Yamaha FX High Output, FX Cruiser High Output Owners Manual

2006
WaveRunner
FX High Output
FX Cruiser High Output
OWNER’S/OPERATOR’S
MANUAL
READ THIS MANUAL
CAREFULLY BEFORE OPERATION!
U.S.A. Edition
LIT-18626-06-53


EJU09890
CAUTION:
To the owner/operator
Thank you for choosing a Yamaha water-
craft.
This Owner’s/Operator’s Manual contains
information you will need for proper operation, maintenance, and care. A thorough
understanding of these simple instructions
will help you to obtain maximum enjoyment
from your new Yamaha. If you have any
questions about the operation or maintenance of your watercraft, please consult a
Yamaha dealer.
Because Yamaha has a policy of continuing product improvement, this product may
not be exactly as described in this Owner’s/
Operator’s Manual. Specifications are subject to change without notice.
This manual should be considered a permanent part of this watercraft and should
remain with it even if the watercraft is subsequently sold.
E
EJU12040
Important manual information:
In this manual, information of particular
importance is distinguished in the following
ways:
The Safety Alert Symbol means
ATTENTION! BECOME ALERT!
YOUR SAFETY IS INVOLVED!
WARNING
@
Failure to follow WARNING instructions
could result in severe injury or death to
the machine operator, passengers, a
bystander, or a person inspecting or
repairing the watercraft.
@
@
A CAUTION indicates special precautions that must be taken to avoid damage
to the watercraft.
@
NOTE:
@
A NOTE provides key information to make
procedures easier or clearer.
@
EJU11730
WaveRunner FX High Output/
FX Cruiser High Output
OWNER’S/OPERATOR’S MANUAL
©2005 by Yamaha Motor Corporation, USA
1st Edition, August 2005
All rights reserved.
Any reprinting or unauthorized use
without the written permission of
Yamaha Motor Corporation, USA
is expressly prohibited.
Printed in USA
P/N LIT-18626-06-53

EJU09920
CONTENTS
GENERAL AND SAFETY
INFORMATION
E
1
FEATURES AND FUNCTIONS
OPERATION
MAINTENANCE AND CARE
TROUBLESHOOTING AND
EMERGENCY PROCEDURES
2
3
4
5
APPENDIX
READ THIS OWNER’S/OPERATOR’S MANUAL CAREFULLY
BEFORE OPERATING YOUR WATERCRAFT.
6
EJU09930
GENERAL AND
SAFETY
E
INFORMATION
Identification numbers
Primary Identification (PRI-ID)
number ...................................................1-1
Hull Identification Number (HIN) ............1-2
Engine serial number .............................1-2
Emission control information
Approval label of Emission control
certificate ................................................1-3
Manufactured date label ........................1-3
Star labels ..............................................1-4
Important labels
Label location .........................................1-6
Warning labels .......................................1-7
Other labels ............................................1-9
Safety information
Limitations on who may operate
the watercraft .......................................1-10
Cruising limitations ...............................1-11
Operation requirements .......................1-12
Recommended equipment ..................1-14
Hazard information ..............................1-15
Watercraft characteristics ....................1-15
Water-skiing .........................................1-16
Rules of the Road
Steering and sailing rules ....................1-18
Rules when encountering vessels ......1-19
Other special situations .......................1-20
Reading buoys and other markers ...... 1-20
To get more boating safety
information
United States Coast Guard .................1-22
Other sources ......................................1-22
Watercraft Education and Training ......1-22
Enjoy your watercraft responsibly
.............................................1-22
............................1-1
................1-3
.......................................1-6
.................................1-10
..................................1-18
......1-23
1
E
EJU18300
Identification numbers
Record the Primary Identification (PRI-ID)
number, Hull Identification Number (HIN)
and engine serial number in the spaces provided for assistance when ordering spare
parts from a Yamaha dealer. Also record
and keep these ID numbers in a separate
place in case your watercraft is stolen.
EJU20141
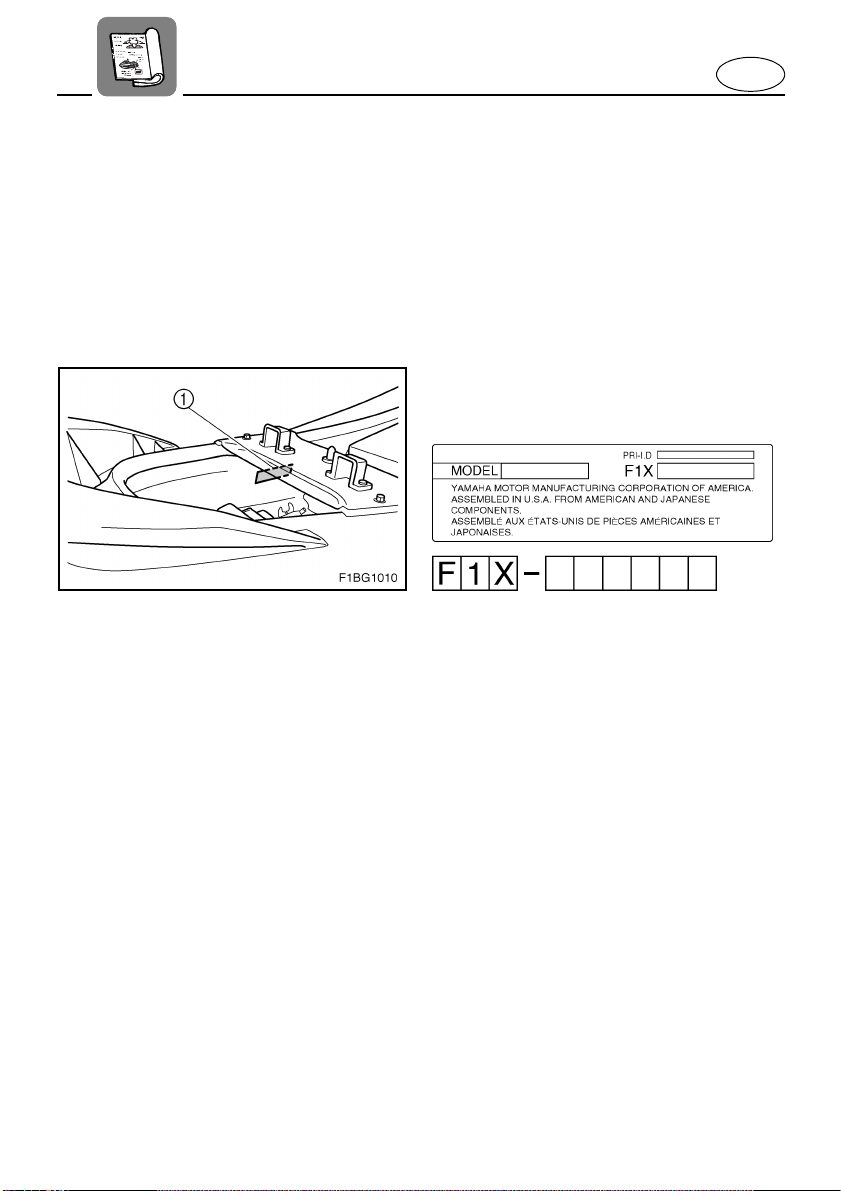
Primary Identification (PRI-ID)
number
MODEL: FX1100-E (FX High Output)
FX1100A-E (FX Cruiser High
Output)
FX1100B-E (FX Cruiser High
Output Limited)
The PRI-ID number is stamped on a
label 1 attached inside the engine compartment.
1-1

