Page 1

Installing vRealize Automation
vRealize Automation 7.2
This document supports the version of each product listed and
supports all subsequent versions until the document is
replaced by a new edition. To check for more recent editions of
this document, see http://www.vmware.com/support/pubs.
EN-002325-02
Page 2

Installing vRealize Automation
You can find the most up-to-date technical documentation on the VMware Web site at:
hp://www.vmware.com/support/
The VMware Web site also provides the latest product updates.
If you have comments about this documentation, submit your feedback to:
docfeedback@vmware.com
Copyright © 2017 VMware, Inc. All rights reserved. Copyright and trademark information.
VMware, Inc.
3401 Hillview Ave.
Palo Alto, CA 94304
www.vmware.com
2 VMware, Inc.
Page 3

Contents
vRealize Automation Installation 7
Updated Information 9
vRealize Automation Installation Overview 11
1
vRealize Automation Installation Components 11
The vRealize Automation Appliance 12
Infrastructure as a Service 12
Deployment Type 14
Minimal vRealize Automation Deployments 15
Distributed vRealize Automation Deployments 16
Choosing Your Installation Method 17
Preparing for vRealize Automation Installation 19
2
Host Names and IP Addresses 19
Hardware and Virtual Machine Requirements 20
Browser Considerations 20
Password Considerations 21
Windows Server Requirements 21
IaaS Database Server Requirements 21
IaaS Web Service and Model Manager Server Requirements 22
IaaS Manager Service 23
Distributed Execution Manager Requirements 23
vRealize Automation Port Requirements 26
User Accounts and Credentials Required for Installation 28
Security 30
Certicates 30
Extracting Certicates and Private Keys 30
Security Passphrase 31
Third-Party Software 31
Time Synchronization 31
VMware, Inc.
Installing vRealize Automation with the Installation Wizard 33
3
Deploy the vRealize Automation Appliance 33
Using the Installation Wizard for Minimal Deployments 35
Run the Installation Wizard for a Minimal Deployment 35
Installing the Management Agent 35
Synchronize Server Times 38
Run the Prerequisite Checker 38
Specify Minimal Deployment Parameters 39
Create Snapshots Before You Begin the Installation 39
Finish the Installation 39
3
Page 4

Installing vRealize Automation
Address Installation Failures 40
Set Up Credentials for Initial Content Conguration 40
Using the Installation Wizard for Enterprise Deployments 41
Run the Installation Wizard for an Enterprise Deployment 41
Installing the Management Agent 42
Synchronize Server Times 44
Run the Prerequisite Checker 45
Specify Enterprise Deployment Parameters 46
Create Snapshots Before You Begin the Installation 46
Finish the Installation 46
Address Installation Failures 47
Set Up Credentials for Initial Content Conguration 48
The Standard vRealize Automation Installation Interfaces 49
4
Using the Standard Interfaces for Minimal Deployments 49
Minimal Deployment Checklist 49
Deploy and Congure the vRealize Automation Appliance 50
Installing IaaS Components 55
Using the Standard Interfaces for Distributed Deployments 60
Distributed Deployment Checklist 60
Distributed Installation Components 61
Disabling Load Balancer Health Checks 62
Certicate Trust Requirements in a Distributed Deployment 63
Congure Web Component, Manager Service and DEM Host Certicate Trust 63
Installation Worksheets 64
Deploy the vRealize Automation Appliance 66
Conguring Your Load Balancer 68
Conguring Appliances for vRealize Automation 68
Install the IaaS Components in a Distributed Conguration 74
Installing vRealize Automation Agents 97
Set the PowerShell Execution Policy to RemoteSigned 98
Choosing the Agent Installation Scenario 98
Agent Installation Location and Requirements 99
Installing and Conguring the Proxy Agent for vSphere 99
Installing the Proxy Agent for Hyper-V or XenServer 104
Installing the VDI Agent for XenDesktop 108
Installing the EPI Agent for Citrix 111
Installing the EPI Agent for Visual Basic Scripting 114
Installing the WMI Agent for Remote WMI Requests 117
vRealize Automation Post-Installation Tasks 121
5
Congure Federal Information Processing Standard Compliant Encryption 121
Replacing Self-Signed Certicates with Certicates Provided by an Authority 122
Change the Master vRealize Automation Appliance Host Name 122
Change a Replica vRealize Automation Appliance Host Name 123
Installing the vRealize Log Insight Agent on IaaS Servers 124
Congure Access to the Default Tenant 124
4 VMware, Inc.
Page 5

Troubleshooting a vRealize Automation Installation 127
6
Default Log Locations 127
Rolling Back a Failed Installation 128
Roll Back a Minimal Installation 128
Roll Back a Distributed Installation 129
Create a vRealize Automation Support Bundle 130
General Installation Troubleshooting 130
Installation or Upgrade Fails with a Load Balancer Timeout Error 130
Server Times Are Not Synchronized 131
Blank Pages May Appear When Using Internet Explorer 9 or 10 on Windows 7 131
Cannot Establish Trust Relationship for the SSL/TLS Secure Channel 132
Connect to the Network Through a Proxy Server 132
Console Steps for Initial Content Conguration 133
Cannot Downgrade vRealize Automation Licenses 134
Troubleshooting the vRealize Automation Appliance 134
Installers Fail to Download 134
Encryption.key File has Incorrect Permissions 134
Identity Manager Fails to Start After Horizon-Workspace Restart 135
Incorrect Appliance Role Assignments After Failover 136
Failures After Promotion of Replica and Master Nodes 136
Incorrect vRealize Automation Component Service Registrations 137
Troubleshooting IaaS Components 138
Validating Server Certicates for IaaS 138
Credentials Error When Running the IaaS Installer 138
Save Seings Warning Appears During IaaS Installation 139
Website Server and Distributed Execution Managers Fail to Install 139
IaaS Authentication Fails During IaaS Web and Model Management Installation 139
Failed to Install Model Manager Data and Web Components 140
IaaS Windows Servers Do Not Support FIPS 141
Adding an XaaS Endpoint Causes an Internal Error 141
Uninstalling a Proxy Agent Fails 142
Machine Requests Fail When Remote Transactions Are Disabled 142
Error in Manager Service Communication 143
Email Customization Behavior Has Changed 143
Troubleshooting Log-In Errors 144
Aempts to Log In as the IaaS Administrator with Incorrect UPN Format Credentials Fails with
No Explanation 144
Log In Fails with High Availability 144
Proxy Prevents VMware Identity Manager User Log In 145
Contents
Silent vRealize Automation Installation 147
7
Perform a Silent vRealize Automation Installation 147
Perform a Silent vRealize Automation Management Agent Installation 148
Silent vRealize Automation Installation Answer File 149
The vRealize Automation Installation Command Line 149
vRealize Automation Installation Command Line Basics 150
vRealize Automation Installation Command Names 150
The vRealize Automation Installation API 151
Convert Between vRealize Automation Silent Properties and JSON 152
VMware, Inc. 5
Page 6

Installing vRealize Automation
Index 153
6 VMware, Inc.
Page 7

vRealize Automation Installation
vRealize Automation Installation explains how to install VMware vRealize ™ Automation.
N Not all features and capabilities of vRealize Automation are available in all editions. For a
comparison of feature sets in each edition, see hps://www.vmware.com/products/vrealize-automation/.
Intended Audience
This information is intended for experienced Windows or Linux system administrators who are familiar
with virtual machine technology and data center operations.
VMware Technical Publications Glossary
VMware Technical Publications provides a glossary of terms that might be unfamiliar to you. For denitions
of terms as they are used in VMware technical documentation, go to
hp://www.vmware.com/support/pubs.
VMware, Inc.
7
Page 8

Installing vRealize Automation
8 VMware, Inc.
Page 9

Updated Information
The following table lists the changes to Installing vRealize Automation for this product release.
Revision Description
EN-002325-02
EN-002325-01 Added Congure a Datastore Cluster permission to “vSphere Agent Requirements,” on page 99.
EN-002325-00 Initial document release.
Added another restart in “Change the Master vRealize Automation Appliance Host Name,” on
n
page 122 and “Change a Replica vRealize Automation Appliance Host Name,” on page 123.
Added “Cannot Downgrade vRealize Automation Licenses,” on page 134.
n
VMware, Inc. 9
Page 10

Installing vRealize Automation
10 VMware, Inc.
Page 11

vRealize Automation Installation
Overview 1
You can install vRealize Automation through dierent means, each with varying levels of interactivity.
To install, you deploy a vRealize Automation appliance and then complete the bulk of the installation using
one of the following options:
A consolidated, browser-based Installation Wizard
n
Separate browser-based appliance conguration, and separate Windows installations for IaaS server
n
components
A command line based, silent installer that accepts input from an answer properties le
n
An installation REST API that accepts JSON formaed input
n
After installation, you start using vRealize Automation by customizing the environment and conguring
one or more tenants, which sets up access to self-service provisioning and life-cycle management of cloud
services.
If you installed earlier versions of vRealize Automation, note the following changes before you begin.
This release of vRealize Automation introduces an installation API that uses a JSON formaed version
n
of the silent installation seings.
See “The vRealize Automation Installation API,” on page 151.
This release supports the changing of vRealize Automation appliance host names.
n
See “Change the Master vRealize Automation Appliance Host Name,” on page 122.
This release of the vRealize Automation Installation Wizard introduces a post-installation option to
n
migrate data from an older deployment.
This chapter includes the following topics:
“vRealize Automation Installation Components,” on page 11
n
“Deployment Type,” on page 14
n
“Choosing Your Installation Method,” on page 17
n
vRealize Automation Installation Components
A typical vRealize Automation installation consists of a vRealize Automation appliance and one or more
Windows servers that, taken together, provide vRealize Automation Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS).
VMware, Inc.
11
Page 12

Installing vRealize Automation
The vRealize Automation Appliance
The vRealize Automation appliance is a precongured Linux virtual appliance. The vRealize Automation
appliance is delivered as an open virtualization le that you deploy on existing virtualized infrastructure
such as vSphere.
The vRealize Automation appliance performs several functions central to vRealize Automation.
The appliance contains the server that hosts the vRealize Automation product portal, where users log in
n
to access self-service provisioning and management of cloud services.
The appliance manages single sign-on (SSO) for user authorization and authentication.
n
The appliance server hosts a management interface for vRealize Automation appliance seings.
n
The appliance includes a precongured PostgreSQL database used for internal vRealize Automation
n
appliance operations.
In large deployments with redundant appliances, the secondary appliance databases serve as replicas to
provide high availability.
The appliance includes a precongured instance of vRealize Orchestrator. vRealize Automation uses
n
vRealize Orchestrator workows and actions to extend its capabilities.
The embedded instance of vRealize Orchestrator is now recommended. In older deployments or special
cases, however, users might connect vRealize Automation to an external vRealize Orchestrator instead.
The appliance contains the downloadable Management Agent installer. All Windows servers that make
n
up your vRealize Automation IaaS must install the Management Agent.
The Management Agent registers IaaS Windows servers with the vRealize Automation appliance,
automates the installation and management of IaaS components, and collects support and telemetry
information.
Infrastructure as a Service
vRealize Automation IaaS consists of one or more Windows servers that work together to model and
provision systems in private, public, or hybrid cloud infrastructures.
You install vRealize Automation IaaS components on one or more virtual or physical Windows servers.
After installation, IaaS operations appear under the Infrastructure tab in the product interface.
IaaS consists of the following components, which can be installed together or separately, depending on
deployment size.
Web Server
The IaaS Web server provides infrastructure administration and service authoring to the
vRealize Automation product interface. The Web server component communicates with the Manager
Service, which provides updates from the Distributed Execution Manager (DEM), SQL Server database, and
agents.
Model Manager
vRealize Automation uses models to facilitate integration with external systems and databases. The models
implement business logic used by the DEM.
The Model Manager provides services and utilities for persisting, versioning, securing, and distributing
model elements. Model Manager is hosted on one of the IaaS Web servers and communicates with DEMs,
the SQL Server database, and the product interface Web site.
12 VMware, Inc.
Page 13

Chapter 1 vRealize Automation Installation Overview
Manager Service
The Manager Service is a Windows service that coordinates communication between IaaS DEMs, the SQL
Server database, agents, and SMTP.
IaaS requires that only one Windows machine actively run the Manager Service. For backup or high
availability, you may deploy additional Windows machines where you manually start the Manager Service
if the active service stops.
I Simultaneously running an active Manager Service on multiple IaaS Windows servers makes
vRealize Automation unusable.
The Manager Service communicates with the Web server through the Model Manager and must be run
under a domain account with administrator privileges on all IaaS Windows servers.
SQL Server Database
IaaS uses a Microsoft SQL Server database to maintain information about the machines it manages, plus its
own elements and policies. Most users allow vRealize Automation to create the database during installation.
Alternatively, you may create the database separately if site policies require it.
Distributed Execution Manager
The IaaS DEM component runs the business logic of custom models, interacting with the IaaS SQL Server
database, and with external databases and systems. A common approach is to install DEMs on the IaaS
Windows server that hosts the active Manager Service, but it is not required.
Each DEM instance acts as a worker or orchestrator. The roles can be installed on the same or separate
servers.
DEM Worker—A DEM worker has one function, to run workows. Multiple DEM workers increase capacity
and can be installed on the same or separate servers.
DEM Orchestrator—A DEM orchestrator performs the following oversight functions.
Monitors DEM workers. If a worker stops or loses its connection to Model Manager, the DEM
n
orchestrator moves the workows to another DEM worker.
Schedules workows by creating new workow instances at the scheduled time.
n
Ensures that only one instance of a scheduled workow is running at a given time.
n
Preprocesses workows before they run. Preprocessing includes checking preconditions for workows
n
and creating the workow execution history.
The active DEM orchestrator needs a strong network connection to the Model Manager host. In large
deployments with multiple DEM orchestrators on separate servers, the secondary orchestrators serve as
backups by monitoring the active DEM orchestrator, and provide redundancy and failover if a problem
occurs with the active DEM orchestrator. For this kind of failover conguration, you might consider
installing the active DEM orchestrator with the active Manager Service host, and secondary DEM
orchestrators with the standby Manager Service hosts.
Agents
vRealize Automation IaaS uses agents to integrate with external systems and to manage information among
vRealize Automation components.
A common approach is to install vRealize Automation agents on the IaaS Windows server that hosts the
active Manager Service, but it is not required. Multiple agents increase capacity and can be installed on the
same or separate servers.
VMware, Inc. 13
Page 14

Installing vRealize Automation
Virtualization Proxy Agents
vRealize Automation creates and manages virtual machines on virtualization hosts. Virtualization proxy
agents send commands to, and collect data from, vSphere ESX Server, XenServer, and Hyper-V hosts, and
the virtual machines provisioned on them.
A virtualization proxy agent has the following characteristics.
Typically requires administrator privileges on the virtualization platform that it manages.
n
Communicates with the IaaS Manager Service.
n
Is installed separately and has its own conguration le.
n
Most vRealize Automation deployments install the vSphere proxy agent. You might install other proxy
agents depending on the virtualization resources in use at your site.
Virtual Desktop Integration Agents
Virtual desktop integration (VDI) PowerShell agents allow vRealize Automation to integrate with external
virtual desktop systems. VDI agents require administrator privileges on the external systems.
You can register virtual machines provisioned by vRealize Automation with XenDesktop on a Citrix
Desktop Delivery Controller (DDC), which allows the user to access the XenDesktop Web interface from
vRealize Automation.
External Provisioning Integration Agents
External provisioning integration (EPI) PowerShell agents allow vRealize Automation to integrate external
systems into the machine provisioning process.
For example, integration with Citrix Provisioning Server enables provisioning of machines by on-demand
disk streaming, and an EPI agent allows you to run Visual Basic scripts as extra steps during the
provisioning process.
EPI agents require administrator privileges on the external systems with which they interact.
Windows Management Instrumentation Agent
The vRealize Automation Windows Management Instrumentation (WMI) agent enhances your ability to
monitor and control Windows system information, and allows you to manage remote Windows servers
from a central location. The WMI agent also enables collection of data from Windows servers that
vRealize Automation manages.
Deployment Type
You can install vRealize Automation as a minimal deployment for proof of concept or development work, or
in a distributed conguration suitable for medium to large production workloads.
14 VMware, Inc.
Page 15

Chapter 1 vRealize Automation Installation Overview
Minimal vRealize Automation Deployments
Minimal deployments include one vRealize Automation appliance and one Windows server that hosts the
IaaS components. In a minimal deployment, the vRealize Automation SQL Server database can be on the
same IaaS Windows server with the IaaS components, or on a separate Windows server.
Figure 1‑1. Minimal vRealize Automation Deployment
N The vRealize Automation documentation includes a complete, sample minimal deployment scenario
that walks you through installation and how to start using the product for proof of concept. See Installing
and Conguring vRealize Automation for the Rainpole Scenario.
VMware, Inc. 15
Page 16

Installing vRealize Automation
Distributed vRealize Automation Deployments
Distributed, enterprise deployments can be of varying size. A basic distributed deployment might improve
vRealize Automation simply by hosting IaaS components on separate Windows servers as shown in the
following gure.
Figure 1‑2. Distributed vRealize Automation Deployment
Many production deployments go even further, with redundant appliances, redundant servers, and load
balancing for even more capacity. Large, distributed deployments provide for beer scale, high availability,
and disaster recovery. Note that the embedded instance of vRealize Orchestrator is now recommended, but
you might see vRealize Automation connected to an external vRealize Orchestrator in older deployments.
16 VMware, Inc.
Page 17

Chapter 1 vRealize Automation Installation Overview
Figure 1‑3. Large Distributed and Load Balanced vRealize Automation Deployment
For more information about scalability and high availability, see the vRealize Automation Reference
Architecture guide.
Choosing Your Installation Method
The consolidated vRealize Automation Installation Wizard is your primary tool for new
vRealize Automation installations. Alternatively, you might want to perform the manual, separate
installation processes in some cases.
The Installation Wizard provides a simple and fast way to install, from minimal deployments to
n
distributed enterprise deployments with or without load balancers. Most users run the Installation
Wizard.
VMware, Inc. 17
Page 18

Installing vRealize Automation
You need the manual installation steps if you want to expand a vRealize Automation deployment or if
n
the Installation Wizard stopped for any reason.
Once you begin a manual installation, you cannot go back and run the Installation Wizard.
18 VMware, Inc.
Page 19

Preparing for vRealize Automation
Installation 2
System Administrators install vRealize Automation into their existing virtualization environments. Before
you begin an installation, prepare the deployment environment to meet system requirements.
This chapter includes the following topics:
“Host Names and IP Addresses,” on page 19
n
“Hardware and Virtual Machine Requirements,” on page 20
n
“Browser Considerations,” on page 20
n
“Password Considerations,” on page 21
n
“Windows Server Requirements,” on page 21
n
“vRealize Automation Port Requirements,” on page 26
n
“User Accounts and Credentials Required for Installation,” on page 28
n
“Security,” on page 30
n
“Time Synchronization,” on page 31
n
Host Names and IP Addresses
vRealize Automation requires that you name the hosts in your installation according to certain
requirements.
All vRealize Automation machines in your installation must be able to resolve each other by fully
n
qualied domain name (FQDN).
While performing the installation, always enter the FQDN when identifying or selecting a machine. Do
not enter IP addresses.
In addition to the FQDN requirement, Windows machines that host the Model Manager Web service,
n
Manager Service, and Microsoft SQL Server database must be able to resolve each other by Windows
Internet Name Service (WINS) name.
Congure your Domain Name System (DNS) to resolve these short WINS host names.
Preplan domain and machine naming so that vRealize Automation machines will begin and end with
n
alphabet (a-z) or digit (0-9) characters, and will only contain alphabet, digit, or hyphen (-) characters.
The underscore character (_) must not appear in the host name or anywhere in the FQDN.
For more information about allowable names, review the host name specications from the Internet
Engineering Task Force. See www.ietf.org.
VMware, Inc.
19
Page 20

Installing vRealize Automation
In general, you should expect to keep the host names and FQDNs that you planned for
n
vRealize Automation systems. You can change a vRealize Automation appliance host name after
installation, but changing other vRealize Automation host names makes vRealize Automation
unusable.
A best practice is to reserve and use static IP addresses for all vRealize Automation appliances and IaaS
n
Windows servers. vRealize Automation supports DHCP, but static IP addresses are recommended for
long-term deployments such as production environments.
You apply an IP address to the vRealize Automation appliance during OVF or OVA deployment.
n
For the IaaS Windows servers, you follow the usual operating system process. Set the IP address
n
before installing vRealize Automation IaaS.
Hardware and Virtual Machine Requirements
Your deployment must meet minimum system resources to install virtual appliances and minimum
hardware requirements to install IaaS components on the Windows Server.
For operating system and high-level environment requirements, including information about supported
browsers and operating systems, see the vRealize Automation Support Matrix.
The Hardware Requirements table shows the minimum conguration requirements for deployment of
virtual appliances and installation of IaaS components. Appliances are pre-congured virtual machines that
you add to your vCenter Server or ESXi inventory. IaaS components are installed on physical or virtual
Windows 2008 R2 SP1, or Windows 2012 R2 servers.
An Active Directory is considered small when there are up to 25,000 users in the OU to be synced in the ID
Store conguration. An Active Directory is considered large when there are more than 25,000 users in the
OU.
Table 2‑1. Hardware Requirements
vRealize Automation appliance
for Small Active Directories
4 CPUs
n
18 GB memory
n
60 GB disk storage
n
Browser Considerations
Some restrictions exist for browser use with vRealize Automation.
Multiple browser windows and tabs are not supported. vRealize Automation supports one session per
n
user.
VMware Remote Consoles provisioned on vSphere support a subset of vRealize Automation-supported
n
browsers.
For operating system and high-level environment requirements, including information about supported
browsers and operating systems, see the vRealize Automation Support Matrix.
vRealize Automation appliance for Large
Active Directories
4 CPUs
n
22 GB memory
n
60 GB disk storage
n
IaaS Components (Windows
Server).
2 CPUs
n
8 GB memory
n
30 GB disk storage
n
Additional resources are
required when you are include
an SQL Server on a Windows
host.
20 VMware, Inc.
Page 21

