
EASY- STOP™ TRAILER
ABS: 2S/1M (BASIC AND
STANDARD), 2S/2M, 4S/2M
AND 4S/3M SYSTEMS
MAINTENANCE MANUAL

Service Notes
WARNING
CAUTION
NOTE
TORQUE
Important Information
This manual contains maintenance procedures for WABCO's Easy-StopTM Trailer Anti-Lock Braking System
(ABS). The information contained in this manual was current at time of publication and is subject to change
without notice or liability.
You must follow company procedures and understand all procedures and instructions before you begin to
service or repair a unit. Some procedures require the use of special tools for safe and correct service.
Failure to use special tools when required can cause serious personal injury to service personnel, as well as
damage equipment and components.
WABCO uses the following notations to warn the user of possible safety issues and to provide information
that will prevent damage to equipment and components.
A WARNING indicates that you must follow
a procedure exactly. Otherwise, serious
personal injury can occur.
A CAUTION indicates that you must follow
a procedure exactly. Otherwise, damage to
equipment or components can occur. Serious
personal injury can also result, in addition to
damaged or malfunctioning equipment
or components.
Also Available from WABCO
ABS Tips
앫 Driver Tips (SP-93161)
앫 How to Brake with ABS audio cassette
(SP-94126)
앫 Driver Tips for Trailer ABS Warning Lamps
(TP-97132)
A NOTE indicates an operation, procedure or
instruction that is important for proper service.
A NOTE can also supply information that can
help to make service quicker and easier.
This symbol indicates that you must tighten
fasteners to a specific torque value.
Copyright 7-18 WABCO

Table of Contents
Asbestos and Non-Asbestos Fiber Warnings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ii
Section 1: Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1
Section 2: System Components . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3
Section 3: ABS Questions and Answers
The Electronic Control Unit (ECU) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
The ABS Warning Lamp . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
Types of Faults . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Section 4: System Configurations
2S/1M Trailer ABS Configuration Installation Diagrams . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .11
2S/2M Trailer ABS Configuration Installation Diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .13
4S/2M Trailer ABS Configuration Installation Diagrams . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .14
4S/3M Trailer ABS Configuration Installation Diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .17
Power Cable Wiring Diagrams . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .18
Section 5: Diagnostics
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
Blink Code Diagnostics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .21
Diagnostic Tools For ECUs with External Diagnostic Connectors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .23
Normal Mode Diagnostics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .23
Repair Existing Faults . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
Section 6: Component Replacement
Wheel Speed Sensor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .27
ABS Relay Valve . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .28
The ECU/Valve Assembly . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .28
How to Install the Blink Code Diagnostic Tool into the SAE J1587 Diagnostic Connector . . . . . . . .30
Section 7: Sensor Adjustment & Component Testing
How to Test Wheel Speed Sensors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .31
Sensor Test Procedure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .31
Sensor Output Voltage Test . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
Check ABS Functions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .31
ABS External Modulator Valve . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
Final Test Before Returning a Trailer to Service:
For ECU/Valve Assembly Part Number 472 500 011 0
(without external diagnostic connector) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .32
For ECU/Valve Assembly Part Numbers 472 500 012 0 and
S 472 500 013 0 (Units with External Diagnostic Connector) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
Trailer Identification . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .36
Section 8: Appendixes
Appendix A: Expert Mode Diagnostics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
Appendix B: Reconfigure Mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
Appendix C: Warning Lamp Diagnostics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
i

ASBESTOS FIBER WARNING
The following procedures for servicing brakes are recommended to reduce
NON-ASBESTOS FIBER WARNING
exposure to asbestos fiber dust, a cancer and lung disease hazard. Material
Safety Data Sheets are available from WABCO.
Hazard Summary
Because some brake linings contain asbestos, workers who service brakes must understand
the potential hazards of asbestos and precautions for reducing risks. Exposure to airborne
asbestos dust can cause serious and possibly fatal diseases, including asbestosis (a chronic
lung disease) and cancer, principally lung cancer and mesothelioma (a cancer of the lining of
the chest or abdominal cavities). Some studies show that the risk of lung cancer among
persons who smoke and who are exposed to asbestos is much greater than the risk for
non-smokers. Symptoms of these diseases may not become apparent for 15, 20 or more years
after the first exposure to asbestos.
Accordingly, workers must use caution to avoid creating and breathing dust when servicing
brakes. Specific recommended work practices for reducing exposure to asbestos dust
follow. Consult your employer for more details.
Recommended Work Practices
1. Separate Work Areas. Whenever feasible, service brakes in a separate area away
from other operations to reduce risks to unprotected persons. OSHA has set a
maximum allowable level of exposure for asbestos of 0.1 f/cc as an 8-hour
time-weighted average and 1.0 f/cc averaged over a 30-minute period. Scientists
disagree, however, to what extent adherence to the maximum allowable exposure
levels will eliminate the risk of disease that can result from inhaling asbestos dust.
OSHA requires that the following sign be posted at the entrance to areas where
exposures exceed either of the maximum allowable levels:
DANGER: ASBESTOS
CANCER AND LUNG DISEASE HAZARD
AUTHORIZED PERSONNEL ONLY
RESPIRATORS AND PROTECTIVE CLOTHING
ARE REQUIRED IN THIS AREA
2. Respiratory Protection. Wear a respirator equipped with a high-efficiency (HEPA)
filter approved by NIOSH or MSHA for use with asbestos at all times when servicing
brakes, beginning with the removal of the wheels.
3. Procedures for Servicing Brakes.
a. Enclose the brake assembly within a negative pressure enclosure. The
enclosure should be equipped with a HEPA vacuum and worker arm sleeves.
With the enclosure in place, use the HEPA vacuum to loosen and vacuum
residue from the brake parts.
b. As an alternative procedure, use a catch basin with water and a biodegradable,
non-phosphate, water-based detergent to wash the brake drum or rotor and
other brake parts. The solution should be applied with low pressure to prevent
dust from becoming airborne. Allow the solution to flow between the brake
drum and the brake support or the brake rotor and caliper. The wheel hub and
brake assembly components should be thoroughly wetted to suppress dust
before the brake shoes or brake pads are removed. Wipe the brake parts clean
with a cloth.
c. If an enclosed vacuum system or brake washing equipment is not available,
employers may adopt their own written procedures for servicing brakes,
provided that the exposure levels associated with the employer's procedures
do not exceed the levels associated with the enclosed vacuum system or brake
washing equipment. Consult OSHA regulations for more details.
d. Wear a respirator equipped with a HEPA filter approved by NIOSH or MSHA for
use with asbestos when grinding or machining brake linings. In addition, do
such work in an area with a local exhaust ventilation system equipped with a
HEPA filter.
e. NEVER use compressed air by itself, dry brushing, or a vacuum not equipped
with a HEPA filter when cleaning brake parts or assemblies. NEVER use
carcinogenic solvents, flammable solvents, or solvents that can damage brake
components as wetting agents.
4. Cleaning Work Areas. Clean work areas with a vacuum equipped with a HEPA filter
or by wet wiping. NEVER use compressed air or dry sweeping to clean work areas.
When you empty vacuum cleaners and handle used rags, wear a respirator equipped
with a HEPA filter approved by NIOSH or MSHA for use with asbestos. When you
replace a HEPA filter, wet the filter with a fine mist of water and dispose of the used
filter with care.
5. Worker Clean-Up. After servicing brakes, wash your hands before you eat, drink or
smoke. Shower after work. Do not wear work clothes home. Use a vacuum equipped
with a HEPA filter to vacuum work clothes after they are worn. Launder them
separately. Do not shake or use compressed air to remove dust from work clothes.
6. Waste Disposal. Dispose of discarded linings, used rags, cloths and HEPA filters
with care, such as in sealed plastic bags. Consult applicable EPA, state and local
regulations on waste disposal.
Regulatory Guidance
References to OSHA, NIOSH, MSHA, and EPA, which are regulatory agencies in the United
States, are made to provide further guidance to employers and workers employed within the
United States. Employers and workers employed outside of the United States should consult
the regulations that apply to them for further guidance.
The following procedures for servicing brakes are recommended to reduce
exposure to non-asbestos fiber dust, a cancer and lung disease hazard. Material
Safety Data Sheets are available from WABCO.
Hazard Summary
Most recently manufactured brake linings do not contain asbestos fibers. These brake linings
may contain one or more of a variety of ingredients, including glass fibers, mineral wool,
aramid fibers, ceramic fibers and silica that can present health risks if inhaled. Scientists
disagree on the extent of the risks from exposure to these substances. Nonetheless,
exposure to silica dust can cause silicosis, a non-cancerous lung disease. Silicosis gradually
reduces lung capacity and efficiency and can result in serious breathing difficulty. Some
medical experts believe other types of non-asbestos fibers, when inhaled, can cause similar
diseases of the lung. In addition, silica dust and ceramic fiber dust are known to the State of
California to cause lung cancer. U.S. and international agencies have also determined that
dust from mineral wool, ceramic fibers and silica are potential causes of cancer.
Accordingly, workers must use caution to avoid creating and breathing dust when servicing
brakes. Specific recommended work practices for reducing exposure to non-asbestos dust
follow. Consult your employer for more details.
Recommended Work Practices
1. Separate Work Areas. Whenever feasible, service brakes in a separate area away
from other operations to reduce risks to unprotected persons.
2. Respiratory Protection. OSHA has set a maximum allowable level of exposure for
silica of 0.1 mg/m
asbestos brake linings recommend that exposures to other ingredients found in nonasbestos brake linings be kept below 1.0 f/cc as an 8-hour time-weighted average.
Scientists disagree, however, to what extent adherence to these maximum allowable
exposure levels will eliminate the risk of disease that can result from inhaling nonasbestos dust.
Therefore, wear respiratory protection at all times during brake servicing, beginning
with the removal of the wheels. Wear a respirator equipped with a high-efficiency
(HEPA) filter approved by NIOSH or MSHA, if the exposure levels may exceed OSHA or
manufacturers' recommended maximum levels. Even when exposures are expected to
be within the maximum allowable levels, wearing such a respirator at all times during
brake servicing will help minimize exposure.
3. Procedures for Servicing Brakes.
a. Enclose the brake assembly within a negative pressure enclosure. The
b. As an alternative procedure, use a catch basin with water and a biodegradable,
c. If an enclosed vacuum system or brake washing equipment is not available,
d. Wear a respirator equipped with a HEPA filter approved by NIOSH or MSHA
e. NEVER use compressed air by itself, dry brushing, or a vacuum not equipped
4. Cleaning Work Areas. Clean work areas with a vacuum equipped with a HEPA filter or
by wet wipi ng. NEVER use compressed air or dry sweeping to clean work areas. When
you empty vacuum cleaners and handle used rags, wear a respirator equipped with a
HEPA filter approved by NIOSH or MSHA, if the exposure levels may exceed OSHA or
manufacturers' recommended maximum levels. When you replace a HEPA filter, wet
the filter with a fine mist of water and dispose of the used filter
with care.
5. Worker Clean-Up. After servicing brakes, wash your hands before you eat, drink or
smoke. Shower after work. Do not wear work clothes home. Use a vacuum equipped
with a HEPA filter to vacuum work clothes after they are worn. Launder them
separately. Do not shake or use compressed air to remove dust from work clothes.
6. Waste Disposal. Dispose of discarded linings, used rags, cloths and HEPA filters with
care, such as in sealed plastic bags. Consult applicable EPA, state and local
regulations on waste disposal.
Regulatory Guidance
References to OSHA, NIOSH, MSHA, and EPA, which are regulatory agencies in the United
States, are made to provide further guidance to employers and workers employed within the
United States. Employers and workers employed outside of the United States should consult
the regulations that apply to them for further guidance.
3
as an 8-hour time-weighted average. Some manufacturers of non-
enclosure should be equipped with a HEPA vacuum and worker arm sleeves.
With the enclosure in place, use the HEPA vacuum to loosen and vacuum
residue from the brake parts.
non-phosphate, water-based detergent to wash the brake drum or rotor and
other brake parts. The solution should be applied with low pressure to prevent
dust from becoming airborne. Allow the solution to flow between the brake
drum and the brake support or the brake rotor and caliper. The wheel hub and
brake assembly components should be thoroughly wetted to suppress dust
before the brake shoes or brake pads are removed. Wipe the brake parts clean
with a cloth.
carefully clean the brake parts in the open air. Wet the parts with a solution
applied with a pump-spray bottle that creates a fine mist. Use a solution
containing water, and, if available, a biodegradable, non-phosphate,
water-based detergent. The wheel hub and brake assembly components should
be thoroughly wetted to suppress dust before the brake shoes or brake pads
are removed. Wipe the brake parts clean with a cloth.
when grinding or machining brake linings. In addition, do such work in an area
with a local exhaust ventilation system equipped with a HEPA filter.
with a HEPA filter when cleaning brake parts or assemblies. NEVER use
carcinogenic solvents, flammable solvents, or solvents that can damage brake
components as wetting agents.
ii

