Page 1

[ Care and Use ManUal ]
WAters seP-PAK dnPH-sILICA CArtrIdGe
Contents
I. IntroduCtIon
a. Sep-Pak DNPH-Silica Cartridge Description
II. usInG seP-PAK dnPH CArtrIdGes
a. Theory of Operation
b. Preventing Contamination
c. Collecting the Sample
d. Eluting the Derivatives
III. AnALYZInG tHe dnPH derIVAtIVes
a. Operating Guidelines
b. Performing HPLC Analysis
c. Analyzing a Cartridge Blank
d. Selecting Separation Conditions
IV. APPLICAtIon eXAMPLes
a. Estimating Sample Volume
b. Analysis of Auto Exhaust Emissions
c. Analysis of Residential Air
d. Analysis of Research Lab Air
I. IntroduCtIon
Waters Sep-Pak® DNPH-Silica cartridges are convenient, reproducible
sampling devices for quantifying aldehydes and ketones in gasses,
including air within a range of 1 to 5,000 parts per billion (ppbv).
V. storAGe And dIsPosAL oF used CArtrIdGes
VI. trouBLesHootInG
VII. reFerenCes And BIBLIoGrAPHY
VIII. orderInG InForMAtIon APPendICes
IX. APPendICes
a. Measuring Acetonitrile Purity
b. Synthesizing DNPH Derivative Standards
c. Measuring Sample Breakthrough
Waters Sep-Pak DNPH-Silica Cartridge
1
Page 2
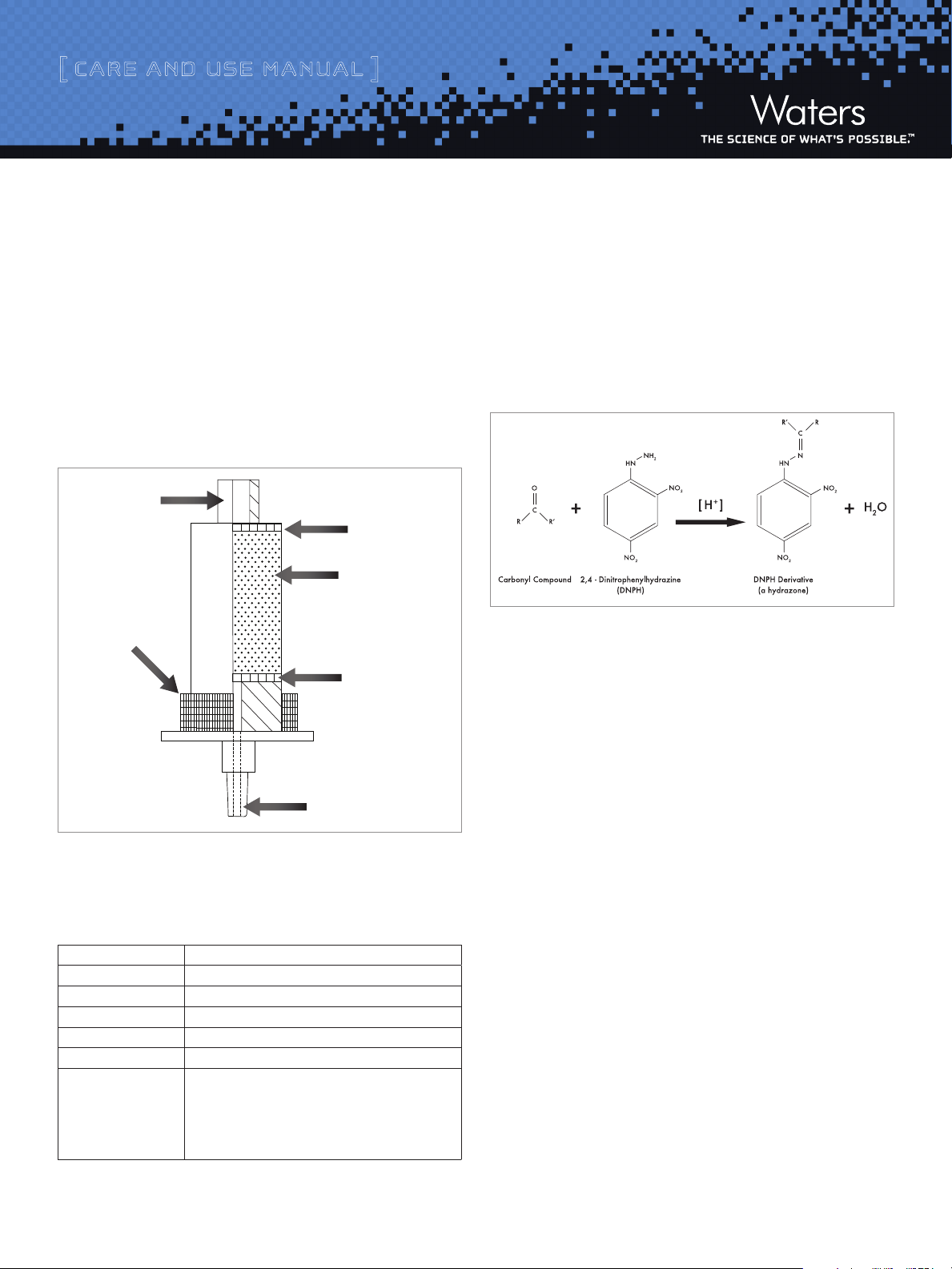
[ Care and Use ManUal ]
Po lyethylene Filter
DNPH-Silica
Po lyethylene Filter
Luer Connector
Aluminum
Compression Ring
Luer Connector
a. Sep-Pak DNPH-Silica Cartridge Description
• WatersSep-PakDNPH-Silicacartridgesconsistofacidified
2,4-dinitrophenylhydrazine-coated silica packed in Waters
Sep-Pak Plus cartridges.