Password Considerations
Character restrictions apply to some passwords.
The VMware vRealize ™ Automation administrator password cannot contain a trailing "=" character. Such
passwords are accepted when you assign them, but result in errors when you perform operations such as
saving endpoints.
Windows Server Requirements
The virtual or physical Windows machine that hosts the IaaS components must meet conguration
requirements for the IaaS database, the IaaS server components, the IaaS Manager Service, and Distributed
Execution Managers.
The Installation Wizard runs a vRealize Automation prerequisite checker on all IaaS Windows servers to
ensure that they meet the conguration necessary for installation. In addition to the prerequisite checker,
address the following prerequisites separately.
As a best practice, place all IaaS Windows servers in the same domain.
n
Create or identify a domain account to use for installation, one that has administrator privileges on all
n
IaaS Windows servers.
Chapter 2 Preparing for vRealize Automation Installation
IaaS Database Server Requirements
The Windows server that hosts the vRealize Automation IaaS SQL Server database must meet certain
prerequisites.
The requirements apply whether you run the Installation Wizard or the legacy setup_vrealize-automation-
appliance-URL.exe installer and select the database role for installation. The prerequisites also apply if you
separately create an empty SQL Server database for use with IaaS.
Use a supported SQL Server version from the vRealize Automation Support Matrix.
n
Enable TCP/IP protocol for SQL Server.
n
Enable the Distributed Transaction Coordinator (DTC) service on all IaaS Windows servers and the
n
machine that hosts SQL Server. IaaS uses DTC for database transactions and actions such as workow
creation.
N If you clone a machine to make an IaaS Windows server, install DTC on the clone after cloning.
If you clone a machine that already has DTC, its unique identier is copied to the clone, which causes
communication to fail. See “Error in Manager Service Communication,” on page 143.
For more about DTC enablement, see VMware Knowledge Base article 2038943.
Open ports between all IaaS Windows servers and the machine that hosts SQL Server. See “vRealize
n
Automation Port Requirements,” on page 26.
Alternatively, if site policies allow, you may disable rewalls between IaaS Windows servers and SQL
Server.
This release of vRealize Automation does not support SQL Server 2016 130 compatibility mode. If you
n
separately create an empty SQL Server 2016 database for use with IaaS, use 100 or 120 compatibility
mode.
If you create the database through a vRealize Automation installer, compatibility is already congured.
AlwaysOn Availability Group (AAG) is only supported with SQL Server 2016.
n
VMware, Inc. 21
Page 22

Installing vRealize Automation
IaaS Web Service and Model Manager Server Requirements
Your environment must meet software and conguration prerequisites that support installation of the IaaS
server components.
Environment and Database Requirements for IaaS
Your host conguration and MS SQL database must meet the following requirements.
Table 2‑2. IaaS Requirements
Area Requirements
Host Conguration The following components must be installed on the host before installing
IaaS:
Microsoft .NET Framework 4.5.2 or later.
n
Microsoft PowerShell 2.0 (included with Windows Server 2008 R2 SP1
n
and later) or Microsoft PowerShell 3.0 on Windows Server 2012 R2.
Microsoft Internet Information Services 7.5.
n
Java must be installed on the machine running the primary Web
n
component to support deployment of the MS SQL database during
installation.
Microsoft SQL Database Requirements The SQL database can reside on one of your IaaS Windows servers, or a
separate host.
If the SQL database is on one of your IaaS Windows servers, congure the
following Java requirements.
Install 64-bit Java 1.8 or later. Do not use 32-bit.
n
Set the JAVA_HOME environment variable to the Java installation folder.
n
Verify that %JAVA_HOME%\bin\java.exe is available.
n
Microsoft Internet Information Services Requirements
Congure Internet Information Services (IIS) to meet the following requirements.
In addition to the conguration seings, avoid hosting additional Web sites in IIS on the IaaS Web server
host. vRealize Automation sets the binding on its communication port to all unassigned IP addresses,
making no additional bindings possible. The default vRealize Automation communication port is 443.
22 VMware, Inc.
Page 23

Chapter 2 Preparing for vRealize Automation Installation
Table 2‑3. Required Configuration for Microsoft Internet Information Services
IIS Component Setting
Internet Information Services (IIS)
modules installed
IIS Authentication seings
IIS Windows Process Activation Service
roles
WindowsAuthentication
n
StaticContent
n
DefaultDocument
n
ASPNET 4.5
n
ISAPIExtensions
n
ISAPIFilter
n
Windows Authentication enabled
n
AnonymousAuthentication disabled
n
Negotiate Provider enabled
n
NTLM Provider enabled
n
Windows Authentication Kernel Mode enabled
n
Windows Authentication Extended Protection disabled
n
For certicates using SHA512, TLS1.2 must be disabled on Windows
n
2012 or Windows 2012 R2 servers
CongurationApi
n
NetEnvironment
n
ProcessModel
n
WcfActivation (Windows 2008 only)
n
HpActivation
n
NonHpActivation
n
IaaS Manager Service
Your environment must meet some general requirements that support the installation of the IaaS Manager
Service.
Microsoft .NET Framework 4.5.2 is installed.
n
Microsoft PowerShell 2.0, 3.0, or 4.0. Some vRealize Automation upgrades or migrations might require
n
you to install an older or newer PowerShell version, in addition to the one that you are currently
running.
SecondaryLogOnService is running.
n
No rewalls can exist between DEM host and Windows Server. For port information, see “vRealize
n
Automation Port Requirements,” on page 26.
IIS is installed and congured.
n
Distributed Execution Manager Requirements
Your environment must meet some general requirements that support the installation of Distributed
Execution Managers (DEMs).
Microsoft .NET Framework 4.5.2 is installed.
n
Microsoft PowerShell 2.0, 3.0, or 4.0. Some vRealize Automation upgrades or migrations might require
n
you to install an older or newer PowerShell version, in addition to the one that you are currently
running.
SecondaryLogOnService is running.
n
VMware, Inc. 23
Page 24

Installing vRealize Automation
No rewalls between DEM host and the Windows server, or ports opened as described in “vRealize
n
Automation Port Requirements,” on page 26.
Servers that host DEM Worker instances might have additional requirements depending on the provisioning
resources that they interact with.
Amazon Web Services EC2 Requirements
A vRealize Automation IaaS Windows server communicates with and collects data from an Amazon EC2
account.
When you use Amazon Web Services (AWS) for provisioning, the IaaS Windows servers that host the DEM
workers must meet the following requirements.
DEM worker hosts must have Internet access.
n
If the DEM worker hosts are behind a rewall, HTTPS trac must be allowed to and from
n
aws.amazon.com as well as the URLs for EC2 regions that your AWS accounts have access to, such as
ec2.us-east-1.amazonaws.com for the US East region.
Each URL resolves to a range of IP addresses, so you might need to use a tool, such as the one available
from the Network Solutions Web site, to list and congure these IP addresses.
If the DEM worker hosts reach the Internet through a proxy server, the DEM service must be running
n
under credentials that can authenticate to the proxy server.
24 VMware, Inc.
Page 25

Chapter 2 Preparing for vRealize Automation Installation
Openstack and PowerVC Requirements
The machines on which you install your DEMs must meet certain requirements to communicate with and
collect data from your Openstack or PowerVC instance.
Table 2‑4. DEM Host Requirements
Your Installation Requirements
All In Windows Registry, enable TLS v1.2 support for .NET
framework. For example:
[HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\.NETFram
ework\v4.0.30319]
"SchUseStrongCrypto"=dword:00000001
[HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Wow6432Node\Micros
oft\.NETFramework\v4.0.30319]
"SchUseStrongCrypto"=dword:00000001
Windows 2008 DEM Host In Windows Registry, enable TLS v1.2 protocol. For
example:
[HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Co
ntrol\SecurityProviders\SCHANNEL\Protocols\TLS
1.2]
[HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Co
ntrol\SecurityProviders\SCHANNEL\Protocols\TLS
1.2\Client]
"DisabledByDefault"=dword:00000000
"Enabled"=dword:00000001
[HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Co
ntrol\SecurityProviders\SCHANNEL\Protocols\TLS
1.2\Server]
"DisabledByDefault"=dword:00000000
"Enabled"=dword:00000001
Self-signed certicates on your infrastructure endpoint host If your PowerVC or Openstack instance is not using trusted
certicates, import the SSL certicate from your PowerVC
or Openstack instance into the Trusted Root Certicate
Authorities store on each IaaS Windows server where you
intend to install a vRealize Automation DEM.
Red Hat Enterprise Virtualization KVM (RHEV) Requirements
When you use Red Hat Enterprise Virtualization for provisioning the IaaS Windows server communicates
with and collects data from that account.
Your environment must meet the following Red Hat Enterprise requirements.
Each KVM (RHEV) environment must be joined to the domain containing the IaaS server.
n
The credentials used to manage the endpoint representing a KVM (RHEV) environment must have
n
Administrator privileges on the RHEV environment. These credentials must also have sucient
privileges to create objects on the hosts within the environment.
SCVMM Requirements
A DEM Worker that manages virtual machines through SCVMM must be installed on a host where the
SCVMM console is already installed.
A best practice is to install the SCVMM console on a separate DEM Worker machine. In addition, verify that
the following requirements have been met.
The DEM worker must have access to the SCVMM PowerShell module installed with the console.
n
VMware, Inc. 25
Page 26

Installing vRealize Automation
The PowerShell Execution Policy must be set to RemoteSigned or Unrestricted.
n
To verify the PowerShell Execution Policy, enter one of the following commands at the PowerShell
command prompt.
help about_signing
help Set-ExecutionPolicy
If all DEM Workers within the instance are not on machines that meet these requirements, use Skill
n
commands to direct SCVMM-related workows to DEM Workers that are.
The following additional requirements apply to SCVMM.
This release supports SCVMM 2012 R2, which requires PowerShell 3 or later.
n
Install the SCVMM console before you install vRealize Automation DEM Workers that consume
n
SCVMM work items.
If you install the DEM Worker before the SCVMM console, you see log errors similar to the following
example.
Workflow 'ScvmmEndpointDataCollection' failed with the following exception: The term 'Get-
VMMServer' is not recognized as the name of a cmdlet, function, script file, or operable
program. Check the spelling of the name, or if a path was included, verify that the path is
correct and try again.
To correct the problem, verify that the SCVMM console is installed, and restart the DEM Worker
service.
Each SCVMM instance must be joined to the domain containing the server.
n
The credentials used to manage the endpoint representing an SCVMM instance must have
n
administrator privileges on the SCVMM server.
The credentials must also have administrator privileges on the Hyper-V servers within the instance.
Hyper-V servers within an SCVMM instance to be managed must be Windows 2008 R2 SP1 Servers
n
with Hyper-V installed. The processor must be equipped with the necessary virtualization
extensions .NET Framework 4.5.2 or later must be installed and Windows Management
Instrumentation (WMI) must be enabled.
To provision machines on an SCVMM resource, you must add a user in at least one security role within
n
the SCVMM instance.
To provision a Generation-2 machine on an SCVMM 2012 R2 resource, you must add the following
n
properties in the blueprint.
Scvmm.Generation2 = true
Hyperv.Network.Type = synthetic
Generation-2 blueprints should have an existing data-collected virtualHardDisk (vHDX) in the
blueprint build information page. Having it blank causes Generation-2 provisioning to fail.
For more information, see “Congure the DEM to Connect to SCVMM at a Dierent Installation Path,” on
page 94.
For additional information about preparing your SCVMM environment, see Conguring vRealize Automation.
vRealize Automation Port Requirements
vRealize Automation uses designated ports for communication and data access.
Although vRealize Automation uses only port 443 for communication, there might be other ports to open on
the system. Because open, unsecured ports might present security vulnerabilities, verify that only ports
required by your business applications are open.
26 VMware, Inc.
Page 27

Chapter 2 Preparing for vRealize Automation Installation
vRealize Automation Appliance
The following ports are used by the vRealize Automation appliance.
Table 2‑5. Incoming Ports for the vRealize Automation appliance
Port Protocol Comments
22 TCP Optional. Access for SSH sessions
80 TCP Optional. Redirects to 443
111 TCP, UDP RPC
443 TCP Access to the vRealize Automation console and API calls
443 TCP Access for machines to download the guest agent and software bootstrap agent
5480 TCP Access to the virtual appliance Web management interface
5480 TCP Used by the Management Agent
5488, 5489 TCP Internally used by the vRealize Automation appliance for updates
4369,
25672,5671,5672
8230, 8280, 8281 TCP Internal vRealize Orchestrator instance.
8444 TCP Console proxy communication for vSphere VMware Remote Console
TCP RabbitMQ messaging
connections.
Table 2‑6. Outgoing Ports for the vRealize Automation appliance
Port Protocol Comments
25, 587 TCP, UDP SMTP for sending outbound notication emails
53 TCP, UDP DNS
67, 68, 546, 547 TCP, UDP DHCP
80 TCP Optional. For fetching software updates. Updates can be downloaded
separately and applied
110, 995 TCP, UDP POP for receiving inbound notication emails
143, 993 TCP, UDP IMAP for receiving inbound notication emails
123 TCP, UDP Optional. For connecting directly to NTP instead of using host time
443 TCP Communication with IaaS Manager Service and infrastructure endpoint hosts
over HTTPS
443 TCP Communication with the software bootstrap agent over HTTPS
902 TCP ESXi network le copy operations and VMware Remote Console connections.
5050 TCP Optional. For communicating with vRealize Business.
5432 TCP, UDP Optional. For communicating with an Appliance Database
8281 TCP Optional. For communicating with an external vRealize Orchestrator instance
Other ports might be required by specic vRealize Orchestrator plug-ins that communicate with external
systems. See the documentation for the vRealize Orchestrator plug-in.
Infrastructure as a Service
The ports in the tables Incoming Ports for Infrastructure as a Service Components and Outgoing Ports for
Infrastructure as a Service must be available for use by the IaaS Windows Server.
VMware, Inc. 27
Page 28

Installing vRealize Automation
Table 2‑7. Incoming Ports for Infrastructure as a Service Components
Component Port Protocol Comments
Manager Service 443 TCP Communication with IaaS components and vRealize
vRealize Automation
appliance
Infrastructure Endpoint
Hosts
SQL Server instance 1433 TCP MSSQL
Table 2‑8. Outgoing Ports for Infrastructure as a Service Components
Component Port Protocol Comments
All 53 TCP, UDP DNS
All 67, 68, 546,
All 123 TCP, UDP Optional. NTP
Manager Service 443 TCP Communication with vRealize Automation appliance over
Distributed Execution
Managers
Proxy agents 443 TCP Communication with Manager Service and infrastructure
Management Agent 443 TCP Communication with the vRealize Automation appliance
Guest agent
Software bootstrap agent
Manager Service
Website
All 5480 TCP Communication with the vRealize Automation appliance.
Automation appliance over HTTPS
443 TCP Communication with IaaS components and vRealize
Automation appliance over HTTPS
443 TCP Communication with IaaS components and vRealize
Automation appliance over HTTPS. Typically, 443 is the
default communication port for virtual and cloud
infrastructure endpoint hosts, but refer to the
documentation provided by your infrastructure hosts for a
full list of default and required ports
TCP, UDP DHCP
547
HTTPS
443 TCP Communication with Manager Service over HTTPS
endpoint hosts over HTTPS
443 TCP Communication with Manager Service over HTTPS
1433 TCP MSSQL
Microsoft Distributed Transaction Coordinator Service
In addition to verifying that the ports listed in the previous tables are free for use, you must enable
Microsoft Distributed Transaction Coordinator Service (MS DTC) communication between all servers in the
deployment. MS DTC requires the use of port 135 over TCP and a random port between 1024 and 65535.
The Prerequisite Checker validates whether MS DTC is running and that the required ports are open.
User Accounts and Credentials Required for Installation
You must verify that you have the roles and credentials to install vRealize Automation components.
vCenter Service Account
If you plan to use a vSphere endpoint, you need a domain or local account that has the appropriate level of
access congured in vCenter.
28 VMware, Inc.
Page 29

Chapter 2 Preparing for vRealize Automation Installation
Virtual Appliance Installation
To deploy the vRealize Automation appliance, you must have the appropriate privileges on the deployment
platform (for example, vSphere administrator credentials).
During the deployment process, you specify the password for the virtual appliance administrator account.
This account provides access to the vRealize Automation appliance management console from which you
congure and administer the virtual appliances.
IaaS Installation
Before installing IaaS components, add the user under which you plan to execute the IaaS installation
programs to the Administrator group on the installation host.
IaaS Database Credentials
You can create the database during product installation or create it manually in the SQL server.
When you create or populate an MS SQL database through vRealize Automation, either with the Installation
Wizard or through the management console, the following requirements apply:
If you use the Use Windows Authentication option, the sysadmin role in SQL Server must be granted
n
to the user executing the Management Agent on the primary IaaS web server to create and alter the size
of the database.
If you do not select Use Windows Authentication, the sysadmin role in SQL Server must be also be
n
granted to the user executing the Management Agent on the primary IaaS web server. The credentials
are used at runtime.
If you populate a pre-created database through vRealize Automation, the user credentials you provide
n
(either the current Windows user or the specied SQL user) need only dbo privileges for the IaaS
database.
N vRealize Automation users also require the correct level of Windows authentication access to log in
and use vRealize Automation.
IaaS Service User Credentials
IaaS installs several Windows services that share a single service user.
The following requirements apply to the service user for IaaS services:
The user must be a domain user.
n
The user must have local Administrator privileges on all hosts on which the Manager Service or Web
n
site component is installed. Do not do a workgroup installation.
The user is congured with Log on as a service privileges. This privilege ensures that the Manager
n
Service starts and generates log les.
The user must have dbo privileges for the IaaS database. If you use the installer to create the database,
n
ensure that the service user login is added to SQL Server prior to running the installer. The installer
grants the service user dbo privileges after creating the database.
The installer is run under the account that runs the Management Agent on the primary Web server. If
n
you want to use the installer to create an MS SQL database during installation, you must have the
sysadmin role enabled under MS SQL. This is not a requirement if you choose to use a pre-created
empty database.
The domain user account that you plan to use as the IIS application pool identity for the Model
n
Manager Web Service is congured with Log on as batch job privileges.
VMware, Inc. 29
Page 30

Installing vRealize Automation
Model Manager Server Specifications
Specify the Model Manager server name by using a fully qualied domain name (FQDN). Do not use an IP
address to specify the server.
Security
vRealize Automation uses SSL to ensure secure communication among components. Passphrases are used
for secure database storage.
For more information see “Certicate Trust Requirements in a Distributed Deployment,” on page 63.
Certificates
vRealize Automation uses SSL certicates for secure communication among IaaS components and instances
of the vRealize Automation appliance. The appliances and the Windows installation machines exchange
these certicates to establish a trusted connection. You can obtain certicates from an internal or external
certicate authority, or generate self-signed certicates during the deployment process for each component.
For important information about troubleshooting, support, and trust requirements for certicates, see
VMware Knowledge Base article 2106583.
You can update or replace certicates after deployment. For example, a certicate may expire or you may
choose to use self-signed certicates during your initial deployment, but then obtain certicates from a
trusted authority before going live with your vRealize Automation implementation.
Table 2‑9. Certificate Implementations
Minimal Deployment (non-
Component
vRealize
Automation
Appliance
IaaS Components During installation, accept the
production) Distributed Deployment (production-ready)
Generate a self-signed certicate
during appliance conguration.
generated self-signed certicates or
select certicate suppression.
For each appliance cluster, you can use a certicate from an
internal or external certicate authority. Multi-use and
wildcard certicates are supported.
Obtain a multi-use certicate, such as a Subject Alternative
Name (SAN) certicate, from an internal or external certicate
authority that your Web client trusts.
Certificate Chains
If you use certicate chains, specify the certicates in the following order.
Client/server certicate signed by the intermediate CA certicate
n
One or more intermediate certicates
n
A root CA certicate
n
Include the BEGIN CERTIFICATE header and END CERTIFICATE footer for each certicate when you
import certicates.
Extracting Certificates and Private Keys
Certicates that you use with the virtual appliances must be in the PEM le format.
The examples in the following table use Gnu openssl commands to extract the certicate information you
need to congure the virtual appliances.
30 VMware, Inc.
Page 31

Chapter 2 Preparing for vRealize Automation Installation
Table 2‑10. Sample Certificate Values and Commands (openssl)
Certificate Authority
Provides Command Virtual Appliance Entries
RSA Private Key openssl pkcs12 -in path _to_.pfx
certicate_le -nocerts -out key.pem
PEM File openssl pkcs12 -in path _to_.pfx
certicate_le -clcerts -nokeys -out
cert.pem
(Optional) Pass Phrase n/a Pass Phrase
RSA Private Key
Chain
Security Passphrase
vRealize Automation uses security passphrases for database security. A passphrase is a series of words used
to create a phrase that generates the encryption key that protects data while at rest in the database.
Follow these guidelines when creating a security passphrase for the rst time.
Use the same passphrase across the entire installation to ensure that each component has the same
n
encryption key.
Use a phrase that is greater than eight characters long.
n
Include uppercase, lowercase and numeric characters, and symbols.
n
Memorize the passphrase or keep it in a safe place. The passphrase is required to restore database
n
information in the event of a system failure or to add components after initial installation. Without the
passphrase, you cannot restore successfully.
Third-Party Software
Some components of vRealize Automation depend on third-party software, including Microsoft Windows
and SQL Server. To guard against security vulnerabilities in third-party products, ensure that your software
is up-to-date with the latest patches from the vendor.
Time Synchronization
A system administrator must set up accurate timekeeping as part of the vRealize Automation installation.
Installation fails if time synchronization is set up incorrectly.
Timekeeping must be consistent and synchronized across the vRealize Automation appliance and Windows
servers. By using the same timekeeping method for each component, you can ensure this consistency.
For virtual machines, you can use the following methods:
Conguration by using Network Time Protocol (directly).
n
Conguration by using Network Time Protocol through ESXi with VMware Tools. You must have NTP
n
set up on the ESXi.
For more about timekeeping on Windows, see VMware Knowledge Base article 1318.
VMware, Inc. 31
Page 32

