Page 1

[ CARE AND USE MANUAL ]
[ CARE AND USE MANUAL ]
Sep-Pak XPoSure Aldehyde Sampler
CONTENTS
I. INTRODUCTION
a. Sep-Pak DNPH-Silica Cartridge Description
II. USING THE SEP-PAK XPOSURE
ALDEHYDE SAMPLER
a. Theory of Operation
b. Preventing Contamination
c. Collecting the Sample
d. Eluting the Derivatives from the Sampler
III. ANALYZING THE DNPH DERIVATIVES
a. Theory of Operation
b. Preventing Contamination
c. Collecting the Sample
d. Calculating Results
IV. APPLICATION EXAMPLES
a. Formaldehyde in Laboratory Air - STEL
b. Glutaraldehyde in Laboratory Air – STEL
I. INTRODUCTION
Waters Sep-Pak® XPoSure™ Aldehyde Samplers are convenient,
reproducible sampling devices for quantifying formaldehyde
concentrations in the workplace and indoor air within a range of
0.001 to 5 parts per million (ppmv).
V. STORAGE AND DISPOSAL OF THE SAMPLERS
a. Storing Unused Samplers
b. Storing Exposed Samplers
c. Disposing of used cartridges
VI. TROUBLESHOOTING
VII. REFERENCES AND BIBLIOGRAPHY
VIII. ORDERING INFORMATION
IX. APPENDIC ES
a. Appendix A: Measuring Acetontrile Purity
b. Appendix B: Synthesizing the DNPH-Derivative Standards
c. Appendix C: Measuring Breakthrough
d. Appendix D: Useful Conversion Factors
d.1. Carbonyl to Hydrazone Conversion Factors
d.2. Equation for converting µg/L to ppmv
d.3. Conversion Factors: µg/L to ppmv
Page 2
[ CARE AND USE MANUAL ]
[ CARE AND USE MANUAL ]
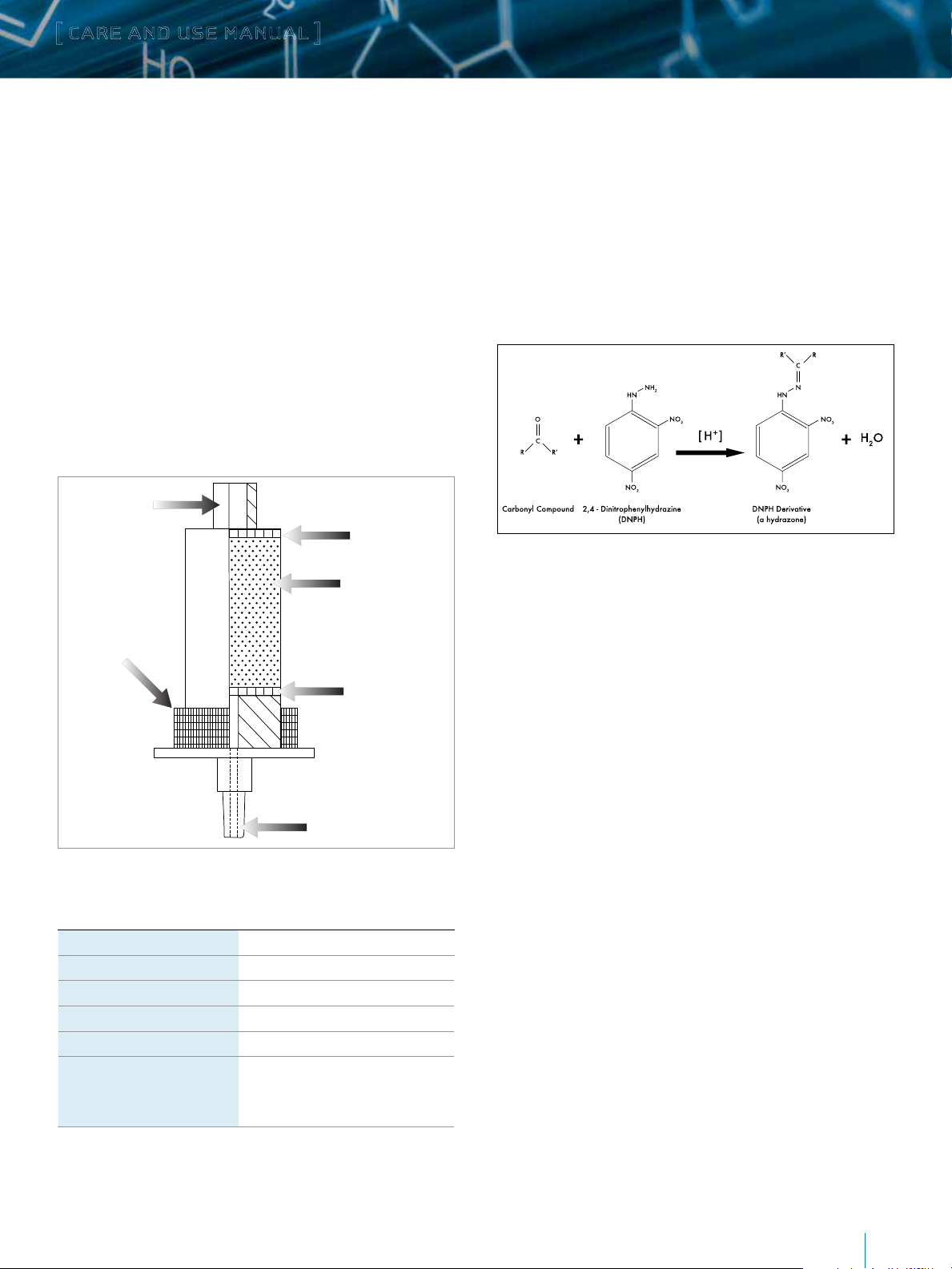
a. Sep-Pak XPoSure Aldehyde Sampler Description
and Features
Sep-Pak XPoSure Aldehyde Samplers contain acidified
2,4-Dinitrophenylhydrazine(DNPH)-coated silica, packed
in Waters Sep-Pak Plus cartridges.