Section 1Introduction
1003290d
SERIAL NUMBER
EASY-STOP™ TRAILER ABS ECU/VALVE ASSEMBLY
DATE CODE
FIRST TWO DIGITS = BUILD WEEK
LAST TWO DIGITS = BUILD YEAR
PART NUMBER
Overview
This manual describes how WABCO's Easy-Stop™
Trailer Anti-Lock Braking System (ABS) works;
answers some basic ABS questions; outlines
procedures on how to adjust, test, remove and
install ABS components, as well as how to test for
faults in the system by using Blink Code
Diagnostics; and illustrates ABS components and
wiring and plumbing installation diagrams. This
manual does not contain Original Equipment
Manufacturer (OEM) installation instructions. New
installations require the following documentation:
앫 Easy-Stop™ Basic (2S/1M without external
diagnostics): TP-97145
앫 Easy-Stop™ Standard (2S/1M, 2S/2M, 4S/2M
with external diagnostics): TP-97147
앫 Easy-Stop™ Standard (4S/3M with external
diagnostics): TP-97153
Section 1
Introduction
Figure 1.1
Scope of Blink Code
Diagnostics in This Manual
This manual contains blink code diagnostics
information and instructions for most of
the ECU/Valve Assemblies listed in Ta bl e A —
Scope of Blink Code Diagnostics.
The serial and part numbers are located on the
ECU/Valve Assembly. Refer to Figure 1.1 .
Table A — Scope of Blink Code Diagnostics
ECU/Valve Assembly Part
Number
472 500 001 0
(Serial Number 3080002745
and lower)
472 500 001 0
(Serial Number 3080002746
and higher)
472 500 011 0
(Serial Number Not
Applicable)
472 500 012 0
(Serial Number Not
Applicable)
472 500 013 0
(Serial Number Not
Applicable)
Blink Code
Diagnostics
Contact WABCO for
blink code
diagnostics
information.
See Section 5 and
Appendix A and B.
See Section 5 and
Appendix C.
See Section 5 and
Appendix A, B
and C.
See Section 5 and
Appendix A, B
and C.
Page 1

Section 1
1002071d
2
1
4
3
Introduction
Easy-Stop™ Trailer ABS Parts
Parts book PB-96133 lists WABCO Easy-Stop™
replacement parts. To obtain a copy, contact
WABCO North America Customer Care at
855-228-3203.
What Is WABCO’s Easy-Stop™
Trailer ABS?
WABCO’s Easy-Stop™ Trailer ABS is an electronic,
self-monitoring system that works
with standard air brakes. The major components
of the system are the Electronic Control Unit
(ECU)/Valve Assembly, ABS relay (modulator)
valve, tooth wheel and wheel speed sensor.
Refer to Figure 1.2 .
ECU Part Numbers 472 500 001 0, 472 500 012 0
and 472 500 013 0 have an external diagnostics
connector for use with a special diagnostic tool.
These models are also compatible with an MPSI
Pro-Link
cartridge. ECU/Valve Assembly 472 500 011 0 does
not have a diagnostic connector port. Diagnostic
procedures for all of these ECUs are detailed in
Section 5, "Diagnostics" of this manual.
Figure 1.2
®
9000 diagnostic tool and WABCO
The ABS configuration defines the number of
wheel speed sensors and ABS relay valves used in
a system. For example, a 2S/1M configuration
includes two wheel sensors and one ABS relay
valve. A 2S/2M configuration includes two wheel
sensors and two relay valves. A 4S/2M
configuration includes four wheel sensors and
two ABS relay valves.
How Trailer ABS Works
WABCO ABS is an electronic system that monitors
and controls wheel speed during braking. The
system works with standard air
brake systems.
ABS monitors wheel speeds at all times and
controls braking during wheel lock situations. The
system improves vehicle stability and control by
reducing wheel lock during braking.
The ECU receives and processes signals from the
wheel speed sensors. When the ECU detects a
wheel lockup, the unit activates the appropriate
modulator valve, and air pressure is controlled.
In the event of a malfunction in the system, the
ABS in the affected wheel(s) is disabled; that wheel
still has normal brakes. The other wheels keep the
ABS function.
An ABS warning lamp lets drivers know the status
of the system.
1 ECU/Valve Assembly
2 External ABS Relay Valve (not used in
1M configurations)
3 Tooth Wheel
4 Wheel Speed Sensor
Page 2

Section 2
1002072d
2S/1M BASIC
STANDARD
1002073c
1002074a
1002075a
1002076a
System Components
Section 2System Components
ECU/Valve Assembly
앫 12 volt
앫 Integrated ECU and ABS relay valve
앫 The 2S/1M Basic ECU/Valve Assembly does not
have an external diagnostics connector.
Figure 2.1
1 2S/1M Basic
2 Standard
Sensor with Molded Socket
앫 Measures the speed of a tooth wheel rotating
with the vehicle wheel.
앫 Produces an output voltage proportional to
wheel speed.
Figure 2.3
Sensor Spring Clip
앫 Holds the wheel speed sensor in close proximity
to the tooth wheel.
ABS External Valve
앫 Controls air pressure to the brake chambers
where it is plumbed.
앫 During ABS operation, the valve adjusts air
pressure to the brake chambers to control
braking and prevent wheel lock.
앫 Used in conjunction with ECU/Valve Assembly
for 2M or 3M systems.
Figure 2.2
Figure 2.4
Sensor Extension Cable
앫 Two-wire cable with molded-on connector.
앫 Connects the wheel speed sensor to the ECU.
Figure 2.5
Page 3

Section 2
1002077a
1002078b
BLUNT END
INDUSTRY
STANDARD
1002079a
1002080a
System Components
Connection Cable for ABS External Valves
앫 Three-wire cable with connector.
앫 Connects the ABS external valve to the ECU.
앫 “Y” cable for use with 4S/3M configurations
also available.
Figure 2.6
Power Cables
앫 Connects power to the ECU and provides a
connection for the warning lamp.
앫 Available with blunt-end four- or five-wire cable
or four- or five-wire industry standard harness
connector at one end.
앫 Molded connector on opposite end used to
attach cable to ECU.
Figure 2.7
Diagnostic Cable
앫 Provides for blink code diagnostics and
diagnostics using the MPSI Pro-Link
®
9000
diagnostic tool.
앫 Five-wire cable with over-molded connector to
ECU on one end and SAE J1587 diagnostic
connector over-molded on the other end.
Figure 2.8
Diagnostic Tool
앫 Sealed switch and lamp that connects to the
SAE J1587 diagnostic connector.
앫 Used to activate blink code diagnostics,
reconfigure the ECU and test the
ECU installation.
앫 Protective dust cap included.
앫 Designed to remain on the trailer at all times.
1 Blunt End
2 Industry Standard
Page 4
Figure 2.9

Section 2
1002081a
1002082a
1002083a
1002084a
1002085a
System Components
Diagnostic Cable Mounting Bracket
앫 Bracket used to mount the diagnostic cable
assembly to the trailer.
Figure 2.10
ECU/Valve Assembly Mounting Bracket
앫 Bracket used to remote mount the ECU/Valve
Assembly to the trailer frame.
Figure 2.11
Diagnostic Cable Assembly with Diagnostic Tool
앫 Diagnostic cable mounted to the bracket with a
diagnostic tool connected to the SAE J1587
diagnostic connector.
앫 Protective dust cap included.
Figure 2.13
Tooth Wheel
앫 A machined ring mounted to the
machined surface on the hub of each
ABS-monitored wheel.
Diagnostic Cable Assembly with Protective Cap
앫 Diagnostic cable mounted to the bracket
with a protective cap on the SAE J1587
diagnostic connector.
Figure 2.12
Figure 2.14
Page 5

Section 2
NOTE
1003296a
1002094a
System Components
Installation Hardware Kit
앫 Contains Schedule 80 NPT pipe nipple fittings
and Grade 8, 3/8-inch SAE bolts for proper
mounting of ABS components to the trailer
frame or reinforced air tanks.
Figure 2.15
Easy-Stop™ Trailer ABS Warning Label
앫 Provides information about the operation of the
ABS warning lamp and illustrates blink code
fault locations.
앫 Label is self-adhesive and is mounted on the
trailer near the ABS warning lamp.
앫 If there is no warning label on your trailer, let
your supervisor know. Labels are available from
WABCO. Ask for Part Number TP-95172.
MPSI Pro-Link
앫 Provides diagnostic and testing capability for
ABS components.
앫 Requires a cartridge (version 4.0 or higher)
designed for use with WABCO ABS.
The Pro-Link® 9000 diagnostic tool is not available
from WABCO. Contact Kent-Moore at
800-328-6657 to order.
Figure 2.16
®
9000 Diagnostic Tool
Page 6

