WELTREND WT6016 Datasheet
WT6016
Digital Monitor Controller
Ver. 1.51 Jul-31-1998
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The WT6016 is a member of WT60XX microcontroller family. It is specially designed for digital
controlled multi-sync monitor. It contains 8-bit CPU, 16K bytes ROM, 288 bytes RAM, 14 PWMs,
parallel I/O, SYNC processor, timer, one DDC interface (slave mode I2C interface with DDC1), one
master/slave I2C interface, two 4-bit A/D convertors and watch-dog timer.
FEATURES
* 8-bit 6502 compatible CPU, 4MHz operating frequency
* 16384 bytes ROM, 288 bytes SRAM
* 8MHz crystal oscillator
* 14 channels 8-bit/62.5kHz PWM outputs (8 open drain outputs & 6 CMOS outputs)
* Sync signal processor with H+V separation, frequency calculation, H/V polarity detection/control
* Three free-running sync signal outputs for burn-in test (64kHz/62.5Hz, 48kHz/75Hz, 31kHz/60Hz)
* Self-test pattern generator generates cross hatch picture
* DDC interface supports VESA DDC1/DDC2B standard
* Master/slave I2C interface
* Watch-dog timer (0.524 second)
* Maximum 25 programmable I/O pins
* One 8-bit programmable timer
* Two 4-bit A/D converter
* One external interrupt request
* Built-in low VDD voltage reset
* +5V power supply
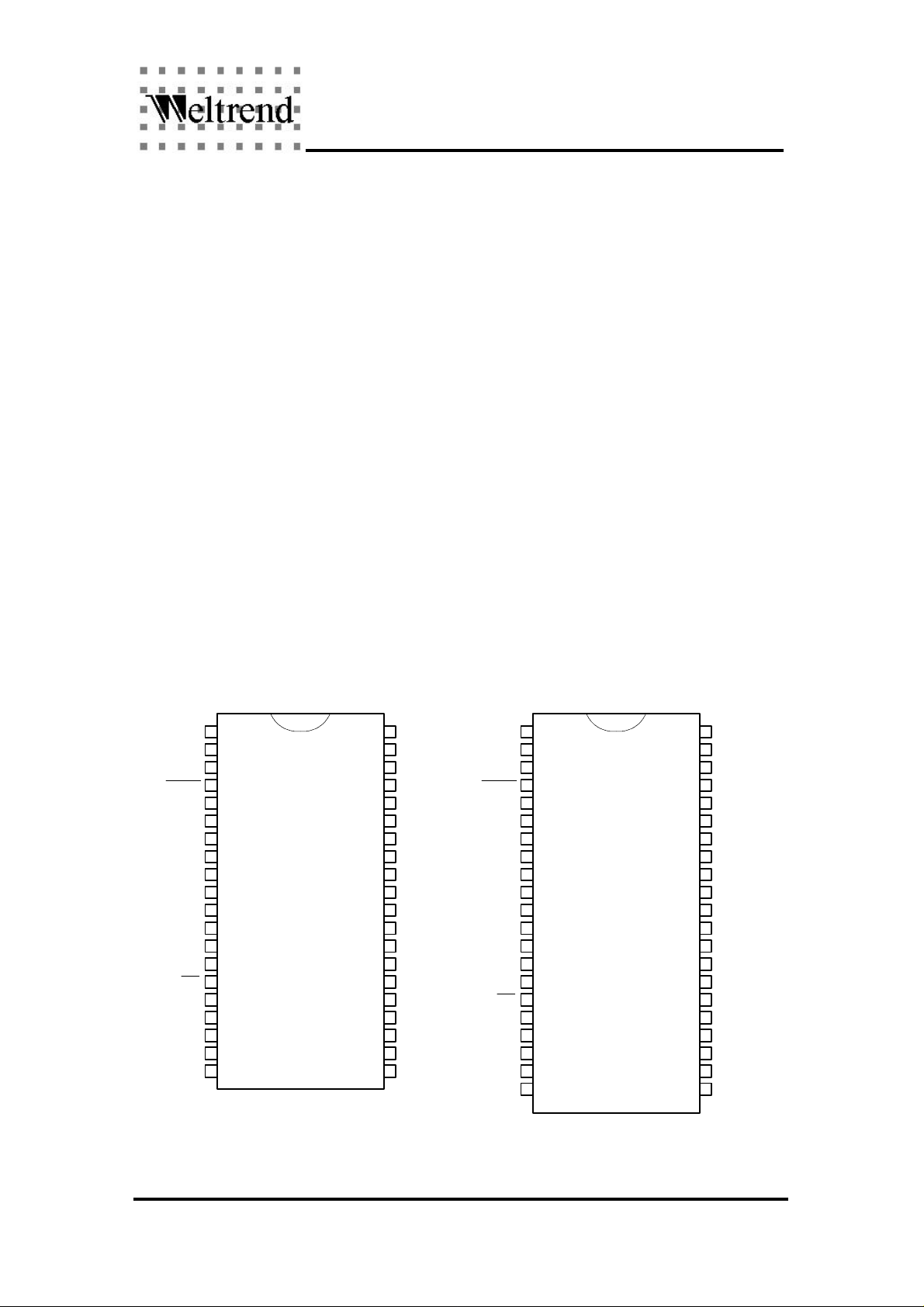
PIN ASSIGNMENT
1
DA2
2
DA1
3
DA0
RESET
OSCO
OSCI
PB5/SDA2
PB4/SCL2
PB3/PAT
PB1/HLFI
PB0/HLFO
PB6/IRQ
4
5
VDD
6
GND
7
8
9
10
11
12
PB2
13
14
15
16
PC7 SCL1/PD0
17
PC6
18
PC5
19
PC4
40
39
38
37
36
35
34
33
32
31
30
29
28
27
26
25
24
23
22
2120
VSYNC
HSYNC
DA3
DA4
DA5
DA6
DA7
PA7/HSO
PA6/VSO
PA5/DA13
PA4/DA12
PA3/DA11
PA2/DA10
PA1/DA9
PA0/DA8
SDA1/PD1
PC0/AD0
PC1/AD1
PC2PC3
42-Pin SDIP40-Pin PDIP
1
DA2
2
DA1
3
DA0
RESET
OSCO
OSCI
PB5/SDA2
PB4/SCL2
PB3/PAT
PB1/HLFI
PB0/HLFO
PB6/IRQ
4
5
VDD
6
7
GND
8
9
10
11
12
13
PB2
14
15
16
17
PC7 SCL1/PD0
18
PC6
19
PC5
20
PC4
42
41
40
39
38
37
36
35
34
33
32
31
30
29
28
27
26
25
24
23
2221
VSYNC
HSYNC
DA3
DA4
DA5
DA6
DA7
PA7/HSO
PA6/VSO
PA5/DA13
PA4/DA12
PA3/DA11
PA2/DA10
PA1/DA9
PA0/DA8
SDA1/PD1
PC0/AD0
PC1/AD1
PC2PC3
* I2C is a trademark of Philips Corporation.
* DDC is a trademark of Video Electronics Standard Association (VESA).
