Page 1

[ Care and Use ManUal ]
CeRtIFIeD seP-PAK CARtRIDGes
Contents
I. IntRoDUCtIon
II. UsInG CeRtIFIeD seP-PAK CARtIDGes
III. stRAteGIes FoR soLID-PHAse eXtRACtIon
IV. FACtoRs AFFeCtInG sePARAtIon eFFICIenCY
V. stoRAGe AnD DIsPosAL oF UseD CARtRIDGes
VI. oRDeRInG InFoRmAtIon
VII. ADDItIonAL InFoRmAtIon
VII. LIteRAtURe ReFeRenCes
I. IntRoDUCtIon
Waters Certified Sep-Pak® cartridges are convenient, reproducible,
disposable solid-phase extraction (SPE) devices for sample
preparation. Certified Sep-Pak cartridges are manufactured in a
Waters ISO 13485 and ISO 9002-registered facility in compliance
with cGMP guidelines for the U.S. Food and Drug Administration for
Class 1 Medical Devices.
Certified Sep-Pak cartridges are available in many styles to
accommodate manual and automated solid-phase extraction and are
available in 3 cc and 6 cc formats in the following chemistries:
Reversed-Phase: C
Normal-Phase: Silica, Alumina A, Alumina B, Alumina N, Florisil
18
®
Certified Sep-Pak Cartridges 1
Page 2
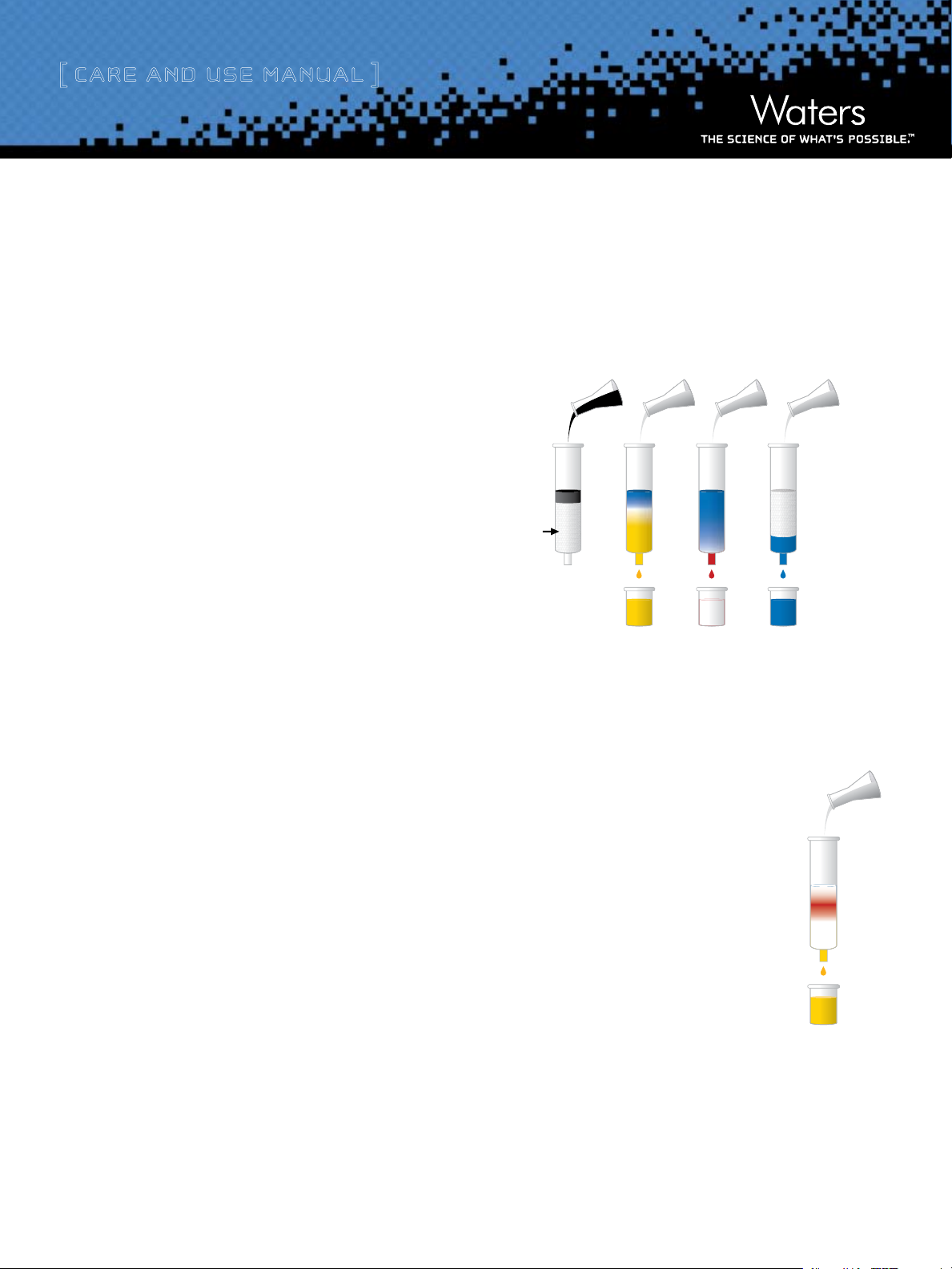
[ Care and Use ManUal ]
Load Sample
(Black)
Step
Elute 1
Step
Elute 2
One cartridge can separate all three dyes
Step
Elute 3
NOTE: Different
strength solvents
can be used to
separate the dyes.
Stationary
Phase
Particles
II. UsInG CeRtIFIeD seP-PAK CARtRIDGes
Below is a five step guideline for using Certified Sep-Pak cartridges.
Each separation is different and not all steps may be required for
your application.
1. Prepare sample: T he sample can be applied to the Certified Sep-Pak
cartridge in either liquid or a gas phase. If the sample is a solid, it must
be dissolved or extracted prior to loading.
2. Condition/equilibrate cartridge: A conditioning step is required for
reversed-phase sorbents (e.g., C
). Use a strong solvent to wet the
18
stationary phase. Conditioning is followed by an equilibration step
using a weak solvent.
3. Load sample: T he sample is loaded onto the cartridge.
4. Wash: The wash step removes interferences while retaining the analyte.
