Page 1

OPERATION, SERVICE & PARTS MANUAL
Before installing hoist, fill in the
information below. Refer to the
Hoist and Motor data plates.
Model No._________________
Serial No. _________________
SERIES Y80
®
Purchase Date _____________
Voltage ___________________
Rated Load _______________
YALE
WIRE ROPE ELECTRIC HOISTS
INCLUDING
WEIGHT WATCHER OVERLOAD CLUTCH MODELS
RA TED LOADS 1/2 THRU 5 TONS
Printed in U.S.A.
May, 2003 Copyright 2003, Yale•Lift-Tech, division of Columbus McKinnon Corporation Part No. 117404-10
Page 1
Page 2
FOREWORD
This manual contains important information to help you install, operate,
maintain and service your new YALE electric hoist. We recommend
that you study its contents thoroughly before putting the hoist into use.
Read ANSI B30.16 safety code for hoists . Then, thru proper installation,
application of correct operating procedures and by practicing the
recommended maintenance suggestions you can expect maximum
lifting service from the hoist.
It will likely be a long time before parts information found in Section IX
is needed; theref ore , after the hoist is installed and y ou ha ve completely
familiarized yourself with operation and preventive maintenance
procedures, we suggest that this book be carefully filed for future
reference.
When ordering replacement parts from this book, it will be necessar y
that you include, with your order, the Hoist Serial Number, Model
Number and Catalog Number which is found on the nameplate attached
to the hoist electrical cover. For your convenience, a space has been
NOTICE: Information contained in this book is subject to change without notice.
SECTION I GENERAL DESCRIPTION Page
Paragraph 1-1 General .................................................................................................................................................................3
Paragraph 1-2 Basic Construction ...............................................................................................................................................3
Paragraph 1-3 Differences Between Models ............................................................................................................................... 3
SECTION II INSTALLATION
Paragraph 2-1 General .................................................................................................................................................................3
Paragraph 2-2 Suspending Hoist .................................................................................................................................................3
Paragraph 2-3 Connecting Hoist to Electr ical Ser vice ................................................................................................................ 4
Paragraph 2-4 Pre-Operation Checks ..........................................................................................................................................4
SECTION III OPERATION
Paragraph 3-1 General .................................................................................................................................................................6
Paragraph 3-2 Push Button Operation ......................................................................................................................................... 6
Paragraph 3-3 Overload Clutch Operation (Optional) ................................................................................................................. 6
Paragraph 3-4 Operating Precautions..........................................................................................................................................6
SECTION IV LUBRICATION
Paragraph 4-1 General .................................................................................................................................................................7
Paragraph 4-2 Change Gear Case Oil ......................................................................................................................................... 7
Paragraph 4-3 Lubr icate Hoist Cable ...........................................................................................................................................7
Paragraph 4-4 Lubricate Upper Sheave and Lower Block Assembly .........................................................................................7
Paragraph 4-5 Lubr icate Limit Stop Lever ....................................................................................................................................8
Paragraph 4-6 Lubr icate Limit Switch ..........................................................................................................................................8
SECTION V INSPECTION AND PREVENTIVE MAINTENANCE
Paragraph 5-1 General .................................................................................................................................................................8
Paragraph 5-2 Inspect Lower Block ............................................................................................................................................. 9
Paragraph 5-3 Inspect Upper Block and Hoist Suspension ........................................................................................................ 9
Paragraph 5-4 Inspect Electrical Controls....................................................................................................................................9
Paragraph 5-5 Inspect Motor Brake ...........................................................................................................................................11
Paragraph 5-6 Inspect Mechanical Load Brake, Gearing and Overload Clutch (Optional) .....................................................11
Paragraph 5-7 Inspect Rope Dr um and Shaft............................................................................................................................13
Paragraph 5-8 Rope Inspection, Maintenance and Replacement ............................................................................................14
Paragraph 5-9 Rope Reeving .....................................................................................................................................................14
Paragraph 5-10 Testing Hoist and Overload Clutch (Optional) ...................................................................................................17
SECTION Vl TROUBLE SHOOTING CHART ............................................................................................................................ 19-20
SECTION Vll ADJUSTMENTS
Paragraph 7-1 Mechanical Load Brake ......................................................................................................................................21
Paragraph 7-2 Motor Brake.........................................................................................................................................................21
Paragraph 7-3 Block Operated Limit Switch ..............................................................................................................................21
Paragraph 7-4 Screw- Type Limit Switch....................................................................................................................................21
Paragraph 7-5 Overload Clutch Adjustment ..............................................................................................................................22
SECTION VIII WIRING DIAGRAMS
SECTION IX PARTS LIST
Paragraph 9-1 General ...............................................................................................................................................................22
Paragraph 9-2 List of Parts Illustrations .....................................................................................................................................22
provided on the front cover of this Manual for enter ing this information.
We recommend that you fill it out immediately so it is readily at hand
when needed.
The contents of this manual are of necessity, general in nature and
may cover features not incorporated on your hoist; therefore, the user
must exercise care in applying instructions given in this manual. If
specific information not in this manual is required, contact the factory
at Muskegon, Michigan 49443.
THE INFORMATION CONTAINED IN THIS MANUAL IS FOR
INFORMATIONAL PURPOSES ONLY AND YALE•LIFT-TECH DOES
NOT WARRANT OR OTHERWISE GUARANTEE (IMPLIEDLY OR
EXPRESSLY) ANYTHING OTHER THAN THE COMPONENTS THAT
YALE•LIFT-TECH MANUFACTURES AND ASSUMES NO LEGAL
RESPONSIBILITY (INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO
CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES) FOR INFORMATION CONTAINED IN
THIS MANUAL.
INDEX
No part of this document may be reproduced in any form, in an electronic retrieval system or otherwise, without prior written permission of the publisher.
Page 2
Page 3
SECTION I — GENERAL DESCRIPTION
This brake requires periodic adjustment.
1-1. GENERAL. YALE electric hoists are precision built wire
rope and drum type hoists which are made in five rated load
sizes (1/2, 1, 2, 3 and 5 tons) with various lifts, lifting speeds
and electrical service. Equipped with an integrally welded
mounting lug, they are designed to be rigidly attached to an
overhead structure or mounted on YALE rigid mount trolleys
for operation on runway beams. On certain models optional
base mounting or other supporting methods may be obtained.
For full information apply to factory at Muskegon, Michigan
49443.
NOTICE
YALE hoists are available with an optional built-in
mechanical overload clutch. Hoists having this device
are identified with words WEIGHT WATCHER on the
hoist.
The WEIGHT WATCHER overload clutch permits operation of
your hoist within its rated load and helps prevent lifting of
excessive loads which could cause permanent deformation
of a properly maintained hoist or trolley.
1-2. BASIC CONSTRUCTION. All models are of the same
basic construction and consist of a rugged welded steel frame
which houses a lifting drum and serves as the suspension for
carrying the entire hoist load. A mounting lug, for attaching
the hoist to a trolley or overhead support, is located on top of
the frame. An aluminum alloy gearcase and cover, attached
to one end of frame, houses a three-reduction gear train and
a mechanical load brake. An electric dr iving motor with disctype motor brake is located beside the frame, face mounted
on the back of the gearcase. Electr ical system components,
located on the end of the frame (opposite gearcase end) and
enclosed by a steel cover, control operation and rotating
direction of a driving motor. A hoisting rope and an enclosed
lower block assembly are used for lifting loads. An upper limit
stop is used to limit travel of the lower block in the raising
direction, to protect hoist from damage. A push button control
station, for operating the hoist, is suspended from the electrical
compartment.
1-3. DIFFERENCES BETWEEN MODELS. The main
differences between models are in rope reeving and frame
size as described below.
a.
Rope Reeving. There are four types of rope reeving used:
Two parts of rope single reeved, four parts of rope single
reeved, six parts of rope single reeved and two par ts of rope
double reeved. Single reeved hoists have one end of the
rope anchored to the drum, whereas, double reeved hoists
have both ends anchored to the drum. On single reeved
models, the lower block travels sideways as rope winds on
drum, double reeved models offer true vertical lift. For
illustrations, refer to Section V, paragraph 5-9, “Rope Reeving”
instructions.
b. Frame Size. Length of frame furnished is dependent on
hoist capacity and lift. Four frame lengths are used; short
frame, long frame, first and second extensions. Short frame
hoists have a rope drum flange to flange distance of
approximately 9-3/4", whereas this distance on a long frame
hoist is approximately 16-3/4". First extension frame hoists
have a flange to flange distance of 22-15/16" and second
extensions have 35-3/8".
c. Motor Brake. Hoists are equipped with a disc brake mounted
on the motor end bell and operated by a short stroke solenoid.
SECTION II — INSTALLATION
2-1.GENERAL. YALE electric hoists are lubricated and tested
before being shipped from the factory. T o place hoist in service,
attach to a suitable suspension (paragraph 2-2), connect to
electrical service (paragraph 2-3) and perform pre-operation
tests and checks (paragraph 2-4).
WARNING
Before attempting installation of hoist or trolley, the
main power switch must be loc ked in the open position
(off).
2-2.SUSPENDING HOIST. The hoist may be suspended in a
fixed location servicing only the area directly below the hoist
(Lug Mounted) or the hoist may be attached to a moveable
trolley or trolleys which in turn may be mounted on an l-beam
attached to a building or crane, servicing a larger area (Trolley
Mounted).
WARNING
DO NOT use small holes f or attaching this hoist unless
rated load on lower block is 1 (one) ton (2000 Ibs.) or
less.
a. Lug Mounted hoists attach to adequate supports welded
or bolted to a building or other structure. The supporting
structure must have sufficient strength with appropriate safety
factor, to suppor t the weight of the hoist and rated load as
well as other loads to which the supporting structure may be
subjected.
WARNING
Design and installation of hoist support shall be
performed only by qualified persons.
Steel angles or plates used to suspend hoist should be spaced
as close to the hoist suspension lug as possible. Mounting
bolts or threaded studs, attaching hoist to mounting structure,
shall have a diameter not less than recommended by
manufacturer and material equivalent to ASTM A 325. Make
certain that mounting bolts or studs are long enough so that
the threads do not engage the mounting support and that
mounting bolts or studs are secured with nuts and
lockwashers, self-locking nuts or cross bolting, if unthreaded.
b. Trolley Mounted hoists are attached to moveable trolleys. If
the hoist is mounted on an existing trolley, a qualified person
shall determine that the trolley and its supporting structure
are adequate to support the rated load and weight of the
hoist. Hoist/trolley units may be shipped from the factory with
trolley packaged separately. If the trolley can be installed
directly over the end of the supporting beam, assemble trolley
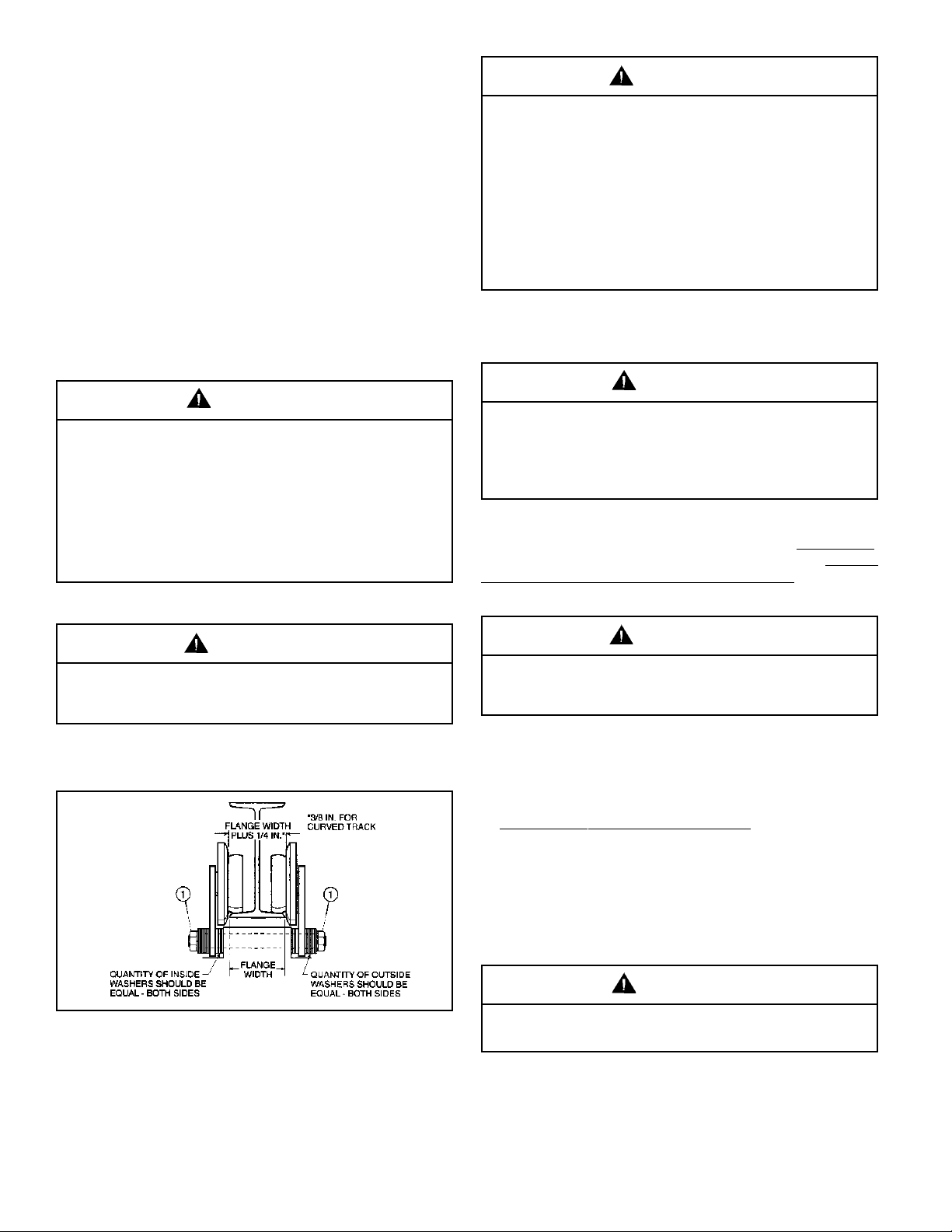
to hoist. Be certain that the spacing between wheel flanges,
after assembly, is 1/4" greater than exact width of beam
flange. (See Figure 2-1 below and instruction sheet fur nished
with trolley.) Using proper equipment, carefully lift trolley and
hoist and install on end of beam.
Page 3
Page 4
For trolleys which are to be mounted along the span of a
beam not having open ends, measure exact width of beam
flange and assemble trolley to hoist so that spacing between
wheel flanges is 1/4" (see Figure 2-1) greater than beam
width (3/8" if beam has curves). This is accomplished by
rearranging the spacer washers on the bolts connecting trolley
side plates to hoist mounting lug. If trolley is shipped separate
from hoist, see instruction sheets furnished with trolley for
orientation and installation.
When proper spacing has been determined, loosen mounting
nuts (item 1, Figure 2-1) to allow trolley wheels to spread far
enough to pass over edges of beam flange. (Some installations
may require complete removal of one trolley side plate.) Using
adequate equipment, carefully lift the hoist and trolley so the
wheel treads will rest on the lower beam flange. Replace side
plate and washers if removed for installation. Replace
suspension stud nuts.
CAUTION
Recheck spacer washers to make certain that the number
of washers between the side plate and hoist suspension lug
are equal, and also the number on the outside of each side
plate are equal. The suspension stud nuts should only be
snugged up on the lockwashers until a load has been
applied on the hook. A partial load (approx. 25% rated hoist
load) placed on the hook will properly seat hoist in the
trolley. Tighten suspension stud nuts only after hoist has
been properly seated in the trolley.
WARNING
Be certain that electrical power supply is off and locked
in the open position before attempting any electrical
connections to the hoist. This equipment must be
effectively grounded according to the National Electric
Code, or other applicable codes. If the grounding
method used is through the trolley wheels, then each
section of track must be grounded by metal-to-metal
connection to the building ground. Certain
environments may prevent proper grounding by this
means. In this case a separate grounding conductor
should be provided.
a. Follow National, State and Local Electrical Codes
when providing electrical service to the hoist.
CAUTION
208/230/460V single speed motors are reconnectable at
the motor. See motor nameplate. Transformer may be
reconnected for 200/230/460/575V. See transformer . Check
with wiring diagram to make certain that motor, transf ormer
and brake leads are properly connected.
b. Make electrical connections using the appropriate wiring
diagrams furnished with the hoist. All electrical connections,
including connections to collectors or power cord, shall be
made only by qualified journeymen electricians.
WARNING
Mounting of the hoist-trolley unit on the monorail and
final pre-operation inspection shall be performed only
by qualified persons properly supervised.
11207A
Figure 2-1. Sectional View of Trolley showing proper wheel
and washer spacing.
2-3. CONNECTING HOIST TO ELECTRICAL SERVICE.
Electrical service to the hoist may be power cable or a guarded
system having sliding shoe collectors.
WARNING
The green wire provided in the power supply cable
(when furnished) is a grounding wire and must be
connected to a proper ground.
c. When trolley is shipped separate from hoist, see special
instructions furnished with trolley for orientation and
installation.
2-4.PRE-OPERATION CHECKS.
a. Check Oil Level and Grease Fittings. The gearcase has
been filled with oil to the proper level and grease points for
lower and upper sheaves have been lubricated at the factory.
However, this should be checked before operating hoist. Check
oil level by removing oil level plug with hoist in a level position.
Oil level should be at the bottom edge of the plug hole. If not,
add oil as specified in Section IV. Grease fittings in lower and
upper sheave pins should show evidence of grease.
CAUTION
Overfilling of the gearcase may result in the excess fluid
being expelled through the breather.
Page 4
Page 5
Check Push Button Operation and Phasing.
b.
WARNING
On three phase hoists it is possible to have “Reverse
Phasing” causing the lower block to lower when the
áá
á button is depressed. When this condition exists,
áá
the automatic limit stop switch is inoperative and
hoist operation will be dangerous.
To properly check the phase of the hoist, follow the steps
below:
(1) With “POWER OFF” operate all the push buttons
and determine that they do not bind or stick in any position
WARNING
If any push button binds or sticks in any position —
DO NOT TURN POWER ON — determine the cause
and correct the malfunction before operating.
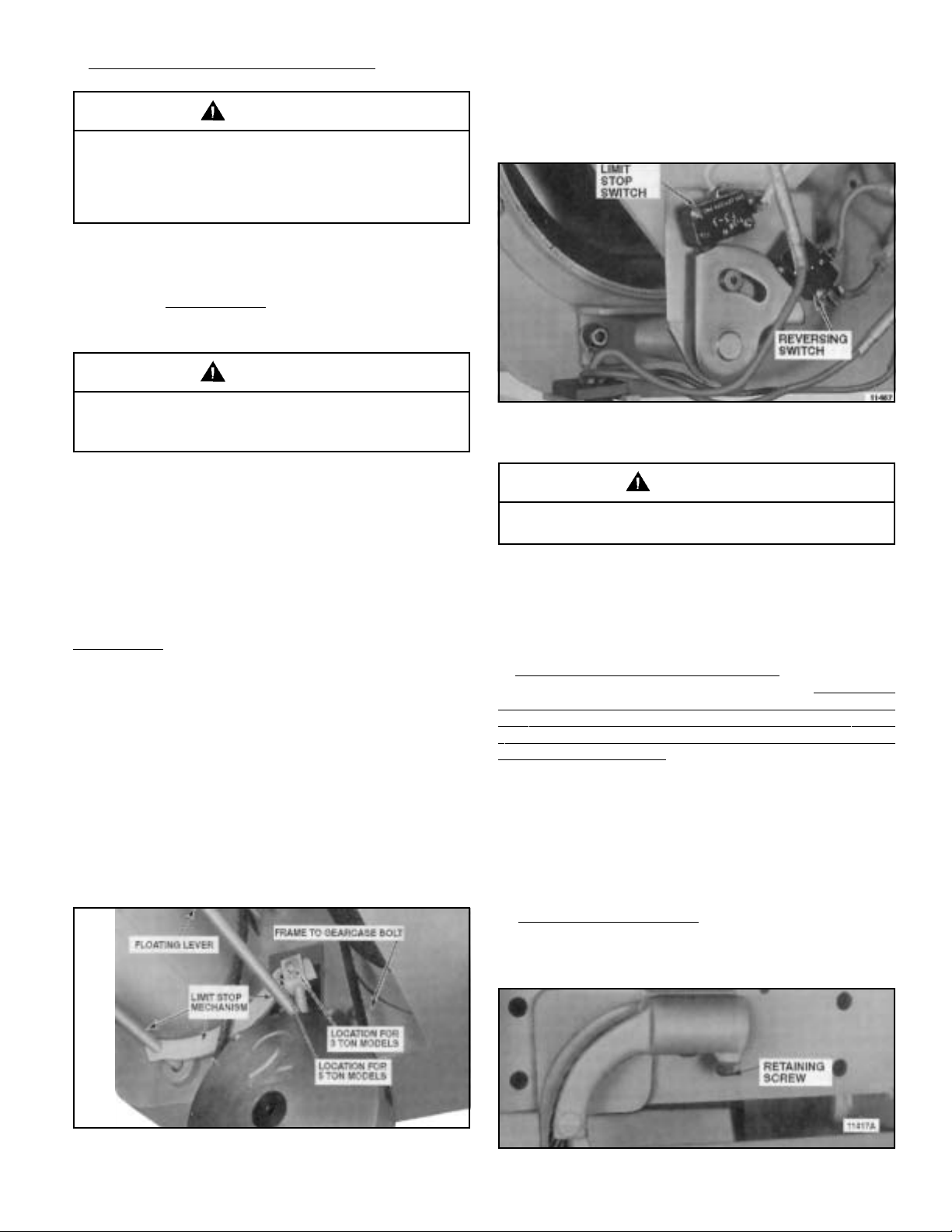
When floating rod is raised, stop switch is actuated first and
then the reversing switch is actuated (Figure 2-3). Stop switch
stops hoist. Reversing switch lowers hook block in case of
floating rod over-travel. If limit switch does not function in this
manner, refer to trouble shooting chart Section Vl for possible
remedy.
Figure 2-3. Electrical Compartment Cover Removed
Showing Limit Switch and Reversing Switch Arrangement.
(2) Temporarily connect hoist to power source.
(3) Operate á button briefly to determine direction of
hook travel.
(4) If hook raises, phase is correct. Turn power off and
make temporary connections permanent.
(5) If hook lowers, hoist is “Reverse Phased”. TURN
POWER OFF and correct by interchanging any two leads at
power source connection. Do not change internal wiring of
hoist.
c. Check Limit Switch Operation.
(1) A block operated upper limit stop (Figure 2-2) is
furnished as standard equipment. This limit stop is factory
set to stop lower block in its high position and guard against
over-travel and possible damage to hoist. (Note mounting
position of floating lever for 3 and 5 ton hoists.) No adjustment
can be made. Limit switch operation should be tested when
hoist is installed. Move hook to a low position by depressing
push button marked â. Now depress button marked
raise hook. While hook is traveling upward, manually (or with
an extension pole) raise limit stop mechanism (Figure 2-2).
áá
á to
áá
WARNING
Do not attempt to make above test with hook in a
high position near hoist.
(2) A screw-type upper and lower limit switch is provided
optionally when both upper and lower limit stops are required
(Figure 7-2). This switch is adjustable and must be adjusted,
at time hoist is installed, to desired high and low limits of
lower block travel. Refer to Section Vll.
d. Check Lower Block and Hoisting Cable. Depress
button and run lower block to its lowest position. No less than
two wraps shall remain on the drum with the loaded hook in
its lowest position, unless hoist is equipped with a lower limit
switch in which case no less than one and one half wraps
shall remain on the drum. Also check to see that lower block
and rope does not twist excessively. If it does twist to the
extent that two ropes rub against each other, disengage rope
from the frame anchor and twist rope four or five turns in a
direction opposite to that which the block turns. Reconnect
rope to anchor (Figure 2-4), holding firmly to eliminate rope
twisting back to its original position. Operate hoist up and
down a few times. If lower block still rotates, repeat process
until twisting is corrected.
e. Lubricate Hoisting Cable. For longer cable life, it is
recommended that the cable be lubricated at time of
installation by applying a Chain and Cable Fluid as outlined
in Section IV, paragraph 4-3.
ââ
â push
ââ
Figure 2-2. Limit Stop Mechanism
Being Tripped By Lower Block.
11403
Figure 2-4. Rope End Anchor.
Page 5
Page 6

