Waters Sep-Pak Cartridges and Plates User Manual
[ Care and Use ManUal ]
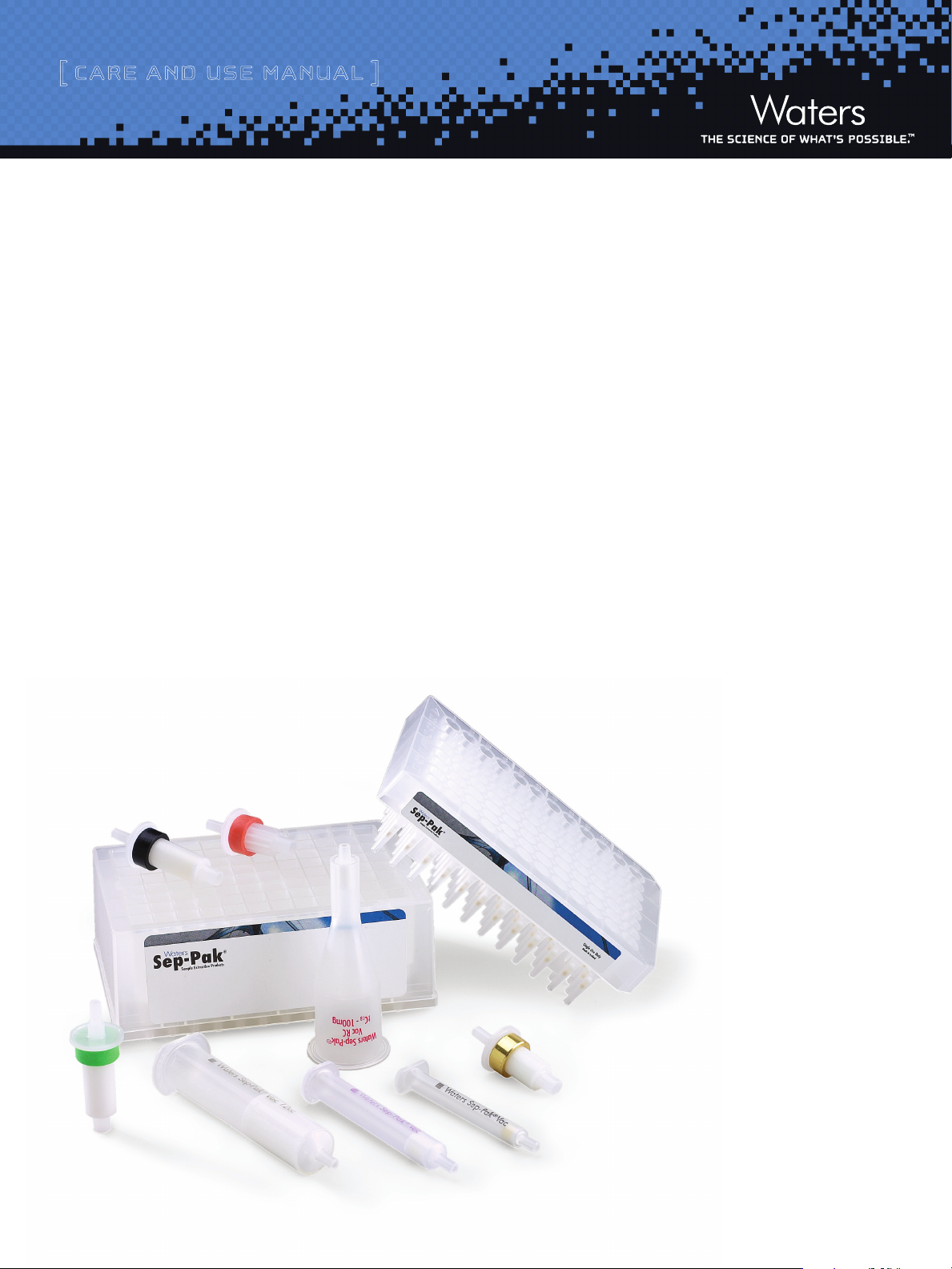
seP-PAK CArtrIdGes And PLAtes
Waters Sep-Pak® cartridges and 96-well plates are convenient,
reproducible, disposable solid-phase extraction (SPE) devices
for sample preparation. Sep-Pak cartridges and plates are
manufactured in a Waters ISO 13485 and ISO 9002-registered
facility in compliance with cGMP guidelines for the U.S. Food and
Drug Administration for Class 1 Medical Devices.