• WatersSep-PakPluscartridgesareconstructedofhigh-purity
polyethylene components with triaxially-compressed packed
beds and Luer fittings equipped with end caps and plugs.
• T hegold-coloredaluminumcompressionringontheSep-Pak
DNPH-Silica cartridge allows for easy identification.
II. usInG seP-PAK dnPH-sILICA CArtrIdGes
a. Theory of Operation
Waters Sep-Pak DNPH-Silica cartridges trap aldehydes and ketones in
gasses by reacting them with the DNPH in the cartridge to form stable
1,2 ,3
hydrazone derivatives
place during sample collection. The derivatives are later eluted and
analyzed. Analysis should take place within two weeks.
Figure 2: Derivitization Reaction
. The derivitization reaction (Figure 2) takes
Figure 1: Cutaway View
Table 1: Physical/Chemical Properties
Hold-Up Volume 0.7 mL
Particle Size 55 to 105 µm
Collection Efficiency >95% for sampling rates up to 2 L/min
Capacity Approximately 75 µg formaldehyde
Quantity of DNPH-Silica 0.35 g/cartridge (1.0 mg DNPH)
Operating Temperature* 10 °C to 100 °C
Dimensions 4.3 cm total length
2.0 cm o.d. at widest point
1.0 cm i.d.
0.9 cm bed length
* Evaluate cartridge performance for individual high-temperature
methods.
b. Preventing Contamination
Contamination is most likely to occur during sample preparation.
Before eluting the derivatives, clean all glassware by rinsing with
acetonitrile and heating to 60 °C in a vacuum oven for at least
30 minutes. Eluting the samples in a nitrogen-purged glove box
further reduces the risk of contamination.
The acetonitrile used to elute the DNPH derivatives can also be a
source of contamination. Even HPLC-grade acetonitrile may have
unacceptable levels of carbonyl contaminants. A concentration of
10 µg/L of any aldehyde or ketone contaminant will add 0.1 µg to
the blank values determined for the DNPH derivatives per cartridge.
Follow the procedure in Appendix A to test your acetonitrile.
c. Collecting the Sample
Caution: Beware of unintentional exposure of the cartridges and
eluted samples to aldehyde and ketone sources. Laboratory air often
holds high concentrations of acetone. Labeling inks and adhesives as
well as packaging containers (including vials with plastic caps) are all
possible sources of contamination.
Waters Sep-Pak DNPH-Silica Cartridge
2
Page 3
[ Care and Use ManUal ]
Caution: Ozone (usually present in urban air) degrades the hydrazone
4
derivatives
. Place an Ozone Scrubber Cartridge (Waters Part
number: WAT054420) on the inlet of the Sep-Pak DNPH-Silica
cartridge.
Notice: Do not use Sep-Pak DNPH-Silica cartridges to process liquid
samples.
To collect the sample:
1. Take the cartridge from its pouch. Remove and save the end cap
and plug.
2. Connect the cartridge to a pump with flexible plastic tubing.
The cartridge is bidirectional (flow can be in either direction).