SECTION III — OPERATION
3-1. GENERAL. Operation of Series 800 YALE electric hoists
is controlled by a convenient pendant push button station.
With it, the hoist can be controlled to give fast lifting and
lowering; or controlled to lift or lower load in small increments,
providing accurate spotting. The push button station has a
built-in interlock to prevent depressing opposing buttons
simultaneously.
When first using hoist, break-in by operating under lighter
loads to full travel before applying maximum load.
3-2. PUSH BUTTON OPERATION.
a. Depress push button marked
b. Depress push button marked
c. Jogging the push button will give “hairline” load movement.
The quickness of the depressing motion will determine the
amount of movement. Excessive use of this “Jogging” feature
will cause premature burning of contact tips and motor
overheating.
d. On two-speed hoists, partial depression of button operates
the hoist at slow speed; depressing b utton completely oper ates
the hoist at fast speed.
3-3. OVERLOAD CLUTCH OPERATION (Optional). The
overload clutch, when furnished with the hoist, is factory
preset and tested so that the hoist will lift its full rated load
but will refuse to lift overloads which could cause deformation
or weakening of your hoist. If the load to be lifted exceeds
the clutch setting, the hoist motor will continue to run when
áá
the
á button is depressed and rotate the load brake gear
áá
without lifting the load. Whenever this slipping occurs,
immediately release the
of the clutch friction surfaces and the hoist motor.
Always know load to be lifted. Lift-Tech does not
recommend lifting loads greater than the rated load of
your hoist.
3-4. OPERATING PRECAUTIONS.
áá
á push button to prev ent o verheating
áá
áá
á to raise load.
áá
ââ
â to lower load.
ââ
NOTICE
WARNING
Equipment covered herein is not designed or suitable
as a power source for lifting or lowering persons.
Safe operation of an overhead hoist is the operator’s
responsibility. Listed below are some basic rules that can
make an operator aware of dangerous practices to avoid and
precautions to take for his o wn safety and the safety of others.
Observance of these rules in addition to frequent examinations
and periodic inspection of the equipment may save injury to
personnel and damage to equipment.
a. DO read ANSI B30.16 Safety Standard for Overhead
Hoists and the Operation, Service and Parts Manual.
b. DO be familiar with hoist operating controls,
procedures and warnings.
c. DO make sure hook travel is in the same direction as
shown on controls.
d. DO make sure hoist limit switches function properly.
e. DO maintain firm footing when operating a hoist.
f. DO make sure that load slings or other approved
single attachments are properly sized and seated in the
hook saddle.
g. DO make sure that the hook latch, is closed and not
supporting any part of the load.
h. DO make sure that load is free to move and will clear
all obstructions.
i. DO take up slack carefully, check load balance, lift a
few inches and check load holding action before
continuing.
j. DO avoid swinging of load or load hook.
k. DO make sure that all persons stay clear of the
suspended load.
l. DO warn personnel of an approaching load.
m. DO protect wire rope from weld splatter or other
damaging contaminants.
n. DO promptly report any malfunction, unusual
performance, or damage of the hoist.
o. DO inspect hoist regularly, replace damaged or worn
parts, and keep appropriate records of maintenance.
p. DO use the hoist manufacturer’s recommended parts
when repairing a hoist.
q. DO use hook latches.
r. DO apply lubricant to wire rope as recommended.
s. DO NOT lift more than rated load.
t. DO NOT use a damaged hoist or a hoist that is not
working correctly.
u. DO NOT use the hoist with twisted, kinked, damaged
or worn wire rope.
v. DO NOT lift a load unless wire rope is properly seated
in its drum groove(s).
w. DO NOT use wire rope as a sling or wrap rope around
the load.
x. DO NOT lift a load if any binding prevents equal
loading on all supporting ropes.
y. DO NOT apply the load to the tip of the hook.
z. DO NOT operate unless load is centered under hoist.
aa. DO NOT allow your attention to be diverted from
operating the hoist.
ab. DO NOT operate the hoist beyond limits of wire rope
travel.
ac. DO NOT use limit switches as routine operating stops
unless recommended. They are emergency devices only.
ad. DO NOT use hoist to lift, support or transport people.
ae. DO NOT lift loads over people.
af. DO NOT leave a suspended load unattended unless
specific precautions have been taken.
ag. DO NOT allow sharp contact between two hoists or
between hoist and obstructions.
ah. DO NOT allow the rope or hook to be used as a
ground for welding.
ai. DO NOT allow the rope or hook to be touched by a
live welding electrode.
aj. DO NOT remove or obscure the warnings on the hoist.
Page 6
Page 7
ak. DO NOT adjust or repair a hoist unless qualified to
perform hoist maintenance.
al. DO NOT attempt to lengthen the wire rope or repair
damaged wire rope.
am. DO NOT allow personnel not physically fit or properly
qualified to operate hoist.
an. DO NOT operate hoist unless limit s witch is operating
properly.
ao. DO be sure there is no twist in wire rope.
ap. DO avoid operating hoist when hook is not centered
under hoist. Avoid side pulls and swinging of load or
load hook when traveling hoist.
WARNING
DO NOT operate hoist with the hoisting rope out of the
drum groves. Such operation may result in the rope
breaking and dropping the load which can cause
damage to equipment and injury to operator and other
personnel. Hoist rope will remain in the drum groves
during operation under normal operating conditions,
however, slack or kinked rope, excessive side pulls,
swinging or jerking of load, or similar ab use, ma y cause
the rope to leave the groves.
SECTION IV — LUBRICATION
4-1.GENERAL. The lubrication services outlined in
paragraphs 4-2 thru 4-6 should be performed at regular
intervals to maintain top hoist performance and ensure long
life. Inter vals of at least six (6) months, coinciding with spring
and fall seasons, are recommended. The reason for this is,
on hoists installed out-of-doors and in unheated areas, a
“cold test” lubricant is required in cold (below freezing)
climates making seasonal changes necessary.
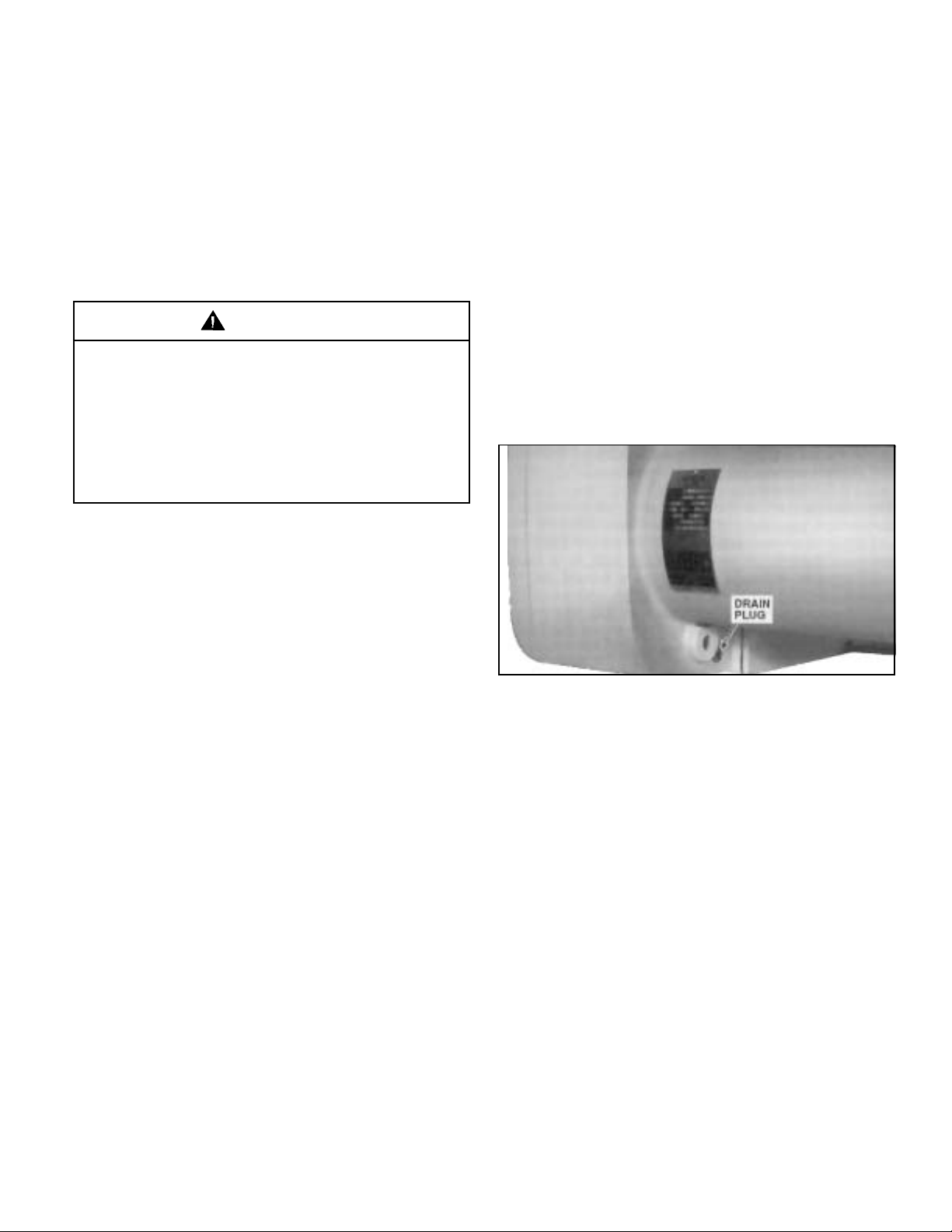
4-2. CHANGE GEARCASE OIL. (Figure 4-1)
a. Remove oil drain plug from bottom of gearcase and drain
out oil. (Two drain plugs, one on front and one on back of
gearcase.)
b. Flush out housing using petroleum solvent. Reinstall drain
plug.
c. Refill thru oil hole cover to proper level (bottom of oil
level plug hole) using 10 pints of Automatic Transmission
Fluid, DEXRON III Type, suitable for all temperature ranges.
aq. DO operate hoist within recommended duty cycle and
do not “jog’’ unnecessarily.
ar. DO conduct regular visual inspections for signs of
damage or wear.
as. DO NOT operate hoist with hooks that have opened
up. See Figure 5-1.
at. DO provide supporting structure or anchoring means
that has a load rating at least equal to that of the hoist.
au. DO NOT use hoists in locations that will not allow
operator movement to be free of the load.
av. DO, when starting to lift or pull, move the load a few
inches at which time the hoist should be checked for
proper load holding action. The operation shall be
continued only after the operator is assured that the hoist
is operating properly.
aw. DO NOT leave a loaded hoist unattended at the end
of a work shift or for extended periods during the work
shift. Where operations are such that this condition cannot
be avoided the operator must be assured that the
condition does not create a hazard to personnel or
property.
ax. DO NOT use the hoist load limiting device to measure
the load.
ay . DO NOT operate hoist unless hook moves in the same
direction as indicated on the pushbutton. If opposite
direction occurs, see pre-operation checks, Paragraph 2-
4.b.
az. Obser ve recommended inspection and maintenance
procedures.
ba. DO use common sense and best judgement whenever
operating a hoist. Observe American National Standard
Safety standard, ANSI B30.16, Iatest issue.
11413A
Figure 4-1. View Showing Location of
One Oil Drain Plug.
4-3.LUBRICATE HOISTING CABLE. Hoists are shipped from
the factory without an exterior coating on hoisting cable. It is
recommended, where conditions permit, that the cable be
thoroughly coated at installation and kept well lubricated with
LUBRIPLATE Chain and Cable Fluid, or equal, suitable for all
temperature ranges.
4-4. LUBRICATE UPPER SHEAVE AND LOWER BLOCK
ASSEMBLY.
a. All hoists have grease fittings located in ends of sheave
pins. Apply (*) NLGI No. 2 grease for operating temperatures
from +50°F to +125°F. For colder temperatures, (-20°F to
+50°F) use NLGI No. 1 grease.
b. Apply a few drops of S.A.E. No. 50 oil to hook thrust
bearings.
(*) National Lubricating Grease Institute.
4-5. LUBRICATE LIMIT STOP LEVER.
a. Apply a few drops of S.A.E. No. 50 oil to pivot points of
limit rod.
b. Apply a few drops of S.A.E. No. 50 oil to shaft bearing at
rear of electrical compartment.
Page 7
Page 8
4-6. LUBRICATE LIMIT SWITCH. Provide a light film of
NLGI No. 2 grease on bevel gear of limit switch.
SECTION V
INSPECTION AND PREVENTIVE
MAINTENANCE
5-1. GENERAL. YALE, Series 800, hoists are inspected
and tested at the factory. Regular in service inspection and
preventiv e maintenance prog rams not only help reduce overall
maintenance costs but may also prevent serious shutdowns
by fore warning of problems that could cause these shutdowns.
Regular inspections, periodic minor adjustments, regular
cleaning and lubrication and replacement of worn par ts can
help preserve good performance and operation of your hoist.
Many factors influence the inspection and preventive
maintenance program required for your hoist. Frequency and
severity of service and material handled, local environmental
conditions and various applicable codes are some of the
factors that the user must consider to adjust inspection and
maintenance program outlined in this section to meet his
specific conditions.
The inspection and maintenance services outlined in this
section are considered minimum. Recommended in the
schedule are minimum inspection and maintenance intervals
based on average daily use in a normal environment. Average
daily use is based on 1000 operational hours per year
maximum and intermittent operation of the hoist eight hours
per day, five days per week with a maximum 40% “on” time
and the average loading not exceeding 65% of rated load.
reports. Inspections are recommended each month and should
be performed thoroughly enough to inform the hoist user of
deficiencies for any item listed. This form does not supersede
the Inspection and Maintenance Schedule listed below but
may be used to record scheduled inspection and maintenance
services required.
The user should revise the inspection interval, add additional
units or provide a similar form to suit particular conditions
which may exist. However, written, dated and signed inspection
reports should be maintained particularly on critical items,
such as hoist hooks, hoisting ropes, sheaves, drums and
brakes. Periodic review of old inspection reports can point
out service life of hoist components, forecasting need for
adjustment, repair or replacement of these components.
As a matter of expedience, appointed maintenance personnel
inspecting the hoist can also take care of minor adjustments,
repairs and cleaning, where required. Note the column on
Inspection Schedule and Maintenance Report form headed
Corrective Action and Notes. When corrective action is made
during inspection, note condition of part or unit as inspected
in appropriate
“during inspection” corrective action taken and date in space
provided. In this manner, items requiring fur ther attention will
be checked (
advise the designated person responsible for hoist operation
and safety, who reviews the reports, that deficiencies exist.
The designated person will check all deficiencies as listed
and reexamine or otherwise determine whether they constitute
a safety
Condition column with a check mark (ü). Note
ü) without showing corrective action. This will
Environmental conditions in which the hoist operates are
also important considerations for the user when adjusting
hoist inspection and maintenance programs to local conditions.
Frequency of inspection and maintenance must be increased
if hoist is subjected to severe atmospheric environmental
conditions, such as corrosive vapors, extreme heat or cold,
cement or dust and other airborne contaminants. The user
should carefully consider all environmental conditions and
adjust frequency and degree of maintenance for his local
conditions. Consult Lift-Tech Field Service Department for
advice for unusual environmental conditions.
Various codes also regulate inspection and maintenance
programs. Attention must be given to applicable Federal
Standards, OSHA regulations, National Standards, state and
local codes which may include mandatory rules relating to
hoist inspection and maintenance. The user should become
familiar with all applicable codes for his area and be guided
accordingly.
Listed on the Recommended Inspection and Maintenance
Schedule are inspection frequencies and requirements.
Perform these inspections regularly as scheduled and
additional inspections as may be required for activity, ser vice
and environment of your hoist. The hoist operator must be
responsible for determining the operating conditions and
severity of service.
Inspection Schedule and Maintenance Report Form.
Shown on page 10 of this manual is a recommended
Inspection Schedule and Maintenance Report form which
lists various components of the hoist. The for m also includes
trolley components, runway components, and miscellaneous
items. This form is suggested as a guide for written inspection
WARNING
Deficiencies may be hazardous to personnel and
equipment. Do not operate a hoist ha ving deficiencies
unless a designated qualified person has determined
that these deficiencies DO NOT constitute a safety
hazard.
Written, dated and signed inspection reports for many items
are mandatory under OSHA regulations, and many state safety
codes. It is strongly recommended that the Inspection
Schedule and Maintenance Report, shown herein, be
completed by a qualified person designated with the
responsibility for hoist operation and safety or an inspector
appointed by this person.
Inspection records can point out the service life of hoist
components and help forecast the need for adjustments,
repairs and ordering of replacement parts. File and review
these reports after each inspection.
WARNING
Do not operate a hoist having unusual vibrations,
sounds or other conditions. Danger may be present
that the hoist operator cannot see. Determine and
correct cause of unusual conditions and make
certain the hoist can be operated safely. Be certain
to disconnect power to the hoist whenever electrical
cover is removed.
Page 8
Page 9
5-2.INSPECT LOWER BLOCK.
a. Check lubrication of all par ts. If the thrust bearing is not
equipped with a grease fitting, lubricate with SAE No. 50 oil.
Also lubricate the shank of the hook which passes through
the lower block body.
b. Check each sheave to ensure rope groove is smooth and
free from burrs, or other surface defects.
c. Check each sheave for freedom of rotation; replace
bearings if defective.
d. Make cer tain that dowel pin, holding the hook nut to the
hook, is securely in position.
c. Make certain that rope guide pins are not bent, loose or
otherwise distorted; guide pins must have close clearance to
sheave flange to keep rope in sheave grooves.
d. Check hoist suspension bolts on lug suspended hoists;
make certain that bolts are secure, properly tightened and
free from damage.
e. Inspect suspension lug at top of hoist frame for damage ,
cracks, hole elongation or other signs of wear. On all hoists,
the suspension lug is integral with hoist frame and the entire
frame must be replaced when suspension lug is damaged
and requires replacement.
e. If hook is equipped with a safety latch or rotational lock,
check to determine that they are in good operating condition.
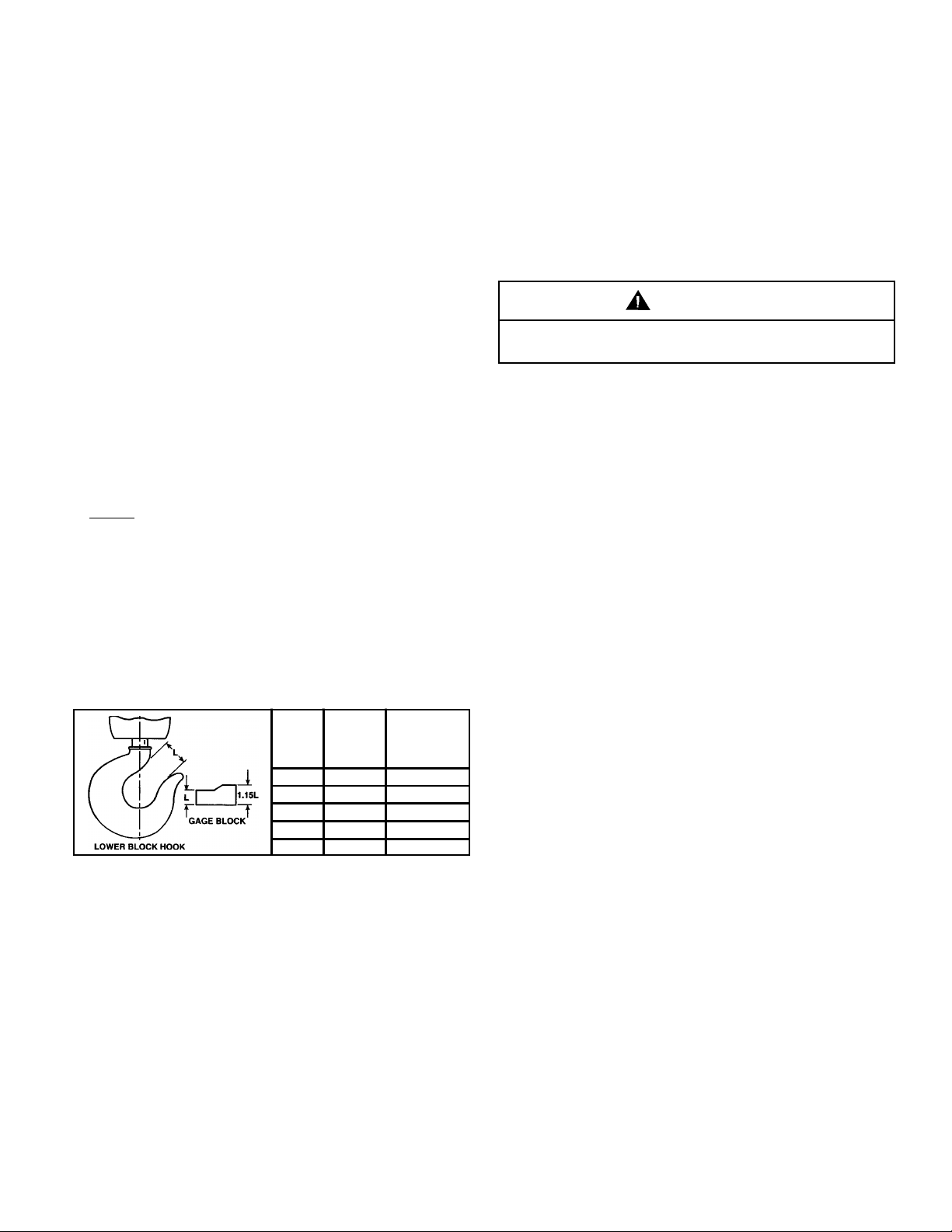
f. Check throat opening of hook. (Refer to Figure 5-1.) It is
recommended that upon receipt of the hoist a measurement
be made and recorded of the hook throat opening. OSHA
Standards require that the hook be replaced if the throat
opening exceeds 15 percent of the original opening, or if the
hook is twisted more than 10 degrees from the unbent plane.
A gage block, properly identified to the hoist, similar to the
one shown in Figure 5-1, is suggested to be made for each
hook for use in these measurements.
NOTE: Hooks and hook openings shown are based on
hooks normally furnished with standard hoists. For
dimensions of hooks having a special size, shape or
material, consult the Muskegon, Michigan factory. For
hooks with certain kinds of safety latches it may be
necessary to remove latch to measure hook opening.
g. Hooks showing signs of cracks must be replaced. Hooks
should be inspected at least once per year using dye
penetrants, magnetic particle or other suitable crack detecting
methods.
11202A
HOIST
RATED
LOAD
(IN TONS)
1/2 G 1-1/8"
HOOK
SIZE
(ST ANDARD)
1 G 1-1/8"
2 H 1-1/4"
3 I 1-1/2"
5 J 1-3/4"
CORRECT "L"
DIMENSION
(NEW HOOK)
WARNING
Do not operate a hoist having worn or damages
suspension bolts.
f. Reinstall all parts following procedure in reverse of
disassembly.
5-4. INSPECT ELECTRICAL CONTROLS. Arrangement of
electrical control equipment varies with the type of control,
physical space and the optional control features ordered with
the hoist.
a. Disconnect electrical power to hoist, remove electrical
compartment cover (Figure 9-1, Ref. No. 29) and inspect
wiring and terminals. Terminals should be securely crimped
to wires and electrical insulation should be sound. Ter minal
screws should be tight.
b. Check condition of contactor assembly, transformer, and
limit stop and reverse switches.
Figure 5-1. Proper Hook Opening.
(Shown with latch removed for clar ity.)
h. Check wear of the hook, especially at the saddle and
replace if badly worn.
5-3. INSPECT UPPER BLOCK AND HOIST SUSPENSION.
a. Check upper block sheaves (when hoist is so equipped)
for wear, damage and freedom of rotation. If sheaves do not
rotate freely, disassemble block and inspect bearings. Replace
worn or damaged bearings, washers, pins or sheaves.
b. Make cer tain that all sheaves, bearings and hanger pins
are free of foreign material and properly lubricated. Bearings
without grease fittings are lubricated for the life of the bearing
and require no further lubrication. After inspection, lubricate
all upper block lubrication fittings.
Page 9
Page 10
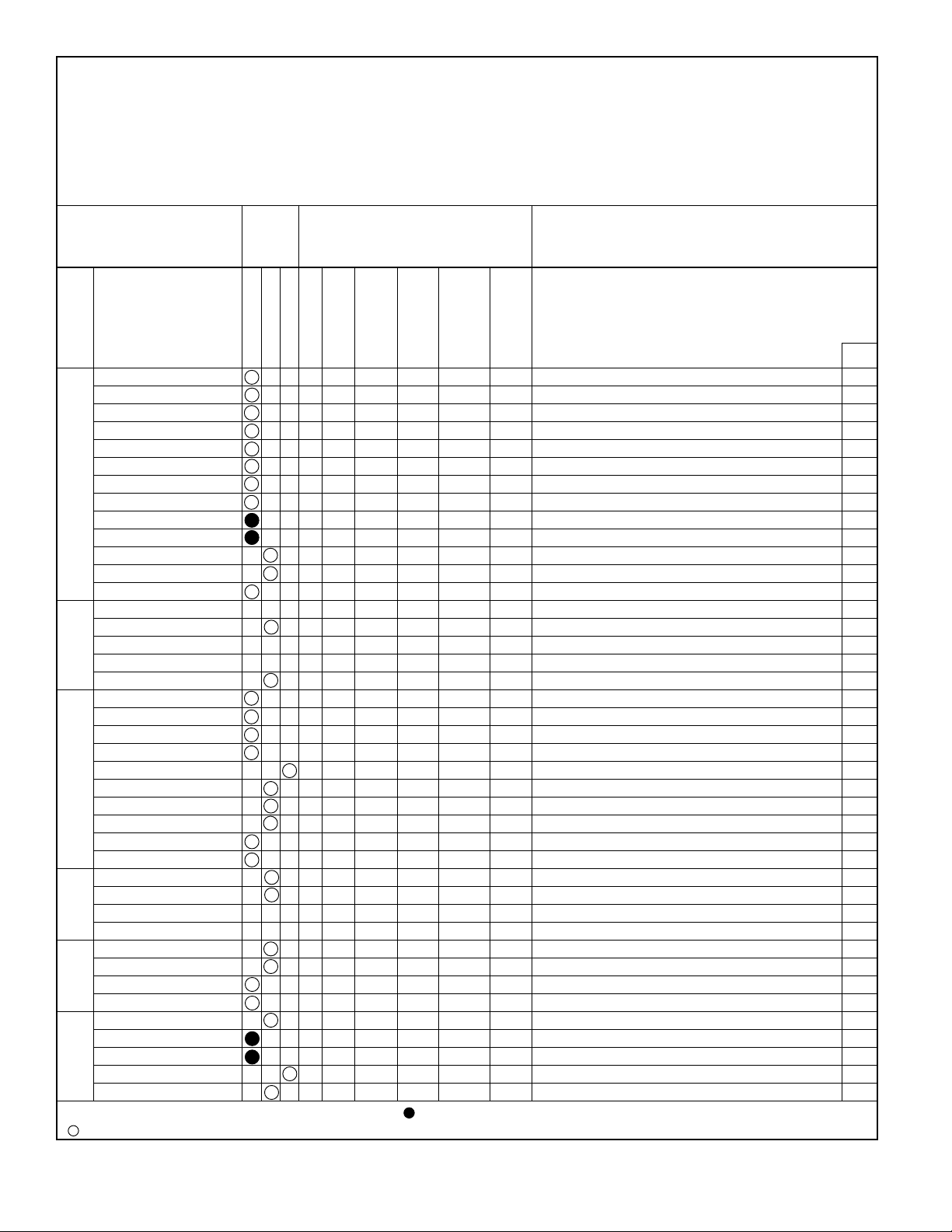
INSPECTION SCHEDULE AND MAINTENANCE REPORT
HOIST SERIAL NO. (MFGRS) _______________________ CUSTOMER CRANE IDENTITY NO. _______________________
RATED LOAD _________________ LOCATION IN PLANT __________________________________
TYPE ________________________ THIS INSPECTION IS MONTHLY o ANNUAL o
VOLTAGE_____________________ SEMI-ANNUAL o
INSPECTED BY: ________________ DATE _____________
*
COMPONENT, UNIT OR PART mended (Check column best indicating condition when CORRECTIVE ACTION
and location Inspection part or unit is inspected. Use note column to NOTES
COMPONENT,
UNIT OR
PART
Motor
Motor Brake
Mechanical Load Brake
Overload Clutch
Couplings
Gears, Shafts & Bearings
Upper Block
HOIST LOCATION
Lower Block
Hook & Throat Opening X Record Hook Throat Opening
Hoist Rope
Rope Drum
Guards
Limit Switch
Recom- CONDITION
Interval the right if condition is not listed below.)
MONTHLY
SEMI-ANNUAL
ADJUSTMENT
GOOD
ANNUAL
REQUIRED
(Loose Parts or
REPAIR REQUIRED
Wires)
REQUIRED
REPLACEMENT
(Worn or Damaged)
REQUIRED
LUBRICATION
(Low Oil or Grease,
PAINTING
CLEANING OR
Rust or Corrosion)
(Indicate corrective action taken during inspection and note date. For corrective
action to be done after inspection, a designated person must determine that
the existing deficiency does not constitute a safety hazard before allowing
unit to operate. When corrective action is completed, describe and note date
in this column.)
REQUIRED
DATE
Pushbutton
CONTROL
STATION OR
PUSH BUTTON
Wiring
Motor
Brake (when so equipped)
Couplings
Gears, Shafts & Bearings
Frame
Wheels
TROLLEYRUNWAYS
Bumpers
Guards
Conductors
Collectors
Hoist
Trolley
RESISTORS
Monorail Joints
Monorail
Main Conductors
Main Collectors
General Condition
Load Attachment Chains
Rope Slings & Connections
MISC.
Change Gearcase Lub.
Grounding Faults
See text for DAILY & WEEKLY REQUIREMENTS.
*
INSPECTION INTERVAL.
SIGNED & DATED REPORT REQUIRED – OSHA.
X MAGNETIC PARTICLE OR EQUIVALENT EXAMINATION REQUIRED.
Typical Inspection Schedule and Maintenance Repor t form.
User must adjust inspection interval and components to suit his individual conditions and usage. 12375B
Page 10
Page 11
TIME INTERVAL INSPECTION OR MAINTENANCE
Daily or start Check operation of all functional mechanisms including limit switch operation,
of each shift brakes and control. Check hoist cable for kinks, abrasions, corrosion or broken
(\/isual) wires or evidence of improper spooling on drum. Inspect hooks, upper and lower
blocks, and all load bearing components for damage.
1 Month * HOIST CABLE — Inspect and lubricate per paragraph 5-8.
1 - 3 Months
6 Months
* ELECTRICAL CONTROLS — Inspect per paragraph 5-4.
Check hoist gearcase oil level — add oil as required per paragraph 4-2.
* LOWER BLOCK — Inspect per paragraph 5-2.
UPPER BLOCK — Inspect per paragraph 5-3.
Motor brake and actuating mechanisms. Inspect and adjust per paragraph 5-5.
Annually * Inspect hooks with suitable crack detecting procedures per paragraph 5-2.
Drain and refill hoist gearcase per paragraph 4-2.
Inspect electrical controls per paragraph 5-4. Change hoist gearcase oil — Fill
6 Months or with oil per paragraph 4-2. Lubricate hoist cable per paragraph 4-3. Lubricate
500 - 750 hours * upper and lower hook block per paragraph 4-4. Lubricate limit stop lever per
“on” time paragraph 4-5. If a screw type limit switch is furnished, add a light film of
NLGI No. 2 grease to bevel gear.
5 Years elapsed Complete inspection, disassembly, and maintenance required. It is recommended
time or 5000 * that your YALE Repair Station be contacted for this ser vice.
hours “on” time
*Perfor m services described by paragraph indicated.
Figure 5-2. Inspection and Maintenance Schedule.
5-5.INSPECT MOTOR BRAKE. See Figure 9-4.
a. Remove acorn nuts holding brake cover and remove
brake cover.
b. Remove brake mounting plate screws and lift brake
assembly off.
c. Check braking surfaces for wear and scoring. Replace
badly worn or scored parts.
d. Reinstall par ts in reverse of disassembly.
e. Adjust brake as explained in Section Vll.
5-6.INSPECT MECHANICAL LOAD BRAKE, GEARING AND
OVERLOAD CLUTCH (Optional).
a. The mechanical load brake and gearing may be inspected
and serviced with hoist suspended. To do so, remove lower
block and wire rope, drain oil from gearcase, remove 12 hex
head bolts and lockwashers holding gearcase cover, and pull
cover from gearcase (Figure 5-3).
11404A
Figure 5-3. View of Gearcase – Cover Removed.
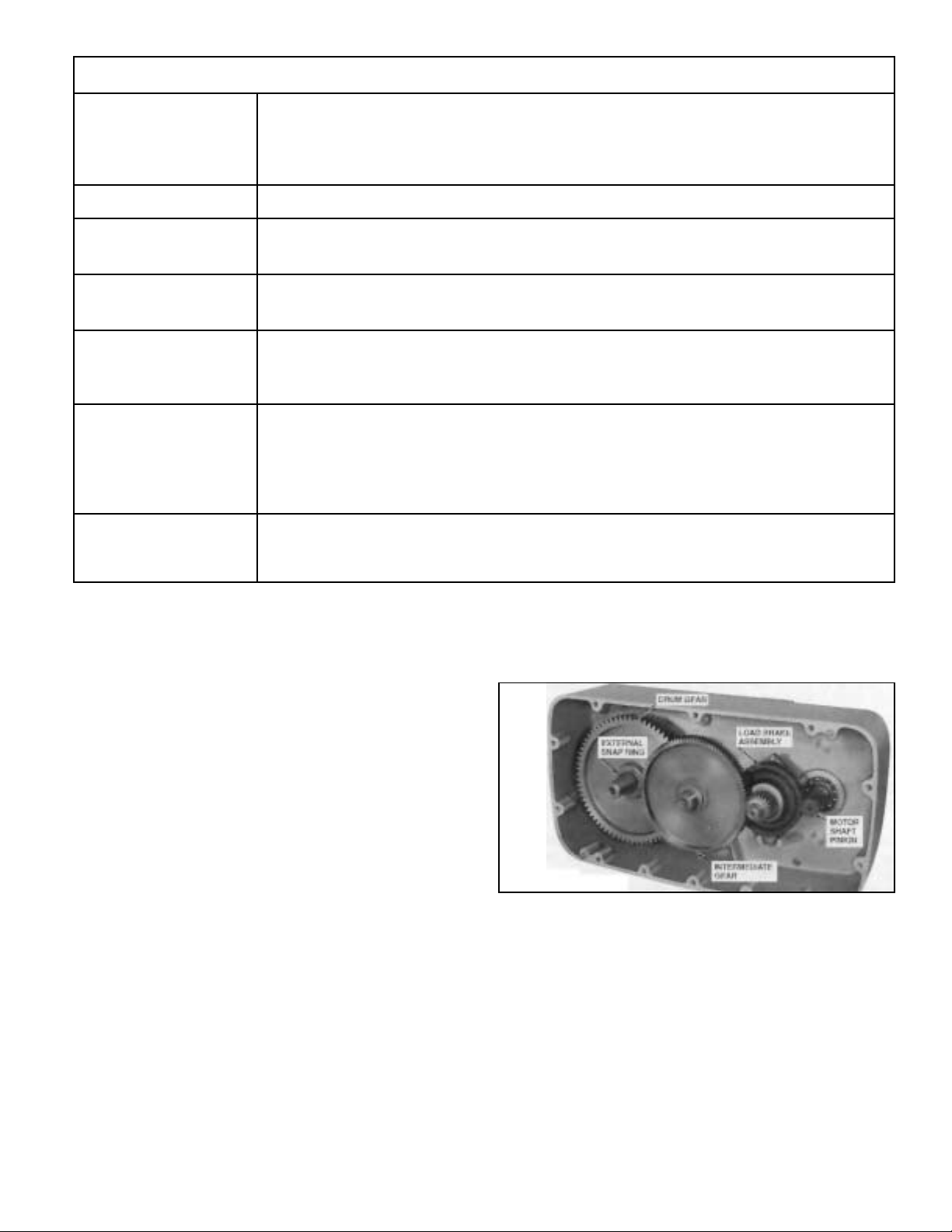
b. To inspect gearing, pull out intermediate gear and pinion
assembly and roller thrust bearings (Figure 5-4), and load
brake assembly (Figure 5-5). Do not remove drum gear unless
visual inspection indicates replacement is necessary.
c. Inspect gears and pinions for signs of tooth wear and
damage. If replacement of any parts appears necessary,
disassemble drum gear, intermediate gear and pinion
assembly, and load brake assembly as directed on following
page.
Page 11
Page 12
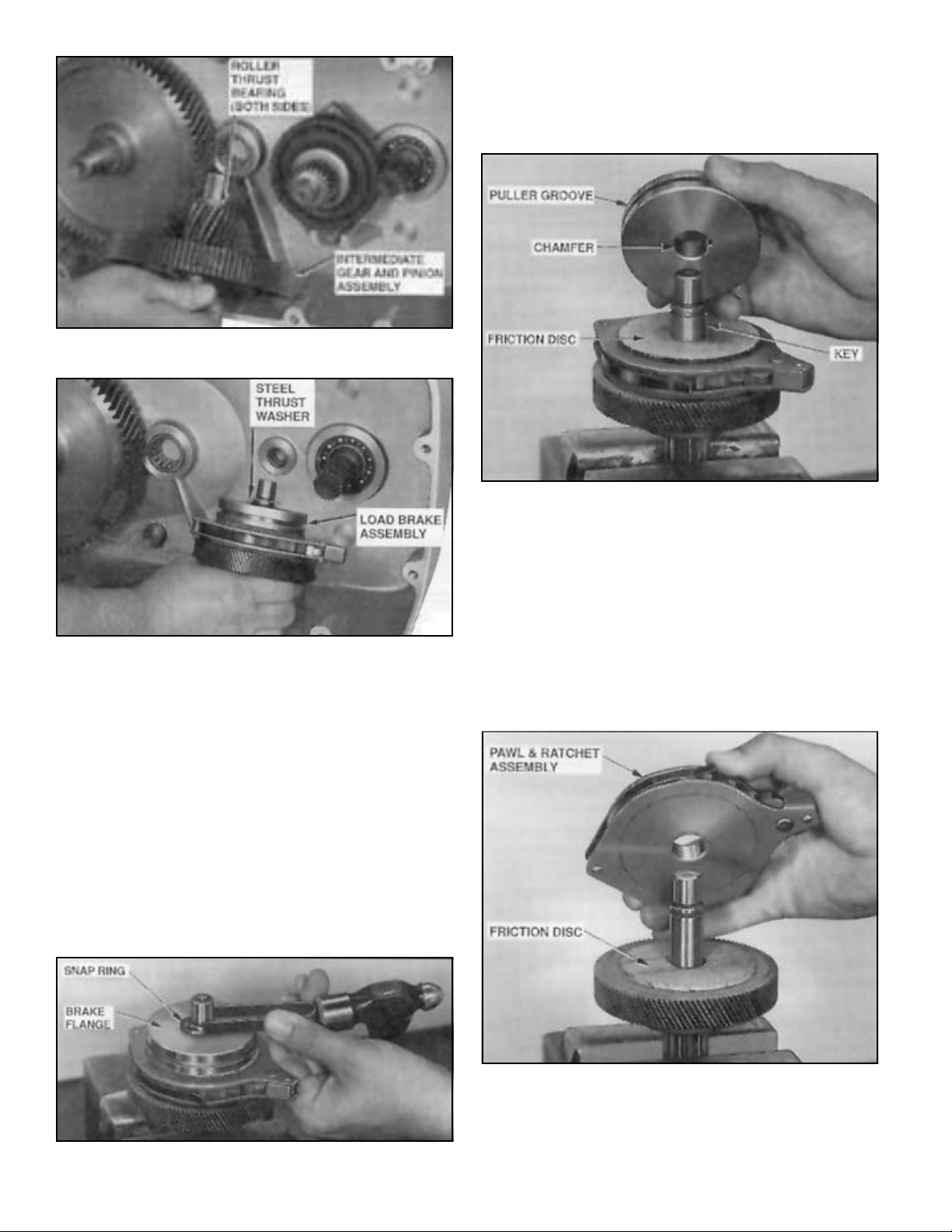
Figure 5-4. Removing Inter mediate Gear and
Pinion Assembly.
(2) Using a puller tool, remove brake flange from shaft.
A groove is provided around outer diameter for this purpose.
See Figure 5-7. Remove key from shaft and lift off 2 friction
discs, and the pawl and ratchet assembly (Figure 5-8).
11421
10334
Figure 5-7. View Showing Load Brake
Flange Removed.
11422
Figure 5-5. Removed Load Brake Assembly.
d. To disassemble drum gear, remove external snap ring
from splined shaft, using heavy-duty snap ring pliers, and
pull off gear.
e. To disassemble intermediate gear and pinion, press
pinion shaft from gear using an arbor press.
f. It is recommended that load brake assembly be retur ned
to an Authorized Repair Station for inspection and repair. If it
is necessary that you make your own inspection and repair,
instructions below must be followed:
(1) Place load brake assembly, flange up, in a vise
equipped with brass or copper jaw plates to protect pinion
gear teeth. Remove snap ring from end of load brake shaft
(Figure 5-6).
(3) Remove load brake gear. If replacement of spring,
spring retainer or cam is necessary, press off shaft (Figure
5-9).
(4) The load brake pawl and ratchet is a riveted
assembly and is not to be disassembled.
(5) Clean all par ts thoroughly and inspect for wear and
damage. Replace all parts that are excessively worn or
damaged. Hard surface or glazed friction discs should be
replaced.
10333
Figure 5-6. Remove Snap Ring From Load Brake Shaft.
Page 12
10335A
Figure 5-8. Removing Pawl and Ratchet Assembly
From Load Brake Shaft.
g. Reassemble gearing and load brake parts following
reverse procedure of disassembly. In assembling load brake,
observe assembly steps (1) through (4) below:
Page 13
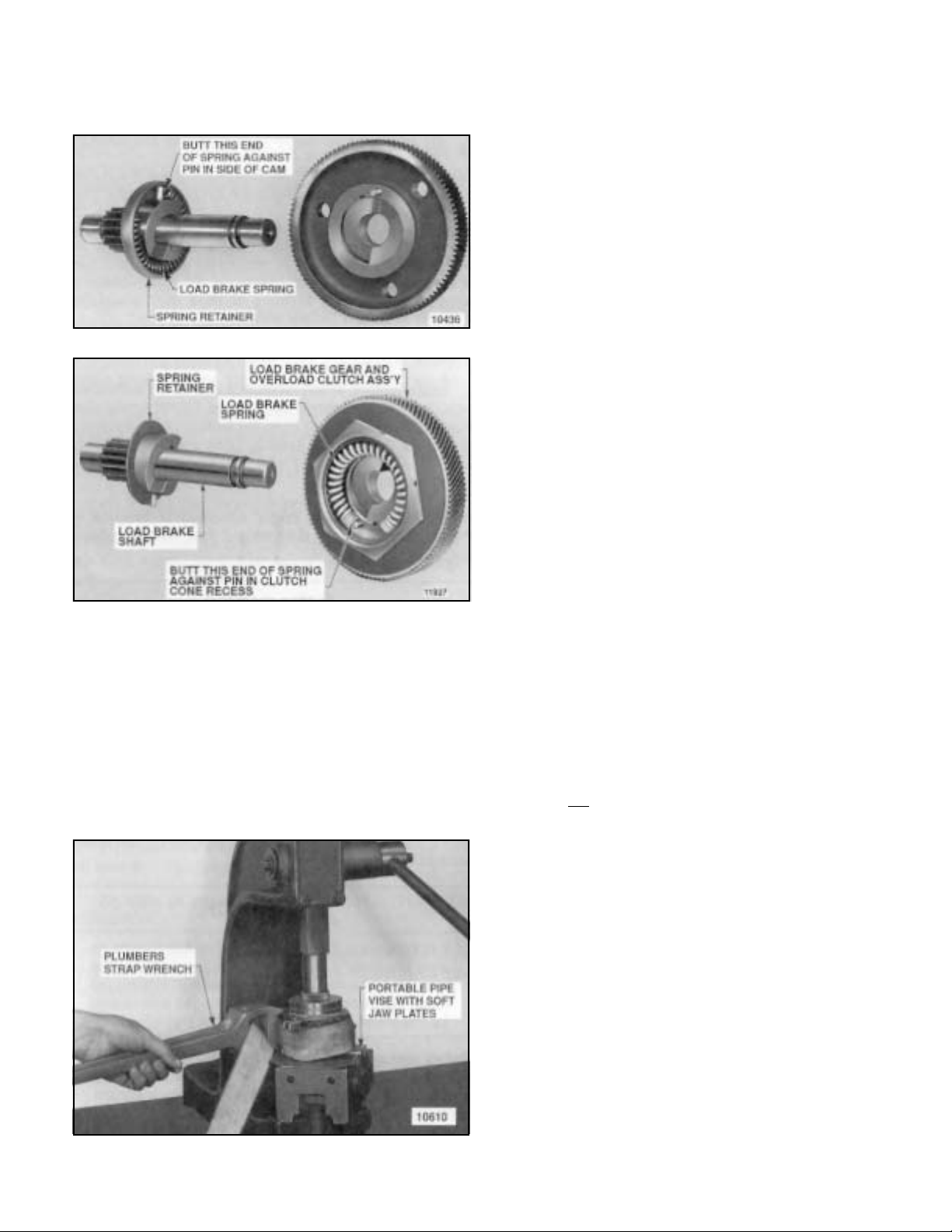
(1) Before installing spring in its retainer (Figure 5-9), apply
a good grade of ball bearing grease to inside of retainer.
Spring must be positioned exactly as illustrated, butted against
pin at side of cam.
LOAD BRAKE — OVERLOAD CLUTCH
(4) The brake spring must be pre-loaded at assembly to
a torque of from 10 to 14 lb.-ft. This is accomplished using a
plumber’s strap wrench to wind (rotate) load brake gear to
set up spring (Figure 5-10) while pressing brake flange into
place using an arbor press. Clamp pinion end of shaft into a
portable vise to keep brake from rotating in press. Use brass
or copper jaw plates on vise to protect pinion gear teeth.
Wind gear counterclockwise (viewing brake from flange end)
with strap wrench and press down on flange until snap ring
groove in shaft is exposed allowing snap ring to be installed.
Use extreme care not to over wind spring as yield will result
and final spring torque will be reduced. Do not wind gear
beyond point necessary to install snap ring in groove.
h. Install gearing and load brake assembly in gearcase in
reverse order of disassembly. Be certain roller thrust bearings
are installed at both ends of intermediate gear shaft as shown
in Figure 5-4 and that thrust washers are properly installed at
both ends of load brake shaft as noted below:
(1) A steel thrust washer with 5/8" I.D. must be installed
on the brake flange end (end opposite pinion) of load brake
as shown in Figure 5-5.
(2) A bronze thrust washer with a lug on one side goes
on pinion end of load brake shaft and it must be installed so
that its lug engages the special slot located on the spot face
surrounding the load brake bearing bore inside gearcase
cover. Use heavy grease to hold it in place on cover as cover
is installed.
LOAD BRAKE — STANDARD
Figure 5-9. Load Brake Gear Removed From
Load Brake Showing Load Brake Spring.
(2) When installing pawl and ratchet assembly on load
brake shaft, be certain that teeth on ratchet face are in the
same direction as shown in Figure 5-8. The ratchet assembly
should rotate freely when turned counterclockwise and the
pawl should engage ratchet teeth when unit is turned
clockwise.
(3) When installing brake flange, position it with chamfer
facing friction disc (Figure 5-7).
On hoists with 18 or 20 tooth load brake pinion, an 11/
16" I.D. steel thrust washer is installed between pinion
and bronze thrust washer.
j. At completion of reassembly of gearing and load brake in
gearcase, refill gearcase to proper level using correct grade
of oil, as outlined in Section IV — LUBRICATION.
k. For hoists equipped with an overload clutch (optional)
which has been functioning properly, visually inspect clutch
adjusting nut and spring washer for signs of damage or
looseness. With a small hex allen wrench, make certain two
set screws in adjusting nut are tight. DO NOT TURN
ADJUSTING NUT OR DISASSEMBLE CLUTCH. If spring
washer, adjusting nut or gear is loose or damaged, or the
clutch did not function properly before disassembly of hoist
for inspection, consult the nearest YALE Authorized Repair
Station for repair or adjustment.
5-7. INSPECT ROPE DRUM AND SHAFT.
a. To remove drum, remove wire rope, electrical
compartment cover and electrical panel assembly (Figure
9-1) and gearing and load brake assembly (paragraph 5-6).
b. Remove four hex socket head bolts secur ing gearcase to
cover. Three bolts are accessible from inside frame (Figure
2-2, Section II) and the fourth is accessible from electrical
end of frame thru special access hole using a socket hex key
wrench with an extension (Figure 5-11). With bolts removed,
pry assembled gearcase and motor from frame. Exercise
caution so that gearcase and motor assembly does not fall
as it comes free of frame. This disassembly operation is not
recommended with hoist suspended. Drum will remain in frame
and can be lifted from drum shaft. To remove shaft, remove
internal retaining ring from bearing bore in frame.
Figure 5-10. Winding Load Brake Gear Using a Strap
Wrench to Set Up Load Brake Spring.
Page 13
Page 14
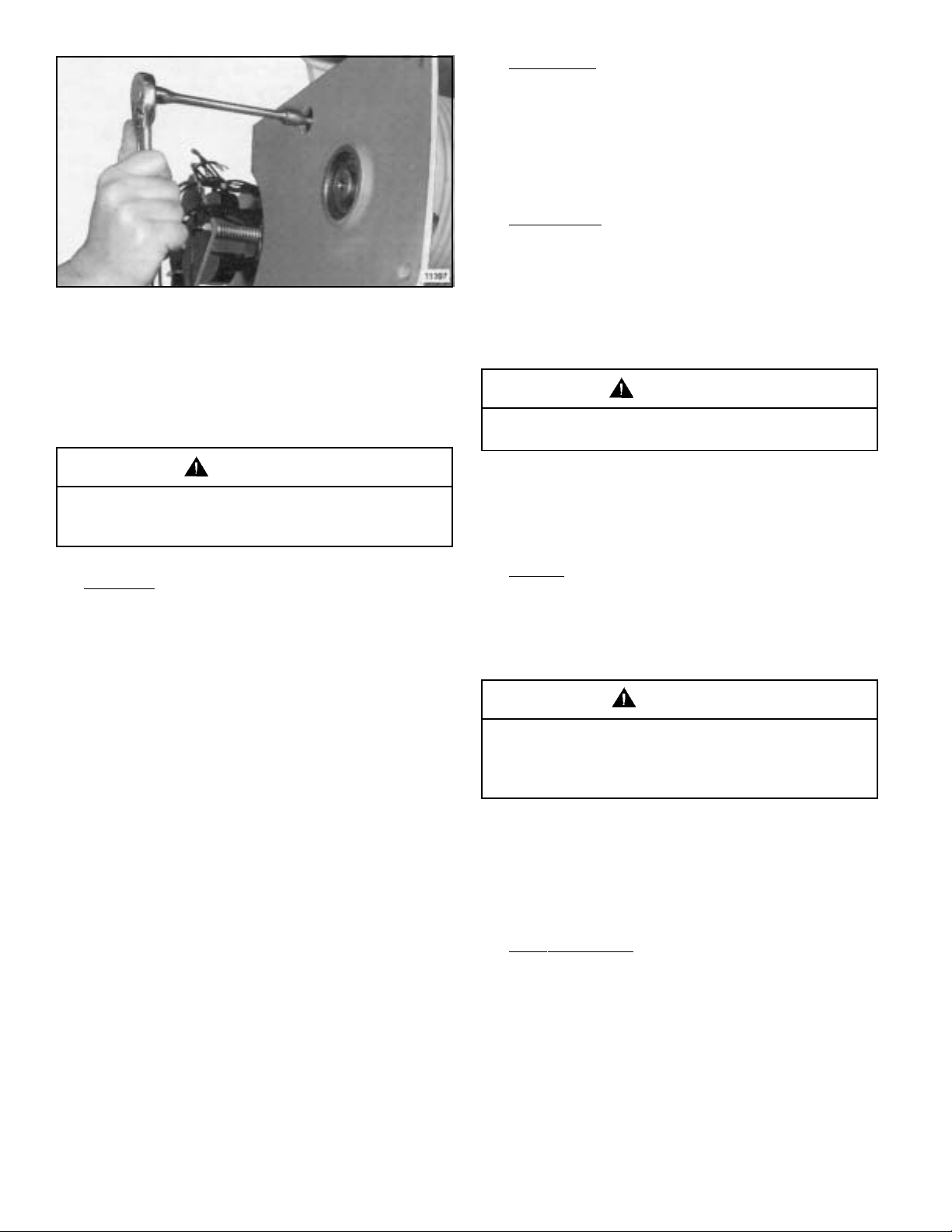
Figure 5-11. Removing Bolt
Securing Gearcase to Frame.
c. Check parts for wear and damage. Replace drum if there
are any signs of cracks or other damage.
5-8. ROPE INSPECTION, MAINTENANCE AND
REPLACEMENT.
b. Maintenance. Keep rope well lubricated to help reduce
internal friction and prevent corrosion. Lubricant, as described
in paragraph 4-3, should be applied as a part of the regular
maintenance program. Special attention is required to lubricate
sections of rope over equalizing sheaves and other hidden
areas.
Avoid dragging ropes in dirt or around shar p objects which
will scrape, nick, crush or induce sharp bends in the rope.
c. Replacement. When recommended by an authorized
inspector, the rope should be replaced. Replacement rope
assemblies are shipped from the factory carefully coiled to
prevent damage by kinking. Care must be taken to avoid
twisting or kinking when uncoiling and handling during reeving.
Before replacing rope, check condition of grooves in sheaves
and drums to determine if they are excessively worn.
WARNING
Use only factory approved rope with swagg ed wire
rope sockets.
WARNING
Wire rope improperly handled or abused can create a
SAFETY HAZARD. Read and comply with inspection,
maintenance and replacement information given herein.
a. Inspection. Wire rope on your hoist is one of the most
important components requiring frequent inspection and
maintenance. All wire ropes will eventually deteriorate to a
point where they are not safe and will require replacement.
WIRE ROPE SHOULD BE THOROUGHLY INSPECTED AT
REGULAR MONTHLY INTERVALS BY AN AUTHORIZED
PERSON AND A DETERMINATION MADE WHEN FURTHER
USE OF THE ROPE WOULD CONSTITUTE A SAFETY
HAZARD. Each inspection should include a written, dated
and signed report of rope condition. Reports should be filed
and reviewed each month and an y rope deterior ation carefully
noted. Inspections revealing but not limited to the following
conditions should cause the inspector to question remaining
strength of rope and consider replacement:
(1) Twelve randomly distributed broken wires in one rope
lay or four broken wires in one strand.
(2) Wear of one-third of the original diameter of outside
individual wires.
(3) Kinking, cr ushing or bird caging.
(4) Heat damage from any cause.
(5) Reductions from nominal diameter of more than
1/64" for 3/16", 1/4", and 5/16" diameter rope.
(6) Rope corrosion, inter nal or external.
(7) Effects from improper lubrication.
(8) Rope idle for month or more due to shutdown.
Special attention should be exercised when inspecting rope
normally hidden during inspecting procedures.
When first using the hoist after rope replacement, break-in
rope by operating under lighter loads to full travel before
applying maximum load.
5-9. ROPE REEVING.
a. General. Before unreeling rope from a coil or reel, be
sure floor is clean. Dirt picked up by the rope can cause
excessive wear and abrasion. Uncoil the rope by rolling the
coil or reel along the floor; or, place reel on a stand with a
shaft thru the center of reel so rope can be pulled straight out
with the reel rotating.
CAUTION
It is imperative that the rope reel or coil rotates as rope
unwinds. If coil or reel does not rotate, the wire will be
twisted as it is uncoiled and kinking will result. A kinked
rope may be damaged and unsafe.
Before removing the old rope, refer to reeving diagrams,
(Figures 5-12, 5-14, 5-15 and 5-17). Face the rope drum on
your hoist from the side which the rope comes off drum. To
assist with rereeving your hoist, select the reeving diagram
for your hoist. Note the description (such as 2 part double
reeved, Figure 5-17) and refer to the paragraph below with
the same description which describes rereeving procedure.
b. Removing old rope — for all reevings.
(1) Lower the bottom block to a scaffold located 6 to 7
feet below hoist to relieve tension on wire rope. (Bottom block
may be lowered to floor if desired; however, to handle less
weight and for ease of rereeving adequate scaffold below the
hoist is recommended.)
(2) Remove bottom block sheave guard.
(3) Remove key plates from both sides of sheave pin
and slide sheave pin from bottom block.
(4) Lift out sheaves from the top of the bottom block and
remove wire rope.
Page 14
Page 15
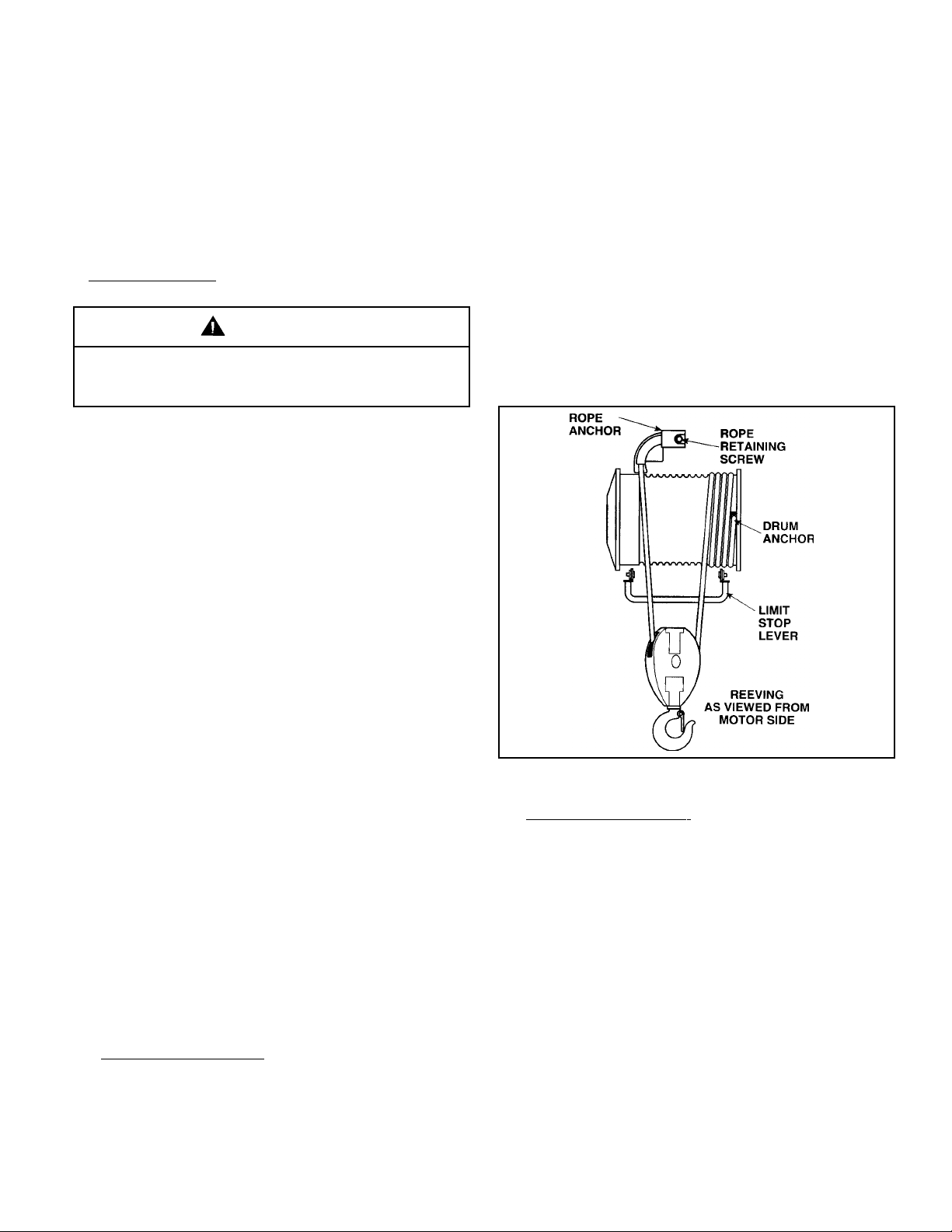
(5) Remove key plates or snap rings from upper block
sheave(s) and slide out upper block sheave pins, releasing
upper block sheaves. Remove wire rope from sheaves.
With new rope installed on the drum as described in paragraph
5-9c single reeved above, proceed with rereeving following
steps below:
(6) Make certain all personnel are clear of hoist and
operate hoist
drum. Stop hoist so drum anchor slot(s) is accessible. Remove
live rope and socket(s) from drum.
(7) TURN OFF POWER TO HOIST.
(8) Remove the bolt and lockwasher in the end of the
rope anchor fitting. Remove rope from slot in top of anchor.
c. Installing new rope.
ââ
â to completely unwind all wire rope from
ââ
WARNING
Winding rope on rope drums with power can be
hazardous. Keep hands safe distance from drum, wear
gloves and use extreme care when handling rope.
SINGLE REEVED HOISTS
Stretch new cable on floor in one continuous length. Make
certain there is no twist in rope.
(1) Place one end of rope in rope dr um anchor slot. Be
sure end fitting is properly seated.
(2) With all personnel clear of hoist — TURN ON
POWER.
(1) Pass other end of rope thru bottom opening of hoist,
between floating limit rod and motor, and attach rope to cast
dead end anchor fitting. A slot is located at top of fitting to
accept cable. Reinstall bolt and lockwasher in end of anchor
fitting to lock rope compression fitting in place.
(2) Grasp loop, formed after installing end anchor, and
place bottom block sheave in loop. Lower sheave into bottom
block and insert sheave pin. Replace key plates and bolts
holding sheave pin in place.
(3) Replace sheave guard. Make certain rope is not
twisted. Should the two parts of rope tend to wind around
each other, remove cable from anchor slot and untwist cable.
Reattach the cable anchor.
(4) Lubr icate cable per paragraph 4-3.
(3) Operate hoist
with gloved hand, until the following lengths remain unwound:
(a) 2 part single reeved — about 14'-0".
(b) 4 part single reeved — about 28'-0".
(c) 6 part single reeved — about 42'-0".
(4) Proceed with reeving as described in appropriate
paragraph below and the reeving diagram for your hoist.
DOUBLE REEVED HOISTS
Stretch new cable on floor in one continuous length. Make
certain there are no twists in rope.
(1) Pull far end of rope toward end of rope nearest hoist,
until both ends are even and a loop is for med. Place fittings
on both ends of rope in anchor slots on rope drum. Be sure
end fittings are properly seated.
(2) With all personnel clear of hoist — TURN ON
POWER.
(3) Operate hoist
ends of drum, until the distance from the drum to the loop is
— about 28' for 2 part double reeved.
(4) Proceed with reeving as described in appropriate
paragraph below and the reeving diagram for your hoist.
d. Reeving — 2 part single.
áá
á, guiding new rope into drum grooves
áá
áá
á guiding rope into grooves at both
áá
12203A
Figure 5-12. Hoist Reeving — Two Part Single.
Reeving — 4 part single.
e.
See Figure 5-14 for diagram.
See Figure 9-13 for block parts.
With new rope installed on the drum as described in
paragraph 5-9c single reeved above, proceed with rereeving
following steps below:
(1) Grasp the cable near the middle (about 14'-0") of
the unwound end and form a loop. Place upper sheave in
this loop. Slide upper sheave with cable into sheave pocket.
(2) Insert sheave pin into sheave. Replace key plates
and bolts to hold sheave pin in place.
See Figure 5-12 for diagram.
See Figure 9-11 for block parts.
Page 15
Page 16

