Page 1

Waters 2996
et
7
C
PDA Detector
Operator’s Guide
34 Maple Stre
Milford, MA 01 75
71500023202, Revision
Page 2

NOTICE
The information in this document is subject to change without notice and should not be
construed as a commitment by Waters Corporation. Waters Corporation assumes no
responsibility for any errors that may appear in this document. This document is believed
to be complete and accurate at the time of publication. In no event shall Waters
Corporation be liable for incidental or consequential damages in connection with, or
arising from, the use of this docum ent.
© 2001 WATERS CORPORATION. PRINTED IN THE UNITED STATES OF
AMERICA. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. THIS DOCUMENT OR PARTS THEREOF
MAY NOT BE REPRODUCED IN ANY FORM WITHOUT THE WRITTEN
PERMISSION OF THE PUBLISHER.
Millennium, PIC, and Waters are register ed t rad emar ks, and busLAC/E and PowerStation
are trademarks of Waters Corporation.
Micromass is a registered trademark, and MassLynx is a trademark of Micromass Ltd.
All other trademarks or registered trademarks are the sole property of their respective
owners.
Page 3

STOP
Note: When you use the instrument, follow generally accepted procedures for quality
control and methods development.
If you observe a change in the retention of a particular compound, in the resolution
between two compounds, or in peak shape, immediately determine the reason for the
changes. Until you determine the cause of a change, do not rely on the separation results.
Note: The Installation Category (Overvoltage Category) for this instrument is Level II. The
Level II Category pertains to equipment that receives its electrical power from a local level,
such as an electrical wall outlet.
Attention: Changes or modifications to this unit not expressly approved by the party
responsible for compliance could void the user’s authority to operate the equipment.
Important : Toute modification sur cette unité n’ayant pas été expressément approuvée
par l’autorité responsable de la conformité à la réglementation peut annuler le droit de
l’utilisateur à exploiter l’équipement.
Achtung: Jedwede Änderungen oder Modifikationen an dem Gerät ohne die
ausdrückliche Genehmigung der für die ordnungsgemäße Funktionstüchtigkeit
verantwortlichen Personen kann zum Entzug der Bedienungsbefugnis des Systems
führen.
Avvertenza: eventuali modifiche o alterazioni apportate a questa unità e non
espressamente approvate da un ente responsabile per la conformità annulleranno
l’autorità dell’utente ad operare l’apparecchiatura.
Atención: cualquier cambio o modificación realizado a esta unidad que no haya sido
expresamente aprobado por la parte responsable del cumplimiento puede anular la
autorización de la que goza el usuario para utilizar el equipo.
Page 4

Caution: Use caution when working with any polymer tubing under pressure:
• Always wear eye protection when near pressurized polymer tubing.
• Extinguish all nearby flames.
• Do not use Tefzel tubing that has been severely stressed or kinked.
• Do not use Tefzel tubing with tetrahydrofuran (THF) or concentrated nitric
or sulfuric acids.
• Be aware that methylene chloride and dimethyl sulfoxide cause Tefzel
tubing to swell, which greatly reduces the rupture pressure of the tubing.
Attention : soyez très prudent en travaillant avec des tuyaux de polymères sous
pression :
• Portez toujours des lunettes de protection quand vous vous trouvez à
proximité de tuyaux de polymères.
• Eteignez toutes les flammes se trouvant à proximité.
• N'utilisez pas de tuyau de Tefzel fortement abîmé ou déformé.
• N'utilisez pas de tuyau de Tefzel avec de l'acide sulfurique ou nitrique, ou
du tétrahydrofurane (THT).
• Sachez que le chlorure de méthylène et le sulfoxyde de diméthyle
peuvent provoquer le gonflement des tuyaux de Tefzel, diminuant ainsi
fortement leur pression de rupture.
Vorsicht: Bei der Arbeit mit Polymerschläuchen unter Druck ist besondere Vorsicht
angebracht:
• In der Nähe von unter Druck stehenden Polymerschläuchen stets
Schutzbrille tragen.
• Alle offenen Flammen in der Nähe löschen.
• Keine Tefzel-Schläuche verwenden, die stark geknickt oder
überbeansprucht sind.
• Tefzel-Schläuche nicht für Tetrahydrofuran (THF) oder konzentrierte
Salpeter- oder Schwefelsäure verwenden.
• Durch Methylenchlorid und Dimethylsulfoxid können Tefzel-Schläuche
quellen; dadurch wird der Berstdruck des Schlauches erheblich
reduziert.
Page 5

Precauzione: prestare attenzione durante le operazioni con i tubi di polimero sotto
pressione:
• Indossare sempre occhiali da lavoro protettivi nei pressi di tubi di
polimero pressurizzati.
• Estinguere ogni fonte di ignizione circostante.
• Non utilizzare tubi Tefzel soggetti a sollecitazioni eccessive o incurvati.
• Non utilizzare tubi Tefzel contenenti tetraidrofurano (THF) o acido
solforico o nitrico concentrato.
• Tenere presente che il cloruro di metilene e il dimetilsolfossido
provocano rigonfiamento nei tubi Tefzel, che riducono notevolmente il
limite di pressione di rottura dei tubi stessi.
Advertencia: manipular con precaución los tubos de polimero bajo presión:
• Protegerse siempre los ojos a proximidad de tubos de polimero bajo
presión.
• Apagar todas las llamas que estén a proximidad.
• No utilizar tubos Tefzel que hayan sufrido tensiones extremas o hayan
sido doblados.
• No utilizar tubos Tefzel con tetrahidrofurano o ácidos nítrico o sulfúrico
concentrados.
• No olvidar que el cloruro de metileno y el óxido de azufre dimetilo inflan
los tubos Tefzel lo que reduce en gran medida la presión de ruptura de
los tubos.
Page 6

Caution: The user shall be made aware that if the equipment is used in a manner not
specified by the manufacturer, the protection provided by the equipment may be impaired.
Attention : L’utilisateur doit être informé que si le matériel est utilisé d’une façon non
spécifiée par le fabricant, la protection assurée par le matériel risque d’être défectueuses.
Vorsicht: Der Benutzer wird darauf aufmerksam gemacht, dass bei unsachgemäßer
Verwenddung des Gerätes unter Umständen nicht ordnungsgemäß funktionieren.
Precauzione: l’utente deve essere al corrente del fatto che, se l’apparecchiatura viene
usta in un modo specificato dal produttore, la protezione fornita dall’apparecchiatura
potrà essere invalidata.
Advertencia: El usuario deberá saber que si el equipo se utiliza de forma distinta a la
especificada por el fabricante, las medidas de protección del equipo podrían ser
insuficientes.
Caution: To protect against fire hazard, replace fuses with those of the same type and
rating.
Attention : Remplacez toujours les fusibles par d’autres du même type et de la même
puissance afin d’éviter tout risque d’incendie.
Vorsicht: Zum Schutz gegen Feuergefahr die Sicherungen nur mit Sicherungen des
gleichen Typs und Nennwertes ersetzen.
Precauzione: per una buona protezione contro i rischi di incendio, sostituire i fusibili con
altri dello stesso tipo e amperaggio.
Precaución: sustituya los fusibles por otros del mismo tipo y características para evitar
el riesgo de incendio.
Page 7

Caution: To avoid possible electrical shock, power off the instrument and disconnect the
power cord before servicing the instrument.
Attention : Afin d’éviter toute possibilité de commotion électrique, mettez hors tension
l’instrument et débranchez le cordon d’alimentation de la prise avant d’effectuer la
maintenance de l’instrument.
Vorsicht: Zur Vermeidung von Stromschlägen sollte das Gerät vor der Wartung
abgeschaltet und vom Netz getrennt werden.
Precauzione: per evitare il rischio di scossa elettrica, spegnere lo strumento e
scollegare il cavo di alimentazione prima di svolgere la manutenzione dello strumento.
Precaución: para evitar choques eléctricos, apague el instrumento y desenchufe el
cable de alimentación antes de realizar cualquier reparación en el instrumento.
Page 8

Commonly Used Symbols
Direct current
Courant continu
Gleichstrom
Corrente continua
Corriente continua
Alternating current
Courant alternatif
Wechselstrom
Corrente alternata
Corriente alterna
Protective conductor terminal
Borne du conducteur de protection
Schutzleiteranschluss
Terminale di conduttore con protezione
Borne del conductor de tierra
Frame or chassis term inal
Borne du cadre ou du châssis
Rahmen- oder Chassisanschluss
Terminale di struttura o telaio
Borne de la estructura o del chasis
Caution or refer to manual
Attention ou reportez-vous au guide
Vorsicht, oder lesen Sie das Handbuch
Prestare attenzione o fare riferimento alla guida
Actúe con precaución o consulte la guía
Caution, hot surface or high temperature
Attention, surface chaude ou température élevée
Vorsicht, heiße Oberfläche oder hohe Temperatur
Precauzione, superficie calda o elevata temperatura
Precaución, superficie caliente o temperatura elevada
Page 9

Commonly Used Symbols (Continued)
Caution, risk of electric shock (high voltage)
Attention, risque de commotion électrique (haute tension)
Vorsicht, Elektroschockgefahr (Hochspannung)
Precauzione, rischio di scossa elettrica (alta tensione)
Precaución, peligro de descarga eléctrica (alta tensión)
Caution, risk of needle-stick puncture
Attention, risques de perfor at io n de la tail le d’u n e aigu il le
Vorsicht, Gefahr einer Spritzenpunktierun g
Precauzione, rischio di puntura con ago
Precaución, riesgo de punción con aguja
Caution, ultraviolet light
UV
Attention, rayonnement ultrviolet
Vorsicht, Ultraviolettes Licht
Precauzione, luce ultravioletta
Precaución, emisiones de luz ultravioleta
Page 10

2996 PDA Detector Information
Intended Use
The Waters® 2996 PDA Detector can be used for in-vitro diagnostic testing to analyze
many compounds, including diagnostic indicators and therapeutically monitored
compounds. When you develop methods, follow the “Protocol for the Adoption of
Analytical Methods in the Clinical Chemistry Laboratory,” American Journal of
Medical Technology, 44, 1, pages 30–37 (1978). This prot ocol covers good operating
procedures and techniques necessary to validate system and method performance.
Biological Hazard
When you analyze physiological fluids, take all necessary precautions and treat all
specimens as potentially infectious. Precautions are outlined in “CDC Guidelines on
Specimen Handling,” CDC – NIH Manual, 1984.
Calibration
Follow acceptable methods of calibration with pure standards to calibrate methods. Use a
minimum of five standards to generate a standard curve. The concentration range should
cover the entire range of quality-control samples, typical specimens, and atypical
specimens.
Quality Control
Routinely run three quality-control samples. Quality-control samples should represent
subnormal, normal, and above-normal levels of a compound. Ensure that quality-control
sample results are with in an ac cept ab le range, and evaluate precision from day to day and
run to run. Data collected when qua lity- contr ol samp les are out of range may not be val id.
Do not report this data until you ensure that chromatographic system performance is
acceptable.
General Maintenance
To clean the outside of the Waters 2996 PDA Detector, use only a soft lint-free paper or
cloth dampened with mild soap and water.
Page 11

Table of Contents xi
Preface................................................................................................................ xix
Chapter 1
Installation
........................................................................................................... 1
1.1 Installation Site Requirements .......................................................................... 1
1.2 Power Connections............................................................................................ 2
1.3 Millennium32 Workstation Connections ........................................................... 3
1.3.1 Connecting the IEEE-488 Cable.......................................................... 4
1.3.2 Setting the IEEE-488 Address ............................................................ 5
1.4 Non-IEEE-488 Communication Connections................................................... 6
1.4.1 Connecting Analog Output Cables ...................................................... 6
1.4.2 Connecting Event Cables .................................................................... 7
1.5 Fluidic Connections........................................................................................... 9
1.6 Starting Up and Shutting Down the Detector.................................................. 11
Chapter 2
Diagnostics and Calibration
.......................................................................... 15
2.1 Diagnostics...................................................................................................... 15
2.2 User-Initiated Diagnostics............................................................................... 17
2.3 PDA Calibration.............................................................................................. 18
Chapter 3
Maintenance
...................................................................................................... 19
3.1 Flow Cell Maintenance ................................................................................... 19
3.1.1 Flushing the Flow Cell....................................................................... 20
3.1.2 Removing the Flow Cell ................................................................... 20
3.1.3 Disassembling and Cleaning the Flow Cell ...................................... 22
3.1.4 Installing the Flow Cell Assembly .................................................... 24
Table of Contents
Page 12

xii Table of Contents
3.2 Replacing the Lamp ........................................................................................ 25
3.3 Replacing the Fuses......................................................................................... 27
Chapter 4
Principles of the 2996 PDA Detector Optics
.............................................. 29
4.1 2996 Detector Optics....................................................................................... 29
4.2 Resolving Spectral Data.................................................................................. 31
4.3 Measuring Light at the Photodiode................................................................. 32
4.4 Computing Absorbance Data Points............................................................... 35
4.4.1 Calculating Absorbance..................................................................... 35
4.4.2 Resolution ......................................................................................... 38
4.4.3 Filtering Data .................................................................................... 38
Chapter 5
Spectral Contrast Theory
.............................................................................. 41
5.1 Comparing Absorbance Spectra...................................................................... 41
5.2 Representing Spectra as Vectors ..................................................................... 42
5.2.1 Vectors Derived from Two Wavelengths .......................................... 43
5.2.2 Vectors Derived from Multiple Wavelengths ................................... 43
5.3 Spectral Contrast Angles................................................................................. 44
5.4 Undesirable Effects ......................................................................................... 47
5.4.1 Detector Noise ................................................................................... 47
5.4.2 Photometric Error ............................................................................. 48
5.4.3 Solvent Changes ............................................................................... 48
5.4.4 Threshold Angle ............................................................................... 48
Page 13

