Page 1

Owner’s Manual & Safety Instructions
Save This Manual Keep this manual for the safety warnings and precautions, assembly,
operating, inspection, maintenance and cleaning procedures. Write the product’s serial number in the
back of the manual near the assembly diagram (or month and year of purchase if product has no number).
Keep this manual and the receipt in a safe and dry place for future reference. 19h
Visit our website at: http://www.harborfreight.com
Email our technical support at: productsupport@harborfreight.com
When unpacking, make sure that the product is intact
and undamaged. If any parts are missing or broken,
please call 1-888-380-0318 as soon as possible.
Copyright© 2017 by Harbor Freight Tools®. All rights reserved.
No portion of this manual or any artwork contained herein may be reproduced in
any shape or form without the express written consent of Harbor Freight Tools.
Diagrams within this manual may not be drawn proportionally. Due to continuing
improvements, actual product may differ slightly from the product described herein.
To ol s re q u ir e d fo r as s e mb l y a n d s e r vi c e m a y n o t b e in c l ud e d .
Read this material before using this product.
Failure to do so can result in serious injury.
SAVE THIS MANUAL.
Page 2

Table of Contents
Safety ......................................................... 2
Specifications ............................................. 7
SAFETY MAINTENANCEBASIC WELDING WELDING TIPSSETUP
Setup .......................................................... 8
Basic Welding ............................................ 15
Welding Tips .............................................. 23
Maintenance .............................................. 27
Parts List and Diagrams ............................ 30
Warranty .................................................... 32
WARNING SYMBOLS AND DEFINITIONS
This is the safety alert symbol. It is used to alert you to potential
personal injury hazards. Obey all safety messages that
follow this symbol to avoid possible injury or death.
Indicates a hazardous situation which, if not avoided,
will result in death or serious injury.
Indicates a hazardous situation which, if not avoided,
could result in death or serious injury.
Indicates a hazardous situation which, if not avoided,
could result in minor or moderate injury.
Addresses practices not related to personal injury.
IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION
Read all safety warnings and instructions.
Failure to follow the warnings and instructions may result in electric shock, fire and/or serious injury.
Save all warnings and instructions for future reference.
General Safety
PROTECT yourself and others. Read and understand this information.
1. Before use, read and understand
manufacturer′s instructions,
Material Safety Data Sheets (MSDS′s),
employer′s safety practices, and ANSI Z49.1.
2. Keep out of reach of children.
Keep children and bystanders away while operating.
3. Place the welder on a stable location before use.
If it falls while plugged in, severe injury,
electric shock, or fire may result.
4. Do not overreach.
Keep proper footing and balance at all times.
5. Stay alert, watch what you are doing and use
common sense when operating a welder.
Do not use a welder while you are tired or under
the influence of drugs, alcohol or medication.
A moment of inattention while operating welders
may result in serious personal injury.
6. Avoid unintentional starting. Make sure you are
prepared to begin work before turning on the Welder.
7. Never leave the Welder unattended while
energized. Turn power off if you have to leave.
8. The warnings, precautions, and instructions
discussed in this instruction manual cannot
cover all possible conditions and situations
that may occur. It must be understood by the
operator that common sense and caution are
factors which cannot be built into this product,
but must be supplied by the operator.
Page 2 For technical questions, please call 1-888-380-0318. Item 63617
Page 3

Fume and Gas Safety
Welding and Plasma Cutting Produce toxic fumes.
1. Exposure to welding or cutting exhaust
fumes can increase the risk of developing
certain cancers, such as cancer of the
larynx and lung cancer. Also, some diseases
that may be linked to exposure to welding
or plasma cutting exhaust fumes are:
• Early onset of Parkinson’s Disease
• Heart disease
• Ulcers
• Damage to the reproductive organs
• Inflammation of the small intestine or stomach
• Kidney damage
• Respiratory diseases such as
emphysema, bronchitis, or pneumonia
Use natural or forced air ventilation and wear
a respirator approved by NIOSH to protect
against the fumes produced to reduce the
risk of developing the above illnesses.
2. Do not use near degreasing or
painting operations.
INHALATION HAZARD:
3. Keep head out of fumes.
Do not breathe exhaust fumes.
4. Use enough ventilation, exhaust at arc, or
both, to keep fumes and gases from breathing
zone and general area. If engineering controls
are not feasible, use an approved respirator.
5. Work in a confined area only if it
is well-ventilated, or while wearing
an air-supplied respirator.
6. Have a recognized specialist in
Industrial Hygiene or Environmental Services
check the operation and air quality
and make recommendations
for the specific welding situation.
Follow OSHA guidelines for
Permissible Exposure Limits (PEL’s) and
the American Conference of Governmental
Industrial Hygienists recommendations for
Threshold Limit Values (TLV’s) for fumes and gases.
SAFETYMAINTENANCE BASIC WELDINGWELDING TIPS SETUP
Arc Ray Safety
ARC RAYS can injure eyes and burn skin.
1. Wear ANSI-approved welding eye protection
featuring at least a number 10 shade lens rating.
2. Wear leather leggings, fire resistant shoes
or boots during use. Do not wear pants with
cuffs, shirts with open pockets, or any clothing
that can catch and hold molten metal or sparks.
3. Keep clothing free of grease, oil,
solvents, or any flammable substances.
Wear dry, insulating gloves and protective clothing.
4. Wear an approved head covering to protect
the head and neck. Use aprons, cape, sleeves,
shoulder covers, and bibs designed and
approved for welding and cutting procedures.
5. When welding/cutting overhead or in confined
spaces, wear flame resistant ear plugs or
ear muffs to keep sparks out of ears.
Page 3For technical questions, please call 1-888-380-0318.Item 63617
Page 4

Electrical Safety
ELECTRIC SHOCK can KILL.
1. Turn off, disconnect power, and
SAFETY MAINTENANCEBASIC WELDING WELDING TIPSSETUP
discharge electrode to ground before setting
down torch/electrode holder and before service.
2. Do not touch energized electrical parts.
Wear dry, insulating gloves. Do not touch electrode
holder, electrode, welding torch, or welding wire with
bare hand. Do not wear wet or damaged gloves.
3. Connect to grounded, GFCI-protected
power supply only.
4. Do not use near water or damp objects.
5. People with pacemakers should consult their
physician(s) before use. Electromagnetic fields
in close proximity to heart pacemaker could cause
pacemaker interference or pacemaker failure.
6. Do not expose welders to rain or wet conditions.
Water entering a welder will increase
the risk of electric shock.
7. Do not abuse the cord. Never use the cord
for carrying, pulling or unplugging the welder.
Keep cord away from heat, oil, sharp edges
or moving parts. Damaged or entangled
cords increase the risk of electric shock.
8. Do not use outdoors.
9. Insulate yourself from the workpiece and
ground. Use nonflammable, dry insulating
material if possible, or use dry rubber mats,
dry wood or plywood, or other dry insulating
material large enough to cover your full
area of contact with the work or ground.
Fire Safety
ARC AND HOT SLAG can cause fire.
1. Clear away or protect flammable objects.
Remove or make safe all combustible materials for a
radius of 35 feet (10 meters) around the work area.
Use a fire resistant material to cover
or block all open doorways, windows,
cracks, and other openings.
2. Keep ABC-type fire extinguisher near
work area and know how to use it.
3. Maintain a safe working environment.
Keep the work area well lit.
Make sure there is adequate
surrounding workspace. Keep the work area free
of obstructions, grease, oil, trash, and other debris.
4. Do not operate welders in atmospheres
containing dangerously reactive or
flammable liquids, gases, vapors, or dust.
Provide adequate ventilation in work areas
to prevent accumulation of such substances.
Welders create sparks which may ignite flammable
substances or make reactive fumes toxic.
5. If working on a metal wall, ceiling, etc.,
prevent ignition of combustibles on the
other side by moving the combustibles to a
safe location. If relocation of combustibles is
not possible, designate someone to serve as
a fire watch, equipped with a fire extinguisher,
during the cutting process and for at least one
half hour after the cutting is completed.
6. Do not weld or cut on materials having
a combustible coating or combustible
internal structure, as in walls or ceilings, without
an approved method for eliminating the hazard.
7. Do not dispose of hot slag in containers
holding combustible materials.
8. After welding, make a thorough examination
for evidence of fire. Be aware that easily
visible smoke or flame may not be present
for some time after the fire has started.
9. Do not apply heat to a container that has held
an unknown substance or a combustible
material whose contents, when heated,
can produce flammable or explosive vapors.
Clean and purge containers before applying heat.
Vent closed containers, including castings,
before preheating, welding, or cutting.
Page 4 For technical questions, please call 1-888-380-0318. Item 63617
Page 5