Figure 5-13. Upper Sheave Installed.
(Typical 3 and 5 Ton)
(3) Pass free end of rope thru bottom opening of hoist
between floating limit rod and motor, and insert rope in anchor
fitting at hoist frame. Be certain power is off before attempting
to place rope in anchor fitting. With end fitting properly seated
in anchor, replace bolt and lockwasher in end of socket. Two
loops have now been for med for bottom block sheaves.
(1) Grasp cable at a point one-third (approx. 14’0") the
distance hanging below the rope drum and form a loop. Place
one upper sheave in this loop. Slide upper sheave with cable
into sheave pocket; partially inser t sheave pin to hold sheave
in place.
(2) Repeat (1) above and install second upper sheave
with rope. Inser t sheave pin and install key plates and bolts
to secure sheave pin.
12204A
Figure 5-14. Hoist Reeving — Four Part Single.
(4) Place one sheave in each loop. Install one sheave
with cable in bottom block, partially insert sheave pin to hold
sheave in place.
NOTE: Some blocks have spacer washers
between sheaves. Be certain that washers are installed
between sheaves, when shown on parts illustration. Install
second sheave with cable into bottom block. Slide sheave pin
through sheave. Replace key plates and bolts securing sheave
pin.
12205A
Figure 5-15. Hoist Reeving — Six Part Single.
(3) Pass free end of rope thru bottom opening of hoist
between floating limit rod and motor and insert in rope anchor
fitting at hoist frame. Be certain power is off before attempting
to place rope in anchor fitting. With end fitting properly seated
in anchor, replace bolt and lockwasher in end of socket.
Three loops have now been formed for bottom block sheaves.
(4) Place sheave in each loop. Install one sheave with
cable in bottom block; partially insert sheave pin to hold
sheave in place. NOTE: Be certain that washers are installed
between sheaves, as shown on parts illustration.
(5) Repeat step 4 for remaining bottom block sheaves.
Install sheave pin through sheaves. Replace key plates and
bolts securing sheave pin.
(6) Replace sheave guard.
(7) Lubr icate cable per paragraph 4-3.
g. Reeving — 2 part double.
See Figure 5-17 for diagram.
See Figure 9-12 for block parts.
(5) Replace sheave guard.
(6) Lubr icate cable per paragraph 4-3.
f. Reeving — 6 part single.
See Figure 5-15 for diagram.
See Figure 9-13 for block parts.
With new rope installed on the drum as described in paragraph
5-9c single reeved above, proceed with rereeving following
steps below:
Page 16
With new rope installed on the drum as described in paragraph
5-9c double reeved above, proceed with rereeving following
steps below:
(1) Form loops in the two ropes coming from rope drum.
Place these loops into bottom block pockets and slide pipe or
rod through sheave pin holes. Note position of ropes passing
limit stop bar.
(2) Partially insert upper block sheave pin in opening
and install one spacer washer. Raise remaining rope up to
hoist, form a loop and place upper sheave in this loop.
Page 17
(d)Turn on power; raise and lower the block
several times to feed the correcting twist in the rope
through the reeving.
(e)If block still tends to twist, repeat the above
procedure until block rotation is corrected.
Figure 5-16. Upper Sheave Installed (Typical).
(3) Place sheave with rope into upper sheave pocket
and slide pin partially thru sheave. Install remaining washer
and push pin thru side plates. Install snap ring on each end
of pin to secure pin in place.
(2) To remove rope twist in
double reeved hoists.
(a)Obser ve direction block tends to rotate.
(b) Lower the bottom b lock unspooling rope from rope
drum until only one quarter (1/4) turn remains to
rope end anchors in drum.
(c) Rotate rope near ends entering drum in a direction
tending to correct block rotation. This rotates rope
end fittings in the drum.
(d)Turn on power; raise and lower the block several
times to feed the correcting twist in the rope through
the reeving.
(e)If block still tends to twist, repeat the above
procedure until block rotation is corrected.
5-10. TESTING HOIST AND OVERLOAD CLUTCH
(Optional).
a. General. Before placing hoist in service or after disassembly and reassembly, hoist should be tested. To test suspend hoist from an overhead supporting member of sufficient
strength to support the weight of the hoist and the rated load.
Hoists having overload clutches, require an overhead supporting structure capable of supporting with appropriate safety
factor, a load equal to 200 percent rated load and the weight
of the hoist. Connect hoist to power supply as shown on hoist
nameplate and perform the checks listed in b and c below.
12206A
Figure 5-17. Hoist Reeving — Two Part Double.
(4) Inser t lower sheave pin into bottom block removing
pipe as sheave pin is inserted. Be certain washers are
replaced as shown on parts illustration. With sheave pin
installed, replace key plates and bolts to secure sheave pin.
(5) Replace sheave guard.
(6) Lubr icate rope per paragraph 4-3.
h. Checking for and removal of rope twisting.
Although rereeving of hoist may have been done carefully,
sometimes after new rope has been installed twisting may
occur. With new rope installed, the hoist block should be
raised and lowered several times with gradually increasing
loads, through full lift. If the block still rotates excessively at
no load, the rope may have twists which should be removed.
(1) To remove rope twist in single reeved hoists.
(a) Observe direction block tends to rotate.
(b) Lower the block to a low position and turn off
power.
b. Check hoist as outlined in PRE-OPERATION CHECKS,
Section II, paragraph 2-4.
c.
Check hoist with capacity load.
(1) Attach rated load to lower hook.
(2) Depress
áá
á push button and raise load. When push
áá
button is released, hoist should immediately stop and hold
load at that level.
(3) Depress
ââ
â push button, lower load a short distance
ââ
and release button. Hoist should stop immediately and hold
load at that level.
NOTE: If load drifts downward slowly in step 2 or
3 above, motor brake requires adjustment — see
MOTOR BRAKE ADJUSTMENT — Section Vll —
paragraph 7-2.
d.
Overload Clutch. The overload clutch (optional) must
be tested for proper operation before placing hoist in service
or after disassembly and reassembly of hoist. For test
procedure follow instructions listed below.
(c) Rotate rope near the anchor end several turns in
a direction tending to correct block rotation. This
rotates rope end fitting in the anchor.
Page 17
Page 18

