Vishay SiC532 Datasheet
www.vishay.com
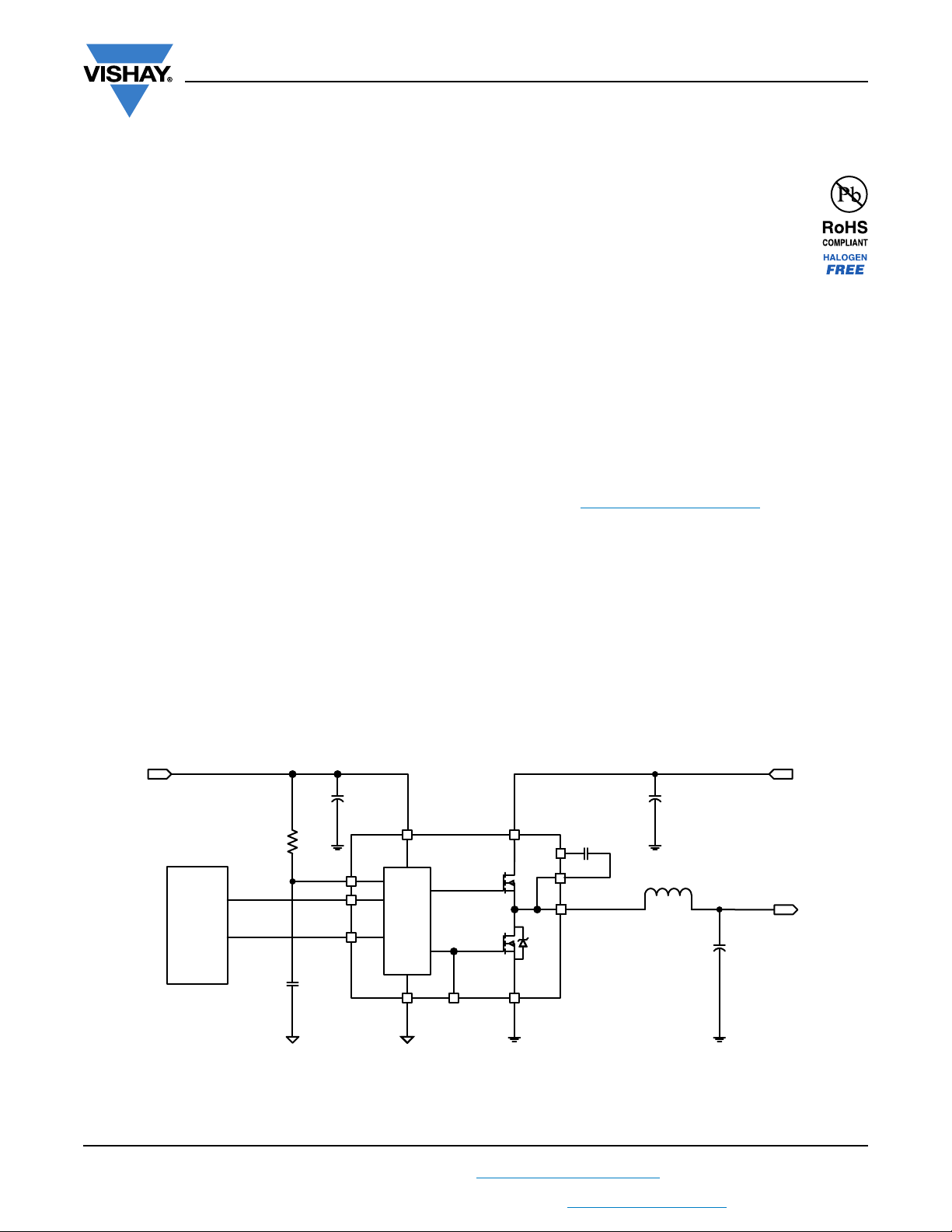
PWM
controller
Gate
driver
5V
V
IN
V
OUT
V
CIN
PWM
V
DRV
V
IN
BOOT
V
SWH
P
GND
GL
C
GND
PHASE
ZCD_EN#
30 A VRPower® Integrated Power Stage
SiC532
Vishay Siliconix
DESCRIPTION
The SiC532 is an integrated power stage solution optimized
for synchronous buck applications to offer high current, high
efficiency, and high power density performance. Packaged
in Vishay’s proprietary 4.5 mm x 3.5 mm MLP package,
SiC532 enables voltage regulator designs to deliver up to
30 A continuous current per phase.
The internal power MOSFETs utilize Vishay’s
state-of-the-art Gen IV TrenchFET
industry benchmark performance to significantly reduce
switching and conduction losses.
