Page 1

VC-EVCC-P
Technical Reference
Version 2.2.0
Authors
Vector Informatik GmbH
Status
Released
Page 2
Technical Reference VC-EVCC-P
© 2021 Vector Informatik GmbH Version 2.2.0 2
based on template version 6.0.2
Document Information
History
Author
Date
Version
Remarks
ssm
2020-07-07
1.0.1
Change Authors’ information
Add Document information
ssm
2020-07-15
1.0.2
Chapter 1: Update graphic
Chapter 2: Update System Overview
vml/ssm
2020-08-04
1.1.0
Chapter “Delivery Content” added
ssm
2020-08-27
1.2.0
Chapter “Industrialization” added
dim
2020-09-24
2.0.0
Updated for SW release 3.0.0:
Chapter 2 “System Architecture” updated (RMP architecture
added)
Chapter 4.14 “Charging Arbitration” added
dim
2020-11-24
2.0.1
Chapter 3.2: Connector description updated
ssm
2021-02-03
2.1.0
Chapter 7.5 “Quality Documents” added
dim
2021-03-31
2.2.0
Chapter 4.8 Remark about HSOUT added
Reference Documents
No.
Source
Title
[1]
OppCharge
Network and application protocol specification for Siemens – Volvo
OppCharge implementation, Version 1.3.0
[2]
Vector
TechnicalReference_CAN-WiFi-GW
[3]
DIN
DIN 70121:2014-12
[4]
DIN
DIN EN 61851-23 - Konduktive Ladesysteme für Elektrofahrzeuge
- Teil 23 Gleichstromladestationen für Elektrofahrzeuge (IEC 61851-
23:2014)
[5]
DIN
DIN EN 61851-23 Berichtigung 1 - Konduktive Ladesysteme für
Elektrofahrzeuge - Teil 23 Gleichstromladestationen für
Elektrofahrzeuge (IEC 61851-23:2014/COR1:2016)
[6]
Vector
User Manual
[7]
ISO
ISO 15118-2:2014(E)
Page 3

Technical Reference VC-EVCC-P
© 2021 Vector Informatik GmbH Version 2.2.0 3
based on template version 6.0.2
Safety Instructions
Caution
To avoid personal injuries and damage to property you have to read and understand
the following safety instructions and hazard warnings prior to installation and use of this
ECU. Keep this documentation always near the ECU.
Proper Use and Intended Purpose
Caution
The ECU may only be operated according to the instructions and descriptions of this
manual. The ECU is exclusively designed for use by skilled personnel as its operation
may result in serious personal injuries and damage to property. Therefore, only those
persons may operate the ECU who have understood the possible effects of the actions
which may be caused by the ECU. Users have to be specifically trained in the handling
(e.g. calibration) with the ECU, the applied embedded software and the system
intended to be influenced. Users must have sufficient experience in using the ECU
safely.
Hazard Warnings
Caution
The ECU may control and/or otherwise influence the behavior of control systems and
electronic control units. Serious hazards for life, body and property may arise, in
particular without limitation, by interventions in safety relevant systems (e.g. by
deactivation or otherwise manipulating the engine management, steering, airbag and/or
braking system) and/or if the ECU is operated in public areas (public traffic). Therefore,
you must always ensure that the ECU is used in a safe manner. This includes inter alia
the ability to put the system in which the ECU is used into a safe state at any time (e.g.
by “emergency shutdown”), in particular without limitation in the event of errors or
hazards. Furthermore, all technical safety and public law directives which are relevant
for the system in which the ECU is used must apply. Provided that serious hazards for
life, body and property may occur and before the use in public areas the system in
which the ECU is used must be tested according to recognized rules of engineering in
a non-public area.
Page 4