Weltrend Semiconductor, Inc.
1
PIN DESCRIPTION
Pin No.
40 42
1 1 DA2 O
2 2 DA1 O
3 3 DA0 O
4 4 /RESET I
5 5 VDD
6 7 GND
7 8 OSCO O
8 9 OSCI I
9 10 PB5/SDA2 I/O
10 11 PB4/SCL2 I/O
11 12 PB3/PAT I/O
12 13 PB2 I/O
13 14 PB1/HLFI I/O
14 15 PB0/HLFO I/O
15 16 PB6/IRQ I/O
16 17 PC7 I/O
17 18 PC6 I/O
18 19 PC5 I/O
19 20 PC4 I/O
20 21 PC3 I/O
21 22 PC2 I/O
22 23 PC1/AD1 I/O
23 24 PC0/AD0 I/O
24 25 SDA1/PD1 I/O
25 26 SCL1/PD0 I/O
26 27 PA0/DA8 I/O
27 28 PA1/DA9 I/O
28 29 PA2/DA10 I/O
29 30 PA3/DA11 I/O
30 31 PA4/DA12 I/O
31 32 PA5/DA13 I/O
32 33 PA6/VSO I/O
33 34 PA7/HSO I/O
34 35 DA7 O
35 36 DA6 O
36 38 DA5 O
37 39 DA4 O
38 40 DA3 O
39 41 HSYNC I
40 42 VSYNC I
Pin Name I/O Descriptions
WT6016
Digital Monitor Controller
Ver. 1.51 Jul-31-1998
D/A converter 2. Open-drain output. External applied voltage can up to 10V.
D/A converter 1. Open-drain output. External applied voltage can up to 10V.
D/A converter 0. Open-drain output. External applied voltage can up to 10V.
Reset. Active low. Schmitt trigger input with internal pull high.
Power supply (+5V).
Ground (0V).
Oscillator Output. Connects a 8MHz crystal.
Oscillator Input. Connects a 8MHz crystal.
I/O Port B5 or I2C data pin. This pin can be an I/O port or I2C serial data pin.
I/O Port B4 or I2C clock pin. This pin can be I/O port or I2C clock pin.
I/O Port B3 or self-test pattern output. When as an I/O port, it is same as PB2.
When it is configured to test pattern output, a vedio signal is output.
I/O Port B2. When it is an input pin, it has an internal pull-up resistor. When it is
an output pin, the source/sink current is 5mA
I/O Port B1 or half frequency input.
I/O Port B0 or half frequency output.
I/O Port B6 or Interrupt Request . When as interrupt request input, it has an
internal pull high resistor. When as an I/O port, it is same as PB3.
I/O Port C7. When it is an input pin, it has an internal pull-up resistor. When it is
an output pin, the sink current is 10mA and the source current is 5mA.
I/O Port C6. Same as PC7.
I/O Port C5. Same as PC7.
I/O Port C4. Same as PC7.
I/O Port C3. Same as PC7.
I/O Port C2. Same as PC7.
I/O Port C1 or A/D converter input 0.
I/O Port C0 or A/D converter input 1.
