Winbond Electronics W25P022AF-6, W25P022AD-7, W25P022AD-6, W25P022AF-7 Datasheet
W25P022A
LBO
CE3
CE3
ZZ
64K × 32 BURST PIPELINED HIGH-SPEED
CMOS STATIC RAM
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The W25P022A is a high-speed, low-power, synchronous-burst pipelined CMOS static RAM
organized as 65,536 × 32 bits that operates on a single 3.3-volt power supply. A built-in two-bit burst
address counter supports both Pentium burst mode and linear burst mode. The mode to be
executed is controlled by the
the FT pin. A snooze mode reduces power dissipation.
The W25P022A supports both 2T/2T mode and 2T/1T mode, which can be selected by pin 42. The
default mode is 2T/1T, with pin 42 low. To switch to 2T/2T mode, bias pin 42 to VDDQ. The state of
pin 42 should not be changed after power up. The 2T/2T mode will sustain one cycle of valid data
output in a burst read cycle when the device is deselected by CE2/
1-1-1-1 in a two-bank, back-to-back burst read cycle. On the other hand, the 2T/1T mode disables
data output within one cycle in a burst read cycle when the device is deselected by CE2/
mode, the device supports only 3-1-1-1-2-1-1-1 in a two-bank, back-to-back burst read cycle.
FEATURES
• Synchronous operation
• High-speed access time: 6/7 nS (max.)
• Single +3.3V power supply
• Individual byte write capability
• 3.3V LVTTL compatible I/O
• Clock-controlled and registered input
• Asynchronous output enable
pin. Pipelining or non-pipelining of the data outputs is controlled by
. This mode supports 3-1-1-1-
. In this
• Pipelined/non-pipelined data output capability
• Supports snooze mode (low-power state)
• Internal burst counter supports Intel burst mode
& linear burst mode
• Supports both 2T/2T & 2T/1T mode
• Packaged in 100-pin QFP or TQFP
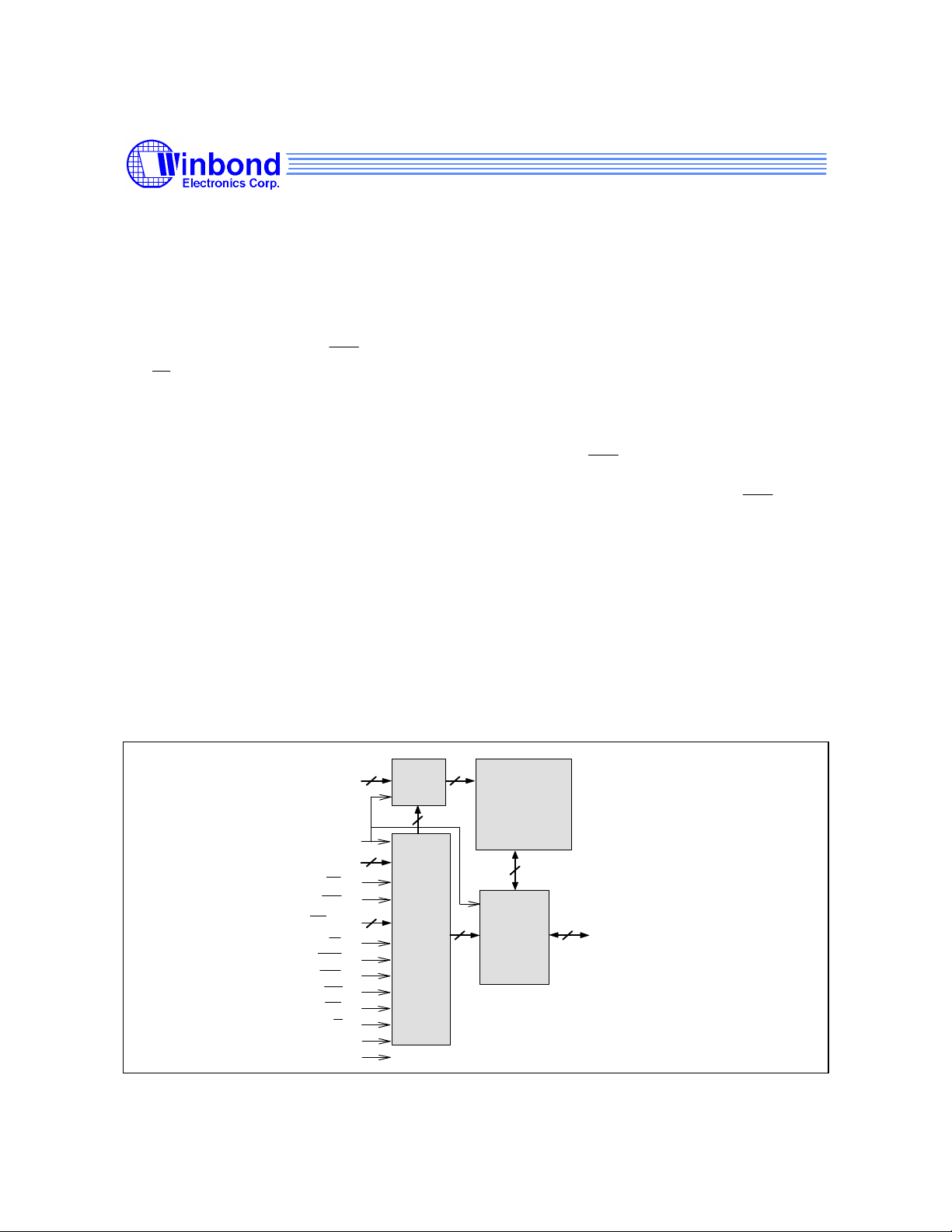
BLOCK DIAGRAM
A(15:0)
CLK
CE(3:1)
GW
BWE
BW(4:1)
ADSC
ADSP
ADV
LBO
INPUT
REGISTER
CONTROL
LOGIC
OE
FT
MS
REGISTE
R
64K X 32
CORE
ARRAY
DATA I/O
REGISTER
I/O(32:1)
Publication Release Date: September 1996
- 1 - Revision A1
