Page 1

VEC-8218K Owner’s Manual Counter-Surveillance Monitor Kit
INTRODUCTION
General Information: Despite lurid tales of the FBI using electronic olives to
spy on private citizens, most of us feel pretty safe from electronic surveillance in
our homes and offices. But, perhaps we shouldn't! A quick scan of the
electronic hobby magazines reveals an astonishing array of affordable microminiature VHF and UHF transmitters being sold for the sole purpose of
"bugging" private conversations. And now, with the advent of low-cost
microchip video cameras, even our most intimate and private acts are easily
transmitted blocks away and committed to videotape! Who would do such a
thing? Recent news reports suggest heavy-handed p rosecutors, angry spouses,
personal or political enemies, dishonest business competitors, internet smut
hucksters, hired sleuths, insurance investigators, criminal sex offenders, and even
curious adolescent snoops--to name only a few! It's not a comforting thought,
but manufacturers are selling hundreds of millions of dollars worth of
inexpensive amateur surveillance products yearly, and somebody out there is
buying this stuff!
The VEC-8218K can help you fight back and reclaim your personal space by
detecting signals from low-power bugging transmitters over a wide frequency
range. Sweep an area, and if a signal is there, you can find its source and
"crunch" the offending bug quickly--before sensitive words and private acts wind
up in the wrong hands! As an ad ded plus, your monitor also checks cel lphones,
cordless phones, RC transmitters, and garage-door openers for operation.
Circuitry: The VEC-8218 Counter-Surveillance Monitor consists of a high-
gain wide-band RF amplifier coupled to a RF detector. This drives a sensitive
VCO (voltage-controlled oscillator) that changes in pitch whenever nearby
signals are picked up. The closer you get, the greater the change in pitch from
the speaker--enabling you to move in quickly for the "kill". Sensitivity is
adjustable down to -60 dBm, which ensures detection of even very-low power or
well-hidden bugs.
TOOLS AND SUPPLIES
Construction Area: Kit construction requires a clean, smooth, and well-lighted
area where you can easily organize and handle small parts without losing them.
An inexpensive sheet of white poster board makes an excellent construction
surface, while providing protection for the underlying table or desk. Diffused
overhead lighting is a plus, and a supplemental high-intensity desk lamp is
especially helpful for close-up work. Safety is always important! Use a suitable
high-temperature stand for your soldering iron, and keep the work area free of
clutter.
1
Page 2

