Page 1

WLAN 11g Broadband Router
User Manual
Page 2
This product is in compl iance with the essential requ irements and other
relevant provisions of the R&TTE directive 1999/5/EC.
Product Nam e: X-Micr o WLAN 11 g Broadband Router
Model Name : XWL-11GRIX
MAX. OUT POWER
COUNTRY CHANNELS
Spain 2400-24 83. 5 MHz 1-13 < 100 mW EIRP < 100 mW EIRP
France 2400-2 454 MHz 1-8 < 100 mW EIRP < 100 mW EIRP
France 2454-24 83. 5 MHz 9-13 < 100 mW EIRP < 10 mW EIRP
Italy 2400-24 83. 5 MHz 1-13 < 100 mW EIRP < 100 mW EIRP
UK 2400-24 83. 5 MHz 1-13 < 100 mW EIRP < 100 mW EIRP
Netherlands 2400-24 83. 5 MHz 1-13 < 100 mW EIRP < 100 mW EIRP
Germany 2400-24 83. 5 MHz 1-13 < 100 mW EIRP < 100 mW EIRP
Austria 2400-24 83. 5 MHz 1-13 < 100 mW EIRP < 100 mW EIRP
Belgium 2400-24 83. 5 MHz 1-13 < 100 mW EIRP < 100 mW EIRP
Switzerland 2400-2483. 5 MHz 1-13 < 100 mW EIRP < 100 mW EIRP
Luxemburg 2400-2483.5 M Hz 1-13 < 100 mW EIRP < 100 mW EIRP
Ireland 2400-2483.5 MHz 1-13 < 100 mW EI RP < 100 mW EIRP
Portugal 2400-24 83. 5 MHz 1-13 < 100 mW EIRP < 100 mW EIRP
Norway 2400-24 83. 5 MHz 1-13 < 100 mW EIRP < 100 mW EIRP
Denmark 2400-24 83. 5 MHz 1-13 < 100 mW EIRP < 100 mW EIRP
Finland 2400-2483.5 MHz 1-13 < 100 mW EIRP < 100 mW EIRP
Iceland 2400-24 83. 5 MHz 1-13 < 100 mW EIRP < 100 mW EIRP
Greece 2400-2483.5 MHz 1-13 < 100 mW EI RP < 100 mW EIRP
Lichtenstein 2400-24 83. 5 MHz 1-13 < 100 mW EIRP < 100 mW EIRP
Sweden 2400-24 83. 5 MHz 1-13 < 100 mW EIRP < 100 mW EIRP
INDOOR OUTDOOR
2
Page 3

FCC INFORMATION
FCC Radiation Exposure Statement
This equipment complies with FCC radiation exposure limits set forth for an
uncontrolled environment. This equipment should be installed and operated with
minimum distance 20cm between the radiator & your bo dy. This transmitter must
not be co-located or operating in conjunction with any other antenna or transmitter.
The equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class
B Digital Device, p ursuant to part 15 o f the FCC Ru les. These limits are des igned
to provide reasonable protection against harmful interference in a residential
installation. This equipment generates, uses and can radiate radio frequency
energy and, if not installed and used in accordance with the instruction, may cause
harmful interference to radio communication. However, there is no grantee that
interference will not occur in a particular installation. If this equipment dose cause
harmful interference t o radio or television re ception, which can be determined by
turning the equipment off and on, the user is encouraged to try to correct the
interference by one or more of the following measures:
--Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
--Increase the separation between the equipment and receiver.
--Connect the equipment into an outlet on a circuit different from that to which the
receiver is connected.
--Consult the dealer or an experienced radio/TV technician for help.
Notice: The Part 15 radio device operates on a non-interference basis with other
devices operating at this frequency. Any changes or modification not expressly
approved by the party responsible could void the user’s authority to operate the
device.
REGULA TOR Y INFORMATION
X-Micro WLAN 11g Broadband Router must be installed and used in strict
accordance with the instructions. This device complies with the following radio
frequency and safety standards.
USA - Federal Communications Commission (FCC)
This device complies with Part 15 of FCC Rules. Operation is subject to the
following two conditions:
1. This device may not cause harmful interference.
2. This device must accept any interference that may cause undesired operation.
3
Page 4

Copyright
Copyright 200 4 by X-Mic ro Tec hnology Corp. , All rights reserv ed. No part of
this publication may be reproduced, transmitted, transcribed, stored in a
retrieval s yste m, or tr anslated into any languag e or c omp uter la nguag e, in
any form or by any means, electronic, mechanical, magnetic, optical,
chemical, manual or otherwise, without the prior written permission of
X-Micro Technology Corp.
Disclaimer
X-Micro Technology Corp. makes no representations or warranties, either
expressed or implied, with respect to the contents hereof and specifically
disclaims any warranties, merchantability or fitness for any particular
purpose. A ny software d escribed in t his m anual is sold or licensed " as is".
Should the programs prove defective following their purchase, the buyer
(and not th is com pany, its distributor, or its dealer) as sumes the entire c ost
of all necessary servicing, repair, and any incidental or consequential
damages resulting from any defect in the software. Further, X-Micro
Technology C orp., reser ves the rig ht to rev ise this p ublication and to make
changes from time to t ime in the co ntents hereof without o bligation to notify
any person of suc h revision or change.
All brand and product names mentioned in this manual are trademarks
and/or registered trademarks of their respective holders.
4
Page 5

Contents
1. OVERVIEW............................................ ................................................... ..........6
1.1 Product Feature..........................................................................................6
1.2 System Requirements ................................................................................ 6
1.3 Appl icati ons... ..... ........ ...... ........ ........ ..... ........ ..... ........ ...... ........ ..... ........ .....6
2. Installing Your Router...........................................................................................7
2.1 Installation Instructions...............................................................................7
3. Preparing Your Network....................................... ................................................8
3.1 Configuring Windows for IP Networking.....................................................8
3.2 To Configure Windows to Receive Dynamic IP Address:............................8
3.3 Collecting ISP Information........................................................................10
4. Basic Fu nction s........ ................................... ......................................................11
4.1 To Open the Web-based Admini stration Tool:...........................................11
4.2 Setup........................................................................................................13
4.3 Global Address.........................................................................................17
4.4. Wireless............. ..... ... ...... ..... ... ..... ... ..... ... ..... ... ..... ... ..... ... ..... ... ..... ... ..... ...20
4.5 Tool s...................................................... ........................................... ........29
4.6 S tatus....... ................................................... ........................................... ...33
4.7 DHCP.......................................................................................................36
4.8 Log...........................................................................................................38
4.9 S tati stics............. ........................... ........................................... ................41
5. Advanc ed Functi on......... ........... ........ .......... ........ ........... ........ ........... ........ ........43
5.1. To Toggle between Basic Functions and Advanced Functions:................43
5.2 Virtual Servers..........................................................................................44
5.3 Filters........................................................................................................47
5.4 IP/URL Block............................................................................................51
5.5 S p ecial Apps....................................................... ......................................54
5.6 DMZ Host.................................................................................................58
5.7 MAC Clone...............................................................................................60
5.8 Dynamic DNS...........................................................................................61
5.9 Proxy DNS ................................................................................................63
5.10 SNMP.....................................................................................................65
5.11 Static Routing............ ... ..... ... ..... ... ..... ... ..... ... ...... .. ...... .. ..... ... ..... ... ...... .. ...68
5
Page 6

1. OVERVIEW
1.1 Product Feature
Compliance w ith IEEE 802.11g a nd 802.1 1b standards
Highly efficient design mechanism to provide unbeatable performance
Strong network s ecurity with WEP and 802.1X encryption
Achieving data rat e up to 54Mbps for 802.11g and 11Mbps for 802.11b with
wide range coverage; high performance to deliver up to 54Mbps raw data
rate for 802.11g
Quick and easy setup with Web-based management utility
1.2 System Requirements
Windows 98, 98SE, Millennium Edition (ME), 2000 and XP operating
systems
Microsoft Internet Explorer 5.5 or higher
DSL/ Cable Modem Broadband I nter net c onnectio n and ISP account
PCs eq uipped wi th 10 Mbps or 1 0/10 0 Mb ps Ether net c onne ction t o support
TCP/IP protocol
One CD-ROM driver
1.3 Applications
Home SOHO networking for device sharing and wireless multimedia
Wireless office provides a wider range for home and SOHO Ethernet
Enables wireless building-t o-building data communicatio n
Built-in infrastruc ture mode
Router provides ideal solut ion for:
Temporary LANs for scenarios such as trade-exhibitions and meetings
Enables LAN adaptability to freq uently changing e nvironments
Enables rem ote access to cor porate netw ork inform ation, for exam p le e-m ai l
and company hom e page
6
Page 7

2. Installing Your Router
In this chapter, you’ll learn how to connect your router.
2.1 Installation Instructions
To Connect the Router:
2.1.1. Mak e sure all equipments are turned off, including the router, Desk top
or Laptop PCs, the cable and DSL modem, and so on.
2.1.2. Connect the WA N Port of t he router to the cable and DS L m odem,
Ethernet Server or t he hub.
2.1.3. Connect your client PCs to t he LAN Ports.
2.1.4. Connect the Power Adaptor (5VDC, 1.2A) to the powe r jack of the
router and plug the power cabl e i nto t he out let .
2.1.5. Turn on our PCs .
7
Page 8