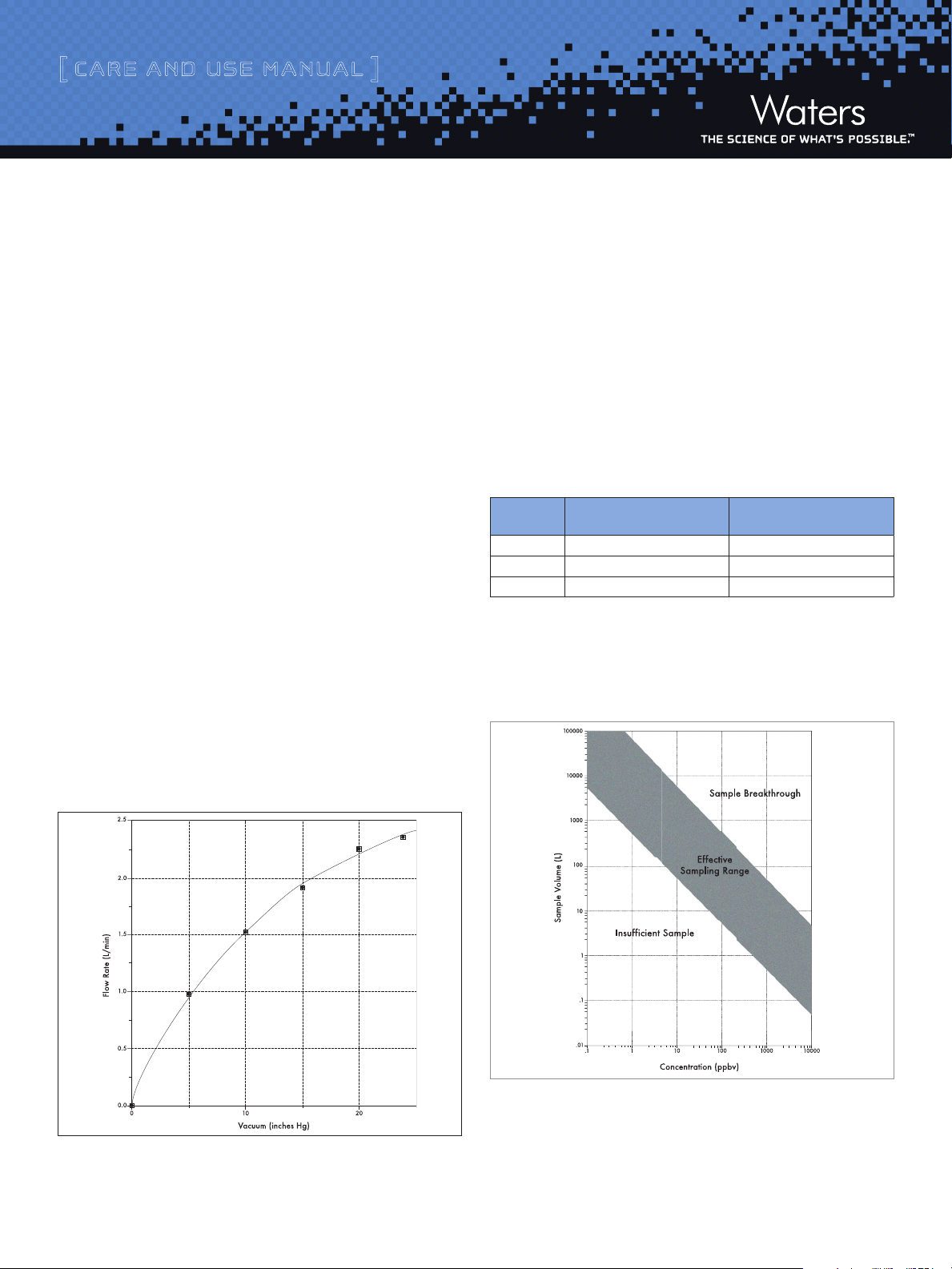
Figure 3 shows the flow rate through a cartridge versus applied
vacuum.
3. Draw the sample through the cartridge. Record the flow rate and
collection time.
4. Reseal the cartridge with its end cap and plug.
5. Store the cartridge in the provided pouch with appropriate
identification. If possible, seal the pouch using a heat sealer,
®
or store the cartridge in a glass container with a Teflon
-lined
cap. Keep the samples cool (<4 °C). Elute the cartridge within
two weeks.
The volume of air passed through the cartridge must be large
enough for the quantity of DNPH derivative formed to be several
times greater than the background level (Table 2). The United
States Environmental Protection Agency (US EPA) recommends
3
that this level be at least 10 times of that of the background
.
Figure 4 shows the ranges of sample volumes to use as a function
of expected concentration. If you can not predict the concentration
of total carbonyl compounds in a sample, follow the procedure in
Appendix C, Measuring Sample Breakthrough.
Table 2: Background Levels of DNPH Derivatives
Compound µg DNPH Derivative per Cartridge µg as Carbonyl Compound per
Cartridge
Formaldehyde <1.0 <0.15
Acetone <2.0 <0.50
Others* <0.75 -
* Individually, as acetone-DNPH, determined using a gradient
from 70/25/5 water/acetonitrile/tetrahydrofuran to 40/60 water/
acetonitrile. Other conditions are as in Section III, d.
Figure 3: Flow Rate versus Applied Vacuum
Waters Sep-Pak DNPH-Silica Cartridge
Figure 4: Range of Sample Volumes vs. Expected Concentration
3
Page 4

[ Care and Use ManUal ]
d. Eluting the Derivatives
There are two recommended methods for elution of the derivatives
from the cartridge:
Volumetric Method:
1. Elute the DNPH derivatives from the cartridge directly into a
5 mL volumetric flask. Use 3 mL HPLC-grade acetonitrile at a
flow rate of less than 3 mL/min. Higher flow rates (>3 mL/min)
can result in reduced recovery.
