Page 1

[ Care and Use ManUal ]
delta-Pak HIGH-Pressure Inert HPlc coluMn
I. IntroductIon
a. Overview
Waters High Pressure Inert (HPI) HPLC columns are a metal free alternative
for both bio-chromatographic and ion-chromatographic applications. In this
®
advanced design, the sample contacts only polyetherether ketone (PEEK
and ultrahigh molecular weight polyethylene (UHMWPE), two materials
which are widely accepted for their biocompatibility and inertness. The
chromatographic performance of these columns is essentially identical
to their metal counterparts with the added advantage of greater chemical
inertness.
b. Delta-Pak Columns
TM
The Delta-Pak
phase. It is synthesized from 5 µm spherical silica particles having an average pore diameter of 100 Å or 300 Å. Delta-Pak
analysis and purification of peptides and proteins.
column packing material is an endcapped C18 or C4 bonded
columns are ideal for the
)
contents
I. IntroductIon
a. Overview
b. Delta-Pak Columns
II. InstallatIon
a. Installing the Column
b. Equilibration
III. MoBIle PHase and saMPle GuIdelInes
a. Solvent Compatibility
b. Mobile Phase Requirements
c. Sample Preparation and Filtration
IV. oPeratIon
a. Chromatography Guidelines
b. Efficiency Testing
c. Typical Column Backpressure and Eluent Viscosity
d. Column Temperature Limits
V. care and MaIntenance
a. Troubleshooting
b. Cleaning the Column
c. Storing the Column
VI. orderInG InforMatIon
1
Page 2
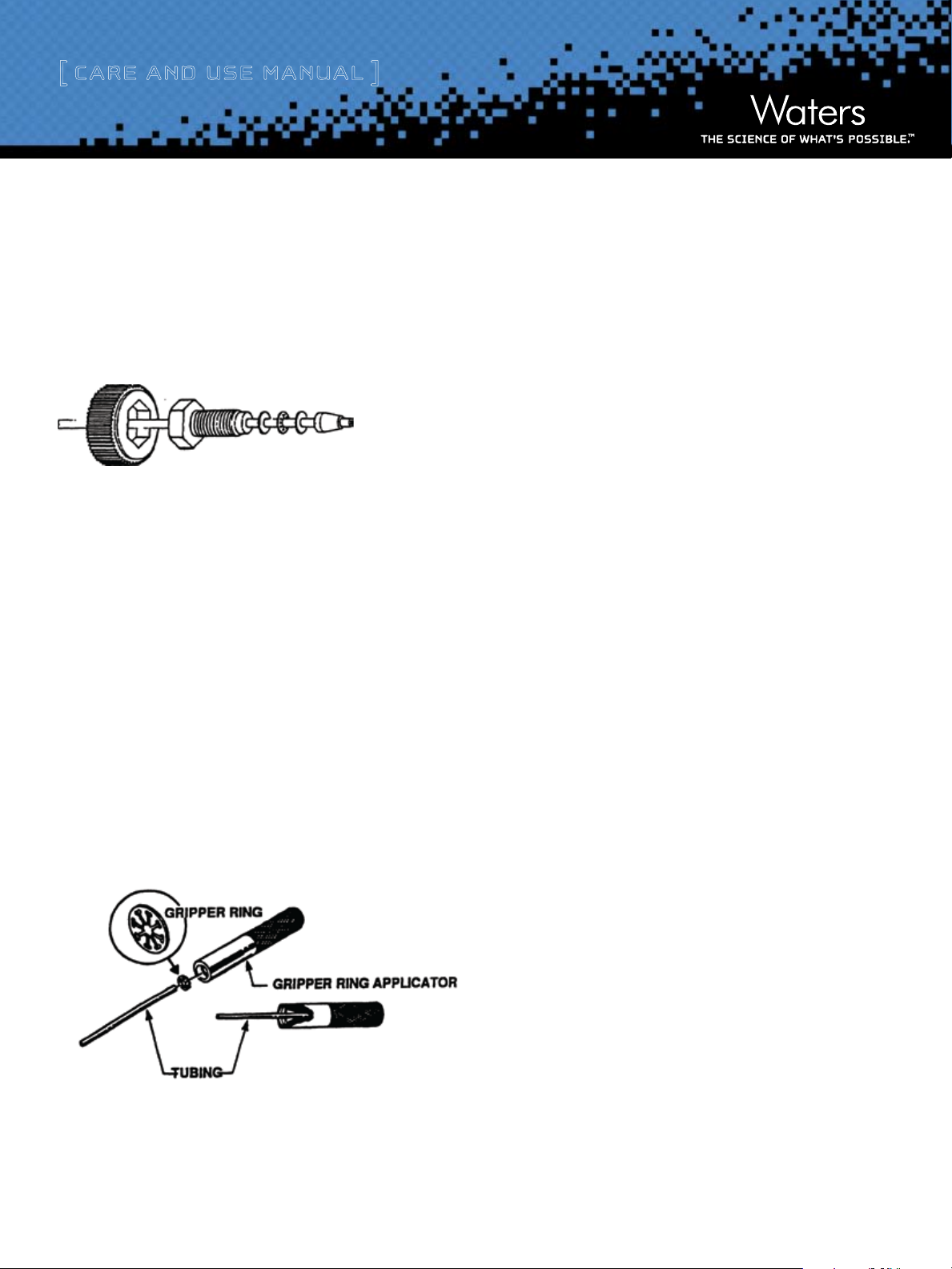
[ Care and Use ManUal ]
II. InstallatIon
a. Installing the column
Use only plastic tubing and plastic finger-tight endfittings with the HighPressure Inert column. The Waters endfitting design is shown in Figure 1.
Over-tightening the endfittings can cause irreversible damage to the filter
housing.
Figure 1: Finger-tight Endtting
To install a new fitting or replace a worn fitting:
1) Using a single-edge razor, make a straight and square cut on the
plastic tubing. Make this cut in front of the compression screw on the
worn endfitting.
2) Slide a compression screw fitting and a washer over the end of the cut
tubing.
3) Place the gripper ring in the top depression of the tool (see Figure 2).
Insert the end of the tubing into the gripper ring tool as far as it will
go. This seats the gripper ring at the proper length of the tubing.
4) Remove the tubing from the tool and slide the other washer and ferrule
