
VBrick
EtherneTV Portal Server
ETV v4.1 Portal Server
Admin Guide
June 21, 2007
4410-0118-0006

Copyright
© 2007 VBrick Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
12 Beaumont Road
Wallingford, Connecticut 06492, USA
www.VBrick.com
This publication contains confidential, proprietary, and trade secret information. No part of this document may be
copied, photocopied, reproduced, translated, or reduced to any machine-readable or electronic format without
prior written permission from VBrick. Information in this document is subject to change without notice and
VBrick Systems assumes no responsibility or liability for any errors or inaccuracies. VBrick, VBrick Systems, the
VBrick logo, StreamPlayer, and StreamPlayer Plus are trademarks or registered trademarks in the United States and
other countries. Windows Media is a trademarked name of Microsoft Corporation in the United States and other
countries. All other products or services mentioned in this document are identified by the trademarks, service
marks, or product names as designated by the companies who market those products. Inquiries should be made
directly to those companies. This document may also have links to third-party web pages that are beyond the
control of VBrick. The presence of such links does not imply that VBrick endorses or recommends the content of
any third-party web pages. VBrick acknowledges the use of third-party open source software and licenses
VBrick products. This freely available source code is posted at http://www.vbrick.com/opensource.
in some
About VBrick Systems
Founded in 1997, VBrick Systems, an ISO 9001 certified vendor, is a privately held company that has enjoyed rapid
growth by helping our customers successfully introduce mission critical video applications across their enterprise
networks. Since our founding, VBrick has been setting the standard for quality, performance and innovation in the
delivery of live and stored video over IP networks—LANs, WANs and the Internet. With thousands of video
appliances installed world-wide, VBrick is the recognized leader in reliable, high-performance, easy-to-use
networked video solutions.
VBrick is an active participant in the development of industry standards and continues to play an influential role in
the Internet Streaming Media Alliance (ISMA), the MPEG Industry Forum, and Internet2. In 1998 VBrick
invented and shipped the world's first MPEG Video Network Appliance designed to provide affordable DVDquality video across the network. Since then, VBrick's video solutions have grown to include Video on Demand,
Management, Security and Access Control, Scheduling, and Rich Media Integration. VBrick solutions are
successfully supporting a broad variety of applications including distance learning and training, conferencing and
remote office communications, security, process monitoring, traffic monitoring, business and news feeds to the
desktop, webcasting, corporate communications, collaboration, command and control, and telemedicine. VBrick
serves customers in education, government, healthcare, and financial services markets among others.

Portal Server v4.1 Admin Guide
Organization . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .vii
Getting Help . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . viii
Font Conventions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . viii
Related Documents . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . viii
Printer-Friendly . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ix
1. Introduction
Portal Server Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1
Server Requirements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
Desktop Requirements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
Copyright Protection. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
MySQL . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
Portal Server Features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
End User Features. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
Administrative Features. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
Portal Server Components. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
VBrick Encoders/Decoders . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
ETV Video-on-Demand Servers. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
ETV Set Top Box . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
ETV Network Video Recorder . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
ETV Live Portal Server. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
VB-PC Remote Controller . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Amino Set Top Box. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
WM IP Receiver . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
Portal Server Installation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .10
Download Components . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
Port Requirements. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
License Files . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .14
Changing the Title, Header, and Logo . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Admin Console Login . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Admin Console Options . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
Internet Explorer 7.0 Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
Contents
2. Global Settings
Global Assignments . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .21
Custom Fields . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
Customize Streams. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
Add Link . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .29
Stream Restrictions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
Servers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
Add/Modify VOD/FTP Servers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
ETV Portal Server Admin Guide iii

Creating a VOD-D FTP Server. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
Add/Modify Video On Demand Content Folders . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
VBricks. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
Advanced Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
Control Devices . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
Adding Control Devices . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
Adding User-Defined VBIRs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
Connecting Control Devices . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
Configuring Control Devices . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
Learning IR Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
Set Top Boxes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
Recorders . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
Synchronizing the Portal Server and the NVR . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 48
Script Devices . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 48
Scripts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 50
Creating a Script . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 50
Finding VBrick Parameters and Values . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 52
URLs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 53
Add/Modify a URL for a Live Video Stream . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 53
Add VOD Content . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 54
Add Non-VOD Content . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 55
Emergency Broadcast . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 56
Program Names . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .60
Access Logging . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 61
Extended Logging Properties . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 62
Viewing the Access Logs. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 63
3. Server Administration
Modify VOD Content . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 65
Diagnostics. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 67
Status . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 67
Expired Content Log . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .68
Access Control. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 69
Single Sign-On. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 71
Using LDAP Servers with SSL . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 73
Live Presentations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 75
Users . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 75
User Groups. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 75
Resource Groups . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .75
Help . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 76
Logout . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 76
4. Users and User Groups
Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 77
Definitions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .77
Configuring for Users and User Groups . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 79
iv Contents

1. Setup and Configure ETV Components . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 79
2. Choose an Authentication Method . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 79
3. Create User Groups on the Portal Server . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .80
4. Create Resource Groups on the Portal Server . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 81
5. Create Users on the ETV Portal Server . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 81
6. Assign Resources to Users or User Groups . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 81
Users . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 81
Add/Modify User Information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 83
Add/Modify User's Group Assignments . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 84
Add/Modify User's Resource Group Assignments . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 84
Add/Modify Live Channel Privileges . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 84
Allow Access to Specific FTP Servers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 85
Allow Access to Specific Recorder Servers. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 85
Allow Access to Specific VOD Servers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 85
Allow Access to Specific VOD Content . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 85
Allow Viewing by Content Type . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 85
Allow Content Publishing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 86
Allow Content Recording . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 86
Default Content Recording . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 86
Allow VBrick Access. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 86
STB Access . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .87
Schedule Privileges . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 87
Emergency Broadcast Privileges . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 87
Copyright Restrictions & Expiration Privileges . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 87
User Groups . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 87
Add/Modify Group Information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 88
Add/Modify Group's User Assignments . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 88
Add/Modify Group's Resource Assignments . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 88
Resource Groups . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 89
Add/Modify Resource Group Information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 89
Add/Modify User's Resource Assignments . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 90
Add/Modify Group's Resource Assignments . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 90
STB Authentication . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .90
Authentication by PIN . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 91
Authentication by Host Name or IP Address. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 91
5. Configuring for SSL
Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 93
1. Generate a Certificate Request . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 93
2. Submit a Certificate Request . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 94
3. Install the Certificate . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 94
4. Configure ETV Resources for SSL . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 95
6. Network Video Recording
NVR Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .99
Standard NVR . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 100
ETV Portal Server Admin Guide v

Standalone NVR . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 100
NVR Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 101
Configuring a Standard NVR . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 101
Configuring a Standalone NVR. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 102
Using an NVR . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 102
NVR Hardware . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 103
7. VBPresenter
Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 105
Working with Presentations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 106
Configuring MCS for VBPresenter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 106
Configuring an FTP User . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 106
Configuring a Presentation User . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 106
Configuring for Live Presentations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 107
Configuring for Stored Presentations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 109
8. Auto Content Ingestion
AutoIngest Content . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .111
AutoIngest Content via XML . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 113
Using the XML Template . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 113
Removing MPEG-4 Closed Captions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 114
9. Database Backup
Introduction. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 117
Database Backup. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 117
Database Restore. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 118
10. Amino Set Top Box
Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 119
Connecting the Amino. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 119
Configuring the Amino . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 120
Changing the IP Address . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 121
Configuring the Remote Control for a TV . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 121
Configuring the Amino for a Widescreen . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 121
Setting the TV Display Format . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 122
11. ACNS Configuration
Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 123
ACNS Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 123
VOD-W Server Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 123
Portal Server Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 124
ACNS Server Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 125
Verify Installation. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 125
Index
vi Contents

Portal Server v4.1 Admin Guide
This Portal Server Admin Guide is written for anyone who will be using or evaluating the
VBrick EtherneTV Portal Server. This includes system administrators, software developers,
network technicians, and others. The ETV Portal Server is a web-based portal for accessing
and managing video assets including both live or stored audio and video files. The ETV
Portal Server is a key component in VBrick's EtherneTV Media Distribution System. The
ETV Portal Server provides a simple, intuitive interface that auto-discovers available media
assets in your network. Key components in VBrick's EtherneTV solution include:
• EtherneTV-VOD Video-on-Demand Server – Provides all standard Video-on-Demand
(VOD) features including support for MPEG-1, MPEG-2, MPEG-4, and Windows
Media for maximum flexibility.
• EtherneTV Digital IP Receivers – Leading edge digital set top boxes that provide a low-
cost standalone decoder for DVD-quality MPEG-1, MPEG-2, MPEG-4, and Windows
Media video assets.
• VBrick Hardware Encoders/Decoders – Rugged, reliable video appliances that can
reside anywhere on your network to provide either distributed or high-density centralized
encoding/decoding of MPEG-1, MPEG-2, MPEG-4, and WM (Windows Media) video.
Note The Amino STB is a compact set top box that plays MPEG-2 streams only. It is fully
integrated with the Portal Server and provides access to most Portal Server viewer
functionality. It does not, however, support Access Logging, Scheduling, Device Control,
Emergency Broadcast, or Copyright Restrictions.
Organization
Introduction
Global Settings
Server Administration
Users and User Groups
Configuring for SSL explains how to securely configure the system using the Secure
Network Video
Recording
provides an overview of the application including server and
desktop requirements and an overview of features and
functionality.
explains high-level configuration settings and parameters that
apply to the entire system.
provides detailed explanations of all ETV Portal Server global
settings and configuration options, as well as diagnostics and
status windows.
explains how to configure the system for access control. It
explains how to create users and groups with specific
permissions and access to resources.
Sockets Layer.
explains how to configure and use an NVR to offload recording
tasks from the Portal Server to a separate "recorder server"
machine.
ETV Portal Server Admin Guide vii
VBPresenter explains how to configure and launch rich media presentation
from the Portal Server including those created with VBPresenter.
Auto Content Ingestion
explains auto content ingestion. This is the process whereby
video content is automatically populated on the portal server.
Database Backup
explains how to backup the MySQL database when you transfer
or remove VOD servers. Note that procedure backs up the
database—not video content.
Amino Set Top Box explains how to connect and use the Amino set top box to view
MPEG-1 and MPEG-2 streams.
ACNS Configuration
explains how to configure the Portal Server and Cisco's
Application and Content Networking System (ACNS) to work
together.
Getting Help
If you need help, or more information about any topic, use the online help system. The
online help is cross-referenced and searchable and can usually find the information in a few
seconds. Use the tree controls in the left pane to open documents and the up and down
arrows to page through them. Use the
one or more words in the box and press Enter. The search results will return pages that have
all of the words you entered—highlighted in yellow (Internet Explorer only). The
is not case-sensitive and does not recognize articles (a, an, the), operators (+ and – ), or
quotation marks. You can narrow the search by adding words.
Search box to find specific information. Simply enter
Search box
If you can't find the information you need from the online help, or from your certified
VBrick reseller, you can contact VBrick Support Services
on the web. Support Services can
usually answer your technical questions in 24 business hours or less. Also note that our
publications team is committed to accurate and reliable documentation and we appreciate
your feedback. If you find errors or omissions in any of our documents, please send e-mail to
documentation@vbrick.com
and let us know. For more information about any VBrick
products, all of our product documentation is available on the web. Go to www.vbrick.com/
documentation to search or download VBrick product documentation.
Font Conventions
Arial bold is used to describe dialog boxes and menu choices, for example: Start > All
Programs > VBrick
Courier fixed-width font is used for code elements (C++, HTML) as well as
filenames, directories, etc.
Bold Courier fixed-width font is used to indicate user input in keyboard commands,
scripts, etc.
Folder names and user examples are displayed in this sans serif font.
Italics are used to emphasize specific words or phrases.
Related Documents
EtherneTV Portal Server User Guide
viii Preface

EtherneTV-STB Admin Guide
EtherneTV-STB Quick Start Guide
EtherneTV-NXG Server Quick Start Guide
EtherneTV-VOD W Server Quick Start Guide
EtherneTV-VOD WM Server Quick Start Guide
VBPresenter User Guide
Printer-Friendly
Click on the following link to print a hard copy of the document.
ETV Portal Server User Guide
ETV Portal Server Admin Guide
ETV Portal Server Release Notes
T To save or print a PDF document:
1. Click once to open the PDF document in Acrobat Reader.
2. To save or print a PDF document, right-click and select
Save Target As or Print Target.
ETV Portal Server Admin Guide ix

x Preface

Introduction
Topics in this chapter
Portal Server Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1
Portal Server Features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
Portal Server Components. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
Portal Server Installation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .10
Admin Console Login . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Portal Server Overview
VBrick's EtherneTV Media Distribution System consists of a group of products that includes
the EtherneTV Portal (ETV Portal Server), EtherneTV Encoders, the EtherneTV-VOD
Video-on-Demand Server, EtherneTV Set-Top Boxes and StreamPlayer software. This
integrated system delivers both live and on-demand audio and video over an IP-based
infrastructure. The ETV Portal Server functions as a video portal, permitting end users to
view live and on-demand MPEG-1, MPEG-2, MPEG-4 and WM (Windows Media) streams
on a Window PC, a Macintosh, a Linux PC (or a set top box). The ETV Portal Server comes
as software-only solution that can be installed on a Windows Server or as a pre-configured
hardware/software combination.
Chapter 1
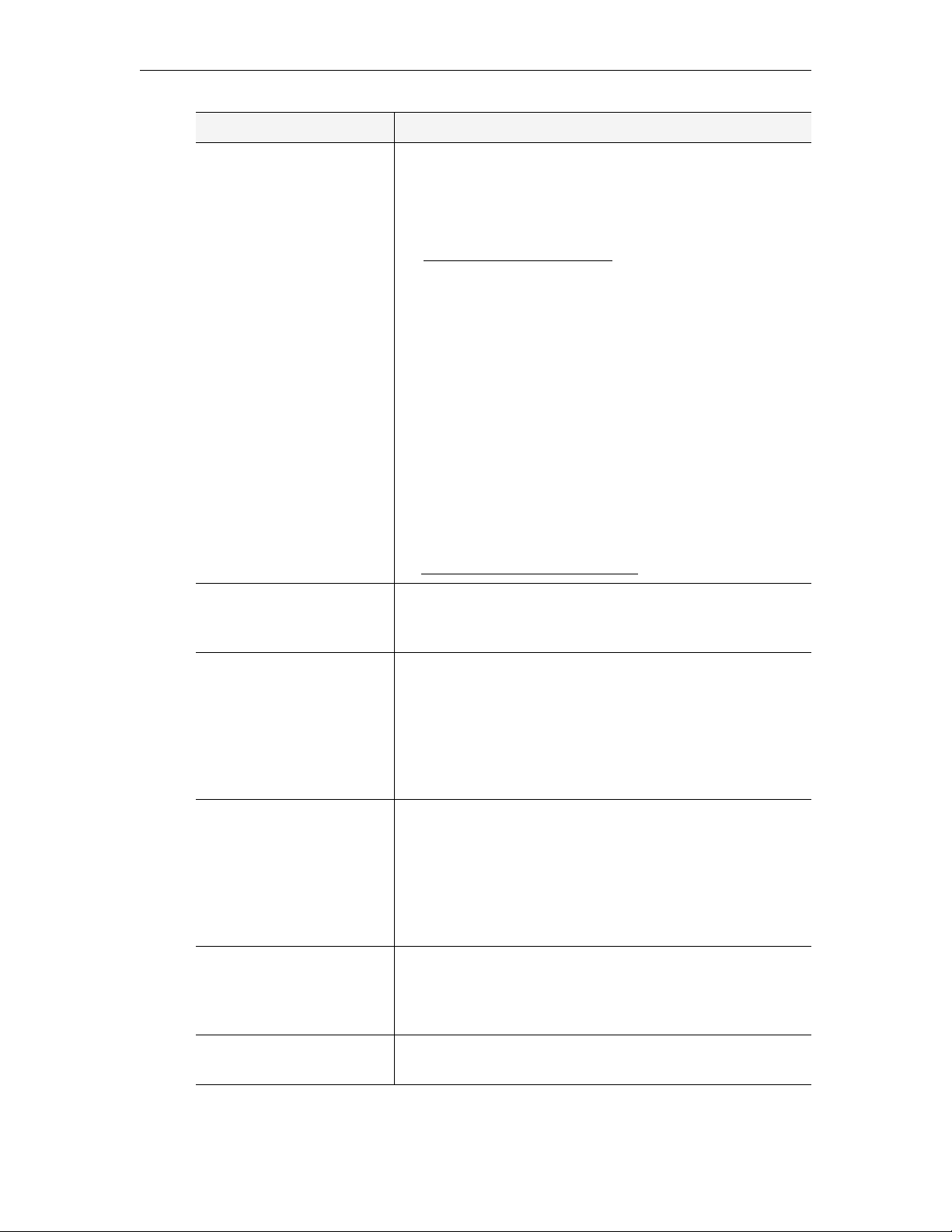
Figure 1. EtherneTV Media Control Server Suite
The VBrick EtherneTV (ETV) Portal Server is a web-based portal for accessing Live and
On-Demand audio and video files. A key component of VBrick's EtherneTV Media
Distribution System, the ETV Portal Server provides a simple interface to easily locate
ETV Portal Server Admin Guide 1

available media assets on your network. Upon accessing the main portal page, users can
navigate or search for specific videos, select the video, and immediately begin viewing DVD
quality video. For on-demand videos, users can Fast Forward/Rewind and Seek to specific
points in the video. Standard access control functionality provides restriction of certain
content to particular users, user groups, or set top boxes. An optional scheduling module
allows users to schedule devices to send video, receive video, record video, or to initiate a
two-way conference.
Server Requirements
The minimum server requirements include:
• Windows 2000 Server or Windows Server 2003 (Web Edition or Standard Edition with
Service Pack 2).
• Pentium IV or Xeon Processor 1.26 GHz Minimum (2 GHz or higher recommended).
• RAM 512 MB Minimum (1 GB or more recommended).
• Hard Drive 36 GB Minimum (larger for frequent recording).
Note VBrick has tested the ETV Portal Server on Windows 2000 Web Server and on
Windows 2003 Server Web Edition and Standard Edition. Note also that ETV Portal
Server also will not operate correctly on a server that is configured as a primary
domain controller or with other network-related services and software.
Desktop Requirements
Windows-based PC and Macintosh users access the ETV Portal Server through a web
browser. For Windows-based PCs, on the first access to the server, VBrick StreamPlayer
software is automatically downloaded to the PC. StreamPlayer software lets end users select a
stream and view TV-quality video directly on a PC. Macintosh users view MPEG-4 video
through the QuickTime player.
Windows PCs
• Windows 98, 2000, or XP (with Service Pack 2).
• 300 MHz Pentium II processor for MPEG-1 streams.
• 500 MHz Pentium III processor for MPEG-2 streams.
• 500 MHz (minimum), 750 MHz Pentium III processor (recommended) for MPEG-4
streams.
• 128 MB RAM.
• SVGA video card 640x480, 256 colors, video card acceleration recommended.
• Windows-compatible sound device.
• Minimum 10 MB hard disk space for installation.
• Microsoft Internet Explorer 6.0 or higher.
• Microsoft Windows Media Player 9.0 or higher.
• Firefox 1.0 or higher
• DirectX Media Version 8.1 and higher.
2 © 2007 VBrick Systems, Inc.