Welder Use and Care
1. Do not use the welder if the switch does not turn
it on and off. Any welder that cannot be controlled
with the switch is dangerous and must be repaired.
2. Disconnect the plug from the power
source before making any adjustments,
changing accessories, or storing welders.
Such preventive safety measures reduce the
risk of starting the welder accidentally.
3. Prevent unintentional starting.
Ensure the switch is in the offposition before connecting to power
source or moving the welder. Carrying
or energizing welders that have the
switch on invites accidents.
Maintenance
1. Maintain welders. Check for misalignment or
binding of moving parts, breakage of parts
and any other condition that may affect the
welder’s operation. If damaged, have the
welder repaired before use. Many accidents
are caused by poorly maintained welders.
2. Have your welder serviced by a qualified
repair person using only identical
replacement parts. This will ensure that
the safety of the welder is maintained.
4. Store idle welders out of the reach of
children and do not allow persons unfamiliar
with the welder or these instructions to
operate the welder. Welders are dangerous
in the hands of untrained users.
5. Use the welder and accessories in
accordance with these instructions, taking
into account the working conditions and
the work to be performed. Use of the welder
for operations different from those intended
could result in a hazardous situation.
6. Do not use the welder for pipe thawing.
3. Maintain labels and nameplates on the Welder.
These carry important information.
If unreadable or missing, contact
Harbor Freight Tools for a replacement.
4. Unplug before maintenance. Unplug the Welder
from its electrical outlet before any inspection,
maintenance, or cleaning procedures.
SAFETYMAINTENANCE BASIC WELDINGWELDING TIPS SETUP
Gas Shielded Welding – Cylinder Safety
Cylinders can explode when damaged.
1. Never weld on a pressurized or a closed cylinder.
2. Never allow an electrode holder,
electrode, welding torch, or welding
wire to touch the cylinder.
3. Keep cylinders away from any electrical circuits,
including welding circuits.
4. Keep protective cap in place over the valve
except when the cylinder is in use.
5. Use only correct gas shielding equipment
designed specifically for the type of welding
you will do. Maintain this equipment properly.
6. Protect gas cylinders from heat, being struck,
physical damage, slag, flames, sparks, and arcs.
7. Always use proper procedures
to move cylinders.
SAVE THESE INSTRUCTIONS.
Page 5For technical questions, please call 1-888-380-0318.Item 63617
Page 6

Grounding
SAFETY MAINTENANCEBASIC WELDING WELDING TIPSSETUP
TO PREVENT ELECTRIC SHOCK AND DEATH
FROM INCORRECT GROUNDING WIRE CONNECTION:
Check with a qualified electrician if you are in doubt as to whether the outlet is
properly grounded.
Do not use the Welder if the power cord or plug is damaged. If damaged, have it repaired by a service
facility before use. If the plug will not fit the outlet, have a proper outlet installed by a qualified electrician,
do not use adapter plugs.
1. The green wire inside the cord is connected to
the grounding system in the Welder. The green
wire in the cord must be the only wire connected
to the Welder’s grounding system and must
never be attached to an electrically “live” terminal.
Never leave the grounding wire disconnected
or modify the Power Cord Plug in any way.
2. Make sure the tool is connected to an outlet having
the same configuration as the plug. If the tool must
be reconnected for use on a different type of electric
circuit, the reconnection should be made by qualified
service personnel; and after reconnection, the tool
should comply with all local codes and ordinances.
Extension Cords
Do not use an extension cord on this Welder.
Replacement Cords
1. Use only one of the supplied power cords for
this Welder or an identical replacement cord.
2. Do not install a thinner or longer
cord on this Welder.
3. Do not patch cords of any length
together for this item. Patches may allow
moisture to penetrate the insulation,
resulting in electric shock.
Page 6 For technical questions, please call 1-888-380-0318. Item 63617
Page 7

Symbology
VAC
A
OCV
KVA
Wire Feed (Speed)
Workpiece Ground Cable
Torch Cable
Overheat Shutdown Indicator
Cooling Fan
Housing Ground Point
Volts Alternating Current
Amperes
Open Circuit Voltage
Kilovolt Amperes
(Volts / 1000 * Amperes)
IPM
AWG
Inches Per Minute
American Wire Gauge
SAFETYMAINTENANCE BASIC WELDINGWELDING TIPS SETUP
Electric Shock Hazard.
Do not touch energized parts.
Inhalation Hazard.
Keep head out of fumes
and use proper ventilation.
Read manual before
setup and/or use.
Fire Hazard.
Keep flammable materials
away during welding. Spatter
can cause accidental fires.
Arc Ray Hazard.
Wear welding helmet with
properly rated filter lens.
Pacemaker Hazard.
Welding processes may
interfere with pacemakers.
Consult doctor before use.
Specifications
Power Input 120 VAC / 60 Hz 240 VAC / 60 Hz
Current Input at Output
Welding Current Range 30 –140 A 30 –220 A
Rated Duty Cycles
Open Circuit Voltage 78 VDC 78 VDC
Welding Wire Capacity
Wire Speed 50 – 500 IPM
Wire Spool Capacity Up to 12 lb spool
15 A: 20.7 A at 100 A
20 A: 24.3 A at 115 A
40% @ 100 A
15 A:
100% @ 75 A
30% @ 115 A
20 A:
100% @ 75 A
Flux Cored: 0.030" / 0.035" / 0.045"
24.8 A at 200 A
25% @ 200 A
100% @ 115 A
Solid Core: 0.025" / 0.030" / 0.035"
Page 7For technical questions, please call 1-888-380-0318.Item 63617
Page 8

Setup
Read the ENTIRE IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION section at the beginning of this manual
SAFETY MAINTENANCEBASIC WELDING WELDING TIPSSETUP
Note: Remove the protective foam and cardboard from the Welder before setup.
including all text under subheadings therein before set up or use of this product.
TO PREVENT SERIOUS INJURY FROM ACCIDENTAL OPERATION:
Turn the Power Switch off and unplug the Welder before setup.
Wire Spool Installation / Wire Setup
1. Turn the Power Switch OFF and unplug
the Welder before proceeding.
Power
Switch
2. Pull up on the Door Latch,
then open the Door.
3. 2 Pound Wire Spool Installation:
Remove the Wingnut and Spacer. If
replacing a Spool, remove the old Spool
and all remaining wire from the liners.
4. Place the new Wire Spool over the Spool Spindle
and against the Spool Brake Pad as illustrated.
To prevent wire feed problems, set the
Spool so that it will unwind clockwise.
5. Replace the Spacer over the
Spool Spindle and secure Spool
in place with the Wingnut.
Notice: If Wire Spool can spin freely, Wingnut is too
loose. This will cause the welding wire to unravel and
unspool which can cause tangling and feeding problems.
Door
Door
Latch
Wingnut
Spacer
Spool
Spindle
2 lb
Wire Spool
Spool
Brake Pad
Welder
Wall
2 lb Spool Loading
Page 8 For technical questions, please call 1-888-380-0318. Item 63617
Page 9