2. Dilute to volume with HPLC-grade acetonitrile.
Gravimetric Method:
1. Elute the DNPH derivatives from the cartridge directly into a
tared vessel. Weigh the eluate and divide by the density of the
acetonitrile to obtain the sample volume. Acetonitrile has a
density of 0.785 g/mL at 20 °C.
III. AnALYZInG tHe dnPH derIVAtIVes
a. Operating Guidelines
To ensure success in your HPLC analysis:
• Useapre-columnfilterbetweentheinjectorandcolumn.
b. Performing HPLC Analysis
To analyze the sample:
1. Prepare the standard solution of the DNPH derivatives that you
need to quantify. The concentrations of the standards should be
in the same range as the expected concentrations in the sample.
To synthesize DNPH derivatives, see Appendix B.
2. Prepare a cartridge blank from the same sample lot as the
c a r t r i d g e u s e d t o c o l l e c t t h e s a m p l e , u s i n g t h e s a m p l e
procedure and same bottled solvent.
3. Analyze the standard solution to determine the response
factor for each derivative. Due to the high linearity of the
detector response, a single point calibration is sufficient for
Waters detectors.
Note: Use an injection volume appropriate for your column. Inject
≤20 µL for a 3.9 x 150 mm Nova-Pak C
3.0 x 75 mm Nova-Pak C
column.
18
column, and ≤10 µL for a
18
4 . A n a l y z e t h e c a r t r i d g e b l a n k t o d e t e r m i n e b a c k g r o u n d l e v e l s .
Ensure that the blank values are in the normal range
(see Table 2).
5. Analyze the samples.
• UseHPLC-gradeunstabilizedtetrahydrofuranformakingmobile
phases.
• UseHPLC-gradewaterandHPLC-gradeacetonitrile.
• Degasthemobilephasesbysimultaneouslyapplyingvacuum
and ultrasound to the mobile phases for 30 seconds. If you are
using a low-pressure mixing gradient system, sparging with
helium may be necessary.
®
• WatersNova-Pak
C18 columns are shipped containing
water/acetonitrile. Equilibrate the column at 1.5 mL/min for
10 minutes in mobile phase before the first analysis.
Waters Sep-Pak DNPH-Silica Cartridge
6. Subtract the blank values from the sample values. Run standards
at regular intervals between samples.
c. Analyzing a Cartridge Blank
Analyze a blank to determine background levels. Figure 5 shows a
typical result from a blank cartridge extraction. Since background
levels may change during storage (see Section V), always compare
samples to blank cartridges from the same lot stored under the same
conditions.
Note: When preparing a blank sample, ensure that you use the exact
bottled reagents that were used for the preparation of the sample.
4
Page 5

[ Care and Use ManUal ]
1 . DNPH
2. Formaldehyde-DNPH
3. Acetaldehyde-DNPH
4. Acetone-DNPH
5. Acrolein-DNPH
6. Propionaldehyde-DNPH
Time (minutes)
Time (minutes)
1 . DNPH
2. Formaldehyde-DNPH
3. Acetaldehyde-DNPH
4. Acetone-DNPH
5. Acrolein-DNPH
6. Propionaldehyde-DNPH
7 . Crotonaldehyde-DNPH
8. Butanone-DNPH
9. Butyraldehyde-DNPH
1 0 . Benzaldehyde-DNPH
1 1 . Isovaleraldeh yde-DNPH
1 2 . V a leraldehyde-DNPH
1 3 . o-T o lualdehyde-DNPH
1 4 . m-T o lualdehyde-DNPH
1 5 . p-T o lualdehyde-DNPH
1 6 . Hexaldehyde-DNPH
1 7 . 2,5-Dimethylbenzaldehyde-DNPH
1 . DNPH
2. Formaldehyde-DNPH
3. Acetaldehyde-DNPH
4. Acetone-DNPH
Time (minutes)
1
1 . DNPH
2
. Formalde
hyd
e-DNP
H
3
. Acetaldehyde-DNP
H
4. Acetone-DNP
H
Cartridge Blank
234
02681 0
1 2
1 4
To prepare a cartridge blank:
1. Elute a fresh DNPH-Silica Sep-Pak cartridge from the same lot as
the cartridges used to collect your sample.
2. Analyze the solution by HPLC using the same conditions as those
used for the sample.
3. Multiply the concentration of each DNPH derivative by the
volume of the eluate to determine the amount of background
DNPH derivative.
Figure 6: Isocratic Separation of C
Aldehyde and Ketone
1-C3
Derivatives
Gradient Separation of Derivatives
Use the gradient conditions listed in Table 4 to separate DNPH and
DNPH derivatives from a complex mixture of aldehydes and ketones
in 15 minutes. Figure 7 shows an example separation.