Introduction
Macintosh PCs
• Mac OS X with Safari 1.0 (or higher)
•Firefox for Mac 1.0.4
•QuickTime Player 6.0 or higher.
• Internet Explorer is not supported.
• Intel-based Macintoshes play all streams except WM.
Copyright Protection
The Portal Server uses copyright restrictions and content expiration to protect the rights of
content owners and to enforce rules against unauthorized usage or distribution. Copyright
restrictions are specifically used to enforce license requirements. Content is often restricted
to a limited number of viewers and you may need a license, for example, to view MPEG-2
content. In the Portal Server,
restrictions for any live, stored, or recorded video. If the number of concurrent viewers
exceeds the configured value, the content will not play. (The
restriction does not apply to viewers who tune in to a scheduled broadcast.)
Content expiration controls the length of time that specific content can be viewed. Content
expiration is used for time-sensitive, copyrighted, or otherwise protected content that cannot
be legally displayed after a specified date or a period of time. Users with appropriate
permissions (see Copyright Restrictions & Expiration Privileges
expiration dates or a viewing period when they use the Add Video feature. The viewing
period starts at the time the content is added to the server. If desired, administrators can
restrict expiration privileges to particular users or groups in which case only those specified
users or groups (and administrators) can set content to expire.
Max. Concurrent Viewers is used to enforce copyright
Max. Concurrent Users
on page 87) can assign
Administrators can also assign an
using the Modify VOD Content
Expiration Date or Viewing Period for any stored video
page. By default, recordings from live streams have no
expiration date. However administrators can set default viewing periods for content recorded
from specific live streams (see "Viewing Periods" in Stream Restrictions on page 30).
The ETV Portal Server enforces content expiration by preventing the streaming or
scheduling of content that is expired or will expire before the scheduled event. Once content
has expired, administrators can set a new expiration date or viewing period. By default,
expired content will remain in storage indefinitely unless you choose to delete it automatically
using the
Set Expired VOD Content Treatment option in Global Assignments.
The Portal Server writes to a log that tracks content expirations; administrators can view or
purge this log as necessary (see Expired Content Log
on page 68). In many installation an
administrator is assigned to monitor and/or renew content that is about to expire. To
facilitate this process, the Portal Server can be configured to automatically generate e-mail
that notifies the designated administrator when content is about to expire by using the option
in Global Assignments
.
ETV Portal Server Admin Guide 3

MySQL
EtherneTV Portal Server is shipped with MySQL as the database. The MySQL database is
installed as part of the Portal Server installation package. If the hardware/software
combination was purchased from VBrick, MySQL will already be installed on your machine;
the default user name is
root. To protect the integrity of the database, you should change the
default password (vbrick_18) after initial installation and periodically thereafter as explained
below. To backup the MySQL database, see Database Backup on page 117.
Note MySQL Query Browser is an Open Source front-end that provides a graphical
interface to the MySQL database. MySQL Query Browser is available with the free
software/open source GNU General Public License at to http://www.mysql.com
T To change the MySQL password:
1. Open a Command Prompt window.
2. At the C: prompt type
3. Type
4. Type
5. Type
mysql -uroot -pvbrick_18 and press Enter.
set password for 'root'@'localhost'=password ('new_password'); (where
'new_password' in single quotes is the new password) and press Enter.
exit.
cd program files\mysql\mysql server 4.1\bin and press Enter.
Portal Server Features
.
End User Features
• Windows-based PCs, Macintoshes, or STBs (connected to televisions or display
monitors) can all access the Portal Server.
• Users can view video at
• Users can view Video-On-Demand assets with full VCR/DVD control, including
Pause, Stop, Fast Forward, Rewind, and Seek.
• Video can be viewed in a preview window or launched in an external, re-sizeable player
window (PC and Macintosh).
4 © 2007 VBrick Systems, Inc.
Full Screen for a television-like user experience.
Play,

Introduction
• Set-Top Box users can use familiar Channel Up/Down keys and other hot keys on the IR
remote control to navigate through video listings.
• Users can search through the list of Live or On-Demand videos by
Description, or other custom fields defined by an ETV Portal Server administrator.
Title, Keyword,
• Users can record and store videos on the EtherneTV-VOD Video-on-Demand server via
ETV Portal Server.
• Users can publish pre-recorded content and thumbnails directly to the VOD server.
• Users can view closed caption text (Windows-based PCs and set-top boxes only).
• Users can launch pre-configured emergency broadcasts. (Optional. Requires Scheduling
module.)
• Users can schedule recordings or broadcasts. (Optional. Requires Scheduling module.)
Figure 2. ETV Portal Server Home Page
Administrative Features
• Access Control - allows administrators to allow/deny access to specific functions of the
ETV Portal Server server. Access control functionality can use the local ETV Portal
Server database or authenticate to an LDAP directory server.
• Clustering support – multiple EtherneTV-VOD Video-on-Demand servers can be
clustered to increase total throughput. The ETV Portal Server will automatically load
balance all servers defined in ETV Portal Server; no additional configuration is
necessary. See Servers
• SSL/TLS security – the ETV Portal Server can be set up to provide encrypted access to
the Login pages and/or the Admin pages. See Configuring for SSL
• Customer defined URLs – can be entered into the system and displayed in the ETV
Portal Server interface. The URLs can point to video assets or other assets such as PDFs
or PowerPoint documents.
ETV Portal Server Admin Guide 5
on page 31 for more.
on page 93.

• Autoingestion to the EtherneTV-VOD server – content placed in autoingestion folders
on the ETV Portal Server will be automatically transferred and ingested into the
EtherneTV-VOD server.
• Customized global messages can display on the ETV Portal Server interface.
• Channel numbers can be assigned to live streams.
• Define a startup channel for STBs – the STB will automatically tune into this channel
when users select the
• Emergency broadcasts – can define pre-configured emergency broadcast templates that
can be launched instantaneously. See Emergency Broadcast
• Status window – shows the status of videos being added, recorded, or ingested.
• Diagnostics window – displays a complete log of system events by source, time, and IP
address.
• Custom fields and streams – the ability to add customized information and search
parameters to live and stored streams.
Live TV option.
Portal Server Components
VBrick Encoders/Decoders
VBrick's VB4000-5000-6000 Series MPEG-2 network video appliances provide DVD quality
video and CD quality audio at 1–15 Mbps of bandwidth. MPEG-2 is the world's most
popular digital compression technology and is used to encode DVDs as well as Digital Cable
and Digital Satellite broadcasts. VBrick's VB4000-5000-6000 Series MPEG-4 encoders and
decoders are versatile and reliable video appliances for one or two-way interactive
communications over low or medium bandwidth IP networks. The VBrick MPEG-4
encoder/decoder can be used for webcasting, multicasting, transcoding, and two-way
interactive video. Designed for streaming over the Internet at lower bit rates (56K, 128K,
384K) and over a LAN at higher rates (1Mbps and above). VBrick's WM (Windows Media)
video appliances provide scalable quality at webcasting rates up to 2 Mbps. It features built-in
live streaming server, automatic multicasting, and state-of-the-art reliability. A key benefit of
the WM appliance is its compatibility with the Windows Media Player, thus eliminating the
need for desktop player installation.
on page 56 for more.
ETV Video-on-Demand Servers
EtherneTV Video on Demand (VOD) servers provide the ETV Portal Server with a source
of available video content organized in folders. The VOD content is displayed by name in the
ETV Portal Server user interface, along with the duration of the video, and associated
descriptions, key words, and other custom information entered by an administrator. You play
content from the VOD server by selecting the program name from the application interface
(see the Portal Server User Guide for details). The ETV Portal Server currently supports all of
the VOD servers shown in Table 1. The configuration for each server is essentially the same
(see Servers
ETV servers can be LAN-based or Internet-based depending on how the range of Internet
addresses is defined (see "Assign LAN/Internet Address Range" in Global Assignments
page 21). VOD servers accessible to Internet users are called Internet-zone servers; VOD
servers assessable to LAN users only (within a secured corporate network and behind a
firewall) are called LAN-zone servers.
6 © 2007 VBrick Systems, Inc.
on page 31 for details) and there is little difference in functionality for end users.
on
Introduction
Content added by users in the LAN zone will be ingested to all VOD servers for which they
have permissions using the Add Video page. Users in the Internet zone have the Add Video
page available only if they have permissions for at least one VOD server that is also in the
Internet zone. Content added by LAN users is added to all configured servers that can handle
the content (for example you cannot add MPEG content to a Windows Media server) and for
which you have permission. The content available for viewing may also be limited by the
server type. For example, Internet users will see only MPEG-4 and Windows Media content
on VOD-D and VOD-WM servers respectively. LAN users however will see all content on
all servers.
Tab le 1 . Supported EtherneTV VOD Servers
Server Type Description Zone
NXG Linux-based NXG1/2 VOD server. LAN only
VOD-W Windows-based VOD-W VOD server. LAN only
VOD-D Darwin Open Source server for Linux, Windows, Mac,
LAN or Internet
etc. Ingests and plays MPEG-4 content only. Requires
an FTP server.
VOD-WMStandard
VOD-WMAdvanced
Microsoft Windows Media Server (unicast only).
Requires an FTP server.
Microsoft Windows Media Server (unicast or
multicast). Requires an FTP server.
LAN or Internet
LAN or Internet
ETV Internet-Based Servers
ETV Portal Server supports the installation of LAN-based servers and Internet-based
servers. As part of an ETV Server installation, you can configure a VOD-D or VOD-WM
server (see Table 1) to run on your LAN or on the public Internet. Before server
configuration, you assign a range of IP addresses that define the LAN domain, or vice versa,
that define the Internet domain. Any IP address outside that range will assumed to be from
an Internet source, or vice versa, from a LAN source. (See "Assign LAN/Internet Address
Range" in Global Assignments
You can purchase an Internet-based Windows Media server from VBrick (in which case it is
configured by VBrick) or you can purchase and configure it yourself using the Microsoft
documentation (not recommended). You can also install a Darwin Open Source server which
is fully-compatible with ETV Portal Server but is not sold or supported by VBrick. (For more
about downloading, installing, and configuring a Darwin server, go to: http://
developer.apple.com/opensource/server/streaming/) As noted, ETV users can be on the
Internet or on a LAN; Internet users can only access MPEG-4 and Windows Media content
stored on Internet-based servers. LAN users can access all content on all servers both inside
and outside the firewall. To summarize, Internet-based servers and users are subject to the
following limitations:
on page 21.)
• Internet servers support MPEG-4 and Windows Media content only.
• Internet servers support unicast only (they do not support multicast).
• Internet ETV users can add video only to VOD servers in the Internet zone.
• Internet users can only see MPEG-4 and Windows Media content stored on Internetbased servers.
ETV Portal Server Admin Guide 7

• Internet servers do not support ETV scheduling features.
ETV Set Top Box
EtherneTV-STBs access the ETV Portal Server through a web browser within the Set Top
Box. Using the Set-Top Box remote control, users can navigate and search for specific ondemand content or live video streams, select a stream, and begin viewing television-quality
video. Set-Top Box users can also record video directly on the ETV Portal Server using the
remote control or the wireless keyboard. See the Set Top Box documentation for more about
how to configure and use an ETV Set Top Box.
ETV Network Video Recorder
The ETV Network Video Recorder and the ETV Live Portal Server are optional components
that are purchased and installed separately. They have different license files that must be
installed separately. See License Files
off-load all recording tasks from the ETV Portal Server machine to one or more separate
"recorder server" machines. This optimizes recording performance and improves ETV Portal
Server performance as well. The Network Video Recorder uses ETV Portal Server
components and typically requires two machines: the ETV Portal Server is installed on one
machine; the Network Video Recorder software is installed on a different machine. Once
installed, the NVR machine is used for all ETV Portal Server recording tasks. See Network
Video Recording on page 99 for more information.
on page 14. The ETV Network Video Recorder lets you
Note A standard ETV Portal Server permits two concurrent recording operations. If you
purchase a Network Video Recorder, the number of concurrent recording operations
(10 or 40) is fixed by the terms of your licensing agreement with VBrick.
ETV Live Portal Server
The ETV Live Portal Server provides ETV functionality that is limited to scheduling and
viewing live streams. It does not integrate with a VOD server and there is no functionality
for browsing a video library. Note the limited options on the navigation footer.
8 © 2007 VBrick Systems, Inc.

Introduction
Figure 3. Live Portal Server User Interface
VB-PC Remote Controller
The VB-PC Remote is a handheld infrared device you can use
to control (stop/start/pause, etc.) any stream running on the
Portal Server. The VB-PC Remote is compatible with Internet
Explorer 6.0 or higher; it is not compatible with Firefox. The
VB-PC Remote can be used for all Portal Server streams
(MPEG-1, MPEG-2, MPEG-4, and WM) and has a
line-of-sight range of approximately 40 feet.
After you manually start a stream using the Portal Server
interface, you can use the VB-PC Remote to control it. When
using the remote controller, the computer running the Portal Server basically acts like a set
top box that you can control with the remote control. The VB-PC Remote includes an IR
Remote Control and an IR Remote Receiver. The computer to which it's attached must have
an available (1.1 or 2.0) USB port. Note that the VB-PC Remote is installed on client machines
connected to the Portal Server. It is not part of the Portal Server installation and must be installed
separately on each client machine. See the VB-PC Remote Product CD for details and installation
instructions.
Amino Set Top Box
The AmiNet110 is a compact set top box for the Portal Server manufactured by Amino
Systems. It connects to a standard TV and only plays MPEG-1 and MPEG-2 streams; no
other streams are selectable for viewing on the Portal Server interface. There is no software
installation required. Simply connect and configure the device as explained in Amino Set Top
Box on page 119. The Portal Server User Guide explains how to use the Amino infrared
remote control unit that comes with the device.
ETV Portal Server Admin Guide 9

WM IP Receiver
VBrick's WM IP Receiver is similar to a conventional set top box but is significantly more
stable, rugged, and reliable. It is designed for 24x7 operation, and built for enterprise
networks that require a high degree of stability, security, and scalability. The WM IP Receiver
is a robust, state-of-art device that meets the demanding requirements of VBrick's
EtherneTV Media Distribution System. The WM IPR plays Windows Media streams from
VBrick WM appliances and Windows Media servers. The WM IPR is also a fully-featured
VBrick EtherneTV client. This means that in addition to the ability to deliver video,
subsequent WM IPR releases will provide scheduling, access logging, and device control
from the Portal Server. For more information about the WM IPR, see the IPR Admin Guide
in the Portal Server online help.
Portal Server Installation
Complete installation instructions for the Portal Server are provided in the ETV Portal Server
Release Notes. Once the Portal Server is installed, end users on Windows, Macintosh, and
Linux machines may be prompted for additional download components as explained below.
This only happens the first time they access the Portal Server. The Portal Server supports a
wide variety of clients and video formats. See Supported VBrick Clients
a complete list.
Download Components
and Video Formats for
Windows PCs
If configured with the appropriate components, Windows PCs (with Internet Explorer
or Firefox) can play all stream types including MPEG-1, MPEG-2, MPEG-4, and
Windows Media. For Windows-based PC users, the Portal Server uses VBrick StreamPlayer
software-based components to decode video streams on user desktops. The Portal Server
downloads these components to each client machine the first time you access the Portal
Server (depending on the
Assignments). No download is necessary for subsequent access. If this is a new installation,
end users must answer
download, you don’t have to restart your computer but must you must close the browser.
These components are downloaded using .cab files.
In certain circumstances however, the use of .cabs is either not allowed or not feasible. In
these cases, VBrick provides an
installs the same components and allows end-users who cannot download .cabs to have full
Portal Server functionality. This installer is located in the
folder.
Note The component download setting will not affect previously-installed components.
For example if you have StreamPlayer installed, you will be able to play MPEG-2
streams regardless of what components you specify for download.
With Firefox, users will also be prompted to install additional components the first time they
launch a stream—if they are configured to receive these download components. Links for the
appropriate stream types (MPEG-1/2/4 and/or WM) will be displayed in the area where the
embedded player is normally displayed. These additional plugins must be installed. Firefox
Specify Components to Download to Clients setting in Global
Yes to security requests to download these components. After a
.msi installer called VBrickComponents.msi. This installer
Program Files\VBrick\MCS\utils
10 © 2007 VBrick Systems, Inc.

Introduction
users will also be required to install an additional plugin when they use Add Video for the
first time (again, if they are configured with this privilege).
Table 2. Supported Operating Systems and Browsers – Windows
Operating System Browser
Windows 2000 Internet Explorer 6.0†, Firefox 1.0†
Windows XP Internet Explorer 6.0†, Firefox 1.0†
†or higher
Locked-Down Windows PCs
As described above, the Portal Server automatically downloads components to client PCs
depending on the Global Assignment setting. This download can be an issue in environments
that have restrictions on client software installation. For playback of WM files, Portal Server
uses the existing Windows Media Player components on the client PC and there is no need
for the extra components to be downloaded. This means that Portal Server and WM can be
used in some but not all restrictive or "locked-down" environments.
Even if downloads are configured, a client PC will still refuse to accept the component
download if the Internet Explorer security feature
disabled. When using Portal Server 4.0 exclusively with WM streams and a WM VOD, the
client PC can refuse to accept the downloaded components and all Portal Server features
except
Add Video will work. In this case you should uncheck the Add Video Utility in Global
Assignments.
Download signed ActiveX controls is
Some sites also require that their PCs be configured with certain Internet Explorer security
settings. The Portal Server will not work on clients with Internet Explorer security set to
High. The Portal Server will work at any level at or below Medium. If you start at High, the
client will still work with Portal Server if you enable Run ActiveX contr ols and plug-i ns,
Script ActiveX controls marked safe for scripting, and Active scripting.
Since firewalls on LAN client PCs can also cause problems with Portal Server, it is
recommended that firewalls be disabled on LAN clients. (In Windows XP with Service Pack
2, the firewall is enabled by default.) Portal Server's support for Internet clients is designed to
work through firewalls. If you have Internet clients with firewalls see the description of
LAN/Internet address ranges in Global Assignments
on page 21.
Macintosh PCs
If configured with the appropriate components, Macintosh PCs (with Safari or Firefox)
can play all stream types including MPEG-1, MPEG-2, MPEG-4, and Windows Media.
(Intel-based Macintoshes play all streams except WM.) In a Macintosh environment, if
downloads are configured in Global Assignments, when you launch the ETV Portal Server
for the first time, the Home page (see Figure 2) displays a link prompting you to download
components that are appropriate for your computer. If you agree, these components are
automatically installed and no additional download is necessary for subsequent access. On
Macintosh PCs, Portal Server functionality is the same as in Windows except that the
feature is not available. Table 3 shows the stream types supported for each
Video
environment; Table 4 shows the operating systems that are tested and supported. Note that
there are certain performance limitations in Macintosh environments; see the ETV Portal
Server Release Notes for information and recommendations.
Add
ETV Portal Server Admin Guide 11
Linux PCs
If configured with the appropriate components, Linux PCs running Fedora or Red Hat
(on Firefox) can play MPEG-1, MPEG-2, and MPEG-4 streams. However, the Portal
Server must download Linux components to each-end user desktop before any streams will
play. This should only be performed by a system administrator. When you access the Portal
Server for the first time, you will see a message in the embedded player window indicating
that the appropriate plugins are not installed. See "Installing Linux Components" in the
Portal Server Release Notes for detailed instructions. On Linux PCs, Portal Server functionality
is the same as in Windows except that the
the stream types supported for each environment; Table 4 shows the operating systems that
are tested and supported. Note that there are certain performance limitations in Linux
environments; see the ETV Portal Server Release Notes for information and
recommendations.
Table 3. Supported Stream Types – Macintosh and Linux
Environment Supported Streams Closed Captions
Add Video feature is not available. Table 3 shows
Macintosh † Safari – MPEG-1, MPEG-2,
MPEG-4, WM ††.
Firefox – MPEG-1,
MPEG-2, MPEG-4, WM.
Linux Firefox – MPEG-1,
MPEG-2, MPEG-4.
† Intel-based Macintoshes play all streams except WM.
†† RTSPU is not supported.
Table 4. Supported Operating Systems and Browsers – Macintosh and Linux
Operating System Browser †
Mac OS X 10.4 (Tiger) Safari 2.0, Firefox 1.0
Mac OS X 10.3 (Panther) Safari 1.2, Firefox 1.0
Linux Red Hat 9.0 Firefox 1.0
Linux Fedora Core 3 Firefox 1.0
Linux Fedora Core 4 Firefox 1.0
† Use version shown or higher.
Supported for MPEG-1/MPEG-2 streams,
and for MPEG-4 with VBrick plugin.
Supported for MPEG-1/MPEG-2 streams,
and for MPEG-4 with VBrick plugin.
Supported for MPEG-1 and MPEG-2
streams.
Port Requirements
The drawing below, and the table that follows, show the required port configuration for
various Portal Server devices. All ports in the drawing are TCP except as noted.
12 © 2007 VBrick Systems, Inc.

Introduction
Table 5. Port Requirements†
Zone Port(s) Protocol Description
Internet >
DMZ
Internet >
DMZ
DMZ >
Internet
LAN > DMZ 80 TCP Web request from client to MCS.
LAN > DMZ 9875/
LAN > DMZ 21 TCP FTP from VBStar to MCS (auto-FTP to MCS Auto-Ingest
DMZ > LAN 21 TCP FTP from MCS to VBStar (content discovery).
DMZ > LAN 80 TCP Management command from MCS to VBrick/STB.
DMZ > LAN 80/8080 TCP Web service request from MCS to VOD Server (VOD-W/
80 TCP Web request from client to MCS.
9876/9878
21 TCP FTP from MCS to VOD Server (Darwin/Windows Media/
UDP
UDP
9876/
9878
Management/RTSP SAP announce from VBrick to MCS.
FTP).
Multicast/Management/RTSP SAP announce from VBrick
to MCS.
directory).
NXG).
ETV Portal Server Admin Guide 13
Zone Port(s) Protocol Description
DMZ > LAN 21 TCP FTP from MCS to VOD Server (Darwin/Windows Media/
FTP).
LAN > DMZ 21 TCP FTP from VOD Server (NXG/VOD-W) to MCS.
DMZ > LAN 135 TCP Management command from MCS to Windows Media
(DCOM).
DMZ > LAN 80 TCP Web service request from MCS to Network Video Recorder.
DMZ > LAN 80 TCP Web service request from Network Video Recorder to MCS.
DMZ > LAN 389 TCP LDAP lookup from MCS to LDAP Server (e.g. Active
Directory).
† All ports are TCP except as noted.
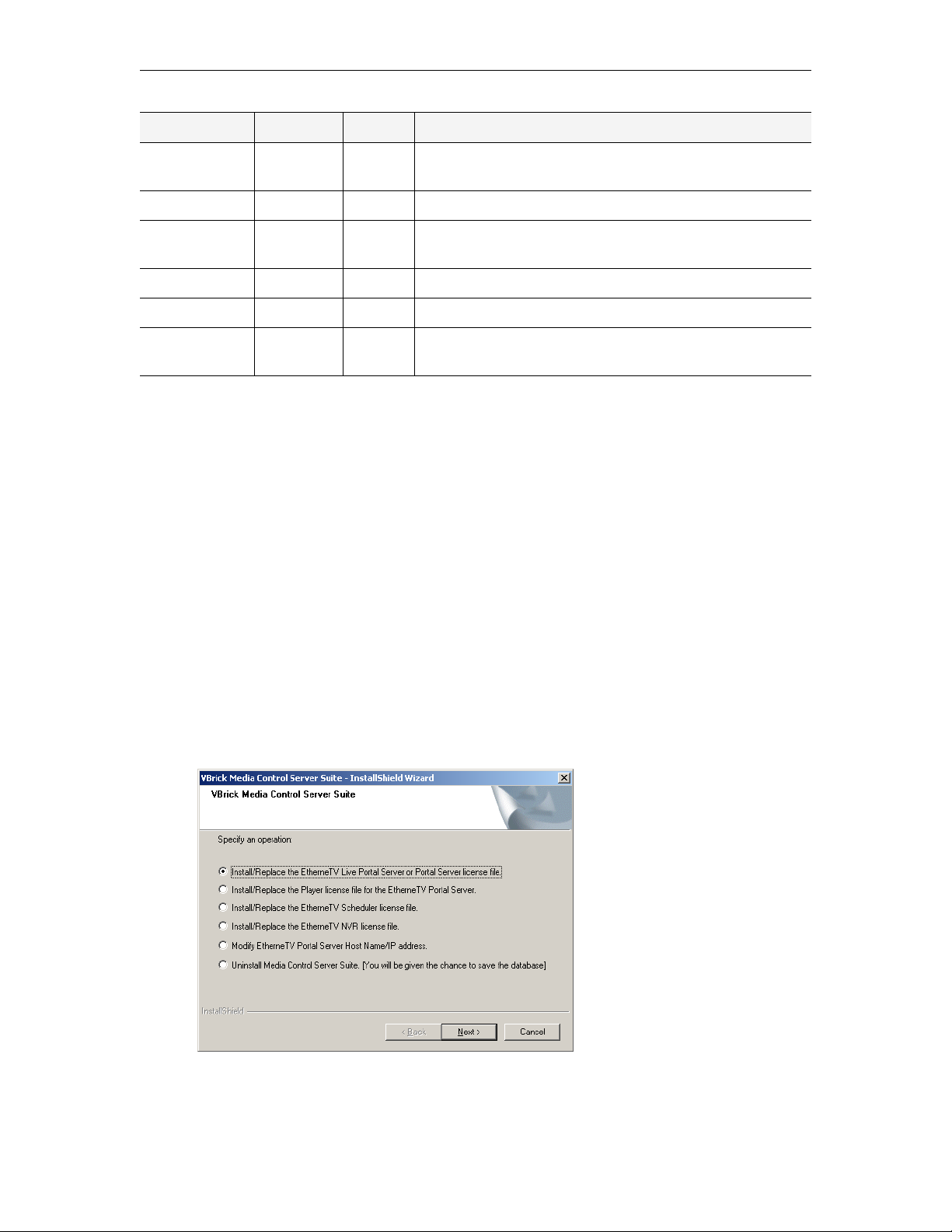
License Files
You are prompted to install a license (.lic) file as part of the ETV Portal Server installation
process. Different Portal Server functionality is available depending on the type of license
you purchase and install. (For example if you do not install a Scheduler license, you will not
see a
Scheduled Programs, as shown above, option in the Portal Server client application.)
After initial installation you can install a different license as necessary by using Add or
Remove Programs
.
T To install or modify a Portal Server license file:
1. Go to
2. Click
3. Click
Start > Control Panel > Add or Remove Programs > VBrick Media Control
Server Suite
.
Change/Remove and select the appropriate license file type (see below).
Next, then browse to the file and click Open.
4. When done, manually close the window and launch the application. There is no need to
restart the host machine.
14 © 2007 VBrick Systems, Inc.