over the end of the tubing. Insert a union over the endfitting assembly
and tighten. This seats the assembly.
Make sure that any mobile phase used for startup is miscible with the shipping solvent. Before placing the column in the flow path:
1) Attach a union between the column inlet and outlet lines.
2) Flush the lines to remove any microparticulates and old solvents. Flush
the injector loop if applicable.
3) Remove the union.
Remove the finger-tight end plugs from our column and save them to store
the column when it is removed from the system. Attach the column so that
flow follows the direction of the arrow on the column label. To install the
column, read the inlet and outlet fittings into the column until finger-tight.
b. Equilibration
The column is delivered in the mobile phase indicated in Table 1. Prior to
use, the column should be equilibrated with the mobile phase that will be
used in a analysis. Check mobile phase/shipping solvent miscibility.
Delta-Pak material is highly hydrophobic. If mobile phases with high concentrations of water are to be used, it is necessary to thoroughly solvate the
packing with the non-aqueous component before starting. To do so, pure the
column with 5 to 10 column volumes of the non-aqueous solvent to be used
in the mobile phase prior to equilibrating the column with the mobile phase.
Should the mobile phase contain a buffer salt, flush the column with 30
mL of water prior to equilibrating the column with the buffer. With PIC
ion- pairing reagents, whose concentration in the mobile phase is very
low (typically 5 mmol/l), 100 to 300 mL of mobile phase is required for
equilibration.
®
Figure 2: Gripper Ring Installation
III. MoBIle PHase and saMPle GuIdelInes
Liquid chromatography columns have a finite lifetime directly related to the
care and use they receive. Column life is reduced by:
• contamination from the mobile phase or sample
• improper storage and handling
• frequent solvent switching
• exposure to high or low pH eluents (for example, less than
2.0, greater than 8.0)
2
Page 3

[ Care and Use ManUal ]
a. Solvent Compatibility
The HPI column is constructed from non-metallic components which
have been chosen on the basis of their chemical inertness. While the
materials of construction are resistant to a wide spectrum of organic
and inorganic chemicals, the following list of chemicals attack the
surface and cause irreparable damage.