3. Prep ar i ng Your Network
In this chapter, you’ll lear n what to do before configuring your
network.
Before configuring your router, you need set up the computers
in your netw ork f or TCP/IP networki ng and collect r el evant ISP
informati on if necessary.
3.1 Configuring Wi ndows for IP Networking
Each computer in your network should be config ured for TCP/IP
networking. There are two ways to configure your computers:
You are c ommended to use DHCP, then you can simp ly choose to
receive an IP address automatically. For detailed instructions, see
Configure Windows to Receive Dynamic IP Address
.
If you don’t use DHCP, you need assign an IP address to each
computer manually. For detailed instructions, refer to your Windows
Documentation.
3.2 To Configure Windows to Receive Dynamic IP
Address:
3.2.1. Click Start, then choose Settings > Network and Dial-up
Connections.
3.2.2. Select the name of your ISP connection.
The Local Area Connection Status dialog box appears, seen
in FIGURE 3-1:
8
Page 9
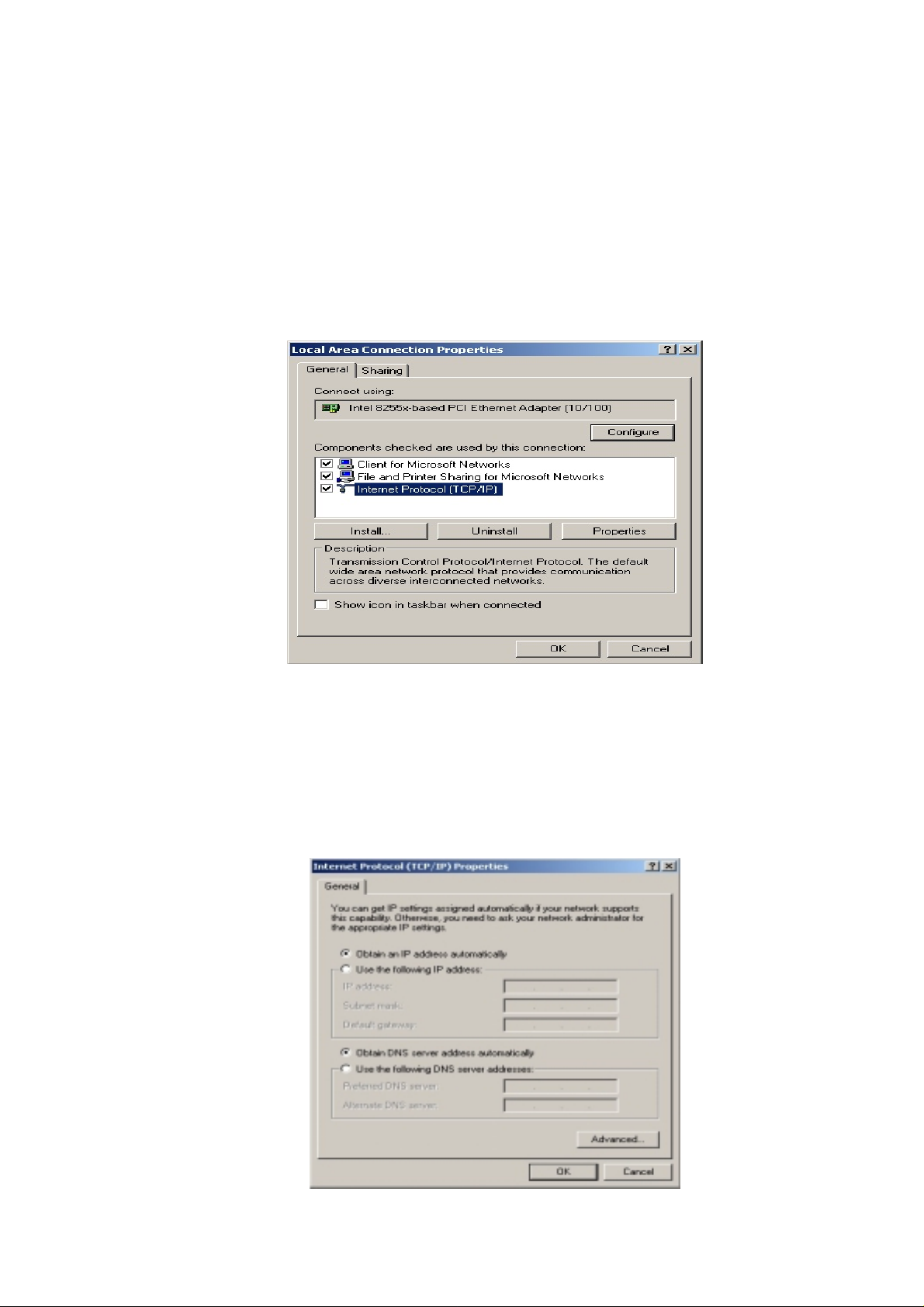
FIGURE 3-1 : Local Ar ea C onnection Status dialog box
3.2.3. Click Properties.
The Local Area Connect ion Propert ies dialog box appears,
seen in FIGURE 3-2:
FIGURE 3-2: Local Area Connection Properties dialog box.
3.2.4. Click Internet Protocol (TCP/IP), then click Properties.
The Internet protocol (TCP/IP) Properties dialog box appears,
seen in FIGURE 3-3:
9
Page 10
FIGURE 3-3: Internet Protocol (TC P /IP) Properties dialog box
3.2.5. Click Obtain an IP address automatically and Obtain DNS
server address automatically.
3.2.6. Click OK.
You need restart your computer now or at a later time.
Note :
The procedural steps above apply to W i ndows 2000 only. For Windows
95/98/ME/NT/XP, refer to your Windows D ocumentation.
3.3 Collecting ISP Information
Yo u need query the relevant information from your ISP before
configur i ng your ro uter, for example:
Has your ISP assigned you a static or dynamic IP address? If you
have obtained one static IP address, what is it?
Does your ISP use PPPoE? If so, what is your PPPoE user name
and password?
If you are not sure of the above questions, call your ISP to clarify them.
10
Page 11
4. Basic Func tio ns
In this chapter, you will learn how to use basi c functions tha t the
Company AP Router provides, including Setup, Global Address,
Wireless Tools, Status, DHCP, Log and Printer.
The X-Micro WLAN 11g Broadband Router provides you a
Web-based Administration Tool with which you can easily set
up the router and cust om ize the basic router settings. You can
use this Web-based Tool from any computer in your network.
Notes :
Micr os of t Inte rn e t Exp l or er 5.0 or later is high l y re com mended for usin g
this W eb-based Tool.
Graphics sampled in this chapter are provided for illustrations only. They
may sligh t l y dif f er fr om you r own r outer scre en s.
4.1 To Open the Web-based Administration Tool:
4.1.1. Open the browser on your PC.
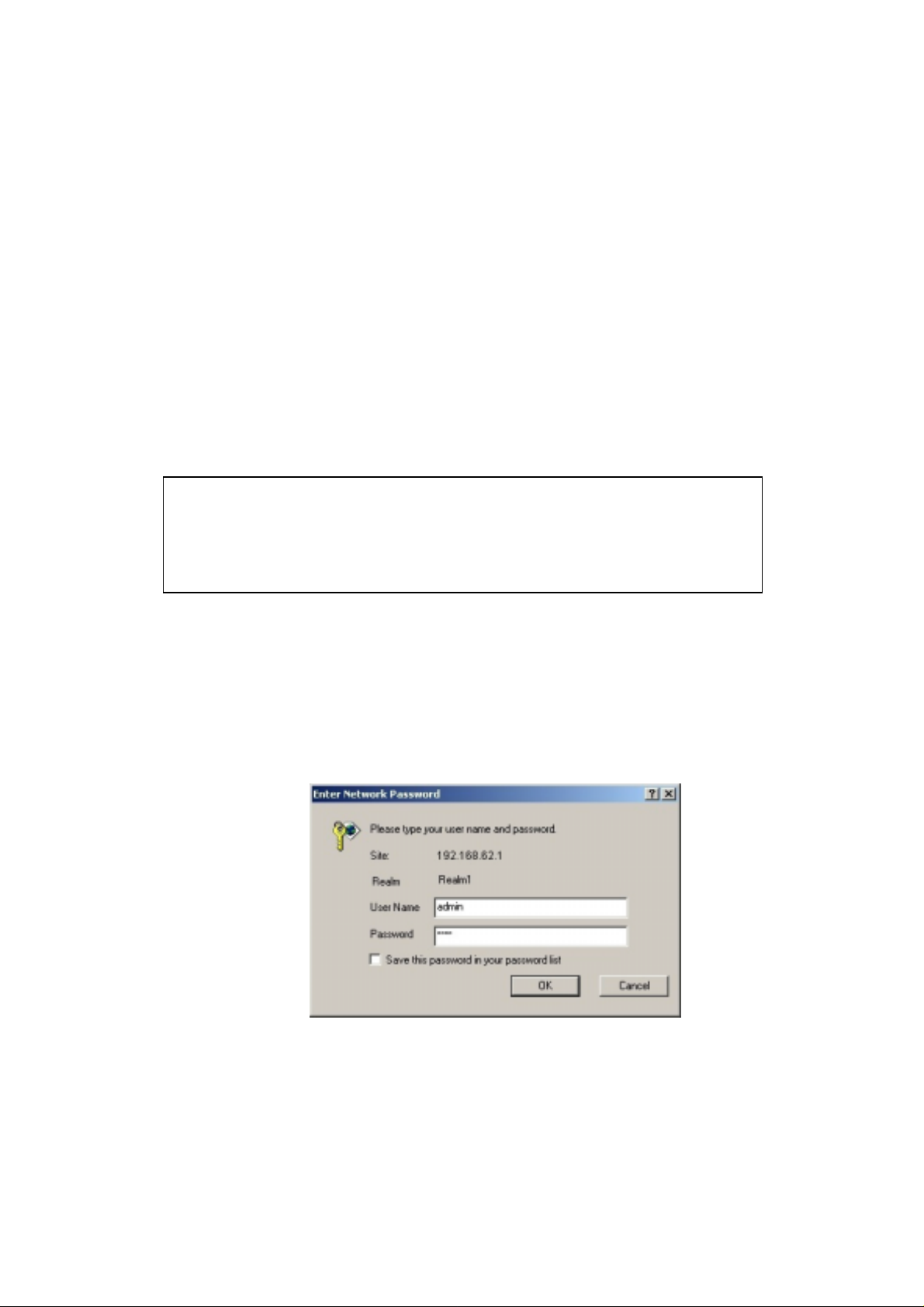
4.1.2. Type http://192.168.62.1 in the Address bar.
The Logon dialog box appears, seen in FIGURE 4-1:
FIGURE 4-1: Logon dialog box
11
Page 12

4.1.3. Type admin in the User Name bo x .
4.1.4. Type the password in the box.
Note :
The default password is “1234”. You can change the password on
th e Tools page. Fo r det ailed instructi o ns, see To Change the
Administrative Password for Your Router.
4.1.5. Optional. To log on to the Administration Tool once for all,
select the check box of Save this password in your password
list.
4.1.6. Click OK.
The Company AP Router Administration Tool appears.
Note :
The Administr ation Tool will ti me out after a pe r iod of idling, the Router
may as k you to log on again.
12
Page 13

4.2 Setup
The Setup page allows you to edit the basic configuration
parameters for your router, such as Host Name, Domain Name, LAN
IP Address, WAN IP Address, PPPoE Logi n, UPNP, and so on.
In most cases, the default sett i ngs will be Ok ay for you. However,
different ISPs ( Internet Service Prov ider) may ask f or spec ific
requirements, please c heck it with your ISP if you are not sure.
4.2.1. To Con figure Setup Parameters:
4.2.1.1. Click Set up on t he navi ga t i on ba r.
The Setup page appears, seen in FIGURE 4-2:
FIGURE 4-2: Setup page
13
Page 14