The samplers are constructed from high-purity and high-
density polyethylene components, triaxially-compressed
packed beds and Luer fittings equipped with end caps and
plugs.
The samplers are designed for flow rates of up to 1.5 L/min
with typical personal pumps.
The gold-colored aluminum compression ring on the
Sep-Pak XPoSure Aldehyde Sampler allows for easy
identification.
Luer Connector
Polyethylene Filter
DNPH-Silica
Aluminum
Compression Ring
Polyethylene Filter
II. USING THE SEP-PAK XPOSURE
ALDEHYDE SAMPLER
a. Theory of Operation
Sep-Pak XPoSure Aldehyde Samplers trap aldehydes in air by
reacting them with acidified 2,4-dinitrophenylhydrazine(DNPH),
forming stable hydrazone derivatives. The derivitization reaction,
as shown in Figure 2, takes place during sample collection. T he
derivatives are later eluted and analyzed using HPLC.
Figure 2. Derivitization Reaction.
b. Preventing Contamination
Contamination is most likely to occur during sample collection.
Before eluting the derivatives, clean all glassware by rinsing with
acetonitrile and heating to 60 °C in a vacuum oven for at least
30 minutes. Eluting the samples in a nitrogen-purged glove box
further reduces the risk of contamination.
Luer Connector
Figure 1. Cutaway View.
Table 1: Physical and Chemical Properties
Hold-up Volume
Collection Efficiency
Capacity
Quantity of DNPH Silica
Sampling Temperature
Dimensions
a.
Based on 50% consumption of DNPH.
b
Evaluate sampler performance for individual high-temperature method.
a
b
>95% for sampling rates up to 1.5 L/min
Approximately 70 µg formaldehyde
0.35 g/sampler (~1 mg DNPH)
0.7 mL
10 °C to 100 °C
4.3 cm total length
2.0 cm o.d. at widest point
1.0 cm i.d.
0.9 cm bed length
The acetonitrile you use to elute the DNPH derivatives can also be
a source of contamination. Even HPLC-grade acetonitrile may have
unacceptable levels of carbonyl contaminants and should be stored
in a carbonyl-free environment. A concentration of 10 µg/L of
any aldehyde or ketone contaminant will add 0.1 µg to the blank
values determined for the DNPH-derivatives per cartridge. Follow
the procedure in Appendix A, Measuring Acetonitrile Purity, to
pre-qualify your acetonitrile.
Sep-Pak XPoSure Aldehyde Sampler
2
Page 3

[ CARE AND USE MANUAL ]
[ CARE AND USE MANUAL ]
c. Collecting the Sample
Caution: Beware of unintentional exposure of the samplers and
eluted samples to aldehyde and ketone sources. Laboratory air
often holds high concentrations of acetone. Labeling inks and
adhesives as well as packaging containers (including vials with
plastic caps) are all possible sources of contamination.
Sampling methods have been developed and validated for both 15
minute short-term exposure limit (STEL), and in 8 hour personal
exposure limit (PEL) measurements following the National
Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH) guidelines
XPoSure Aldehyde Samplers have been tested under controlled
laboratory conditions. Table 2 lists the equipment needed to
collect air samples using XPoSure Aldehyde Samplers. The
recommended measurement range for formaldehyde is:
STEL: 0.022 to 2 ppmv
PEL: 0.01 to 1 ppmv
Table 2: Sample Collection Equipment
Suggested Personal Pump Specifications
Operating Range 100 to 1,500 mL/min
Compensation Range 1,500 mL/min – 0 to 20 inches water
Flow Control ±5% set point constant flow
Flow Indicatora Built-in flow indicatora
a.
A flow calibrator may also be required.