Table of Contents xiii
Appendix A
Detector Specifications
................................................................................... 51
Appendix B
Spare Parts
........................................................................................................ 53
Appendix C
Mobile Phase Absorbance
.............................................................................. 55
Index ................................................................................................................... 59
Page 14

xiv Table of Contents
Page 15

List of Figures xv
1-1 Waters 2996 PDA Detector Dimensions.................................................... 2
1-2 Detector Rear Panel ................................................................................... 3
1-3 Example of IEEE-488 Cable Connections................................................. 4
1-4 Locating the IEEE-488 Switches............................................................... 5
1-5 Analog Out Terminal Strip......................................................................... 7
1-6 Event Input/Output Terminal Strip ............................................................ 8
1-7 Compression Screw Assembly ................................................................ 11
1-8 2996 Detector Indicator Lights................................................................ 12
3-1 Removing the Flow Cell Assembly......................................................... 21
3-2 Flow Cell and Fluidic Connections Assemblies...................................... 22
3-3 Disassembling the Flow Cell................................................................... 23
3-4 Lamp Power Connector and Mounting Screws....................................... 26
3-5 Fuse Block ............................................................................................... 27
4-1 Optics Assembly Light Path.................................................................... 30
4-2 Benzene Spectrum at 1.2 nm Resolution................................................. 32
4-3 Photodiodes Discharged by Light............................................................ 33
4-4 Absorbance as a Function of Concentration............................................ 36
5-1 Comparing Spectra of Two Compounds.................................................. 42
5-2 Plotting Vectors for Two Spectra............................................................. 43
5-3 Spectra with a Large Spectral Contrast Angle......................................... 45
5-4 Spectra with a Small Spectral Contrast Angle......................................... 46
5-5 Absorbance Spectra of a Compound at Two Concentrations .................. 47
5-6 Effects of pH and Solvent Concentration on the Absorbance Spectrum of
p-Aminobenzoic Acid ............................................................................. 49
List of Figures
Page 16

xvi List of Figures
Page 17

List of Tables xvii
1-1 Site Requirements..................................................................................... 1
1-2 Event In Terminal Specifications on TTL or Switch Closure................... 9
1-3 Event Out Terminal Specifications on Contact Closure ........................... 9
1-4 LED Indicator Sequences During Startup............................................... 12
2-1 2996 Detector Troubleshooting .............................................................. 15
4-1 Optics Assembly Components................................................................ 30
A-1 2996 Detector Specifications.................................................................. 51
B-1 Spare Parts.............................................................................................. 53
C-1 Mobile Phase Absorbance Measured Against Air or Water................... 55
List of Tables
Page 18

xviii List of Tables
Page 19

xix
Preface
The Waters 2996 PDA Detector Operator’s Guide describes the p rocedures for installi ng,
maintaining, and troubleshooting the Waters
®
2996 PDA Detector. It also describes
detector optics and th e principle s of Spectral Contrast used in the Millenni um®
32
software
for analyzing the data from the PDA detector. Also included is information on vector
analysis, mobile phase absorbance, specifications.
This guide is intended for individuals who need to install, operate, maintain, and
troubleshoot the 2996 PDA Detector. It is also intended for users who need to understand
the Spectral Contrast principles underlying the processing of PDA Detector data by
Millennium
32
software.
Organization
This guide contains the following:
Chapter 1 describes how to install and set up the 2996 Detector.
Chapter 2 describes how to troubleshoot the 2996 Detect or.
Chapter 3 describes how to replace the flow cell, the lamp, and the fuse.
Chapter 4 explains the principles involved in resolving spectral data, measuring light
at the photodiode, verifying wavelengths, and computing absorbance data.
Chapter 5 describes the calculations used for Spectral Contrast.
Appendix A provides the specifications of the 2996 PDA Detector.
Appendix B lists recommended spare parts.
Appendix C provides a table of absorbances at several wavelengths for common
mobile phases.
Related Documentation
W at ers Li censes , Warranties, and Supp ort: Provi des software lic ense and warranty
information, describes training and extended support, and tells how Waters handles
shipments, damages, claims, and returns.
Millennium
32
Help: Describes al l Millennium32 windows, menus, menu selections,
and dialog boxes. Also includes reference information and procedures for performing
Page 20

all tasks required to use the Millennium32 software. Included as part of the
Millennium
Millennium
Millennium
32
software.
32
Software Ge tting Started Guide : Provides an introduction to the
32
System. Describes the basics of how to use Millennium32 software to
acquire data, develop a processing method, review results, and print a report. Also
covers basics for managing projects and configuring systems.
Millennium
to use Millennium
32
PDA Software Ge tting Started Guide : Describes the basics of how
32
PDA software to dev elop a PDA proces sing method an d to review
PDA results.
32
Millennium
Millennium
System Installation an d Configu ration Gui de: Describes
32
software installation, including the stand-alone workstation,
PowerStation™ system, and client/server system. Discusses how to configure the
computer and chromatographic instruments as part of the Millennium
covers the installation, config uration, a nd use of ac quisition s e rvers such as the
LAC/E
32
module, the busLAC/E card, and interface cards used to com municate with
serial instruments
Water s 29 96 PD A De tector Qual ificati on Workbook: Describes qualification
procedures for the 2996 PDA Detector.
Documentation Conventions
The following conventions may be used in this guide:
Convention Usage
32
system . Also
Bold Bold indicates user action such as keys to press, menu selections,
Italic Italic indicat es infor mation that you s upply such as varia bles. It also
Courier
Courier Bold
xx
and commands. For example, “Click Next to go to the next page.”
indicates emphasis and document titles. For example, “Replace
file_name with the actual name of your file.”
Courier indicates examples of source code and system output. For
example, “The
SVRMGR> prompt appears.”
Courier bold indicates characters that you type or keys you press in
examples of source code. For example, “At the
enter
set password oracle to access Oracle.”
LSNRCTL> prompt,
Page 21

Convention Usage
Keys The word key refers to a computer key on the keypad or keyboard.
Screen keys refer to the key s on the instrument located im mediately
below the screen. For example, “The A/B screen key on the 2414
Detector displays the selected channel.”
… Three periods indicate that more of the same type of item can
optionally follow. For example, “You can store filename1,
filename2, … in each folder.”
> A right arrow between menu options indicates you should choose
each option in sequence. For example, “Select File > Exit” me ans
you should selec t File from the menu bar, then select Exit from the
File menu.
Notes
Notes call out information that is helpful to the operator. For example:
Note: Record your result before you proceed to the next step.
Attentions
Attentions provide information about preventing possible damage to the system or
equipment. For example:
Attention: To avoid damaging the detector flow cell, do not touch the flow cell
STOP
Cautions
window.
Cautions provide information essential to the safety of the operator. For example:
Caution: To avoid possible burns, turn off the lamp at least 15 minutes before
removing it for replacement or adjustment.
Caution: To avoid possible electrical shock and injury, always turn off the detector
and unplug the power cord before performing maintenance procedures.
Caution: To avoid chemical or electrical hazards, always observe safe laboratory
practices when operating the system.
xxi
Page 22

xxii
Page 23

Installation Site Requirements 1
1
Chapter 1
Installation
The Waters® 2996 Photodiode Array (PDA) Detector operates in any standard laboratory
environment. The detector requires electrical power, sample and wast e fluidic lines, and
either the Millennium®
32
or MassLynx™ workstations. Optional connections on the
detector rear panel allow communication with chart recorders, data integrators, and other
instruments that are not compatible with Millennium
32
or MassLynx software control.
1.1 Installation Site Requirements
Install the 2996 PDA Detector at a site that meets the specifications in Table 1-1 and
Figure 1-1.
Table 1-1 Site Requirements
Factor Specification
Ambient temperature 4 to 40 °C (39 to 104 °F), not to vary more
than 1 °C per hour (to prevent drift)
Relative humidity 20 to 80%, noncondensing
Bench space Width: 11.5 in. (29 cm)
Depth: 24 in. (61 cm)
Height: 8.5 in. (22 cm)
Bench support Capable of supporting 31.5 pounds (14.3 kg)
Clearance At least 4 in. (10 cm) on the back side for
ventilation
Power Grounded ac, 100 to 240 Vac
Page 24

1
11.5 in. (29 cm)
WATERS 996
Photodiode Array
8.5 in.
(22 cm)
24 in.
(61 cm)
Sample Outlet
Figure 1-1 Waters 2996 PDA Detector Dimensions
1.2 Power Connections
Ensure that power connections for the 2996 PDA Detector are made according to the
procedures that follow.
Operating Voltage
The 2996 PDA Detector has a universal input power supply that requires no voltage
adjustmen t. The electrical power requiremen ts for the Waters 2996 PDA De tector are:
LAMP
Sample Inlet
Drain Line
• Voltage range: 100 to 240 Vac
• Total power: 100 VA
• Frequency range: 50 to 60 Hz
Fuses
The 2996 PDA Detector is shipped with fuses rated for North American operation. If you
operate the 2996 P DA Detect or in anot her loca tion, install t he IEC-rat ed fuses (supplie d in
2Installation
Page 25

Millennium32 Workstation Connections 3
1
the Waters 2996 Detector St ar tup Kit ) in the fu se h older in the rear of the de tecto r (re fer t o
Section 3.3, Replacing the Fuses).
Connecting the Power Cord
Connect one end of the 2996 Detector power cord to the rear panel power receptacle
(Figure 1-2) and the other end to a power outlet.
Figure 1-2 Detector Rear Panel
1.3 Millennium32 Workstation Connections
The 2996 Detector requires signal connections to the Millennium32 Work station over the
IEEE-488 bus. All detector control and data acquisition communications take place over
the IEEE-488 bus.
Note: If an inject start signal is not available over the IEEE-488 bus, you must provide a
signal at the Event In 1 terminals on the 2996 Detector rear panel (Section 1.4.2,
Connecting Event Cables).
TP01452
AC Input
Page 26
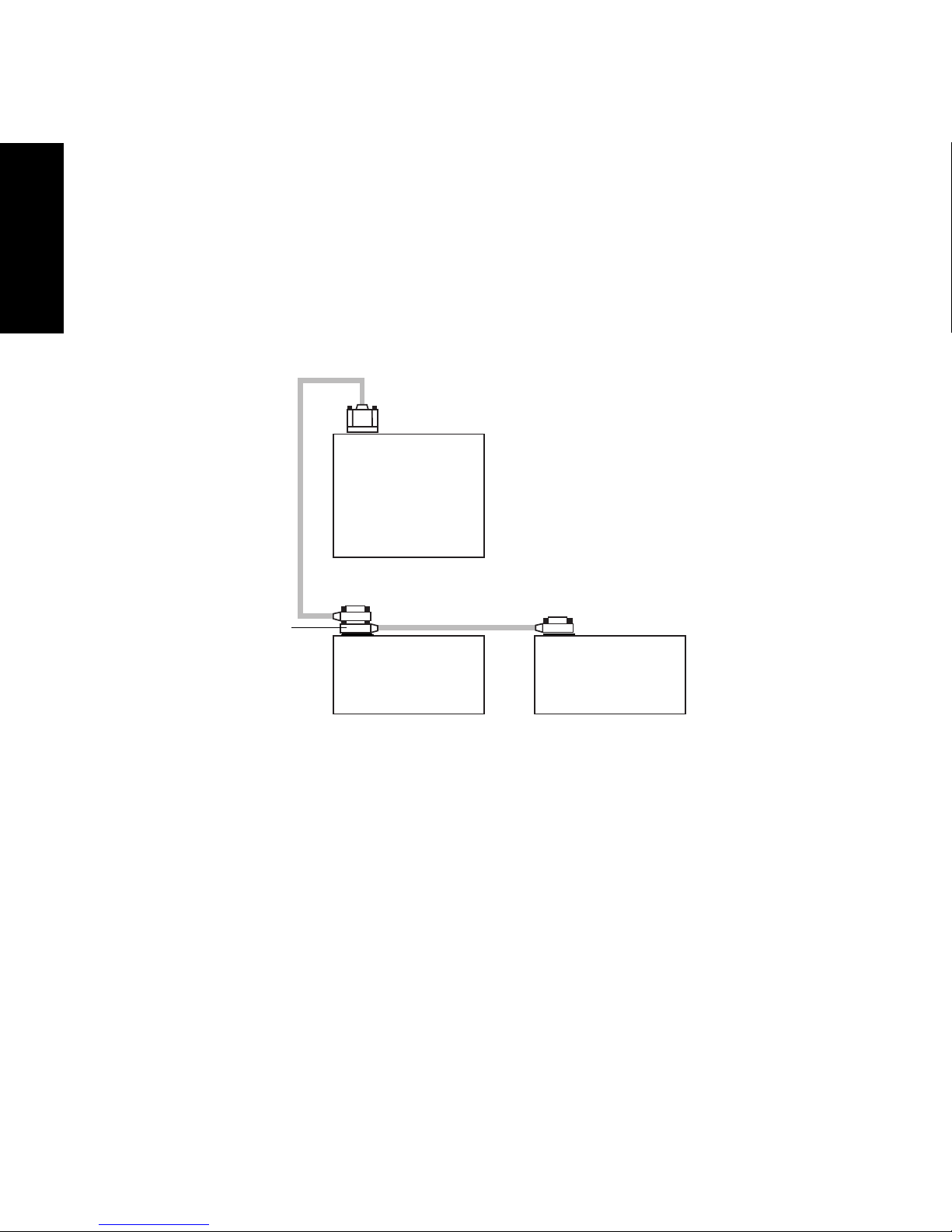
1.3.1 Connecting the IEEE-488 Cable
To connect the 2996 Detector to a Millennium32 Workstation:
1
1. Connect one end of the IEEE-488 ca ble to t he IEEE-488 recepta cle on t he rear panel
of the 2996 Detector. Connect the other end of the cable (stackable connector for
daisy-chaining additional instruments) to the IEEE-488 connector on any of the
other instruments in your chromatographic system (Figure 1-3).
Waters
IEEE-488
Cable
IEEE-488
Connector
Millennium
busLAC/E Card
(on Workstation)
Waters
Alliance
Separations Module
32
IEEE-488 Cable
Waters 2996
Detector
Note: The order in which you connect IEEE-488 devices to the busLAC/E card on
the workstation is not important. For example, you can connect the 2690
Separations Module before or after the 2996 Detector.
2. Use another IEEE-488 cable to connect to the stackable connector on the first
instrument and the IEEE-488 connector on another instrument.
3. Repeat step 2 for each IEEE-488 instrument in your chromatographic system, up to
a maximum of 14 IEEE-488 instruments.
Note: Keep in mind cable-length limitations when you set up your system. For a list
of IEEE-488 interface guidelines, refer to the Millennium
Configuration Guide.
4Installation
TP01544
Figure 1-3 Example of IEEE-488 Cable Connections
32
System Installation and
Page 27
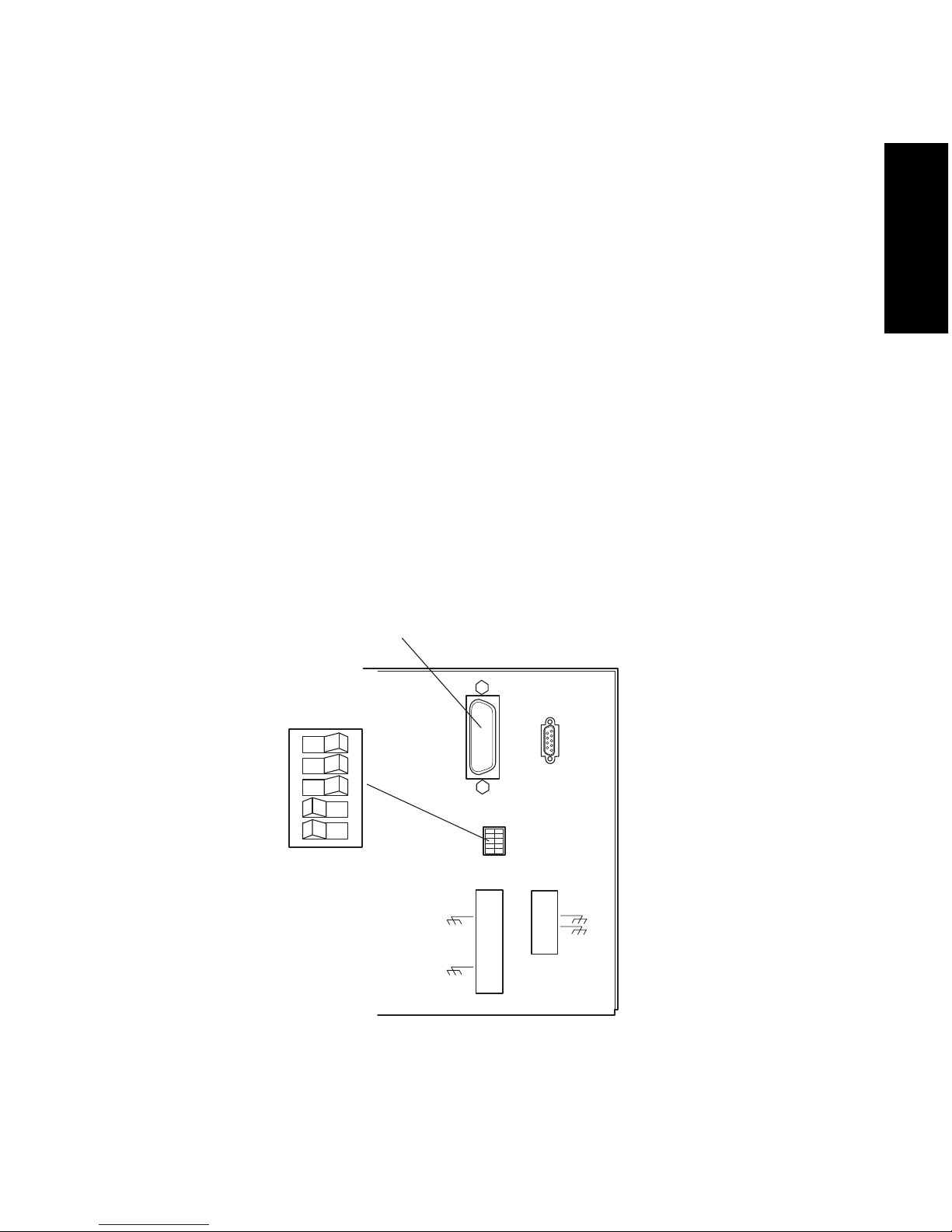
Millennium32 Workstation Connections 5
1
4. Ensure that all IEEE-488 cable screws are fastened finger-tight.
Cable Lengths
The maximum length of all cables connecting instruments to one busLAC/E is 2 meters
multiplied by the numb er of devices (or 20 mete rs, whichever is smaller).
The maximum length of cable between devices is 4 meters.
Note: The maximum number of devices to be connected together is 14.
1.3.2 Setting the IEEE-488 Address
To set the IEEE-488 address for the 2996 Detector:
Use a small screwdriver (or similar device) to set the IEEE-488 switches on the detector
rear panel (Figure 1-4) to the IEEE-488 address of the 2996 Detec tor. The address must be
a number from 2 to 29 and must be different than that of any other component connected
to your acquisition server.
Refer to the Millennium
32
System Installation and Configuration Guide for the correct
IEEE-488 GPIB switch settings.
Figure 1-4 Locating the IEEE-488 Switches
IEE 488 ADDRESS
12345
OPEN
TP01457
IEEE-488
Address
Switches
IEEE-488 Cable Connection
Page 28