DDC serial data or I/O Port D1. When it is a DDC interface pin, It is an open-
drain output. When as an I/O port, it is same as Port B.
DDC serial clock or I/O Port D0. When it is a DDC interface pin, It is an opendrain output. When as an I/O port, it is same as Port B.
I/O Port A0 or D/A converter 8. This pin can be the output of D/A converter 8
(source/sink = 5mA) or an I/O pin (source = -100uA, sink = 5mA).
I/O Port A1 or D/A converter 9. Same as PA0/DA8.
I/O Port A2 or D/A converter 10. Same as PA0/DA8.
I/O Port A3 or D/A converter 11. Same as PA0/DA8.
I/O Port A4 or D/A converter 12. Same as PA0/DA8.
I/O Port A5 or D/A converter 13. Same as PA0/DA8.
I/O Port A6 / VSYNC OUT. This pin can be the output of VSYNC or an I/O pin.
When as an I/O pin, it is same as PA0.
I/O Port A7 / HSYNC OUT. This pin can be the output of HSYNC or an I/O pin.
When as an I/O pin, it is same as PA0.
D/A converter 7. Open-drain output. External applied voltage can up to 10V.
D/A converter 6. Open-drain output. External applied voltage can up to 10V.
D/A converter 5. Open-drain output. External applied voltage can up to 10V.
D/A converter 4. Open-drain output. External applied voltage can up to 10V.
D/A converter 3. Open-drain output. External applied voltage can up to 10V.
HSYNC input. Schmitt trigger input.
VSYNC input. Schmitt trigger input.
Weltrend Semiconductor, Inc.
2
WT6016
Digital Monitor Controller
Ver. 1.51 Jul-31-1998
FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
CPU
The CPU core is 6502 compatible, operating frequency is 4MHz. Address bus is 16-bit and data bus is
8-bit. the non-maskable interrupt (/NMI) of 6502 is changed to maskable interrupt and is defined as
the INT0. The interrupt request (/IRQ) of 6502 is defined as the INT1.
Default stack pointer is 01FFH.
Please refer the 6502 reference menu for more detail.
ROM
16384 bytes maskable ROM is provided for program codes.
Address is located from C000H to FFFFH.
The following addresses are reserved for special purpose :
FFFAH (low byte) and FFFBH (high byte) : INT0 interrupt vector.
FFFCH (low byte) and FFFDH (high byte) : program reset vector.
FFFEH (low byte) and FFFFH (high byte) : INT1 interrupt vector.
RAM
Built-in 288 bytes SRAM, address is located from 0080H to 019FH. Because the initial stack pointer
is 01FFH, so program must set proper stack pointer when program starts. A recommended value is
019FH.
0000H
:
0020H
0021H
:
007FH
0080H
:
019FH
01A0H
:
BFFFH
C000H
:
:
:
FFFFH
REGISTERS
Reserved
RAM
Reserved
ROM
Low VDD Voltage Reset