Technical Reference VC-EVCC-P
© 2021 Vector Informatik GmbH Version 2.2.0 4
based on template version 6.0.2
Contents
1 General .......................................................................................................................... 7
2 System Architecture ..................................................................................................... 8
2.1 OppCharge Architecture ..................................................................................... 8
2.2 Roof-Mounted Pantograph Architecture ............................................................. 9
2.3 Supported Peripherals ....................................................................................... 9
3 ECU ................................ .............................................................................................. 10
3.1 ECU Overview ................................................................................................. 10
3.2 Key ECU Characteristics .................................................................................. 11
4 Functional Overview ................................................................................................... 12
4.1 CP Communication .......................................................................................... 12
4.2 WiFi Communication (OppCharge only) ........................................................... 12
4.3 Power Line Communication ............................................................................. 13
4.3.1 Low Level communication with EVSE .............................................. 13
4.3.2 DC Charging with High Level Communication .................................. 13
4.4 Stop Button ...................................................................................................... 14
4.5 StopCharge CAN Signal .................................................................................. 14
4.6 Clamp 15 Signal Input ...................................................................................... 14
4.7 Status LEDs ..................................................................................................... 14
4.8 High Side Outputs ............................................................................................ 14
4.9 Reprogramming of the ECU Software .............................................................. 15
4.10 Self-Diagnostics ............................................................................................... 15
4.11 ECU State Handling ......................................................................................... 15
4.12 Vehicle Immobilization (OppCharge only) ........................................................ 16
4.13 Configuration of Software ................................................................................. 16
4.14 Charging Arbitration ......................................................................................... 16
5 Qualification ................................ ................................................................................ 17
5.1 Configuration ................................................................................................... 17
5.2 Electrical Tests ................................................................................................. 17
5.3 EMC Test ......................................................................................................... 18
5.4 Climatic Tests ................................................................................................... 18
5.5 Mechanical Tests ............................................................................................. 19
5.6 Life Tests.......................................................................................................... 19
5.7 Chemical Tests................................................................................................. 19
6 Industrialization .......................................................................................................... 21
Page 5

Technical Reference VC-EVCC-P
© 2021 Vector Informatik GmbH Version 2.2.0 5
based on template version 6.0.2
7 Delivery Content ......................................................................................................... 22
7.1 ECU ................................................................................................................. 22
7.2 Packaging ........................................................................................................ 22
7.3 Software .......................................................................................................... 23
7.4 Technical Documents ....................................................................................... 23
7.5 Quality Documents ........................................................................................... 23
8 Glossary and Abbreviations ...................................................................................... 25
Page 6

Technical Reference VC-EVCC-P
© 2021 Vector Informatik GmbH Version 2.2.0 6
based on template version 6.0.2
Illustrations
Figure 1-1 VC-EVCC-P ................................................................................................ 7
Figure 2-1 System Overview OppCharge (Inverted Pantograph) ................................. 8
Figure 2-2 System Overview Roof-Mounted Pantograph (RMP) .................................. 9
Figure 3-1 VC-EVCC-P Interfaces ............................................................................. 10
Figure 7-1 VC-EVCC-P packed in Cardboard Package ............................................. 22
Tables
Table 1-1 Delivery Content ......................................................................................... 7
Table 3-1 VC-EVCC-P Key Characteristics .............................................................. 11
Table 4-1 Low Level Communication – Duty Cycle of CP PWM ............................... 13
Table 5-1 Qualification Configuration ........................................................................ 17
Page 7