4.2.1.2. Type the Host Name, System Name or Account Name in
the Host Name box if your ISP requires.
4.2.1.3. Type the Domain Name of your ISP in the box if your ISP
requires, such as xyz.isp.com.
4.2.1.4. Optional. Review the firmware version number and date
information that you are currently using.
4.2.1.5. Select a specific Time Zone from the Set Time Zone
drop-down list, such as (GMT+08:00) Bei ji ng, Ch ongqing, Hong
Kong, Urumqi.
4.2.1.6. If you want to use Daylight Savings time, click Enable
and select the start date and end date from the Daylight Period
drop-dow n lists .
4.2.1.7. If you don’t want to use Daylight Savings time, click
Disable. If you select to disable the Daylight Savings, Daylight
Period will not take effect any more.
4.2.1.8. Optional. Review the Device IP Address and Subnet
Mask next to LAN IP Address and change the information if
necessary.
Notes :
Device I P Address and Subnet Mask are invisible to users on the LAN
(Local Area Network) only.
In most cases, you need not make any ch ange to LAN IP Address. If y ou
change the LAN I P Address with DHCP enable d, you need to restart
your client PCs; otherwise, you need reconfigure your client’s IP
addresses manually.
4.2.1.9. If you have enabled the DMZ feature on the DHCP page,
review the DMZ IP Address and Subnet Address next to DMZ IP
Address and change the information if necessary.
4.2.1.10. For WAN IP Address (Wide Area Network, also called
Public IP), choose either Obtain an IP Address automatically or
Specify an IP Address if your ISP has assigned you with static
IP).
14
Page 15

y
Note :
ou choose to obtain an IP Addres s automatically, skip Step 11.
If
4.2.1.11. Optional. If you select Specify an IP Address, type the
WAN IP Address, Subnet Mask, ISP Gateway Address and DNS
in the boxes, seen in FIGURE 4-3. You can collect such
information from your ISP.
FIGURE 4-3: WAN IP Address - Specify an IP Address
4.2.1.12. If your ISP uses PPPoE (Point to Point Protocol over
Ethernet), click Enable next to PPPoE Login; otherwise, click
Disable. For detailed instructions on how to set the PPPoE
Login parameters in FIGURE 3-4, see To Set PPPoE Login
Parameters below.
Notes :
Using PPPoE, your ISP can authenticate your connection with a specific
user name and password for security issues.
If you enable PPPoE, make sure to uninstall all existing applications on
any computer in your net w ork
.
4.2.113. If you want to use UPNP (Universal Plug and Play) to
plug devices lik e PCs , rout ers and others int o a net work and to
automatically know about each other, cl ick Enabl e next to UPNP;
otherwise, click Disable.
4.2.1.14. When you have completed all the settings, click Apply,
or click Cancel to und o your ch a nges .
15
Page 16

4.2.2. To Set PPPoE Login Parameters:
4.2.2.1. Click Enable next to PPPoE Login.
FIGURE 4-4: Set PPPoE Login Parameters
4.2.2.2. Type the User Name and Password provided by your
ISP.
4.2.2.3. For connection types, you can select either Connect on
Demand or Connect Manually.
4.2.2.4. Optional. If you want to limit the idling minutes, select
Max Idle Time and type a maximum number in minutes.
16
Page 17

4.3 Global Address
On the Global Address page, you can set up NAT (Network Address
Translation) to provide internal-to-external IP address mappings.
Have you enabled DMZ on the DHCP page? Depending on whether DMZ
is enabled, you may follow different procedural ste ps.
Notes :
If you want to use Global Address mapping, you must enable NAT
on the Filters page. For detailed instructions, see To Set up a Port
Filtering or Raw IP Filter.
If you have chosen to retrieve an IP address automatically, you w ill
not need to use this function. Instead, the default public IP address
will display on the Global Address page.
What do you want to do?
Set up Global Address with DMZ Disabled
Set up Global Address with DMZ Enabled
Remove Global Addresses
4.3.1. To Set up G loba l Ad dre ss wit h DMZ Disa b led :
4.3.1.1. Click Global Address on the navigation bar.
The Global Address page with DMZ Disabled appears, seen in
FIGURE 4-5:
FIGURE 4-5: Global Address Page with DMZ Disabled
17
Page 18
4.3.1.2. Review the first line in the above figure. It shows the
default WAN I P ad dre ss whi c h is s peci f ie d on t he Setup page. If
your ISP assigns you an IP address automatically, it will display
here.
4.3.1.3. In Line 2 – Line 8, you can list up to 7 additional static,
external IP addresses provided by your ISP.
4.3.1.4. When you have completed editing all the settings, click
Apply, or click Cancel to undo your changes.
4.3.2. To S et up Globa l Ad dre ss wit h DMZ E nab led :
4.3.2.1. Click Global Address on the navigation bar.
The Global Address page with DMZ Enabled appears, seen in
FIGURE 4-6:
FIGURE 4-6: Global Address Page with DMZ Enabled
18
Page 19

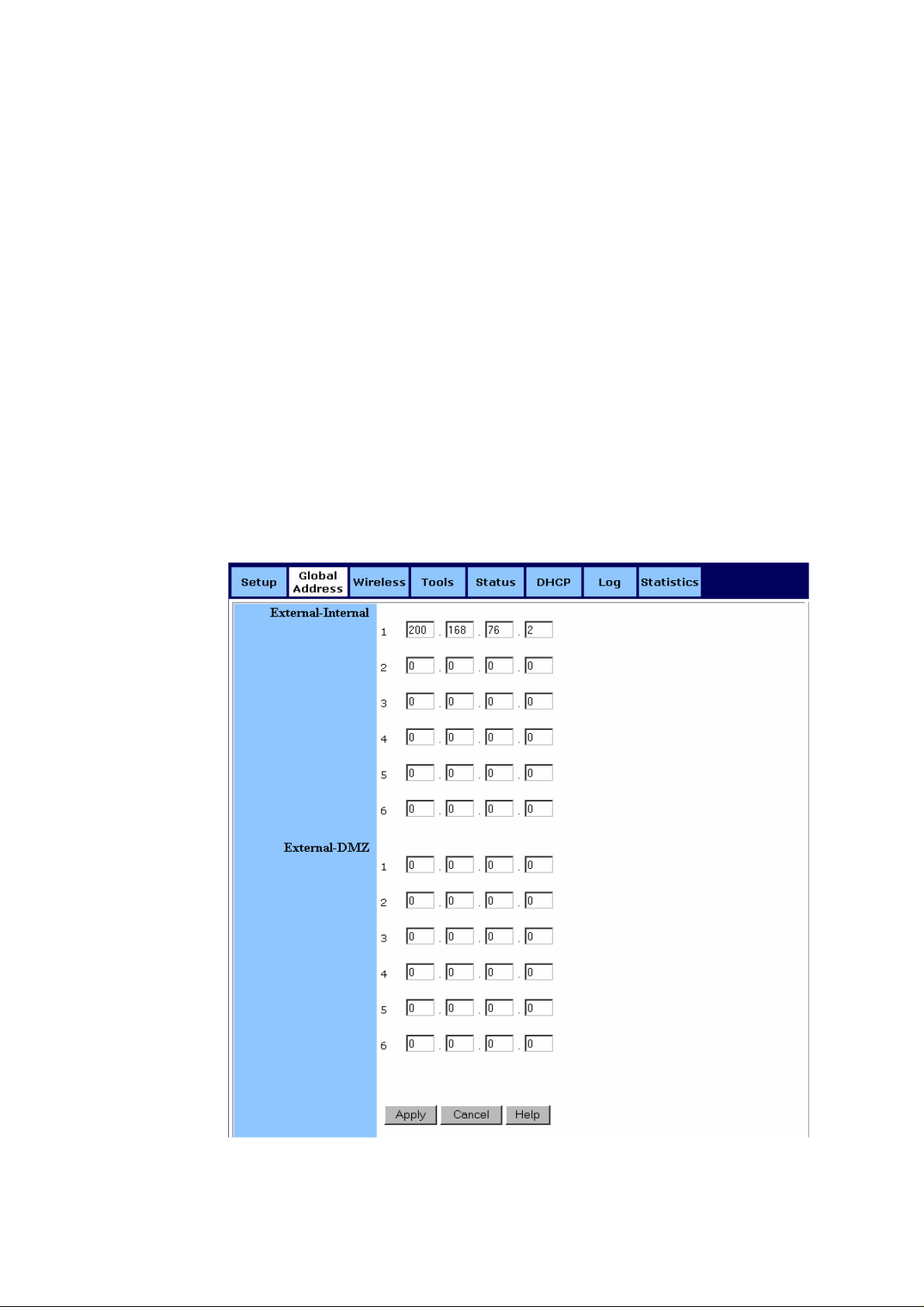
4.3.2.2. Review the first line in the above figure. It shows the
default WAN I P ad dre ss whi c h is s peci f ie d on t he Setup page. If
your ISP assigns you an IP address automatically, it will display
here.
4.3.2.3. Next to External - Internal, you can list up to 6 static,
external IP addresses provided by your ISP.
4.3.2.4. Next to External – DMZ, define for your DMZ network up
to 6 static, external global IP addresses provided by your ISP.
4.3.2.5. When you have completed editing all the settings, click
Apply, or click Cancel to undo your changes.
4.3.3. T o Remove Globa l Addres ses:
4.3.3.1. Click Global Address on the navigation bar.
4.3.3.2. For any entry you want to delete, enter 0.0.0.0, and click
Apply.
19
Page 20

4.4. Wireless
Using Wireless, you can c onf igure your router for wireless access.
There are three p arts on the Wireless page:
Radio Settings: Allows you to configure your Gateway for wireless
access, including Wireless Enable/Disable, Mode, ESSID, Beacon
Interval, RTS Threshold, Preamble Type, Distribution System, and
so on.
Sec urit y Setting : Allows you t o conf igure your Gatewa y for secur ity
issues.
Status: Allows you to find out your Gateway’s AP Radio statistics
and wireless devices of which the AP (Ac cess Point) is aware.
You can easily toggle between the above three parts on the Wireless
page.
On the Radio Sett ing s page, Wire les s Distribution System as defined
by the IEEE 802.11 standard has been made av ailable on the
Company AP Router now. Hence, it is possible to wirelessly connect
Access Points using up to 8 MAC Addresses of PC cards, so that
you can extend a wired infrastructure to locations where cabling is
not available. Thus those user s can roam or st ay connected to the
availab le network resourc es.
What do you want to do?
Set the Wireless R adio Parameters
Set the Wirele ss Security Parameters
Review Wireless Status
Disable Wireless
4.4.1. T o Set th e Wireless Radio Parameters:
4.4.1.1. On the Wireless page, select Radio Settings.
The Radio Setti ngs pag e appears, seen in FIGUR E 4-7:
20
Page 21