6. 10-12 Pound Wire Spool Installation:
Remove the Wingnut and Spacer. If
replacing a Spool, remove the old Spool
and all remaining wire from the liners.
Spool Knob
Wingnut
7. Place the Spool Adapter over the Spool Spindle
and against the Spool Brake Pad as illustrated.
8. Place the new Wire Spool over the Adapter and
line up pin on Adapter with hole in Spool.
To prevent wire feed problems, set the
Spool so that it will unwind clockwise.
9. Replace the Spacer over the Spool Spindle
and secure Spool in place with the Wingnut.
Notice: If Wire Spool can spin freely, Wingnut
is too loose. This will cause the welding
wire to unravel and unspool which can
cause tangling and feeding problems.
10. Screw the Spool Knob into the Spool Adapter.
10-12 lb
Spool
Adapter
Wire
must
unwind
in this
direction
10-12 lb Spool Loading
Spacer
10-12 lb
Wire Spool
Spool Spindle
Spool
Brake Pad
Welder
Wall
SAFETYMAINTENANCE BASIC WELDINGWELDING TIPS SETUP
11. DCEN Direct Current Electrode Negative
Wire Setup for Flux-Cored (gasless) welding:
Remove the two Wingnuts securing the cables.
Connect the Black Ground Cable to the positive (+)
Terminal using the Wingnut.
Connect the Red Cable to the negative (–)
Terminal using the other Wingnut.
Make sure the Cable connectors
sit flush in the grooves.
DCEN
Flux-Cored (Gasless) Polarity Setup
Page 9For technical questions, please call 1-888-380-0318.Item 63617
Page 10
Reset
Power Input
Gas Inlet
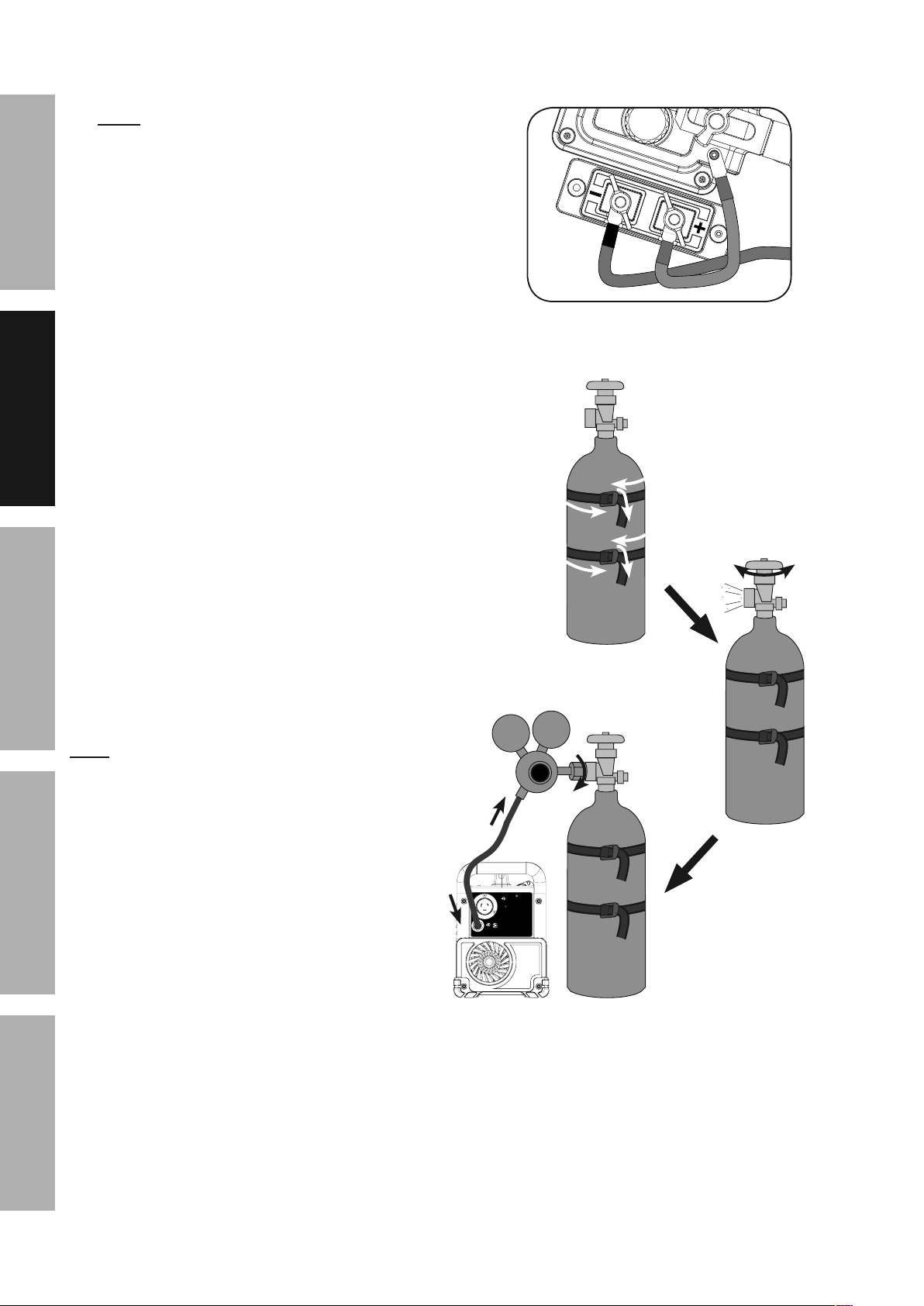
12. DCEP Direct Current Electrode Positive Wire
SAFETY MAINTENANCEBASIC WELDING WELDING TIPSSETUP
Setup for Solid Core (gas shielded) welding:
a. Remove the two Wingnuts securing the
cables. Connect the Black Ground Cable to the
negative (–) Terminal using the Wingnut.
Connect the Red Cable to the positive (+)
Terminal using the other Wingnut.
Make sure the Cable connectors
sit flush in the grooves.
b. Determine which type of shielding gas
would be appropriate for the welding
you will do. Refer to the Settings Chart
on the inside of the Welder door.
DCEP
Solid Core (Gas Shielded) Polarity Setup
c. With assistance, set the cylinder (not included)
onto a cabinet or cart near the Welder
and secure the cylinder in place with two
straps (not included) to prevent tipping.
d. Remove the cylinder’s cap. Stand to the
side of the valve opening, then open the
valve briefly to blow dust and dirt from the
valve opening. Close the cylinder valve.
e. Locate the Regulator (included) and close its
valve until it is loose, then thread Regulator
onto cylinder and wrench tighten connection.
Note: When using C100 shielding gas, connect the
enclosed CGA 580/320 adapter to the inlet connection
of the Regulator and wrench tighten. Thread the
adapter onto the gas cylinder and wrench tighten.
f. Attach the Gas Hose (included) to the
Regulator’s outlet and the Welder’s gas
inlet. Wrench-tighten both connections.
c
Briefly open valve
d
to clean,
then close
valve.
f
e
Page 10 For technical questions, please call 1-888-380-0318. Item 63617
Page 11

13. Turn the Feed Tensioner knob counterclockwise to
loosen it enough to pull it down to remove tension.
The spring-loaded Idler Arm will move up as shown.
Feed Tensioner
Idler Arm
SAFETYMAINTENANCE BASIC WELDINGWELDING TIPS SETUP
14. Feed Roller Instructions:
Check that the Feed Roller is correct for the
type of wire being used (solid core or fluxcored) and that it is turned to properly match
the wire size marked on the Wire Spool:
a. Unscrew the Feed Roller Knob counterclockwise.
b. Remove the Feed Roller Knob to
expose the Feed Roller.
Feed Roller
Knob
Solid Core
V-Groove
groove
0.030 / 0.035
0.025
groove
A
Feed
Roller
B
c. Flip or replace the Feed Roller as needed and
confirm that it is the correct Roller for the type of
wire being used and that the number showing
is the same as the wire diameter on the Spool.
d. Screw the Feed Roller Knob back into
place to secure the Feed Roller.
0.045
groove
0.030 / 0.035
Flux-Cored
Knurled Groove
C
groove
D
Page 11For technical questions, please call 1-888-380-0318.Item 63617
Page 12

Wire Feed
Mechanism
15. Loosen the Knob on the Wire Feed
SAFETY MAINTENANCEBASIC WELDING WELDING TIPSSETUP
mechanism, then insert the Gun Cable
Connector through the hole on the Welder
front and into the socket on the Wire Feed.
16. Ensure that the Gun Cable Connector
is fully inserted into the socket on
the Wire Feed mechanism as shown,
then tighten the Knob securely.
If Connector is not fully inserted, the gas
connection will leak, preventing shielding
gas from reaching the welding arc.
NOTICE: To prevent damage, do
not overtighten the Knob.
Gun Cable
Connector
Knob
Incorrect – Connector not fully inserted
Wire
Feed
Control
Cable
17. Connect the Wire Feed Control Cable to the
Wire Feed Control Socket located on the front
of the machine and tighten the lock ring on the
Cable plug. Note that the plug on the Cable fits
into the Socket in one specific orientation only.
Securely hold onto the end of the welding wire and keep
tension on it during the following steps.
If this is not done, the welding wire will unravel and unspool
which can cause tangling and feeding problems.
18. Cut off all bent and crimped wire.
The cut end must have no burrs or
sharp edges; cut again if needed.
IMPORTANT
Welding
Wire
Correct – Connector fully inserted
HOLD WIRE
SECURELY
Feed
Guide
19. Keep tension on the wire and guide at
least 12 inches of wire into the Wire
Inlet Liner and Feed Guide.
Page 12 For technical questions, please call 1-888-380-0318. Item 63617
Wire
Spool
Wire Inlet
Liner
Page 13