Section 3ABS Qu estions and Answers
The Electronic Control
Unit (ECU)
Section 3
ABS Questions and Answers
The ABS Warning Lamp
What is the function of the warning lamp?
How do you activate the ECU?
In a constant-powered system, the ECU activates
and then begins a self-diagnostic check of the
system when you turn the ignition ON. In a
stoplight-powered system, the ECU activates when
you apply the brakes. All trailers manufactured on
or after March 1, 1998 will be equipped with ABS
that has constant power capability with stoplight
power as back-up.
What if the ECU finds a fault in an ABS component
during normal operation?
If the ECU senses a fault in the system (with an
ABS valve, for example), the ECU turns the trailer
ABS warning lamp on and returns the wheel
controlled by that valve to standard braking. Or, if
the ECU finds a fault with one wheel speed sensor
in a system that has four sensors on a tandem
axle, the ECU uses information from the other
sensor on the same side of the tandem to ensure
continuous ABS function. The ECU continues to
provide full ABS function to the wheels unaffected
by system faults. However, the ECU will turn the
trailer ABS warning lamp on to tell the driver a
fault has been detected in the system.
How does the ECU respond to a wheel
approaching lock-up?
The ECU directs the ABS relay valve to function as
a modulator valve and adjust air pressure to the
chambers up to five times a second. This pressure
adjustment allows a wheel (or wheels) to rotate
without locking.
The warning lamp enables a driver to monitor the
ABS at all times. Refer to the OEM operating
manual for the mounting location of the
warning lamp.
How does the warning lamp operate?
How the warning lamp operates depends on
whether the ABS is powered by stoplight or
constant power:
앫 If the trailer was manufactured prior to February
28, 1998, or was manufactured outside of the
United States, the ABS may be either stoplight
or constant powered.
앫 If the trailer was manufactured March 1, 1998 or
later — and was manufactured in the United
States — it will have constant power capability.
This is mandated by Federal Motor Vehicle
Safety Standard (FMVSS) 121.
Check your vehicle specification sheet to
determine the type of ABS power. Ta b le B —
Stoplight Power and Table C — Constant Power,
in this section, illustrate warning lamp operation
on stoplight and constant powered
ABS systems.
Table B — Stoplight Power
System Power Comes from Activating the Stoplight Circuit.
Brakes Fault in System Vehicle Speed Warning Lamp
Released N.A. N.A. OFF
Applied NO Less than 4 mph ON for 3 seconds, then goes OFF.
Applied NO Greater than 4 mph Flashes once, then stays OFF for
Applied YES N.A. ON
remainder of stop.
Page 7

Section 3
ABS Questions and Answers
Table C — Constant Power
System Is Powered When Ignition Is Switched ON.
Brakes Ignition Fault in System Vehicle Speed Warning Lamps (Trailer and Dash)
Released OFF N.A. N.A. OFF
Released ON NO Less than 4 mph ON for 3 seconds, then go OFF.
Released ON NO Greater than 4 mph OFF
Released ON YES N.A. ON
Applied OFF NO Less than 4 mph ON for 3 seconds, then go OFF.
Applied OFF NO Greater than 4 mph Flash once, then stay OFF for
remainder of stop.
Applied OFF YES N.A. ON
Applied ON NO Less than 4 mph ON for 3 seconds, then go OFF.
Applied ON NO Greater than 4 mph OFF
Applied ON YES N.A. ON
An ECU with part number 472 500 001 0
manufactured prior to September 1997 requires all
sensed wheels to detect a 4 mph signal to shut off
the ABS warning lamp. Do not confuse this with a
faulty ABS system. If the warning lamp stays on
when the brakes are applied to a moving vehicle,
service the ABS system.
Most trailers manufactured prior to February 1998
require that the brakes be applied to operate the
ABS warning lamp. If the warning lamp stays on
when the brakes are applied to a moving vehicle,
service the ABS system.
What does the trailer ABS warning lamp mean to
service personnel?
The trailer ABS warning lamp indicates the status
of the trailer ABS. If it comes ON and stays ON
when you apply the brakes to a moving vehicle,
there is an ABS malfunction. It is normal for the
lamp to come ON and go OFF to perform a bulb
check, but it should not stay ON when the vehicle
is moving above 4 mph. As with any safety system,
it is important not to ignore this warning. If the
warning lamp indicates a malfunction, the vehicle
can be operated to complete the trip, but it is
important to have it serviced as soon as possible
using the appropriate maintenance manual to
ensure proper braking performance and that the
benefits of ABS remain available to your drivers.
Typical ABS warning lamp mounting locations are
illustrated in Figure 3.1 .
Figure 3.1
1 Prior to March 1, 1998
2 On or after March 1, 1998
Typical ABS Warning Lamp Mounting Locations
For more information, contact WABCO North
America Customer Care at 855-228-3203.
Page 8

ABS Questions and Answers
NOTE
Can you continue to operate a vehicle when the
warning lamp indicates a fault?
Yes. When a fault exists in the ABS, standard
braking returns to the affected wheel, and the ABS
still controls other monitored wheels. This lets you
complete the trip. You should not ignore the
warning lamp and should have the vehicle
serviced as soon as possible after the lamp
comes ON and stays ON.
Types of Faults
What is a “fault” in the system?
A fault in the system is a problem that can exist in
the ABS or in the system’s components. Faults
can be either existing faults or intermittent
stored faults.
What is an existing fault?
An existing fault is a problem that exists currently
in the system. For example, a damaged sensor
cable is an existing fault that the ECU will detect
and store into memory until you identify the cause,
repair the cable and clear the fault from the ECU.
Section 3
What is an intermittent fault?
An intermittent fault is a problem that usually
occurs only under certain driving conditions. For
example, the ECU may detect a loose cable or wire
or receive an erratic signal from a wheel sensor.
Since intermittent faults can be unpredictable and
may only happen periodically, you can use
information stored in ECU memory to find and
correct the loose cable or wire.
Is an intermittent fault difficult to locate
and repair?
It can be, because you may not be able to easily
see the cause of the problem. WABCO
recommends that you write down intermittent
faults to help you isolate a fault that recurs over a
period of time.
Can the ECU store more than one fault
in memory?
Yes. And the ECU retains existing and intermittent
faults in memory even when you turn OFF the
power to the ECU.
For part number information, refer to PB-96133.
Copies are available from the WABCO North
America Customer Care at 855-228-3203.
Page 9

Notes
Page 10

Section 4
NOTE
1003292e
AIR TANK
ECU/VALVE
ASSEMBLY (YE)
YE1
YE2
A Service/Control Lines
B Sensor Cables
C Service to Brake Lines (Delivery Lines)
D Air Supply/Emergency Lines
AIR TANK
System Configurations
Section 4System Configurations
2S/1M Trailer ABS Configuration Without External Diagnostics
Capability Installation Diagram
Figure 4.1
A Service/Control Lines
B Sensor Cables
C Service to Brake Lines (Delivery Lines)
D Air Supply/Emergency Lines
1 ECU/Valve Assembly (YE)
2 Air Tanks
For direct tank-mounted installations, see “How to
Install the ECU/Valve Assembly,” in Section 6,
"Component Replacement".
Typical Application:
Sensors may be installed on either axle,
depending upon suspension and other
vehicle characteristics.
앫 Single-Axle Dolly
앫 Single- and Tandem-Axle Semi-Trailer
Page 11

Section 4
NOTE
1002086f
AIR TANK
ECU/VALVE
ASSEMBLY (YE)
A Service/Control Lines
B Sensor Cables
C Service to Brake Lines (Delivery Lines)
D Air Supply/Emergency Lines
AIR TANK
YE1
YE2
System Configurations
2S/1M Trailer ABS Configuration with External Diagnostics
Capability Installation Diagram
Figure 4.2
For direct tank-mounted installations, see “How to
Install the ECU/Valve Assembly” in Section 6,
"Component Replacement".
A Service/Control Lines
B Sensor Cables
C Service to Brake Lines (Delivery Lines)
D Air Supply/Emergency Lines
1 ECU/Valve Assembly (YE)
2 Air Tanks
Typical Application:
앫 Single-Axle Dolly
앫 Single- and Tandem-Axle Semi-Trailer
Page 12
Sensors may be installed on either axle,
depending upon suspension and other
vehicle characteristics.

System Configurations
NOTE
1002087e
BU1
AIR TANK
ECU/VALVE
ASSEMBLY (YE)
AIR TANK
YE1
A Service/Control Lines
B Sensor Cables
C Service to Brake Lines (Delivery Lines)
D Air Supply/Emergency Lines
EXTERNAL
VALVE (BU)
2S/2M Trailer ABS Configuration Installation Diagram
Figure 4.3
Section 4
For direct tank-mounted installations, see “How to
Install the ECU/Valve Assembly” in Section 6,
"Component Replacement".
A Service/Control Lines
B Sensor Cables
C Service to Brake Lines (Delivery Lines)
D Air Supply/Emergency Lines
1 ECU/Valve Assembly (YE)
2 Air Tanks
3 External Valve (BU)
Typical Application:
앫 Single- and Tandem-Axle Semi-Trailer
Sensors may be installed on either axle,
depending upon suspension and other
vehicle characteristics.
Page 13

Section 4
1002088e
YE1
YE2
EXTERNAL
VALVE (BU)
AIR TANK
BU1
BU2
AIR TANK
ECU/VALVE
ASSEMBLY (YE)
A Service/Control Lines
B Sensor Cables
C Service to Brake Lines (Delivery Lines)
D Air Supply/Emergency Lines
System Configurations
4S/2M Trailer ABS Configuration Installation Diagram
Figure 4.4
A Service/Control Lines
B Sensor Cables
C Service to Brake Lines (Delivery Lines)
D Air Supply/Emergency Lines
1 ECU/Valve Assembly (YE)
2 Air Tanks
3 External Valve (BU)
For direct tank-mounted installations, see “How to
Install the ECU/Valve Assembly” in Section 6,
"Component Replacement".
Typical Application:
앫 Tandem and Tri-Axle Semi-Trailer
Page 14

Section 4
1002089e
EXTERNAL
VALVE (BU)
AIR TANK
ECU/VALVE
ASSEMBLY (YE)
AIR TANK
A Service/Control Lines
B Sensor Cables
C Service to Brake Lines (Delivery Lines)
D Air Supply/Emergency Lines
BU2 BU1
YE2
YE1
LIFT AXLE
FIXED AXLE
LIFT AXLE
FIXED AXLE
System Configurations
4S/2M Trailer ABS Configuration Diagram for Lift Axle Applications
(Forward Lift Axle Installation Diagram)
Figure 4.5
A Service/Control Lines
B Sensor Cables
C Service to Brake Lines (Delivery Lines)
D Air Supply/Emergency Lines
1 ECU/Valve Assembly (YE)
2 External Valve (BU)
3 Air Tanks
4 Lift Axle
5 Fixed Axle
For direct tank-mounted installations, see “How to
Install the ECU/Valve Assembly” in Section 6,
"Component Replacement".
Typical Application:
앫 Tandem and Tri-Axle Semi-Trailer
Page 15