FIGURE 4-7: Wireless – Radio Settings Page
4.4.1.2. Click Enable next to Wireless.
4.4.1.3. Optional. Review the firmware version number and date
information that you are currently using.
4.4.1.4. Enter the following basic radio parameters:
Paramet
Description
er
Mode
ESSID
Selects the Wirel ess Mode that your
Company AP Router support s from th e
drop-down list.
A vailable options ar e 802.11B, 802.11G, and
MIXED which supports both 8 02.11B and
802.11G.
Type the uniq u e identi fier fo r th e Exte nde d
Service S et which is shared b y client st ati ons
in an infrastructur e asso ci ation, such as
WLAN-test.
21
Page 22
It is case-sensitive and cannot exceed 32
characters.
Channel
Selects one IEEE 802.11G channel for
wirele ss LAN tran smissio ns from th e
drop-down list.
Specifi es the bandwidth which the wireless
radio operates. AP and the cli en t stations t hat
is associated work in one of channels from 1
to 14.
4.4.1.5. Enter the following advanced radio parameters:
Parameter Description
Beacon
Interval
RTS
Threshold
Type the time interval in milliseconds
between beacons bro adc ast by AP
(Access Po i nt) in th e Beacon Interval box,
such as 100.
Type a number in the RTS Threshold box.
Also called Request-to-Send Threshold.
This field specifi es the mini mum size of
data frames above which RTS protocol
is used, ran ging from 256 to 2432. RTS
helps prevent data collision from hidden
nodes.
Fragmentatio
n Threshold
DTIM Interval
Preamble
Type
Distribution
System
Type a number in the Fragmentation
Threshold box.
For efficiency in hig h -traffic situ ations,
large files are spli t into fr agment s. This
field spe cifies the defaul t p acket size, an
even number ranging f ro m 256 to 2346.
Type a number in the DTIM Interval box.
Also called Deli very Tr affic I ndi cati on
Map . Th is fiel d specif i e s t he numb er of
beacon intervals between successive
DTIMs, rangi ng from 1 to 255.
Select either Short Preamble (72 bits) or
Long Preamble (144 bits).
If you want to use Wireless Distr ib utio n
System on your Router, click Enable
next to Distribution System, then type the
dist r i b uted cli ent P C s’ physical
addresses, as described in Step 6.
Otherwi se, cl ick Disable.
22
Page 23
Note :
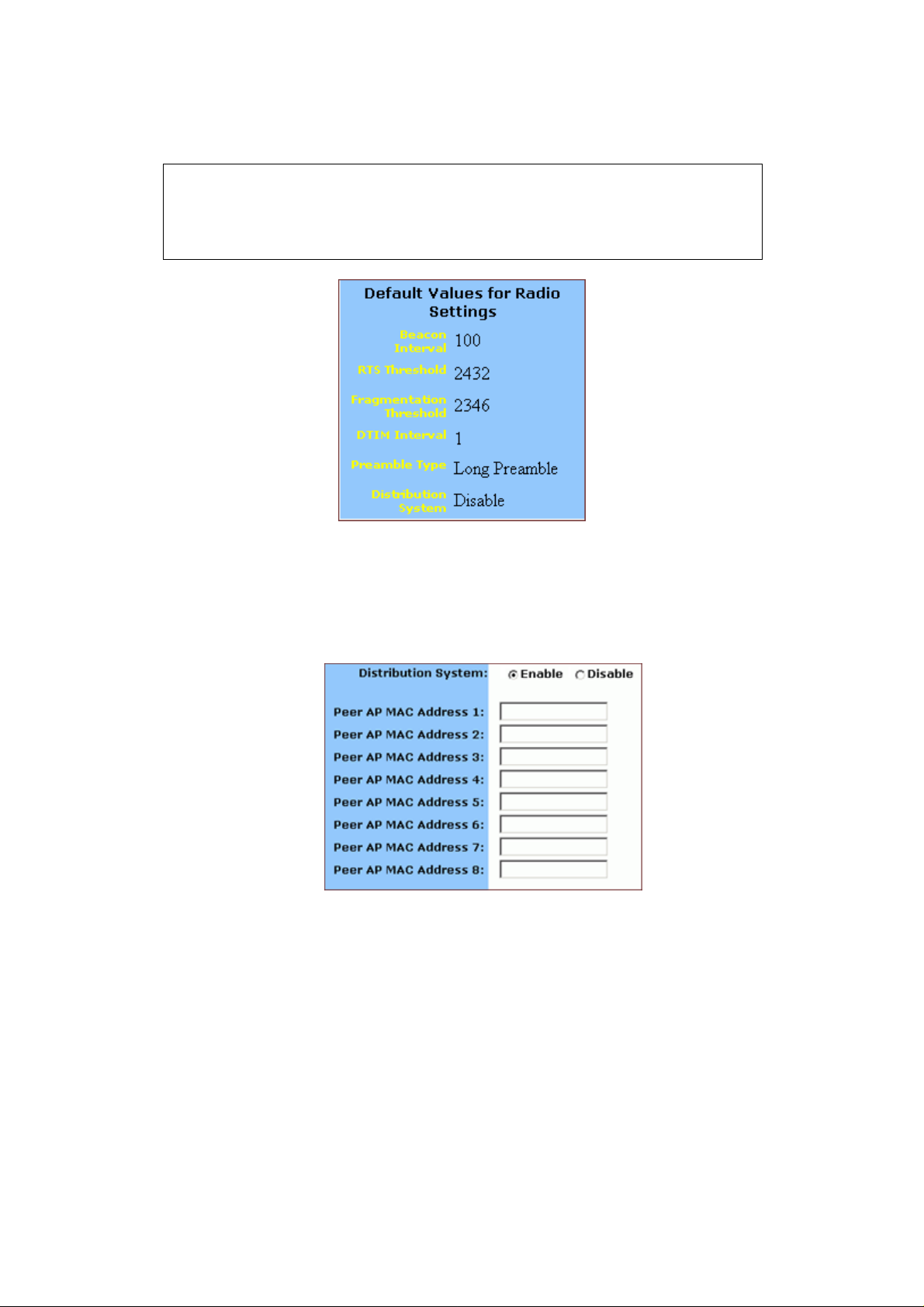
You can see the defaul t values of the above advanced wireless settings on
the right of the page. If you don’t know how to change the settings, please
leave as they are in Figur e 4-8:
FIGURE 4-8: Default Values for Radio Settings
4.4.1.6. Optional. If you have enabled Distribution System, type
the physical addresses of distributed client PCs in a wireless
network in the Peer AP MAC Address 1-8 boxes, seen in
FIGURE 4-9:
FIGURE 4-9: Peer AP MAC Addresses for Distribution
Systems
4.4.1.7. When you have completed editing all the settings, click
Apply, or click Cancel to undo your changes.
4.4.2. To Set Wireless Se curity Parameters:
4.4.2.1. Click Security Settings on the Wireless page.
The Security Settings appears, seen in FIGURE 4-10:
23
Page 24

FIGURE 4-10: Wireless – Security Settings Page
4.4.2.2. Select one of Open System, Shared Key and Both from
the Authenti cation Type drop-down list.
Notes :
Authentication Type indicates an authentication algorithm which can be
supported by the Access Point:
Open System: The simplest of available auth e ntication alg or i thms.
Essentially it is a null algorithm. Any station that requests authent ication
with this algorit hm may become authenticated if Open System is set at the
recipient station.
Shared Key: Allows stations with a specific WEP (Wired Equivalent
Privacy) Keys to be authenticated.
Both: Supports the authentications of either stations who know a shared
key or those wh o do not.
If you want to prevent other stations without specific WEP
(Wired Equivalent Privacy) keys from linking to the AP, select
Enable next to Encryption and then click Set WEP Keys to
specify relevant keys; otherwise, select Disable. For detailed
instructions on how to set the WEP Keys, see below To Set
WEP Keys.
If you want to allow access to the Internet based on user’s MAC
(Media Access Control) address, select On next to Wireless
Access Control and then click Set Access List to specify
relevant MAC addresses; otherwise, click Off. For detailed
instructions on how to specify relevant MAC addresses, see
below To Set Wireless Ac c ess C ontrol
.
24
Page 25

4.4.2.3. Next to Enhanced Security, select either Enable or
Disable. If you choose to enable the enhanced security feature,
go to Step 6.
4.4.2.4. Optional. If you have enabled Enhanced Security, you
can choose to hide your SSID (Service Set Identifier) in Beacon
frame.
4.4.2.5. When you have completed editing all the settings, click
Apply, or click Cancel to undo your changes.
4.4.3. T o Set WEP Keys:
4.4.3.1. On the Security Settings page, enable the Encryption
and click Set WEP Keys.
The Set WEP Keys window appears, seen in FIGURE 4-11:
FIGURE 4-11: Set WEP Keys Window
4.4.3.2. Select either 64 Bit or 128 Bit next to Encryption Level.
25
Page 26

Note :
128 Bit encryption can provide you a more secure encryption algorithm ,
but it will slow down your ne twor k data transmission rates.
4.4.3.3. If you want to generate WEP Keys automatically, do the
following action:
4.4.3.3.1. Select Automatic next to WEP Key Type.
4.4.3.3.2. Type a string of any words in the Passphrase
box, and click Generate.
Four newly generated WEP Keys will display
in the Key 1 – Key 4.
4.4.3.3..3. Optional. Click Clear Keys to reset all the keys
to null.
Note :
Make sure that you write down the passphrase string, so that you can
refer to it if necessary.
4.4.3.4. If you want to enter the key elements manually, do the
following action:
4.4.3.4.1. Select Manually next to WEP Key Type.
4.4.3.4.2. If you select Alphanumeric: 5 characters, type
a string of 5 alphanumeric characters in the Key
1 – Key 4 boxes respectively.
4.4.3.4.3. If you select Hexadecimal: 10 digits (0-9, A-F),
type a string of 10 hexadecimal digits in the Key
1 – Key 4 boxes respectively.
4.4.3.4.4. Optional. Click Clear Keys to reset all the keys
to null.
26
Page 27

4.4.3.5. Select the default encryption key from the Default TX
Key drop-down list, such as Key 1.
4.4.3.6. When you have completed editing all the settings, click
Apply, or click Cancel to undo your changes.
4.4.4. T o Set Wireless Access Control:
4.4.4.1. On the Security Settings page, set the Wireless Access
Control On and click Set Access List.
The Window Control List window appears, s een i n FIGUR E
4-12:
FIGURE 4-12: Wireless Control List window
4.4.4.2. Type the MAC addresses that you want to allow to access
the Internet. You can specify up to 80 MAC addresses in the
list.
4.4.4.3. When you have complete editing all the MAC addresses,
click Submit, or click Cancel to undo your changes.
4.4.4.4. Optional. You can click Refresh to see the most current MAC
addresses in effect.
4.4.5. T o Review W ir eless Status:
4.4.5.1. On the Wireless page, select Status.
The Status page appears with your GateWay’s AP Radio
statistics including Status, Max.Mb/s, IP Addr, MAC Addr, Radio
SSID, Receive data and Transmit data . Seen in FIGURE 4-13:
27
Page 28