Table 6. License Files
License File Description License Errors
Introduction
Live Portal Server
or Portal Server
Either a standard ETV Portal Server license file
or a Live Portal Server (see ETV Live Portal
Server on page 8.) license file.
Player The embedded Windows Media Player has
restrictions on the number of licensed users. Use
this option to select a license file that modifies
the number of allowed users for various
MPEG-1, MPEG-2, and MPEG-4 streams.
Scheduler Enables the broadcast or recording of future
events. See the ETV Portal Server User Guide for
more information.
Network Video
Recorder
A Network Video Recorder is a standalone
recorder option that can speed up recording
operations and/or enhance Portal Server
performance. (See ETV Network Video Recorder
on page 8.)
Modify Host Name
or IP Address
Lets you auto-detect or manually change the
Portal Server Host Name. This name must match
the machine name on which ETV Portal Server is
installed. If you change the host machine name,
use this option to change the Portal Server Host
Name.
If not installed, error page
displayed at login.
If not installed, popup
message displayed when
you try to launch a
stream.
If not installed, the Add
option will not be shown
on Scheduler page.
If not installed, there will
be a "record" failure for
more than two concurrent
record requests.
Not applicable.
Uninstall Media
Control Server
Suite
Changing the Title, Header, and Logo
You can change various images on the Portal Server client, the VBrick set top box, and the
Amino set top box as explained below. On the Portal Server you can also change the default
title (
VBrick Systems) that is superimposed on the header image Figure 4) of the user
interface. To change this title go to
title or leave the title blank by entering at least one space. (Note that the title is always
displayed in white text and may not be visible if you use a light-colored background image.)
This change will be retained through subsequent software upgrades. You can also change the
header and logo images on the Portal Server and the set top boxes but these changes are not
retained when you upgrade the application. Use care when making any changes. It is always a
good idea to copy and save the orignal image files. For best results, open and view each image
in an editor before making any changes. Note that you cannot change any images on the
Admin user interface.
Figure 4. Header Image
Remove all ETV Portal Server components. You
are prompted to save the database as desired.
Global Assignments > Change Title, then enter a new
Not applicable.
ETV Portal Server Admin Guide 15
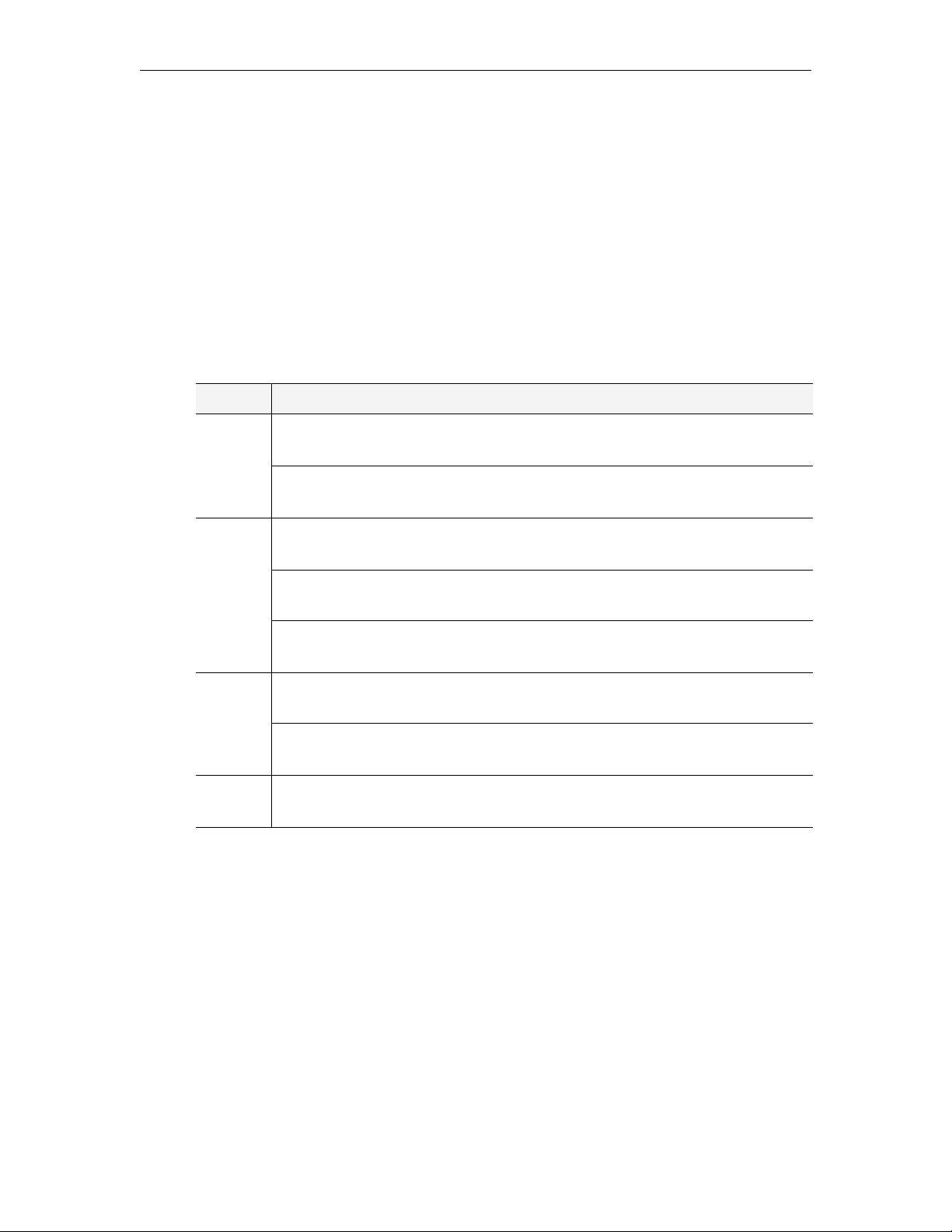
Figure 5. Logo Image
Table 7 shows the images you can change on the Portal Server and the set top boxes. Do not
modify or change any other images. You can replace any .jpg image but it must have the same
dimensions in pixels (for example 1003x50) as the original image. It must also have the same
security settings. To view the security settings, right-click on the image, then select Properties
and go to the Security tab. If you are prompted for a user name and password when opening
the Portal Server user interface after replacing an image, it is likely that the security profile of
the new image does not match the profile of the image you just replaced.
Table 7. User Interface Images
Interface Image
Portal
Server
Header image:
C:\Program Files\VBrick\MCS\Images\topBanner-1003x50_PS.jpg
Logo image:
C:\Program Files\VBrick\MCS\Images\main_VBrick_logo.gif
VBrick
STB
Header image for MCS Portal Server:
C:\sfwapp\Components\WebApp\MCS\images\STB\EtherneTV-Top-STB_PS.jpg
Header image for MCS Live Portal Server:
C:\sfwapp\Components\WebApp\MCS\images\STB\EtherneTV-Top-STB _LPS.jpg
Logo image:
C:\sfwapp\Components\WebApp\MCS\images\STB\PoweredByVBrick.gif
Amino
STB
Header image:
C:\sfwapp\Components\WebApp\MCS\MCS_Amino\images\EtherneT V_logo_STB_20.jpg
Logo image:
C:\sfwapp\Components\WebApp\MCS\MCS_Amino\images\vbrick_logo_st b.gif
WM IPR Logo image:
C:\sfwapp\Components\WebApp\MCS\WMIPR\banner.jpg
Admin Console Login
The ETV Portal Server can be administered from Windows-based PCs using Internet
Explorer 6.0 or higher only. The Admin Console pages are best viewed at 1024x768
resolution. The Admin Console is not supported on Macintoshes or Set Top Boxes, or with
Firefox or other browsers. In order to access the administrative functions enter the following
address in the Internet Explorer browser of the PC where
myserveraddress is the host name
or IP address of the ETV Portal Server. The session will timeout after 20 minutes of
inactivity.
http://myserveraddress/admin/
16 © 2007 VBrick Systems, Inc.
admin is both the default user name and password.
Introduction
Note As a standard best practice, VBrick recommends changing the default administrator
User Name and Password. Go to
Global Settings > Global Assignments on the
Admin Console.
Admin Console Options
Login to the ETV Portal Server Admin pages with a valid user name and password to display
the following window. This window provides access to all admin configuration options.
ETV Portal Server Admin Guide 17
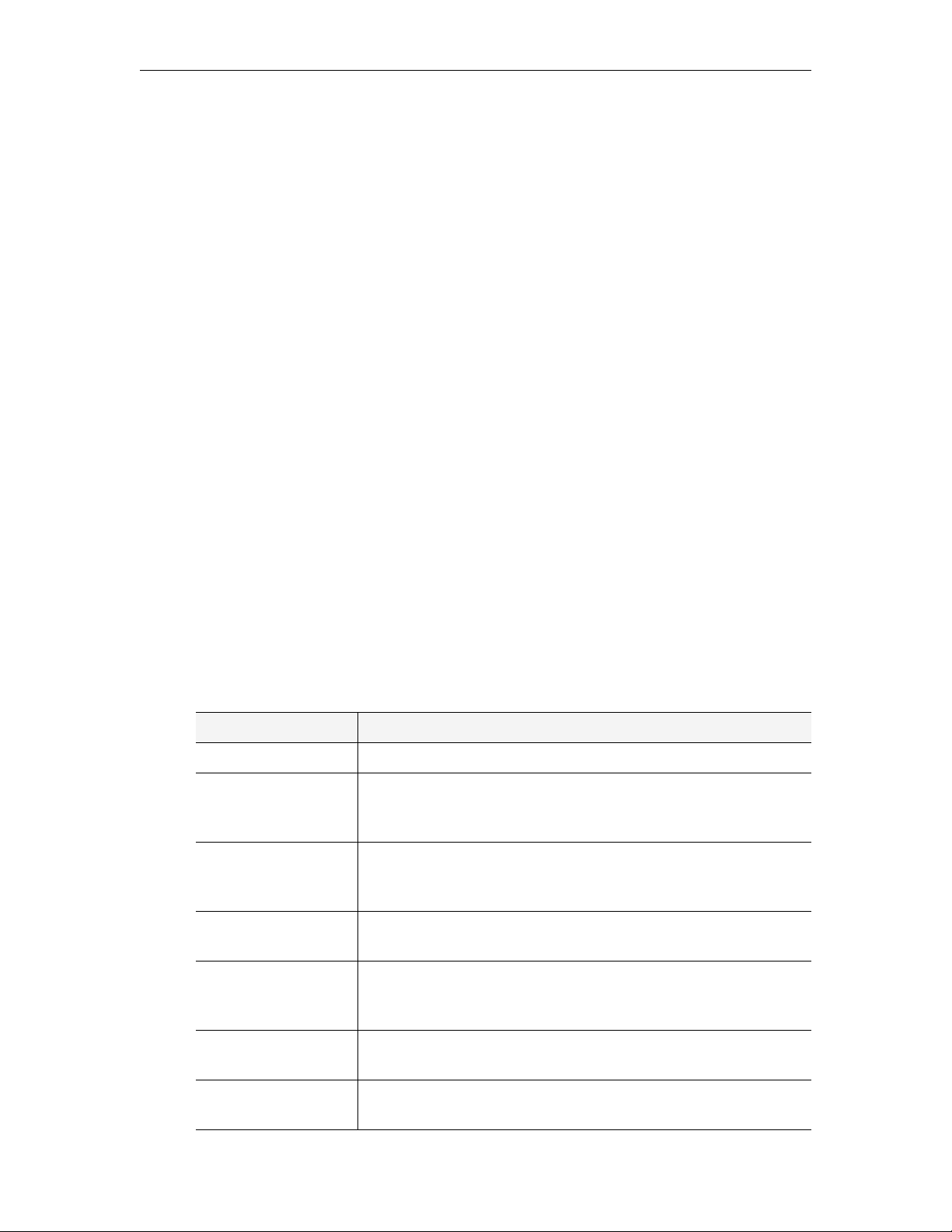
Table 8. Admin Options
Option Description
Getting Started The ETV Portal Server splash page shown above.
Global Settings Provides system-wide configuration parameters to connect to
VBrick encoders and VOD servers as well as to customize the look
of the ETV Portal Server pages.
Modify VOD Content Provides the ability to Move, Rename, or Delete assets on the
EtherneTV-VOD Video-on-Demand server. (Not supported on
some legacy NXG servers.)
Diagnostics Displays system log messages by source, time, and (generally) IP
address.
Status Shows the status of events in progress including recordings, Add
Video commands, ingestion to the VOD server, and FTP
downloads.
Expired Content Log Shows all expired content still present on the Portal Server. Use
Purge All to delete unwanted content.
Access Control Provides the ability to limit access to the ETV Portal Server
system to different users or groups of users.
18 © 2007 VBrick Systems, Inc.

Introduction
Option Description
Live Presentations Provides the ability to view and remove current live presentations
from the Live Broadcasts page.
Users† Used in conjunction with Access Control to limit access to the
ETV Portal Server system to different users.
User Groups† Used in conjunction with Access Control to limit access to the
ETV Portal Server system to different groups of users.
Resource Groups† Used in conjunction with Access Control to group resources
which can then be provided to users or user groups.
Help Displays the ETV Portal Server online help system in a new
window.
Logout Logs out the user who is currently logged in.
† Users, User Groups, and Resource Groups are only displayed if Access Control is
enabled. See Users and User Groups
on page 77 for a description of these functions.
Internet Explorer 7.0 Configuration
The Admin Console and the Portal Server user interface support the browsers shown in
Table 2 and in Table 4. When using Internet Explorer 7.0, there are additional security
settings required for compatibility with the Portal Server.
T To configure the Portal Server for Internet Explorer 7.0:
1. Go to
2. Under
Tools > Internet Options > Security and select Custom level.
Active X controls and plugins set the following parameters:
•
Allow previously unused ActiveX controls to run without prompt – Enable
Automatic prompting for ActiveX controls – Disable
•
Display video and animation on a webpage that does not use external media
•
player
– Enable
Download signed ActiveX controls – Prompt
•
Run ActiveX controls and plug-ins – Enable
•
Script ActiveX controls marked as safe for scripting – Enable
•
ETV Portal Server Admin Guide 19

20 © 2007 VBrick Systems, Inc.

Global Settings
Global Settings include configuration settings and parameters that apply to the entire system.
Global Settings include all of the following.
Topics in this chapter
Global Assignments . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .21
Custom Fields . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
Customize Streams. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
Stream Restrictions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
Servers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
VBricks. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
Control Devices . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
Set Top Boxes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
Recorders . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
Script Devices . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .48
Scripts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .50
URLs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 53
Emergency Broadcast . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 56
Program Names . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .60
Access Logging . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 61
Chapter 2
Global Assignments
Global Assignment are listed below. Most are self-explanatory and consist of text boxes
where you enter appropriate values.
ETV Portal Server Admin Guide 21

