Page 1

ACQUITY APC Columns
CONTENTS
I. INTRODUCTION
II. GETTING STARTED
a. Preparing the System
b. Column Connections
c. Column Installations
d. eCord Installation
e. Column Equilibration
III. COLUMN USE
a. Guidelines
b. Calibration
c. Useable Flow-Rate Ranges
d. Minimizing Band Spread
IV. TROUBLESHOOTING
V. COLUMN CLEANING, REGENERATION
AND STORAGE
a. Cleaning and Regeneration
b. Storage
VI. eCORD INTELLIGENT CHIP TECHNOLOGY
a. Introduction
b. Installation
c. Column Use Information
I. INTRODUCTION
Thank you for choosing an ACQUITY APC™ Column. The ACQUITY APC
Columns are designed to achieve maximum separation performance
when used with the ACQUITY® Advanced Polymer Chromatography®
(APC™) System. Please take a few moments to read this manual carefully.
Following the recommendations in this manual will prolong column life
and enhance chromatographic reproducibility.
ACQUITY APC Columns are packed with sub-3-µm ethylene bridged
hybrid (BEH) particles that provide mechanical strength, packedbed stability and high separation efficiency. They deliver superior
chromatographic performance for all polymer classes, including low
molecular weight aqueous and organic soluble polymers, up to a
molecular weight of 2,000,000 g/mole (Table 1).
To maximize separation selectivity and performance ACQUITY APC
Columns are available in two bonding technologies optimized for each
solvent class:
ACQUITY APC XT: Packed with a high-coverage trimethyl silane bonded to
a BEH substrate. These columns are recommended for extended temperature
(< 90 °C) separations in organic solvents.
ACQUITY APC AQ: Feature unbonded BEH substrate. Recommended for
room temperature (< 45 °C) separations in aqueous solvents.
ACQUITY APC Columns are manufactured in an ISO 9001 facility and are
held to narrow specification ranges to ensure reproducible performance.
Every column is individually tested and a Certificate of Batch Analysis is
provided on the attached eCord™ Intelligent Chip.
Page 2

Table 1. Physical Characteristics
Recommended
Separation Solvent
ACQUITY APC XT 45 Organic 90 1-11 45 1.7 200-5,000
ACQUITY APC XT 125 Organic 90 1-11 125 2.5 1,000-30,000
ACQUITY APC XT 200 Organic 90 1-11 200 2.5 3,000-70,000
ACQUITY APC XT 450 Organic 90 1-11 450 2.5 20,000-400,000
ACQUITY APC XT 900 Organic 90 1-11 900 2.5 300,000-2,000,000
ACQUITY APC AQ 45 Aqueous 45 1-9 45 1.7 200-5,000
ACQUITY APC AQ 125 Aqueous 45 1-9 125 2.5 1,000-30,000
ACQUITY APC AQ 200 Aqueous 45 1-9 200 2.5 3,000-70,000
ACQUITY APC AQ 450 Aqueous 45 1-9 450 2.5 20,000-400,000
*Linear range based on polystyrene standards
Temperature Limit
(°C)
pH Range
Pore Size
(Å)
dp
(µm)
Linear Range
(g/mol e)*
II. GET TING STARTED
a. Preparing the System
Before attaching the column, the system must be prepared as follows:
1. Remove the old columns and connect the tubing ends with a
zero-dead-volume connector.
2. Convert the system to the solvent required for the separation by
flushing the system and injector pathway to remove old solvents.
For additional information, refer to the ACQUITY APC System’s
operator guide.
b. Column Connections
The ACQUITY APC System uses tubing and connectors that have
been designed to meet stringent tolerances to minimize extracolumn volume within the system. It is highly recommended that
you use the column connection hardware that is supplied with the
system, and, when needed, replace with original manufacturer’s
hardware. For applications that require a bank of columns connected
in series, a u-shaped column-joining tube (which has been optimized
to fit within the column heater compartment) is available separately.
c. Column Installations
Generally, analytical results are independent of the sequence in
which a column bank is arranged. However, to improve resolution
and column life, arrange the columns in order of decreasing
pore size, with the largest pore size closest to the injector. This
is recommended because the species with the highest molecular
weight in the sample contributes the most to the viscosity of the
sample. If the largest species are separated first, the viscosity of
the sample plug decreases more quickly, placing less strain on
the column bank. In the case of higher molecular weight polymers,
there is less chance of shear degradation of the polymer sample.
