Page 1
Verabar V400S (Single Rod)
1.0 SCOPE
These instructions provide procedures for installing the
V400 (Single Rod) Verabar flow sensor. Procedures are
given for all industrial flow measurement applications
including liquid, steam and gas service for both horizontal
and vertical piping configurations.
2.0 RECEIVING INSPECTION
The following tasks should be performed as part of the
receiving inspection procedure:
• Check items received against the packing list.
• Check sensor nameplate for proper model number,
serial number and customer number.
• Verify that the actual pipe diameter matches the ID
stated on the sensor nameplate.
• Check the bullet shaped sensor tube for any signs
of damage. Damage to the sensor tube may result
in erroneous flow readings.
• Check the round cover tube for any damage,
especially axial gouges or scratches. Damage to
the cover tube may prevent the packing from
sealing properly.
3.0 SAFETY PRECAUTIONS
Prior to installation of the Verabar flow sensor, check
maximum operating conditions on the flow sensor
nameplate and verify that they exceed the maximum
conditions of the installation. If any pressure,
temperature or flow limits will be exceeded, consult the
factory before proceeding.
INSTALLATION INSTRUCTIONS
4.0 INSTALLATION PREPARATIONS
4.1 Location
For the most accurate flow measurement, a minimum
straight run of pipe is required. Table 1 shows the
minimum straight run requirements. If longer straight
runs are available, position the Verabar such that the
ratio of upstream straight run to downstream straight run
is approximately 4 to 1. If straight run lengths are less
than the values stated in Table 1, consult the factory for
additional accuracy and location information. For
additional piping configurations, see Drawing SUB -4521.
Position straightening vanes such that the end closest to
the Verabar is half way between the Verabar and the
