Page 1
[ Care and Use ManUal ]
CarbaMate analysIs ColuMn
I. IntroduCtIon
The Waters Carbamate Analysis Column (3.9 x 150 mm) is packed
with a durable, high efficiency, 4μ spherical silica-based stationary
phase ideally suited for the reversed-phase separation of carbamate
pesticides and related compounds.
Waters exclusive sequential bonding and packing processes coupled
with stringent quality control procedures ensure precise surface
chemistry, reproducibility, and stability. When used as a component
of Waters Carbamate Analysis System with the Waters Carbamate
Analysis Method, this column is guaranteed to provide the resolution
and sensitivity needed for successful analysis of the analytes listed
in Figure 1.
Contents
I. IntroduCtIon
II. InstallatIon
a. Attaching the Column
b. Equilibration
III. MobIle phase and saMple guIdelIne
a. Solvent Preparation and Filtration
b. Sample Preparation and Filtration
IV. operatIon
a. Chromatography Guidelines
b. Efficiency Testing
V. Care and MaIntenanCe
a. Troubleshooting
b. Shutdown and Storage
VI. ColuMn and supplIes orderIng and InforMatIon
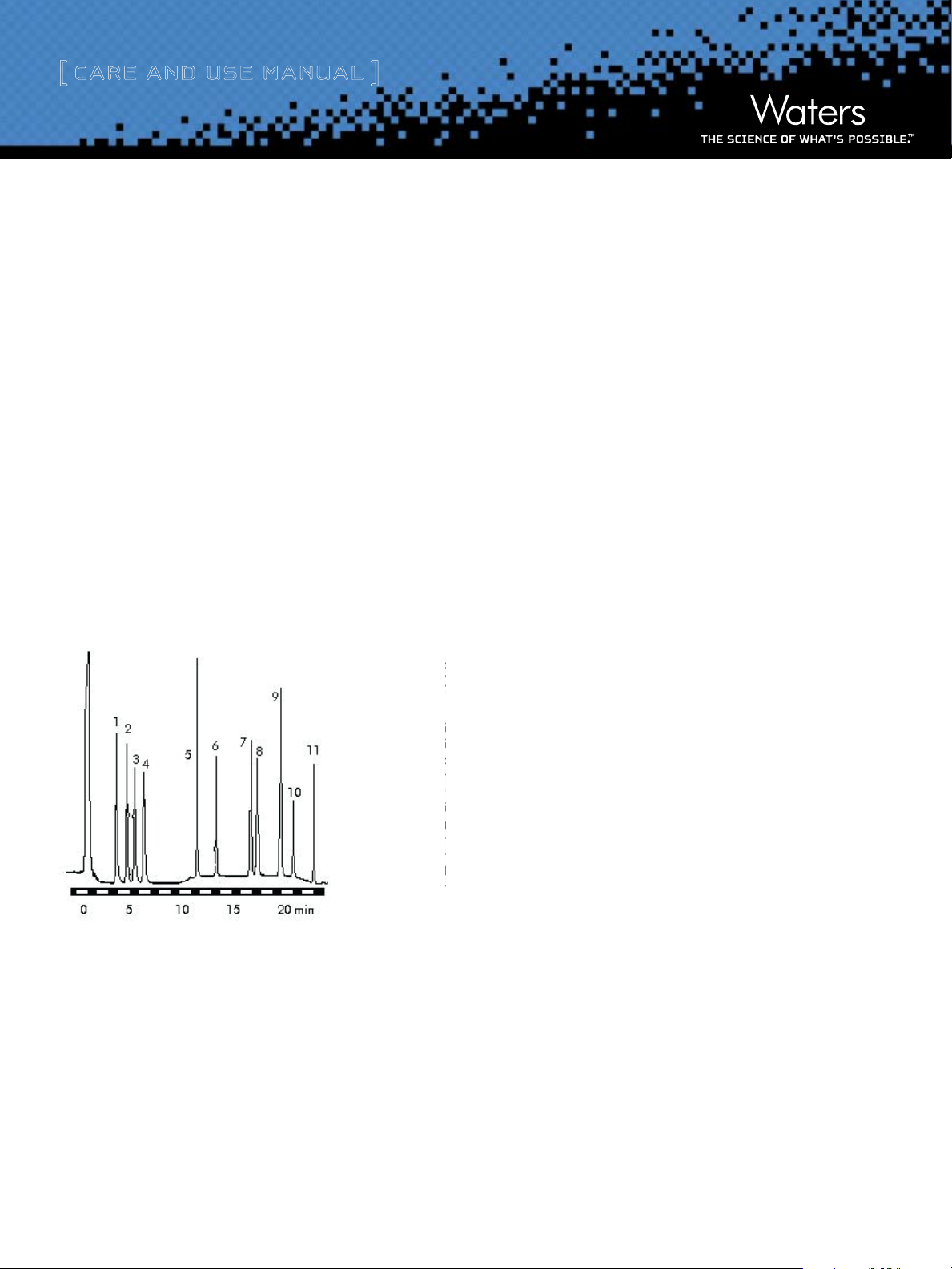
Figure 1: A Typical Separation of Carbamate Pesticides & Related
Compounds using Waters Carbamate Analysis System*
Please take a few moments to read this manual carefully. Use the
information it contains to ensure that you obtain quality results and
take full advantage of the features your Waters column offers.