A VDD voltage detector is built inside the chip. When VDD is below 4.0 volts, the whole chip will be
reset just like power-on-reset.
Note that the 4.0 volts varies with temperature and process. Please refer the electrical characteristics.
Weltrend Semiconductor, Inc.
3
WT6016
Digital Monitor Controller
Ver. 1.51 Jul-31-1998
PWM D/A Converter
The WT6018 provides 14 PWM D/A converters. DA0 to DA7 are open-drain outputs and external
applied voltage on these pins can be up to 10 volts. DA8 to DA13 are 5 volts push-pull CMOS outputs
and are shared with I/O Port PA0 to PA5. All D/A converters are 62.5kHz frequency with 8-bit
resolution. Each D/A converter is controlled by the corresponding register (REG#00H to REG#0DH),
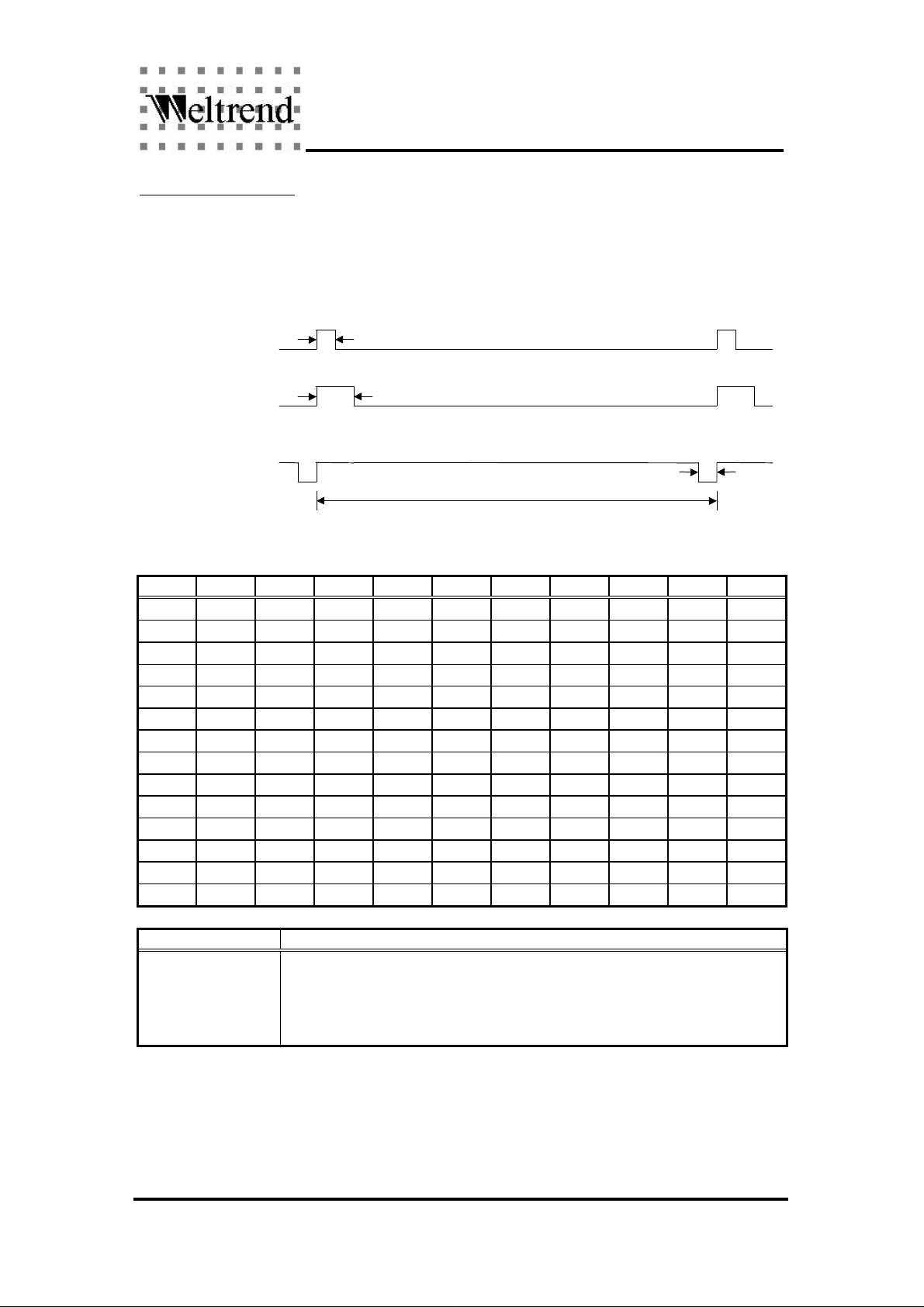
the duty cycle can be programmed from 1/256 (data = 01H) to 255/256 (data = FFH).
Duty cycle = 1/256
62.5ns
Duty cycle = 2/256
125ns
62.5ns
Duty cycle = 255/256
1/62.5kHz=16us
To program the PWM D/A converters, write the corresponding registers ( REG#00H to REG#0DH).
Address R/W Initial Bit7 Bit6 Bit5 Bit4 Bit3 Bit2 Bit1 Bit0
0000H R/W 80H DA07DA06DA05DA04DA03DA02DA01DA0
0001H R/W 80H DA17DA16DA15DA14DA13DA12DA11DA1
0002H R/W 80H DA27DA26DA25DA24DA23DA22DA21DA2
0003H R/W 80H DA37DA36DA35DA34DA33DA32DA31DA3
0004H R/W 80H DA47DA46DA45DA44DA43DA42DA41DA4
0005H R/W 80H DA57DA56DA55DA54DA53DA52DA51DA5
0006H R/W 80H DA67DA66DA65DA64DA63DA62DA61DA6
0007H R/W 80H DA77DA76DA75DA74DA73DA72DA71DA7
0008H R/W 80H DA87DA86DA85DA84DA83DA82DA81DA8
0009H R/W 80H DA97DA96DA95DA94DA93DA92DA91DA9
000AH R/W 80H DA107DA106DA105DA104DA103DA102DA101DA10
000BH R/W 80H DA117DA116DA115DA114DA113DA112DA111DA11
000CH R/W 80H DA127DA126DA125DA124DA123DA122DA121DA12
000DH R/W 80H DA137DA136DA135DA134DA133DA132DA131DA13
Bit Name Bit value
DAx7-DAx0 01H : 1/256 duty cycle
02H : 2/256 duty cycle
03H : 3/256 duty cycle
:
FFH : 255/256 duty cycle
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
** Do not write 00H to the PWM registers. This will cause unstable
output on the corresponding pin.
Weltrend Semiconductor, Inc.
4
WT6016
Digital Monitor Controller
Ver. 1.51 Jul-31-1998
I/O Ports
Port_A :
Pin PA0/DA8 - general purpose I/O shared with DA8 output.
Pin PA1/DA9 - general purpose I/O shared with DA9 output.
Pin PA2/DA10 - general purpose I/O shared with DA10 output.
Pin PA3/DA11 - general purpose I/O shared with DA11 output.
Pin PA4/DA12 - general purpose I/O shared with DA12 output.
Pin PA5/DA13 - general purpose I/O shared with DA13 output.
Pin PA6/VSO - general purpose I/O shared with VSYNC output.
Pin PA7/HSO - general purpose I/O shared with HSYNC output.