To install the columns:
1. Remove the end plugs from each column and save them.
2. Connect the first column to the injector outlet tubing. Note the
direction of flow. A flow direction arrow is etched on the inlet
side end nut of the column.
3. Finger-tighten the fitting, then tighten with a wrench by
another turn using the flats machined into the column end nut.
Do not use a wrench on the column tubing. Figure 1 shows a
proper tubing-to-column connection.
2
ACQUITY APC Columns
4. Connect the next column to the previous column using
u-shaped tube connectors. Ensure that the solvent flow
continues in the direction shown on the column end fittings.
Thread the inlet and outlet fittings of the u-shaped tube until
finger tight, then tighten with a wrench.
5. Repeat Step 4 until all columns in the bank are connected.
6. Connect the last column to the detector inlet tubing.
Page 3

In a proper tubing/column connection (Figure 1), the tubing touches
the bottom of the column endfitting, with no void between them.
Figure 1. Proper Tubing Column Connection.
The presence of a void in the flow stream reduces column
performance. This can occur if a Parker ferrule is connected
to a Waters style endfitting (Figure 2).
Table 2. Empty Column Volumes in mL
Column Length
(mm)
30 4.6 0.50
50 4.6 0.83
75 4.6 1.25
150 4.6 2.50
Column Internal Diameter
(mm)
Volume
(mL)
The rigid hybrid particle bed used for the ACQUIT Y APC Columns
allows the user to rapidly switch solvents without damaging the
column packing material. Changing solvents works best between
compatible solvents. For example, when changing between two
immiscible solvents, an intermediate solvent/co-solvent that is
miscible in both initial and final conditions should be used. For highly
viscous solvents, reduce the flow rate to avoid over pressuring the
system. Once the exchange is complete, equilibrate the column using
the final solvent conditions with a minimum of 20-column empty
volumes, or until a stable detector baseline is achieved.
III. COLUMN USE
Figure 2. Parker Ferrule in a Waters Style Endfitting.
d. eCord Installation
Attach the eCord button for each column to the side of the column
heater module noting their sequence. Up to four columns can
be installed at one time. The eCord button is magnetized and
does not require specific orientation. Once connected, column
identification and usage will be available though the instrument’s
control software.
e. Column Equilibration
ACQUITY APC Columns are shipped dry giving the user full
option of the solvent needed for the separation. Equilibrate the
column with a minimum of 20-column volumes, or until a stable
detector baseline is achieved. For a column bank, use the sum of
the column volumes in series to determine the total equilibration
volume. Refer to Table 2 for a listing of column volumes.
a. Guidelines
ACQUITY APC Columns have a finite lifetime directly related to
their care and use. Column lifetime is reduced by contamination
from samples and eluents; improper handling and storage; and
exceeding operational conditions. To maximize ACQUITY APC
Column lifetime, pay attention to these guidelines:
For best resolution and maximum column life, do not exceed
the flow rate recommendations found in Section III c.
Protect the column from vibration and mechanical shock.
Avoid precipitation by dissolving samples in the mobile
phase. If the sample is not dissolved in the mobile phase,
ensure that the sample, solvent and mobile phase are
miscible to avoid precipitation.
Always use high-quality, particle-free, HPLC-grade solvents.
Dedicate, whenever possible, the column to specific
applications. Frequent switching of samples and solvents
accelerates column deterioration and loss of resolution.
Exceeding the upper temperature limit of the column.
3
ACQUITY APC Columns
For aqueous mobile phases, take steps to avoid bacterial
contamination. For additional information refer to "Controlling
Contamination in UPLC®/MS and HPLC/MS Systems", Waters
part number 715001307.