Column Nova-Pak C18 3.9 x 150 mm
Mobile Phase A: Water/Acetonitrile/Tetrahydrofuran 60/30/10 v/v
B: Water/Acetonitrile 40/60 v/v
Gradient 100%Afor1min(adjustasnecessarytogivegradientdelay>
Figure 5: Typical DNPH-Silica Sep-Pak Cartridge.
3mL) then a linear gradient from 100% A to 100% B in 10 min
Flow Rate 1.5 mL/min
d. Selecting Separation Conditions
InjectionVolume 20 µL
Detection Adsorbance at 360 nm
Isocratic Separation of Derivatives
Aldehyde and Ketone
1-C9
Use the conditions in Table 3 to separate DNPH and DNPH
derivatives of C
through C3 a l d e h y d e s a n d k e t o n e s i n l e s s t h a n
1
Table 4: Gradient Separation of C
Derivatives
10 minutes. This separation requires a relatively weak mobile phase
(high water content) to separate the formaldehyde-DNPH derivative
from trace impurities. Figure 6 shows a representative chromatogram
using the isocratic conditions listed in Table 3.
Table 3: Isocratic Separation of C
Derivatives
Column Nova-Pak C18 3.9 x 75 mm
Aldehyde and Ketone
1-C3
Mobile Phase Water/Acetonitrile/Tetrahydrofuran 65/30/5 v/v
Flow Rate 1.5 mL/min
InjectionVolume 10 µL
Figure 7: Gradient Separation of C
Derivatives
Aldehyde and Ketone
1-C9
Detection Adsorbance at 360 nm
Waters Sep-Pak DNPH-Silica Cartridge
5
Page 6

[ Care and Use ManUal ]
Time (minutes)
1 . DNPH
2. Formaldehyde-DNPH
3. Acetaldehyde-DNPH
4. Acetone-DNPH
5. Acrolein-DNPH
6. Propionaldehyde-DNPH
7 . Crotonaldehyde-DNPH
8. Butanone-DNPH
9. Butyraldehyde-DNPH
1 0 . Benzaldeh yde-DNPH
1 1 . o-T o lualdehy de-DNPH
1 2 . m, p-T o lualdehy de-DNPH
1 3 . 2,5-Dimethylbenzaldehy de-DNPH
Time (minutes)
Lab Air Sample
Cartridge Blank
1 . DNPH
2. Formaldehyde-DNPH
3. Acetaldehyde-DNPH
4. Acetone-DNPH
5. Butanone-DNPH
6. Isovaleraldeh yde-DNPH
Time (minutes)
Residential Air
Cartridge Blank
1 . DNPH
2. Formaldehyde-DNPH
3. Acetaldehyde-DNPH
4. Acetone-DNPH
5. Hexaldehyde-DNPH
IV. APPLICAtIon eXAMPLes
a. Estimating Sample Volume
An expected formaldehyde concentration in a paper mill is estimated
to be 1000 ppbv. Refer to Figure 4 to find the sample volume to
collect. For this example, a sample volume of 10 liters is sufficient.
The pump used in this example generates 17 inches (Hg) of vacuum,
resulting in a flow rate through the cartridge of 2 L/min. Therefore,
five minutes of pumping at 2 L/min yields the 10 liter sample
required for the analysis.
b. Analysis of Auto Exhaust Emissions
A typical analysis of diluted exhaust emissions from car fueled by
gasoline is shown in Figure 8. The sample* was collected using a
constant volume sampler dilution tunnel. The car was operated on a
prescribed driving schedule on a chassis dynamometer.
The cartridge was connected to a heated (100 °C) sampling manifold
using a short piece of Teflon tubing. The sample was collected using
a metal bellows pump and a mass flow controller.
c. Analysis of Residential Air
A n e x a m p l e o f a n a n a l y s i s o f i n d o o r a i r i n a c o n v e n t i o n a l h o m e i s
s h o w n i n F i g u r e 9 . A 1 0 8 l i t e r s a m p l e w a s c o l l e c t e d a t 0 . 6 L / m i n
us ing a port abl e s amplin g p ump . T he chromat ogr am sho ws
formaldehyde (31 ppbv), acetaldehyde (9 ppbv), acetone (62 ppbv),
and hexaldehyde (2 ppbv).
Figure 9: Analysis of Residential Air
d. Analysis of Research Lab Air
Figure 8 represents an 8.4 liter sample collected at 1 L/min.
F or m al d e hy d e i s t h e m o st a bu n da n t c a rb o ny l c o mp o un d em it te d
(ca. 2000 ppbv). Smaller amounts of other aldehydes and ketones
al so appe ar.
* The sample was provided by Dr. S.B. Tejada of the US EPA
Atmospheric Research and Exposure Assessment Laboratory.