Section 4
1002090e
EXTERNAL
VALVE (BU)
AIR TANK
ECU/VALVE
ASSEMBLY (YE)
AIR TANK
FIXED AXLE
LIFT AXLE
FIXED AXLE
LIFT AXLE
BU1
BU2
YE1
YE2
A Service/Control Lines
B Sensor Cables
C Service to Brake Lines (Delivery Lines)
D Air Supply/Emergency Lines
System Configurations
4S/2M Trailer ABS Configuration Diagram for Lift Axle Applications
(Rear Lift Axle Installation Diagram)
Figure 4.6
For direct tank-mounted installations, see “How to
Install the ECU/Valve Assembly” in Section 6,
"Component Replacement".
Typical Application:
앫 Tandem and Tri-Axle Semi-Trailer
A Service/Control Lines
B Sensor Cables
C Service to Brake Lines (Delivery Lines)
D Air Supply/Emergency Lines
1 ECU/Valve Assembly (YE)
2 External Valve (BU)
3 Air Tanks
4 Fixed Axle
5 Lift Axle
Page 16

System Configurations
NOTE
1003293e
BU1
BU2
YE2
YE1
AIR TANK
ECU/VALVE
ASSEMBLY (YE)
AIR TANK
EXTERNAL
VALVE (BU)
EXTERNAL
VALVE (RED)
A Service/Control Lines
B Sensor Cables
C Service to Brake Lines (Delivery Lines)
D Air Supply/Emergency Lines
4S/3M Trailer ABS Configuration Installation Diagram
Figure 4.7
Section 4
A Service/Control Lines
B Sensor Cables
C Service to Brake Lines (Delivery Lines)
D Air Supply/Emergency Lines
1 ECU/Valve Assembly (YE)
2 External Valve (RED)
3 External Valve (BU)
4 Air Tanks
Typical Application:
앫 Tandem with Lift Axle
앫 Tri-Axle Semi-Trailer
앫 Semi-Trailer with Lift Axle
앫 Full Trailer (Drawbar Trailers)
Sensors may be installed on either axle,
depending upon suspension and other
vehicle characteristics.
Page 17

Section 4
1003302e
4 OR 5 WIRE SCHEMATIC
P/N 449 315 XX0 0 OR 894 60X XXX 0 (INDUSTRY STANDARD CABLE)
ECU INTERNAL GROUND (5 WIRE CABLE ONLY)
TRAILER ABS
INDICATOR LAMP
IN TRACTOR
7 WAY
POWER
SOURCE
WHITE AND YELLOW
WHITE
(GROUND)
BLUE
(CONSTANT POWER)
RED
(STOP LAMP)
GREEN AND WHITE
TRAILER ABS
INDICATOR LAMP
GROUND
Trailers Produced March 1, 1998 or Later
ECU POWER CONNECTOR
1003305d
CONSTANT POWER/STOPLIGHT POWER CIRCUIT
BLACK
YELLOW
BLUE
WHITE
BROWN
GREEN
RED
RED
GREEN
RED/WHITE
RED
WHITE
Connect to
Easy-Stop™.
SWITCHED 12 VOLTS DC
FROM TRACTOR
P/N 449 312 XX0 0
4 CONDUCTOR CABLE
Trailers produced prior to March 1, 1998.
Tractors produced during 1997 model
year and later have the blue wire of the
7-way (SAE J560) connector wired to
provide constant power to trailer ABS.
System Configurations
Power Cable Wiring Diagrams
Figure 4.8
Figure 4.9
Page 18

Power Cable Wiring Diagrams
1003303c
STOPLIGHT POWER CIRCUIT
WHITE
BLUE
BLACK
YELLOW
RED
BROWN
GREEN
RED
RED
GREEN
INDICATOR LAMP
WHITE
Connect to
Easy-Stop™.
P/N 894 604 19X 2
3 CONDUCTOR CABLE
Trailers produced prior to March 1998.
1003304c
WHITE
BLUE
BLACK
YELLOW
RED
GREEN
BROWN
WHITE
RED
RED/WHITE
RED
INDICATOR LAMP
GREEN
Connect to
Easy-Stop™.
STOPLIGHT POWER CIRCUIT
P/N 449 312 XX0 0
4 CONDUCTOR CABLE
Trailers produced prior to March 1998.
Figure 4.10
Section 4
System Configurations
Figure 4.11
Page 19

Notes
Page 20

Section 5 Diag nosti cs
NOTE
WARNINGS
Section 5
Diagnostics
To prevent serious eye injury, always wear
safe eye protection when you perform vehicle
maintenance or service.
The ABS is an electrical system. When you
work on the ABS, take the same precautions that
you must take with any electrical system to avoid
serious personal injury. As with any electrical
system, the danger of electrical shock or sparks
exists that can ignite flammable substances. You
must always disconnect the battery ground cable
before working on the electrical system.
Introduction
Blink code diagnostic procedures in this
section cover:
앫 ECU Part Number 472 500 011 0
WABCO Basic ECU without an external
diagnostic connector
앫 ECU Part Number:
472 500 001 0
472 500 012 0
472 500 013 0
WABCO ECUs with external diagnostic
connectors
This section covers Normal Mode diagnostics
(Codes for system faults that cause the ABS
warning lamp to come on and stay on when the
vehicle is in operation.)
For ECU Part Numbers 472 500 012 0 and
472 500 013 0 ONLY:
If you do not have a diagnostic blink code tool,
follow the procedure given for ECU 472 500 011 0
(see “Using the Blink Code” in this section), but
use Table E — Normal Mode Fault Code Table
to identify the fault codes.
For additional diagnostic procedures refer to:
Appendix A Expert Mode Diagnostics
(ECU P/Ns 472 500 001 0,
472 500 012 0, 472 500 013 0)
This mode is used to identify
intermittent faults, such as a loose
connector.
Appendix B Reconfigure Mode. Use only as
indicated in the reconfiguration
table in Appendix B.
Appendix C Warning Lamp Diagnostics
(ECU P/Ns 472 500 011 0,
472 500 012 0, 472 500 013 0)
Blink Code Diagnostics
To use blink code diagnostics you need to know
whether or not the ECU has an external diagnostic
connector. See Section 2, "System Components" in
this manual for details. If you are unable to make
this determination, contact WABCO North America
Customer Care at 855-228-3203 for assistance.
On-Site Assistance
WABCO has provided an ABS Trailer warning label
that illustrates possible system fault locations. This
label should be mounted on the trailer near the
ABS warning lamp. If there is no ABS warning
label on the trailer, let your supervisor know.
Labels are available from WABCO. Ask for Part
Number TP-95172.
Page 21

Section 5
1003306a
1
Diagnostics
Using the Blink Code
For ECU Part Number 472 500 011 0 without
diagnostic connector:
1. Make sure the vehicle is stationary:
앫 Emergency brake ON
앫 Wheels properly chocked
2. Provide 12 volts DC power (9.5 to 14 volts is
acceptable range) to the ECU/Valve Assembly.
3. Check the ABS warning lamp on the trailer. If:
앫 The warning lamp comes ON briefly, then
goes OFF: There is no fault in system.
앫 The warning lamp comes ON and stays ON:
There is an existing fault. Go to Step 4.
4. Check the blink code lamp on the ECU. See
Figure 5.1 .
앫 If blink code lamp is OFF, there is no
system fault.
앫 If the blink code lamp is flashing, count the
number of flashes to identify the fault. Check
Table D — ECU Part Number 472 500 011 0
Blink Codes to determine the problem.
Follow the suggested corrective action.
Figure 5.1
1 Blink Code Lamp
Table D — ECU Part Number 472 500 011 0 Blink Codes
Blink Code Problem Area Action
4 Sensor YE1 (curbside sensor) Check sensor installation and connections.
Verify proper sensor resistance and air gap.
Make necessary repairs.
6 Sensor YE2 (roadside sensor) Check sensor installation and connections.
Verify proper sensor resistance and air gap.
Make necessary repairs.
10 ECU/Valve Assembly Verify proper installation. Make sure all connections
are secure.
If code continues, contact WABCO for assistance.
14 Power Supply Verify proper electrical installation and connections.
Check power supply.
Make necessary corrections.
15 ECU Failure Verify proper installation.
If code continues, contact WABCO for assistance.
Page 22

Section 5
NOTE
NOTE
1002094a
1002092a
Diagnostics
Diagnostic Tools For ECUs with
External Diagnostic Connectors
MPSI Pro-Link® 9000
Diagnostic Tool
(WABCO Cartridge Model J 38500-404)
The MPSI Pro-Link® 9000 diagnostic tool can test
for existing and stored faults, read and clear fault
codes, and test components, for WABCO tractor
and trailer ABS.
Figure 5.2
MPSI Pro-Link
Kent-Moore offers Kit J 38500-404 that contains
the WABCO ABS diagnostic cartridge, version 4.0
or higher, and the manual “WABCO ABS/ATC
Systems,” which contains complete information
and operating instructions for the MPSI Pro-Link
9000 diagnostic tool. Order the kit from KentMoore, 28635 Mound Road, Warren, MI 480923499; phone 800-345-2233.
®
Diagnostic Tool
®
Diagnostic Activation Tool
For ECU Part Numbers 472 500 001 0,
472 500 012 0 and 472 500 013 0.
Figure 5.3
The blink code diagnostic tool inserts into the
SAE J1587 diagnostic connector to activate the
blink code diagnostics, reconfigure the ECU and
test ECU installation. (See “How to Install
the Blink Code Diagnostic Tool into the
SAE J1587 Diagnostic Connector” in Section 6,
"Component Replacement".)
Normal Mode Diagnostics
If the blink code lamp displays a blink code for a
fault that is not listed in the Normal Mode Fault
Code Table or the Expert Mode Fault Code Table in
Appendix A:
A J 38500-60A Deutsch cable is also required. It is
available from Kent-Moore.
1. Visually inspect all connections
and components.
2. Try to erase the fault from ECU memory. If you
cannot erase the fault, a problem can exist
within the ECU/Valve Assembly.
3. Contact the contact WABCO North America
Customer Care at 855-228-3203.
Page 23