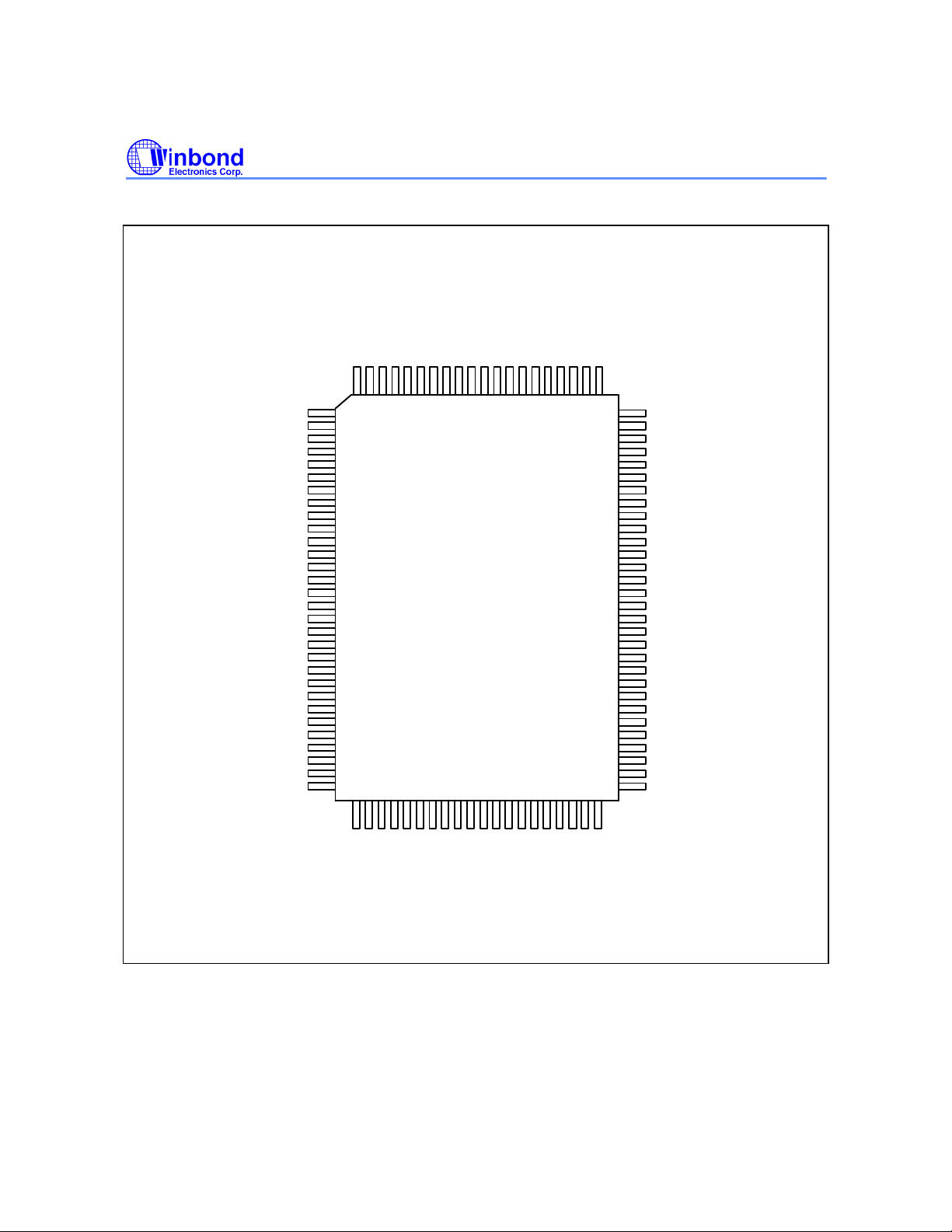
PIN CONFIGURATION
NC
I/O 17
I/O 18
VDDQ
VSSQ
I/O 19
I/O 20
I/O 21
I/O 22
VSSQ
VDDQ
I/O 23
I/O 24
/FT
VDD
NC
VSS
I/O 25
I/O 26
VDDQ
VSSQ
I/O 27
I/O 28
I/O 29
I/O 30
VSSQ
VDDQ
I/O 31
I/O 32
NC
/
/
/
/
/
/
C
C
A6A
1
0
0
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
313233343536373839404142434445464748495
30
B
E
E
W
7
1
2
4
/
B
B
B
C
V
V
W
W
W
3
2
1
C
E
D
S
L
3
D
S
K
100-pin
TQFP MO-136
QFP MO-108
/
G
W
/
/
A
A
B
/
D
D
W
O
S
S
E
E
C
P
/
A
DVA8A
W25P022A
9
818283848586878889909192939495969798991
80
NC
I/O 16
79
78
I/O 15
VDDQ
77
VSSQ
76
75
I/O 14
74
I/O 13
I/O 12
73
72
I/O 11
VSSQ
71
VDDQ
70
69
I/O 10
68
I/O 9
67
VSS
NC
66
VDD
65
ZZ
64
63
I/O 8
I/O 7
62
61
VDDQ
VSSQ
60
I/O 6
59
58
I/O 5
I/O 4
57
56
I/O 3
VSSQ
55
54
VDDQ
I/O 2
53
I/O 1
52
51
0
NC
/
A5A4A3A2A1A0NCNCV
L
B
O
S
S
- 2 -
V
A
A
A
A
A
N
N
D
1
1
CMS
D
0
1
A
1
1
1
C
1
2
3
4
5
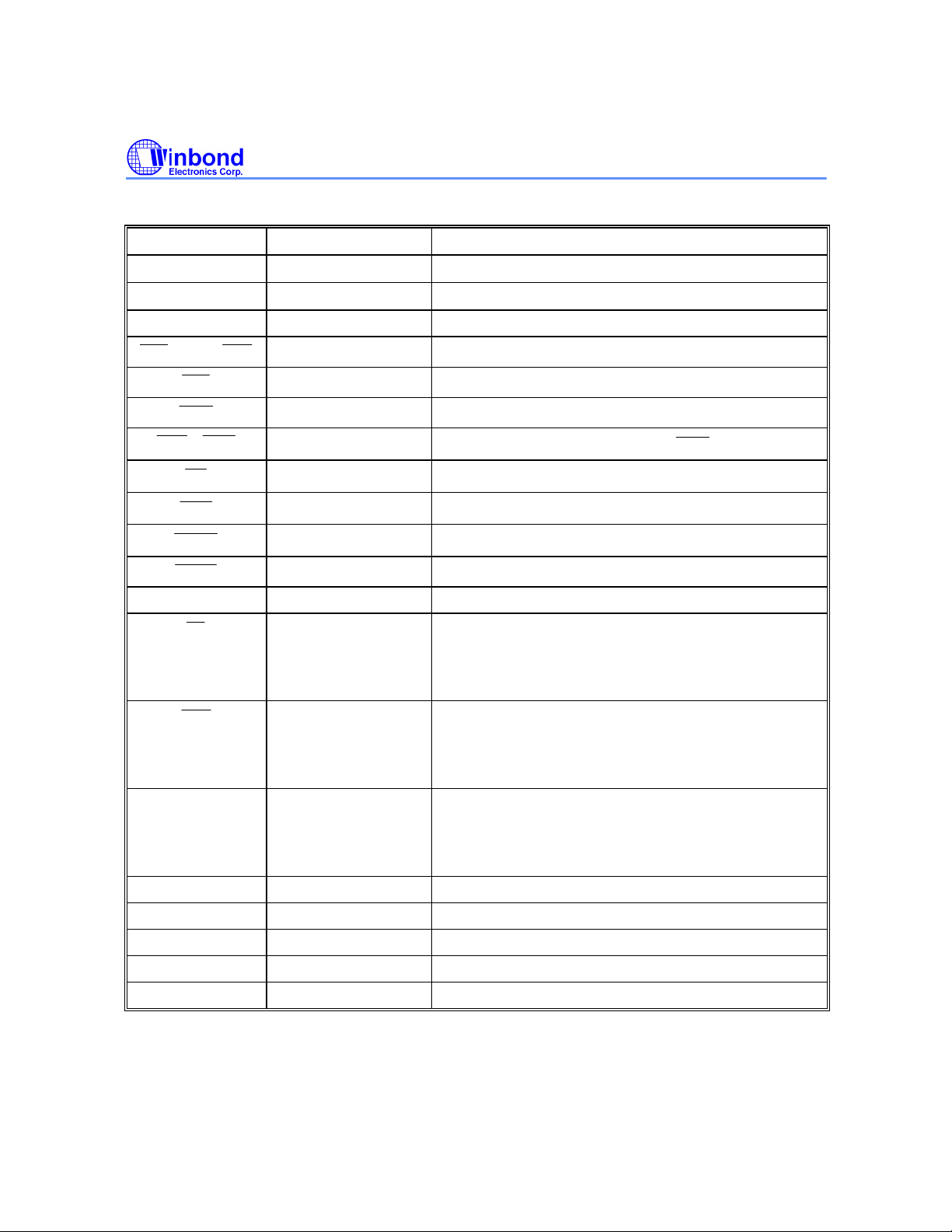
PIN DESCRIPTION
CE1
CE3
GW
BWE
BW1
BW4
BWE
OE
ADV
ADSC
ADSP
FT
LBO
SYMBOL TYPE DESCRIPTION
W25P022A
A0−A15
I/O1−I/O32
CLK Input, Clock Processor Host Bus Clock
, CE2,
−
ZZ Input, Asynchronous Snooze Pin for Low-power State, internally pulled low
Input, Synchronous Host Address
I/O, Synchronous Data Inputs/Outputs
Input, Synchronous Chip Enables
Input, Synchronous Global Write
Input, Synchronous Byte Write Enable from Cache Controller
Input, Synchronous
Input, Asynchronous Output Enable Input
Input, Synchronous Internal Burst Address Counter Advance
Input, Synchronous Address Status from chip set
Input, Synchronous Address Status from CPU
Input, Static Connected to VSSQ: Device operates in flow-through
Input, Static Lower Address Burst Order
Host Bus Byte Enables used with
(non-pipelined) mode.
Connected to VDDQ or unconnected: Device operates
in piplined mode.
Connected to VSSQ: Device operates in linear mode.
Connected to VDDQ or unconnected: Device is in nonlinear mode.
MS Input, Static Mode Select for 2T/2T or 2T/1T
When unconnected or pulled low, device is in 2T/1T
mode; if pulled high (VDDQ), device enters 2T/2T
mode.