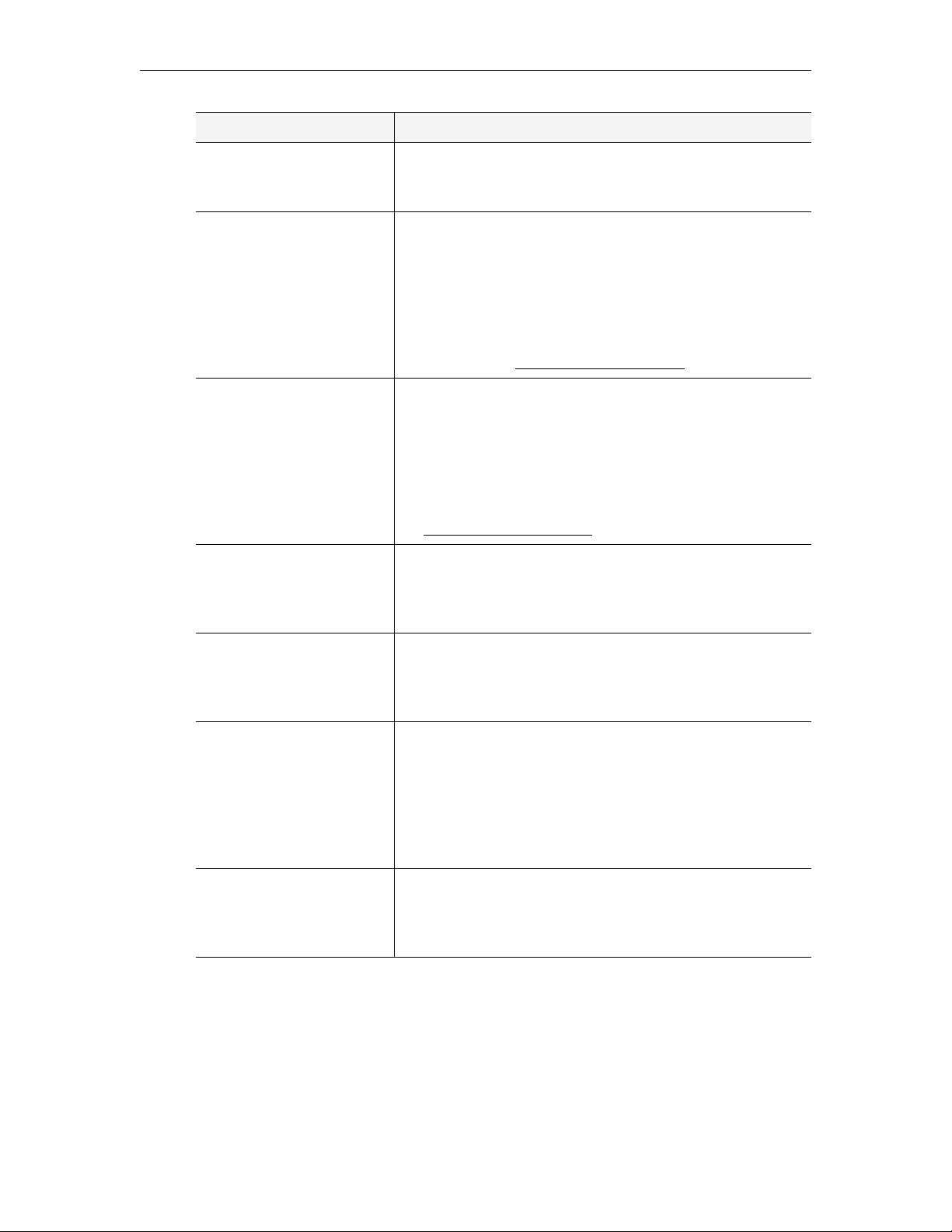
Table 9. Global Assignments
Item Description
Assign a Global Message The global message will be displayed in the message area of
the Portal Server user interface when there is no program
information available. Enter the message text and click
Submit. Example: There will be an all hands meeting today at
4:00 PM in the boardroom. Note that if you are running the
Portal Server on a Set Top Box, the message area will not
display more than 4 lines of text.
Define Set Top Box Startup
Channel
When an STB (in ETV Portal Server Start mode) accesses
Watch live broadcasts page, it can be set to
the
automatically play a defined channel in the Preview Window.
Highlight that channel from the list and click Submit. If there
are no channels listed, channels must first be defined as
Customized Live Streams.
Change Admin User Name Change the default admin user name of
admin. Use any
combination of alphanumeric and special characters except
slashes, quotes, or commas.
22 © 2007 VBrick Systems, Inc.
Global Settings
Item Description
Change Admin Password Change the default admin password of admin. Use any
combination of alphanumeric and special characters except
slashes, quotes, or commas.
Define FTP User Name ETV Portal Server is defaulted for "anonymous" FTP access
which is configured in Windows IIS Default FTP Site. If a
more secure FTP access is desired, the User Name can be
changed in IIS (see the Windows Server documentation for
details). The same User Name should be entered here. Use
any combination of alphanumeric and special characters
except slashes, quotes, or commas. If configuring for
VBPresenter, see Configuring an FTP User
on page 106.
Define FTP User Password ETV Portal Server is defaulted for "anonymous" FTP access
which is configured in Windows IIS Default FTP Site. If a
more secure FTP access is desired, the Password can be
changed in IIS (see the Windows Server documentation for
details). The same Password should be entered here. Use any
combination of alphanumeric and special characters except
slashes, quotes, or commas. If configuring for VBPresenter,
see Configuring an FTP User
on page 106.
Define a Record Duration Applies to the on-demand
Record pushbutton only (not to
scheduled recording). Defines the maximum duration
(default 120 minutes) allowed for a continuous recording.
Maximum record duration limited only by size of hard drive.
Change Title Changes the text (i.e. VBrick Systems) that is displayed on
the upper left hand corner of the Portal Server User
Interface. To leave blank, enter at least one space. Note that
the title text is white and cannot be changed.
Change Announcement
Addresses
Changing these from the defaults is highly discouraged and should
only be done if advised by a VBrick technician or Network
Administrator. Changes the Management, Multicast, and
RTSP addresses on which Announcements (SAPs) are
received. By default all VBrick devices are set to the same
addresses and ports as the defaults in ETV Portal Server.
These have to match on all devices for proper functionality.
Change Announcement
Filter
Filters SAP announcements so that only the specified IP
addresses are shown in ETV Portal Server. Wildcards are
allowed. For example 255.*.*.* displays only those addresses
in the range 255.0.0.0 – 255.255.255.255.
ETV Portal Server Admin Guide 23
Item Description
Assign LAN/Internet
Address Range(s)
Assign Multicast Address
Range
Define the range(s) of IP addresses that define the LAN or
the Internet domain. Any IP addresses outside the range are
assumed to be from the domain you did not select. Check one
option and, if necessary, use the text box to enter the range(s)
separated by a comma, a semicolon, or a new line. For details,
see ETV Internet-Based Servers
on page 7.
• All Users, Servers, and VBricks are in the LAN Domain
(default).
• All Users, Servers, and VBricks are in the Internet
Domain.
• Specify LAN Address Range(s); assume users/servers/
VBricks outside this range(s) are in the Internet domain.
• Specify Internet Address Range(s); assume users/servers/
VBricks outside this range(s) are in the LAN domain.
• Always use TCP protocol (HTTP Tunneling/RTSP
Interleaving) for MPEG-4 and Windows Media content –
Use only with Internet-compatible (VOD-D and
VOD-WM) servers. If checked, the Portal Server will
always use HTTP tunneling or RTSP interleaving using
the
HTTP Tunneling Port defined for the server (see
Add/Modify VOD/FTP Servers on page 31).
Defines the current multicast IP address range and port
range. The default multicast IP range is 225.1.1.0–
239.128.255.255. The default port range is 1040–65534.
Assign VOD Polling
Interval
Assign VoD Content
Ingestion Maximum
Assign Default Max.
Concurrent Viewers
Set Expired VOD Content
Treatment
Not generally changed. Defines the interval at which the
Portal Server polls the VOD server(s) for new content
(default 120 minutes). This is only used to poll for content
added to the VOD from an interface other than ETV Portal
Server. When adding a server, use Sync Now to sync the
program listings on the client Browse Video Library page
with the content on the new server.
Defines the maximum number of simultaneous video files
that can be ingested to the VOD Video-on-Demand server.
The default is set to 2. Increasing the default may increase
the speed at which files will be transferred to the VOD
server, but may result in playback issues from the Video-onDemand server. VBrick recommends keeping the default of 2
for all supported VOD servers.
Defines the default maximum concurrent viewers allowed for
new live or stored (VOD) content. An entry on the
Restrictions
page or the Modify VOD Content page will
Stream
override these value for live and stored streams respectively.
Specifies whether expired content will be kept or
automatically deleted at the expiration date.
24 © 2007 VBrick Systems, Inc.
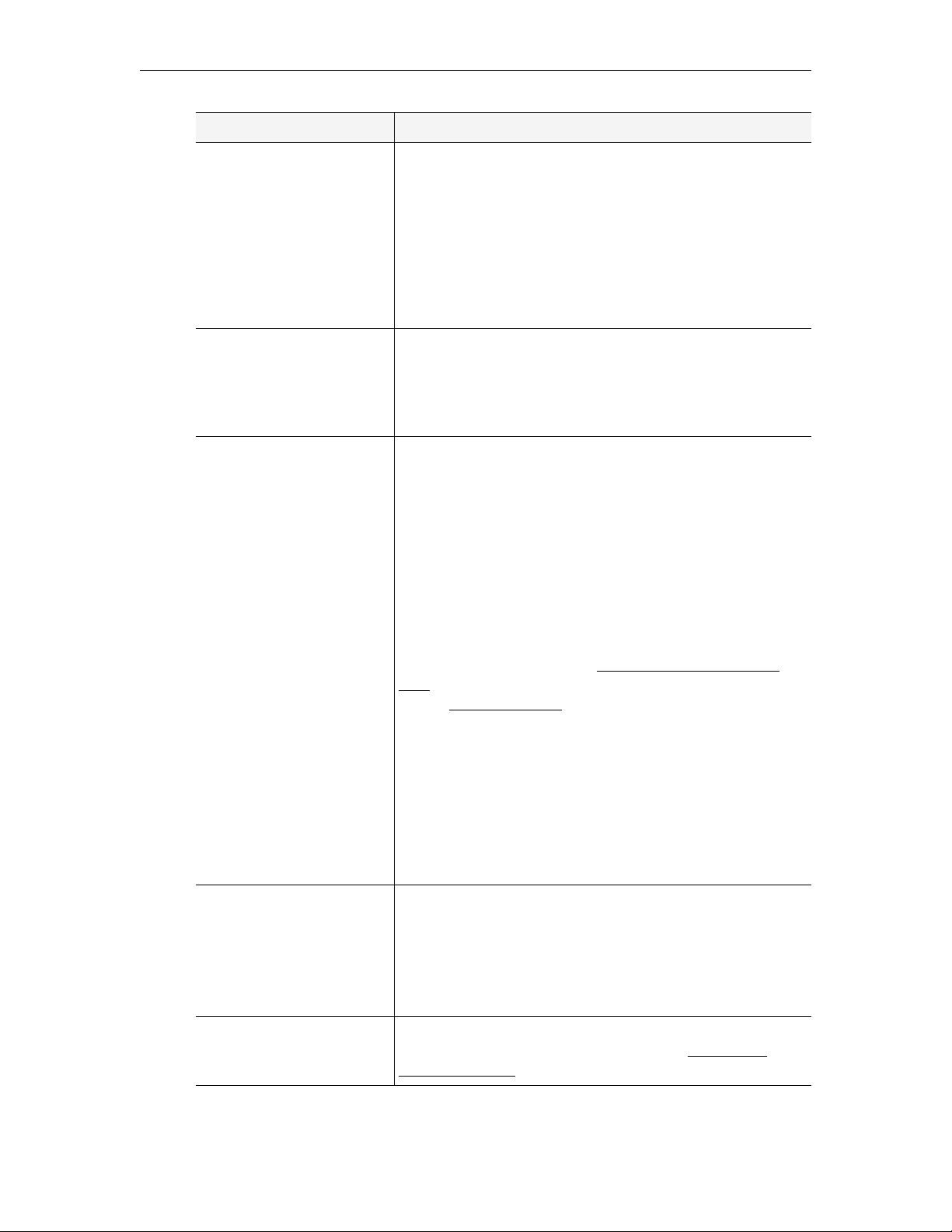
Item Description
Global Settings
Assign Content Expiration
Warning Recipient
Enter the semicolon-separated e-mail address(es) of the
person(s) responsible for renewing copyrighted or otherwise
protected content. When you configure or change either the
recipient or the mail server, the Portal Server will attempt to
send a test message. Check that this message is successfully
delivered. The Portal Server validates the e-mail address but
cannot detect other mail delivery failures. If the user's mail
box is full, for example, the message will not reach its
intended recipient to warn of impending content expiration.
Assign Mail Server Required field. SMTP mail server name. In Microsoft
Exchange, for example, go to Tools > E-mail Accounts > Email > Microsoft Exchange Server > servername. An e-mail
to the assigned Content Expiration Warning Recipient is
generated when you configure or change this field.
Assign Presentations VBPresenter is used to create multimedia presentations that
can be launched from the Portal Server. The
Presentations Directory
defines the virtual directory on the
Current
Portal Server where the live presentations are stored—the
default is
Presentations. During a new Portal Server
installation, the required virtual and physical directories are
automatically created. To use a different virtual directory,
create the virtual directory in IIS and enter only the virtual
directory name in this field—do not enter the complete path.
Current Presentations User is a pseudo VBPresenter
The
user who will be given permission to publish to specified
directories and VOD servers. Configuring a Presentation
User on page 106 explains how to create this user; contact
VBrick Support Services
if you need help.
If you are upgrading from Portal Server v4.0.1 or earlier and
using VBPresenter, you will need to manually create two
virtual directories (
MCSPresentations for stored presentations), giving the user
Everyone full permissions, and mapping the local paths
Presentations for live presentations and
respectively to:
C:\Program Files\VBrick\MCS\Presentations
C:\Program Files\VBrick\MCS\MCSPresentations
Select Macintosh Player for
MPEG4 Content
Select the player to use for MPEG-4 content on Macintosh
clients:
• VBrick Player – users will be prompted to install a VBrick
plugin the first time they launch MPEG-4 content.
• Apple QuickTime Player – no plugin required. Does not
support access logging.
Assign AutoIngest The current autoingest via XML user name that has access
and publishing rights to a VOD ser ver. See AutoIngest
Content via XML on page 113 for more information.
ETV Portal Server Admin Guide 25
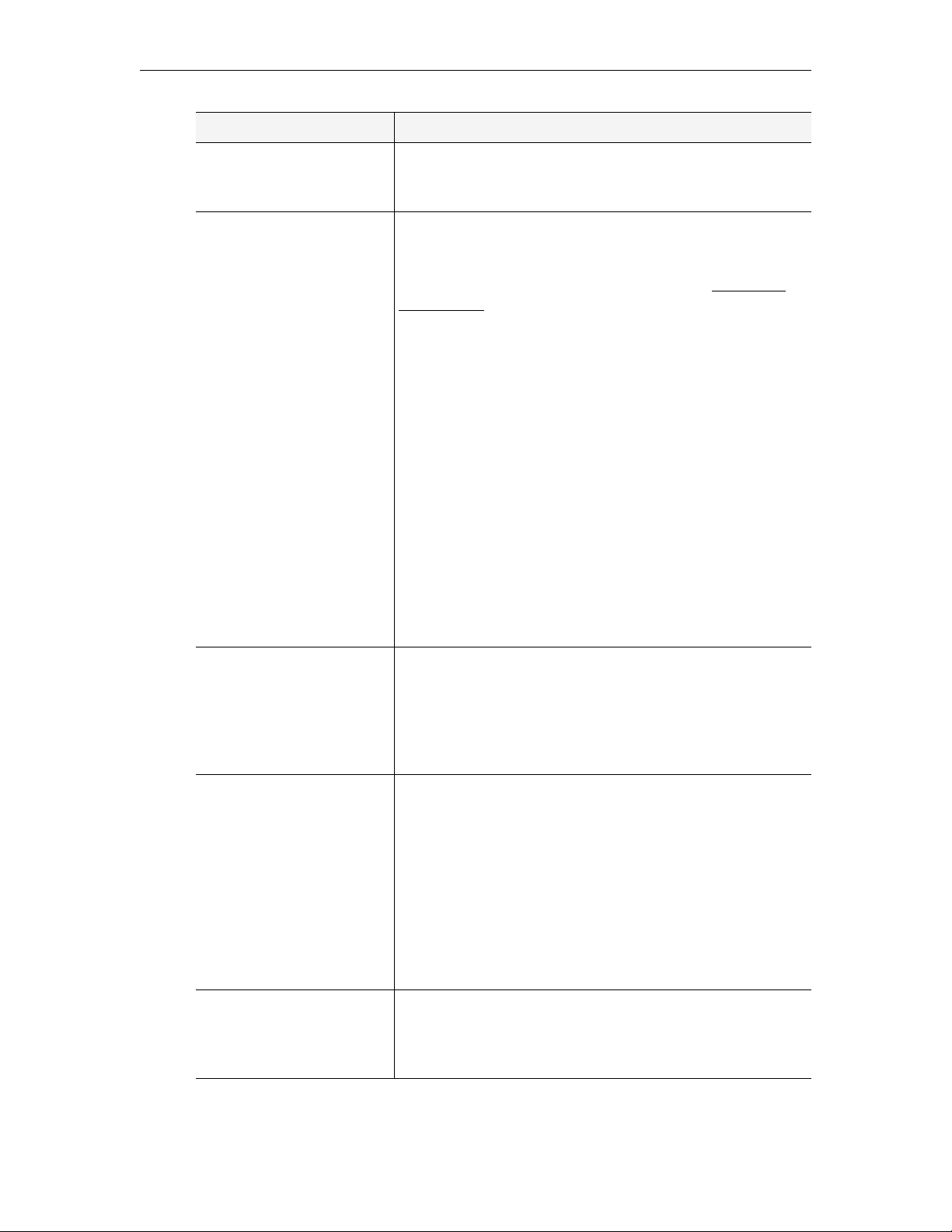
Item Description
Delete Recorded Files After
Ingestion
Specify Components to
Download to Clients
Used with scheduled recording and push button recording.
Specifies whether or not to delete the recorded file from the
NVR after ingestion. Enabled by default.
This setting defines whether the Portal Server will download
additional components to client machines when the client
first makes contact with the Portal Server—before any
streams or assets are selected for playback (see Download
Components on page 10 for more information.) Any changes
to these settings apply to new client machines only and will not affect
previously configured machines. The settings here apply to
Internet and/or LAN users as defined in the
Internet Address Range(s)
in Global Assignments (see
Assign LAN/
above). The default is to download all components to all
clients. For Windows clients you can selectively choose any
combination of settings; for Macintosh or Linux clients, any
one selection will download all components for all clients.
• MPEG-1 Video Support – makes MPEG-1 files playable.
• MPEG-2/1 Video Support – makes both MPEG-2 and
MPEG-1 files playable.
• MPEG-4 – makes MPEG-4 files playable.
• WM Video Support for Firefox on Windows PC – makes
Windows Media files playable on Firefox.
• 'Add Video' Utility – enables or disables the "add video"
functionality on client machines.
MPEG-2 Packet Ordering
at Schedule End
Network hardware infrastructure determines the order in
which packets arrive at a destination. To improve video
quality, VBrick MPEG-2 appliances reorder packets by
default. Since this reordering can cause an increase in latency
and affect applications like video conferencing, you can set
packet ordering to disabled at schedule end.
Stored Schedule Mode Used when creating a live broadcast schedule for stored
content. Note that the following parameters are "sticky."
They remain associated with the schedule even if the Stored
Schedule Mode is subsequently changed.
• Content Centric – content titles are shown; content
servers are not shown. The content is downloaded from
load-balanced servers.
• Server Centric – content servers are shown with a tree
control for selecting content. The content is downloaded
from a specific server and is not load balanced.
External Player Mode Windows only. Determines whether or not multiple streams
can be displayed by launching external player windows.
Default = Single. You can launch multiple windows but you
can only record one stream at a time.
26 © 2007 VBrick Systems, Inc.
Item Description
Global Settings
Set Cisco ACNS Manifest
Options
Custom Fields
Custom fields are used to add additional fields to the Info pages associated with stored
videos and live broadcast streams. All stored videos, and those live streams that have been
"customized," have an Info hyperlink. By default, the Info page has fields for Description
and
Keywords. The Custom Fields functionality lets you add additional "custom" fields that
are appropriate to your business or application. This lets you provide more information on
the page and it also makes it easier to search for specific streams. (All defined fields are listed
in the dropdown list box next to the
When you add a custom field using this function, the field is available to administrators as a
selection in the
Info
button on the Info pages associated with stored videos (if they have content publishing
permissions).
Check the box to enable generation of a Cisco ACNS
Manifest File. (The Cisco ACNS server must be configured
to point to this file.) Select the files (MPEG-4 and/or WM)
to include in the file, and specify a Manifest Generation
Interval (default = 10 minutes) that defines how often the
file will be regenerated. Click Generate Now to create an "on
demand" file. ACNS copies all MPEG-2 and WM video files
to all (Windows Media, Darwin, and VOD-W) servers in your
EtherneTV system. Additional configuration steps are
required on the VOD-W server only. See ACNS
Configuration on page 123 for more about ACNS.
Search button.)
Customize Streams window. It is also available to end users as the Modify
T To create a Custom Field:
1. Go to
Global Settings > Custom Fields.
ETV Portal Server Admin Guide 27
2. Enter a Field Name and a Field Type. If you select Dropdown, you can add items one at
a time followed by Add Item. These items will populate a dropdown list box on the
Customize Streams page.
3. When done, click
Add Custom Field. The field will be added to the panel at the top of
the window; it will also be available as an option when you are customizing a stream.
Add/Modify
Custom Field
This panel shows the existing custom fields that have previously been
defined.
Field Name The field name you want to display on the Info page for this stream or
video.
Field Type This determines how the field will be displayed on the
Streams
Customize Streams
Customizing streams refers to changing the way live streams are displayed in the ETV Portal
Server. (VOD streams are customized by end users rather than by administrators.)
Customizing a live stream allows you to change the displayed Program Name, assign a
Channel number, and enter a Description that displays in the Messages area of the window.
You can also enter Keywords for searching, and values for any custom fields that have been
defined (see Custom Fields above).
The ETV Portal Server auto-discovers live streams on the network by listening for
announcements, also known as SAPs (Session Announcement Protocols). On a network with
many live streams, the administrator can keep the stream list organized by assigning channel
numbers. This also provides an environment for end users that is similar to television.
T To customize a stream:
1. Go to
Global Settings > Customize Streams:
Customize
page, either as a text field or as a dropdown list box.
28 © 2007 VBrick Systems, Inc.

Global Settings
2. Choose an Available Live Stream (one that has not been customized), enter an optional
Channel number, and click Add Customization. This moves the customized stream to
the panel on the right.
3. Optionally, add a
on the broadcast list page and on the
4. You can also add
Description of the channel that will be displayed in the Messages area
Info page.
Keywords and Links (see below) that are displayed on the Info pages
associated with a stream. They make it easier to search for specific content.
Program Name Required. Name that will display in the directory of Live
Broadcasts.
Channel Optional. Unique number that will display in the directory.
Description Optional. Description that will display on the Info page.
Keywords Optional. Enter each searchable keyword(s) separated by commas
or spaces.
Links Optional. Add hyperlinks that will display on the Info page.
Add Link
This feature lets you add a hyperlink to the page you get by clicking the Info hyperlink
associated with each live stream.
T To add a link to a customized stream:
1. Highlight a stream in the
2. Click
3. Click
ETV Portal Server Admin Guide 29
Add New Link and enter a Link Title and Link Type.
Add Link when done. Repeat as many times as necessary.
Customized Live Streams panel.

Link Title The title actually displayed on the Info page, for example
"Additional Information."
Link Type • Web page URL – Enter a valid URL or copy and paste one
• Uploaded File – Browse to select an upload file. This can be a
Stream Restrictions
Use this page to set and the viewing period for live stream recordings and the maximum
number of concurrent viewers. There are no default expiration dates for live streams when a
recording is made but administrators can automatically set the content from a specific stream
to expire by setting a viewing period. For more about content expiration see Copyright
Protection on page 3.
from your web browser.
PowerPoint, an image, or any file you want to make available
to end users. The file is automatically uploaded to the Portal
Server, and the Portal Server creates a URL for end users to
access it.
30 © 2007 VBrick Systems, Inc.

Global Settings
Live Stream Click on any live stream shown in the list to populate this field.
Max. Concurrent
Viewers
Viewing Period of
Stream Recordings
Servers
Use the Servers page to add/modify VOD servers or to add/modify VOD content folders.
Note that you can cluster multiple servers to increase throughput. The ETV Portal Server
will automatically load balance all servers defined on the Servers page; no additional
configuration is necessary. Note that content added by users in the Internet zone will only be
ingested to VOD servers in the Internet zone for which they have permissions. Content
added by users in the LAN zone will be ingested to all VOD servers to which they have
permissions. See ETV Video-on-Demand Servers
Add/Modify VOD/FTP Servers
Use this window to add Video-On-Demand Server(s) to the ETV Portal Server. If the
network supports Windows 98 users, you must use the IP address of the VOD server—not
the host name. After selecting a
settings for FTP Password, Publishing Local Path, Publishing Directory, etc. unless there is a
compelling reason to change them. Nor is it necessary to create a Streaming Alias. Unless you
are using HTTP Tunneling, leave this parameter blank.
Set the maximum number of concurrent viewers for this stream to
unlimited or any number greater than zero.
Set the length of the viewing period for a file recorded with this
stream in hours, days, weeks, months, or years. The file will no
longer be available for viewing at the end of the period and will be
deleted or saved as configured in Global Assignments > Set
Expired VOD Content Treatment.
on page 6 for more about ETV servers.
Server Type VBrick recommends you keep the default
ETV Portal Server Admin Guide 31

IP or Domain This is the primary IP address or Host Name of the VOD server
for LAN users (see also
Secondary Server Address below). The
Server Name or IP address entered into the ETV Portal Server
must be accessible by the ETV Portal Server. (If the network
supports Windows 98 users, you must use the IP address.)
Server Description This allows the administrator to define a descriptor such as
location.
FTP User Name This is the FTP user name that the Portal Server uses when
publishing content to the server. The default for NXG servers is
vbrickuser; the default for all others is anonymous. The FTP User
Name refers to a user account that already exists on the server. If
the FTP User Name is changed on any VOD server, it must be
changed here as well. Use any combination of alphanumeric and
special characters.
Server Type • NXG – Linux-based Kasenna VOD server.
• VOD-W – Windows-based InfoValue VOD server.
• VOD-D – Darwin Open Source server for Linux, Windows,
Mac, etc. Ingests and plays MPEG4 content only. Requires an
FTP server. See Creating a VOD-D FTP Server
on page 34.
• VOD-WM-Standard – Microsoft Windows Media Server
(unicast only). Requires an FTP server.
• VOD-WM-Advanced – Microsoft Windows Media Server
(unicast or multicast). Requires an FTP server.
• FTP – Use FTP only if you want to copy from the Recorder
server to another FTP server in which case it records to
ftp:\root.
32 © 2007 VBrick Systems, Inc.