WARNING
BEFORE ATTEMPTING TO TEST THE OVERLOAD
CLUTCH, MAKE CERTAIN THE FOLLOWING
PREREQUISITES ARE STRICTLY OBSERVED:
a. An appointed person must determine, before
starting, that all structures supporting the hoist are
adequately strong to withstand the test load of 200%
of the rated load, plus the weight of the hoist, whether
hoist is tested in installed position or moved to a
designated test facility.
b. Loads used for testing must be accurately known.
c. Test must be made ONLY by a qualified operator,
thoroughly familiar with the hoist and the purpose of
the test.
d. Adequate and proper rigging must be provided to
ensure that test loads are securely attached, properly
balanced, and lifted level. Failure to provide adequate
support could cause injury to personnel and/or damage
to equipment.
(1) Using a known load, equal to the hoist rated load,
energize hoist to lift the load. Raise this load just high enough
to be certain hoist is lifting the entire load. Clutch should not
slip with the rated load. Lower load to rest position. If clutch
slips with rated load, adjustment is required. (See paragraph
7-5. — “OVERLOAD CLUTCH ADJUSTMENT”.) If hoist will lift
rated load, proceed to step (2).
(2) Increase load in steps from rated load, TO A MAXIMUM
OF 200% of the rated load, attempting to lift load with each
increase in weight. Hoist Overload Clutch should slip and refuse
to lift load before 200% of the rated load is reached. Should
hoist lift 200% of the rated load — STOP TEST — A CLUTCH
ADJUSTMENT IS REQUIRED. (See paragraph 7-5 —
“OVERLOAD CLUTCH ADJUSTMENT”.)
(3) Run hoist with load causing clutch to slip (hoist refusing
load) five cycles of approximately 1 second each.
CAUTION
To prevent overheating, release the hoist control button at
once when the hoist refuses to lift the load.
(4) Remove weights added in step (2) and return to hoist rated
load. Lift rated load one final time. Clutch should not slip.
WARNING
Do not lift more than rated load except for test
purposes.
NOTICE
ALWAYS KNOW LOAD TO BE LIFTED, LIFT-TECH
DOES NOT RECOMMEND LIFTING LOADS GREATER
THAN THE RATED LOAD OF YOUR HOIST.
Page 18
Page 19