VEC-8218K Owner’s Manual Counter-Surveillance Monitor Kit
Universal Kit-building Tools: No special tools are required to complete this
kit beyond common items normally used for bench construction. We
recommend the following:
! Soldering Iron (grounded-tip and temperature-controlled preferred)
! High-temperature Iron Holder with Cleaning Sponge
! Solder, 60/40 or 37/63 with rosin or "no-clean" flux (.031" dia. is good size).
! Needle Nose Pliers or Surgical Hemostats
! Diagonal Cutters or "Nippy Cutters"
! Solder Sucker (squeeze or vacuum pump type), or Desoldering Braid
! Bright Desk Lamp
! Magnifying Glass
BEFORE YOU START BUILDING
Experience shows there are four common mistakes builders make. Avoid these,
and your kit will probably work on the first try! Here's what they are:
1. Installing the Wrong Part: It always pays to double-check each step. A 1K
and a 10K resistor may look almost the same, but they may act very
differently in an electronic circuit! Same for capacitors--a device marked
102 (or .001 uF) may have very different operating characteristics from one
marked 103 (or .01uF).
2. Installing Parts Backwards: Always check the polarity of electrolytic
capacitors to make sure the positive (+) lead goes in the (+) hole on the
circuit board. ICs have a notch or dot at one end indicating the correct
direction of insertion. Always double-check--especially before applying
power to the circuit!
3. Faulty Solder Connections: Inspect for cold-solder joints and solder
bridges. Cold solder joints happen when you don't fully heat the connection-or when metallic corrosion and oxide contaminate a component lead or pad.
Solder bridges form when a trail of excess solder shorts pads or tracks
together (see solder tips below).
4. Omitting or Misreading a Part: This is easier to do than you might think!
Always double-check to make sure you completed each step in an assembly
sequence.
Soldering Tips: Cleanliness and good heat distribution are the two secrets of
professional soldering. Before you install and solder each part, inspect leads or
2
Page 3
VEC-8218K Owner’s Manual Counter-Surveillance Monitor Kit
pins for oxidation. If the metal surface is dull, sand with fine emery paper until
shiny. Allow the tip of your iron to contact both the lead and pad for about one
second (count "one-thousand-one") before feeding solder to the connection.
Surfaces must become hot enough for solder to flow smoothly. Feed solder to
