Wasp Bar Code WWS500 User Manual

Barcode Scanning Made Easy
WWS500 Programming Guide

Table of Contents
Chapter 1. Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2
Chapter 2. Barcode Symbologies . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3
Chapter 3. Quick Start . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .4
Chapter 4. WWS500 Setup & Configuration . . . . . . . .6-28
1. Setup & Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .6
2. Factory Default & Autosense Stand Mode . .7
3. Beep and Delay . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .8-9
4. Upper/Lower Case . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .10
5. Keyboard Language . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .11
6. Preamble/Postamble Configuration . . . . . .12
7. Terminator/Code ID . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .13
Enable/Disable Barcode Symbologies
8.
9. Barcode Symbology Settings . . . . . . . .16-28
Code 39 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .16
Interleaved 2 of 5 and Code 93 . . . . . . . . .17
Code 128 and UCC/EAN 128 . . . . . . . . . . .18
MSI/Plessey . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .19
Codabar . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .20
UPC-A . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .21
UPC-A Supplemental / UPC-A to EAN-13 .22
UPC-E . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .23
UPC-E Supplemental . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .24
EAN-8 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .25
EAN-8 Supplemental . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .26
EAN-13 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .27
EAN-13 Supplemental . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .28
Chapter 5. Bluetooth Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .29
. . .14-15
Appendix A Barcode Test Symbols . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .30-32
Appendix B ASCII Table . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .33-36
Appendix C Codes for PC . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .37
Appendix D Technical Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .38
Warranty . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .39
FAQ / Product Support . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .40

Chapter 1
Introduction
Barcoding is the most common Automated Data Collection (ADC)
technology providing timely, error-free information that can be used to
increase productivity, accuracy, and efficiency in the workplace. Virtually
every type of industry is using bar codes to replace keyboard data entry.
Studies have shown that a proficient data entry operator will make one
error for every 300 characters that are manually entered. The error rate
using barcodes is almost negligible and can be error-free using barcode
symbologies with the check digit enabled.
The Wasp Charged Coupled Device (CCD) technology is a technique
whereby a barcode is photographed, digitized, and electronically sampled
by built-in photodetectors. The detectors process the measurement of
every bar and space using the number of adjacent photodetectors which
contrast a black mark and a white space. The Wasp WWS500 Freedom
Scanner is extremely rugged since it has no moving parts.
Of all the hand held barcode scanning devices on the market, the CCD
reader is the easiest to use and most cost effective for the typical business
user. The Wasp WWS500 Freedom Scanner is an extended distance
scanner with a depth of reading of up to one foot depending on the mil
size of the barcode. To activate the scanner, the user simply points the
scanning aperture towards the barcode, pulls the trigger, and aims the red
LED beam across the barcode.
2

Chapter 2
Barcode Symbologies
Barcodes are symbols consisting of a series of bars and spaces which can
be applied to packages, cartons, bottles, and other commercial products.
The bars and spaces in each symbol are grouped in such a way to
represent a specific ASCII character or function. The interpretation of
these groups is based on a particular set of rules called symbologies.
Various symbologies have been developed for particular applications.
Some examples are shipping and receiving, manufacturing, retail,
healthcare, transportation, document processing and tracking, and
libraries.
The resolution of a barcode is dependent on the narrowest element of a
barcode (X dimension), and can vary from high density (nominally less
than 0.009 in./0.23 mm), medium density (between 0.009 in./0.23 mm and
0.020 in./0.50 mm), and low density (greater than 0.020 in./0.50 mm).
Medium and low densities are the most common since these are the
easiest to read (scan) with nearly all scanning devices. The Wasp
WWS500 Freedom Scanner can read barcodes with X-dimensions as low
as 5 mils (0.005 in/0.13mm).
The Wasp WWS500 Freedom Scanner can read the most popular barcode
symbologies including Code 39, Code 93, Code 128, Interleaved 2 of 5,
UPC-A, UPC-E, EAN/JAN-8, EAN/JAN-13, Codabar, and MSI/Plessey.
Please see test chart on pages 28-30.
3