20. Make sure the welding wire is resting in the groove
Reset
Power Input
Gas Inlet
of the Feed Roller, then push the wire Idler Arm
down, and swing the Feed Tensioner up to latch it
across the tip of the arm.
After the wire is held by the Tensioner,
you may release it.
Note: The tension should be 3 – 5 for solid wire and
2 – 3 for flux-cored wire. Too much force on flux-cored
wire will crush it and may cause feeding issues.
21. Pull the Nozzle to remove it.
Idler Arm
Feed Tensioner
SAFETYMAINTENANCE BASIC WELDINGWELDING TIPS SETUP
MIG Gun
22. Unscrew the Contact Tip
counterclockwise and remove.
23. Lay the MIG Gun Cable out in a straight line so
that the welding wire moves through it easily.
Leave the cover open, so that the feed
mechanism can be observed.
Nozzle
Contact
IMPORTANT
Stainless steel wire is less flexible than other welding wire. Therefore, it is
more difficult to feed through the liner and gun. It is especially important
to keep the gun cable straight while feeding stainless steel wire.
DANGER
PARTS MAY BE AT WELDING VOLTAGE
TO PREVENT ELECTRIC SHOCK AND DEATH:
1. Keep hands away from Wire Feed mechanism.
Tip
2. Close door before plugging in, unless using Cold
3. Do not touch Trigger while feeding wire through to gun.
24. Plug either 120 VAC or 240 VAC Power
Cord into Power Input Socket.
Note: Plug will only fit one way.
Wire Feed to feed wire through to gun.
Power
Input
Page 13For technical questions, please call 1-888-380-0318.Item 63617
Page 14

25. Do not touch the Gun’s Trigger. Plug the Power
Cord into a properly grounded, GFCI protected
SAFETY MAINTENANCEBASIC WELDING WELDING TIPSSETUP
120 VAC (20 amp rated) or 240 VAC receptacle that
matches the plug and turn the Power Switch ON.
The circuit must be equipped with delayed
action-type circuit breaker or fuses.
Power
Switch
26. Point the Gun away from
all objects. Press and
hold the Cold Wire Feed
Switch until the wire feeds
through two inches.
The wire liner may come
out with the welding
wire. This is normal,
just push the wire liner
back into the Gun.
If the wire does not feed
properly and the Spool
is stationary, turn OFF
and unplug the Welder
and slightly tighten the
Feed Tensioner clockwise
before retrying.
27. To check the wire’s drive tension, press and hold
Trigger to feed the wire against a piece of wood
from 2 to 3 inches away.
Note: After pressing Trigger, wire will stop
feeding after 3 seconds if there is no arc.
Check tension for less than 3 seconds.
If the wire stops instead of bending, unplug
the Welder, slightly tighten the Feed Tensioner
clockwise, and try again. If the wire bends from
the feed pressure, then the tension is set properly.
Cold Wire
Feed Switch
2"
Welding
Wire
Incrementally
increase tension
until
wire bends.
MIG Gun
2–3"
28. Turn OFF the Power Switch and unplug the
Power Cord from its electrical outlet.
29. Close the Door. Make sure
Door is securely latched.
30. Select a Contact Tip that is compatible with
the welding wire used. Slide the Contact
Tip over the wire and thread it clockwise into
the MIG Gun. Tighten the Contact Tip.
31. Replace the Nozzle and cut the wire
off at 1/2" from tip (1/2" stickout).
Page 14 For technical questions, please call 1-888-380-0318. Item 63617
Nozzle
Contact
Tip
MIG Gun
Page 15

Basic Welding
Read the ENTIRE IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION section at the beginning of this manual
including all text under subheadings therein before welding.
TO PREVENT SERIOUS INJURY:
Protective gear must be worn when using the Welder; minimum shade number 10 full face shield
(or welding mask), ear protection, welding gloves, sleeves and apron, NIOSH-approved respirator, and fire
resistant work clothes without pockets should be worn when welding.
Light from the arc can cause permanent damage to the eyes and skin.
Do not breathe arc fumes.
Flux-cored wire welding is used to weld mild steel
and stainless steel without shielding gas.
MIG welding uses solid wire and shielding gas,
and is used to weld mild steel and stainless steel.
MIG welding can also be used to weld thinner
workpieces than flux-cored welding can.
Aluminum welding can be performed with an
optional Spool Gun (sold separately) using
aluminum wire and shielding gas.
Good welding takes a degree of skill and experience.
Practice a few sample welds on scrap before
welding your first project. Additional practice
periods are recommended whenever you weld:
• a different thickness of material
• a different type of material
• a different type of connection
• using a different process (MIG vs. Flux)
Make practice welds on pieces of scrap to practice
technique before welding anything of value.
SAFETYMAINTENANCE BASIC WELDINGWELDING TIPS SETUP
TO PREVENT SERIOUS INJURY,
FIRE AND BURNS:
Keep welding tip clear of grounded
objects whenever unit is plugged
in and turned on.
Practice your welding
technique on scrap
pieces before welding
anything of value.
Power
On
=
Page 15For technical questions, please call 1-888-380-0318.Item 63617
Page 16

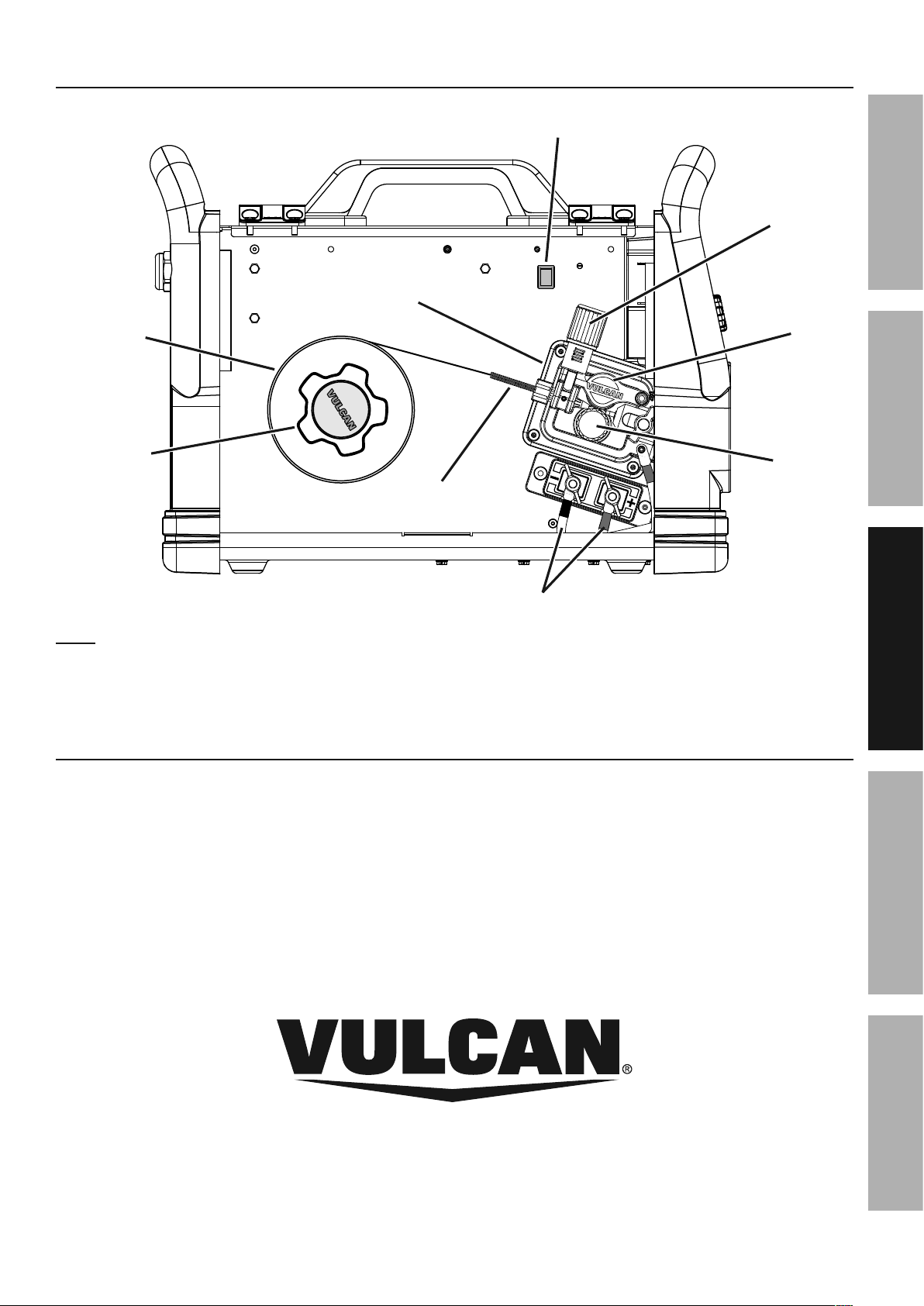
Front Panel Controls
Voltage
Input /
SAFETY MAINTENANCEBASIC WELDING WELDING TIPSSETUP
Thermal
Overload
Indicator
Power ON
Indicator
Material
Thickness /
Voltage Knob
Synergic
Indicator
Power
Switch
Process
Selection Knob
Wire Speed
Knob
MIG Gun /
Spool Gun
Cable Socket
Wire Feed
Control Socket
Ground
Cable
Voltage Input / Thermal Overload Indicator:
Lights up if the input voltage is outside the
machine’s specifications or duty cycle has been
exceeded, resulting in overheating the Welder.
Power ON Indicator: When illuminated
indicates that the Power Switch is on.
Material Thickness / Voltage Knob: This
controls the output voltage of the Welder.
Synergic Indicator: Lights when using Auto Settings
and flashes if chosen settings are incorrect.
Power Switch: Turns on power to the
Welder and internal cooling fan.
MIG Gun / Spool Gun Cable Socket: The MIG Gun
and Spool Gun Cables connect here. The wire,
welding current, and shielding gas (if performing
MIG) feed to the weld through here.
Wire Diameter
Selection Knob
Spool Gun
Gas Outlet
Wire Feed Control Socket: The MIG Gun and
Spool Gun Control Cables connect here.
Ground Cable: This connects to the base
metal to provide a good connection for the
current to travel back to the Welder.
Spool Gun Gas Outlet: When using optional Spool
Gun (sold separately), gas hose connects here.
Wire Diameter Selection Knob: Sets the
diameter of the welding wire to be used.
Wire Speed Knob: Controls the speed that the
welding wire feeds out of the MIG Gun or Spool
Gun and the output amperage of the Welder.
Process Selection Knob: Adjust to select
the welding process to be used.
Page 16 For technical questions, please call 1-888-380-0318. Item 63617
Page 17
Interior Controls
Wire Spool
Wire Feed
Mechanism
Cold Wire
Feed Switch
Feed
Tensioner
Idler
Arm
SAFETYMAINTENANCE BASIC WELDINGWELDING TIPS SETUP
Spool Knob
Wire Inlet
Liner
Polarity Cables
Note: When using an optional Spool Gun (sold separately), connect the Spool Gun gas
hose to the Spool Gun Gas Outlet (see Front Panel Controls on previous page).
Weld Settings
Refer to the Settings Chart on the inside of the Welder door for Flux-Cored and MIG Weld
settings. The chart is only intended to show general guidelines for different wire sizes and for
different thicknesses of material. The initial settings used at the beginning of a weld may need to be
adjusted after stopping and carefully inspecting the weld. Proper welding takes experience.
Feed
Roller Knob
Page 17For technical questions, please call 1-888-380-0318.Item 63617
Page 18