Installing vRealize Automation
32 VMware, Inc.
Page 33

Installing vRealize Automation with
the Installation Wizard 3
The vRealize Automation Installation Wizard provides a simple and fast way to install minimal or
enterprise deployments.
Before you launch the wizard, you deploy a vRealize Automation appliance and congure IaaS Windows
servers to meet prerequisites. The Installation Wizard appears the rst time you log in to the newly
deployed vRealize Automation appliance.
To stop the wizard and return later, click Logout.
n
To disable the wizard, click Cancel, or log out and begin manual installation through the standard
n
interfaces.
The wizard is your primary tool for new vRealize Automation installations. If you want to expand an
existing vRealize Automation deployment after running the wizard, see the procedures in Chapter 4, “The
Standard vRealize Automation Installation Interfaces,” on page 49.
This chapter includes the following topics:
“Deploy the vRealize Automation Appliance,” on page 33
n
“Using the Installation Wizard for Minimal Deployments,” on page 35
n
“Using the Installation Wizard for Enterprise Deployments,” on page 41
n
Deploy the vRealize Automation Appliance
To deploy the vRealize Automation appliance, a system administrator must log in to the vSphere client and
select deployment seings.
Some restrictions apply to the root password you create for the vRealize Automation administrator.
Prerequisites
Download the vRealize Automation appliance from the VMware Web site.
n
Log in to the vSphere client as a user with system administrator privileges.
n
Procedure
1 Select File > Deploy OVF Template from the vSphere client.
2 Browse to the vRealize Automation appliance le you downloaded and click Open.
3 Click Next.
4 Click Next on the OVF Template Details page.
5 Accept the license agreement and click Next.
VMware, Inc.
33
Page 34

Installing vRealize Automation
6 Enter a unique virtual appliance name according to the IT naming convention of your organization in
the Name text box, select the datacenter and location to which you want to deploy the virtual appliance,
and click Next.
7 Follow the prompts until the Disk Format page appears.
8 Verify on the Disk Format page that enough space exists to deploy the virtual appliance and click Next.
9 Follow the prompts to the Properties page.
The options that appear depend on your vSphere conguration.
10 Congure the values on the Properties page.
a Enter the root password to use when you log in to the virtual appliance console in the Enter
password and password text boxes.
b Select or uncheck the SSH service checkbox to choose whether SSH service is enabled for the
appliance.
This value is used to set the initial status of the SSH service in the appliance. If you are installing
with the Installation Wizard, enable this before you begin the wizard. You can change this seing
from the appliance management console after installation.
c Enter the fully qualied domain name of the virtual machine in the Hostname text box.
d Congure the networking properties.
11 Click Next.
12 Depending on your deployment, vCenter, and DNS conguration, select one of the following ways of
nishing OVA deployment and powering up the vRealize Automation appliance.
If you deployed to vSphere, and Power on after deployment is available on the Ready to Complete
n
page, take the following steps.
a Select Power on after deployment and click Finish.
b After the le nishes deploying into vCenter, click Close.
c Wait for the machine to start, which might take up to 5 minutes.
If you deployed to vSphere, and Power on after deployment is not available on the Ready to
n
Complete page, take the following steps.
a After the le nishes deploying into vCenter, click Close.
b Power on the vRealize Automation appliance.
c Wait for the machine to start, which might take up to 5 minutes.
d Verify that you can ping the DNS for the vRealize Automation appliance. If you cannot ping
the DNS, restart the virtual machine.
e Wait for the machine to start, which might take up to 5 minutes.
If you deployed the vRealize Automation appliance to vCloud using vCloud Director, vCloud
n
might override the password that you entered during OVA deployment. To prevent the override,
take the following steps.
a After deploying in vCloud Director, click your vApp to view the vRealize Automation
appliance.
b Right-click the vRealize Automation appliance, and select Properties.
c Click the Guest OS Customization tab.
d Under Password Reset, clear the Allow local administrator password option, and click OK.
34 VMware, Inc.
Page 35

Chapter 3 Installing vRealize Automation with the Installation Wizard
e Power on the vRealize Automation appliance.
f Wait for the machine to start, which might take up to 5 minutes.
13 Open a command prompt and ping the FQDN to verify that the fully qualied domain name can be
resolved against the IP address of vRealize Automation appliance.
Using the Installation Wizard for Minimal Deployments
Minimal deployments demonstrate how vRealize Automation works but usually do not have enough
capacity to support enterprise production environments.
Install a minimal deployment for proof-of-concept work or to become familiar with vRealize Automation.
Run the Installation Wizard for a Minimal Deployment
Minimal deployments typically consist of one vRealize Automation appliance, one IaaS Windows server,
and the vSphere agent for endpoints. Minimal installation places all IaaS components on a single Windows
server.
Minimal deployments typically consist of one vRealize Automation appliance, one IaaS Windows server,
and the vSphere agent for endpoints.
Prerequisites
Verify that you have met the prerequisites described in Chapter 2, “Preparing for vRealize Automation
n
Installation,” on page 19.
“Deploy the vRealize Automation Appliance,” on page 66.
n
Procedure
1 Open a Web browser to the vRealize Automation appliance management interface URL.
hps://vrealize-automation-appliance-FQDN:5480
2 Log in with the user name root and the password you specied when the appliance was deployed.
3 When the Installation Wizard appears, click Next.
4 Accept the End User License Agreement and click Next.
5 On the Deployment Type page, select Minimal deployment and Install Infrastructure as a Service, and
click Next.
6 On the Installation Prerequisites page, you pause to log in to your IaaS Windows server and install the
Management Agent. The Management Agent allows the vRealize Automation appliance to discover
and connect to the IaaS server.
What to do next
See “Installing the Management Agent,” on page 35.
Installing the Management Agent
You must install a Management Agent on each Windows machine hosting IaaS components.
For enterprise installations, a Management Agent is not required for the MS SQL host.
If your primary vRealize Automation appliance fails, you must reinstall Management Agents.
Management Agents are not automatically deleted when you uninstall an IaaS component. Uninstall the
Management Agent as you would uninstall any Windows program with the Add or Remove program tool.
VMware, Inc. 35
Page 36

Installing vRealize Automation
Procedure
1 Find the SSL Certicate Fingerprint for the Management Site Service on page 36
When you install a management agent, you must validate the ngerprint of the SSL certicate for the
Management Site service.
2 Download and Install the Management Agent on page 36
You install the Management Agent on the IaaS Windows server in your deployment.
Find the SSL Certificate Fingerprint for the Management Site Service
When you install a management agent, you must validate the ngerprint of the SSL certicate for the
Management Site service.
You can obtain the ngerprint at the command prompt on the vRealize Automation appliance.
Procedure
1 Log in to the vRealize Automation appliance console as root.
2 Enter the following command:
openssl x509 -in /opt/vmware/etc/lighttpd/server.pem -fingerprint -noout -sha1
The SHA1 ngerprint appears. For example:
SHA1 Fingerprint=E4:F0:37:9A:32:52:FA:7D:2E:91:BD:12:7A:2F:A3:75:F8:A1:7B:C4
3 Copy the ngerprint UID. For validation, you might need to remove the colons.
What to do next
Keep the ngerprint you copied for use with the Management Agent installer.
Download and Install the Management Agent
You install the Management Agent on the IaaS Windows server in your deployment.
The Management Agent registers the IaaS Windows server with the vRealize Automation appliance,
automates the installation and management of IaaS components, and collects support and telemetry
information. The Management Agent runs as a Windows service.
If you host the vRealize Automation SQL Server database on a separate Windows machine that does not
host the IaaS components, the SQL Server machine does not need the Management Agent.
Prerequisites
Note the vRealize Automation appliance certicate ngerprint by following the steps in “Find the SSL
n
Certicate Fingerprint for the Management Site Service,” on page 36.
Note the user name and password of a domain account with administrator privileges on the IaaS
n
Windows server. The Management Agent service must run under this account.
Procedure
1 Log in to the IaaS Windows server using an account that has administrator rights.
2 Open a Web browser to the vRealize Automation appliance installer URL.
hps://vrealize-automation-appliance-FQDN:5480/installer
3 Click Management Agent installer, and save vCAC-IaaSManagementAgent-Setup.msi.
4 Run vCAC-IaaSManagementAgent-Setup.msi.
5 Read the welcome and click Next.
36 VMware, Inc.
Page 37
Chapter 3 Installing vRealize Automation with the Installation Wizard
6 Accept the EULA and click Next.
7 Conrm or change the installation folder, and click Next.
The default folder is %Program Files(x86)%\VMware\vCAC\Management Agent.
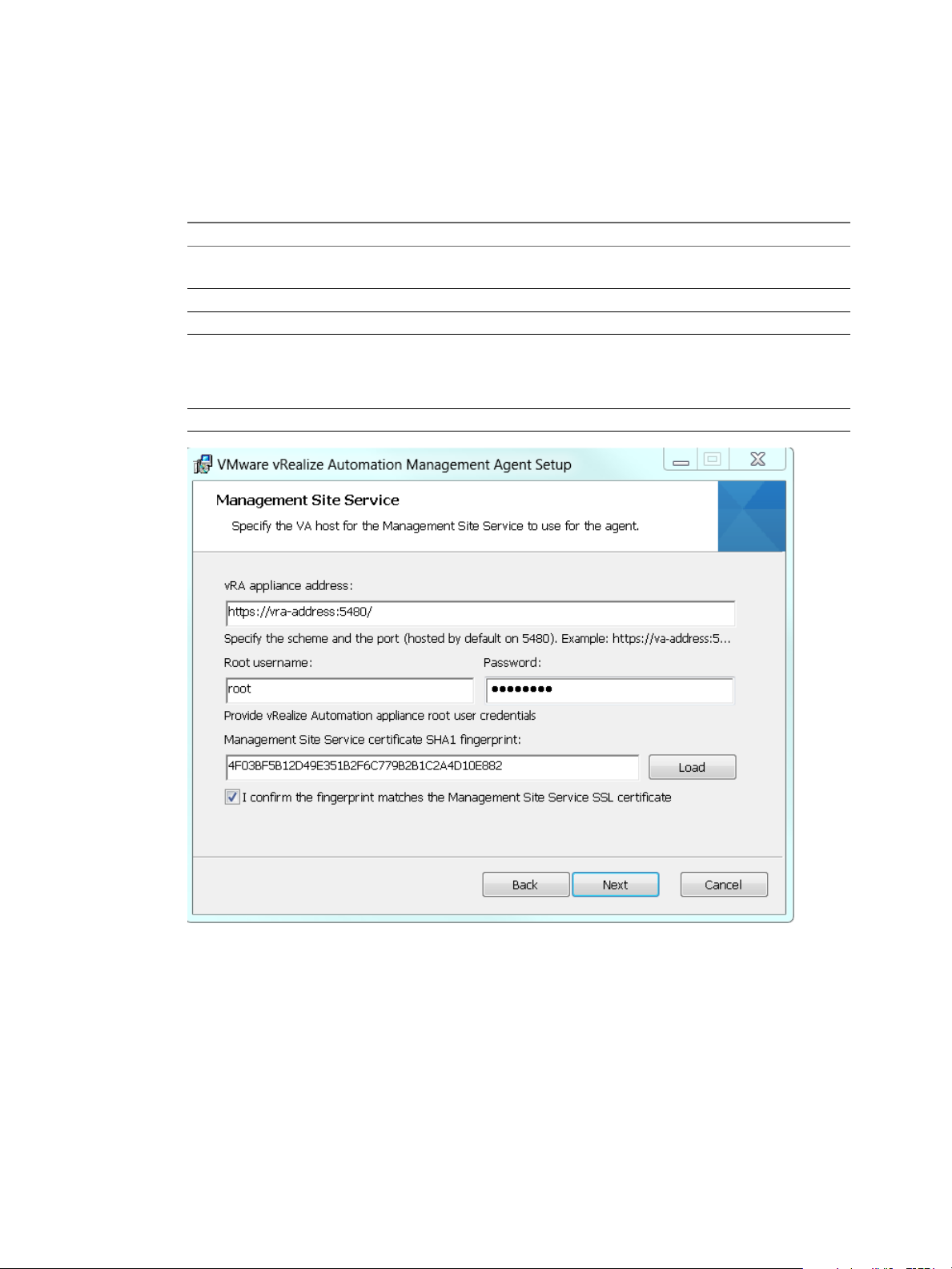
8 Enter Management Site Service details.
Text box Input
vRA appliance address
Root username
Password
Management Site server certificate
Load
https://vrealize-automation-appliance-FQDN:5480
You must include the port number.
The root user name for the vRealize Automation appliance.
The root user password for the vRealize Automation appliance.
The SHA1 ngerprint for the Management Site Service certicate. The
Management Site Service is hosted on the vRealize Automation appliance.
Sample SHA1 ngerprint:
DFF5FA0886DA2920D227ADF8BC9CDE4EF13EEF78
Click Load to load the default ngerprint.
9 Verify that the ngerprint matches the one from the vRealize Automation appliance certicate, and
select the conrmation checkbox.
If the ngerprints do not match, verify that the correct address appears in vRA appliance address.
Make changes and reload the ngerprint, if necessary.
10 Click Next.
11 Enter the service account user name and password, and click Next.
12 Click Install.
13 Click Finish.
VMware, Inc. 37
Page 38

Installing vRealize Automation
After you install the Management Agent, the IaaS Windows server appears on the Installation Prerequisites
page of the Installation Wizard.
Synchronize Server Times
Clocks on vRealize Automation servers and Windows servers must be synchronized to ensure a successful
installation.
Options on the Prerequisites page of the Installation Wizard let you select a time synchronization method
for your virtual appliances. The IaaS host table informs you of time osets.
Procedure
1 Select an option from the Time Sync Mode menu.
Option Action
Use Time Server
Use Host Time
2 Click Change Time .
Select Use Time Server from the Time Sync Mode menu to use Network
Time Protocol . For each time server that you are using, enter the IP
address or the host name in the Time Server text box.
Select Use Host Time from the Time Sync Mode menu to use
VMware Tools time synchronization. You must congure the connections
to Network Time Protocol servers before you can use VMware Tools time
synchronization.
3 Click Next.
What to do next
Verify that your IaaS servers are congured correctly.
Run the Prerequisite Checker
Run the Prerequisite Checker to verify that the Windows server for IaaS components is correctly congured.
Procedure
1 Click Run on the Prerequisite Checker screen.
As the checks are done, the Windows server for IaaS components is listed with a status.
2 If you see a warning, you can get more information on the error or choose to automatically correct the
error.
Click Show Details for more information on the error and the course of action to follow to address
u
it.
Click Fix to automatically x the error.
u
The Fix option applies corrections and restarts the IaaS Windows server.
3 Click Run to verify corrections.
4 Click Next when all errors are resolved.
Your Windows server is correctly congured for installation of IaaS components.
What to do next
Continue to the vRealize Automation Host screen.
38 VMware, Inc.
Page 39

Chapter 3 Installing vRealize Automation with the Installation Wizard
Specify Minimal Deployment Parameters
Use the vRealize Automation Installation Wizard to enter conguration seings for the minimal deployment
components.
Procedure
Follow the Installation Wizard pages to enter vRealize Automation appliance and IaaS Windows server
u
FQDNs, account credentials, default tenant password, and other seings.
The wizard checks systems for prerequisites before you begin to enter seings, and validates your
seings before it begins product installation.
What to do next
In vSphere, create a snapshot of each vRealize Automation appliance and IaaS Windows server before you
begin product installation.
Create Snapshots Before You Begin the Installation
Take snapshots of all your appliances and Windows servers. If the installation fails, you can revert to these
snapshots and try to install again.
The snapshots preserve your conguration work. Be sure to include a snapshot of the vRealize Automation
appliance on which you are running the wizard.
Instructions are provided for vSphere users.
N Do not exit the installation wizard or cancel the installation.
Procedure
1 Open another browser and log in to the vSphere Client.
2 Locate your server or appliance in the vSphere Client inventory.
3 Right-click the server the inventory and select Take Snapshot.
4 Enter a snapshot name.
5 Select Snapshot the virtual machine's memory checkbox to capture the memory of the server and click
OK.
The snapshot is created.
Repeat these steps to take snapshots of each of your servers or appliances.
What to do next
“Finish the Installation,” on page 60
Finish the Installation
There are a couple nal seings to apply before initiating the vRealize Automation installation and waiting
for the process to complete.
Procedure
1 Return to the installation wizard.
2 Review the installation summary and click Next.
3 Enter the product license key and click Next.
VMware, Inc. 39
Page 40

Installing vRealize Automation
4 Accept or change the default telemetry seings and click Next.
5 Click Next.
6 Click Finish.
The installation starts. Depending on your network, installation might take up to an hour to nish.
What to do next
Set up vRealize Automation for initial content creation.
Address Installation Failures
When you install from the Installation Details page, you are informed of any issues that are preventing the
installation from nishing.
When problems are found, the component is agged and you are presented with detailed information about
the failure along with steps to investigate solutions. After you have addressed the issue, you retry the
installation step. Depending on the type of failure, you follow dierent remediation steps.
Procedure
1 If the Retry Failed buon is enabled, use the following steps.
a Review the failure.
b Assess what needs to be changed and make required changes.
c Return to the Installation screen and click Retry Failed.
The installer aempts to install all failed components.
2 If the Retry All IaaS buon is enabled, use the following steps.
a Review the failure.
b Assess what needs to be changed.
c Revert all IaaS servers to the snapshots you created earlier.
d Delete the MS SQL database, if you are using an external database.
e Make required changes.
f Click Retry All IaaS.
3 If the failure is in the virtual appliance components use the following steps.
a Review the failure.
b Assess what needs to be changed.
c Revert all servers to snapshots, including the one from which you are running the wizard,
d Make required changes.
e Refresh the wizard page.
f Logon and rerun the wizard again.
The wizard opens at the pre-installation step.
Set Up Credentials for Initial Content Configuration
Optionally, you can start an initial content workow for a vSphere endpoint.
The process uses a local user called congurationadmin that is granted administrator rights.
40 VMware, Inc.
Page 41

Chapter 3 Installing vRealize Automation with the Installation Wizard
Procedure
1 Create and enter a password for the congurationadmin account in the Password text box.
2 Reenter the password in the password text box. Make a note of the password for later use.
3 Click Create Initial Content.
4 Click Next.
A conguration admin user is created and a conguration catalog item is created in the default tenant. The
conguration admin is granted the following rights:
Approval Administrator
n
Catalog Administrator
n
IaaS Administrator
n
Infrastructure Architect
n
Tenant Administrator
n
XaaS Architect
n
What to do next
When you nish the wizard, you can log in to the default tenant as the congurationadmin user and
n
request the initial content catalog items. For an example of how to request the item and complete the
manual user action, see Installing and Conguring vRealize Automation for the Rainpole Scenario.
Congure access to the default tenant for other users. See “Congure Access to the Default Tenant,” on
n
page 124.
Using the Installation Wizard for Enterprise Deployments
You can tailor your enterprise deployment to the needs of your organization. An enterprise deployment can
consist of distributed components or high-availability deployments congured with load balancers.
Enterprise deployments are designed for more complex installation structures with distributed and
redundant components and generally include load balancers. Installation of IaaS components is optional
with either type of deployment.
For load-balanced deployments, multiple active Web server instances and vRealize Automation appliance
appliances cause the installation to fail. Only a single Web server instance and a single vRealize Automation
appliance should be active during the installation.
Run the Installation Wizard for an Enterprise Deployment
Enterprise deployments are used for production environment. You can use the Installation Wizard to deploy
a distributed installation or a distributed installation with load balancers for high availability and failover.
If you install a distributed installation with load balancers for high availability and failover, notify the team
responsible for conguring your vRealize Automation environment. Your tenant administrators must
congure Directories Management for high availability when they congure the link to your Active
Directory.
Prerequisites
Verify that you have met the prerequisites described in Chapter 2, “Preparing for vRealize Automation
n
Installation,” on page 19.
“Deploy the vRealize Automation Appliance,” on page 66.
n
VMware, Inc. 41
Page 42

Installing vRealize Automation
Procedure
1 Open a Web browser to the vRealize Automation appliance management interface URL.
hps://vrealize-automation-appliance-FQDN:5480
2 Log in with the user name root and the password you specied when the appliance was deployed.
3 When the Installation Wizard appears, click Next.
4 Accept the End User License Agreement and click Next.
5 On the Deployment Type page, select Enterprise deployment and Install Infrastructure as a Service.
6 On the Installation Prerequisites page, you pause to log in to your IaaS Windows servers and install the
Management Agent. The Management Agent allows the vRealize Automation appliance to discover
and connect to those IaaS servers.
What to do next
See “Installing the Management Agent,” on page 42.
Installing the Management Agent
You must install a Management Agent on each Windows machine hosting IaaS components.
If your primary vRealize Automation appliance fails, you must reinstall Management Agents.
Management Agents are not automatically deleted when you uninstall an IaaS component. Uninstall the
Management Agent as you would uninstall any Windows program with the Add or Remove program tool.
Find the SSL Certificate Fingerprint for the Management Site Service
When you install a management agent, you must validate the ngerprint of the SSL certicate for the
Management Site service.
You can obtain the ngerprint at the command prompt on the vRealize Automation appliance.
Procedure
1 Log in to the vRealize Automation appliance console as root.
2 Enter the following command:
openssl x509 -in /opt/vmware/etc/lighttpd/server.pem -fingerprint -noout -sha1
The SHA1 ngerprint appears. For example:
SHA1 Fingerprint=E4:F0:37:9A:32:52:FA:7D:2E:91:BD:12:7A:2F:A3:75:F8:A1:7B:C4
3 Copy the ngerprint UID. For validation, you might need to remove the colons.
What to do next
Keep the ngerprint you copied for use with the Management Agent installer.
Download and Install the Management Agent
You install the Management Agent on each IaaS Windows server in your deployment.
The Management Agent registers the IaaS Windows server with the vRealize Automation appliance,
automates the installation and management of IaaS components, and collects support and telemetry
information. The Management Agent runs as a Windows service.
If you host the vRealize Automation SQL Server database on a separate Windows machine that does not
host any other IaaS components, the SQL Server machine does not need the Management Agent.
42 VMware, Inc.
Page 43