EJU12051
Hull Identification Number
(HIN)
The HIN is stamped on a plate 1
attached to the aft deck.
EJU09971
Engine serial number
The engine serial number is stamped on
a label 1 attached to the engine unit.
E
1-2
E
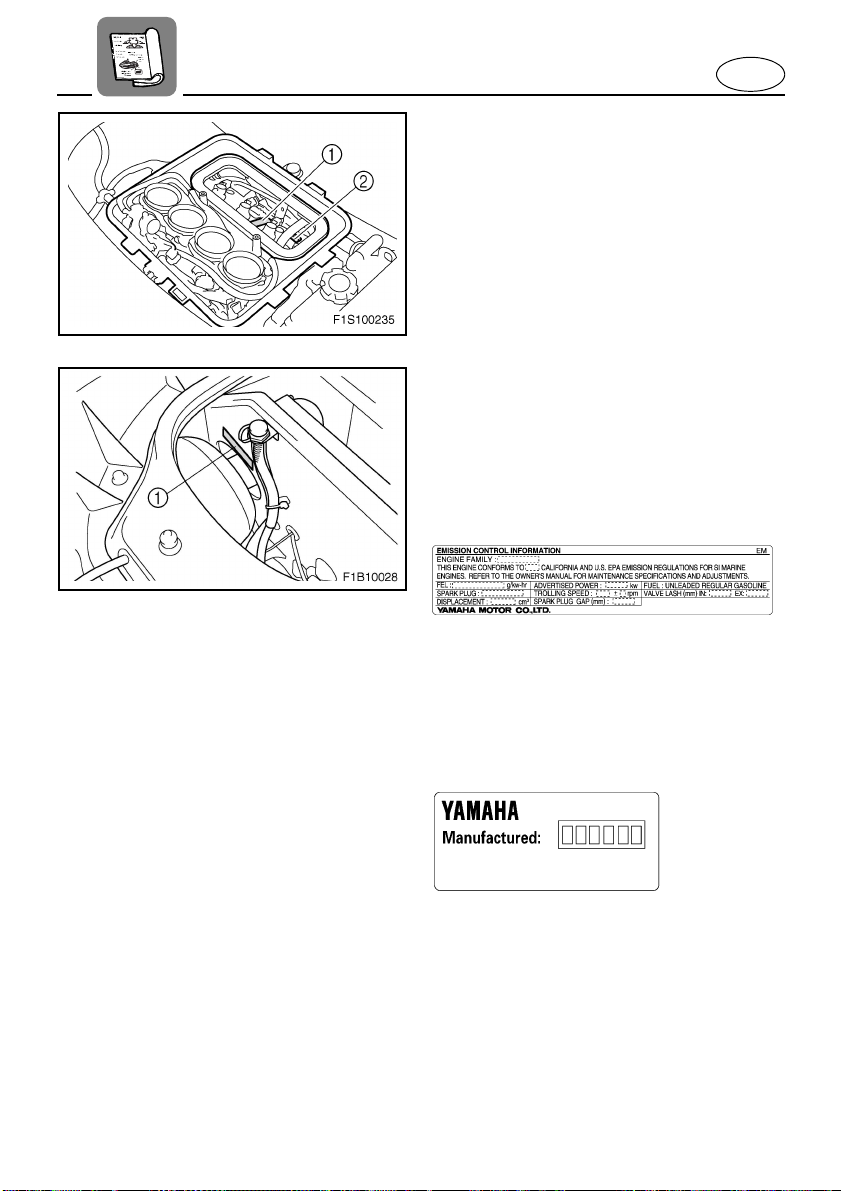
EJU13881
Emission control
information
This engine conforms to 2006 U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) and/or
California Air Resouces Board (CARB) regulations for marine SI engines.
This engine is certified to operate on regular unleaded gasoline.
EJU17790
Approval label of Emission
control certificate
This label is attached to the top of the cylinder head and to the bulkhead.
1
Emission control information label
EJU17800
Manufactured date label
This label is attached to the top of the cylinder head.
2
Manufactured date label
1-3

E
EJU18761
Star labels
This watercraft is labeled with a California
Air Resources Board (CARB) star label 1.
See below for a description of your particular label.
One Star - Low Emission
The one-star label identifies engines that
meet the Air Resources Board’s Personal
Watercraft and Outboard marine engine
2001 exhaust emission standards. Engines
meeting these standards have 75% lower
emissions than conventional carbureted
two-stroke engines. These engines are
equivalent to the U.S. EPA’s 2006 standards
for marine engines.
Two Stars - Very Low Emission
The two-star label identifies engines that
meet the Air Resources Board’s Personal
Watercraft and Outboard marine engine
2004 exhaust emission standards. Engines
meeting these standards have 20% lower
emissions than One Star-Low-Emission
engines.
Three Stars - Ultra Low Emission
The three-star label identifies engines
that meet the Air Resources Board’s Personal Watercraft and Outboard marine
engine 2008 exhaust emission standards or
the Sterndrive and Inboard marine engine
2003-2008 exhaust emission standards.
Engines meeting these standards have 65%
lower emissions than One Star-Low Emission engines.
1-4

E
Four Stars - Super Ultra Low Emission
The four-star label identifies engines that
meet the Air Resources Board’s Sterndrive
and Inboard marine engine 2009 exhaust
emission standards. Personal Watercraft
and Outboard marine engines may also
comply with these standards. Engines meeting these standards have 90% lower emissions than One Star-Low Emission engines.
1-5
EJU09980
EJU13510
Label location
E
Important labels
1-6

