Page 1

vacon nx
ac drives
basic i/o boards
expander i/o boards
adapter i/o boards
user manual
®
Page 2

Page 3

vacon • 1
Local contacts: http://drives.danfoss.com/danfoss-drives/local-contacts/
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Document: DPD00884B
Release date : 1/9/16
1. General information.........................................................................................2
1.1 Board slots on the control board of VACON® NXS and NXP............................................2
1.2 Board Slots on the control board of VACON® NXL...........................................................3
1.3 Option board types .............................................................................................................4
1.4 Technical data ....................................................................................................................5
1.4.1 Isolation..............................................................................................................................6
1.4.2 Analogue inputs (mA/V) .....................................................................................................6
1.4.3 Analogue outputs (mA/V) ...................................................................................................6
1.4.4 Control voltage (+24V/EXT +24V)........................................................................................6
1.4.5 Digital input signal conversion ..........................................................................................7
1.5 Hardware protections ........................................................................................................9
1.5.1 Terminal block coding .......................................................................................................9
1.5.2 Board slot guides and allowed slots..................................................................................9
1.6 Type identification number ..............................................................................................10
1.7 Defining functions to inputs and outputs.........................................................................10
1.8 Defining a terminal for a certain function with NCDrive programming tool ..................11
1.9 Option board related parameters ....................................................................................12
2. Installation of VACON® Option Boards .......................................................... 13
2.1 Control cables ..................................................................................................................15
2.1.1 Cable grounding...............................................................................................................15
2.2 Board information sticker................................................................................................16
3. Descriptions of VACON® option boards .........................................................17
3.1 Basic boards OPTA_.........................................................................................................17
3.1.1 OPTA1 ...............................................................................................................................18
3.1.2 OPTA2 ...............................................................................................................................21
3.1.3 OPTA3 ...............................................................................................................................22
3.1.4 OPTA4 ...............................................................................................................................23
3.1.5 OPTA5 ...............................................................................................................................29
3.1.6 OPTA7 ...............................................................................................................................33
3.1.7 OPTA8 ...............................................................................................................................39
3.1.8 OPTA9 ...............................................................................................................................42
3.1.9 OPTAL...............................................................................................................................43
3.1.10 OPTAE...............................................................................................................................45
3.1.11 OPTAN ..............................................................................................................................49
3.2 I/O Expander Boards OPTB_............................................................................................53
3.2.1 OPTB1...............................................................................................................................54
3.2.2 OPTB2...............................................................................................................................56
3.2.3 OPTB4...............................................................................................................................57
3.2.4 OPTB5...............................................................................................................................58
3.2.5 OPTB8...............................................................................................................................60
3.2.6 OPTB9...............................................................................................................................63
3.2.7 OPTBB ..............................................................................................................................64
3.2.8 OPTBH ..............................................................................................................................69
3.3 Adapter Boards OPTD_ ....................................................................................................71
3.3.1 OPTD1...............................................................................................................................71
3.3.2 OPTD2...............................................................................................................................73
3.3.3 OPTD3...............................................................................................................................77
3.3.4 OPTD6...............................................................................................................................79
4. VACON® Option Boards – operational details................................................81
Page 4
1
vacon • 2 General information
Local contacts: http://drives.danfoss.com/danfoss-drives/local-contacts/
1. GENERAL INFORMATION
VACON® NX range embodies a wide selection of expander and adapter boards with which the
available I/O of VACON
®
NX AC drive can be increased and its versatility improved.
The input and output configuration (I/O) of VACON
®
NX is designed with modularity in mind. The
total I/O is comprised of option boards, each having its own input and output configuration. The
boards contain not only normal analogue and digital inputs and outputs, but also fieldbuses and
additional application-specific hardware.
The basic, expander and adapter boards are placed in the board slots on the control board of the AC
drive. The I/O boards are usually interchangeable between different VACON
®
types, i.e. NXS and
NXP. However, the control boards of these types differ from each other to some extent which means
that the use of some I/O boards in different VACON
®
AC drive types may be restricted.
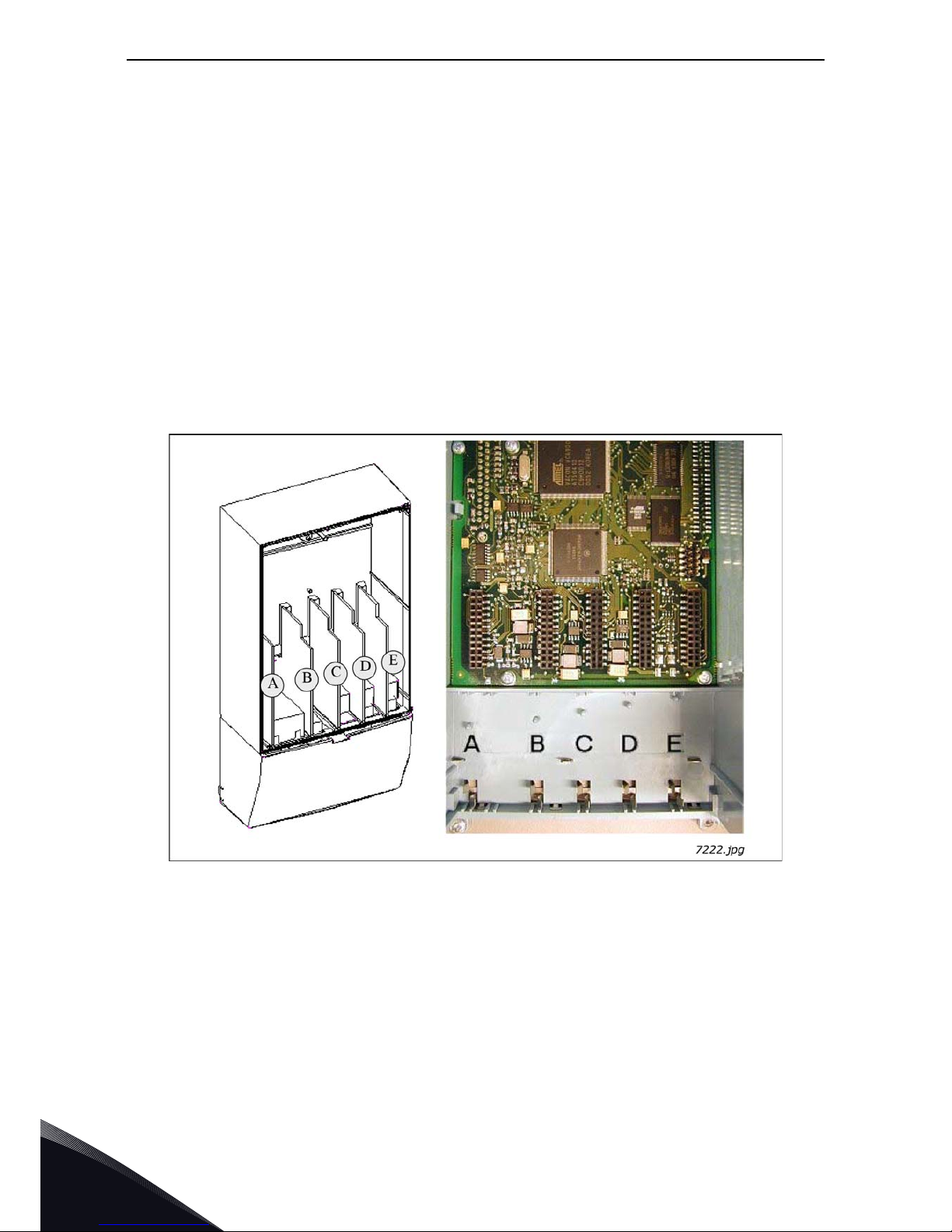
1.1 Board slots on the control board of VACON® NXS and NXP
Figure 1. Board slots on control board of the VACON® NXS and NXP
The control board is situated inside the control unit of the VACON
®
NX AC drive. There are five board
slots (labelled A to E) on the control board of NXS and NXP (See NXS/P User Manual): The
connectability of different option boards to different slots depends greatly on the type of the board.
For more information on this, see Chapter 1.2. See also the descriptions of the options boards on
pages 18 to 79.
Usually, when the AC drive is delivered from the factory, the control unit includes at least the
standard compilation of two basic boards (I/O board and relay board) which are normally installed
in slots A and B. The I/O boards mounted at the factory are indicated in the type code of the AC drive.
The three expander slots C, D and E are available for different option boards i.e. I/O expander
boards, fieldbus boards and adapter boards.
Page 5
General information vacon • 3
Local contacts: http://drives.danfoss.com/danfoss-drives/local-contacts/
1
1.2 Board Slots on the control board of VACON® NXL
Figure 2. Board slots on control board of VACON® NXL.
The control board of NXL includes fixed standard I/O and one place for option boards (see NXL User
Manual of NXL). The most typical option board for NXL, OPT-AA, is specified in the NXL
User Manual.
Page 6