Trouble Probable Cause Remedy
6-1. Hoist Will Not Operate.
SECTION Vl - TROUBLE SHOOTING
a. No power to hoist.
a. Check switches, circuit breakers or fuses and
connections in power supply lines. Check power
collectors.
6-2. Hook Moves in Wrong
Direction.
b. Wrong voltage.
c. Loose or broken wire
connections in hoist electrical
system.
d. Contactor assembly not
functioning.
e. No control voltage.
f. Motor bur ned out.
a. Reverse phasing on three-
phase hoists.
b. Check voltage required on motor data plate
against power supply.
c. Shut off power supply, remove electrical cover on
hoist and check wiring connections. Also check
connections in push button station and limit
switches.
d. See that necessary jumper wires are properly
installed. Verify that the contactor armatures are
free to move. If binding occurs, replace contactor.
Check for burned out contactor coils.
e. Check transformer fuse. If blown, check for
grounding and/or shorts in the push button station.
Check the transformer coil for signs of
overheating. Replace transformer if burned out.
Verify the transformer secondary is the same
voltage as the coils to which it is connected.
f. Replace motor. Check input power supply. Check
hoist motor connections.
a. Interchange any two power supply line leads.
Refer to Section II, paragraph 2-4 b.
6-3. Hook Will Raise But
Not Lower.
6-4. Hook Will Lower But
Not Raise.
b. Hoist wired wrong.
a. Lower electrical circuit open.
b. Contactor assembly not
functioning.
c. Down, push button inoperative.
a. Excessive load.
b. Hoist electr ical circuit open.
c. Contactor assembly not
functioning.
b. Check wiring connections with appropr iate wiring
diagram.
a. Check for loose connections. See that necessary
jumper wires are properly installed on contactor.
b. See that necessary jumper wires are properly
installed. Verify that the contactor armatures are
free to move. If binding occurs, replace contactor.
Check for burned out contactor coils.
c. Check push button contacts and wires.
a. Reduce loading to rated load of hoist, as shown
on nameplate.
b. Check for loose connections. See that necessary
jumper wires are properly installed on contactor.
Check limit switch mounting and connections.
c. See that necessary jumper wires are properly
installed. Verify that the contactor armatures are
free to move. If binding occurs, replace contactor.
Check for burned out contactor coils.
d. Up, push button inoperative.
d. Check push button contacts and wires.
Page 19
Page 20