Note: Liquid chromatography columns have a finite life, which is
directly related to the care and use they receive. Column life is
affected by contamination from samples and solvents, frequent
solvent changeovers, and improper handling and storage.
* For additional information on the complete method, please refer to Waters Carbamate
Analysis System Manual.
Carbamate Analysis Column 1
VII. Warranty/serVICe InforMatIon
Page 2

[ Care and Use ManUal ]
Compression Screw or Nut
Ferrule
End must be straight
and smooth to achieve
maximum column efficiency
Tu be
Critical Distance to be determined by
the union or column fitting, etc.
Follow generally accepted procedures for quality control and methods
development when using this column.
If you observe a change in peak shape, retention of a particular
compound, or resolution between two compounds, take immediate
steps to determine the reason for the changes. Until the cause of the
change is determined, do not rely on the results of the analyses.
II. InstallatIon
a. Attaching the Column
1. If this column is to be used with an LC system previously used
for a purpose other than carbamate analysis, then before
installing the column in the flow path connect the column
inlet and outlet lines to each other with a union and flush the
lines, as well as the sample injector and injector loops, free of
previous solvents. Make certain that the final flushing solvent
is miscible with water. Remove the union.
2. Remove the end plugs from your column with a 5/16-inch
wrench.
5. Grasp the tubing on both sides of the scribe mark with cloth-
covered pliers (to prevent marring the tube surface) and gently
work the tub back and forth until it breaks cleanly. Check that
the end is straight and smooth with no burrs. Flush the tube
from the opposite end with mobile phase to remove any metal
particles that may have lodged in the interior of the tube.
6. Slide the compression screw head first followed by the ferrule
(large end of the taper first) over the tube. Insert the end of
the tube into the fitting seat to which it will be connected.
Tighten the compression screw in the fitting seat as in Step 3.
Assembly details are shown in Figure 2.
CAUTION: Properly bottom the tubing in the fitting seat
while tightening the compression screw to the column.
Tubing not completely seated will result in dead volume
which could cause excessive sample band spreading.
NOTE: Be sure to replace and tighten the end plugs when the
column is removed from the system for storage.
3. The column outlet is indicated by an arrow on the label
showing the direction solvent should flow. Thread the inlet and
outlet tubing fittings into the column until finger tight and then
tighten the fittings with a wrench turning each - turn.
CAUTION: Do not over-tighten. Over-tightening will damage
the connection. Follow the next three steps of this procedure
if you must remove a damaged compression screw or worn
ferrule.
4. Using a miniature tubing cutter, scribe deeply the
circumference of the tubing at the desired break point. Or,
alternatively, using a three-cornered file with a cutting edge,
cut 1/3 of the way through the tubing at the desired break
point.
Carbamate Analysis Column 2
Figure 2: Ferrule and Compression Screw Assembly
b. Equilibration
The Waters Carbamate Analysis Column is shipped in the mobile
phase used for column storage: 50/50 v/v methanol/acetonitrile.