The SiC532 incorporates an advanced MOSFET gate driver
IC that features high current driving capability, adaptive
dead-time control, an integrated bootstrap Schottky diode,
and zero current detection to improve light load efficiency.
The driver is also compatible with a wide range of PWM
controllers, supports tri-state PWM, and 5 V PWM logic.
A user selectable diode emulation mode (ZCD_EN#) is
included to improve the light load performance. The device
also supports PS4 mode to reduce power consumption
when system operates in standby state.
®
technology that delivers
FEATURES
• Thermally enhanced PowerPAK® MLP4535-22L
package
• Vishay’s Gen IV MOSFET technology and a
low-side MOSFET with integrated Schottky
diode
• Delivers up to 30 A continuous current, 35 A at 10 ms peak
current
• High efficiency performance
• High frequency operation up to 2 MHz
• Power on reset
• 5 V PWM logic with tri-state and hold-off
• Supports PS4 mode light load requirement for IMVP8 with
low shutdown supply current (5 V, 3 μA)
• Under voltage lockout for V
CIN
• Material categorization: for definitions of compliance
please see www.vishay.com/doc?99912
APPLICATIONS
• Multi-phase VRDs for computing, graphics card and
memory
• Intel IMVP-8 VRPower delivery
- V
- V
• Up to 24 V rail input DC/DC VR modules
CORE
, V
GRAPHICS
, V
platforms
for Apollo Lake platforms
CCGI
SYSTEM AGENT
Skylake, Kabylake
TYPICAL APPLICATION DIAGRAM
S20-0485-Rev. C, 29-Jun-2020
THIS DOCUMENT IS SUBJECT TO CHANGE WITHOUT NOTICE. THE PRODUCTS DESCRIBED HEREIN AND THIS DOCUMENT