Caution: Use of any of these solvents with the column will result in a
void of the warranty:
• Chlorinated hydrocarbons
• Concentrated sulfuric acid
• Tetrahydrofuran (THF)
• Concentrated nitric acid
b. Mobile Phase Requirements
The following precautions are recommended for the preparation
of eluents:
• Use LC-grade solvents which have been filtered to remove
microparticulate matter above 0.45 µm. Ultrapure water
(18 megohm) is recommended.
• Use Gelman Sciences Aerodisc
to filter samples and prevent the high backpressure that results
from a blocked column inlet filer.
®
syringe filters from Waters
IV. oPeratIon
Simple procedures such as those outlined in this and the previous
chapter can significantly extend the column lifetime.
Should a change in peak shape, retention of a particular compound,
or resolution between two compounds be observed, take immediate
steps to determine a reason for the changes (see Section V. a.,
Troubleshooting). Until the cause of the change is determined, do not
rely on the results of the analyses.
Note: Before running the first analyses on your new column, perform
the test sample separation given in Efficiency Testing, Section IV, b.
a. Chromatography Guidelines
The following operating guidelines will help you obtain the best
performance from your Waters analytical HPIC column.
• Do not exceed an operating pressure of 40 Mpa (400 atm or
6,000 psi).
• Use vacuum filtration and/or sonification to remove dissolved
gases which could affect your pump. Care should be exercised
when vacuum filtering or sparging mixtures of solvents, because
the composition of the mixture could change. The best way to
degas the mobile phase is to place it into an ultrasonic bath and
apply vacuum and ultrasonic power simultaneously for about
30 seconds.
• Use ultrapure water as an intermediate solvent when changing
from aqueous salt solutions to organic solvents. Perform this
changeover gradually. Use care when adding organic solvents to
aqueous buffer solutions, as salt precipitation may occur.
c. Sample Preparation and Filtration
If the sample contains dissolved contaminants or particulates that
may bind irreversibly to the column, the following procedure is
recommended:
®
• Use Sep-Pak
sample that may be adsorbed onto the packing material surface
causing changes in performance and reduced column lifetime.
cartridges to remove contaminants from the
• Avoid using concentrated acids and bases. T he use of mobile
phases whose pH is below 2.0 or above 8.0 results in significantly reduced column lifetime due to the hydrolysis of the
bonded phase.
• Filter all aqueous buffers through a 0.45 µm filter prior to use.
Never use turbid or cloudy mobile phases.
• Protect the column from vibration, mechanical shock, and rapid
changes in pressure which can result from rapidly changing the
composition of the eluent.
• Use ultrapure water (18 megohn). Deionized water is not accept
able because it contains organic compounds that may alter
column selectivity.
b. Efficiency Testing
Waters’ columns are tested for compliance with our specifications. It
is possible that columns may be damaged during shipment. Test the
column before using it. The results of the efficiency test may be used
as a benchmark or future references.
3
Page 4

[ Care and Use ManUal ]
INJECT
N = 25
2
(
)
To perform an efficiency test, prepare the test sample as follows:
1) Prepare an acetone/acenaphthene sample by dissolving 0.05 g
acenaphthene and 600 µl acetone in 100 mLs of mobile phase.
While acenaphthene is the recommended sample, you can
substitute the following simple aromatic hydrocarbons:
Figure 3: 5 Sigma Test Method
• naphthalene
• p-cymene
• xylene
• dibutyl-, dipropyl-, or diethylphthalate
• propylbenzene
• toluene
• ethylbenzene
Toluene and diethylphthalate are the least desirable substitutes
since they have the lowest k.
2) Equilibrate the column employing the conditions summarized
below. Note: Incomplete equilibration results in tailing, fronting
or split peaks.