1
vacon • 4 General information
Local contacts: http://drives.danfoss.com/danfoss-drives/local-contacts/
1.3 Option board types
The VACON® option boards are divided in four groups according to their characteristics: types A, B,
C and D. Short descriptions of the types below:
OPTA_
• Basic boards used for basic I/O (NXS, NXP); normally pre-installed at the factory.
• This board type uses slots A, B or C.
See pages 17 to 49 for a detailed presentation of the boards of this type. See also the principle
diagram on the options boards and their equipment on page 81.
OPTB_
• Option boards used for I/O expansion.
• Normally pluggable into slots B, C, D and E.
See pages 53 to 64 for a detailed presentation of the boards of this type. See also the principle
diagram on the options boards and their equipment on page 81.
OPTC_
• Fieldbus boards (e.g. Profibus or Modbus).
• These boards are connected to slots D and E.
See a separate manual on each individual Fieldbus Board. Ask factory or your nearest distributor
for more information.
OPTD_
• Adapter boards
• Boards with fiber optic adapters, e.g. System Bus Fiber Optic Adapter Board.
• Connect the adapter boards to slots D and E (see however page 77).
See pages 69 to 79 for a detailed presentation of the boards of this type. See also the principle
diagram on the option boards and their equipment on page 81.
Page 7
General information vacon • 5
Local contacts: http://drives.danfoss.com/danfoss-drives/local-contacts/
1
1.4 Technical data
The data in the table below applies to the inputs and outputs on all basic and expander boards.
Table 1. Tec hn ica l d at a
Safety (all boards)
Comply with EN50178, C-UL and EN60204-1
Inputs/outputs galvanically isolated; Isolation voltage
rate 500V
Input/output type Specification
Analogue inputs (AI), voltage
0…±10V, R
i
≥ 200 kΩ, single-ended;
Resolution 10 bits/0.1%, accuracy ±1% of the full display
(–10…+10V joystick control)
Analogue inputs (AI), current
0(4)…20mA, R
i
= 250Ω, differential
Resolution 10 bits/0.1%, accuracy ±1% of the full display
Digital inputs (DI), DC voltage controlled
24V: "0"≤10V, "1"≥18V, R
i
> 5kΩ
Digital inputs (DI), AC voltage controlled
Control voltage 42…240 VAC
"0"<33V, "1">35V
Auxiliary voltage (output) (+24V)
24V (±15%), max 250mA (total summarized load from
ext. +24V outputs, max. 150 mA from one board.
Auxiliary voltage (input) (ext. +24V)
24VDC (±10%, max. ripple voltage 100mV RMS), max. 1A.
In special applications where PLC type functions are
included in the control unit the input can be used as
external auxiliary power supply for control boards as
well as I/O boards.
Reference voltage (output) (+10V
ref
)
10V – 0% – +2%, max. 10mA
Analogue output (AO), current (mA)
0(4)…20mA, R
L
<500Ω, resolution 10 bits/0.1%, accuracy
≤ ±2%
Analogue output (AO), voltage (V) 0(2)…10V, RL ≥ 1kΩ, resolution 10 bits, accuracy ≤ ±2%
Relay outputs (RO)
Switching capacity
Max. continuous load
Min.switching load:
24VDC/8A
250VAC/8A
125VDC/0.4A
2A rms
5V/10mA
Thermistor input (TI)
R
trip
= 4 kΩ (PTC type)
Encoder control voltage (+5V/+12V/
+15V/+24V)
See OPTA4, OPTA5, OPTA7, OPTAE and OPTBB technical
data
Encoder connections (inputs, outputs)
See OPTA4, OPTA5, OPTA7, OPTAE and OPTBB technical
data
Environment (all boards)
Ambient operating temperature –10…55°C
Storing temperature –40…60°C
Humidity <95%, no condensation allowed
Altitude Ma 1000m
Vibration 0.5 G at 9…200 Hz
Page 8
1
vacon • 6 General information
Local contacts: http://drives.danfoss.com/danfoss-drives/local-contacts/
1.4.1 Isolation
The control connections are isolated from the mains potential and the I/O ground is connected
directly to the frame of the AC drive. Digital inputs and relay outputs are isolated from the I/O
ground. For digital input arrangements, see Chapter Digital input signal conversions on page 7.
1.4.2 Analogue inputs (mA/V)
Analogue inputs of I/O boards can be used as either current inputs or voltage inputs (see detailed
description of each board). The signal type is selected with a jumper block on the board. In case the
voltage type input is used you still have to define the voltage range with another jumper block. The
factory default value for the analogue signal type is given in the description of the board. For detailed
information, see the description of the board in question.
1.4.3 Analogue outputs (mA/V)
In the same way as in the analogue inputs, the output signal type (current/voltage) can be selected
with jumper except for some expander boards with analogue outputs used only with current signals.
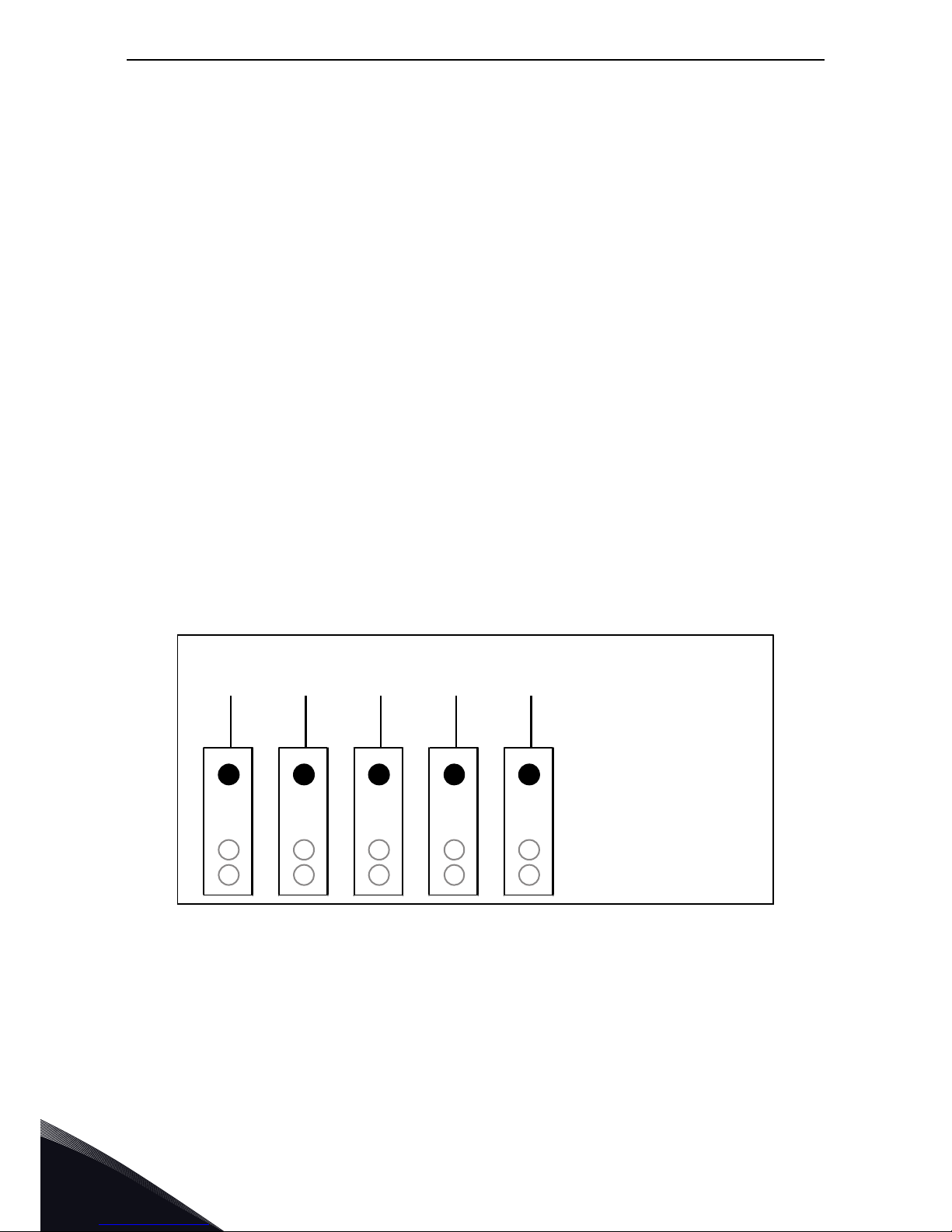
1.4.4 Control voltage (+24V/EXT +24V)
The control voltage output +24V/EXT+24V can be used in two ways. Typically, the +24V control voltage
is wired to digital inputs through an external switch. The control voltage can also be used to powerup external equipment, such as encoders and auxiliary relays.
Observe that the specified total load on all available +24V/EXT+24V output terminals must not
exceed 250mA. The maximum load on the +24V/EXT+24V output per board is 150mA. See Figure 3.
Figure 3. Maximum loads on +24V/EXT+24V output
The +24V/EXT+24V outputs can further be used to externally power-up the control board as well as
the basic and expander boards. If an external power supply is connected to EXT+24V output, the
control board, basic boards and expander boards remain live even if mains is lost on the AC drive.
This ensures sufficient functioning of the control logic (not the motor control, however) and some
alarms in exceptional power-loss situations. Furthermore, fieldbus links remain powered which
enables e.g. the Profibus Master to read valuable data on the AC drive.
NOTE: The power unit is not powered through the EXT+24V and therefore the motor control does not
work if the mains is lost.
+24V
out
+24V
out
+24V
out
+24V
out
+24V
out
++++
= max. 250mA
max.
150mA
max.
150mA
max.
150mA
max.
150mA
max.
150mA
7224.emf
Page 9
General information vacon • 7
Local contacts: http://drives.danfoss.com/danfoss-drives/local-contacts/
1
Requirements for an external power back-up:
- output voltage +24DC±10%, max. ripple voltage 100mV RMS
-max. current 1A
- 1A external fuse (no internal short-circuit protection on the control board
NOTE: Analogue outputs and inputs do not work with only +24V supplied to the control unit.
If there is a +24V/EXT+24V output on the board it is short-circuit protected locally. If one of the +24V/
EXT+24V outputs short-circuits, the others remain powered because of the local protection.
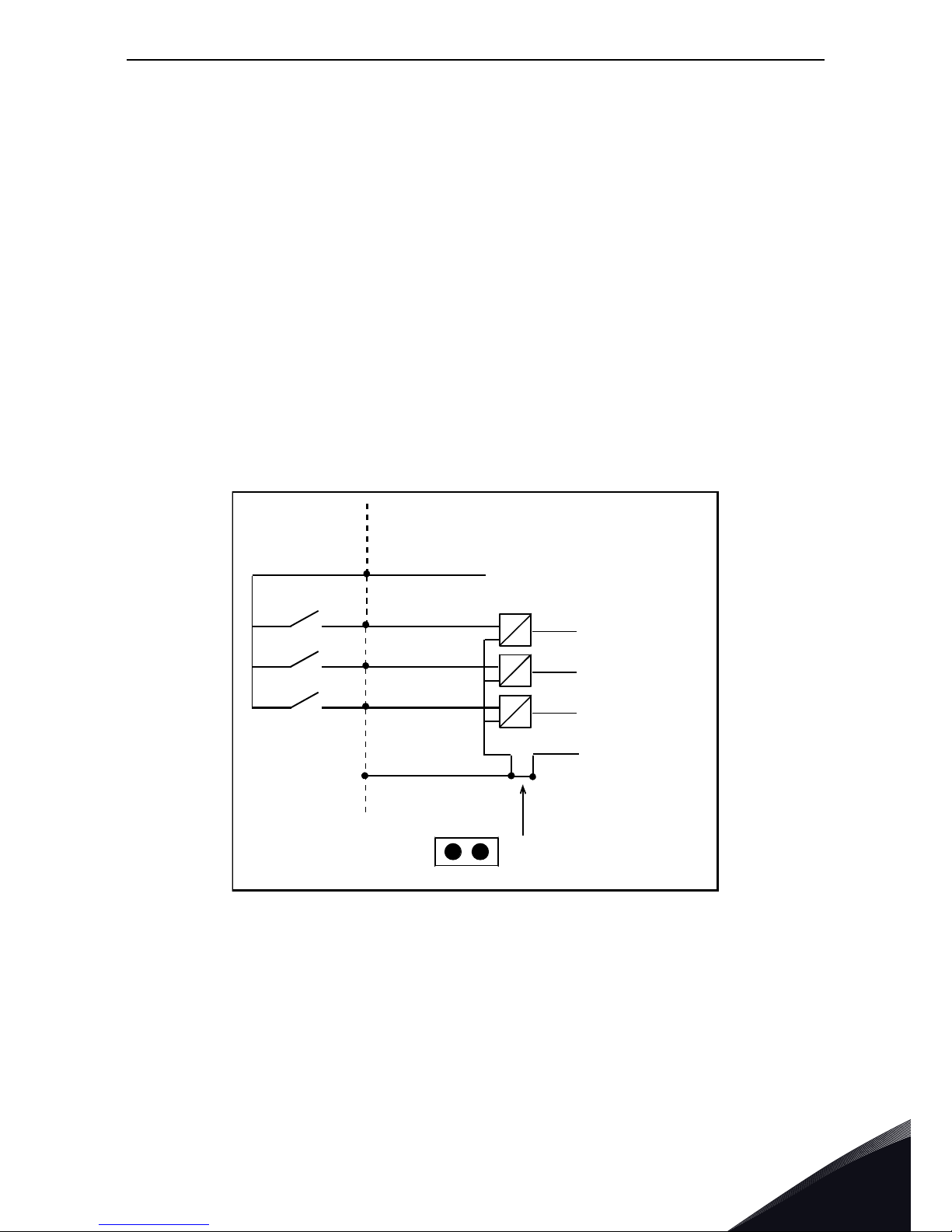
1.4.5 Digital input signal conversion
The active signal level depends on which potential the common input CMA (and CMB if available) is
connected to. The alternatives are +24V or Ground (0V). See Figure 4, Figure 5 and Figure 6.
The 24-volt control voltage and the ground for the digital inputs and the common input (CMA) can
be either internal or external.
Some typical input signal conversion examples are shown below. If you use the internal +24V from
the AC drive, the following arrangements are possible:
Figure 4. If CMA is connected to GND with inboard jumper the internal +24V is used and the CMA terminal
ed not be wired
+24V/EXT+24V
DI1
DI2
DI3
GND
Jumper setting: = CMA connected to GND
7225.emf
Page 10
1
vacon • 8 General information
Local contacts: http://drives.danfoss.com/danfoss-drives/local-contacts/
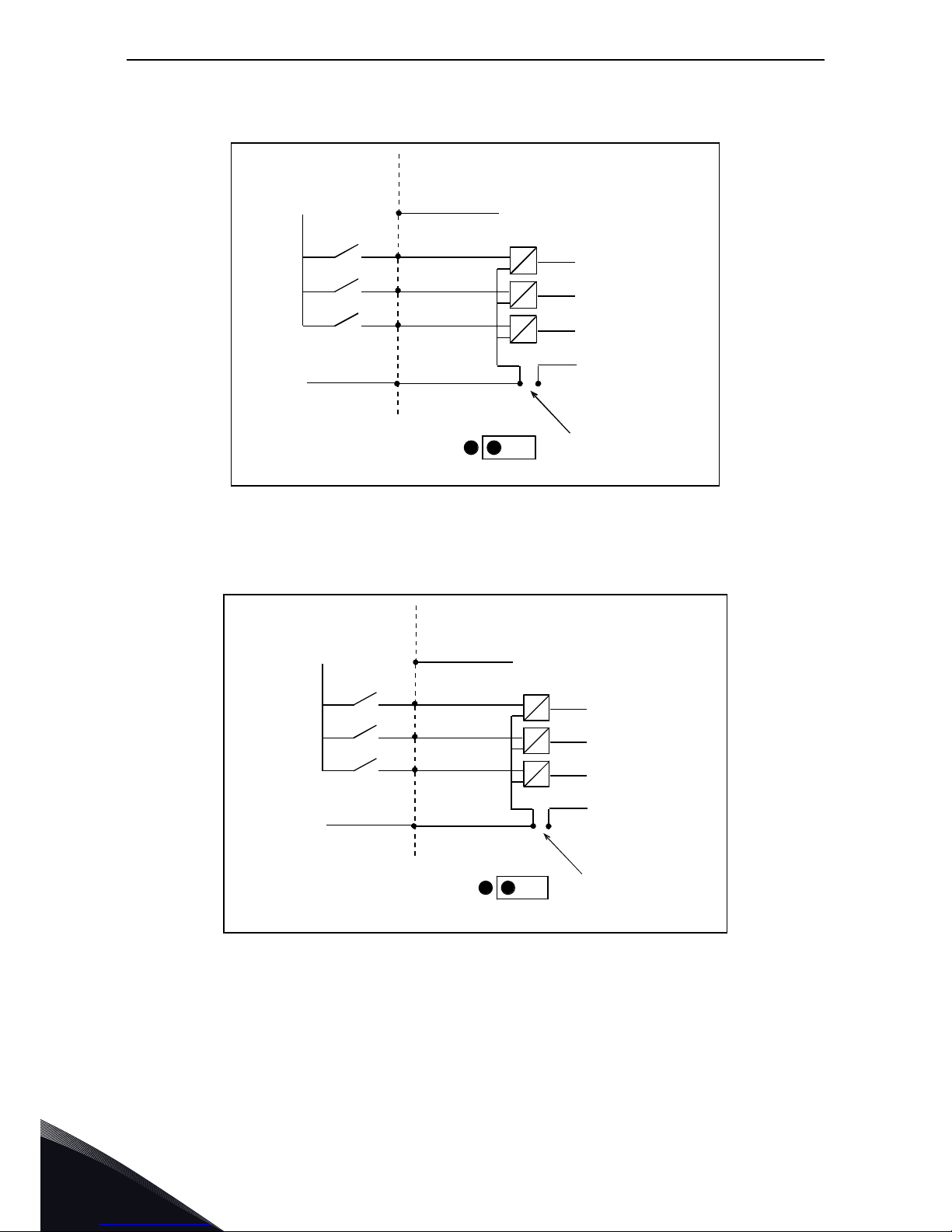
If you use an external +24V the following arrangements are possible:
Figure 5. Positive logic with external +24V when CMA is isolated from GND using onboard jumper. The
input is active when the switch is closed
Figure 6. Negative logic with external +24V when CMA is isolated with onboard jumper. The input is active
when the switch is closed (0V is the active signal)
You can make the positive and negative logic arrangements also with the internal +24V. Place the
jumper block in the 'CMA isolated from GND' position (as above) and wire the CMA terminal to the
GND terminal of the AC drive.
+24V/EXT+24V
DI1
DI2
DI3
GND
Jumper setting:
= CMA isolated from GND
Ground
External +24V
7226.emf
+24V/EXT+24V
DI1
DI2
DI3
GND
Jumper setting:
= CMA isolated from GND
External +24V
Ground
7227.emf
Page 11
General information vacon • 9
Local contacts: http://drives.danfoss.com/danfoss-drives/local-contacts/
1
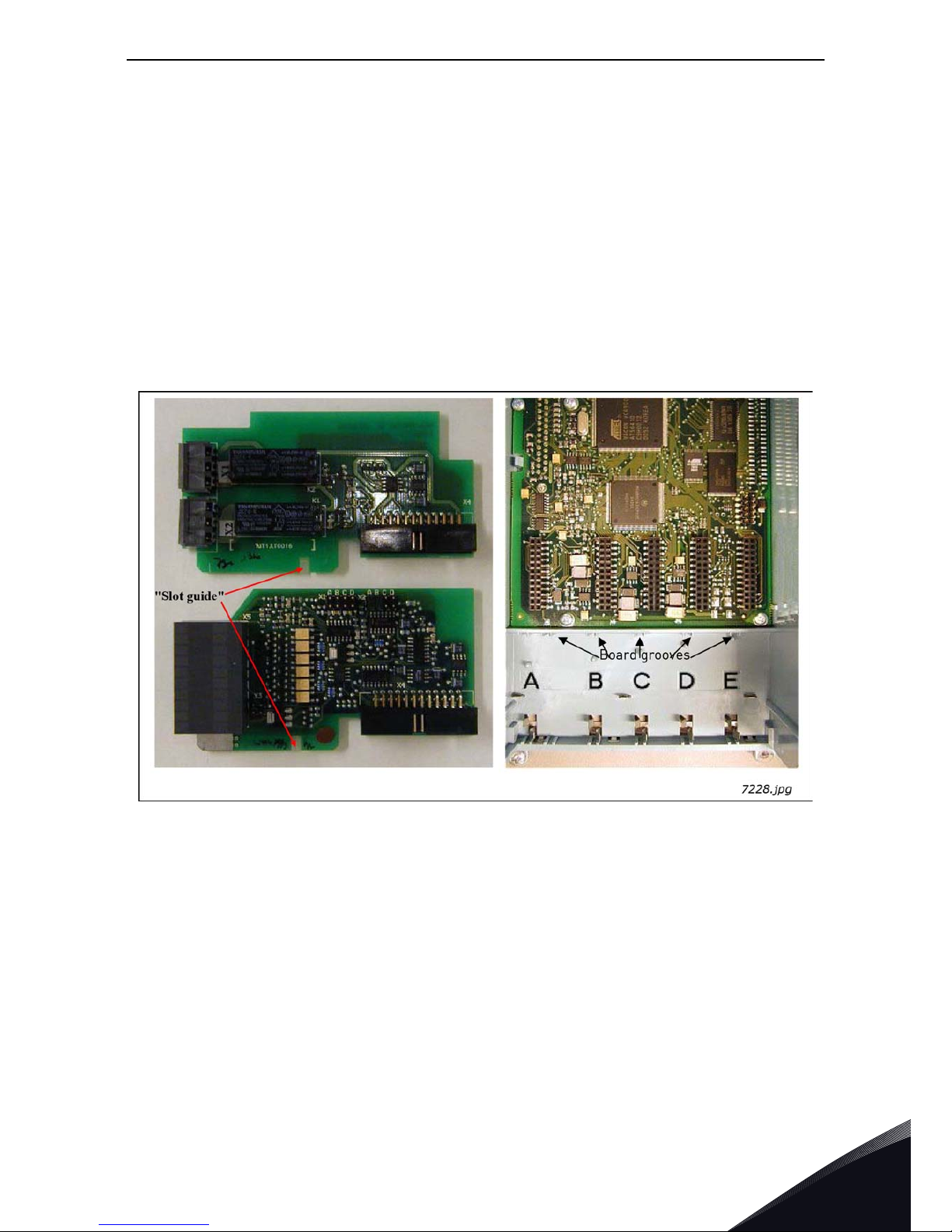
1.5 Hardware protections
1.5.1 Terminal block coding
In order to avoid incorrect connections of terminal blocks to boards, some terminal blocks as well
as related terminal connectors on the board are uniquely coded. For more information, see the
description of the individual board.
1.5.2 Board slot guides and allowed slots
You cannot mount an option board into any slot.Table 46 and Table 47 show which slots are allowed
for which option boards. For reasons of safety, slots A and B are protected in hardware against
mounting of unallowed boards. As regards mounting of unallowed boards into slots C, D and E, the
boards just will not work, there is no danger of health or equipment damage.
Figure 7. Board guide to prevent incorrect mountings
Page 12
1
vacon • 10 General information
Local contacts: http://drives.danfoss.com/danfoss-drives/local-contacts/
1.6 Type identification number
NOTE: This information is relevant only for special applications designers using the VACON®
NC1131-3 engineering tool.
Each VACON
®
OPTxx board has a unique type designation code. Besides the type designation code,
each board has a unique Type identification number which is used by the system program to identify
which board is plugged into which board slot. The system program and the application use the Type
ID also to establish the needed connections in order to achieve the desired functionality of the
available I/O boards in the control unit. The ID code is loaded in the memory of the board.
1.7 Defining functions to inputs and outputs
How to connect functions and the available I/O depends on the application you use. The VACON® All
in One Application Package includes seven applications: Basic Application, Standard Application,
PID Control Application, Multi-Step Speed Control Application, Local/Remote Control Application,
Pump and Fan Control Application with Autochange and Multipurpose Control Application (see Allin-One Application Manual). All but two applications of these use the conventional VACON
®
method
to connect functions and the I/O. In the Function to Terminal Programming Method (FTT), you have
a fixed input or output that you define a certain function for. The mentioned two applications, Pump
and Fan Control and Multipurpose Control Application, however, use the Terminal to Function
Programming Method (TTF) in which the programming process is carried out the other way round:
Functions appear as parameters which the operator defines a certain input/output for.
Connecting a certain input or output to a certain function (parameter) is done by giving the
parameter an appropriate value, the address code. The code is formed of the Board slot on the
VACON
®
NX control board (see page 2 and 3) and the respective input/output number. See below.
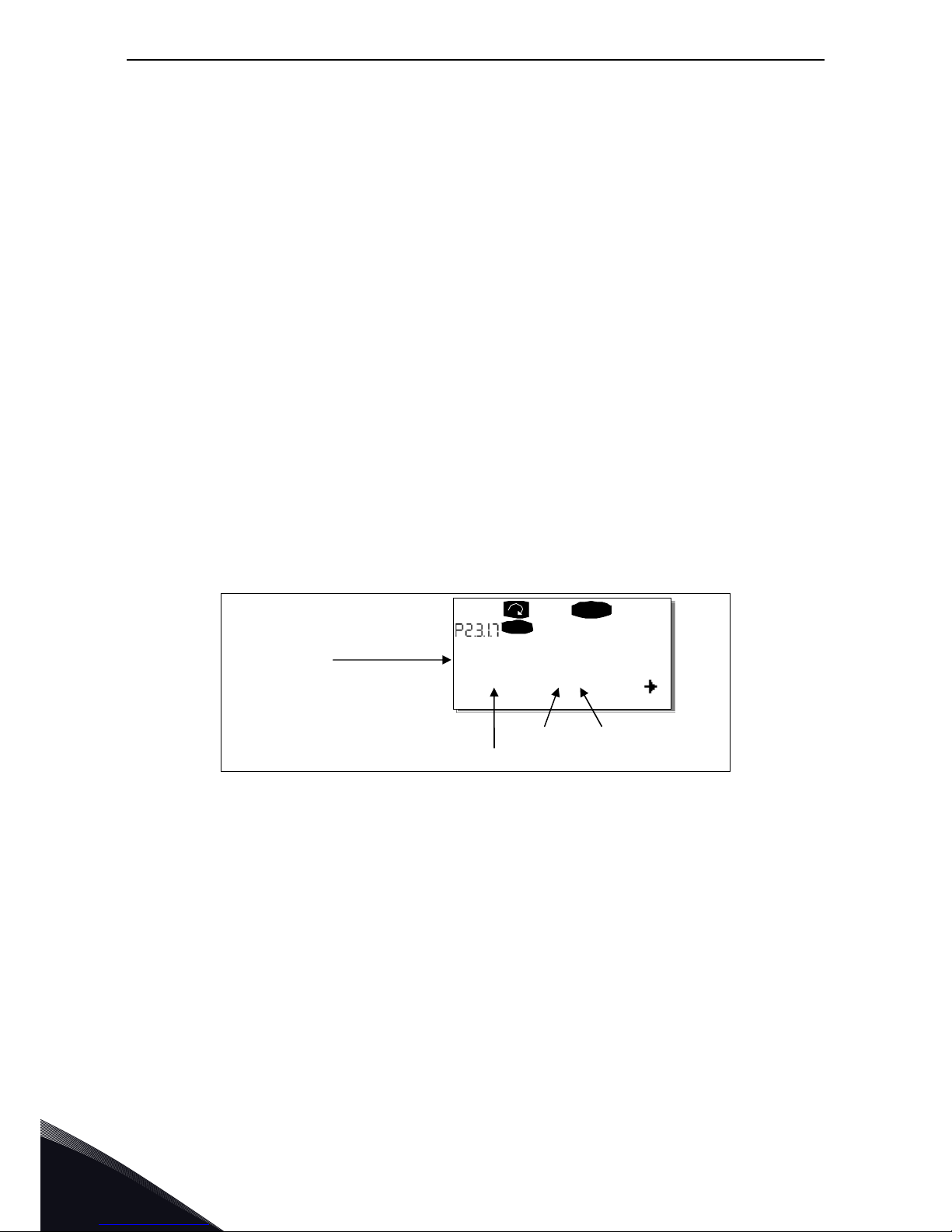
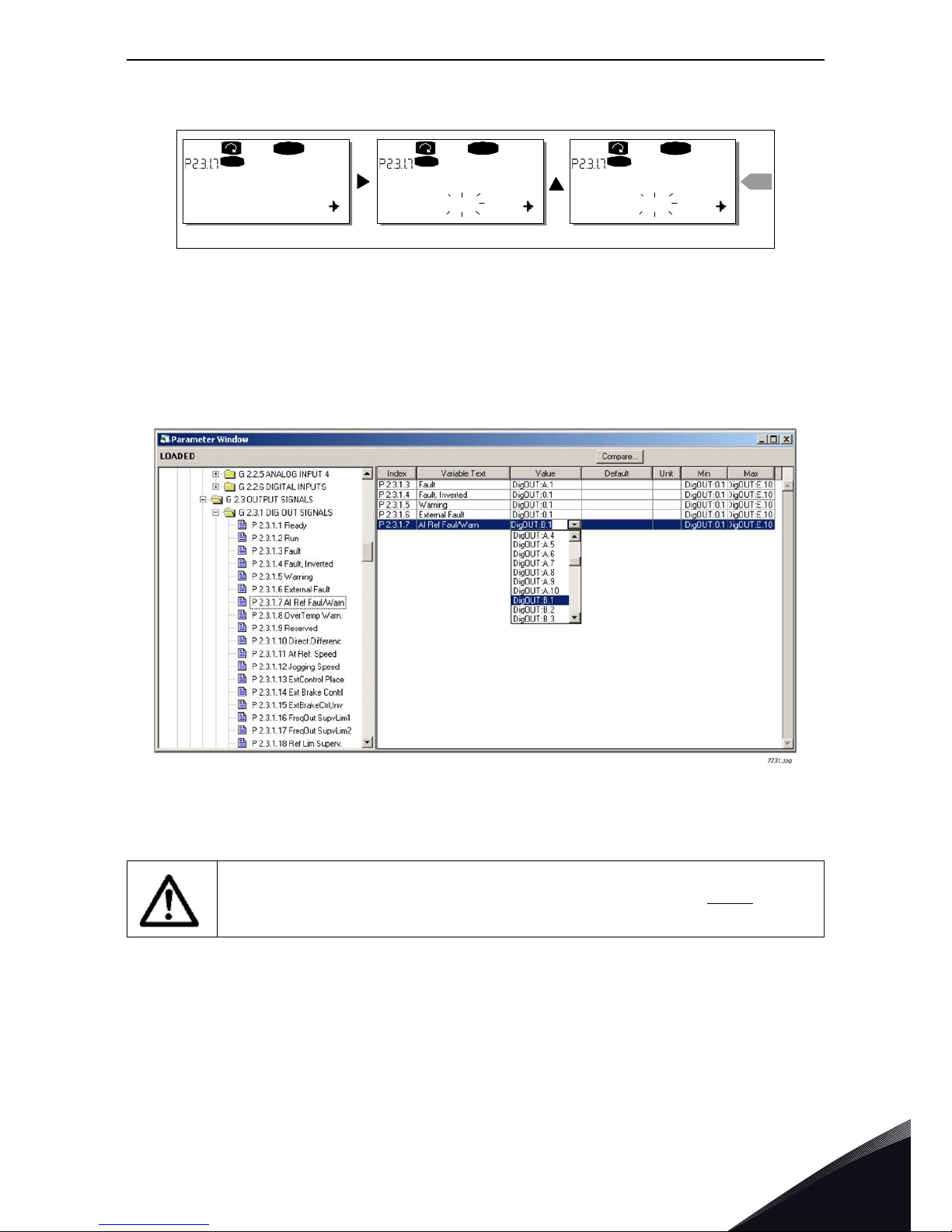
Example: You use the Pump and Fan Control Application. You want to connect the digital output
function Reference fault/warning (parameter 2.3.1.7) to the digital output DO1 on the basic board
OPTA1.
First find the parameter 2.3.1.7 on the keypad. Press the Menu button right once to enter the edit
mode. On the value line, you will see the terminal type on the left (DigIN, DigOUT, An.IN, An.OUT)
and on the right, the present input/output the function is connected to (B.3, A.2 etc.), or if not
connected, a code 0.#.
When the value is blinking, hold down the Browser button up or down to find the desired board slot
and input/output number. The program will scroll the board slots starting from 0 and proceeding
from A to E and the I/O numbers from 1 to 10.
READY
I/O term
DigOUT:B.1
AI
R
ef Faul/Warn
Function name
rebmunlanimreTtolS
epytlanimreT
7229.emf
Page 13
General information vacon • 11
Local contacts: http://drives.danfoss.com/danfoss-drives/local-contacts/
1
Once you have set the desired code, press the Enter button once to confirm the change.
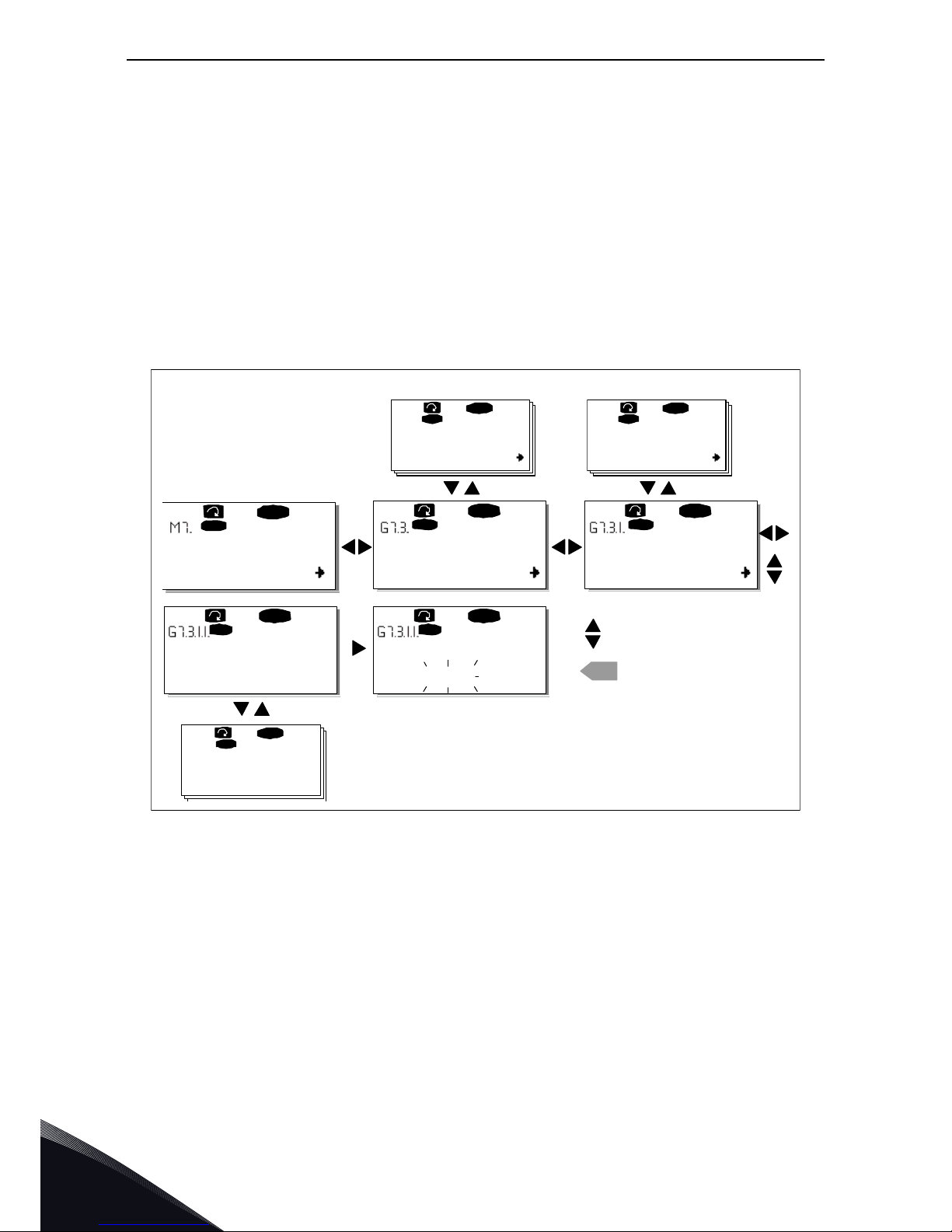
1.8 Defining a terminal for a certain function with NCDrive
programming tool
If you use the NCDrive Programming Tool for parametrizing you will have to establish the
connection between the function and input/output in the same way as with the control panel. Just
pick the address code from the drop-down menu in the Value column (see Figure 8 below).
Figure 8. Screenshot of NCDrive programming tool; Entering the address code
NOTE: The inputs, unlike the outputs, cannot be changed in RUN state.
Be ABSOLUTELY sure not to connect two functions to one and same output
in order
to avoid function overruns and to ensure flawless operation.
READ Y
I/Oterm
DigOUT:0.0
READ Y
I/Oterm
DigOUT:0.0
READ Y
I/Oter m
DigOUT:A.1
ent er
AIRefFaul/Warn AIRefFaul/Warn AIRefFaul/Warn
7230.emf
Page 14
1
vacon • 12 General information
Local contacts: http://drives.danfoss.com/danfoss-drives/local-contacts/
1.9 Option board related parameters
Some of the input and output functions of certain option boards are controlled with associated
parameters. The parameters are used to set the signal ranges for analogue inputs and outputs as
well as values for different encoder functions.
The board-related parameters can be edited in the Expander Board Menu (M7) of the control
keypad.
Enter the following menu level (G#) with the Menu button right. At this level, you can browse through
slots A to E with the Browser buttons to see what expander boards are connected. On the lowermost
line of the display you also see the number of parameters associated with the board. Edit the
parameter value as shown below. For more information on the keypad operation, see VACON
®
NXS/
P User Manual. See Figure 9.
Figure 9. Board parameter value editing
NOTE: Fieldbus boards (OPTC_) also have fieldbus-related parameters. These boards are, however,
described in the separate fieldbus board manuals (see http://drives.danfoss.com/knowledgecenter/technical-documentation/).
G1
G5
READY
I/Oter m
C:NXOPTC1
READY
I/Oter m
G1G2
READY
I/Oter m
READY
I/Oterm
enter
P1P4
D:NXOPTC2
READY
I/ Ot e r m
G1G2
READY
I/O te rm
V1V2
READY
I/Oter m
READY
I/Oterm
Exp ander boards
Parameters
Slave address
126
CHANGE VALUE
CONFIRM CHANGE
Slave address
126
Baud rate
Auto
Monitor
7232.emf
Page 15