1.4 Non-IEEE-488 Communication Connections
1
Non-IEEE-488 communication connections on the 2996 Detector include:
• Analog Outputs – The 2996 Detect or provides two, unattenuated, 1 volt-per
absorbance-unit analog output channels to integrators, chart recorders, or other
components.
• Event Inputs and Outputs – The 2996 Detector sends and receives contact closure
signals to and from other instruments.
You make all non-I EEE-488 c ommunicat ion ca ble c onne ction s to t he 299 6 Detec tor a t the
rear panel on the analog/event terminal (Figure 1-2).
Attention: To meet the regulatory requirements of immunity from external electrical
STOP
disturbances that may affect the performance of this instrument, do not use cables longer
than 9.8 feet (3 meters) when you make connections to the screw-type barrier terminal
strips. In addition, ensure that you always connect the shield of each cable to chassis
ground.
1.4.1 Connecting Analog Output Cables
The values of the analog output signals generated by the 2996 Detector are specified by
parameter values set from the Millennium
Millennium
32
Help.
32
Workstation. For details, refer to the
Required Materials
• One small, flat-blade screwdriver
• One electrical insulation stripping tool
• Analog signal cables (included with the Waters 2996 Detector Startup Kit)
Procedure
To connect the 2996 Detector to a device that receives analog output signals:
1. Pull off the ana log out te rminal strip from the 2996 Detec tor rear pa nel (Figure 1-5).
This step simplifies the following steps.
2. Insert the appropriate bare wires at one end of an analog signal cable into the
positive (+) and negative (–) terminals of Analog Out 1 (Figure 1-5). Tighten the
two screws to secure the + and – wires.
6Installation
Page 29

3. Connect the other end of the analog signal cable to the appropriate analog input
terminal on the external device, being sure to maintain negative-to-negative and
positive-to-positive continuity.
4. Reinstall the Ana log Output Terminal strip.
Removable Analog Output
Terminal Strip
+
Analog Out 1
-
123456
+
Analog Out 2
-
Figure 1-5 Analog Out Terminal Strip
1
IEE 488 ADDRESS
TP01456
1.4.2 Connecting Event Cables
The 2996 Detector has four terminal strip connections for contact closure signals:
• Two input signal terminals (generally used for inject start)
• Two output (programmable event table) signal terminals
If an inject start s ignal is not ava ilable over the IEEE-488 bus , you must provide a signal at
Event In 1 terminal on the 2996 Detector rear panel. Manual injectors such as the
Rheodyne 7725i provide a cable that connects the injector to an Event In terminal on the
2996 Detector rear panel.
The values of the event output signals generated by the 2996 Detector are specified by
parameter values set from the Millennium
Millennium
32
Help.
32
Workstation. For details, refer to the
Non-IEEE-488 Communication Connections 7
Page 30

Required Materials
• Small flat-blade screwdriver
1
• One electrical insulation stripping tool
• Event signal cables (included in the Waters 2996 Detector Startup Kit)
Procedure
To connect the 2996 Detector to an external event input or output device:
Pull off the event terminal strip from the rear panel (Figure 1-6). This simplifies the
following steps:
1. Insert the bare wires at one end of the event signal cable into the positive (+) and
negative (–) slots of the appropriate event input or output terminal (Figure 1-6).
Tighten the two screws to secure the + and – wires.
2. Connect the other end of the event signal cable to the appropriate event input or
event output terminal on the external device.
3. Reinstall the event terminal strip.
Removable Event
Input/Output
Terminal Strip
8Installation
Event
Out 2
Event
Out 1
Event
In 2
+
1234567890
+
Event
In 1
IEE 488 ADDRESS
Figure 1-6 Event Input/Output Terminal Strip
TP01455
Page 31

Fluidic Connections 9
1
Electrical Specifications
Before you connect an external device to an event input or output terminal, refer to the
electrical specifications in Table 1-2 and Table 1-3.
1.5 Fluidic Connections
Required Materials
• 5/16-inch open-end wrench
• 0.009-inch (0.23 m m) ID stainless steel tubing (included in the 2996 Detector
Startup Kit)
Table 1-2 Event In Terminal Specifications on TTL or Switch Closure
Parameter Specification
Low trigger <1.8 V
High trigger >3.0 V
Protected to ±30 V
Minimum pulse width 30 msec (this may lim it compatibility
with valves that require a quick pulse)
Maximum current 5 mA
Table 1-3 Event Out Terminal Specifications on Contact Closure
Parameter Specification
Maximum power 10 W
Maximum current 0.5 A at 20 V
Maximum voltage 24 V RMS
STOP
Attention: To avoid damage to the 2996 Detector electronics, be sure you make the
proper electrical connections as outlined in this section.
Caution: To avoid chemical hazards, always observe safe laboratory practices when
handling solvents. Refer to the Material Safety Data Sheets for the solvents in use.
Page 32