SECTION Vl - TROUBLE SHOOTING (Continued)
Trouble Probable Cause Remedy
6-5. Hoist Will Not Lift Rated
Load.
6-6. Hoist Motor Overheats.
6-7. Load Drifts Excessively
When Hoist Is Stopped.
a. Low voltage
b. Overload Clutch not properly
adjusted.
a. Excessive load.
b. Excessive duty-cycle.
c. Wrong voltage or frequency.
d. Defective motor or worn bear-
ings in hoist frame.
e. Overload Clutch slipping without
lifting load.
a. Excessive load.
a. See that power supply current is same voltage
Iisted on motor data plate. Check hoist motor
connections. Check size of power supply lines.
b. See Section VII, paragraph 7-5.
a. Reduce loading to rated load of hoist, shown on
nameplate.
b. Reduce frequency of lifts or amount of jogging.
c. Check current rating on motor data plate against
power supply. Check hoist motor connections.
d. Disassemble hoist and inspect for defective, wor n
or damaged parts.
e. See Section VII, paragraph 7-5.
a. Reduce loading to rated load, as shown on
nameplate.
6-8. Hoist Operates
Intermittently
b. Motor brake not holding.
c. Load brake not holding.
a. Collectors make poor contact.
b. Loose connections.
b. With No Load, check hoist for drift. If drifting is
excessive, inspect motor brake (Section V,
paragraph 5-5) and adjust as outlined in Section
VII, paragraph 7-2.
c. (1) After determining that the motor brake is working
properly, attach rated load to hook and operate
hoist. If the load accelerates during lowering, the
load brake is not functioning properly. See Section
V, paragraph 5-6 for replacing worn or damaged
parts.
(2) If load brake checks O .K., magnetic motor br ake
needs adjustment (see b. above).
a. Check collectors for free movement of spring arm,
weak spring or electrical connections.
b. Check all wiring for loose connections.
Page 20
Page 21

SECTION Vll — ADJUSTMENTS
7-1. MECHANICAL LOAD BRAKE. The mechanical load
brake on Series 800 YALE hoists is a pawl and ratchet “Weston”
type automatic brake. The brake is not adjustable and requires
only periodic inspection and occasional replacement of the
friction washers.
7-2. MOTOR BRAKE. Instructions for adjusting the brake are
inside the brake cover and are repeated below. Check brake
adjustment after the first 30 days of service and regularly
thereafter during the six-month inspection procedure. Two
versions of the motor brake occur in this manual.
c. On the early version of the brake (Figure 7-1), if the tang is
below the midway position of the two adjustment points shown
on the brake, the brake should be adjusted to br ing the tang
back up alongside the NORMAL position on the brake.
d. Remove the hex key (1/8" size) from the holster on the
cover mounting stud and carefully turn the ADJUSTING SCREW
(located above the solenoid coil) clockwise. The indicating tang
will move a large distance for a small turn of the adjusting
screw, therefore turn the screw no more than one quarter turn
before checking adjustment.
e. After adjustment operate the brake b y hand to assure brake
disc running clearance. The outboard brake pad should separate
from the brake disc by approximately .010".
f. Replace hex key in holster.
g Replace brake cover.
7-3. BLOCK OPERATED LIMIT SWITCH. The block operated
upper limit stop, furnished as standard equipment, is
nonadjustable and designed to stop lower block at its high
point of travel to guard against o v er-tr a v el with possib le damage
to hoist. When high point is reached, limit stop switch
automatically stops hook travel. If hook drifts upward slightly
after stop switch is actuated, a reversing switch will close and
automatically reverse direction of hook travel.
12759C
12759
Figure 7-1A. Motor Brake - Later Version.
7-4. SCREW-TYPE LIMIT SWITCH. This limit switch has a
rotary screw driven by a gear reduction which is coupled to the
end of the drum shaft. Adjustment discs operate the contacts of
separate switches; one for the hoisting circuit and one for the
lowering circuit. The switch assembly must be wired in
accordance with the appropriate wiring diagram, which is
packaged with hoist. Adjustment of this screw-type limit switch
is accomplished as follows: (Refer to Figure 7-2).
WARNING
Before attempting actual adjustments, be certain main
power switch is OFF and locked in the open position.
Figure 7-1. Motor Brake - Early Version.
a. Examine position of indicating tang located below the
solenoid coil (Figure 7-1 or 7-1A).
b. On the
later version of the brake (Figure 7-1A), if the tang
is below the line by more than 1/8", the brake should be adjusted
to bring the top of the tang back up alongside the line on the
adjust label.
12758B
SWITCH
LOCKING
PLATE
ADJUSTMENT
DISCS
SWITCH
Figure 7-2. Screw-Type Limit Switch Adjustment.
(Wires not Shown for Clarity.)
a. Remove four screws and lift off switch cover.
b. Loosen locking plate screws. Slide locking plate away from
adjustment discs.
Page 21
Page 22

c. Turn proper adjustment disc (right for up, left for down)
toward stitch to reduce hook travel or away from switch to
increase hook travel.
hoist is furnished as a separate insert and shipped with hoist.
We suggest you carefully file the wiring diagram with this book
for future reference.
d. Slide locking plate back into position ensuring slots on
adjustment discs are fully engaged, tighten locking plate screws
to 4 in-lbs.
e. Replace cover.
WARNING
Check limit switch operation carefully, without load,
before placing hoist in service. If misadjusted, SEVERE
DAMAGE AND/OR A DROPPED LOAD COULD RESULT.
Allow 6" for hook drift in both directions. Never allow
less than 1-1/2 complete wraps of rope on drum with
hook in lowest position.
Provide a light film of NLGI No. 2 grease on bevel gear of limit
switch.
7-5. OVERLOAD CLUTCH ADJUSTMENT. When properly
adjusted, the overload device is designed so that the hoist will
lift its full rated load but will refuse to lift an excessive overload.
The overload clutch is not externally adjustable. It is necessary
to remove the ov erload clutch assembly from the hoist for proper
adjustment. Therefore, it is strongly recommended that when
adjustment and/or replacement parts are required, a SHAWBO X
Authorized Repair Station be contacted. Consult y our SHAWBOX
Distributor for nearest Repair Station.
SECTION VIII — WIRING DIA GRAMS
Wiring diagrams for SHA WBOX electric hoists have been omitted
from this book because of many possible variations. This is due
to different currents and types of electrical components used in
their construction. A print of the correct wiring diagram for each
WHEN ORDERING PARTS OR INFORMATION ON THIS
EQUIPMENT, ALWAYS INCLUDE MODEL AND SERIAL
NUMBER ON ORDER.
SECTION IX — PARTS LIST
9-1. GENERAL. The parts lists and illustrations in this section
of the manual, cover parts for all standard 800 SHAWBOX
Electric Hoists. A typical hoist is shown as the basis for the
exploded parts illustrations; therefore, certain variations may
occur from the information given. For this reason, always give
the Hoist Serial Number, Catalog Number, Motor Horsepower,
Voltage, Phase, Frequency and Rated Load of Hoist when
ordering parts.
Certain parts of your hoist will, in time, require replacement
under normal wear conditions. It is suggested that these parts
be purchased for your hoist as spares for future use. These
parts are indicated by a (†) symbol at the right side of the par ts
reference numbers.
WARNING
NON-FACTORY AUTHORIZATIONS OR MODIFICATION
OF EQUIPMENT AND USE OF NON-FACTORY REPAIR
PARTS CAN LEAD TO DANGEROUS OPERATION AND
INJURY.
TO AVOID INJURY:
• Do not alter or modify equipment without factor y
authorization.
• Do use only factory provided replacement parts.
The numbers assigned to the parts of our various assemblies in our parts lists are not the part numbers used in
manufacturing the part. They are identification numbers, that when given with the model number, permit us to
identify, select or manufacture, and ship the correct part needed.
9-2. INDEX OF EXPLODED VIEW PARTS ILLUSTRATIONS
Figure No. Title Page No.
9-1 Frame, Gearcase and External Parts ...........................................................................................................23
9-2 Gear ing and Load Brake Parts .....................................................................................................................26
9-3 Hoist Motor Brake - Later Version.................................................................................................................28
9-4 Hoist Motor Brake - Early Version............................................................................................ ..................30
9-5 Three Phase Motor Assembly .......................................................................................................................32
9-6 Upper Limit Switch Parts...............................................................................................................................33
9-7 Electr ical Control Equipment .........................................................................................................................34
9-8 Push Button Station Assembly and Conductor Cable (Single Speed) ........................................................35
9-9 Push Button Station Assembly and Conductor Cable (Two Speed) - Later Version...................................36
9-10 Push Button Station Assembly and Conductor Cable (Two Speed) - Early Version................................... 38
9-11 Lower Block Assembly — 2 parts rope, single reeved ................................................................................40
9-12 Lower Block Assembly — 2 part double reeved...........................................................................................41
9-13 Upper and Lower Block Parts (3 & 5 Ton) ....................................................................................................42
9-14 Screw-Type Limit Switch Parts......................................................................................................................43
Page 22
Page 23

11455C
Figure 9-1. Frame, Gearcase and External Parts.
Ref. Part Qty.
No. Number Description Req’d
1 800-197 Plug — Oil Level 2
2 800-192 Cover & Bearing Assembly — Gearcase 1
3 800-105 Dowel 2
4† 800-106 Gasket — Gearcase 1
5 800-107 Gearcase & Bearing Assembly 1
6 Drum & Hub Assembly (Double Reeved Models) 1
1/2 & 1 Ton (3/6" Dia. Rope)
800-109 18' Lift
800-111 34' Lift
800-2100 47' Lift
2 Ton (1/4" Dia. Rope)
800-108 14' Lift
800-110 25' Lift
800-2101 36' Lift
7 Drum & Hub Assembly (Single Reeved Models) 1
1/2 & 1 Ton (1/4" Dia. Rope)
800-113 25' Lift
800-115 50' Lift
2 Ton (5/16" Dia. Rope)
800-112 20' Lift
800-114 40' Lift
3 Ton (5/16" Dia. Rope)
800-2102 30' Lift
800-2103 45' Lift
5 Ton (5/16" Dia. Rope)
800-2104 20' Lift
800-2105 30' Lift
Page 23
Page 24

Figure 9-1. Frame, Gearcase & External Parts. (Cont’d.)
Ref. Part Qty.
No. Number Description Req’d.
8 800-116 Screw — Hex, Socket Button Head — Self-Locking 4
9 Frame Assembly (Single Reeved Models) 1
1/2, 1 & 2 Ton
800-117 Short Frame
800-118 Long Frame
3 Ton
800-2106 First Extension
800-2107 Second Extension
5 Ton
800-2108 First Extension
800-2109 Second Extension
9A Frame Assembly (Double Reeved Models) 1
1/2, 1 & 2 Ton
800-2110 Short Frame
800-2111 Long Frame
800-2112 First Extension
12 800-121 Closure — 1/2" Plug 3
14 800-124 Nut — Hex (Double Reeved Models) 4
15 800-125 Lockwasher (Double Reeved Models) 4
19 Shaft — Extension, Drum 1
800-130 Short Frame
800-131 Long Frame
800-2113 First Extension
800-2114 Second Extension
20 800-132 Key — Woodruff (“Hi-Pro” Type) 1
21 800-133 Ring — Retaining, Hub (Inter nal) 1
22† 800-134 Bearing — Drum Shaft 1
23 800-135 Ring — Retaining, External 1
24 800-136 Ring — Retaining, Beveled Hub (Internal) 1
25 800-137a Plate Assembly — Base 1
26 800-138 Lockwasher 16
27 800-139 Screw — Hex Socket Head Cap 4
29 800-194c Cover Assembly — Electrical 1
30 800-2121 Screw — Self-Tapping 2
32 800-146a Plate Assembly — Base (Short Frame) 1
34 800-2122 Shell — Brake, Short Frame 1
35 800-149 Screw — Self-Tapping 2
41 See Fig. 9-3 Motor & Brake 1
& Fig. 9-4
43 800-155 Screw — Hex Socket Head 1
44 800-156 Lockwasher 1
45† Rope & Thimble Assembly (Single Reeved Models) 1
1/2 & 1 Ton (1/4" Dia. Rope)
800-158 25' Lift
800-161 50' Lift
2 Ton (5/16" Dia. Rope)
800-157 20' Lift
800-160 40' Lift
3 Ton (5/16" Dia. Rope)
800-2115 30' Lift
800-2116 45' Lift
5 Ton (5/16" Dia. Rope)
800-2117 20' Lift
800-2118 30' Lift
47 800-164 Screw — Hex Socket Head 4
48 800-165 Roll Pin 2
Page 24
Page 25