1,2
Sample Collection – STEL (0.02 to 2.0 ppmv)
To collect the STEL air sample:
1. 1Calibrate the sampling pump with a representative sampler
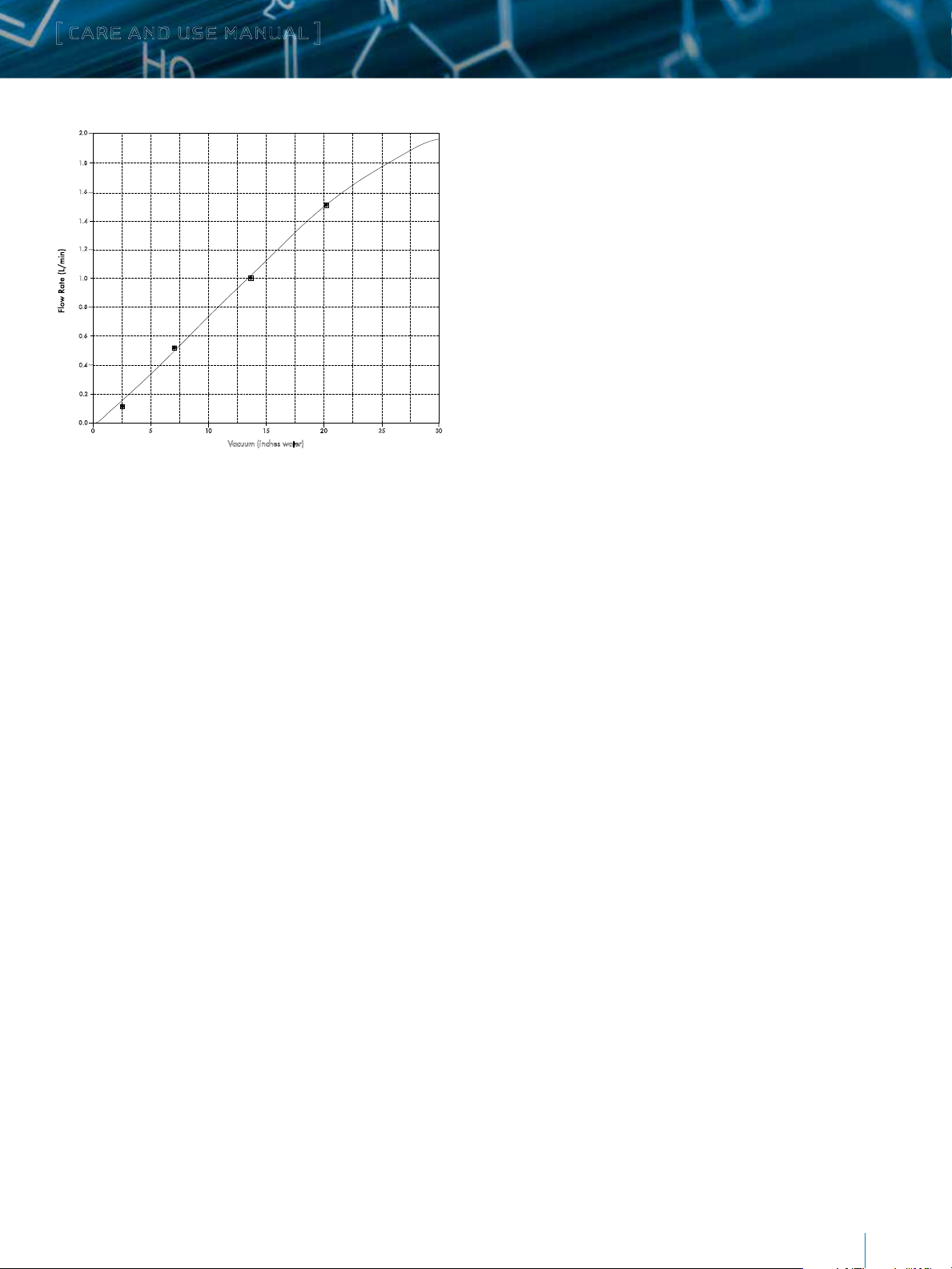
in line. Set the flow to 1.5 L/min. Figure 3 shows the flow rate
through a sampler versus applied vacuum. Once calibrated,
remove and store this representative sampler for future
calibrations.
2. Take a fresh sample from its pouch. Remove and save the end
cap and plugs.
.
3. Connect the sampler to a pump with flexible plastic tubing. The
sampler is bidirectional (flow can be in either direction).
4. Draw air for 15 minutes, yielding a sample volume of
22.5 liters.
5. Reseal the sampler with its end cap and plug.
6. Store the sampler in the pouch provided with appropriate
identification. Seal the pouch by folding the edge over twice
and stapling it shut. Avoid exposing the samplers to heat.
A 22.5 L air sample is sufficient for quantifying formaldehyde in
the range of 0.02 to 2 ppmv. Formaldehyde concentrations lower
than 0.02 ppmv in air will require longer sampling times and a
larger air sample. Conversely, formaldehyde concentrations that
exceed 2.0 ppmv will require shorter sampling times or reduced
sampling flow rates in order to avoid overloading the sampler and
obtaining nonlinear results.
The background levels of aldehydes and ketones in the sampler
determine the sensitivity of the method. The volume of air passed
through the sampler must be large enough for the quantity of
DNPH derivatives formed to be several times greater than the
background level. The United States Environmental Protection
Agency (US EPA) recommends that this level be at least 10 times
the background level.3 Table 3 lists the sampler background
specifications.