Installation of VACON® Option Boards vacon • 13
Local contacts: http://drives.danfoss.com/danfoss-drives/local-contacts/
2
2. INSTALLATION OF VACON® OPTION BOARDS
Do not add or replace option boards or fieldbus boards on an AC drive with the power
switched on. This may damage the boards.
A
VACON® NX AC drive.
B
Remove the cable cover.
C
Open the cover of the control unit.
Page 16

2
vacon • 14 Installation of VACON® Option Boards
Local contacts: http://drives.danfoss.com/danfoss-drives/local-contacts/
D
Install the option board in a correct slot on the control board of the AC drive. On
attaching (also removing) the board, hold it in horizontally straight position to avoid
twisting the connector pins. See the photos below.
Make sure that the board (see below) fits tightly in the metal clamp and the plastic
groove. If the board seems to be difficult to fit in the slot you may have to check the
allowed slots for your option board.
NOTE: Check that the jumper settings on the board correspond to you needs.
Finally, close the cover of the AC drive and the cable cover.
Page 17

Installation of VACON® Option Boards vacon • 15
Local contacts: http://drives.danfoss.com/danfoss-drives/local-contacts/
2
2.1 Control cables
The control cables used must be at least 0.5mm2 screened multicore cables. The maximum
terminal wire size is 2.5mm
2
for the relay terminals and 1.5 mm2 for other terminals.
Find the tightening torques of the option board terminals in the table below.
2.1.1 Cable grounding
We recommend to ground the control cables in the manner presented above.
Strip the cable at such distance from the
terminal that you can fix it to the frame with the
grounding clamp.
Figure 10. Grounding of control cable
Table 2. Tightening torques of terminals
Termin al sc rew Tightening torque
Nm lb-in.
Relay and thermistor terminals
(screw M3)
0.5 4.5
Other terminals
(screw M2.6)
0.2 1.8
Table 3. Cable types required to meet standards
Cable type Level H, C Level L
Control cable 4 4
Level H =
EN 61800-3+A11, 1
st
environment, restricted distribution
EN 61000-6-4
Level L =
EN61800-3, 2
nd
environment
4 =
Screened cable equipped with compact low-impedance shield
(NNCABLES /Jamak, SAB/ÖZCuY-O or similar).
Page 18
2
vacon • 16 Installation of VACON® Option Boards
Local contacts: http://drives.danfoss.com/danfoss-drives/local-contacts/
2.2 Board information sticker
Each I/O option board package delivered by the factory includes a sticker (shown below) where
possible modifications made in the AC drive are noted. Please check Option board (1), mark the
board type (2), the slot into which the board is mounted (3) and the mounting date (4) on the sticker.
Finally, attach the sticker on your drive.
Drive mod if ied :
Option board:
NXOPT................
IP54 upgrade/ Collar
in slot:
Date:...................
ABCDE
EMC level modifi ed: H to T / T to H
Date:...................
Date:...................
3
2
4
1
7241.emf
Page 19
Descriptions of VACON® option boards vacon • 17
Local contacts: http://drives.danfoss.com/danfoss-drives/local-contacts/
3
3. DESCRIPTIONS OF VACON® OPTION BOARDS
3.1 Basic boards OPTA_
• Basic boards used for basic I/O; normally pre-installed at the factory.
• This board type uses slots A, B and C.
The standard VACON
®
NXS and NXP AC drives contain two boards placed in slots A and B. The board
in slot A (OPTA1, OPTA8 or OPTA9) has digital inputs, digital outputs, analogue inputs and an
analogue output. The board in slot B (OPTA2) has two change-over relay outputs. As an alternative
to OPTA2, a board of type OPTA3 can also be placed in slot B. In addition to the two relay outputs,
this board has one thermistor input.
The boards you wish to have installed in your AC drive have to be defined in the type designation code
of the AC drive when ordering it from the factory.
Table 4. VACON
®
NX Basic boards and their equipment
FC
type
I/O
board
Allowed
slots
DI DO AI AO RO TI Other
NXS
NXP
OPTA1 A 6 1
2 (mA/V), incl.
-10…+10V
1
(mA/V)
+10Vref
+24V/ EXT+24V
NXS
NXP
OPTA2 B
2
(NO/NC)
NXS
NXP
OPTA3 B
1
(NO/NC)
+ 1 NO
1
NXS
1)
NXP
OPTA4 C
3 DI encoder
(RS-422) +
2 DI
(qualifier &
fast input)
+5V/+15V/+24V
(progr.)
NXS
1)
NXP
OPTA5 C
3 DI encoder
(wide range) +
2 DI
(qualifier &
fast input)
+15V/+24V
(progr.)
NXP OPTA7 C 6 (enc.) 2 (enc)
+15V/+24V
(progr.)
NXS
NXP
OPTA8 A 6 1
2 (mA/V), incl.
-10…+10V (decoupled from
GND)
1 (mA/V)
(decoupled
from GND)
+10Vref (decoupled from GND)
+24V/ EXT+24V
NXS
NXP
OPTA9 A 6 1
2 (mA/V),
incl. -10…+10V
1 (mA/V)
+10ref (2.5 mm
terminals)
+24V/ EXT+24V
NXS
1)
NXP
OPTAE C
3 DI encoder
(wide range)2 (Enc.)
+15V/+24V
(progr.)
NXS
NXP
OPTAL A
6
42…240 VAC
1
2 (AI1 0-10V)
(AI2 +-10V)
2 (AO1 mA)
(AO2 V)
+15V/+24V
NXP OPTAN A 6
2 (mA/V),
incl.
-10…+10V
2 (mA/V),
incl.
-10…+10V
+10Vref
-10Vref
+24V/ EXT+24V
1)
Encoder board can be used in VACON® NXS with special applications only.
DI = Digital input DO = Digital output TI = Thermistor input
AI = Analogue input AO = Analogue output RO = Relay output
Page 20
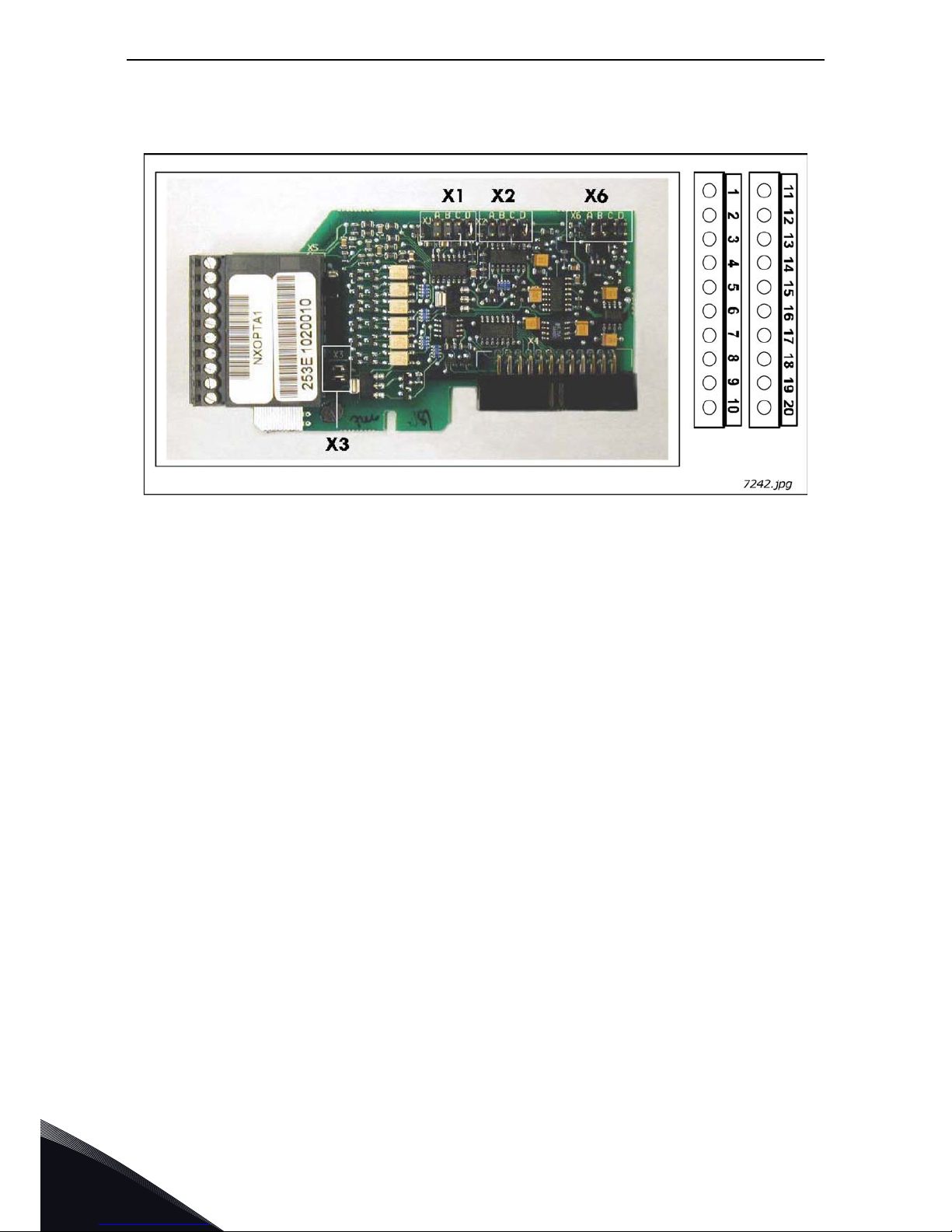
3
vacon • 18 Descriptions of VACON® option boards
Local contacts: http://drives.danfoss.com/danfoss-drives/local-contacts/
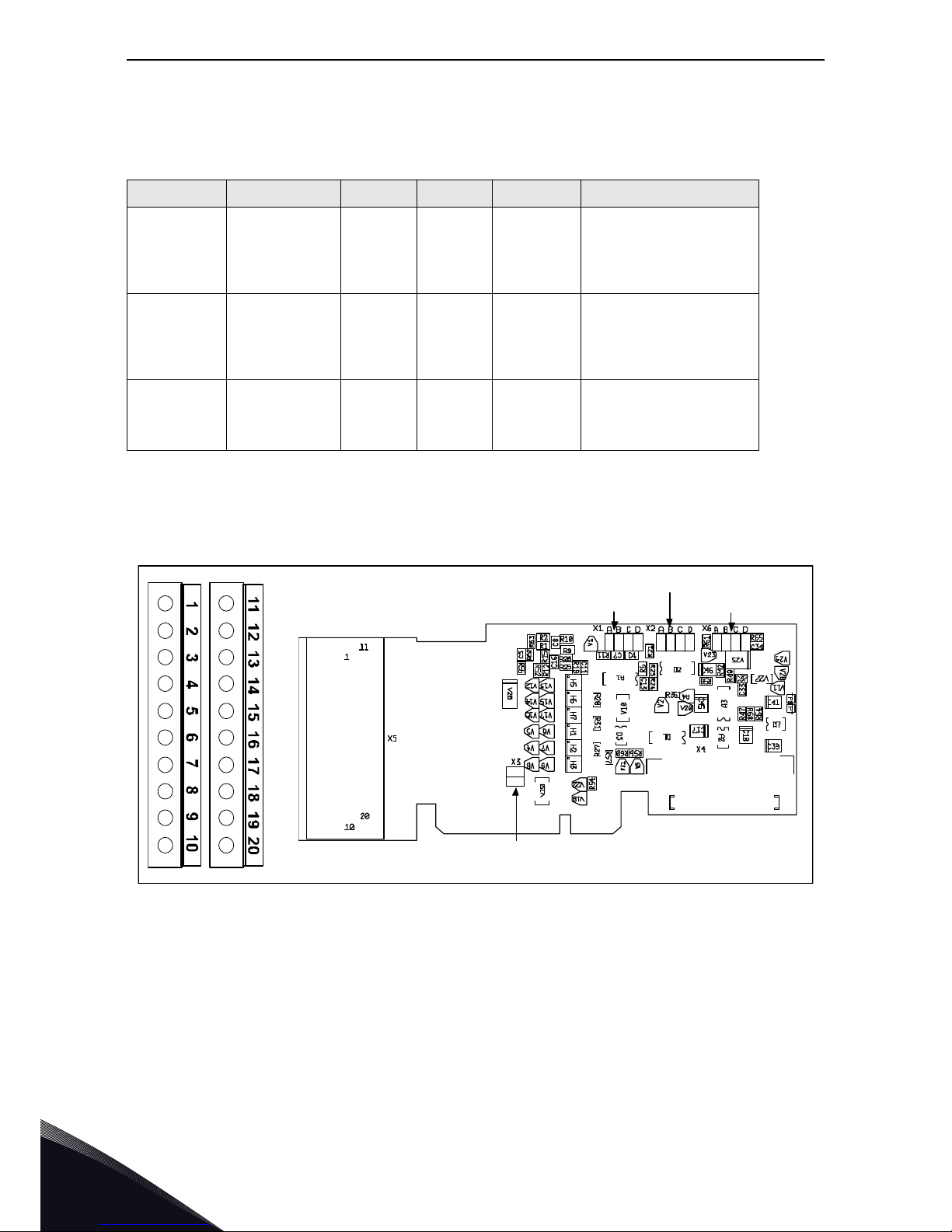
3.1.1 OPTA1
Figure 11. VACON
®
OPTA1 option board
Description: Standard I/O board with digital inputs/outputs and analogue inputs/outputs
Allowed slots: A
Type ID: 16689
Termi nal s: Two terminal blocks (coded = mounting of blocks in wrong order prevented,
terminals #1 and #12);
Screw terminals (M2.6)
Jumpers: 4; X1, X2, X3 and X6 (See Figure 12)
Board parameters: Board parameters:Yes (See page 21)
Page 21
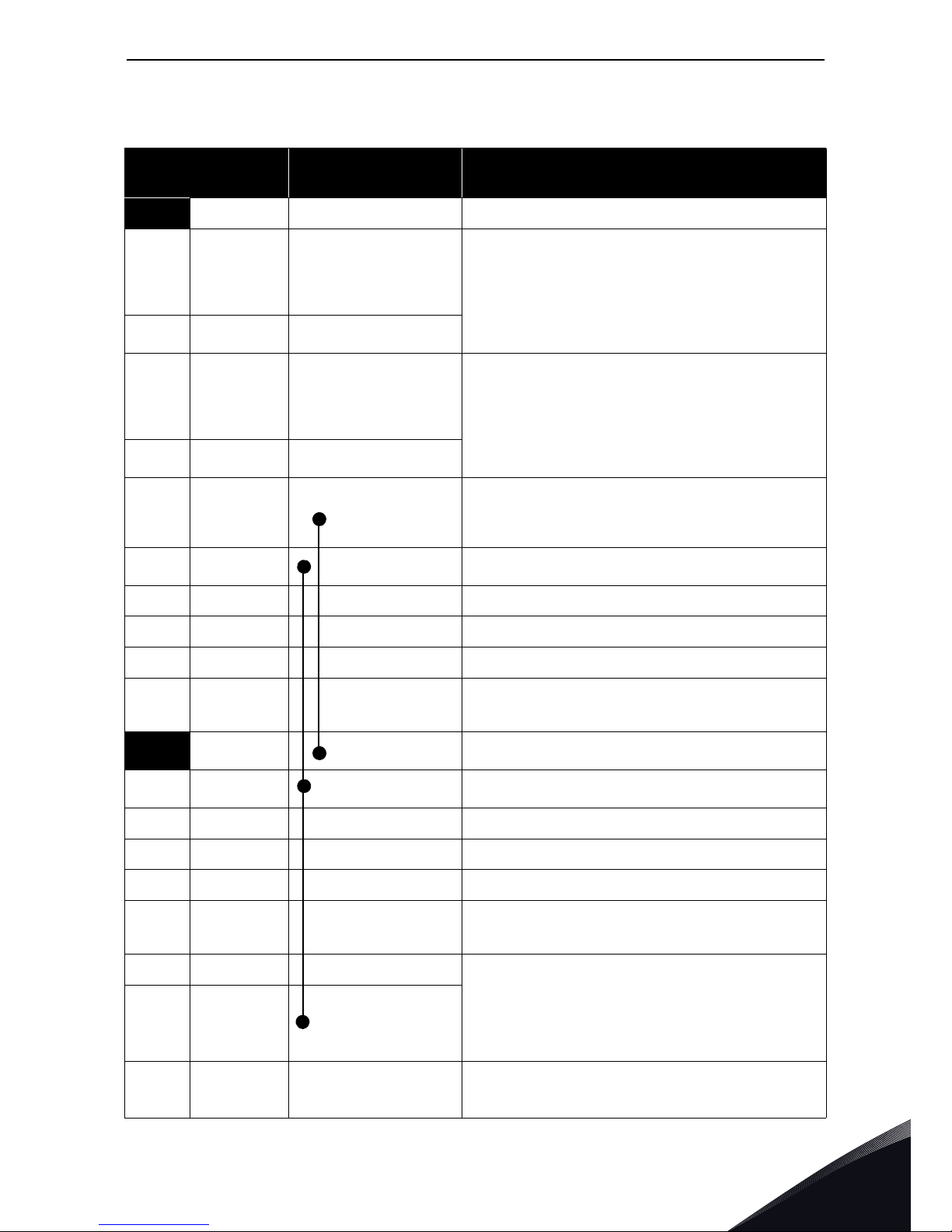
Descriptions of VACON® option boards vacon • 19