VDDQ I/O Power Supply
VSSQ I/O Ground
VDD Power Supply
VSS Ground
NC No Connection
Publication Release Date: September 1996
- 3 - Revision A1
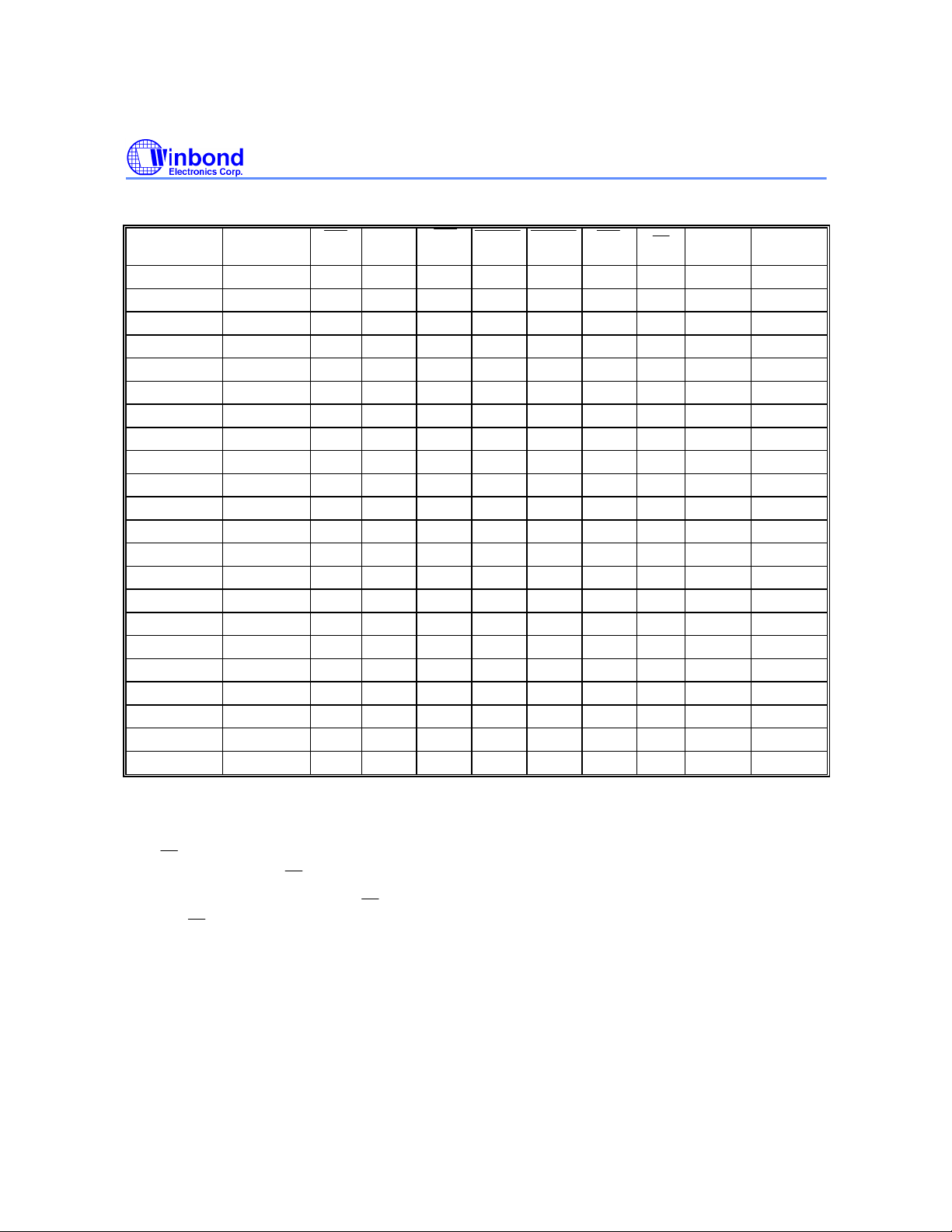
TRUTH TABLE
W25P022A
CYCLE
Unselected No 1 X X X 0 X X Hi-Z X
Unselected No 0 X 1 0 X X X Hi-Z X
Unselected No 0 0 X 0 X X X Hi-Z X
Unselected No 0 X 1 1 0 X X Hi-Z X
Unselected No 0 0 X 1 0 X X Hi-Z X
Begin Read External 0 1 0 0 X X X Hi-Z X
Begin Read External 0 1 0 1 0 X X Hi-Z Read
Continue Read Next X X X 1 1 0 1 Hi-Z Read
Continue Read Next X X X 1 1 0 0 D-Out Read
Continue Read Next 1 X X X 1 0 1 Hi-Z Read
Continue Read Next 1 X X X 1 0 0 D-Out Read
Suspend Read Current X X X 1 1 1 1 Hi-Z Read
Suspend Read Current X X X 1 1 1 0 D-Out Read
Suspend Read Current 1 X X X 1 1 1 Hi-Z Read
Suspend Read Current 1 X X X 1 1 0 D-Out Read
Begin Write Current X X X 1 1 1 X Hi-Z Write
Begin Write Current 1 X X X 1 1 X Hi-Z Write
Begin Write External 0 1 0 1 0 X X Hi-Z Write
Continue Write Next X X X 1 1 0 X Hi-Z Write
Continue Write Next 1 X X X 1 0 X Hi-Z Write
Suspend Write Current X X X 1 1 1 X Hi-Z Write
Suspend Write Current 1 X X X 1 1 X Hi-Z Write
Notes:
1. For a detailed definition of read/write, see the Write Table below.
2. An "X" means don't care, "1" means logic high, and "0" means logic low.
ADDRESS
USED
CE1
CE2
CE3 ADSP ADSC ADV
OE
DATA WRITE*
3. The OE pin enables the data output but is not synchronous with the clock. All signals of the SRAM are sampled synchronous
to the bus clock except for the OE pin.
4. On a write cycle that follows a read cycle, OE must be inactive prior to the start of the write cycle to allow write data to set up
the SRAM. OE must also disable the output buffer prior to the end of a write cycle to ensure the SRAM data hold timings
are met.
- 4 -
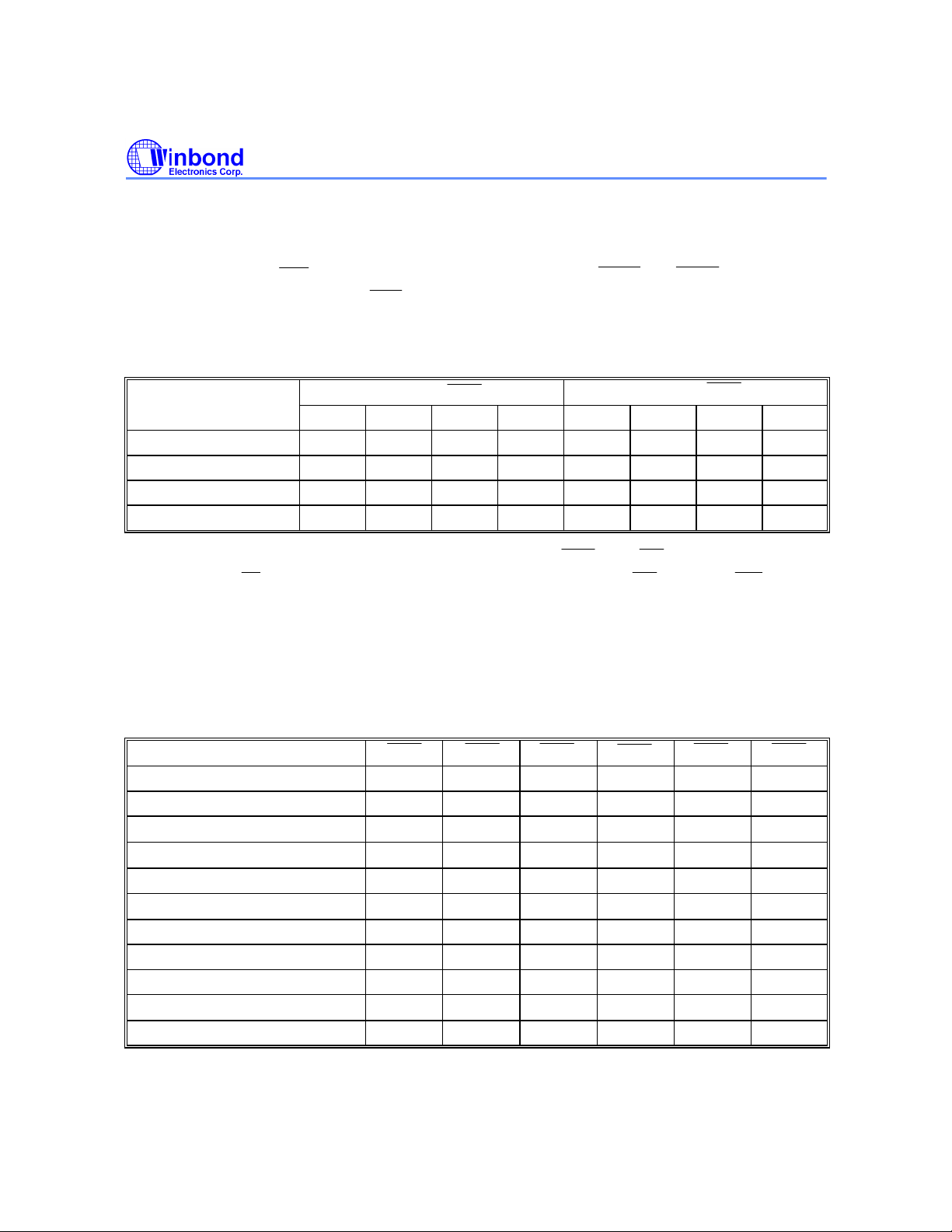
W25P022A
LBO
ADSP
ADSC
ADV
BWE
GW
FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
The W25P022A is a synchronous-burst pipelined SRAM designed for use in high-end personal
computers. It supports two burst address sequences for Intel systems and linear mode, which can
be controlled by the
counter is incremented whenever
pipelined mode if necessary.