Port_A is controlled by REG#10H & REG#11H. In REG#10H, each corresponding bit enables
HSYNC output, VSYNC output or D/A converter output when it is "1". If the corresponding bit is "0",
the output level is decided by REG#11H. In REG#11H, if the I/O corresponding bit (PAn) is "0", the
output is low level (IOL=5mA). If PAn bit is "1", the output is high level (IOH= -100uA) and can be
used as an input.
Address R/W Initial Bit7 Bit6 Bit5 Bit4 Bit3 Bit2 Bit1 Bit0
0010H W 00H EHO EVO EDA13 EDA12 EDA11 EDA10 EDA9 EDA8
0011H W FFH PA7W PA6W PA5W PA4W PA3W PA2W PA1W PA0W
0011H R -- PA7R PA6R PA5R PA4R PA3R PA2R PA1R PA0R
Bit Name Bit value = “1” Bit value = “0”
EHO Enable PA7 as HSYNC output. PA7 as general purpose I/O.
EVO Enable PA6 as VSYNC output. PA6 as general purpose I/O.
EDA13 Enable PA5 as DA13 output. PA5 as general purpose I/O.
EDA12 Enable PA4 as DA12 output. PA4 as general purpose I/O.
EDA11 Enable PA3 as DA11 output. PA3 as general purpose I/O.
EDA10 Enable PA2 as DA10 output. PA2 as general purpose I/O.
EDA9 Enable PA1 as DA9 output. PA1 as general purpose I/O.
EDA8 Enable PA0 as DA8 output. PA0 as general purpose I/O.
PA7W - PA0W Outputs high level (IOH= -100uA). Outputs low level (IOL= 5mA).
PA7R- PA0R Pin is high level. Pin is low level.
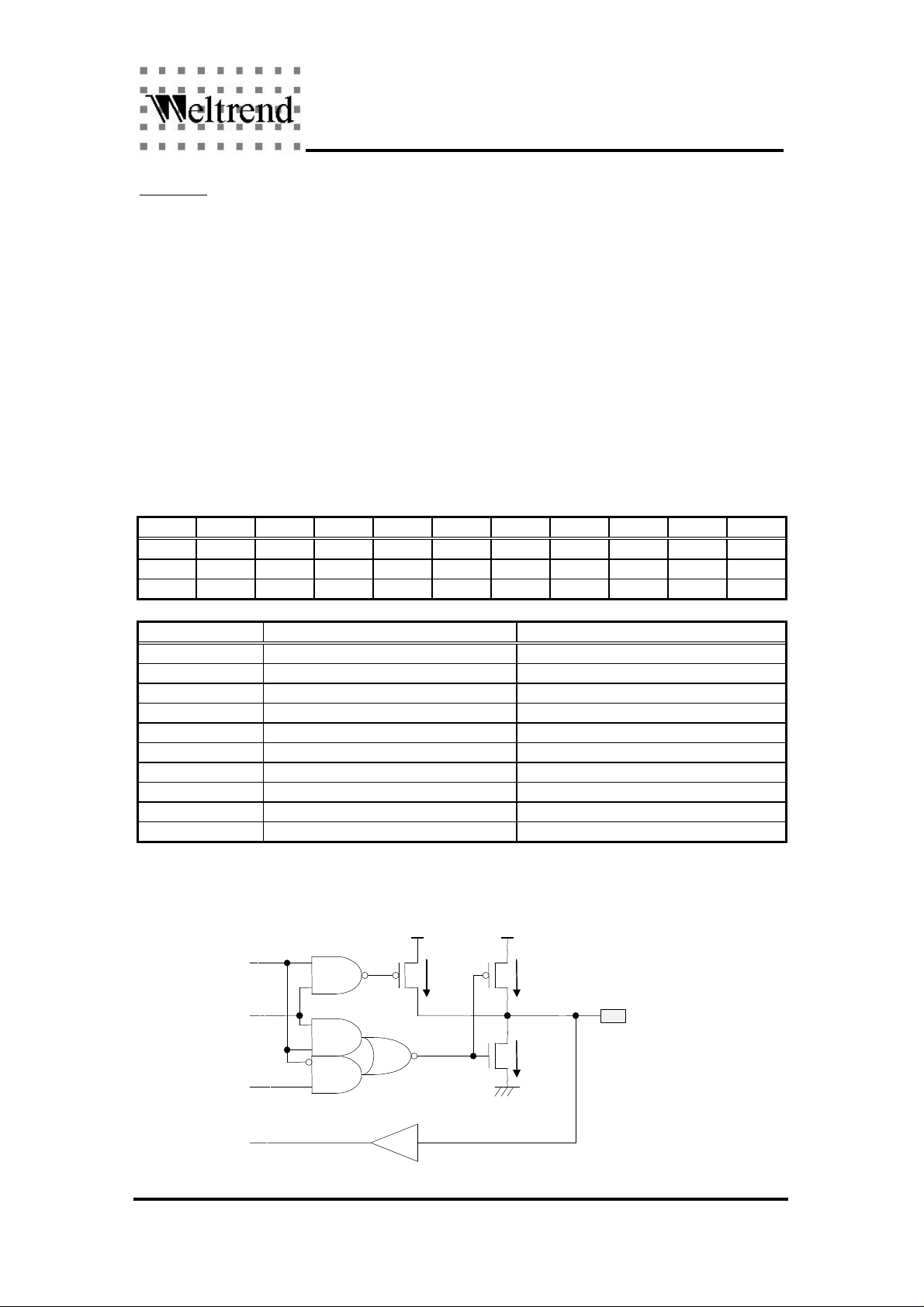
* If the program wants to force VSYNC output (VSO pin) in low state, write "0" to PA6 bit first, then
write "0" to EVO bit. This is used to prevent high frequency output on VSO pin when the VSYNC
frequency is increased to read EDID data in DDC1 mode.