the opposite side of the lead from your iron tip--solder will wick around the lead
toward the tip, wetting all exposed surfaces. Apply solder sparingly, and do not
touch solder directly to the hot iron tip to promote rapid melting. Keep a damp
sponge handy to wipe your so ldering tip on. This removes excess solde r, and
keeps the tip properly tinned. If the iron is going to sit idling for long periods,
wipe the tip, add some fresh solder, and unplug the iron.
Desoldering Tips: If you make a mistake and need to remove a part, follow
these instructions carefully! First, grasp the component with hemostats, needlenose pliers, or your fingers. Heat the pad beneath the lead you intend to extract,
and pull gently. The lead should come out. Repeat for the other lead. Solder
may fill in behind the lead as you extract it--especially if you are working on a
double-sided b o ar d with plat e-thr o ugh hol es. Sho uld this ha pp e n, tr y heat ing the
pad again and inserting a common pin into the hole. Solder won't stick to the
pin's chromium plating. When the pad cools, remove the pin and insert the
correct component. For ICs or multiple-pin parts, use desoldering braid to
remove excess solder before attempting to extract the part. Alternatively, a lowcost vacuum-bulb or spring-loaded solder sucker may be used. Parts damaged or
severely overheated during extraction should be replaced rather than reinstalled.
Work Habits: Kit construction requires the ability to follow detailed
instructions and, in many cases, to perform new and unfamiliar tasks. To avoid
making needless mistakes, work for short periods when you're fresh and alert.
Recreational construction projects are more informative and more fun when you
take your time. Enjoy!
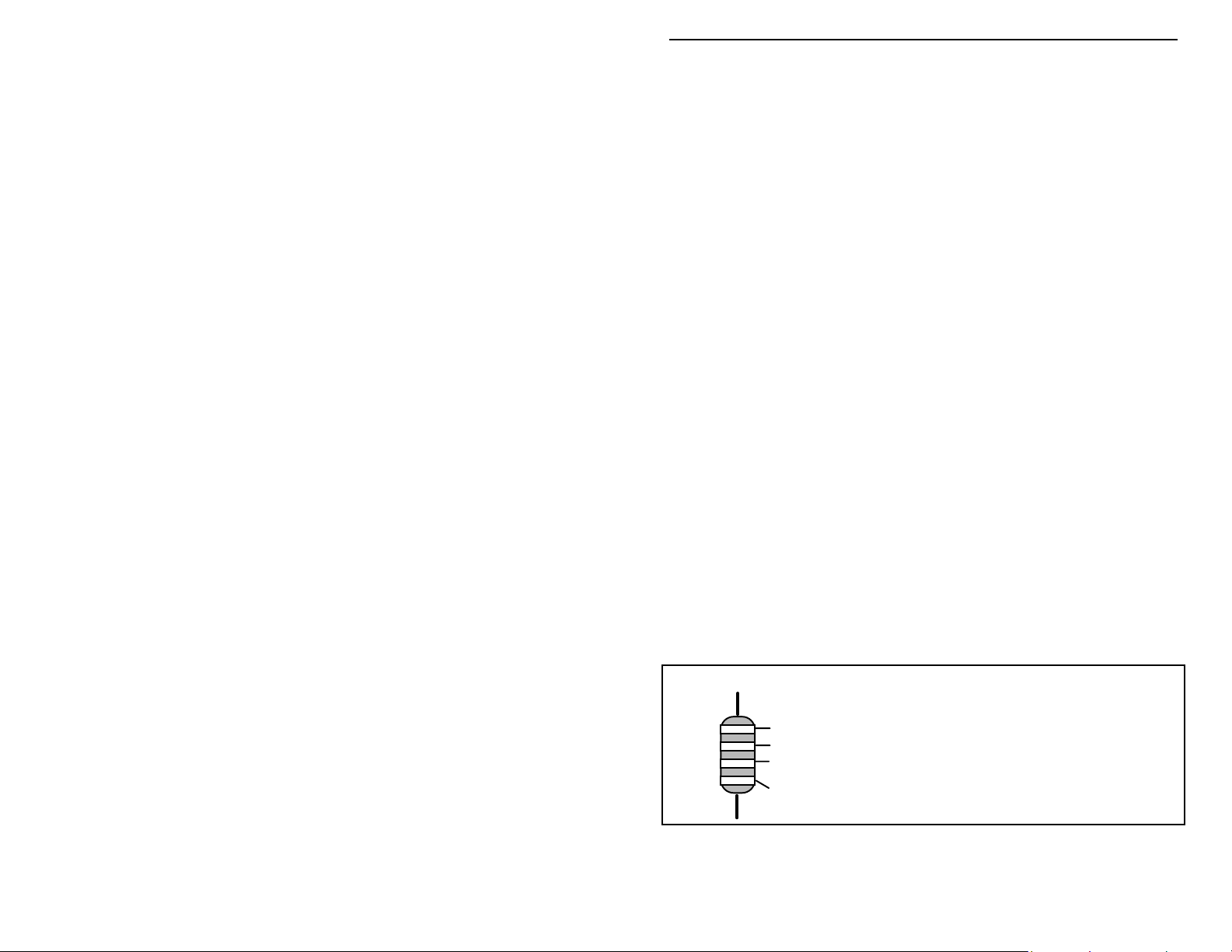
Sorting and Reading Resistors: The electrical value of resistors is indicated by
a color code (shown below). You don't have to memorize this code to work with
resistors, but you do need to understand how it works:
Resistor Color Code
1st Digit
2nd Digit
Multiplier
Tolerence
(gold or silver)
Black = 0 (tens)
Brown = 1 (hundreds)
Red = 2 (K)
Orange = 3 (10K)
Yellow = 4 (100K)
Green = 5 (1Meg)
Blue = 6
Violet = 7
Gray = 8
White = 9
Silver = 10%
Gold = 5%
When you look at a resistor, check its multiplier code first. Any resistor with a
black multiplier band falls between 10 and 99 ohms in value. Brown designates
3
Page 4

