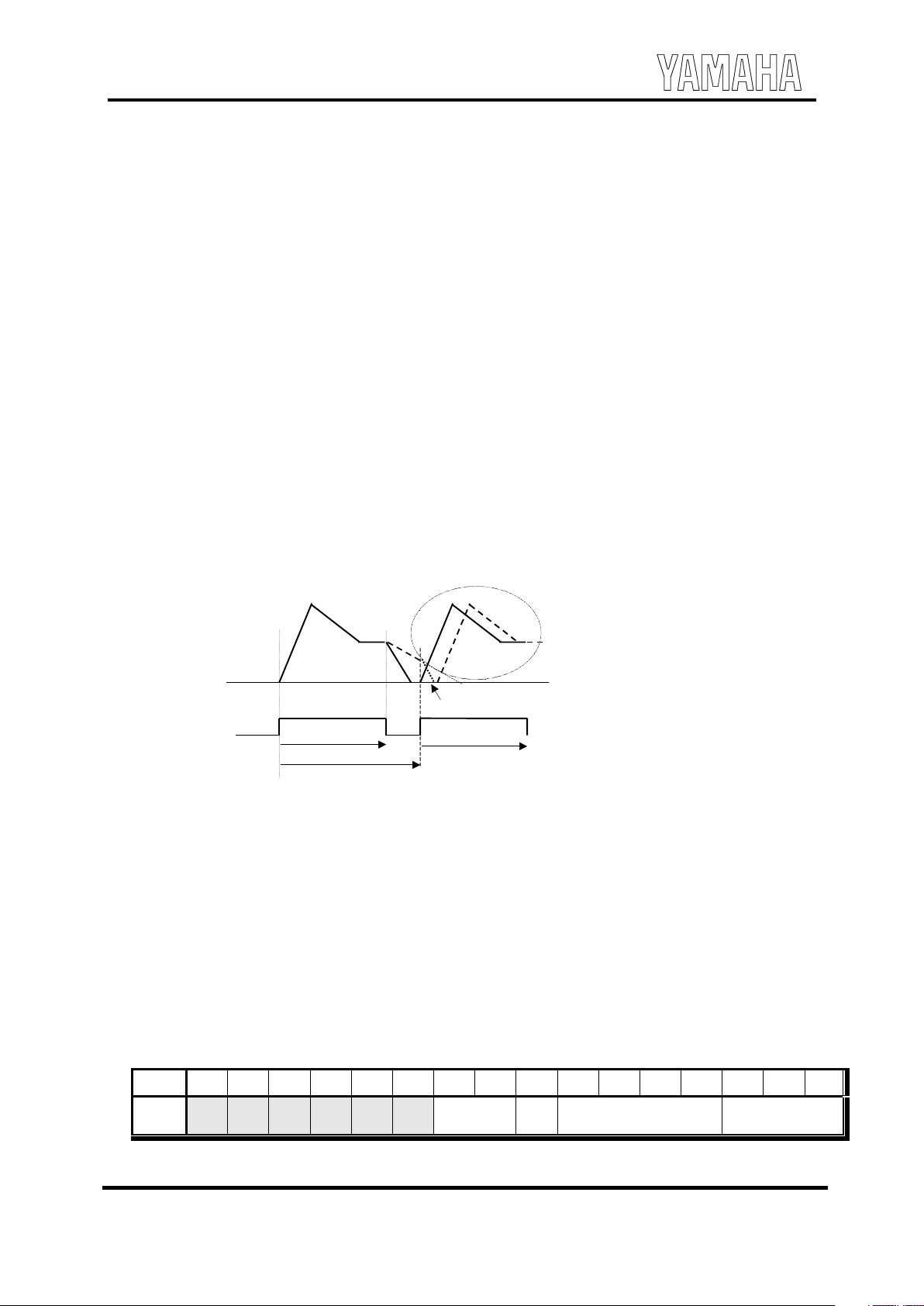
When KEY is tur ned on agai n under the condi tion that a rel ease isn' t fini shed com pl et el y, a tone may
change.(It is limited when enve lope wave shape is sustai ned s ound.)
This happe ns because enve lope wave shape of the career side of FM sound source and m odulat or
side are shifted.
The movement of envelope is expl ai ned.
As for the condi tion that it stops com pl et el y, it moves to at tack rat e at the sam e time with KEYON.
If the last pronunciat ion is condi tion that in rel ease and isn’t stopped com pl et el y, the est abl ishm ent of a
rel ease is made for ci bly early (8.94m s ). And it moves to at tack rat e from the condi tion that it stops. (A
in figur e)
An exam pl e is given to it, and the cause that a tone changes is expl ai ned.
It thinks that there is a tone which only rel ease time is different from with the car eer and m odulat or .
Though envelope of the solid line changes to at tack rat e soon at the time of the second KEYON.
But can't move to at tack rat e s oon, because s ound does n 't stop com pl et el y, envelope of the dotted line.
It moves to attack rat e after be speed up rel ease time and it becom es the condi tion that rel ease time is
stops com pl et el y.
Both enve lope are shifted by thi s movement.
And the sym ptom that a tone changes in the period when it is surrounded by a ci rcl e occur s.
It asks for the follow ing consi de rat ion to avoi d this sym ptom .
-It is pr onounc e d unde r the condi tion that a rel ease st ops com pl et el y.
-The rel ease time of the tone is shortened with the career , m odulat or side as well.
If sustai n level setting of the career side and m odulat or side are sam e value, the method of avoi dance
is as follow s .
- The rel ease time of career side and m odulat or side is made the sam e length.
Rest data
Default: 0000h
Index
b15 b14 B13 b12 b11 b10 b9 b8 b7 b6 b5 b4 b3 b2 b1 b0
$00h
0 0 1 1 0 0 CH1 CH0 VCHE TI3 TI2 TI1 TI0 VCH2 VCH1 VCH0
7.#
7,#
7.#
$#WRQH#FKDQJHV1#

YMU757
#
#
-13-
CH1 - CH 0 : Part setting
Using CH 1 or 0 bit, set the part for each rest .
CH[1:0] Part
00b 0
01b 1
10b 2
11b 3
TI3 - TI0 : Interval setting
These bits ar e us ed to set the inter val befor e the note and rest are processed next.
The interva l " 48" repr esent s the time for the w hole note.
TI [3:0] Interval
0h 3
1h 2
2h 3
3h 4
4h 6
5h 8
6h 9
7h 12
8h 18
9h 24
Ah 48
Bh 1
Ch 16
Dh 24
Eh 36
Fh 48
VCHE, VCH 2 - 0 : Timbre change function
Although the maximum num ber of timbres that can be us e d simultaneousl y is four , the timbre can be changed during
sound reproduct ion by set ting t hes e bi ts. Se t "1" for VC H E and us e V CH 2 t o V C H 0 t o set the t imbre N o.. The n
starting with the note whos e sound is to be generat ed next, the timbre for the part which ha s been set by us ing CH 0
and 1 will be changed.
Change a tone af ter the pr onunc iat ion of a part to change stops com pl et el y.
The condition t ha t pr onunciation stops i s not t he condition t ha t TK ( pr onunci ation l ength) i s f inished , but the
condition that the time when rel eases of envel ope is fini shed.
B e caref ul because st range sound m om entarily i s pronounced when you c hange a tone unde r t he c ondi tion t ha t
pronunciat ion does n't stop com pl et el y.
If the timbre al lotment is changed by us ing this function, the $30h regi ster itself will be rew ritten.
 Loading...
Loading...