Chapter 3 Installing vRealize Automation with the Installation Wizard
Prerequisites
Note the vRealize Automation appliance certicate ngerprint by following the steps in “Find the SSL
n
Certicate Fingerprint for the Management Site Service,” on page 36.
Note the user name and password of a domain account with administrator privileges on the IaaS
n
Windows server. The Management Agent service must run under this account.
Procedure
1 Log in to the IaaS Windows server using an account that has administrator rights.
2 Open a Web browser directly to the vRealize Automation appliance installer URL. Do not use a load
balancer address.
hps://vrealize-automation-appliance-FQDN:5480/installer
3 Click Management Agent installer, and save vCAC-IaaSManagementAgent-Setup.msi.
4 Run vCAC-IaaSManagementAgent-Setup.msi.
5 Read the welcome and click Next.
6 Accept the EULA and click Next.
7 Conrm or change the installation folder, and click Next.
The default folder is %Program Files(x86)%\VMware\vCAC\Management Agent.
8 Enter Management Site Service details.
Text box Input
vRA appliance address
Root username
Password
https://vrealize-automation-appliance-FQDN:5480
You must include the port number.
The root user name for the vRealize Automation appliance.
The root user password for the vRealize Automation appliance.
VMware, Inc. 43
Page 44

Installing vRealize Automation
Text box Input
Management Site server certificate
Load
The SHA1 ngerprint for the Management Site Service certicate. The
Management Site Service is hosted on the vRealize Automation appliance.
Sample SHA1 ngerprint:
DFF5FA0886DA2920D227ADF8BC9CDE4EF13EEF78
Click Load to load the default ngerprint.
9 Verify that the ngerprint matches the one from the vRealize Automation appliance certicate, and
select the conrmation checkbox.
If the ngerprints do not match, verify that the correct address appears in vRA appliance address.
Make changes and reload the ngerprint, if necessary.
10 Click Next.
11 Enter the service account user name and password, and click Next.
12 Click Install.
13 Click Finish.
14 Repeat the process for each IaaS Windows server.
After you install the Management Agent, the IaaS Windows server appears on the Installation Prerequisites
page of the Installation Wizard.
Synchronize Server Times
Clocks on vRealize Automation servers and Windows servers must be synchronized to ensure a successful
installation.
Options on the Prerequisites page of the Installation Wizard let you select a time synchronization method
for your virtual appliances. The IaaS host table informs you of time osets.
44 VMware, Inc.
Page 45

Chapter 3 Installing vRealize Automation with the Installation Wizard
Procedure
1 Select an option from the Time Sync Mode menu.
Option Action
Use Time Server
Use Host Time
Select Use Time Server from the Time Sync Mode menu to use Network
Time Protocol . For each time server that you are using, enter the IP
address or the host name in the Time Server text box.
Select Use Host Time from the Time Sync Mode menu to use
VMware Tools time synchronization. You must congure the connections
to Network Time Protocol servers before you can use VMware Tools time
synchronization.
2 Click Change Time .
3 Click Next.
What to do next
Verify that your IaaS servers are congured correctly.
Run the Prerequisite Checker
Run the Prerequisite Checker to verify that the Windows servers for IaaS components are correctly
congured.
Procedure
1 Click Run on the Prerequisite Checker screen.
As the checks are done, each Windows server for IaaS components is listed with a status.
2 If you see a warning, you can get more information on the error or choose to automatically correct the
error.
Click Show Details for more information on the error and the course of action to follow to address
u
it.
Click Fix to automatically x the error.
u
The Fix option applies corrections and restarts all IaaS machines, including those that might not
have had xes.
3 Click Run to verify corrections.
4 Click Next when all errors are resolved.
Your Windows servers are correctly congured for installation of IaaS components.
What to do next
Continue to the vRealize Automation Host screen.
VMware, Inc. 45
Page 46

Installing vRealize Automation
Specify Enterprise Deployment Parameters
Use the vRealize Automation Installation Wizard to enter conguration seings for the enterprise
deployment components.
Prerequisites
Procedure
Follow the Installation Wizard pages to enter vRealize Automation appliance and IaaS Windows server
u
FQDNs, account credentials, default tenant password, and other seings.
The wizard checks systems for prerequisites before you begin to enter seings, and validates your
seings before it begins product installation.
What to do next
In vSphere, create a snapshot of each vRealize Automation appliance and IaaS Windows server before you
begin product installation.
Create Snapshots Before You Begin the Installation
Take snapshots of all your appliances and Windows servers. If the installation fails, you can revert to these
snapshots and try to install again.
The snapshots preserve your conguration work. Be sure to include a snapshot of the vRealize Automation
appliance on which you are running the wizard.
Instructions are provided for vSphere users.
N Do not exit the installation wizard or cancel the installation.
Procedure
1 Open another browser and log in to the vSphere Client.
2 Locate your server or appliance in the vSphere Client inventory.
3 Right-click the server the inventory and select Take Snapshot.
4 Enter a snapshot name.
5 Select Snapshot the virtual machine's memory checkbox to capture the memory of the server and click
OK.
The snapshot is created.
Repeat these steps to take snapshots of each of your servers or appliances.
What to do next
“Finish the Installation,” on page 60
Finish the Installation
After creating snapshots, you initiate the installation of vRealize Automation and wait for the installation to
complete successfully.
Procedure
1 Return to the installation wizard.
2 Review the installation summary and click Next.
46 VMware, Inc.
Page 47

Chapter 3 Installing vRealize Automation with the Installation Wizard
3 Click Next.
4 Click Finish.
The installation starts. Depending on your network conguration, installation can take between fteen
minutes and one hour.
A conrmation message appears when the installation nishes.
What to do next
You are now ready to congure your deployment.
Address Installation Failures
When you install from the Installation Details page, you are informed of any issues that are preventing the
installation from nishing.
When problems are found, the component is agged and you are presented with detailed information about
the failure along with steps to investigate solutions. After you have addressed the issue, you retry the
installation step. Depending on the type of failure, you follow dierent remediation steps.
Procedure
1 If the Retry Failed buon is enabled, use the following steps.
a Review the failure.
b Assess what needs to be changed and make required changes.
c Return to the Installation screen and click Retry Failed.
The installer aempts to install all failed components.
2 If the Retry All IaaS buon is enabled, use the following steps.
a Review the failure.
b Assess what needs to be changed.
c Revert all IaaS servers to the snapshots you created earlier.
d Delete the MS SQL database, if you are using an external database.
e Make required changes.
f Click Retry All IaaS.
3 If the failure is in the virtual appliance components use the following steps.
a Review the failure.
b Assess what needs to be changed.
c Revert all servers to snapshots, including the one from which you are running the wizard,
d Make required changes.
e Refresh the wizard page.
f Logon and rerun the wizard again.
The wizard opens at the pre-installation step.
VMware, Inc. 47
Page 48

Installing vRealize Automation
Set Up Credentials for Initial Content Configuration
Optionally, you can start an initial content workow for a vSphere endpoint.
The process uses a local user called congurationadmin that is granted administrator rights.
Procedure
1 Create and enter a password for the congurationadmin account in the Password text box.
2 Reenter the password in the password text box. Make a note of the password for later use.
3 Click Create Initial Content.
4 Click Next.
A conguration admin user is created and a conguration catalog item is created in the default tenant. The
conguration admin is granted the following rights:
Approval Administrator
n
Catalog Administrator
n
IaaS Administrator
n
Infrastructure Architect
n
Tenant Administrator
n
XaaS Architect
n
What to do next
When you nish the wizard, you can log in to the default tenant as the congurationadmin user and
n
request the initial content catalog items. For an example of how to request the item and complete the
manual user action, see Installing and Conguring vRealize Automation for the Rainpole Scenario.
Congure access to the default tenant for other users. See “Congure Access to the Default Tenant,” on
n
page 124.
48 VMware, Inc.
Page 49

The Standard vRealize Automation
Installation Interfaces 4
After running the Installation Wizard, you might need or want to perform certain installation tasks
manually, through the standard interfaces.
The Installation Wizard described in Chapter 3, “Installing vRealize Automation with the Installation
Wizard,” on page 33 is your primary tool for new vRealize Automation installations. However, after you run
the wizard, some operations still require the older, manual installation process.
You need the manual steps if you want to expand a vRealize Automation deployment or if the wizard
stopped for any reason. Situations when you might need to refer to the procedures in this section include
the following examples.
You chose to cancel the wizard before nishing the installation.
n
Installation through the wizard failed for some reason.
n
You want to add another vRealize Automation appliance for high availability.
n
You want to add another IaaS Web server for high availability.
n
You need another proxy agent.
n
You need another DEM worker or orchestrator.
n
You might use all or only some of the manual processes. Review the material throughout this section, and
follow the procedures that apply to your situation.
This chapter includes the following topics:
“Using the Standard Interfaces for Minimal Deployments,” on page 49
n
“Using the Standard Interfaces for Distributed Deployments,” on page 60
n
“Installing vRealize Automation Agents,” on page 97
n
Using the Standard Interfaces for Minimal Deployments
You can install a standalone, minimal deployment for use in a development environment or as a proof of
concept. Minimal deployments are not suitable for a production environment.
Minimal Deployment Checklist
A system administrator can deploy a complete vRealize Automation in a minimal conguration. Minimal
deployments are typically used in a development environment or as a proof of concept and require fewer
steps to install.
The Minimal Deployment Checklist provides a high-level overview of the sequence of tasks you must
perform to complete a minimal installation.
VMware, Inc.
49
Page 50

Installing vRealize Automation
Print out a copy of the checklist and use it to track your work as you complete the installation. Complete the
tasks in the order in which they are given.
Table 4‑1. Minimal Deployment Checklist
Task Details
Plan and prepare the installation environment and
verify that all installation prerequisites are met.
Set up your vRealize Automation appliance “Deploy and Congure the vRealize Automation
Install IaaS components on a single Windows server. “Installing IaaS Components,” on page 55
Install additional agents, if required. “Installing vRealize Automation Agents,” on
Perform post-installation tasks such as conguring the
default tenant.
Chapter 2, “Preparing for vRealize Automation
Installation,” on page 19
Appliance,” on page 50
page 97
Deploy and Configure the vRealize Automation Appliance
The vRealize Automation appliance is a precongured virtual appliance that deploys the vRealize
Automation appliance server and Web console (the user portal). It is delivered as an open virtualization
format (OVF) template. The system administrator downloads the appliance and deploys it into the
vCenter Server or ESX/ESXi inventory.
1 Deploy the vRealize Automation Appliance on page 50
To deploy the vRealize Automation appliance, a system administrator must log in to the vSphere
client and select deployment seings.
2 Enable Time Synchronization on the vRealize Automation Appliance on page 52
Clocks on the vRealize Automation server and Windows servers must be synchronized to ensure a
successful installation.
3 Congure the vRealize Automation Appliance on page 52
To prepare the vRealize Automation appliance for use, you congure host seings, generate an SSL
certicate, and provide SSO connection information.
Deploy the vRealize Automation Appliance
To deploy the vRealize Automation appliance, a system administrator must log in to the vSphere client and
select deployment seings.
Some restrictions apply to the root password you create for the vRealize Automation administrator.
Prerequisites
Download the vRealize Automation appliance from the VMware Web site.
n
Log in to the vSphere client as a user with system administrator privileges.
n
Procedure
1 Select File > Deploy OVF Template from the vSphere client.
2 Browse to the vRealize Automation appliance le you downloaded and click Open.
3 Click Next.
4 Click Next on the OVF Template Details page.
5 Accept the license agreement and click Next.
50 VMware, Inc.
Page 51

Chapter 4 The Standard vRealize Automation Installation Interfaces
6 Enter a unique virtual appliance name according to the IT naming convention of your organization in
the Name text box, select the datacenter and location to which you want to deploy the virtual appliance,
and click Next.
7 Follow the prompts until the Disk Format page appears.
8 Verify on the Disk Format page that enough space exists to deploy the virtual appliance and click Next.
9 Follow the prompts to the Properties page.
The options that appear depend on your vSphere conguration.
10 Congure the values on the Properties page.
a Enter the root password to use when you log in to the virtual appliance console in the Enter
password and password text boxes.
b Select or uncheck the SSH service checkbox to choose whether SSH service is enabled for the
appliance.
This value is used to set the initial status of the SSH service in the appliance. If you are installing
with the Installation Wizard, enable this before you begin the wizard. You can change this seing
from the appliance management console after installation.
c Enter the fully qualied domain name of the virtual machine in the Hostname text box.
d Congure the networking properties.
11 Click Next.
12 Depending on your deployment, vCenter, and DNS conguration, select one of the following ways of
nishing OVA deployment and powering up the vRealize Automation appliance.
If you deployed to vSphere, and Power on after deployment is available on the Ready to Complete
n
page, take the following steps.
a Select Power on after deployment and click Finish.
b After the le nishes deploying into vCenter, click Close.
c Wait for the machine to start, which might take up to 5 minutes.
If you deployed to vSphere, and Power on after deployment is not available on the Ready to
n
Complete page, take the following steps.
a After the le nishes deploying into vCenter, click Close.
b Power on the vRealize Automation appliance.
c Wait for the machine to start, which might take up to 5 minutes.
d Verify that you can ping the DNS for the vRealize Automation appliance. If you cannot ping
the DNS, restart the virtual machine.
e Wait for the machine to start, which might take up to 5 minutes.
If you deployed the vRealize Automation appliance to vCloud using vCloud Director, vCloud
n
might override the password that you entered during OVA deployment. To prevent the override,
take the following steps.
a After deploying in vCloud Director, click your vApp to view the vRealize Automation
appliance.
b Right-click the vRealize Automation appliance, and select Properties.
c Click the Guest OS Customization tab.
d Under Password Reset, clear the Allow local administrator password option, and click OK.
VMware, Inc. 51
Page 52

Installing vRealize Automation
e Power on the vRealize Automation appliance.
f Wait for the machine to start, which might take up to 5 minutes.
13 Open a command prompt and ping the FQDN to verify that the fully qualied domain name can be
resolved against the IP address of vRealize Automation appliance.
Enable Time Synchronization on the vRealize Automation Appliance
Clocks on the vRealize Automation server and Windows servers must be synchronized to ensure a
successful installation.
If you see certicate warnings during this process, continue past them to nish the installation.
Prerequisites
“Deploy the vRealize Automation Appliance,” on page 33.
Procedure
1 Open a Web browser to the vRealize Automation appliance management interface URL.
2 Log in with the user name root and the password you specied when the appliance was deployed.
3 Select Admin > Time .
4 Select an option from the Time Sync Mode menu.
Option Action
Use Time Server
Use Host Time
Select Use Time Server from the Time Sync Mode menu to use Network
Time Protocol . For each time server that you are using, enter the IP
address or the host name in the Time Server text box.
Select Use Host Time from the Time Sync Mode menu to use
VMware Tools time synchronization. You must congure the connections
to Network Time Protocol servers before you can use VMware Tools time
synchronization.
5 Click Save .
6 Click Refresh.
7 Verify that the value in Current Time is correct.
You can change the time zone as required from the Time Zone Seing page on the System tab.
8 (Optional) Click Time Zone from the System tab and select a system time zone from the menu choices.
The default is Etc/UTC.
9 Click Save .
Configure the vRealize Automation Appliance
To prepare the vRealize Automation appliance for use, you congure host seings, generate an SSL
certicate, and provide SSO connection information.
Prerequisites
“Enable Time Synchronization on the vRealize Automation Appliance,” on page 52.
Procedure
1 Open a Web browser to the vRealize Automation appliance management interface URL.
hps://vrealize-automation-appliance-FQDN:5480
52 VMware, Inc.
Page 53

Chapter 4 The Standard vRealize Automation Installation Interfaces
2 Continue past the certicate warning.
3 Log in with the user name root and the password you specied when the appliance was deployed.
4 Select vRA > Host .
Option Action
Resolve Automatically Select Resolve Automatically to specify the name of the current
host for the vRealize Automation appliance.
Update Host For new hosts, select Update Host. Enter the fully qualied domain
name of the vRealize Automation appliance, vra-
hostname.domain.name, in the Host Name text box.
For distributed deployments that use load balancers, select Update
Host. Enter the fully qualied domain name for the load balancer
server, vra-loadbalancername.domain.name, in the Host Name text
box.
N Congure SSO seings as described later in this procedure whenever you use Update Host to
set the host name.
VMware, Inc. 53
Page 54

Installing vRealize Automation
5 Select the certicate type from the Action menu.
If you are using a PEM-encoded certicate, for example for a distributed environment, select Import.
Certicates that you import must be trusted and must also be applicable to all instances of vRealize
Automation appliance and any load balancer through the use of Subject Alternative Name (SAN)
certicates.
N If you use certicate chains, specify the certicates in the following order:
a Client/server certicate signed by the intermediate CA certicate
b One or more intermediate certicates
c A root CA certicate
Option Action
Keep Existing
Generate Certificate
Import
6 Click Save to save host information and SSL conguration.
Leave the current SSL conguration. Select this option to cancel your
changes.
a The value displayed in the Common Name text box is the Host Name
as it appears on the upper part of the page. If any additional instances
of the vRealize Automation appliance available, their FQDNs are
included in the SAN aribute of the certicate.
b Enter your organization name, such as your company name, in the
Organization text box.
c Enter your organizational unit, such as your department name or
location, in the Organizational Unit text box.
d
Enter a two-leer ISO 3166 country code, such as US, in the Country
text box.
a Copy the certicate values from BEGIN PRIVATE KEY to END
PRIVATE KEY, including the header and footer, and paste them in the
RSA Private Key text box.
b Copy the certicate values from BEGIN CERTIFICATE to END
CERTIFICATE, including the header and footer, and paste them in the
Chain text box. For multiple certicate values, include a
BEGIN CERTIFICATE header and END CERTIFICATE footer for each
certicate.
N In the case of chained certicates, additional aributes may be
available.
c (Optional) If your certicate uses a pass phrase to encrypt the
certicate key, copy the pass phrase and paste it in the Passphrase text
box.
7 Congure the SSO seings.
8 Click Messaging. The conguration seings and status of messaging for your appliance is displayed.
Do not change these seings.
9 Click the Telemetry tab to choose whether to join the VMware Customer Experience Improvement
Program (CEIP).
Details regarding the data collected through CEIP and the purposes for which it is used by VMware are
set forth at the Trust & Assurance Center at hp://www.vmware.com/trustvmware/ceip.html.
Select Join the VMware Customer Experience Improvement Program to participate in the
n
program.
Deselect Join the VMware Customer Experience Improvement Program to not participate in the
n
program.
54 VMware, Inc.
Page 55

Chapter 4 The Standard vRealize Automation Installation Interfaces
10 Click Services and verify that services are registered.
Depending on your site conguration, this can take about 10 minutes.
N You can log in to the appliance and run tail -f /var/log/vcac/catalina.out to monitor startup
of the services.
11 Enter your license information.
a Click vRA > Licensing.
b Click Licensing.
c Enter a valid vRealize Automation license key that you downloaded when you downloaded the
installation les, and click Submit Key.
N If you experience a connection error, you might have a problem with the load balancer. Check
network connectivity to the load balancer.
12 Conrm that you can log in to vRealize Automation.
a Open a Web browser to the vRealize Automation product interface URL.
hps://vrealize-automation-appliance-FQDN/vcac
b Accept the vRealize Automation certicate.
c Accept the SSO certicate.
d Log in with administrator@vsphere.local and the password you specied when you congured
SSO.
The interface opens to the Tenants page on the Administration tab. A single tenant named
vsphere.local appears in the list.
You have nished the deployment and conguration of your vRealize Automation appliance. If the
appliance does not function correctly after conguration, redeploy and recongure the appliance. Do not
make changes to the existing appliance.
What to do next
See “Install the Infrastructure Components,” on page 56.
Installing IaaS Components
The administrator installs a complete set of infrastructure (IaaS) components on a Windows machine
(physical or virtual). Administrator rights are required to perform these tasks.
A minimal installation installs all of the components on the same Windows server, except for the SQL
database, which you can install on a separate server.
Enable Time Synchronization on the Windows Server
Clocks on the vRealize Automation server and Windows servers must be synchronized to ensure that the
installation is successful.
The following steps describe how to enable time synchronization with the ESX/ESXi host by using VMware
Tools. If you are installing the IaaS components on a physical host or do not want to use VMware Tools for
time synchronization, ensure that the server time is accurate by using your preferred method.
Procedure
1 Open a command prompt on the Windows installation machine.
VMware, Inc. 55
Page 56