Chapter 3
Quick Start
1. Unpack
Open the box and remove all the pieces from their protective packaging.
2. Charging the WWS500
You must charge the scanner for 4 hours before first using it. To charge
the scanner plug the power supply in to the bottom of the scanner.
3. Setting up the Bluetooth Adaptor
If you already have Bluetooth setup on your PC or device, please
continue to the next step.
To setup Bluetooth on your PC you will need to insert the Bluetooth
adapter into an available USB port. Windows will detect the adapter and
install the required Microsoft Bluetooth software. If Windows does not
detect the Bluetooth adapter, please remove the adapter and insert the CD
with the adapter’s Bluetooth software on it. Follow the instruction on the
CD for installing the Bluetooth software.
4. Connecting the scanner to a Bluetooth device.
The scanner will connect to most Bluetooth devices that support HID
connection.
You will need to open your Bluetooth software and search for Bluetooth
devices. The Bluetooth software can be found by clicking the Bluetooth
symbol on the start bar near the computer time. If the Bluetooth symbol is
not found, there could be a problem with the Bluetooth adapter installation.
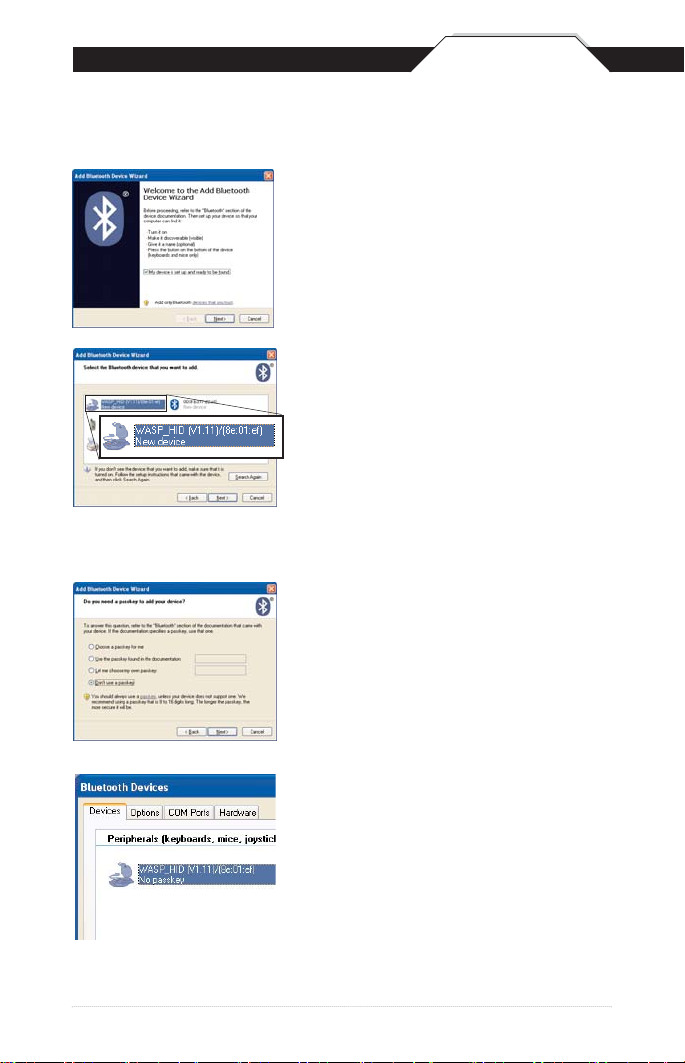
Once you have the Bluetooth software open
you will need to scan the Set Connection
barcode (right). This will make the scanner ready
to be detected by the Bluetooth software.
Set Connection
4
Chapter 3
The following screens are Microsoft’s standard Bluetooth wizard.
*Most Bluetooth wizards will have similar steps.
Check the “My device is setup and
ready to be found.” and click Next.
The scanner will show up in the list of
Bluetooth devices found. Select the
WASP_HID and click Next.
* If WASP_HID does not show up in the
available devices please check the following.
- Make sure the scanner is on by pressing
the trigger.
- If you are using a pre-installed Bluetooth
adapter, make sure the adapter supports HID.
The next step will ask you to setup a passkey
for the device. By default the scanner will not
have a passkey set. Please select “Don’t use
a passkey” and click Next.
The last screen of the wizard will be complete
the wizard. Just click Finish to complete.
Once the wizard is complete the scanner will
show up as a WASP_HID Device. Click OK to
close the screen. You are now ready to use
the WWS500.
5