FIGURE 4-13: Wireless – Status Page
4.4.5.2. To see the wireless devices of which the AP (Access
Point) is aware, click Display Association Table.
4.4.5.3. Optional. You can click Refresh to see the most current
data.
4.4.6. To Disable Wireless:
4.4.6.1. On the Wireless page, select Radio Settings.
The Radio Setti ngs pag e ap pea rs, s een i n FIGURE 4-7.
If you don’t want the router to support Wireless, select Disable.
Note :
None of the router’ s wireless functions will work unless you enable it.
28
Page 29

4.5 Tools
On the Tools page, you can:
Change the Administrative Password for Your Router
Restore the Fac tory Default Configuration
Reset Gateway
Upgrade the Firmware
Important:
We strongly recommend that you change the administrative password
after the first login.
Restoring the default factory settings will reset all of the router
configurations in every page, so we recommend that you backup the
confi gu r ation dat a from the Gateway to your PC simply using DOS
commands. In addition, you can also restore the factory defaults under the
DOS window . For detailed ins tructions, see To Backup or Restore the
Configuration Data Using DOS Commands.
If you want to res et the hard ware, you need reset the Gateway.
Before upgrading the firmware, you need download the firmware image
file from the Gateway Web site and save it to your root local drive first.
4.5.1. To Change the Administrative Password for Your Router:
4.5.1.1. Click Tools on the navigation bar.
The Tools page appears, seen in FIGURE 4-14:
FIGURE 4-14: Tools Page
29
Page 30

4.5.1.2. Type the Old Pas s word in the box. The defaul t password
is 1234.
4.5.1.3. Type a New
Password in the box.
Note :
Password must be less than 64 characters.
4.5.1.4. Type the new password in the Confirm Password box.
4.5.2. T o Resto re the Factory Default Confi gurati on:
4.5.2.1. On the Tools page, click Restore to Default next to
Restore Factory Defaults.
The Warning dialog box appears, see FIGURE 4-15:
FIGURE 4-15: Warning Dialog Box
4.5.2.2. Click OK.
Important:
Restoring the default factory settings will reset all of the router
configurations in every page, so we recommend that you backup the
configuration data from the Gateway to your PC first using DOS
comman ds. For details, s ee To Backup or Restore the Conf iguration Data
Using DOS Commands.
In addi tion, you c an also restore the factory defaults using DOS
comman ds. For detailed instructions, see To Backup or Restore the
Configuration Data U sing DOS Comm ands.
4.5.3. To Backup or R estore the Configura tion Dat a Using
DOS Command s :
For the backu p of the configurati on dat a fr om the Gateway to you r
PC, Gateway acts as a TFTP server.
30
Page 31

To back up the co nfiguration data, under the DOS window, use the
following command:
tftp –i gateway_Ip_address GET filename
To restore the configuration data, under the DOS window, use the
following command:
tftp –i gateway_Ip_address PUT filename
gateway_Ip_address: The IP address of the Gateway where you
want to back the configuration data.
filename: T he f ile name for backup from the Gate way. It m ust begin
with “nvram” which is not case-sensitive, such as
“nvram__11032003”.
4.5.4. T o Reset Gateway:
If you want to reset the hardware, click Reset next to Reset
Gateway on the Tools page.
4.5.5. To Upgrade the Firmware:
4.5.5.1. Download a firmware image file from the Gateway Web
site and save it to yo ur root loc a l drive.
4.5.5.2. Type the file path and file name in the Upgrade Firmware
box, or click Browse to launch a Choose file dialog box, seen in
31
Page 32

FIGURE 4-15:
FIGURE 4-15: Choose File Dialog Box for Upgrading
Firmware
4.5.5.3. Locate the firmware you have downloaded and click
Open.
4.5.5.4. The Choose file dialog box closes.
4.5.5.5. Click Upgrade Now. The firmware of the device will be
Caution :
The firmware upgrade may t ake about 10 secon ds, please DONOT
power off the unit wh en it is being upgraded .
upgraded.
32
Page 33

4.6 Status
On the Status page, you can vie w the m ost current information about
your Router whic h w i ll be continuously refreshed per 10 seconds ,
such as Host Name, Domain, PPPoE Log i n, LAN/WAN and DDNS
Status. Different conf ig urat io n may bring you to different data,
compare d in FIGURE 3-16 and FIGURE 4 - 17.
Note :
If you w ant to change the configuration, go to the Setup page. For detailed
instructions, see Setup
If you have enabled the PPPoE Login, the Stat us page will display
as illustrated in FIGURE 4-16:
.
FIGURE 4-16: Status Page with PPPoE Login Enabled
If you hav e chosen the Dynamic IP a nd disabled PPPoE Login, t he
Status page wi ll dis play as illustrated in FIGURE 4-17:
33
Page 34

Notes :
If you have chosen the Dynamic IP and disabled PPPoE Login, you can see
the DHCP Release and DHCP Renew buttons:
T o release the most current W AN IP address, click DHCP Release.
To renew the WAP IP address, click DHCP Renew.
FIGURE 4-17: Status Page with PPPoE Login Disabled
Status Detail:
Paramet
er
Host
Name
Domain
Shows the name of the device.
Shows the domain name of the device.
Description
PPPoE
Login
Shows the current statu s of PPP oE Logi n:
Disabled
Enabled: Connected, Connecting or
34
Page 35

Disconnected.
LAN
WAN
DDNS
Shows the current IP Addr ess and Subnet
Mask of the device, as seen by users in your
internal n etwork.
Shows the IP Address, Subnet M ask, Default
Gateway, and DNS of th e router, as seen by
external users on the Internet.
Shows the Dynamic DNS Server and Status.
If you want to change the setti n g , go to th e
Advanced Dynamic DNS page. For details
instructions, see To Config u re a Dynamic
DNS Server.
35
Page 36

4.7 DHCP
On the DHCP page, you can set your NAT/Firewall Gateway as a
DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) server, and DHCP
servers will automatically assign IP addresses to all the client PCs in
Notes
If you want to enable DHCP, make sure that there is not already a D HCP
server on your router.
If you don’t enable DHCP on your router , you will need to manually
configure an IP address for each PC in your network; if you do enable
DHCP, make sure that each PC is configured to receive an IP address
automatically.
your network.
What do you want to do then?
Set Your Router as a DHCP Server
View the Active IP Table
Disable DHCP on Your Router
4.7.1. T o Set Y our Router as a DH CP Server:
4.7.1.1. Make sure that there is not already a DHCP server on
your router.
4.7.1.2. Make sure that each PC in your network is configured to
receive an IP address automatically.
4.7.1.3. Click DHCP on the navigation bar.
The DHCP page appears, seen in FIGURE 4-18:
36
Page 37

FIGURE 4-18: DHCP Page
4.7.1.4. Click Enable next to DHCP Server.
4.7.1.5. Type a IP Pool Starting Address to designate the first IP
address that can be assigned to a PC in your network.
4.7.1.6. Type a IP Pool Ending Address to designate the last IP
address that can be assigned to a PC in your network.
4.7.1.7. When you have completed editing all the settings, click
Apply, or click Cancel to undo your changes.
4.7.2. To Disable DHCP on Your Router:
4.7.2.1. On the DHCP page, click Disabled next to DHCP Server.
4.7.2.2. Click Apply.
4.7.3 To View the Activ e IP Tab le :
If you want to find out the information about PCs that have been
assigned IP addresses by the DHCP server, click Display DHCP
Table.
DHCP Server IP Address, Client H ost Name, IP Address and
MAC Address for each active client PC will be listed out in the
table, seen in FIGURE 4-19:
FIGURE 4-19: DHCP Active IP Tab le
Note :
If you have enabled the DMZ and LAN features, you can also find the
relevant information in the DHCP Active IP Table for DMZ Zone and the
DHCP Active IP Table for LAN.
Optional. Click Refresh to obtain the most current data.
37
Page 38

4.8 Log
On the Log pag e, you can set up Access Log and view log file s that
record the ac cess activity of LAN and WAN client PCs, including
Session Event Log, Block Event Log, Intrusion Event Log and
Wireless Event Log.
What do you want to do?
Set up Access Log on Your Router
View Session Event Log
View Block Event Log
View Intrusion Event Log
View Wireless Event Log
4.8.1. To S et up Access Log on Your Router:
4.8.1.1. Click Log on the navigation bar.
The Log page appears, seen in FIGURE 4-20:
FIGURE 4-20: Log Page
4.8.1.2. Select Enable.
4.8.1.3. Click Apply, or click Cancel to undo your changes.
4.8.2. To Vi e w Sessi on Ev ent Log :
4.8.2.1. Click Session Event Log on the Log page.
38
Page 39

The Session Event Log Table appears, including each
session event entry information like Record Name, Transport type,
Source IP and so on, seen in FIGURE 4-21:
FIGURE 4-21: Sessio n Event Log Table
4.8.2.2. Optional. Clic k Refresh to obtain the most curren t data.
4.8.2.3. Optional. Click Clear to delete all the log informatio n.
4.8.3. To Vi e w Bloc k Ev ent Log :
4.8.3.1. Click Block Event Log on the Log page.
The Block Event Log Table appears, including each block
event entry information like Record Name, Transport type, Source
IP and so on, see n in FIGURE 4-22 :
FIGURE 4-22: Block Even t Log Ta ble
4.8.3.2. Optional. Clic k Refresh to obtain the most curren t data.
4.8.3.3. Optional. Click Clear to delete all the log informatio n.
4.8.4. To Vi e w Intr usi on Ev ent Lo g:
39
Page 40

4.8.4.1. Click Intrusion Event Log on the Log page.
The Intrusion Event Log Table appears, including each
intrusion event entry’s Record Name and Int r us ion Type , seen in
FIGURE 4-23:
FIGURE 4-23: Intr usion Event Log Table
4.8.4.2. Optional. Clic k Refresh to obtain the most curren t data.
4.8.4.3. Optional. Click Clear to delete all the log informatio n.
4.8.5. To View Wir eless Event Log:
4.8.5.1. Click Wireless Event Log on the Log page.
The Session Event Log Table appears, including each
wireless event entry’s Time, Severity and Description, seen in
FIGURE 4-24:
FIGURE 4-24: Wireless Event Log Table
4.8.5.2. Optional. Clic k Refresh to obtain the most curren t data.
4.8.5.3. Optional. Click Clear to delete all the log informatio n.
4.8.6. To Disable Acce ss Lo g on Your Router :
4.8.6.1. On the Log page, click Disabled next to Access Log.
4.8.6.2. Click Apply.
40
Page 41