Installing vRealize Automation
2 Type the following command to navigate to the VMware Tools directory.
cd C:\Program Files\VMware\VMware Tools
3 Type the command to display the timesync status.
VMwareToolboxCmd.exe timesync status
4 If timesync is disabled, type the following command to enable it.
VMwareToolboxCmd.exe timesync enable
IaaS Certificates
vRealize Automation IaaS components use certicates and SSL to secure communications between
components. In a minimal installation for proof-of-concept purposes, you can use self-signed certicates.
In a distributed environment, obtain a domain certicate from a trusted certicate authority. For information
about installing domain certicates for IaaS components, see “Install IaaS Certicates,” on page 75 in the
distributed deployment chapter.
Install the Infrastructure Components
The system administrator logs into the Windows machine and follows the installation wizard to install the
infrastructure components (IaaS) on the Windows virtual or physical machine.
Prerequisites
Verify that your installation machine meets the requirements described in “IaaS Web Service and Model
n
Manager Server Requirements,” on page 22.
“Enable Time Synchronization on the Windows Server,” on page 55.
n
Verify that you have deployed and fully congured the vRealize Automation appliance, and that the
n
necessary services are running (plugin-service, catalog-service, iaas-proxy-provider).
Procedure
1 Download the vRealize Automation IaaS Installer on page 57
To install IaaS on your minimal virtual or physical Windows server, you download a copy of the IaaS
installer from the vRealize Automation appliance.
2 Select the Installation Type on page 57
The system administrator runs the installer wizard from the Windows 2008 or 2012 installation
machine.
3 Check Prerequisites on page 58
The Prerequisite Checker veries that your machine meets IaaS installation requirements.
4 Specify Server and Account Seings on page 58
The vRealize Automation system administrator species server and account seings for the Windows
installation server and selects a SQL database server instance and authentication method.
5 Specify Managers and Agents on page 59
The minimum installation installs the required Distributed Execution Managers and the default
vSphere proxy agent. The system administrator can install additional proxy agents (XenServer, or
Hyper-V, for example) after installation using the custom installer.
6 Register the IaaS Components on page 59
The system administrator installs the IaaS certicate and registers the IaaS components with the SSO.
7 Finish the Installation on page 60
The system administrator nishes the IaaS installation.
56 VMware, Inc.
Page 57

Chapter 4 The Standard vRealize Automation Installation Interfaces
Download the vRealize Automation IaaS Installer
To install IaaS on your minimal virtual or physical Windows server, you download a copy of the IaaS
installer from the vRealize Automation appliance.
If you see certicate warnings during this process, continue past them to nish the installation.
Prerequisites
Microsoft .NET Framework 4.5.2 or later. You can download the .NET installer from the same Web page
n
as the IaaS installer.
If you are using Internet Explorer for the download, verify that Enhanced Security Conguration is not
n
enabled. Point Internet Explorer to res://iesetup.dll/SoftAdmin.htm on the Windows server.
Procedure
1 Log in to the IaaS Windows server using an account that has administrator rights.
2 Open a Web browser directly to the vRealize Automation appliance installer URL.
hps://vrealize-automation-appliance-FQDN:5480/installer
3 Click IaaS Installer.
4 Save setup__vrealize-automation-appliance-FQDN@5480 to the Windows server.
Do not change the installer le name. It is used to connect the installation to the vRealize Automation
appliance.
Select the Installation Type
The system administrator runs the installer wizard from the Windows 2008 or 2012 installation machine.
Prerequisites
“Download the vRealize Automation IaaS Installer,” on page 76.
Procedure
1 Right-click the setup__vrealize-automation-appliance-FQDN@5480.exe setup le and select Run as
administrator.
2 Click Next.
3 Accept the license agreement and click Next.
4 On the Log in page, supply administrator credentials for the vRealize Automation appliance and verify
the SSL Certicate.
a Type the user name, which is root, and the password.
The password is the password that you specied when you deployed the vRealize Automation
appliance.
b Select Accept .
c Click View .
Compare the certicate thumbprint with the thumbprint set for the vRealize Automation
appliance. You can view the vRealize Automation appliance certicate in the client browser when
the management console is accessed on port 5480.
5 Select Accept .
6 Click Next.
VMware, Inc. 57
Page 58

Installing vRealize Automation
7 Select Complete Install on the Installation Type page if you are creating a minimal deployment and
click Next.
Check Prerequisites
The Prerequisite Checker veries that your machine meets IaaS installation requirements.
Prerequisites
“Select the Installation Type,” on page 57.
Procedure
1 Complete the Prerequisite Check.
Option Description
No errors
Noncritical errors
Critical errors
2 Click Next.
Click Next.
Click Bypass.
Bypassing critical errors causes the installation to fail. If warnings appear,
select the warning in the left pane and follow the instructions on the right.
Address all critical errors and click Check Again to verify.
The machine meets installation requirements.
Specify Server and Account Settings
The vRealize Automation system administrator species server and account seings for the Windows
installation server and selects a SQL database server instance and authentication method.
Prerequisites
“Check Prerequisites,” on page 58.
Procedure
1 On the Server and Account Seings page or the Detected Seings page, enter the user name and
password for the Windows service account. This service account must be a local administrator account
that also has SQL administrative privileges.
2 Type a phrase in the Passphrase text box.
The passphrase is a series of words that generates the encryption key used to secure database data.
N Save your passphrase so that it is available for future installations or system recovery.
3 To install the database instance on the same server with the IaaS components, accept the default server
in the Server text box in the SQL Server Database Installation Information section.
If the database is on a dierent machine, enter the server in the following format.
machine-FQDN,port-number\named-database-instance
4 Accept the default in the Database name text box, or enter the appropriate name if applicable.
58 VMware, Inc.
Page 59

Chapter 4 The Standard vRealize Automation Installation Interfaces
5 Select the authentication method.
Select Use Windows authentication if you want to create the database using the Windows
u
credentials of the current user. The user must have SQL sys_admin privileges.
Deselect Use Windows authentication if you want to create the database using SQL authentication.
u
Type the User name and Password of the SQL Server user with SQL sys_admin privileges on the
SQL server instance.
Windows authentication is recommended. When you choose SQL authentication, the unencrypted
database password appears in certain conguration les.
6 (Optional) Select the Use SSL for database connection checkbox.
By default, the checkbox is enabled. SSL provides a more secure connection between the IaaS server and
SQL database. However, you must rst congure SSL on the SQL server to support this option. For
more about conguring SSL on the SQL server, see Microsoft Knowledge Base article 316898.
7 Click Next.
Specify Managers and Agents
The minimum installation installs the required Distributed Execution Managers and the default vSphere
proxy agent. The system administrator can install additional proxy agents (XenServer, or Hyper-V, for
example) after installation using the custom installer.
Prerequisites
“Specify Server and Account Seings,” on page 58.
Procedure
1 On the Distributed Execution Managers And Proxy vSphere Agent page, accept the defaults or change
the names if appropriate.
2 Accept the default to install a vSphere agent to enable provisioning with vSphere or deselect it if
applicable.
a Select Install and vSphere agent.
b Accept the default agent and endpoint, or type a name.
Make a note of the Endpoint name value. You must type this information correctly when you
congure the vSphere endpoint in the vRealize Automation console or conguration may fail.
3 Click Next.
Register the IaaS Components
The system administrator installs the IaaS certicate and registers the IaaS components with the SSO.
Prerequisites
“Download the vRealize Automation IaaS Installer,” on page 57.
Procedure
1 Accept the default Server value, which is populated with the fully qualied domain name of the
vRealize Automation appliance server from which you downloaded the installer. Verify that a fully
qualied domain name is used to identify the server and not an IP address.
If you have multiple virtual appliances and are using a load balancer, enter the load balancer virtual
appliance path.
2 Click Load to populate the value of SSO Default Tenant (vsphere.local).
VMware, Inc. 59
Page 60

Installing vRealize Automation
3 Click Download to retrieve the certicate from the vRealize Automation appliance.
You can click View to view the certicate details.
4 Select Accept to install the SSO certicate.
5 In the SSO Administrator panel, type administrator in the User name text box and the password you
dened for this user when you congured SSO in Password and password.
6 Click the test link to the right of the User name eld to validate the entered password.
7 Accept the default in IaaS Server, which contains the host name of the Windows machine where you
are installing.
8 Click the test link to the right of the IaaS Server eld to validate connectivity.
9 Click Next.
If any errors appear after you click Next, resolve them before proceeding.
Finish the Installation
The system administrator nishes the IaaS installation.
Prerequisites
“Register the IaaS Components,” on page 59.
n
Verify that machine on which you are installing is connected to the network and is able to connect to the
n
vRealize Automation appliance from which you download the IaaS installer.
Procedure
1 Review the information on the Ready to Install page and click Install.
The installation starts. Depending on your network conguration, installation can take between ve
minutes and one hour.
2 When the success message appears, leave the Guide me through initial check box
selected and click Next, and Finish.
3 Close the the System message box.
The installation is now nished.
What to do next
“Verify IaaS Services,” on page 97.
Using the Standard Interfaces for Distributed Deployments
In a distributed, enterprise deployment, the system administrator installs components on multiple machines
in the deployment environment.
Distributed Deployment Checklist
A system administrator can deploy vRealize Automation in a distributed conguration, which provides
failover protection and high-availability through redundancy.
The Distributed Deployment Checklist provides a high-level overview of the steps required to perform a
distributed installation.
60 VMware, Inc.
Page 61

Table 4‑2. Distributed Deployment Checklist
Task Details
Plan and prepare the installation environment
and verify that all installation prerequisites are
met.
Plan for and obtain your SSL certicates.
Deploy the lead vRealize Automation
appliance server, and any additional appliances
you require for redundancy and high availability.
Congure your load balancer to handle
vRealize Automation appliance trac.
Congure the lead vRealize Automation
appliance server, and any additional appliances
you deployed for redundancy and high
availability.
Congure your load balancer to handle the
vRealize Automation IaaS component trac and
install vRealize Automation IaaS components.
If required, install agents to integrate with
external systems.
Congure the default tenant and provide the
IaaS license.
Chapter 2, “Preparing for vRealize Automation Installation,” on
page 19
“Certicate Trust Requirements in a Distributed Deployment,” on
page 63
“Deploy the vRealize Automation Appliance,” on page 66
“Conguring Your Load Balancer,” on page 68
“Conguring Appliances for vRealize Automation,” on page 68
“Install the IaaS Components in a Distributed Conguration,” on
page 74
“Installing vRealize Automation Agents,” on page 97
“Congure Access to the Default Tenant,” on page 124
Chapter 4 The Standard vRealize Automation Installation Interfaces
vRealize Orchestrator
The vRealize Automation appliance includes an embedded version of vRealize Orchestrator that is now
recommended for use with new installations. In older deployments or special cases, however, users might
connect vRealize Automation to a separate, external vRealize Orchestrator. See
hps://www.vmware.com/products/vrealize-orchestrator.html.
For information about connecting vRealize Automation and vRealize Orchestrator, see Using the vRealize
Orchestrator Plug-In for vRealize Automation.
Directories Management
If you install a distributed installation with load balancers for high availability and failover, notify the team
responsible for conguring your vRealize Automation environment. Your tenant administrators must
congure Directories Management for high availability when they congure the link to your Active
Directory.
For more information about conguring Directories Management for high availability, see the Conguring
vRealize Automation guide.
Distributed Installation Components
In a distributed installation, the system administrator deploys virtual appliances and related components to
support the deployment environment.
VMware, Inc. 61
Page 62

Installing vRealize Automation
Table 4‑3. Virtual Appliances and Appliance Database
Component Description
vRealize Automation appliance A precongured virtual appliance that deploys the
Appliance Database Stores information required by the virtual appliances. The
You can select the individual IaaS components you want to install and specify the installation location.
Table 4‑4. IaaS Components
Component Description
Website Provides the infrastructure administration and service
Manager Service The Manager Service coordinates communication between
Model Manager The Model Manager communicates with the database, the
Distributed Execution Managers (Orchestrator and Worker) A Distributed Execution Manager (DEM) executes the
Agents Virtualization, integration, and WMI agents that
vRealize Automation server. The server includes the
vRealize Automation console, which provides a single
portal for self-service provisioning and management of
cloud services, as well as authoring and administration.
database is embedded on one or two instances of vRealize
Automation appliance.
authoring capabilities to the vRealize Automation console.
The Website component communicates with the Model
Manager, which provides it with updates from the
Distributed Execution Manager (DEM), proxy agents and
database.
agents, the database, Active Directory, and SMTP. The
Manager Service communicates with the console Web site
through the Model Manager. This service requires
administrative privileges to run.
DEMs, and the portal website. The Model Manager is
divided into two separately installable components — the
Model Manager Web service and the Model Manager data
component.
business logic of custom models, interacting with the IaaS
database and external databases. DEMs also manage cloud
and physical machines.
communicate with infrastructure resources.
Disabling Load Balancer Health Checks
Health checks ensure that a load balancer sends trac only to nodes that are working. The load balancer
sends a health check at a specied frequency to every node. Nodes that exceed the failure threshold become
ineligible for new trac.
For workload distribution and failover, you may place multiple vRealize Automation appliances behind a
load balancer. In addition, you may place multiple IaaS Web servers and multiple IaaS Manager Service
servers behind their respective load balancers.
When using load balancers, do not allow the load balancers to send health checks at any time during
installation. Health checks might interfere with installation or cause the installation to behave unpredictably.
When deploying vRealize Automation appliance or IaaS components behind existing load balancers,
n
disable health checks on all load balancers in the proposed conguration before installing any
components.
After installing and conguring all of vRealize Automation, including all vRealize Automation
n
appliance and IaaS components, you may re-enable health checks.
62 VMware, Inc.
Page 63

Chapter 4 The Standard vRealize Automation Installation Interfaces
Certificate Trust Requirements in a Distributed Deployment
For secure communication, vRealize Automation relies on certicates to create trusted relationships among
components.
The specic implementation of the certicates required to achieve this trust depends on your environment.
To provide high availability and failover support, you might deploy load-balanced clusters of components.
In this case, you obtain a multiple-use certicate that includes the IaaS component in the cluster, and then
copy that multiple-use certicate to each component. You can use Subject Alternative Name (SAN)
certicates, wildcard certicates, or any other method of multiple-use certication appropriate for your
environment as long as you satisfy the trust requirements. If you use load balancers in your deployment,
you must include the load balancer FQDN in the trusted address of the cluster multiple-use certicate.
For example, if you have a load balancer on the Web components cluster, one that requires a certicate on
the load balancer as well as the Web components behind it, you might obtain a SAN certicate to certify
web-load-balancer.mycompany.com, web1.mycompany.com, and web2.mycompany.com. You would copy
that single multiple-use certicate to the load balancer and vRealize Automation appliances, and then
register the certicate on the two Web component machines.
The Certicate Trust Requirements table summarizes the trust registration requirements for various
imported certicates.
Table 4‑5. Certificate Trust Requirements
Import Register
vRealize Automation appliance cluster Web components cluster
Web component cluster
Manager Service component cluster
vRealize Automation appliance cluster
n
Manager Service components cluster
n
DEM Orchestrators and DEM Worker components
n
DEM Orchestrators and DEM Worker components
n
Agents and Proxy Agents
n
Configure Web Component, Manager Service and DEM Host Certificate Trust
Customers who use a thumb print with pre installed PFX les to support user authentication must congure
thumb print trust on the web host, manager service, and DEM Orchestrator and Worker host machines.
Customers who import PEM les or use self-signed certicates can ignore this procedure.
Prerequisites
Valid web.pfx and ms.pfx available for thumb print authentication.
Procedure
1 Import the web.pfx and ms.pfx les to the following locations on the web component and manager
service host machines:
Host Computer/Certificates/Personal certificate store
n
Host Computer/Certificates/Trusted People certificate store
n
2 Import the web.pfx and ms.pfx les to the following locations on the DEM Orchestrator and Worker
host machines:
Host Computer/Certificates/Trusted People certificate store
VMware, Inc. 63
Page 64

Installing vRealize Automation
3 Open a Microsoft Management Console window on each of the applicable host machines.
N Actual paths and options in the Management Console may dier somewhat based on Windows
versions and system congurations.
a Select Add/Remove Snap-in.
b Select .
c Select Local Computer.
d Open the certicate les that you imported previously and copy the thumb prints.
What to do next
Insert the thumb print into the vRealize Automation wizard Certicate page for the Manager Service, Web
components and DEM components.
Installation Worksheets
Worksheets record important information that you need to reference during installation.
Seings are case sensitive. Note that there are additional spaces for more components, if you are installing a
distributed deployment. You might not need all the spaces in the worksheets. In addition, a machine might
host more than one IaaS component. For example, the primary Web server and DEM Orchestrator might be
on the same FQDN.
Table 4‑6. vRealize Automation Appliance
Variable My Value Example
Primary vRealize Automation
appliance FQDN
Primary vRealize Automation
appliance IP address
For reference only; do not enter IP
addresses
Additional vRealize Automation
appliance FQDN
Additional vRealize Automation
appliance IP address
For reference only; do not enter IP
addresses
vRealize Automation appliance load
balancer FQDN
vRealize Automation appliance load
balancer IP address
For reference only; do not enter IP
addresses
Management interface
(hps://appliance-FQDN:5480)
username
Management interface password admin123
Default tenant vsphere.local (default) vsphere.local
Default tenant username administrator@vsphere.local (default) administrator@vsphere.local
Default tenant password login123
root (default) root
automation.mycompany.com
123.234.1.105
automation2.mycompany.com
123.234.1.106
automation-balance.mycompany.com
123.234.1.201
64 VMware, Inc.
Page 65

Chapter 4 The Standard vRealize Automation Installation Interfaces
Table 4‑7. IaaS Windows Servers
Variable My Value Example
Primary IaaS Web Server with Model
Manager Data FQDN
Primary IaaS Web Server with Model
Manager Data IP address
For reference only; do not enter IP
addresses
Additional IaaS Web Server FQDN web2.mycompany.com
Additional IaaS Web Server IP address
For reference only; do not enter IP
addresses
IaaS Web Server load balancer FQDN web-balance.mycompany.com
IaaS Web Server load balancer IP
address
For reference only; do not enter IP
addresses
Active IaaS Manager Service host
FQDN
Active IaaS Manager Service host IP
address
For reference only; do not enter IP
addresses
Passive IaaS Manager Service host
FQDN
Passive IaaS Manager Service host IP
address
For reference only; do not enter IP
addresses
IaaS Manager Service host load
balancer FQDN
IaaS Manager Service host load
balancer IP address
For reference only; do not enter IP
addresses
For IaaS services, domain account with
administrator rights on hosts
Account password login123
web.mycompany.com
123.234.1.107
123.234.1.108
123.234.1.202
mgr-svc.mycompany.com
123.234.1.109
mgr-svc2.mycompany.com
123.234.1.110
mgr-svc-balance.mycompany.com
123.234.203
SUPPORT\provisioner
Table 4‑8. IaaS SQL Server Database
Variable My Value Example
Database instance IAASSQL
Database name vcac (default) vcac
Passphrase (used at installation,
upgrade, and migration)
VMware, Inc. 65
login123
Page 66

Installing vRealize Automation
Table 4‑9. IaaS Distributed Execution Managers
Variable My Value Example
DEM host FQDN dem.mycompany.com
DEM host IP address
For reference only; do not enter IP
addresses
DEM host FQDN dem2.mycompany.com
DEM host IP address
For reference only; do not enter IP
addresses
Unique DEM Orchestrator name Orchestrator-1
Unique DEM Orchestrator name Orchestrator-2
Unique DEM Worker name Worker-1
Unique DEM Worker name Worker-2
Unique DEM Worker name Worker-3
Unique DEM Worker name Worker-4
123.234.1.111
123.234.1.112
Deploy the vRealize Automation Appliance
To deploy the vRealize Automation appliance, a system administrator must log in to the vSphere client and
select deployment seings.
Some restrictions apply to the root password you create for the vRealize Automation administrator.
Prerequisites
Download the vRealize Automation appliance from the VMware Web site.
n
Log in to the vSphere client as a user with system administrator privileges.
n
Procedure
1 Select File > Deploy OVF Template from the vSphere client.
2 Browse to the vRealize Automation appliance le you downloaded and click Open.
3 Click Next.
4 Click Next on the OVF Template Details page.
5 Accept the license agreement and click Next.
6 Enter a unique virtual appliance name according to the IT naming convention of your organization in
the Name text box, select the datacenter and location to which you want to deploy the virtual appliance,
and click Next.
7 Follow the prompts until the Disk Format page appears.
8 Verify on the Disk Format page that enough space exists to deploy the virtual appliance and click Next.
9 Follow the prompts to the Properties page.
The options that appear depend on your vSphere conguration.
66 VMware, Inc.
Page 67

Chapter 4 The Standard vRealize Automation Installation Interfaces
10 Congure the values on the Properties page.
a Enter the root password to use when you log in to the virtual appliance console in the Enter
password and password text boxes.
b Select or uncheck the SSH service checkbox to choose whether SSH service is enabled for the
appliance.
This value is used to set the initial status of the SSH service in the appliance. If you are installing
with the Installation Wizard, enable this before you begin the wizard. You can change this seing
from the appliance management console after installation.
c Enter the fully qualied domain name of the virtual machine in the Hostname text box.
d Congure the networking properties.
11 Click Next.
12 Depending on your deployment, vCenter, and DNS conguration, select one of the following ways of
nishing OVA deployment and powering up the vRealize Automation appliance.
If you deployed to vSphere, and Power on after deployment is available on the Ready to Complete
n
page, take the following steps.
a Select Power on after deployment and click Finish.
b After the le nishes deploying into vCenter, click Close.
c Wait for the machine to start, which might take up to 5 minutes.
If you deployed to vSphere, and Power on after deployment is not available on the Ready to
n
Complete page, take the following steps.
a After the le nishes deploying into vCenter, click Close.
b Power on the vRealize Automation appliance.
c Wait for the machine to start, which might take up to 5 minutes.
d Verify that you can ping the DNS for the vRealize Automation appliance. If you cannot ping
the DNS, restart the virtual machine.
e Wait for the machine to start, which might take up to 5 minutes.
If you deployed the vRealize Automation appliance to vCloud using vCloud Director, vCloud
n
might override the password that you entered during OVA deployment. To prevent the override,
take the following steps.
a After deploying in vCloud Director, click your vApp to view the vRealize Automation
appliance.
b Right-click the vRealize Automation appliance, and select Properties.
c Click the Guest OS Customization tab.
d Under Password Reset, clear the Allow local administrator password option, and click OK.
e Power on the vRealize Automation appliance.
f Wait for the machine to start, which might take up to 5 minutes.
To verify that you successfully deployed the appliance, open a command prompt and ping the FQDN of the
vRealize Automation appliance.
What to do next
Repeat this procedure to deploy additional instances of the vRealize Automation appliance for redundancy
in a high-availability environment.
VMware, Inc. 67
Page 68