Global Settings
FTP Password The FTP password the Portal Server uses when publishing content
to the server. The default for NXG servers is
default for all others is
anonymous. If the FTP Password is changed
vbrickuser; the
on the server, it must be changed here as well. Use any
combination of alphanumeric and special characters.
Publishing Local Path Maps the Publishing Directory to the physical location on the
VOD server.
Publishing Directory Used for Add Video, FTP, or Record. The logical path to a folder
under FTP root. This is the staging area on the VOD server from
which files are ingested to the destination folder.
Streaming Alias (IP
or Domain)
HTTP Tunneling
Port
Secondary Server
Address
Publishing Point
Name
Some content hosts (PowerStream, Akamai, etc.) use one host
name for FTPing and indexing content, and another host name for
streaming content. If necessary, use this field to identify the host
name alias for streaming content.
VOD-WM and VOD-D only. VOD-WM and VOD-D servers can
stream to clients via the HTTP protocol. By default this uses port
80. If another process on the server (for example a web server) is
also using the HTTP protocol, there will be a conflict on this port.
This setting lets you select a different port (1–65535 with
limitations) to be used when streaming via HTTP. This setting must
correspond with the port setting on the server. See also "Assign
LAN/Internet Address Range > Always use TCP protocol for
MPEG-4 content" in Global Assignments
on page 21.
A VOD server can have two addresses: one for Internet users and
one for LAN users (see also
IP or Domain name above). This is the
secondary server address for Internet users. It is the IP address or
domain name of a second NIC or a NAT.
VOD-WM only. The publishing point on the VOD-WM server
where content will be accessed and managed by the ETV Portal
Server. Note: this setting must correspond with a valid publishing
point on the server.
Domain or Machine
Name
VOD-WM-Advanced only. When the ETV Portal Server and the
VOD-WM server reside in the same domain, this is the name of
that domain. When workgroups are being used, this is the machine
name of the VOD-WM server. Note: the machine name is not the
IP address of the server.
ETV Portal Server Admin Guide 33

User Name VOD-WM-Advanced only. The name of a valid user that has
administration privileges on the VOD-WM server. If the VODWM Server is within a domain, the name entered here will be a
domain user. That domain user must have administration privileges
on the VOD-WM Server. If the VOD-WM Server is part of a
workgroup, the name entered here will be a local user with
administration privileges on the VOD-WM Server. A local user
with administrator privileges having the same name must also exist
on the MCS Portal Server.
Note: The MCS Portal Server and VOD-WM Server(s) must all be
within a domain or part of a workgroup. Any topology that mixes
servers in domains and servers in workgroups will not function.
User Password VOD-WM-Advanced only. The valid password of the user specified
above.
Note It may take up to 20 minutes for new server content to be displayed in the ETV
Portal Server. To make content available immediately, go to
Assignments > Assign VOD Polling Interval
and click Sync Now.
Global Settings > Global
Creating a VOD-D FTP Server
If you are using a VOD-D (Darwin) server, you must install and configure a standard FTP
server on the VOD-D server as explained below. (For more about Darwin servers see ETV
Video-on-Demand Servers on page 6.)
T To create a Darwin FTP Server:
1. Install a standard FTP server on port 21.
2. Set the default FTP directory to the Darwin server's Media Folder directory (also called
the Publishing Point) or create a virtual directory of the FTP root pointing to the Darwin
server's Media Folder.
3. Create and configure a user account with full permissions (read/write, rename/delete
etc.) on the Add/Modify VOD/FTP Servers
page.
Add/Modify Video On Demand Content Folders
Add/Modify Video On Demand Content Folders can be used to organize content on a
specific Video-on-Demand server. The Portal Server periodically polls certain folders for
presence of content and if found ingests the content onto multiple VOD servers. Any files
FTPed into a particular folder in the Autoingest folder will automatically be ingested into the
corresponding folder on the VOD server(s). You must add these folders using the window
shown below. (See Auto Content Ingestion
Existing folder structures on a VOD server will be mirrored in the Portal Server. However
you will still need to associate those folders with other server(s) if the file is to be autoingested onto multiple servers.
on page 111 for more about auto-ingestion.)
34 © 2007 VBrick Systems, Inc.

Global Settings
This function is useful for VBrick VBStar appliances to easily transfer content from their
hard drives to the VOD server. (It can also be helpful for users who acquire content outside
of the ETV Portal Server, for example from StreamPlayer Plus.) When a folder is created, you
must check a box in
Add/Modify Folders on Selected Servers to associate the folder with a
server for autoingestion. ETV Portal Server checks these folders every 5 minutes and ingests
new content if present. This feature only applies to Autoingest; it does not apply to
Record
or Add Video.
As the folder structure is created in this section, autoingest folders will be created in the FTP
root path. For example, if the FTP root path is
d:\inetpub\ftproot, then folders that are
created in the Add/Modify On-Demand content folders will also be created in the
d\inetpub\ftproot\mcs\autoingest folder.
Autoingested content can go into any folder that has been associated with a server or servers
using the
Add/Modify Folders on Selected Servers check boxes shown above. If using a
VBStar, be sure to associate a folder with a server for autoingest. This enables the folder that
the VBStar will FTP files into. This function is not associated with a user or group
permission and is controlled only by the Administrator. See Auto Content Ingestion
on
page 111 for a more detailed description of the Auto-ingestion functionality.
Note Use the Delete button to remove non-empty folders only. Use the Modify button to
change AutoIngest settings in the
Add/Modify Folders on Selected Servers pane.
Creating Subfolders
Use the following steps to create a subfolder in an existing folder.
T To create a subfolder:
1. Highlight any existing folder name, for example
and click
ETV Portal Server Admin Guide 35
New.
/Bill as shown in the previous window,

2. Type the new subfolder name in the text field, preceded by a forward slash, for example
VBricks
All VBricks must be configured in ETV Portal Server before they can be managed and used
for scheduled events. (VBrick configuration is only required if you are using the Scheduling
feature. Once configured, all VBricks in the system are shown on the following window. In
the ETV Portal Server, SAP (Session Announcement Protocol) announcements are sent to
the Portal Server by network-connected VBrick devices (encoders and/or decoders). The
Select VBrick panel in the next screen shows VBrick appliances (encoders and decoders) that
have announced their presence on the network but have not been configured for use in ETV
Portal Server. (Note that if you delete a VBrick from the
it will not be shown as available until you logout and log back in to the Admin Console.)
T To add a VBrick configuration:
1. Go to
/Bill/temp, and click Submit when done.
Currently Configured VBrick List,
Global Settings > VBricks.
2. Select
36 © 2007 VBrick Systems, Inc.
Add VBricks and click Submit.

Global Settings
3. In Select VBrick, select one or more existing VBricks for which a SAP has been received.
If you select one VBrick, this populates the VBrick Configuration panel. (If you select
multiple VBricks, it does not populate the panel; if you need to configure the VBricks,
you must add them one at a time.)
4. Complete or modify the fields in
VBrick Configuration as necessary. Note that you must
enter a User Name and Password and confirm that Password or the configuration will
fail.
5. Click
Submit when done. This adds the new configuration to the list of configured
VBricks shown on the previous page.
Note The only time you will manually complete the VBrick Configuration fields is when
you are defining the configuration for a VBrick that will be added to the network at a
later time. In this case, you will need to know the following configuration data in
advance.
Host Name Required. Host name of VBrick.
IP Address Required. IP address of VBrick.
User Name Defaults to system-defined value if blank.
User Password Defaults to system-defined value if blank.
Confirm Password Defaults to system-defined value if blank. Must match User Password
if entered above.
Software Revision Optional. To get the Software Revision in IWS, go to
System Information >
Release Revision.
HTTP Port Optional. To get the HTTP Port in IWS, go to
System > Security > IWS Server Port
ETV Portal Server Admin Guide 37
.
Status >
Configuration >

VBrick Model Select from dropdown. Advanced settings are enabled if you select an
encoder or a VBStar.
Advanced Settings
Advanced settings are enabled if you select a VBrick encoder or a VBStar. Note that the Portal
Server will attempt to retrieve and autofill the Multicast IP addresses and Port numbers. You can
modify these fields as necessary.
Note The following values are stored in the Portal Server database only. Depending on
how a scheduled event is configured, they may be saved and written back to the
VBrick device after the scheduled event runs.
Multicast IP Destination multicast IP address.
Video Port Destination video port.
Audio Port MPEG-4 devices only. Destination audio port.
CC Port MPEG-4 devices only. Closed captioning port.
38 © 2007 VBrick Systems, Inc.

Control Devices
Control devices let you configure a video source device so that it can be controlled by end
users from the Portal Server user interface. (An example of a video source device is a DVD
or VCR directly connected to a VBrick encoder.) Once configured, a special icon on the
Broadcasts
as shown in Figure 6 below. VBrick currently supports DVDs and VCRs from several
different manufacturers as well as the VBrick VBIR remote controller that can be customized
for use with a wide variety of source devices. See Adding User-Defined VBIRs
more about VBIRs.
Note In some cases you may be able to control a source device using the front panel or the
page indicates you can control the stream using a "virtual" remote control panel
handheld remote that came with the unit, but this is not always possible. For
example, if the remote gets lost or the source DVD and/or VCRs are rack-mounted
in an inaccessible metal enclosure, you must use the Portal Server interface or a VBIR.
Global Settings
Live
below for
Figure 6. "Virtual" Remote Control Panel on Live Broadcasts Page
As shown in Figure 7 below, the remote control panel will have a different graphical user
interface depending on whether the source device is directly attached (via a serial port
connection) or uses a VBIR. The control panel interface for direct-connect devices varies
according to the specific device you select; the control panel interface for VBIR-connected
devices is the same for all VBIR devices.
ETV Portal Server Admin Guide 39

Figure 7. Control Panel for Direct-Connect Devices (left) and VBIRs (right)
Note The Amino set top box does not recognize "control devices." Any video source
devices configured as
Control Devices in the Portal Server will not display a "virtual"
remote control panel on the Amino set top box.
Adding Control Devices
Use the following windows to define or modify control devices. As noted, these devices will
be displayed on the
encoder. If the device is used as a source encoder for a scheduled broadcast, however, only the user who
actually created the schedule will have access during the scheduled period. This prevents other users
from potentially interrupting the broadcast. If the Portal Server does not have a Scheduling
license, all control devices are available at any time to any user with VBrick access and other
permissions. See "Using the Scheduler" in the Portal Server User Guide for an explanation of
how to schedule events for control devices.
T To define a control device:
Live Broadcasts page with a special icon for any users with access to that
1. Go to
Global Settings > Control Devices and select Add Control Devices.
2. Complete the fields on the next screen as explained below and click
Submit.
40 © 2007 VBrick Systems, Inc.
Global Settings
Name Enter a unique, descriptive name that will be displayed on the
virtual remote. For example in Figure 6, "Sony DVD" is the
configured name shown on the controller. No embedded spaces or
special characters are allowed.
Source Device Select a source DVD or VCR from the dropdown list. The list
shows serial port direct-connect devices and VBIR (SpitFire)
devices that are tested and supported by VBrick. It also shows any
custom VBIR devices you have added (note that you cannot add
serial port direct-connect devices). You add custom devices by
creating a User Defined VBIR as explained below. If the source
device you wish to control does not have a serial port, you must use
a VBIR for remote control.
VBrick Encoder Select the specific encoder to which the selected Source Device
above is connected from the dynamically populated list of encoders
on your network.
User Defined VBIRs Select the SpitFire version you have (SpitFire II or III) and enter a
Description and a three-digit Code (see Adding User-Defined
VBIRs below).
Adding User-Defined VBIRs
The VBrick VBIR is an external hardware device that uses the passthough port on a VBrick
to send control commands via an infrared link to third-party devices like VCRs, DVDs, etc.
(see Figure 8 for a visual schematic). You must use a VBIR if the target third-party device
does not have a serial port that can directly connect to a VBrick encoder. The VBIR can be
programmed with codes representing IR command sets that are compatible with devices
from many manufacturers. Use the following window to create a custom
Enter a device description (20 characters or less), a three-digit code, and select the SpitFire
model. When done, the new device is added to the
Source Device dropdown list. For a current list of VCR/ DVD device codes for SpitFire II
models, go to http://innotech.com/spitfire-ii-device-codes.pdf
User Defined VBIRs list as well as to the
For SpitFire III models, go
User Defined VBIR.
ETV Portal Server Admin Guide 41

to http://innotechsystems.com/Spitfire/SpitFire III.pdf Be aware that the device codes at
this link are not tested or supported by VBrick. If you can't find the code you need, or have
trouble controlling a non-supported device, check the product documentation or contact the
manufacturer.
Note The VBIR (SpitFire III model only) can also "learn" (i.e. be programmed to use) IR
commands much like a universal remote controller. Learned commands are stored in
VBIR memory areas called slots and are accessed by reserved three-digit codes. The
six slots are available are: AUX (994), TV (995), VCR (996), DVD (997), AUD (998),
and CBL/SAT (999). For a detailed explanation of how a VBIR "learns" commands,
see the Application Note Learning IR Commands on the VBIR
Product Documentation website.
on the VBrick
Connecting Control Devices
To set up a device that can be remotely controlled from the Portal Server, you connect the
serial interface on the source device (the DVD or VCR) to the passthrough port (COM1 or
COM2 for Slots 1 and 2 respectively) on the VBrick encoder using an appropriate cable (see
Table 10) from those shipped with the encoder. For more about Serial Port Passthrough, see
the online help for the encoder. You can also control devices using VBrick's VBIR remote
controller. To use the VBIR remote controller, you connect the VBIR SpitFire device to
COM1 or COM2 on the VBrick encoder. The VBIR subsequently communicates with the
DVD or VCR via infrared commands (see Figure 8) at the configured baud rate.
If necessary, connect one end of the XIR emitter cable to the SpitFire and the other to the
DVD or VCR making sure the adhesive lead is securely attached to the device. The emitter is
used when there is no direct line-of-sight to a control device (for example when the VCR is in
a cabinet) and you can't use the remote control. On the back of the VBIR, be sure the
SpitFire is in RS-232 mode.
42 © 2007 VBrick Systems, Inc.
Figure 8. Connecting Control Devices
Tab le 1 0 . Device Connectors
Device Connector
Global Settings
VCR
DVD
MPEG-1 Encoder DB-9
MPEG-2/4/WM Encoders RJ-45
† Typical device connector.
DB-9
DB-15
†
†
Configuring Control Devices
You also need to configure the baud rate and passthrough state of the VBrick associated with
a control device. In IWS, go to the Configuration: Passthrough page and set these values as
follows:
Tab le 1 1 . Baud Rate and Passthrough State
Device Baud Rate Passthrough State
DVD 4800 Responder
VCR 9600 Responder
VBIR 2400 N/A
ETV Portal Server Admin Guide 43
Learning IR Commands
The Portal Server VBIR also supports the SpitFIRE device internal library. This library is a
database in flash memory of several thousand IR command sets accessed by a three-digit
code. In the EtherneTV Portal Server Admin Console a three-digit internal library code is
specified by selecting a SpitFire source device from the dropdown list during configuration.
If none of the codes in the SpitFire internal library represent the IR command set used by a
particular source device, the SpitFire VBIR can be set to learn and store IR commands like a
universal remote. Once commands are learned on a SpitFire they can be written as an
extended (download) command library to a storage file on a PC. The learned commands in
the stored file can be uploaded and "cloned" to another SpitFire. For more information, go
to www.VBrick.com/documentation
Commands on the VBIR."
Set Top Boxes
STBs (Set Top Boxes) must be configured in ETV Portal Server before they can be managed
and used for scheduled events. (STB version must also be 3.7.1 or higher.) Once configured,
all STBs in the system are shown on the following window. The
screen shows STBs that have announced their presence on the network but have not been
configured for use in the Portal Server. (Note: to schedule
T To add an STB configuration:
and see the application note "EtherneTV: Learning IR
Select STB panel in the next
1. Go to
44 © 2007 VBrick Systems, Inc.
Global Settings > Set Top Boxes.

Global Settings
2. Select Add STBs and click Submit.
3. In
Select STB, select one or more existing STB for which a SAP has been received. This
populates the STB Configuration panel. (If you select multiple STBs, it does not
populate the panel; if you need to configure the STBs, you must add them one at a time.)
4. Complete or modify the fields in
STB Configuration as necessary and click Submit. This
adds the new configuration to the list of configured STBs shown on the previous page.
ETV Portal Server Admin Guide 45

Note The only time you will manually complete the STB Configuration fields is when you
are defining the configuration for an STB that will be added to the network at a later
time. In this case, you will need to know the configuration data in advance.
Host Name Required. Host name of STB.
IP Address Required. IP address of STB.
User Name Defaults to system-defined value if blank.
User Password Defaults to system-defined value if blank.
Confirm Password Defaults to system-defined value if blank. Must match User Password
Software Revision Optional.
STB Model Select from the dropdown.
Start Mode Select from the dropdown: ETV Portal Server, Local, or Local-
Recorders
A Recorder server enables recording by Portal Server users. If a recorder server is not created
here, any attempt to record a live stream or a stored video will fail. Once enabled, users must
also be assigned the appropriate permissions (see Allow Content Recording
(Note: Do not confuse a Recorder server with a Network Video Recorder which is a a
separate product. See the ETV Network Video Recorder Release Notes for more information.)
if entered above.
Fullscreen
on page 86).
Note By installation default, all recordings are stored on the D: drive. If you install ETV
Portal Server on a system without a D: drive, you must subsequently go to
Settings > Recorders
Recording
field shows the default number of concurrent recording sessions allowed.
and change the record path as necessary. Also, the Max
Global
If you need more than 2 concurrent recording sessions, you must purchase a Network Video
Recorder.
T To add a Recorder configuration:
1. Go to
Global Settings > Recorders.
46 © 2007 VBrick Systems, Inc.

2. Select Add Recorders and click Submit.
Global Settings
3. Complete the fields in
Recorder Configuration window and click Submit. This adds the
newly configured recorder to the previous window. If necessary see Synchronizing the
Portal Server and the NVR below.
Recorder Server IP address or host name of recorder server. Defaults to localhost if
recorder server is on the same machine as ETV Portal Server.
ETV Portal Server Admin Guide 47

Record Path Path and folder where all recording are stored. By default, recordings
are stored on the D: drive. If you install ETV Portal Server on a
system without a D: drive, you must change the path. Also, in order to
record multiple streams, the Record Path must be under FTP root.
For example, if root is
C:\Inetpub\ftproot\<your_folder>
C:\Inetpub\ftproot the Record Path must be
Max. Recording The default number of concurrent recording sessions allowed is 2. If
you exceed 2, you must purchase a Network Video Recorder. Without
an NVR, any attempt to record more than 2 concurrent sessions will
fail.
FTP User Name FTP user name in operating system of Recorder server.
FTP Password FTP password in operating system of Recorder server.
Confirm Password FTP password in operating system of Recorder server.
Domain Name This field is required only if the Recorder server is not on the local network.
Enter the domain name if the Record Path above points to a server in
a different domain,
User Name The user name who has access to the specified path.
User Password The corresponding password for this user name.
Synchronizing the Portal Server and the NVR
The internal clocks on the Portal Server and the NVR must be synchronized for recording
functionality to work properly. You can use the Net time command as explained below or you
can use an external time server. In order to run the
server must be on the domain, and the user logged onto the server must have admin
privileges and be part of the domain. To synchronize the Portal Server and the NVR use the
command that corresponds to your operating system.
• Windows 2003 Server – Open a command prompt on the Portal Server and type:
Net time \\{NVR IP Address} /SET
• Windows 2000 Server – Open a command prompt on the NVR and type:
Net time \\{Portal Server IP Address} /SET
Script Devices
Script devices work with scripts and can be used to control VBricks, or other devices
attached to a VBrick via the serial port. In order to use a script, the device (a VBrick, STB,
camera, VCR, etc.) must be defined in the Portal Server database as a script device. Once
defined, they can be subsequently controlled by a script (see Scripts
from the Portal Server Scheduler. A script device must be physically connected to the
network and must be available at the runtime of a scheduled event. For example, PTZ
cameras respond to pan, tilt, and zoom commands. Once defined as a script device, pan,
zoom, and tilt commands can be scripted and executed from ETV Portal Server to control
the movement of the camera at a specific date, time, and recurrence.
Net time command on either server, the
on page 50) launched
T To add a Script Device configuration:
1. Go to
48 © 2007 VBrick Systems, Inc.
Global Settings > Script Devices.