4.9 Statistics
On the Statistics page, you can vie w the statistics information of LAN,
WAN an d AP ( A ccess Point) Radio ports, inclu di n g Status,
Max.Mb/s, IP Addr and MAC Addr, Rec eiv e data and Transmit data.
You can click Statistics on the nav ig at ion bar, and then the Statistics
page appears, seen in FIGURE 4-25:
FIGURE 4-25: Statistics Page
4.9.1. The Statistics page includes three parts:
4.9.1.1. LAN Stat is tics: Lists out the data on the LA N port .
4.9.1.2. WAN Statistics: Lists out the data on the WAN port .
41
Page 42

4.9.1.3. AP Radio : Lists out the data o n the Access Point’s radio.
Note :
You c an also c lick R e f resh in any p art above t o obtai n the most c urre nt
data.
42
Page 43

5. Advance d Function
In this chapter, you will learn how to use the advance d
administr ati ve functions that th e Company AP Router provides,
including Virtual Server, Filters, IP/URL Block, Special Apps,
DMZ Host, MAC Clone, Dynamic DNS, Proxy DNS and SNMP.
The Web-based Administra tio n Tool provides you some advanced
services on t he Advanced Function naviga t ion bar , such as Filte ri ng
and cloning your MAC addresses.
In most cases, basic functions are Okay. If you want to set the
advance d configuration, you will need to toggle to the Advanced
Function navigation bar first.
5.1. To Toggle between Basic Functions and
Advance d Functions:
5.1.1. To toggle to the Advanced window, click Advanced on the
right side of the Basic window, seen in FIGURE 5-1:
FIGURE 5-1: Advanced Button on the Basic Window
5.1.2. Once you are already in the Advanced window, click Basic
on the right side of t he Advan ced window to return to the Basic
Window, seen in FIGURE 5-2:
FIGURE 5-2: Advanced Button on the Basic Window
43
Page 44

5.2 Virtual Servers
In some situatio ns, you m ight want users on the Interne t to be able
to acce ss servers on your LAN, such as an FTP Server , Teln et
Server or Web Server. Such remote services are accomplished by
creating Virtual Server.
Each virtual server has its own IP address and shares a single public
IP address. It is defined by the Protocol type (TCP, UDP or Both)
and a TCP/UDP/Both port number. Only the enabled virtual servers
Note :
Configuring virtual servers may cause fi lters to be au tomatically cr eated
on the Filters pag e.
can be accessed by remote users over the Internet.
What do you want to do?
Set up a Client PC on the LAN as a Virtual Server
Delete Virtual Servers on the L AN
5.2.1. To Set up a Client PC on the LAN as a Virtual Server:
5.2.1.1. On the Advanced navigation bar, click Virtual Servers.
The Virtual Servers page appears with a list of existing virtual
servers, seen in FIGURE 5-3:
44
Page 45

FIGURE 5-3: Virtual Servers Page
5.2.1.2. If you have enabled DMZ and your Gateway is not
configured to retrieve an IP address automatically, sel ect either
of the following options from the Choose Interface drop-down
list:
(1) External – Interna l : To set up Virt ual Server in your LAN
network.
(2) External – DMZ: To se t up Vi rt ua l Serv ers in your DMZ
network.
5.2.1.3. If you are using the Windows XP operating system, type
a remote service name in the Service box.
Note :
It is only available for client PCs using Windows XP. Because Windows XP
takes an advantage of the UPnP (Universal Plug and Play) feature of the
Company AP Router, it allows c lient PCs that support UPnP to identify
the router automatically.
5.2.1.4. Select a Public IP Address from the drop-down list.
Note :
The IP Address of a DMZ host will not appear in the list.
Type a port number in the Public Port and Private Port boxes,
such as 80 for HTTP. For help on which port to choose, refer
to Well-known Ports on the right of the page, seen in FIGURE
5-4:
FIGURE 5-4: Well-know Ports
45
Page 46

Notes :
Public Port is the TCP/UDP/Both port number used by the server PC on
the WAN. It is also called the external port number because this port
number is visi bl e to the users on the Intern et .
Private Port is the TCP/UDP/Both por t number used by the server PC on
the LAN. The designated P ublic Port wi ll be translated i nto this internal
port number
.
5.2.1.5. Select one of TCP, UDP and Both from the Protocol
drop-down list.
5.2.1.6. Type a local IP address of the server PC on the LAN in
the Private IP Address box.
5.2.1.7. When you have completed editing all the settings, click
Apply, or click Cancel to undo your changes.
5.2.2. To De lete Vir tual Ser vers on the LAN :
5.2.2.1. On the Advanced navigation bar, click Virtual Servers.
A list of existing virtual servers appears.
5.2.2.2. For any virtual server you want to delete, select 0.0.0.0
from the Public IP Address drop- down list.
5.2.2.3. Click Apply.
46
Page 47

5.3 Filters
On the Filters page, you can set up f ilters that can selectively a l lo w
traffic to pass in and out of your net work. The Company AP Ro uter
comes wit h 9 factory default filters for you.
In addition to 9 def ault filters, some f il t e r s may be cre ated
automatically to allow Virtual Servers or Special Applications to
function.
We strong ly rec ommend that yo u choose an empty row when you
want to set up new f i lters, because overwriting or de let i ng these
filters may cause some services to be disabled, for example, your
client PCs m ay NOT be able to access the Internet.
Note – If you have overwritten or deleted the factory default filters,
you can retrieve them at a later time using the Restore Factory
Defaults function on the Tools page. For detailed instructions, see To
Restore the Factory Default Configuration.
What do you want to do?
Set up a Port Filter ing or Raw IP Filter
Delete a Port Filtering o r Raw IP Fi lter
5.3.1. To Set up a Port Filter ing or Ra w IP Fi lter:
5.3.1.1. On the Advanced navigation bar, click Filters.
The Filters page appears, seen in FIGURE 5-5:
47
Page 48

FIGURE 5-5: Filters Page
5.3.1.2. Select an option from the Filtering Page drop-down list:
1~12, 13~24, 25~36.
5.3.1.3. If you select Port Filtering from the Filtering Layer
drop-down list, do the following action:
5.3.1.3.1. Select a traffic direction from the
drop-down list: Inbound, Outbound and
Both.
5.3.1.3.2. Type the start port number and end port
number that you want t o allow in the Private
Port Range boxe s.
5.3.1.3.3 . Sele c t a p rotocol type from the drop- down
list: TCP, UDP and Both.
5.3.1.4. If you select Raw IP from the Filtering Layer drop-down
list, do the following action:
48
Page 49

5.3.1.4.1. Type an IP Protocol Number in the Proto
Note - It ranges from 0 to 255, but can not be 6 (TCP)
Num box.
or 17 (UDP); otherwise, this port filt er will not work.
5.3.1.4.2. Select a traffic direction from the
dr op-dow n list : Inbound Outbound and
Both.
5.3.1.4.3. Select an option from the Protocol
dr op-dow n list : TCP, UDP and Both.
5.3.1.5. Optional. Select Enable or Disable for the following
additional f i ltering options:
Paramet
er
NAT
Firewall
Remote
Manage
ment
IPSec
Pass
Through
PPTP
Pass
Through
Intrusion
Detect
Description
Allows you to set up NAT (Network Access
Translation).
Allows you to protect your network with a
firewall.
Allows you to access your router’s
Web-based A dm i nistration Tool through your
WAN connection.
Allows you to use IP Security Pass Through.
Allows yo u to use PP TP (Point-to-Poin t
Tunneling Protocol), used to enable VPN
sessions.
Allows you to detect and record intrusion
attempts into your network.
5.3.1.6. When you have completed editing all the settings, click
Apply, or click Cancel to undo your changes.
49
Page 50

5.3.2. To De let e Filt ers:
You can delete any existing Port Filtering or Raw IP filer, but make
sure that yo u are deleting an unwanted one, otherwise delet ing the
filters associated with Virtual Servers or Special Applications may
cause to services to collapse down.
5.3.2.1 . To De lete a Por t Filt ering Filte r:
5.3.2.1.1. On the Filters page, for any Raw IP filter you want to
delete, type 0 in the Private Port Rang e boxes.
5.3.2.1.2. Click A pp ly.
5.3.2.2 . To De lete a Ra w IP Filter :
5.3.2.2.1. On the Filters page, for any Raw IP filter you want to
delete, ty pe 0 in the Pr ot o Num box.
5.3.2.2.2. Click Apply.
50
Page 51

5.4 IP/URL Block
On the IP/URL Block pag e, you can create filters t hat c an selectively
block users from specific IP addresses and domain names to pass in
and out of your ne t work. The Comp any AP Router provides t wo
ways of blocki ng users:
IP Block: Allows you to block a single IP address or a range of IP
addresses.
URL Block: Allows you to block up to 36 domain names.
Note – This IP/URL Block feature will block in both directions from
specified IP addresses or domain names.
What do you want to do?
Block a Single IP Address
Block a Range of IP Address
Block a Specific Domain Name
Delete a Specific or All IP Blocks
Delete a Specific or All URL Blocks
5.4.1. T o Block a Single IP Address:
Do either of the following:
5.4.1.1. Click IP/URL Block on the Advanced navigation bar.
5.4.1.2. If you are on the URL Block page, select IP Block on the
upper of the page.
The IP Block page appears, seen in FIGURE 5-6:
FIGURE 5-6: IP Block Page
51
Page 52

5.4.1.3. In Line 1 – Line 6, type the same IP addresses in both IP
Block Starting Address and IP Block Ending Address boxes
respectively.
5.4.1.4. Optional. You can click Clear All to conveniently delete
all the existing IP addresses and then do Step 2.
5.4.1.5. When you have completed editing all the IP addresses
you want to block, click Apply, or click Cancel to undo your
changes.
5.4.2. T o Block a Range of IP Address:
5.4.2.1. Do either of the following:
Click IP/URL Block on the Adv anced navigation bar.
If you are on the URL Block page, select IP Block on the
upper of the page.
The IP Block page appears, seen in FIGURE 4-6.
5.4.2.2. In Line 1 – Line 6, type the different IP addresses in both
IP Block Starting Address and IP Block Ending Address boxes
respectively.
5.4.2.3. Optional. You can click Clear All to conveniently delete
all the existing IP addresses and then do Step 2.
5.4.2.4. When you have completed editing all the IP addresses
you want to block, click Apply, or click Cancel to undo your
changes.
5.4.3. To Block a Specific Domain Nam e:
5.4.3.1. Click IP/URL Block on the advanced navigation bar.
The IP Block page appears, seen in FIGURE 5-6.
5.4.3.2. Select URL Block on the IP Block page.
The URL Block page appears, seen in FIGURE 5-7:
52
Page 53