For equilibration, flush the column with the initial mobile phase
used for the gradient analysis. This can be conveniently done while
the post-column reaction system, column oven, and detector are
warming up to stable operating conditions (about 30 minutes at 1.5
mL/min). Refer to the Waters Carbamate Analysis System Manual
for details.
Page 3

[ Care and Use ManUal ]
III. MobIle phase and saMple guIdelIne
a. Solvent Preparation and Filtration
1. Use only HPLC Grade or better solvents suitable for high sensitivity
fluorescence analysis, filtered to remove micro-particulate matter
about 0.45 µm.
NOTE: All glassware used for solvent and sample preparation must
be scrupulously clean. Detergent, fingerprint, cigarette smoke, breath
residues, etc., may contain amines which can cause interference with the
analysis.
Acetonitrile and methanol, even HPLC grade, may contain traces of
amines or ammonia, which will react with OPA/mercaptoethanol to
form highly fluorescent impurities. These derivatives may cause base-
line shifts or increased baseline noise. If this becomes a problem, clean
the reservoirs and use fresh solvent. If necessary, switch to a different
lot of solvent or to a different solvent vendor until a suitable grade is
found.
Distill or HPLC grade water. De-ionized water is not acceptable because
it contains organic compounds which may alter column selectivity.
2. Use vacuum filtration, sonication, and/or helium sparging to remove
dissolved gases, which could affect your solvent delivery system.
Waters Solvent Clarification Kit is designed to assist in the degassing
and preparation of mobile phases. Waters Carbamate Analysis System
has provision for continuous sparging of each mobile phase component.
3. Use a Waters In-Line Pre column Filter to capture system particulates
and extend column life. Note: a Waters In-Line Pre column Filter is
supplied with the Waters Carbamate Analysis System.
IV. o pe rat Io n
a. Chromatography Guidelines
Liquid chromatography columns have a finite life which, is directly
related to the care and use they receive. Column life is affected
by contamination from; samples and solvents, frequent solvent
changeovers, and improper handling and storage.
If you observe a change in peak shape, retention of a particular
compound, or resolution between two compounds, take immediate
steps to determine the reason for the changes. Until the cause of the
change is determined, do not rely on the results of the analyses.
Follow generally accepted procedures for quality control and
methods development when using this column
NOTE: Before running the first analysis on your new column, perform
the test sample separation given in Section IV. b., Efficiency Testing
PRECAUTIONS
a. Pressure
Maximum pressure should not exceed: 28 Mpa (4000 psi or 275
bars). Typical operating pressure in the Waters Carbamate Analysis
System: 10-20 Mpa (1500-3000 psi or 100-200 bars).
b. Temperature
Recommended column operating temperature range: 20 °C - 40
°C. Typical operating pressure in the Waters Carbamate Analysis
System: 30 °C.
c. Flow Rate
b. Sample Preparation and Filtration
1. Use a Waters Sample Clarification Kit or 0.45 μ Membrane Filter
Units to filter samples and prevent excessive pressure buildup.
2. Do not inject a sample that is dissolved in a solvent, which is not
miscible with the mobile phase.
3. If samples contain contaminants which become irreversibly bound
to the column packing under normal operating conditions, it may be
®
desirable to use Waters Sep-Pak
column module and Guard-Pak Cartridges to remove the contaminants
off-line or on-line, respectively.
Carbamate Analysis Column 3
Cartridges or Waters Guard-Pak™ Pre
There are not flow rate restrictions as long as the recommended
pressure limits are not exceeded. Typical operating flow rate is
1.5mL/min. Flow rate should be increased gradually (in 0.5 mL/min
increments) to reach operating flow rate and decreased gradually to
zero upon system shutdown.
d. pH Range
Maintain pH of mobile phase and samples between 3 and 8. Avoid
using concentrated acids or bases.
Page 4

[ Care and Use ManUal ]
INJ ECT
W
V
R
= Column efficency (plates)
= Volume to peak apex (mL)
= Volume at 4.40% of peak height (mL)
N25
=
()
2
V
R
W
e. Particular Contamination
Filter all mobile phases. Never use turbid or cloudy solvents or
solutions.
f. Shock
Protect column from vibration, mechanical shock, and rapid changes in
operating pressure. Any thermal, physical, or chemical shock (such as
changing solvent composition rapidly) may cause the particles to shift and
may result in void and a loss of efficiency.