VEC-8218K Owner’s Manual Counter-Surveillance Monitor Kit
a value between 100 and 999 ohms. Red indicates a value from 1000 to 9999
ohms, which is also expressed as 1.0K to 9.9K. An orange multiplier band
designates 10K to 99K, etc. To inventory resistors, first separate them into
groups by multiplier band (make a pile of 10s, 100s, Ks, 10Ks, etc.). Next, sort
each group by specific value (1K, 2.2K, 4.7K, etc). This procedure makes the
inventory easier, and also makes locating specific parts more convenient later on
during construction. Some builders find it especially helpful to arrange resistors
in ascending order along a strip of double-sided tape.
Reading Capacitors: Unlike resistors, capacitors no longer use a color code for
value identification. Instead, the value, or a 3-number code, is printed on the
body.
Value Code
10 pF = 100
100 pF = 101
1000 pF = 102
.001 uF = 102*
.01 uF = 103
.1 uF = 104
Multilayer
(270 pF)
271
Ceramic Discs
(.001 uF) (.1 uF)
102
104
Electrolytic
1 uF
|
1uF
|
35V
+
-
As with resistors, it's helpful to sort capacitors by type, and then to arrange them
in ascending order of value. Small-value capacitors are characterized in pF (or
pico-Farads), while larger values are labeled in uF (or micro-Farads). The
transition from pF to uF occurs at 1000 pF (or .001 uF)*. Today, most
monolithic and disc-ceramic capacitors are marked with a three-number code.
The first two digits indicate a numerical value, while the last digit indicates a
multiplier (same as resistors).
Electrolytic capacitors are always marked in uF. Electrolytics are polarized
devices and must be oriented correctly during installation. If you become
confused by markings on the case, remember the uncut negative lead is slightly
shorter than the positive lead.
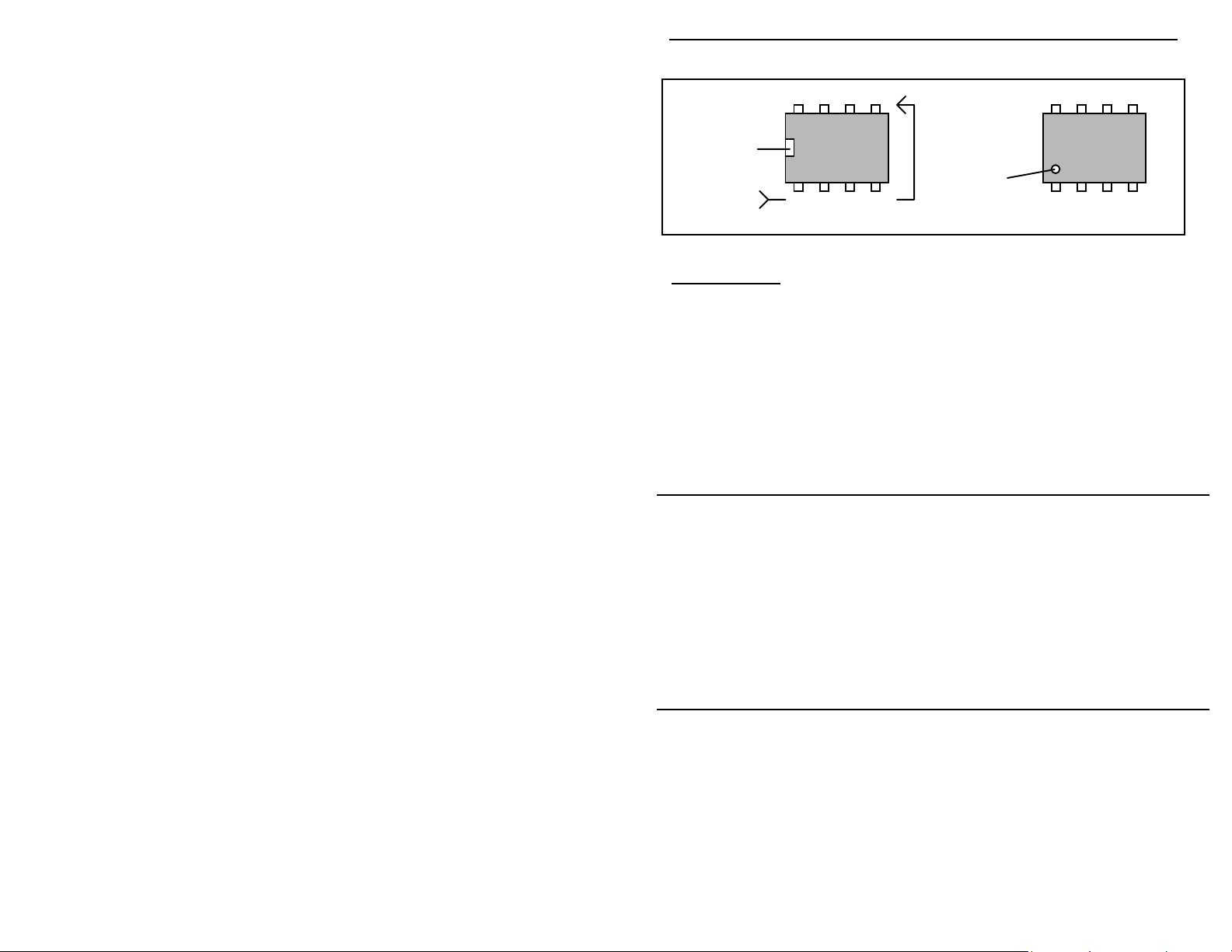
Integrated Circuits: Proper IC positioning is indicated by a dot or square
marking located on one end of the device. A corresponding mark will be silkscreened on the PC board and printed on the kit's parts-placement diagram. To
identify specific IC pin numbers for testing purposes, see the diagram below.
Pin numbers always begin at "1" at the keyed end of the case and progress along
the device, as shown:
4
Page 5
VEC-8218K Owner’s Manual Counter-Surveillance Monitor Kit
8 7 6 5
Installation
Key
Installation
Key
1 2 3 4
Pin Numbers
PARTS LIST
Your kit should contain all of the parts listed below. Please identify and
inventory each item on the checklist before you start building. If any parts are
missing or damaged, refer to the manual's warranty section for replacement