ARE SUBJECT TO SPECIFIC DISCLAIMERS, SET FORTH AT www.vishay.com/doc?91000
For technical questions, contact: powerictechsupport@vishay.com
Fig. 1 - SiC532 Typical Application Diagram
1
Document Number: 74770
www.vishay.com
V
V
V
V
V
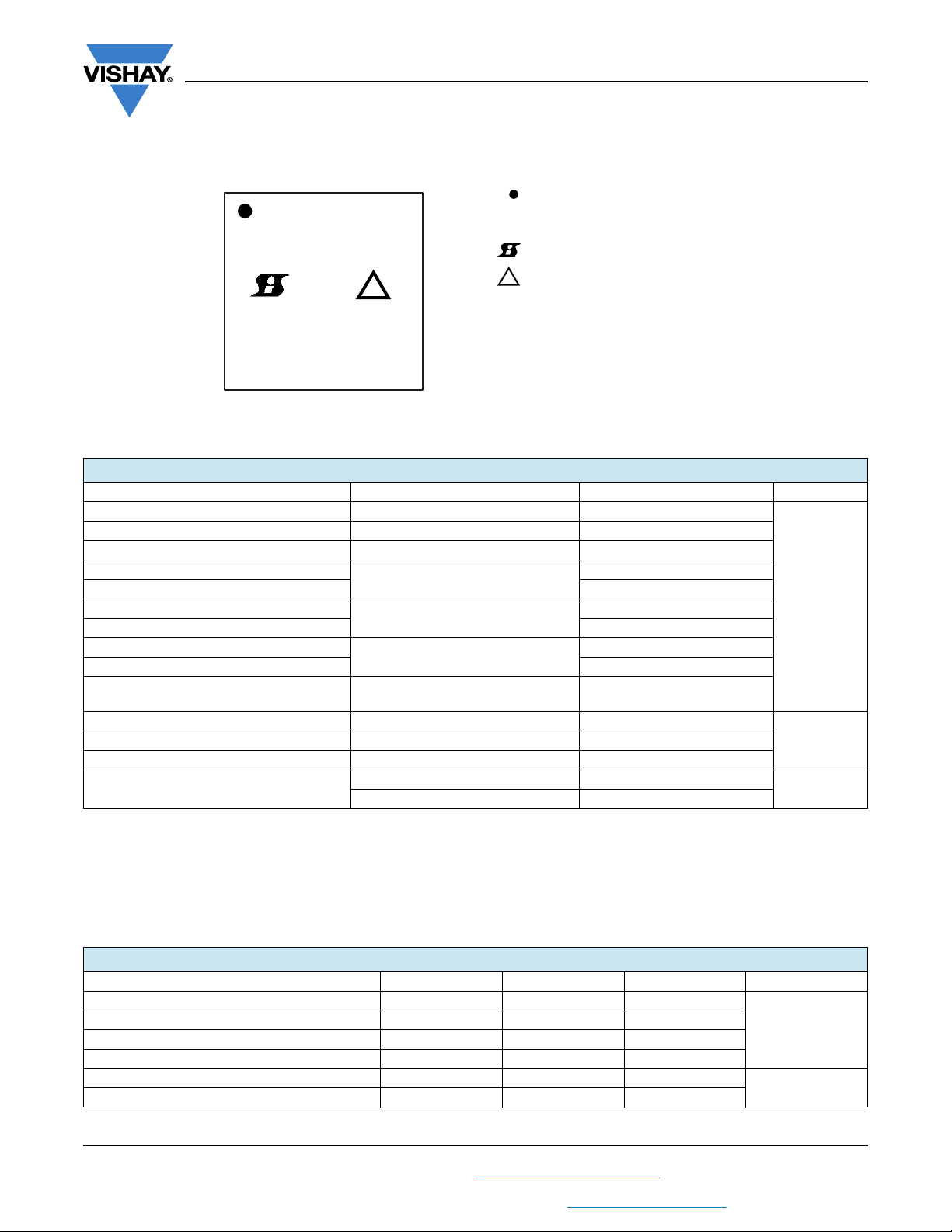
PINOUT CONFIGURATION
SiC532
Vishay Siliconix
SWH
SWH
SWH
SWH
SWH
GNDPGNDPGND
P
11 10 9 8 7 6
12
26
13
14
15
16
P
GND
24
GL
17 18 19 20 21 22
GND
GND
P
P
GL
VINVINV
25
V
23
C
GND
GND
P
IN
PHASE
IN
DRV
V
PWM
5
BOOT
4
3
V
2
ZCD_EN#
1
N.C.
CIN
Fig. 2 - SiC532 Pin Configuration
PIN DESCRIPTION
PIN NUMBER NAME FUNCTION
The ZCD_EN# pin enables or disables Diode Emulation. When ZCD_EN# is LOW, diode
1 ZCD_EN#
2V
23 C
CIN
GND
3N.C.
4 BOOT High-side driver bootstrap voltage
5 PHASE Return path of high-side gate driver
6 to 8, 25 V
9 to 11, 17, 18, 20, 26 P
12 to 16 V
IN
GND
SWH
19, 24 GL Low-side gate signal
21 V
DRV
22 PWM PWM control input
emulation is allowed. When ZCD_EN# is HIGH, continuous conduction mode is forced.
ZCD_EN# can also be put in a high impedance mode by floating the pin. If both ZCD_EN#
and PWM are floating, the device shuts down and consumes typically 3 μA (9 μA max.)
current
Supply voltage for internal logic circuitry
Analog ground for the driver IC
This pin can be either left floating or connected to C
Internally it is either connected to GND or not internally
connected depending on manufacturing location.
Factory code “G” on line 3, pin 3 = C
Factory code “T” on line 3, pin 3 = not internally connected
GND
GND
.