Chapter 4
Setup & Configuration
In order to configure Wasp WWS500 Freedom Scanner, you must
familiarize yourself with the setup procedures on the following pages. The
default settings of the scanners are identified on each page and clearly
marked using an asterisk (*).
preprogrammed for the most common barcode configurations.
Use the setup & configuration barcodes only to customize the
WWS500 Freedom Scanner settings. If you need to configure the
Scanner, the default settings will be overwritten. All the programmed
settings are stored permanently in non-volatile memory.
In order to configure Wasp WWS500 Freedom Scanner,
two basic steps need to be followed:
(1) Locate the group that contains the options to be changed.
(2) Scan the barcode representing the option to be changed.
The scanner will sound two beeps.
To change Minimum/Maximum Length:
The default settings have been
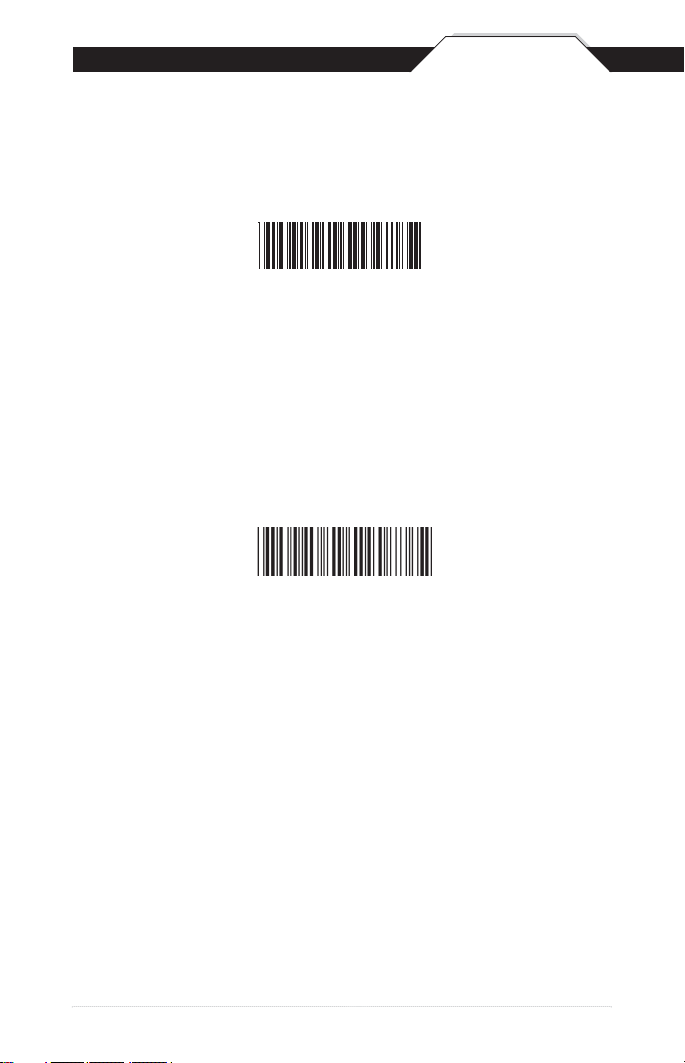
(1) Scan the Minimum or Maximum Length barcode on page 15.
(2) Scan a 2 digit value from the ASCII table on pages 31-34
(3) Scan the Minimum or Maximum Length barcode again.
Example: To have a minimum length barcode of 1, you must scan a
0 then 1, then scan the minimum barcode again. To have a maximum
length barcode of 10, you must scan a 1 then 0, then scan the
maximum barcode again.
6
FACTORY DEFAULT & KEYBOARD CONNECTION
Chapter 4
Factory Default
Use the Factory Default barcode to reset the scanner to the Default settings.
Factory Default
Autosense Stand Mode
Scan this Autosense Stand Mode bar code to enable the hands-free autosense
feature of the WWS500 Freedom Scanner. If you desire to turn this mode “off,”
please scan the default bar code above.
Autosense Flash Mode Enable
Note: Enabling this option will significantly increase the WWS500
Freedom Scanners battery consumption.
7