• Stainless st eel tubing cutter or scri bing file
• Pliers, plastic- covered, or with cloth
1
• Compression screw assemblies, three
Procedure
To make fluidic connections to the 2996 Detector:
1. Measure the lengths of tubing needed to connect:
• The column outlet to the 2996 Detector inlet
Note: Keep the length of this tubing as short as possible to prevent band
broadening.
• The 2996 Detector outlet to a waste collection bottle
Note: Ensure the length of this tubing is at least 1 to 2 feet (30 to 60 cm) to prevent
air bubbles from forming in the flow cell.
2. Cut the two lengths of tubing as follows:
a. Use a Waters 1/16-inch stain less stee l tubing cu tter o r a file with a cu tting edge to
scribe the circumference of the tubing at the desired break point.
b. Grasp the tubing on both sides of the sc ri bed mark with cl ot h- or pl ast ic-covered
pliers (to prevent marring the surface), then gently work the tubing back and
forth until it separates.
c. File the tubing ends smooth and straight to minimize dead volume and band
3. Assem ble a compre ssion fittin g (Figure 1-7 ) at both ends of the col umn outlet line
and at one end of the detector outlet line.
10 Installation
broadening.
Page 33
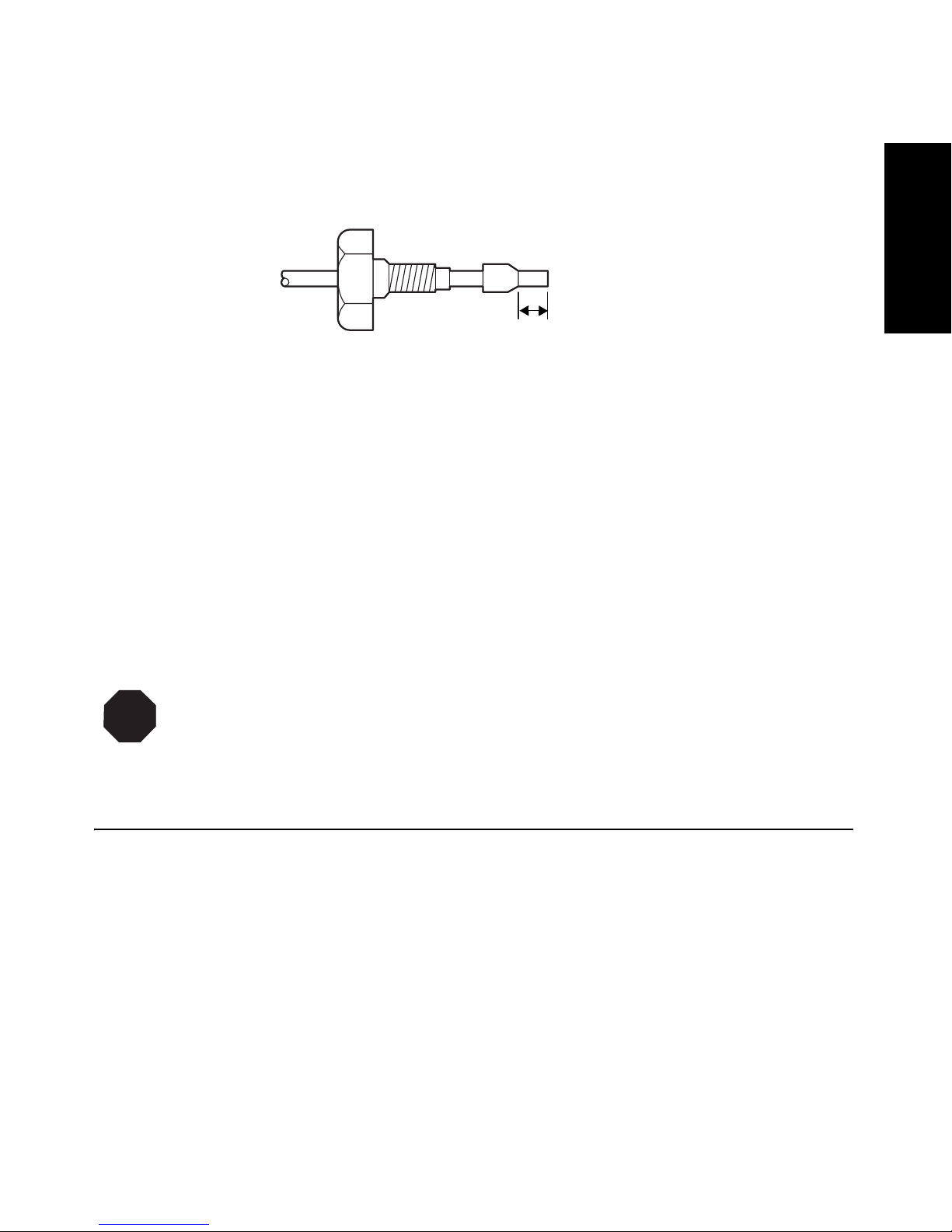
Compression
Screw
Ferrule
Tubing
Distance Determined by
the Union or Column Fitting
TP01139
Figure 1-7 Compression Screw Assembly
End Must be Straight
and Smooth to Prevent
Dead Volume
4. Seat one end of the column outlet tubing in the fitting of the column outlet, then
tighten the compression screw about 3/4-turn past finger-tight (using the 5/16-inch
open-end wrench).
5. Seat the other end of the tubi ng in the fitt ing of the detector inlet, then tighten the
compression screw as in step 4.
6. Seat the end of the detect or ou tl et tu bing wi th t he compress ion f itting in the detect or
outlet fitting, then tighten the compression screw about 3/4-turn past finger-tight.
Insert the other end of the tubing in the waste container.
1
STOP
Attention: To avoid damage to the flow cell, avoid pressures approaching its maximum
allowable pressure, 1000 psi (70 kg/cm
2
).
1.6 Starting Up and Shutting Down the Detector
The entire startup procedure takes less than 1 minute. Once completed, you should allow
the 2996 Detector to warm up for at least 1 hour before running an analysis. Follow the
procedures in this section to ensure reliable detector performance.
Starting Up the Detector
To start up the 2996 Detector:
1. In your instrument method, set the solvent delivery system or pump to deliver
1 mL/min of degassed mobile phase. For details, refer to the Millennium
Starting Up and Shutting Down the Detector 11
32
Help.
Page 34
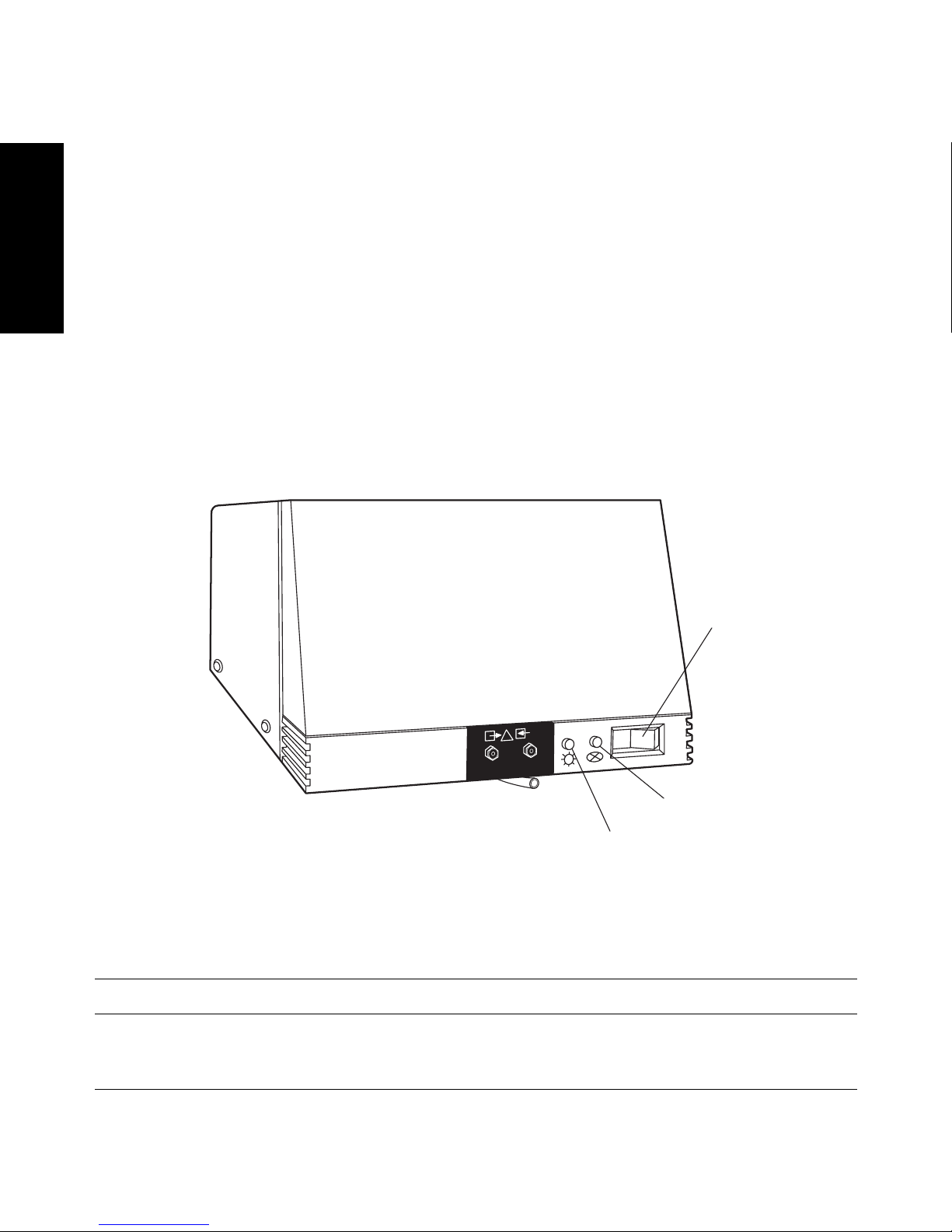
12 Installation
1
Note: Use only thoroughly degassed HPLC-grade solvents. Gas in the mobile
phase may form bubbles in the flow cell and cause the detector to fail the Reference
Energy diagnostic.
2. Flush the detector for 10 minutes or until no bubbles appear in the outlet line.
3. Press the 0/1 (Off/On) switch on the front panel of the detector (Figure 1-8) to the
1 (On) position.
4. Observe the Lamp and Status indicator LEDs on the front panel of the detector
(Figure 1-8).
• If both lights remain illuminated, the detector passed the internal diagnostics.
• If either indicator light blinks or is off, refer to the troubleshooting tables in
Chapter 2, Diagnostics and Calibration.
5. Wait 1 hour for the 2996 Detector to stabilize before acquiring data.
Figure 1-8 2996 Detector Indicator Lights
Table 1-4 LED Indicator Sequences During Startup
Lamp LED Status LED Indicates Troubleshooting
OFF OFF No power or CPU
failure.
Check ac source and main
fuse. Contact Waters Technical Service.
TP01460
LAM
P
WATERS 2996
Photodiode Array
Detector
Lamp Indicator
Status Indicator
On/Off Switch
Page 35

Starting Up and Shutting Down the Detector 13
1
Shutting Down the Detector
To shut down the 2996 Detector:
1. If the mobile phase contains buffers, set the solvent delivery syst em or pump to
deliver 1 mL/min of HPLC-grade water for 10 minutes. Otherwise, set the solvent
delivery system or pump to deliver 1 mL/min of degassed methanol for 10 minutes.
2. Press the 0/1 (Off/On) switch on the front panel of the detector to the 0 (Off)
position.
OFF FLASHING The 2996 is running
power-on self-tests.
FLASHING FLASHING 2996 has failed one of
the self-tests.
Contact Waters Technical
Service.
OFF FLASHING The 2996 is running
Confidence tests.
ON FLASHING Lamp start was
successful. The 2996
is starting calibration.
ON FLASHING for more
than 30 seconds
The 2996 may not
have calibrated
correctly.
Could be air bubble in flow
cell (Table 2-1). Contact
Waters Technical Service.
ON ON Calibration was
successful.
Table 1-4 LED Indicator Sequences During Startup (Continued)
Lamp LED Status LED Indicates Troubleshooting
Page 36

1
14 Installation
Page 37

Diagnostics 15
2
Chapter 2
Diagnostics and Calibration
The Waters 2996 Photodiode Array Detector automatically runs a series of internal
diagnostics upon sta rt up. The indica tor LEDs on the front of the detec tor and message s at
the Millennium
32
Wor kstation show the results of the start up interna l diagnostics
(Figure 1-8).
If you need to determine the cause of a problem during operation of the detector, you can
run the same internal diagnostics from the Millennium
32
Workstation. Additional
information about the performance of the detector is also available through the PDA
Calibration window, accessed from Run Samples in the Millennium
32
software.
If you encounter a problem that you cannot troubleshoot (Section 2.1, Diagnostics),
contact Waters T e chnical Servi ce at (800) 25 2-4752, U.S. and Canadian customers only.
Other customers, cal l you r l ocal Waters sub sidiary or your local Waters Technical Service
Representative in Milford, Massachusetts (U.S.A.) for assistance.
2.1 Diagnostics
Refer to Table 2-1 to troubleshoot problems encountered during startup diagnostics and
during detector operation.
Table 2-1 2996 Detector Troubleshooting
Symptom Possible Cause Corrective Action
Both LEDs off No power 1. Check line cord connections.
2. Check outlet for power.
Blown fuse Replace fuse (Section 3.3, Replacing
the Fuses).
Status light bl inks and
lamp light is off
The 2996 is running
Confidence tests.
Page 38

16 Diagnostics and Calibration
2
Status light bl inks and
lamp light on
Failed startup
diagnostics
Reseat and check alignment of flow
cell.
Flush the flow cell (Section 3.1.1,
Flushing the Flow Cell).
Insuffic ie nt energy
reaching photodiode
array because of air
bubble, or dirty flow
cell can cause shutter
diagnostic to fail
Flush the flow cell (Section 3.1.1,
Flushing the Flow Cell).
To prevent air bubbles from forming,
check that there is a 1- to 2-foot (30 - to
60-cm) length of 0.009-inch
(0.23-mm) ID tubing connected to the
detector waste outlet.
Weak lamp Replace lamp (Section 3.1.2,
Removing the Flow Cell).
Shutter failure
message
Shutter failed Run the Shutter diagnostic. For details,
see Millennium
32
Help.
Detector not
responding to
Millennium
32
Workstation
Detector not
connected to
busLAC/E or to
LAC/E
32
Acquisition
Server in t he
Millennium
32
Workstation
Check IEEE-488 cable connections,
tighten connectors.
Incorrect IEEE-488
address
1. Ensure that the 2996 Detector
IEEE-488 address is unique and
within the range 2 to 29 (see the
Millennium
32
System Instal lation
and Configuration Guide).
2. Rescan the IEEE-488 bus. For
details, see Millennium
32
Help.
Table 2-1 2996 Detector Troubleshooting (Continued)
Symptom Possible Cause Corrective Action
Page 39

User-Initiated Diagnostics 17
2
2.2 User-Initiated Diagnostics
Note: The system administrator can restrict access to the 2996 Detector diagnostics by
disabling user access to Run Samples. For details, refer to the Millennium
32
Help.
There are two types of user-initiated PDA diagnostic tests:
• Internal Tests – Tests run by the instrument firmware that help you determine the
source of a malfunction. These tests do not require connections to external devices.
• Interactive Tests – Tests that check analog output and event input/output signal
communications between the detector and connected external devices. These tests
require connections to pump flow and/or test equipment.
You can run all user -initia ted diagnos tics from Run Sampl es in the Mill ennium
32
software.
For more information on Run Samples and PDA diagnostics, refer to
the Millennium
32
Help.
Change in reference
spectrum
Mobile phase contain s
gas or is contaminated
Prepare fresh mobile phase and degas
thoroughly.
Air bubbles trapped in
flow cell
Reseat and check alignment of flow
cell.
Flush the flow cell, or apply slight
backpressure on the detector waste
outlet.
T o prevent ai r bubbles, check that there
is a 1- to 2-foot (30- to 60-cm) length
of 0.009-inch (0.23-mm) ID tubing
connected to the detector waste outlet.
Solvent in drain line Leak from flow cell
gasket
Rebuild flow cell with a new gasket
(Section 3.1.3, Disassembling and
Cleaning the Flow Cell).
Leak from flow cell
fittings
Check fittings for overtightening or
undertightening, and replace fittings if
necessary.
Table 2-1 2996 Detector Troubleshooting (Continued)
Symptom Possible Cause Corrective Action
Page 40

18 Diagnostics and Calibration
2
2.3 PDA Calibration
You can adjust, or calibrate, the 2996 Detector to ensure that wavelength readings are
accurate. Recalibrate the 2996 Detector only if the Wavelength Accuracy diagnostic (in
the Internal Diagnostics tests) fails. Calibration allows you to correct small errors in
wavelength which may be caused by aging optics or excessive vibration.
You calibrate the 2996 Detector using the PDA Calibration window, which you access
from Run Samples and which allows you to:
• View the effects of exposure time on photodiode saturation for a given wavelength
range.
• Verify the wavelength location of the deuterium spectrum Balmer lines (486.0 nm
and 656.1 nm).
• Recalibrate to set the 486-nm peak at the proper wavelength.
• Ensure precise data for library matching.
Note: The system administrator can restrict access to the PDA Calibration window by
disabling access to Run Samples.
Note: Ensure that the flow cell is clean before you check calibration (Section 3.1.1,
Flushing the Flow Cell).
To prepare for calibration:
1. Set the pump t o deli ver 1 mL/min of degassed methan ol fo r 10 minut es. If metha nol
is not miscible with the previous solvent, flush with a miscible sovent before
switching to methanol.
2. If you have been using buffers, flush with HPLC-quality water at 1 mL/min for
10 minutes, then switch to methanol for 10 minutes.
Note: Ensure that the solvent is miscible with the previous mobile phase.
For information on pe rforming calibration, refer to the M illen nium32 Help.
STOP
Attention: Recalibrating the wavelength requires that spectral libraries be reentered.
Page 41

Flow Cell Maintenance 19
3
Chapter 3
Maintenance
This chapter covers main tenanc e of the Waters 2996 Photo diode Ar ray De tect or flow cel l,
lamp, and fuse.
3.1 Flow Cell Maintenance
The flow ce ll requires m aintenance w hen:
• The reference spectrum changes.
• The cell fluid leaks out of the drain tube.
• The Lamp diagnostic (in the Millennium
32
PDA Diagnostics window) fails and the
lamp status light is on (Table 2-1).
• The 2996 Detector causes high backpressure.
Note: Conditions other than a dirty flow cell may cause decreased lamp intensity. For
more information, refer to Chapter 2, Diagnostics and Calibration.
Flow cell maintenance consists of:
• Flushing the flow cell
• Removing the flow cell
• Disassembling and cleaning the flow cell
• Installing the flow cel l assembly
Caution: To avoid possible electric shock, do not remove the 2996 Detector power
supply covers. The power supply does not contain user-serviceable components.
Page 42