FIGURE 5-7: URL Block Page
5.4.3.3. In Line 1 – Line 36, type the URLs you want to block.
5.4.3.4. Optional. You can click Clear All to conveniently delete
all the existing URLs and then do Step 2.
5.4.3.5. When you have completed editing all the domain names
you want to block, click Apply, or click Cancel to undo your
changes.
5.4.4. To De lete a Specific or All I P Blocks:
5.4.4.1. On the IP Block page, do either of the following:
For any IP block yo u wa nt t o delete , type 0.0.0.0 in both IP Block
Starting Address and IP Block Ending Address boxes respectively.
If you want to delete all IP blocks, click Clear All.
5.4.4.2. Click Apply.
5.4.5. T o Delete a Specific or A ll URL Blocks:
5.4.5.1. On the URL Block page, do either of the following:
For any domain name block you want to delete, clear out the URL in
the box.
If you want to delete all URL blocks, click Clear All.
5.4.5.2. Click Apply.
53
Page 54

5.5 Special Apps
On the Special Ap ps page, you can authorize certain ports to
commun ic ate with PCs outside your network . It may be necessary
for multi-sessi o n appli cations, such as online games and voice
conferencing.
There are two wa ys of set up new sp ecial applicatio ns on your
router:
Popular Application Copy: Allows you to select one of frequently
used app lications from the Pop ular Applications d rop-down list and
copy it to your Spec ial Applicatio n Table. Available opt ions are AIM,
Diablo II (1), Diablo II (2), StarCraft, StarCraft III, ICUII, FTP,
CUseeMe, MSN Messenger and Real Play er.
Man ua l Conf igur atio n: If the a ppl icat ion you wa nt to conf igur e is not
in the Popular Applications list, you can configure its settings
manually.
Before conf ig uri ng a new special application, wo uld you please
check the list of those popular applic ations first? If it is alre ady in
the list, we recommend that yo u use the Popular Appl ic ation Copy
unless you know exactly which settings to choose.
Notes
Configuring special applications may cause filters to be automat ically
created on the Filters pa ge.
The Com pany AP Router provides two factory default special appl icat ions
for FTP and N e tMeeting, if you overwrite them or any other existing
application, they will not work.
What do you want to do?
Copy a Popular Application to a Spec ific Line
Configure a Special Application Manually
Delete Special Applications
5.5.1. To Cop y a Popular App lication to a Specific Line:
5.5.1.1. On the Advanced navigation bar, click Special Apps.
The Popular Applications list appears on the Special Apps
page, seen in FIGURE 5-8:
54
Page 55

FIGURE 5-8: Popu la r Applications List
5.5.1.2. Select an option from the Popular Applications drop-down
list, including AIM, Diablo II (1), Diablo II (2), StarCraft, StarCraft III,
ICUII, FTP, CUseeMe, MSN Mess enger and Real Pla yer.
Note :
Make sure the specif ied ID presents an empty line unless you want to
overwrite an exist i ng application.
Select a specific line number from the ID drop-down list.
5.5.1.3. Click Copy to.
5.5.1.4. The selected applicatio n’s conf igurat ion is added to
your Special Applications Table on the upper of the page.
5.5.1.5. When you have completed editing all the settings, click
Apply, or click Cancel to undo your changes.
5.5.2. To Configure a Spec ial Application Ma nually:
5.5.2.1. On the Advanced navigation bar, click Special Apps.
5.5.2.2. The Special Apps page appears, seen in FIGURE 5-9:
55
Page 56

FIGURE 5-9: Special Apps Page
5.5.2.3. Select a line corresponding to a specific ID.
Note :
Make sure you have selected an empty line unless you want to overwrite
an existing application.
Enter the following configuration information:
Paramet
Description
er
Protocol
Trigger
Port
Range
Maximu
m
Activity
Interval
Specifies the comm unication protocol us ed
by the appl i c at ion.
A vailable options ar e TCP, UDP and Both.
Range of ports used for outg oing traffic. It
will trigger the Gateway to accept certain
incoming request s.
Maximum num ber of mil iseco nds aft er the
port trigger function, within which incoming
requests will be accepted.
Session
Chaining
Chaining
Allows you to select either Enable or Disable.
Specifi es wheth er dyn ami c session s can be
chained, allowing mu l ti-session trig gering.
Allows you to select Enable or Disable only
56
Page 57

on UDP
Address
Replace
when Session Chaining is enabled.
Specifi es wheth er th e session ch aini ng is
allowed on UDP.
Allows you to select Enable or Disable only
when Chaining on UDP is enabled.
ment
Specifi es wheth er binary ad dres s
replacement should be performed.
Address
Translati
Allows you to select TCP or UDP only when
Address Replacement is enabled.
on Type
Specifi es wheth er addr e ss translati o n is
performed on TCP or U DP packets.
Two
Allows you to select either Enable or Disable.
Way
Only
Specifies that a new ses si on is allowed to be
initiated from the same remote host.
5.5.2.4. When you have completed editing all the settings, click
Apply, or click Cancel to undo your changes.
5.5.3. To De let e Speci a l Appli c atio n s:
5.5.3.1. On the Special Apps page, for any application you want
to delete, type 0 – 0 in the Trigge r Port R an g e box.
5.5.3.2. Click Apply.
57
Page 58

5.6 DMZ Host
On the DMZ Host page, you can expos e one or more client PCs in
your network to the Internet. It is often used for o nl ine games that
require uns tricted two- way com municatio ns.
The total number of DMZ (Demil itarized Zone) ho sts you can hav e
depends on how many Global Addresses you have configured on
the Gl ob al Address page. Fo r example, if you have defined 5 Global
Addresses (including the defa ul t IP), you are limited to 5 DMZ hosts.
Since the maximum number of Globa l Addresses is 8, the total
number of DMZ host s you can conf ig ure is als o 8.
Caution :
Once a PC in your network is designated as DMZ host, it will not have any
firewall protection.
What do you want to do?
Designate a PC in Your Net work as a DMZ Hos t
Delete DMZ Hosts
5.6.1. T o Designate a PC in Your Network as a DMZ Host:
5.6.1.1. On the Advanced navigation bar, click DMZ Host.
The DMZ Host page appears, seen in FIGURE 5-10:
FIGURE 5-10: DMZ Host Page
5.6.1.2. Select a Public IP Address from the drop-down list.
5.6.1.3. Type the IP address of a PC in your network that you
want to designate as a DMZ Host in the Private IP Address box.
58
Page 59

5.6.1.4. When you have completed editing all the settings, click
Apply, or click Cancel to undo your changes.
5.6.2. To De lete D MZ Hos ts:
5.6.2.1. On the DMZ Host page, for any DMZ host you want to
delete, sel e c t 0.0.0.0 from the Public IP Address drop-down list.
5.6.2.2. Click Apply.
59
Page 60

5.7 MA C Clone
If your ISP restricts services at a PC level, using MAC Clone, you
can copy a PC MAC (Media Ac cess C ontrol) address to the ro uter.
Then what story will begin? The router will appear as a single PC,
and multiple PCs i n your network wil l ac cess the Internet via this
“Single PC”.
5.7.1. To Clone the MAC Address:
5.7.1.1. On the Advanced navigation bar, click MAC Clone.
The MAC Clone page appe ar s with the current WAN port
address and the factory default MAC address for your
convenience, seen in FIGURE 5-11:
Note :
You may need to use the Ethernet MAC address of the NIC (Network
Interface Card) that your PC is registered with your ISP.
FIGURE 5-11: MAC Clone Page
5.7.1.2. Click Mac Clone, or click Restore to retrieve the default
settings.
60
Page 61

5.8 Dynamic DNS
On the Dynamic DNS page, you can tie up your domain name to a
dynamic DNS pr ovider. These providers allo w you to associate a
static hostname with a dynamic IP addres s, then you can connect to
the Internet with a dynamic IP address and use applications t hat
require a static IP address.
The Company AP Router supports three dynamic DNS providers :
DynDNS.org
no-IP.com
no-IP.com
What do you want to do?
Configure a Dynamic DNS Server
Disable a Dynamic D N S Serv er
5.8.1. T o Confi gure a D ynamic DNS Server:
5.8.1.1. On the Advanced navigation bar, click Dynamic DNS.
The Dynamic Server page appears, seen in FIGURE 5-12:
FIGURE 5-12: Dynamic DNS page
5.8.1.2. Select Enable next to Dynamic DNS.
5.8.1.3. Select one of DynDNS.org , no-IP.com, no-IP.com from
the Dynamic DNS Provider drop-down list.
5.8.1.4. Type your Domain Name in the box.
5.8.1.5. Type your Account or E-mail in the box.
5.8.1.6. Type your Password or Key in the box.
61
Page 62

5.8.1.7. When you have completed editing all the settings, click
Apply, or click Cance l t o undo you r changes.
5.8.2. To Disable a Dynam ic DNS Ser v er :
5.8.2.1. On the Dynamic DNS page, select Disable next to
Dynamic DNS.
5.8.2.2. Click Apply.
62
Page 63

5.9 Proxy DNS
On the Proxy DNS page, you can map a domain name to a server IP
address. Acting as a DNS se rver for internal and DMZ networks, it
allows you to connect to local machines in your network without
using an extern al DNS server. It si mp lifies th e configuration and
management of your network.
What do you want to do?
Configure a Proxy D NS Server
Delete a Specific or All Proxy DNS Servers
Disable the Proxy DNS on Your Router
5.9.1. To Configure a Proxy DNS Server:
5.9.1.1. On the Advanced navigation bar, click Proxy DNS.
The Proxy DNS page appears, seen in FIGURE 5-13:
FIGURE 5-13: Proxy DNS Page
5.9.1.2. Select Enable next to Proxy DNS.
5.9.1.3. Type a nam e f or one PC in your network that you want
to use as a Proxy DNS server in the Domain Name box.
63
Page 64

5.9.1.4. Type the IP address for the PC in the Virtual IP Address
box.
5.9.1.5. Optional. If you want to delete all the existing Proxy DNS
servers first, click Clear All and do Step 3 and Step 4.
5.9.1.6. When you have completed editing all the settings, click
Apply, or click Cancel to undo your changes.
5.9.2. To Delete a Specific or A ll Proxy DNS S e rvers:
5.9.2.1. On the Proxy DNS page, for any Proxy DNS server you
want to delete, type 0.0.0.0 in the Virtual IP Address box.
5.9.2.2. If you want to delete all the existing Proxy DNS servers,
click Clear All.
5.9.2.3. Click Apply.
5.9.3. To Disable the Proxy DNS on Your Router:
5.9.3.1. On the Proxy DNS page, for any Proxy DNS server you
want to delete, type 0.0.0.0 in the Virtual IP Address box.
5.9.3.2. If you want to delete all the existing Proxy DNS servers,
click Clear All.
5.9.3.3. Click Apply.
64
Page 65