Installing vRealize Automation
Configuring Your Load Balancer
After you deploy the appliances for vRealize Automation, you can set up a load balancer to distribute trac
among multiple instances of the vRealize Automation appliance.
The following list provides an overview of the general steps required to congure a load balancer for
vRealize Automation trac:
1 Install your load balancer.
2 Enable session anity, also known as sticky sessions.
3 Ensure that the timeout on the load balancer is at least 100 seconds.
4 If your network or load balancer requires it, import a certicate to your load balancer. For information
about trust relationships and certicates, see “Certicate Trust Requirements in a Distributed
Deployment,” on page 63. For information about extracting certicates, see “Extracting Certicates and
Private Keys,” on page 30
5 Congure the load balancer for vRealize Automation appliance trac.
6 Congure the appliances for vRealize Automation. See “Conguring Appliances for vRealize
Automation,” on page 68.
N When you set up virtual appliances under the load balancer, do so only for virtual appliances that
have been congured for use with vRealize Automation. If uncongured appliances are set up, you see fault
responses.
For information about scalability and high availability, see the vRealize Automation Reference Architecture
guide.
Configuring Appliances for vRealize Automation
After deploying your appliances and conguring load balancing, you congure the appliances for
vRealize Automation.
Configure the Primary vRealize Automation Appliance
The vRealize Automation appliance is a precongured virtual appliance that deploys the
vRealize Automation server and Web console (the user portal). It is delivered as an open virtualization
format (OVF) template. The system administrator downloads the appliance and deploys it into the vCenter
Server or ESX/ESXi inventory.
If your network or load balancer requires it, the certicate you congure for the primary instance of the
appliance is copied to the load balancer and additional appliance instances in subsequent procedures.
Prerequisites
“Deploy the vRealize Automation Appliance,” on page 66.
n
Get a domain certicate for the vRealize Automation appliance.
n
Procedure
1 Enable Time Synchronization on the vRealize Automation appliance on page 69
Clocks on the vRealize Automation appliance server and Windows servers must be synchronized to
ensure a successful installation.
2 Congure the vRealize Automation Appliance on page 69
To prepare the vRealize Automation appliance for use, you congure host seings, generate an SSL
certicate, and provide SSO connection information.
68 VMware, Inc.
Page 69

Chapter 4 The Standard vRealize Automation Installation Interfaces
Enable Time Synchronization on the vRealize Automation appliance
Clocks on the vRealize Automation appliance server and Windows servers must be synchronized to ensure
a successful installation.
If you see certicate warnings during this process, continue past them to nish the installation.
Procedure
1 Open a Web browser to the vRealize Automation appliance management interface URL.
2 Log in with the user name root and the password you specied when the appliance was deployed.
3 Select Admin > Time .
4 Select an option from the Time Sync Mode menu.
Option Action
Use Time Server
Use Host Time
Select Use Time Server from the Time Sync Mode menu to use Network
Time Protocol . For each time server that you are using, enter the IP
address or the host name in the Time Server text box.
Select Use Host Time from the Time Sync Mode menu to use
VMware Tools time synchronization. You must congure the connections
to Network Time Protocol servers before you can use VMware Tools time
synchronization.
5 Click Save .
6 Verify that the value in Current Time is correct.
You can change the time zone as required from the Time Zone Seing page on the System tab.
Configure the vRealize Automation Appliance
To prepare the vRealize Automation appliance for use, you congure host seings, generate an SSL
certicate, and provide SSO connection information.
Procedure
1 Open a Web browser to the vRealize Automation appliance management interface URL.
hps://vrealize-automation-appliance-FQDN:5480
2 Continue past the certicate warning.
3 Log in with the user name root and the password you specied when the appliance was deployed.
4 Select vRA > Host .
Option Action
Resolve Automatically Select Resolve Automatically to specify the name of the current
host for the vRealize Automation appliance.
Update Host For new hosts, select Update Host. Enter the fully qualied domain
name of the vRealize Automation appliance, vra-
hostname.domain.name, in the Host Name text box.
For distributed deployments that use load balancers, select Update
Host. Enter the fully qualied domain name for the load balancer
server, vra-loadbalancername.domain.name, in the Host Name text
box.
N Congure SSO seings as described later in this procedure whenever you use Update Host to
set the host name.
VMware, Inc. 69
Page 70

Installing vRealize Automation
5 Select the certicate type from the Action menu.
If you are using a PEM-encoded certicate, for example for a distributed environment, select Import.
Certicates that you import must be trusted and must also be applicable to all instances of vRealize
Automation appliance and any load balancer through the use of Subject Alternative Name (SAN)
certicates.
N If you use certicate chains, specify the certicates in the following order:
a Client/server certicate signed by the intermediate CA certicate
b One or more intermediate certicates
c A root CA certicate
Option Action
Keep Existing
Generate Certificate
Import
6 Click Save to save host information and SSL conguration.
Leave the current SSL conguration. Select this option to cancel your
changes.
a The value displayed in the Common Name text box is the Host Name
as it appears on the upper part of the page. If any additional instances
of the vRealize Automation appliance available, their FQDNs are
included in the SAN aribute of the certicate.
b Enter your organization name, such as your company name, in the
Organization text box.
c Enter your organizational unit, such as your department name or
location, in the Organizational Unit text box.
d
Enter a two-leer ISO 3166 country code, such as US, in the Country
text box.
a Copy the certicate values from BEGIN PRIVATE KEY to END
PRIVATE KEY, including the header and footer, and paste them in the
RSA Private Key text box.
b Copy the certicate values from BEGIN CERTIFICATE to END
CERTIFICATE, including the header and footer, and paste them in the
Chain text box. For multiple certicate values, include a
BEGIN CERTIFICATE header and END CERTIFICATE footer for each
certicate.
N In the case of chained certicates, additional aributes may be
available.
c (Optional) If your certicate uses a pass phrase to encrypt the
certicate key, copy the pass phrase and paste it in the Passphrase text
box.
7 If required by your network or load balancer, copy the imported or newly created certicate to the
virtual appliance load balancer.
You might need to enable root SSH access in order to export the certicate.
a If not already logged in, log in to the vRealize Automation appliance Management Console as root.
b Click the Admin tab.
c Click the Admin sub menu.
d Select the SSH service enabled check box.
Deselect the check box to disable SSH when nished.
70 VMware, Inc.
Page 71

Chapter 4 The Standard vRealize Automation Installation Interfaces
e Select the Administrator SSH login check box.
Deselect the check box to disable SSH when nished.
f Click Save .
8 Congure the SSO seings.
9 Click Services.
All services must be running before you can install a license or log in to the console. They usually start
in about 10 minutes.
N You can also log in to the appliance and run tail -f /var/log/vcac/catalina.out to monitor
service startup.
10 Enter your license information.
a Click vRA > Licensing.
b Click Licensing.
c Enter a valid vRealize Automation license key that you downloaded when you downloaded the
installation les, and click Submit Key.
N If you experience a connection error, you might have a problem with the load balancer. Check
network connectivity to the load balancer.
11 Click Messaging. The conguration seings and status of messaging for your appliance is displayed.
Do not change these seings.
12 Click the Telemetry tab to choose whether to join the VMware Customer Experience Improvement
Program (CEIP).
Details regarding the data collected through CEIP and the purposes for which it is used by VMware are
set forth at the Trust & Assurance Center at hp://www.vmware.com/trustvmware/ceip.html.
Select Join the VMware Customer Experience Improvement Program to participate in the
n
program.
Deselect Join the VMware Customer Experience Improvement Program to not participate in the
n
program.
13 Click Save
14 Conrm that you can log in to vRealize Automation.
a Open a Web browser to the vRealize Automation product interface URL.
hps://vrealize-automation-appliance-FQDN/vcac
b If prompted, continue past the certicate warnings.
c Log in with administrator@vsphere.local and the password you specied when you congured
SSO.
The interface opens to the Tenants page on the Administration tab. A single tenant named
vsphere.local appears in the list.
VMware, Inc. 71
Page 72

Installing vRealize Automation
Configuring Additional Instances of the vRealize Automation Appliance
The system administrator can deploy multiple instances of the vRealize Automation appliance to ensure
redundancy in a high-availability environment.
For each vRealize Automation appliance, you must enable time synchronization and add the appliance to a
cluster. Conguration information based on seings for the initial (primary) vRealize Automation appliance
is added automatically when you add the appliance to the cluster.
If you install a distributed installation with load balancers for high availability and failover, notify the team
responsible for conguring your vRealize Automation environment. Your tenant administrators must
congure Directories Management for high availability when they congure the link to your Active
Directory.
Enable Time Synchronization on the vRealize Automation Appliance
Clocks on the vRealize Automation appliance server and Windows servers must be synchronized to ensure
a successful installation.
If you see certicate warnings during this process, continue past them to nish the installation.
Prerequisites
“Congure the Primary vRealize Automation Appliance,” on page 68.
Procedure
1 Open a Web browser to the vRealize Automation appliance management interface URL.
2 Log in with the user name root and the password you specied when the appliance was deployed.
3 Select Admin > Time .
4 Select an option from the Time Sync Mode menu.
Option Action
Use Time Server
Use Host Time
Select Use Time Server from the Time Sync Mode menu to use Network
Time Protocol . For each time server that you are using, enter the IP
address or the host name in the Time Server text box.
Select Use Host Time from the Time Sync Mode menu to use
VMware Tools time synchronization. You must congure the connections
to Network Time Protocol servers before you can use VMware Tools time
synchronization.
5 Click Save .
6 Verify that the value in Current Time is correct.
You can change the time zone as required from the Time Zone Seing page on the System tab.
Add Another vRealize Automation Appliance to the Cluster
For high availability, distributed installations can use a load balancer in front of a cluster of vRealize
Automation appliance nodes.
You use the management console on the new vRealize Automation appliance to join it to an existing cluster
of one or more appliances. The join operation copies conguration information to the new appliance that
you are adding, including certicate, SSO, licensing, database, and messaging information.
You must add appliances to a cluster one at a time and not in parallel.
72 VMware, Inc.
Page 73

Chapter 4 The Standard vRealize Automation Installation Interfaces
Prerequisites
You must have one or more vRealize Automation appliance nodes already in the cluster, where one
n
node is the primary node. See “Congure the Primary vRealize Automation Appliance,” on page 68.
You can set a new node to be the primary node only after joining the new node to the cluster.
Verify that the load balancer is congured for use with the new vRealize Automation appliance.
n
Verify that trac can pass through the load balancer to reach all current nodes and the new node that
n
you are about to add.
Enable time synchronization on the new node. See “Enable Time Synchronization on the vRealize
n
Automation Appliance,” on page 72.
Verify that all vRealize Automation services have started, on the existing cluster appliance nodes and
n
the new node that you are adding.
Procedure
1 Open a Web browser to the vRealize Automation appliance management interface URL.
2 Continue past any certicate warnings.
3 Log in with user name root and the password you specied when deploying the vRealize Automation
appliance.
4 Select vRA > Cluster.
5 Enter the FQDN of a previously congured vRealize Automation appliance in the Leading Cluster
Node text box.
You can use the FQDN of the primary vRealize Automation appliance, or any vRealize Automation
appliance that is already joined to the cluster.
6 Type the root password in the Password text box.
7 Click Join Cluster.
8 Continue past any certicate warnings.
Services for the cluster are restarted.
9 Verify that services are running.
a Click the Services tab.
b Click the Refresh tab to monitor the progress of service startup.
Disable Unused Services
To conserve internal resources in cases where an external instance of vRealize Orchestrator is used, you may
disable the embedded vRealize Orchestrator service.
Prerequisites
“Add Another vRealize Automation Appliance to the Cluster,” on page 72
Procedure
1 Log in to the vRealize Automation appliance console.
2 Stop the vRealize Orchestrator service.
service vco-server stop
chkconfig vco-server off
VMware, Inc. 73
Page 74

Installing vRealize Automation
Validate the Distributed Deployment
After deploying additional instances of the vRealize Automation appliance, you validate that you can access
the clustered appliances.
Procedure
1 In the load balancer management interface or conguration le, temporarily disable all nodes except
the node that you are testing.
2 Conrm that you can log in to vRealize Automation through the load balancer address:
hps://vrealize-automation-appliance-load-balancer-FQDN/vcac
3 After verifying that you can access the new vRealize Automation appliance through the load balancer,
re-enable the other nodes.
Install the IaaS Components in a Distributed Configuration
The system administrator installs the IaaS components after the appliances are deployed and fully
congured. The IaaS components provide access to vRealize Automation Infrastructure features.
All components must run under the same service account user, which must be a domain account that has
privileges on each distributed IaaS server. Do not use local system accounts.
Prerequisites
“Congure the Primary vRealize Automation Appliance,” on page 68.
n
If your site includes multiple instances of vRealize Automation appliance, “Add Another vRealize
n
Automation Appliance to the Cluster,” on page 72.
Verify that your installation servers meet the requirements described in “IaaS Web Service and Model
n
Manager Server Requirements,” on page 22.
Obtain a certicate from a trusted certicate authority for import to the trusted root certicate store of
n
the machines on which you intend to install the Component Website and Model Manager data.
If you are using load balancers in your environment, verify that they meet the conguration
n
requirements.
Procedure
1 Install IaaS Certicates on page 75
For production environments, obtain a domain certicate from a trusted certicate authority. Import
the certicate to the trusted root certicate store of all machines on which you intend to install the
Website Component and Manager Service (the IIS machines) during the IaaS installation.
2 Download the vRealize Automation IaaS Installer on page 76
To install IaaS on your distributed virtual or physical Windows servers, you download a copy of the
IaaS installer from the vRealize Automation appliance.
3 Choosing an IaaS Database Scenario on page 77
vRealize Automation IaaS uses a Microsoft SQL Server database to maintain information about the
machines it manages and its own elements and policies.
4 Install an IaaS Website Component and Model Manager Data on page 81
The system administrator installs the Website component to provide access to infrastructure
capabilities in the vRealize Automation web console. You can install one or many instances of the
Website component, but you must congure Model Manager Data on the machine that hosts the rst
Website component. You install Model Manager Data only once.
74 VMware, Inc.
Page 75

Chapter 4 The Standard vRealize Automation Installation Interfaces
5 Install Additional IaaS Web Server Components on page 85
The Web server provides access to infrastructure capabilities in vRealize Automation. After the rst
Web server is installed, you might increase performance by installing additional IaaS Web servers.
6 Install the Active Manager Service on page 87
The active Manager Service is a Windows service that coordinates communication between IaaS
Distributed Execution Managers, the database, agents, proxy agents, and SMTP.
7 Install a Backup Manager Service Component on page 90
The backup Manager Service provides redundancy and high availability, and may be started manually
if the active service stops.
8 Installing Distributed Execution Managers on page 92
You install the Distributed Execution Manager as one of two roles: DEM Orchestrator or DEM Worker.
You must install at least one DEM instance for each role, and you can install additional DEM instances
to support failover and high-availability.
9 Conguring Windows Service to Access the IaaS Database on page 95
A system administrator can change the authentication method used to access the SQL database during
run time (after the installation is complete). By default, the Windows identity of the currently logged
on account is used to connect to the database after it is installed.
10 Verify IaaS Services on page 97
After installation, the system administrator veries that the IaaS services are running. If the services
are running, the installation is a success.
What to do next
Install a DEM Orchestrator and at least one DEM Worker instance. See “Installing Distributed Execution
Managers,” on page 92.
Install IaaS Certificates
For production environments, obtain a domain certicate from a trusted certicate authority. Import the
certicate to the trusted root certicate store of all machines on which you intend to install the Website
Component and Manager Service (the IIS machines) during the IaaS installation.
Prerequisites
On Windows 2012 machines, you must disable TLS1.2 for certicates that use SHA512. For more
information about disabling TLS1.2, see Microsoft Knowledge Base article 245030.
Procedure
1 Obtain a certicate from a trusted certicate authority.
2 Open the Internet Information Services (IIS) Manager.
3 Double-click Server from Features View.
4 Click Import in the Actions pane.
a Enter a le name in the text box, or click the browse buon (…), to navigate to the
name of a le where the exported certicate is stored.
b Enter a password in the Password text box if the certicate was exported with a password.
c Select Mark this key as exportable.
5 Click OK.
6 Click on the imported certicate and select View.
VMware, Inc. 75
Page 76

Installing vRealize Automation
7 Verify that the certicate and its chain is trusted.
If the certicate is untrusted, you see the message, This CA root certificate is not trusted.
N You must resolve the trust issue before proceeding with the installation. If you continue, your
deployment fails.
8 Restart IIS or open an elevated command prompt window and type iisreset.
What to do next
“Download the vRealize Automation IaaS Installer,” on page 76.
Download the vRealize Automation IaaS Installer
To install IaaS on your distributed virtual or physical Windows servers, you download a copy of the IaaS
installer from the vRealize Automation appliance.
If you see certicate warnings during this process, continue past them to nish the installation.
Prerequisites
“Congure the Primary vRealize Automation Appliance,” on page 68 and, optionally, “Add Another
n
vRealize Automation Appliance to the Cluster,” on page 72.
Verify that your installation servers meet the requirements described in “IaaS Web Service and Model
n
Manager Server Requirements,” on page 22.
Verify that you imported a certicate to IIS and that the certicate root or the certicate authority is in
n
the trusted root on the installation machine.
If you are using load balancers in your environment, verify that they meet the conguration
n
requirements.
Procedure
1 (Optional) Activate HTTP if you are installing on a Windows 2012 machine.
a Select Features > Add Features from Server Manager.
b Expand WCF Services under .NET Framework Features.
c Select HTTP Activation.
2 Log in to the IaaS Windows server using an account that has administrator rights.
3 Open a Web browser directly to the vRealize Automation appliance installer URL. Do not use a load
balancer address.
hps://vrealize-automation-appliance-FQDN:5480/installer
4 Click IaaS Installer.
5 Save setup__vrealize-automation-appliance-FQDN@5480 to the Windows server.
Do not change the installer le name. It is used to connect the installation to the vRealize Automation
appliance.
6 Download the installer le to each IaaS Windows server on which you are installing components.
What to do next
Install an IaaS database, see “Choosing an IaaS Database Scenario,” on page 77.
76 VMware, Inc.
Page 77

Chapter 4 The Standard vRealize Automation Installation Interfaces
Choosing an IaaS Database Scenario
vRealize Automation IaaS uses a Microsoft SQL Server database to maintain information about the
machines it manages and its own elements and policies.
Depending on your preferences and privileges, there are several procedures to choose from to create the
IaaS database.
N You can enable secure SSL when creating or upgrading the SQL database. For example, when you
create or upgrade the SQL database, you can use the Secure SSL option to specify that the SSL conguration
which is already specied in the SQL server be enforced when connecting to the SQL database. SSL provides
a more secure connection between the IaaS server and SQL database. This option, which is available in the
custom installation wizard, requires that you have already congured SSL on the SQL server. For related
information about conguring SSL on the SQL server, see Microsoft Knowledge Base article 316898.
Table 4‑10. Choosing an IaaS Database Scenario
Scenario Procedure
Create the IaaS database manually using the provided
database scripts. This option enables a database
administrator to review the changes carefully before
creating the database.
Prepare an empty database and use the installer to
populate the database schema. This option enables the
installer to use a database user with dbo privileges to
populate the database, instead of requiring sysadmin
privileges.
Use the installer to create the database. This is the simplest
option but requires the use of sysadmin privileges in the
installer.
“Create the IaaS Database Manually,” on page 77.
“Prepare an Empty Database,” on page 78.
“Create the IaaS Database Using the Installation Wizard,”
on page 79.
Create the IaaS Database Manually
The vRealize Automation system administrator can create the database manually using VMware-provided
scripts.
Prerequisites
Microsoft .NET Framework 4.5.2 or later must be installed on the SQL Server host.
n
Use Windows Authentication, rather than SQL Authentication, to connect to the database.
n
Verify the database installation prerequisites. See “IaaS Database Server Requirements,” on page 21.
n
Open a Web browser to the vRealize Automation appliance installer URL, and download the IaaS
n
database installation scripts.
hps://vrealize-automation-appliance-FQDN:5480/installer
Procedure
1 Navigate to the Database subdirectory in the directory where you extracted the installation zip archive.
2 Extract the DBInstall.zip archive to a local directory.
3 Log in to the Windows database host with sucient rights to create and drop databases sysadmin
privileges in the SQL Server instance.
VMware, Inc. 77
Page 78