Table 1: Column Efciency Test Conditions
Column Mobile Phase Flow Rate Test Samples
Delta-Pak C
Delta-Pak C
18
4
and
50/50
acetonitrile/
0.7 ml/min Acenaphthene
water
Do not substitute methanol for acetonitrile in reversed-phase
column tests due to the much higher viscosity of methanol/water
mixtures.
If problems occur during normal operation of the column, repeat th
efficiency test and compare the results. This may help locate the
source of the problem.
c. Typical Column Backpressure and Eluent Viscosity
The column hardware has been designed to withstand operating
pressures as high as 50 Pa (500 atm or 7,000 psi). However, normal
operating backpressure should not exceed 40 Mpa (400 atm or
6,000 psi).
The normal operating backpressure of a column varies considerably
and is affected by column length, flow rate, mobile phase viscosity,
temperature, and particle size. The backpressure may rise significantly during the course of a gradient.
The following equation can be used to calculate the backpressure of
your column:
Pressure (atm) at 1 L/min in H
0 = 210 x l • v
2
dp2 x d2
Where:
L = column length, mm
dp = particle diameter, µm
d = column diameter, mm
v = mobile phase viscosity, centipose (see Table 2)
3) Set a UV detector at 254 nm with an attenuation of 0.05 AUFS.
The resulting detector deflection should be approximately 90
percent of full scale. The minimum deflection is 60%.
4) Inject about 2 µL of sample. Large amount may overload the
column.
5) Measure and record plate count, asymmetry, backpressure, and
instrument settings. Waters uses the 5 sigma method, shown
in Figure 3, to measure column efficiency. Unlike the tangent
method, this more stringent method takes peak asymmetry into
account
4
Page 5

[ Care and Use ManUal ]
Table 2: Viscosity
Mobile Phase Viscosity (20 °C),
Centipoise
n-Pentane 0.24
n-Hexane 0.33
wn-Heptane 0.42
Isoctane 0.50
Acetone 0.32
Dioxane 1.54
Nitromethane 0.65
Acetonitrile 0.37
n-Propanol 2.3
Ethanol 1.2
Methanol 0.6
Water 1.0
60/40 Methanol/Water 2.0
The typical operating backpressure for Waters® Delta-PakTM columns
is summarized below.
Table 3: Typical Operating Backpressure at 1 mL/min
Column Dimension Mpa Methanol
DeltaPak
DeltaPak
2.1 x 150
TM
mm
3.9 x 150
TM
mm
(Water)
17 (28) 170 (285) 2500 (4200)
6.0 (10.0) 60 (100) 900 (1500)
Atm Methanol (Water)
Psi Methanol
(Water)
A variation of plus or minus 10-15% is acceptable.
d. Column Temperature Limits
The column hardware has been designed to operate between 4 °C and
50 °C.
Note: Column failure due to operation outside of these temperature
limits voids the warranty.
V. care and MaIntenance
a. Troubleshooting
Table 4, on the following page, provides the corrective action for
specific problems that may occur with the Waters HPLC High Pressure
Inert columns.
b. Cleaning the Column
Flush reversed-phase columns with methanol or acetonitrile. It is
useful to monitor the UV absorbance during this procedure to see if
contaminants are being removed from the column.
If flushing does not resolve the problem, wash the column with solvents of decreasing polarity, always making sure the solvent in the
column and a washing solvent are miscible. Return the column to the
standard reversed-phase conditions by reversing the wash sequence.
If you suspect a particular contaminant is building up on the column,
use solvents or chemicals that are known to dissolve a material.
Be sure to remain within the limits of pH 2.0 to pH 8.0. Also,
ensure that no precipitate forms as a result of mixing the washing
solution with the solvent in the column. Proteinaceous material can
sometimes be removed by making repeated injections of 200 µL of
dimethylsulfoxide (DMSO).
c. Storing the Column
Leaving the column unused for less than 72 hours does not generally
require specialized storage procedures. However, never let columns
dry out. For longer storage:
• DO NOT store the column in water alone, as this may result
in bacterial growth in the column. Storing the column in a 10%
aqueous solution of isopropanol or methanol will hinder
bacterial growth.
• DO NOT store the column in buffered solution or solutions
containing salts, as these may precipitate.
