Page 1

User Manual
WI-I/O-EX Serial I/O Module
Weidmuller Inc., 821 Southlake Blvd., Richmond, VA 23236
Tel: (800) 849-9343 Fax: (804) 897-4136 Email: support@weidmuller.com
Web: www.weidmuller.com
Page 2
WI-I/O-EX Serial I/O Module User Manual v1.11
Thank you for your selection of the WI-I/O-EX Serial I/O Module. We trust
it will give you many years of valuable service.
ATTENTION!
Incorrect termination of supply wires may cause internal damage and will void warranty.
To ensure your WI-I/O-EX product enjoys a long life,
double check ALL your connections with the User Manual
before turning the power on.
All equipment must be properly grounded for safe operation.
All equipment should be serviced only by a qualified technician.
Important Notice
Weidmuller, Inc. products are designed to be used in industrial environments, by
experienced industrial engineering personnel with adequate knowledge of safety design
considerations. These products should not be used in non-industrial applications, or lifesupport systems, without consulting Weidmuller, Inc. first.
Limited Lifetime Warranty, Disclaimer and Limitation of Remedies
Weidmuller, Inc. products are warranted to be free from manufacturing defects for the
“serviceable lifetime” of the product. The “serviceable lifetime” is limited to the
availability of electronic components. If the serviceable life is reached in less than three
years following the original purchase from Weidmuller, Inc., Weidmuller, Inc. will
replace the product with an equivalent product if an equivalent product is available.
This warranty does not extend to:
- failures caused by operation of the equipment outside the particular product's
specification, or
- use of the module not in accordance with this User Manual, or
- abuse, misuse, neglect or damage by external causes, or
- repairs, alterations, or modifications undertaken other than by an authorized
Service Agent.
Weidmuller, Inc.’s liability under this warranty is limited to the replacement or repair of
the product. This warranty is in lieu of and exclusive of all other warranties. This
warranty does not indemnify the purchaser of products for any consequential claim for
damages or loss of operations or profits and Weidmuller, Inc. is not liable for any
consequential damages or loss of operations or profits resulting from the use of these
products. Weidmuller, Inc. is not liable for damages, losses, costs, injury or harm incurred
as a consequence of any representations, warranties or conditions made by Weidmuller,
Inc. or its representatives or by any other party, except as expressed solely in this
document.
Page 2 February 2010
Page 3

WI-I/O-EX Serial I/O Module User Manual v1.11
CONTENTS
1 OVERVIEW ............................................................................................................... 4
1.1 MODULE TYPES AND FEATURES .........................................................................................5
1.1.1 Digital inputs / outputs................................................................................................6
1.1.2 Pulsed outputs.............................................................................................................6
1.1.3 Pulsed inputs...............................................................................................................7
1.1.4 Analog inputs..............................................................................................................7
1.1.5 Analog outputs............................................................................................................8
1.1.6 Communications.........................................................................................................9
2 INSTALLATION ..................................................................................................... 10
2.1 GENERAL INSTALLATION .................................................................................................10
2.1.1 Power Connection.....................................................................................................10
2.1.2 Address Switches......................................................................................................10
2.2 SIGNAL CONNECTIONS.....................................................................................................12
2.2.1 Digital Inputs (and Pulsed Inputs) ............................................................................12
2.2.2 Digital Outputs (and Pulsed Outputs).......................................................................13
2.2.3 Analog Inputs............................................................................................................13
2.2.4 Analog Outputs.........................................................................................................17
3 CONFIGURATION ................................................................................................. 20
3.1 ADD A RADIO MODULE TO CONNECT THE WI-I/O-EX TO THE RADIO NETWORK.............20
3.2 ADD THE SERIAL MODULE...............................................................................................20
4 HARDWARE CONFIGURATION........................................................................ 23
4.1 CONNECTING TO THE WI-I/O-EX MODULE......................................................................23
4.2 CONFIGURATION COMMON TO ALL MODULES .................................................................24
4.2.1 Communications.......................................................................................................24
4.2.2 Pulsed outputs...........................................................................................................25
4.3 WI-I/O-EX-11 CONFIGURATION ......................................................................................26
4.3.1 Pulsed Inputs.............................................................................................................26
4.4 WI-I/O-EX-12 CONFIGURATION ......................................................................................27
4.4.1 Voltage input ............................................................................................................27
4.4.2 Current input.............................................................................................................30
4.5 WI-I/O-EX-13 CONFIGURATION ......................................................................................33
4.5.1 Voltage output ..........................................................................................................33
4.5.2 Current output...........................................................................................................35
5 OPERATION............................................................................................................ 37
5.1 WI-I/O-EX-11 MODULE ...................................................................................................37
5.2 WI-I/O-EX-12 MODULE ...................................................................................................39
5.3 WI-I/O-EX-13 MODULE ...................................................................................................40
5.4 HEXADECIMAL REPRESENTATION OF VOLTAGE AND CURRENT LEVELS..........................42
APPENDIX A. MODBUS ADDRESS MAP................................................................. 43
A.1. WI-I/O-EX-11.....................................................................................................................43
A.2. WI-I/O-EX-12.....................................................................................................................45
A.3. WI-I/O-EX-13.....................................................................................................................47
APPENDIX B. MODBUS FUNCTIONALITY............................................................ 49
APPENDIX C. COMMS RECOVERY ........................................................................ 50
APPENDIX D. SPECIFICATIONS .............................................................................. 53
WI-IO-EX Manual v1.11 Page 3
Page 4

WI-I/O-EX Serial I/O Module User Manual v1.11
APPENDIX E. RS232 WIRING .................................................................................... 55
1 Overview
The WI-I/O-EX modules are designed to provide I/O expansion for other products like
WI-I/O 9, WI-MOD-9-E and WI-MOD-E modules. The WI-I/O-EX modules support the
WI Series protocol, and communicate serially via RS232 or RS485. Configuration is
done via the WI Series configuration utility.
The WI-I/O-EX modules also support ModBus protocol. They may be used as a ModBus
slave with any 3rd-party ModBus device, or with the WI-GTWY modules using ModBus.
They support both ModBus ASCII protocol, and serial un-signed ModBus RTU, also
known as “ModBus binary”. The ModBus slave address of the WI-I/O-EX is selected via
two rotary switches on the bottom panel of the case.
All WI-I/O-EX models provide digital inputs and outputs. Specific models provide
analog inputs or analog outputs. Pulsed inputs and pulsed outputs are also available.
Several modules may be connected to one master, allowing any combination of I/O types.
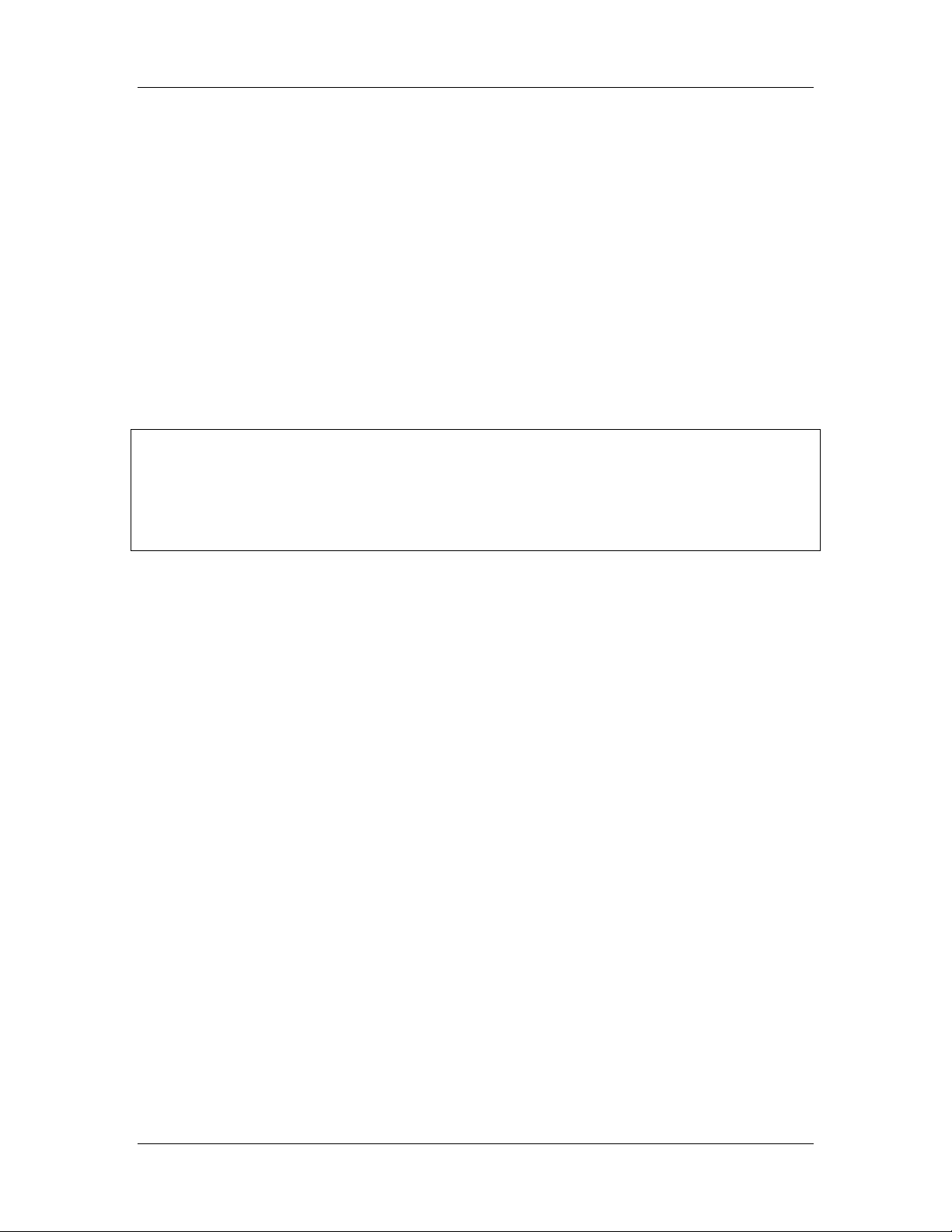
Figure 1-1 shows a diagram of a WI-I/O-EX module with parts labelled.
Page 4 February 2010
Page 5
WI-I/O-EX Serial I/O Module User Manual v1.11
access panel
Status LEDs
RS485 and
power connector
Address switches
I/O connector
RS485
termination
switch
RS232 configuration
connector
DIN rail mount
Power
OK
Transmit
Receive
Analog
configuration
Figure 1-1: WI-I/O-EX unit with significant parts labeled.
Two ports allow configuration and communications on the WI-I/O-EX. The RS232 port
is intended for configuration. The RS485 port allows the unit to be in a multi-drop
configuration.
Overvoltage protection and supply monitoring is provided to minimize the risk of failure
due to faulty connections or supply surges.
1.1 Module types and features
The module types and I/O are summarized in Table 1-1.
WI-IO-EX Manual v1.11 Page 5
Page 6
WI-I/O-EX Serial I/O Module User Manual v1.11
WI-I/O-EX -11 -12 -13
Digital inputs/outputs
Pulse outputs
Pulse inputs
Analog inputs
Analog outputs
Up to 16 Up to 8 Up to 8
8 8 8
4 - -
- 4 floating or 8 commoned -
- - 8
Table 1-1: Summary of WI-I/O-EX module types and I/O.
1.1.1 Digital inputs / outputs
Each digital I/O channel on the WI-I/O-EX modules can act as either an input or an
output. The input/output direction does not need to be user configured.
Digital inputs are suitable for voltage-free contacts, or NPN-transistor switch devices.
Digital outputs are open-collector transistor outputs, able to switch loads up to 30VDC,
200mA.
If you have wired an input/output channel as an input, it is recommended that you do not
write values to it as an output. No electrical damage will occur if you attempt to use a
channel wired as an input as an output, or vice-versa, however the I/O system will not
operate correctly.
We recommend that the required digital inputs be assigned consecutively from channel 1.
Then use the remaining channels as digital outputs.
1.1.2 Pulsed outputs
The first eight digital channels on each WI-I/O-EX module can be used as pulse outputs.
The maximum output frequency is 100Hz.
A pulse output on the WI-I/O-EX will output the number of pulses equal to the register
value sent by the master. When the master sends a new register value, the WI-I/O-EX
will output additional pulses until the output count is the same as the new value.
Three register values are associated with creating each pulsed output:
• The Count keeps a tally of how many pulses have been output - this is a 16-bit
register and overflows to 0.
• The Target is set by the master, and is the trigger for pulses to be created. The
digital channel outputs pulses until the Count value reaches the Target value. If
the Target register is set to 0, the pulses stop and the Count register is cleared.
• The Update Time is the interval in which the WI-I/O-EX expects to receive
updates to the Target value. The module will output enough pulses for the Count
Page 6 February 2010
Page 7