Installing vRealize Automation
4 Review the database deployment scripts as needed. In particular, review the seings in the DBSettings
section of CreateDatabase.sql and edit them if necessary.
The seings in the script are the recommended seings. Only ALLOW_SNAPSHOT_ISOLATION ON and
READ_COMMITTED_SNAPSHOT ON are required.
5 Execute the following command with the arguments described in the table.
BuildDB.bat /p:DBServer=db_server;
DBName=db_name;DBDir=db_dir;
LogDir=[log_dir];ServiceUser=service_user;
ReportLogin=web_user;
VersionString=version_string
Table 4‑11. Database Values
Variable Value
db_server Species the SQL Server instance in the format
db_name
db_dir Path to the data directory for the database, excluding the nal
log_dir Path to the log directory for the database, excluding the nal
service_user User name under which the Manager Service runs.
Web_user User name under which the Web services run.
version_string The vRealize Automation version, found by logging in to the
dbhostname[,port number]\SQL instance. Specify a port
number only if you are using a non-default port. The
Microsoft SQL default port number is 1433. The default value
for db_server is localhost.
Name of the database. The default value is vra. Database
names must consist of no more than 128 ASCII characters.
slash.
slash.
vRealize Automation appliance and clicking the Update tab.
For example, the vRealize Automation 6.1 version string is
6.1.0.1200.
The database is created.
What to do next
“Install the IaaS Components in a Distributed Conguration,” on page 74.
Prepare an Empty Database
A vRealize Automation system administrator can install the IaaS schema on an empty database. This
installation method provides maximum control over database security.
Prerequisites
Verify the database installation prerequisites. See “IaaS Database Server Requirements,” on page 21.
n
Open a Web browser to the vRealize Automation appliance installer URL, and download the IaaS
n
database installation scripts.
hps://vrealize-automation-appliance-FQDN:5480/installer
Procedure
1 Navigate to the Database directory within the directory where you extracted the installation zip archive.
2 Extract the DBInstall.zip archive to a local directory.
78 VMware, Inc.
Page 79

Chapter 4 The Standard vRealize Automation Installation Interfaces
3 Log in to the Windows database host with sysadmin privileges within the SQL Server instance.
4 Edit CreateDatabase.sql and replace all instances of the variables in the table with the correct values for
your environment.
Table 4‑12. Database Values
Variable Value
$(DBName) Name of the database, such as vra. Database names must
consist of no more than 128 ASCII characters.
$(DBDir) Path to the data directory for the database, excluding the nal
slash.
$(LogDir) Path to the log directory for the database, excluding the nal
slash.
5 Review the seings in the DB Settings section of CreateDatabase.sql and edit them if needed.
The seings in the script are the recommended seings for the IaaS database. Only
ALLOW_SNAPSHOT_ISOLATION ON and READ_COMMITTED_SNAPSHOT ON are required.
6 Open SQL Server Management Studio.
7 Click New Query.
An SQL Query window opens.
8 On the Query menu, ensure that SQLCMD Mode is selected.
9 Paste the entire modied contents of CreateDatabase.sql into the query pane.
10 Click Execute.
The script runs and creates the database.
What to do next
“Install the IaaS Components in a Distributed Conguration,” on page 74.
Create the IaaS Database Using the Installation Wizard
vRealize Automation uses a Microsoft SQL Server database to maintain information about the machines it
manages and its own elements and policies.
The following steps describe how to create the IaaS database using the installer or populate an existing
empty database. It is also possible to create the database manually. See “Create the IaaS Database Manually,”
on page 77.
Prerequisites
If you are creating the database with Windows authentication, instead of SQL authentication, verify that
n
the user who runs the installer has sysadmin rights on the SQL server.
“Download the vRealize Automation IaaS Installer,” on page 76.
n
Procedure
1 Right-click the setup__vrealize-automation-appliance-FQDN@5480.exe setup le and select Run as
administrator.
2 Click Next.
3 Accept the license agreement and click Next.
VMware, Inc. 79
Page 80

Installing vRealize Automation
4 On the Log in page, supply administrator credentials for the vRealize Automation appliance and verify
the SSL Certicate.
a Type the user name, which is root, and the password.
The password is the password that you specied when you deployed the vRealize Automation
appliance.
b Select Accept .
c Click View .
Compare the certicate thumbprint with the thumbprint set for the vRealize Automation
appliance. You can view the vRealize Automation appliance certicate in the client browser when
the management console is accessed on port 5480.
5 Click Next.
6 Select Custom Install on the Installation Type page.
7 Select IaaS Server under Component Selection on the Installation Type page.
8 Accept the root install location or click Change and select an installation path.
Even in a distributed deployment, you might sometimes install more than one IaaS component on the
same Windows server.
If you install more than one IaaS component, always install them to the same path.
9 Click Next.
10 On the IaaS Server Custom Install page, select Database.
11 In the Database Instance text box, specify the database instance or click Scan and select from the list of
instances. If the database instance is on a non-default port, include the port number in instance
specication by using the form dbhost,SQL_port_number\SQLinstance. The Microsoft SQL default port
number is 1443.
12 (Optional) Select the Use SSL for database connection checkbox.
By default, the checkbox is enabled. SSL provides a more secure connection between the IaaS server and
SQL database. However, you must rst congure SSL on the SQL server to support this option. For
more about conguring SSL on the SQL server, see Microsoft Knowledge Base article 316898.
13 Choose your database installation type from the Database Name panel.
Select Use existing empty database to create the schema in an existing database.
n
Enter a new database name or use the default name vra to create a new database. Database names
n
must consist of no more than 128 ASCII characters.
14 Deselect Use default data and log directories to specify alternative locations or leave it selected to use
the default directories (recommended).
15 Select an authentication method for installing the database from the Authentication list.
To use the credentials under which you are running the installer to create the database, select User
n
Windows identity....
To use SQL authentication, deselect Use Windows identity.... Type SQL credentials in the user and
n
password text boxes.
By default, the Windows service user account is used during runtime access to the database, and must
have sysadmin rights to the SQL Server instance. The credentials used to access the database at runtime
can be congured to use SQL credentials.
Windows authentication is recommended. When you choose SQL authentication, the unencrypted
database password appears in certain conguration les.
80 VMware, Inc.
Page 81

Chapter 4 The Standard vRealize Automation Installation Interfaces
16 Click Next.
17 Complete the Prerequisite Check.
Option Description
No errors
Noncritical errors
Critical errors
Click Next.
Click Bypass.
Bypassing critical errors causes the installation to fail. If warnings appear,
select the warning in the left pane and follow the instructions on the right.
Address all critical errors and click Check Again to verify.
18 Click Install.
19 When the success message appears, deselect Guide me through initial and click Next.
20 Click Finish.
The database is ready for use.
Install an IaaS Website Component and Model Manager Data
The system administrator installs the Website component to provide access to infrastructure capabilities in
the vRealize Automation web console. You can install one or many instances of the Website component, but
you must congure Model Manager Data on the machine that hosts the rst Website component. You install
Model Manager Data only once.
Prerequisites
Install the IaaS Database, see “Choosing an IaaS Database Scenario,” on page 77.
n
If you previously installed other components in this environment, verify that you know the passphrase
n
that was created. See “Security Passphrase,” on page 31.
If you are using load balancers in your environment, verify that they meet the conguration
n
requirements.
Procedure
1 Install the First IaaS Web Server Component on page 81
You install the IaaS Web server component to provide access to infrastructure capabilities in
vRealize Automation.
2 Congure Model Manager Data on page 83
You install the Model Manager component on the same machine that hosts the rst Web server
component. You only install Model Manager Data once.
You can install additional Website components or install the Manager Service. See “Install Additional IaaS
Web Server Components,” on page 85 or “Install the Active Manager Service,” on page 87.
Install the First IaaS Web Server Component
You install the IaaS Web server component to provide access to infrastructure capabilities in
vRealize Automation.
You can install multiple IaaS Web servers, but only the rst one includes Model Manager Data.
Prerequisites
“Create the IaaS Database Using the Installation Wizard,” on page 79.
n
Verify that your environment meets the requirements described in “IaaS Web Service and Model
n
Manager Server Requirements,” on page 22.
VMware, Inc. 81
Page 82

Installing vRealize Automation
If you previously installed other components in this environment, verify that you know the passphrase
n
that was created. See “Security Passphrase,” on page 31.
If you are using load balancers in your environment, verify that they meet the conguration
n
requirements.
Procedure
1 If using a load balancer, disable the other nodes under the load balancer, and verify that trac is
directed to the node that you want.
In addition, disable load balancer health checks until all vRealize Automation components are installed
and congured.
2 Right-click the setup__vrealize-automation-appliance-FQDN@5480.exe setup le and select Run as
administrator.
3 Click Next.
4 Accept the license agreement and click Next.
5 On the Log in page, supply administrator credentials for the vRealize Automation appliance and verify
the SSL Certicate.
a Type the user name, which is root, and the password.
The password is the password that you specied when you deployed the vRealize Automation
appliance.
b Select Accept .
c Click View .
Compare the certicate thumbprint with the thumbprint set for the vRealize Automation
appliance. You can view the vRealize Automation appliance certicate in the client browser when
the management console is accessed on port 5480.
6 Click Next.
7 Select Custom Install on the Installation Type page.
8 Select IaaS Server under Component Selection on the Installation Type page.
9 Accept the root install location or click Change and select an installation path.
Even in a distributed deployment, you might sometimes install more than one IaaS component on the
same Windows server.
If you install more than one IaaS component, always install them to the same path.
10 Click Next.
11 Select Website and ModelManagerData on the IaaS Server Custom Install page.
12 Select a Web site from available Web sites or accept the default Web site on the Administration &
Model Manager Web Site tab.
13 Type an available port number in the Port number text box, or accept the default port 443.
14 Click Test Binding to conrm that the port number is available for use.
82 VMware, Inc.
Page 83

Chapter 4 The Standard vRealize Automation Installation Interfaces
15 Select the certicate for this component.
a If you imported a certicate after you began the installation, click Refresh to update the list.
b Select the certicate to use from Available .
c If you imported a certicate that does not have a friendly name and it does not appear in the list,
deselect Display using friendly names and click Refresh.
If you are installing in an environment that does not use load balancers, you can select Generate a Self-
Signed instead of selecting a certicate. If you are installing additional Web site components
behind a load balancer, do not generate self-signed certicates. Import the certicate from the main IaaS
Web server to ensure that you use the same certicate on all servers behind the load balancer.
16 (Optional) Click View , view the certicate, and click OK to close the information window.
17 (Optional) Select Suppress mismatch to suppress certicate errors. The installation ignores
certicate name mismatch errors as well as any remote certicate-revocation list match errors.
This is a less secure option.
Configure Model Manager Data
You install the Model Manager component on the same machine that hosts the rst Web server component.
You only install Model Manager Data once.
Prerequisites
“Install the First IaaS Web Server Component,” on page 81.
Procedure
1 Click the Model Manager Data tab.
2 In the Server text box, enter the vRealize Automation appliance fully qualied domain name.
vrealize-automation-appliance.mycompany.com
Do not enter an IP address.
3 Click Load to display the SSO Default Tenant.
The vsphere.local default tenant is created automatically when you congure single sign-on. Do not
modify it.
4 Click Download to import the certicate from the virtual appliance.
It might take several minutes to download the certicate.
5 (Optional) Click View , view the certicate, and click OK to close the information window.
6 Click Accept .
7 Type administrator@vsphere.local in the User name text box and the password you created when you
congured the SSO in the Password and text boxes.
8 (Optional) Click Test to verify the credentials.
VMware, Inc. 83
Page 84

Installing vRealize Automation
9 In the IaaS Server text box, identify the IaaS Web server component.
Option Description
With a load balancer
Without a load balancer
The default port is 443.
10 Click Test to verify the server connection.
11 Click Next.
12 Complete the Prerequisite Check.
Option Description
No errors
Noncritical errors
Critical errors
13 On the Server and Account Seings page, in the Server Installation Information text boxes, enter the
user name and password of the service account user that has administrative privileges on the current
installation server.
Enter the fully qualied domain name and port number of the load
balancer for the IaaS Web server component, web-load-
balancer.mycompany.com:443.
Do not enter IP addresses.
Enter the fully qualied domain name and port number of the machine
where you installed the IaaS Web server component, web.mycompany.com:
443.
Do not enter IP addresses.
Click Next.
Click Bypass.
Bypassing critical errors causes the installation to fail. If warnings appear,
select the warning in the left pane and follow the instructions on the right.
Address all critical errors and click Check Again to verify.
The service account user must be one domain account that has privileges on each distributed IaaS
server. Do not use local system accounts.
14 Provide the passphrase used to generate the encryption key that protects the database.
Option Description
If you have already installed
components in this environment
If this is the first installation
Type the passphrase you created previously in the Passphrase and
text boxes.
Type a passphrase in the Passphrase and text boxes. You must
use this passphrase every time you install a new component.
Keep this passphrase in a secure place for later use.
15 Specify the IaaS database server, database name, and authentication method for the database server in
the Microsoft SQL Database Installation Information text box.
This is the IaaS database server, name, and authentication information that you created previously.
16 Click Next.
17 Click Install.
18 When the installation nishes, deselect Guide me through the initial and click Next.
What to do next
You can install additional Web server components or install the Manager Service. See “Install Additional
IaaS Web Server Components,” on page 85 or “Install the Active Manager Service,” on page 87.
84 VMware, Inc.
Page 85

Chapter 4 The Standard vRealize Automation Installation Interfaces
Install Additional IaaS Web Server Components
The Web server provides access to infrastructure capabilities in vRealize Automation. After the rst Web
server is installed, you might increase performance by installing additional IaaS Web servers.
Do not install Model Manager Data with an additional Web server component. Only the rst Web server
component hosts Model Manager Data.
Prerequisites
“Install an IaaS Website Component and Model Manager Data,” on page 81.
n
Verify that your environment meets the requirements described in “IaaS Web Service and Model
n
Manager Server Requirements,” on page 22.
If you previously installed other components in this environment, verify that you know the passphrase
n
that was created. See “Security Passphrase,” on page 31.
If you are using load balancers in your environment, verify that they meet the conguration
n
requirements.
Procedure
1 If using a load balancer, disable the other nodes under the load balancer, and verify that trac is
directed to the node that you want.
In addition, disable load balancer health checks until all vRealize Automation components are installed
and congured.
2 Right-click the setup__vrealize-automation-appliance-FQDN@5480.exe setup le and select Run as
administrator.
3 Click Next.
4 Accept the license agreement and click Next.
5 On the Log in page, supply administrator credentials for the vRealize Automation appliance and verify
the SSL Certicate.
a Type the user name, which is root, and the password.
The password is the password that you specied when you deployed the vRealize Automation
appliance.
b Select Accept .
c Click View .
Compare the certicate thumbprint with the thumbprint set for the vRealize Automation
appliance. You can view the vRealize Automation appliance certicate in the client browser when
the management console is accessed on port 5480.
6 Click Next.
7 Select Custom Install on the Installation Type page.
8 Select IaaS Server under Component Selection on the Installation Type page.
9 Accept the root install location or click Change and select an installation path.
Even in a distributed deployment, you might sometimes install more than one IaaS component on the
same Windows server.
If you install more than one IaaS component, always install them to the same path.
10 Click Next.
VMware, Inc. 85
Page 86

Installing vRealize Automation
11 Select Website on the IaaS Server Custom Install page.
12 Select a Web site from available Web sites or accept the default Web site on the Administration &
Model Manager Web Site tab.
13 Type an available port number in the Port number text box, or accept the default port 443.
14 Click Test Binding to conrm that the port number is available for use.
15 Select the certicate for this component.
a If you imported a certicate after you began the installation, click Refresh to update the list.
b Select the certicate to use from Available .
c If you imported a certicate that does not have a friendly name and it does not appear in the list,
deselect Display using friendly names and click Refresh.
If you are installing in an environment that does not use load balancers, you can select Generate a Self-
Signed instead of selecting a certicate. If you are installing additional Web site components
behind a load balancer, do not generate self-signed certicates. Import the certicate from the main IaaS
Web server to ensure that you use the same certicate on all servers behind the load balancer.
16 (Optional) Click View , view the certicate, and click OK to close the information window.
17 (Optional) Select Suppress mismatch to suppress certicate errors. The installation ignores
certicate name mismatch errors as well as any remote certicate-revocation list match errors.
This is a less secure option.
18 In the IaaS Server text box, identify the rst IaaS Web server component.
Option Description
With a load balancer
Without a load balancer
Enter the fully qualied domain name and port number of the load
balancer for the IaaS Web server component, web-load-
balancer.mycompany.com:443.
Do not enter IP addresses.
Enter the fully qualied domain name and port number of the machine
where you installed the IaaS rst Web server component,
web.mycompany.com:443.
Do not enter IP addresses.
The default port is 443.
19 Click Test to verify the server connection.
20 Click Next.
21 Complete the Prerequisite Check.
Option Description
No errors
Noncritical errors
Critical errors
Click Next.
Click Bypass.
Bypassing critical errors causes the installation to fail. If warnings appear,
select the warning in the left pane and follow the instructions on the right.
Address all critical errors and click Check Again to verify.
22 On the Server and Account Seings page, in the Server Installation Information text boxes, enter the
user name and password of the service account user that has administrative privileges on the current
installation server.
The service account user must be one domain account that has privileges on each distributed IaaS
server. Do not use local system accounts.
86 VMware, Inc.
Page 87

Chapter 4 The Standard vRealize Automation Installation Interfaces
23 Provide the passphrase used to generate the encryption key that protects the database.
Option Description
If you have already installed
components in this environment
If this is the first installation
Type the passphrase you created previously in the Passphrase and
text boxes.
Type a passphrase in the Passphrase and text boxes. You must
use this passphrase every time you install a new component.
Keep this passphrase in a secure place for later use.
24 Specify the IaaS database server, database name, and authentication method for the database server in
the Microsoft SQL Database Installation Information text box.
This is the IaaS database server, name, and authentication information that you created previously.
25 Click Next.
26 Click Install.
27 When the installation nishes, deselect Guide me through the initial and click Next.
What to do next
“Install the Active Manager Service,” on page 87.
Install the Active Manager Service
The active Manager Service is a Windows service that coordinates communication between IaaS Distributed
Execution Managers, the database, agents, proxy agents, and SMTP.
Your IaaS deployment requires that only one Windows machine actively run the Manager Service. For
backup or high availability, you may deploy additional Windows machines where you manually start the
Manager Service if the active service stops.
I Simultaneously running an active Manager Service on multiple IaaS Windows servers makes
vRealize Automation unusable.
Prerequisites
If you previously installed other components in this environment, verify that you know the passphrase
n
that was created. See “Security Passphrase,” on page 31.
(Optional) If you want to install the Manager Service in a Website other than the default Website, rst
n
create a Website in Internet Information Services.
Microsoft .NET Framework 4.5.2 is installed.
n
Verify that you have a certicate from a certicate authority imported into IIS and that the root
n
certicate or certicate authority is trusted. All components under the load balancer must have the
same certicate.
Verify that the Website load balancer is congured and that the timeout value for the load balancer is
n
set to a minimum of 180 seconds.
“Install an IaaS Website Component and Model Manager Data,” on page 81.
n
Procedure
1 If using a load balancer, disable the other nodes under the load balancer, and verify that trac is
directed to the node that you want.
In addition, disable load balancer health checks until all vRealize Automation components are installed
and congured.
VMware, Inc. 87
Page 88

Installing vRealize Automation
2 Right-click the setup__vrealize-automation-appliance-FQDN@5480.exe setup le and select Run as
administrator.
3 Accept the license agreement and click Next.
4 On the Log in page, supply administrator credentials for the vRealize Automation appliance and verify
the SSL Certicate.
a Type the user name, which is root, and the password.
The password is the password that you specied when you deployed the vRealize Automation
appliance.
b Select Accept .
c Click View .
Compare the certicate thumbprint with the thumbprint set for the vRealize Automation
appliance. You can view the vRealize Automation appliance certicate in the client browser when
the management console is accessed on port 5480.
5 Click Next.
6 Select Custom Install on the Installation Type page.
7 Select IaaS Server under Component Selection on the Installation Type page.
8 Accept the root install location or click Change and select an installation path.
Even in a distributed deployment, you might sometimes install more than one IaaS component on the
same Windows server.
If you install more than one IaaS component, always install them to the same path.
9 Click Next.
10 Select Manager Service on the IaaS Server Custom Install page.
11 In the IaaS Server text box, identify the IaaS Web server component.
Option Description
With a load balancer
Without a load balancer
Enter the fully qualied domain name and port number of the load
balancer for the IaaS Web server component, web-load-
balancer.mycompany.com:443.
Do not enter IP addresses.
Enter the fully qualied domain name and port number of the machine
where you installed the IaaS Web server component, web.mycompany.com:
443.
Do not enter IP addresses.
The default port is 443.
12 Select Active node with startup type set to automatic.
13 Select a Web site from available Web sites or accept the default Web site on the Administration &
Model Manager Web Site tab.
14 Type an available port number in the Port number text box, or accept the default port 443.
15 Click Test Binding to conrm that the port number is available for use.
88 VMware, Inc.
Page 89

Chapter 4 The Standard vRealize Automation Installation Interfaces
16 Select the certicate for this component.
a If you imported a certicate after you began the installation, click Refresh to update the list.
b Select the certicate to use from Available .
c If you imported a certicate that does not have a friendly name and it does not appear in the list,
deselect Display using friendly names and click Refresh.
If you are installing in an environment that does not use load balancers, you can select Generate a Self-
Signed instead of selecting a certicate. If you are installing additional Web site components
behind a load balancer, do not generate self-signed certicates. Import the certicate from the main IaaS
Web server to ensure that you use the same certicate on all servers behind the load balancer.
17 (Optional) Click View , view the certicate, and click OK to close the information window.
18 Click Next.
19 Check the prerequisites and click Next.
20 On the Server and Account Seings page, in the Server Installation Information text boxes, enter the
user name and password of the service account user that has administrative privileges on the current
installation server.
The service account user must be one domain account that has privileges on each distributed IaaS
server. Do not use local system accounts.
21 Provide the passphrase used to generate the encryption key that protects the database.
Option Description
If you have already installed
components in this environment
If this is the first installation
Type the passphrase you created previously in the Passphrase and
text boxes.
Type a passphrase in the Passphrase and text boxes. You must
use this passphrase every time you install a new component.
Keep this passphrase in a secure place for later use.
22 Specify the IaaS database server, database name, and authentication method for the database server in
the Microsoft SQL Database Installation Information text box.
This is the IaaS database server, name, and authentication information that you created previously.
23 Click Next.
24 Click Install.
25 When the installation nishes, deselect Guide me through the initial and click Next.
26 Click Finish.
What to do next
To ensure that the Manager Service you installed is the active instance, verify that the vCloud
n
Automation Center Service is running and set it to "Automatic" startup type.
You can install another instance of the Manager Service component as a passive backup that you can
n
start manually if the active instance fails. See “Install a Backup Manager Service Component,” on
page 90.
A system administrator can change the authentication method used to access the SQL database during
n
run time (after the installation is complete). See “Conguring Windows Service to Access the IaaS
Database,” on page 95.
VMware, Inc. 89
Page 90