Table 3: Sampler Background Specifications
Compound
Formaldehyde <0.45 <0.06
Adetaldehyde <0.75 <0.15
Acetone <1.5 <0.38
Othersa <0.75 -
a.
Individually, as acetone-DNPH.
µg DNPH Derivatives
per Sampler
µg Carbonyl Compounds
per Sampler
Note: The maximum recommended sampler capacity is
2.3 µmoles total carbonyl species. This calculates to 50% of
the DNPH consumed. Contaminated air may contain significant
concentrations of other aldehydes and ketones and the total may
exceed the capacity of the sampling device. Follow the procedure in
Appendix C, Measuring Breakthrough for more information.
Sep-Pak XPoSure Aldehyde Sampler
3
Page 4
2.0
[ CARE AND USE MANUAL ]
[ CARE AND USE MANUAL ]
1.8
1.6
1.4
1.2
1.0
Note: The maximum recommended sampler capacity is 2.3 µmoles
total carbonyl species. This calculates to 50% of the DNPH consumed.
Contaminated air may contain significant concentrations of other
aldehydes and ketones and the total may exceed the capacity
of the sampling device. Follow the procedure in Appendix C,
Measuring Breakthrough for more information.
0.8
0.6
0.4
0.2
5
Figure 3: Typical Sampler Backpressure Profile.
15
Vacuum (inches water)
Sample Collection – PEL (0.01 to 1.0 ppmv)
To collect the PEL air sample:
1. Calibrate the sampling pump with a representative sampler in
line. Set the flow to 100 mL/min. Figure 3 shows the flow rate
through a sampler versus applied vacuum. Once calibrated,
remove and store this representative sampler for future
calibrations.
2. Take a fresh sample from its pouch. Remove and save the end
cap and plugs.
3. Connect the sampler to a pump with flexible plastic tubing. The
sampler is bidirectional (flow can be in either direction).
4. Draw air for 8 hours, yielding a sample volume of 48 liters.
5. Reseal the sampler with its end cap and plug.
6. Store the sampler in the pouch provided with appropriate
identification. Seal the pouch by folding the edge over twice
and stapling it shut. Avoid exposing the samplers to heat.
A 48 L air sample is sufficient for quantifying formaldehyde in the
range of 0.01 to 1 ppmv. Formaldehyde concentrations lower than
0.01 ppmv in air will require longer sampling times and a larger
air sample. Conversely, formaldehyde concentrations that exceed
1.0 ppmv will require shorter sampling times or reduced sampling
flow rates in order to avoid overloading the sampler and obtaining
nonlinear results.
d. Eluting the Derivatives from the Sampler
To elute the derivatives from the sampler:
1. Remove the sampler from the stapled pouch.
2. Elute the DNPH derivatives from the sampler with pre-qualified
25
30
acetonitrile directly into a 10 mL volumetric flask. Use a flow
rate of <3 mL/min. Higher flow rates (>3 mL/min) can result in
reduced recovery.
3. Cap the volumetric flask and mix by inverting it several times.
4. Analyze the eluate using HPLC.
Note: Since background levels may change during storage, always
compare samples to a blank sampler from the same lot, stored
under the same conditions.
III. ANALYZING THE DNPH DERIVATIVES
a. Operating Guidelines
To ensure success in your HPLC analysis:
Use a pre-column filter between the injector and column.
Use HPLC-grade water and HPLC-grade acetonitrile.
Degas the mobile phases by simultaneously applying
vacuum and ultrasound to the mobile phases for 30 seconds.
If you are using a low-pressure mixing gradient system,
sparging with helium may be necessary.
Waters Symmetry® C18 columns are shipped containing
water/acetonitrile. Before the first analysis, equilibrate the
column with mobile phase at 1.3 mL/min for 10 minutes in
mobile phase or until the baseline is stable. See Table 4 for
separation conditions.
Sep-Pak XPoSure Aldehyde Sampler
4
Page 5

0246810
12
14
0
.0005
.0010
.0015
.0020
.0025
1. DNPH
2. DNPH-Formaldehyde
3. DNPH-Acetaldehyde
4. DNPH-Acetone
.0030
1
2
3
4
[ CARE AND USE MANUAL ]
[ CARE AND USE MANUAL ]
b. Performing the HPLC Analysis
To analyze the sample:
1. Prepare the standard solution of the DNPH derivatives that you
need to quantify. T he concentrations of the standards should
be in the same range as the expected concentrations in the
sample. To synthesize DNPH derivatives, see Appendix B.
2. Prepare a cartridge blank from the same sample lot as
the cartridge used to collect the sample, using the sample
procedure and same bottled solvent.
3. Analyze the standard solution to determine the response factor
for each derivative. Due to the high linearity of the detector
response, a single point calibration is sufficient for Waters
detectors.
Note: Use an injection volume appropriate for your column.
Inject ≤ 20 µL for a 3.9 x 150 mm Waters Symmetry C18 column,
and ≤ 10 µL for a 3.0 x 75 mm Waters Symmetry C18 column.