5.10 SNMP
The Simple Netw ork Managemen t Prot ocol (S NM P ) is an a ppl ication
layer protocol that facil it ies the exchange of managem ent
information between network devices. It is part of TCP/IP
(Transmission Control protocol/Internet Protocol) suite and e nables
you to control and monitor the network in a simple way.
On the SNMP page, you can edit the basic Agent information and
also configure up to 6 SNM P trap receiver’s IP Addr e sses. When a
trap condition occurs, your router will send an SNMP trap message
to any NMS (Network Management System) specified as trap
receivers, for example, when power supply errors occur.
Notes :
NMS (Network Management System) is an SNMP management
application together with the computer it runs on.
Currently the Company AP Router supports SNMPv1 (SNMP version 1)
and SNMPv2 (SNMP version 2) which have a number of features in
common except for some enhancements.
An d mor e over, y ou can specify differ ent community names for
authentic at ing access to the management informatio n, whic h
functio n as embedded pass wo rds:
Read: Gives you READ access to all the management information,
but does not allo w WRITE access.
Write: Gives you both READ and WRITE access to all the
Note :
The community name definitions on your NMS must match at least one of
the above two community name definitions.
managemen t i nformation.
What do you want to do?
Configure Agent Information, SNMP Trap Host IP Addresses and
Community Names on Your Router
Delete an Existing SNMP Trap Receiver
Delete SNMP Community Names
65
Page 66

5.10.1. To Confi gure Agent Infor m ati on , SNM P Trap Host IP
Addres se s and Com mu nity Names on Your Router:
5.10.1.1. On the Advanced navigation bar, click SNMP.
The SNMP page appears, seen in FIGURE 5-14:
FIG URE 5-14: SNMP Page
Enter the following Agent informa tion :
Paramet
er
Name
Contact
Location
Specifi es an admin istrativel y-as si gne d name
for this managed node, like SOHO Rou t er .
It is a string of the maximum 31 alphanumeric
characters.
Specifies the contact person of this managed
node, plus phone number , Email address, etc.
It is a string of the maximum of 255
alphanum eric characters.
Specifies the phy sical lo cation of thi s
managed node, for example, city, address
and specific office location.
Description
It is a string of the maximum of 255
alphanum eric characters.
66
Page 67

5.10.1.2. To send SNMP trap messages to any NMS, type up to 6
trap receiver IP addresses in the SNMP Trap Host IP Address
1 – SNMP Trap Host IP Address 6 boxes.
5.10.1.3. To secure SNMP with community names, do the
following action:
5.10.1.3.1. Type a string in the SNMP Community box,
like Public.
5.10.1.3.2. Select an option from the SNMP Access
drop-down list, for example, Read.
Note :
Usually, we define a string of “Public” for Read acces s and “Private” for
Read-Write access.
5.10.1.3.3. Click Add. If you want to add more community
names, do Step 4.1 – Step 4.3 again.
5.10.1.4. When you have completed editing all the settings, click
Apply, or click Cancel to undo your changes.
5.10.2. To Delete an Existing SNMP Trap Receiver:
5.10.2.1. On the SNMP page, for any SNMP trap receiver that you
want to delete, enter 0.0.0.0 in the SNMP Trap Host IP Address
box.
5.10.2.2. Click Apply.
5.10.3. To Delete SNMP Community Names:
5.10.3.1. On the SNMP page, for any SNMP community name
that you want to delete, click Delete in the corresponding row.
5.10.3.2. Click Apply.
67
Page 68

5.11 Static Routing
The Static Routing is used to configure static routes to remote networks
manually, where the route is predefined and is not supervised by the
Routing Information Protocol (RIP). It can explicitly reduce the network
traffic and speed the Internet connects for a small network.
However, it may fall into a certain disadvantage. When a static router
involves more than one Hop, if the connection to the next hop goes
down, the router cannot be aware of the invalid path and continues to
route traffic on this hop.
On the Static Routing page, you can add up to 20 static routes by
indicating:
Destination LAN IP address and Subnet Mask
Remote gateway
Hop
Router interface through which to forward the packets to the destination.
Note :
If the network topology changes, you m ay ha ve to make chang e s to the static
routing tables for relevant static routes.
What do you want to do?
Add a New Static Route
Delete a Static Route
Page 69

5.11.1. To Add a New Stati c Rou te:
5.11.1.1. On the Advanced navigation bar, click Routing.
The Stat ic Rout ing page appea rs, s een in F I G U RE 5-1 5:
FIGURE 5-15: Static Routing Page
5.11.1.2. Enter the following static route information:
Paramet
er
Destinati
on LAN
IP
Subnet
Mask
Gateway
Hop
Description
Speci f ies the networ k a d dress of the remote
LAN segm ent. For sta ndard cla s s "C" LA Ns,
the network address is the first 3 fields of this
Destination LAN IP, t h e 4t h f ield c an be left at
0.
Speci f ies the Sub net Mask us e d on t he
remote LAN segment. For cla s s " C" network s,
the standard Network Mask is 255.255.255.0.
Speci f ies the I P Addres s o f t he router on t h e
local LAN segment to which this device is
attached.
Note that it is NOT the router on the remote
LAN se g ment.
Speci f ies the num ber of routers that must b e
traversed to rea c h t he remo te LAN segment.
Valid values are 1 to 16.
Interface
Specifies the interface through which the
router go e s t o the next ho p or a p art i cul ar
net wo r k. Available options are WAN, LAN and
DMZ.
Page 70

5.11.1.3. Click <<Add.
The new static route appears in the static routing list.
5.11.2. To Delete a Static Rou te:
5.11.2.1. On the Static Routing page, for any static route that you
want to delete, review the relevant information, seen in FIGURE 5 –
15.
5.11.2.2. Click Delete.
Page 71

6. Glossary
IEEE 802.11 Standard
The IEEE 802.11 Wireless LAN standards su bco mmitt ee, w hi ch is formulati ng
a standard for the industry.
A cces s point
An Internet working device that seamlessly connects wired and wireless networks together.
Ad hoc
An ad hoc wireless LAN is a group of computers, each with a WLAN adapter, connected as
an independent wireless LAN. Ad hoc wireless LAN is applicable at a departmental scale for a
branch or SOHO o p eration.
BSSID
A specific ad hoc LAN is called a Basic Service Set (BSS). Computers in a BSS must be
configured with the same BSSID.
DHCP
Dynamic Hos t Co nfiguration Prot ocol - a method in w hich IP addres ses are assigne d by a
serv er dynamically to clients on the network. DHCP is used for dynamic IP ad dressing a n d
requires a dedi cated DHCP ser ver on the network.
DSSS
Direct Sequence Spread Spectrum. This is the method the wireless adapters use to transmit
data over the frequency spectrum. An alternative method is frequency hopping. Direct
sequence spreads the data over one frequency range (channel) while frequency hopping
jumps from one narrow frequency band to another many times per second.
ESSID
An infrastructure configuration could also support roaming capability for mobile workers. More
than one BSS can be configured as an extended servi ce set (ESS). Users wit hin an ESS can
roam freely between BSSs while served as a continuous connection to the network wireless
stations and access points wit hi n an ESS must be configured with the same ESSID and the
same radio channel.
Ethernet
Ethernet is a 10/10 0Mbps netw ork that r u ns over dedi cat ed home /office wiring.
Users mu s t be wired to the n et work at all times to g ain access.
Gateway
A gateway is a hardware and software device that connects two dissimilar systems, such as a
LAN and a mai nfra me. I n Intern et terminol ogy, a gateway i s another name for a router.
Generally a gateway is used as a funnel for all traffic to the Internet.
Page 72

IEEE
Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers
Infrastructure
An integrated wireless an d w ired LAN is ca l led an infrastr u cture co nfiguration. I nf r a s tructure is
applicable on an enterprise scale for wireless access to a central database, or wireless
applicat ion for mobi le workers.
ISM Band
The FCC and their c ount erparts outs ide of the U.S . have s et asi de bandwidth for unlicensed
use in the so-called I SM (Indus trial, Scient ific and Medical) band. Spectrum in the vicinity of
2.4 GHz, i n par ti cu l ar , is being made available worl dwide. This presents a truly r evol ut ionary
opportunity to place convenient high speed wireless capabilities in the hands of users around
the globe.
LAN
Local A rea Networ k. A LA N is a group of computers, e ach eq uipped with the ap propriate
network adapter connected by cable/air that share applications, data, and peripherals. All
connections are made via cable or wireless media, but a LAN does not use telephone
serv ices. I t typically spa ns a s ingle buil ding or campus .
Network
A network is a system of computers that is connected. Data, .les, and messages can be
transmitted over this networ k. Net w orks may be l o c al or wide area netw orks.
Protocol
A protocol is a standardized set of r ules that sp ecify how a communication i s to take place,
including the format, timing, sequencing and/ or error checking.
SSID
Serv ice Set Identifi er . A networ k ID unique to a network. Only clients and ac c es s points that
shar e the same SSID are able to c ommu nicate with each other. This s tring is case- sensitive.
SNMP
Simple Network Management Protocol is the network management protocol of TCP/IP. In
SNMP , agents-w hich can be har dware as we ll as sof twar e-moni tor th e activ ity i n the various
devices on the network and report to the n etwor k c onso l e workstation. C ontro l information
about each d evice is mai ntained in a s truct ure known as a manag ement information block.
Static IP addressing
A method of as signing I P ad dresses to clients on the network. In netw orks with s tatic IP
address, the network administrator manually assigns an IP address to each computer. Once a
stat ic IP address is ass igned, a compu ter uses the same IP address every ti me it r eb oots and
logs on to the network, unless it is manually changed.
TCP/IP
Tran smission Control P rotocol / Internet Protocol. TCP/IP is the pr otoco l s uite developed by
Page 73

the Advanced Research Projects Agency (ARPA). TCP governs how a packet is sequenced
for transmission the network. The term “TCP/IP” is often used generically to refer to the entire
suite of relate d proto c ols.
Transmit / Receive
The wireless thr oughput in bytes per sec ond (B ps) av erag ed over two seconds.
WAN
Wide Area Network. A WAN consists of multiple LANs that are tied together via telephone
serv ices and / or fiber optic cabling. WANs may span a city , a s tate, a co untry, or even the
world.
Page 74

www.x-micro.com
 Loading...
Loading...