EJU13521
Warning labels
1
E
2
1-7
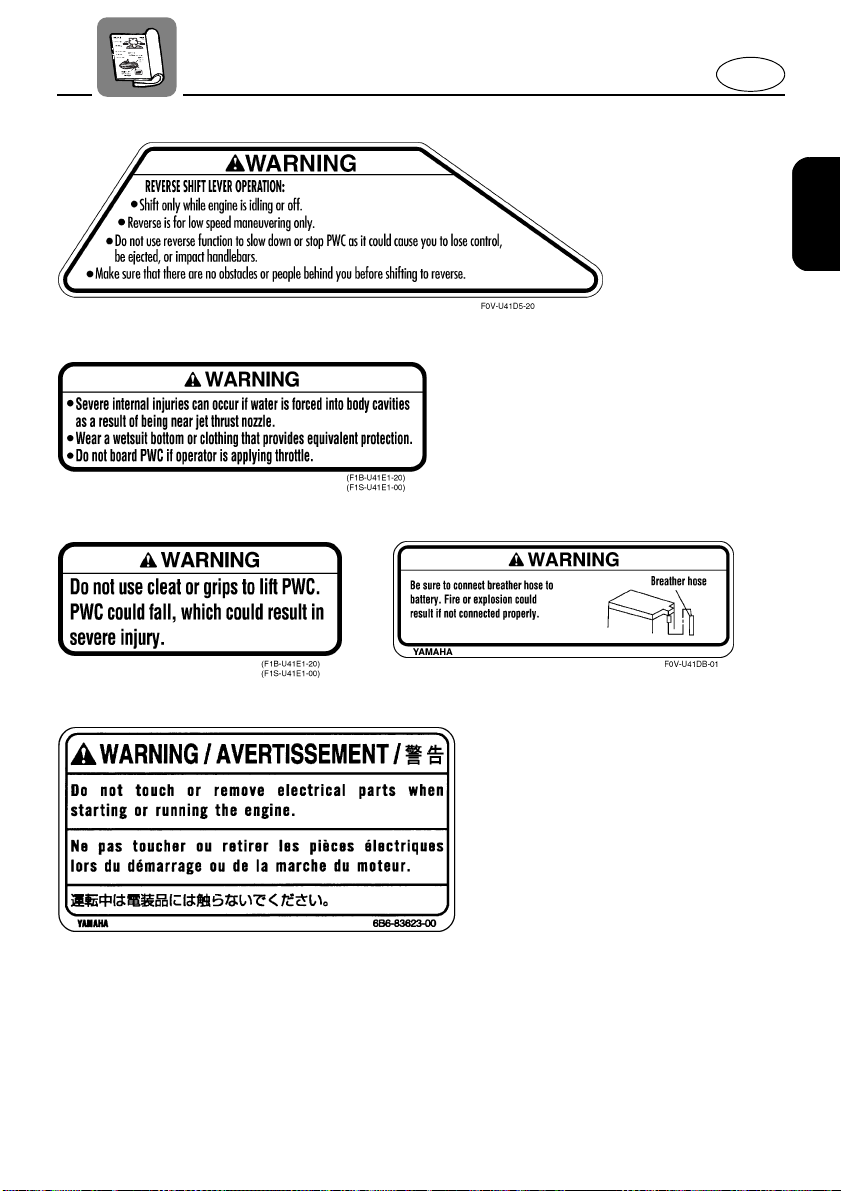
3
4
56
E
7
1-8

EJU13541
Other labels
8
This label indicates the
correct direction to upright
a capsized watercraft.
A
BC
9
0
E
D
1-9

E
EJU11770
Safety information
The safe use and operation of this
watercraft is dependent upon the use of
proper riding techniques, as well as upon
the common sense, good judgment, and
expertise of the operator. Every operator
should know the following requirements
before riding the watercraft.
Before operating the watercraft, read the
●
Owner’s/Operator’s Manual, the Riding
Practice Guide, the Riding Instruction
card and all warning and caution labels
on the watercraft. Also, watch the Basic
Orientation Video provided with your
watercraft. These materials should give
you an understanding of the watercraft
and its operation.
Never allow anyone to operate this water-
●
craft until they too have read the Owner’s/
Operator’s Manual, the Riding Practice
Guide, the Riding Instruction card and all
warning and caution labels, and if possi-
ble watched the Basic Orientation Video.
Showing them the video may help rein-
force the information contained in these
materials.
EJU11590
Limitations on who may
operate the watercraft
Yamaha recommends a minimum opera-
●
tor age of 16 years old.
Adults must supervise use by minors.
Know the operator age and training
requirements for your state. A boating
safety course is recommended and may
be required in your state. You can find
local rules by contacting the United
States Coast Guard (USCG), the National
Association of State Boating Law Administrators, or your local Power Squadron.
This watercraft is designed to carry the
●
operator and up to 2 passengers. Never
exceed the maximum load limit or allow
more than 3 persons (or 2 persons if a
water-skier is being pulled) to ride the
watercraft at one time.
Maximum load: 240 kg (530 lb)
Load is the total weight of cargo, operator and passengers.
Do not operate the watercraft with any
●
passengers on board until you have considerable practice and experience riding
alone. Operating the watercraft with passengers requires more skill. Take the time
to become accustomed to the handling
characteristics of the watercraft before
trying any difficult maneuvers.
1-10
E
EJU10011
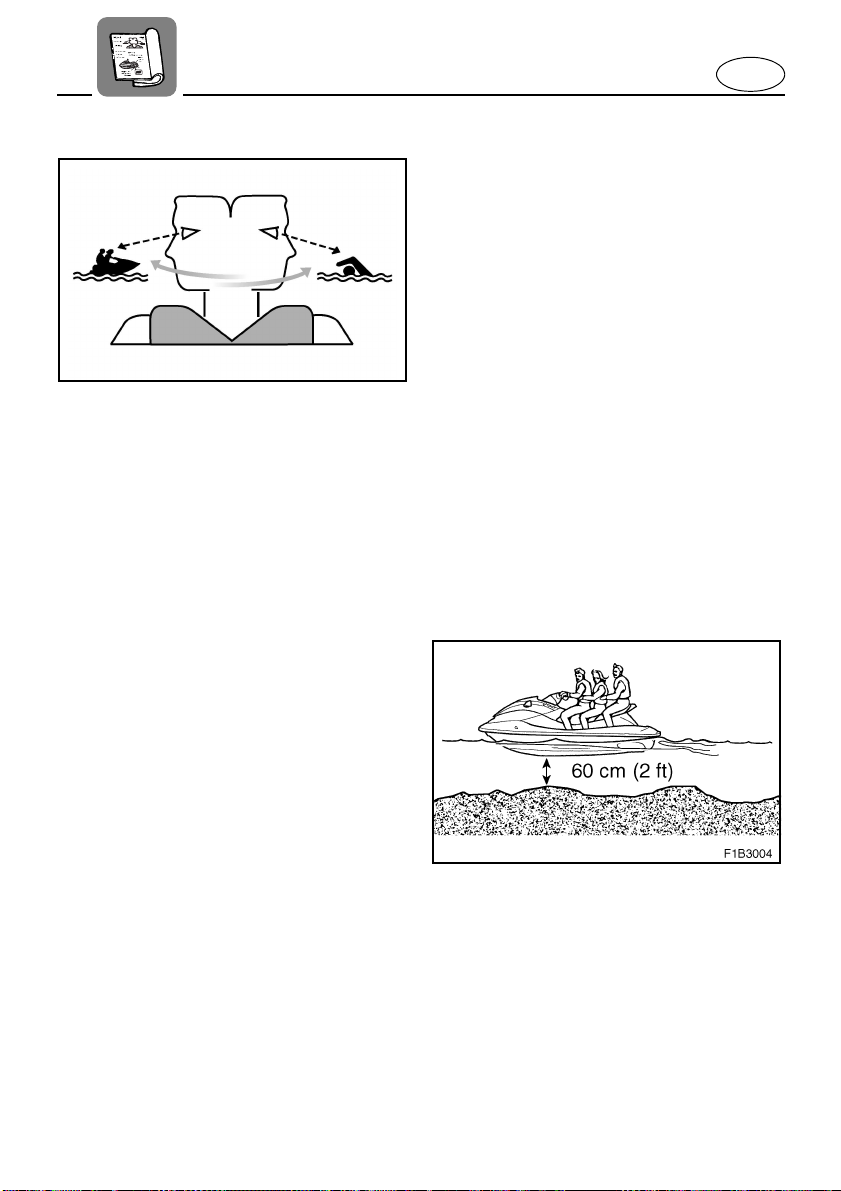
Cruising limitations
Scan constantly for people, objects, and
●
other watercraft. Be alert for conditions
that limit your visibility or block your vision
of others.
Operate defensively at safe speeds and
●
keep a safe distance away from people,
objects, and other watercraft.
Do not follow directly behind watercraft or
●
other boats.
Do not go near others to spray or splash
●
them with water.
Avoid sharp turns or other maneuvers
●
that make it hard for others to avoid you or
understand where you are going.
Avoid areas with submerged objects or
●
shallow water.
Take early action to avoid collisions.
●
Remember, watercraft and other boats do
not have brakes.
Do not release the throttle when trying to
●
steer away from objects—you need throt-
tle to steer. Always check throttle and
steering controls before starting the
watercraft.
Ride within your limits and avoid aggres-
●
sive maneuvers to reduce the risk of loss
of control, ejection, and collision.
This is a high performance boat—not a
●
toy. Sharp turns or jumping wakes or
waves can increase the risk of back/spinal
injury (paralysis), facial injuries, and broken legs, ankles and other bones. Do not
jump wakes or waves.
Do not operate the watercraft in rough
●
water, bad weather or when visibility is
poor; this may lead to an accident causing injury or death. Be alert to the possibility of adverse weather. Take note of
weather forecasts and the prevailing
weather conditions before setting out on
your watercraft.
As with any water sport, you should not
●
operate your watercraft without someone
else nearby. If you operate further than
swimming distance from shore, you
should be accompanied by another boat
or watercraft, but make sure you stay a
safe distance away. It’s good, common
sense!
Never operate in water that is less than
●
60 cm (2 ft) deep, otherwise you increase
your chance of hitting a submerged
object, which could result in injury.
1-11