Technical Reference VC-EVCC-P
© 2021 Vector Informatik GmbH Version 2.2.0 7
based on template version 6.0.2
1 General
The Vector Controller - Electric Vehicle Communication Controller for Pantograph (VC-
EVCC-P) is a generic ECU for 24V environments.
It realizes electrical charging according to OppCharge V1.3.0 (see [1]) in combination with
an additional CAN-WiFi-Gateway for communication with the charging infrastructure.
In addition, charging with a roof-mounted pantograph is supported.
The hardware is the VC36PLC-24 with an integrated flash bootloader. VC-EVCC-P includes
a modern MICROSAR stack with all relevant application modules to realize electrical
charging communication.
Figure 1-1 VC-EVCC-P
The following parts are included in the delivery:
Part
Description
VC-EVCC-P
ECU with integrated software
Documentation
Customer receives a Technical Reference (this
document) as well as a User Manual and
Charging Sequence Diagrams
Remaining Bus Simulation
CANoe bus simulation for the VC-EVCC-P for
bus test and evaluation purposes
CAN database description (dbc)
Diagnostic description file (cdd)
Table 1-1 Delivery Content
Page 8
Technical Reference VC-EVCC-P
© 2021 Vector Informatik GmbH Version 2.2.0 8
based on template version 6.0.2
2 System Architecture
The VC-EVCC-P is designed to be integrated into the vehicle with one of the following
system architectures.
2.1 OppCharge Architecture
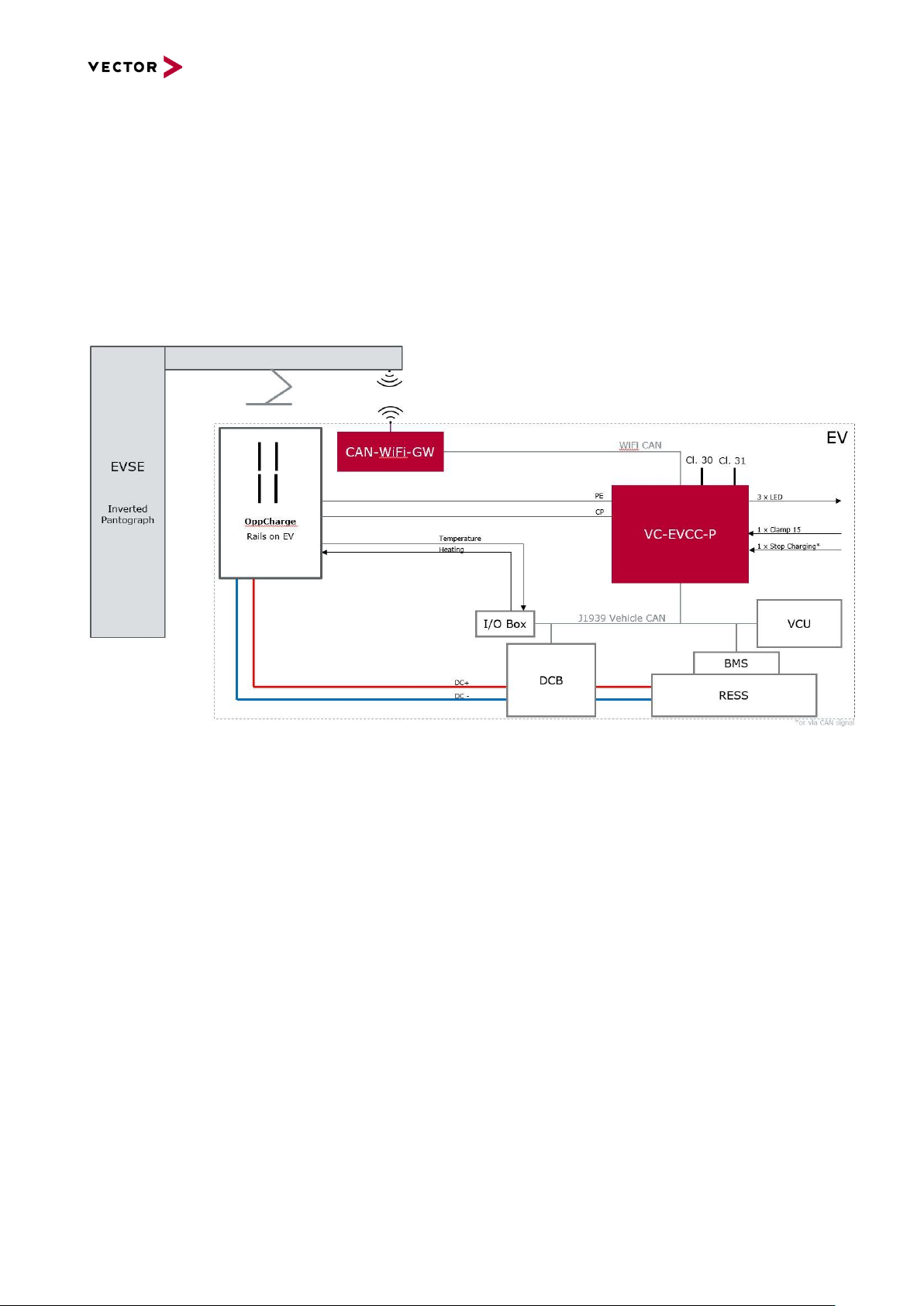
Figure 2-1 System Overview OppCharge (Inverted Pantograph)
Red components are in focus of VC-EVCC-P system context and are provided by Vector.
Non-red components, e.g. CAN-I/O Interface, have to be supplied alternatively in case
Temperature or Heater control shall be implemented.
Page 9