Global Settings
Note You can also write a script (launched from the Portal Server) that uses TCP/IP to
communicate with any compatible device on the network. Contact VBrick Support
Services for more information.
2. Select Add Script Devices and click Submit.
3. In
Script Device Configuration, complete the following fields and click Submit. This
adds the newly configured script device to the list of devices shown in the previous
window. To modify a Script Device, first delete the device and then repeat these steps.
Device Name Any user-defined name.
ETV Portal Server Admin Guide 49

Address Hard-coded device IP address. This is usually the address of the
VBrick or the address of the VBrick to which a device is connected
but it can be the address of any device.
Port TCP/IP port number range =
Scripts
Scripts work with previously defined script devices such as VBricks, STBs, or other devices
attached to a VBrick. Scripts can be used to control any type of VBrick or to control other
devices like cameras and VCRs that are attached to a VBrick. To script VBrick commands,
you select the VBrick and build a script by choosing parameters from a dropdown list—the
parameters vary depending on the type of VBrick you select (MPEG1, MPEG2, etc.). You
can script commands to change any of the parameters (in the MIB database) that are available
through IWS.
For non-VBrick (
that device. This scripting functionality is designed for advanced users and you must know
the instruction set for the device in order to script commands that will control that device.
You can use a text-based script or a binary script to control devices connected to the serial
passthrough port (COM1 or COM2) on a VBrick encoder.
You can control devices that require binary input by pasting binary input into the
Content
require binary input. This type of script will pass binary input through the serial passthrough
port on a VBrick to the specified device. You will typically connect your device to the serial
passthrough port using the port number previously defined for the device (
4414 for COM2).
1040–65534. If using serial port
passthrough, use the VBrick's passthrough port number:
COM1,
Other) devices, you write a script from scratch using the native language for
4414 for COM2
4439 for
Script
text box. Binary scripts let you provide a sequence of commands for devices that
4439 for COM1,
Note If you are scheduling an event, any device for which you write a script must be
available to the network at runtime. If the device is not available the script will fail.
Creating a Script
T To create a script that can be executed from the Portal Server:
1. Go to
50 © 2007 VBrick Systems, Inc.
Global Settings > Scripts.

Global Settings
2. Select Add Scripts and click Submit.
3. In
Script Configuration, enter a Script Name and select a Device Type (MPEG1,
MPEG2/MPEG4/WM, or Other) from the dropdown list—and wait a few seconds for
ETV Portal Server to populate the panel with a list of devices.
4. In
Select Device, highlight one or more devices and use the arrow buttons to populate
the right panel.
5. Create the
ETV Portal Server Admin Guide 51
Script Content.

a. For VBrick devices, select a Parameter Name from the dropdown list , enter a
Parameter Value, and click Add. Repeat as many times as necessary and click Submit
when done. Note that the order in which you add parameters is critical. This is the
order in which the commands will be executed at runtime. (See Finding VBrick
Parameters and Values for more information.
b. For non-VBrick (
Other) devices, write the script in a native language compatible with
the device (or copy and paste binary input) and click Submit when done.
To run a previously created script, login to ETV Portal Server and click Schedul ed
Programs
pattern. When done, click
. Then create a schedule by selecting a date, time, and (optionally) a recurrence
Script and select the script you want to run on the schedule you
just defined.
Example
The following example shows binary input for a VBrick VBIR device. In a typical scenario
you will need to set the Passthrough State and other parameters on the encoder before you
can run the script. See "Serial Port Passthrough" in the VB4000-5000-6000 Admin Guide for
more information. The following example programs a VBrick VBIR device to device code
351 and sends the Play command. This is just a brief example. If you need help or want more
information about using binary scripts, please contact VBrick Support
Begin instruction set, program for following device code. This set of instructions is used in all
scripts.
Services.
<-script->
<-send binary 0xc1 0x0d->
<-receive 2->
<-send binary 0xc0 0x0d->
<-receive 2->
Program three-digit device code. Here code is 351.
<-send binary 0x83 0x0d->
<-receive 2->
<-send binary 0x85 0x0d->
<-receive 2->
<-send binary 0x81 0x0d->
<-receive 2->
End device code programming, set for command. This set of instructions is used in all scripts.
<-send binary 0xc0 0x0d->
<-receive 2->
<-send binary 0xd3 0x0d->
<-receive 2->
Command. Here Play.
<-send binary 0x91 0x0d->
<-receive 2->
Finding VBrick Parameters and Values
In order to create scripts, you need to determine the correct parameters and values to use.
The following procedures explain how to locate parameters from the IWS page and how to
52 © 2007 VBrick Systems, Inc.

Global Settings
find the value associated with that parameter using a standard MIB browser or text editor.
These brief procedures simply outline the basic steps which are typically performed by a
programmer or a system administrator. Contact VBrick Customer Service or see the VBrick
SDK User Guide for more information.
T To locate a parameter name by viewing the source code:
T To find the parameter value:
URLs
1. Find the
Parameter Name in the Integrated Web Server (IWS) page.
2. Then locate the parameter name by viewing the source code of the page.
1. Locate the parameter name as described above.
2. Find the
Parameter Value by examining the MIB file with either a standard MIB browser
or a text editor.
Add/Modify a URL for a Live Video Stream
Administrators can manually enter URLs to live video streams that will not automatically be
displayed by the Portal Server. For example, the administrator may wish to have the
Announcements (SAPs) disabled on the VBrick encoders for security purposes. Or the
Administrator may want to enter the address of an off-network stream such as an MPEG-4
Stream from an Apple Darwin Server or a stream coming from a hosting provider.
Additionally, this feature lets you enter the addresses of non-MPEG streams such as
Windows Media and Real Networks. Note that the Access Control feature Allow Viewing by
Content Type does not apply to manually added URLs.
Note For any non-MPEG video, the correct player (such as Windows Media Player or Real
Player) must be present on the desktop for the client to be able to receive the stream.
Set Top Boxes will not be able to receive non-MPEG streams because the Set Top
Box only includes decoders for MPEG-1, MPEG-2, and MPEG-4.
The following examples show valid URL syntax for live video streams. All URLs are case
sensitive. The syntax must be accurate and there is no internal validation of user input:
Valid for Types MPEG-1 and MPEG-2
vbricksys://ip=239.1.1.1&port=4444
Where 239.1.1.1 is the multicast IP address and 4444 is the multicast port.
Valid for Type MPEG-4
rtsp://172.1.1.1/vbrickvideo1
vbrtsp://172.1.1.1/vbrickvideo1
Where 172.1.1.1 is the source IP address and vbrickvideo1 is the program name.
vbhttp://172.1.1.1/vbs2d1.sdp
Where 172.1.1.1 is the source IP address and vbs2d1.sdp is the SDP file name.
Valid for Type Other
ASX Files
http://172.1.1.1/file.asx
ETV Portal Server Admin Guide 53

http://myHost/file.asx
http://www.myCompany.com/files/file.asx
MP3 and WMA Files
http://172.1.1.1/file.mp3
http://myHost/file.mp3
http://172.1.1.1/file.wma
http://myHost/file.wma
WMV Files
http://www.myCompany.com/files/file.wmv
mms://www.myCompany.com/files/file.wmv
To add a URL for a live video stream:
T
1. Enter the URL or IP address in the
2. Enter the
Type and Title and click Add to add the URL to the list of streams shown.
URL field.
URL Enter a valid URL or IP address. See examples above.
Type Choose MPEG-1, MPEG-2, MPEG-4, WM or Other. (Select Other for
non-MPEG streams.)
Title Title is what will display to clients in the ETV Portal Server viewing pages.
Add VOD Content
Administrators can manually enter URLs to VOD content that is not automatically displayed
by the Portal Server. These URLs can be to content that is located on a non-NXG Video-onDemand server, such as the QuickTime/Darwin server, a Windows Media server, or a Helix
Real server. This is valuable feature if you want to enter an off-network stream such as an
MPEG-4 Stream from an Apple Darwin Server or if there is Windows Media or Real
Networks content that needs to be displayed through the Portal Server interface.
54 © 2007 VBrick Systems, Inc.

Global Settings
URL Enter a valid URL or IP address. For example:
rtsp://ipaddress/programname
mms://ipaddress/videoname.wmv
Type Choose MPEG-1, MPEG-2, MPEG-4, MPEG-4 NXG, Document,
WM, or Other. If you are creating a URL for stored video that points
www.yahoo.com, for example, select Document in this field—not
to
Other.
Title This is what will display to clients in the ETV Portal Server viewing
pages
Folder This is the folder on the VOD server in which the video will be
displayed.
Keywords Enter keywords that can be searched from the user interface.
Max. Concurrent
Users
Set the maximum number of concurrent viewers for this stream to
unlimited or any number greater than zero.
Press Add to add the VOD content to the list. VOD content also can be Modified or
Deleted. Simply select the VOD content, make modifications (if required), and click
or
Delete.
Modify
Add Non-VOD Content
PC Users Only. In the VoD Content section, administrators can also link to external
documents such as PDF files, PowerPoint files, web pages, or anything that can be displayed
in a browser or other external program. For content that needs to run with a specific
application (for example, PowerPoint slides), the application must be present on the desktop
for that file to be viewed. Use the content
Type field to identify the content. Select a stream
type (MPEG-1, MPEG-2, etc.) to add video content from an outside source. Select type
ETV Portal Server Admin Guide 55

Document for PDFs or Word documents, or type Other for PowerPoint presentations, Flash
demos, etc. Each content type has a different icon on the Video Library page.
The URL must point to a web server or a local drive. The Portal Server server can act as the
web server for this content, if the content is placed in the
directory on the ETV Portal Server (or in any subdirectory you create, e.g.
... mcs\test_files\test.doc). A local path or network shared path also can be entered.
Content accessed from a local drive (or network shared path) needs to be entered in the
format c:/path/file (it will fail if you use back slashes, for example c:\path\file). Also, this
drive needs to be accessible by those that have access to the link.
Emergency Broadcast
These pages are used to create emergency broadcast templates that Portal Server users can
subsequently use to launch an emergency broadcast. Emergency broadcasts are launched from the
Portal Server user interface—not from the Admin console. An emergency broadcast is a schedule
that can be executed by Portal Server users with appropriate permissions. This schedule
broadcasts a live or stored video to specified VBricks or set top boxes in case of an
emergency. The schedule is executed instantly, for a specified duration or indefinitely. When
done (or manually stopped) all preempted schedules automatically resume.
An emergency broadcast template pre-defines all parameters for the broadcast so that it can
be launched immediately; it pre-empts all other broadcasts. Very simply, you define the
source stream (live or stored) and the downstream targets (VBricks or STBs) and then save
the template for future use. It is important to note that emergency broadcast streams are
shown only on monitors or TVs attached to VBricks and STBs respectively. They are not shown
on the Portal Server user interface. If you are watching a stream in the embedded player on the
user interface browser, you will not see an emergency broadcast.
c:\program files\vbrick\mcs
Note Live and stored broadcasts, in this context, refer to content that is being streamed
over your IP multicast-enabled network. This does not mean there is IP broadcasting
to your entire network.
T To create an Emergency Broadcast Template:
1. Go to
Global Settings > Emergency Broadcast. This page shows a list of previously
defined templates (if any).
56 © 2007 VBrick Systems, Inc.

Global Settings
2. Select Add Template and click Submit to display the following window.
3. Enter a
Template Name, select a Schedule Type, and click Next. (Duplicate template
names are allowed but not recommended.)
Each
Schedule Type subsequently has a different wizard depending on the selections
you make but basically, you select the video source (which can be a live or stored
broadcast), the downstream targets (VBricks or STBs) to which it will be broadcast, and
configure any
Advanced Settings (see note below) for the VBricks or STBs. When done
the template you created is available to authorized Portal Server users as an Emergency
Broadcast template. See the ETV Portal Server User Guide for more information.
ETV Portal Server Admin Guide 57
Note
Advanced Settings are available to configure VBricks and STBs with exceptional
configuration parameters. It is unlikely you will ever need to change these settings. In
all cases you can safely ignore the
Advanced Settings and use the defaults provided
by ETV Portal Server.
Template name Alphanumeric characters or spaces. No special characters.
Schedule Type Live Broadcast
• VBrick – Select a live stream by VBrick Name. Then select the
destination VBricks or STBs.
• Program Name – Select a live stream by Program Name from all
available. Then select the destination STBs.
• Enter Manually – Select an MPEG source residing at a specified IP
address. Then select the destination STBs.
Stored Broadcast
• VoD Name – Select a VOD server and a source video. Then select
the destination VBricks or STBs.
• VBrick Name – Select a VBrick (or VBStar) and a source video.
Then select the destination VBricks or STBs.
4. Configure Advanced Settings for VBricks and STBs as necessary. As noted, it is unlikely
you will ever need to change these settings. In all cases you can safely ignore these
settings and use the defaults provided by the Portal Server.
These settings generally set configuration options for source devices and destination
devices (VBricks and STBs) so that they are configured properly (e.g. transmit/receive
enabled/disabled) at the beginning and end of an emergency broadcast. All required
devices must be present and enabled for a successful emergency broadcast. The settings
differ depending on the device (e.g. MPEG-1, MPEG-2 or MPEG-4) you select and may
include some or all of the fields explained below.
58 © 2007 VBrick Systems, Inc.
Global Settings
Schedule Start
Options
Enter values that describe the device state at schedule start.
• Program Name – Program name selected above.
• Template – MPEG only. Screen varies for MPEG-1, 2, or 4.
• Destination – Destination 1, Destination 2, RTSP Server.
• Destination Address – Enter value.
•Video Port – Enter value.
• Audio Port – Enter value.
• Closed Captioning Port – Enter value.
• Video – Enabled, Disabled, As Configured.
• Audio – Enabled, Disabled, As Configured.
• Closed Captioning – Enabled, Disabled, As Configured.
Schedule End
Options
Enter values that describe the device state at schedule end.
• Video – Enabled, Disabled, As Configured.
• Audio – Enabled, Disabled, As Configured.
• Closed Captioning – Enabled, Disabled, As Configured.
5. Click Next to page through each wizard.
6. Click
7. Verify the information and click
Finish when done.
Create Schedule when prompted (or use the Back
button to make changes). When finished, the template is added to the list of Emergency
ETV Portal Server Admin Guide 59

Broadcast Templates available to ETV Portal Server users from the Portal Server
application. See the ETV Portal Server User Guide for more information.
Program Names
Program Names are used with live presentations. A Program Name is the title that will be
displayed on the Live Broadcasts page during a live, rich media presentation—if users have
Live Channel privileges. Program names are also used to set permissions for live
presentations and all defined Program Names are displayed in the
Privileges
in this window. A
permissions) in advance for use with VBPresenter. When you use this same name in the
Program Name
Portal Server's
for more about program names.
window. You can allow or deny viewing of any presentation by adjusting privileges
Program Name (e.g. HR Presentation) can be pre-configured (with
field in VBPresenter for example, HR Presentation will be displayed on the
Live Broadcasts page. See Configuring for Live Presentations on page 107
Add/Modify Live Channel
MCS
60 © 2007 VBrick Systems, Inc.

Global Settings
Access Logging
Access logging tracks Portal Server usage. It creates logs that let you review who has watched
what content, when, and for how long. Specifically, it logs access to live or VOD content, and
to user-initiated recordings. There are two output logs; one is used for live/VOD content
and the other is for recordings. The logs are created in a standard format and can be viewed
with a customized template (see Viewing the Access Logs
tools like Web Log Explorer. Use the various configuration options described below to save
the logs to a different computer, set log time periods, etc. By default, access logging is set to
off and the logs are saved in
the log file only after viewing or recording is complete. To se e w hat is currently being viewed or
recorded, open the Logged Programs table in MCS using MySQL Query Browser or a similar
tool. (MySQL Query Browser is available free of charge with the free software/open source
GNU General Public License at http://www.mysql.com
certain constraints; for example, it:
• does not log web page access. This is an IIS function that can be set and controlled by
system administrators.
• does not work with the Apple QuickTime player.
• does not have a built-in parser. The logs can be viewed as text files or can be managed
and viewed using third-party reporting and analysis tools.
on page 63) or with log analysis
Program Files\VBrick\MCS\Logs. Note that log entries are written to
.) Be aware that the access logger has
ETV Portal Server Admin Guide 61
Enable Access Logging Sets access logging on or off.
Log Cycle Time New log files can be created daily, weekly, or when the file reaches
a certain size. Old files are never deleted or written over.
Log File Directory Specifies where the log files are saved. This can be on the same
machine as the Portal Server or on a different machine in the
same network.
Cycle Log File Click
Cycle Now to close the existing log files and create new
files.
Extended Logging
See below. Determines what fields are logged.
Properties
Logger Timeout Values The timeout values (default two hours for stored content, four
hours for live content) are typically used when a client machine
crashes or hangs.
Extended Logging Properties
Use the following window to specify which fields are logged. The items in parentheses (e.g.
cs-username) refer to the header field shown in the actual log file (see Figure 9 below). The
fields are self-explanatory and most are standard W3C fields. (See http://www.w3.org/TR/
WD-logfile.html for more about W3C log file formats.) Note that the fields used in each log
will vary slightly and unused fields are marked with a hyphen "-". Note that the following
non-standard fields may be incompatible with some reporting tools and can be de-selected:
x-address, x-port, and x-duration. For best results with log analysis tools, do not de-select any
other fields.
62 © 2007 VBrick Systems, Inc.

Global Settings
Viewing the Access Logs
The log files are saved in Program Files\VBrick\MCS\Logs.You can view these file using a
standard editor like Notepad or you can use the Excel spreadsheet template provided by
VBrick. The
can also use this template to build Pivot Tables to analyze the log data in greater detail. Pivot
Tables are a powerful tool used to analyze multi-dimensional data. Pivot Tables are beyond
the scope of this document and are not explained here. For an introduction to Pivot Tables,
there are a variety of resources on the web including the Microsoft Office online demo at
http://office.microsoft.com/en-us/assistance/HA011989031033.aspx
T To create a pivot table:
1. Navigate to
2. When prompted, select Enable Macros.
3. Click
4. Select one or more log files by holding down the Ctrl or Shift keys while selecting files.
5. Once the window is populated with log data (Figure 9) you can view or sort any of the
columns as necessary.
6. Click
MCSS Access Log.xlt template file makes to easy to view and sort log files. You
C:\Program Files\VBrick\MCS\Utils and double-click MCSS Access Log.xlt
Import Log(s) and navigate to the log files in Program Files\VBrick\MCS\Logs
Pivot Table Wizard and follow the prompts to build a Pivot Table.
ETV Portal Server Admin Guide 63

Figure 9. Imported Access Log
64 © 2007 VBrick Systems, Inc.

Server Administration
Topics in this chapter
Modify VOD Content . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 65
Diagnostics. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 67
Status . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 67
Expired Content Log . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .68
Access Control. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 69
Live Presentations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 75
Users . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 75
User Groups. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 75
Resource Groups . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .75
Help . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 76
Logout . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 76
Chapter 3
Modify VOD Content
Video on Demand Servers only. Administrators and authorized users can modify and delete
content located on their video on-demand servers. (Note that you cannot delete or modify
any content files that are currently in use.) Administrators can find or filter the displayed
assets by clicking on
set Expiration and to define the maximum number of concurrent viewers for a stream. Also,
be aware that a user with publishing permissions can delete content by clicking the Info
hyperlink and then
publishing permissions (see Allow Content Publishing on page 86).
Note NXG1 only. You cannot rename or otherwise manage VOD files stored on some
legacy NXG1 servers. This feature is supported on all NXG2 servers and on all other
servers currently available with ETV Portal Server.
All, Keyword, Title, or Expiration Date. You can also use this window to
Delete Video. To disable this user option, disable the user's content
ETV Portal Server Admin Guide 65

Search box (All) Search for specific assets by selecting All, Keyword, Title, or
Expiration Date. Then click Refresh.
Filter Pattern Search for specific assets using a filter pattern. Type any text string
and click Refresh. For example, type
mp4 in the title. The filter does not recognize "wildcards" and is not
mp4 to search for assets with
case-sensitive.
Name Video content name. Click on Refresh to re-paint the screen or Purge
button to remove the artifacts of failed Delete operations.
Expiration Expiration date if any.
Folders Use to navigate to a specific folder.
Filename Click once on any named content in the list to populate this field.
Expiration • Expiration Date – set date in
mm/dd/yyyy 12:00 AM format.
• Viewing Period – set a value for viewing period in hours, days,
weeks, months, or years.
Max. Concurrent
Users
T To modify VOD Content:
Defines the maximum number of users who can view this stream at
the same time. Select unlimited or enter a value greater than zero.
1. Click on the content to be changed.
2. Enter a new filename and/or path for that file. Note that the file must be alphanumeric
characters and cannot contain embedded spaces.
3. Set the
4. To delete a file, select the file and click
66 © 2007 VBrick Systems, Inc.
Expiration Date or Viewing Period as necessary.
Delete.

Diagnostics
This window displays information about Scheduler events only. It displays system log
messages by source and time and (generally) IP address. Use Clear All to empty the log.
Server Administration
Status
This window shows the status of videos being added or recorded. Use Refresh and Purge as
necessary. Use the tree controls on the left to expand (or contract) individual entries. Click
the Cancel icon to the left of each to cancel a recording or ingestion in progress. This also
cancels the recording on the
Live Broadcasts page.
ETV Portal Server Admin Guide 67

Expired Content Log
This window shows all expired content in chronological order with the oldest expiration date
first. Click Purge All to delete all records in the log. See Modify VOD Content on page 65
and Stream Restrictions
on page 30 for more information.
68 © 2007 VBrick Systems, Inc.