Chapter 4
The 'Beep and Delay' configuration supports the general control options for the
Wasp WWS500 Freedom Scanner. These options include the volume,
intercharacter delay, and interblock delay.
Interblock delay is the minimum time interval between two adjacent scans. If the
processing speed of your host device is slower than your scanning speed, a longer
interblock delay may ensure the data integrity.
Intercharacter delay is the time period that the scanner will wait before transmitting
the next character. If data sent by the scanner has incorrect or missing characters,
a longer intercharacter delay may solve the problem. The intercharacter delay
should be changed only if the transfer rate cannot be maintained between the
scanner and the keyboard buffer of the computer.
Note: The default for the intercharacter delay is set to '140us' and is the most
common configuration; however, your PC may be different. When you scan a bar
code, if some stray or scrambled characters appear, increase the intercharacter
delay to slow down the transfer rate.
BEEP AND DELAY
Beep Settings
Beep Off
Beep Medium *
Beep High to Low
Beep Hi
Beep Low to High
Beep Low
*Default
8

BEEP AND DELAY
Chapter 4
Interblock Delay Intercharacter Delay
0ms *
10ms
50ms
100ms
200ms
140us *
500us
1ms
4ms
16ms
500ms
*Default
9

Chapter 4
• Caps Lock Auto (For PC XT/AT only):
In Auto mode, the scanner will keep track of the Caps Lock
status automatically. For some PCs, the scanning performance
may be compromised because of the auto tracing. If the
scanning performance is poor (or cannot scan) or the scanner
cannot output the upper/lower case characters correctly, try to
select one of the next two choices instead of auto tracing.
• Caps Lock Off:
When the keyboard is in the unshifted state
(Caps Lock is not pressed), select “Lower Case.”
• Caps Lock On:
When the keyboard is in the shifted state (Caps Lock is on),
select “Upper Case.”
UPPER/LOWER CASE
Caps Lock On
Caps Lock Off *
Caps Lock Auto
10
*Default

KEYBOARD LANGUAGE
The ‘Keyboard Language’ setting controls the key codes for your
keyboard’s language.
U.S. *
German
French
Chapter 4
Spanish
Italian
11
*Default

Chapter 4
The ‘Preamble/Postamble’ configuration is used to add a prefix or suffix
set of characters to the barcode value. Up to 8 characters may be added
for each option separately. Preamble and postamble characters can
function concurrently, but need to be configured separately.
To add preamble or postamble characters, follow the steps below:
1) Scan the ‘Clear Pre/Postamble’ barcode on this page.
2) Scan the ‘Preamble’ or ‘Postamble’ barcode.
3) Use Appendix B on pages 32-35 to locate the characters you want to
add as preamble or postamble characters. Make sure that you scan
the barcode associated with each letter before preceding to the next
character. For example, to add the letter “A,” scan the barcode
corresponding to the letter “A” on page 34. The letter “A” will always
appear in your data as prefix or suffix to the barcode value.
4) Scan the corresponding 'Pre/Postamble' barcode on this page to exit
this setting.
PREAMBLE/POSTAMBLE CONFIGURATION
Clear Pre/Postamble
Preamble
Postamble
12
 Loading...
Loading...