Protect the column from rapid changes in solvent composition which may
alter the mobile phase viscosity, and thereby, the system back pressure
drastically.
g. Efficiency Testing
Waters columns are tested in our quality control laboratories for
adherence to our specifications. Slight variations in your results will
occur depending on:
• EquipmentUsed
Save the chromatogram from this test. With the calculated column
efficiency, record the retention times, system settings, and all
experimental conditions so that they can be reproduced exactly in
the future. If problems occur during normal operation of the column,
repeat the initial efficiency test under the original conditions and
compare the results.
Differences in the results may indicate the source of the problem.
Refer to Table 1 and also the Waters Carbamate Analysis System
Manual for troubleshooting guidelines.
• TestSystemmakeup
• Equipmentsettingsandexperimentalconditions
Each new column’s performance should be checked on your system to
provide an initial efficiency standard for future comparison. After the
column has been installed and equilibrated, run the test sample as
described in the Waters Carbamate Analysis System Manual.
Choose a peak for one of the following analytes: aldicarb sulfoxide,
aldicarb sulfone, oxamyl, or methomyl. Measure the column effi-
ciency as shown in Figure 3.
NOTE: For convenience, VR and W can be expressed in units of length
rather than volume as measure with a scale from the chromatogram.
The “5-Sigma” method shown in Figure 3 is a more stringent way
to calculate plate count, N, than “half-peak height” and “tangent”
methods. It takes into account naturally occurring peak asymmetry
which can significantly reduce the resolution between adjacent peaks.
Figure 3: 5-Sigma Method for Measuring Column Efciency
V. Care and MaIntenanCe
a. Troubleshooting
Table 1 provides the corrective action for some typical column
problems that may occur with the Carbamate Analysis Column.
Refer also to the Waters Carbamate Analysis System Manual for
more detailed information on troubleshooting Waters Carbamate
Analysis Method.
NOTE: Eventually, column performance will degrade over time below
an acceptable level as determined by periodic efficiency testing.
When this happens, replace the old column with a new Waters
Carbamate Analysis Column. See Section VI. for reorder information.
Carbamate Analysis Column 4
Page 5

[ Care and Use ManUal ]
Table 1: Troubleshooting the Carbamate Analysis Column
Symptom Conditions Corrective Action
Excess pressure
buildup
Loss of resolution,
broad peaks, or
low plate counts
Filters plugged with
particulates.
Sample precipitates on
column (sample not
soluble in mobile
phase).
Clogged tubing. Replace tubing.
Mass overload Dilute sample and run it again.
Incorrect tubing size
(0.040” or 0.020”
i.d.)
Contaminated column. Slowly flush with a 50-100
Insufficient equilibrium Continue equilibration
Filters partially plugged Replace or clean (inlet and
Failing Injector Repair Injector.
Replace filter element or clean
in an ultrasonic bath. Always
filter solvents and samples
Slowly purge with a solvent
appropriate to dissolve the
precipitate.
Install correct 0.009” ID stainless steel tubing to column
inlet & outlet.
mL of 50/50 v/v acetonitrile/
MeOH; then equilibrate with
initial mobile phase and run
sample again.
outlet) the Filter Retainer Disc
and the Filter.
Long-term Storage (more than 72 hours)
Flush the column with 15-30 mL of 50/ v/v acetonitrile/methanol.
Then turn the pump off. Allow the column to cool to ambient
temperature. Disconnect the inlet and outlet tubes from the column
and join them with a union. Install the end plugs in the column inlet
and outlet fittings. Tighten the end plugs firmly in place with 5/16”
open end wrench.
CAUTION: Do not overtighten – Overtightening will damage the
column fittings. Allowing columns to dry out may result in poor
chromatographic performance. Return the column to its box for
storage
VI. ColuMn and supplIes orderIng InforMatIon
Item Part Number
Carbamate Analysis Column, 3.9x150mm WAT035577
Filter Retainer WAT088084
Filter Retainer Disc WAT089567
In-Line Pre column Filter WAT084560
Solvent Clarification Kit with pump WAT085113
b. Shutdown and Storage
Between Analyses
During the course of a working day, between analyses, continue
to pump the initial mobile phase mixture through the column. This
will maintain the equilibrium in the column necessary for good
retention time reproducibility. If a few hours will pass before the
next injection, the flow rate may be slowed down in the interim to a
few tenths of a mL/min to conserve solvent.