Installing vRealize Automation
Install a Backup Manager Service Component
The backup Manager Service provides redundancy and high availability, and may be started manually if the
active service stops.
Your IaaS deployment requires that only one Windows machine actively run the Manager Service. Machines
that provide the backup Manager Service must have the service stopped and congured to start manually.
I Simultaneously running an active Manager Service on multiple IaaS Windows servers makes
vRealize Automation unusable.
Prerequisites
If you previously installed other components in this environment, verify that you know the passphrase
n
that was created. See “Security Passphrase,” on page 31.
(Optional) If you want to install the Manager Service in a Web site other than the default Web site, rst
n
create a Web site in Internet Information Services.
Microsoft .NET Framework 4.5.2 is installed.
n
Verify that you have a certicate from a certicate authority imported into IIS and that the root
n
certicate or certicate authority is trusted. All components under the load balancer must have the
same certicate.
Verify that the Website load balancer is congured.
n
“Install an IaaS Website Component and Model Manager Data,” on page 81.
n
Procedure
1 If using a load balancer, disable the other nodes under the load balancer, and verify that trac is
directed to the node that you want.
In addition, disable load balancer health checks until all vRealize Automation components are installed
and congured.
2 Right-click the setup__vrealize-automation-appliance-FQDN@5480.exe setup le and select Run as
administrator.
3 Click Next.
4 Accept the license agreement and click Next.
5 On the Log in page, supply administrator credentials for the vRealize Automation appliance and verify
the SSL Certicate.
a Type the user name, which is root, and the password.
The password is the password that you specied when you deployed the vRealize Automation
appliance.
b Select Accept .
c Click View .
Compare the certicate thumbprint with the thumbprint set for the vRealize Automation
appliance. You can view the vRealize Automation appliance certicate in the client browser when
the management console is accessed on port 5480.
6 Click Next.
7 Select Custom Install on the Installation Type page.
8 Select IaaS Server under Component Selection on the Installation Type page.
90 VMware, Inc.
Page 91

Chapter 4 The Standard vRealize Automation Installation Interfaces
9 Accept the root install location or click Change and select an installation path.
Even in a distributed deployment, you might sometimes install more than one IaaS component on the
same Windows server.
If you install more than one IaaS component, always install them to the same path.
10 Click Next.
11 Select Manager Service on the IaaS Server Custom Install page.
12 In the IaaS Server text box, identify the IaaS Web server component.
Option Description
With a load balancer
Without a load balancer
Enter the fully qualied domain name and port number of the load
balancer for the IaaS Web server component, web-load-
balancer.mycompany.com:443.
Do not enter IP addresses.
Enter the fully qualied domain name and port number of the machine
where you installed the IaaS Web server component, web.mycompany.com:
443.
Do not enter IP addresses.
The default port is 443.
13 Select Disaster recovery cold standby node.
14 Select a Web site from available Web sites or accept the default Web site on the Administration &
Model Manager Web Site tab.
15 Type an available port number in the Port number text box, or accept the default port 443.
16 Click Test Binding to conrm that the port number is available for use.
17 Select the certicate for this component.
a If you imported a certicate after you began the installation, click Refresh to update the list.
b Select the certicate to use from Available .
c If you imported a certicate that does not have a friendly name and it does not appear in the list,
deselect Display using friendly names and click Refresh.
If you are installing in an environment that does not use load balancers, you can select Generate a Self-
Signed instead of selecting a certicate. If you are installing additional Web site components
behind a load balancer, do not generate self-signed certicates. Import the certicate from the main IaaS
Web server to ensure that you use the same certicate on all servers behind the load balancer.
18 (Optional) Click View , view the certicate, and click OK to close the information window.
19 Click Next.
20 Check the prerequisites and click Next.
21 On the Server and Account Seings page, in the Server Installation Information text boxes, enter the
user name and password of the service account user that has administrative privileges on the current
installation server.
The service account user must be one domain account that has privileges on each distributed IaaS
server. Do not use local system accounts.
VMware, Inc. 91
Page 92

Installing vRealize Automation
22 Provide the passphrase used to generate the encryption key that protects the database.
Option Description
If you have already installed
components in this environment
If this is the first installation
Keep this passphrase in a secure place for later use.
23 Specify the IaaS database server, database name, and authentication method for the database server in
the Microsoft SQL Database Installation Information text box.
This is the IaaS database server, name, and authentication information that you created previously.
24 Click Next.
25 Click Install.
26 When the installation nishes, deselect Guide me through the initial and click Next.
27 Click Finish.
What to do next
To ensure that the Manager Service you installed is a passive backup instance, verify that the
n
vRealize Automation Service is not running and set it to "Manual" startup type.
Type the passphrase you created previously in the Passphrase and
text boxes.
Type a passphrase in the Passphrase and text boxes. You must
use this passphrase every time you install a new component.
A system administrator can change the authentication method used to access the SQL database during
n
run time (after the installation is complete). See “Conguring Windows Service to Access the IaaS
Database,” on page 95.
Installing Distributed Execution Managers
You install the Distributed Execution Manager as one of two roles: DEM Orchestrator or DEM Worker. You
must install at least one DEM instance for each role, and you can install additional DEM instances to
support failover and high-availability.
The system administrator must choose installation machines that meet predened system requirements. The
DEM Orchestrator and the Worker can reside on the same machine.
As you plan to install Distributed Execution Managers, keep in mind the following considerations:
DEM Orchestrators support active-active high availability. Typically, you install one DEM Orchestrator
n
on each Manager Service machine.
Install the Orchestrator on a machine with strong network connectivity to the Model Manager host.
n
Install a second DEM Orchestrator on a dierent machine for failover.
n
Typically, you install DEM Workers on the IaaS Manager Service server or on a separate server. The
n
server must have network connectivity to the Model Manager host.
You can install additional DEM instances for redundancy and scalability, including multiple instances
n
on the same machine.
There are specic requirements for the DEM installation that depend on the endpoints you use. See
“Distributed Execution Manager Requirements,” on page 23.
92 VMware, Inc.
Page 93

Chapter 4 The Standard vRealize Automation Installation Interfaces
Install the Distributed Execution Managers
You must install at least one DEM Worker and one DEM Orchestrator. The installation procedure is the same
for both roles.
DEM Orchestrators support active-active high availability. Typically, you install a single DEM Orchestrator
on each Manager Service machine. You can install DEM Orchestrators and DEM workers on the same
machine.
Prerequisites
“Download the vRealize Automation IaaS Installer,” on page 76.
Procedure
1 Right-click the setup__vrealize-automation-appliance-FQDN@5480.exe setup le and select Run as
administrator.
2 Click Next.
3 Accept the license agreement and click Next.
4 On the Log in page, supply administrator credentials for the vRealize Automation appliance and verify
the SSL Certicate.
a Type the user name, which is root, and the password.
The password is the password that you specied when you deployed the vRealize Automation
appliance.
b Select Accept .
c Click View .
Compare the certicate thumbprint with the thumbprint set for the vRealize Automation
appliance. You can view the vRealize Automation appliance certicate in the client browser when
the management console is accessed on port 5480.
5 Click Next.
6 Select Custom Install on the Installation Type page.
7 Select Distributed Execution Managers under Component Selection on the Installation Type page.
8 Accept the root install location or click Change and select an installation path.
Even in a distributed deployment, you might sometimes install more than one IaaS component on the
same Windows server.
If you install more than one IaaS component, always install them to the same path.
9 Click Next.
10 Check prerequisites and click Next.
11 Enter the log in credentials under which the service will run.
The service account must have local administrator privileges and be the domain account that you have
been using throughout IaaS installation. The service account has privileges on each distributed IaaS
server and must not be a local system account.
12 Click Next.
VMware, Inc. 93
Page 94

Installing vRealize Automation
13 Select the installation type from the DEM role drop-down menu.
Option Description
Worker
Orchestrator
14 Enter a unique name that identies this DEM in the DEM name text box.
If you plan to use the migration tool, this name must exactly match the name you used in your vCloud
Automation Center 5.2.3 installation. The name cannot include spaces and cannot exceed 128 characters.
If you enter a previously used name, the following message appears: "DEM name already exists. To
enter a dierent name for this DEM, click Yes. If you are restoring or reinstalling a DEM with the same
name, click No."
15 (Optional) Enter a description of this instance in DEM description.
16 Enter the host names and ports in the Manager Service Host name and Model Manager Web Service
Host name text boxes.
Option Description
With a load balancer
Without a load balancer
The default port is 443.
The Worker executes workows.
The Orchestrator oversees DEM worker activities, including scheduling
and preprocessing workows, and monitors DEM worker online status.
Enter the fully qualied domain name and port number of the load
balancers for the Manager Service component and the Web server that
hosts Model Manager, mgr-svc-load-balancer.mycompany.com:443 and web-
load-balancer.mycompany.com:443.
Do not enter IP addresses.
Enter the fully qualied domain name and port number of the machine
where you installed the Manager Service component and the Web server
that hosts Model Manager, mgr-svc.mycompany.com:443 and
web.mycompany.com:443.
Do not enter IP addresses.
17 (Optional) Click Test to test the connections to the Manager Service and Model Manager Web Service.
18 Click Add.
19 Click Next.
20 Click Install.
21 When the installation nishes, deselect Guide me through the initial and click Next.
22 Click Finish.
What to do next
Verify that the service is running and that the log shows no errors. The service name is VMware DEM
n
Role - Name where role is Orchestrator or Worker. The log location is Install Location\Distributed
Execution Manager\Name\Logs.
Repeat this procedure to install additional DEM instances.
n
Configure the DEM to Connect to SCVMM at a Different Installation Path
By default, the DEM Worker conguration le uses the default installation path of Microsoft System Center
Virtual Machine Manager (SCVMM) 2012 console. You must update the conguration when the SCVMM
console is installed to another location.
This release supports the SCVMM 2012 R2 console, so you must update the path to 2012 R2. You also might
need to update the path if you installed the SCVMM console to a non-default path.
94 VMware, Inc.
Page 95

Chapter 4 The Standard vRealize Automation Installation Interfaces
You only need this procedure if you have SCVMM endpoints and agents.
Prerequisites
Know the actual path where the SCVMM console is installed.
n
The following is the default 2012 path that you must replace in the conguration le.
path="{ProgramFiles}\Microsoft System Center 2012\Virtual Machine Manager\bin"
Procedure
1 Stop the DEM Worker service.
2 Open the following le in a text editor.
Program Files (x86)\VMware\vCAC\Distributed Execution Manager\instance-
name\DynamicOps.DEM.exe.config
3 Locate the <assemblyLoadConfiguration> section.
4 Update each path, using the following example as a guideline.
<assemblyLoadConfiguration>
<assemblies>
<!-- List of required assemblies for Scvmm -->
<add name="Errors" path="{ProgramFiles}\Microsoft System Center 2012 R2\Virtual Machine
Manager\bin"/>
<add name="Microsoft.SystemCenter.VirtualMachineManager" path="{ProgramFiles}\Microsoft
System Center 2012 R2\Virtual Machine Manager\bin"/>
<add name="Remoting" path="{ProgramFiles}\Microsoft System Center 2012 R2\Virtual Machine
Manager\bin"/>
<add name="TraceWrapper" path="{ProgramFiles}\Microsoft System Center 2012 R2\Virtual
Machine Manager\bin"/>
<add name="Utils" path="{ProgramFiles}\Microsoft System Center 2012 R2\Virtual Machine
Manager\bin"/>
</assemblies>
</assemblyLoadConfiguration>
5 Save and close DynamicOps.DEM.exe.config.
6 Restart the DEM Worker service.
For more information, see “SCVMM Requirements,” on page 25.
Additional information about preparing the SCVMM environment and creating an SCVMM endpoint is
available in Conguring vRealize Automation.
Configuring Windows Service to Access the IaaS Database
A system administrator can change the authentication method used to access the SQL database during run
time (after the installation is complete). By default, the Windows identity of the currently logged on account
is used to connect to the database after it is installed.
VMware, Inc. 95
Page 96

Installing vRealize Automation
Enable IaaS Database Access from the Service User
If the SQL database is installed on a separate host from the Manager Service, database access from the
Manager Service must be enabled. If the user name under which the Manager Service will run is the owner
of the database, no action is required. If the user is not the owner of the database, the system administrator
must grant access.
Prerequisites
“Choosing an IaaS Database Scenario,” on page 77.
n
Verify that the user name under which the Manager Service will run is not the owner of the database.
n
Procedure
1 Navigate to the Database subdirectory within the directory where you extracted the installation zip
archive.
2 Extract the DBInstall.zip archive to a local directory.
3 Log in to the database host as a user with the sysadmin role in the SQL Server instance.
4 Edit VMPSOpsUser.sql and replace all instances of $(Service User) with user (from Step 3) under which
the Manager Service will run.
Do not replace ServiceUser in the line ending with WHERE name = N'ServiceUser').
5 Open SQL Server Management Studio.
6 Select the database (vCAC by default) in Databases in the left-hand pane.
7 Click New Query.
The SQL Query window opens in the right-hand pane.
8 Paste the modied contents of VMPSOpsUser.sql into the query window.
9 Click Execute.
Database access is enabled from the Manager Service.
Configure the Windows Services Account to Use SQL Authentication
By default, the Windows service account accesses the database during run-time, even if you congured the
database for SQL authentication. You can change run-time authentication from Windows to SQL.
One reason to change run-time authentication might be when, for example, the database is on an untrusted
domain.
Prerequisites
Verify that the vRealize Automation SQL Server database exists. Begin with “Choosing an IaaS Database
Scenario,” on page 77.
Procedure
1 Using an account with administrator privileges, log in to the IaaS Windows server that hosts the
Manager Service.
2 In Administrative Tools > Services, stop the VMware vCloud Automation Center service.
3 Open the following les in a text editor.
C:\Program Files (x86)\VMware\vCAC\Server\ManagerService.exe.config
C:\Program Files (x86)\VMware\vCAC\Server\Model Manager Web\Web.config
4 In each le, locate the <connectionStrings> section.
96 VMware, Inc.
Page 97

Chapter 4 The Standard vRealize Automation Installation Interfaces
5 Replace
Integrated Security=True;
with
User Id=database-username;Password=database-password;
6 Save and close the les.
ManagerService.exe.config
Web.config
7 Start the VMware vCloud Automation Center service.
8 Use the iisreset command to restart IIS.
Verify IaaS Services
After installation, the system administrator veries that the IaaS services are running. If the services are
running, the installation is a success.
Procedure
1 From the Windows desktop of the IaaS machine, select Administrative Tools > Services.
2 Locate the following services and verify that their status is Started and the Startup Type is set to
Automatic.
VMware DEM – Orchestrator – Name where Name is the string provided in the DEM Name box
n
during installation.
VMware DEM – Worker – Name where Name is the string provided in the DEM Name box during
n
installation.
VMware vCloud Automation Center Agent Agent name
n
VMware vCloud Automation Center Service
n
3 Close the Services window.
Installing vRealize Automation Agents
vRealize Automation uses agents to integrate with external systems. A system administrator can select
agents to install to communicate with other virtualization platforms.
vRealize Automation uses the following types of agents to manage external systems:
Hypervisor proxy agents (vSphere, Citrix Xen Servers and Microsoft Hyper-V servers)
n
External provisioning infrastructure (EPI) integration agents
n
Virtual Desktop Infrastructure (VDI) agents
n
Windows Management Instrumentation (WMI) agents
n
For high-availability, you can install multiple agents for a single endpoint. Install each redundant agent on a
separate server, but name and congure them identically. Redundant agents provide some fault tolerance,
but do not provide failover. For example, if you install two vSphere agents, one on server A and one on
server B, and server A becomes unavailable, the agent installed on server B continues to process work items.
However, the server B agent cannot nish processing a work item that the server A agent had already
started.
VMware, Inc. 97
Page 98

Installing vRealize Automation
You have the option to install a vSphere agent as part of your minimal installation, but after the installation
you can also add other agents, including an additional vSphere agent. In a distributed deployment, you
install all your agents after you complete the base distributed installation. The agents you install depend on
the resources in your infrastructure.
For information about using vSphere agents, see “vSphere Agent Requirements,” on page 99.
Set the PowerShell Execution Policy to RemoteSigned
You must set the PowerShell Execution Policy from Restricted to RemoteSigned or Unrestricted to allow
local PowerShell scripts to be run.
For more information about the PowerShell Execution Policy, see Microsoft Technet article hh847748. If your
PowerShell Execution Policy is managed at the group policy level, contact your IT support for about their
restrictions on policy changes, and see Microsoft Technet article jj149004.
Prerequisites
Log in as a Windows administrator.
n
Verify that Microsoft PowerShell is installed on the installation host before agent installation. The
n
version required depends on the operating system of the installation host. See Microsoft Help and
Support.
For more information about PowerShell Execution Policy, run help about_signing or help Set-
n
ExecutionPolicy at the PowerShell command prompt.
Procedure
1 Select Start > All Programs > Windows PowerShell version > Windows PowerShell.
2 For Remote Signed, run Set-ExecutionPolicy RemoteSigned.
3 For Unrestricted, run Set-ExecutionPolicy Unrestricted.
4 Verify that the command did not produce any errors.
5 Type Exit at the PowerShell command prompt.
Choosing the Agent Installation Scenario
The agents that you need to install depend on the external systems with which you plan to integrate.
Table 4‑13. Choosing an Agent Scenario
Integration Scenario Agent Requirements and Procedures
Provision cloud machines by integrating with a cloud
environment such as Amazon Web Services or
Red Hat Enterprise Linux OpenStack Platform.
Provision virtual machines by integrating with a vSphere
environment.
Provision virtual machines by integrating with a
Microsoft Hyper-V Server environment.
Provision virtual machines by integrating with a XenServer
environment.
Provision virtual machines by integrating with a
XenDesktop environment.
You do not need to install an agent.
“Installing and Conguring the Proxy Agent for vSphere,”
on page 99
“Installing the Proxy Agent for Hyper-V or XenServer,” on
page 104
“Installing the Proxy Agent for Hyper-V or XenServer,”
n
on page 104
“Installing the EPI Agent for Citrix,” on page 111
n
“Installing the VDI Agent for XenDesktop,” on
n
page 108
“Installing the EPI Agent for Citrix,” on page 111
n
98 VMware, Inc.
Page 99
Chapter 4 The Standard vRealize Automation Installation Interfaces
Table 4‑13. Choosing an Agent Scenario (Continued)
Integration Scenario Agent Requirements and Procedures
Run Visual Basic scripts as additional steps in the
provisioning process before or after provisioning a
machine, or when deprovisioning.
Collect data from the provisioned Windows machines, for
example the Active Directory status of the owner of a
machine.
Provision virtual machines by integrating with any other
supported virtual platform.
“Installing the EPI Agent for Visual Basic Scripting,” on
page 114
“Installing the WMI Agent for Remote WMI Requests,” on
page 117
You do not need to install an agent.
Agent Installation Location and Requirements
A system administrator typically installs the agents on the vRealize Automation server that hosts the active
Manager Service component.
If an agent is installed on another host, the network conguration must allow communication between the
agent and Manager Services installation machine.
Each agent is installed under a unique name in its own directory, Agents\agentname, under the
vRealize Automation installation directory (typically Program Files(x86)\VMware\vCAC), with its
conguration stored in the le VRMAgent.exe.config in that directory.
Installing and Configuring the Proxy Agent for vSphere
A system administrator installs proxy agents to communicate with vSphere server instances. The agents
discover available work, retrieve host information, and report completed work items and other host status
changes.
vSphere Agent Requirements
vSphere endpoint credentials, or the credentials under which the agent service runs, must have
administrative access to the installation host. Multiple vSphere agents must meet vRealize Automation
conguration requirements.
Credentials
When creating an endpoint representing the vCenter Server instance to be managed by a vSphere agent, the
agent can use the credentials that the service is running under to interact with the vCenter Server or specify
separate endpoint credentials.
The following table lists the permissions that the vSphere endpoint credentials must have to manage a
vCenter Server instance. The permissions must be enabled for all clusters in vCenter Server, not just clusters
that will host endpoints.
Table 4‑14. Permissions Required for vSphere Agent to Manage vCenter Server Instance
Attribute Value Permission
Datastore Allocate Space
Browse Datastore
Datastore Cluster Congure a Datastore Cluster
Folder Create Folder
Delete Folder
Global Manage Custom Aributes
Set Custom Aribute
VMware, Inc. 99
Page 100

Installing vRealize Automation
Table 4‑14. Permissions Required for vSphere Agent to Manage vCenter Server Instance (Continued)
Attribute Value Permission
Network Assign Network
Permissions Modify Permission
Resource Assign VM to Res Pool
Virtual Machine Inventory Create from existing
Migrate Powered O Virtual Machine
Migrate Powered On Virtual Machine
Create New
Move
Remove
Interaction Congure CD Media
Console Interaction
Device Connection
Power O
Power On
Reset
Suspend
Tools Install
Conguration Add Existing Disk
Add New Disk
Add or Remove Device
Remove Disk
Advanced
Change CPU Count
Change Resource
Extend Virtual Disk
Disk Change Tracking
Memory
Modify Device Seings
Rename
Set Annotation (version 5.0 and later)
Seings
Swaple Placement
Provisioning Customize
Clone Template
Clone Virtual Machine
Deploy Template
Read Customization Specs
State Create Snapshot
100 VMware, Inc.
 Loading...
Loading...