Contents
I. IntroduCtIon
II. usInG seP-PAK CArtIdGes And PLAtes
III. strAteGIes For soLId-PHAse eXtrACtIon
a. Retention-Cleanup-Elution Strategy
b. Pass-Through Cleanup Strategy
IV. stePs oF An sPe ProCedure
V. storAGe And dIsPosAL oF used CArtrIdGes
VI. AddItIonAL InForMAtIon
VII. LIterAture reFerenCes
Sep-Pak Cartridges and Plates 1
[ Care and Use ManUal ]
I. IntroduCtIon
Sep-Pak devices are available in many styles to accommodate
manual and automated solid-phase extraction. Devices are available
in convenient Plus, Light, Classic, Vac, Vac RC, and 96-well plate
formats.
Available Sorbent Chemistries:
Reversed Phase: C18, tC18, C8, tC
Normal Phase: Silica, Alumina A, Alumina B, Alumina N, Florisil
2
®
Ion Exchange and Mixed Mode: Aminopropyl, PSA, Accell™ Plus
QMA, Accell Plus CM, Cyanopropropyl, Diol
Speciality Products: Porapak® RDX, DNPH-Silica, XPoSure™, Ozone
Scrubber, Dry, PS2, AC2, Carbon Black/Aminopropyl
II. usInG seP-PAK CArtrIdGes And 96-WeLL PLAtes
Below is a five step guideline for using Sep-Pak cartridges. Each separation
is different and not all steps may be required for your application. Typical
strong and weak solvents used in the sample preparation steps are listed in
Table 1 below.
Table 1: Typical strong and weak solvents used in the
sample preparation.
Separation Mode Typical Weak
Solvents
Reversed Phase Water or bufer.
May contain low
concentrations of organics,
such as methanol.
Typical Strong
Solvents
Acetonitrile,
methanol, or
aqueous/organic
mixture
Prepare sample: The sample can be applied to the Sep-Pak Cartridge in
either liquid or a gas phase. If the sample is a solid, it must be dissolved or
extracted prior to loading.
Condition/Equilibrate Cartridge: A conditioning step is required for
reversed-phase sorbents (e.g., C18). Use a strong solvent to wet the station-
ary phase. Conditioning is followed by an equilibration step using a weak
solvent.
Load Sample: The sample is loaded onto the cartridge.
Wash: The wash step removed interferences while retaining the analyte. If
weakly retained interferences are present in the sample matrix, wash with an
appropriate weak solvent.
Elute: Use an appropriate stronger solvent to elute the analyte while retain-
ing more strongly bound interferences.
III. strAteGIes For soLId-PHAse eXtrACtIon
Purification: Use as a “chemical filter” to retain the component of interest
while interferences elute, or to retain the interferences while the analyte
passes through unretained.
Trace Enrichment or Concentration: Use to concentrate an analyte from
a dilute solution. This is done when the analyte concentration is below the
detection limit of the analytical method.
Fractionation: Use with a step gradient of increasing solvent strength to
selectivity elute and isolate analytes based on differences in polarity.
Solvent Exchange: Use to adsorb the analyte and elute with a
desirable solvent. This is helpful of the sample is dissolved in a solvent
that is incompatible with the analytical method.
Normal Phase Hexane, toluene Methylene chloride,
methanol
Weak Cation
Exchange
Strong Anion
Exchange
Sep-Pak Cartridges and Plates 2
Low ionic strength
buffer, pH >4
Low ionic strength
buffer, pH <8
High ionic strength
buffer, or pH <2
High ionic strength
buffer, or pH >10
 Loading...
Loading...