Duty Cycle (Duration of Use)
Avoid damage to the Welder by not welding
for more than the prescribed duty cycle
SAFETY MAINTENANCEBASIC WELDING WELDING TIPSSETUP
time. The Duty Cycle defines the number of
minutes, within a 10 minute period, during
which a given welder can produce a particular
welding current without overheating.
For example, a welder with a 40% duty
cycle at 100 A welding current must be
allowed to rest for at least 6 minutes after
every 4 minutes of continuous welding.
40% Use at 100A
For 10 Continuous Minutes
4
Minutes
Welding
6
Minutes
Resting
Failure to carefully observe duty cycle limitations
can easily over-stress a welder’s power generation
system contributing to premature welder failure.
This Welder has an internal thermal protection
system to help prevent this sort of over-stress.
When the Welder overheats, it automatically
shuts down and the Overload Indicator
lights. The Welder automatically returns to
service after cooling off. Should this occur,
rest the MIG Gun on an electrically nonconductive, heat-proof surface, such as a
concrete slab, well clear of the ground clamp.
Allow the Welder to cool with the Power
Switch on, so that the internal Fan will help
cool the Welder.
When the Overload Indicator is no longer
lit and the Welder can be used again, use
shorter welding periods and longer rest
periods to prevent needless wear.
Overload
Indicator
100% Continuous Use at 75A
25% Use at 200A
For 10 Continuous Minutes
2-1/2
Minutes
Welding
7-1/2
Minutes
Resting
100% Continuous Use at 115A
MIG Gun
Power
Switch
concrete slab
(or other heat-proof,
non-conductive surface)
Page 18 For technical questions, please call 1-888-380-0318. Item 63617
Page 19

Setting Up The Weld
1. Make practice welds on pieces of scrap the
same thickness as your intended workpiece
to practice technique before welding anything
of value. Clean the weld surfaces thoroughly
with a wire brush or angle grinder; there
must be no rust, paint, oil, or other materials
on the weld surfaces, only bare metal.
2. Use clamps (not included) to hold the workpieces
in position so that you can concentrate on
proper welding technique. The distance
(if any) between the two workpieces must be
controlled properly to allow the weld to hold
both sides securely while allowing the weld
to penetrate fully into the joint. The edges of
thicker workpieces may need to be chamfered
(or beveled) to allow proper weld penetration.
Notice: When welding equipment on a vehicle,
disconnect the vehicle battery power from both the
positive connection and the ground before welding.
This prevents damage to some vehicle electrical
systems and electronics due to the high voltage
and high frequency bursts common in welding.
clamps
SAFETYMAINTENANCE BASIC WELDINGWELDING TIPS SETUP
workpieces
Clean
surfaces to
bare metal.
Chamfer thick workpieces.
3. Clamp Ground Cable to bare metal on the
workpiece near the weld area, or to metal work
bench where the workpiece is clamped.
4. Turn the Power Switch to the OFF position,
then plug the Power Cord into a properly
grounded, GFCI protected 120 VAC (20 amp
rated) or 240 VAC receptacle that matches
the plug. The circuit must be equipped with
delayed action-type circuit breaker or fuses.
Ground
Power
Switch
Workpiece
Clean
surface to
bare metal.
Clamp
Page 19For technical questions, please call 1-888-380-0318.Item 63617
Page 20

5. Set MIG Gun down on nonconductive,
SAFETY MAINTENANCEBASIC WELDING WELDING TIPSSETUP
nonflammable surface away from any grounded
objects. Turn the Power Switch ON.
6. Settings - Refer to Label on the
inside of the Welder door.
a. Auto (Synergic) Settings – Synergic
Indicator will light:
• Set Process
• Set Wire Diameter
Note: If using 0.045" flux-cored wire, set Wire
Diameter to MANUAL. In this case, Synergic welding
will be turned off. Refer to Manual Settings below.
• Set Material Thickness – If Synergic
Indicator flashes, Material Thickness
setting is incorrect – refer to Settings
Chart for proper weld settings
b. Manual Settings:
• Set Process
• Set Wire Diameter to MANUAL
• Set Wire Feed Speed according
to Settings Chart
• Set Voltage according to Settings Chart
Note: The initial settings may need to be
adjusted after stopping and carefully inspecting
the weld. Proper welding takes experience.
Power
Switch
DANGER! TO PREVENT DEATH
FROM ASPHYXIATION:
Do not open gas without proper ventilation. Fix
gas leaks immediately.
Shielding gas can displace air and cause rapid loss of
consciousness and death.
Shielding gas without carbon dioxide can be even
more hazardous because asphyxiation can start
without feeling shortness of breath.
7. Gas shielded, solid-core wire only:
a. Open gas cylinder valve all the way.
b. Set Flow Gauge to SCFH value
indicated on Settings Chart.
Page 20 For technical questions, please call 1-888-380-0318. Item 63617
Page 21

Basic Welding Technique
1. Press (and hold) MIG Gun Trigger and contact the
area to be welded with electrode wire to ignite arc.
2. For a narrow weld, you can usually draw the wire in
a steady straight line.
This is called a stringer bead.
For a wider weld, draw the wire back and forth
across the joint.
This is called a weave bead and takes
practice to perform properly.
3. Direct the welding wire straight into the joint.
This gives an angle of 90° (straight up and
down) for butt (end to end) welds, and an
angle of 45° for fillet (T-shaped) welds.
stringer bead weave bead
Weld MIG Gun angles,
viewed from front of weld joint.
45°
SAFETYMAINTENANCE BASIC WELDINGWELDING TIPS SETUP
90°
4. For MIG welding using solid wire and
shielding gas, the end of the MIG Gun should
be tilted so that wire is angled anywhere
in-between straight on and 15° away
from the direction you are welding. The
amount of tilt is called the push angle.
5. When using flux-cored wire without
shielding gas, the end of the MIG Gun
should be tilted so that wire is angled
anywhere in-between straight on and
15° in the direction you are welding. The
amount of tilt is called the drag angle.
fillet weld joint
Push Angle
0-15°
Weld
Direction
Solid Wire with Shielding Gas Flux-Cored Wire without Gas
butt weld joint
Drag Angle
0-15°
Weld
Direction
CTWD
(up to 1/2")
6. The Contact Tip should remain within 1/2"
of the work surface. This distance is called
CTWD - Contact Tip to Work Distance.
Page 21For technical questions, please call 1-888-380-0318.Item 63617
Page 22