Section 5
1002095a
3 Flashes = Existing Fault = Sensor BU1
1S 1S
1S
Power ON;
ECU activated
S = Second(s)
Diagnostics
How to Test for Existing Faults
Using the Normal Mode
When you use Normal Mode diagnostics, the blink
code lamp displays a numerical fault code
sequence for each existing fault, one at a time.
If the ECU stores more than one existing fault in
memory, you must repair the first fault before
Normal Mode diagnostics will display the second
existing fault. In the Normal Mode, the lamp only
identifies the component that needs repair; for
example, THREE FLASHES = SENSOR BU1. To
identify and display intermittent faults, use
Expert Mode diagnostics. (See Appendix A.)
The ECU stores existing faults into memory in the
order in which they occur, but the blink code lamp
displays the most recent fault first. To identify and
display intermittent stored faults (such as a loose
cable or wire) from ECU memory, you must use
Expert Mode diagnostics.
To activate Normal Mode diagnostics:
1. The vehicle must be stationary. Power the
ECU with 12 volts DC (9.5–14 is an acceptable
range). The warning lamp on the trailer will
come ON.
2. Locate the diagnostic tool: Plug the diagnostic
tool into the diagnostic cable socket
located usually on the right side of the
trailer sub-frame.
Figure 5.4
1 Blink Code Switch
2 LED Lamp
6. When there are existing faults: You must repair
existing faults.
7. After you identify an existing fault, turn the
power to the ECU OFF. Repair the fault. Turn
the power to the ECU back ON.
8. ECU Part Number 472 500 001 0: Repeat
Steps 3, 5, 6, and 7 until the blink code lamp
goes OFF, comes back ON and remains ON.
This sequence signals that there are no other
existing faults.
ECU Part Numbers 472 500 012 0 and
472 500 013 0: Repeat Step 3. If there are no
other existing faults in the system, the blink
code lamp will come ON, go
remain OFF.
9. If you have just repaired a sensor fault, the
ECU is “waiting” to see a 4-mph signal on
sensed wheels. Until this 4 mph is sensed by
the ECU, the ABS warning lamp on the trailer
will remain ON.
OFF and
Table E — Normal Mode Fault Code Table
Blink Code Location
0 No Faults
3Sensor BU1
4Sensor YE1
5Sensor BU2
6Sensor YE2
7 Ext. Modulator (Red) 4S/3M Only
9 Ext. Modulator (BU)
10 ECU Modulator (YE)
14 System Configuration/Power
Supply
15 ECU Failure
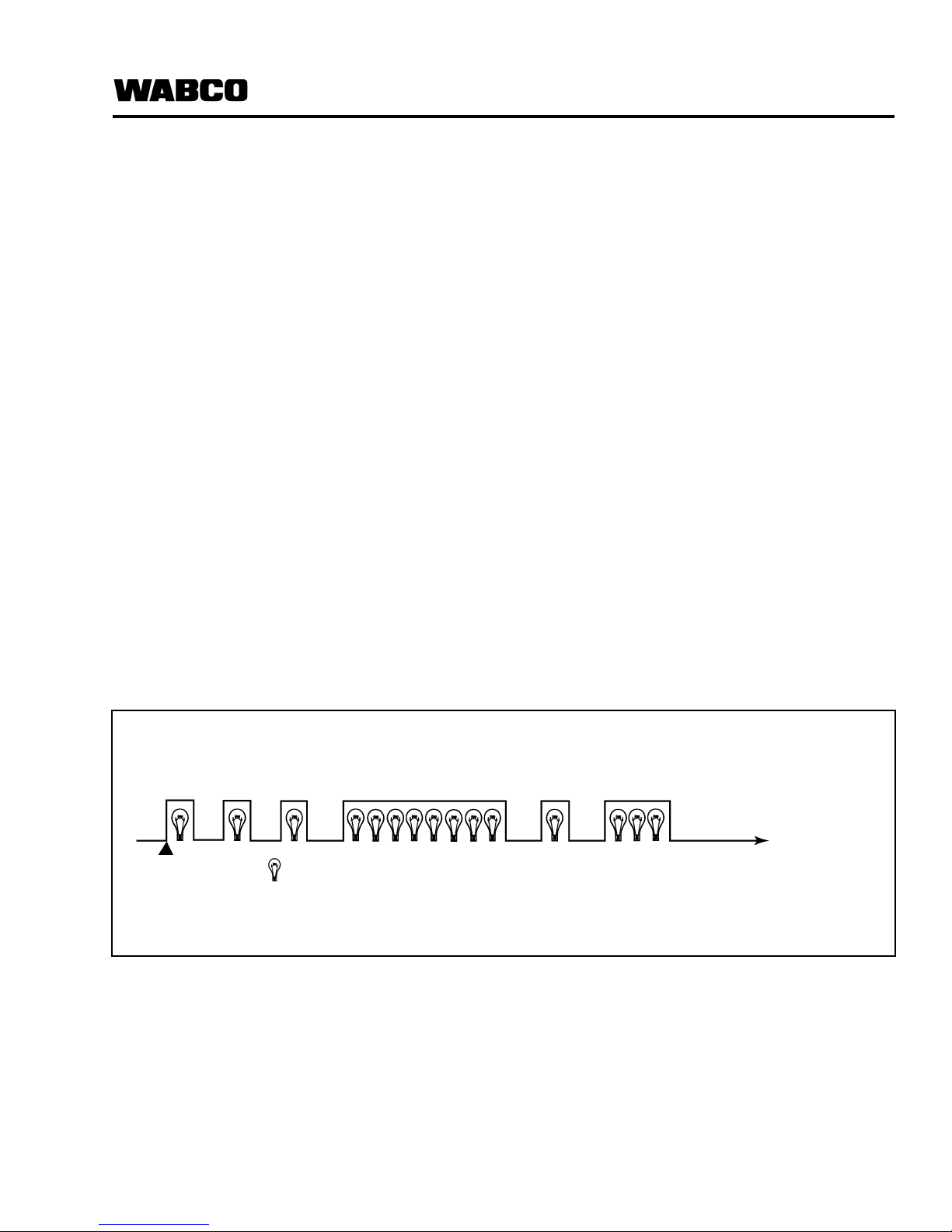
Figure 5.5
3. Press the blink code switch once for one
second and release the switch.
4. If there are no existing faults in the system:
When activated, the blink code lamp will
–Come ON
–Go OFF
– Remain OFF
5. When there is an existing fault: The blink code
lamp will flash between three and fifteen times
to identify the existing fault. Refer to Table E —
Normal Mode Fault Code Table, below, for
Normal Mode fault codes. See Figure 5.5 .
Page 24
Section 5
1002097b
1 S
1 S
1 S
8 Rapid Flashes =
ECU Faults Cleared
2.5 S
3 Flashes = I.D.
= 4S/2M
OFF
1 S
OFF
1 S
OFF
2.5 S
OFF
2.5 S
OFF
2.5 S
Continuously
Identifies
Configuration
Power ON;
ECU activated
= light ON
S = Second(s)
Perform the ECU
Installation Test.
Diagnostics
Repair Existing Faults
앫 With Normal Mode diagnostics, you must repair
an existing fault before you can identify and
repair the next existing fault stored in ECU
memory. Follow these steps:
앫 Turn off the power to the ECU.
앫 Repair the fault.
앫 Repeat Normal Mode diagnostics.
앫 Clear stored faults (if necessary).
How to Clear Repaired Faults from
the ECU
1. Power the ECU with 12 volts DC (9.5–14.0 is an
acceptable range).
2. To clear repaired faults from ECU memory,
press the blink code lamp switch three times
for one second each time as follows:
a. Depress the blink code lamp switch once
for one second. The lamp will come ON.
b. Release the switch for one second. The
lamp will go OFF.
c. Immediately depress the switch once for
one second. The blink code lamp will come
back ON.
d. Immediately release the switch once
for one second. The blink code lamp will
go OFF.
e. Immediately depress the switch once for
one second. The blink code lamp will come
back ON.
f. Release the switch.
g. The blink code lamp will flash rapidly for
eight times to indicate that the repaired
faults have been erased from ECU memory.
h. The lamp will continue to flash the
system configuration until you turn OFF
the power to the ECU. System
configuration codes are:
– 2 Flashes = 4S/3M
– 3 Flashes = 4S/2M
– 4 Flashes = 2S/2M
– 5 Flashes = 2S/1M
Blink Code Example (4S/2M Configuration)
Clear-All Mode
Figure 5.6
Page 25

Notes
Page 26

Section 6
NOTE
CAUTION
SENSOR
HOLDER
SPRING
CLIP
SPRING
CLIP TAB
SENSOR
1002100b
3"
SENSOR
CABLE
1002101b
Component Replacement
Section 6Component Replacement
WARNINGS
To prevent serious eye injury, always wear
safe eye protection when you perform vehicle
maintenance or service.
Block the wheels to prevent the vehicle from
moving. Support the vehicle with safety stands.
Do not work under a vehicle supported only by
jacks. Jacks can slip and fall over. Serious personal
injury can result.
The ABS is an electrical system. When you
work on the ABS, take the same precautions that
you must take with any electrical system to avoid
serious personal injury. As with any electrical
system, the danger of electrical shock or sparks
exists that can ignite flammable substances. You
must always disconnect the battery ground cable
before working on the electrical system.
Disconnect power from the ECU/Valve Assembly
before you remove any components. Failure to
disconnect power from the ECU can cause faults
to be recorded and stored in ECU memory.
1. Apply a mineral oil-based grease that contains
molydisulfide to the sensor spring clip and to
the body of the sensor. The grease must be
anti-corrosive and contain adhesive properties
that will continuously endure temperatures
from –40° to 300°F (–40° to 150°C).
2. Push the spring clip into the sensor holder
from the inboard side, until the spring clip tabs
are against the sensor holder. Push the sensor
into the spring clip as far as possible. Refer to
Figure 6.1 .
Figure 6.1
Use the following procedures to avoid damage to
the electrical system and ABS components.
When welding on an ABS-equipped vehicle is
necessary, disconnect the power connector from
the ECU.
Wheel Speed Sensor
How to Remove a Sensor
1. Follow the vehicle manufacturer's instructions
to back off the slack adjuster and remove the
tire, wheel and drum.
2. Hold the sensor, not the cable, and use a
twisting motion to pull the sensor out of its
mounting block.
3. Remove the spring clip from the
mounting block.
4. Remove any fasteners that hold the sensor
cable to other components.
5. Disconnect the sensor cable from the
extension cable.
How to Install a Sensor
1 Sensor Holder
2 Spring Clip
3 Spring Clip Tab
4 Sensor
3. Route the sensor cable toward the brake
chamber, over the brake spider, and behind the
axle. Secure the cable to the axle between the
brake spider and the suspension brackets.
Continue to route the sensor cable behind the
spring seats. Secure the cable to the axle one
inch from the molded sensor plug. Refer to
Figure 6.2 .
Figure 6.2
Sensor locations vary according to suspension
types. Typically, a spring suspension has sensors
on the forward axle, and an air suspension has
sensors on the rear axle.
1 Sensor Cable
Page 27
Section 6
WARNING
CAUTION
WARNING
CAUTION
1002102b
Component Replacement
4. Install the wheel hub carefully, so that the
tooth wheel pushes against the sensor as you
adjust the wheel bearings. After installation
there should be no gap between the sensor
and the tooth wheel. During normal operation
a gap of 0.04-inch is allowable.
5. Sensor Output Voltage Test: Use a
Volt/Ohm meter to check the AC output voltage
of the sensors while rotating the wheel at
approximately one-half revolution per second.
Minimum output must be greater than
0.2 volts AC. If minimum output is less than
0.2 volts AC, push the sensor toward the tooth
wheel. Recheck the sensor output.
ABS Relay Valve
Figure 6.3
How to Install a Standard ABS
Relay Valve
You must use Schedule 80 pipe nipple (3/4-inch
NPT) to nipple-mount the ABS relay valve securely
to the reinforced air tank to avoid possible serious
personal injury and damage to components.
1. Install the valve with two lock nuts and
washers as required. Tighten the hex nuts to
a torque of 18 lb-ft (24 N폷m) or nipple-mount
the valve directly to the air tank with
Schedule 80 pipe nipple (3/4-inch NPT).
2. Connect the air lines to the ports according
to the labels installed when the air lines
were disconnected.
3. Connect the cable to the valve.
4. Pressurize the brake system. Apply the brakes
and verify there are no air leaks.
The ECU/Valve Assembly
Release all pressure from the air system before
you disconnect any components. Pressurized air
can cause serious personal injury.
How to Remove a Standard ABS
Relay Valve
1. Release all pressure from the air system.
2. Disconnect the cable from the valve.
3. Attach labels to identify all of the air lines.
4. Disconnect the air lines from the valve.
5. Remove the mounting fasteners if the valve is
not nipple-mounted directly to the air tank.
6. Remove the valve.
Release all pressure from the air system before
you disconnect any components. Pressurized air
can cause serious personal injury.
The ECU and valve assembly are sealed together
as one unit. To ensure product integrity and avoid
possible damage to the components, do not
attempt to separate the ECU from the valve.
How to Remove the
ECU/Valve Assembly
1. Release all pressure from the air system.
2. Attach labels to identify all air lines.
3. Disconnect the air lines from the
ECU/Valve Assembly.
4. Disconnect the power cable, diagnostic cable,
additional relay valve cable (if used), and all
sensor cables from the ECU/Valve Assembly.
Refer to Figure 6.4 .
5. Remove the ECU/Valve Assembly from its
mounting location:
a. Bracket-mounted: Loosen and remove the
two mounting bolts and lock nuts that hold
the assembly to the mounting bracket.
Remove the assembly.
b. Nipple-mounted to Air Tank: Unscrew the
assembly from the air tank.
Page 28