Page 4
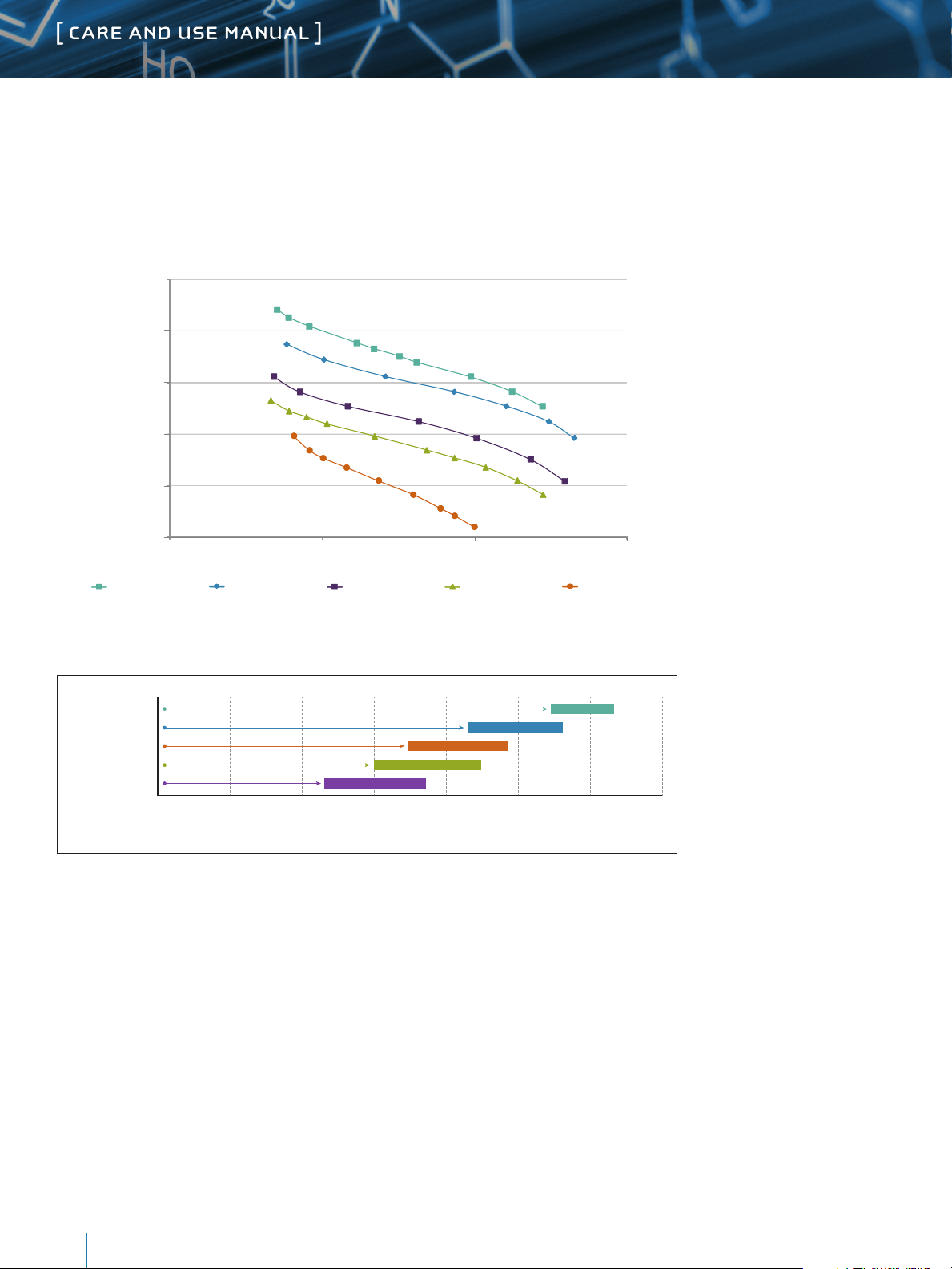
b. Calibration
Whenever replacing a single column of a complete column bank, generate a new calibration curve to
ensure the reproducibility of the application. Figure 3 shows typical calibration curves for each column.
The calibration curves were obtained with polystyrene standards. Figure 4 shows the expected linear
range based on the calibration data.