Figure 8: Analysis of Auto Exhaust Emissions
Waters Sep-Pak DNPH-Silica Cartridge
The sample in Figure 10 was collected in a chemical research labora-
tory using a portable sampling pump. A 100 L air sample was drawn
through the cartridge at flow rate 0.65 L/min. The chromatogram
shows formaldehyde (4.8 ppbv), acetaldehyde (1.2 ppbv), acetone
(118 ppbv), butanone (0.8 ppbv), and isovaleradehyde (0.7 ppbv).
Figure 10: Analysis of Research Lab Air
6
Page 7

[ Care and Use ManUal ]
V. storAGe And dIsPosAL oF used CArtrIdGes
Storing unused Cartridges
Always store any unused Waters Sep-Pak DNPH-Silica cartridges in
their protective pouches to prevent contamination.
Store the sealed pouches in a refrigerator at (4 °C or lower) for up to
six months. Cartridges may be stored in their unopened pouches at
room temperature (20 to 25 °C) for up to two weeks.
Background levels of hydrazone derivatives increase slightly with
time and temperature. Before using cartridges exposed to high
temperatures or stored longer than the recommended periods, run a
blank.
Storing Exposed Cartridges
Once a cartridge has been used to collect a sample, be careful to
cap and seal it until it is time to elute it. Inadvertent exposure of an
exposed cartridge can ruin a carefully collected sample. Elute the
derivatives from the cartridge within two weeks.
VI. trouBLesHootInG
Use Table 5 to solve common problems that may arise while using
the cartridges. Most errors occur as a result of contamination during
sample preparation. If resolution problems persist, validate the HPLC
5
.
system
Table 5: Troubleshooting Common Problems
Symptom Possible Cause Solution
High carbonyl values
in unused cartridges
Formaldehyde
coelutes with other
peaks
Broad peaks Injectionvolumetoohigh Useinjectionvolumeappropriate
Contaminated acetonitrile Certify acetonitrile quality prior
to use, see Appendix A
Contaminated glassware Use only pre-cleaned glassware.
Air contamination of
sample during elution
Cartridge age and storage
conditions
Improper mobile phase
composition
Separation conditions Check separation conditions. Use
Prepare sample in a glove box.
Buy new cartridges. Refrigerate
unused cartridges. Rotate stock.
Prepare fresh mobile phase,
decrease acetonitrile content.
a gradient separation.
to column (≤ 20 µL for 150 mm
or ≤ 10 µL for 75 mm Nova-Pak
columns).
C
18
Disposing of Used Cartridges
Dispose of used cartridges according to applicable government
regulations.
VII. reFerenCes And BIBLIoGrAPHY
1. Committee on Aldehydes, Board of Toxicology and
Environmental Hazards, National Research Council,
Formaldehyde and Other Aldehydes; National Academy Press,
Washington, DC, 1981.
2. Tejada,S.B.,“EvaluationofSilicaGelCartridgesCoatedIn
Situ With Acidified 2,4-Dinitrophenylhydrazine for Sampling
Aldehydes with Ketones in Air”, Intern. J. Environ. Chem. 1986,
26 , 167-185.
3. Riggins,R.M.,“CompendiumofMethodsfortheDetermination
of Toxic Organic Compounds in Ambient Air”, US Environmental
Protection Agency Report EPA-600/4-84-041, US
Environmental Protection Agency: Research Triangle Park, NC,
198 4.
Waters Sep-Pak DNPH-Silica Cartridge
7
Page 8

[ Care and Use ManUal ]
4. Arnts,R.R.andTejada,S.B.,“2,4-Dinitrophenylhydrazine-
Coated Silica Gen Cartridge Method for Determination of
Formaldehyde in Air: Identification of an Ozone Interference”,
Environ. Sci. Technol. 1989, 23, 1428-1430.
5. Guide to Successful Operation of Your LC System; Millipore
Corporation, Waters Chromatography Division: Milford, MA
1991. See Appendix E to order.
6. ASTM Method E411; Standard Test Method for Trace Quantities
of Carbonyl Compounds with 2,4-Dinitrophenylhydrazine.
VIII. orderInG InForMAtIon
Waters Sep-Pak DNPH-Silica cartridges are shipped in boxes of 20
individually-packaged cartridges. Pouches are supplied for storage
after sampling.
Table 6: Ordering Information
If your acetonitrile is unacceptable for your application, contact your
solvent supplier, or purify the acetonitrile. To purify acetonitrile,
distill it from an acidified DNPH solution using a procedure
a n a l o g o u s t o t h e o n e d e s c r i b e d i n A S T M M e t h o d E 4 1 1 f o r t h e
6
purification of methanol
.
To measure acetonitrile purity:
1. Clean all glassware by rinsing with acetonitrile and heating in a
60 °C vacuum oven for at least 30 minutes.