Note: If Welder is used too long, the Overload
Indicator lights up and the unit automatically
shuts down. The Welder automatically returns
to service after cooling off. Should this occur,
rest the MIG Gun on an electrically non-
SAFETY MAINTENANCEBASIC WELDING WELDING TIPSSETUP
conductive, heat-proof surface, such as a
concrete slab, away from the ground clamp.
Allow the Welder to cool with the
Power Switch on, so that the internal
Fan will help cool the Welder.
When the Overload Indicator is no longer
lit and the Welder can be used again, use
shorter welding periods and longer rest
periods to help prevent needless wear.
7. After welding the test weld on a piece
of scrap for a few seconds, stop, and
check your progress. Clean, then compare
your weld’s appearance with the diagrams
and descriptions in the Welding Tips section
starting on the next page. After making any
necessary adjustments, continue to weld
while carefully following the DUTY CYCLE
guidelines as explained on page 18.
CAUTION! Weld will be hot, do not touch.
Overload
MIG Gun
Indicator
Power
Switch
concrete slab
(or other heat-proof,
non-conductive surface)
After practice welding for a few seconds,
STOP and examine your weld using the
guidelines starting on the next page.
FOLLOW DUTY CYCLE!
120 VAC
40% Use at 100 A
For 10 Continuous Minutes
4
Minutes
Welding
100% Continuous Use at 75 A
6
Minutes
Resting
For 10 Continuous Minutes
2-1/2
Minutes
Welding
100% Continuous Use at 115 A
240 VAC
25% Use at 200 A
7-1/2
Minutes
Resting
8. When welding is complete, set the MIG
Gun down on a heat-proof, electrically
non-conductive surface.
Turn the Power Switch OFF.
9. Allow Welder to cool down, then
unplug the Power Cord.
10. Remove Ground Clamp from workpiece
or table and disconnect MIG Gun.
11. Respool wire by clipping wire, removing gas
nozzle/contact tip on MIG gun, releasing Idler
Arm on Wire Feed mechanism, and rotating
the Wire Spool counterclockwise. Be sure
to securely hold wire as it is being respooled
because the end of wire has a tendency to
quickly unravel once it clears the wire feeder.
12. MIG ONLY:
Close shielding gas cylinder valve
securely. Remove Regulator and
replace cap. Disconnect Gas Hose from
Welder. Store and secure gas cylinder.
MIG Gun
concrete slab
(or other heat-proof,
non-conductive surface)
Power
Switch
Page 22 For technical questions, please call 1-888-380-0318. Item 63617
Page 23

Welding Tips
A good way to test welding technique is to examine a
weld’s appearance after it has cooled and the slag
has been removed. Then, better welding can be
learned by adjusting your weld technique to remedy
any problems found.
Cleaning the Weld
TO PREVENT SERIOUS INJURY:
Continue to wear ANSI-approved
safety goggles and protective wear
when cleaning a weld.
Sparks or chips may fly when cleaning.
1. A weld from flux-cored wire will be
covered by slag. Use a chipping hammer
to knock this off. Be careful not to
damage the weld or base material.
2. Use a wire brush to further clean the weld
or use an angle grinder (sold separately) to
shape the weld.
A typical flux-cored wire (FCAW) weld
before cleaning.
slag
base metal
A typical solid wire (GMAW) weld
before cleaning.
weld bead
base metal
Chipping
Hammer
weld bead
spatter
SAFETYMAINTENANCE BASIC WELDINGWELDING TIPS SETUP
spatter
Wire Brush
Strike Test
A test weld on a PIECE OF SCRAP can be tested by
using the following procedure.
WEAR ANSI-APPROVED SAFETY GOGGLES
DURING THIS PROCEDURE.
WARNING! This test WILL damage the weld it is
performed on. This test is ONLY an indicator of weld
technique and is not intended to test working welds.
1. After two scraps have been welded together and the
weld has cooled, clamp one scrap in a sturdy vise.
2. Stay clear from underneath while you strike
the opposite scrap with a heavy hammer,
preferably a dead-blow hammer.
3. A GOOD WELD will deform but not break,
as shown on top.
A POOR WELD will be brittle and snap at the weld,
as shown on bottom.
dead-blow hammer
dead-blow hammer
clamp
SCRAP
workpiece
GOOD WELD
bends and is not brittle
clamp
SCRAP
workpiece
POOR WELD
snaps or cracks
Page 23For technical questions, please call 1-888-380-0318.Item 63617
Page 24

Weld Diagnosis
Workpiece Heat Control / Weld Penetration
SAFETY MAINTENANCEBASIC WELDING WELDING TIPSSETUP
Not hot enough Too hotIdeal heat
How to increase workpiece heat
and increase penetration:
(to weld THICKER workpieces properly)
a. Increase weld current
b. Decrease travel speed
c. Use faster wire feed
d. Use shorter CTWD
Example Weld Diagrams
PROPER PENETRATIONINADEQUATE PENETRATION
EXCESS PENETRATION OR
BURN-THROUGH
How to reduce workpiece heat
and limit penetration:
(to weld THINNER workpieces properly)
a. Decrease weld current
b. Increase travel speed
c. Use slower wire feed
d. Use longer CTWD
Good
Weld
Page 24 For technical questions, please call 1-888-380-0318. Item 63617
Voltage
Too Low or
Wire Feed
Too Slow
TO CORRECT:
or
Voltage
Too High or
Wire Feed
Too Fast
TO CORRECT:
or
Travel Speed
Too Fast
TO CORRECT:
travel
slower
Travel Speed
Too Slow
TO CORRECT:
travel
faster
CTWD
Too Long
or
Wrong Polarity
TO CORRECT:
Check Polarity
and
maintain
less
than 1/2"
CTWD
Page 25

Weld Problems
Penetration (Workpiece Heat Control)
EXCESS PENETRATION OR
BURN-THROUGH
Weld droops on top and
underneath, or falls through
entirely, making a hole.
POSSIBLE CAUSES AND SOLUTIONS
1. Workpiece overheating:
Reduce wire feed speed.
Decrease weld current.
2. Travel speed too slow:
Increase travel speed and ensure
that travel speed is kept steady.
3. Excessive material at weld:
Reduce wire feed speed.
Bend at Joint
PROPER PENETRATION
Weld is visible underneath and
bulges slightly on top.
PROFILE VIEWS
POSSIBLE CAUSES AND SOLUTIONS
1. Incorrect welding technique:
Maintain 1/2" or less CTWD.
Keep arc on leading edge of weld puddle.
Hold MIG Gun at proper angles.
2. Insufficient weld heat:
Reduce travel speed.
Increase weld current.
3. Workpieces too thick/close:
Bevel thick workpieces, allow slight
gap, and weld in several passes.
4. Insufficient weld material:
Increase wire feed speed.
INADEQUATE PENETRATION
Weld does not penetrate the
joint fully, just on the surface.
SAFETYMAINTENANCE BASIC WELDINGWELDING TIPS SETUP
PROFILE
VIEW
POSSIBLE CAUSES AND SOLUTIONS
1. Improper clamping:
Clamp workpieces securely.
Make tack welds to hold workpieces.
2. Excessive heat:
Weld a small portion and allow to cool before
proceeding.
Increase travel speed.
Reduce wire feed speed.
Coat of Slag Over Weld
TOP
VIEW
PARTIALLY CHIPPED AWAY TO SHOW WELD
Slag is a necessary part of a flux-cored wire
weld. It shields the weld from impurities.
Clean off the slag with a Chipping Hammer
and Wire Brush after welding.
Gas-shielded MIG welds are protected by the
shielding gas and do not need slag to protect them.
Weld Not Adhering Properly
Gaps present between weld and previous bead or
between weld and workpiece. See areas below.
PROFILE
VIEW
POSSIBLE CAUSES AND SOLUTIONS
1. Incorrect welding technique:
Place stringer bead at correct place in joint.
Adjust workpiece position or weld angle to permit
proper welding to bottom of piece.
Pause briefly at sides during weave bead.
Keep arc on leading edge of weld puddle.
Hold MIG Gun at proper angles.
2. Insufficient weld heat:
Increase current.
Increase wire feed speed.
3. Dirty workpiece:
Clean workpiece down to bare metal.
4. Insufficient weld material:
Increase wire feed speed.
5. Workpiece gap too narrow:
Widen groove or increase bevel.
Page 25For technical questions, please call 1-888-380-0318.Item 63617
Page 26