Access Control
Under the Access Control section, administrators have the ability to enable Authentication
and Authorization which requires users to login and be authenticated. By default Enable
Authentication and Authorization
and all functions (recording, publishing, etc.). When Access Control is enabled,
Groups
what functionality is available to each user. For example some users may have unlimited
access, while others can only view certain live channels and may not have permission to
record live channels or add videos to the VOD server. Users and User Groups
explains in detail how configure users and groups.
Access control also lets you specify which folders are used when individual users record live
broadcasts, add videos, or autoingest content. If you do not enable
Authorization
,and Resource Groups are shown on the navigation bar. Access control determines
, all of these actions default to the root folder (which can quickly get cluttered).
Server Administration
is unchecked which allows everyone to access all content
User
on page 77
Authentication and
Note As soon as you check
Enable Authentication and Authorization, users will be
prompted for User Names and Passwords. VBrick recommends configuring the
system prior to user access or during off hours when the network is idle.
Administrators have the option of using the onboard
VBrick database for authentication,
using an LDAP database, or using both. VBrick supports major LDAP vendors but only
Microsoft Active Directory, Novell eDirectory, and OpenLDAP are fully tested and supported. If
ETV Portal Server Admin Guide 69
authenticating against Microsoft's Active Directory, check the LDAP Server is Microsoft
Active Directory
check box and enter the path to the LDAP server in the LDAP Path box. If
authenticating against a directory other than Microsoft Active Directory, do not check LDAP
Server is Microsoft Active Directory
. LDAP (Lightweight Directory Access Protocol) is a
standardized method to access directories from multiple vendors. A complete discussion of
LDAP is beyond the scope of this document.
Enable Authentication and
Authorization
Enable authentication and authorization which requires users
to login and be authenticated. If not checked, all users have
access to all functionality and content.
Use VBrick database Use the VBrick (non LDAP) database provided with ETV
Portal Server.
Use LDAP database Use an LDAP database. VBrick supports major LDAP
vendors but only Microsoft Active Directory and Novell
eDirectory are fully tested and supported.
LDAP Server is Microsoft
Check only if using Microsoft Active Directory.
Active Directory
Use Integrated Windows
Authentication
Use "single sign-on." This means that once you login to your
local network, you can open ETV Portal Server without reentering your login credentials. See below Single Sign-On
Use Independent Group
Entries
If unchecked (the default), the user's group memberships are
stored as attributes of the user's directory entry identified by
Attribute for Groups field. If checked, MCS will support
the
LDAP models where group entries are independent of user
entries. If checked, the Independent Group ObjectClass and
Independent Group Identifier fields are required.
LDAP Path† Required by ETV Portal Server. Case sensitive. Must begin
LDAP:// Points to a specific position in the LDAP tree
with
and also includes the machine IP address (or Domain name)
on which the server is running. For example use
myLDAPServer
myLDAPServer:636
with Microsoft Active Directory; use LDAP://
with Novell eDirectory. For more
information, see Installing the Root Certificate
LDAP://
on page 73.
.
Attribute for Usernames† Required by ETV Portal Server. Attribute to identify a user.
The following sample username attributes are widely used but
refer to a specific LDAP schema:
• Microsoft Active Directory:
sAMAccountName
• Novell eDirectory: uid
Attribute for Groups† Required by ETV Portal Server. Attribute to identify the group
to which a user belongs. The following sample group
attributes are widely used but refer to a particular LDAP
schema:
• Microsoft Active Directory:
memberOf
• Novell eDirectory: groupMembership
User Base DN Base distinguishing name (DN) of user nod and/or the Base
DN for the Master Username.
70 © 2007 VBrick Systems, Inc.

Server Administration
Username Prefix Used in non-Active Directory environments where the user
name is prefixed with a specific string such as
uid= or cn=.
The following sample prefixes are widely used but refer to a
specific LDAP schema:
• uid=
• cn=
Master Username Required for single-sign-on. User name that has admin
permission to browse the LDAP tree. Used to browse the
LDAP tree to get user groups.
Master Password Required for single-sign-on. Password for Master Username.
Ind. Group ObjectClass A group attribute in the LDAP database. Identifies which
entries will be searched for user memberships.
Ind. Group Identifier The group attribute that uniquely identifies a group. MCS will
match the values returned for this attribute with group names
entered on the
User Groups page.
† ETV Portal Server required field. All others are optional.
Note The Softerra LDAP Browser 2.6 provides an Explorer-like LDAP client you can use
to browse the LDAP tree. It is available for Windows only and can be downloaded
free of charge from Softerra at http://www.ldapbrowser.com
Single Sign-On
To use single sign-on, go to Access Control and then check Enable Authentication and
Authorization
you can select Use Integrated Windows Authentication to enable "MCS Single Sign-on."
This means that once you login to your local network with your assigned credentials, you can
open ETV Portal Server without re-entering your login credentials. ETV Portal Server uses
your assigned credentials to authenticate and authorize your defined permissions within the
application. (If using an LDAP directory other than Microsoft's Active Directory, VBrick
strongly recommends using SSL to encrypt the communication between the Portal Server
server and the LDAP directory. Please consult your LDAP vendor documentation for
instructions on how to configure SSL.) When configuring for Integrated Windows
Authentication, keep the following points in mind:
• Integrated Windows Authentication is only valid when using LDAP Authentication with
Microsoft Active Directory.
• You must perform an additional configuration step in IIS as explained below in
Configuring IIS for Single Sign-On
• Integrated Windows Authentication only works seamlessly with Microsoft Internet
Explorer browsers (Windows and Macintosh). When accessing ETV Portal Server, you
will get a popup login window only if you have not previously logged in to the network.
• When using Integrated Windows Authentication, all single-sign-on users must have an
Active Directory account and the Portal Server must be part of the Windows domain.
• When using Integrated Windows Authentication, Microsoft Internet Explorer's default
behavior is that it will not prompt for an ID/password when the server is in the
Intranet Zone
and Use LDAP Database. If the LDAP server is Microsoft Active Directory,
.
Local
. (By default, Internet Explorer assumes a URL without a period (.). This
ETV Portal Server Admin Guide 71
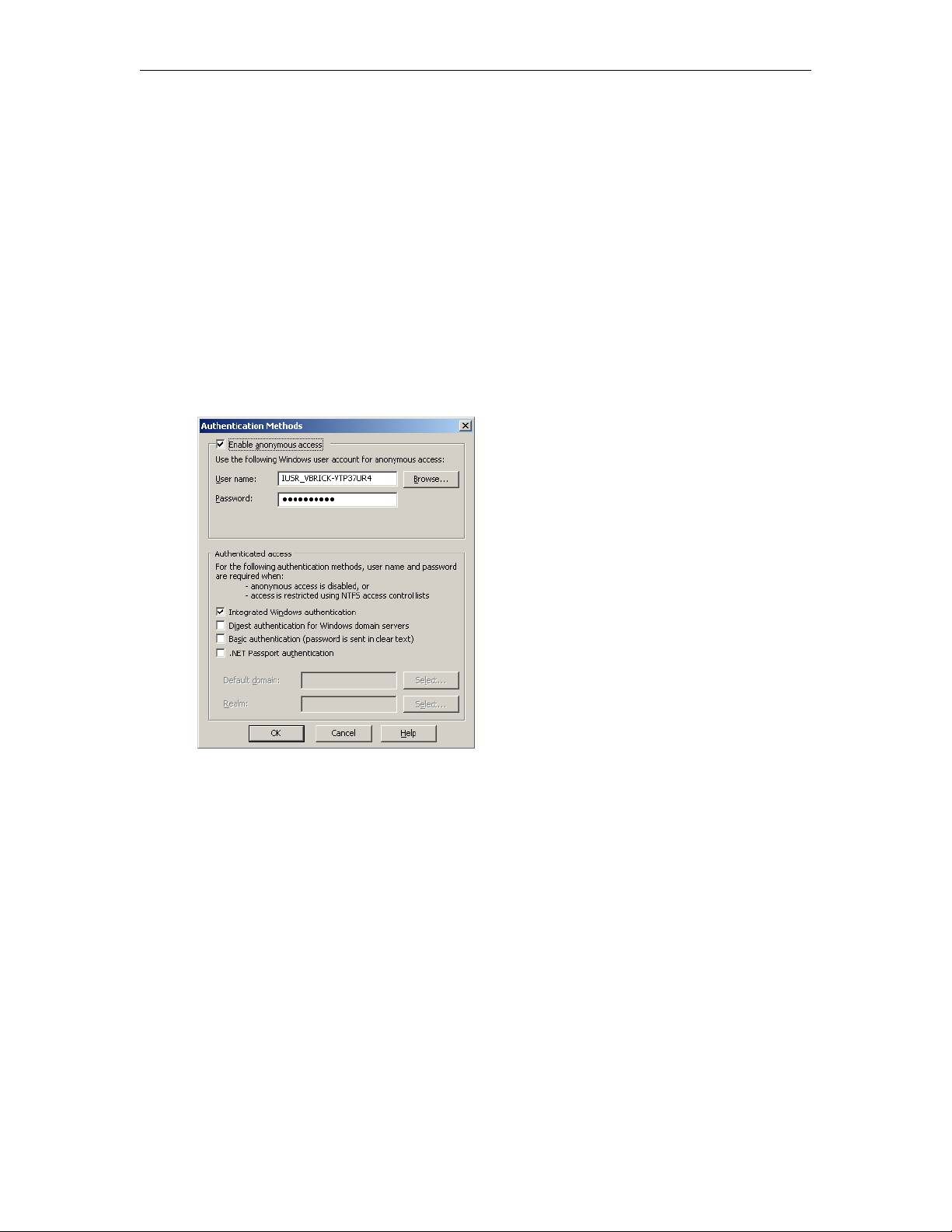
means http://yourserver/ is in the Local Intranet Zone while http://
yourserver.yourcompany.com
(or http://199.88.7.11)) is in the Internet Zone.
Configuring IIS for Single Sign-On
Use the following steps to configure IIS for single sign-on. If you do not perform these steps,
the login page will likely be blank when you launch the Portal Server.
T To configure IIS for single sign-on:
1. Go to
2. Expand
3. Expand
4. Go to
Start > Administrative Tools > Computer Management.
Services and Applications and expand Internet Information Services (IIS)
Manager
Integrated Windows authentication is checked on the following window.
.
Web Sites and then right-click on Default Web Site and select Properties.
Directory Security > Authentication and access control and make sure that
Using Single Sign-On
T To use single-sign-on (and avoid username/password prompts), you must do one of the
following:
• Access the Portal Server by the alphabetical name (for example
• Access the Portal Server by the IP address in which case you must also add the Portal
Server to the
Local Intranet Zone (Internet Options > Security > Sites). This setting can
be pushed company-wide by an administrator using security policies.
5. Change Internet Explorer's default settings to allow
username and password
Authentication
72 © 2007 VBrick Systems, Inc.
).
(Go to Internet Options > Security > Custom Level > User
Automatic logon with current
http://yourserver).

Server Administration
Using LDAP Servers with SSL
Installing the Root Certificate
If the LDAP server requires SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) for encryption and authentication,
you will need to install the certificate locally on the ETV Portal Server as a Trusted Root
Certificate Authority
T To install the root certificate locally on the ETV Portal Server as Trusted Root
Certificate Authority:
1. Open Internet Explorer.
2. In the address bar type
LDAP Server associated with Certificate Authority (See Resolving Other Security Alerts
on page 74) and
3. When Internet Explorer displays a Security Alert dialog (Internet Explorer 6) or
certificate error screens (Internet Explorer 7), click
Note Internet Explorer 6 only. All three items in the Security Alert window below must be
in compliance. The first item can easily be installed using these instructions; for the
middle item, the local CA will need to create a new certificate if it is out of date; for
the last item, the name of the certificate will need to match the address entered in the
address bar of your browser.
.
https://LDAPSERVER:636 where LDAPSERVER is the address of the
636 is the SSL port used to authenticate with the LDAP Server.
View Certificate.
4. A Certificate window will open, click on the
5. If there is more than on certificate listed in the
Certificate Path tab.
Certificate Path tab, choose the root
certificate by selecting the top-most certificate and then clicking View Certificate.
6. Choose the
7. Click
General tab. and click Install Certificate.
Next.
ETV Portal Server Admin Guide 73
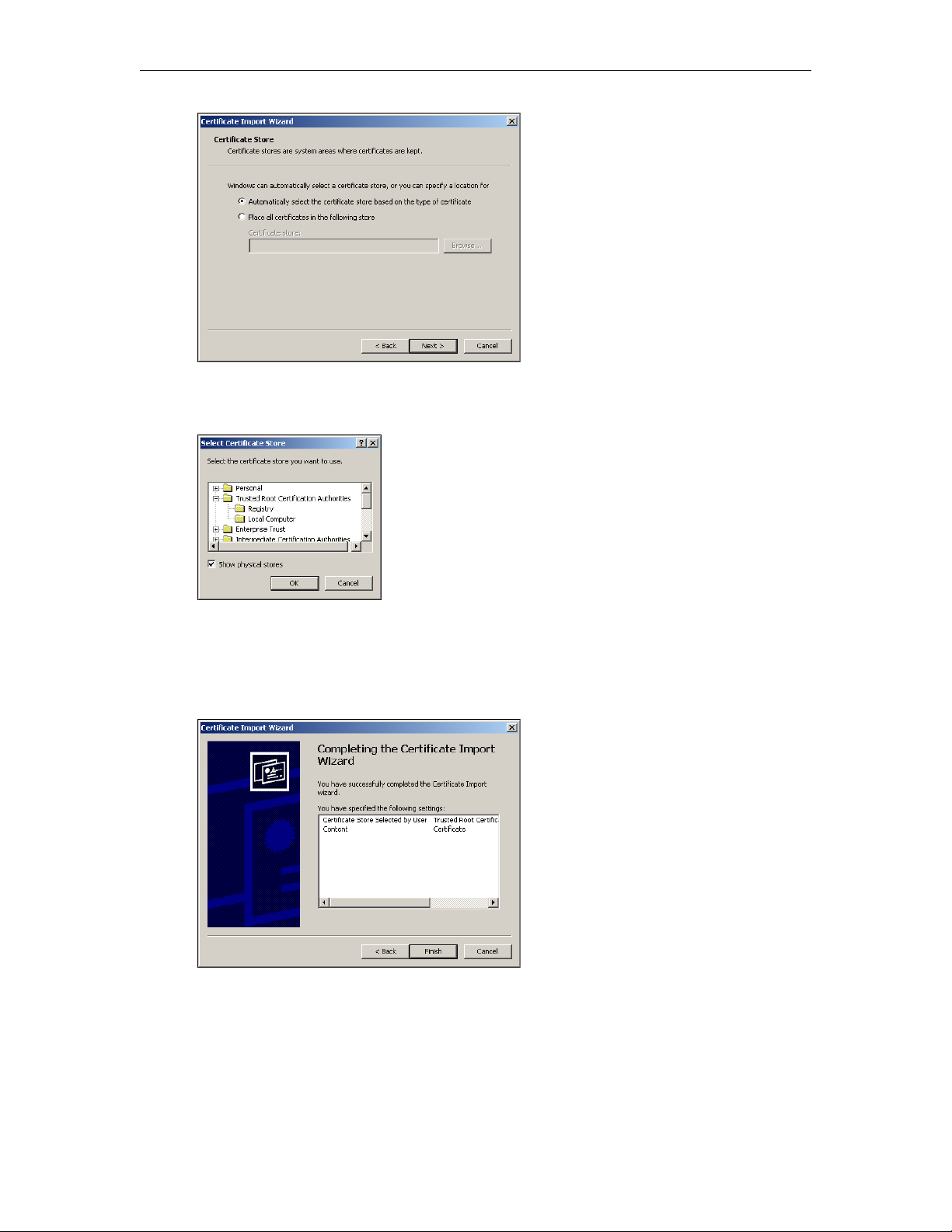
8. Click Place all certificates in the following store.
9. Click
Browse.
10. Check Show physical stores check box.
11. Click the plus sign (+) next to
12. Select
13. Click
Local Computer and click OK.
Next and Finish when done.
Trusted Root Certificate Authorities.
Resolving Other Security Alerts
If you are receiving any other Security Alerts you will need to identify the problem as either
"out of date" or
invalid name, follow the steps below to determine the valid name. If the certificate has an
"out of date" error, a new certificate must be created.
74 © 2007 VBrick Systems, Inc.
The name on the security certificate is invalid. If the certificate has an

T To determine the valid certificate name:
Server Administration
1. Click
2. The
For example: if the information is
/edirldap.vb.loc:636
out if the address is accessible, ping the address given in a command prompt. If the address is
not accessible you must create or add a DNS entry to the Host file on the local server or
generate a new certificate with the correct information.
View Certificate.
General tab shows who the Certificate is issued to; the address shown is the address
that will need to be used in the browser address bar, as well as in the configuration of the
LDAP Server.
Live Presentations
Use this window to manually remove a live presentation listing from the Live Broadcasts
page. If the presentation is terminated abnormally for any reason (for example if the
presenter exits PowerPoint without going
presentation links. See VBPresenter on page 105 for more about configuring live
presentations.
edirldap.vb.loc then the address bar should read https:/
and the LDAP Path should read LDAP://edirldap.vb.loc:636 To find
OFFLINE), you may need to manually remove the
Users
See Users on page 81.
User Groups
See User Groups on page 87.
Resource Groups
See Resource Groups on page 89.
ETV Portal Server Admin Guide 75

Help
This command launches the ETV Portal Server online help system in a new window. This
online help system provide fast full-text search and makes it easy to find the information you
need. To navigate in the help window, use the tree controls on the left to expand a topic and
the navigation buttons at the top to move to a different page. Go to
this Help
for information about how to Print pages and use the full text Search feature.
About this Help > Using
Logout
This command logs you out of the application and lets you log back in as a different user.
This may be necessary to gain access to certain functionality. For example, some users may
not be allowed to create thumbnails and you may want to login as a user who has the
permissions to do this.
76 © 2007 VBrick Systems, Inc.

Users and User Groups
Topics in this chapter
Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 77
Configuring for Users and User Groups . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 79
Users . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 81
User Groups . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 87
Resource Groups . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 89
STB Authentication . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .90
Overview
Adding the EtherneTV system to a network provides many benefits in the form of increasing
access to rich media. However, because of the sensitive nature of some video assets, many
customers want to limit access to different users or groups of users. VBrick's EtherneTV
Portal Server allows Administrators to setup the system in just this manner. The ETV Portal
Server makes it easy to provide different Users or User Groups access to different resources.
The ETV Portal Server Access Control system allows administrators to allow/deny access to
the portal server for Windows-based PCs, Macintoshes, and Set Top Boxes:
Chapter 4
• Viewing of certain Live Channels
• Viewing of stored content from specific VOD folders
• Publishing content to specific VOD folders
• Recording content to a specific VOD folder
• Allow the viewing of content from only specific VOD servers on the network
• The ability to place bandwidth restrictions for viewing content
• The ability to limit certain users to only access Multicast or RTSP (unicast) content
• The ability to group content resources (Live Channels and/or VOD content) into
Resource Groups, which allows the setup and modification of the Access Control
functionality to take place much more easily.
The ETV Portal Server is permissive by default, meaning, authentication is not enabled and
access to the entire functionality of the server is allowed. However, to follow good security
practices, once the Access Control functionality is enabled on the Portal Server, all resources
are by default not available to any users. Administrators need to provide access to resources to
different users or user groups.
Definitions
The ability to provide different users different access to resources on a network is typically
referred to as access control, authentication and authorization, and/or access management.
VBrick refers to this functionality as Access Control. In order to fully understand the range
of functionality of the ETV Portal Server Access Control system, it is beneficial to define
some of terms that are used in this section.
ETV Portal Server Admin Guide 77

Authentication
Authentication is the process of identifying an individual, usually based on a username and
password. In security systems, authentication is distinct from authorization (see below), which is
the process of providing individuals access to resources based on their identity.
Authentication merely ensures that the individual is who he or she claims to be, but says
nothing about the access rights of the individual.
The ETV Portal Server Access Control system allows administrators to authenticate users
against the ETV Portal Server database or authenticate users against an LDAP directory.
More details on the different authentication databases are given below.
Authorization
Authorization is the process of granting or denying access to a network resource. Most
computer security systems are based on a two-step process. The first stage is authentication,
which ensures that a user is who he or she claims to be. The second stage is authorization,
which allows the user access to various resources based on the user's identity. In the ETV
Portal Server, all authorization is done directly on the ETV Portal Server, through the ETV
Portal Server database.
LDAP
LDAP stands for Lightweight Directory Access Protocol which is a set of protocols for
accessing information directories. The LDAP standard defines both a network protocol for
accessing information from the directory and an extensible structure for defining how the
information is organized in the directory. The advantage of using an LDAP directory is
centralized management of users. For example, a new user needs only to be entered once into
the LDAP directory and all future modifications to that user can be done in the same central
location. Different applications can authenticate and/or authorize users against the LDAP
directory.
There are numerous LDAP directory products on the market today, but the most popular are
Microsoft Active Directory, Novell eDirectory, Sun iPlanet, and OpenLDAP. VBrick supports
major LDAP vendors but only Microsoft Active Directory and Novell eDirectory are fully tested and
supported.
VBrick Database
The ETV Portal Server server ships by default with the MySQL database, which is a fully
ODBC-compliant database. (Open Database Connectivity is a standard database access
method.) For those environments that have not migrated to an LDAP directory-based user
management system, all of the authentication functionality can be done directly in the ETV
Portal Server database itself. Also, for those environments that are using LDAP directories
for Authentication, all of the Authorization functionality also takes place in the ETV Portal
Server database. Additionally, to reduce the chance of system lockout, all Administrative
Users are located in the ETV Portal Server database.
Resources and Resource Groups
In the ETV Portal Server, providing a user with Resources refers to providing them access to
a particular functionality of the EtherneTV system. These include the ability to view Live
Channels, to view VOD content, to publish content to the VOD, and to record content or
schedule a recording. A unique feature of the ETV Portal Server software is the ability to
78 © 2007 VBrick Systems, Inc.