20 Maintenance
3
3.1.1 Flushing the Flow Cell
Required Materials
• HPLC-grade water
• HPLC-grade methanol
If the flow cell requires cleaning, first try flushing it with solvent.
Procedure
To flush the flow cell:
1. Select a solvent compatible with the samples and mobile phases that you have been
using. If you have been using buffers, flush with HPLC-grade water for 10 minutes
at 1 mL/min, then switch to a low-su rface-tension solvent s uch as metha nol.
2. Set pump flow to 1 mL/min, then run the pump for 10 minutes.
3. Test the lamp energy by perf orming the Lamp diagnostic test. For details, refer to
the Millennium
32
Help.
If the lamp diagn ost ic fails and the lamp has not been used more than 2000 hours or
1 year (whichever comes first), disassemble the flow cell and clean the flow cell
components using the procedure described in Section 3.1.2, Removing the Flow
Cell.
3.1.2 Removing the Flow Cell
Note: You do not need to shut down the 2996 Detector to remove and replace the
flow cell.
Required Materials
• 5/16-inch open-end wrench
• Phillips screwdriver
• Powder-fr ee gloves
STOP
Attention: Ensure that the solvent is miscible with the previous mobile
phase.
Page 43
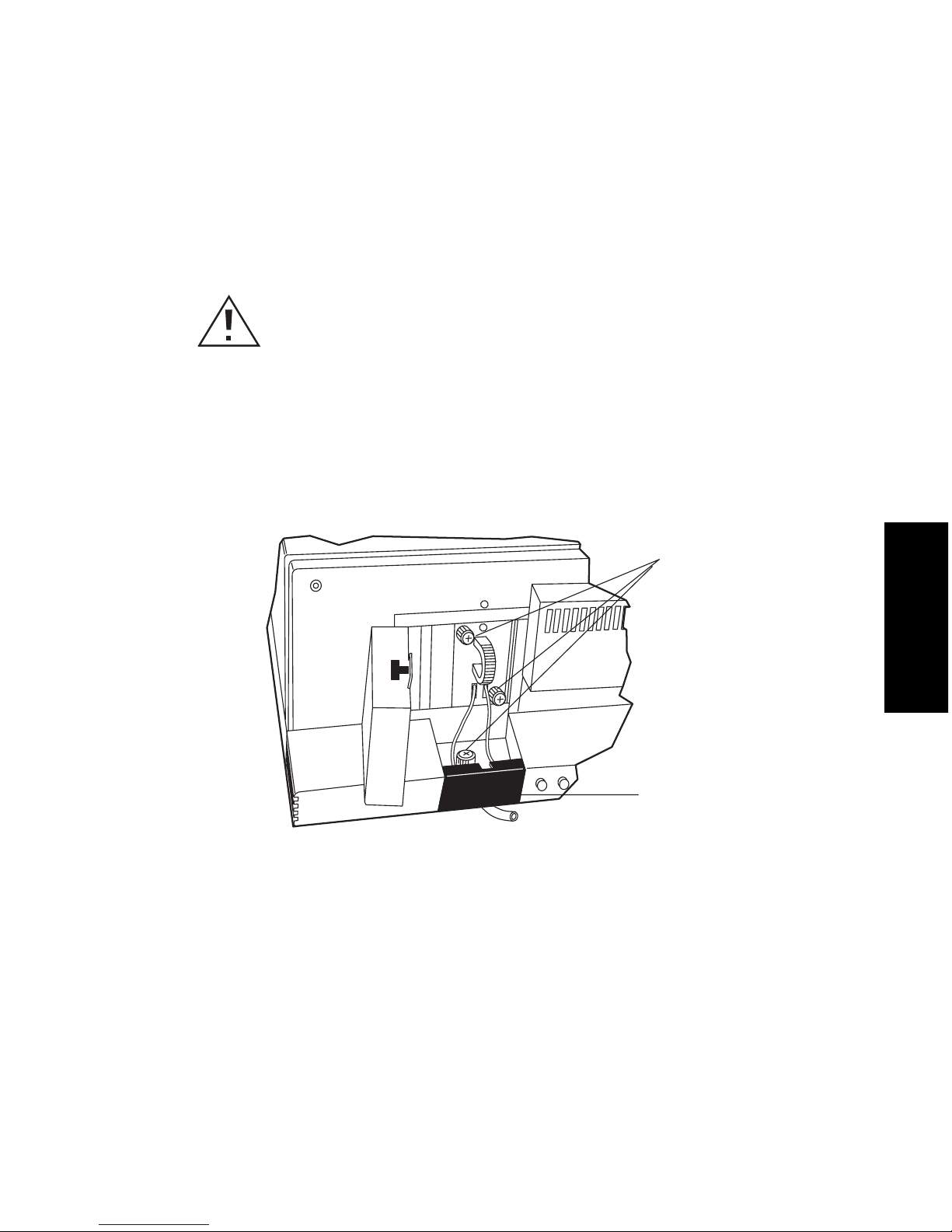
Flow Cell Maintenance 21
3
Procedure
To remove the 2996 Detector flow cell:
1. Set the flow to 0.0 mL/min.
2. Power off the solvent delivery system or pump to avoid exposure to chemicals.
3. Use the 5/16-inch wrench to disconnect the fluidic lines at the front of the detector.
4. Lift up the 2996 detector front cover and pull the front cover from the detector
chassis.
5. Open the flow cell access door by pulling the black thumbtab, then pull the door
gently toward you (Figure 3-1).
Figure 3-1 Removing the Flow Cell Assembly
6. Use the Phillips screwdr iver to loosen the thr ee thumbs crew s that hold the flo w
cell assembly to the optics bench and the thumbscrew that secures the bracket
holding the flui dic co nne ction s, then detach th e bra cket .
7. Pull the flow cell assembly gently toward you to remove it from the detector
(Figure 3-2).
Caution: To avoid the possibility of leaking mobile phase, do not disconnect
the inlet or outlet fluidic lines while there is pressure in the chromatographic
system. Always vent your system before disconnecting fluidic lines.
TP01462
Thumbscrews
Holding Flow
Cell Assembly
and Bracket
Fluidic Connections
(Inside Bracket)
Thumbscrews
Holding Flow
Cell Assembly
and Bracket
Page 44

Flow Cell Body
Lens Holder
Assembly
3
Fluidic
Connections
Figure 3-2 Flow Cell and Fluidic Connections Assemblies
Bracket
TP01463
3.1.3 Disassembling and Cleaning the Flow Cell
Attention: The lens surface finish and the alignment of the lenses are critical to the
STOP
STOP
performance of the 2996 Detector. Be careful not to touch or damage the lenses and the
lens holders.
Attention: To prevent lens contamination, use powder-free gloves when disassembling,
inspecting, cleaning, or replacing parts within the flow cell or when removing or replacing
the flow cell within its assembly.
Required Materials
• TORX™ T10 screwdriver
• Small, flat-blade screwdriver
• Lens tissue or nonparticulating swab
22 Maintenance
Page 45

Flow Cell Maintenance 23
3
• HPLC-grade methanol
• Belleville spring washer
• Flow cell gasket
• Powder-fr ee gloves
Procedure
To disassemble and clean the flow cell (and lenses):
1. Use the TORX T10 screwdriver to remove the three screws that secure one of the
lens holder assemblies (Figure 3-3).
Figure 3-3 Disassembling the Flow Cell
2. Use the small, flat-blade screwdriver to gently pry the lens assembly from the flow
cell body at the slots.
3. Use a lens tissue or a nonparticulating swab to wipe the lens with methanol.
STOP
Attention: Solvents other than methanol may damage a disassembled flow
cell. In normal use, the gasket protects the lens holder from solvents.
TP01464
Gasket
Flow Cell Disk
Lens Assembly
Flow Cell Disk
Belleville
Spring
Washer
Lens Assembly
Flow Cell
Body
Spring
Washer
Slot for
Removing
Lens
Assembly
Screws
Page 46

24 Maintenance
3
4. Remove and discard the gasket.
5. Repeat steps 1 through 4 to remove, disassemble, and clean the other lens holder
assembly.
6. Use methanol and a nonparticulating swab to clean the flow cell body.
Reassembling the Flow Cell
To reassemble the flow cell (Figure 3-3):
1. Insert a replacement gasket into one side of the flow cell body.
2. Align the screw holes of the lens assembly with the holes in the flow cell body.
3. Place the new Belleville spring washers (with the concave side facing out) onto the
lens assembly.
4. Place the flow cell disk over the lens assembly.
5. Insert the three screws using the TORX T10 driver to gradually tighten each screw,
alternating between the screws in a clockwise pattern. Tighten until the screws meet
the flow cell disk, the n tighten each screw 1/4-turn. If a torque screwdriver is
available, tighten the screws to 16 in-oz (0.113 N-m).
6. Check for leaks. If you find any leaks, repeat step 5.
7. Repeat steps 1 through 5 to reassemble the other side of the flow cell.
3.1.4 Installing the Flow Cell Assembly
To in stall the flow cell assembly:
1. While you hold the flow cell assembly in a vertical orientation (Figure 3-2), insert
the assembly into the optics bench. Note that the flow cell is self-aligning and uses
the guide pins on the optics bench.
2. Gently push the front of the assembly until it seats on the front alignment pins.
3. Hand-tighten the thumbscrews.
4. Reconnect the fluidic lines.
STOP
Attention: Be careful not to overtighten the screws.
STOP
Attention: The alignment of the flow cell in the optics bench is critical to detector
operation. Be careful not to damage the flow cell body.
Page 47

Replacing the Lamp 25
3
5. Replace the front cover.
6. Flush the flow cell (Section 3.1.1, Flushing the Flow Cell).
3.2 Replacing the Lamp
Replace the lamp in the 2996 Detector when either of the following conditions exists:
• The sampling rate requires an excessively long exposure time (more than
100 milliseconds).
• Intensity is low enough that sensitivity is not sufficient for your method.
Note: An improperly inserted flow cell could appear to be a problem with the lamp.
Note: If lamp intensity is low, but the lamp has not been used for 2000 hours, you may be
able to increase lamp intensity by cleaning the flow cell (Section 3.1, Flow Cell
Maintenance).
Absorbance by the mo bile phase also affects the apparent lamp intensity. For example,
acetonitrile is more transparent than methanol at wavelengths less than 220 nm.
Caution: To avoid electrical hazards and exposure to UV light, turn off the power and
disconnect the power cord before you begin this procedure.
Caution: The lamp and housing are extremely hot. To avoid the possibility of contacting
hot surfaces, allow the lamp to cool for 15 minutes before you handle the lamp assembly
or surfaces close to the lamp.
STOP
Attention: Do not touch the lamp glass while unpacking or inserting the lamp. Touching
lamp glass damages the lamp and reduces life expectancy.
STOP
Attention: To prevent lamp glass contamination, use powder-free gloves when
removing or replacing the lamp.
Caution: The lamp may be very hot! Please allow it to cool for at least 15 minutes before
you attempt to remove it.
Page 48

3
Required Materials
• Slotted head screwdriver
• Powder-fr ee gloves
Caution: To avoid electrical hazards when you perform the following procedure, power
off the 2996 Detector and disconnect the power cord.
Procedure
To replace the la mp:
1. Power off the 2996 Detector, disconnec t t he power cord, and allow the lamp to cool
for at least 15 minutes.
Caution: To avoid the possibility of contacting hot surfaces, wait at least
15 minutes after powering off the detector before you handle the lamp.
2. Lift up the front panel cover and pull it away from the chassis.
3. Open lamp secure panel.
Alignment
Notch
Mounting
Screws
Figure 3-4 Lamp Power Connector and Mounting Screws
26 Maintenance
Lamp
Lamp Power
Connector
Lamp Usage
Indicator
TP01466
Page 49

Replacing the Fuses 27
3
4. Use a slotted head screwdriver to unscrew the two mounting screws.
5. Grip the metal base of the lamp, pull the lamp out, and set it aside. Do not pull the
wires to remove the lamp.
6. Carefully unpack the replacement lamp.
7. While wearing powder-free gloves and holding the lamp by its base, position the
lamp so that the not ch in the base aligns with the pos it ioning pin in the optics bench.
8. Insert the lamp and secure it with the two screws. Make sure that the lamp base is
flush against the lamp housing.
9. Reconnect the lamp power connector (Figure 3-4).
10. Secure the lamp access panel.
11. Install the front panel cover.
12. Reconnect the power cord and power on the 2996 Detector.
3.3 Replacing the Fuses
Replace the fuses unde r the conditions indicated in the troub les hooting table (Section 2.1,
Diagnostics). The 2996 Detector requires two 2 A, 250 V fuses (5 mm × 20 mm).
To replace the two fuses in the 2996 Detector:
1. Power off the 2996 Detector and remove the power cord.
2. Locate the fuse block below the power cord plug (Figure 3-5) on the rear panel.
Figure 3-5 Fuse Block
Caution: To avoid electrical hazards, power off the 2996 Detector and disconnect the
power cord before you perform the following procedure.
Squeeze Side Clips to
Access Fuses
Page 50

3. Squeeze the two side clips on the fuse block while you pull out the block.
4. Remo ve the fuses from the block, then ins tall the new fuses.
5. Position the fuse block with the small tab pointing down, then push in the block
until the side clips engage.
6. Connect the power cord, then power on the 2996 Detector.
3
28 Maintenance
Page 51