• Return the column to its box with the end plugs firmly in place
for storage. Allowing the column to dry out may result in poor
chromatographic performance.
• DO NOT leave a column at elevated temperatures with no mobile
phase flow.
5
Page 6

[ Care and Use ManUal ]
Table 4: Troubleshooting
Symptom Cause Corrective Action Prevention
Buildup in system operating
pressure.
Loss of resolution, low plate
count.
Inlet filter plugged with
particulates from dirty sample
or mobile phase. Injector seal or
pump seal shredding.
Sample precipitates on the
column (sample not soluble in
the mobile phase).
Clogged tubing Replace the tubing. Identify and eliminate the source
Sample solvent is incompatible
with or stronger than the mobile
phase.
Failing injector (measure system
band spreading periodically).
Contaminated column. Wash with strong solvent. Isolate the source of the con-
Insufficient equilibration. Continue equilibration.
Replace the filter. Install an in-line filter between
the pump and the injector. Filter
the sample and/or mobile phase.
Wash the column using a solvent
that will dissolve the sample.
Dissolve sample in another
solvent.
Repair the injector. Filter mobile phases and use an
Use a mobile phase in which the
sample is soluble.
of the material clogging the
tubing.
Dissolve sample in another
mobile phase. If not possible,
change mode of separation.
in-line filter.
tamination and use a Sep-Pak
cartridge to clean up the sample.
If this is not possible, use a
Guard-Pak™ holder and insert
to protect the column from
contaminants. Use HPLC grade
solvents.
®
Incorrect connecting tubing. Replace with 0.0009” internal
diameter tubing.
All tubing from injector to the
detector should be 0.0009”
internal diameter.
VI orderInG InforMatIon
Delta-Pak HPI (High Pressure Inert Analytical Columns (PEEK)
Column (non metallic) Particle Size Pore Size Dimensions Part No.
DeltaPak HPI C18 5 µm 100 Å 2.1 mm x 150 mm WAT052750
DeltaPak HPI C18 5 µm 300 Å 2.1 mm x 150 mm WAT052765
DeltaPak HPI C4 5µm 100 Å 2.1 mm x 150 mm WAT052760
DeltaPak HPI C4 5 µm 300 Å 2.1 mm x 150 mm WAT052755
DeltaPak HPI C18 5 µm 300 Å 3.9 mm x 150 mm WAT035571
6
Page 7

[ Care and Use ManUal ]
Sales Offices:
Austria and European Export
(Central South Eastern Europe,
CIS and Middle East) 431 877 18 07
Australia 2 9933 1777
Belgium 32 2 726 1000
Brazil 55 11 5094 3788
Canada 800 252 4752
China 8621 6495 6999
CIS/Russia +7 495 3367000
Czech Republic 42 02 617 11384
Denmark 45 46 59 8080
Finland +358 9 5659 6288
France (33) 1 30 48 72 00
Germany 49 6196 400600
Hong Kong 852 29 64 1800
Hungary 36 1 350 5086
India and India Subcontinent
91 80 2 837 1900
Ireland 353 1 448 1500
Italy 39 02 274 211
Japan (81) 3 3471 7191
Korea (82) 2 820 2700
Mexico 5255 5200 1860
The Netherlands +31 (0)76-50 87 200
Norway 47 63 84 60 50
Poland (48) 22 833 4400
Puerto Rico 787 747 8445
Singapore 65 6273 1221
Spain 34 93 600 93 00
Sweden 46 8 555 11500
Switzerland 41 62 889 2030
Taiwan 886 2 2543 1898
United Kingdom 44 208 238 6100
©2007 Waters Corporation, Waters, The Science of W hat’s Possible, Delta-Pak, Guard-Pak, PIC and Sep-Pak are trademarks of
Waters Corporation. Aerodisc is a trademark of Gelman Sciences.
PEEK is a trademark of Victrex plc.
October 2007 WAT035904 Rev 4 V W-PDF
Waters Corporation
34 Maple Street
Milford, MA 01757 U.S.A.
T: 1 508 478 2000
F: 1 508 872 1990
www.waters.com
7
 Loading...
Loading...