Porosity
SAFETY MAINTENANCEBASIC WELDING WELDING TIPSSETUP
Small cavities or holes in the bead.
Excessive Spatter
Fine spatter is normal.
Spatter that is grainy and large is a problem.
TOP
VIEW
POSSIBLE CAUSES AND SOLUTIONS
1. Incorrect polarity:
Check that polarity is set correctly
for type of welding.
2. Insufficient shielding gas (MIG only):
Increase flow of gas.
Clean nozzle.
Maintain proper CTWD.
3. Incorrect shielding gas (MIG only):
Use shielding gas recommended by wire supplier.
4. Dirty workpiece or welding wire:
Clean workpiece down to bare metal.
Make certain that wire is clean and free
from oil, coatings, and other residues.
5. Inconsistent travel speed:
Maintain steady travel speed.
6. CTWD too long:
Reduce CTWD.
TOP
VIEW
POSSIBLE CAUSES AND SOLUTIONS
1. Dirty workpiece or welding wire:
Clean workpiece down to bare metal.
Make certain that wire is clean and free
from oil, coatings, and other residues.
2. Incorrect polarity:
Check that polarity is set correctly
for type of welding.
3. Insufficient shielding gas (MIG only):
Increase flow of gas.
Clean nozzle.
Maintain proper CTWD.
4. Wire feeding too fast:
Reduce wire feed speed.
5. CTWD too long:
Reduce CTWD.
Crooked/Wavy Bead
TOP
VIEW
POSSIBLE CAUSES AND SOLUTIONS
1. Inaccurate welding:
Use two hands or rest hand on steady surface.
2. Inconsistent travel speed:
Maintain steady travel speed.
3. CTWD too long:
Reduce CTWD.
Page 26 For technical questions, please call 1-888-380-0318. Item 63617
Burn-Through
Base material melts away,
leaving a hole in the weld.
TOP
VIEW
POSSIBLE CAUSES AND SOLUTIONS
1. Workpiece overheating:
Reduce current and/or wire feed speed.
2. Travel speed too slow:
Increase travel speed and ensure
that travel speed is kept steady.
3. Excessive material at weld:
Reduce wire feed speed.
Page 27

Maintenance
TO PREVENT SERIOUS INJURY, FIRE AND BURNS:
Unplug the Welder, rest the MIG Gun on a heat-proof, electrically non-conductive surface, and
allow all parts of the Welder to cool thoroughly before service.
SAFETYMAINTENANCE BASIC WELDINGWELDING TIPS SETUP
1. BEFORE EACH USE, inspect the general
condition of the Welder. Check for:
• loose hardware
• misalignment or binding of moving parts
• damaged cord / electrical wiring
• frayed or damaged cables
• cracked or broken parts
• any other condition that may
affect its safe operation.
2. Periodically, have a qualified
technician remove the Rear Panel
and use compressed air to blow
out all dust from the interior.
3. Store in a clean and dry location.
4. For optimal weld quality, clean and
inspect the Contact Tip and Nozzle
before each use, as explained below.
Nozzle and Contact Tip Inspection and Cleaning
1. Make sure that the entire MIG Gun is completely
cool and that the Power Cord is unplugged
from the electrical outlet before proceeding.
2. Pull the Nozzle to remove it.
3. Scrub the interior of the Nozzle
clean with a wire brush.
MIG Gun
4. Examine the end of the Nozzle. The end should be
flat and even. If the end is uneven, chipped, melted,
cracked, or otherwise damaged, the Nozzle will
adversely effect the weld and should be replaced.
5. Unscrew the Contact Tip counterclockwise
and slide it off the welding wire to remove.
6. Scrub the outside of the Tip clean with a wire brush.
Clean out the inside of the tip with a tip
cleaner (sold separately). Check that the Tip
is the proper type for the wire size used.
7. Examine the shape of the hole at the end of
the Contact Tip. It should be an even circle; it
should not be oblong or have any bulges in it.
8. If any problems are noted, replace the
Contact Tip. Select a new Tip of the
correct size for the welding wire used.
9. Reinstall the Tip and securely
reinstall the Nozzle as well.
Nozzle
Contact
Tip
Page 27For technical questions, please call 1-888-380-0318.Item 63617
Page 28

Troubleshooting
IMPORTANT!
SAFETY MAINTENANCEBASIC WELDING WELDING TIPSSETUP
Be CERTAIN to shut off the Welder, disconnect it from power, and discharge the MIG Gun to
ground before adjusting, cleaning, or repairing the unit.
Problem Possible Causes Likely Solutions
1. Insufficient wire feed pressure.
2. Incorrect wire feed roll size.
Wire feed motor
runs but wire does
not feed properly
Wire creates a bird’s
nest during operation
Wire stops
during welding
Welding arc
not stable
Weak arc strength
3. Damaged MIG Gun, cable, or liner assembly.
4. Feed Tensioner is too tight.
1. Excess wire feed pressure.
2. Incorrect Contact Tip size.
3. MIG Gun Cable Connector not fully
inserted into Wire Feed mechanism.
4. Damaged liner.
1. Gun cable is severely bent and Wire
Feed mechanism cannot feed wire.
2. Gun liner is clogged or worn.
3. Gun liner is too small for welding
wire being used.
4. Wire is tangled on the spool.
5. Wire is not making contact with Feed Rollers.
6. Feed Roller is not making enough contact
with wire or is crushing flux-cored wire.
1. Wire not feeding properly.
2. Incorrect Contact Tip or liner
size or excessive wear.
3. Incorrect wire feed speed.
4. Loose MIG Gun cable or ground cable.
5. Damaged MIG Gun or loose
connection within Gun.
6. Incorrect polarity for process being run.
7. Gas coverage may be insufficient or too high.
8. Poor connection with workpiece.
1. Incorrect line voltage.
2. Improper gauge or length of cord.
3. Not enough current.
1. Increase wire feed pressure properly.
Follow step 27 on page 14.
2. Flip roll to correct size. Follow the Wire Spool
Installation instructions on page 8.
3. Have a qualified technician inspect these
parts and replace as necessary.
4. Loosen Feed Tensioner so it applies only
enough pressure to prevent continued
spinning after the Gun Trigger is released.
1. Adjust wire feed pressure properly.
Follow step 27 on page 14.
2. Replace with the proper tip for wire used.
3. Insert Gun Cable Connector properly. Follow
steps 15 and 16 on page 12.
4. Have a qualified technician inspect and
repair/replace as necessary.
1. Straighten Gun cable.
2. Check gun liner for obstruction. Replace if necessary.
3. Check that gun liner is correct size for wire.
4. Check wire for cross winding or tangled spool.
5. Check Feed Rollers and ensure correct
groove for wire diameter is being used.
6. Check Feed Tensioner and ensure it is set properly.
1. See first Troubleshooting section above.
2. Replace with the proper tip or liner size for wire used.
3. Adjust wire feed speed to achieve a more stable arc.
4. Check to ensure that all connections are tight.
5. Have a qualified technician inspect and
repair/replace as necessary.
6. Ensure polarity is correct for operation:
DCEP for MIG welding and DCEN for
Flux-Cored self-shielded welding.
7. Ensure gas flow rate is set according to Settings Chart.
Make sure MIG Gun Cable Connector is fully inserted
into Wire Feed mechanism with no O-Rings exposed.
8. Check the ground clamp connection to
the workpiece and machine. Ensure
the MIG Gun is properly secured.
1. Check the line voltage and, if insufficient, have
a licensed electrician remedy the situation.
2. Do not use an extension cord on this Welder.
Use only one of the supplied power cords for
this Welder or an identical replacement cord.
3. Switch current to proper setting for metal thickness.
Follow all safety precautions whenever diagnosing or servicing the equipment.
Page 28 For technical questions, please call 1-888-380-0318. Item 63617
Page 29