Overnight
When shutting down overnight or over a weekend, first flush the
column with 15-30 mL of 50/50 v/v acetonitrile/methanol. Then
turn the flow rate to zero mL/min and leave the column connected
in the system. The oven temperature may be maintained at 30 °C,
if desired.
Carbamate Analysis Column 5
Solvent Clarification Kit without pump WAT085124
Aqueous Replacement Filters (HATF 04700),
pkg. of 100
Organic Replacement Filters (FHUP 04700),
pkg. of 100
Aqueous Sample Clarification Kit WAT026865
Guard-Pak Pre column Module: Kit WAT080040
®
Nova-Pak
Sep-Pak C
Sep-Pak C
Sep-Pak C
C18 Guard-Pak Cartridges (10/Pkg.) WAT015220
Cartridges (50/Box) WAT051910
18
Plus Cartridges (24/Box) WAT011191
18
Plus Cartridges (96/Box) WAT015402
18
WAT085147
WAT085118
Page 6

[ Care and Use ManUal ]
VII. Warrant y/serVICe InforMatIon
Waters Corporation staff of experienced specialists provides
maintenance assistance on both preventative and/or corrective
levels. For complete information and assistance, please call Waters
Service Department at 1-800-252-HPLC. For solutions to particular
applications questions, Waters team of technical support personnel
are available to help you with specialized support. They may be
contacted at 1-800-252-HPLC in Milford, MA, USA.
Wa r r a nt y
Waters Corporation warrants its high performance liquid
chromatography columns in accordance with the following terms
and conditions:
Waters will repack or replace (at our discretion) without cost any
steel column that fails to perform satisfactorily if notice within 90
days from your receipt. Any column returned mush have a Return
Authorization Number granted by the Waters Customer Service
Depart. Approval is subject to the following exclusions:
Sales Offices:
Austria and European Export
(Central South Eastern Europe,
CIS and Middle East) 431 877 18 07
Australia 2 9933 1777
Belgium 32 2 726 1000
Brazil 55 11 5094 3788
Canada 800 252 4752
China 8621 6495 6999
CIS/Russia +7 495 3367000
Czech Republic 42 02 617 11384
Denmark 45 46 59 8080
Finland +358 9 5659 6288
France (33) 1 30 48 72 00
Germany 49 6196 400600
Hong Kong 852 29 64 1800
Hungary 36 1 350 5086
India and India Subcontinent
91 80 2 837 1900
Ireland 353 1 448 1500
Italy 39 02 274 211
Japan (81) 3 3471 7191
Korea (82) 2 820 2700
Mexico 5255 5200 1860
The Netherlands +31 (0)76-50 87 200
Norway 47 63 84 60 50
Poland (48) 22 833 4400
Puerto Rico 787 747 8445
Singapore 65 6273 1221
Spain 34 93 600 93 00
Sweden 46 8 555 11500
Switzerland 41 62 889 2030
Taiwan 886 2 2543 1898
• Physicaldamagetothecolumnduetomisuseorabuse.
• Chemicaldamagetothepackingmaterialbecauseofusewithincom-
patible solvents or buffers, or at an incorrect pH.
• Physicaldamagetothepackingmaterialbecauseofoperationatincor-
rect temperatures or pressures.
• Particulatebuilduporprecipitationinthecolumnorendfittingscausing
high internal pressure which has occurred due to improper solvent or
sample filtration practices.
© 2007 Waters Corporation. Waters, The Science of W hat’s
Possible, Sep-Pak, Nova-Pak, and Guard-Pak are trademarks of
Waters Corporation.
November WAT035583 Rev 2 VW-PDF
Carbamate Analysis Column 6
United Kingdom 44 208 238 6100
Waters Corporation
34 Maple Street
Milford, MA 01757 U.S.A.
T: 1 508 478 2000
F: 1 508 872 1990
www.waters.com
 Loading...
Loading...