Local contacts: http://drives.danfoss.com/danfoss-drives/local-contacts/
3
I/O terminals on OPTA1 (coded terminals painted black)
Table 5. OPTA1 I/O terminals
Ter mi na l
Parameter reference
on keypad and NCDrive
Technical information
1
+10 Vref Reference output +10V; Maximum current 10 mA
2
AI1+ An.IN:A.1
Selection V or mA with jumper block X1 (see page 20):
Default: 0– +10V (Ri = 200 kΩ)
(-10V..+10V Joy-stick control, selected with ajumper)
0– 20mA (Ri = 250 Ω)
Resolution 0.1%; Accuracy ±1%
3
AI1–
Differential input if not connected to ground;
Allows ±20V differential mode voltage to GND
4
AI2+ An.IN:A.2
Selection V or mA with jumper block X2 (see page 20):
Default: 0– 20mA (Ri = 250 Ω)
0– +10V (Ri = 200 kΩ)
(-10V..+10V Joy-stick control, selected with a jumper)
Resolution: 0.1%; Accuracy ±1%
5
AI2–
Differential input if not connected to ground;
Allows ±20V differential mode voltage to GND
6
24 Vout (bidirectional)
24V auxiliary voltage output. Short-circuit protected.
±15%, maximum current 150 mA, see 1.4.4.
+24Vdc external supply may be connected.
Galvanically connected to terminal #12.
7
GND
Ground for reference and controls
Galvanically connected to terminals #13,19.
8
DIN1 DigIN:A.1
Digital input 1 (Common CMA); R
i
= min. 5kΩ
9
DIN2 DigIN:A.2
Digital input 2 (Common CMA); R
i
= min. 5kΩ
10
DIN3 DigIN:A.3
Digital input 3 (Common CMA); R
i
= min. 5kΩ
11
CMA
Digital input common A for DIN1, DIN2 and DIN3.
Connection by default to GND.
Selection with jumper block X3 (see page 20):
12
24 Vout (bidirectional)
Same as terminal #6
Galvanically connected to terminal #6.
13
GND
Same as terminal #7
Galvanically connected to terminals #7 and 19
14
DIN4 DigIN:A.4
Digital input 4 (Common CMB); R
i
= min. 5kΩ
15
DIN5 DigIN:A.5
Digital input 5 (Common CMB); R
i
= min. 5kΩ
16
DIN6 DigIN:A.6
Digital input 6 (Common CMB); R
i
= min. 5kΩ
17
CMB
Digital input common B for DIN4, DIN5 and DIN6.
Connection by default to GND.
Selection with jumper block X3 (see page 20):
18
AO1+ AnOUT:A.1
Analogue output
Output signal range:
Current 0(4)–20mA, R
L
max 500Ω or
Voltage 0—10V, R
L
>1kΩ
Selection with jumper block X6 (see page 20):
Resolution: 0.1% (10 bits); Accuracy ±2%
19
AO1–
20
DO1 DigOUT:A.1
Open collector output
Maximum U
in
= 48VDC
Maximum current = 50 mA
Page 22
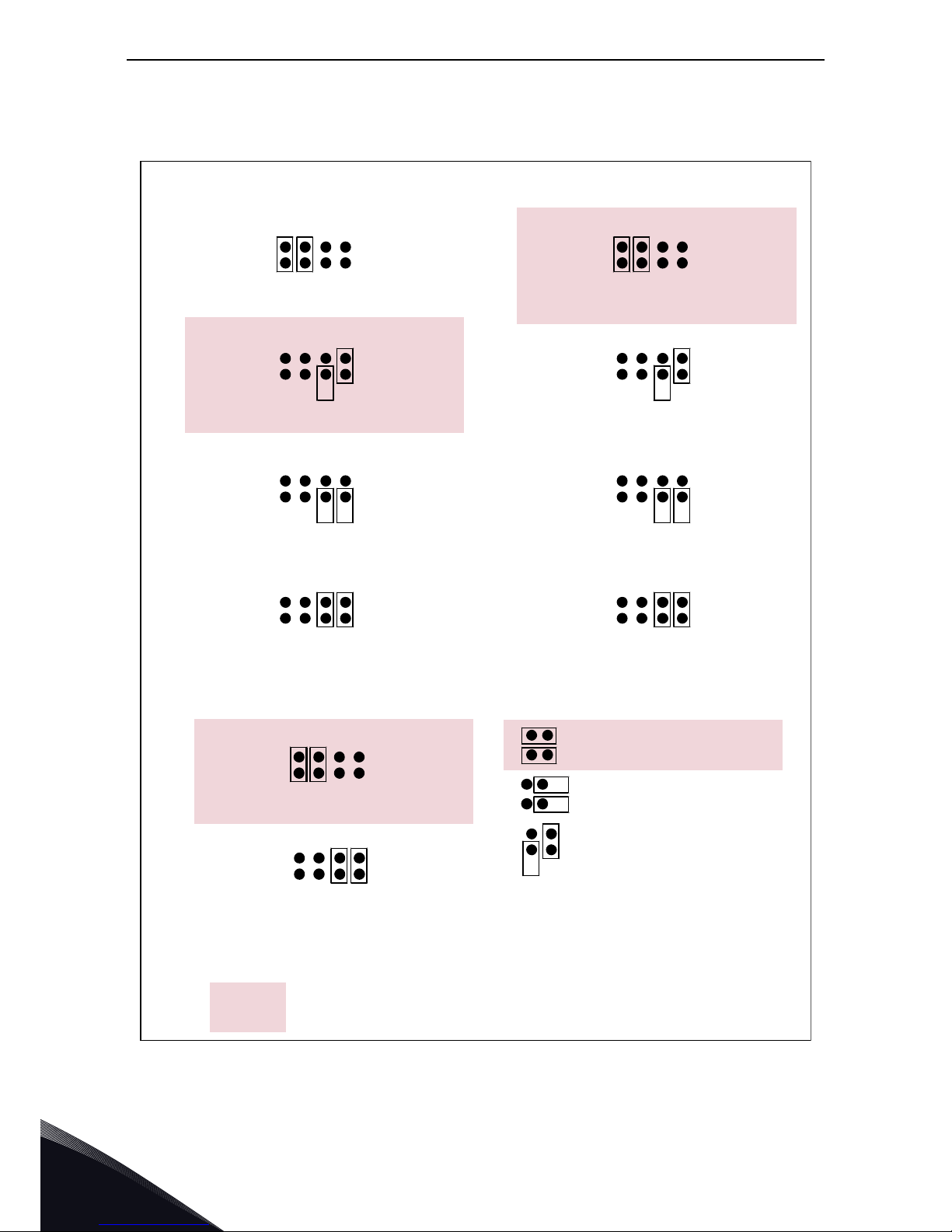
3
vacon • 20 Descriptions of VACON® option boards
Local contacts: http://drives.danfoss.com/danfoss-drives/local-contacts/
Jumper selections
There are four jumper blocks on the OPTA1 board. The factory defaults and other available jumper
selections are presented below.
Figure 12. Jumper block selection on OPTA1
ABCD
ABCD
ABCD
ABCD
ABCD
ABCD
ABCD
ABCD
ABCD
ABCD
Jum per block X 1 :
AI1 mode
AI1 mode: Voltage input; 0...10V
AI1 mode: Voltage input; 0...10V (differential)
AI1 mode: Voltage input; -10...10V
Jum per blockX2:
AI2 mode
AI2 mode: 0...2 0 mA; Current input
AI2 mode: Voltage i np ut; 0 . ..10 V
AI2 mode: Voltage input; 0...1 0V (differential)
AI2 mode: Voltage input; -10 ...10V
Jumper block X 3:
CMA a nd CMB grounding
CMB connected to GN D
CMA connected to GND
CMB isolated from GN D
CMA isolated from GN D
CMB and CM A
interna lly connected to g ether,
isolated from GND
=Factorydefault
Jumper block X 6:
AO1 m ode
AO 1 mode: 0... 2 0 mA; Current output
AO1 mode: Voltage output; 0...10V
AI1 mode: 0...20mA; Current input
7243.emf
Page 23
Descriptions of VACON® option boards vacon • 21
Local contacts: http://drives.danfoss.com/danfoss-drives/local-contacts/
3
OPTA1 parameters
3.1.2 OPTA2
Table 6. OPTA1 board-related parameters
Number Parameter Min Max Default Note
1 AI1 mode 1 5 3
1 = 0...20mA
2 = 4...20mA
3 = 0...10V
4 = 2...10V
5 = -10...+10V
2 AI2 mode 1 5 1
1 = 0...20mA
2 = 4...20mA
3 = 0...10V
4 = 2...10V
5 = -10...+10V
3AO1 mode 141
1 = 0...20mA
2 = 4...20mA
3 = 0...10V
4 = 2...10V
Description:
Standard VACON
®
NX AC drive relay board with two relay outputs
Allowed slots: B
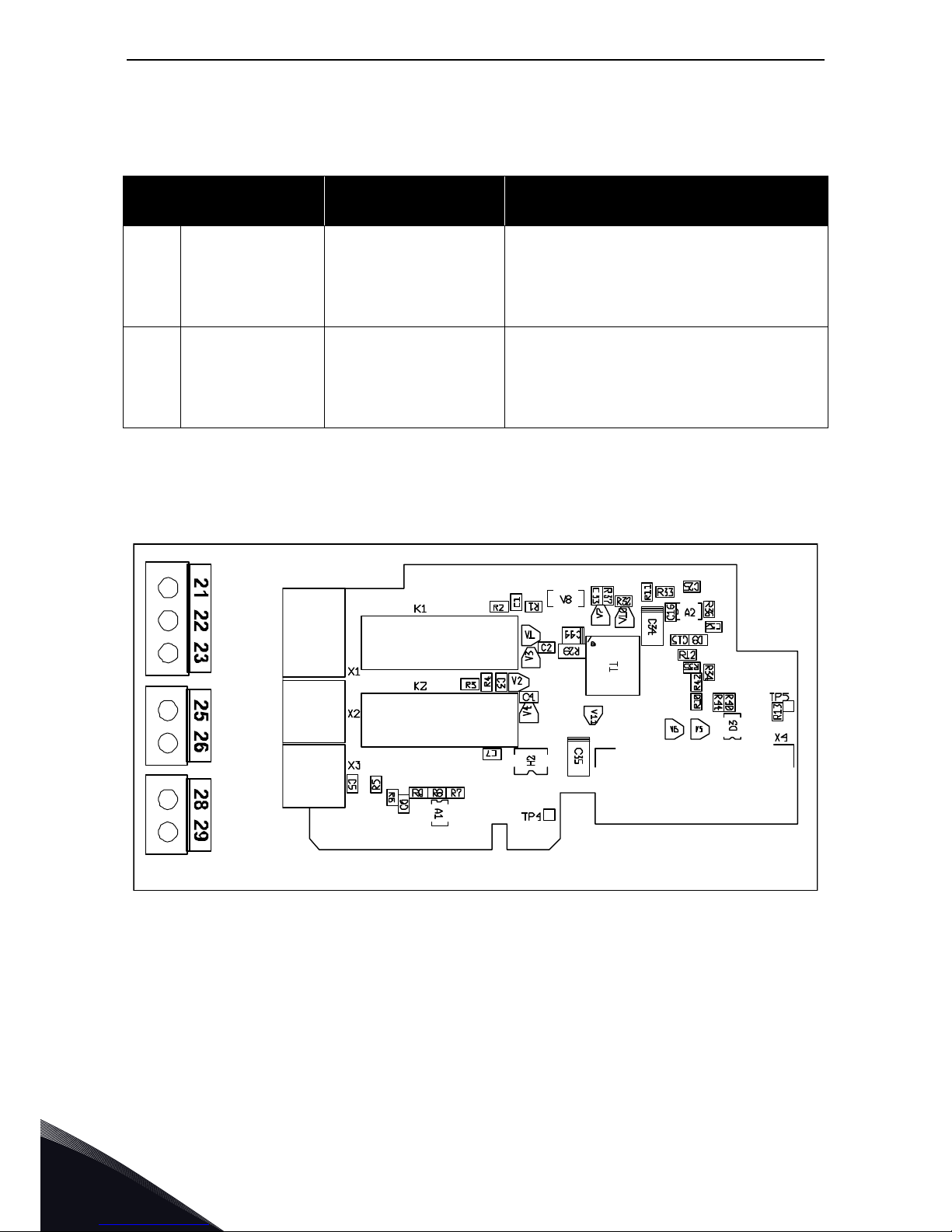
Type ID: 16690
Termi nal s: Two terminal blocks; Screw terminals (M3); No coding
Jumpers: None
Board parameters: None
7244.emf
Page 24
3
vacon • 22 Descriptions of VACON® option boards
Local contacts: http://drives.danfoss.com/danfoss-drives/local-contacts/
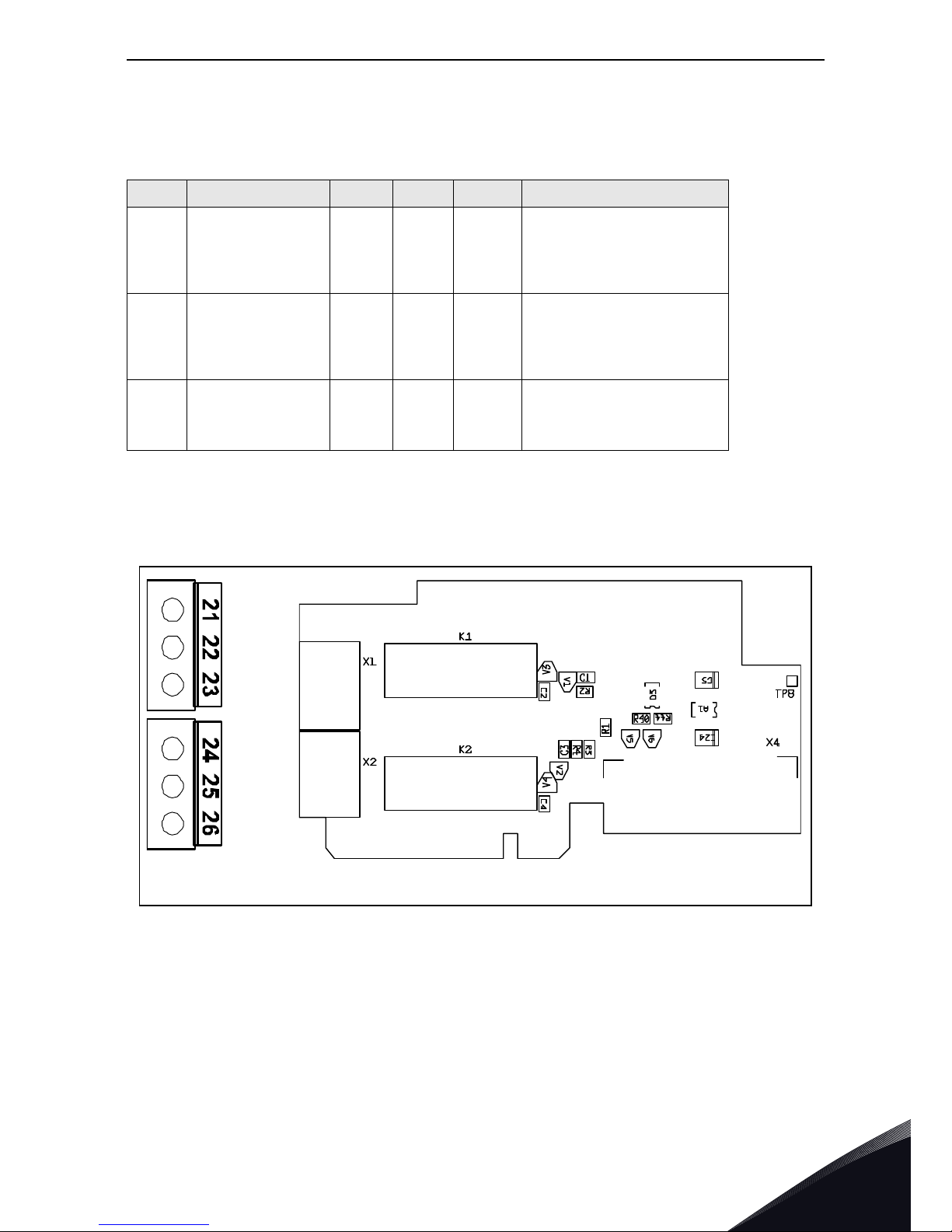
I/O terminals on OPTA2
3.1.3 OPTA3
Table 7. OPTA2 I/O terminals
Ter mi na l
Parameter reference
on keypad and NCDrive
Technical information
21
22
23
RO1/normal closed
RO1/common
RO1/normal open
DigOUT:B.1
Relay output 1 (NO/NC)
Switching capacity
Min. switching load
24VDC/8A
250VAC/8A
125VDC/0.4A
5V/10mA
24
25
26
RO2/normal closed
RO2/common
RO2/normal open
DigOUT:B.2
Relay output 2 (NO/NC)
Switching capacity
Min. switching load
24VDC/8A
250VAC/8A
125VDC/0.4A
5V/10mA
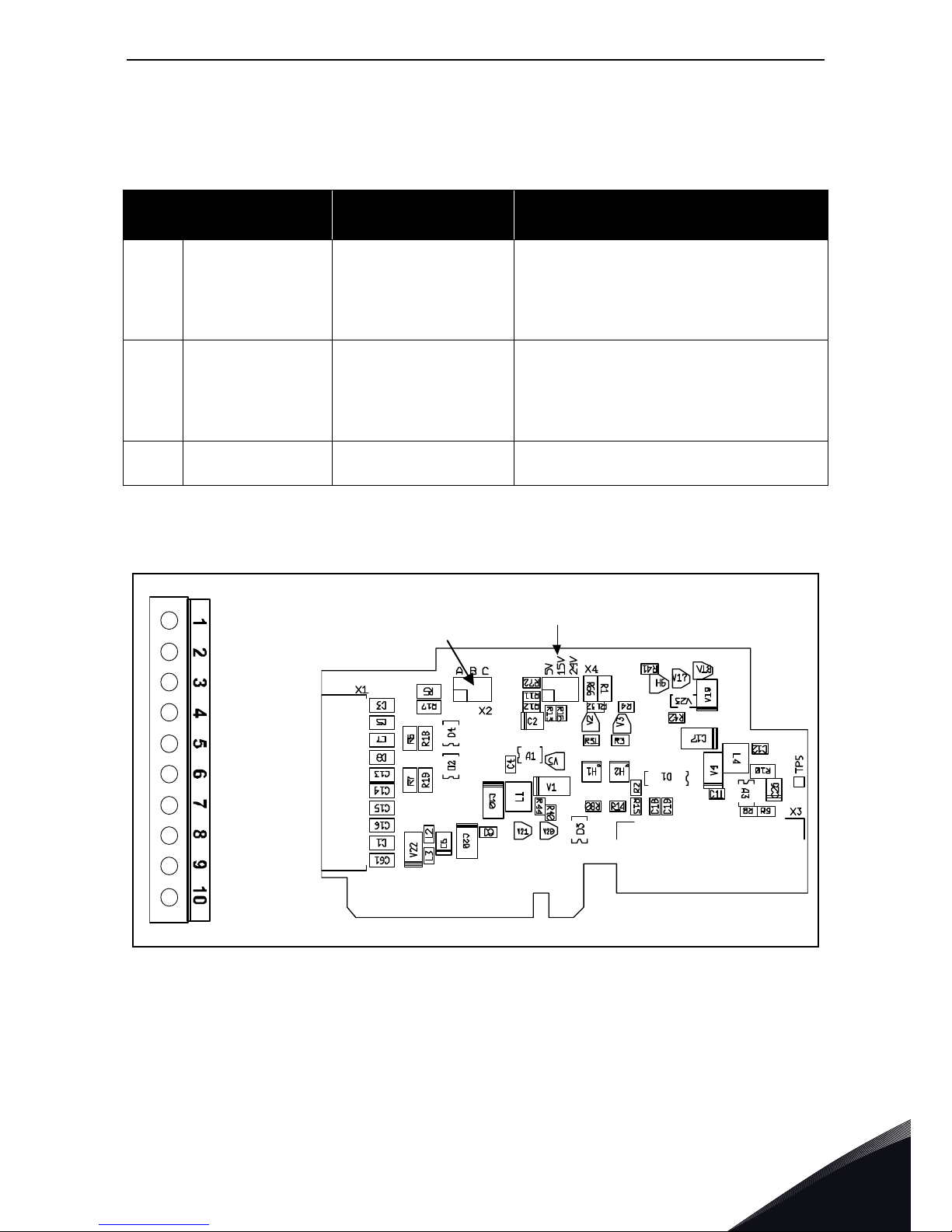
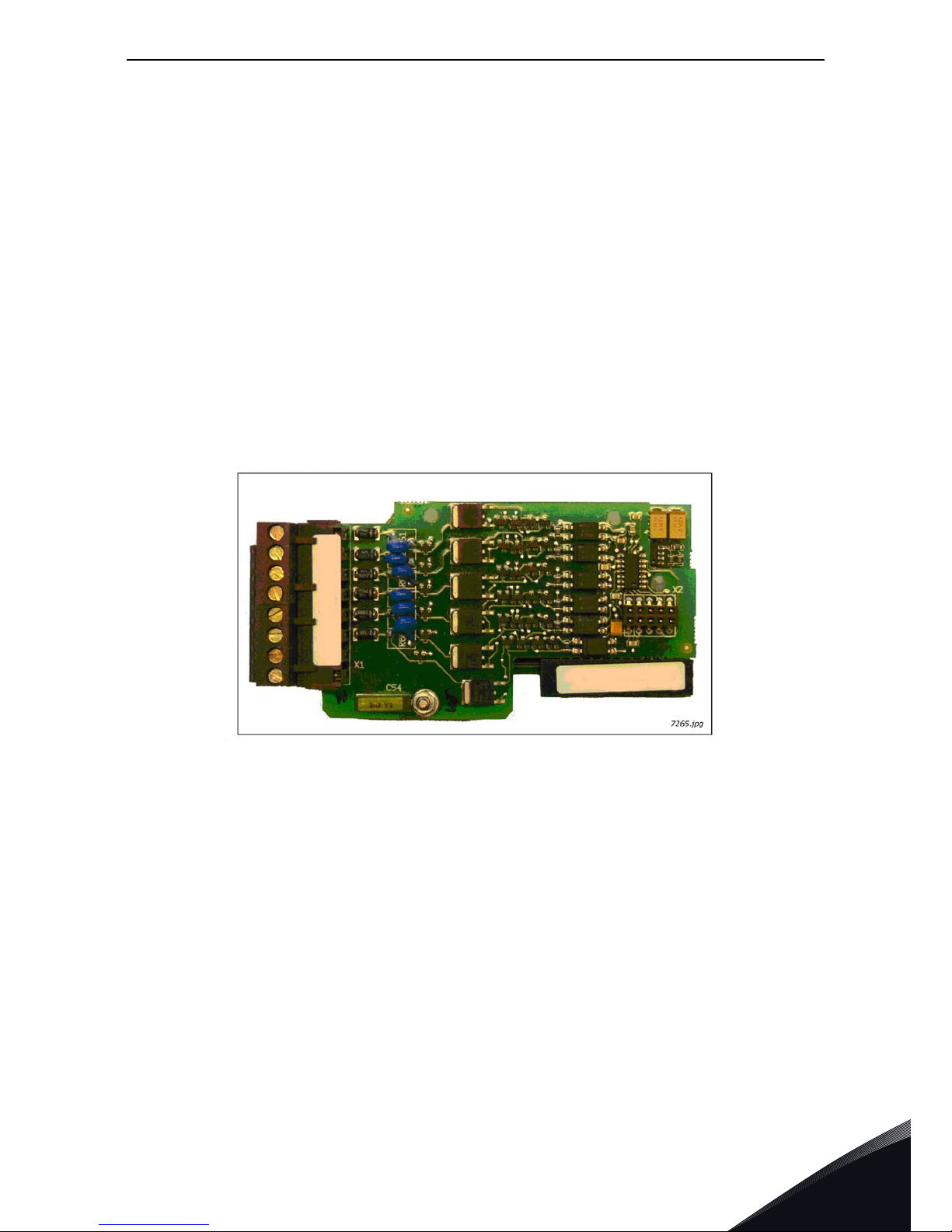
Description:
Relay board with two relay outputs and one thermistor input for VACON
®
NX
AC drive
Allowed slots: B
Type ID: 16691
Termi nal s: Three terminal blocks; Screw terminals (M3); No coding.
Jumpers: None
Board parameters: None
7245.emf
Page 25
Descriptions of VACON® option boards vacon • 23
Local contacts: http://drives.danfoss.com/danfoss-drives/local-contacts/
3
I/O terminals on OPTA3
3.1.4 OPTA4
Table 8. OPTA3 I/O terminals
Ter mi na l
Parameter reference
on keypad and NCDrive
Technical information
21
22
23
RO1/normal closed
RO1/common
RO1/normal open
DigOUT:B.1
Relay output 1 (NO/NC)
Switching capacity
Min. switching load
24VDC/8A
250VAC/8A
125VDC/0.4A
5V/10mA
2526RO2/common
RO2/normal open
DigOUT:B.2
Relay output 2 (NO)
Switching capacity
Min. switching load
24VDC/8A
250VAC/8A
125VDC/0.4A
5V/10mA
2829TI1+
TI1–
DigIN:B.1
Thermistor input; R
trip
= 4 kΩ (PTC)
JumperX4
Jumper X2
7246.emf
Page 26