10,000,000
1,000,000
100,000
10,000
Polystyrene Molecular Weight (Da)
1,000
100
0.50 1.00 1.50 2.00
Elution volume (mL)
ACQUITY APC
XT 900
ACQUITY APC
XT 450
ACQUITY APC
XT 200
ACQUITY APC
XT 125
ACQUITY APC
XT 45
Figure 3. Calibration Curves for ACQUITY APC XT and ACQUITY APC AQ Columns (4.6 x 150 mm) Using Polystyrene Standards.
ACQUITY APC (XT) 900
ACQUITY APC (AQ/XT) 450
ACQUITY APC (AQ/XT) 200
ACQUITY APC (AQ/XT) 125
ACQUITY APC (AQ/XT) 45
10 10
1
2
10
Effective Molecular Weight Range
3
10
4
10
5
10
6
10
7
10
Figure 4. Effective Molecular Weight Range for ACQUITY APC Columns.
c. Useable Flow-Rate Ranges
Excessive mobile-flow rates can create backpressure that can damage the column packing material.
For any given particle size, as the pore volume increases, the base particle loses mechanical strength
due to the reduction in particle wall thickness surrounding the open pore. Table 3 shows the maximum
flow rate recommendation for a single column for each pore size, independent of column length. When
connecting multiple columns in series, the column that specifies the lowest flow rate will dictate the
maximum flow rate for the column bank. Higher viscosity solvents will limit the flow rate due to flow
restriction. Table 4 provides viscosity data for common solvents.
4
ACQUITY APC Columns
Page 5

Diluted/Distor ted Sample Band
0.005 inches
0.020 inches
0.040 inches
For example, if you were to select a three-column bank using
45Å, 200Å and 450Å columns and require that DMF to be used
as the mobile-phase solvent, you would be limited to a maximum
flow rate of 1.0 mL/min. In this case, DMF has a solvent viscosity
of 0.92 cP at 25 °C. Under these conditions the 450Å column
limits the flow to 1.0 mL/min, even though the other columns
can support a higher flow.
Note: When connecting multiple columns in series, the maximum flow rate may
not be achievable due to pressure limitations of the instrumentation. Please
refer to the system's owner manual for more information.
Table 3. Recommended Mobile Phase
Flow Rate for a Single ACQUITY APC Column
Pore Size
(Å)
45 1.8 m L/min 1.1 m L/min
125 2.0 mL/min 1.6 mL/min
200 2.0 mL/min 1.4 mL /min
450
900 0.90 mL/min 0.60 mL/min
Maximum Flow
Rate at Solvent
Viscosity < 0.6 cP
1.7 m L/min 1.0 mL/min
Maximum Flow
Rate at Solvent
Viscosity > 0.6 cP
Table 4. Viscosity of Common Solvents at
Different Temperatures **
Solvent
Acetone 0.32 0.26
Chloroform 0.57 0.45
Dimethyl formamide (DMF) 0.92 0.68
Dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) 2.00 1.50
Ethyl Acetate 0.44 0.36
Hexane 0.33 0.26
Methanol 0.60 0.44
Methylene chloride 0.44 N/A
N-Methylpyrrolidone (NMP) 1.70 1.30
Tetrahydrofuran (THF) 0.55 0.39
Toluene 0.59 0.46
Water 1.00 0.67
**References:
1. Reid, R.C., Prausnitz, J.M., Poling, B.E. The Properties of Gases and Liquids,
4th Edition, McGraw Hill, 1987, Table 9-8.
2. http://www.wolframalpha.com
3. Yang, J. Chem Eng Data (2008), 53, 1639 -1642.
Vi scosity (cP)
20 °C 40 °C
d. Minimizing Band Spread
The ACQUITY APC System was designed to minimize band
spreading. Deviation from Waters specified tubing could result
in deterioration of chromatographic performance. Figure 5
shows the influence of tubing inner diameter. Using larger
tubing causes excessive peak broadening, lower sensitivity,
and loss in resolution.
Figure 5. Effect of Connecting Tubing on System.
IV. TROUBLESHOOTING
Changes in retention time, resolution or backpressure are
often due to column contamination. See the Column Cleaning,
Regeneration and Storage section of the care and use manual.