Troubleshooting (continued)
IMPORTANT!
Be CERTAIN to shut off the Welder, disconnect it from power, and discharge the MIG Gun to
ground before adjusting, cleaning, or repairing the unit.
Problem Possible Causes Likely Solutions
When switched on,
Power ON Indicator
lights but Welder
does not function
Power ON Indicator
does not light when
Welder is switched on
Wire feeds, but arc
does not ignite
Porosity in the
weld metal
1. Tripped thermal protection device.
2. Faulty or improperly connected Trigger.
3. Machine is in low- or
over-voltage protection.
4. Machine is in the incorrect mode.
1. Unit is not connected to outlet properly.
2. Outlet is unpowered.
3. Circuit supplies insufficient input voltage or
amperage.
4. Plug does not have correct rating.
5. Circuit breaker has tripped due
to high input amperage.
6. Input Power Cord is not seated properly.
1. Improper ground connection.
2. Improperly sized Contact Tip.
3. Excessively worn Contact Tip.
4. Dirty Contact Tip.
1. Shielding gas bottle is empty.
2. Not enough or too much shielding gas.
3. Dirty workpiece.
4. Gun is being used too far away from workpiece.
5. Polarity is incorrect for the application.
6. Dirty welding wire is introducing
contamination into the weld.
1. If the Voltage Input/Thermal Overload Indicator
is illuminated, Welder has overheated and shut
down. Stop and wait with the Power Switch ON
for the Welder to cool. The Welder automatically
returns to service after cooling off. Reduce
duration or frequency of welding periods to
help reduce wear on the Welder. Refer to Duty
Cycle (Duration of Use) on page 18.
2. Ensure the gun connection is properly
seated on machine. Qualified technician
must check and secure/replace Trigger.
3. Check input voltage and ensure it falls within
the specified range. If input voltage is correct,
press Reset Button on back of machine.
4. Ensure the Process Selection Knob is
switched to the correct process.
1. Verify the voltage at the outlet and
the connection to the outlet.
2. Check circuit breaker/GFCI devices; if any are tripped,
determine and remedy cause before resetting.
3. Verify that the circuit is designed to supply the
required input voltage and amperage as detailed on
the Specifications table. If the Voltage Input/Thermal
Overload Indicator is illuminated on machine, check
the input voltage to ensure it is within specified range.
4. Make sure installed plug is correct rating.
See Specifications on page 7.
5. Press Reset Button on back of
machine to reset circuit breaker.
6. Ensure the twist lock input Power
Cord is fully secured.
1. Make certain that the workpiece is contacted
properly by the Ground Clamp and that
the workpiece is properly cleaned near the
ground clamp and the welding location.
2. Verify that Contact Tip is the proper size
for welding wire. If needed, replace
Contact Tip with proper size and type.
3. Check that the hole in the tip is not
deformed or enlarged. If needed, replace
Contact Tip with proper size and type.
4. Properly clean Contact Tip.
1. Check gas bottle and replenish as necessary.
2. Check gas regulator to ensure proper flow.
3. Clean workpiece down to bare metal.
4. Check CTWD (contact tip to work
distance) for the proper procedure.
5. Check the polarity and ensure it is DCEP
for MIG and DCEN for Flux-Cored.
6. Make certain that welding wire is clean
and free of rust and residues.
SAFETYMAINTENANCE BASIC WELDINGWELDING TIPS SETUP
Follow all safety precautions whenever diagnosing or servicing the equipment.
Page 29For technical questions, please call 1-888-380-0318.Item 63617
Page 30

Parts List and Diagrams
Wiring Diagram
SAFETY MAINTENANCEBASIC WELDING WELDING TIPSSETUP
Switch
AC1
AC2
F
Fuse
G
Gas Valve 1 Gas Valve 2
Touch Switch
3
4
1
2
CN6
2
1
〜
+
4
3
〜
-
v
15V
J
2 1
FAN2
FAN2
RECITIFIER
1
2
〜
+
3
4
〜
-
IGBT
34
-t
FAN1
1
2
1
2
LED3
PFC
M3
control panel
CN5
10111213141516171819202122232425262728293031323334
123456789101112131415161718192021222324252627282930313233
LED2
Main Board
34
123456789
VR2
Remote Control Board
20
19
12
11
Gas Valve 1
5
6
CN1
Gas Valve 2
4
CN3
1
2
3
4
7
8
9
10
4
1
CN8
1234567
123
1234567
2
CN3
1
Drawing Wire MotorWire Feed Motor
M
12345
CN4
34
Gun switch
M
123
CN7
Hall Sensor
*
OUT+
OUT-
CN1
123
4
FAN1
VR1
LED1
Parts List
Part Description Qty
1 Right Cover 1
2 Handle Cover 1
3 Handle Base 1
4 Hinge – Right 2
5 Hinge – Left 2
6 Left Cover 1
7 Door Latch 1
8 Middle Panel 1
9 PFC Inductor 1
10 Spool 1
11 Wire Feeder 1
12 Remote Control PCB 1
13 Insulation Block 1
14 Display PCB 1
15 Front Handle Cover Plate 1
16 Ground Clamp Subassembly 1
17 Control Panel 1
18 Knob 2
19 Knob 2
20 Switch 1
21 Front Plate 1
22 Plug Connector 1
23 Bottom Housing 1
24 MIG Welding Torch 1
25 Output Inductor 1
26 Pneumatic Connector 3
27 Solenoid Valve 2
28 Pneumatic Connector 2
K1
K2
Part Description Qty
29 Copper Output Bracket 1
30 Board Insulation Paper 1
31 Main PCB 1
32 Fast Recovery Diode 6
33 Control PCB 1
34 Sheet Metal Air Duct 1
35 Rectifier Heatsink 1
36 Rectifier Heatsink Support Bar 1
37 Transformer 1
38 DC Fan 1
39 IGBT 2
40 Bridge Heatsink 1
41 Bridge Rectifier 2
42 Fast Recovery Diode 2
43 IGBT 4
44 IGBT Heatsink Support Bar 1
45 IGBT Heatsink 1
46 IGBT Heatsink 2
47 DC Fan 1
48 Y-Type Threaded Tee 1
49 Air Fitting 1
50 Overload Protector 1
51 120 Volt Power Cord 1
52 Rear Plate 1
53 Rear Handle Cover Plate 1
54 Power Socket 1
55 Rear Panel 1
56 240 Volt Power Cord 1
Page 30 For technical questions, please call 1-888-380-0318. Item 63617
Page 31

Assembly Diagram
14
15
16
13
12
3 2
11
4
10 9
8
5
6
7
1
55
54
53 52
56
51
50
49
48
47
46
45
SAFETYMAINTENANCE BASIC WELDINGWELDING TIPS SETUP
17
18
19
44
43
42
41
40
39
38
2725
23222120
24
26
28
29
30
32 3331
34
3635
37
Record Serial Number Here:
Note: If product has no serial number, record
month and year of purchase instead.
Note: Some parts are listed and shown for
illustration purposes only, and are not available
individually as replacement parts.
Page 31For technical questions, please call 1-888-380-0318.Item 63617
Page 32

PLEASE READ THE FOLLOWING CAREFULLY
THE MANUFACTURER AND/OR DISTRIBUTOR HAS PROVIDED THE PARTS LIST AND ASSEMBLY DIAGRAM
IN THIS MANUAL AS A REFERENCE TOOL ONLY. NEITHER THE MANUFACTURER OR DISTRIBUTOR
MAKES ANY REPRESENTATION OR WARRANTY OF ANY KIND TO THE BUYER THAT HE OR SHE IS
QUALIFIED TO MAKE ANY REPAIRS TO THE PRODUCT, OR THAT HE OR SHE IS QUALIFIED TO REPLACE
ANY PARTS OF THE PRODUCT. IN FACT, THE MANUFACTURER AND/OR DISTRIBUTOR EXPRESSLY
STATES THAT ALL REPAIRS AND PARTS REPLACEMENTS SHOULD BE UNDERTAKEN BY CERTIFIED AND
LICENSED TECHNICIANS, AND NOT BY THE BUYER. THE BUYER ASSUMES ALL RISK AND LIABILITY
ARISING OUT OF HIS OR HER REPAIRS TO THE ORIGINAL PRODUCT OR REPLACEMENT PARTS
THERETO, OR ARISING OUT OF HIS OR HER INSTALLATION OF REPLACEMENT PARTS THERETO.
Limited 90 Day Warranty
Harbor Freight Tools Co. makes every effort to assure that its products meet high quality and durability standards,
and warrants to the original purchaser that this product is free from defects in materials and workmanship for the
period of 90 days from the date of purchase. This warranty does not apply to damage due directly or indirectly,
to misuse, abuse, negligence or accidents, repairs or alterations outside our facilities, criminal activity, improper
installation, normal wear and tear, or to lack of maintenance. We shall in no event be liable for death, injuries
to persons or property, or for incidental, contingent, special or consequential damages arising from the use of
our product. Some states do not allow the exclusion or limitation of incidental or consequential damages, so the
above limitation of exclusion may not apply to you. THIS WARRANTY IS EXPRESSLY IN LIEU OF ALL OTHER
WARRANTIES, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING THE WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS.
To take advantage of this warranty, the product or part must be returned to us with transportation charges
prepaid. Proof of purchase date and an explanation of the complaint must accompany the merchandise.
If our inspection verifies the defect, we will either repair or replace the product at our election or we may
elect to refund the purchase price if we cannot readily and quickly provide you with a replacement. We will
return repaired products at our expense, but if we determine there is no defect, or that the defect resulted
from causes not within the scope of our warranty, then you must bear the cost of returning the product.
This warranty gives you specific legal rights and you may also have other rights which vary from state to state.
26541 Agoura Road • Calabasas, CA 91302 • 1-888-380-0318
 Loading...
Loading...