P/N
LL
G Y W W
P/N
LL
T Y W W
Power stage input voltage. Drain of high-side MOSFET
Power ground
Switch node of the power stage
Supply voltage for internal gate driver
ORDERING INFORMATION
PART NUMBER PACKAGE MARKING CODE
SiC532CD-T1-GE3 PowerPAK
®
MLP4535-22L SiC532 5 V PWM optimized
SiC532DB Reference board
S20-0485-Rev. C, 29-Jun-2020
2
Document Number: 74770
For technical questions, contact: powerictechsupport@vishay.com
THIS DOCUMENT IS SUBJECT TO CHANGE WITHOUT NOTICE. THE PRODUCTS DESCRIBED HEREIN AND THIS DOCUMENT
ARE SUBJECT TO SPECIFIC DISCLAIMERS, SET FORTH AT www.vishay.com/doc?91000
SiC532
= pin 1 indicator
P/N = part number code
= Siliconix logo
=ESD symbol
F = assembly factory code
Y = year code
WW = week code
LL = lot code
F Y W W
P/N
LL
www.vishay.com
PART MARKING INFORMATION
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS
ELECTRICAL PARAMETER CONDITIONS LIMIT UNIT
Input voltage V
Control logic supply voltage V
Drive supply voltage V
Switch node (DC voltage)
Switch node (AC voltage)
BOOT voltage (DC voltage)
BOOT voltage (AC voltage)
BOOT to PHASE (DC voltage)
BOOT to PHASE (AC voltage)
All logic inputs and outputs
(PWM and ZCD_EN#)
Max. operating junction temperature T
Storage temperature T
Electrostatic discharge protection
Note
• Stresses beyond those listed under “Absolute Maximum Ratings” may cause permanent damage to the device. These are stress ratings
only, and functional operation of the device at these or any other conditions beyond those indicated in the operational sections of the
specifications is not implied. Exposure to absolute maximum rating conditions for extended periods may affect device reliability
(1)
The specification values indicated “AC” is V
(2)
The specification value indicates “AC voltage” is V
(3)
The specification value indicates “AC voltage” is V
(1)
(2)
(3)
Human body model, JESD22-A114 2000
Charged device model, JESD22-C101 1000
to P
SWH
, -8 V (< 20 ns, 10 μJ), min. and 35 V (< 50 ns), max.
GND
to P
BOOT
to V
BOOT
IN
CIN
DRV
V
SWH
V
BOOT
V
BOOT- PHASE
J
A
stg
, 40 V (< 50 ns) max.
GND
, 8 V (< 50 ns) max.
PHASE
-0.3 to +28
-0.3 to +7
-0.3 to +7
-0.3 to +28
-8 to +35
33
40
-0.3 to +7
-0.3 to +8
-0.3 to V
150
-40 to +125
-65 to +150
Vishay Siliconix
+ 0.3
CIN
V
°CAmbient temperature T
V
RECOMMENDED OPERATING RANGE
ELECTRICAL PARAMETER MINIMUM TYPICAL MAXIMUM UNIT
Input voltage (V
Drive supply voltage (V
Control logic supply voltage (V
BOOT to PHASE (V
Thermal resistance from junction to PCB - 5 -
Thermal resistance from junction to case - 2.5 -
S20-0485-Rev. C, 29-Jun-2020
THIS DOCUMENT IS SUBJECT TO CHANGE WITHOUT NOTICE. THE PRODUCTS DESCRIBED HEREIN AND THIS DOCUMENT
)4.5-24
IN
) 4.555.5
DRV
BOOT-PHASE
) 4.555.5
CIN
, DC voltage) 4 4.5 5.5
V
°C/W
For technical questions, contact: powerictechsupport@vishay.com
ARE SUBJECT TO SPECIFIC DISCLAIMERS, SET FORTH AT www.vishay.com/doc?91000
3
Document Number: 74770
www.vishay.com
Vishay Siliconix
ELECTRICAL SPECIFICATIONS
(ZCD_EN# = 5 V, V
PARAMETER SYMBOL TEST CONDITION
POWER SUPPLY
Control logic supply current I
Drive supply current I
PS4 mode supply current I
BOOTSTRAP SUPPLY
Bootstrap diode forward voltage V
PWM CONTROL INPUT
Rising threshold V
Falling threshold V
Tri-state voltage V
Tri-state rising threshold V
Tri-state falling threshold V
Tri-state rising threshold hysteresis V
Tri-state falling threshold hysteresis V
PWM input current I
ZCD_EN# CONTROL INPUT
Rising threshold V
Falling threshold V
Tri-state voltage V
Tri-state rising threshold V
Tri-state falling threshold V
Tri-state rising threshold hysteresis V
Tri-state falling threshold hysteresis V
ZCD_EN# input current I
PS4 exit latency t
TIMING SPECIFICATIONS
Tri-state to GH/GL rising
propagation delay
Tri-state hold-off time t
GH - turn off propagation delay t
GH - turn on propagation delay
(dead time rising)
GL - turn off propagation delay t
GL - turn on propagation delay
(dead time falling)
PWM minimum on-time T
PROTECTION
Under voltage lockout V
Under voltage lockout hysteresis V
Notes
(1)
Typical limits are established by characterization and are not production tested
(2)
Guaranteed by design
S20-0485-Rev. C, 29-Jun-2020
THIS DOCUMENT IS SUBJECT TO CHANGE WITHOUT NOTICE. THE PRODUCTS DESCRIBED HEREIN AND THIS DOCUMENT
= 12 V, V
IN
DRV
and V
= 5 V, TA = 25 °C, unless otherwise stated)
CIN
LIMITS
MIN. TYP. MAX.