If weakly retained interferences are present in the sample matrix, wash
with an appropriate weak solvent.
5. Elute: Use an appropriate stronger solvent to elute the analyte while
retaining more strongly bound interferences.
III. stRAteGIes FoR soLID-PHAse eXtRACtIon
a. Retention-Cleanup-Elution Strategy
As the sample is loaded onto the cartridge, the analytes of interest are
retained by the sorbent. If needed, an optimized series of washes are
used to remove matrix interference from the cartridge. A strong solvent
is used to elute the analytes from the cartridge. Sample enrichment
results when the final elution volume is smaller than the load volume.
b. Pass-Through Cleanup Strategy
Pass-through cleanup methods optimize matrix retention while the
analytes of interest pass-through the cartridge unretained. No sample
enrichment occurs during the solid-phase extraction (SPE) step.
Purification: Use as a “chemical filter” to retain the component
of interest while interferences elute, or to retain the interferences
while the analyte passes through unretained.
Trace enrichment or concentration: Use to concentrate an analyte
from a dilute solution. This is done when the analyte concentration is
below the detection limit of the analytical method.
Fractionation: Use with a step gradient of increasing solvent
strength to selectivity elute and isolate analytes based on differences
in polarity.
Solvent exchange: Use to adsorb the analyte and elute with a desir-
able solvent. This is helpful of the sample is dissolved in a solvent
that is incompatible with the analytical method.
Certified Sep-Pak Cartridges 2
1. Sample is passed through sorbent and collected
• No sample enrichment
2. Matrix interferences are retained on sorbent
Pass-Through
Page 3

[ Care and Use ManUal ]
c. SPE Procedure Steps
The following section describes the steps involved in a complete
solid-phase extraction procedure:
1. Pretreatment
Solid samples (soil, tissue, etc.)
• Shake, sonicate, or use soxhlet extraction.