Technical Reference VC-EVCC-P
© 2021 Vector Informatik GmbH Version 2.2.0 9
based on template version 6.0.2
2.2 Roof-Mounted Pantograph Architecture
Figure 2-2 System Overview Roof-Mounted Pantograph (RMP)
Red components are in focus of VC-EVCC-P system context and are provided by Vector.
Non-red components, e.g. CAN-I/O Interface, have to be supplied alternatively in case
Temperature or Heater control shall be implemented.
2.3 Supported Peripherals
Supported peripherals of the VC-EVCC-P:
> CAN-WiFi-Gateway (Vector article no.: 180109):
Due to radio admission restrictions the CAN-WiFi-Gateway is only available for the
European Market. For further information about restrictions of usage see [2].
Page 10

Technical Reference VC-EVCC-P
© 2021 Vector Informatik GmbH Version 2.2.0 10
based on template version 6.0.2
3 ECU
This chapter contains an overview about the VC-EVCC-P. A detailed description of the
electronics and housing can be found in the User Manual of the VC-EVCC-P.
3.1 ECU Overview
The following diagram and tables give an abstract overview of the interfaces of the hardware.
Note
There are many different configuration options for the hardware of the VC-EVCC-P.
The following figure shows the configuration of the VC-EVCC-P.
Figure 3-1 VC-EVCC-P Interfaces
Page 11

Technical Reference VC-EVCC-P
© 2021 Vector Informatik GmbH Version 2.2.0 11
based on template version 6.0.2
3.2 Key ECU Characteristics
Parameter
Description
CPU
SPC564B74L7, 120MHz
Memory
3,0 MB Code-Flash, 4x16 kB Data-Flash, 192
kB RAM
Voltage range
10V … 32V (ISO 16750, Code E)
Connector
Molex CMC36 Hybrid Sealed (36 Pins)
Communication
3x CAN 2.0B (incl. shielding)
1x PLC – Power Line Communication based on
IEC61851
I/O
Extensive Inputs and Outputs typically needed
for in vehicle powerline charging systems
Temperature Range
-35°C … +85°C (ISO 16750, Code H)
Typical Current Consumption without loads
150mA
Quiescent Current
114µA
Weight
560 g
IP protection
IP6K6K / IP6K7 / IP6K9K (not valid for
unsealed housing
Functional Safety
Not considered, development based on QM
process
Table 3-1 VC-EVCC-P Key Characteristics
Page 12

Technical Reference VC-EVCC-P
© 2021 Vector Informatik GmbH Version 2.2.0 12
based on template version 6.0.2
4 Functional Overview
4.1 CP Communication
The CP connection to rails is detected by measurement of CP voltage.
4.2 WiFi Communication (OppCharge only)
The VC-EVCC-P controls DC charging communication between EV and EVSE according to
OppCharge V1.3.0 [1] communication via an additional CAN-WiFi-Gateway [2].
The DC charging via ACD (inverted pantograph) is done according to the following
sequence:
WiFi Communication Setup
Setup of High Layer Communication
Charge Parameter Discovery
Cable Check incl. ACD connection, isolation measurement and immobilization of the
vehicle
Pre-Charge
Power Delivery True
Current Demand incl. monitoring of charging progress
Power Delivery False
Session Stop incl. retraction of ACD to home position and mobilization of the vehicle
Stop Communication Session
Caution
Plug and Charge is not supported by the VC-EVCC-P.
Page 13