Figure 9-1. Frame, Gearcase & External Parts. (Cont’d.)
Ref. Part Qty.
No. Number Description Req’d.
49 800-166 Lockwasher 2
50 800-167 Screw — Hex Head Cap 2
51 800-168 Key Plate 1
52 800-169 Shaft — Sheave (Double Reeved Models) 1
53 800-170 Bracket, Sheave (Double Reeved Models) 1
54† 800-171 Bearing, Sheave (Double Reeved Models) 1
55† 800-172 Sheave Assembly, Upper (Double Reeved Models) Includes Bearing 1
56† Rope & Thimble Assembly (Double Reeved Models) 1
1/2 & 1 Ton (3/16" Dia. Rope)
800-174 18' Lift
800-176 34' Lift
800-2119 47' Lift
2 Ton (1/4" Dia. Rope)
800-173 14' Lift
800-175 25' Lift
800-2120 36' Lift
57 800-177 Plug, Pin 2
58 800-178 Bolt, Hex Head 12
61 800-196 Label, Rated Load (Specify Rated Load) 1
†Recommended spares.
NOTES
Page 25
Page 26

11456LC
Figure 9-2. Gearing and Load Brake Parts.
Ref. Part Qty.
No. Number Description Req’d.
1† 800-201 Bearing Assembly — Needle, Intermediate & Drum Gear Shaft 2
2† 800-202 Race — Thrust Bear ing 4
3† 800-203 Bearing Assembly — Needle Thrust 2
4 Gear — Intermediate 1
800-204 104 Teeth
800-205 109 Teeth
800-266 103 Teeth
800-206 90 Teeth
800-2205A 107 Teeth
5 800-207 Key — Woodruff 1
7 Gear — Drum 1
800-209 71 Teeth
800-210 61 Teeth
800-2209 71 Teeth
8 Shaft — Intermediate Gear 1
800-211 14 Teeth
800-212 24 Teeth
800-2211 14 Teeth
Page 26
Page 27
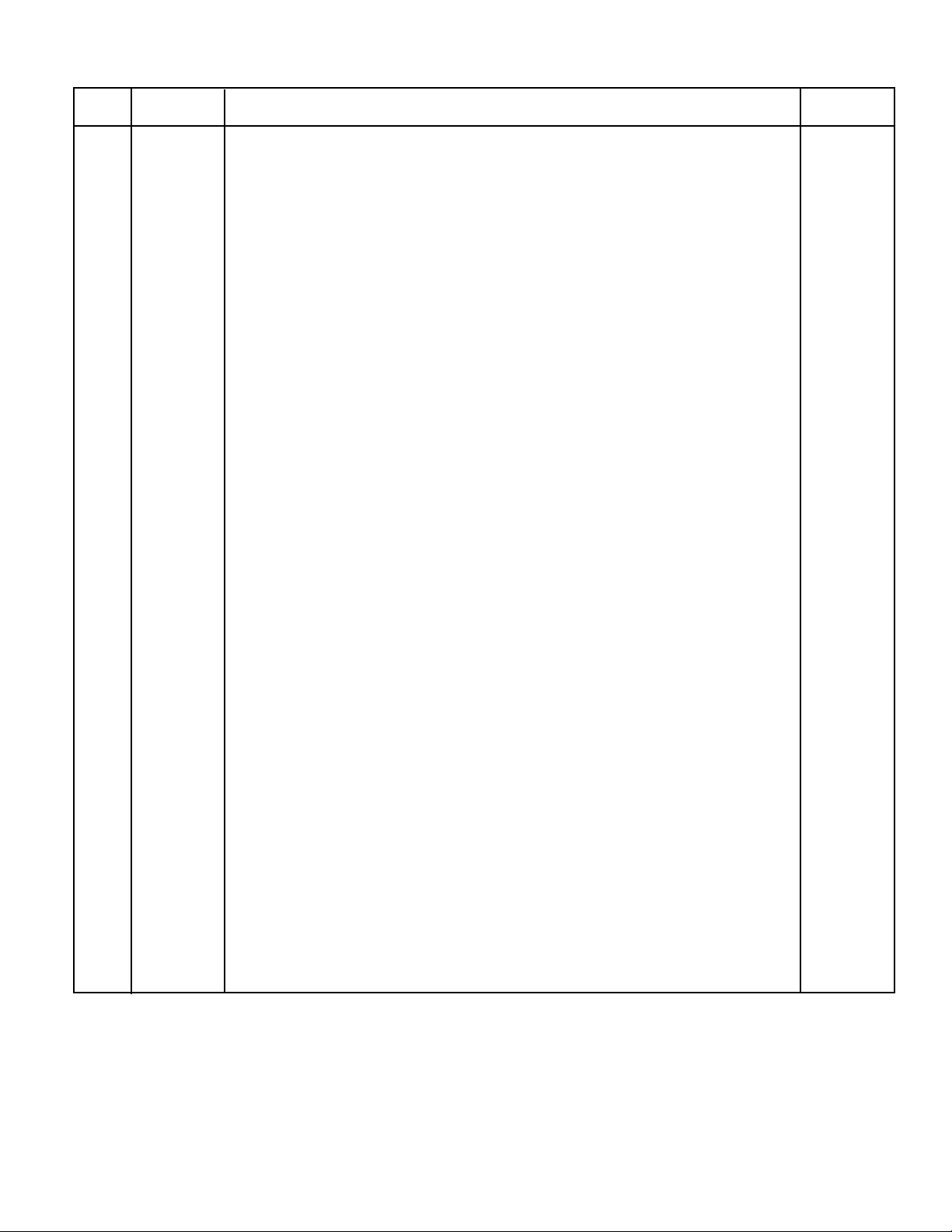
Figure 9-2. Gearing and Load Brake Par ts. (Cont’d.)
Ref. Part Qty.
No. Number Description Req’d.
15 800-219 Ring — Retaining, Drum Shaft Bearing 1
17 800-221 Ring — Retaining 1
18† 800-222 Bearing Assembly — Roller, Inter mediate Shaft 1
19 800-269 Cover — Oil Hole 1
20 800-224 Pipe Plug — Hex Socket 1
21† 800-225 Oil Seal — Motor Shaft 1
22† 800-226 Bearing Assembly — Ball, Motor Shaft 1
23† 800-227 Bearing Assembly — Needle, Load Brake Shaft 1
24 800-228 Ring — Retaining, Motor Shaft Bearing 1
25 800-229 Washer — Thrust (Steel) 1
Brake Assembly — Load, Complete (Includes Items 26 thru 37) 1
800-230 23 Teeth
800-231 36 Teeth
800-267 24 Teeth
800-232 18 Teeth
800-2232A 20 Teeth
26 800-233 Ring — Retaining, Brake Flange 1
27 800-234 Flange — Load Brake 1
28* 800-235 Washer — Friction 2
29 800-236 Pawl & Ratchet Assembly — Load Brake (Available Only As An Assembly) 1
30 800-237 Bushing — Ratchet 1
31 800-238 Gear & Center Assembly 1
32 800-239 Pin — Groove 2
33† 800-240 Cam — Load Brake 1
34† 800-241 Spring — Load Brake 1
35 800-242 Retainer — Spring, Load Brake 1
36 800-243 Key — Woodruff 2
37 Shaft & Integral Pinion — Load Brake 1
800-244 23 Teeth
800-245 36 Teeth
800-268 24 Teeth
800-246 18 Teeth
800-2246A 20 Teeth
38† 800-247 Washer — Thrust (Used With 800-246 Only) 1
39† 800-248 Washer — Thrust (Bronze) 1
40† 800-249 Bearing Assembly — Needle, Load Brake Shaft 1
* 800-250 Load Brake — Clutch Assembly With Bearings (Complete) 1
** 800-251 Load Brake — Clutch Assembly (Includes Items 26 thru 30, 34, 36 thru 38
and 43 thru 45) 1
43 800-254 Spring Retainer
44 800-253 Brake Gear, Center
45 800-252 Clutch Assembly
46 800-260 Ring — Retaining 3
47 800-263 Oil Seal — Drum Shaft 1
48 800-261 Bearing Assembly — Ball, Drum Shaft 1
49 800-262 Shaft — Drum 1
† Recommended spares.
* Recommended Replacement Kit for Load Brake Clutch (Complete).
** Replacement Complete, Less Bearings and Thrust Washers.
For hoists built prior to March, 1997, gearing part numbers, with four digits (rather than three) after “800-”, must be replaced in sets.
For hoists built between March 1, 1997 and July 1, 1997, contact the factory for gearing requirements.
Available only as par t of
800-250 or 800-251 above
}
Page 27
Page 28
12756H
Figure 9-3. Hoist Motor Brake - Later Version.
Ref. Part Qty.
No. Number Description Req’d.
800-2401 Motor Brake Assembly (Includes Ref. Nos. 1 thr u 31) 1
1 * Acorn Nut - Plated (#10-32) 2
2 800-2402 Brake Cover Assembly (Includes Brake Cover and Label Inside Cover) 1
3 * Cover Stud 2
4 * Gasket 1
5 * Phillips Pan Head Self Tapping Screw - Plated (#10-32 x 1-3/4) 4
6 * Solenoid Frame Cover Assembly 1
7 * Hex Key (1/8 - 3/4 x 2) 1
8 800-2410† Solenoid Coil Assembly 1
9 * Tubing 3
10 * Hex Nut - Plated (#10-32) 2
11 800-2411 Solenoid Frame 1
14 * Hex Head Self Locking Nut - Plated (#10-32) 2
15 800-2403 Solenoid Support 1
16 * Hex Washer Head Thread Forming Screw - Plated (#10-32 x 1/4) 2
17 * Solenoid Plunger 1
18 * Hex Socket Head Set Screw - Oval Point (1/4-28 x 1) 1
19 * Hex Socket Shoulder Screw (#10-24 x 1)** 1
20 * Hex Head Self Locking Nut - Plated (#10-24)** 1
21 * Brake Spring (Use Red Spring Only) 1
22 * Brake Lever Assembly 1
23 * Pressure Pad 2
24 Brake Disc (Non-asbestos) 1
25 * Brake Support Stud 2
26 * Separating Spring 2
27 800-2404 Brake Mounting Plate 1
28 * Hex Socket Head Self Locking Set Screw - Cup Point (1/4-20 x 3/8) 2
29 * Brake Hub 1
30 * Hex Socket Head Screw (3/8-16 x 3/4) 2
31 Lock Washer (3/8) 2
Wire Nuts — Not Shown (No. 22 thru 14 AWG) 4
* Not available as individual parts. See replacement kits listed below.
** Later models have a hex socket head screw (1/4-20 x 1-1/2) with a hex head self locking nut - plated (1/4-20).
Kits include quantities shown above.
Page 28
Page 29

Figure 9-3. Hoist Motor Brake. (Cont’d.)
Kit Description Part Number Reference Numbers Included
Brake Disc 800-2405† 23, 24, 26
Brake Lever 800-2406 6, 15, 17, 18, 19, 20, 21 (Red Color), 22,
Adjusting Screw Label, Brake Adjust Label —
Discard Zinc Colored Spring
Rectifier 800-2407 12, 13, 4 Wire Nuts
Hardware 800-2408 1, 3, 4, 5, 7, 9, 10, 12, 16, 18, 20, 25, 28, 30, 31,
Instruction Label, Power Warning Label
Brake Hub 800-2409 28, 29, Hub Drive Key (Shown Elsewhere)
† Recommended spares.
NOTES
Page 29
Page 30

12756A
Figure 9-4. Hoist Motor Brake - Early Version.
Ref. Part Qty.
No. Number Description Req’d.
Motor Brake Assembly (Includes Ref. Nos. 1 thru 32) 1
800-1400 Short Frame Models Only
800-1401 Other Models
1 * Acor n Nut (#10-32) 2
2 800-1402 Brake Cover Assembly (Includes Brake Cover and Label Inside Cover) 1
3 * Cover Stud 2
4 * Gasket 1
5 * Hex Washer Head Thread For ming Screw (#10-32 x 1 -3/4) 4
6 * Solenoid Frame Cover Assembly 1
7 * Hex Key (1/8-3/4 x 2-1/4) 1
8 * Solenoid Coil Assembly 1
9 * Tubing 3
10 * Hex Nut (#10-32 Pltd.) 2
11 * Solenoid Frame 1
14 * Hex Head Self-Locking Nut (#10-24) 2
15 800-1403 Solenoid Support 1
16 * Hex Washer Head Thread Forming Screw (#10-32 x 1/4) 2
17 * Solenoid Plunger 1
18 800-1404 Hex Socket Head Self-Locking Set Screw - Oval Point (1/4 - 28 x 1) 1
20 * Clevis Pin (3/16 x 1-1/4) 1
21 * Flat Washer 2
22 * Brake Spring 1
23 * Brake Lever Assembly 1
24 * Pressure Pad 2
25 * Brake Disc (Non-asbestos) 1
26 * Brake Support Stud 2
27 * Separating Spr ing 2
28 * Hex Socket Head Self-Locking Set Screw - Cup Point (1/4 - 20 x 3/8) 2
29 * Brake Hub 1
30 * Hex Socket Head Screw (3/8 - 16 x 3/4) 2
31 800-1405 Brake Mounting Plate 1
32 * Wire Nuts — Not Shown (No. 22 thru 16 AWG) 4
* Not available as individual parts. See replacement kits listed below. Kits include quantities shown above.
Page 30
Page 31

Figure 9-4. Hoist Motor Brake. (Cont’d.)
Kit Description Part Number Reference Numbers Included
Brake Disc 800-1406 24, 25, 27
Solenoid 800-1407 5, 6, 8, 11, 17
Brake Lever 800-1408 18, 20, 21, 22, 23
Brake Hub 800-1409 28, 29, Hub Drive Key (Shown Elsewhere)
Special Hardware 800-1410 3, 4, 9, 26, Instruction Label inside cover,
Adjust Label, Adjusting Screw Label on
brake lever assembly, Power Warning Label
on cover
Hardware 800-1411 1, 5, 7, 10, 12, 14, 16, 18, 20, 21, 28, 30
NOTES
Page 31
Page 32

12724
Figure 9-5. Three Phase Motor Assembly.
Ref. Part Qty.
No. Number Description Req’d.
Motor Assembly (Includes Ref. Nos. 1 thru 8) 1
1 Horsepower (1 Speed)
800-1301 200 Volt
800-1302 230/460 Volt
800-1303 575 Volt
2 Horsepower (1 Speed)
800-1304 200 Volt
800-1305 230/460 Volt
800-1306 575 Volt
4 Horsepower (1 Speed)
800-1307 200 Volt
800-1308 230/460 Volt
800-1309 575 Volt
1 - 1/3 Horsepower (2 Speed)
800-1310 200 Volt
800-1311 230 Volt
800-1312 460 Volt
800-1313 575 Volt
2 - 2/3 Horsepower (2 Speed)
800-1314 200 Volt
800-1315 230 Volt
800-1316 460 Volt
800-1317 575 Volt
3 - 1 Horsepower (2 Speed)
800-1318 200 Volt
800-1319 230 Volt
800-1320 460 Volt
800-1321 575 Volt
4 - 2 Horsepower (2 Speed)
800-1322 200 Volt
800-1323 230 Volt
800-1324 460 Volt
800-1325 575 Volt
1 * Bell — End 1
2 * Ring — Retaining 1
3 * Bearing — Ball 1
4 * Ring — Retaining 1
5 * Key — Brake 1
6 * Rotor and Shaft Assembly 1
7 * Stator Assembly 1
8 * Bolt — Motor 4
* Furnished only as par t of motor assembly.
Page 32
Page 33

11460
Figure 9-6. Upper Limit Switch Par ts.
Ref. Part Qty.
No. Number Description Req’d.
1 800-501 Pin — Pivot 2
2 Arm — Lever 1
800-502 Shor t Frame
800-503 Long Frame
800-526 First Extension
800-527 Second Extension
3 Lever — Floating 1
800-504 Shor t Frame
800-505 Long Frame
800-528 First Extension
800-529 Second Extension
4 800-506 Washer 2
5 800-507 Pin — Cotter 2
6 800-525 Coupling 1
7 800-509 Pin — Roll 2
8† 800-510 Switch Assembly — Limit, Reversing (Includes Wire Leads) 1
9 800-511 Connector — Wire 3
10† 800-512 Switch Assembly — Limit, Stop (Includes Wire Leads) 1
11 800-513 Screw — Round Head 4
12 800-514 Screw — Socket Head Shoulder 1
13 800-515 Shaft & Cam Assembly 1
14 800-516 Insulator — Limit Switch 1
15 800-517 Bearing — Nylon 2
16 800-518 Screw — Socket Head Cap 2
17 800-519 Lockwasher 2
18 800-520 Nut — Lock 1
19 800-521 Bracket Assembly — Mounting 1
20 800-522 Nut — Hex 2
† Recommended Spares.
Page 33
Page 34

12748A
Figure 9-7. Electrical Control Equipment.
Ref. Part Qty.
No. Number Description Req’d.
3 800-670 Cord Grip — Conductor 2
5 800-654 Screw — Self-Tapping 4
6† 800-655 Contactor — Two Speed 1
7† 800-656 Contactor 1
8 800-657 Screw — Self-Tapping 2
9† 800-671 Transformer 1
10 800-663 Screw — Self-Tapping 4
11† 800-672 Terminal Board (Reconnectable Hoist Only) 1
12 800-673 Fuse, Fuse Holder and Wire Assembly 1
800-674 Fuse Only (2A, 300V) 1
13 800-675 Brake Module 1
14 800-676 Screw — Self Tapping 2
† Recommended Spares.
NOTES
Page 34
Page 35