Derivative Concentration (µg/mL)
Formaldehyde-DNPH 0.08
Acetaldehyde-DNPH 0.12
Acetone-DNPH 0.40
All other hydrazones <0.05
2. Elute a fresh cartridge with 3 mL acetonitrile.
Derivative Concentration (µg/mL)
Formaldehyde-DNPH 0.09
Acetaldehyde-DNPH 0.14
Acetone-DNPH 2.00
All other hydrazones <0.05
Product Part Number
Sep-Pak DNPH-Silica Cartridges, 20/
box
Sep-Pak DNPH-Silica Long Body
Cartridges, 20/box
Nova-Pak C
Nova-Pak C
In-line Pre-Column Filter (0.5µm) 600000180
HVLP Mobile Phase Filter, 100/pkg WAT200530
Beginners Guide to Liquid
Chromatography
Ozone Scrubber Cartridge, 20/box WAT54420
Column, 3.9 x 75 mm WAT011670
18
Column, 3.9 x 150 mm WAT086344
18
WAT037500
WAT039550
715001531
IX. APPendICes
Appendix A: Measuring Acetonitrile Purity
HPLC-grade acetonitrile may contain traces of aldehydes and
ketones, especially acetone. 10 µg/L of an aldehyde or ketone
i n t h e a c e t o ni t r i l e a d d s 0 .1 µ g D N P H d e r i v a t i v e p e r c a r t r i d g e t o
background values.
3. Within3minutes,injecttheeluateontotheHPLCsystemto
measure the concentration of DNPH derivatives.
Derivative Concentration
after Reaction
with Acid
FormaldehydeDNPH
AcetaldehydeDNPH
Acetone-DNPH 2.00 µg/mL - 0.40 µg/mL = 1.60 µg/mL
0.09 µg/mL - 0.08 µg/mL = 0.01 µg/mL
0.14 µg/mL - 0.12 µg/mL = 0.02 µg/mL
Minus
Concentration in
Blank
Equals
Contribution from
Acetonitrile
4. Add 1 drop of concentrated HCl to the eluate and allow it to
react at room temperature for 30 minutes.
Derivative Contribution
from
Acetonitrile
FormaldehydeDNPH
AcetaldehydeDNPH
Acetone-DNPH
0.01 ÷÷ 0.08 x 100 = 12%
0.02 ÷÷ 0.12 x 100 = 17%
1.60 ÷ ÷ 0.40 x 100 =
Divided by
Background
Value
Times 100 Equals Percent
Relative to
Background
400%
Waters Sep-Pak DNPH-Silica Cartridge
8
Page 9

[ Care and Use ManUal ]
5. Remeasure the concentration of DNPH derivatives by HPLC.
6. Calculate the difference in the concentration of each DNPH
derivative measured in steps 3 and 5 to yield the contribution
from the acetonitrile.
7. Calculate the percent hydrazone contributed by the acetonitrile
relative to the background level. The value for any hydrazone
should not exceed 25% of its value in the blank.
Example: Measuring Acetonitrile Purity
1. HPLC analysis of a fresh cartridge shows the sample contains:
2. Analysis of the concentrations of hydrazones after reacting with
acid yields:
3. The different between the concentrations of hydrazone from
steps 3 and 5 represent the amount of hydrazone contributed by the
acetonitrile.
4. The percent of the hydrazones contributed by the acetonitrile are:
2. Saturate the 2 M HCl solution with DNPH: Add 8 g DNPH and stir
for one hour at 20 to 25 °C. Filter through a 0.45 µm hydrophilic
membrane (HVLP) filter (Waters Part number: WAT200530).
3. Form hydrazone derivative: Add a two-fold molar excess of
reagent-grade aldehyde or ketone to the filtered 2 M HCl DNPH
solution. Stir for 30 minutes to one hour at 20 to 25 °C.
4. Filter the hydrazone slurry. Wash the hydrazone with 50 mL 2 M
HCl 3 times. Wash with 50 mL water 3 times. Dry the filter cake
in an oven at 50 to 60°C overnight.
5. Prepare standard solutions in acetonitrile at concentrations
between 1 to 10 mg hydrazone/L. The solutions are stable for
at least one month when stored in tightly-capped glass vials
at 4 °C.
Appendix C: Measuring Sample Breakthrough
Note: If several aldehydes and ketones are present in significant
concentration, estimate the maximum sample size from the total
concentration of all species.
Since the percent for formaldehyde and acetaldehyde arising from the
acetonitrile is less than 25% of the background level in the cartridge,
the acetonitrile is considered clean for these compounds. If the analysis
considers only these compounds, the acetonitrile is acceptable.
However, the amount of acetone arising from the acetonitrile is four
times the amount in the blank (much higher than the 25% suggested
maximum). Therefore, it is suggested that this lot of acetonitrile may
be unacceptable for the analyses.
Appendix B: Synthesizing DNPH Derivative Standards
DNPH-derivative standards are easily synthesized from DNPH supplied
by Aldrich Chemical Co. (70% DNPH and 30% water). To synthesize
98-99% pure hydrazones:
1. Prepare one liter of 2 M HCl solution: Add 172 mL concentrated
reagent-grade hydrochloric acid (HCl) to a 1 L volumetric flask.