WI-I/O-EX Serial I/O Module User Manual v1.11
to reach the Target within the update time. The output pulse rate is determined by
the update time, and the difference between the count and the target.
If the calculated pulse rate is more than the maximum rate (100Hz), the WI-I/O-EX will
output pulses at the maximum rate. At the end of the update time, the count value will be
less than the target. The WI-I/O-EX will then calculate the new required pulse rate for
the next update period, based on the difference between Count and Target values.
If the calculated pulse rate is greater than around three times the maximum rate, pulses
are not output. The Count value will be set to the value of the Target without any pulses
output. Pulses will be output again when the calculated pulse rate falls within the
maximum possible rate.
1.1.3 Pulsed inputs
The first four digital channels on the WI-I/O-EX-1-S-11 module can be used as pulsed
inputs. The maximum input pulse frequency is 1 KHz.
The pulse input channel calculates two register variables, each of which can be read by
the master.
• The Pulse Count is a count of the pulses detected on the channel since the WI-I/O-
EX powered up. The pulse input counts are 32-bit values (2 x 16-bit registers, a low
and a high register), and wrap around to zero on overflow.
• The Pulse Rate is a measure of the rate of pulses detected on the channel. The pulse
rate value is decimal 16,384 (hex 4000) for zero rate and decimal 49,152 (hex C000)
for the maximum rate configured by the user. These zero and maximum values are
the same as 0% and 100% used for analog values. (See section 5.4 for hex to decimal
conversion.)
The maximum pulse input rate is set during configuration. The value is in pulses per
minute and is limited to 60000 (1 KHz), the maximum rate capable of the module.
1.1.4 Analog inputs
The analog inputs on the WI-I/O-EX-1-S-12 can be connected as either grounded singleended inputs or as floating differential inputs. The WI-I/O-EX-1-S-12 has eight
grounded inputs or four floating inputs.
• Grounded single-ended inputs connect between the AIN terminal and the GND
terminal.
• Floating differential inputs each take up two terminals. There are four differential
pairs on the WI-I/O-EX-1-S-12: [AIN1-AIN2], [AIN3-AIN4], [AIN5-AIN6], [AIN7AIN8]. For example, the first input is connected to terminals AIN1 (positive) and
AIN2 (negative).
WI-IO-EX Manual v1.11 Page 7
Page 8

WI-I/O-EX Serial I/O Module User Manual v1.11
The two types of input cannot be mixed - all inputs must be either “grounded” or
“floating”.
Inputs can also be selected as mA current, or voltage input - all inputs must be the same,
either all current or all voltage. The scale of each analog input is chosen during hardware
configuration, with scale options as follows:
Voltage input scale options: [0 to 5V], [0 to 10V], [1 to 5V]
Current input scale options: [0 to 10mA], [0 to 20mA], [4 to 20mA]
For compatibility with E-Series modules, 4-20mA current is recommended. See section
4.4 for more information on compatibility.
The values on the analog input are decimal 16,384 (hex 4000) for minimum signal (0%)
and decimal 49,152 (hex C000) for maximum (100%).
The analog channel will measure over-scale, up to 150% which will have value 65,536
(hex FFFF). For 4-20mA signals, the channel will measure under-scale down to 0mA
which has a value of 8,192 (hex 2000). (See section 5.4 for hex to decimal conversion.)
The WI-I/O-EX-12 provides a 24V analog loop supply (“ALS”) for powering analog
loops.
1.1.5 Analog outputs
The WI-I/O-EX-1-S-13 has eight analog output channels and can be configured to output
voltage or current. For current signals, “source” or “sink” can be selected. The scale of
each analog output is specified during configuration, with scale options as follows:
Voltage output scale options: [0 to 5V], [0 to 10V], [1 to 5V]
Current output scale options: [0 to 10mA], [0 to 20mA], [4 to 20mA], source or sink
• Voltage outputs are measured with respect to the ground terminal.
• Current source outputs are measured with respect to the ground terminal.
• Current sink outputs are measured with respect to the 24V “ALS” terminal.
Writing to the output register by the master produces the analog output. Minimum to
maximum signals (0 – 100%) are produced by register values from decimal 16,384 to
49,152 (hex 4000 - C000). (See section 5.4 for hex to decimal conversion.)
The analog channel can output over-scale, up to 150% corresponding to register value
65,536 (hex FFFF). For 4-20mA signals, the channel can output under-scale down to
0mA from a register value of 8,192 (hex 2000) or less. Note that the over-scale output is
limited by the maximum levels capable of the WI-I/O-EX module (12V or 24mA).
Page 8 February 2010
Page 9