4. Analyze the cartridge blank to determine background levels.
Ensure that the blank values are in the normal range (see Table
3). Figures 4 and 5 show a representative separation and blank
sample, respectively.
1. DNPH
2. Formaldehyde-DNPH
3. Acetaldehyde-DNPH
4. Acetone-DNPH
5. Acrolein-DNPH
6. Propionaldehyde-DNPH
Time (minutes)
Figure 4. Isocratic Separation of C1-C3 Hydrazone Derivatives.
5. Analyze the samples.
6. Subtract the blank values from the sample values. Run
standards at regular intervals between samples.
Table 4: HPLC Separation Conditions
Column Waters Symmetry C18, 3.9 x 150 mm
Mobile Phase 45:55 Acetonitrile/Water
Flow Rate 1.3 mL /min
Injection Volume 20 µL
Detection Wavelength
Limit of Detection for
Formaldehyde
Limit of Quantification for
Formaldehyde
Absorbance at 360 nm
(<50 mV of baseline noise)
Based on a signal to noise ration of 3
(55 picograms in 20 µL injection)
Based on a signal to noise ratio of 10
(183 picograms in 20 µL injection)
Figure 5: Typical Sampler Blank.
c. Analyzing a Cartridge Blank
Analyze a blank to determine background levels. Since
background levels may change during storage, always compare
samples to blank cartridges from the same lot stored under the
same conditions.
Note: When preparing a blank sample, ensure that you use the
exact bottled reagents that were used for the preparation of the
sample.
To prepare a cartridge blank:
1. Elute a fresh DNPH-Silica Sep-Pak cartridge from the same lot
as the cartridges used to collect your sample
2. Analyze the solution by HPLC using the same conditions as
those used for the sample.
3. Multiply the concentration of each DNPH derivative by the
volume of the eluate to determine the amount of background
DNPH derivative.
Sep-Pak XPoSure Aldehyde Sampler
5
Page 6

2
de
3
e
e
0
6
0
.002
4
2a
[ CARE AND USE MANUAL ]
[ CARE AND USE MANUAL ]
d. Calculating Results
To calculate the aldehyde concentration in air:
1. Prepare a calibration line of peak area to standard
concentration on µg/mL of analyte as carbonyl compound.
2. Use the calibration line to determine the analyte concentration
in the blank and sample eluates.
3. Determine the mass of each analyte in the blank (Wb) in
µg. This is done by multiplying each analyte concentration
by the eluate volume in mL. Compare these vales to the
specifications listed in Table 3. If these values are higher than
the specifications, contamination occurred during sample
preparation or storage.
4. Determine the mass of each analyte in the sample (Ws) in µg.
This is done by multiplying each analyte concentration by the
eluate volume in mL.
5. Calculate the analyte concentration (C) in µg/L*. This is done
by dividing the weight of the analyte in the air (Ws-Wb) by the
volume of the air sampled (V) in liters.
C = Ws – W
V
*The units, µg/L, is equivalent to mg/m3. For converting µg/L to ppmv at 1 atm
and 20 °C, see Appendix D.
b
b. Glutaraldehyde in Laboratory Air – STEL
The sample in Figure 7 was collected in chemical research
laboratory using a portable sampling pump. The 22.5 liter air
sample was collected at 1.5 L/min. The chromatogram shows
0.02 ppmv of glutaraldehyde. Under these chromatographic
conditions the DNPH-glutaraldehyde diastereomers are resolved.
1
.00
.004
.002
0
0246
Figure 7. Analysis of Glutaraldehyde in Lab Air.
1. DNPH
2a & 2b. DNPH-Glutaraldehyde Diastereomers
2b
2a
8
8
V. STORAGE AND DISPOSAL OF T HE SAMPLERS
a. Storing unused samplers
Always store any unused Waters Sep-Pak XPoSure Aldehyde
Samplers in their protective pouches to prevent contamination.
Store the sealed pouches in a refrigerator at (4 °C ± 2 °C) for up to
six months. Cartridges may be stored in their unopened pouches at
room temperature (20 to 25 °C) for up to two weeks.
IV. APPLICATION EXAMPLES
a. Formaldehyde in Laboratory Air - STEL
The sample in Figure 6 was collected in a chemical research
laboratory using a portable sampling pump. The 22.5 liter air
sample was collected at 1.5 L/min. The chromatogram shows
0.02 ppmv formaldehyde, with trace levels of both acetonitrile
and acetone detected.
1. DNPH
.004
.002
0
02 46810
Figure 8. Analysis of Formaldehyde in Lab Air.
1
2
1. DNPH
2. DNPH-Formaldehyde
3. DNPH-Acetaldehyde
4. DNPH-Acetone
4. DNPH-Aceton
3
. DNPH-Formaldehy
. DNPH-Acetaldehyd
4
12
14
Background levels of hydrazone derivatives increase slightly with
time and temperature. Before using cartridges exposed to high
temperatures or stored longer than the recommended periods, run
a blank.
b. Storing exposed samplers
Once a sampler has been used for collection, be careful to cap
and seal it until it is time to elute it. Inadvertent exposure of an
exposed cartridge can ruin a carefully collected sample. Elute
the derivatives from the cartridge within two weeks. T he sample
eluates are stable at 4 °C ± 2 °C for up to one month.
c. Disposing of used cartridges
Dispose of used cartridges according to applicable government
regulations.