instructions. If you can't positively identify an unfamiliar item on the basis of the
information given, set it aside until all other items are checked off. You may
then be able to identify it by process of elimination. Finally, your kit will go
together more smoothly if parts are organized by type and arranged by value
ahead of time. Use this inventory as an opportunity to sort and arrange parts so
you can identify and find them quickly.
""""
Qty Part Description Designation VEC P/N
!
1 22 ohm resistor (red-red-black) R6 100-1220
!
1 100 ohm resistor (brown-black-brown) R16 100-2100
!
2 220 ohm resistor (red-red-brown) R1,R9 100-2220
!
2 470 ohm resistor (yellow-violet-brown) R4,R14 100-2470
!
1 560 ohm resistor(green-blue-brown) R5 100-2560
!
1 1K resistor (brown-black-red) R22 100-3100
!
1 1.5K resistor (brown-green-red) R8 100-3150
!
1 4.7K resistor (yellow-violet-red) R7 100-3470
!
4 10K resistor (brown-black-orange) R10,R11,R21
R23
""""
Qty Part Description Designation VEC P/N
!
2 15K resistor (brown-green-orange) R13,R17 100-4150
!
1 39K resistor (orange-white-orange) R3 100-4390
!
3 47K resistor (yellow-violet-orange) R15,R18,R19 100-4470
!
2 100K resistor (brown-black-yellow) R2,R20 100-5100
!
1 1M resistor (brown-black-green) R12 100-6100
!
1 10K potentiometer w/switch R24
!
1 .001 uF multilayer capacitor (102) C1 220-1100
!
1 .0047 uF multilater capacitor (472) C8 220-1470
100-4100
5
Page 6
VEC-8218K Owner’s Manual Counter-Surveillance Monitor Kit
!
6 .01 uF multilayer capacitor (103) C2,C3,C4,C5
C6,C7
!
2 10 uF electrolytic capacitor C9,C10 270-5100-1
!
1 LM324 quad op-amp IC (14 pins) U1 324-0324
!
1 MRF901 transistor (4 leads) Q1 306-5901
!
2 PN2222 transistor Q2,Q3 305-2222-1
!
1 1N270 detector diode D1 300-0034
!
1 Sub-miniature speaker SPK1 410-0011
!
1 9V battery snap BAT1 730-3005
!
6 3” length of insulated wire 871-2444-0300
!
1 Telescoping antenna ANT 758-1120
!
1 Solder lug 720-1213
!
1 3.5 x .6 - 6mm screw 675-0006B
!
1 Printed circuit board 861-VEC8218
!
1 Owner’s Manual 925-VEC8218K
220-2100
PARTS PLACEMENT
STEP-BY-STEP ASSEMBLY INSTRUCTIONS
In these instructions, when you see the term install, this means to locate, identify,
and insert the part into its mounting holes on the PC board. T his includes prebending or straightening leads as needed so force is not required to seat the part.
Once a component is mounted, bend each lead over to hold it in place. Use
sharp side-cutters to clip off excess lead length before soldering. Make sure
trimmed leads don't touch other pads and tracks, or a short circuit may result:
Good
6
Not Good
Page 7