2996 Detector Optics 29
4
Chapter 4
Principles of the 2996 PDA
Detector Optics
To use the Millennium32 PDA software effectively, you must be familiar with the
principles of operation of the optics and electronics of the Waters 2996 PDA Detector.
4.1 2996 Detector Optics
The 2996 Detector is an ultraviolet/visible light (UV/Vis) spectrophotometer with:
• 512 photodiodes
• Optical resolution of 1.2 nm per diode
• Operating wavelength range from 190 to 800 nm
The light path through the optics assembly of the 2996 Detector is shown in Figure 4-1.
Page 52
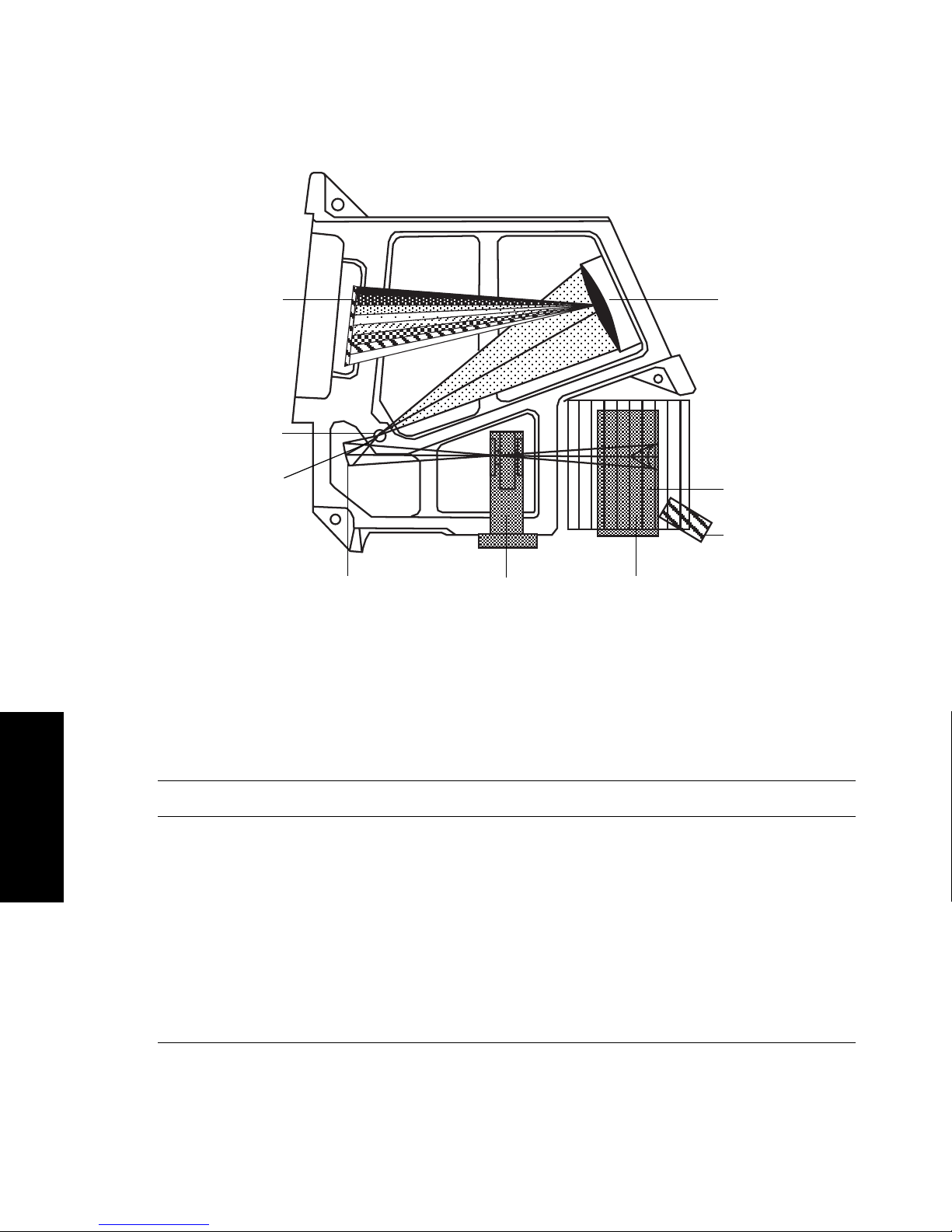
30 Principles of the 2996 PDA Detector Optics
4
Figure 4-1 Optics Assembly Light Path
Table 4-1 describes the optics assembly components in the 2996 Detector.
Table 4-1 Optics Assembly Components
Component Function
Lamp and lamp
optics
Focuses light from the deuterium so urce lamp via a mirror through a
beamsplitter to the flow cell.
Beamspl itter and
reference diode
Reflects part of the light back to a reference diode, which measures
the intensity of the li ght emitted by the lamp. The detector uses this
measurement to keep the lamp output constant.
Flow cell
assembly
Houses the segment of the flow path (conta ining eluent and sa mple)
through which the polychromatic light beam passes. This arrangement of optical components, with the flow cell positioned between
the lamp and the grating, is commonly called reversed optics.
Reference
Diode
Beamsplitter
Assembly
50-µm Aperture
Lamp and
Lamp Optics
Spectrographic
Mirror and Mask
Shutter
Assembly
Flow Cell
Assembly
Grating
Photodiode
Array
Page 53

Resolving Spectral Data 31
4
4.2 Resolving Spectral Data
The ability to distinguish similar spectra depends on photodiode spacing and the
bandwidth of the light striking the photodiode. The bandwidth of the light striking the
photodiodes depends on the aperture width.
The apertu re width determines:
• Attainable wavelength bandwidth at the photodiode array
• Intensity of the light reaching the photodiode array (optical throughput)
The aperture creates a narrow beam that reflects from the grating to the photodiode array.
The wavelength that strikes a particular diode depends on the angle of reflection from the
grating.
Figure 4-2 shows an absorbance spectrum of benzene obtained from the 2996 Detector
using the 50-µm aperture. In this spectrum, the wavelength resolution is sufficient to
resolve five principal benzene absorption peaks.
Spectrograph
mirror and mask
The mirror focuses light transmitted through the flow cell onto the
aperture at the entrance to the spectrographic portion of the optic s.
The mirror mask defines the beam of light focused on the spectrograph mirror.
Aperture Controls wavelength resolution and intensity of light striking the
photodiodes. The width of the aperture is 50 µm.
Shutter assembly Prevents light from reaching the photodiode array except during
sampling and calibration. For details on the dark current, see
Section 4.4.1, Calculating Absorbance.
Grating Disperses the light into bands of wavelengths and focuses those
wavelength bands onto the plane of the photodiode array.
Second-order
filter
Reduces the contribution of second-order reflection of UV light
(less than 370 nm) to the light intensity observed at visible wavelengths (greater than 370 nm).
Photodiode array An array of 512 photodiodes arranged li nearl y. The diode width and
spacing provide a single wavelength resolution of 1.2 nm.
Table 4-1 Optics Assembly Components (Continued)
Component Function
Page 54

32 Principles of the 2996 PDA Detector Optics
4
Figure 4-2 Benzene Spectrum at 1.2 nm Resolution
4.3 Measuring Light at the Photodiode
The 2996 Photodiode Array Det ector mea sures the amount of light s triking the photodi ode
array to determine the absorbance of the sample in the flow c ell.
The array consists of 512 photodiodes arranged in a row. Each photodiode acts as a
capacitor by holding a fixed amount of charge.
Light striking a photodiode discharges the diode (Figure 4-3). The magnitude of the
discharge depends on the amount of light striking the photodiode.
nm
Absorbance
Page 55
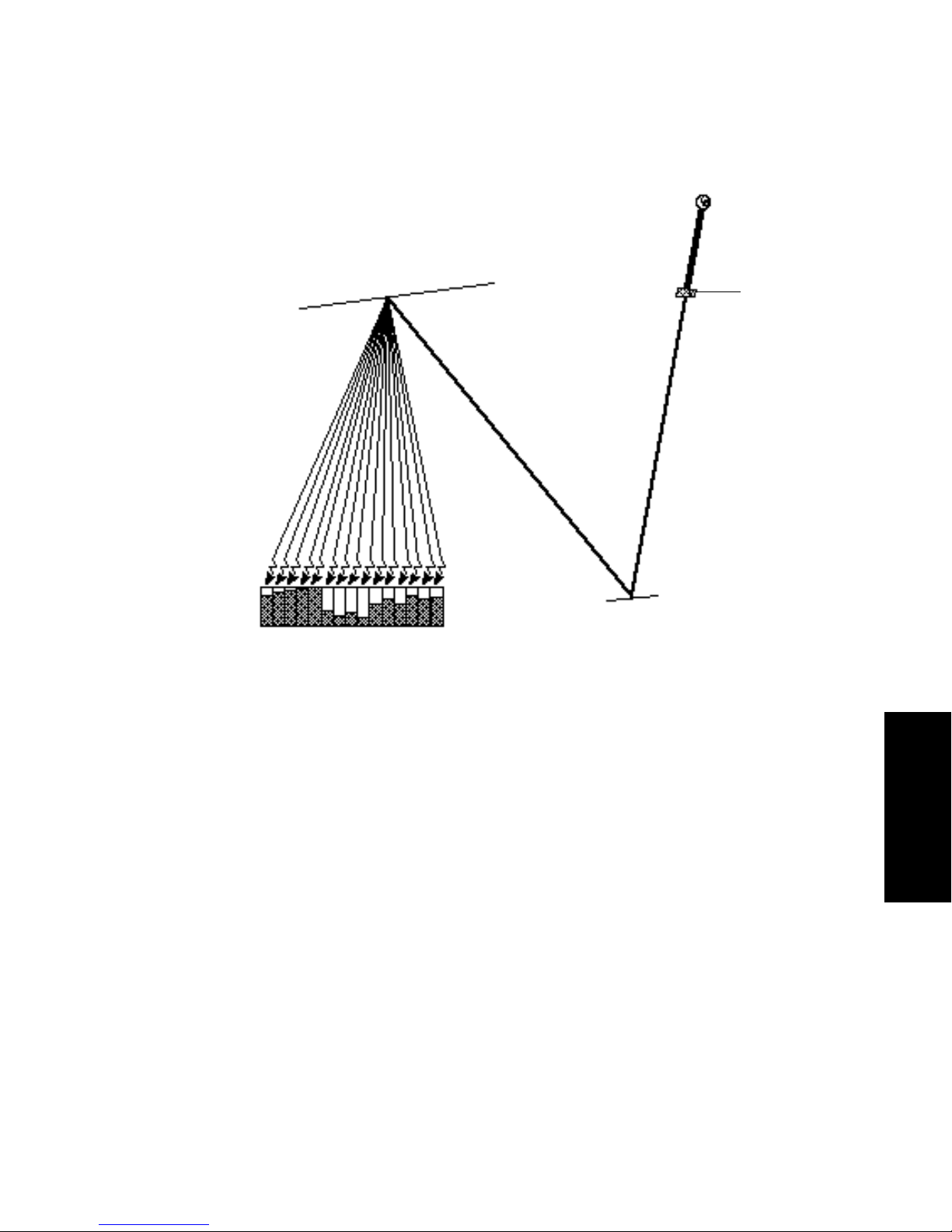
Sample in flow cell
absorbs at specific
wavelengths.
Deuterium
Lamp
Grating
Light from grating
dispersed into 1.2-nm
wavelength beams
continuously
discharges diodes.
Mirror
Figure 4-3 Photodiodes Discharged by Light
Flow
Cell
The 2996 Detector measures the amount of current required to recharge each photodiode.
The current is proportional to the amount of light transmitted through the flow cell over
the interval specified by the diode exposure time.
Exposure Time
The 2996 Detector recharges each diode and reads the recharging current one diode at a
time. The interval between two readings of an individual diode is the exposure time. The
2996 Detector requires less than 10 msec to sequentially read all of t h e d iod es in the array
and process the data. The minimum exposure time is 10 msec. You can set exposure time
from 10 to 500 msec.
For example, if an exposure time is set to 50 milliseconds, the 2996 Detector:
1. Recharges diode 1 and reads the current required to recharge diode 1
2. Recharges diode 2 and reads the current required to recharge diode 2
4
Measuring Light at the Photodiode 33
Page 56
3. Sequentially recharges and reads the current required to recharge all the remaining
510 photodiodes
4. Waits approximately 45 msec before beginning the recharge-and-reading sequence
with diode 1 after all diodes have been recharged and read.
You set the exposure time parameter in the General tab of the 2996 PDA Instrument
Method Editor. You can specify either Auto Expo sure or Expo sur e T i me. For det ails, refe r
to the Millennium
32
Help.
4
Note: For best signal-to-noise performance, adjust the wavelength range optimize
autoexposure computations. For details, refer to the Millennium
32
Help.
Using the Auto Exposure Parameter
The Auto Exposure time parameter allows the 2996 Detector optics to calculate the
optimum exposure time needed to recharge the diodes based on lamp energy, lamp
spectrum, mobile phase absorbance, and the chosen wavelength range using a single
Deuterium light source from 190 to 800 nm. To minimize detector noise, Auto Exposure
adjusts the exposure time from 50 to 90% of full scale.
The Auto Exposure time setting ensures that the photodiodes are:
• Not saturating due to overexposure
• Operating above the range of normal, dark current discharge
With auto exposure enabled, the 2996 Detector:
• Calculates exposure time at the start of a run based on maximum light intensity
within the selected wavelength range
• Limits the exposure so that no diode within the given wavelength range discharges
more than 90%
• Provides proper settings for signal-to-noise and dynamic range for each run
The Auto Exposure time setting may not support certain combinations of sampling rates,
wavelength ranges, or filter time-constant settings required for your analysis. If this is the
case, you can set the exposure time manuall y to adjus t the exposure time from expe riment
to experim ent.
Using the Exposure Time Parameter
The Exposure Time parameter enables you to manually set the length of tim e the
photodiodes are exposed to light before they are read. The supported range is 10 to
500 msec.
34 Principles of the 2996 PDA Detector Optics
Page 57

Computing Absorbance Data Points 35
4
Note: Changing exposure times within a set of samples can cause changes in baseline
noise.
Be aware that increasing the Exposure Time parameter has the potential to saturate the
photodiodes. A longer exposure time may cause the 2996 Detector to lose the signal at
certain wavelengths because of diode saturation. When specifying the Exposure Time,
select a value that provides settings for an optimum signal-to-noise ratio over the
wavelength range of your analysis (see the next topic “Optimizing the Signal-to-Noise
Ratio”).
Optimizing the Signal-to-Noise Ratio
To optimize signal-to-noise ratios, choose an acquisition wavelength range that includes
only the wavelengths of interest and over which the mobile phase absorbs minimally
(Appendix C, Mobile Phase Absorbance). Setting the bandwidth to higher values can
improve signal-to-noise ratios.
4.4 Computing Absorbance Data Points
The 2996 Detector calculates absorbance values before transmitting the data to the
Millennium
32
database. To calculate absorbance, the 2996 Detector:
• Computes the absorb ance at each diode using the dark current and reference
spectrum (Section 4.4.1, Calculating Absorbance)
• Averages the absorbances at a particular wavelength as specified in the spectra per
second sample rate and reports the average as a single data point (Section 4.4.2,
Resolution)
• Can apply a filter (Section 4.4.3, Filtering Data)
4.4.1 Calculating Absorbance
The detector computes absorbance by subtracting the dark current and referenc e s pec tr um
from the acquired spectrum. Absorbance is based on the principles of Beer’s Law.
Page 58

36 Principles of the 2996 PDA Detector Optics
4
Beer’s Law
The relationship between the quantity of light of a particular wavelength arriving at the
photodiode and the concentration of the sample passing through the flow cell is described
by the Beer-Lambert Law (commonly called Beer’s Law). Beer’s Law is expressed as:
A = εlc
where:
A = absorbance
ε = molar absorptivi ty
l = path length (1.0 cm in the 2996 Detector normal flow cell)
c = molar concentration
Beer’s Law applies only to well-equilibrated dilute solutions. It assumes that the refractive
index of the sample remains constant, that the light is monochromatic, and that no stray
light reaches the detector element. As concentration increases, the chemical and
instrumental requirements of Beer’s law may be violated, resulting in a deviation from
(absorbance versus concentration) linearity (Figure 4-4). The absorbance of mobile phase
can reduce the linear range by the amounts shown in Appendix C, Mobile Phase
Absorbance.
Figure 4-4 Absorbance as a Function of Concentration
Ideal
Actual
Absorbance
Working Range
Background Absorbance
Concentration
Page 59