WI-I/O-EX Serial I/O Module User Manual v1.11
1.1.6 Communications
The WI-I/O-EX modules have two communication ports: RS232 and RS485. The RS485
port communicates using E-Series protocol. Both ports support ModBus protocol.
The RS232 port is intended for configuration. The RS485 port is intended for normal
operation and can be used in a multi-drop setup.
There are two address switches on the base of the module. Setting both address switches
to 00 configures the module to use E-Series protocol on the RS485 port. When the
switches are set within the range 01-99, the module uses ModBus protocol on the RS485
port, with the ModBus address defined by the switches. Whenever these address switches
are changed the unit should be reset by disconnecting power.
When using E-Series protocol, the port settings are fixed at 9600 baud, 8 data bits, no
parity, 1 stop bit.
The ModBus communications settings are configurable as follows:
ModBus type: RTU, ASCII with 8 data bits, ASCII with 7 data bits. (Note that the
configuration software only supports ModBus RTU. A ModBus Master can select ASCII
protocol by writing to the appropriate register. See Appendix A.)
Baud rate: 1200, 2400, 4800, 9600, 14400, 19200, 28800, 38400, 57600, 76800, 115200
Parity: none, odd, even
Stop bits: 1 or 2.
The modules are fitted with a termination switch for the RS485. Set this switch only on
the last module in a multi-drop RS485 configuration.
The WI Series software is used to configure the WI-I/O-EX modules as part of a network.
The hardware set-up for items such as expected pulse rates and analog signals is also
available through this software.
When used as a ModBus-only device, stand-alone configuration software (cfg_WI-I/OEX_Vx.xx.exe) is available to set up the modules. All required software may be
downloaded from the Weidmuller website (http://wireless.weidmuller.com).
WI-IO-EX Manual v1.11 Page 9
Page 10
WI-I/O-EX Serial I/O Module User Manual v1.11
B A
-
+
2 Installation
All connections to the module should be SELV only. Normal 110/220/240V mains
supply should not be connected to any input terminal of the module.
2.1 General installation
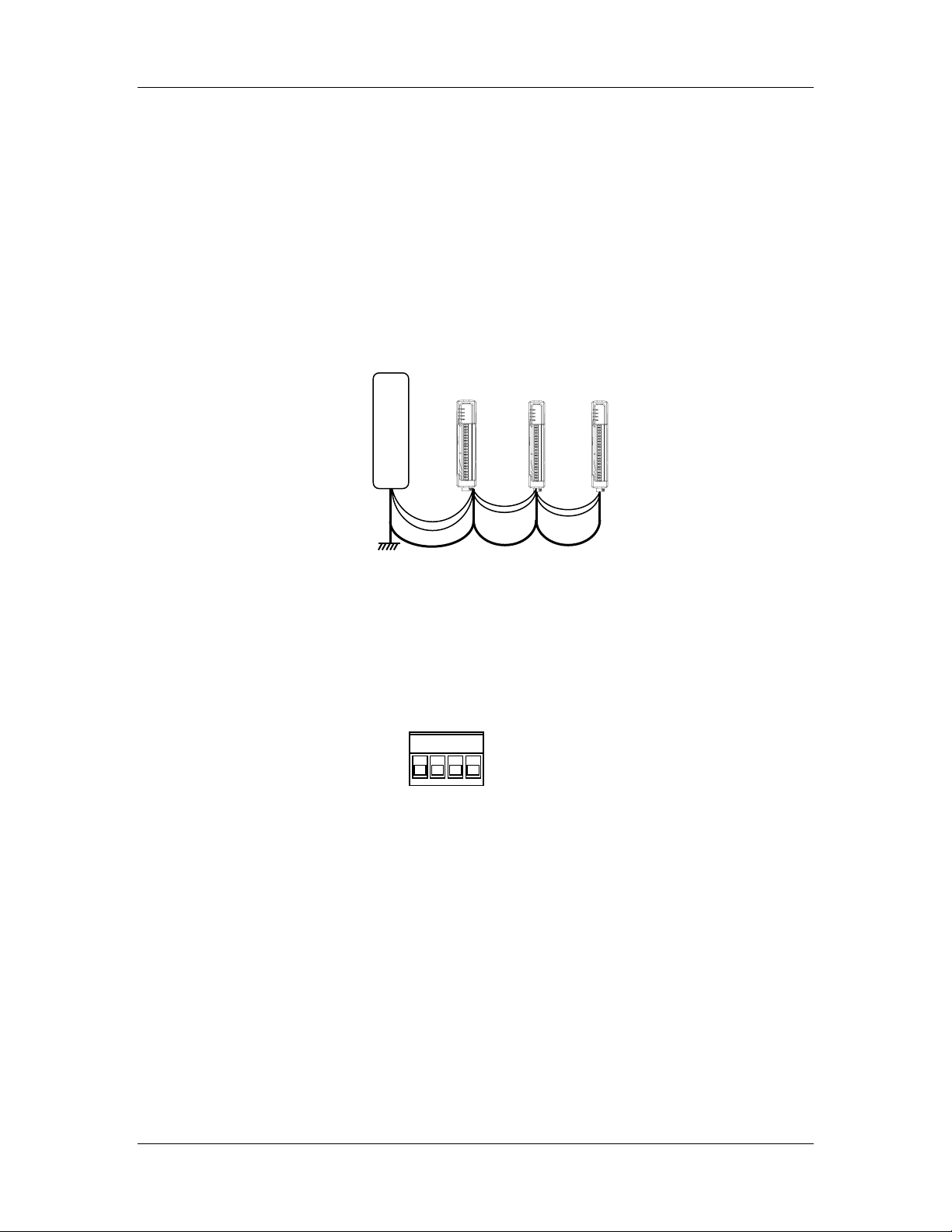
Several WI-I/O-EX modules may be connected to one master via RS485 multi-drop
connection as shown in Figure 2-1. Ensure there is good grounding between the WI-I/OEX units and the master. A 2.5 mm2 / 12 gauge earth wire is recommended.
Master
WI-I/O-EX
WI-I/O-EX WI-I/O-EX
Figure 2-1: Several WI-I/O-EX units connected to a master.
2.1.1 Power Connection
The WI-I/O-EX modules require a 10.8-30 VDC ** power supply. This is supplied to the
4-way connector, shown in Figure 2-2.
Figure 2-2: Power and RS485 connector. Connect 10.8-30 VDC** to + and earth to -.
Connect RS485 to B and A.
** Model Dependent. Check rear label for actual operating voltages
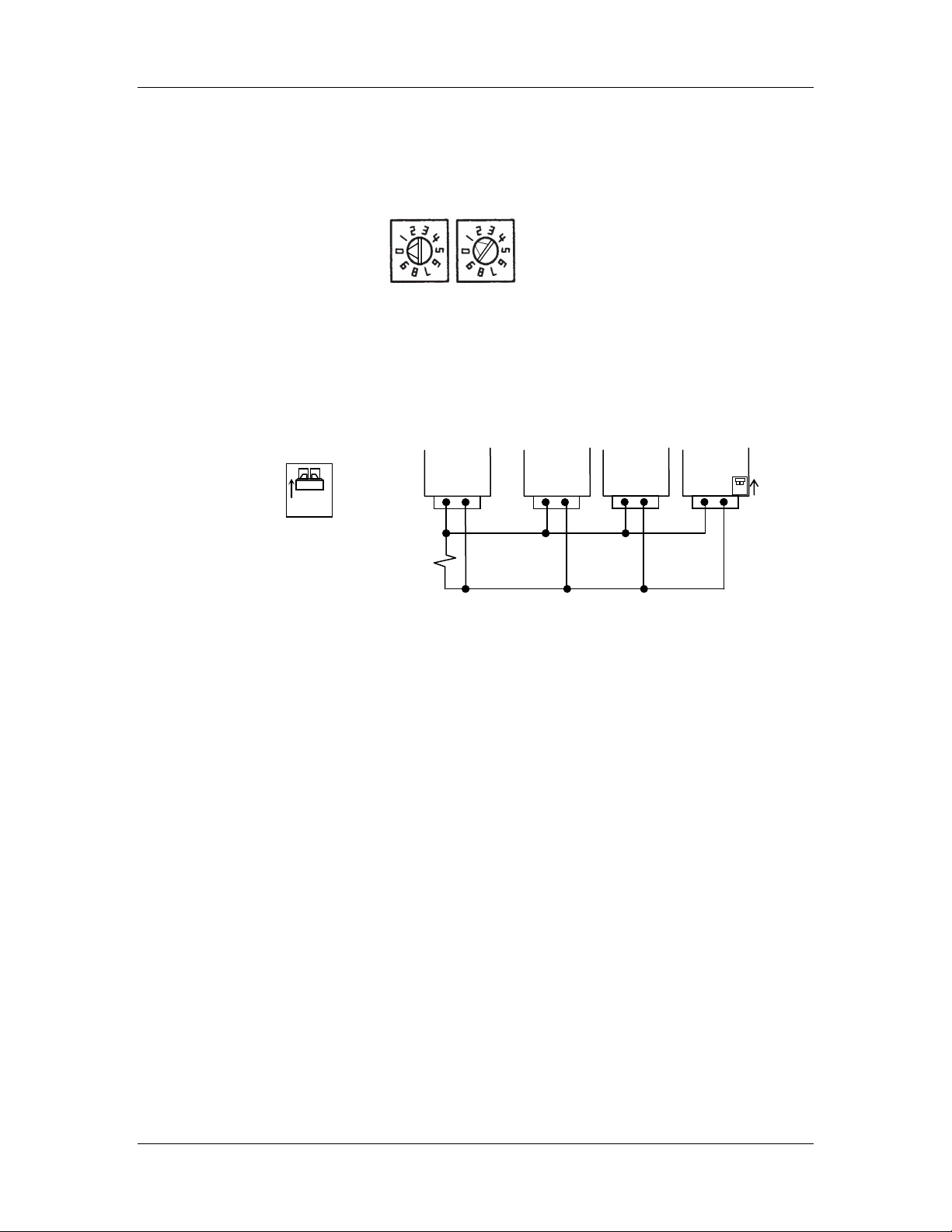
2.1.2 Address Switches
The address switches are found on the bottom panel of the module, as shown in Figure
2-3. If you are using the WI-I/O-EX module with other modules WI-I/O 9, WI-MOD-9-E
and WI-MOD-E modules), the address switches must be set to “00”. This enables ESeries protocol mode.
If you are using a ModBus Master device, ensure each WI-I/O-EX connected to the same
ModBus master has a unique ModBus address.
Note that the module must be reset after changing the address switches.
Page 10 February 2010
Page 11
WI-I/O-EX Serial I/O Module User Manual v1.11
A B
A B A B A B
Ω
You can connect to an WI-GTWY-9-MD1 Module using either MODBUS protocol or ESeries protocol. E-Series protocol is easier to set up, and we recommend using this
protocol for most applications.
x10 x1
Figure 2-3: Address switches. The address shown is 01.
Connect the RS485 B and A wires to the 4-way connector shown previously in Figure
2-2. An RS485 termination switch is provided. Terminate the last WI-I/O-EX module in
the multi-drop setup as shown in Figure 2-4.
Up = terminate
Down = unterminated
ON
RS485
termination
switch.
120
Master
WI-I/O-
EX
WI-I/O-
EX
WI-I/O-
EX
Termination
switch up
(terminated)
Figure 2-4: RS485 multi-drop connection and termination (only use external
termination for the master if it does not have internal termination).
WI-IO-EX Manual v1.11 Page 11
Page 12
WI-I/O-EX Serial I/O Module User Manual v1.11
DIO1
DIO2
EARTH
2.2 Signal Connections
All connections to the module should be SELV only. Normal 110/220/240V mains
supply should not be connected to any input terminal of the module.
2.2.1 Digital Inputs (and Pulsed Inputs)
The WI-I/O-EX-1-S-11 supports 16 digital signals, and the WI-I/O-EX-1-S-12 and WII/O-EX-1-S-13 support 8 digital signals. Additionally, digital inputs DIO1-4 on the WII/O-EX-1-S-11 operate as pulse inputs.
Digital output signals share the same terminals as the Digital input signals, marked DIO18, and DIO1-16 on the WI-I/O-EX-1-S-11 module.
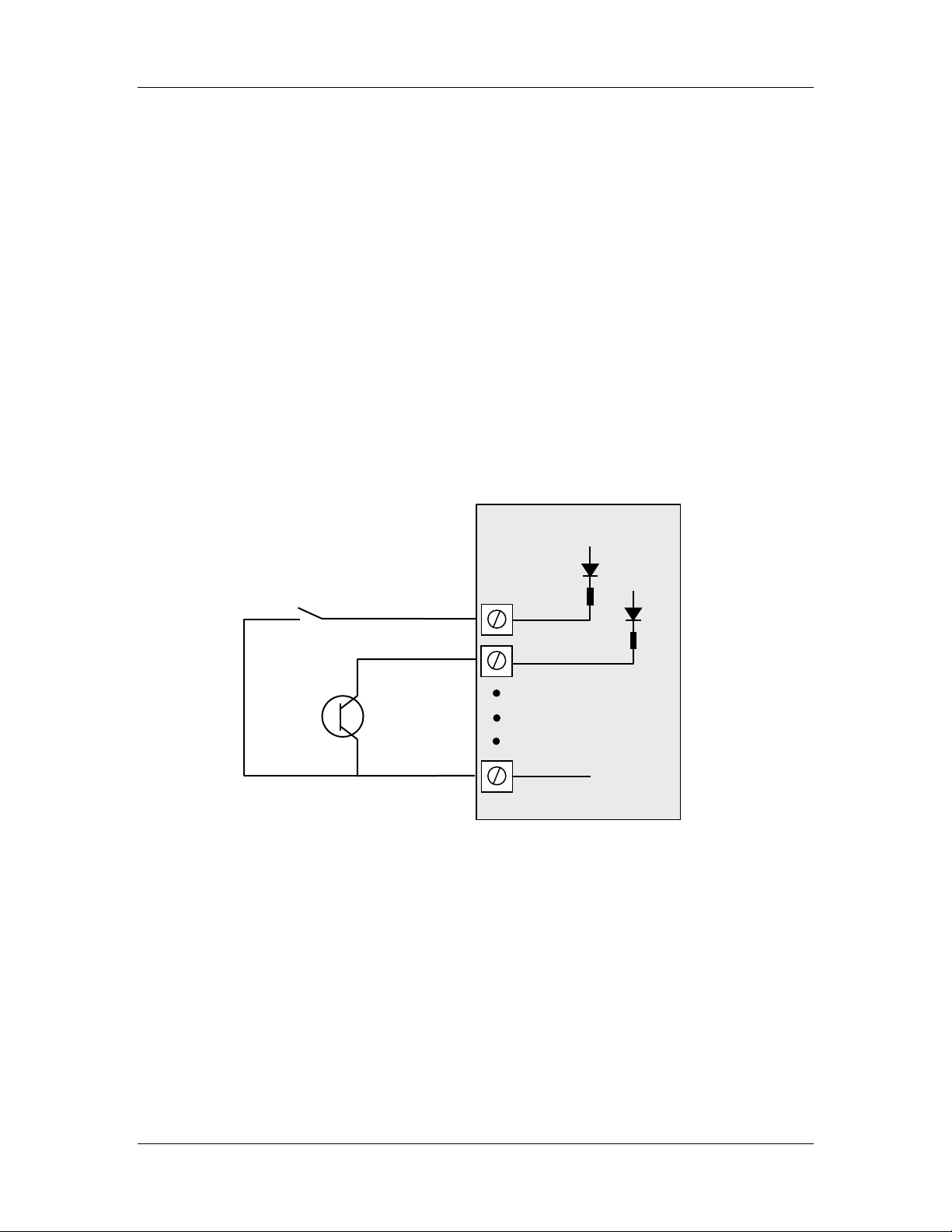