Page 8

VEC-8218K Owner’s Manual Counter-Surveillance Monitor Kit
The term solder means to solder the part's leads in place, and to inspect both (or
all) solder connections for flaws or solder bridges. Nip off excess protruding
leads with a sharp pair of side cutters.
This kit has 23 fi xed-value resistors. Mount these now,
starting with the smallest value and moving to the
largest. Before mounting each one, carefully bend both
leads close to the resistor body to form right-angles, as
shown.
"
! ! 1.#Find a 22 ohm resistor (red, red, black). Install at R6 and solder.
! ! 2.#Find a 100 ohm resistor (brown-black-brown). Install R16 and solder.
Locate two (2) 220 ohm resistors (red-red-brown).
! ! 3.#Install a 220 ohm at R1 and solder.
! ! 4.#Install a 220 ohm at R9 and solder.
Locate two (2) 470 ohm resistors (yellow-violet-brown).
! ! 5.#Install a 470 ohm at R4 and solder.
! ! 6.#Install a 470 ohm at R14 and solder.
! ! 7.#Find a 560 ohm resistor (green-blue-brown). Install at R5 and solder.
! ! 8.#Find a 1K resistor (brown-black-red). Install at R22 and solder.
! ! 9.#Find a 1.5K resistor (brown-green-red). Install at R8 and solder.
! ! 10.#Find a 4.7K resistor (yellow-violet-red). Install at R7 and solder.
Locate four (4) 10K resistors (brown-black-orange).
! ! 11.#Install a 10K at R10 and solder.
! ! 12.#Install a 10K at R11 and solder.
! ! 13.#Install a 10K at R21 and solder.
! ! 14.#Install a 10K at R23 and solder.
Locate two (2) 15K resistors (brown-green-orange).
! ! 15.#Install a 15K at R13 and solder.
! ! 16.#Install a 15K at R17 and solder.
! ! 17.#Find a 39K resistor (orange-white-orange). Install at R3 and solder.
Locate three (3) 47K resistors (yellow-violet-orange).
! ! 18.#Install a 47K at R15 and solder.
7
Page 9

VEC-8218K Owner’s Manual Counter-Surveillance Monitor Kit
! ! 19.#Install a 47K at R18 and solder.
! ! 20.#Install a 47K at R19 and solder.
Locate two (2) 100K resistors (brown-black-yellow).
! ! 21.#Install a 100K at R2 and solder.
! ! 22.#Install a 100K at R20 and solder.
! ! 23.#Find a 1M resistor (brown-black-green). Install at R12 and solder.
This concludes installation of the resistors provided in your kit. Double-check
for placement, making sure each value is installed where it belongs.
Next, install the kit's 8 multilayer capacitors. Avoid using force or excessive
heat when installing these. If the spacing isn't right, pre-form leads to the correct
spacing before inserting into the PC board.
Incorrect
Ooops!
Correct
! ! 24.#Find a .001 uF multilayer capacitor (marked 102). Install at C1 and
solder.
! ! 25.#Find a .0047 uF multilayer capacitor (marked 472). Install at C8 and
solder.
Locate six (6) .01 uF multilayer capacitor (marked 103).
! ! 26.#Install a .01 uF at C2 and solder.
! ! 27.#Install a .01 uF at C3 and solder.
! ! 28.#Install a .01 uF at C4 and solder.
! ! 29.#Install a .01 uF at C5 and solder.
! ! 30.#Install a .01 uF at C6 and solder.
! ! 31.#Install a .01 uF at C7 and solder.
The last two capacitors in your kit are electrolytic.
Electrolytic caps are polarized and must be installed the
correct way in order to work. Each capacitor's plus (+)
mounting hole is marked on both the circuit board and
+
parts placement diagram. If the markings on the capacitor
body are unclear, the plus (+) lead is always the longer of
Plus Lead
8
Page 10