Burst Address Sequence
External Start Address 00 01 10 11 00 01 10 11
Second Address 01 00 11 10 01 10 11 00
Third Address 10 11 00 01 10 11 00 01
Fourth Address 11 10 01 00 11 00 01 10
pin. The burst cycles are initiated by
is sampled low. The device can also be switched to non-
INTEL SYSTEM (LBO = VDDQ) LINEAR MODE (LBO = VSSQ)
A[1:0] A[1:0] A[1:0] A[1:0] A[1:0] A[1:0] A[1:0] A[1:0]
or
and the burst
The device supports several types of write mode operations.
byte writes. The BE[7:0] signals can be directly connected to the SRAM BW[4:1]. The
used to override the byte enable signals and allows the cache controller to write all bytes to the
SRAM, no matter what the byte write enable signals are. The various write modes are indicated in the
Write Table below. Note that in pipelined mode, the byte write enable signals are not latched by the
SRAM with addresses but with data. In pipelined mode, the cache controller must ensure the SRAM
latches both data and valid byte enable signals from the processor.
and BW[4:1] support individual
signal is
WRITE TABLE
READ/WRITE FUNCTION GW BWE BW4 BW3 BW2 BW1
Read 1 1 X X X X
Read 1 0 1 1 1 1
Write byte 1 I/O1−I/O8
Write byte 2 I/O9−I/O16
Write byte 2, byte 1 1 0 1 1 0 0
Write byte 3 I/O17−I/O24
Write byte 3, byte 1 1 0 1 0 1 0
Write byte 3, byte 2 1 0 1 0 0 1
Write byte 3, byte 2, byte 1 1 0 1 0 0 0
Write byte 4 I/O25−I/O32
Write byte 4, byte 1 1 0 0 1 1 0
1 0 1 1 1 0