A digital input is activated by connecting to EARTH, either by voltage-free contact or by
a transistor switch. Refer to Figure 2-5:
WI-I/O-EX Module
V+
V+
Voltage-free contact
Transistor
switch device
V-
Figure 2-5: Connection of digital inputs.
Page 12 February 2010
Page 13
WI-I/O-EX Serial I/O Module User Manual v1.11
_
DIO1
DIO2
EARTH
2.2.2 Digital Outputs (and Pulsed Outputs)
The WI-I/O-EX-1-S-11 supports up to 16 digital outputs, shared with the digital input
function on the same terminals. The WI-I/O-EX-1-S-12 and WI-I/O-EX-1-S-13 both
provide 8 digital output signals. These signals are marked DIO1-8, and DIO1-16 for the
WI-I/O-EX-1-S-11. On all WI-I/O-EX modules, DIO1-8 can also operate as pulsed
outputs.
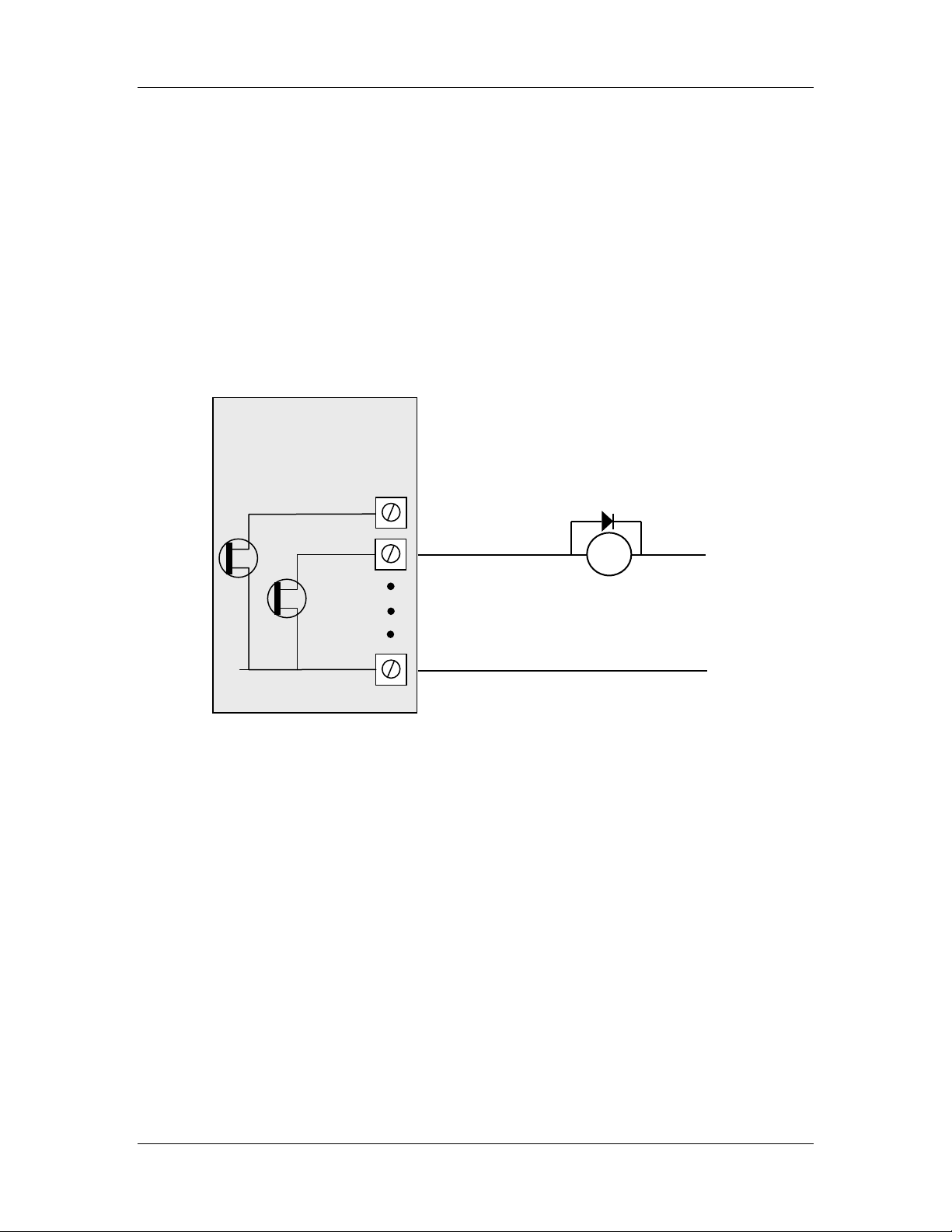
When active, digital outputs provide a transistor switch to EARTH. To connect a digital
output, refer to the diagram in Figure 2-6. A bypass diode is recommended to protect
against switching surges for inductive loads such as relay coils.
WI-I/O-EX Module
DC
Load
+
Max 30VDC
0.2A
V-
Figure 2-6: Connection of digital outputs.
Note that digital outputs will only switch DC circuits, with maximum voltage 30VDC.
2.2.3 Analog Inputs
The WI-I/O-EX-1-S-12 provides eight grounded single-ended or four floating differential
analog inputs. These provide measurement of voltage signals (0-10V) or current (0-20
mA) signals. An internal 24V analog loop supply (ALS) is generated for current loops.
Refer to Section 4.4 for detail on configuring single-ended, differential, current-mode or
voltage mode inputs.
WI-IO-EX Manual v1.11 Page 13
Page 14
WI-I/O-EX Serial I/O Module User Manual v1.11
AIN1
AIN2
AGND
ALS +24V
+
-
+
-
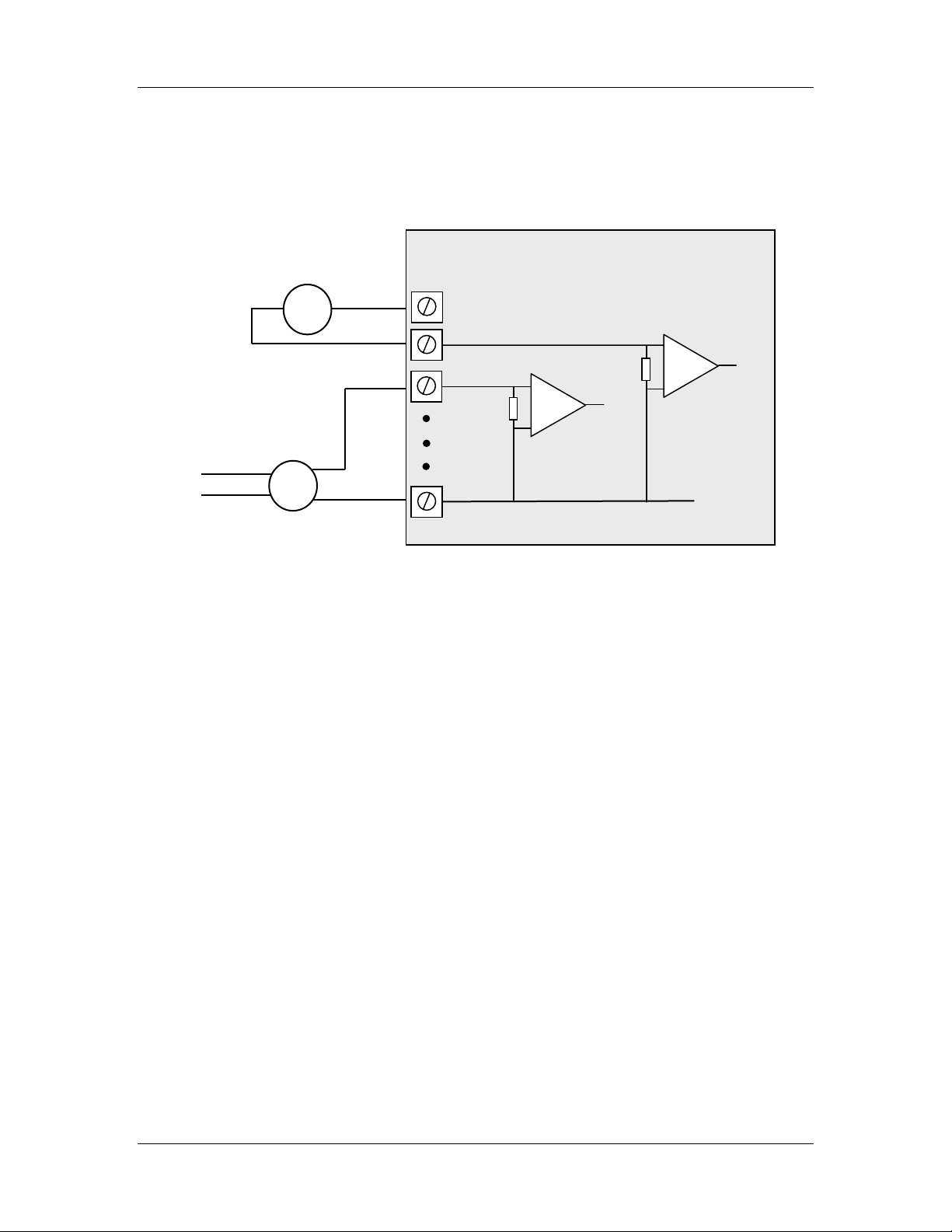
2.2.3.1 Grounded Single-Ended mA Inputs
Single-ended current inputs allow twice as many inputs as the differential mode. This
mode is useful when the sensor loop can be grounded to the WI-I/O-EX module. Devices
may also be powered by the 24V supplied by the WI-I/O-EX. Refer to Figure 2-7:
Loop powered
sensor
WI-I/O-EX Module
Externally powered
sensor
V-
Figure 2-7: Connection for single-ended current inputs. Transducers may be
externally powered or powered by the WI-I/O-EX +24V loop supply (ALS).
Note:
- The module is configured at the factory for this type of input
- To change the input configuration, refer to section 4.4
Page 14 February 2010
Page 15
WI-I/O-EX Serial I/O Module User Manual v1.11
AIN3
AIN4
AGND
ALS +24V
Externally powered
+
-
AIN1
AIN2
+
-
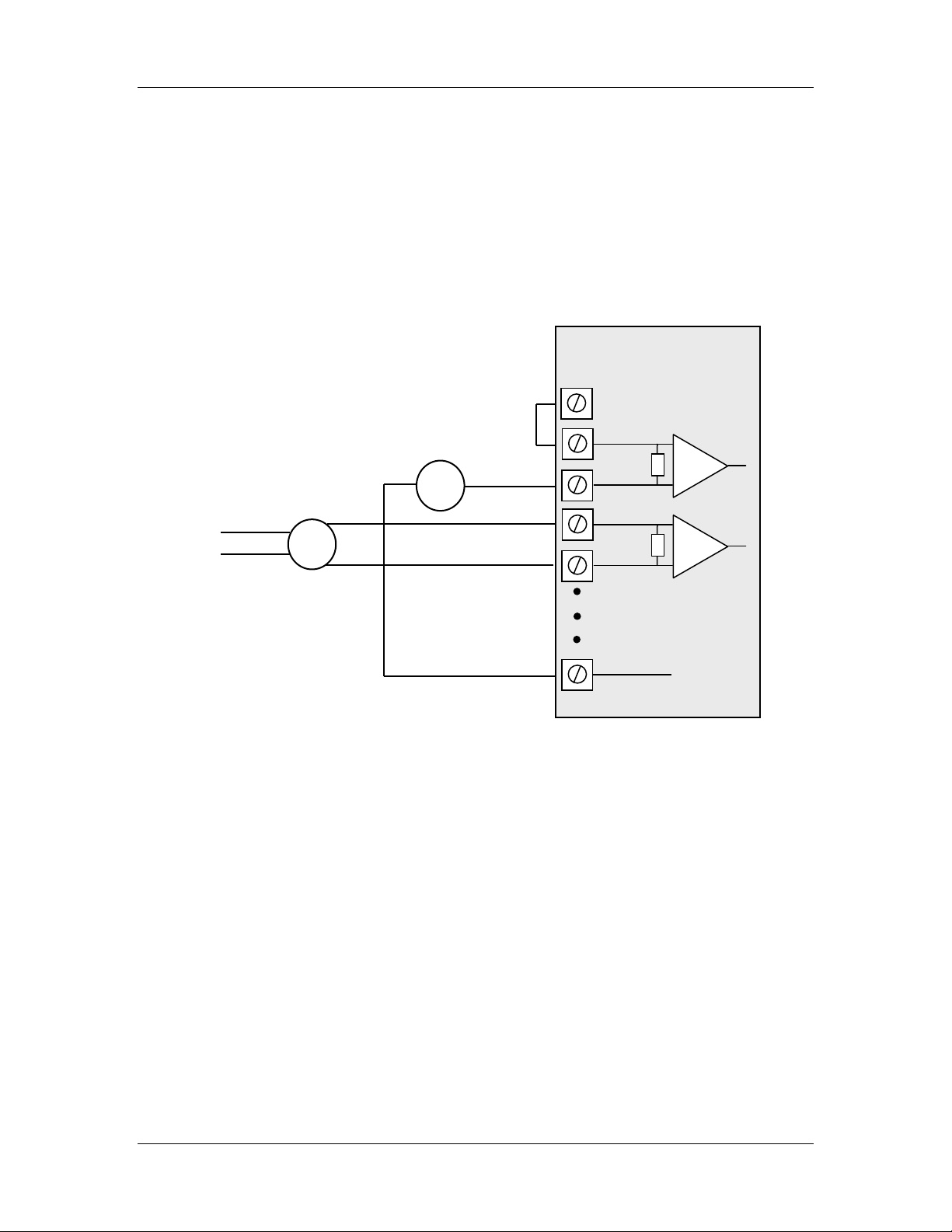
2.2.3.2 Floating Differential Mode mA Inputs
Differential mode current inputs should be used when measuring a current loop which
cannot be connected to earth or ground. This allows the input to be connected anywhere
in the current loop. Common mode voltage can be up to 27VDC.
Up to four loops can be connected, to terminal pairs [AIN1-AIN2], [AIN3-AIN4],
[AIN5-AIN6], [AIN7-AIN8] - the former terminal is positive and the latter negative.
The diagram in Figure 2-8 indicates how to connect devices for differential mode current
inputs.
WI-I/O-EX-1-S-12 Module
Loop powered
sensor
Power
supply
sensor
V-
Figure 2-8: Connections for differential current inputs.
Note:
- The module configuration needs to be changed for this type of input
- To change the input configuration, refer to section 4.4
WI-IO-EX Manual v1.11 Page 15
Page 16
WI-I/O-EX Serial I/O Module User Manual v1.11
AIN3
AIN4
AGND
AIN1
AIN2
+
-
+
-
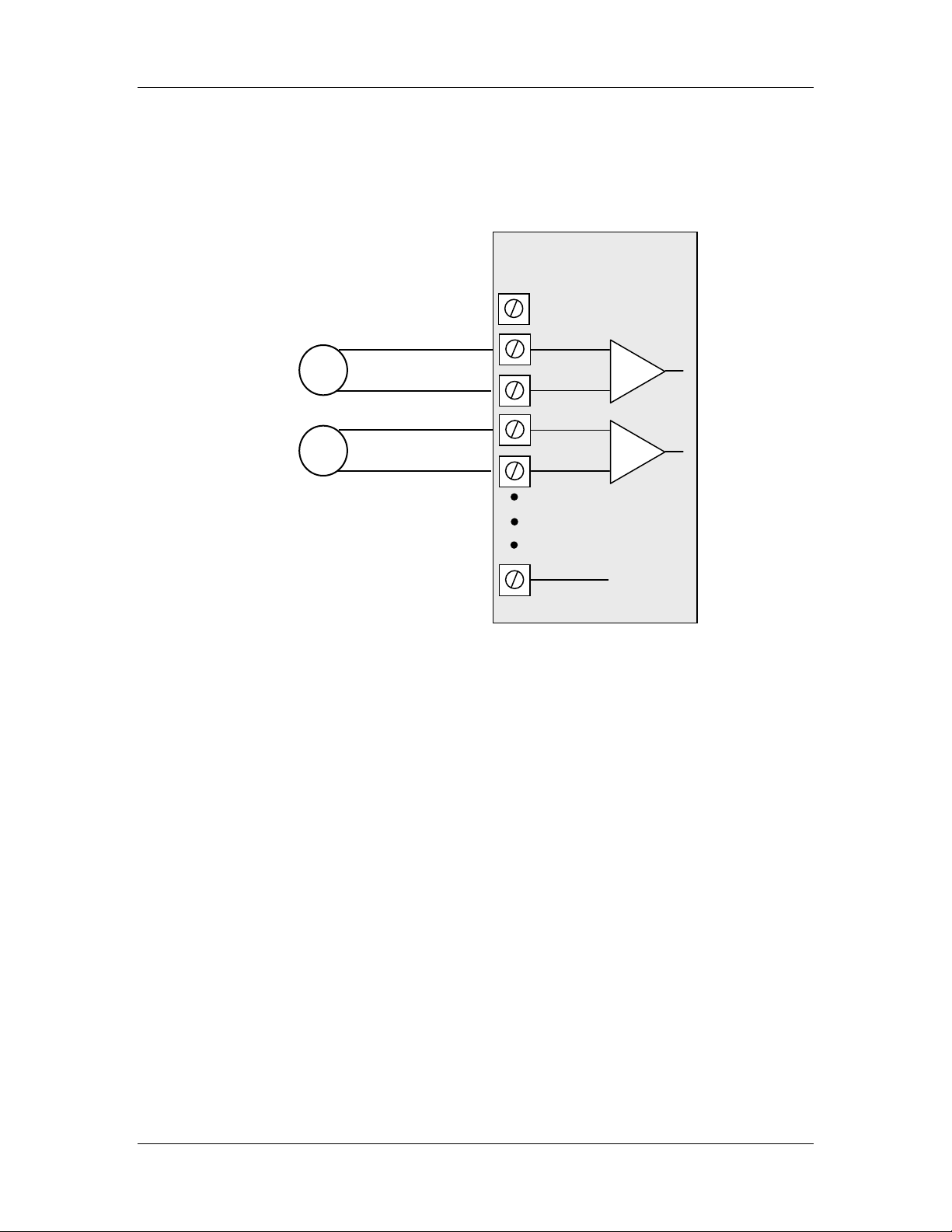
2.2.3.3 Floating Differential Voltage Inputs
Differential voltage inputs allow a voltage to be measured when it cannot be referenced
to earth or ground. The diagram in Figure 2-9 shows how to connect differential voltage
inputs. The module has a 27V common mode input range.
WI-I/O-EX-1-S-12 Module
ALS +24V
Sensors with
voltage signals
V-
Figure 2-9: Connection for differential voltage input mode.
Note:
- The module configuration needs to be changed for this type of input
- To change the input configuration, refer to section 4.4
Page 16 February 2010
Page 17
WI-I/O-EX Serial I/O Module User Manual v1.11
AIN1
AIN2
AGND
ALS +24V
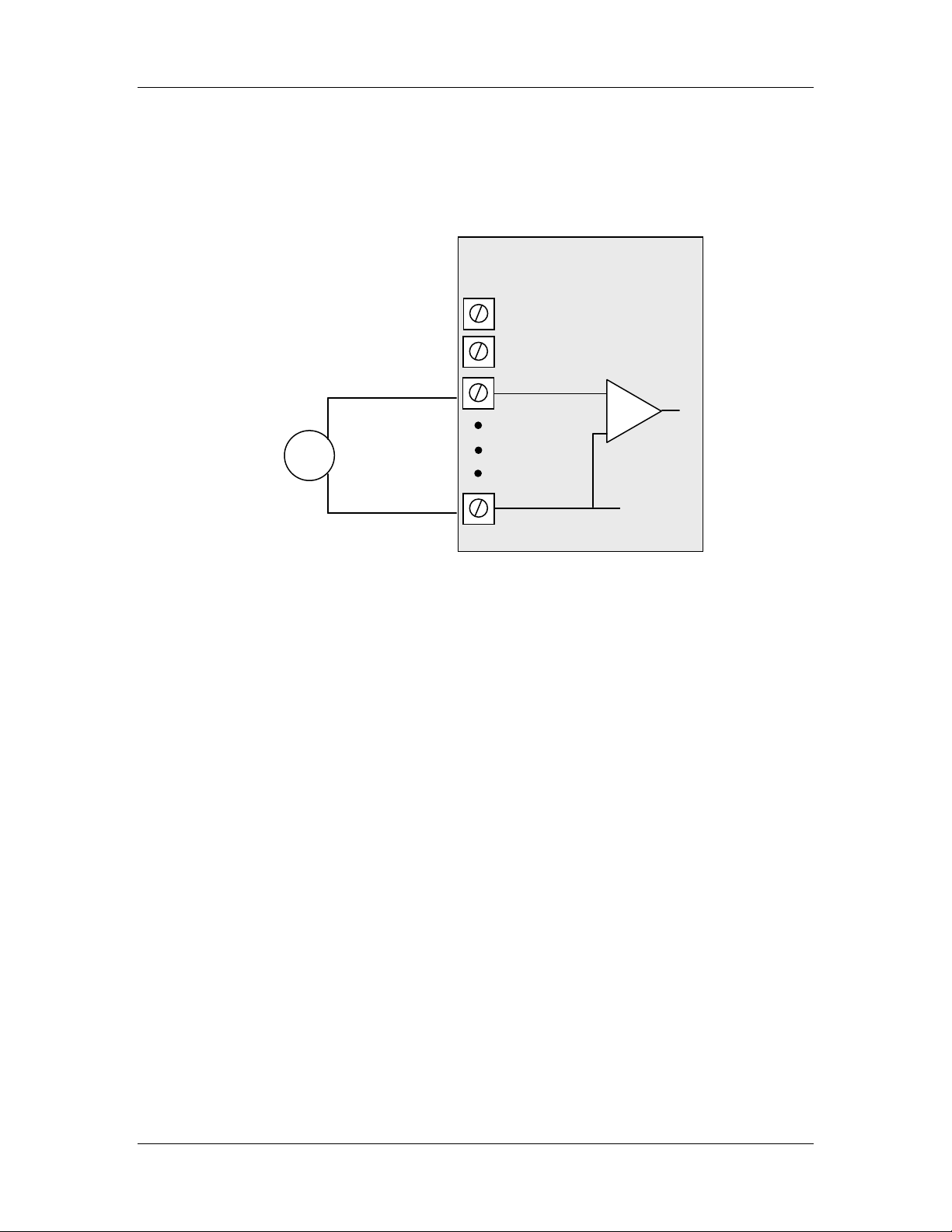
2.2.3.4 Single-ended Voltage Input
Single-ended voltage inputs allow twice as many inputs as differential mode. This mode
is useful when one end of the input voltage can be connected to the ground of the WI-I/OEX module. Figure 2-10 shows connections for single-ended voltage input.
WI-I/O-EX-1-S-12 Module
Sensor with voltage
signal
V-
Figure 2-10: Connection for single-ended voltage input.
Note:
- The module configuration needs to be changed for this type of input
- To change the input configuration, refer to section 4.4
2.2.4 Analog Outputs
The WI-I/O-EX-1-S-13 provides eight analog outputs. These may be configured as
voltage or current outputs. The current output may be selected as “sink” or “source”
current.
Refer to Section 4.5 for detail on configuring analog outputs.
WI-IO-EX Manual v1.11 Page 17
Page 18