VEC-8218K Owner’s Manual Counter-Surveillance Monitor Kit
the two.
Locate two (2) 10 uF electrolytic capacitors.
! ! 32.#Install 10 uF at C9 and solder.
! ! 33.#Install 10 uF at C10 and solder.
This completes capacitor installation. Before moving on, check each electrolytic
for correct polarity.
Locate two (2) PN2222 plastic transistors. Like the
electrolytic caps, transistors must be oriented correctly to
work.
PN2222
! ! 34.#Install a PN2222 at Q2 and solder.
! ! 35.#Install a PN2222 at Q3 and solder.
Locate the MRF 901. This device resembles
a small black plastic pill with four leads. The
longest lead is the collector, also
distinguished by the letter “M”. Carefully
Collector
MRF901
bend each lead down, forming a right-angle to
the component body (make sure the "M" is on
top).
Now, locate the silk-screened footprint for Q1.
! ! 36.#Gently insert all four leads into the board, making sure the collector
lead is positioned correctly. The body should rest flush with the PC
board surface. Turn the board over, keeping an index finger on Q1,
and bend the leads to secure the device in place.
! ! 37.#Solder all four leads of Q1.
Find the 1N270 diode (glass body). Like transistors, diodes are polarized
devices that must be installed correctly. Always look for the banded end when
installing.
! ! 38.#Install the 1N270 diode at D1 and solder.
Find the LM324 IC. The IC is keyed at one end to indicate proper positioning.
During installation, orient the IC so the notch corresponds to the key on the PC
layout.
9
Page 11

VEC-8218K Owner’s Manual Counter-Surveillance Monitor Kit
Key
LM324
Key
When installing ICs, make sure all pins enter the mounting holes and appear on
the opposite side of the PC board (it's easy to fold one or more under the IC).
Also, when soldering, make sure the IC remains flat against the board surface.
! ! 39.#Observing the key, install the LM324 at U1 and solder.
Locate the 9V battery snap clip, and note the red+ lead and black- lead.
! ! 40.#Install the red lead at SW (+) and solder.
! ! 41.#Install the black lead at GND (-) and solder.
Locate three (3) lengths of insulated wire. These will be installed at the
mounting points next to R7.
! ! 42.#Install an insulated wire at MID and solder.
! ! 43.#Install an insulated wire at CCW and solder.
! ! 44.#Install an insulated wire at CW and solder.
Next, locate the 10K 16mm potentiometer (with off/on switch). Position as
shown, and connect the control leads as follows:
CCW
MID
CW
Back of Pot
CCW = Counter-clockwise Terminal
MID = Middle Terminal
CW = Clockwise Terminal
Be sure to wrap the lead end around the pot terminal before soldering:
Pot Teminal
! ! 45.#Connect the lead from MID to the middle terminal of the 10K pot and
solder.
! ! 46.#Connect the lead from CCW to the top lead of the 10K pot and solder..
10
Page 12

VEC-8218K Owner’s Manual Counter-Surveillance Monitor Kit
! ! 47.#Connect the lead from CW to the bottom lead of the 10K pot and
solder.
Locate the red (+) lead going from the battery snap connector to SW (+) on the
PC board. Perform the following steps:
! ! 48.#Measure back 2" from the SW (+) end and snip the wire.
! ! 49. Dress both ends, removing 1/4" of insulation and tinning the leads.
Find the two off/on switch terminals on the back of 10K pot R24:
Red Leads
Switch Terminals
! ! 50.#Install the snap-clip end of the red lead to one switch terminal.
! ! 51.#Install the SW (+) red battery lead to the other switch terminal.
Locate the small 8 ohm speaker supplied with your kit. Also, find two (2) equal
lengths of insulated wire:
Speaker Leads
Speaker
! ! 52.#Solder a lead to each of the two (2) speaker connections on the plastic
frame.
! ! 53.#Install one speaker lead at SPK1 on the PC board (either hole).
! ! 54.#Install the second lead at the other SPK1 hole on the PC board.
Find one last length of hook-up wire. This will be used for connecting the
collapsible whip later on.
! ! 55.#Install one end of the wire at ANT on the PC board.
This concludes wiring of your VEC-8218 Surveillance Monitor Kit. Before
moving on to the next section, give your kit a thorough QC (quality control)
inspection. This will help you discover accidental assembly errors that might
prevent it from working properly--or that might cause damage to sensitive parts
when you apply power. Follow this procedure:
11
Page 13