Information on column troubleshooting problems may be
found in HPLC Column Theory, Technology and Practice, U.D.
Neue, (Wiley-VCH, 1997); Waters HPLC Troubleshooting Guide
(Literature Code # 720000181EN); or by visiting www.waters.com
V. COLUMN CLEANING, REGENERATION
AND STORAGE
Assuming that there is no damage to the column bed, changes
in peak shape, peak splitting, shoulders on the peak, shifts in
retention, change in resolution or increasing backpressure
may indicate contamination of the column. Flushing with high
concentrations of organic solvent, taking care not to precipitate
buffers, is usually sufficient to remove the contaminant. If the
flushing procedure does not solve the problem, purge the column
using the following cleaning and regeneration procedures.
a. Cleaning and Regeneration
Use a cleaning routine that matches the properties of the samples
and/or what you believe is contaminating the column. The
columns are stable using a wide range of solvents to improve the
dissolution of the contaminant. Before beginning any cleaning
procedure it is best to isolate the column from downstream
5
ACQUITY APC Columns
Page 6

connections to protect further contamination post column.
Increasing column temperature increases cleaning efficiency. If
the column performance is poor after cleaning and regenerating,
call your local Waters office for additional support.
If the inlet for the first column in the column bank series is
plugged with precipitated material or sample, it is possible to
disconnect the column and reverse the flow to dislodge the
blockage. This must be done extremely carefully at a low flow rate
(not to exceed 0.1 mL/min) to prevent disruption of the packed
sorbent bed. Once the blockage is removed, the column must be
returned to its proper flow direction. If inlet plugging is a concern,
a column in-line filter unit is available (Waters part number
205000343).
Note: The addition of an in-line filter increases the likelihood of shear
degradation, especially for large molecular weight polymer species.
If the column performance is poor after cleaning and regenerating,
call your local Waters office for additional support.
VI. eCORD INTELLIGENT CHIP TECHNOLOGY
a. Introduction
The eCord Intelligent Chip will provide the history of a column’s
performance throughout its lifetime. The eCord is permanently
attached to the column to assure that the column’s performance
history is maintained in the event that the column is moved from
one instrument to another.
Figure 6. eCord Intelligent Chip.
b. Storage
If you will be using the column again within 24 hours, special
storage procedures are unnecessary. For longer storage periods,
return the column to its box with the end plugs firmly in place. Do
not leave a column at elevated temperature without solvent flow.
For maximum column life, avoid temperature cycling. Maintain
operating temperature and reduce the flow rate to 0.1 mL/min
when columns are not in use.
b. Installation
Install the column into the ACQUITY APC Column Manager. Plug
the eCord into the side of the column heater noting the order of
the attachment point. Once the eCord is inserted into the column
heater (see Figure 7) the identification and overall column usage
information will be available allowing the user to access column
information on their desktop. Up to four columns can be connected
at one time.
eCord Fob
Figure 7. Installing the eCord Intelligent Chip.
6
ACQUITY APC Columns
Page 7

c. Column Use Information
The eCord Chip provides the customer with column use data, column dimensions and serial number. The overall
column usage information includes the total number of samples, total number of injections, total sample sets,
date of first injection, date of last injection, maximum pressure and temperature. The information also details
the column history by sample set including date started, sample set name, user name, system name, number
of injections in the sample set, number of samples in the sample set, maximum pressure and temperature in
the sample set, and if the column met basic system suitability requirements. Up to 50 sample sets can be
stored on the eCord Chip. In addition, the eCord provides two-way communications between the eCord Chip and
Empower® Software.
Waters, The Science of W hat’s Possible, Empower, UPLC, Advanced Polymer Chromatography, and ACQUITY are registered
trademarks of Waters Corporation. ACQUITY APC, APC, and eCord are trademarks of Waters Corporation.
©2014 Waters Corporation. Produced in the U.S.A. July 2014 720004667EN Rev. B TC-PDF
Waters Corporation
34 Maple Street
Milford, MA 01757 U.S.A.
T: 1 508 478 2000
F: 1 508 872 1990
www.waters.com
 Loading...
Loading...