Fill the flask to the mark with distilled deionized water.
The collection efficiency for Waters Sep-Pak DNPH-Silica cartridges is
greater than 95% for gaseous sampling rates of up to 2 L/min. The
sample may exhibit breakthrough if:
• Thesamplingflowrateisgreaterthan2L/min
• Theamountofsamplecollectedisenoughtoreactwithmore
than 50% of the DNPH (equivalent to 0.5 mg DNPH)
To measure DNPH-Silica cartridges for collection efficiency:
1. Connect two unused cartridges together by the Luer fittings and
mark each cartridge for identification.
2. Connect the cartridges to a pump with a short length of flexible
tubing.
3. Collect the sample.
4. Elute both cartridges and an unused third blank cartridge.
Waters Sep-Pak DNPH-Silica Cartridge
9
Page 10

[ Care and Use ManUal ]
5. Analyze all three cartridges by HPLC.
6. Subtract the value from the blank cartridge from the values
determined from the other two cartridges.
7. Calculate and sum of the total captured DNPH-derivative from
both cartridges 1 and 2.
8. Divide the amount of DNPH-derivative determined from the first
cartridge by the total amount determined form cartridges 1 and
2. Multiply by 100. This is the percentage of DNPH-derivatives
captured on the first cartridge. This value should exceed 95%
otherwise, some of the sample broke through to the second
cartridge.
Example: Measuring Sample Breakthrough
To measure breakthrough:
Expected concentration of formaldehyde is 500 ppbv. Flow rate is
2.0 L/min. A sample volume if 100 liters yields:
Table 7: Breakthrough Example HPLC Results
Sampler Amount (µg) Quantity Captured
Sampler – blank (µg)
Sampler 1 75.06 75.00 91.8
Sampler 2 6.72 6.66 8.2
Blank 0.06 - -
In the above example, only a single carbonyl source was present.
Under many test conditions more than one carbonyl source may be
present in significant concentrations. These other compounds will
consume DNPH, effectively reducing the capacity of the sampler for
the compound of interest. To assure that the capacity of the sampler
has not been exceeded, compare the DNPH peak areas of the sample to
a similarly eluted blank. The DNPH peak area in all samples must be
no less than 50% of the DNPH peak area of the blank. This ensures
the sampler capacity has not been exceeded.
Percent Captured on
Sampler
Analyte ppmv Carbonyl Collected
concentration x molecular x air volume = µg Carbonyl
weight
Analyte molar volume at 1 atm/25 °C
This calculates to:
0.66 µL x 30.03 g/mole x 100 L = 81 µg formaldehyde
24.46 L/mole
The actual results are shown in Table 7. To calculate the percent
captured on the first sampler, divide the quantity captured on sampler
1 by the total quantity captured, then multiply by 100. Since this
value is less than 95%, and the total carbonyl amount exceeded
2.3 µmoles, breakthrough occurred.
Waters Sep-Pak DNPH-Silica Cartridge
10
Page 11

[ Care and Use ManUal ]
Austria and European Export
(Central South Eastern Europe, CIS
and Middle East) 43 1 877 18 07
Australia 61 2 9933 1777
Belgium 32 2 726 1000
Brazil 55 11 5094-3788
Canada 1 800 252 4752 x2205
China 86 10 8586 8899
CIS/Russia +7 495 3367000
Czech Republic 420 2 617 1 1384
Denmark 45 46 59 8080
Finland 09 5659 6288
France 33 1 30 48 72 00
Germany 49 6196 400600
Hong Kong 852 29 64 1800
The Netherlands 31 76 508 7200
Norway 47 6 384 60 50
Poland 48 22 833 4400
Puerto Rico 1 787 747 8445
Singapore 65 6273 1221
Spain 34 93 600 9300
Sweden 46 8 555 11 500
Switzerland 41 56 676 70 00
Taiwan 886 2 2543 1898
United Kingdom 44 208 238 6100
All other countries:
Waters Corporation U.S.A.
1 508 478 2000
1 800 252 4752
www.waters.com
Hungary 36 1 350 5086
India and India Subcontinent
91 80 2837 1900
Ireland 353 1 448 1500
Italy 39 02 265 0983
Japan 81 3 3471 7191
Korea 82 2 6300 4800
Mexico 52 55 5200 1860
© 2009 Waters Corporation. Waters, The Science of W hat’s Possible,
Sep-Pak and Nova-Pak are trademarks of Waters Corporation.
March 2009 WAT037506 Rev B KK-PDF
Waters Corporation
34 Maple Street
Milford, MA 01757 U.S.A.
T: 1 508 478 2000
F: 1 508 872 1990
www.waters.com
Waters Sep-Pak DNPH-Silica Cartridge
11
 Loading...
Loading...