VEC-8218K Owner’s Manual Counter-Surveillance Monitor Kit
1. Compare parts locations with the parts-placement diagram. Was each part
installed where it is supposed to be? Was the correct value used? Start at
one side of the board and work your way across in an organized pattern.
2. Inspect the solder side of the board for cold-solder joins and solder bridges
between tracks or pads. Use a magnifying glass to obtain a clear view of the
track area. If you suspect a solder bridge, hold the board in front of a bright
light for a better view. All joints should be smooth and shiny, indicating
good solder wetting and flow. Resolder any beaded or dull-appearing
connections. Also, check the front-panel jacks, switches, and connectors for
defective solder connections.
3. Finally, check electrolytic capacitors and diodes for correct polarity. Does
the plus (+) polarity symbol on the part agree with the pictorial and with the
pattern on the PC board? Is the banded end of each diode positioned
correctly? Were all ICs and transistors installed correctly?
Be sure to correct all errors before moving on.
12
Page 14

VEC-8218K Owner’s Manual Counter-Surveillance Monitor Kit
TESTING AND ALIGNMENT
This kit has no internal alignment adjustments. To test the circuit board for
proper operation prior to installation in its case, begin as follows:
1. Temporarily connect the monitor's collapsible antenna with the hardware
provided.
2. Turn the power switch off (pot fully counter-clockwise).
3. Install a fresh 9V alkaline battery on the battery snap clip.
4. Collapse t he antenna for minimum length.
5. Turn the power switch on and advance the control slowly clockwise.
With no strong nearby radios signals present, you should hear a steady low-
frequency tone in the speaker that increases in pitch as you advance the
sensitivity control. If you fail to hear the oscillation, check battery condition. If
the battery's okay, re-check for construction errors.
To check the RF detector for proper operation, you'll need a signal source in the
1-1000 MHz range. A cordless phone, RC-model transmitter, garage door
opener, cellphone, baby monitor, ham-radio HT, CB rig, or PCS walkie-talkie
should work fine for this purpose.
6. Extend your monit or's antenna for full length.
7. Set the VCO control for the lowest sustained tone you can get.
8. Place the monitor close to the transmitter or RF source you've chosen.*
9. Activate the transmitter or RF source.
When the transmitter is on, audio pitch should increase. If it doesn't, try a
different transmitter source. If that fails, re-check for construction errors.
Important Note:
commercial-band walkie-talkies, and mobile or base-station transceivers emit
extremely high RF levels that could damage your kit if the antennas get too
close. Keep your unit at least 10 feet from these sources--or remove the
monitor's collapsible antenna during your test. At the opposite extreme, note
that your monitor's sensitivity is considerably lower at 900-MHz than at 100 MHz.
Therefore, some 900-MHz short-range cordless phones may not provide a very
strong signal indication unless the antennas are practically touching.
High-power RF sources such as ham-radio HTs, CBs,
If your surveillance monitor is operating properly, you may install it in the case
at this time. If it fails to operate in the manner described, recheck your work and
refer to the "In Case Of Difficulty" section of this manual.
13
Page 15

Page 16

VEC-8218K Owner’s Manual Counter-Surveillance Monitor Kit
15
Page 17

Page 18

VEC-8218K Owner’s Manual Counter-Surveillance Monitor Kit
17
 Loading...
Loading...