Section 6
NOTE
CAUTION
1002103c
8
3
4
5
6
7
1
2
1002104b
BRACKET
Plug unused port
.
MODULATOR
POWER
DIAGN.
YE2
YE1
BU1
BU2
1002105c
Component Replacement
6. If the assembly being replaced is under
warranty, please return it to the trailer OEM
for replacement.
How to Install the
ECU/Valve Assembly
The ECU/Valve Assembly is supplied with black
protective caps on each sensor connector.
When a sensor cable is not plugged into a sensor
connector, the black cap must remain on the
connector to protect it from dirt and
contamination. See Figure 6.4 .
Figure 6.4
Figure 6.5
1 Bracket
Plug unused port.
You must use a Schedule 80 pipe nipple (3/4-inch
NPT) to nipple mount the ECU/Valve Assembly
securely to the air tank to avoid possible serious
personal injury and damage to components.
1. Attach the ECU/Valve Assembly to the vehicle:
a. Bracket-mounted: Use two 3/8-inch Grade
8 bolts with prevailing torque nuts to attach
the assembly to the mounting bracket.
Tighten to 18 lb-ft (24 N폷m).
Plug unused supply port (Port 1). Refer to
Figure 6.5 .
b. Nipple-mounted to air tank: Attach the
ECU/Valve Assembly to the air tank, using a
Schedule 80 pipe nipple (3/4-inch NPT).
Tighten securely with exhaust port facing
down. Do not overtighten.
1 Control Port (Port 4)
2 Black Protective Caps on Unused
Cable Connectors
3 External Relay Valve Cable
Plug unused supply port (Port 1). Refer to
Figure 6.6 .
Figure 6.6
4 Supply Port (Port 1)
5 Sensor Cables
6 Port 2 (Any Port May Be Used)
7 Diagnostic Cable (if applicable)
8 Power Cable
* Plug unused port. Use front supply port
for bracket-mounted. Use rear port for nipple
mount.
Plug unused port.
Page 29

Section 6
NOTE
NOTE
1002106b
SAE J1587
CONNECTOR
1002107b
1
Component Replacement
2. Connect the air lines to the ports. Follow the
label markers installed when the air lines were
disconnected.
3. Connect the sensor cables, external relay valve
cable (if used), diagnostic cable, and power
cable to the ECU/Valve Assembly. Use the black
protective connector caps included with the
replacement assembly to cover unused cable
connectors.
4. Test the installation using blink
code diagnostics
5. Perform the “Final Test Before Returning A
Trailer to Service” test in Section 7.
How to Install the Blink Code
Diagnostic Tool into the SAE J1587
Diagnostic Connector
The blink code switch and LED lamp are sealed
against dust and contaminants. The red dust cap
protects the switch and lamp during use but is not
an integral part of the diagnostic tool.
1. Remove the grey protective cap from the
SAE J1587 diagnostic connector. Figure 6.7 .
a. Turn the cap counterclockwise.
b. Pull off the cap.
2. Install the diagnostic tool into the
diagnostic connector.
a. Align the notch on the diagnostic tool with
the notch on the diagnostic connector.
Refer to Figure 6.8 .
b. Push the diagnostic tool firmly into the
connector. Refer to Figure 6.8 .
You must replace the grey protective cap if you
remove the diagnostic tool from the diagnostic
connector. Dirt and contaminants can damage
the connector.
c. Rotate the grey ring on the diagnostic tool
to securely lock the diagnostic tool into
the plug.
Figure 6.8
1 Diagnostic Connector
3. If the diagnostic tool will remain permanently
installed into the connector:
a. Remove the protective cap and guide wire
that are attached to the mounting bracket.
Figure 6.7
1 SAE J1587 Connector
Page 30
b. Attach the diagnostic tool and guide wire to
the mounting bracket.

Sensor Adjustment & Component Testing
NOTE
1003297a
GROUND
TERMINAL
EXHAUST
SOLENOID
INLET
SOLENOID
1
23
4
5
4003950a
Section 7Sensor Ad justment & Compone nt Testing
How to Test Wheel
Speed Sensors
At initial installation, no gap must exist between
the sensor and the tooth wheel.
After you install a hub, always check that the
sensor is adjusted properly.
Operating the trailer can cause a gap to develop
between the sensor and the tooth wheel. If the
gap exceeds 0.040-inch, the system may not
function correctly.
To adjust the sensor, twist and push the sensor
through the sensor bracket as far as possible or
until the sensor touches the tooth wheel.
Section 7
Check ABS Functions
앫 WABCO recommends that you test a vehicle's
ABS after a new installation and after you
diagnose, repair and erase faults in the ABS.
앫 Perform installation tests and blink code
diagnostics using the blink code diagnostic tool
or the MPSI Pro-Link
Model J 38500-404, version 4.0
or higher).
®
9000 (WABCO Cartridge
ABS External Modulator Valve
Measure resistance across each valve solenoid coil
terminal and ground on the ABS valve to ensure
4.0 to 8.0 ohms. Valve and cable pinouts are
illustrated in Figure 7.1 .
Sensor Test Procedure
1. Disconnect power to the ECU/Valve Assembly.
2. Disconnect the sensor electrical connector
from the ECU/Valve Assembly.
3. Connect the Volt/Ohm meter leads to the two
wire component terminals inside the
disconnected connector.
4. When checking the resistance, the meter must
read 500–2000 ohms.
5. Check and replace the sensor and cables
as required.
6. Repeat Steps 1-5 for each sensor in the system.
Sensor Output Voltage Test
1. Disconnect power from the
ECU/Valve Assembly.
2. Connect the AC Volt/Ohm meter leads to the
sensor terminals inside the connector.
3. Rotate the corresponding wheel at a constant
speed of one-half revolution per second.
4. The output voltage must be greater than
0.2 volts AC.
5. When there is no reading:
a. Trace the cable to verify that the cable
connects to the wheel you turned.
b. Check that you turned the correct wheel.
c. Check that the system is wired correctly.
d. Check that the sensor touches the
tooth wheel.
6. If the Volt/Ohm meter still indicates no reading
or a low reading after following the above
procedures, check and replace the component
and cables as required.
7. Repeat Steps 1-5 for each sensor in the system.
Figure 7.1
앫 To check the cable and the ABS valve as one
unit, measure resistance across the pins on the
ECU connector of the harness. See Figure 7.2 .
– For 2S/1M, 2S/2M, and 2S/4M systems,
measure the resistance across pins 1 and 3
and pins 2 and 3.
– For 4S/3M systems (“Y” cable connectors),
measure across pins 3 and 4 and pins 3 and 5.
– Resistance should be between 4.0 and
8.0 ohms for each measurement. Figure 7.2 .
Figure 7.2
1 Exhaust Solenoid
2 Inlet Solenoid
3 Ground Terminal
4 Exhaust Solenoid (4S/3M only)
5 Inlet Solenoid (4S/3M only)
앫 If the resistance is greater than 8.0 ohms clean
the electrical contacts in the solenoid. Check the
resistance again.
Page 31

Section 7
NOTE
Sensor Adjustment & Component Testing
Final Test Before Returning a Trailer to Service
For ECU/Valve Assembly Part Number 472 500 011 0
(without external diagnostic connector)
If you are testing ECU 472 500 001 0, contact
WABCO North America Customer Care at
855-228-3203.
ABS Electrical/Hardware Installation Test
1. Provide 12 volts DC power (9.5–14 volts is an
acceptable range) to the ECU/Valve Assembly.
– Suggested power source: 12-volt battery.
Table F — ECU Part Number 472 500 011 0
If Status Action
Trailer ABS warning lamp does
not come ON.
OR
Blink code lamp on ECU does not
come ON.
Trailer ABS warning lamp
comes ON.
AND # Blinks Location
Blink code lamp on ECU
continues to flash.
Trailer ABS warning lamp comes
ON and stays ON.
AND
ECU clicks twice.
AND
Blink code lamp on ECU comes
ON briefly, then goes OFF.
Trailer ABS warning lamp
comes ON for 3 seconds, then
goes OFF.
AND
ECU clicks twice.
AND
Blink code lamp on ECU comes
ON briefly, then goes OFF.
Minimum power requirement
not met or wiring problem
exists.
Hardware fault code Identify fault location. Make
Proper hardware installation. Perform Sensor Installation Test.
Proper hardware installation.
Proper sensor installation.
2. Observe the ABS warning lamp and the blink
code lamp on the ECU. Check the results
in Ta bl e F.
Check electrical connections
and power source. Make
necessary repairs.
necessary repairs to the installation:
4 Sensor YE1 (curbside)
6 Sensor YE2 (roadside)
10 ECU/Valve Assembly
14 Power Supply
15 ECU Failure
None required.
Page 32