This watercraft is not equipped with light-
●
ing required for night operation. Do not
operate the watercraft after sunset or
before dawn, otherwise you increase the
risk of colliding with another boat, which
could result in severe injury or death.
Follow navigation rules, and state/provin-
●
cial and local laws that apply to water-
craft.
EJU11605
Operation requirements
All riders must wear a U.S. Coast Guard
●
(USCG) approved personal flotation
device (PFD) that is suitable for personal
watercraft use.
Wear protective clothing. Severe internal
●
injuries can occur if water is forced into
body cavities as a result of falling into
water or being near the jet thrust nozzle.
Normal swimwear does not adequately
protect against forceful water entry into
the rectum or vagina. All riders must wear
a wetsuit bottom or clothing that provides
equivalent protection. Such clothing
includes thick, tightly woven, sturdy and
snug-fitting apparel such as denim, but
does not include spandex or similar fabrics, like those used in bicycle shorts.
E
1
USCG approved PFD
2
Wetsuit bottom
Eye protection is recommended to keep
●
wind, water, and glare from the sun out of
your eyes while you operate your watercraft. Restraining straps for eyewear are
made which are designed to float should
your eyewear fall in the water.
Footwear and gloves are recommended.
1-12

Helmets meeting Snell or DOT standards
●
are required for IJSBA-sanctioned races.
You must decide whether to wear a hel-
met while you ride for recreation. You
should know that a helmet could help pro-
tect you in certain kinds of accidents and
that it could injure you in others.
A helmet is designed to provide some
head protection. Although helmets cannot
protect against all foreseeable impacts, a
helmet might reduce your injuries in a col-
lision with a boat or other obstacle.
A helmet may have potential safety haz-
ards, as well. Falling into the water could
risk the chance of the helmet catching
water, commonly known as “bucketing,”
and the resulting strain on your neck
could cause choking, severe and perma-
nent neck injuries, or death. A helmet
could also increase the risk of an accident
if it reduces your vision or hearing, or if it
distracts you or increases your fatigue.
How should you decide if a helmet’s
potential safety benefits outweigh its
potential risks for you? Consider your par-
ticular riding conditions. Consider factors
such as your riding environment and your
riding style and ability. Also consider the
likelihood of traffic congestion, and the
water surface conditions. If you decide to
wear a helmet based upon your riding cir-
cumstances, choose one carefully. Look
for a helmet designed for personal water-
craft use, if possible. Consider a helmet
meeting Snell or DOT standards. If you
will be engaging in closed-course compe-
tition, follow the helmet requirements of
the sanctioning organization.
NEVER operate the watercraft after con-
●
suming alcohol or taking other drugs.
For reasons of safety and proper care of
●
the watercraft, always perform the preoperation checks listed on page 3-4
before operating the watercraft.
The operator and passengers should
●
always keep both feet in the footwell when
the watercraft is in motion. Lifting your
feet increases the chances of losing your
balance, or hitting objects outside the
watercraft with your feet. Do not give a
ride to children if their feet cannot reach
the floor of the footwell.
The passengers should hold on firmly,
●
either to the person in front of them or to
the handgrip provided.
Never allow a passenger to ride in front of
●
the operator.
Always consult your doctor on whether it
●
is safe for you to ride this watercraft if you
are pregnant or in poor health.
E
1-13
Do not attempt to modify this watercraft!
●
Modifications to your watercraft may
reduce safety and reliability, and render
the watercraft unsafe or illegal for use.
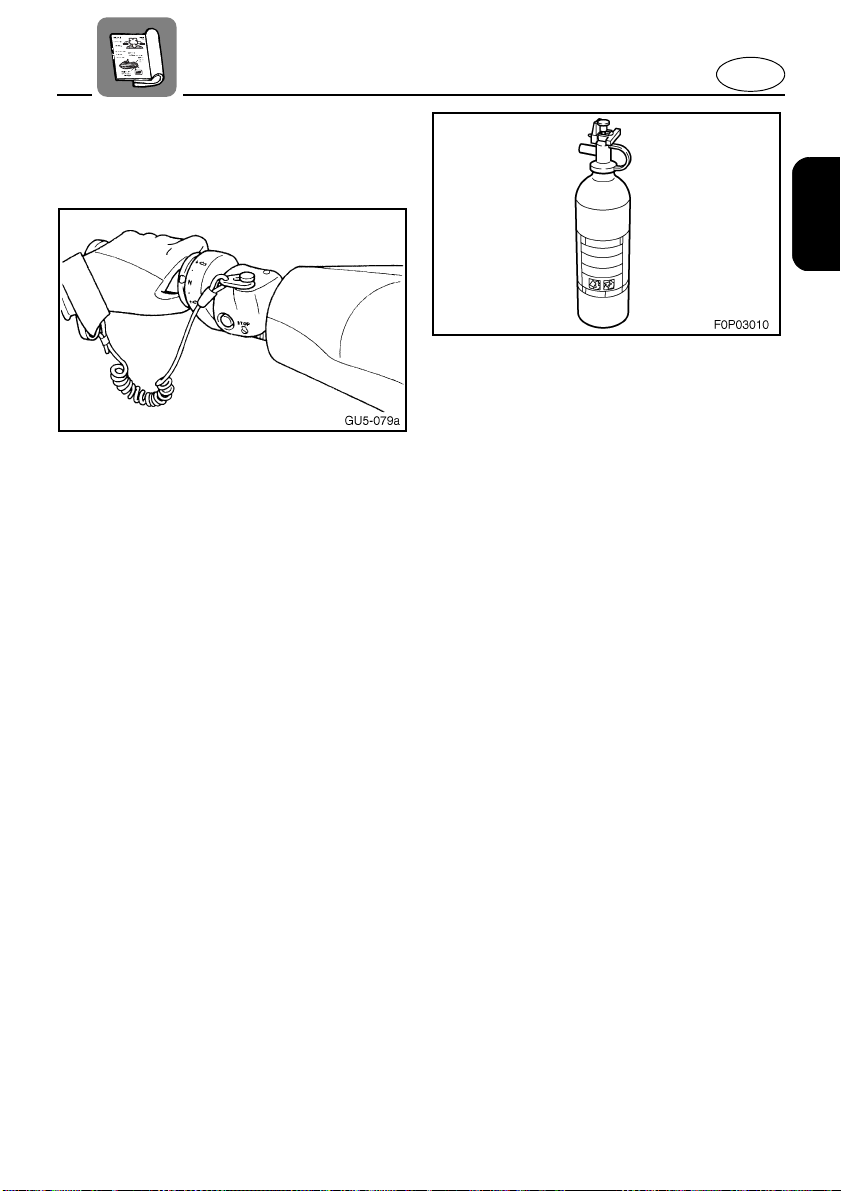
Attach the engine shut-off cord (lanyard)
●
to your wrist and keep it free from the
handlebars so that the engine stops if the
operator falls off. After riding, remove the
engine shut-off cord from the watercraft to
avoid accidental starting or unauthorized
use by children or others.
Scan carefully for swimmers and stay
●
away from swimming areas. Swimmers
are hard to see and you could acciden-
tally hit someone in the water.
Avoid being hit by another boat! You
●
should always take the responsibility to
watch for traffic; other boaters may not be
watching for you. If they do not see you,
or if you maneuver more quickly than
other boaters expect, you risk a collision.
Maintain a safe distance from other boats
●
and watercraft, and also watch for ski
ropes or fishing lines. Obey the “Rules of
the Road,” and be sure to check behind
you before making a turn. (See Rules of
the Road on pages 1-18 to 1-21.)
According to the USCG, boats under
●
6.1 m (20 ft) in length like your watercraft
MUST carry a fire extinguisher of a B-1
classification, with a capacity of two
pounds or more when navigating in
waters under USCG jurisdiction. In addition, most state and local boating laws
also require that the fire extinguisher be
approved by the USCG.
EJU13810
Recommended equipment
The following items should be carried on
board your watercraft:
Sound-signaling device
●
You should carry a whistle or other soundsignaling device that can be used to signal other boats. See Rules of the Road for
more information.
Visual distress signals
●
It is recommended that a USCG approved
pyrotechnic device be stored in a waterproof container on your watercraft. A mirror can also be used as an emergency
signal. Contact your Yamaha dealer or the
Coast Guard for more information.
Watch
●
A watch is helpful so you will know how
long you have been operating.
Towline
●
A towline can be used to tow a disabled
watercraft in an emergency.
E
1-14