EDAx
DAx
PAnW
5mA
100uA
Pin PAn
5mA
PAnR
Weltrend Semiconductor, Inc.
5
WT6016
100uA
Digital Monitor Controller
Ver. 1.51 Jul-31-1998
Port_B :
Pin PB0/HLFO - general purpose I/O pin shared with half frequency output.
Pin PB1/HLFI - general purpose I/O pin shared with half frequency input.
Pin PB2 - general purpose I/O pin.
Pin PB3/PAT - general purpose I/O pin shared with self-test pattern output.
Pin PB4/SCL2 - general purpose I/O pin shared with I2C interface clock pin.
Pin PB5/SDA2 - general purpose I/O pin shared with I2C interface data pin.
Pin PB6/IRQB - general purpose I/O pin shared with interrupt request input.
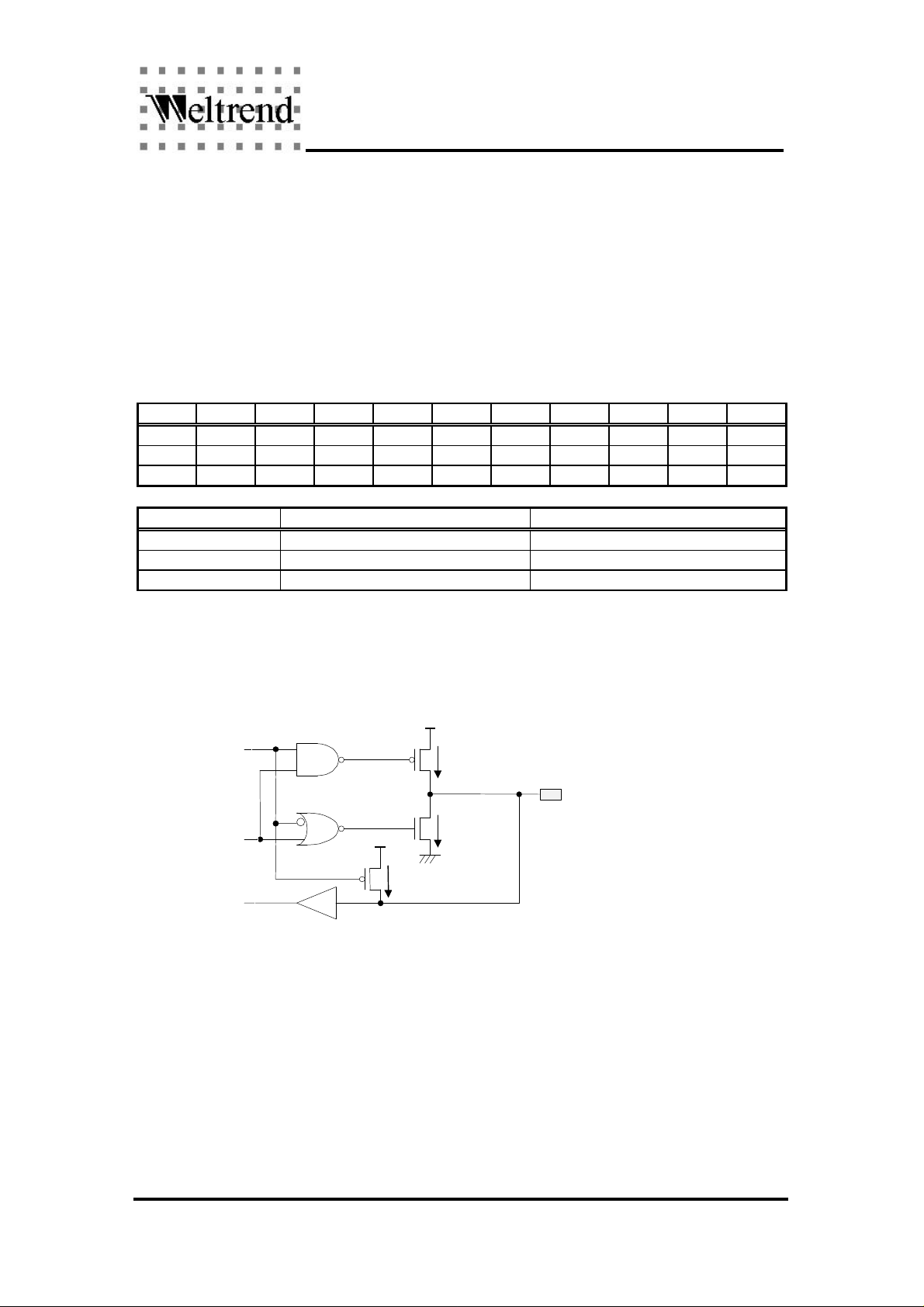
The source/sink current of port_B is 5mA when as an output. When it is input, an internal pull high
resistor is connected.