3
vacon • 24 Descriptions of VACON® option boards
Local contacts: http://drives.danfoss.com/danfoss-drives/local-contacts/
I/O terminals on OPTA4 (coded terminal painted black)
Description:
Encoder board for VACON
®
NXP. Encoder input board with programmable
control voltage for an encoder.
The encoder board OPTA4 is for TTL type encoders (TTL, TTL(R)) providing
input signal levels that meet the RS_422 interface standard. Encoder inputs
A, B and Z are not galvanically isolated. The OPTA4 board includes, too, the
qualifier input ENC1Q (meant to trace the Z-pulse in certain situations) and a
special/fast digital input DIC4 (used to trace very short pulses). These two
inputs are used in special applications.
The TTL type encoders do not have an internal regulator and use therefore a
supply voltage of +5V±5% whereas the TTL(R) type encoders have an internal
regulator and the supply voltage can be e.g. +15V±10% (depending on the
encoder manufacturer).
Allowed slots: C
Type ID: 16692
Termi nal s: One terminal block; Screw terminals (M2.6); Coding in terminal #3.
Jumpers: 2; X4 and X2 (see page 25)
Board parameters: Yes (see page 27)
Table 9. OPTA4 I/O terminals
Ter mi na l
Parameter reference
Keypad/NCDrive
Technical information
1DIC1A+ Pulse input A
2DIC1A–
3 DIC2B+
Pulse input B; phase shift of 90 degrees compared
to Pulse input A
4 DIC2B–
5 DIC3Z+ Pulse input Z; one pulse per revolution
6DIC3Z–
7 ENC1Q Reserved for future use
8 DIC4 Reserved for future use
9 GND Ground for control and inputs ENC1Q and DIC4
10 +5V/+15V/+24V
Control voltage (auxiliary voltage) output to
encoder;
Output voltage selectable with jumper X4. See
chapter 1.4.4.
Page 27
Descriptions of VACON® option boards vacon • 25
Local contacts: http://drives.danfoss.com/danfoss-drives/local-contacts/
3
Technical data:
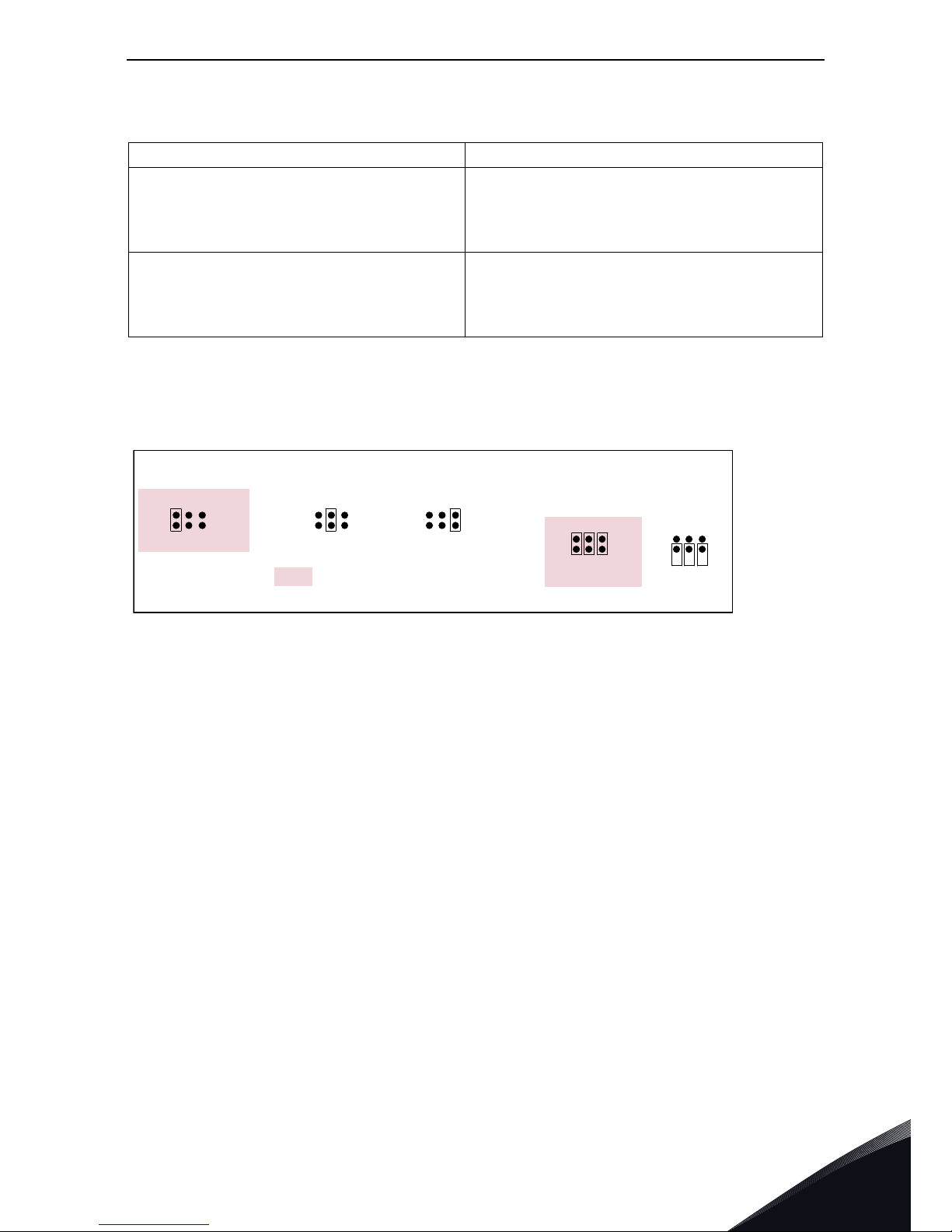
Jumper selections
On the OPTA4 board, there are two jumper blocks. The jumper X2 is used to define the status of the
termination resistor (R=135Ω). The jumper X4 is used to program the control voltage (auxiliary
voltage). The factory default and other available jumper selections are presented below.
Encoder control voltage, +5V/+15V/+24V Control voltage selectable with jumper X4.
Encoder input connections,
inputs A+, A–, B+, B–, Z+, Z–
Max. input frequency ≤150kHz
Inputs A, B and Z are differential
Encoder inputs are RS-422 interface compatible
Max. load per encoder input I
low
= I
high
≈ 25mA
Qualifier input ENC1Q
Fast digital input DIC4
Max. input frequency ≤10kHz
Min. pulse length 50μs
Digital input 24V; R
i
>5kΩ
Digital input is single-ended; connected to GND
ABC ABC
Jump er blockX2:
Ter m i na t io n r esi st or
Termination resistor
used
Termination resistor
not used
5V
15V
24V
=
Fa ct o r y d ef a ul t
5V
15V
24V
5V
15V
24V
Jump er block X 4:
Auxiliary voltage level
Auxiliary voltage +15 V Auxiliary voltage +24VAuxiliary voltage +5V
7247.emf
NOTE: If one encoder is connected to one
drive only, the termination resistor on the
board must be used. If the encoder is connected to several drives, the termination
resistor of the last drive must be used.
Page 28

3
vacon • 26 Descriptions of VACON® option boards
Local contacts: http://drives.danfoss.com/danfoss-drives/local-contacts/
Encoder connection – Differential
Figure 13. RS-422 type encoder connection using differential inputs
NOTE:
The encoder pulses are handled by VACON
®
software as presented below:
GND
A-
B-
+5V**
5V/15V/24V fro m the OPT-A4board or from external supply*
OPT-A4
board
.
.
10 +5V/+15V/+24V
9GND
1DIC1A+
2DIC1A3DIC2B+
4DIC2B5DIC3Z+
6DIC3Z7ENC1Q
8DIC1
.
.
*If external supply is used remember
to connectthe ground of external
supply to terminal #9 of theOPT-A4
and t o the en code r grou nd
**+5V/15V/+24V
Encoder
Tw i st e d p a ir s
with ow n shield
A+
B+
7248.emf
A
OUTPUT SIGNALS
Clockwise, seen from shaft
B
360º el.
1period
90º el. (channel separation)
7249.emf
Page 29

Descriptions of VACON® option boards vacon • 27
Local contacts: http://drives.danfoss.com/danfoss-drives/local-contacts/
3
OPTA4 parameters
Par 7.3.1.4 Encoder Type (can be selected with boards A4, A5 and A7 (encoder 2 mode))
Table 10. OPTA4 board-related parameters
Number Parameter Min Max Default Note
7.3.1.1 Pulse/revolution 1 65535 1024
7.3.1.2 Invert direction 0 1 0
0 = No
1 = Yes
7.3.1.3 Reading rate 0 4 1
Time used to calculate speed actual value.
NOTE: Use value 1 in Closed Loop mode.
0 = No
1 = 1 ms
2 = 5 ms
3 = 10 ms
4 = 50 ms
7.3.1.4 Encoder type 1 3 1
1 = A,B = speed
2 = A = REF, B = DIR
3 = A= FORW, B = REV
1 = A, B = Speed
Only with this input type it is possible to use Closed Loop speed control in an NXP
drive. NXS drives do not have Closed Loop possibility, but encoder signal can be
used e.g. for reference or positioning.
This input mode requires that both channels A and B are receiving pulses, differential connection is recommended.
Direction of speed is determined from 90° difference in signals.
2 = A = Ref, B = Dir
This type cannot be used for Closed Loop control!
In this mode only channel A is receiving pulses. Channel B will determine if direction is negative or positive. Input in channel B must be static signal.
A
B
90°
7250.emf
Page 30

3
vacon • 28 Descriptions of VACON® option boards
Local contacts: http://drives.danfoss.com/danfoss-drives/local-contacts/
3 = A = Forw, B = Rev
This type cannot be used for Closed Loop control!
In this mode both channels are receiving signal but not at the same time.
Pulses on channel A means positive direction.
Pulses on channel B means negative direction.
A
B
-25 Hz
+25 Hz
7251.emf
A
B
+25 Hz
-25 Hz
7252.emf
Page 31

Descriptions of VACON® option boards vacon • 29
Local contacts: http://drives.danfoss.com/danfoss-drives/local-contacts/
3
3.1.5 OPTA5
Description:
Encoder board for VACON
®
NXP. Encoder input board with programmable
control voltage for an encoder.
The OPTA5 board is designed for HTL (High voltage Transistor Logic) type
encoders (voltage output type push-pull HTL, open collector output type HTL)
which provide input signal levels dependent on the supply voltage of the
encoder. The encoder inputs A, B and Z are galvanically isolated. The OPTA5
board includes, too, the qualifier input ENC1Q (meant to trace the Z-pulse in
certain situations) and a fast digital input DIC4 (used to trace very short
pulses). These two inputs are used in special applications.
The OPTA5 is similar to the OPTA4 in connections but the encoder inputs A, B
and Z have different signal levels (voltage level). The input levels for A, B and
Z of the OPTA4 are compatible with RS-422 while those of the OPTA5 are
more general wide range inputs. Inputs ENC1Q and DIC4 are identical in both
boards.
Allowed slots: C
Type ID: 16693
Termi nal s: One terminal block; Screw terminals (M2.6); Coding in terminal #3.
Jumpers: 4; X2, X4, X5, X6 (see page 31)
Board parameters: Yes (see page 27)
X4
X2
X5
X6
Jumpers
7253.emf
Page 32

3
vacon • 30 Descriptions of VACON® option boards
Local contacts: http://drives.danfoss.com/danfoss-drives/local-contacts/
I/O terminals on OPTA5 (coded terminal painted black)
NOTE: Encoder inputs are wide range inputs that can be used with encoders using +15V or +24V.
Technical data:
NOTE: A high pulse frequency combined with a great cable capacitance places a considerable load
on the encoder. Apply therefore as low a voltage as possible for the encoder supply, rather lower
than 24V. The manufacturer also recommends to place jumper X4 to position +15V, if allowed in the
voltage range specification of the encoder.
Table 11. OPTA5 I/O terminals
Ter mi na l
Parameter reference
Keypad/NCDrive
Technical information
1 DIC1A+ Pulse input A (differential); Voltage range 10…24V
2 DIC1A–
3 DIC2B+
Pulse input B; phase shift of 90 degrees compared to
Pulse input A (differential); Voltage range 10…24V
4 DIC2B–
5
DIC3Z+
Pulse input Z; one pulse per revolution (differential);
Voltage range 10…24V
6 DIC3Z–
7 ENC1Q Reserved for future use
8 DIC4 Reserved for future use
9 GND Ground for control and inputs ENC1Q and DIC4
10
+15V/+24V
Control voltage (auxiliary voltage) output to encoder;
Output voltage selectable with jumper X4. See chapter
1.4.4.
Encoder control voltage, +15V/+24V Control voltage selectable with jumper X4.
Encoder input connections,
inputs A+, A–, B+, B–, Z+, Z–
Max. input frequency ≤150kHz
Inputs A, B and Z are differential
Qualifier input ENC1Q
Fast digital input DIC4
Max. input frequency ≤10kHz
Min. pulse length 50μs
Digital input 24V; R
i
>5kΩ
Digital input is single-ended; connected to GND
Page 33

Descriptions of VACON® option boards vacon • 31
Local contacts: http://drives.danfoss.com/danfoss-drives/local-contacts/
3
Jumper selections
On the OPTA5 board, there are four jumper blocks; X4 is used to program the control voltage
(auxiliary voltage), X2, X5 and X6 are set according the voltage of the encoder. The factory default
and other available jumper selections are presented below.
Jumper blocks X2, X5 and X6:
When these jumpers are set to High (default and typically good for 24V encoders), it means that
when the voltage at the channel goes above 8V, it will acknowledge a new pulse.
When they are set to Low = 2.3 V, it means that when the voltage at the channel goes above 2.3V, it
will acknowledge a new pulse.
Usage: Closed Loop Vector Control. The OPTA5 board is mainly used in conventional industrial
applications where encoder cable lengths are relatively long.
Encoder connection – Differential
Figure 14. HTL type encoder connection using differential inputs
24V
15V
24V
15V
High
Low
High
Low
Jumper block X4:
Auxiliary voltage level
Auxiliary voltage +24V Auxiliary voltage +15V
=
Factory default
Jumper blocks X2, X5 and X6:
encoder voltage level
7254.emf
GND
A-
B-
15V**
15V/24V from the OPT-A5board or from external supply*
OPT-A5
board
.
.
10 + 15V/ +24 V
9GND
1DIC1A+
2DIC1A3DIC2B+
4DIC2B5DIC3Z+
6DIC3Z7ENC1Q
8DIC1
.
.
*If external supply is usedremember
to connect the ground of external
supply to termi nal #9 of the OPT-A5
and t o the enco der gr ou nd
**+ 15V/+24 V
Encoder
Tw i s te d p a i rs
with own shield
A+
B+
DIC4
7255.emf
Page 34

3
vacon • 32 Descriptions of VACON® option boards
Local contacts: http://drives.danfoss.com/danfoss-drives/local-contacts/
Encoder connection – Single-ended
Figure 15. HTL type encoder connection (open source) using single-ended inputs
NOTE! Grounding is to be connected only at the AC drive to avoid circulating current in the shield.
Isolate shield at the encoder.
It is recommended to use double shielded cable for encoder connection.
Figure 16. HTL type encoder connection (open collector) using single-ended inputs
NOTE! Grounding is to be connected only at the AC drive to avoid circulating current in the shield.
Isolate shield at the encoder.
It is recommended to use double shielded cable for encoder connection.
OPTA5 parameters
See page 27 and 27.
GND
GND
GND
15V/24V from the OPT-A5board or from external supply*
OPT-A5
board
.
.
10 +15V/+24V
9GND
1DIC1A+
2DIC1A3DIC2B+
4DIC2B5DIC3Z+
6DIC3Z7ENC1Q
8DIC1
.
.
*If external supply is used remember
to connect the ground ofexternal
supply to terminal #9 of the OPT-A5
and t o the en co der gr ound
**+1 5V/ +24V
Encoder
Tw i st e d pa i r s
with o wn s hield
+
A+
B+
DIC4
7256.emf
GND
A-
B-
15V /24V f ro m t he O PT-A 5board or from external supply*
OPT-A5
board
.
.
10 +1 5V/+ 24V
9GND
1DIC1A+
2DIC1A3DIC2B+
4DIC2B5DIC3Z+
6DIC3Z7ENC1Q
8DIC1
.
.
*If external supply is usedremember
to connectthe groundof external
supply to terminal #9 of the OPT- A5
andtotheencoderground
**+ 15V /+ 24V
Encoder
Tw i st e d p a ir s
with ow n shield
+
+
+
DIC4
7257.emf
Page 35

Descriptions of VACON® option boards vacon • 33
Local contacts: http://drives.danfoss.com/danfoss-drives/local-contacts/
3
3.1.6 OPTA7
Description:
Duplicate encoder board for VACON
®
NXP. Encoder input board with
programmable control voltage for the encoder.
The OPTA7 board is designed for HTL (High voltage Transistor Logic) type
encoders (voltage output type push-pull HTL, open collector output type HTL)
which provide input signal levels dependent on the supply voltage of the
encoder. The encoder inputs A, B and Z are galvanically isolated. The OPTA7
board includes, too, the qualifier inputs ENC1Q and ENC2Q meant to trace
positions in positioning applications.
The board can be used as both Master and Slave device. The encoder input
signal is repeated on the board and carried to the next device through the
digital output.
Allowed slots: C
Type ID: 16695
Termi nal s: Two terminal blocks; Screw terminals (M2.6); Coding in terminals #3 and
#14.
Jumpers: 4; X4, X5, X15 and X16 (see page 35)
Board parameters: Yes, see page 38.
Jumper X4
Jumper X5 Jumpers X15 and X16
7258.emf
Page 36

3
vacon • 34 Descriptions of VACON® option boards
Local contacts: http://drives.danfoss.com/danfoss-drives/local-contacts/
I/O terminals on OPTA7
NOTE: Encoder inputs are wide range inputs that can be used with encoders using +15V or +24V.
Table 12. OPTA7 I/O terminals
Ter mi na l
Parameter reference
Keypad/NCDrive
Technical information
1 DIC1A+ Pulse input A (differential); Voltage range 10…24V
2 DIC1A–
3 DIC2B+
Pulse input B; phase shift of 90 degrees compared to
Pulse input A (differential); Voltage range 10…24V
4 DIC2B–
5
DIC3Z+
Pulse input Z; one pulse per revolution (differential);
Voltage range 10…24V
6 DIC3Z–
7 ENC1Q Qualifier input. Single-ended input with GND
8 ENC2Q Qualifier input. Single-ended input with GND
9 GND Ground for control and inputs ENC1Q and ENC2Q
10
+15V/+24V
Control voltage (auxiliary voltage) output to encoder;
Output voltage selectable with jumper X4.
11
DID1A+
Pulse input A (differential input), voltage range
10…24V
12 DID1A–
13
DID2B+
Pulse input B; 90 degrees phase shift compared to the
pulse input A (differential input), voltage range 10…24V
14 DID2B–
15
DID3Z+
Pulse input Z; one pulse per revolution (differential
input), voltage range 10…24V
16 DID3Z–
17
DOD1A+
Pulse output A (differential), output voltage +24V.
Pulse input DIC1A or DID1A is internally repeated in
the card and connected to the DOD1A output.
18
DOD1A–
19
DOD2B+
Pulse output B (differential), output voltage +24V.
Pulse input DIC2A or DID2A is internally repeated in
the card and connected to the DOD2A output.
20
DOD2B–
Page 37

Descriptions of VACON® option boards vacon • 35
Local contacts: http://drives.danfoss.com/danfoss-drives/local-contacts/
3
Technical data:
NOTE: A high pulse frequency combined with a great cable capacitance places a considerable load
on the encoder. Apply therefore as low a voltage as possible for the encoder supply, rather lower
than 24V. The manufacturer also recommends to place jumper X4 to position +15V, if allowed in the
voltage range specification of the encoder.
Jumper selections
On the OPTA7 board, there are four jumper blocks.
Jumper X4 is used to program the control voltage (auxiliary voltage).
The setting of jumper X5 defines the encoder channel (DIC/DID) used to carry the signal to the
repeater.
The setting of jumpers X15 and X16 is changed according to whether the board is used as a Master
or Slave device.
In Slave function input, signals DID1A are directly connected to outputs DOD1A and signals DID2B
are directly connected to outputs DOD2B.
In Master Function input signals DIC_ or DID_, as selected with Jumper Block X5 "Encoder
Channel", DIC1A or DID1A are actively connected to outputs DOD1A and DIC2A or DID2A are actively
connected to outputs DOD2B.
The factory default and other available jumper selections are presented below.
Encoder control voltage, +15V/+24V Control voltage selectable with jumper X4.
Encoder input connections,
inputs A+, A–, B+, B–, Z+, Z–
Max. input frequency ≤150kHz
Inputs A, B and Z are differential
Qualifier input ENC1Q
Fast digital input DIC1
Max. input frequency ≤10kHz
Min. pulse length 50μs
Digital input 24V; R
i
>5kΩ
Digital input is single-ended; connected to GND
Page 38

3
vacon • 36 Descriptions of VACON® option boards
Local contacts: http://drives.danfoss.com/danfoss-drives/local-contacts/
Usage: Closed Loop Vector Control, positioning applications. The OPTA7 encoder board is mainly
used in demanding system applications, e.g. when measuring the motor speed with two encoders.
24V
15V
24V
15V
Jumper block X4:
Auxiliary voltage level
Auxiliary voltage +24V Auxiliary voltage +15V
= Factory default
Jumper block X5:
Encoder channel
Channel DIC
selected
Channel DID
selected
Master function
selected
Slave function
selected
Jumper blocks
X15 and X16:
Master/Slave
function
7259A_uk
X5
X5
X16X15
X16X15
Page 39
Descriptions of VACON® option boards vacon • 37
Local contacts: http://drives.danfoss.com/danfoss-drives/local-contacts/
3
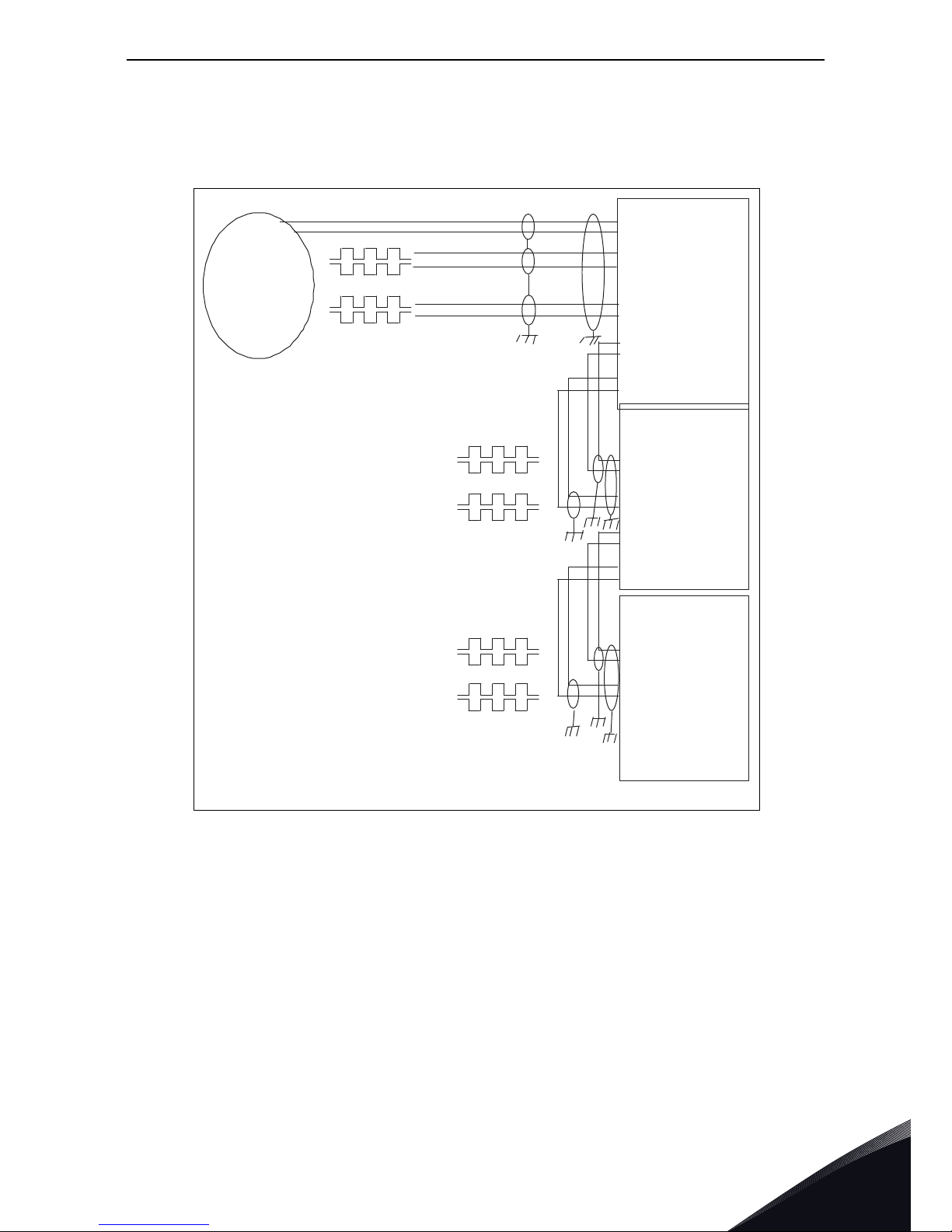
Encoder connection
The figures below present examples of a chain connection of several OPTA7 boards (Figure 17) and
a connection of two encoders to the OPTA7 option board (Figure 18).
Figure 17. Connection of encoder and three OPTA7 boards
B+
B-
A+
A-
B+
B-
A+
A-
B+
B-
A+
A-
O
PT-A7
10 +15V/+24V
9 GND
1/11 DIC1A+/DID1A+
2/12 DIC1A-/DID1A-
3/13 DIC2B+/DID2B+
4/14 DIC2B-/DID2B-
17 DOD1A +
18 DOD1A -
19 DOD2B +
20 DOD2B -
OPT-A7
1/11 DIC1A+/DID1A+
2/12 DIC1A-/DID1A-
3/13 DIC2B+/DID2B+
4/14 DIC2B-/DID2B-
17 DOD1A+
18 DOD1A-
19 DOD2B+
20 DOD2B-
OPT-A7
1/11 DIC1A+/DID1A+
2/12 DIC1A-/DID1A-
3/13 DIC2B+/DID2B+
4/14 DIC2B-/DID2B-
17 DOD1A+
18 DOD1A-
19 DOD2B+
20 DOD2B-
Encoder
7260A_uk
Page 40