group Resources into Resource Groups. This allows the administrator to quickly and easily
assign several resources at once to specific Users or User Groups.
Configuring for Users and User Groups
1. Setup and Configure ETV Components
The following products need to be setup and properly configured prior to configuring Access
Control.
1. ETV Portal Server – The ETV Portal Server needs to be properly setup and configured
on the network. The following items should be configured in the Portal Server interface:
a. If there is a VOD server(s) in the system, the proper addresses for these servers need
to be entered into the Portal Server Administrative pages and connectivity to those
servers should be ensured.
b. The folder structure on the VOD server should be defined (even if there is no
content in these folders) as folders are how the Access Control functionality
provides access to end users to view VOD content, publish content, and record
content. When setting up the folder structure, the Administrator should be thinking
about how they plan to provide access to different groups of users. For example, if a
corporation wanted to provide certain content to the Engineering group and certain
content to the Marketing group, then they would want to set up an Engineering
folder and a Marketing folder on their VOD server.
c. If there are live streams on the network, then those streams should be provided a
channel number if the Administrator wants to provide access to live streams via
channel number.
d. If security is a concern, SSL should be turned on between clients and the ETV Portal
Server server. This allows User Names and Passwords to be encrypted between the
client and the server. See the section Configuring for SSL
on how to configure this.
Users and User Groups
on page 93 for instructions
2. VBrick – If there are VBricks in the network, they are auto-discovered but still need to be
added to the Portal Server database.
3. VOD Server – If there are VOD servers in the network, again they need to have
connectivity to the Portal Server and the folder structure needs to be configured.
4. Set-Top Boxes – If there are STBs to be deployed in the system, they should be
configured with a Host Name, and should be configured to point to the ETV Portal Server.
Additionally, if an LDAP server is going to be used to authenticate users, then the
administrator should know the address of the server, the group structures on the LDAP
server, and the Context (if the server is not Microsoft's Active Directory).
Note In order to scan the Groups available in Microsoft's Active Directory, in Windows
Explorer, go to
Show common tasks in folders is selected. Then go to Start > My Network Places
and select
Tools > Folder Options. On the General tab, make sure that the
Network Tasks > Search Active Directory.
2. Choose an Authentication Method
Select one of the following methods:
ETV Portal Server Admin Guide 79

VBrick Database The native ETV Portal Server user database provides local
authentication for users and administrators.
LDAP Database Enables the ETV Portal Server to authenticate against, and retrieve
user and group data from, an existing LDAP server.
Both methods can be used simultaneously. If LDAP authentication is enabled, the ETV
Portal Server will attempt to authenticate against the LDAP server first, and if this is
unsuccessful, will attempt to authenticate against the local ETV Portal Server User Database.
VBrick Database
If authentication is enabled, you must select a database (either VBrick or LDAP). The VBrick
(ETV Portal Server) user database contains user, group, and resource information that
provides the Portal Server with information to allow it to provide the appropriate privileges
to users and Set-Top Boxes that are accessing the system. Administrators should authenticate
users with the native Portal Server user database if:
• User authentication is required, but the organization does not have an LDAP server.
• For STBs, the organization wishes to use User PINs. Since User PINs are not available in
the LDAP directory, the users need to be created in the ETV Portal Server database
(Note: only those users that need PINs to access STBs need to be created in the ETV
Portal Server database. PC or Mac users can still be authenticated against LDAP).
LDAP Directory Server
An LDAP directory server contains User and Group information which the ETV Portal
Server can authenticate against to verify User's identities. The Portal Server then uses this
information to authorize users to access the system. Administrators should authenticate users
with an LDAP Directory server if:
• The organization has an LDAP server that they actively manage to allow products to
authenticate.
• The ETV Portal Server administrator can obtain the necessary configuration information
from the LDAP administrator to allow the authentication to occur.
Using LDAP reduces the amount of administrative time necessary to add and modify users
from the ETV Portal Server system. VBrick Systems encourages customers who have LDAP
directories implemented to use them for authentication with the ETV Portal Server.
3. Create User Groups on the Portal Server
Grouping users is common practice and makes administering access to the ETV Portal
Server less complicated than administering access by individual user. The ETV Portal Server
allows the administrator to create groups, specify group memberships for users, and set
access privileges for the group. A user can be a member of one group or multiple groups.
Group access privileges also can be set and modified on a per group basis.
If an LDAP directory is being used for Authentication, the same group information that is
available in the directory can be used to Authorize end users to access the ETV Portal Server.
For example, if the organization has three User Groups in its LDAP directory—Marketing,
Engineering, and Sales—they can simply create these groups in the ETV Portal Server
system, and assign privileges to the groups.
80 © 2007 VBrick Systems, Inc.

Users and User Groups
4. Create Resource Groups on the Portal Server
In the Portal Server software, providing a user with Resources refers to providing them
access to a particular functionality of the EtherneTV system. These include the ability to:
• View Live Channels.
• View VOD content.
• Publish content to the VOD.
• Record content or schedule a recording.
• Launch an emergency broadcast.
A unique feature of the Portal Server software is the ability to group Resources into Resource
Groups. This allows the administrator to quickly and easily assign several resources at once to
more than one User or User Groups. This also makes the ongoing management of this
content for these Users or User Groups much easier.
For example, if the organization has three User Groups—Marketing, Engineering, and
Sales—they might create four resource groups. These Resource Groups would be Full
Access, which are resources that everyone can see, and one Resource Group for each of the
user groups. Full Access would be assigned to all user groups, and the Marketing Resource
Group would be assigned to the Marketing User Group, the Engineering Resource Group to
the Engineering User Group, and the Sales Resource Group to the Sales User Group.
Resource Groups provide the added bonus that they allow the Administrator to quickly
provide access to new content to Users and User Groups. For example, if the organization
originally had ten Live Channels on the network, and another Live Channel was added, the
Administrator would simply need to add that Channel to the appropriate Resource Groups
and the channel would be available.
5. Create Users on the ETV Portal Server
Creating users is an optional step that can be completed for the following reasons.
• The organization needs to provide a single user with additional privileges above and
beyond what is available to his or her User Group or Resource Group.
• The organization wants to authenticate STB users using a PIN.
• Users can be assigned to multiple User Groups.
6. Assign Resources to Users or User Groups
The final step is to provide access to Resources to Users and/or User Groups. The
administrator can assign individual resources to Users or User Groups, or can assign
Resource Groups (if created) to Users or User Groups. Detailed information on the steps to
configure access control and provide access to resources to Users and/or User Groups is
provided in the following sections.
Users
There are several different ways to provide privileges to different User and User Groups with
the ETV Portal Server. The easiest way is to use the group structure of an existing LDAP
database. LDAP User Groups can be added to the ETV Portal Server system and assigned
permissions (see User Groups below). All of the users in this group will have the same
ETV Portal Server Admin Guide 81

permissions. For ease of implementation, VBrick recommends configuring User Groups and
Resource Groups (see these sections below), prior to configuring users.
However, if further individual permissions need to be assigned, administrators can add them
as a user. Under the users section, administrators have the ability to add, modify and delete
users. Submit may be pressed at anytime during the process or can be done when everything
has been added/modified. Users will have the permissions of the group as well as the
additional permission that are assigned to them. The ETV Portal Server is additive in its
permissions, meaning that it takes all of the permissions that are provided to a particular user
and provides all of these to the user.
Users can be added by using the VBrick Database if LDAP authentication is not available or
desired. Finally, in order to assign user PINs to access Set-Top Boxes, a user assignment is
needed (see Set-Top Box Authentication section below). Note that STB PIN access is
dependent on the VBrick Database being enabled. See Access Control
on page 69 for details.
Submit Save changes and/or navigate to the next window.
Add New Takes the administrator to the Add New User, User Group, or Resource
Group screen (depending on which section you are in)
Clear All Clears any entries that have been entered in the individual sections.
Revert All Returns all entries to the last state entered in the database. This selection is
important if a mistake is made during entry.
Cancel Cancels out of the page. Changes are not saved.
Clear Clear eliminates or de-selects any entries in the particular section.
Revert Returns the selection to the last state entered in the database. This selection is
important if a mistake is made during entry.
82 © 2007 VBrick Systems, Inc.

Users and User Groups
Once all selections have been made, you can press Submit in the bottom right hand corner of
the screen (or any of the other buttons shown above) to submit the information to the
database. User privileges include the following options:
Add/Modify User Information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 83
Add/Modify User's Group Assignments . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 84
Add/Modify User's Resource Group Assignments . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 84
Add/Modify Live Channel Privileges . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 84
Allow Access to Specific FTP Servers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 85
Allow Access to Specific Recorder Servers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 85
Allow Access to Specific VOD Servers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 85
Allow Access to Specific VOD Content . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 85
Allow Viewing by Content Type . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 85
Allow Content Publishing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 86
Allow Content Recording . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 86
Default Content Recording . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 86
Allow VBrick Access . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .86
STB Access . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .87
Schedule Privileges. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 87
Emergency Broadcast Privileges . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 87
Copyright Restrictions & Expiration Privileges . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 87
Add/Modify User Information
To add or modify users, select Users from the navigation bar on the left.
User •
Username To authenticate using an LDAP database, the user name must match
Password For LDAP authentication a password is not needed (the user will use
User – Use this option if the EtherneTV system will be accessed
by a PC or Mac user, or if Users will be authenticated to STBs via
PIN numbers. This access is not limited to a specific PC or STB.
•
Set Top Box – Use this option if the EtherneTV system will be
accessed via a STB attached to a television or other video display.
If Set-Top Box is selected, then the privilege to the system will be
on a per STB basis. The authentication will take place
automatically, so no end user interaction is required. When
choosing STB, the STB's host name or IP address must be entered,
as well as an optional location/description of the STB.
exactly what is in the LDAP database (the Portal Server is case
sensitive). A new user can also be assigned (if using the VBrick
database option) that does not exist in the LDAP database.
their normal network login password). If using the VBrick database a
password must be entered (passwords are case sensitive).
ETV Portal Server Admin Guide 83

STB Pin Optional. A PIN number can be assigned to a user that allows them to
access their content from any STB, regardless of the STB's privilege
level. This works well when an STB is going to be a shared resource.
Note: STB PIN access is dependent on VBrick Database being
enabled.
First Name Optional. User first name.
Last Name Optional. User last name.
E-mail address Optional. User e-mail address.
Location Optional. User location.
Assigning Privileges to Users
There are three ways to assign privileges to users:
• Assign the User to a User Group that has privileges assigned to it.
• Assign the User to a Resource Group that has privileges assigned to it.
• Individually assign resources to the User.
These methods all can be combined. For example, to provide a User with access to the
resources provided to a User Group but also provide them access to additional resources, the
administrator can a) Assign the User to that Resource Group and b) Individually assign the
additional resources to that user. Each of these methods is discussed below.
Add/Modify User's Group Assignments
Users can be assigned to specific User Groups, and they will inherit the privileges of that
group. If no User Groups appear, then none have been defined. Click User Groups in the
main navigation to the left to create User Groups.
Add/Modify User's Resource Group Assignments
Users can be assigned to specific Resource Groups, and they will inherit the privileges of that
Resource Group. If no Resource Groups appear, then none of been defined. Click Resource
Groups in the main navigation to the left to create Resource Groups.
Add/Modify Live Channel Privileges
A list of available live video streams will be displayed. A user can be provided access to all live
streams or to specified individual streams. (Note that a
has been customized using
assignments, both the Channel Number and the Program Name will appear in the Channel
list. If the Channel number is selected, the ETV Portal Server will always provide access to
the particular channel (for example, Channel 1) even if the Program Name of that channel
changes. If the Program Name is selected, the ETV Portal Server will always provide access
to the Program Name (for example, CNN), even if the channel that it is associated with
changes (for example, from Channel 2 to Channel 4).
Customize Streams.) For live streams that have channel
Live Program is a Live Channel that
84 © 2007 VBrick Systems, Inc.

Users and User Groups
Note The live streams shown in the Portal Server may also be restricted by a bit mask on a
VBrick encoder. The Portal Server will parse the bitmask and send the live stream
only to ETV clients with a IP address that matches the masked IP of the source
VBrick. You can use this feature in addition to the Portal Server authorization
features. See the Announce(SAP) parameter in the encoder appliance Admin Guide
for more information.
Allow Access to Specific FTP Servers
Allow or deny access to defined FTP servers.
Allow Access to Specific Recorder Servers
Allow or deny access to defined recorder servers.
Allow Access to Specific VOD Servers
Choose from a list of available VOD server(s) to which a user has access. A user can have
access to multiple servers. This feature is particularly useful when VOD servers are located in
different physical locations that are separated by low bandwidth links. For example, if a
company has offices and VOD servers in both New York and Chicago, and these offices are
separated by a T-1 link, then they would want to limit the users in the Chicago office to the
Chicago VOD server and those in New York to the New York VOD server.
Note When a user is provided access to particular VOD server(s), and they are given the
privilege to Publish or Record to a particular folder, when they Publish or Record,
the video will be Published or Recorded to each server that they have access to. This
is important for clustering purposes.
Allow Access to Specific VOD Content
Choose from a list of folders to which a user can have access. A user can have access to
multiple folders on multiple servers. If the user has access to multiple VOD servers, and the
folder names are the same on both servers, only one folder name will show up in the list.
Allow Viewing by Content Type
The Administrator can limit the types of content that a user can view and/or limit the
bandwidth that specific users can view. Note that this setting does not apply to URLs that
were manually added by an administrator (see
Do Not Allow
Multicast viewing
Restrict Multicast to
Kbps
This will limit users that are on a non-multicast capable part of
the network from trying to view multicast video.
This will limit users to only viewing multicast streams that are a
certain size or smaller. This works well to maintain bandwidth
utilization over a particular WAN port.
URLs on page 53).
ETV Portal Server Admin Guide 85
Do Not Allow RTSP
viewing
This will limit users from viewing RTSP Unicast Streams from
MPEG-4 Encoders and from accessing RTSP unicast streams
from a Video-on-Demand server (MPEG-1, MPEG-2, or
MPEG-4). T his works well to maintain bandwidth utilization over
a particular LAN or WAN port.
Restrict RSTP viewing
to Kbps
This will limit users to only viewing RTSP streams that are a
certain size or smaller. This works well to maintain bandwidth
utilization over a particular LAN or WAN port.
Allow Content Publishing
Administrators can allow a user the ability to publish content to folder(s) on an VOD VideoOn-Demand Server. This function allows the user access to the Add Video page, where users
can add pre-recorded video content to a VOD. It also allows users to (1) create (and upload)
Thumbnails for video files in the folders to which they can publish, to (2) delete video
content from the VOD server, and (3) to add keyword and description data using the Modify
Info
button. To prevent users from deleting content, be sure this option is disabled.
Note If users are provided access to more than one VOD server, when they publish
content, it will be published to each of the servers to which they have access. This is
important for clustering purposes.
Allow Content Recording
Used for scheduled recording. Administrators can allow a user the ability to schedule the
recording of live content to a specific folder(s) on a VOD Video-On-Demand Server. They
cannot record content to any other folder(s). You must select a folder here to enable
Content Recording
shown as an option and
below. If there is no schedule license, Allow Content Recording is not
Default Content Recording lets you select any folder. If you add a
schedule license later (using Start > Control Panel > Add or Remove Programs), Allow
Content Recording
will be shown as an option with all folders selected. You may want to
unselect specific folders in order to restrict recording privileges.
Default
Default Content Recording
Used for on-demand recording. You must select a folder above for Allow Content Recording
before you can make a folder selection here. Administrators can allow a user the ability to
record live content to a specific default folder on an VOD Server by pressing the
Record
push button below the Preview Window. For ease of use, the Administrator can only assign
one default folder where a particular user can record content. This allows one button
recording on the ETV Portal Server and is particularly important for Set-Top Box users, who
may not be able to enter a recording path with their IR remote control.
Allow VBrick Access
Administrators can allow a user the ability to access all VBricks or only specific VBricks when
scheduling events. When scheduling an event, users will see only those VBricks for which
they have been granted access.
86 © 2007 VBrick Systems, Inc.

Users and User Groups
STB Access
Administrators can allow a user the ability to access all STBs or only specific STBs when
scheduling events. When scheduling an event, users will see only those STBs for which they
have been granted access.
Schedule Privileges
Users may have full, partial, or no permission to schedule VBrick event. Users with full
privileges can modify all configuration parameters in a schedule. Users with partial privileges
cannot modify
• Super – can change all schedules.
• Full – can change only "owned" schedules.
• Partial – can change only "owned" schedules; no
• None – cannot create schedules; no
Advanced Settings.
Advanced features.
Add button shown on Scheduling page.
Emergency Broadcast Privileges
Administrators can specify whether or not a user can launch Emergency Broadcasts.
Copyright Restrictions & Expiration Privileges
Administrators can allow users to set Copyright Restrictions and Expiration Privileges when
adding stored content or scheduling a recording. Note that copyright restrictions apply only
to Portal Server-initiated playback sessions (and not, for example to direct RTSP requests to
a VOD server).
User Groups
Grouping users is common practice and makes administering access to the ETV Portal
Server less complicated than administering access by individual user. The ETV Portal Server
server allows the administrator to create User Groups, specify group memberships for users,
and set access privileges for the group. A user can be a member of one group or multiple
groups. Group access privileges also can be set and modified on a per group basis.
If an LDAP directory is being used for Authentication, the same group information that is
available in the directory can be used to Authorize end users to access the ETV Portal Server.
For example, if the organization has three User Groups in its LDAP directory—Marketing,
Engineering, and Sales—they can simply create these groups in the ETV Portal Server
system, and assign privileges to the groups.
ETV Portal Server Admin Guide 87

Add/Modify Group Information
If LDAP is being used for authentication, then the group name has to exactly match the
group name in the LDAP directory. If LDAP is not being used, Group Names can be entered
directly into the ETV Portal Server database. If Microsoft's Active Directory is used, to find
the available list of active groups in
the left-hand menu Search Active Directory. A new window will open. Click Find now to see
all available groups. In Windows 2000, go to My Network Places > Entire Network >
Directory
, the domain, and Users.
Windows XP, browse to My Network Places and click on
Note Windows XP needs to be configured to
configure this, in
> Tasks
section, select the radio button called Show common tasks in folders.
My Network Places, go to Tools > Folder Options. In the General
Show Common Tasks in Folders. To
Add/Modify Group's User Assignments
Users can be assigned to specific User Groups, and they will inherit the privileges of that
group. If no Users appear, then none have been defined. However, if LDAP is being used for
Authentication, no users need to be defined. When a user Authenticates to the system, the
Authentication process will return the User's group information. The user will receive the
privileges that are provided to that group.
Add/Modify Group's Resource Assignments
Resource groups can be assigned to User Groups, and the User Group will inherit the
privileges of that Resource Group. If no Resource Groups appear, then none of been
defined. Click
Groups.
Resource Groups in the main navigation to the left to create Resource
88 © 2007 VBrick Systems, Inc.

Note The remaining options for User Groups (beginning with Add/Modify Live Channel
Privileges
The only difference is that the descriptions will apply to groups of users rather than
to individual users.
) are the same as those described earlier for individual Users on page 81.
Resource Groups
In the ETV Portal Server software, providing a user with Resources refers to providing them
access to a particular functionality of the EtherneTV system. These include the ability to
view Live Channels, to view VOD content, to publish content to the VOD, and to record
content. A unique feature of the ETV Portal Server software is the ability to group Resources
into Resource Groups. This allows the administrator to quickly and easily assign several
resources at once to more than one User or User Groups. This also makes the ongoing
management of this content for these Users or User Groups much easier.
Users and User Groups
For example, if the organization has three User Groups—Marketing, Engineering, and
Sales—they might create four resource groups. These Resource Groups would be Full
Access, which are resources that everyone can see, and one Resource Group for each of the
user groups. Full Access would be assigned to each user group, and the Marketing Resource
Group would be assigned to the Marketing User Group, the Engineering Resource Group to
the Engineering User Group, and the Sales Resource Group to the Sales User Group.
Resource Groups provide the added bonus that they allow the Administrator to quickly
provide access to new content to Users and User Groups. For example, if the organization
originally had ten Live Channels on the network, and another Live Channel was added, the
Administrator would simply need to add that Channel to the appropriate Resource Groups
and the channel would be available.
Add/Modify Resource Group Information
Add the Resource Group Name that is relevant for the Resource Group being created.
ETV Portal Server Admin Guide 89
Add/Modify User's Resource Assignments
Users can be assigned to specific Resource Groups, and they will inherit the privileges of that
Resource Group. If no Users appear, then none have been defined. Click on the Users section
to add Users.
Add/Modify Group's Resource Assignments
User Groups can be assigned to Resource Groups, and the User Group will inherit the
privileges of that Resource Group. If no User Groups appear, then none have been defined.
Click User Groups in the main navigation to the left to create User Groups.
Note The remaining options for
Channel Privileges
) are the same as those described earlier for individual Users on
Resource Groups (beginning with Add/Modify Live
page 81. The only difference is that the descriptions will apply to resource groups
rather than to individual users.
STB Authentication
There are two ways (STB IP address or user PIN) to authenticate and authorize Set-Top
Boxes in the ETV Portal Server. STB access control is slightly different from PC and
Macintosh-based authentication (which uses the commonly employed User Name and
Password mechanism). The two methods are outlined in the table below.
Tab le 1 2 . Authentication Methods
Method Description User Interaction Comment
User PIN If Access Control is
enabled, but the STB is
not defined in the system,
then Access Control
works based on a user
PIN. This PIN is defined
per user (not per STB)
on a
basis, so that users need to
be defined for this to
work.
When the user logs
into the system, they
will be prompted for
their PIN. The user
simply enters the PIN
with the remote
control or the wireless
keyboard, and can
then access the video.
This implementation is appropriate
for environments where multiple
users with different privileges will
be accessing the same STB. An
example of this would be a shared
classroom where multiple teachers
are accessing the STB at different
times.
STB IP
Address or
Host Name
90 © 2007 VBrick Systems, Inc.
The ETV Portal Server
system determines the
content that the STB can
view based on its IP
Address or Host Name.
No user interaction is
required. The user
simply turns on the
STB and only the
content that the STB
user can view id
displayed.
This implementation is similar to a
cable TV setup, e.g. if the cable
plan does not include CNN, that
channel cannot be viewed. This
implementation is easiest for end
users because you do not have to
remember user names or PINs. It is
appropriate for environments
where one or a few people with the
same privileges access the same
STB.
 Loading...
Loading...