Sep-Pak XPoSure Aldehyde Sampler
6
Page 7

[ CARE AND USE MANUAL ]
[ CARE AND USE MANUAL ]
VI. TROUBLESHOOTING
Table 5 describes solutions to problems that may arise while
using the samplers. Most errors occur as a result of contamination
during sample preparation. To resolve chromatographic problems
not listed, refer to your HPLC system manual.
Table 5: Troubleshooting
Symptom Possible Cause Solution
Contaminated
acetonitrile
High carbonyl values
in sampler blank
High formaldehyde
levels in sampler
blank
Broad peaks
Contaminated
glassware
Air contamination
during elution
Sampler age and
storage conditions
Coelution of
formaldehyde with
an impurity
Injection volume
too high
System or
column failure
4
Certify acetonitrile quality
prior to use, see Appendix A.
Use only pre-cleaned
glassware.
Prepare sample in
a glove box.
Replace samplers.
Refrigerate fresh samplers.
Prepare a fresh mobile
phase or decrease the
acetonitrile content.
Reduce t he
injection volume.
Consult the HPLC
System manual.
To order, contact your Waters representative, call Waters at
(800) 252-4752 or order online at www.waters.com.
Table 6: Ordering Information
Product Part Number
Sep-Pak XPoSure Aldehyde Samplers, 20/box WAT047205
In-Line Pre-Column Filter
Symmetry C
Solvent Filter, PV DF, 47 mm, 0.45 µm, Protein, 100/pkg
Beginners Guide to Liquid Chromatography
Guide to Successful Operation of Your LC System
Column, 3.9 x 150 mm WAT046980
18
WAT084560
WAT200530
715001531
WAT022378T P
IX. APPENDIC ES
a. Appendix A: Measuring Acetontrile Purity
HPLC-grade acetonitrile may contain traces of aldehydes and
ketones, and especially acetone. A concentration of 10 µg/L of
an aldehyde or ketone in the acetonitrile adds 0.1 µg to the blank
values determined for the DNPH-derivatives per cartridge.
VII. REFERENCES AND BIBLIOGRAPHY
1. Committee on Aldehydes, Board of Toxicology and
Environmental Hazards, National Research Council,
Formaldehyde and Other Aldehydes; National Academy Press,
Washington, DC, 1981.
2. Tejada, S. B. “Evaluation of Silica Gel Cartridges Coated in
Situ With Acidified 2,4-Dinitrophenylhydrazine for Sampling
Aldehydes and Ketones in Air”, Intern. J. Environ. Chem.
1986, 26, 167-185.
3. Riggins, R.M. “Compendium of Methods for the Determination
of Toxic Organic Compounds in Ambient Air”, U.S.
Environmental Protection Agency Report EPA-600/4-84-041,
U.S. Environmental Protection Agency; Research Triangle Park,
NC, 1984.
4. Guide to Successful Operation of Your LC System; Waters
Corporation, Milford, MA 1991.
5. ASTM Method E411; Standard Test Method for Trace Quantities
of Carbonyl Compounds with 2,4-Dinitrophenylhydrazine.
If you acetonitrile is unacceptable for your application, contact
your solvent supplier, to purify the acetonitrile. To purify
acetonitrile, distill it from an acidified DNPH solution, using a
procedure analogous to the one described in ASTM Method E411
for the purification of methanol.
5
To measure acetonitrile purity:
1. Clean all glassware by rinsing with acetonitrile and heating
in a 60 °C vacuum oven for at least 30 minutes.
2. Elute a fresh sampler with 3 mL acetonitrile.
3. Within 3 minutes, inject the eluate into the HPLC system to
measure the concentration of DNPH derivatives.
4. Add 1 drop of concentrated HCl to the eluate, and allow to
react at room temperature for 30 minutes.
5. Remeasure the concentration of DNPH derivatives by HPLC.
6. Calculate the difference in the concentration of each DNPH
derivative measured in steps 3 and 5 to yield the contribution
form the acetonitrile.
VIII. ORDERING INFORMATION
Waters Sep-Pak XPoSure Aldehyde Samplers are shipped in boxes
of 20 individually-packaged cartridges. Pouches are supplied for
storage after sampling.
7. Calculate the percent hydrazone contributed by the acetonitrile
relative to the background level. The value for any hydrazone
should not exceed 25% of its value in the blank.