E
EJU17810
Hazard information
Never start the engine or let it run for any
●
length of time in an enclosed area.
Exhaust fumes contain carbon monoxide,
a colorless, odorless gas that may cause
loss of consciousness and death within a
short time. Always operate the watercraft
in an open area.
Hot oil tank, muffler, and engine surfaces
●
can cause serious burns. Do not touch
the oil tank, muffler, or engine immedi-
ately after turning the engine off.
EJU19970
Watercraft characteristics
Jet thrust turns the watercraft. Releasing
●
the throttle lever completely produces
only minimum thrust. If you are traveling
at speeds above trolling, you will have
rapidly decreasing ability to steer without
throttle. This model has the Yamaha
Engine Management System (YEMS)
that includes an Off-Throttle Steering
(OTS) system. It will activate at planing
speeds should you attempt to steer the
watercraft after releasing the throttle lever.
The OTS system assists in turning by
continuing to supply some thrust while the
watercraft is decelerating, but you can
turn more sharply if you apply throttle
while turning the handlebars. The OTS
system does not function below planing
speeds or when the engine is off. Once
the engine slows down, the watercraft will
no longer turn in response to handlebar
input until you apply throttle again or you
reach trolling speed. Practice turning in
an open area without obstructions until
you have a good feel for this maneuver.
This watercraft is water-jet propelled. The
●
jet pump is directly connected to the
engine. This means that jet thrust will produce some movement whenever the
engine is running. There is no “neutral”
position. You are in either “forward” or
“reverse,” depending upon the shift lever
position.
Do not use the reverse function to slow
●
down or stop the watercraft as it could
cause you to lose control, be ejected, or
impact the handlebars. You could also
damage the shift mechanism.
This could increase the risk of back/spinal
injury (paralysis), facial injuries, and broken legs, ankles, and other bones.
1-15