V
= FLOAT - 80 -
PWM
VCIN
VDRV
+ I
VCIN
VDRV
F
TH_PWM_R
TH_PWM_F
TRI
TRI_TH_R
TRI_TH_F
HYS_TRI_R
HYS_TRI_F
PWM
TH_ZCD_EN#_R
TH_ZCD_EN#_F
TRI_ZCD_EN#
TRI_ZCD_EN#_R
TRI_ZCD_EN#_F
HYS_TRI_ZCD#_R
HYS_TRI_ZCD#_F
ZCD_EN#
PS4EXIT
t
PD_TRI_R
TSHO
PD_OFF_GH
t
PD_ON_GH
PD_OFF_GL
t
PD_ON_GL
PWM_ON_MIN
UVLO
UVLO_HYST
= FLOAT, V
PWM
f
= 300 kHz, D = 0.1 - 300 -
S
fS = 300 kHz, D = 0.1 - 10 15
= 1 MHz, D = 0.1 - 20 -
f
S
V
= V
PWM
ZCD_EN#
T
= -10 °C to +100 °C
A
IF = 2 mA - - 0.65 V
V
= FLOAT - 2.5 -
PWM
V
= 5 V - - 350
PWM
= 0 V - - -350
V
PWM
V
= FLOAT - 2.5 -
ZCD_EN#
V
ZCD_EN#
V
ZCD_EN#
No load, see fig. 4
V
rising, on threshold - 3.4 3.9
CIN
falling, off threshold 2.4 2.9 -
V
CIN
= 0 V - 120 -
ZCD_EN#
= FLOAT,
-39μA
3.6 3.9 4.2
0.72 1 1.3
1.11.351.6
3.4 3.7 4
- 325 -
- 250 -
3.3 3.6 3.9
1.1 1.4 1.7
1.5 1.8 2.1
2.93.153.4
- 375 -
- 450 -
= 5 V - - 100
= 0 V - - -100
--5μs
-20-
- 150 -
-20-
-20-
-20-
-20-
30 - -
- 500 - mV
4
For technical questions, contact: powerictechsupport@vishay.com
ARE SUBJECT TO SPECIFIC DISCLAIMERS, SET FORTH AT www.vishay.com/doc?91000
Document Number: 74770
SiC532
UNIT
μAV
mA
V
mV
μA
V
mV
μA
ns
V

www.vishay.com
DETAILED OPERATIONAL DESCRIPTION
PWM Input with Tri-state Function
The PWM input receives the PWM control signal from the VR
controller IC. The PWM input is designed to be compatible
with standard controllers using two state logic (H and L) and
advanced controllers that incorporate tri-state logic (H, L,
and tri-state) on the PWM output. For two state logic, the
PWM input operates as follows. When PWM is driven above
V
PWM_TH_R
turned on. When PWM input is driven below V
high-side is turned off and the low-side is turned on. For
tri-state logic, the PWM input operates as previously stated
for driving the MOSFETs when PWM is logic high and logic
low. However, there is a third state that is entered as the
PWM output of tri-state compatible controller enters its high
impedance state during shut-down. The high impedance
state of the controller’s PWM output allows the SiC532 to
pull the PWM input into the tri-state region (see definition of
PWM logic and tri-state, fig. 4). If the PWM input stays in this
region for the tri-state hold-off period, t
and low-side MOSFETs are turned off. The function allows
the VR phase to be disabled without negative output voltage
swing caused by inductor ringing and saves a Schottky
diode clamp. The PWM and tri-state regions are separated
by hysteresis to prevent false triggering. The SiC532
incorporates PWM voltage thresholds that are compatible
with 5 V logic.