closest upstream configuration. For elbow installations,
mount the Verabar in the same plane as the closest
upstream elbow.
4.2 Orientation
Verify the proper sensor orientation by checking for an “H” (horizontal piping) or a “-V” (vertical piping) in the
model number on the Verabar name plate. Verify that
the flow arrow stamped on the instrument head is
pointing downstream in the direction of flow.
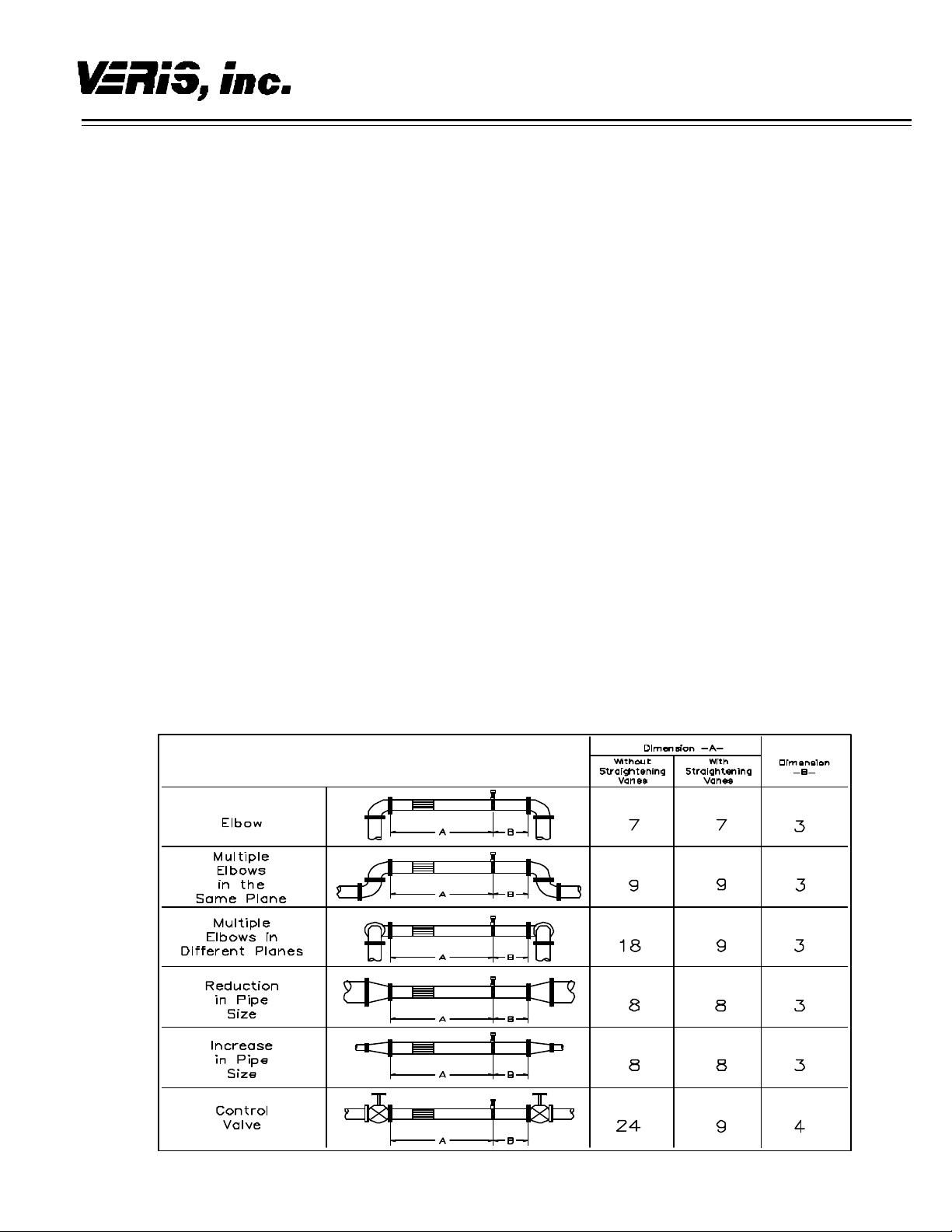
4.2.1 Horizontal Piping
For air or gas installations, mount the Verabar in the
upper 160° of the pipe to allow any condensate to drain
into the pipe (Figure 1). For liquid or steam installations,
mount the Verabar in the lower 160° of the pipe. This
allows any entrained air to bleed back into the pipe for
liquid applications and allows condensate to collect in
the instrument piping for steam applications.
Piping Configuration
Table 1. Straight Run Requirements
Page 2
4.2.2 Vertical Piping
The Verabar may be mounted in any location around the
circumference of the pipe for vertical piping applications
(Figure 1).
Figure 1. Verabar Orientation in Horizontal Pipe
4.3 DP Transmitter/Local Indicator
Location
When choosing a Verabar location, consider the DP
transmitter/local indicator location:
• The transmitter must be mounted below the
Verabar for liquid and steam applications.
• The transmitter must be mounted above the
Verabar for air and gas applications.
4.4 Installation Drawings and Bill of
Materials
Additional information is available in the Installation
Drawings and Bill of Materials VB-7061 (also on the
VeraData CD). It contains standard and alternate
transmitter locations and a complete bill of materials
based on the fluid type and sensor orientation on the
pipe.
4.5 Piping Support
For sensors that extend more than 36” (915mm) beyond
the pipe wall or for sensors mounted in thin-walled pipes,
external support of the Verabar is recommended. This
will reduc e stresses on the pipe wall.