Sensor Adjustment & Component Testing
ABS Sensor Installation Test
(ECU Part Number 472 500 011 0)
1. Remove power.
2. Raise both sensed wheels off of the ground.
Apply air to emergency line to fill air tanks and
release parking brake.
3. Provide 12 volts DC power (9.5–14 volts is an
acceptable range) to ECU/Valve Assembly.
(Make sure trailer ABS warning lamp and ECU
blink code lamp operate correctly, as described
in “ABS Electrical/Hardware Installation Test”.)
4. Rotate the sensed wheels — ONE AT A TIME —
at a rate of 1/2 revolution per second.
5. Check Table G — Sensor Installation Test,
“Sensor Installation Test.”
Table G — Sensor Installation Test
If Status Action
Trailer ABS warning lamp
goes OFF.
Trailer ABS warning lamp does not
go OFF.
AND
There is no blink code flashing on
the ECU.
ECU senses proper speed.
Sensors properly installed.
There is a sensor
gap problem.
No further testing required.
Adjust sensor gap. Push sensor
into its holder until it contacts the
tooth wheel.
Measure the AC voltage output.
Value should be 0.2 volts AC when
wheel is rotated at a rate of
1/2 revolution per second.
Section 7
Trailer ABS warning lamp does not
go OFF.
AND
Blink code is on and flashing
on ECU.
Table H — Blink Code Table
Blink
Code
4Sensor YE1
6Sensor YE2
10 ECU/Valve
Problem
Area Action
Check sensor installation.
(curbside
sensor)
(roadside
sensor)
Assembly
Make necessary repairs.
Check sensor installation.
Make necessary repairs.
Verify proper installation.
If blink code continues,
contact WABCO for
assistance.
Make necessary repairs.
System fault exists. Count the number of flashes.
This is the blink code.
Using Table H — Blink Code Table,
identify the blink code.
Make necessary repairs.
Blink
Code
14 Power
15 ECU
After making the necessary corrections, repeat
the sensor installation test to verify proper
sensor installation.
Problem
Area Action
Verify proper electrical
Supply
Failure
installation. Check
power supply. Make
necessary corrections.
Verify proper installation.
If code continues,
contact WABCO for
assistance.
Page 33

Section 7
NOTE
Sensor Adjustment & Component Testing
For ECU/Valve Assembly Part
Numbers 472 500 012 0 and
S 472 500 013 0 (Units with External
Diagnostic Connector)
If you are testing ECU Part Number 472 500 001 0,
contact WABCO North America Customer Care at
855-228-3203.
ABS Electrical/Hardware Installation Test
1. Provide 12 volts DC (9.5–14 volts is an
acceptable range) to the ECU/Valve Assembly.
Suggested power source: 12-volt battery.
2. Observe the ABS warning lamp and the blink
code lamp on the ECU. Check the results
in Ta bl e I .
Ta b le I
If Status Action
Trailer ABS warning lamp does
not come ON.
OR
Blink code lamp on ECU does not
come ON.
Trailer ABS warning lamp
comes ON.
AND # Blinks Location
Blink code lamp on ECU
continues to flash.
Trailer ABS warning lamp comes
ON and stays ON.
AND
ECU clicks twice.
AND
Blink code lamp on ECU comes
ON briefly then goes OFF or
flashes 14 times, then goes out.
Trailer ABS warning lamp
comes ON for 3 seconds, then
goes OFF.
AND
ECU clicks twice.
AND
Blink code lamp on ECU comes
ON briefly, then goes OFF.
Minimum power requirement
not met or wiring problem
exists.
Hardware fault code Identify fault location. Make
Proper hardware installation. Perform Sensor Installation Test.
Proper hardware installation.
Proper sensor installation.
Check electrical connections
and power source. Make
necessary repairs.
necessary repairs to the installation:
3Sensor BU1
4Sensor YE1
5Sensor BU2
6Sensor YE2
7 External Modulator (Red)
9 External Modulator (BU)
10 ECU Modulator (YE)
14 System Configuration or
15 ECU (contact WABCO)
None required.
4S/3M only
Power Supply
Page 34

Section 7
1002093a
1
2
1003299a
SLACK
ADJUSTER
Sensor Adjustment & Component Testing
Sensor Installation Test (ECU Part
Numbers 472 500 012 and 472 500 013 0)
Purpose of Test: To verify proper sensor gap,
sensor hook-up to the ECU, ABS valve operation,
and pneumatic plumbing connections of the
WABCO Easy-Stop™ ABS on a new trailer.
1. Remove power from the ABS.
2. Raise sensed wheels so that they may
be rotated.
3. Go to the diagnostic tool. Reapply power to
the ABS.
앫 If there is no diagnostic tool on the trailer,
temporarily install one for this test. You
must use a diagnostic tool to complete the
Sensor Installation Test.
4. Check the diagnostic tool to verify the status of
the yellow LED. Figure 7.3 .
앫 If LED comes ON and stays ON, go to Step 5.
앫 If LED does not light, verify adequate power
is applied to the system. Make the
necessary repairs.
앫 If this does not occur, repeat Step 4.
앫 Attach the emergency and control air lines to
the trailer. Fill air tanks to release the spring
brakes.
6. Rotate each sensed wheel — ONE AT A TIME —
at a rate of 1/2 revolution per second. Apply
control pressure to activate the brakes. Refer to
Figure 7.4 .
Figure 7.4
Figure 7.3
1 Blink Code Switch
2 LED Lamp
5. Press and release the blink code switch three
times for Sensor Installation Test Mode, one
second each time, separated by a release time
of one second.
앫 The LED should display eight rapid flashes.
This indicates the Sensor Installation Test
Mode. Then, the LED will continuously
display the system configuration code:
– 2 Flashes = 4S/3M
– 3 Flashes = 4S/2M
– 4 Flashes = 2S/2M
– 5 Flashes = 2S/1M
1 Slack Adjuster
7. Observe the automatic slack adjuster on the
rotated wheel. It must move in and out as
the ABS valve cycles. This indicates a
proper installation.
앫 If the slack adjuster on the rotated wheel
does not move — but the slack adjuster on
the opposite wheel does move — the sensor
leads are reversed or the air line is plumbed
wrong. Correct the installation.
앫 If the slack adjuster on the rotated wheel
does not move, there may be a sensor gap
problem. Check the sensor gap and make
the necessary repairs.
8. Repeat Steps 6 and 7 on the remaining
sensed wheels.
9. If you installed a diagnostic blink code tool for
this test, remove it. Replace the protective cap
over the connector.
Page 35

Section 7
Sensor Adjustment & Component Testing
Trailer Identification
An Easy-Stop™ Trailer ABS warning label is generally affixed to the
trailer near the ABS trailer warning lamp.
If this label is not on the trailer, let your supervisor know. Labels are
available from WABCO. Ask for Part Number TP-95172.
For additional assistance, contact WABCO North America Customer Care at 855-228-3203.
Before calling the WABCO North America Customer Care, be prepared
to provide the following information about the trailer you are
working on:
1. Trailer make and model year.
2. What is the symptom/complaint? What is the component doing
or not doing?
3. What is the ABS blink code or MPSI Pro-Link
4. Have any resistance and/or voltage measurements been taken?
5. What is the result of visual inspection of connectors, harness
and components?
6. When does the symptom occur (vehicle moving, compressor
unloading, etc.)?
7. Does the trailer have any unusual characteristics (for example,
mismatched tires or larger than normal air consumption)?
8. Were maintenance manuals available? If so, which ones
were used?
9. What is the part number of the ECU/Valve Assembly? What is the
system configuration?
By having the above information ready when you call, your customer
support technician will be better equipped to assist you.
®
9000 reading?
WABCO North America
Customer Care, 855-228-3203
Page 36

Section 8
NOTE
NOTES
Appendixes
Section 8Appendixes
Appendix A
Expert Mode Diagnostics
When you use Expert Mode diagnostics, the blink
code lamp identifies and displays existing and
intermittent faults consecutively in three-digit fault
code sequences, with a short pause between each
fault. Refer to Expert Mode Blink Code Example
(4S/2M Configuration) and Table J — Expert Mode
Fault Code, all in this section.
Expert Mode identifies:
앫 System configuration
앫 Components that need repair;
앫 Cause (or type) of fault, such as a cut sensor
cable; and
앫 Number of times a fault has occurred.
The ECU stores intermittent and existing faults
into memory in the order in which they occur.
However, the blink code lamp displays the most
recent fault first.
How to Test for Intermittent Stored Faults
Using the Expert Mode
Before you use Expert Mode diagnostics, be
prepared to count and write down the blink code
lamp flashes for each fault.
1. The vehicle must be stationary to activate the
blink code. Power the ECU with a minimum of
12 volts DC (9.5–14 is an acceptable range). The
warning lamp on the trailer will come ON.
2. Identify the fault. If not already attached, plug
the diagnostic tool into the diagnostic cable
socket usually located on the right side of
the trailer.
b. Release the switch. The blink code lamp
will go OFF.
c. Depress the blink code lamp switch once
for one second. The blink code lamp will
come ON.
d. As soon as the blink code lamp comes ON,
release the blink code button.
4. Determine whether or not there are
Intermittent Stored faults in the system.
If there are no Intermittent Stored faults, the
blink code lamp will come back ON and
identify the system configuration one time
by displaying:
– 2 Flashes = 4S/3M
– 3 Flashes = 4S/2M
– 4 Flashes = 2S/2M
– 5 Flashes = 2S/1M
After the blink code lamp displays the system
configuration once, the lamp will remain OFF.
If There Are Intermittent Stored Faults in
the System
1. The blink code lamp will come back ON and
identify the system configuration one time
by displaying:
– 2 Flashes = 4S/3M
– 3 Flashes = 4S/2M
– 4 Flashes = 2S/2M
– 5 Flashes = 2S/1M
2. The blink code lamp will go OFF for
2.5 seconds, come back ON for 2.5 seconds,
and go OFF for 2.5 seconds.
앫 The blink code lamp will display the most
recent fault in a three-digit fault code
sequence. For example, a fault code
sequence of 3-5-2 reads as follows:
앫 For an alternate blink code access procedure,
see “Warning Lamp Diagnostics” in
Appendix C.
앫 You can restart the Expert Mode fault sequence
at any time by depressing the blink code lamp
switch as described in Step 3 below.
3. Depress the blink code lamp switch located in
the diagnostic tool two times for one second
each time as follows:
a. Depress the blink code lamp switch once
for one second. The lamp will come ON.
First Digit 3 Flashes = Sensor BU1
Second Digit 5 Flashes = Cut Sensor Cable
Third Digit
(X)
3. The blink code lamp will then go OFF for
2.5 seconds, then display each remaining fault
code sequence.
4. When all fault code sequences have been
displayed, the blink code lamp will come ON
and go OFF, and remain OFF.
2 Flashes = Number of
= Fault Occurrences
Page 37

Section 8
1002096b
1 S 1 S
OFF
1 S
OFF
1 S
OFF
2.5 S
OFF
2.5 S
OFF
2.5 S
OFF
2.5 S
OFF
2.5 S
1st Digit
3 Flashes = I.D.
= 4S/2M 2nd Digit 3rd Digit
FAULT CODE
Lamp stays ON after all
fault code sequences
have been displayed.
Power ON;
ECU activated
= Light ON S = Second(s)
BLINK CODE 3-5-2 = CUT SENSOR CABLE
Appendixes
Blink Code Example (4S/2M Configuration)
Expert Mode
Figure 8.1
Table J — Expert Mode Fault Code
Blink Code
1st
Digit
2nd
Digit
3rd
Digit (X)
Component or
Location
000 No Faults No action needed.
35X Sensor BU1 Cable Break,
37X Sensor BU1 Out of Adjustment Adjust sensor.
310X Sensor BU1 Speed Erratic Check for excessive hub
45X Sensor YE1 Cable Break,
47X Sensor YE1 Out of Adjustment Adjust sensor.
410X Sensor YE1 Speed Erratic Check for excessive hub
55X Sensor BU2 Cable Break,
57X Sensor BU2 Out of Adjustment Adjust sensor.
510X Sensor BU2 Speed Erratic Check for excessive hub
65X Sensor YE2 Cable Break,
X = Number of Fault Occurrences
Cause or Type
of Fault Solution
Short Circuit
Short Circuit
Short Circuit
Short Circuit
Check sensor, sensor cable and
cable connection.
runout, a sensor gap that is
too wide or damage to the
tooth wheels.
Check sensor, sensor cable and
cable connection.
runout, a sensor gap that is too
wide or damage to the
tooth wheels.
Check sensor, sensor cable and
cable connection.
runout, a sensor gap that is too
wide or damage to the
tooth wheels.
Check sensor, sensor cable and
cable connection.
Page 38