Address R/W Initial Bit7 Bit6 Bit5 Bit4 Bit3 Bit2 Bit1 Bit0
0012H W 00H 0 PB6OE PB5OE PB4OE PB3OE PB2OE PB1OE PB0OE
0013H W FFH 1 PB6W PB5W PB4W PB3W PB2W PB1W PB0W
0013H R -- -- PB6R PB5R PB4R PB3R PB2R PB1R PB0R
Bit Name Bit value = “1” Bit value = “0”
PB6OE - PB0OE Output enable. Output disable (internal pull-up).
PB6W - PB0W Outputs high level (IOH= -5mA). Outputs low level (IOL= 5mA).
PB6R- PB0R Pin is high level. Pin is low level.
* If IEN_D bit in REG#1AH is “1” and PB6OE bit is "0", the PB6 pin becomes interrupt request
input.
* If ENI2C bit in REG#1EH is “1”, the PB5 and PB4 pins becomes I2C interface pins.
* If ENPAT bit in REG#16H is “1”, the PB3 pin becomes self-test pattern output.
* If ENHALF bit in REG#17H is “1”, the PB1 pin becomes half frequency input and PB0 pin becomes
half frequency output pin.
PBnOE
PBnW
PBnR
Structure of Port B
5mA
Pin PB0 to PB6
5mA
Weltrend Semiconductor, Inc.
6

WT6016
Digital Monitor Controller
Ver. 1.51 Jul-31-1998
Port_C :
Pin PC0 - general purpose I/O pin shared with 4-bit A/D converter 0 input.
Pin PC1 - general purpose I/O pin shared with 4-bit A/D converter 1 input
Pin PC2 to PC7 - general purpose I/O pins.
The REG#14H defines the I/O direction and the REG#15H controls the output level.
The structure of Port_C is same as the Port_B except the sink current is 10mA. When PC0 and
PC1 are programmed as the A/D converter inputs, the pull high transistor is disconnected.
Address R/W Initial Bit7 Bit6 Bit5 Bit4 Bit3 Bit2 Bit1 Bit0
0014H W 00H PC7OE PC6OE PC5OE PC4OE PC3OE PC2OE PC1OE PC0OE
0015H W FFH PC7W PC6W PC5W PC4W PC3W PC2W PC1W PC0W
0015H R -- PC7R PC6R PC5R PC4R PC3R PC2R PC1R PC0R
Bit Name Bit value = “1” Bit value = “0”
PC7OE - PC0OE Output enable. Output disable (internal pull-up).
PC7W - PC0W Outputs high level (IOH= -5mA). Outputs low level (IOL= 10mA).
PC7R - PC0R Pin is high level. Pin is low level.
Port_D :
Pin SCL1/PD0 - general purpose I/O pin shared with DDC interface serial clock.
Pin SDA1/PD1 - general purpose I/O pin shared with DDC interface serial data.
The structure of these two pins are same as the PB4 and PB5. Default is DDC interface and can be
changed to I/O port D by setting ENPD bit.
Address R/W Initial Bit7 Bit6 Bit5 Bit4 Bit3 Bit2 Bit1 Bit0
000FH W 00H -- -- -- ENPD PD1OE PD0OE PD1W PD0W
000FH R -- -- -- -- -- -- -- PD1R PD0R
Bit Name Bit value = “1” Bit value = “0”
ENPD Enable I/O Port_D. DDC interface.(open drain)
PD1OE - PD0OE Output enable. Output disable (internal pull-up).
PD1W - PD0W Outputs high level (IOH= -5mA). Outputs low level (IOL= 5mA).
PD1R- PD0R Pin is high level. Pin is low level.
* If program wants to read current status on the I/O pins (any I/O port), do not set output enable bit to
“0”. Because the registers for reading I/O are always indicating the current state on the I/O pins, set
output enable bit to “0” will change the level on the I/O pin. Please reference the I/O pin structure.
Weltrend Semiconductor, Inc.