5.0 INSTALLATION PROCEDURE
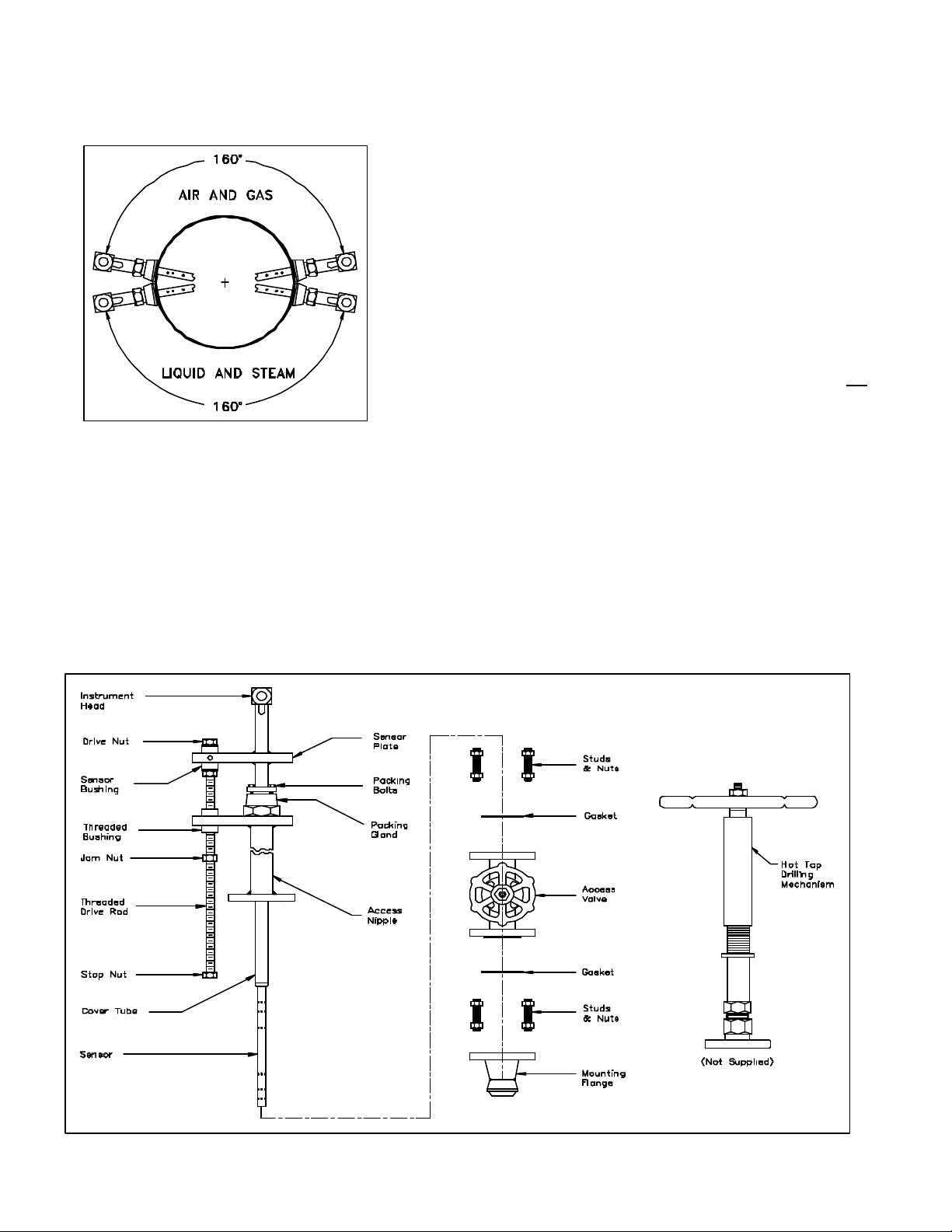
5.1 Assemble the Verabar
Your Verabar is shipped loosely assembled and is not
properly tightened for proper pressure retention. Follow
all assembly steps to ensure a safe installation (see
Figure 2).
5.2 Install Instrument Valves or Manifold
5.2.1 Valves
If the Verabar does not have a valve head, install
instrument valves using proper thread sealant. Be sure
instrument shut-off valves are installed and shut prior to
repressurizing the pipe.
5.2.2 Manifold
If the Verabar has a direct or integral manifold, be sure
the high and low pressure block valves are shut off prior
to repressurizing the pipe.
Figure 2. Verabar Model V400S (Single Rod)
Page 3

5.3 Retract Sensor and Tighten Packing
Retract the Verabar such that the tip of the sensor is
flush with the end of the access nipple (Figure 3).
Tighten the packing bolts on the packing gland.
Cover
Tube
Figure 3. Access Nipple
5.4 Weld Mounting Flange to Pipe
Mark the location where the Verabar is to be mounted.
Position the mounting flange over the center of the mark.
Using the appropriate weld gap, tack weld the mounting
flange into position. Note the flange orientation per
Figure 4. The bolt holes on the flange should straddle
the centerline of the pipe (2-holing pattern). Finish
welding the mounting flange to the pipe per applicable
codes.
per the chart below). Follow the instructions given
by the Hot Tap Drilling Machine.