Technical Reference VC-EVCC-P
© 2021 Vector Informatik GmbH Version 2.2.0 13
based on template version 6.0.2
4.3 Power Line Communication
4.3.1 Low Level communication with EVSE
According to [4] and [5] a low-level communication via PWM on the CP pin is supported.
The following PWM duty cycles are valid:
Duty Cycle of CP PWM
Description
0% <= DC < 3%
No charging allowed
3% <= DC <= 7%
Usage of high-level protocol according to ISO
15118 and DIN 70121. Charging without this
high-level protocol is not possible.
7% < DC < 8%
No charging allowed
8% < DC < 10%
Max current consumption is 6A
10% <= DC <= 85%
Available current = Duty Cycle * 0,6A
85% < DC <= 96%
Available current = (Duty Cycle – 64) * 2,5A
96% < DC <= 97%
Max current consumption is 80A
97% < DC <= 100%
No charging allowed
Table 4-1 Low Level Communication – Duty Cycle of CP PWM
4.3.2 DC Charging with High Level Communication
According to [3] and [7], high level communication for DC charging is supported. The
supported charging profile is EIM (External Identification Means).
Caution
Plug and Charge is not supported by the VC-EVCC-P.
The DC charging is done in the following sequence:
> Get charging clearance from vehicle
> Session setup with EVSE
> Parameter exchange with EVSE (charging mechanism, schedule tables…)
> Isolation measurement with EVSE
> Start pre-charge
> Start charging
> Continuously monitoring of charging progress
> Vehicle state monitoring; Stop button monitoring; Temperature monitoring; EVSE
communication; Self-diagnostic of actuators/sensors
> Stop charging
Page 14

Technical Reference VC-EVCC-P
© 2021 Vector Informatik GmbH Version 2.2.0 14
based on template version 6.0.2
Note
For detailed information, please refer to the DC Charging diagram.
The first schedule table from EVSE will always be accepted on the protocol layer but
ignored in the application (charging will start immediately, independent from the received
schedule table).
4.4 Stop Button
The button is monitored continuously when the VC-EVCC-P is active. If the button is
pressed, the charging is stopped.
Alternatively, the VC-EVCC-P checks a CAN signal for charge abortion information.
In case of an error during ACD retraction the VC-EVCC-P disables immobilization of the
vehicle after driver confirmation of full clearance of the vehicle via pushing the Stop Button.
4.5 StopCharge CAN Signal
The StopCharge CAN Signal is monitored continuously when the VC-EVCC-P is active and
the feature is activated. If the StopCharge CAN Signal is set to pressed, the charging is
stopped.
4.6 Clamp 15 Signal Input
For a discrete wakeup of the ECU instead of a CAN network wakeup the Clamp 15 signal
input may be used to wake the ECU and keep it awake. Clamp 15 has to be available during
the whole OppCharge sequence.
4.7 Status LEDs
The charging status can be displayed via three LEDs which can be controlled via CAN
messages by an external ECU. For more details please refer to the User Manual of the VC-
EVCC-P.
4.8 High Side Outputs
Caution
If the VC-EVCC-P suffers from an unintentional GND contact loss, the freewheeling
diode inside HSOUT4 may lead to an unexpected flow of current from HSOUT4 via its
external load to GND.
As this may lead to undefined behavior of the external load (e.g. a BMS relay), the
usage of HSOUT4 must be considered with care.
If in doubt, please contact the Vector support.
Page 15

Technical Reference VC-EVCC-P
© 2021 Vector Informatik GmbH Version 2.2.0 15
based on template version 6.0.2
Three High Side Outputs are available for general purposes which can be controlled via
CAN signals by an external ECU. For more details please refer to the User Manual of the
VC-EVCC-P.
Caution
If the High Side Outputs of the VC-EVCC-P are used, measures must be taken to
ensure a load current greater than 15mA (HSOUT0, HSOUT1) respectively 330mA
(HSOUT4).
An appropriate load resistor must be calculated depending on the supply voltage.
Otherwise, the VC-EVCC-P will detect an OpenLoad error which leads to a switch-off
of the respective High Side Output.
4.9 Reprogramming of the ECU Software
Reprogramming will be done via diagnostic CAN (CAN0). Therefore, the ISO 14229 UDS
protocol will be used. The following reprogramming features are supported:
Download of one logic block of application and basic software
Download of one logic block of Ethernet transceiver firmware
Download of CWG software
Security via CRC (no signature)
Updater for the flash bootloader itself is not supported
4.10 Self-Diagnostics
The VC-EVCC-P continuously monitors all relevant inputs and outputs. The information is
available in the self-diagnostic messages of the outputs.
In addition to that the self-diagnostic also includes faults during charging or in case of internal
faults.
4.11 ECU State Handling
An ECU wakeup is performed due to following reasons:
Clamp 15 signal
CAN wakeup
Stop button pressed
Control Pilot Pin active
Wake up from real time clock
Page 16