3
vacon • 38 Descriptions of VACON® option boards
Local contacts: http://drives.danfoss.com/danfoss-drives/local-contacts/
Figure 18. Connection of two encoders to OPTA7 board
OPTA7 parameters
Table 13. OPTA7 parameters
Number Parameter Min Max Default Note
7.3.1.1 Encoder 1 Pulse/revolution 0 65535 1024
7.3.1.2 Invert encoder 1 direction 0 1 0
0 = No
1 = Yes
7.3.1.3 Reading rate 0 4 1
Time used to calculate speed actual value.
NOTE: Use value 1 in Closed Loop mode.
0 = No
1 = 1 ms
2 = 5 ms
3 = 10 ms
4 = 50 ms
7.3.1.4 Encoder 2 Pulse/revolution 0 65535 1024
7.3.1.5 Encoder 2 type 1 3 1
1 = A,B = speed
2 = A = REF, B = DIR
3 = A= FORW, B = REV
See page 27 for explanations!
B+
B-
B+
B-
A+
A-
B+
B-
A+
A-
A+
A-
15V/24V from OPT-A7
OPTA-7
10 +15V/+24V
9GND
1DIC1A+
2DIC1A-
3DIC2B+
4DIC2B.
.
.
11 D ID1A+
12 DID1A-
13 DID2B+
14 DID2B-
17 DOD1A+
18 DOD1A-
19 DOD2B+
20 DOD2B-
Encoder 1
Encode r 2
GND
7261.emf
Page 41

Descriptions of VACON® option boards vacon • 39
Local contacts: http://drives.danfoss.com/danfoss-drives/local-contacts/
3
OPTA7 monitoring values
3.1.7 OPTA8
Table 14. OPTA7 monitoring values
Number Monitored value Unit Description
Mon 7.3.2.1 Encoder 1 frequency Hz Motor speed in Hz calculated from encoder 1 pulses
Mon 7.3.2.2 Encoder 1 speed rpm
Motor speed in rpm calculated from encoder 1
pulses
Mon 7.3.2.3 Encoder 2 frequency Hz Motor speed in Hz calculated from encoder 2 pulses
Mon 7.3.2.4 Encoder 2 speed rpm
Motor speed in rpm calculated from encoder 2
pulses
Description:
VACON
®
NX basic I/O board similar to OPTA1 except that the analogue inputs
and output are galvanically isolated.
Allowed slots: A
Type ID: 16696
Termi nal s: Two terminal blocks; Screw terminals (M2.6); Coding in terminals #1 and
#12.
Jumpers: 4; X1, X2, X3 and X6 (see page 41)
Board parameters: Yes (see page 42)
Jumper X1
Jumper X2
Jumper X6
Jumper X3
7262.emf
Page 42

3
vacon • 40 Descriptions of VACON® option boards
Local contacts: http://drives.danfoss.com/danfoss-drives/local-contacts/
I/O terminals on OPTA8 (coded terminals painted black)
Table 15. OPTA8 I/O terminals
Ter mi na l
Parameter reference
Keypad/NCDrive
Technical information
1
+10 Vref Refer.output +10V; Max.current 10mA; Decoupled from FC GND
2
AI1+ An.IN:A.1
Selection V or mA with jumper block X1 (see page 41):
Default: 0– +10V (Ri = 200 kΩ)
(-10V…..+10V Joy-stick control, selected with a jumper)
0– 20mA (Ri = 250 Ω)
Resolution 0.1%; Accuracy ±1%
3
AI1–
(GND ISOL)
GND ISOL/Voltage input;
Connected to GND ISOL (selected with jumper)
4
AI2+ An.IN:A.2
Selection V or mA with jumper block X2 (see page 41):
Default: 0– 20mA (Ri = 250 Ω)
0– +10V (Ri = 200 kΩ)
(-10V…..+10V Joy-stick control, selected with a jumper)
5
AI2–
(GND ISOL)
Resolution: 0.1%; Accuracy ±1%
GND ISOL/Voltage input;
Connected to GND ISOL (selected with jumper)
6
24 Vout
(bidirectional
24V auxiliary voltage output. Short-circuit protected.
±15%, maximum current 150 mA, see 1.4.4.
+24Vdc external supply may be connected.
Galvanically connected to terminal #12.
7
GND
Ground for reference and controls
Galvanically connected to terminal #13.
8
DIN1 DigIN:A.1
Digital input 1 (Common CMA); R
i
= min. 5kΩ
9
DIN2 DigIN:A.2
Digital input 2 (Common CMA); R
i
= min. 5kΩ
10
DIN3 DigIN:A.3
Digital input 3 (Common CMA); R
i
= min. 5kΩ
11
CMA
Digital input common A for DIN1, DIN2 and DIN3.
Connection by default to GND.
Selection with jumper block X3 (see page 41):
12
24 Vout (bidi-
rectional
Same as terminal #6
Galvanically connected to terminal #6.
13
GND
Same as terminal #7
Galvanically connected to terminals #7
14
DIN4 DigIN:A.4
Digital input 4 (Common CMB); R
i
= min. 5kΩ
15
DIN5 DigIN:A.5
Digital input 5 (Common CMB); R
i
= min. 5kΩ
16
DIN6 DigIN:A.6
Digital input 6 (Common CMB); R
i
= min. 5kΩ
17
CMB
Digital input common A for DIN4, DIN5 and DIN6.
Connection by default to GND.
Selection with jumper block X3 (see page 41):
18
AO1+ AnOUT:A.1
Analogue output
Output signal range:
Current 0(4)–20mA, R
L
max 500Ω or
Voltage 0—10V, R
L
>1kΩ
Selection with jumper block X6 (see page 41):
Resolution: 0.1% (10 bits); Accuracy ±2%;
19
AO1–
20
DO1 DigOUT:A.1
Open collector output; Max. U
in
= 48VDC; Max. current = 50 mA
Page 43

Descriptions of VACON® option boards vacon • 41
Local contacts: http://drives.danfoss.com/danfoss-drives/local-contacts/
3
Jumper selections
There are four jumper blocks on the OPTA8 board. The factory defaults and other available jumper
selections are presented below.
Figure 19. Jumper positions for OPTA8
ABCD
ABCD
ABCD
ABCD
ABCD
ABCD
ABCD
ABCD
ABCD
ABCD
Jum per block X 1 :
AI1 mode
AI1 mode: Voltage input; 0...10V
AI1 mode: Voltage input; 0...10V (differential)
AI1 mode: Voltage input; -10...10V
Jum per blockX2:
AI2 m ode
AI2 mode: 0...2 0mA; Current input
AI2 mode: Voltage i np ut; 0 . ..10 V
AI2 mode: Voltage input; 0...1 0V (differential)
AI2 mode: Voltage input; -10 ...10V
Jumper block X 3:
CMA a nd CMB grounding
CMB connected to GN D
CMA connected to GND
CMB isolated from GN D
CMA isolated from GN D
CMB and CM A
interna lly connected to g ether,
isolated from GND
=Factorydefault
Jumper block X 6:
AO1 m ode
AO 1 mod e: 0... 2 0 mA; Current output
AO1 mode: Voltage output; 0...10V
AI1 mode: 0...20mA; Current input
7263.emf
Page 44
3
vacon • 42 Descriptions of VACON® option boards
Local contacts: http://drives.danfoss.com/danfoss-drives/local-contacts/
OPTA8 parameters
3.1.8 OPTA9
Table 16. OPTA8 board-related parameters
Number Parameter Min Max Default Note
1AI1 mode153
1 = 0...20mA
2 = 4...20mA
3 = 0...10V
4 = 2...10V
5 = -10...+10V
2AI2 mode151
1 = 0...20mA
2 = 4...20mA
3 = 0...10V
4 = 2...10V
5 = -10...+10V
3AO1 mode14 1
1 = 0...20mA
2 = 4...20mA
3 = 0...10V
4 = 2...10V
Description:
VACON
®
NX basic I/O board similar to the OPTA1 except that the I/O termi-
nals are bigger (for 2.5mm
2
wires; M3 screws).
Allowed slots: A
Type ID: 16697
Termi nal s: Two terminal blocks; Screw terminals (M3); Coding in terminals #1 and #12.
Jumpers: 4; X1, X2, X3 and X6 (see page 20)
Board parameters: Yes (see page 21)
Jumper X1
Jumper X2
Jumper X6
Jumper X3
7264.emf
Page 45
Descriptions of VACON® option boards vacon • 43
Local contacts: http://drives.danfoss.com/danfoss-drives/local-contacts/
3
I/O terminals on OPTA9
See page 19.
Jumper selections
See page 20.
OPTA9 parameters
See page 21.
3.1.9 OPTAL
Description: Dual I/O expander board with six 42…240 VAC digital inputs, 2 analog inputs,
two analog outputs, one digital output and 15 and 24 V out.
Allowed slots: A
Type ID: 16716
Termi nal s:
Two terminal blocks; Screw terminals (M2.6, 1.5 mm
2
wire terminals 1 – 10;
M3, 2.5 mm
2
wire terminals 11-18); No coding
Jumpers: None
Board parameters: None
Page 46

3
vacon • 44 Descriptions of VACON® option boards
Local contacts: http://drives.danfoss.com/danfoss-drives/local-contacts/
I/O terminals on OPTAL
Table 17. OPTAL I/O terminals
Ter mi na l
Parameter reference
Keypad/NCDrive
Technical information
1 +15 V 15 V out – together with terminal 2 max 200 mA
2 +15 V 15 V out
3 AI1 An.IN:A.1 Analog input 0 – 10 V
4 AI2 An.IN:A.2 Analog input ± 10 V
5 GND Ground for analog signals
6 AO1+ AnOUT:A.1 Analog output 0 (4) – 20 mA
7 AO2+ AnOUT:A.2 Analog output 0 – 10 V
8 DO1 Open collector digital output , 48 V, 50 mA allowed
9 GND Ground for analog signals
10 + 24 V 24 V out – max 200 mA
11
ACIN1 DigIN:X.1
Digital input, 42…240 VAC (threshold 35V)
Control voltage: "0"<33V, "1">35V
12
ACIN2 DigIN:X.2
Digital input, 42…240 VAC (threshold 35V)
Control voltage: "0"<33V, "1">35V
13
ACIN3 DigIN:X.3
Digital input, 42…240 VAC (threshold 35V)
Control voltage: "0"<33V, "1">35V
14
ACIN4 DigIN:X.4
Digital input, 42…240 VAC (threshold 35V)
Control voltage: "0"<33V, "1">35V
15
ACIN5 DigIN:X.5
Digital input, 42…240 VAC (threshold 35V)
Control voltage: "0"<33V, "1">35V
16
ACIN6 DigIN:X.6
Digital input, 42…240 VAC (threshold 35V)
Control voltage: "0"<33V, "1">35V
17
18
COMMON Common input for DI1 - 6
Page 47

Descriptions of VACON® option boards vacon • 45
Local contacts: http://drives.danfoss.com/danfoss-drives/local-contacts/
3
3.1.10 OPTAE
Description:
Encoder board for VACON
®
NXP. Encoder input board with programmable
control voltage for an encoder.
The OPTAE board is designed for HTL (High voltage Transistor Logic) type
encoders (voltage output type push-pull HTL, open collector output type HTL)
which provide input signal levels dependent on the supply voltage of the
encoder. The encoder inputs A, B and Z are galvanically isolated.
In addition, the board includes an Encoder Direction Signal and an Encoder
Pulse Output Signal. The Encoder Direction Signal value ‘1’ indicates a backward motor direction and ‘0’ a forward motor direction. The Encoder Pulse
Output signal is produced from The Encoder input signals (channel A) divided
by the divider parameter (see page 48).
Allowed slots: C
Type ID: 16709
Termi nal s: One terminal block; Screw terminals (M2.6); Coding in terminal #3.
Jumpers: 1; X4 (see page 46 )
Board parameters: Yes
Jumper X4
7266.emf
Page 48

3
vacon • 46 Descriptions of VACON® option boards
Local contacts: http://drives.danfoss.com/danfoss-drives/local-contacts/
I/O terminals on OPTAE (coded terminal painted black)
NOTE: Encoder inputs are wide range inputs that can be used with encoders using +15V or +24V.
Technical data:
Jumper selections
On the OPTAE board, there is one jumper block used to program the control voltage (auxiliary
voltage). The factory default and other available jumper selections are presented below.
Table 18. OPTAE I/O terminals
Ter mi na l
Parameter reference
Keypad/NCDrive
Technical information
1 DIC1A+ Pulse input A (differential); Voltage range 10…24V
2 DIC1A–
3 DIC2B+
Pulse input B; phase shift of 90 degrees compared to
Pulse input A (differential); Voltage range 10…24V
4 DIC2B–
5
DIC3Z+
Pulse input Z; one pulse per revolution (differential);
Voltage range 10…24V
6 DIC3Z–
7
DO1
Encoder divider output. Encoder input signals are
divided by divider paramater (see parameter list on
page 48)
8
DO2
Encoder direction output. The signal value ‘1’ means
that the motor direction is backward and ‘0’ is forward.
9 GND Ground for control
10
+15V/+24V
Control voltage (auxiliary voltage) output to encoder;
Output voltage selectable with jumper X4.
Encoder control voltage, +15V/+24V Control voltage selectable with jumper X4.
Encoder input connections,
inputs A+, A–, B+, B–, Z+, Z–
Max. input frequency ≤150kHz
Inputs A, B and Z are differential
Encoder divider output DO1,
Encoder direction output DO2
Max.load voltage 60Vdc
Max. load current 50mA
Max. output frequency ≤300kHz
=
Fa c to r y d e f a u lt
24V
15V
24V
15V
Auxiliary voltage +24V Auxiliary voltage +15V
7267.emf
Jumper block X4:
Auxilia ry voltage level
Page 49

Descriptions of VACON® option boards vacon • 47
Local contacts: http://drives.danfoss.com/danfoss-drives/local-contacts/
3
Usage: Closed Loop Vector Control. The OPTAE board is mainly used in conventional industrial
applications where encoder cable lengths are relatively long.
Encoder connection - single-ended
Figure 20. HTL type encoder connection (open source) using single-ended inputs
NOTE! Grounding is to be connected only at the AC drive to avoid circulating current in the shield.
Isolate shield at the encoder.
It is recommended to use double shielded cable for encoder connection.
Figure 21. HTL type encoder connection (open collector) using single-ended inputs
NOTE! Grounding is to be connected only at the AC drive to avoid circulating current in the shield.
Isolate shield at the encoder.
It is recommended to use double shielded cable for encoder connection.
GND
GND
GND
15V /24V f ro m t he O PT-A E
board or from external supply*
OPT-AE
board
.
.
10 +15V/+24V
9GND
1DIC1A+
2DIC1A3DIC2B+
4DIC2B5DIC3Z+
6DIC3Z7ENC1Q
8DIC1
.
.
*If external supply is usedr emember
to connectthe ground of external
supply to terminal #9 of theOPT-AE
and t o the en code r grou nd
**+ 15V/ +24 V
Encoder
Tw i st e d p ai r s
with ow n shie ld
+
A+
B+
7268.emf
GND
A-
B-
15V/24V from the OPT-AEboard or from external supply*
OPT-AE
board
.
.
10 +1 5V/ +24V
9GND
1DIC1A+
2DIC1A3DIC2B+
4DIC2B5DIC3Z+
6DIC3Z7ENC1Q
8DIC1
.
.
*If external supply is usedremember
to connectthe groundof external
supply to terminal #9 of the OPT- AE
andtotheencoderground
**+ 15V /+ 24V
Encoder
Tw i st e d p a ir s
with ow n shield
+
+
+
DO2
DO1
7269.emf
Page 50

3
vacon • 48 Descriptions of VACON® option boards
Local contacts: http://drives.danfoss.com/danfoss-drives/local-contacts/
Encoder connection – differential
Figure 22. HTL type encoder connection using differential inputs
OPTAE parameters
Table 19. OPTAE board-related parameters
Number Parameter Min Max Default Note
7.3.1.1 Pulse/revolution 1 65535 1024
7.3.1.2 Invert direction 0 1 0
0 = No
1 = Yes
7.3.1.3 Reading rate 0 4 1
Time used to calculate speed actual value.
NOTE: Use value 1 in Closed Loop mode.
0 = No calculation
1 = 1 ms
2 = 5 ms
3 = 10 ms
4 = 50 ms
7.3.1.4 Divider Value 1 2048 64 Input pulses / Divider = Divider Output
7.3.1.5
Hysteresis for
Direction Out
0511 8
Number of pulses before direction signal
change state
DO2
DO1
GND
15V /24V f ro m t he O PT-A E
board or from external supply*
OPT-AE
board
.
.
10 + 15V/+2 4V
9GND
1DIC1A+
2DIC1A3DIC2B+
4DIC2B5DIC3Z+
6DIC3Z7ENC1Q
8DIC1
.
.
**+ 15V /+ 24V
Encoder
+15V**
DO2
DO1
7270.emf
Page 51

Descriptions of VACON® option boards vacon • 49
Local contacts: http://drives.danfoss.com/danfoss-drives/local-contacts/
3
3.1.11 OPTAN
Description:
Standard I/O board for VACON
®
NXP with 6 galvanically isolated digital inputs
and two analogue inputs/outputs. The Analogue channels are programmable:
1 = 0...20mA
2 = 4...20mA
3 = 0...10V
4 = 2...10V
5 = -10...+10V
Allowed slots: A
Type ID: 16718
Termi nal s: Two terminal blocks (coded = mounting of blocks in wrong order prevented,
terminals #1 and #12);
Jumpers: J1, J2, J3, J4
Board parameters: Yes (see page 51)
7271.emf
Page 52

3
vacon • 50 Descriptions of VACON® option boards
Local contacts: http://drives.danfoss.com/danfoss-drives/local-contacts/
I/O terminals on OPTAN
Table 20. OPTAN I/O terminals
Ter mi na l Technical information
1 AI1-
Selection V or mA with jumper block J1
Default: 0– +10V (Ri = 200 kΩ)
(-10V..+10V Joy-stick control, selected with jumper)
0– 20mA (Ri = 250 Ω)
Resolution 0.1%; Accuracy ±1%
Differential input if not connected to ground;
Allows ±20V differential mode voltage to GND
2 AI1+
3 AI2-
Selection V or mA with jumper block J2
Default: 0– +10V (Ri = 200 kΩ)
(-10V..+10V Joy-stick control, selected with jumper)
0– 20mA (Ri = 250 Ω)
Resolution 0.1%; Accuracy ±1%
Differential input if not connected to ground;
Allows ±20V differential mode voltage to GND
4 AI2+
5 -10V_POT_REF 10V reference voltage 10mA
6 GND POT COM Common for POT
7 +10V_POT_REF +10V reference voltage 10mA
8 AO1+ Analogue output
9 GND AO COM
Output signal range:
10 AO2+
Current 0(4)–20mA, RL max 500Ω,
Voltage 0—10V, RL >1kΩ or
Voltage -10-+10, RL>1kΩ
Selection V or mA with jumper blocks J3 for AO1, J4 for AO2
Resolution: 0.1% (10 bits); Accuracy ±2%
11 DIN1 Digital input 1 (Common DI COM); Ri = min. 5kΩ
12 DIN2 Digital input 2 (Common DI COM); Ri = min. 5kΩ
13 DIN3 Digital input 3 (Common DI COM); Ri = min. 5kΩ
14 DIN4 Digital input 4 (Common DI COM); Ri = min. 5kΩ
15 DIN5 Digital input 5 (Common DI COM); Ri = min. 5kΩ
16 DIN6 Digital input 6 (Common DI COM); Ri = min. 5kΩ
17 DI COM DI COM isolated from GND
18 DI COM DI COM isolated from GND
19
24 V out (bi-
directional)
24V auxiliary voltage output. Short-circuit protected.
±15%, maximum current 150 mA,
+24Vdc external supply may be connected.
20 GND 24V COM Ground for reference and controls
Page 53

Descriptions of VACON® option boards vacon • 51
Local contacts: http://drives.danfoss.com/danfoss-drives/local-contacts/
3
Jumper selections
OPTAN board parameters
J1 (AI1), J2 (AI2) Analog Input Mode 0 ... 10 D (default)
J1 (AI1), J2 (AI2) Analog Input Mode –10 ... +10V CD
J1 (AI1), J2 (AI2) Analog Input Mode 0 ... 20mA AB
J3 (AO1), J4 (AO2) Analog Output 0 ... 10V BC (default)
J3 (AO1), J4 (AO2) Analog Output –10 ... +10V CD
J3 (AO1), J4 (AO2) Analog Output 0 ... 20mA AB
Table 21. OPTAN board-related parameters
Number Parameter Min Max Default Note
7.1.1.1 AI1 mode 1 5 3
1 = 0...20mA
2 = 4...20mA
3 = 0...10V
4 = 2...10V
5 = -10...+10V
7.1.1.2 AI2 mode 1 5 3
1 = 0...20mA
2 = 4...20mA
3 = 0...10V
4 = 2...10V
5 = -10...+10V
7.1.1.3 AO1 mode 1 5 3
1 = 0...20mA
2 = 4...20mA
3 = 0...10V
4 = 2...10V
5 = -10...+10V
J1 J2 J3 J4
ABCD ABCD ABCD ABCD
7272.emf
Page 54