Sensor Size Hole Dia
V400-05 1/2" (13mm)
V400-10 1” (25mm)
V400-15 1-1/2” (38mm)
• After the hole is completely drilled, retract the Hot
Tap Drilling Machine. Shut off the access valve
prior to removal of the Hot Tap Drilling Machine.
Figure 6. Hot Tap Drilling Machines
Note: There are numerous Hot Tap Drilling Machines on
the market with various pressure and temperature
ratings. These devices can usually be rented at a local
utility company. For more information concerning Hot
Tap Drilling Machines, the following companies can be
contacted: Mueller Co., Decatur, IL (217) 423-4471 or
T.D. Williamson Inc., Tulsa, OK (918) 446-1941.
Figure 4. Flange Orientation
5.5 Install Access Valve
Bolt the access valve to the mounting flange using the
gasket, studs and nuts provided.
5.5.1 Horizontal Pipes
Orient the valve such that the valve stem is parallel with
the centerline of the pipe (Figure 5).
5.5.2 Vertical Pipes
Orient the valve such that the valve stem is perpendicular
with the centerline of the pipe (Figure 5).
ACCESS VALVE
STEM PARALLEL TO
CENTER LINE
GAP (1/16” TYP)
TACK WELD, THEN
COMPLETE WELD
HORIZONTAL VERTICAL
ACCESS VALVE
STEM 90° FROM
CENTER LINE
90°
Figure 5. Access Valve
Verify that the access valve is properly tightened to the
mounting flange, because beyond this point it will not be
serviceable without depressurizing the line.
5.6 Drill Hole in Pipe
• With the access valve in the full open position,
install an appropriate Hot Tap Drilling Machine
(Figure 6) and drill a hole in the pipe (hole sizes
5.7 Mount Sensor Assembly to Access
Valve
Orient the sensor such that the arrow labeled “flow” on
the instrument head is in the direction of the flow in the
pipe to within 3° (orientation per Figure 7). Bolt the
access nipple to the access valve using the gasket,
studs and nuts provided.
5.8 Vent Access Valve to Verify No
Leaks are Present
With the instrument valves shut, slowly crack open the
access valve and verify that there are no process fluid
leaks. If leaks are present, shut off the access valve and
tighten the leaky joint.
5.9 Insert Verabar Sensor Assembly
Warning: The flow rate must be decreased to the
amount stated on the Verabar tag: the maximum
insertion/withdrawn DP/flow limit.
• The Verabar should be oriented such that the
arrow on the head is pointing in the direction of
flow.
• Completely open the access valve. Then, using
the drive nut, insert the sensor.
• The tip of the sensor should completely bottom on
the opposite end of the pipe. Continue to insert
the sensor until firm resistance is met. This will
occur when the sensor plate is approximately 2”
(51mm) from the top of the packing gland.
• Thread the jam nut toward the threaded bushing.
The jam nut should press tightly against the
threaded bushing. This will lock the drive rod in
place and maintain the sensor position in the pipe.
Page 4

Figure 7. Orientation of Flow Arrow
The Verabar is now properly installed (Figure 8).
The assembly should be periodically checked. Verify
that no leaks are present. The jam nut and packing bolts
should be tight.
Periodic Maintenance
Sensor Removal Procedure
• Shut off instrument valves.
• Reduce flow rate to below the maximum insertion
withdrawn DP/flow limit stated on the Verabar tag.
• Loosen jam nut.
• Using the drive nut, retract the sensor until the
stop nut and jam nut are pressing against the
threaded bushing.
• Completely shut off the access valve. Slowly
crack open one of the Verabar instrument valves
and bleed off any remaining pressure contained in
the access nipple. The sensor assembly can now
be removed.
Figure 8. Installed V400 (Single)
6315 Monarch Park Place • Niwot, CO 80503 USA • Phone: (303) 652-8550 IO -400S VWI-CS-027 REV B (6/08)
Fax: (303) 652-8552 • Email: contact@veris-inc.com • Website: www.veris-inc.com Printed in USA
 Loading...
Loading...