Diode Emulation Mode and PS4 Mode (ZCD_EN#)
The ZCD_EN# pin enables or disables diode emulation
mode. When ZCD_EN# is driven below V
emulation is allowed. When ZCD_EN# is driven above
V
TH_ZCD_EN#_R
Diode emulation mode allows for higher converter efficiency
under light load situations. With diode emulation active, the
SiC532 will detect the zero current crossing of the output
inductor and turn off the low-side MOSFET. This ensures
that discontinuous conduction mode (DCM) is achieved.
Diode emulation is asynchronous to the PWM signal,
therefore, the SiC532 will respond to the ZCD_EN# input
immediately after it changes state.
The ZCD_EN# pin can be floated resulting in a high
impedance state. High impedance on the input of ZCD_EN#
combined with a tri-stated PWM output will shut down the
SiC532, reducing current consumption to typically 5 μA.
This is an important feature in achieving the low standby
current requirements required in the PS4 state in ultrabooks
and notebooks.
Voltage Input (V
This is the power input to the drain of the high-side power
MOSFET. This pin is connected to the high power
intermediate BUS rail.
the low-side is turned off and the high-side is
PWM_TH_F
, both high-side
TSHO
TH_ZCD_EN#_F
the
, diode
, continuous conduction mode is forced.
)
IN
SiC532
Vishay Siliconix
Switch Node (V
The switch node, V
This is the output applied to the power inductor and output
filter to deliver the output for the buck converter. The PHASE
pin is internally connected to the switch node, V
is to be used exclusively as the return pin for the BOOT
capacitor.
Ground Connections (C
P
(power ground) should be externally connected to
GND
C
(control signal ground). The layout of the printed circuit
GND
board should be such that the inductance separating C
and P
is minimized. Transient differences due to
GND
inductance effects between these two pins should not
exceed 0.5 V.
Control and Drive Supply Voltage Input (V
V
is the bias supply for the gate drive control IC. V
CIN
the bias supply for the gate drivers. It is recommended to
separate these pins through a resistor. This creates a low
pass filtering effect to avoid coupling of high frequency gate
drive noise into the IC.
Bootstrap Circuit (BOOT)
The internal bootstrap diode and an external bootstrap
capacitor form a charge pump that supplies voltage to the
BOOT pin. An integrated bootstrap diode is incorporated so
that only an external capacitor is necessary to complete the
bootstrap circuit. Connect a boot strap capacitor with one
leg tied to BOOT pin and the other tied to PHASE pin.
Shoot-through Protection and Adaptive Dead Time
The SiC532 has an internal adaptive logic to avoid shoot
through and optimize dead time. The shoot through
protection ensures that both high-side and low-side
MOSFETs are not turned on at the same time. The adaptive
dead time control operates as follows. The high-side and
low-side gate voltages are monitored to prevent the
MOSFET turning on from tuning on until the other
MOSFET’s gate voltage is sufficiently low (< 1 V). Built in
delays also ensure that one power MOSFET is completely
off, before the other can be turned on. This feature helps to
adjust dead time as gate transitions change with respect to
output current and temperature.
Under Voltage Lockout (UVLO)
During the start up cycle, the UVLO disables the gate
drive, holding high-side and low-side MOSFET gates low,
until the supply voltage rail has reached a point at which
the logic circuitry can be safely activated. The SiC532 also
incorporates logic to clamp the gate drive signals to zero
when the UVLO falling edge triggers the shutdown of the
device.
and PHASE)
SWH
, is the circuit power stage output.
SWH
GND
and P
GND
. This pin
SWH
)
GND
, V
CIN
)
DRV
is
DRV
S20-0485-Rev. C, 29-Jun-2020
For technical questions, contact: powerictechsupport@vishay.com
THIS DOCUMENT IS SUBJECT TO CHANGE WITHOUT NOTICE. THE PRODUCTS DESCRIBED HEREIN AND THIS DOCUMENT
ARE SUBJECT TO SPECIFIC DISCLAIMERS, SET FORTH AT www.vishay.com/doc?91000
5
Document Number: 74770
 Loading...
Loading...