Dark Current
Photodiodes los e char ge over t ime even when t hey are not exposed t o light. Th e amount of
charge lost is called dark c urrent.
At the start of a chromatographic run, the 2996 Detector closes the shutter to take a dark
current reading for each d iode. Th e shutt er cl os es after th e exposu re ti me is c alcul ated an d
stays closed for the same interval as the exposure time.
The detector subtracts the dark current values from the current values recorded during
absorbance measurements for both the sample and the reference spectra.
Reference Spectrum
Immediately after the dark current measurement and before any components are eluted,
the 2996 Detector records a reference spectrum. The reference spectrum is a measure of
lamp intensity and mobile phase absorbance over the interval specified in the exposure
time taken with the shutter open.
Note: For best results, the reference spectrum should be representative of the initial
mobile phase.
Note: For extremely long exposure times, the dark current and reference spectrum
readings may take several seconds to finish.
Absorbance
The 2996 Detector calculates the absorbance for each diode at the end of each exposure
time using the following equation:
Sn Dn–()
Absorbance
n
where:
S = obtained during sample analysis
D = obtained during the dark current test
R = obtained from the reference spectrum
n = diode number
-------------------------
log=
Rn Dn–()
4
Computing Absorbance Data Points 37
Page 60

4.4.2 Resolution
The data reported by t he 2996 Detec tor to the Mill ennium32 database can be th e average of
a number of data points. After calculating absorbance, the detector averages absorbance
values based on:
• Spectral resolution
• Sample rate
Averaging Spectral Data Based on Resolution
Spectral resolution (or bandwidth) is the wavelength interval (in nanometers) between
data points in an acquired spectrum. The minimal resolution of the 2996 Detector is
1.2 nm. For example, in 3D mode, the 2996 Detector averages three adjacent diodes for
each reported wavelength when the spectral resolution is set in the Millennium
to 3.6 nm. In 2D mode, absorbance values are computed based on the bandwidth setting.
2D mode is supported in Millennium
Averaging Chromatographic Data Based On Sample Rate
Sample rate i s the nu mber of da ta point s per se cond r eported to the Mil lennium32 database.
The number of ti mes the p hotodio des are read d uring the sample r ate i nterv al is de pendent
on the exposure tim e. For example, if exposure time is 25 msec, and sample rate is 1 sec,
then readings per data point are:
32
software versions 4.0 or higher.
1000 msec
------------------------25 msec
40=
32
software
4
The readings are averaged and reported as a single data point.
Combining Spectral Resolution and Sample Rate
Spectral resolution and sample rate have opposite effects on noise and spectral detail.
Increasing the value of the spectral resolution parameter and decreasing the number of
spectra per second decrease the size of the data file.
Note: The data storage rate is based on wavelength range, spectral resolution, and
sample rate, which are set in the General tab of the 2996 PDA Instrument Method Editor.
For details, refer to the Millennium
32
Help.
4.4.3 Filtering Data
Use the General tab of the 2996 PDA Instrument Method Editor (for details, refer to the
Millennium
38 Principles of the 2996 PDA Detector Optics
32
Help) to apply an optional noise filter (the Filter Response parameter) to
Page 61

the data sent to the Millennium32 software database. A noise filter of 1 second is the
default value, which provides a good signal-to-noise ratio for most chromatographic
separations.
Note the fo llowing with regard to fi ltering data:
• The noise filter is a digital (low pass) filter.
• The filte r calculates a data point that is a modified rolling average for a wavelength
over a number of readings.
• The filter values are comparable to the effects of a 0.1- to 3-second RC filter.
4
Computing Absorbance Data Points 39
Page 62

4
40 Principles of the 2996 PDA Detector Optics
Page 63

Comparing Absorbance Spectra 41
5
Chapter 5
Spectral Contrast Theory
This chapter explains the theory behind the Spectral Contrast technique, which is used to
compare UV/Vis absorbance spectra collected by the 2996 Detector. Spectral Contrast
makes use of the fact that different compounds have differently shaped absorbance
spectra. This chapter describes how Spectral Contrast represents absorbance spectra as
vectors. When applied to the UV/Vis absorbance data collected by the 2996 Detector, the
Spectral Contrast technique determine s whether di ffe rences bet ween spe ctra are due t o the
presence of multiple compounds in the same peaks (coelution) or due to nonideal
conditions such as noise, photometric error, or solvent effects.
5.1 Comparing Absorbance Spectra
The shape of an absor bance sp ectru m is det ermine d by the re la tive a bsorban ce at di f fere nt
wavelengths. The shape of a compound’s absorbance spectrum is a characteristic of that
compound at the solvent and pH conditions under which the absorbance spectrum is
measured.
Figure 5-1 shows the absorbance spectra for the two compounds, A and B. The ratio of t he
absorbance at 245 nm to the absorbance at 257 nm is approximately 2.2 for compound A
and 0.7 for compound B.
The absorbance rati os of two wavel en gth pairs is a limited spectral comparison. For more
information, you need to compare the absorbance ratios of multiple wavelength pairs.
Page 64

Compound A:
245 nm
257 nm
Compound A
Figure 5-1 Comparing Spectra of Two Compounds
Compound B:
Compound B
Ab
245
----------- ---- 2 . 2=
Ab
257
Ab
245
---------- ----- 0 . 7=
Ab
257
5
5.2 Representing Spectra as Vectors
The Spectral Contrast technique uses vectors to quantify differences in the shapes of
spectra. Spectral Contrast converts baseline-corre cted spectr a to vectors and then
compares the vectors. Spectral vectors have two properties:
• Length – Proportional to analyte concentration.
• Direction – Determined by the relative absorbance of the analyte at all wavelengths
(its absorbance spectrum). Direction is independent of concentration for peaks that
are less than 1.0 AU across the collected wavelength range.
Vector direction contributes to the identification of a compound, since the direction is a
function of the absorbance spectrum of the compound. The ability of spectral vectors to
differentiate compounds depends on the resolution of spectral features. As both
wavelength range and spec tral resolut ion increase , the precision of a spectral vecto r for the
resultant spectrum increases. A vector derived from the 2996 PDA Detector can include
absorbances in any range from 190 to 800 nm. To enhance spectral sensitivity, set the
bench resolution to 1.2 nm.
42 Spectral Contrast Theory
Page 65

Representing Spectra as Vectors 43
5
5.2.1 Vectors Derived from Two Wavelengths
The Spectral Contrast algorithm uses vectors to characterize spectra (Figure 5-2). To
understand the vector principle, consider two vectors (Figure 5-2) based on the spectra
depicted in Figure 5-1.
Figure 5-2 Plotting Vectors for Two Spectra
The axes in Figure 5-2 are in absorbance units at the two wavelengths used to calculate the
absorbance ratio shown in Figure 5-1. The head of the vector for Compound A is at the
intersection of the absorbance values (for Compound A) at the two wavelengths
represented by each axis. The other vector is similarly derived for the spectrum of
Compound B.
The vector for Compound B points in a direction different from that of the vector for
Compound A. The difference in direction, which reflects the difference in the absorbance
ratios of the two compounds at wavelengths 245 nm and 257 nm, is called the Spectral
Contrast angle. A Spec tral Cont rast angle (e .g., θ in Figure 5-2) greater than zero ind icates
a shape difference between spectra (Section 5.3, Spectral Contrast Angles). The length of
the vector is proportional to the concentration.
5.2.2 Vectors Derived from Multiple Wavelengths
When absorbance ratios are limited to two wavelengths, the chance that two different
spectra will have the same absorbance ratio is much gr eater than if comparison is made
using absorbance ratios at many wavelengths. Therefore, the Spectral Contrast technique
AU at 257 nm
AU at 245 nm
Page 66

44 Spectral Contrast Theory
5
uses absorbances from multiple wavelengths to form a vector in an n-dimensional vector
space, where n is the number of wav elengths from the spectrum.
To compare two spectra, the Spectral Contrast techni que for ms a vector for each sp ectru m
in an n-dimensional space. The two spectral vectors are compared mathematically to
compute the angle between the two vectors.
Just as in the two-wavelength comparison, a Spectral Contrast angle of zero in
n-dimensional space means that all ratios of absorbances at corresponding wavelengths
match. Conversely, if any comparison of ratios doe s not mat ch, the corresponding vectors
point in different directions.
5.3 Spectral Contrast Angles
Spectra that have the same sha pe have vectors tha t point in the same dire ction. Spectra th at
have differ ent shapes have vector s that poi nt in dif ferent directi ons. The angl e between t he
two vectors of any two spectra, the Spectral Contrast angle, quantifies the magnitude of
the shape difference between the spectra. The Spectral Contrast angle is the difference
in direction between the spectral vectors of two spectra.
A Spectral Contrast angle can vary from 0° to 90°. A Spectral Contrast angle near 0°
indicates little shape difference between the compared spectra. Matching a spectrum to
itself produces a Spectral Contrast angle of exactly 0°. The maximum Spectral Contrast
angle, 90°, indicates that the two spectra do not overlap at any wavelength.
To illustrate the relationship between Spectral Contrast angle and spectral shape
differences, consider the pairs of spectra shown in Figure 5-3, Figure 5-4, and Figure 5-5.
Spectra with Different Shapes
In Figure 5-3, the absorbance spectra of two compounds, A and B, are distinctl y di fferent,
and therefore, have a large Spectral Contrast angle.
Page 67

Spectral Contrast Angles 45
5
Figure 5-3 Spectra with a Large Spectral Contrast Angle
Spectra with Similar Shapes
In Figure 5-4, the absorbance spectra of two compounds, A and B, are similar, and
therefore, have a small Spectral Contrast angle (3.0°).
Normalized Absorbance
Wavelength (nm)
Compound A
Compound B
Spectral Contrast Angle: 62.3°
Page 68

46 Spectral Contrast Theory
5
Figure 5-4 Spectra with a Small Spectral Contrast Angle
Differences Between Spectra of the Same Compound
Small but significa nt dif fe rence s between a bsor bance sp ectra can occur because of facto rs
other than those due to the absorbance properties of different compounds. For example,
multiple spectra of the same compound may exhibit slight differences because of det ect or
noise, photometri c error, high sample concentration, or variations in solvent conditions.
The spectra in F igure 5-5, for example, show how inst rument n ois e can a f fect the sha pe o f
an absorbance spectrum of one compound. This effect is most likely to occur at low
concentratio ns wher e the signa l-to -no ise r atio is l ow. Note that th e S pectra l Cont rast angle
between these absorbance spectra of the same compound is 3.4°.
Normalized Absorbance
Wavelength (nm)
Compound A
Compound B
Spectral Contrast Angle: 3.0°
Page 69
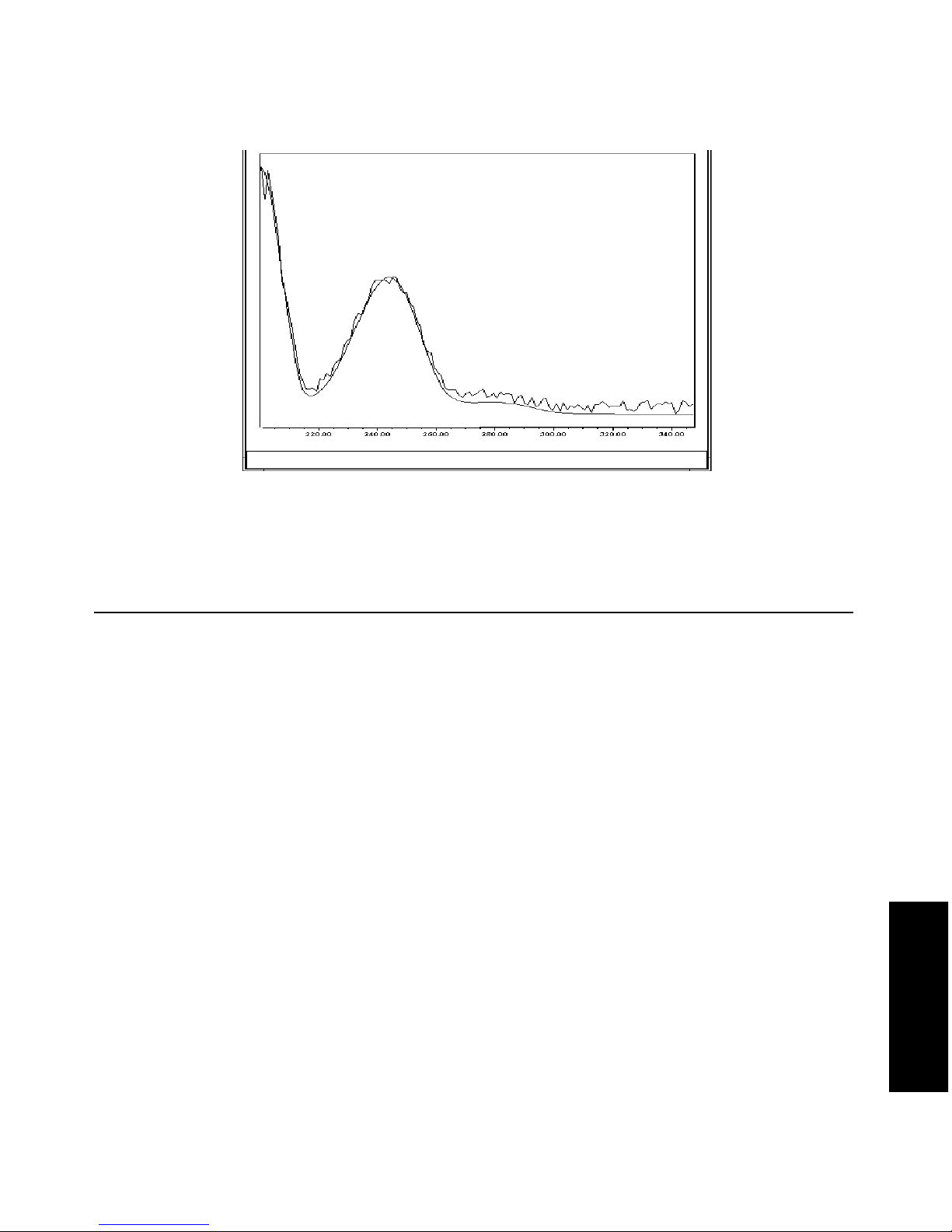
Undesirable Effects 47
5
Figure 5-5 Absorbance Spectra of a Compound at Two Concentrations
5.4 Undesirable Effects
Shape differences between absorbance spectra can be caused by one or more of the
following undesirable effects:
• Detector noise
• Photometric error caused by high sample concentration
• Variation in solvent co mposition
These sources of spectral variation can cause chemically pure, baseline-resolved peaks to
exhibit a sma ll leve l of s pectra l in homogenei ty. You can assess the signi fica nce of s pectr al
inhomogeneity by comparing a Spectral Contrast angle to a Threshold angle
(Section 5.4.4).
5.4.1 Detector Noise
Statistical and thermal variations add electrical noise to the absorbance measurements
made by the 2996 Detector. The noise manifests itself as fluctuations in the baseline,
known as baseline noise. The magnitude of any absorbance differences caused by
statistical an d thermal varia tions can be pre dicted from the i nstrument nois e in the base line
region of a chromatogram.
Normalized Absorbance
Wavelength (nm)
Spectral Contrast Angle: 3.4°
Normalized Spectra of a Compound at Different
Concentrations
Page 70