WI-I/O-EX Serial I/O Module User Manual v1.11
AOT2
AGND
AI+
AI-
AOT1
AGND
AI
COM
+
-
2.2.4.1 Current Output
Current output mode may be configured for current source or current sink. Figure 2-11
shows the connections for current source mode. Figure 2-12 shows the connections for
current sink.
WI-I/O-EX-1-S-13 Module
ALS +24V
AOT2
+
PLC
V-
-
Figure 2-11: Connection for current source output.
Note:
- The module is configured at the factory for this type of output connection
- To change the input configuration, refer to section 4.5
WI-I/O-EX-1-S-13 Module
ALS +24V
AOT1
PLC
V-
Figure 2-12: Connection for current sink output.
Page 18 February 2010
Page 19

WI-I/O-EX Serial I/O Module User Manual v1.11
AOT1
AOT2
AGND
ALS +24V
AI
COM
Note:
- The hardware configuration needs to be changed for this type of output
connection
- To change the hardware configuration, refer to section 4.5
2.2.4.2 Voltage Output
Voltage output mode produces a voltage referenced to the module’s AGND. Figure 2-13
shows the connection for voltage output configuration.
WI-I/O-EX-1-S-13 Module
PLC
VOLTAGE
INPUT
+
V-
-
Figure 2-13: Connection for voltage output configuration.
WI-IO-EX Manual v1.11 Page 19
Page 20

WI-I/O-EX Serial I/O Module User Manual v1.11
3 Configuration
Use the WI Series Configuration utility to configure the WI-I/O-EX module to
communicate to WI-I/O 9, WI-MOD-9-E and WI-MOD-E modules.
- If you want to communicate using ModBus, then simply set the address using the
address switches on the bottom of the module. Refer to section 2.1.2 for details on
setting the address switches
- Ensure the Address switches are set to “00” for E-Series protocol mode. Refer to
section 2.1.2 for details on setting the address switches.
The WI Series Configuration utility allows you to configure systems consisting of a
mixture of Module types. You can download this software from the Weidmuller web site
at (http://wireless.weidmuller.com)
3.1 Add a radio module to connect the WI-I/O-EX to the radio network.
To configure a Serial module you must first create configuration for a radio module – For
example a WI-I/O-9 module. This is the radio module you plan to connect the serial
module to.
- Refer to your radio module user manual for an explanation on how to create the
radio module configuration.
3.2 Add the Serial Module
Once you have created the new radio module configuration, you can add the serial
module. Select the new radio module that you want to connect the WI-I/O-EX serial
module to, and select the “Serial Units” item. Select “Add a new Serial Unit” to create
the new configuration, or select “Load a New Serial Unit” to load the configuration from
an existing module. See Figure 3-1.
Page 20 February 2010
Page 21

WI-I/O-EX Serial I/O Module User Manual v1.11
Figure 3-1: Configuration of WI-I/O-EX modules using Configuration Utility.
When you select “Add a new Serial Unit”
you will need to select the unit type. Select
the correct module type here.
Figure 3-2: Select the unit type.
WI-IO-EX Manual v1.11 Page 21
Page 22

WI-I/O-EX Serial I/O Module User Manual v1.11
Finally, you will be prompted to select the
module address. You can choose to allow
the configuration software to select an
unused address for you, or you can select
the module address manually.
- Serial Module address must be in the
range 96 to 127.
- Every serial module that is
connected to the same radio module
needs a separate address.
- You can use the same address on
two different serial modules if they
are connected to different radio
modules.
Once you have added the new module you can configure it in the same way as for 105
series modules.
For more information on configuring these modules using the WI Series software, refer to
the WI-I/O-9 user manual.
Figure 3-3: Select unit address.
Page 22 February 2010
Page 23

WI-I/O-EX Serial I/O Module User Manual v1.11
4 Hardware Configuration
Hardware Set-up allows the WI-I/O-EX hardware function to be adjusted to suit the
application. To configure the hardware settings, you need:
- Access to the DIP switches under the Analog Configuration Panel (refer Figure
1-1: WI-I/O-EX unit with significant parts labeled.)
- Configuration Software to run on your PC.
Configuration of the WI-I/O-EX modules is performed by either the dedicated WI-I/OEX configuration software (cfg_WI-I/O-EX_Vx.xx.exe), or by the WI Series
configuration software (from the Utilities / Advanced - SXM menu).
4.1 Connecting to the WI-I/O-EX module
To use the configuration software, perform the following steps:
• Connect the WI-I/O-EX to the PC COM port with a standard serial cable (straight-
through, DB9 female to DB9 male. See Appendix for wiring.)
• Set the address switches to 00
• Supply power to the WI-I/O-EX via the “+” and “-” terminals on the bottom of the
module (10.8-30 VDC **).
** Model Dependent. Check rear label for actual operating voltages
• Start the configuration software on your PC or laptop (cfg_WI-I/O-EX_Vx.xx.exe)
Figure 4-1: Main configuration screen.
WI-IO-EX Manual v1.11 Page 23
Page 24

WI-I/O-EX Serial I/O Module User Manual v1.11
• Set the “Port” setting to match the computer com port you have connected to.
• Set the “Slave Address” to match the address switch setting of the WI-I/O-EX. If you
are using address “00” for E-Series Protocol, set the Slave Address to 100.
• Set the communications parameters. The default communications parameters are:
Baud rate: 9600
Parity: NONE
Stop bits: 1
Click the button labeled Connect to WI-I/O-EX.
If you are unable to communicate with the WI-I/O-EX, refer to Appendix C: Comms
Recovery.
If connection has been successful, several folder tabs will become available, depending
on the module type. The panel on the right-hand side of the form shows the WI-I/O-EX
detected and its settings.
4.2 Configuration common to all modules
4.2.1 Communications
Select the Comms folder tab. This page allows you to change the communications
settings of the WI-I/O-EX.
These settings are applied to both the RS-232 configuration port and to the RS-485
ModBus interface port.
Choose the required settings, then click Set comms. You will need to power off / on the
WI-I/O-EX for the new settings to take effect.
Figure 4-2: Communications configuration screen.
Page 24 February 2010
Page 25