- Extract sample with polar organic solvent (methanol,
acetonitrile) for polar analytes.
- Extract sample with organic solvent and drying agent
(dichloromethane, acetone) for non-polar analytes and
multi-residue extraction.
Non-Aqueous liquid
• If the sample is soluble in water, dilute it with water for
reversed-phase SPE.
• If the sample is soluble in hexane, dilute it with (or exchange to)
hexane for SPE.
Wastewater
• Filter or centrifuge as necessary.
2. Condition
For reversed-phase sorbents, preconditioning of the sorbent with
an organic solvent, such as methanol, acetonitrile, isopropanol, or
tetrahydrofuran, is usually necessary to obtain reproducible results.
Without this step, a highly aqueous solvent cannot penetrate the
hydrophobic surface and wet the sorbent. Thus, only a small fraction
of the sorbent surface area would be available for interaction with the
analyte. For the same reason, it is important not to let silica-based
SPE cartridges dry out between the solvation step and the addition of
the sample. A complete preconditioning of a reversed-phase cartridge
includes the solvation step and an equilibration with a low-strength
solvent such as water or buffer.
3. Load
When the analytes of interest are not retained by the sorbent,
this is called analyte breakthrough. For some methods, such as
pass-through cleanup, analyte breakthrough is desirable and is
maximized for those specific methods. However, in all other cases,
analyte breakthrough is unwanted and contributes to poor recovery
and method reproducibility. Breakthrough occurs when:
• T here is too high an organic concentration in the load solution for very
polar analytes. Dilute sample at least 1:1 with water or buffer prior to
loading.
• T he analytes are bound to proteins, they may pass through
the sorbent. Ensure that analytes are not bound to proteins by
acidifying or basifying the sample.
• Sorbent is overloaded by the matrix component. Therefore, it is
important to choose the correct sorbent mass (see table 1).
• T he flow rate of the load step is too fast. T here is not enough
contact time between the analytes and the sorbent. Look at the drops
and adjust the vacuum so that you see discrete droplets, not a stream
of liquid.
Table 1. Choice of Cartridges Based on Sample Size
Sample Size Cartridge
10-100 mL 3 cc/200 mg or 6 cc/500 mg
100-500 mL 3 cc/200 mg or 6 cc/500 mg
500-1000 mL 6 cc/500 mg (LP) or 6 cc/1 g
4. Wash
The wash steps are designed to remove unwanted matrix components
that remain from the loading step. The ideal wash solvent removes
only the matrix while keeping the analytes bound to the sorbent. For
complex samples this is impossible, so the wash steps are optimized
using pH, solvent strength, and solvent polarity to remove as much
matrix as possible while maintaining acceptable analyte recovery.
Certified Sep-Pak Cartridges 3
Page 4

[ Care and Use ManUal ]
5. Elute
Once the interferences are washed off the cartridge, a strong solvent is introduced to elute the analytes of interest. T he volume and flow rate
of the eluting solvents should be precisely controlled as in the load step to ensure reproducible results.
Table 2. Guidelines on the Various Types of Separation Mechanisms
Reversed Phase Normal Phase Ion Exchange
Analyte
Matrix Aqueous Non-polar organic solvent Aqueous/low ionic strength
Low to moderate polarity/
hydrophobic
Moderate to highly polar/uncharged Charged or ionized
Condition/Equilibrate
Wash Aqueous/buffer Non-polar Low ionic strength buffer
Elute
IV. FACtoRs AFFeCtInG sePARAtIon eFFICIenCY
Separation efficiency varies with flow rate and sample load. Here
are some guidelines to consider when optimizing your separation.
a. Flow Rate
If the sample flow rate is too high, components may not interact
sufficiently with he sorbent. The result is loss of resolution, analyte
breakthrough, and poor recovery. To condition the cartridge, use a
flow rate of 5-10 mL/min. To load and elute Certified Sep-Pak Vac 3
cc 200 mg, and 500 mg cartridges, use a flow rate or 0.2-1 mL/min.