Table J — Expert Mode Fault Code (continued)
Blink Code
Section 8
Appendixes
1st
Digit
67X Sensor YE2 Out of Adjustment Adjust sensor.
610X Sensor YE2 Speed Erratic Check for excessive hub
73X External Modulator
75X External Modulator
76X External Modulator
712X External Modulator
93X External Modulator
95X External Modulator
96X External Modulator
912X External Modulator
10 3 X ECU/Valve Assembly
10 5 X ECU/Valve Assembly
10 6 X ECU/Valve Assembly
10 1 2 X ECU/Valve Assembly
14 2 X ECU Data Erratic Unexpected System.
14 3 X Power Supply Over Voltage Repair vehicle power supply.
14 4 X Power Supply Under Voltage Check vehicle voltage output
14 5 X Power Supply Current Low Check for proper ground on
14 9 X ECU/Valve Assembly Internal Failure Erase fault.
14 12 X ECU/Valve Assembly Internal Failure Erase fault.
15 9 X Electromagnetic
15 12 X ECU/Valve Assembly Internal Failure
X = Number of Fault Occurrences
2nd
Digit
3rd
Digit (X)
Component or
Location
(Red)
(Red)
(Red)
(Red)
(BU)
(BU)
(BU)
(BU)
Modulator (YE)
Modulator (YE)
Modulator (YE)
Modulator (YE)
Interference
Cause or Type
of Fault Solution
runout, a sensor gap that is too
wide or damage to the
tooth wheels.
Short to Power Check ABS valve and cable.
Replace as required.
Cable Break or Open Check ABS valve and cable.
Replace as required.
Short to Ground or
Cable Damaged
ECU/Valve
Assembly Failure
Short to Power Check ABS valve and cable.
Cable Break or Open Check ABS valve and cable.
Short to Ground or
Cable Damaged
ECU/Valve
Assembly Failure
Short to Power Check ABS valve and cable.
Cable Break or Open Check ABS valve and cable.
Short to Ground or
Cable Damaged
ECU/Valve
Assembly Failure
Various
Check ABS valve and cable.
Replace as required.
Check ABS valve and cable.
Replace as required.
Replace as required.
Replace as required.
Check ABS valve and cable.
Replace as required.
Check ABS valve and cable.
Replace as required.
Replace as required.
Replace as required.
Check ABS valve and cable.
Replace as required.
Check ABS valve and cable.
Replace as required.
and connector.
power cable.
Contact WABCO North America
Customer Care, 855-228-3203.
Contact WABCO North America
Customer Care, 855-228-3203.
Page 39

Section 8
1002098b
1 S 1 S 1 S
OFF
2.5 S
OFF
2.5 S
OFF
2.5 S
OFF
2.5 S
OFF
2.5 S
OFF
2.5 S
OFF
1 S
OFF
1 S
3 Flashes = I.D.
= 4S/2M
3 Flashes = I.D.
= 4S/2M
3 Flashes = I.D.
= 4S/2M2.5 S 2.5 S
8 Rapid Flashes =
ECU Reconfigured
Power ON;
ECU activated
= Light ON
S = Second(s)
Depress Switch
3 Seconds
Continuously
Identifies
Configuration
Appendixes
Appendix B
Reconfigure Mode
Blink Code Example (4S/2M Configuration)
Reconfigure Mode
Figure 8.2
Page 40

Section 8
NOTE
NOTE
2002111b
THREE FLASHES LAMP GOES OFF 2.5 SECONDS
LAMP COMES ON 2.5 SECONDS LAMP GOES OFF 2.5 SECONDS
THREE FLASHES
LAMP GOES OFF 2.5 SECONDS
LAMP GOES OFF 2.5 SECONDS
LAMP GOES OFF 2.5 SECONDS
LAMP GOES OFF 2.5 SECONDS
LAMP COMES ON 2.5 SECONDS
LAMP COMES ON 2.5 SECONDS
THREE FLASHES
4S/2M SYSTEM IDENTIFICATION
Appendixes
When to Use the Reconfigure Mode
Use the Reconfigure Mode to (1) reconfigure
the ECU if necessary (see Table K — ECU
Reconfiguration); or (2) to clear repaired faults
from ECU memory. (Refer to Figure 8.2 for a
Reconfigure blink code example.)
Table K — ECU Reconfiguration
ECU Part
Number
472 500 001 0 Manual reconfiguration required
472 500 011 0 2S/1M only. No reconfiguration
471 500 012 0
&
472 500 013 0
Reconfiguration
Requirements
if ECU is installed on other than a
2S/2M configuration.
See “How to Use the
Reconfigure Mode”.
required.
Automatic reconfiguration for
upward configurations (e.g.,
2S/2M to 4S/2M). If downward,
manual reconfiguration required.
Do NOT reconfigure the ECU
unless system usage has
changed. Contact WABCO North
America Customer Care at 855228-3203 for assistance.
d. Release the switch once for one second.
The blink code lamp will go OFF.
e. Depress the switch once for one second.
The blink code lamp will come back ON.
f. Release the switch. The blink code lamp
will go OFF.
4. The blink code lamp will display the system's
identification three times. For example, three
flashes identify a 4S/2M system. (Refer to the
system identification example shown below.)
Figure 8.3
How to Use the Reconfigure Mode
For an alternate blink code access procedure, see
“Warning Lamp Diagnostics”, in Appendix C.
1. The vehicle must be stationary to activate
and reconfigure the ECU. Power the ECU with
12 volts DC (9.5–14 is an acceptable range).
2. If the diagnostic tool is not attached to the
diagnostic cable: Plug the diagnostic tool into
the diagnostic cable socket usually located on
the right side of the sub-frame.
3. Activate the Reconfigure Mode: Press the blink
code lamp switch three times for one second
each time as follows:
a. Depress the blink code lamp switch once
for one second.
b. Release the switch for one second. The
lamp will go OFF.
c. Depress the switch once for one second.
The blink code lamp will come back ON.
To accept the ECU reconfiguration, you must
depress the blink code lamp switch for three
seconds during the third display of the
system's identification.
5. During the third time the lamp displays the
system's identification, depress the blink code
lamp switch for three seconds and release the
switch to accept the system reconfiguration.
6. The blink code lamp will flash rapidly eight
times to acknowledge that the ECU is
reconfigured. The lamp will continue to flash
the system's identification until you turn OFF
the power to the ECU.
7. If you repaired or replaced the ECU/Valve
Assembly or ABS Modulator Valve, refer to
“Final Test Before Returning a Trailer to
Service” in Section 7, "Sensor Adjustment &
Component Testing".
Page 41

Section 8
Appendixes
Appendix C
Warning Lamp Diagnostics
ECU Part Numbers 472 500 011 0, 472 500 012 0,
and 472 500 013 0
If you do not have easy access to either the
diagnostic tool or blink code lamp on the ECU, the
ABS warning lamp on the trailer may be used to
display blink codes.
The lamp is capable of displaying faults in Normal,
Expert, Clear-All, and Sensor Installation
Tes t m od es .
System requirements:
앫 Trailer with mandated ABS (with ECU/Valve
Assembly part number listed above).
앫 Tractor/trailer hook-up with switched ignition
power on tractor/trailer connector or a
DC-powered tester.
앫 Technician and assistant recommended.
Read the description of each mode and use the
blink code tables for Normal, Expert, and
Reconfigure/Clear-All modes that appear in
this manual.
To display the blink codes on the ABS
warning lamp:
1. Make sure the vehicle is stationary and that the
trailer is hooked to a properly equipped tractor
(see system requirements).
2. Remove power from the tractor and trailer
(Turn off ignition).
3. Step on the brake pedal. Foot must remain on
the brake for the entire procedure.
4. Provide Power. Turn on ignition for desired
mode (Normal, Expert, or Clear-All). Once you
enter the mode you plan to use, follow the
instructions for that mode.
Reminder:
Brakes must be applied (foot on brake pedal)
for the entire procedure.
For Normal Mode:
앫 Turn ignition ON ONCE for ONE SECOND.
앫 Turn ignition OFF for ONE SECOND.
앫 Turn ignition back ON.
– Warning lamp will display the blink code one
time. See Table E — Normal Mode Fault Code
Ta b l e , in Section 5, "Diagnostics", for blink
code identification.
For Expert Mode:
앫 Turn ignition ON ONCE for ONE SECOND.
앫 Turn ignition OFF for ONE SECOND.
앫 Turn ignition ON A SECOND TIME for
ONE SECOND.
앫 Turn ignition OFF for ONE SECOND.
앫 Turn ignition back ON.
– Warning lamp will display the blink code one
time. See Table J — Expert Mode Fault Code,
in “Appendixes”, for blink code identification.
For Clear-All or Sensor Installation
Te s t M o d e :
앫 Turn ignition ON ONCE for ONE SECOND.
앫 Turn ignition OFF for ONE SECOND.
앫 Turn ignition ON A SECOND TIME for
ONE SECOND.
앫 Turn ignition OFF.
앫 Turn ignition ON A THIRD TIME for
ONE SECOND.
앫 Turn ignition OFF for ONE SECOND.
앫 Turn ignition back ON.
– The blink code lamp will flash rapidly eight
times to indicate that stored faults have been
cleared from ECU memory.
NOTE
To exit any mode, release foot brake pedal and
turn ignition off for AT LEAST 10 SECONDS.
Page 42


© 2018 WABCO North America – All rights reserved – MM-33 / 07.2018
connects trucks, trailers, cargo,
drivers, business partners and
fl eet operators through advanced
fl eet management systems and
mobile solutions. WABCO reported sales of $2.8 billion in
2016. Headquartered in Brussels,
Belgium, WABCO has 13,000 employees in 40 countries. For more
information, visit:
www.wabco-na.com
(NYSE: WBC) is a
leading global supplier of technologies and services that improve
the safety, effi ciency and con-
nectivity of commercial vehicles.
Founded nearly 150 years ago,
WABCO continues to pioneer
breakthrough innovations for advanced driver assistance, braking, stability control, suspension,
transmission automation and
aerodynamics. Partnering with
the transportation industry as it
maps a route toward autonomous
driving, WABCO also uniquely
 Loading...
Loading...