1 0 1 1 0 1
1 0 1 0 1 1
1 0 0 1 1 1
Publication Release Date: September 1996
- 5 - Revision A1
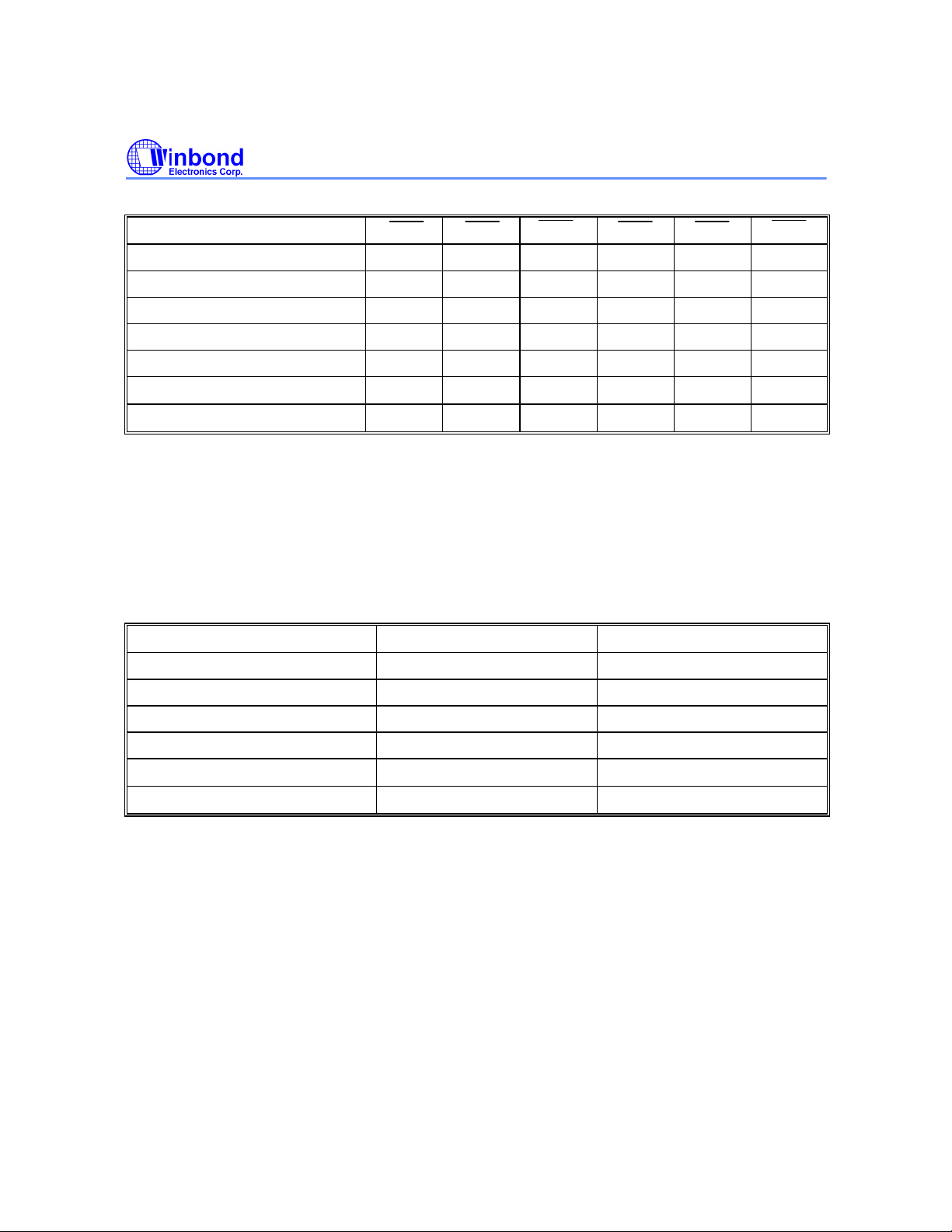
W25P022A
Write Table, continued
READ/WRITE FUNCTION GW BWE BW4 BW3 BW2 BW1
Write byte 4, byte 2 1 0 0 1 0 1
Write byte 4, byte 2, byte 1 1 0 0 1 0 0
Write byte 4, byte 3 1 0 0 0 1 1
Write byte 4, byte 3, byte 1 1 0 0 0 1 0
Write byte 4, byte 3, byte 2 1 0 0 0 0 1
Write all bytes I/O1−I/O32
Write all bytes I/O1−I/O32
The ZZ state is a low-power state in which the device consumes less power than in the unselected
mode. Enabling the ZZ pin for a fixed period of time will force the SRAM into the ZZ state. Pulling the
ZZ pin low for a set period of time will wake up the SRAM again. While the SRAM is in ZZ mode, data
retention is guaranteed, but the chip will not monitor any input signal except for the ZZ pin. In the
unselected mode, on the other hand, all the input signals are monitored.
1 0 0 0 0 0
0 X X X X X
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS
PARAMETER RATING UNIT
Core Supply Voltage to Vss -0.5 to 4.6 V
I/O Supply Voltage to Vss -0.5 to 4.6 V
Input/Output to VSSQ Potential VSSQ -0.5 to VDDQ +0.5 V
Allowable Power Dissipation 1.0 W
Storage Temperaure -65 to 150
Operating Temperature 0 to +70
Note: Exposure to conditions beyond those listed under Absolute Maximum Ratings may adversely affect the life and reliability
of the device.
°C
°C
- 6 -
 Loading...
Loading...