WI-I/O-EX Serial I/O Module User Manual v1.11
Note that you will need to change the connection settings on the “Connect” page, and reconnect to the WI-I/O-EX.
4.2.2 Pulsed outputs
Choose the folder tab labeled Pulsed Outputs Setup, as shown in Figure 4-3.
Figure 4-3: Pulsed outputs setup page for a WI-I/O-EX-11. The pulsed outputs are
available on all models.
Clicking the button Read from WI-I/O-EX will read the pulse out update times from the
WI-I/O-EX and display them on the form.
The Pulse Out Update Times should be set to the approximate interval at which the WII/O-EX will receive updates to its pulse out target register. The pulse output circuitry will
attempt to generate pulses at a rate that will reach the target pulse count within the update
time. For example, if the ModBus master unit is configured to send the register value for
the pulse output channel every 1 minute, then the Update Time should be set to 1 minute.
The maximum allowed pulse out update time is 34 minutes 57 seconds. Set the update
times for each channel in hours, minutes, and seconds. An update time of zero will never
produce any pulses.
After the update times have been set, click the Save Update Times button.
The pulse output feature can be tested on the Check folder tab (refer section 5).
WI-IO-EX Manual v1.11 Page 25
Page 26

WI-I/O-EX Serial I/O Module User Manual v1.11
4.3 WI-I/O-EX-11 configuration
4.3.1 Pulsed Inputs
Choose the Pulse Inputs Setup page, as shown in Figure 4-4.
Figure 4-4: Pulse inputs setup. Only available on a WI-I/O-EX-11 module.
Clicking the Read from WI-I/O-EX button reads the existing maximum pulse rate settings
from the WI-I/O-EX and displays them on the form.
If pulse rate is to be used, the maximum pulse input rate must be set. The pulse rate value
is calculated as a fraction of the maximum pulse input rate. Specify the maximum pulse
input rate in pulses per minute. The highest allowable pulse input rate is 60000 pulses per
minute, or 1kHz.
Once the maximum pulse rates are specified, click the Save Max Rates button to save the
data to the WI-I/O-EX module.
The pulse input feature can be tested on the DIO Check page (refer section 5.1).
Page 26 February 2010
Page 27

WI-I/O-EX Serial I/O Module User Manual v1.11
4.4 WI-I/O-EX-12 configuration
4.4.1 Voltage input
Voltage inputs may be selected in the scales 0 to 5V, 0 to 10V, or 1 to 5V. For each scale,
the minimum to maximum signal levels are represented by 4000 hex to C000 hex. Table
4-1 shows how the WI-I/O-EX-12 voltage readings translate to outputs in other wireless
products.
WI-I/O-EX-
12 Voltage
scale
WI-I/O-EX-
12
Input voltage
WI-GTWY
Register value
(hex)
WI-I/O 9-1
Output current
(mA)
WI-I/O 9-3
Output current
(mA)
(V)
0 4000 4 4 0 to 5V
5 C000 20 20
0 4000 4 4 0 to 10V
10 C000 20 20
1 to 5V
0 2000 0.5* 0
1 4000 4 4
5 C000 20 20
Table 4-1: Compatibility of WI-I/O-EX-12 voltage inputs with other products.
*
Reduced accuracy for less than 4mA in WI-I/O-9-1.
WI-IO-EX Manual v1.11 Page 27
Page 28

WI-I/O-EX Serial I/O Module User Manual v1.11
4.4.1.1 Single-ended voltage input
If the WI-I/O-EX-1-S-12 is to measure voltage with respect to ground, choose the Singleended voltage input page, as shown in Figure 4-5.
Remove the access panel from the front of the WI-I/O-EX-1-S-12 case to
gain access to the dip switches. Replace the access panel after setting the
switches.
Set the switches according to the picture shown. The unit should be orientated with the
20-way connector towards you.
Figure 4-5: Setup page for single-ended voltage input.
Once the dip switches on the unit are set, tick the checkbox on the form, and click Save
configuration. Check the WI-I/O-EX Detected panel to ensure that the analog mode has
been updated (to Voltage, single-ended).
Clicking Read from WI-I/O-EX will read the scales out of the unit (if any) and display
them in the scales grid. Note that the dip switches should be set correctly for this result to
be relevant.
Choose the desired scale for each channel in the Scale box. Click the Save scales to WI-
I/O-EX button, and check that the scales are updated in the WI-I/O-EX Detected panel.
Page 28 February 2010
Page 29

WI-I/O-EX Serial I/O Module User Manual v1.11
4.4.1.2 Differential voltage input
The WI-I/O-EX-1-S-12 can be configured to measure differential voltage. Neighbouring
channels serve as reference voltages in this mode. The four differential pairs are: AIN1AIN2, AIN3-AIN4, AIN5-AIN6, and AIN7-AIN8.
Choose the page to configure the WI-I/O-EX-1-S-12 for differential voltage input, as
shown in Figure 4-6.
Remove the access panel from the front of the WI-I/O-EX-1-S-12 case to
gain access to the dip switches. Replace the access panel after setting the
switches.
Set the switches according to the picture shown. The unit should be orientated with the
20-way connector towards you.
Figure 4-6: Setup page for differential voltage input.
Once the dip switches on the unit are set, tick the checkbox on the form, and click Save
configuration. Check the WI-I/O-EX Detected panel to ensure that the analog mode has
been updated (to Voltage, differential).
WI-IO-EX Manual v1.11 Page 29
Page 30

WI-I/O-EX Serial I/O Module User Manual v1.11
Clicking Read from WI-I/O-EX will read the scales out of the unit (if any) and display
them in the scales grid. Note that the dip switches should be set correctly for this result to
be relevant.
Choose the desired scale for each channel in the Scale box. Click the Save scales to WI-
I/O-EX button, and check that the scales are updated in the WI-I/O-EX Detected panel.
4.4.2 Current input
Current inputs may be selected in the scales 0 to 10mA, 0 to 20mA, or 4 to 20mA. For
each scale, the minimum to maximum signal levels are represented by 4000 hex to C000
hex. Table 4-2 shows how the WI-I/O-EX-12 current readings translate to outputs in
other wireless products.
WI-I/O-EX-
12 Current
scale
WI-I/O-EX-
12
Input current
WI-GTWY
Register value
(hex)
WI-I/O 9-1
Output current
(mA)
WI-I/O 9-3
Output current
(mA)
(mA)
0 4000 4 4 0 to 10mA
10 C000 20 20
0 4000 4 4 0 to 20mA
20 C000 20 20
4 to 20mA
0 2000 0.5* 0
4 4000 4 4
20 C000 20 20
Table 4-2: Compatibility of WI-I/O-EX-12 current inputs with other products.
*
Reduced accuracy for less than 4mA in WI-I/O 9-1.
Page 30 February 2010
Page 31

WI-I/O-EX Serial I/O Module User Manual v1.11
4.4.2.1 Single-ended current input
The WI-I/O-EX-1-S-12 can also measure current input. To measure current with respect
to ground, choose the Single-ended current input page, as shown in Figure 4-7.
Remove the access panel from the front of the WI-I/O-EX-1-S-12 case to
gain access to the dip switches. Replace the access panel after setting the
switches.
Set the switches according to the picture shown. The unit should be orientated with the
20-way connector towards you.
Figure 4-7: Setup page for single-ended current input.
Once the dip switches on the unit are set, tick the checkbox on the form, and click Save
configuration. Check the WI-I/O-EX Detected panel to ensure that the analog mode has
been updated (to Current, single-ended).
Clicking Read from WI-I/O-EX will read the scales out of the unit (if any) and display
them in the scales grid. Note that the dip switches should be set correctly for this result to
be relevant.
Choose the desired scale for each channel in the Scale box. Click the Save scales to WI-
I/O-EX button, and check that the scales are updated in the WI-I/O-EX Detected panel.
WI-IO-EX Manual v1.11 Page 31
Page 32

WI-I/O-EX Serial I/O Module User Manual v1.11
4.4.2.2 Differential current input
The WI-I/O-EX-1-S-12 can be configured to measure differential current. The differential
pairs are: AIN1-AIN2, AIN3-AIN4, AIN5-AIN6, AIN7-AIN8. To use this configuration,
choose the differential current input page, as shown in Figure 4-8.
Remove the access panel from the front of the WI-I/O-EX-1-S-12 case to
gain access to the dip switches. Replace the access panel after setting the
switches.
Set the switches according to the picture shown. The unit should be orientated with the
20-way connector towards you.
Figure 4-8: Setup page for differential current configuration.
Once the dip switches on the unit are set, tick the checkbox on the form, and click Save
configuration. Check the WI-I/O-EX Detected panel to ensure that the analog mode has
been updated (to Current, differential).
Clicking Read from WI-I/O-EX will read the scales out of the unit (if any) and display
them in the scales grid. Note that the dip switches should be set correctly for this result to
be relevant.
Page 32 February 2010
Page 33

WI-I/O-EX Serial I/O Module User Manual v1.11
Choose the desired scale for each channel in the Scale box. Click the Save scales to WII/O-EX button, and check that the scales are updated in the WI-I/O-EX Detected panel.
4.5 WI-I/O-EX-1-S-13 configuration
4.5.1 Voltage output
Voltage outputs may be selected in the scales 0 to 5V, 0 to 10V, or 1 to 5V. For each
scale, the minimum to maximum signal levels are represented by 4000 hex to C000 hex.
Table 4-3 shows how signals from other wireless products translate to WI-I/O-EX-13
voltage levels.
WI-I/O-EX-1-
S-13
Voltage scale
WI-I/O 9-1
Input current
(mA)
WI-I/O 9-2
Input current
(mA)
WI-GTWY
Register value
(hex)
WI-I/O-EX-1-
S-13
Output voltage
(V)
4 4 4000 0 0 to 5V
20 20 C000 5
4 4 4000 0 0 to 10V
20 20 C000 10
1 to 5V
N/A* 0 2000 0
2* 2 3000 0.5
4 4 4000 1
20 20 C000 5
Table 4-3: Compatibility of other products with WI-I/O-EX-13 voltage outputs.
*
Reduced accuracy for less than 4mA in WI-I/O 9-1.
WI-IO-EX Manual v1.11 Page 33
Page 34

WI-I/O-EX Serial I/O Module User Manual v1.11
To configure the WI-I/O-EX-1-S-13 for voltage output, select the page as shown in
Figure 4-9.
Remove the access panel from the front of the WI-I/O-EX-1-S-13 case to
gain access to the dip switches. Replace the access panel after setting the
switches.
Set the switches according to the picture shown. The unit should be orientated with the
20-way connector towards you.
Figure 4-9: Voltage output setup page.
Once the dip switches on the unit are set, tick the checkbox on the form, and click Save
configuration. Check the WI-I/O-EX Detected panel to ensure that the analog mode has
been updated (to Voltage).
Clicking Read from WI-I/O-EX will read the scales out of the unit (if any) and display
them in the scales grid. Note that the dip switches should be set correctly for this result to
be relevant.
Choose the desired scale for each channel in the Scale box. Click the Save scales to WI-
I/O-EX button, and check that the scales are updated in the WI-I/O-EX Detected panel.
Page 34 February 2010
Page 35

WI-I/O-EX Serial I/O Module User Manual v1.11
4.5.2 Current output
Current outputs may be selected in the scales 0 to 10mA, 0 to 20mA, or 4 to 20mA. For
each scale, the minimum to maximum signal levels are represented by 4000 hex to C000
hex. Table 4-4 shows how signals from other wireless products translate to WI-I/O-EX1-S-13 current levels.
WI-I/O-EX-
1-S-13
Current scale
WI-I/O 9-1
Input current
(mA)
WI-I/O 9-2
Input current
(mA)
WI- GTWY
Register value
(hex)
WI-I/O-EX-1-
S-13
Output current
(mA)
4 4 4000 0 0 to 10mA
20 20 C000 10
4 4 4000 0 0 to 20mA
20 20 C000 20
4 to 20mA
N/A* 0 2000 0
2* 2 3000 2
4 4 4000 4
20 20 C000 20
Table 4-4: Compatibility of other products with WI-I/O-EX-1-S-13 voltage outputs.
*
Reduced accuracy for less than 4mA in WI-I/O 9-1.
WI-IO-EX Manual v1.11 Page 35
Page 36