48 Spectral Contrast Theory
5
5.4.2 Photometric Error
At high absorbances (generally greater than 1 AU), a combination of effects can produce
slight departures (about 1%) from Beer’s Law due to photometric error. Although
photometric errors at thi s le vel may have a neg li gib le effect on quantitation, they can be a
significant sour ce of spe ctr al inh omogen eity. To minimize the effects of pho tometr ic error
for all Spectral Contrast operations, the maximum spectral absorbance of a compound
should be less than 1 AU. Keep in mind that the absorbance of the mobile phase reduces
the working linear dynamic range by the amount of mobile phase absorbance at each
wavelength. For examples of mobile phase absorbance, see Appendix C, Mobile Phase
Absorbance.
Note: For more information about the effects of the photometric error curve, refer to
Principles of Instrumental Analysis, third edition, by Douglas A. Skoog, Saunders College
Publishing, 1985, pp 168–172.
5.4.3 Solvent Changes
As long as solvent concentration and composition do not change (isocratic operation), the
background absorba nce, if any, by the solvent remains con stant. A change, however, in
solvent pH or composition, such as occurs in gradient operation, can affect the intrinsic
spectral shape of a compound, as shown in Figure 5-6.
5.4.4 Threshold Angle
In addition to com puting Spectral Contrast angles, the Spectral Contrast technique also
computes a Threshold angle. The Threshold angle is the maximum Spectral Contras t angle
between spectra that can be attributed to nonideal phenomena.
Comparison of a Spectr al Contras t angle to its Thr eshold angle can assi st in dete rmining if
the shape difference between spectra is genuine, that is, generated by mixtures that are
dissimilar. In general, a Spectral Contrast angle le ss than its Thres hold angle indicat es that
shape differences can be attributed to nonideal phenomena alone, and that there is no
evidence for genuine differences between the spectra. A Spectral Contrast angle greater
than its Thresh old angle indi cates that the sha pe differences are due to ge nuine dif fer ences
between the spectra. When automating the spectra contrast comparison, the maximum
absorbance of the spectra must not exceed 1 AU.
Page 71

Absorbance
Effect of pH
pH 6.9
pH 5.1
pH 3.1
Wavelength (nm)
Effect of Concentration
Absorbance
Note position of Maxima can be shifted.
Figure 5-6 Effects of pH and Solvent Concentration
on the Absorbance Spectrum of p-Aminobenzoic Acid
Wavelength (nm)
5
Undesirable Effects 49
Page 72

5
50 Spectral Contrast Theory
Page 73

Detector Specifications 51
A
Appendix A
Detector Specifications
Table A-1 lists the 2996 PDA Detector specifications.
Table A-1 2996 Detector Specifications
Item Specification
Dimensions Width: 11.5 in. (29 cm)
Depth: 24 in. (61 cm)
Height: 8.5 in. (22 cm)
Weight 31.5 lbs (14.3 kg)
Wavelength range 190 to 800 nm
Wavelength accuracy ±1 nm
Linearity range
*
*Per ASTM 685-79
5% at 2.0 AU, propylparaben, at 256 nm
Spectral resolution 1.2 nm
Baseline noise ±1.5 × 10
–5
AU peak-to-peak, dry, at 254 nm
Drift 1 × 10
–3
AU/hour at 254 nm (after warmup)
∆T ≤ 1°C per hour
Flow cells
Standard
Semi-preparative
Variable path flow cell
Microbore
Inert
Autopurification
Pathlength (mm): Tubing (ID):
10 0.009 in.
3 0.040 in.
0.15 to 3 0.004 in.
3 0.005 in.
10 0.010 in.
0.5 0.009 in. (A Inlet)
0.020 in. (P Inlet)
0.040 in. (Common Outlet)
Page 74

A
52 Detector Specifications
Page 75

Spare Parts 53
B
Appendix B
Spare Parts
The spare parts listed in Table B-1 are recommended for customer installation. Damage
incurred by performing unauthorized work on your 2996 Detector may invalidate certain
warranties.
Table B-1 Spare Parts
Item Part Number
Flow cell, standard WAT057919
Flow cell, semi-preparative WAT057463
Flow cell, microbore WAT057462
Flow cell, inert WAT057461
Flow cell, Autopurification 289000612
Variable pathlength flow cell WAT057664
Gasket, flow cell (2) WAT057924
Belleville washer (2) WAT057925
Lens mount and lens (2) WAT057923
Semi-prep lens kit WAT057968
Deuterium lamp WAT052586 (PM Kit)
Fuse, fast 4A, 250 V (5 × 20 mm) WAT057337
Waters
®
Erbium Perchlorate Wavelength
Accuracy Solution
WAT042885
Waters Absorbance Detector Linearity
Solution
WAT042881
Page 76
B
54 Spare Parts
Page 77

Mobile Phase Absorbance 55
C
Appendix C
Mobile Phase Absorbance
This appendix lists the absorbances at several wavelengths for commonly used mobile
phases. Choose your mobile phase carefully to reduce baseline noise.
The best mobile phase for your application is one that is transparent at the chosen
detection wavelen gths. Suc h a mobile ph ase ensure s that any absorbanc e is due only to the
sample. Absorbance by the mobile phase also reduces the linear dynamic range of the
detector by the am ount of absorbance that is autozeroed out. Wavelength, pH, and
concentration of the mobile phase will affect its absorbance. Examples of several mobile
phases are provided in Table C-1.
Table C-1 Mobile Phase Absorbance Measured Against Air or Water
Absorbance at Specified Wavelength (nm)
200 205 210 215 220 230 240 250 260 280
Solvents
Acetonitrile 0.050.030.020.010.01<0.01————
Methanol (not
degassed)
2.06 1.00 0.53 0.37 0.24 0.11 0.05 0.02 <0.01 —
Methanol
(degassed)
1.91 0.76 0.35 0.21 0.15 0.06 0.02 <0.01 — —
Isopropanol 1.80 0.68 0.34 0.24 0.19 0.08 0.04 0.03 0.02 0.02
Unstablized
Tetrahydrofuran
(THF, fresh)
2.44 2.57 2.31 1.80 1.54 0.94 0.42 0.21 0.09 0.05
Unstablized
Tetrahydrofuran
(THF, old)
>2.5 >2.5 >2.5 >2.5 >2.5 >2.5 >2.5 >2.5 2.5 1.45
Page 78

Table C-1 Mobile Phase Absorbance Measured Against Air or Water (Continued)
Absorbance at Specified Wavelength (nm)
200 205 210 215 220 230 240 250 260 280
Acids and Bases
Acetic acid, 1% 2.61 2.63 2.61 2.43 2.17 0.87 0.14 0.01 <0.01 —
C
Hydrochloric
acid, 0.1%
Phosphoric acid,
0.1%
Trifluoroacetic
acid
Diammonium
phosphate,
50 mM
Triethylamine,
1%
Buffers and Salts
Ammonium
acetate, 10 mM
Ammonium
bicarbonate,
10 mM
0.110.02<0.01———————
<0.01—————————
1.20 0.78 0.54 0.34 0.22 0.06 <0.02 <0.01 — —
1.850.670.150.02<0.01—————
2.33 2.42 2.50 2.45 2.37 1.96 0.50 0.12 0.04 <0.01
1.88 0.94 0.53 0.29 0.15 0.02 <0.01 — — —
0.410.100.01<0.01——————
EDT A, disodium,
1 mM
HEPES, 10 mM,
pH 7.6
MES, 10 mM,
pH 6.0
56 Mobile Phase Absorbance
0.11 0.07 0.06 0.04 0.03 0.03 0.02 0.02 0.02 0.02
2.45 2.50 2.37 2.08 1.50 0.29 0.03 <0.01 — —
2.42 2.38 1.89 0.90 0.45 0.06 <0.01 — — —
Page 79

Table C-1 Mobile Phase Absorbance Measured Against Air or Water (Continued)
Absorbance at Specified Wavelength (nm)
200 205 210 215 220 230 240 250 260 280
Potassium
phosphate,
monobasic
(KH
10 mM
Potassium
phosphate,
dibasic,
(K
2
10 mM
Sodium acetate,
10 mM
Sodium chloride,
1 M
Sodium citrate,
10 mM
Sodium formate,
10 mM
2PO4
HPO4),
),
0.03<0.01————————
0.530.160.050.01<0.01—————
1.85 0.96 0.52 0.30 0.15 0.03 <0.01 — — —
2.001.670.400.10<0.01—————
C
2.48 2.84 2.31 2.02 1.49 0.54 0.12 0.03 0.02 0.01
1.00 0.73 0.53 0.33 0.20 0.03 <0.01 — — —
Sodium
phosphate,
100 mM, pH 6.8
Tris HCl, 20 mM,
pH 7.0
Tris HCl, 20 mM,
pH 8.0
1.99 0.75 0.19 0.06 0.02 0.01 0.01 0.01 0.01 <0.01
1.400.770.280.100.04<0.01————
1.801.901.110.430.13<0.01————
Mobile Phase Absorbance 57
Page 80

Table C-1 Mobile Phase Absorbance Measured Against Air or Water (Continued)
Absorbance at Specified Wavelength (nm)
200 205 210 215 220 230 240 250 260 280
Wat er s P IC® Reagents
PIC A, 1 vial/L 0.67 0.29 0.13 0.05 0.03 0.02 0.02 0.02 0.02 <0.01
PIC B6, 1 vial/L 2.46 2.50 2.42 2.25 1.83 0.63 0.07 <0.01 — —
C
PIC B6, low UV,
1 vial/L
PIC D4, 1 vial/L 0.03 0.03 0.03 0.03 0.02 0.02 0.02 0.02 0.02 0.01
Detergents
J 35, 1% 0.06 0.03 0.02 0.02 0.02 0.01 <0.01 — — —
BRI
CHAPS, 0.1% 2.40 2.32 1.48 0.80 0.40 0.08 0.04 0.02 0.02 0.01
SDS, 0.1% 0.020.01<0.01———————
®
Triton
X-100, 0.1%
Tween™
0.1%
20,
0.01<0.01————————
2.48 2.50 2.43 2.42 2.37 2.37 0.50 0.25 0.67 1.42
0.21 0.14 0.11 0.10 0.09 0.06 0.05 0.04 0.04 0.03
58 Mobile Phase Absorbance
Page 81

Index 59
I
N
D
E
X
A
Absorbance
maximum 48
mobile phase 55
photometric error 48
solvent change effects 49
Waters 2996 calculations 35, 37
Acquisition
Auto Exposure parameter 34
Exposure Time parameter 34
Analog output specifications 6, 7
Aperture width 31
Auto Exposure parameter 34
B
Beer’s law 36, 48
C
Calibration 18
Column, connecting 10
Compression fittings 10
Connections
column 10
events 8
fluidic 10
non-IEEE-488 6
rear panel 3
terminal strip 8
Contact closures 6
Contacting Waters Te chni ca l Service 15, 17
Conventions, documentation x x
D
Dark current 37
Data acquisition
Auto Exposure parameter 3 4
Exposure Time parameter 34
Derived vectors 43, 44
Diagnostics 17
Documentation convention s xx
E
Electrical connections 2
Events
connections 6, 8
electrical specifications 9
terminal strip connections 7
Exposure Time parameter 3 4
F
Fittings 10
Flow cell
cleaning 23
exploded view 23
flushing 20
maintenance 19
removing 20
Fluid
connecting lines 10
fittings 10
Fuses
IEC-rated 2
maintenance 27
replacement 27
Index
Page 82

60 Index
I
N
D
E
X
I
IEC-rated fuses 2
Inputs 6, 8, 9
Installation
electrical 2
fluidic 10
site selection 1
Instrument method
Auto Exposure parameter 34
Exposure Time parameter 34
L
Lamp
hardware theory 30
replacement 25, 26
M
Maintenance
flow cell 19
fuse 27
lamp 25
PDA detector 19–28
Match Angle, photometric error effe cts 48
Maximum absorbance 48
Millennium Chromatography Manager,
connections 3
Mobile phase
absorbances 55
wavelengths 55
N
Noise effects 47
Nonidealities 47
Non-IEEE-488 connections 6
O
Outputs 6, 8, 9
P
Parts, spare 53
Photodiode array 32
Photometric error 48
Power connections 2
Purity Angle, photometric error effects 4 8
R
Rear panel connections 3
Reference spectrum 37
S
Shutdown, procedure 13
Solvent A ngle, photometric error effects 48
Solvent changes 48
Spare parts 53
Specifications
analog output 6, 7
event inputs 9
event outputs 9
Waters 2996 51
Spectra
derived vectors 43, 44
spectral shape differences 47
vectors 42
Spectral Contrast
derived vectors 43, 44
spectral shape differences 47
theory 4 1–49
vectors 42
Spectral resolution 31
Page 83

Index 61
I
I
N
D
E
X
Spectrum match, spectral shape differences
47
Start up, procedure 11
T
Terminal strip
connections 7, 8
diagram 8
Threshold angle 47
Troubleshooting 15–18
Tubing, cutting 10
U
Undesirable effects, shape differences 47
V
Vectors
derived from multiple wavelengths 44
derived from two wavelengths 43
spectra, representing 42
spectral contrast 4 2
W
Waters 2996
absorbance calculations 35, 37
aperture width 31
dark current 37
detector optics, overview 29–31
hardware theory 29–39
photodiode array overview 32
reference spectrum 37
spare parts 53
specifications 51
spectral resolution 31
Waters Technical Ser vi ce, contacting 15, 17
Wavelength
accuracy 18
derived vectors 43, 44
mobile phase absorbances 55
Page 84

I
N
D
E
X
62 Index
 Loading...
Loading...