Sep-Pak XPoSure Aldehyde Sampler
7
Page 8

[ CARE AND USE MANUAL ]
[ CARE AND USE MANUAL ]
Example: Measuring Acetonitrile Purity
1. HPLC analysis of a fresh sampler shows the sample contains:
Derivative
FormaldehydeDNPH
AcetaldehydeDNPH
Acetone-DNPH 1.60 ÷ 0.40 x 100 = 400%
Contribution
from
Acetonitrile
0.01 ÷ 0.08 x 100 = 12%
0.02 ÷ 0.12 x 100 = 17%
Divided by
Background
Value
Times
100
Equals
Percent
Relative to
Background
2. Analysis of the concentrations of hydrazones after reacting
with acid yields:
Derivative Concentration (µg/mL)
Formaldehyde-DNPH 0.08
Acetaldehyde-DNPH 0.12
Acetone-DNPH 0.40
All other hydrazones <0.05
3. The difference between the concentrations of hydrazone from
steps 3 and 5 represents the amount of hydrazone
contributed by the acetonitrile:
Derivative Concentration (µg/mL)
Formaldehyde-DNPH 0.09
Acetaldehyde-DNPH 0.14
Acetone-DNPH 2.00
All other hydrazones <0.05
4. The percent of the hydrazones contributed by the acetonitrile is:
Derivative
FormaldehydeDNPH
AcetaldehydeDNPH
Acetone-DNPH 2.00 µg/mL - 0.40 µg/mL = 1.60 µg/mL
Concentration
after Reaction
with Acid
0.09 µg/mL - 0.08 µg/mL = 0.01 µg/mL
0.14 µg/mL - 0.12 µg/mL = 0.02 µg/mL
Minus
Concentration
in Blank
Equals
Contribution
form Acetonitrile
Since the percent for formaldehyde and acetaldehyde arising
from the acetonitrile is less than 25% of the background level
in the sampler, the acetonitrile is considered clean for these
compounds. If the analysis considers only these compounds, the
acetonitrile is acceptable.
However, the amount of acetone arising for the acetonitrile is
4 times the amount found in the the background level. Therefore,
it is suggested that this lot of acetonitrile may be unacceptable
for use in the analysis of acetone.
b. Appendix B: Synthesizing the DNPH-Derivative Standards
High purity (99%) DNPH derivatives are commercially available
or can be synthesized from DNPH supplied by Aldrich Chemical
Company (70% DNPH and 30% water). To synthesize 98-99%
pure hydrozones:
1. Prepare one liter of 2 M HCl solution: Add 172 mL concentrated
reagent-grade hydrochloric acid (HCl) to a 1 L volumetric
flask. Fill the flask to the mark with distilled deionized water.
2. Saturate the 2 M HCl solution with DNPH: Add 8 g DNPH and
stir for one hour at 20 to 25 °C. Filter through a 0.45 µm
hydrophilic membrane (HVLP) filter (Waters Part number:
WAT200530).
3. Form the hydrazone derivative by adding a two-fold molar
excess of reagent-grade aldehyde or ketone to the filtered
2 M HCl DNPH solution. Stir for 30 minutes to one hour at
20 to 25 °C.
4. Filter the hydrazone slurry. Wash the hydrazone with 50 mL
2 M HCl 3 times. Wash with 50 mL water 3 times. Dry the
filter cake in an oven at 50 to 60 °C overnight.
5. Prepare a standard stock solution of the DNPH-derivatives
by dissolving an accurately weighed amount in acetonitrile.
Prepare a set of calibration standards using the stock
solution. The concentration of the standards should be in the
same range as the expected concentration of the samples.
The solutions are stable for at least one month when stored in
tightly-capped glass vials at 4 °C ± 2 °C.
Sep-Pak XPoSure Aldehyde Sampler
8
Page 9

[ CARE AND USE MANUAL ]
[ CARE AND USE MANUAL ]
c. Appendix C: Measuring Breakthrough
Note: If several aldehydes and ketones are present in significant
concentration, estimate the maximum sample size from the total
concentration of all species. Collection efficiency determinations
are best made during times expected to yield peak formaldehyde
concentrations. This will enable appropriate sampling rates and
intervals to be selected to avoid breakthrough.
Figure 8 shows the predicted total carbonyl concentration versus
the range of sample volumes.
To measure Waters Sep-Pak XPoSure Aldehyde Sampler for
collection efficiency:
1. Connect two unused cartridges together by the Luer fittings
and mark each cartridge for identification.
2. Connect the cartridges to a calibrated pump with a short
length of flexible tubing.
3. Collect the sample.
4. Elute both cartridges and a third blank cartridge.
5. Analyze all three cartridges by HPLC.
6. Subtract the blank value from the values determined from the
other two cartridges.
7. Calculate and sum of the total captured DNPH-derivative from
both cartridges.
8. Divide the amount of DNPH-derivative determined from
the first cartridge by the total amount determined form
cartridges 1 and 2. Multiply by 100. This is the percentage of
DNPH-derivatives captured on the first cartridge. This value
should exceed 95%; otherwise, some of the sample broke
through to the second cartridge.
Figure 8. Total Carbonyl Concentration vs. Range of Sample Volumes.
Collection efficiency for Waters Sep-Pak XPoSure Aldehyde
Sampler is greater than 95% for air sampling rates of up to
1.5 L/min. The sampler may exhibit breakthrough if:
The sampling flow rate is greater than 1.5 L/min
The amount of sample collected is enough to react with
more than 50% of the DNPH (~2.3 µmoles)
Example: Measuring Sample Breakthrough
The expected concentration of formaldehyde is 0.66 ppmv (µL/L).