WI-I/O-EX Serial I/O Module User Manual v1.11
To configure the WI-I/O-EX-1-S-13 for current output, select the page as shown in
Figure 4-10.
Remove the access panel from the front of the WI-I/O-EX-1-S-13 case to
gain access to the dip switches. Replace the access panel after setting the
switches.
Set the switches according to the picture shown. The unit should be orientated with the
20-way connector towards you.
Figure 4-10: Current output setup page.
Once the dip switches on the unit are set, tick the checkbox on the form, and click Save
configuration. Check the WI-I/O-EX Detected panel to ensure that the analog mode has
been updated (to Current).
Clicking Read from WI-I/O-EX will read the scales out of the unit (if any) and display
them in the scales grid. Note that the dip switches should be set correctly for this result to
be relevant.
Choose the desired scale for each channel in the Scale box. Click the Save scales to WI-
I/O-EX button, and check that the scales are updated in the WI-I/O-EX Detected panel.
Page 36 February 2010
Page 37

WI-I/O-EX Serial I/O Module User Manual v1.11
5 Operation
5.1 WI-I/O-EX-11 module
The I/O terminal block for the WI-I/O-EX-1-S-11 is shown in Figure 5-1.
DIO DIO DIO DIO DIO DIO DIO DIO DIO DIO DIO DIO DIO DIO DIO DIO
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Earth Earth 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 Earth Earth
Figure 5-1: I/O terminal block for WI-I/O-EX-1-S-11.
Pulse inputs coincide with DIO terminals 1-4. Pulse outputs coincide with DIO terminals
1-8.
The operation of the digital I/O may be confirmed using the configuration software. Start
the software as described in section 4, and choose the DIO Check page as shown in
Figure 5-2.
WI-IO-EX Manual v1.11 Page 37
Page 38

WI-I/O-EX Serial I/O Module User Manual v1.11
Figure 5-2: Check the operation of the WI-I/O-EX-11 module using the DIO Check
page.
Test the digital outputs by setting the select-buttons to ON or OFF - this will force the
DO to the selected state.
Digital inputs are reflected in the software by blacking (ON) or greying (OFF) of the
associated label in the Digital Inputs column.
The pulsed input count values are shown, as well as the pulse rate. The rate can be
viewed in decimal or hexadecimal and represents a fraction of the maximum pulse rate,
where hex 4000 is 0% and hex C000 is 100% of the maximum pulse rate.
The pulse output count values are also shown. The pulse out target may be set by clicking
the Edit Targets button. Pulses will be produced until the count reaches the target.
Page 38 February 2010
Page 39

WI-I/O-EX Serial I/O Module User Manual v1.11
5.2 WI-I/O-EX-1-S-12 module
The I/O terminal block for the WI-I/O-EX-1-S-12 is shown in Figure 5-3.
DIO DIO DIO DIO DIO DIO DIO DIO ALS AI+1 AI-1 AI+2 AI-2 AI+3 AI-3 AI+4 AI-4 A ALS
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Earth +24 AI 1 AI 2 AI 3 AI 4 AI 5 AI 6 AI 7 AI 8 GND +24
Figure 5-3: I/O terminal block for WI-I/O-EX-1-S-12.
Pulse outputs coincide with DIO terminals 1-8.
The operation of the WI-I/O-EX-1-S-12 may be confirmed using the configuration
software. Start the software as described in section 4, and choose the AIN Check page as
shown in Figure 5-4.
Figure 5-4: Check the operation of the WI-I/O-EX-1-S-12 module with the AIN
Check page.
Test the digital outputs by setting the select-buttons to ON or OFF - this will force the
DO to the selected state.
WI-IO-EX Manual v1.11 Page 39
Page 40

WI-I/O-EX Serial I/O Module User Manual v1.11
Digital inputs are reflected in the software by blacking (ON) or greying (OFF) of the
associated label in the Digital Inputs column.
The pulse output count values are also shown. The pulse out target may be set by clicking
the Edit Targets button. Pulses will be produced until the count reaches the target.
The analog inputs can be viewed in decimal or hexadecimal and represents a fraction of
the analog signal, where hex 4000 is 0% and hex C000 is 100%.
In differential configuration, only the value of the first channel in the differential pair
shows the quantity being measured. The second channel of each differential pair should
be ignored.
5.3 WI-I/O-EX-1-S-13 module
The I/O terminal block for the WI-I/O-EX-1-S-13 is shown in Figure 5-5.
DIO DIO DIO DIO DIO DIO DIO DIO ALS AOT AOT AOT AOT AOT AOT AOT AOT A ALS
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Earth +24 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 GND +24
Figure 5-5: I/O terminal block for WI-I/O-EX-1-S-13.
Pulse outputs coincide with DIO terminals 1-8.
The operation of the WI-I/O-EX-1-S-13 may be confirmed using the configuration
software. Start the software as described in chapter 4, and choose the AOT Check page.
Page 40 February 2010
Page 41

WI-I/O-EX Serial I/O Module User Manual v1.11
Figure 5-6: Check the operation of the WI-I/O-EX-1-S-13 module using the AOT
Check page.
Test the digital outputs by setting the select-buttons to ON or OFF - this will force the
DO to the selected state.
Digital inputs are reflected in the software by blacking (ON) or greying (OFF) of the
associated label in the Digital Inputs column.
The pulse output count values are also shown. The pulse out target may be set by clicking
the Edit Targets button. Pulses will be produced until the count reaches the target.
The analog outputs can be viewed in decimal or hexadecimal and represents a fraction of
the analog signal, where hex 4000 is 0% and hex C000 is 100%.
The analog output values can be set by the user for testing, and the output signal
measured to confirm the analog operation. If you are using hexadecimal values (which is
the easiest) ensure the $ symbol precedes the value to denote a hex number.
WI-IO-EX Manual v1.11 Page 41
Page 42

WI-I/O-EX Serial I/O Module User Manual v1.11
5.4 Hexadecimal representation of voltage and current levels
The voltage and current levels are represented as a fraction of the configured scale. 4000
hex represents the minimum level in the scale, and C000 hex represents the maximum
level in the scale.
Levels and their hex representation are summarized in Table 5-1 for easy reference.
Voltage scale Current scale
Hex
value
0000 0.00% 0 N/A N/A N/A N/A N/A N/A
0800 3.13% 2048 N/A N/A N/A N/A N/A N/A
1000 6.25% 4096 N/A N/A N/A N/A N/A N/A
1800 9.38% 6144 N/A N/A N/A N/A N/A N/A
2000 12.50% 8192 N/A N/A 0.00
2800 15.63% 10240 N/A N/A 0.25
3000 18.75% 12288 N/A N/A 0.50
3800 21.88% 14336 N/A N/A 0.75
4000 25.00% 16384 0.00 0.00 1.00 0.00 0.00 4.00
4800 28.13% 18432 0.31 0.63 1.25 0.63 1.25 5.00
5000 31.25% 20480 0.63 1.25 1.50 1.25 2.50 6.00
5800 34.38% 22528 0.94 1.88 1.75 1.88 3.75 7.00
6000 37.50% 24576 1.25 2.50 2.00 2.50 5.00 8.00
6800 40.63% 26624 1.56 3.13 2.25 3.13 6.25 9.00
7000 43.75% 28672 1.88 3.75 2.50 3.75 7.50 10.00
7800 46.88% 30720 2.19 4.38 2.75 4.38 8.75 11.00
8000 50.00% 32768 2.50 5.00 3.00 5.00 10.00 12.00
8800 53.13% 34816 2.81 5.63 3.25 5.63 11.25 13.00
9000 56.25% 36864 3.13 6.25 3.50 6.25 12.50 14.00
9800 59.38% 38912 3.44 6.88 3.75 6.88 13.75 15.00
A000 62.50% 40960 3.75 7.50 4.00 7.50 15.00 16.00
A800 65.63% 43008 4.06 8.13 4.25 8.13 16.25 17.00
B000 68.75% 45056 4.38 8.75 4.50 8.75 17.50 18.00
B800 71.88% 47104 4.69 9.38 4.75 9.38 18.75 19.00
C000 75.00% 49152 5.00 10.00 5.00 10.00 20.00 20.00
C800 78.13% 51200 5.31 10.63 5.25 10.63 21.25 21.00
D000 81.25% 53248 5.63 11.25 5.50 11.25 22.50 22.00
D800 84.38% 55296 5.94 11.88 5.75 11.88 23.75 23.00
E000 87.50% 57344 6.25 12.50 6.00 12.50 N/A 24.00
E800 90.63% 59392 6.56 13.13 6.25 13.13 N/A N/A
F000 93.75% 61440 6.88 13.75 6.50 13.75 N/A N/A
Percent
Dec
value
0-5V 0-10V 1-5V 0-10mA 0-20mA 4-20mA
N/A N/A 0.00
N/A N/A 1.00
N/A N/A 2.00
N/A N/A 3.00
Table 5-1: Hex representation of voltage and current levels.
Page 42 February 2010
Page 43

WI-I/O-EX Serial I/O Module User Manual v1.11
Appendix A. ModBus address map
A.1. WI-I/O-EX-11
Data ModBus I/O Type ModBus
Addresses
Digital input 1 Input status 10001
Digital input 2 Input status 10002
Digital input 3 Input status 10003
Digital input 4 Input status 10004
Digital input 5 Input status 10005
Digital input 6 Input status 10006
Digital input 7 Input status 10007
Digital input 8 Input status 10008
Digital input 9 Input status 10009
Digital input 10 Input status 10010
Digital input 11 Input status 10011
Digital input 12 Input status 10012
Digital input 13 Input status 10013
Digital input 14 Input status 10014
Digital input 15 Input status 10015
Digital input 16 Input status 10016
Digital output 1 Coil status 00001
Digital output 2 Coil status 00002
Digital output 3 Coil status 00003
Digital output 4 Coil status 00004
Digital output 5 Coil status 00005
Digital output 6 Coil status 00006
Digital output 7 Coil status 00007
Digital output 8 Coil status 00008
Digital output 9 Coil status 00009
Digital output 10 Coil status 00010
Digital output 11 Coil status 00011
Digital output 12 Coil status 00012
Digital output 13 Coil status 00013
Digital output 14 Coil status 00014
Digital output 15 Coil status 00015
Digital output 16 Coil status 00016
Pulse input count 1 Input registers 30017 – 30018
Pulse input count 2 Input registers 30019 – 30020
Pulse input count 3 Input registers 30021 – 30022
Pulse input count 4 Input registers 30023 – 30024
Pulse input rate 1 Input registers 30001
Pulse input rate 2 Input registers 30002
WI-IO-EX Manual v1.11 Page 43
Page 44

WI-I/O-EX Serial I/O Module User Manual v1.11
Data ModBus I/O Type ModBus
Addresses
Pulse input rate 3 Input registers 30003
Pulse input rate 4 Input registers 30004
Maximum input pulse rate 1 Input registers 30101
Maximum input pulse rate 2 Input registers 30102
Maximum input pulse rate 3 Input registers 30103
Maximum input pulse rate 4 Input registers 30104
Pulse output count 1 Input registers 30009
Pulse output count 2 Input registers 30010
Pulse output count 3 Input registers 30011
Pulse output count 4 Input registers 30012
Pulse output count 5 Input registers 30013
Pulse output count 6 Input registers 30014
Pulse output count 7 Input registers 30015
Pulse output count 8 Input registers 30016
Pulse output target 1 Holding registers 40009
Pulse output target 2 Holding registers 40010
Pulse output target 3 Holding registers 40011
Pulse output target 4 Holding registers 40012
Pulse output target 5 Holding registers 40013
Pulse output target 6 Holding registers 40014
Pulse output target 7 Holding registers 40015
Pulse output target 8 Holding registers 40016
Pulse out update time 1 Input registers 30109
Pulse out update time 2 Input registers 30110
Pulse out update time 3 Input registers 30111
Pulse out update time 4 Input registers 30112
Pulse out update time 5 Input registers 30113
Pulse out update time 6 Input registers 30114
Pulse out update time 7 Input registers 30115
Pulse out update time 8 Input registers 30116
Module supply voltage* Input registers 30033
Serial port transmission mode Input registers 30201
Serial port baud rate Input registers 30202
Serial port parity and stop bit Input registers 30203
*
0x4000 = 8V; 0xC000 = 16V
Page 44 February 2010
Page 45