12763
Figure 9-8. Push Button Station and Conductor Cable Assembly.
Single Speed Hoists.
Ref. Pa rt Qty.
No. Number Description Req’d.
800-2701 Push Button Station and Conductor Cable Assembly
(Includes Ref. Nos. 1 thru 17) 1
800-2702 Push Button Station (Includes Ref. Nos. 1 thru 15) 1
1 * Type 1 Pan Head Machine Screw (M 3.5 x 0.6 x 12 Pltd.) 7
2 * Lockwasher (M 3.5 Pltd.) 7
3 * Rear Cover 1
4 800-2703 Gasket 1
5 * Type 1 Pan Head Thread Cutting Screw (M 4 x 15 Pltd.) 2
6 800-2704 Contact Assembly 1
7 800-2705 Button Assembly 1
8 * Type 1 Pan Head Machine Screw (M 6 x 1 x 12 Pltd.) 1
9 * Lockwasher (M 6 Pltd.) 1
10 * Plain Washer (M 6 Pltd.) 1
11 * Type 1 Pan Head Machine Screw (M 3.5 x 1 x 14 Pltd.) 2
12 * Lockwasher (M 3.5 Pltd.) 2
13 * Housing Cap 1
14 800-2706 Grommet 1
15 * Housing 1
16 800-2707 Conductor Cable Assembly 1
17 800-2708 Plastic Warning Tag 1
* Not available separately. Order Push Button Station.
Page 35
Page 36

12721A
Figure 9-9. Push Button Station and Conductor Cable Assembly.
Two Speed Hoists Only - Later Version.
Ref. Part Qty.
No. Number Description Req’d.
800-1821 Push Button Station and Conductor Cable Assembly
(Includes Ref. Nos. 1 thru 30) 1
1 800-1822 Grommet 1
7 800-1823 Conductor Cable As Req’d
11 800-1812 Operator Warning Label 1
800-1813 Push Button Station (Includes Ref. Nos. 12 thru 30) 1
12 800-1814 Sleeve — Conductor 1
13 * Support — Strain Cable 1
14 * Screw — Slotted Head 4
15 * Lockwasher 4
16 * Enclosure — Rear 1
17 * Gasket 1
18 * Screw — Slotted Head 2
19 * Screw — Slotted Head 2
Page 36
Page 37

Figure 9-9. Push Button Station and Conductor Cable Assembly. (Cont’d.)
Ref. Pa rt Qty.
No. Number Description Req’d.
20 * Clamp — Conductor 1
21 * Contact Block Assembly 1
800-1815 Contact Block (ZB2-BE101) 2
800-1816 Contact Block (ZB2-BE201) 2
22 * Interlock—Mechanical 1
800-1817 Up Push Button Assembly (Includes 1 Each of Ref. Nos. 23 and
25 thru 29) 1
800-1818 Down Push Button Assembly (Includes 1 Each of Ref. Nos. 23,
25 thru 28 and 30) 1
23 * * Ring — Retaining 2
24 * Enclosure — Front 1
25 * * Seat — Spring 2
26 ** Spr ing 2
27 ** Seal 2
28 * * Plate — Push Button 2
29 * * Push Button — Up 1
30 * * Push Button — Down 1
* Not available separately. Order Push Button Station.
** Not available separately. Order Push Button Assembly.
NOTES
Page 37
Page 38

12721
Figure 9-10. Push Button Station and Conductor Cable Assembly.
Two Speed Hoists Only - Early Version.
Ref. Part Qty.
No. Number Description Req’d.
800-1801 Push Button Station and Conductor Cable Assembly
(Includes Ref. Nos. 1 thru 30) 1
1 800-1802 Anchor Bracket — Strain Cable 1
2 800-1803 Grip Assembly — Conductor 1
3 800-1804 Connector — Strain Cable 1
4 800-1805 Thimble — Strain Cable 2
5 800 1806 Connector — Conductor to Strain Cable 1
6 800-1807 Clamp — Conductor 1
7 800-1808 Conductor Cable 1
8 800-1809 Strain Cable 1
9 800-1810 Sleeve — Pressure 1
10 800-1811 Tie — Conductor As Req’d.
11 800-1812 Operator Warning Label 1
800-1813 Push Button Station (Includes Ref. Nos. 12 thru 30) 1
12 800-1814 Sleeve — Conductor 1
Page 38
Page 39

Figure 9-10. Push Button Station and Conductor Cable Assembly. (Cont’d.)
Ref. Part Qty.
No. Number Description Req’d.
13 * Suppor t — Strain Cable 1
14 * Screw — Slotted Head 4
15 * Lockwasher 4
16 * Enclosure — Rear 1
17 * Gasket 1
18 * Screw — Slotted Head 2
19 * Screw — Slotted Head 2
20 * Clamp — Conductor 1
21 * Contact Block Assembly 1
800-1815 Contact Block (ZB2-BE101) 2
800-1816 Contact Block (ZB2-BE201) 2
22 * Interlock — Mechanical 1
800-1817 Up Push Button Assembly (Includes 1 Each of Ref. Nos. 23 and
25 thru 29) 1
800-1818 Down Push Button Assembly (Includes 1 Each of Ref. Nos. 23,
25 thru 28 and 30) 1
23 ** Ring — Retaining 2
24 * Enclosure — Front 1
25 ** Seat — Spring 2
26 ** Spring 2
27 ** Seal 2
28 ** Plate — Push Button 2
29 ** Push Button — Up 1
30 ** Push Button — Down 1
* Not available separately. Order Push Button Station.
** Not available separately. Order Push Button Assembly.
NOTES
Page 39
Page 40

11464
Figure 9-11. Lower Block Assembly — Two Parts Rope, Single Reeved.
Ref. Part Qty.
No. Number Description Req’d.
800-801 Block Assembly — Lower, Complete, 2 Ton 1
800-802 Block Assembly — Lower, Complete, 1 Ton 1
800-803 Block Assembly — Lower, Complete, 1/2 Ton 1
1 800-804 Screw — Flat Head, Self-Threading 2
2 800-805 Cover — 2 Ton 1
800-806 Cover — 1 Ton 1
800-807 Cover — 1/2 Ton 1
3 800-808 Ring — Retaining, 2 Ton 2
800-809 Ring — Retaining, 1/2 & 1 Ton 2
4 800-810 Lube Fitting 1
5 800-811 Pin — Sheave, 2 Ton 1
800-812 Pin — Sheave, 1/2 & 1 Ton 1
6 800-813 Spacers — 2 Ton 2
800-814 Spacers — 1/2 Ton & 1 Ton 2
† 800-815 Sheave Assembly — 2 Ton (Consists of Items 7 and 8) 1
7 800-816 Bearing 1
8 800-817 Sheave 1
† 800-818 Sheave Assembly — 1/2 & 1 Ton (Consists of Items 7 and 8) 1
7 800-819 Bearing 1
8 800-820 Sheave 1
9 800-821 Cover — Lower Block, 2 Ton 1
800-822 Cover — Lower Block, 1 Ton 1
800-823 Cover — Lower Block, 1/2 Ton 1
10† 800-824 Hook Assembly — (Consists of Hook, Nut & Grooved Pin), 2 Ton 1
† 800-825 Hook Assembly — (Consists of Hook, Nut & Grooved Pin), 1/2 & 1 Ton 1
11 800-826 Shroud — Thrust Bearing, 2 Ton 1
800-827 Shroud — Thrust Bearing, 1/2 & 1 Ton 1
12† 800-828 Bearing Washer -— Thrust, 2 Ton 1
† 800-829 Bearing Washer — Thrust, 1/2 & 1 Ton 1
13 800-830 Body — Lower Block, 2 Ton 1
800-831 Body — Lower Block, 1/2 & 1 Ton 1
14 800-832 *Safety Hook Latch Kit — 2 Ton 1
800-833 *Safety Hook Latch Kit — 1/2 & 1 Ton 1
15 800-834 Screw — Flat Head, Self-Threading 2
† Recommended Spares.
Page 40
Page 41

11465
Figure 9-12. Lower Block Assembly—Two Parts Double Reeved.
Ref. Part Qty.
No. Number Description Req’d .
800-851 Block Assembly — Lower, Complete, 2 Ton 1
800-852 Block Assembly — Lower, Complete, 1 Ton 1
800-853 Block Assembly — Lower, Complete, 1/2 Ton 1
1 800-804 Screw — Flat Heads Self-Threading 4
2 800-854 Cover — Lower Block, 2 Ton 2
800-806 Cover — Lower Block, 1 Ton 2
800-807 Cover — Lower Block, 1/2 Ton 2
3 800-809 Ring — Retaining 2
4 800-810 Fitting — Lube 1
5 800-855 Pin — Sheave 1
6 800-814 Spacer 4
† 800-818 Sheave Assembly — (Consists of Items 7 and 8) 2
7 800-819 Bearing 2
8 800-820 Sheave 2
9 800-856 Cover — Intermediate 1
10 800-834 Screw — Flat Head, Self-Threading 4
11 † 800-824 Hook Assembly — (Consists of Hook, Nut & Grooved Pin), 2 Ton 1
† 800-825 Hook Assembly — (Consists of Hook, Nut & Grooved Pin), 1/2 & 1 Ton 1
12 800-826 Shroud — Thrust Bearing, 2 Ton 1
800-827 Shroud — Thrust Bearing, 1/2 & 1 Ton 1
13 † 800-828 Bearing — Thrust, 2 Ton 1
† 800-829 Bear ing — Thrust, 1/2 & 1 Ton 1
14 800-857 Body — Lower Block, 2 Ton 1
800-858 Body — Lower Block, 1/2 & 1 Ton 1
15 800-832 *Safety Hook Latch Assembly — 2 Ton 1
800-833 *Safety Hook Latch Assembly — 1/2 & 1 Ton 1
† Recommended Spares.
* Furnished as Standard with hook.
Page 41
Page 42

12197LA
Figure 9-13. Upper and Lower Block Parts (3 & 5 Ton — Typical).
Quantity Required
Ref. Part
No. Number Description
3-Ton/4 PS 5-Ton/6 PS
Reeving
800-1501 Block Assembly — Lower, 4 Par t Single (Complete) 1 —
800-1502 Block Assembly — Lower, 6 Par t Single (Complete) — 1
1 800-1503 Screw — Hex Head Cap 2 2
2 800-1504 Lockwasher 2 2
3 800-1505 Key Plate 1 1
4 800-1506 Fitting — Grease 1 1
5 800-1507 Pin — Upper Sheave 1 1
6 800-1508 Spacer Washer — Upper Sheave 2 4
7† 800-1509 Bearing — Upper Sheave (Includes Outer Race) 1 2
8† 800-1510 Sheave — Upper 1 2
9 800-1535 Pin — Rope Guide 2 2
11 800-1513 Spacer Washer — Lower Sheave 4 6
12† 800-1514 Bearing — Lower Sheave (Includes Outer Race) 2 3
13† 800-1515 Sheave — Lower 2 3
14 800-1516 Pin — Roll, Hook Nut 1 1
15 800-1517 Nut — Hook* 1 1
16† 800-1518 Bearing — Thrust, Hook 1 1
800-1530 Shield — Bearing (Not Shown) 1 —
800-1531 Washer — Thrust (Not Shown) 2 —
17 800-1519 Fitting — Grease 1 1
18† 800-1520 Hook Assembly — (includes Hook, Latch & Nut) 1 1
19 800-1521 Plate — Capacity 2 2
20 800-1522 Screw — Round Head, Self-Tapping (Capacity Plate) 4 4
21 800-1523 Guard — Sheave 1 1
22 800-1524 Body — Lower Block 1 1
23 800-1525 Pin — Lower Sheave 1 1
24 800-1526 Screw — Button Head Cap, Self-Locking (Sheave Guard) 4 4
25 800-1527 Ring — Retaining, External 2 2
26 800-1528 Lockwasher — (Capacity Plate) 4 4
27 800-1529 Spacer — Upper Block, 9/16" 2 —
† Recommended Spares.
* Hook Nuts with roll pins are not interchangeable — Available only as an assembly.
Page 42
Page 43
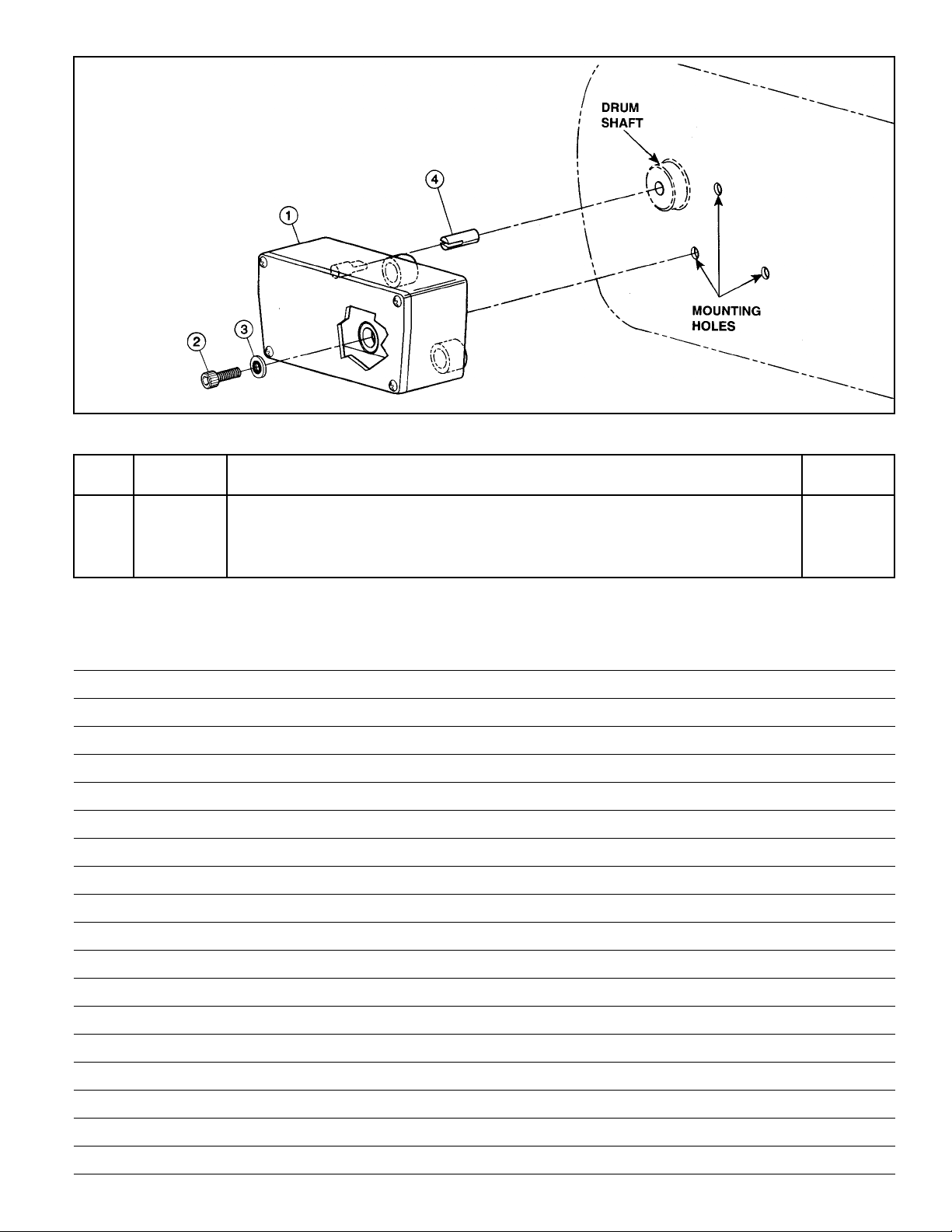
12757A
Figure 9-14. Screw-Type Limit Switch Parts.
Ref. Part Qty.
No. Number Description Req’d.
1 800-1655 Limit Switch Assembly (Includes Ref. Nos. 2, 3 and 4) 1
2 800-1651 Cap Screw — Hex Socket Head 3
3 800-1652 Sealing Washer 3
4 800-1657 Drum Shaft Inser t 1
For switch element replacement order 800-1654.
NOTES
Page 43
Page 44
Recommended Spare Parts for Your Yale Hoist
Certain par ts of your hoist will, in time, require replacement under normal wear conditions.
It is suggested that the following parts be purchased for your hoist as spares for future use.
One Friction Disc Kit
One Motor Brake Solenoid Coil
One Set Of Contactors
One Transformer
One Wire Rope Assembly
One Gearcase Gasket
Note: When ordering parts alwa ys furnish Hoist Serial Number, Catalog Number , Motor Hor sepower , Voltage,
Phase, Frequency and Rated Load of Hoist on which the parts are to be used.
Parts for your hoist are available from your local authorized SHAW-BOX repair station.
For the location of your nearest repair station, write:
IN USA
Yale
Lift-Tech
P.O. Box 769
Muskegon, MI 49443-0769
Phone: 800 742-9269
Fax: 800 742-9270
WARRANTY
WARRANTY AND LIMITATION OF REMEDY AND LIABILITY
A. Seller warrants that its products and parts, when shipped, and its
work (including installation, construction and start-up), when performed,
will meet applicable specifications, will be of good quality and will be
free from defects in material and workmanship. All claims for defective
products or parts under this warranty must be made in writing
immediately upon discovery and in any event, within one (1) year from
shipment of the applicable item unless Seller specifically assumes
installation, construction or start-up responsibility. All claims for
defective products or parts when Seller specifically assumes
installation, construction or start-up responsibility and all claims for
defective work must be made in writing immediately upon discovery
and in any event, within one (1) year from completion of the applicable
work by Seller, provided; however, all claims for defective products
and parts made in writing no later than eighteen (18) months after
shipment. Defective items must be held for Seller’s inspection and
returned to the original f.o.b. point upon request. THE ‘FOREGOING
IS EXPRESSLY IN LIEU OF ALL OTHER WARRANTIES
WHATSOEVER, EXPRESS, IMPLIED AND STATUTORY,
INCLUDING, WITHOUT LIMITATION, THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES
OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS.
B. Upon Buyer’s submission of a claim as provided above and its
substantiation, Seller shall at its option either (i) repair or replace its
product, part or work at either the original f.o.b. point of delivery or at
Seller’s authorized service station nearest Buyer or (ii) refund an
equitable portion of the purchase price.
C. This warranty is contingent upon Buyer’s proper maintenance and
care of Seller’s products, and does not extend to normal wear and
tear. Seller reserves the right to void warranty in event of Buyer’s use
of inappropriate materials in the course of repair or maintenance, or
if Seller’s products have been dismantled prior to submission to Seller
for warranty inspection.
D. The foregoing is Seller’s only obligation and Buyer’s exclusive
remedy for breach of warranty and is Buyer’s exclusive remedy
hereunder by way of breach of contract, tort, strict liability or otherwise.
In no event shall Buyer be entitled to or Seller liable for incidental or
consequential damages. Any action for breach of this agreement
must be commenced within one (1) year after the cause of action has
accrued.
 Loading...
Loading...