Flow rate is 1.25 L/min for 80 minutes. A sample volume of 100
liters is collected. The theoretical quantity of carbonyl is:
Analyte ppmv Carbonyl Collected
concentration x molecular x air volume = µg Carbonyl
weight
Analyte molar volume at 1 atm/25 °C
This calculates to:
0.66 µL x 30.03 g/mole x 100 L = 81 µg formaldehyde
24.46 L/mole
The actual results are shown in Table 7. To calculate the percent
captured on the first sampler, divide the quantity captured on
sampler 1 by the total quantity captured, then multiply by 100.
Since this value is less than 95%, and the total carbonyl amount
exceeded 2.3 µmoles, breakthrough occurred.
Sep-Pak XPoSure Aldehyde Sampler
9
Page 10

[ CARE AND USE MANUAL ]
[ CARE AND USE MANUAL ]
In the above example, only a single carbonyl source was present.
Under many test conditions more than one carbonyl source may be
present in significant concentrations. These other compounds will
consume DNPH, effectively reducing the capacity of the sampler for
the compound of interest. To assure that the capacity of the sampler
has not been exceeded, compare the DNPH peak areas of the sample
to a similarly eluted blank. T he DNPH peak area in all samples
must be no less than 50% of the DNPH peak area of the blank. This
ensures the sampler capacity has not been exceeded.
Table 7: Breakthrough Example HPLC Results
Sampler
Sampler 1 75.06 75.00 91.8
Sampler 2 6.72 6.66 8.2
Blank 0.06 - -
Amount
(µg)
Quantity Captured
Sampler – blank (µg)
Percent Captured
on Sampler
d. Appendix D: Useful Conversion Factors
This appendix contains:
Carbonyl to hydrazone conversion factors
Equation for converting µg/L to ppmv
Conversion factors: µg/L ppmv
Table 9: Conversion Factors,
Carbonyl Weights ↔ Derivative Weights
Carbonyl
Compounds
Formaldehyde 6.998 0.1429
Adetaldehyde 5.089 0.19 65
Adetone 4.101 0.2438
Glutaraldehyde
Carbonyl → Derivative,
(MWD /MWC)
4.589 0.2175
Derivative → Carbonyl,
(MWC /MWD)
d.2. Equation for converting µg/L to ppmv
Carbonyl concentrations can be converted from µg/L to ppmv
(µL/L) by using the following expression:
(Result in ppmv) = (Result in µg/L) x 22.41 x T2 x P1
MWC T1 P2
Where values are:
22.41 = Molar volume of an ideal gas at STP (273.15 °K and
1 atm), L/mole
MWC = Molecular weight of carbonyl, g/mole
Obtaining carbonyl concentrations in eluates and air samples
required the use of several constants and conversion factors. The
factors described in this appendix can be used when converting
carbonyl weights to:
Equivalent derivative weights for preparing standard
solutions
Volumes for reporting air samples in ppmv
d.1. Carbonyl to Hydrazone Conversion Factors
Table 8 lists the molecular weights (MW) for some carbonyl
compounds. These values were used to derive the conversion
factors listed in Table 9. Multiply the carbonyl or derivative
weights by the appropriate factor for the desired conversion.
Table 8: Carbonyl and Hydrazone Molecular Weights
Carbonyl
Compounds
Formaldehyde 30.03 210.15
Adetaldehyde 44.05 22 4.17
Adetone 58.08 238.20
Glutaraldehyde
Carbonyl Compounds
Molecular Weight, (MWC)
100.12 460.36
Hydrazone Derivative
Molecul ar Weight (MWD)
T1 = Standard temperature, 273.15 °K
T2 = Air sample temperature, ºK
P1 = Standard pressure, 1 atm
P2 = Air sample pressure, atm
d.3. Conversion Factors: µg/L to ppmv
Table 10 lists the factors for converting between µg/L and ppmv at
25 °C and 1 atm. Results are converted between µg/L (or mg/m3)
and ppmv, by multiplying by the appropriate factor.
Table 10: Factors for Converting Between µg/L and ppmv at
25 °C and 1 atm.
Carbonyl
Compounds
Formaldehyde 1.23 0.813
Adetaldehyde 1.8 0 0.555
Adetone 2.38 0.420
Glutaraldehyde
ppmv → µg/L µg/L p → ppmv
4.09 0.244
Sep-Pak XPoSure Aldehyde Sampler
10
Page 11

[ CARE AND USE MANUAL ]
Waters, The Science of W hat’s Possible, Symmetry, and Sep-Pak are registered trademarks of Waters Corporation.
XPoSure is a trademark of Waters Corporation. All other trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
©2014 Waters Corporation. Produced in the U.S.A. March 2014 Rev C WAT047204EN KP-PDF
Waters Corporation
34 Maple Street
Milford, MA 01757 U.S.A.
T: 1 508 478 2000
F: 1 508 872 1990
www.waters.com
 Loading...
Loading...