3
vacon • 52 Descriptions of VACON® option boards
Local contacts: http://drives.danfoss.com/danfoss-drives/local-contacts/
OPTAN board I/O monitor values
7.1.1.4 AO2 mode 1 5 3
1 = 0...20mA
2 = 4...20mA
3 = 0...10V
4 = 2...10V
5 = -10...+10V
Table 22. OPTAN board monitor values
Number Parameter Description
7.1.2.1 DigIN:A.1 DIN1 Status
7.1.2.2 DigIN:A.2 DIN2 Status
7.1.2.3 DigIN:A.3 DIN3 Status
7.1.2.4 DigIN:A.4 DIN4 Status
7.1.2.5 DigIN:A.5 DIN5 Status
7.1.2.6 DigIN:A.6 DIN6 Status
7.1.2.7 DigIN:A.8 Not in use
7.1.2.8 DigOUT:A.1 Not in use
7.1.2.9 AnIN:A.1 AI1 Status
7.1.2.10 AnIN:A.2 AI2 Status
7.1.2.11 AnOUT:A.1 AO1 Status
7.1.2.12 AnOUT:A.2 AO2 Status
Table 21. OPTAN board-related parameters
Number Parameter Min Max Default Note
Page 55

Descriptions of VACON® option boards vacon • 53
Local contacts: http://drives.danfoss.com/danfoss-drives/local-contacts/
3
3.2 I/O Expander Boards OPTB_
• Option boards used for I/O expansion
• This board type can normally be plugged into slots B, C, D or E.
The number of control inputs and outputs on your VACON
®
AC drive can be increased with the I/O
Expander boards. This kind of boards can usually be placed in any board slot inside the AC drive
control unit except for slot A.
There are no board-related parameters for OPTB_ I/O expander boards (except for board OPTBB).
The boards you wish to have installed in your AC drive have to be defined in the type designation code
of the AC drive when ordering it from the factory.
Table 23 . VACON
®
NX I/O Expander boards and their equipment
FC
type
I/O
board
Allowed
slots
DI AI TI AO DO RO Pt-100
42-240
VAC
input
Other
NXS
NXP
OPTB1 B,C,D,E (6) (6)
NXS
NXP
NXL
OPTB2 B,C,D,E 1 2
NXS
NXP
NXL
OPTB4 B,C,D,E
1
(iso-
lated);(mA)
2
(isolated
mA)
+24V/
EXT+24V
NXS
NXP
NXL
OPTB5 B,C,D,E 3
NXS
NXP
OPTB8 B,C,D,E 3
NXS
NXP
OPTB9 B,C,D,E 1 5
NXS
NXP
OPTB9 B,C,D,E
2
(enc)
NXS
NXP
OPTBB C
NXS
NXP
OPTBH B,C,D,E
DI = Digital input Pt-100 = Sensor input for Pt-100
AI = Analogue input AO = Analogue output
TI = Thermistor input RO = Relay output
Page 56

3
vacon • 54 Descriptions of VACON® option boards
Local contacts: http://drives.danfoss.com/danfoss-drives/local-contacts/
3.2.1 OPTB1
I/O terminals on OPTB1
Description:
VACON
®
NX I/O expander board with six bidirectional terminals.
Allowed slots: B, C, D, E
Type ID: 16945
Termi nal s: One terminal block; Screw terminals (M2.6); No coding
Jumpers: 2; X2 and X4 (see page 55)
Board parameters: None
Table 24. OPTB1 I/O terminals
Ter mi na l
Parameter reference
Keypad/NCDrive
Technical information
1
DIO1
DigIN: X.1
DigOUT: X.1
Digital input:
24V; Ri>5kΩ
Digital output:
Open collector, 50mA/48V
2
DIO2
DigIN: X.2
DigOUT: X.2
See above.
3
DIO3
DigIN: X.3
DigOUT: X.3
See above.
4
CMA
Common for DIO1…DIO3.
Note: CMA is internally connected to GND with jumper by
default.
5
DIO4
DigIN: X.4
DigOUT: X.4
Digital input:
24V; Ri>5kΩ
Digital output:
Open collector, 50mA/48V
6
DIO5
DigIN: X.5
DigOUT: X.5
See above.
7
DIO6
DigIN: X.6
DigOUT: X.6
See above.
8 CMB Common for DIO4…DIO6
9 GND I/O ground; Ground for reference and controls.
Jumper X2
Jumper X4
7273.emf
Page 57

Descriptions of VACON® option boards vacon • 55
Local contacts: http://drives.danfoss.com/danfoss-drives/local-contacts/
3
Jumper selections
On the OPTB1 board, there are two jumper blocks. The jumper block X2 is used to define the
bidirectional terminal as either input or output. The other jumper block, X4, is used to connect the
common terminals to GND. The factory default and other available jumper selections are presented
below.
Figure 23. Jumper positions for OPTB1
10
+24V
Control voltage output; Voltage for switches etc.;
max. current 150mA; Short-circuit protected.
Table 24. OPTB1 I/O terminals
Ter mi na l
Parameter reference
Keypad/NCDrive
Technical information
DIO 1
DIO 2
DIO 3
DIO 4
DIO 5
DIO 6
DIO1 to DIO6
mod e O UT
DIO 1
DIO 2
DIO 3
DIO 4
DIO 5
DIO 6
DIO1 to DIO6
mod e I N
=
Fa c t or y d e f a u l t
CMA and CM B
connected to GN D
CMA
CMB
CMA
CMB
CMA and CM B
floating
Jumper block X 2:
DIO mo de
Ju m pe r b l ock X4:
CMA/ CMB connection
to G ND
7274.emf
Page 58

3
vacon • 56 Descriptions of VACON® option boards
Local contacts: http://drives.danfoss.com/danfoss-drives/local-contacts/
3.2.2 OPTB2
I/O terminals on OPTB2
NOTE: This expander board can be placed into four different slots on the control board. Therefore,
the 'X' given in the Parameter reference must be replaced by the slot letter (B, C, D, or E) depending
on the slot which the expander board is plugged into. See Chapter 1.7.
Description:
VACON
®
NX I/O expander board with a thermistor input and two relay out-
puts.
Allowed slots: B, C, D, E
Type ID: 16946
Termi nal s: Three terminal blocks; Screw terminals (M3); No coding
Jumpers: None
Board parameters: None
Table 25. OPTB2 I/O terminals
Ter mi na l
Parameter reference
Keypad/NCDrive
Technical information
21
22
23
RO1/normal closed
RO1/common
RO1/normal open
DigOUT:X.1
Switching capacity
Min. switching load
24VDC/8A
250VAC/8A
125VDC/0.4A
5V/10mA
25
26 RO2/common
RO2/normal open
DigOUT:X.2
Switching capacity
Min. switching load
24VDC/8A
250VAC/8A
125VDC/0.4A
5V/10mA
28
29
TI1+
TI1–
DigIN:X.1
Thermistor input (galvanically isolated)
R
trip
= 4 kΩ
7275.emf
Page 59

Descriptions of VACON® option boards vacon • 57
Local contacts: http://drives.danfoss.com/danfoss-drives/local-contacts/
3
3.2.3 OPTB4
Description:
VACON
®
NX I/O expander board with one galvanically isolated analogue input
and two galvanically isolated analogue outputs (standard signals
0(4)…20mA).
Allowed slots: B, C, D, E
Type ID: 16948
Termi nal s: One terminal block; Screw terminals (M2.6); No coding
Jumpers: None
Board parameters: None
7276.emf
Page 60

3
vacon • 58 Descriptions of VACON® option boards
Local contacts: http://drives.danfoss.com/danfoss-drives/local-contacts/
I/O terminals on OPTB4
NOTE: This expander board can be placed into four different slots on the control board. Therefore,
the 'X' given in the Parameter reference must be replaced by the slot letter (B, C, D, or E)
depending on the slot which the expander board is plugged into. See Chapter1.7.
3.2.4 OPTB5
Table 26. OPTB4 I/O terminals
Te rm in al
Parameter reference
Keypad/NCDrive
Technical information
1 AI1+ AnIN:X.1 0(4)…20mA; R
i
=250Ω; galvanically isolated
Resolution 10 bits/0.1%; Accuracy ±1% of the full display
2
AI1–
3 AO1+ AnOUT:X.1
0(4)…20mA; R
L
<500Ω; Resolution 10 bits/0.1%;
Accuracy ≤ ±2% (galvanically isolated)
4 AO1–
5 AO2+ AnOUT:X.2
0(4)…20mA; R
L
<500Ω; Resolution 10 bits/0.1%;
Accuracy ≤ ±2% (galvanically isolated)
6 AO2–
7 GND 24V (±15%); Max. load 250mA (total load from
EXT+24V outputs), max. 150mA from one board. See
Figure 3 on page 6.
8
GND
9 GND 24V (±15%), in special applications where PLC type
functions are included in the control module, this
input can be used as external auxiliary power supply
for control boards as well as for I/O boards.
10
+24V
Description: I/O expander board with three relay outputs.
Allowed slots: B, C, D, E
Type ID: 16949
Termi nal s: Three terminal blocks; Screw terminals (M3); No coding
Jumpers: None
Board parameters: None
7277.emf
Page 61

Descriptions of VACON® option boards vacon • 59
Local contacts: http://drives.danfoss.com/danfoss-drives/local-contacts/
3
I/O terminals on OPTB5
NOTE: This expander board can be placed into four different slots on the control board. Therefore,
the 'X' given in the Parameter reference shall be replaced by the slot letter (B, C, D, or E) depending
on the slot which the expander board is plugged into. See chapter 1.7.
Table 27. OPTB5 I/O terminals
Ter mi na l
Parameter reference
Keypad/NCDrive
Techni ca l informa ti on
22
23 RO1/common
RO1/normal open
DigOUT:X.1
Switching capacity
Min. switching load
24VDC/8A
250VAC/8A
125VDC/0.4A
5V/10mA
25
26 RO2/common
RO2/normal open
DigOUT:X.2
Switching capacity
Min. switching load
24VDC/8A
250VAC/8A
125VDC/0.4A
5V/10mA
28
29 RO3/common
RO3/normal open
DigOUT:X.3
Switching capacity
Min. switching load
24VDC/8A
250VAC/8A
125VDC/0.4A
5V/10mA
Page 62
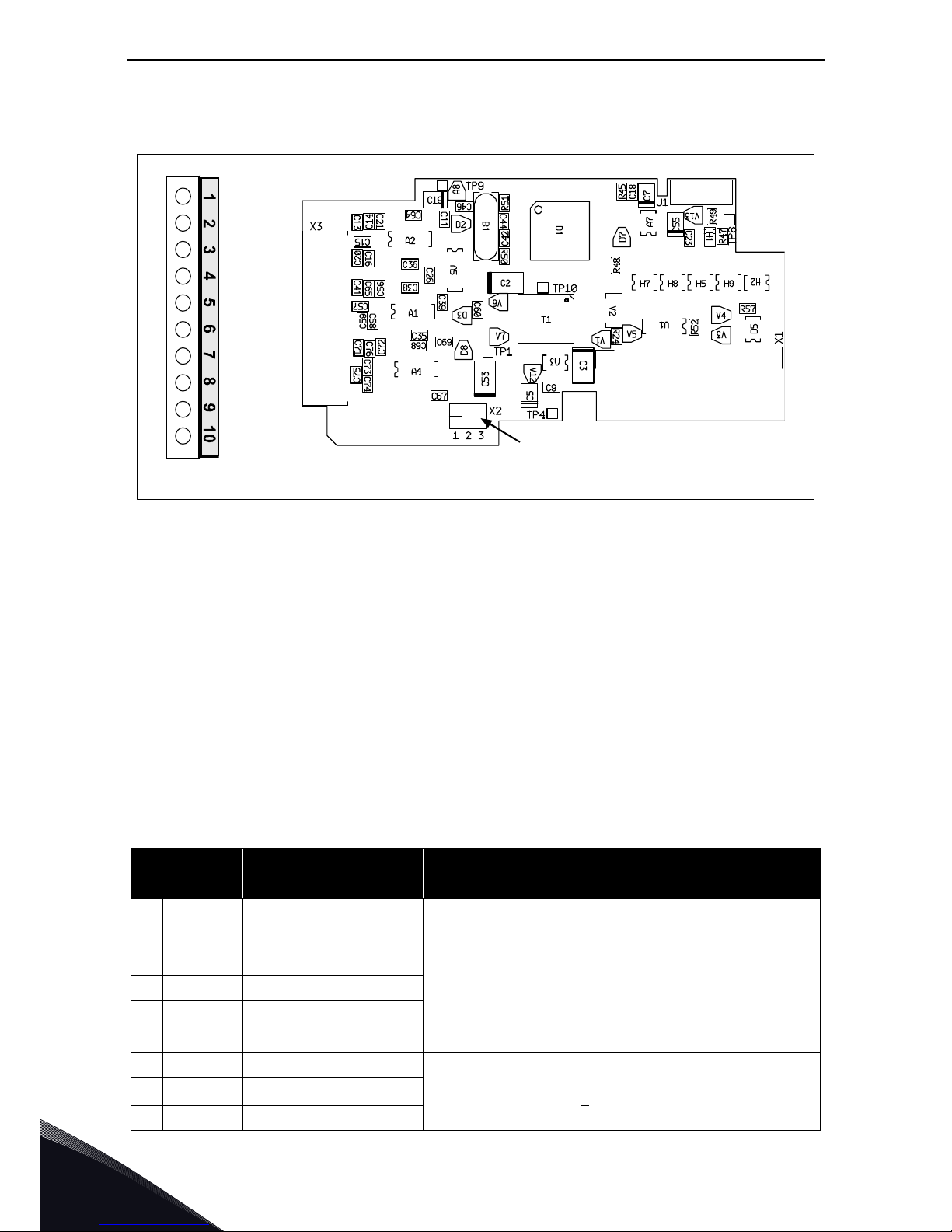
3
vacon • 60 Descriptions of VACON® option boards
Local contacts: http://drives.danfoss.com/danfoss-drives/local-contacts/
3.2.5 OPTB8
I/O terminals on OPTB8
Description: Temperature measuring board with three Pt-100 sensor (3-wire) inputs. The
measurable temperature range is –30...200 Cº on Pt-100 input. Both 3-wire
and 2-wire elements can be used.
Allowed slots: B, C, D, E
Type ID: 16952
Termi nal s: One terminal block; Screw terminals (M2.6); No coding
Jumpers: X2
Board parameters: None
Table 28. OPTB8 I/O terminals
Ter mi na l
Parameter reference
Keypad/NCDrive
Techni ca l informa ti on
1 R1 + AnIN:X.1
PT100 Input, -30 … 200 °C, one sensor.
Sensor current 10 mA.
2 R
m
1
3 R1 -
4 R2 + AnIN:X.2
PT100 Input, -30 … 200 °C, one sensor.
Sensor current 10 mA.
5 R
m
2
6 R2-
7 R3 + AnIN:X.3
PT100 Input, -30 … 200 °C 1 - 3 sensors (see X2 jumper
selections). Accuracy <
1°C. Sensor current 10 mA.
8 R
m
3
9 R3 -
Jumper block X2
7278.emf
Page 63

Descriptions of VACON® option boards vacon • 61
Local contacts: http://drives.danfoss.com/danfoss-drives/local-contacts/
3
OPTB8 accuracy
The following table represents the results of accuracy measurements in laboratory environment. In
the tests we used Draga JAMAK cable. The testing covered different sensor setups.
NOTE: Because of accuracy reasons OPTBH is recommended for newer installations. Please note
that using of OPTBH requires support from NX application.
Connection of PT100 sensors
One PT100-sensor can be connected to the first two inputs (terminals 1 to 3 and 4 to 6) and up to
three sensors to the third input (terminals 7 to 9). The sensors must be connected in series with a
two- or three-wire connection. See Chapter Jumper selections below.
NOTE:
• This expander board can be placed into four different slots on the control board. Therefore,
the 'X' given in the Parameter reference must be replaced by the slot letter (B, C, D, or E)
depending on the slot which the expander board is plugged into. See chapter 1.7.
• Insulation level 4kV/sqrt(2) (DIN VDE 01 10-1). 2kV in sensor and 2kV in option board.
10 NC Not connected
Table 29. PT100 accuracy for OPTB8
Cable length (m) 3-wire 2-wire Accuracy (°C)
300 x -20 < x < 8
150 x -13 < x < 3
50 x -8 < x < 2
50 x -10 < x < 10
Table 28. OPTB8 I/O terminals
Ter mi na l
Parameter reference
Keypad/NCDrive
Techni ca l informa ti on
R+
R
m
R-
R+
R-
R+
R
m
R-
R+
R-
3-wire connection 2-wire connection
Connection of one sensor
3-wire connection 2-wire connection
Connection of several sensors
7279.emf
Page 64

3
vacon • 62 Descriptions of VACON® option boards
Local contacts: http://drives.danfoss.com/danfoss-drives/local-contacts/
Jumper selections
Up to three PT100 sensors can be connected to the third PT100 input. You can select the number of
sensors in use with jumper block X2:
123123123
1 Sensor 2 Sensors 3 Sensors
= Factory default
7280.emf
Page 65

Descriptions of VACON® option boards vacon • 63
Local contacts: http://drives.danfoss.com/danfoss-drives/local-contacts/
3
3.2.6 OPTB9
I/O terminals on OPTB9
NOTE: This expander board can be placed into four different slots on the control board. Therefore,
the 'X' given in the Parameter reference must be replaced by the slot letter (B, C, D, or E)
Description: I/O expander board with five 42…240 VAC digital inputs and one normal relay
output.
Allowed slots: B, C, D, E
Type ID: 16953
Termi nal s: One terminal block; Screw terminals (M2.6); No coding
Jumpers: None
Board parameters: None
Table 30. OPTB9 I/O terminals
Ter mi na l
Parameter reference
Keypad/NCDrive
Technical information
1
ACIN1 DigIN:X.1
Digital input, 42…240 VAC (threshold 35V)
Control voltage: "0"<33V, "1">35V
2
ACIN2 DigIN:X.2
Digital input, 42…240 VAC (threshold 35V)
Control voltage: "0"<33V, "1">35V
3
ACIN3 DigIN:X.3
Digital input, 42…240 VAC (threshold 35V)
Control voltage: "0"<33V, "1">35V
4
ACIN4 DigIN:X.4
Digital input, 42…240 VAC (threshold 35V)
Control voltage: "0"<33V, "1">35V
5
ACIN5 DigIN:X.5
Digital input, 42…240 VAC (threshold 35V)
Control voltage: "0"<33V, "1">35V
6
COMA
Digital input, 42…240 VAC (threshold 35V)
Control voltage: "0"<33V, "1">35V
7
8
RO1/common
RO1/normal open
DigOUT:X.1 Switching capacity
24VDC/8A
250VAC/8A
125VDC/0.4A
7281.emf
Page 66
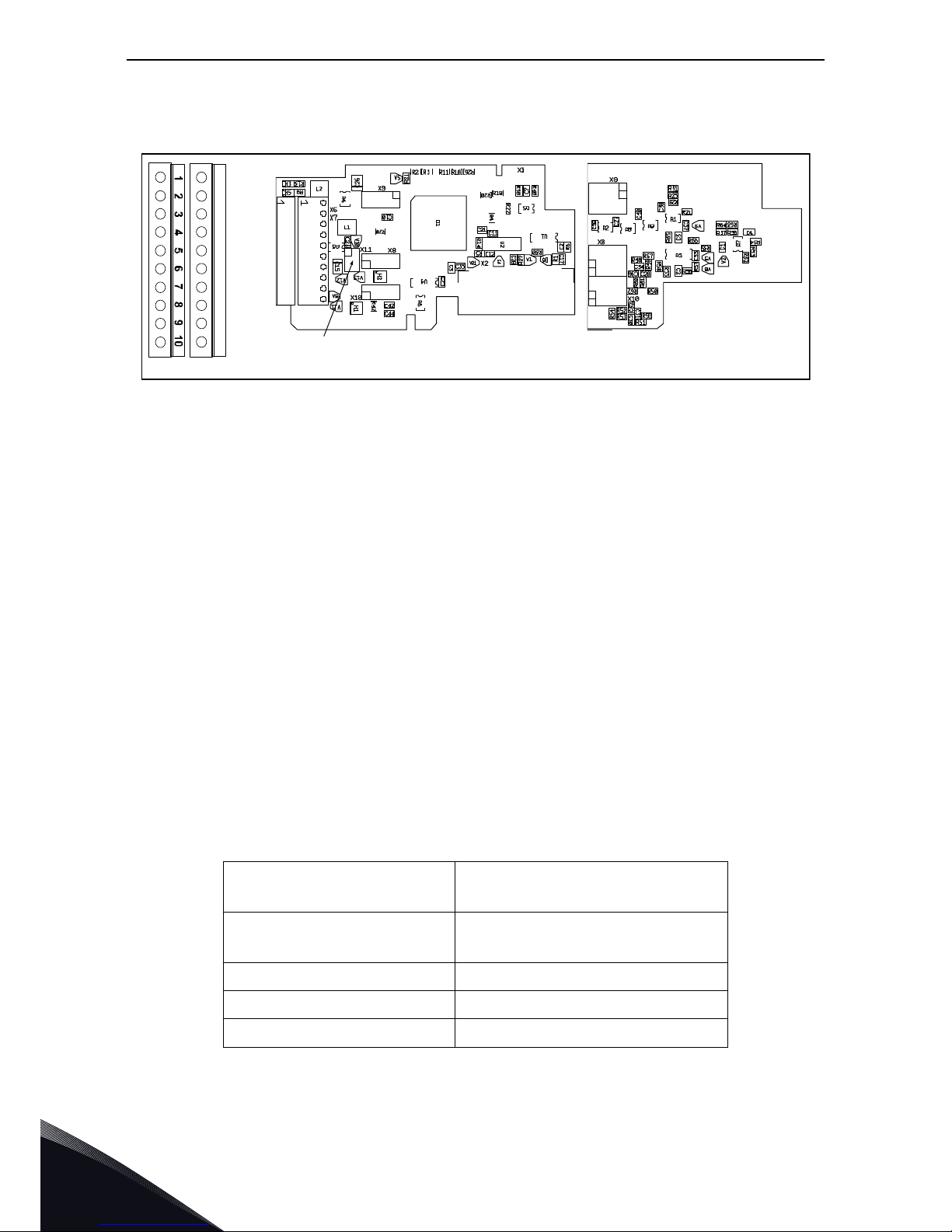
3
vacon • 64 Descriptions of VACON® option boards
Local contacts: http://drives.danfoss.com/danfoss-drives/local-contacts/
depending on the slot which the expander board is plugged into. See chapter 1.7.
3.2.7 OPTBB
An absolute encoder is a type of encoder capable of specifying its absolute position. The position
data is retained even during a power failure or breakdown. The position data carried by the absolute
encoder can be used by the AC drive motor control in the control of a synchronous motor.
ENDAT is a bidirectional synchronic serial interface for absolute encoders. For example, the
encoder position data can be read and encoder parameters can be set via the ENDAT connection. It
also forwards the messages related to the encoder functions.
All Endat connections are available in terminal X6. The board uses Endat version 2.
Description:
Absolute encoder board for VACON
®
NXP with inputs for an Endat type
encoder. Programmable control voltage, fast digital inputs and simulation
pulse output.
The output pulse is produced from sinusoidal input signals.
The galvanically isolated fast digital inputs are used to trace very short
pulses.
Allowed slots: C
Type ID: 16962 (main board), 16963 (secondary board); The secondary board is
mounted on top of the main board
Termi nal s: Two terminal blocks; Screw terminals (M2.6); No coding
Jumpers: 1; X11 (see page 66)
Board parameters: Yes (see page 67)
Encoder cable Heidenhain cable;
Max. length 100m
Encoder voltage 5V, 12V or 15V
Max. current consumption 300mA
Measuring steps/ revolution 4.2 billion (max. 32bit)
Distiguishable revolutions 0—65535 (max. 16bit)
Signal periods/revolution 1—65535
X6 X7
Main bo ard
Jumper block X11
Secondary board
7282.emf
Page 67