E
Reverse can be used to slow down or
●
stop during low-speed maneuvering, such
as when docking. Once the engine is
idling, shift to reverse and gradually
increase engine speed. Make sure that
there are no obstacles or people behind
you before shifting into reverse.
Keep away from the intake grate 1 while
●
the engine is on. Items such as long hair,
loose clothing, or PFD straps can become
entangled in moving parts resulting in
severe injury or drowning.
Never insert any object into the jet thrust
●
nozzle 2 while the engine is running.
Severe injury or death could result from
coming in contact with the rotating parts
of the jet pump.
Stop the engine and remove the clip 3
●
from the engine shut-off switch 4 before
removing any debris or weeds, which may
have collected around the jet intake.
EJU17820
Water-skiing
You can use the watercraft for water-skiing if it has the seating capacity to carry the
operator, a rearward-facing spotter, and the
water-skier when he or she is not skiing.
The watercraft must also have a cleat 1
designed to pull a ski towrope; do not attach
the towrope to any other location.
It is the watercraft operator’s responsibility
to be alert to the safety of the water-skier
and others. Know and follow all state and
local water-skiing regulations in effect for the
waters in which you will be operating.
The operator should be comfortable carrying passengers before attempting to pull a
skier.
The following are some important considerations for minimizing risks while water-skiing.
The skier should wear an approved PFD,
●
preferably a brightly colored one so boat
operators can see the skier.
The skier should wear protective clothing.
●
Severe internal injuries can occur if water
is forced into body cavities as a result of
falling into the water. Normal swimwear
does not adequately protect against
forceful water entry into rectum or vagina.
The skier should wear a wetsuit bottom or
clothing that provides equivalent protec-
tion.
1-16
E
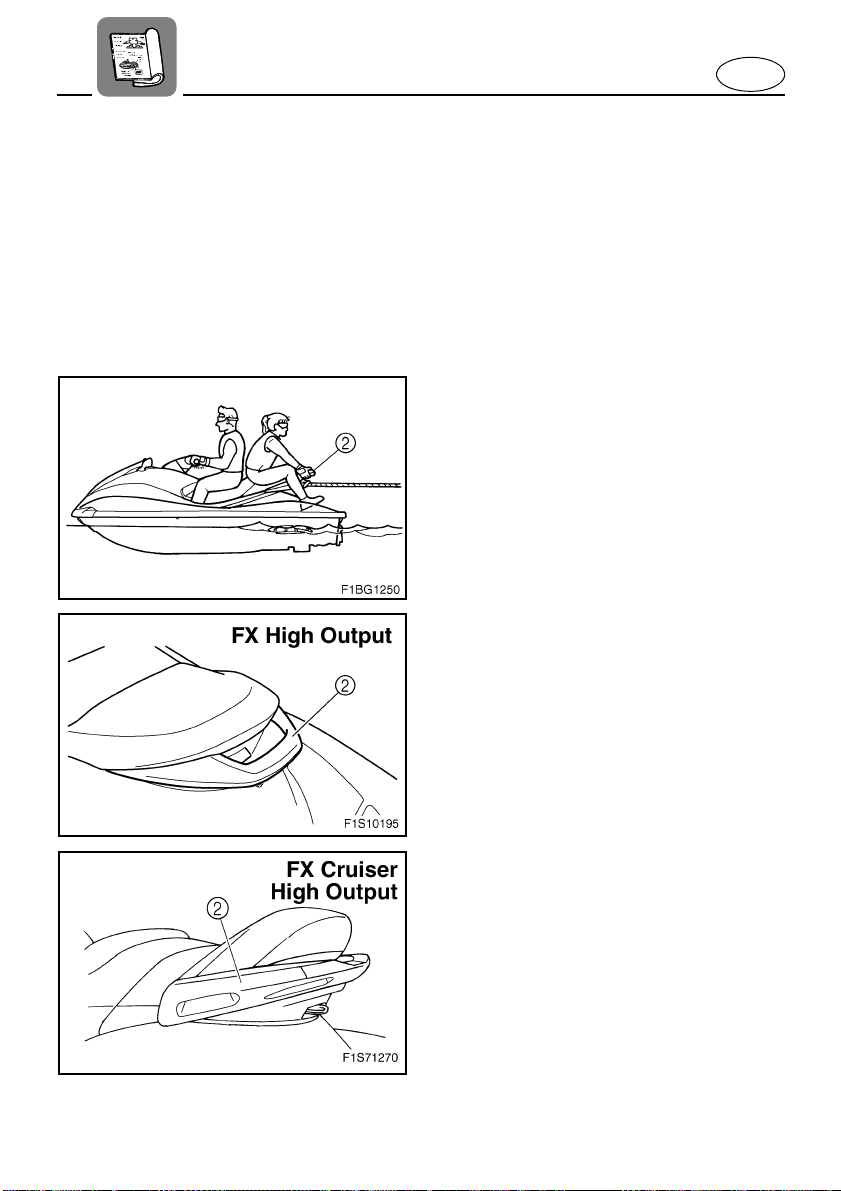
A second person should be on board as a
●
spotter to watch the skier; in most states it
is required by law. Let the skier direct the
operator’s control of speed and direction
with hand signals.
The spotter should sit securely on the
passenger seat and hold onto the handgrip 2 with feet firmly on the floor of the
footwell for proper balance while facing to
the rear to watch the skier’s hand signals
and his or her condition.
Your control while pulling a skier is
●
affected by the skier’s ability, as well as
water and weather conditions.
When preparing to pull a skier, operate
●
the watercraft at the slowest possible
speed until the watercraft is well away
from the skier and slack in the towrope is
taken up. Make sure that the rope is not
looped around anything.
After checking that the skier is ready and
that there is no traffic or other obstacles,
apply enough throttle to raise the skier.
Make smooth, wide turns. The watercraft
●
is capable of very sharp turns, which
could exceed the abilities of the skier.
Keep the skier at least 50 m (150 ft),
about twice the distance of a standard
towrope, from any potential hazard.
Be alert to the hazard of the towrope han-
●
dle snapping back at the watercraft when
the skier falls or is unable to get up on the
skis.
Towing heavy or bulky objects other than
●
skiers, such as another boat or watercraft,
can cause loss of steering control and
create a hazardous condition. If you must
tow another boat in an emergency situa-
tion, operate slowly and cautiously.
1-17

E
EJU11800
Rules of the Road
Yamaha watercraft is legally considered a powerboat. Operation of the
watercraft must be in accordance with
the rules and regulations governing the
waterway on which it is used.
Just as there are rules that apply when
you are driving on streets and highways,
there are waterway rules that apply when
you are operating your watercraft. These
rules are used internationally, and are also
enforced by the United States Coast Guard
and local agencies. You should be aware of
these rules, and follow them whenever you
encounter another vessel on the water.
Several sets of rules prevail according to
geographic location, but are all basically the
same as the International Rules of the
Road. The rules presented here in this
Owner’s/Operator’s Manual are condensed,
and have been provided for your convenience only. Consult your local U.S. Coast
Guard Auxiliary or Department of Motor
Vehicles for a complete set of rules governing the waters in which you will be operating
your watercraft.
Steering and sailing rules
Whenever two vessels on the water meet
one another, one vessel has the right-ofway; it is called the “stand-on” vessel. The
vessel that does not have the right-of-way is
called the “give-way” or “burdened” vessel.
These rules determine which vessel has the
right-of-way, and what each vessel should
do.
Stand-on vessel
The vessel with the right-of-way has the
duty to continue its course and speed,
except to avoid an immediate collision.
When you maintain your direction and
speed, the other vessel will be able to determine how best to avoid you.
Give-way vessel
The vessel which does not have the rightof-way has the duty to take positive and
timely action to stay out of the way of the
stand-on vessel. Normally, you should not
cross in front of the vessel with the right-ofway. You should slow down or change directions briefly and pass behind the other vessel. You should always move in such a way
that the operator of the other vessel can see
what you are doing.
The General Prudential Rule regarding
the right-of-way is that if a collision appears
unavoidable, neither boat has the right-ofway. Both boats must avoid the collision.
In other words, follow the standard rules
except when a collision will occur unless
both vessels try to avoid each other. If that is
the case, both vessels become give-way
vessels.
1-18

E
Rules when encountering
vessels
There are three main situations that you
may encounter with other vessels which
could lead to a collision unless the Steering
Rules are followed:
Meeting: you are approaching another
vessel head-on
Crossing: you are traveling across
another vessel’s path
Overtaking: you are passing or being
passed by another vessel
In the following illustration, your watercraft
is in the center. You should give the right-ofway to any vessels shown in the white area
(you are the give-way vessel). Any vessels
in the shaded area must yield to you (they
are the give-way vessels). Both you and the
meeting vessel must alter course to avoid
each other.
Meeting
If you are meeting another power vessel
head on, and are close enough to run the
risk of collision, neither of you has the rightof-way! Both of you should alter course to
avoid an accident. You should keep the
other vessel on your port (left) side. This
rule does not apply if both of you will clear
one another if you continue on your set
course and speed.
Crossing
When two power-driven vessels are
crossing each other’s path close enough to
run the risk of collision, the vessel which has
the other on the starboard (right) side must
keep out of the way of the other. If the other
vessel is on your starboard (right) side, you
must keep out of its way; you are the giveway vessel. If the other vessel is on your
port (left) side, remember that you should
maintain course and direction, provided the
other vessel gives you the right-of-way as it
should.
1-19