Technical Reference VC-EVCC-P
© 2021 Vector Informatik GmbH Version 2.2.0 16
based on template version 6.0.2
If the ECU is active there are the following awake reasons possible to stay active:
Clamp 15 signal
Control Pilot activity
CAN active
Active Diagnostic session
Active OppCharge charging session
In all other cases, the VC-EVCC-P will go to sleep.
4.12 Vehicle Immobilization (OppCharge only)
The VC-EVCC-P starts immobilization of the vehicle as soon as the EVSE is requested to
start movement of the ACD. The immobilization of the vehicle is kept active until the EVSE
is requested to retract the ACD and the EVSE successfully responds about the ACD back
at its home position.
In case of errors during ACD movement the VC-EVCC-P keeps the vehicle immobile and
indicates an error value via CAN (see dbc. for details). In this case the driver has to confirm
safe position of the ACD via pushing the Stop Button.
4.13 Configuration of Software
The VC-EVCC-P allows configurations of the firmware on the diagnostic channel:
Baudrate adjustment between 250 kBaud, 500 kBaud and 1 MBaud on the J1939 CAN
Automatic switch of high side output to wakeup other ECUs
Charging stop user interaction via charging stop button or dedicated CAN message
Configurable message cycle times of several messages
Security Key Constant
4.14 Charging Arbitration
The charging arbitration enables the operation of a VC-EVCC-P together with a VC-VCCU
on the same CAN channel. It targets use cases which require two charging options
(pantograph and charging inlet) per vehicle but only one option is used at a time.
For charging arbitration, the VC-EVCC-P provides the following configurations on the
diagnostic channel:
> Configuration of Primary Source Address
> Configuration of Secondary Source Address
> Activation/Deactivation of Charging Arbitration
For more details, please refer to the User Manual of the VC-EVCC-P [6].
Page 17

Technical Reference VC-EVCC-P
© 2021 Vector Informatik GmbH Version 2.2.0 17
based on template version 6.0.2
5 Qualification
This section describes the qualification of the VC-EVCC-P. The qualification of Vector ECUs
is executed by accredited test labs according to international standards. Documents with
detailed test specification and test results are not provided. Further details on the performed
tests could be available on individual request.
5.1 Configuration
The qualification of the VC-EVCC-P design has been performed in the following
configuration of the hardware.
Feature
Configuration
High-speed CAN
Channel
Termination
Ground coupling
CAN0
not populated
capacitive (100nF)
CAN1
120Ω
directly connected
CAN2
120Ω
capacitive (100nF)
20mA LED Output
> PWM dimming
200mA High-Side Output
> Static digital
5A High-Side Output
> Freewheeling diode
> Static digital
5A H-Bridge
> Static digital
IP Protection Class
> Housing sealed
Table 5-1 Qualification Configuration
5.2 Electrical Tests
The following electrical tests have been performed:
E-01 Overvoltage
E-05 Load dump
E-06 Superimposed alternating voltage
E-07 Slow decrease and increase of supply voltage
E-08 Slow decrease, quick increase of the supply voltage
E-08 Reset behavior at voltage drop
E-10 Short interruptions
E-11 Starting profile
Page 18