7
WT6016
SELF
Digital Monitor Controller
Ver. 1.51 Jul-31-1998
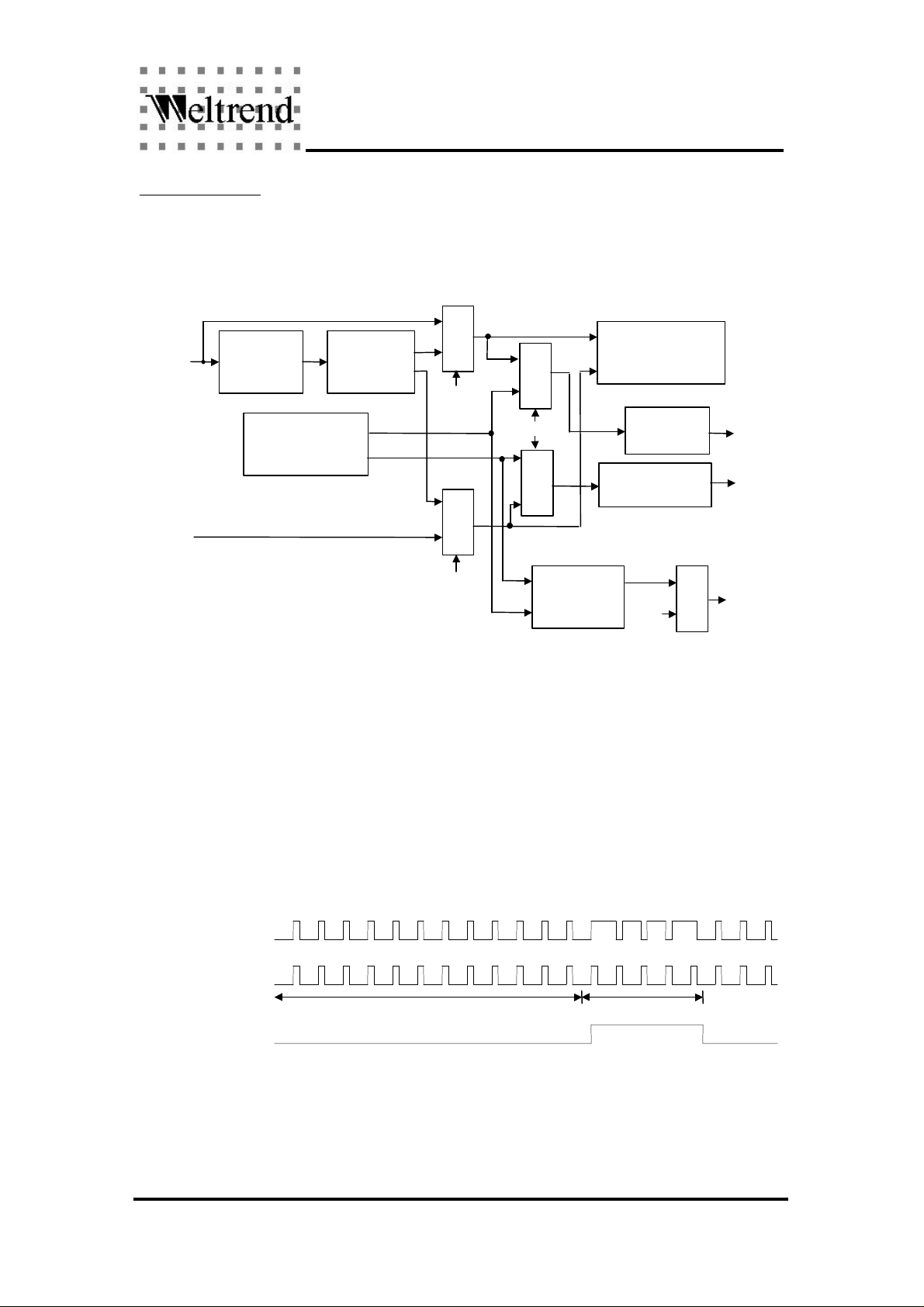
SYNC Processor
The SYNC processor can : (1) separate the composite sync signal; (2) calculate HSYNC and
VSYNC frequencies; (3) detect polarities of HSYNC and VSYNC inputs; (4) control the output
polarities of HSO and VSO pins. (5) generate free-running horizontal and vertical sync signals for
burn-in test; (6) generate self-test pattern signal.
Mux
H+V
Mux
Mux
Mux
H/V Freq. Counter
H Polarity
Control
V Polarity
detect & control
HSYNC
H Polarity
detect
H/V SYNC
Generator
Sync
Separator
H
V
VSYNC
H+V
Test Pattern
Generator
PB3
Mux
PB3/PAT
Composite Sync Signal Separation
The composite sync signal comes from HSYNC pin and is separated by the sync separator.
The operations of sync separator are:
- detect the polarity and convert composite sync signal to positive polarity.
- extract Vsync
Pulse width less than 8us will be filtered, but the Vsync will be widened about 8us.
- count the pulses during the separated Vsync is low and save the counter value (NH).
- bypass the composite sync pulses before the counter equals to N
H.
- start inserting Hsync pulses after the counter equals to NH until the separated Vsync is low.
- the period of inserted Hsync is decided by the last two bypassed Hsync.
- the pulse width of the inserted Hsync is 2us.
HSO
VSO
Positive H+V
separated Hsync
bypass insert HSYNC
separated Vsync
To decide whether the HSYNC input is a composite sync signal or not, program should check the
frequency of VSYNC first (reset H+V bit to “0”). If the VSYNC frequency is lower than 15.25Hz
(OVF2=1), set H+V bit to “1” and check VSYNC frequency again. If VSYNC still has no frequency,
that is power saving condition, program should reset H+V bit. If it has a valid frequency, the HSYNC
input is composite signal.
Weltrend Semiconductor, Inc.
8
 Loading...
Loading...