To load and elute all other cartridges, use a flow rate or 2-10 mL/min.
b. Sample Load
1. Solvate polar organic
2. Water
Increase polar organic content
in steps
Non-polar organic Low ionic strength buffer
Increase moderate to high polarity
organic content in steps
Stronger buffers ionic strength or
pH to neutralize the charge
V. stoRAGe AnD DIsPosAL oF UseD CARtRIDGes
Cartridges stored in their original sealed pouch remain stable
for long periods. Once opened, special care must be taken to
ensure that the SPE cartridges are not exposed to the laboratory
environment for long periods. The highly active sorbents will readily
accumulate background contaminants from the environment and
will affect the quality of the device. Waters recommends that you
open and use only those cartridges that will be needed. If this is not
possible, store the exposed cartridges in clean contaminant free
container such as a desiccator.
Dispose of used cartridges safely in accordance with applicable
government or local regulations.
Cartridge capacity depends upon the mass of all components in the
sample, volume of solvent, solvent strength, sorbent type, sorbent
quality, and retention factor (k) of components. Overloading results in
sample breakthrough which leads to variability in sample recovery.
Certified Sep-Pak Cartridges 4
Page 5

[ Care and Use ManUal ]
VI. oRDeRInG InFoRmAtIon
Description Part Number
Alumina A
Certified Sep-Pak Vac, 3 cc, 500 mg, 50/box 186004602
Certified Sep-Pak Vac, 6 cc, 500 mg, 30/box 186004603
Certified Sep-Pak Vac, 6 cc, 1 g, 30/box 186004604
Alumina B
Certified Sep-Pak Vac, 3 cc, 500 mg, 50/box 186004605
Certified Sep-Pak Vac, 6 cc, 500 mg, 30/box 186004606
Certified Sep-Pak Vac, 6 cc, 1 g, 30/box 186004607
Alumina N
Certified Sep-Pak Vac, 3 cc, 500 mg, 50/box 186004608
Certified Sep-Pak Vac, 6 cc, 500 mg, 30/box 186004609
Certified Sep-Pak Vac, 6 cc, 1 g, 30/box 186004610
Florisil
Certified Sep-Pak Vac, 3 cc, 500 mg, 50/box 186004611
Certified Sep-Pak Vac, 6 cc, 500 mg, 30/box 186004612
Certified Sep-Pak Vac, 6 cc, 1 g, 30/box 186004613
Silica
Certified Sep-Pak Vac, 3 cc, 200 mg, 50/box 186004614
Certified Sep-Pak Vac, 3 cc, 500 mg, 50/box 186004615
Certified Sep-Pak Vac, 6 cc, 500 mg, 30/box 186004616
Certified Sep-Pak Vac, 6 cc, 1 g, 30/box 186004617
18
C
Certified Sep-Pak Vac, 3 cc, 200 mg, 50/box 18 60 04618
Certified Sep-Pak Vac, 3 cc, 500 mg, 50/box 186004619
Certified Sep-Pak Vac, 6 cc, 500 mg, 30/box 186004620
Certified Sep-Pak Vac, 6 cc, 1 g, 30/box 186004621
VII. ADDItIonAL InFoRmAtIon
Sep-Pak accessories are available to help with your solid-phase
extraction. Ordering information for these products is below.
Sep-Pak Cartridge Accessories
Description Qty. Part No.
30 cc Reservoir 48/pkg WAT011390
60 cc Reservoir 12/pkg WAT024659
Reservoir Adapters for 3, and 6 cc VAC 12/pkg WAT054260
Male-Male Adapter 100/pkg WAT024310
Male Luer Plugs WAT044395
Female Luer Plugs WAT044385
Extraction Manifolds
20 position extraction manifold without rack
20 position extraction manifold with 13 x 75 mm test tube rack
20 position extraction manifold with 13 x 100 mm test tube rack
WAT200677
WAT200606
WAT200607
Description Qty. Part No.