Technical Reference VC-EVCC-P
© 2021 Vector Informatik GmbH Version 2.2.0 18
based on template version 6.0.2
E-12 Voltage curve with interactive generator regulation
E-13 Single line interruption
E-14 Multiple line interruption
E-15 Reversed voltage
E-16 Ground reference and supply offset
E-17 Short circuit protection
E-19 Quiescent current
E-22 Overcurrent
E-23 Direct current supply voltage
E-24 Voltage transient to engine rpm steps
E-25 Momentary drop in supply voltage
5.3 EMC Test
The following tests have been performed:
EMC1 - RF-emissions - Measurements at the artificial network (AN-Test, CISPR
25:2008-03)
EMC2 - RF-emissions – Measurements with antennas (RE-Test, CISPR 25: 2008-03)
EMC7 - Transient emissions on supply cables (CTE-Test, ISO 7637-2: 2011-03)
EMC9 - RF-immunity to interference – Bulk current injection (BCI-Test, ISO/DIS 11452-
4: 2010-01)
EMC10 - RF-immunity to interference – Using antennas (ALSE-Test, ISO 11452-2:
2004-11)
EMC14 - Transients on supply lines (TSUP-Test, ISO 11452-2: 2004-11)
EMC15 - Transients on lines except supply lines (TOL-Test, ISO 7637-3: 2007-07)
EMC16 - Electrostatic discharge – Handling Test (ESDH, ISO 10605: 2008-07)
EMC17 - Electrostatic discharge – Direct discharge (ESDD, ISO 10605: 2008-07)
EMC18 - Electrostatic discharge – Indirect discharge (ESDI, ISO 10605: 2008-07)
5.4 Climatic Tests
The following climatic tests have been performed:
K-01 High / Low temperature storage test
K-02 Temperature step test
K-03 High / Low temperature operation test
K-05 Rapid change of temperature with specified transition duration
Page 19

Technical Reference VC-EVCC-P
© 2021 Vector Informatik GmbH Version 2.2.0 19
based on template version 6.0.2
K-06 Salt spray tests - Leakage and function test
K-07 Salt spray tests - Corrosion test
K-09 Humid heat, cyclic test - Composite temperature/humidity cyclic test
K-10 Protection against water
K-11 Steam jet test
K-12 Ice water shock test - Splash water test
K-13 Ice water shock test - Submersion test
K-14 Damp heat, steady-state test
K-15 Humid heat, cyclic test - Dewing test
K-19 Temperature cycle with specified change rate
5.5 Mechanical Tests
The following mechanical tests have been performed:
M-01 Free fall
M-03 Dust test
M-04 Vibration test (Profile D)
M-06 Mechanical shock (Severity II, Drivers door)
5.6 Life Tests
The following life tests have been performed:
L-02 High temperature endurance test
L-03 Alternating temperature endurance test
Assumed Life time: 50,000h / 15 Years
5.7 Chemical Tests
The following chemical tests have been performed:
AA - Diesel fuel
BA - Engine oil
BE - Greases
BF - Silicone oil
CC - Antifreeze fluid
CD - Urea
CG - Protective lacquer remover
Page 20

Technical Reference VC-EVCC-P
© 2021 Vector Informatik GmbH Version 2.2.0 20
based on template version 6.0.2
CA - Battery fluid
CE - Cavity protection
CF - Protective lacquer
DF - Cold cleaning agent
DJ - Ammonium containing cleaner
EB - Transpiration
ED - Refreshment containing caffeine and sugar
EF - Cream, coffee whitener
DB - Vehicle washing chemicals
DC - Interior cleaner
DD - Glass cleaner
DE - Wheel cleaner
EE - Runway de-icer
AE - Methanol
DG - Acetone
DH - Cleaning solvent
DK - Denatured alcohol
Page 21

Technical Reference VC-EVCC-P
© 2021 Vector Informatik GmbH Version 2.2.0 21
based on template version 6.0.2
6 Industrialization
This section describes the elements of the VC-EVCC-P industrialization, which are installed
and released by Vector:
> Production engineering
> Production requirements
> Quality requirements
> Control plan
> P-FMEA
> D-FMEA
> Production installation
> Series Production line for electronic parts
> Automated Optical Inspection (AOI)
> In Circuit Test (ICT)
> Production line for mechanical assembly
> Leakage test
> Generic End of Line Test (EOL)
> Production Specification
> The common part of production is described in the Production Specification and is
released by Vector.
Note
The documents listed in this chapter are for internal documentation of processes only.
They are not released for external use or delivery to Customer.
Page 22