E
Overtaking
If you are passing another vessel, you are
the give-way vessel. This means that the
other vessel is expected to maintain its
course and speed. You must stay out of its
way until you are clear of it. Likewise, if
another vessel is passing you, you should
maintain your speed and direction so that
the other vessel can steer itself around you.
Other special situations
There are three other rules you should be
aware of when riding your watercraft around
other vessels.
Narrow channels and bends
When navigating in narrow channels, you
should keep to the right when it is safe and
practical to do so. If the operator of a powerdriven vessel is preparing to go around a
bend that may obstruct the view of other
water vessels, the operator should sound a
prolonged blast of four to six seconds on the
whistle. If another vessel is around the bend,
it too should sound the whistle. Even if no
reply is heard, however, the vessel should
still proceed around the bend with caution. If
you navigate such waters with your watercraft, you will need to carry a portable air
horn, available from local marine supply
stores.
Fishing vessel right-of-way
All vessels fishing with nets, lines or
trawls are considered to be “fishing vessels”
under the International Rules. Vessels with
trolling lines are not considered fishing vessels. Fishing vessels have the right-of-way
regardless of position. Fishing vessels cannot, however, impede the passage of other
vessels in narrow channels.
Sailing vessel right-of-way
Sailing vessels should normally be given
the right-of-way. The exceptions to this are:
1. When the sailing vessel is overtaking the
power-driven vessel, the power-driven
vessel has the right-of-way.
2. Sailing vessels should keep clear of any
fishing vessel.
3. In a narrow channel, a sailing vessel
should not hamper the safe passage of a
power-driven vessel that can navigate
only in such a channel.
Reading buoys and other
markers
The waters of the United States are
marked for safe navigation by the lateral
system of buoyage. Simply put, buoys and
markers have an arrangement of shapes,
colors, numbers and lights to show which
side of the buoy a boater should pass on
when navigating in a particular direction.
The markings on these buoys are oriented
from the perspective of being entered from
seaward (the boater is going towards the
harbor). Red buoys are passed on your starboard (right) side when proceeding from
open water into the harbor, and black buoys
are to your port (left) side. An easy way to
remember the meaning of the colors is the
phrase “red right returning.” When navigating out of the harbor, your position with
respect to the buoys should be reversed; red
buoys should be to port and black buoys to
starboard.
Many bodies of water used by boaters are
entirely within the boundaries of a particular
state. The Uniform State Waterway Marking
System has been devised for these waters.
1-20

E
This system uses buoys and signs with
distinctive shapes and colors to show regulatory or advisory information. These markers are white with black letters and orange
borders. They signify speed zones,
restricted areas, danger areas, and general
information.
Remember, markings may vary by geographic location. Always consult local boating authorities before riding your watercraft
in unfamiliar waters.
1-21

E
EJU11810
To get more boating
safety information
Be informed about boating safety. Additional publications and information can be
obtained from many organizations, including
the following.
United States Coast Guard
Consumer Affairs Staff (G-BC)
Office of Boating, Public, and Consumer
Affairs
U.S. Coast Guard Headquarters
Washington, D.C. 20593-0001
Boating Safety Hotline: 1-800-368-5647
Other sources
You can find local rules by contacting the
National Association of State Boating Law
Administrators, or your local Power Squadron.
Watercraft Education and
Training
The Online Boating Safety Course, available through the watercraft section of the
yamaha-motor.com website, is a free,
50 question learning course available to the
public. Upon successful completion of
80 percent or better, the user can request a
certificate of completion by mail or can
download one immediately. The Online
Boating Safety Course, provided by the
Boat/US Foundation, is approved by the
National Association of State Boating Law
Administrators (NASBLA) and recognized
by the United States Coast Guard. This
course meets the education requirement for
those states that recognize non-proctored,
NASBLA-approved courses.
Yamaha is the watercraft industry’s lead-
ing manufacturer to build awareness and
support for boating education. In 1997,
Yamaha launched its GET W.E.T. (Watercraft Education and Training) initiative and
has since reached out to over one million
Americans promoting the benefits of boating
education.
The Online Boating Safety Course:
http://www.boatus.com/onlinecourse/
1-22

E
EJU10061
Enjoy your watercraft
responsibly
You share the areas you enjoy when
riding your watercraft with others and with
nature. So your enjoyment includes a
responsibility to treat these other people,
and the lands, waters, and wildlife with
respect and courtesy.
Whenever and wherever you ride, think of
yourself as the guest of those around you.
Remember, for example, that the sound of
your watercraft may be music to you, but it
could be just noise to others. And the exciting splash of your wake can make waves
others won’t enjoy. Avoid riding close to
shoreline homes and waterfowl nesting
areas or other wildlife areas, and keep a
respectful distance from fishermen, other
boats, swimmers, and populated beaches.
When travel in areas like these is unavoidable, ride slowly and obey all laws.
Proper maintenance is necessary to
ensure that the exhaust emission and sound
levels of your watercraft will continue to be
within regulated limits. You have the responsibility to make sure that the recommended
maintenance in this Owner’s/Operator’s
Manual is carried out.
Remember that pollution can be harmful
to the environment. Do not refuel or add oil
where a spill could cause damage to nature.
Remove your watercraft from the water and
move it away from the shoreline before refueling. And keep your surroundings pleasant
for the people and wildlife that share the
waterways: don’t litter!
When you ride responsibly, with respect
and courtesy for others, you help ensure
that our waterways stay open for the enjoyment of a variety of recreational opportunities.
1-23