20 position extraction manifold with 16 x 75 mm test tube rack
20 position extraction manifold with 16 x 100 mm test tube rack
WAT200608
WAT200609
Accessories and Spare Parts for the Waters Extraction Manifolds
Needle valves, 20/pkg (required when using silicabased SPE cartridges)
Needle tips, 20/pkg WAT200691
Cover, 20 position without gauge assembly WAT200686
Gauge assembly, vacuum WAT200687
Reservoir, glass with outlet valve WAT200687
Outlet valve kit WAT200688
Gasket for cover WAT200689
Ejector tool WAT200690
Luer Plugs 25/pkg WAT058839
Rubber ball ring (for vacuum gauge assembly) WAT058851
Reversible Vial Rack for 1 mL or 4 mL
autosampler vials
13 x 75 mm test tube rack WAT058871
13 x 100 mm test tube rack WAT200678
16 x 75 mm test tube rack WAT200679
16 x 100 mm test tube rack WAT200680
Adapter (to attach reservoir to 1, 3, and 6 cc
Sep-Pak Vac cartridges)
Adapter (to attach reservoir to 12, 20, and 35 cc
Sep-Pak Vac cartridges)
Vacuum pump (110 V, 60 Hz) 10/pkg WAT048160
Vacuum pump (220 V, 50 Hz) WAT085114
Vacuum pump (220 V, 50 Hz) WAT085115
100/pkg WAT024310
12/pkg WAT054260
WAT200685
WAT058840
For more detailed information, consult the Chromatography Columns
and Supplies Catalog by visiting www.waters.com (literature code
720002419EN), or contact your Waters representative.
If you require technical assistance, or have any questions
regarding sample preparation, visit www.waters.com or call us at
1-800-252-4752.
VIII. LIteRAtURe ReFeRenCes
Description Literature Code
Certified Sep-Pak Brochure 720002806EN
Sorbent Selection Guide Wall Chart 720002007EN
A Sample Preparation Primer and Guide to Solid-Phase
Extraction Methods Development
Sample Preparation Solutions Brochure 720000848EN
Sep-Pak Sample Extraction Products Brochure 720000860EN
Food Safety Application Notebook 720002565EN
Environmental Chromatography Methods Guide 720002543EN
WA20300
Certified Sep-Pak Cartridges 5
Page 6

[ Care and Use ManUal ]
Sales Offices
Austria and European Export
(Central South Eastern Europe, CIS
and Middle East) 43 1 877 18 07
Australia 61 2 9933 1777
Belgium 32 2 726 1000
Brazil 55 11 5094-3788
Canada 1 800 252 4752 x2205
China 86 21 6879 5888
CIS/Russia +497 727 4490/290 9737
Czech Republic 420 2 617 1 1384
Denmark 45 46 59 8080
Finland 09 5659 6288
France 33 1 30 48 72 00
Germany 49 6196 400600
Hong Kong 852 29 64 1800
The Netherlands 31 76 508 7200
Norway 47 6 384 60 50
Poland 48 22 833 4400
Puerto Rico 1 787 747 8445
Singapore 65 6273 7997
Spain 34 93 600 9300
Sweden 46 8 555 11 500
Switzerland 41 56 676 70 00
Taiwan 886 2 2543 1898
United Kingdom 44 208 238 6100
All other countries:
Waters Corporation U.S.A.
1 508 478 2000
1 800 252 4752
www.waters.com
Hungary 36 1 350 5086
India and India Subcontinent
91 80 2837 1900
Ireland 353 1 448 1500
Italy 39 02 265 0983
Japan 81 3 3471 7191
Korea 82 2 6300 4800
Mexico 52 55 5524 7636
© 2009 Waters Corporation. Waters, The Science of W hat’s
Possible, and Sep-Pak are trademarks of Waters Corporation.
Florisil is a trademark of U.S. Silica.
Sep-Pak Cartridges are covered by U.S. Patents # 4,211,658
and/or # 4,250,035 and several foreign patents.
March 2009 720002966EN Rev A V W-PDF
Waters Corporation
34 Maple Street
Milford, MA 01757 U.S.A.
T: 1 508 478 2000
F: 1 508 872 1990
www.waters.com
Certified Sep-Pak Cartridges 6
 Loading...
Loading...