WI-I/O-EX Serial I/O Module User Manual v1.11
A.2. WI-I/O-EX-1-S-12
Data ModBus I/O Type ModBus
Addresses
Digital input 1 Input status 10001
Digital input 2 Input status 10002
Digital input 3 Input status 10003
Digital input 4 Input status 10004
Digital input 5 Input status 10005
Digital input 6 Input status 10006
Digital input 7 Input status 10007
Digital input 8 Input status 10008
Digital output 1 Coil status 00001
Digital output 2 Coil status 00002
Digital output 3 Coil status 00003
Digital output 4 Coil status 00004
Digital output 5 Coil status 00005
Digital output 6 Coil status 00006
Digital output 7 Coil status 00007
Digital output 8 Coil status 00008
Pulse output count 1 Input registers 30009
Pulse output count 2 Input registers 30010
Pulse output count 3 Input registers 30011
Pulse output count 4 Input registers 30012
Pulse output count 5 Input registers 30013
Pulse output count 6 Input registers 30014
Pulse output count 7 Input registers 30015
Pulse output count 8 Input registers 30016
Pulse output target 1 Holding registers 40009
Pulse output target 2 Holding registers 40010
Pulse output target 3 Holding registers 40011
Pulse output target 4 Holding registers 40012
Pulse output target 5 Holding registers 40013
Pulse output target 6 Holding registers 40014
Pulse output target 7 Holding registers 40015
Pulse output target 8 Holding registers 40016
Pulse out update time 1 Input registers 30109
Pulse out update time 2 Input registers 30110
Pulse out update time 3 Input registers 30111
Pulse out update time 4 Input registers 30112
Pulse out update time 5 Input registers 30113
Pulse out update time 6 Input registers 30114
Pulse out update time 7 Input registers 30115
Pulse out update time 8 Input registers 30116
Analog inputs 1 Input registers 30001
WI-IO-EX Manual v1.11 Page 45
Page 46

WI-I/O-EX Serial I/O Module User Manual v1.11
Data ModBus I/O Type ModBus
Addresses
Analog inputs 2 Input registers 30002
Analog inputs 3 Input registers 30003
Analog inputs 4 Input registers 30004
Analog inputs 5 Input registers 30005
Analog inputs 6 Input registers 30006
Analog inputs 7 Input registers 30007
Analog inputs 8 Input registers 30008
Module supply voltage* Input registers 30033
Analog supply voltage (24V)+ Input registers 30034
Serial port transmission mode Input registers 30201
Serial port baud rate Input registers 30202
Serial port parity and stop bit Input registers 30203
*
0x4000 = 8V; 0xC000 = 16V
+
0x4000 =12V; 0xC000 = 36V
Page 46 February 2010
Page 47

WI-I/O-EX Serial I/O Module User Manual v1.11
A.3. WI-I/O-EX-1-S-13
Data ModBus I/O Type ModBus
Addresses
Digital input 1 Input status 10001
Digital input 2 Input status 10002
Digital input 3 Input status 10003
Digital input 4 Input status 10004
Digital input 5 Input status 10005
Digital input 6 Input status 10006
Digital input 7 Input status 10007
Digital input 8 Input status 10008
Digital output 1 Coil status 00001
Digital output 2 Coil status 00002
Digital output 3 Coil status 00003
Digital output 4 Coil status 00004
Digital output 5 Coil status 00005
Digital output 6 Coil status 00006
Digital output 7 Coil status 00007
Digital output 8 Coil status 00008
Pulse output count 1 Input registers 30009
Pulse output count 2 Input registers 30010
Pulse output count 3 Input registers 30011
Pulse output count 4 Input registers 30012
Pulse output count 5 Input registers 30013
Pulse output count 6 Input registers 30014
Pulse output count 7 Input registers 30015
Pulse output count 8 Input registers 30016
Pulse output target 1 Holding registers 40009
Pulse output target 2 Holding registers 40010
Pulse output target 3 Holding registers 40011
Pulse output target 4 Holding registers 40012
Pulse output target 5 Holding registers 40013
Pulse output target 6 Holding registers 40014
Pulse output target 7 Holding registers 40015
Pulse output target 8 Holding registers 40016
Pulse out update time 1 Input registers 30109
Pulse out update time 2 Input registers 30110
Pulse out update time 3 Input registers 30111
Pulse out update time 4 Input registers 30112
Pulse out update time 5 Input registers 30113
Pulse out update time 6 Input registers 30114
Pulse out update time 7 Input registers 30115
Pulse out update time 8 Input registers 30116
WI-IO-EX Manual v1.11 Page 47
Page 48

WI-I/O-EX Serial I/O Module User Manual v1.11
Data ModBus I/O Type ModBus
Addresses
Analog outputs 1 Holding registers 40001
Analog outputs 2 Holding registers 40002
Analog outputs 3 Holding registers 40003
Analog outputs 4 Holding registers 40004
Analog outputs 5 Holding registers 40005
Analog outputs 6 Holding registers 40006
Analog outputs 7 Holding registers 40007
Analog outputs 8 Holding registers 40008
Module supply voltage* Input registers 30033
Analog supply voltage (28V) + Input registers 30034
Serial port transmission mode Input registers 30201
Serial port baud rate Input registers 30202
Serial port parity and stop bit Input registers 30203
*
0x4000 = 8V; 0xC000 = 16V
+
0x4000 =12V; 0xC000 = 36V
Page 48 February 2010
Page 49

WI-I/O-EX Serial I/O Module User Manual v1.11
Appendix B. ModBus Functionality
Table B-1 specifies the maximum query and response data parameters for the WI-I/OEX modules. See the Gould ModBus Protocol Reference guide (PI-MBUS 300 Rev
B) for more detail.
Function
code
1,2 Read coil / input status 1160 coils / inputs
Description Maximum Data
Size
3 Read holding (output) registers
4 Read input registers 145 registers
5 Force single coil 1 coil
6 Set single register 1 register
7 Read exception status 8 coils
8 Loopback test N/A
9,10 NOT SUPPORTED NOT SUPPORTED
11 Communications event counter
12-14 NOT SUPPORTED NOT SUPPORTED
15 Force multiple coils 1160 coils
16 Set multiple registers 145 registers
17-255 NOT SUPPORTED NOT SUPPORTED
Table B-1: Supported ModBus functions and limitations for WI-I/O-EX modules.
145 registers
N/A
WI-IO-EX Manual v1.11 Page 49
Page 50

WI-I/O-EX Serial I/O Module User Manual v1.11
Appendix C. Comms Recovery
If the communications setting of the WI-I/O-EX has been forgotten or mistakenly set,
there is a way of recovering serial communications with the WI-I/O-EX. WI-I/O-EX
firmware versions 1.04 and earlier require ModScan to do this. With later firmware
versions, this can be done using the configuration software, cfg_WI-I/O-EX_Vx.xx.exe.
Procedure for recovering communications with recent firmware (V1.05 and later):
1. Set the ModBus address switches to 00. This fixes the communications setting to
ModBus RTU, 9600 baud, no parity, and one stop bit.
2. Connect a standard (straight-through) RS232 cable to the module and the PC.
3. Start the configuration software, cfg_WI-I/O-EX_Vx.xx.exe.
4. Set the slave address to 100.
5. Ensure the comms settings are 9600 baud, no parity, one stop bit.
6. Click Connect to WI-I/O-EX
7. The module should connect successfully.
8. Choose the Comms page and change the settings to the desired parameters.
9. If the module did not connect successfully, try the steps listed below for using
ModScan.
Procedure for recovering communications with firmware V1.04 and earlier:
1. Set the ModBus address switches to 00. This fixes the communications setting to
those specified in step 6.
2. Connect the RS232 port to the PC and start ModScan.
3. Supply power to the WI-I/O-EX.
4. In ModScan, set the following
- Address: 0201
- Length: 3
- Device ID: 100
- ModBus Point Type: Holding register
5. Click Connection / Connect.
6. Choose the appropriate COM port. Also choose
- Baud rate: 9600
- Word length: 8
- Parity: none
- Stop bits: 1
7. Click Protocol Selection. Choose STANDARD ASCII for Transmission mode. Click
OK, OK.
8. ModScan should connect to the module with no errors.
9. The registers displayed in ModScan represent the serial port settings that are used
when the address switches are set to other than 00, as follows:
Page 50 February 2010
Page 51

WI-I/O-EX Serial I/O Module User Manual v1.11
Address Description
40201 Serial port transmission mode
40202 Serial port baud rate
40203 Serial port parity and stop bit
10. Use the tables below to work out the current communications settings, or write to the
registers using ModScan to change the settings to the desired values. Note that the
module transmission mode should be set to ModBus RTU.
ModBus address 40201, serial port transmission mode:
Setting Register
Value
ModBus RTU 0x0101
ModBus ASCII, 8 data
bits
ModBus ASCII, 7 data
bits
ModBus address 40202, serial port baud rate:
Setting Register
Value
1200 0x000C
2400 0x0018
4800 0x0030
9600 0x0060
14400 0x0090
19200 0x00C0
28800 0x0120
38400 0x0180
57600 0x0240
76800 0x0300
115200 0x0480
ModBus address 40203, serial port parity and stop bit:
Parity Setting Register’s High Byte
None 0x00
Odd 0x11
Even 0x22
Stop-bit
Setting
1 stop bit 0x11
2 stop bits 0x22
Register’s Low Byte
0x0201
0x0202
Value
Value
WI-IO-EX Manual v1.11 Page 51
Page 52

WI-I/O-EX Serial I/O Module User Manual v1.11
11. Once the new comms setting are correct, be sure to change the address switches back
to a non-zero setting for normal operation.
Page 52 February 2010
Page 53

WI-I/O-EX Serial I/O Module User Manual v1.11
Appendix D. Specifications
EMC Approval EN 55024:1998
EN 61000-3-2: 2002
EN 61000-3-3: 2002
EN 55022: 1998
FCC Part 15
Operating temperature
range
Power supply 10.8 – 30.0 VDC
Supply current (idle 13.8V)
-11
-12
-13
Supply current for I/O
per digital input
per digital output
per analog input
per analog output
Loop supply 24V nominal * * Loop supply will follow
Loop supply max current WI-I/O-EX-12 : 270mA
RS232 port ModBus protocol
RS485 port ModBus protocol
ModBus protocol
Transmission modes ModBus ASCII 8 data bits
Baud rates 1200; 2400; 4800; 9600;
Parity Odd, even, none
Stop bits 1, 2
Slave address 01 - 99
Default settings If slave address = 0 ModBus RTU, 9600, N, 1
Digital inputs
-40 to +60 deg C
13.8V / 24VDC nom
100mA
100mA
120mA
13mA
13mA
50mA
50mA
WI-I/O-EX-13 : 160mA
WI-Series protocol
ModBus ASCII 7 data
bits**
ModBus RTU
14,400; 19,200; 28,800;
38,400; 57,600; 76,800;
115,200
Model Dependent. Check
rear label for actual
operating voltages
If using 24V loop supply
WI-I/O-EX-xx power
supply voltage above 24V
input.
** If no parity, use 2 stop
bits. If using parity, use 1
stop bit.
WI-IO-EX Manual v1.11 Page 53
Page 54

WI-I/O-EX Serial I/O Module User Manual v1.11
On-state voltage <2.1VDC
Wetting current 5mA
Max pulse input rate 1kHz
Minimum pulse width 0.5mS
Max pulse input count 4294967295 (32-bit)
Digital outputs
Output voltage range 0-30VDC
Output current max 200mA
Max pulse output rate 100Hz
Max pulse output count 65535
Analog Inputs
Input voltage range 0-12V
Voltage resolution 16 bits
Input current range 0-24mA
Current resolution 16 bits
Input impedance (voltage) 100k
Input impedance (current) 100ohm
Common mode voltage
range
Calibrated accuracy 0.10%
Analog Outputs
Output voltage range 0-12V
Voltage resolution 12 bits
Output current range 0-24mA Total output current 160mA
Current resolution 12 bits
Calibrated accuracy 0.10%
27VDC
Table D-1: WI-I/O-EX Specifications.
WI-I/O-EX-1-S -11 -12 -13
Digital
inputs/outputs
Pulse outputs
Pulse inputs
Analog inputs
Analog outputs
Table D-2: WI-I/O-EX module types and I/O.
Page 54 February 2010
Up to 16 Up to 8 Up to 8
8 8 8
4 - -
- 4 floating / 8
commoned
- - 8
-
Page 55

WI-I/O-EX Serial I/O Module User Manual v1.11
DB9
PC
DB9
Appendix E. RS232 Wiring
The RS232 connection to the WI-I/O-EX modules requires a standard straight-through
serial cable (modem cable). The wiring is shown in Figure E-1.
WI-I/O-EX
MALE
FEMALE
Figure E-1: Wiring for RS232 cable for PC-WI-I/O-EX communications.
WI-IO-EX Manual v1.11 Page 55
 Loading...
Loading...