EJU10070
FEATURES AND
FUNCTIONS
E
Location of main components
Operation of controls and other
functions
Rear seat ................................................2-5
Front seat ...............................................2-6
Hood .......................................................2-7
Fuel tank filler cap ..................................2-7
Remote control transmitter ....................2-8
Engine stop switch .................................2-9
Engine shut-off switch ..........................2-10
Start switch ...........................................2-10
Throttle lever ........................................2-11
Cooling water pilot outlet .....................2-11
Steering system ...................................2-12
Tilt lever ................................................2-13
Shift lever .............................................2-14
Quick Shift Trim System (QSTS)
selector .................................................2-15
Handgrip ...............................................2-17
Reboarding step (for FX Cruiser High
Output) ..................................................2-17
Pull-up cleats (for FX Cruiser High
Output) .................................................2-18
Yamaha Engine Management System
(YEMS) .................................................2-19
Yamaha Security System/Low-RPM
mode ....................................................2-19
Multifunction meter ...............................2-22
Analog speedometer/tachometer and
indicator lights ......................................2-23
Left multifunction display and
operation buttons .................................2-26
Right multifunction display and
operation buttons (for FX Cruiser High
Output) .................................................2-31
Storage compartments ........................2-35
...................................................2-5
..............2-1
2
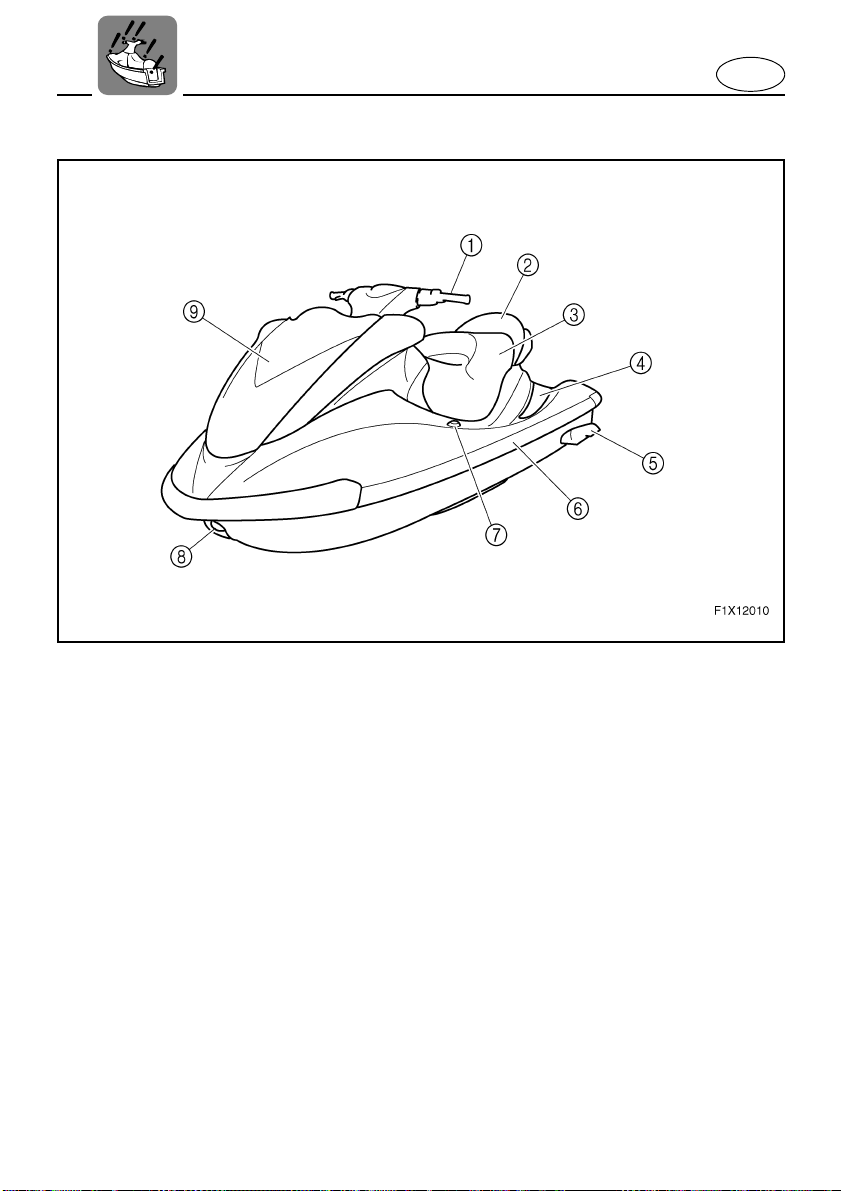
EJU10080
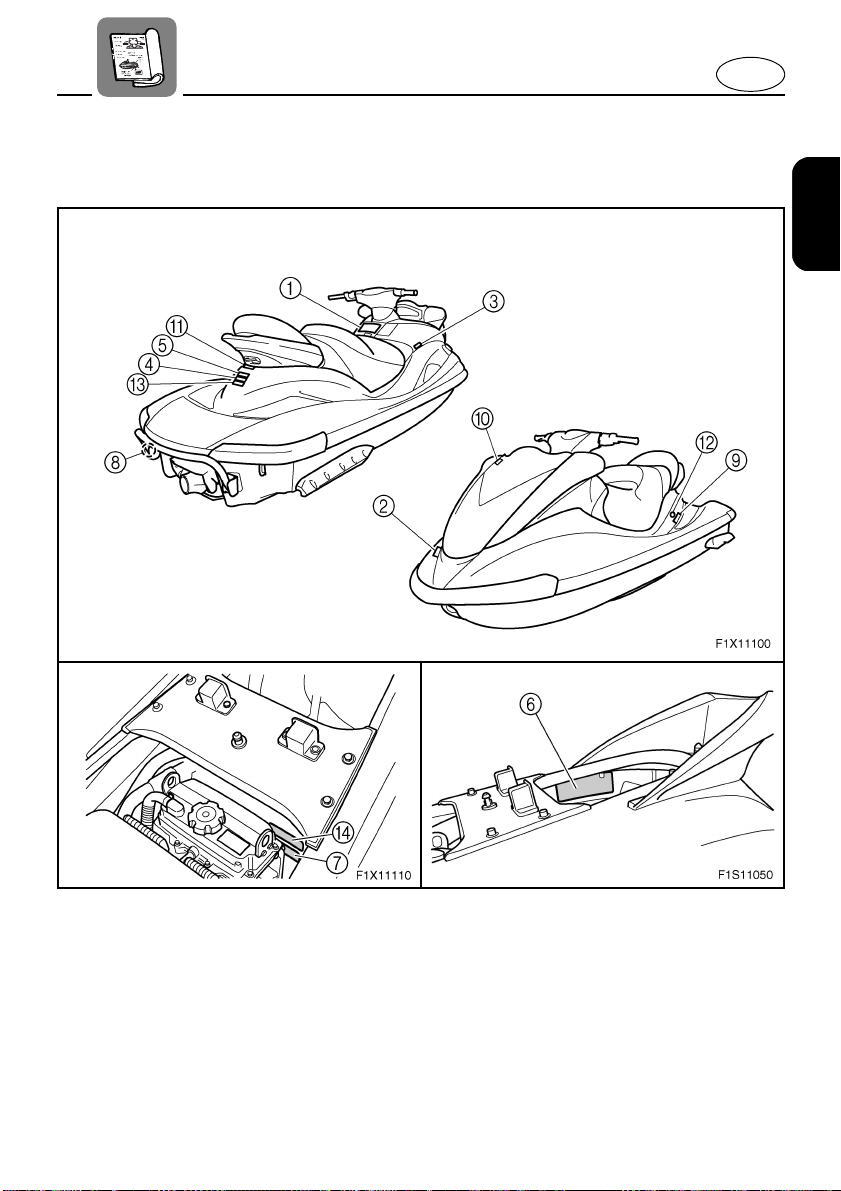
E
Location of main components
Handlebars
1
Use to control direction.
Rear seat
2
Front seat
3
Footwell
4
Use to place feet for balance.
To keep proper balance while facing to the rear
to watch the skier.
Sponsons
5
Gunwale
6
Pull-up cleat (for FX Cruiser High Output)
7
Use to attach rope for mooring.
Bow eye
8
Use to attach rope for transporting, mooring or
towing the watercraft in an emergency.
Hood
9
2-1
 Loading...
Loading...