Technical Reference VC-EVCC-P
© 2021 Vector Informatik GmbH Version 2.2.0 22
based on template version 6.0.2
7 Delivery Content
The VC-EVCC-P hardware is packed in a single packaging and shipped as off-the-shelf
product from Vector warehouse. The standard delivery for software and documents takes
place via download link as ZIP file from the Vector homepage.
7.1 ECU
Based on the offer and order the customer will receive an off-the-shelf product:
> VC-EVCC-P Series (No.: 89518)
> VC-EVCC-P Evaluation (No.: 89519)
The ECUs are stored inside the cardboard package. The goods will be extracted from the
stock as per ordered quantity and packed individually within our logistics department in
Stuttgart.
7.2 Packaging
The VC-EVCC-P is packed in a single box (non ESD) with the following description:
> Approximate sizing of a single package: 250 mm x 191 mm x 64 mm (L x W x H,
approximately)
> Approximate weight: 0,74 kg (approximately, Cardboard 0,18 kg + ECU 0,56 kg)
Figure 7-1 VC-EVCC-P packed in Cardboard Package
Several ECUs in one shipment are packed in overpacks, e.g.:
> 5 ECUs: Approximately 450 x 320 x 320 mm, 5 kg
> 10 ECUs: Approximately 560 x 360 x 310 mm, 10 kg
> 25 ECUs: Approximately 800 x 600 x 400 mm, 25 kg
Page 23

Technical Reference VC-EVCC-P
© 2021 Vector Informatik GmbH Version 2.2.0 23
based on template version 6.0.2
7.3 Software
> VC-EVCC-P for vFlash package (.vflashpack)
> CANoe project (.cfg)
> CAN J1939 communication matrix (.dbc)
> WiFi CAN communication matrix (.dbc)
> Diagnosis CAN communication matrix (.dbc)
> Diagnosis description file for CANdela Studio (.cdd)
7.4 Technical Documents
> Release Notes VC-EVCC-P (.pdf)
> Technical Reference VC-EVCC-P (.pdf)
> Technical Reference CAN-WiFi-Gateway (.pdf)
> User Manual VC-EVCC-P (.pdf)
> User Manual CAN-WiFi-Gateway (.pdf)
> Charging Sequence Description OppCharge (.pdf)
> Charging Sequence Description Roof-mounted Pantograph (.pdf)
> Envelope model 3D (STEP)
> VC-EVCC-P technical drawing (2D)
> VV-Report VC36PLC-24 (.pdf)*
7.5 Quality Documents
The following quality documents can be made accessible to a customer representative
remotely:
> PFMEA (Top 10)
> Control Plan
Page 24

Technical Reference VC-EVCC-P
© 2021 Vector Informatik GmbH Version 2.2.0 24
based on template version 6.0.2
*will be provided if required
Page 25

Technical Reference VC-EVCC-P
© 2021 Vector Informatik GmbH Version 2.2.0 25
based on template version 6.0.2
8 Glossary and Abbreviations
Term
Description
AC
Alternating Current
ACD
Automatic Connection Device
AUTOSAR
AUTomotive Open System ARchitecture
CAN
Controller Area Network
.cdd
CANdela Diagnostic Description File
CP
Control Pilot
CPU
Central Processing Unit
CRC
Cyclic Redundancy Check
CWG
CAN-WiFi-Gateway
DC
Direct Current
DCB
Disconnecting Circuit Breaker
ECU
Electronic Control Unit
EV
Electric Vehicle
EVSE
Electric Vehicle Supply Equipment
LED
Light Emitting Diode
PLC
Power Line Communication
PE
Physical Earth
PP
Proximity Pin / Plug Present
PWM
Pulse-Width Modulation
QM
Quality Management
RAM
Random Access Memory
RESS
Rechargeable Energy Storage System
RMP
Roof-mounted Pantograph
UDS
Unified Diagnostic Services
V2G
Vehicle-to-Grid
VAS
Value Added Services
VC-EVCC-P
Vector Controller – Electric Vehicle Communication Controller for
Pantograph
VDV
Verband Deutscher Verkehrsunternehmen
WiFi
Wireless communication according to IEEE-802.11
 Loading...
Loading...