Descriptions of VACON® option boards vacon • 65
Local contacts: http://drives.danfoss.com/danfoss-drives/local-contacts/
3
Sinus signals require some precautions for noise immunity that may be a little more demanding
than conventional square wave encoders. Use of twisted pairs (possibly with individual shielding of
each pair) is recommended. Use one pair for sinus+ and sinus-, another pair for cosinus+ and
cosinus-, another pair for data+ data- of the absolute serial channel, another pair for clock+ and
clock- of absolute channel.
I/O terminals on OPTBB, encoder terminal X6
I/O terminals on OPTBB, terminal X7
Table 31. I/O terminals on OPTBB, terminal X6
Te rm in al
Heidenheim
colour code
Technical data
1 DATA+ Grey
Data line 120Ω/RS-485
2 DATA– Pink
3 CLOCK+ Violet
Clock line 120Ω/RS-485
(200—400kHz)
4 CLOCK– Yellow
5 A+ Green/black
1Vpp (±0.5V); impedance 120Ω; Max.input 350 kHz
6 A– Yellow/black
7 B+ Blue/black
1Vpp (±0.5V); impedance 120Ω; Max.input 350 kHz
8 B– Red/black
9 GND White/green Input ground
10 Encoder
voltage
Brown/green
Selectable encoder voltages: 5V, 12V and 15V
Max.current consumption 300mA
Table 32. I/O terminals on OPTBB, terminal X7
Ter mi na l Technical data
1 SimA+ Incremental pulse output A (differential), 0°
(square wave, signal level RS-422);
Impedance 120Ω; Input hysteresis ±5mV
2
SimA–
3 SimB+ Incremental pulse output B (differential), 0°
(square wave, signal level RS-422);
Impedance 120Ω; Input hysteresis ±5mV
4
SimB–
5 Not used
6 Not used
7 FDIN1 Fast digital input 1; HTL; Min.pulse length 50μs
8 CMA Common FDIN1
9 FDIN2 Fast digital input 2; HTL; Min.pulse length 50μs
10 CMB Common FDIN2
Page 68
3
vacon • 66 Descriptions of VACON® option boards
Local contacts: http://drives.danfoss.com/danfoss-drives/local-contacts/
Jumper selections
On the OPTBB board, there is one jumper block used to program the control voltage (auxiliary
voltage). The factory default and other available jumper selections are presented below.
NOTE! It is recommended to use a +12 or +15 supply voltage instead of 5 V.
This is because our interface does not support "sense" function to compensate voltage drop which
results in a cable length limit of about 60 m with 0.5 mm
2
wire section for the supply. The problem
does not exist with 12 or 15 v supply.
If 5V is used, it is recommended to use two or more wires in parallel for supply connection.
5V
12V
15V
5V
12V
15V
5V
12V
15V
JumperblockX11
Auxiliary vo ltage le v e l
=
Fa c t o r y d e f a u l t
7283.emf
Page 69
Descriptions of VACON® option boards vacon • 67
Local contacts: http://drives.danfoss.com/danfoss-drives/local-contacts/
3
OPTBB board parameters
OPTBB board monitoring values
OPTBB board information pages
Table 33. OPTBB board parameters
Code Parameter Min Max Default Selections Description
7.3.1.1 Reverse 0 1 0
0 = No
1 = Yes
Manually selectable rotation direction
7.3.1.2 Reading rate 0 4 1
0 = Not used
1 = 1 ms
2 = 5 ms
3 = 10 ms
4 = 50 ms
Incremental pulse reading rate.
NOTE: Use value 1 in Closed Loop mode.
7.3.1.3 Interpolation 0 1 0
0 = No
1 = Yes
If activated, the sinusoidal incremental pulses
are used to calculate the polar angle in order
to optimize the encoder accuracy
Table 34. OPTBB board monitoring values
Code Monitored value Unit Description
7.3.2.1 Encoder frequence Hz Motor speed in Hz calculated from encoder pulses
7.3.2.2 Encoder speed rpm Motor speed in rpm calculated from encoder pulses
7.3.2.3 Encoder position - Absolute position of encoder read from Endat
7.3.2.4 Encoder revolution
7.3.2.5 Encoder fault
7.3.2.6 Encoder warning
7.3.2.7 Encoder messages Number of messages between encoder and NXOPTBB
Table 35. OPTBB board information pages
Code Information Unit Description
7.3.3.1 Encoder type
0 = No encoder connected
1—4 = Incremental linear encoder
5 = Linear absolute encoder
6 = Unknown
7 = Linear absolute encoder
8 = Unknown
9—12 = Rotational incremental/angular encoder
13 = Absolute encoder (singleturn)
14 = Unknown
15 = Absolute encoder (multiturn)
16 = Unknown
7.3.3.2 Pulses/Revolution Sinusoidal pulses/revolution
7.3.3.3 Position bits bit
Accurate position 1—1024 (10bit = 2
10
= 1024)
7.3.3.4 Revolution bits bit
Accurate number of revolutions 1—1024 (10bit = 2
10
= 1024)
Page 70

3
vacon • 68 Descriptions of VACON® option boards
Local contacts: http://drives.danfoss.com/danfoss-drives/local-contacts/
OPTBB option board status LEDs
Yellow LED
Green LED
LED Meaning
OFF Option board not activated
ON
Option board in initialisation state waiting for activation
command from the AC drive
Blinking fast
(once/sec)
Option board is activated and in RUN state
• Option board is ready for external communication
Blinking slow
(once/5 s)
Option board is activated and in FAULT state
• Internal fault of option board
LED Meaning
OFF
Option board not activated
ON
Encoder is being initialised
Option board is reading encoder parameters
Blinking fast
(once/s)
Encoder detected by option board
Option board receives data from encoder
Blinking slow
(once/5 s)
Encoder detected by option board
Option board cannot read encoder data or data is invalid
(CRC error, broken cable etc.)
Page 71

Descriptions of VACON® option boards vacon • 69
Local contacts: http://drives.danfoss.com/danfoss-drives/local-contacts/
3
3.2.8 OPTBH
I/O Terminals on OPTBH
OPTBH accuracy
The following tables represent the results of accuracy measurements in laboratory environment. In
the tests we used Draga JAMAK cable. The testing covered different sensor setups and sensor type
combinations.
Description: Temperature measurement board with three individual channels.
Allowed slots: B, C, D, E
Supported sensors: PT100, PT1000, NI1000, KTY84-130, KTY84-150, KTY84-131
Type ID: 16968
Terminals: One terminal block; Screw terminals (M3); No coding
Jumpers: None
Terminal
Parameter reference
Keypad
Technical information
1
2
3
R1.1
R1.2
R1.3
AnIn:X.1 Temperature sensor input 1, -50...200 °C
4
5
6
R2.1
R2.2
R2.3
AnIn:X.2 Temperature sensor input 2, -50...200 °C
7
8
9
R3.1
R3.2
R3.3
AnIn:X.3 Temperature sensor input 3, -50...200 °C
10 NC
Table 36. PT100 accuracy for OPTBH
Cable length (m) 3-wire 2-wire Accuracy (°C)
≤300 x -1 < x < 3
50 x -1 < x < 14
3025.emf
12345678910
Page 72

3
vacon • 70 Descriptions of VACON® option boards
Local contacts: http://drives.danfoss.com/danfoss-drives/local-contacts/
Connecting Temperature sensors to OPTBH option board:
Use shielded cables and connect the cable shield to grounding clamp in the drive.
Allowed sensor configurations are shown on figures below:
Two-wire configuration Three-wire configuration
Two-wire configuration Three-wire configuration
OPTBH board parameters
Table 37. PT100, KTU84 and Ni1000 (Ni1000 DIN) accuracy for OPTBH
Cable length (m) 3-wire 2-wire Accuracy (°C)
≤300 x -1 < x < 1
150 x -1 < x < 5
50 x -1 < x < 3
Code Parameter Min Max Unit Default ID Description
7.x.1.1 Sensor 1 type 0 6 0
0 = No Sensor
1 = PT100
2 = PT1000
3 = Ni1000
4 = KTY84
5 = 2 x PT100
6 = 3 x PT100
7.x.1.2 Sensor 2 type 0 6 0 See above
7.x.1.3 Sensor 3 type 0 6 0 See above
Page 73

Descriptions of VACON® option boards vacon • 71
Local contacts: http://drives.danfoss.com/danfoss-drives/local-contacts/
3
3.3 Adapter Boards OPTD_
The adapter boards do not provide any additional I/O but are used to connect the AC drive to a
VACON
®
communication bus (System Bus, SPI, CAN). Note that if you use any of the major
fieldbuses (Profibus, Modbus etc.) for communication you will need a corresponding fieldbus board.
For more information, see the specific fieldbus board manual.
NOTE: Do not plug two adapter boards into the same control board in order to avoid incompatibility
problems.
3.3.1 OPTD1
Table 38 . VACO N
®
NX adapter boards
FC type I/O board Allowed slots Description
NXP OPTD1 D,E System Bus adapter board
NXP
OPTD2 (B,)D,E
System Bus adapter board with interface to fast monitoring bus
NXS
NXP
OPTD3 D,E RS-232 adapter board
NXP
OPTD6 B,D,E
Monitor Bus adapter board for
VACON
®
NXP
Description:
System Bus adapter board for VACON
®
NXP
Allowed slots: D, E
Type ID: 17457
Termi nal s: Double optical input and output terminals.
Agilent HFBR-1528 (Receiver), HFBR-2528 (Transmitter).
Jumpers: None
Board parameters: None
Page 74

3
vacon • 72 Descriptions of VACON® option boards
Local contacts: http://drives.danfoss.com/danfoss-drives/local-contacts/
I/O terminals on OPTD1
NOTE: The terminals of the board are protected with a rubber pin. Be sure to leave the pin in the
unused terminals in order to avoid disturbances.
Connections between AC drives with OPTD1
Basic connection:
Connect the output 1 of Device 1 to the input 2 of Device 2 and the input of Device 1 to the output 2
of Device 2. Note that in the end devices one terminal pair remains unused. See Figure 24 below.
Table 39. OPTD1 I/O terminals
Ter mi na l Technical information
1
H1
System Bus optical input 1 (RX1)
Use 1-mm optical cable (e.g. Agilent HFBR-RUS500 &
HFBR-4531/4532/ 4533 connectors)
2
H2
System Bus optical input 2 (RX2)
Use 1-mm optical cable (e.g. Agilent HFBR-RUS500 &
HFBR-4531/4532/4533 connectors)
3
H3
System Bus optical output 1 (TX1)
Use 1-mm optical cable (e.g. Agilent HFBR-RUS500)
4
H4
System Bus optical output 2 (TX2)
Use 1-mm optical cable (e.g. Agilent HFBR-RUS500)
Table 40.
Max.
number of devices in line
Max.
speed achieved [Mbit/s]
312
66
12 3
24 1.5
Page 75
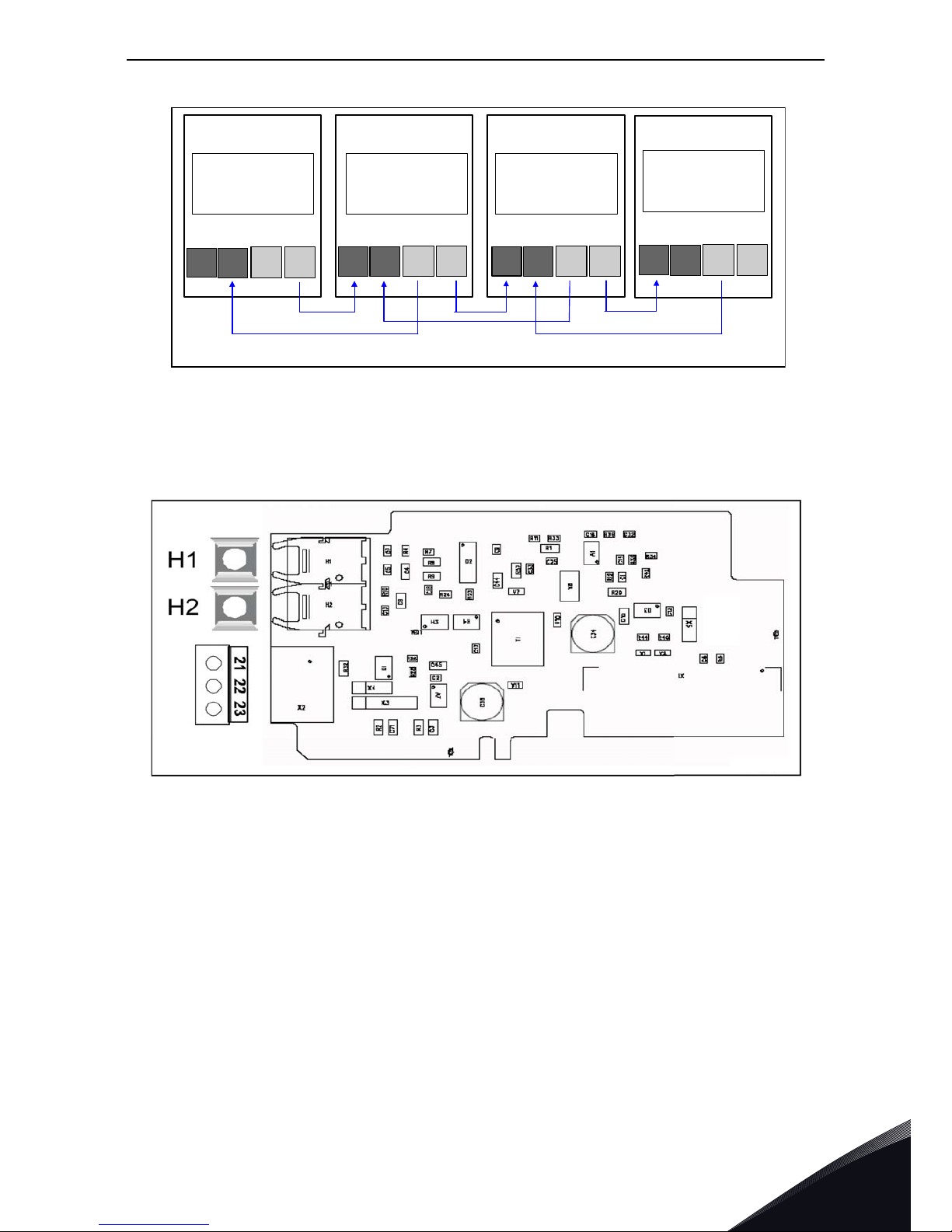
Descriptions of VACON® option boards vacon • 73
Local contacts: http://drives.danfoss.com/danfoss-drives/local-contacts/
3
Figure 24. Basic connection of AC drives with OPTD1
3.3.2 OPTD2
Note! This figure presents the layout of D2 board version H or later. See Chapter
Jumper selections below.
Description:
System Bus adapter board for VACON
®
NXP with single optical input and
output; Interface to fast monitor bus used by the NCDrive PC tool.
Allowed slots: (B,)D, E; Note: If only the Monitor Bus (terminals 21 to 23) will be used, the
board can also be placed in slot B. The System Bus is then unavailable.
Remove therefore jumpers X5 and X6. See page 74.
Type ID: 17458
Termi nal s: Single optical input and output; one screw terminal block (M3),
Agilent HFBR-1528 (Receiver), HFBR-2528 (Transmitter).
Jumpers: Jumpers:4; X3, X4 and X5. See page 74.
Board parameters: None
OPTD1OPTD1OPTD1
Master
SBInUse = Yes
SBID =1
SBNextID = 2
SBLastID = 4
Follower
SBInUse =Yes
SBID = 2
SBNextID = 3
Follower
SBInUse =Yes
SBID = 3
SBNextID =4
H1
(RX)
H3
(TX)
H2
(RX)
H4
(TX)
OPTD1
Follower
SBInUse =Yes
SBID = 4
SBNextID =3
H1
(RX)
H3
(TX)
H2
(RX)
H4
(TX)
H1
(RX)
H3
(TX)
H2
(RX)
H4
(TX)
H1
(RX)
H3
(TX)
H2
(RX)
H4
(TX)
7285.emf
7286A_00
Page 76

3
vacon • 74 Descriptions of VACON® option boards
Local contacts: http://drives.danfoss.com/danfoss-drives/local-contacts/
I/O terminals on OPTD2
Jumper selections
There are four jumper blocks on the OPTD2 board. The factory defaults and other available jumper
selections are presented below.
Figure 25. Jumper selections for OPTD2, up to version G
Table 41. OPTD2 I/O terminals
Ter mi na l Technical information
1
H1
System Bus optical input 1 (RX1)
Use 1-mm optical cable (e.g. Agilent HFBR-RUS500 &
HFBR-4531/4532/ 4533 connectors)
NOTE: Not available if the board is placed in slot B
2
H2
System Bus optical output 1/2 (TX1/TX2);
Selected with jumper X5
Use 1-mm optical cable (e.g. Agilent HFBR-RUS500 &
HFBR-4531/4532/4533 connectors)
NOTE: Not available if the board is placed in slot B
21 CAN_L Monitor Bus negative data
22 CAN_H Monitor Bus positive data
23 CAN_SHIELD Monitor Bus shield
Jumper block X3:
CAN grounding
Connected to shield Not connected to shield
Jumper block X4:
CAN termination
Terminated Not terminated
Jumper block X5*:
System bus output
Output TX1 Output TX2
= Factory default
*If the board is placed in slot B the SystemBus
is not available. Remove jumpers X5 and X6.
7287A_uk
Page 77

Descriptions of VACON® option boards vacon • 75
Local contacts: http://drives.danfoss.com/danfoss-drives/local-contacts/
3
Figure 26. X3 jumper selections for OPTD2, version H and later
NOTE! Position C can be used with 3- or 4-wire can cable to interconnect isolated CAN ground levels
in the network. It is recommended to connect the cable shield to the grounding clamp of the drive.
Figure 27. CAN grounding alternatives
Jumper block X3:
CAN grounding
ABC
A: Connected toground
B: Connected to ground via LC filter
C: Connected to CAN isolated ground
Not assembled: No connection
S
ee further clarifications of the alternatives next page!
7288.emf
PE NC GND
PE NC GND
PE NC GND
A
23
chassis
CAN GND
chassis
- Used when the shield is connected to terminal 23
andthedistance between the dev ices is short
B
chassis
chassis
23
CAN GND
-Usedwhentheshieldisconnectedtoterminal23
and the distance between the devices is long
C
23
CAN GND
chassis
- Used when CAN GND is connected to terminal 23.
This setting is recommended for best noise immunity
= Factory default
= Recommended setting
7289.emf
Page 78

3
vacon • 76 Descriptions of VACON® option boards
Local contacts: http://drives.danfoss.com/danfoss-drives/local-contacts/
Alternative connection of “CAN GND” signal: connect ‘CAN GND’ together between all nodes. Use
the signal wire inside the shield for this purpose, see figure below:
Figure 28. Alternative connection of ”CAN GND” signal
Connections between AC drives with OPTD2
Special connection:
In this connection example, the leftmost device is the Master and the others are slaves. The Master
can send and receive data from the slaves. The slaves cannot communicate with each other.
Changing of masters is not possible, the first device is always the Master.
The OPTD2 board in the Master has the default jumper selections, i.e. X5:1-2. The jumper positions
have to be changed for the slaves: X5:2-3.
Table 42.
Max.
number of devices
in line
Max.
speed achieved
[Mbit/s]
312
66
12 3
24 1.5
Shield
CAN HI CAN HI
CAN LO CAN LO
CAN
GND
CAN
GND
21 22 23
OPTD2 /
OPTD6
OPTD2 /
OPTD6
OPTD2 /
OPTD6
Grounding cla mp
Connect the
data GND
tight ly to the
chassis on
one point
in t he n et
21 22 23
21 22 23
7290.emf
Page 79

Descriptions of VACON® option boards vacon • 77
Local contacts: http://drives.danfoss.com/danfoss-drives/local-contacts/
3
Figure 29. Connection example of AC drives with OPTD2
3.3.3 OPTD3
Description: RS-232 adapter board. Galvanically decoupled. Used mainly for application
engineering to connect another keypad.
Allowed slots: D, E.
Type ID: 17459
Termi nal s: 9-pin female sub-D-connector
Jumpers: 1; X3 (see page 78)
Board parameters: None
OPTD2
Jumper X5 : TX2
OPTD2
Jumper X5 : TX2
OPTD2
Jumper X5 : TX2
OPTD2
Jumper X5 : TX1
H1
(RX)
H2
(TX)
Master
SBInUse = Yes
SBID = 1
SBNextID = 2
SBLastID = 4
Follower
SBInUse = Yes
SBID = 2
SBNextID = 3
Follower
SBInUse = Yes
SBID = 3
SBNextID = 4
Follower
SBInUse = Yes
SBID = 4
SBNextID = 1
H1
(RX)
H1
(RX)
H1
(RX)
H2
(TX)
H2
(TX)
H2
(TX)
7291A_uk
LED 1
LED 2
Jum per bl ock X 3
54321
9876
7292.emf
Page 80

3
vacon • 78 Descriptions of VACON® option boards
Local contacts: http://drives.danfoss.com/danfoss-drives/local-contacts/
I/O terminals on OPTD3
NOTE:
If OPTCI Ethernet Option board is used for NC Tools connection, like NCLoad, the OPTD3 board
cannot be used.
Jumper selections
There is one jumper block on the OPTD3 board. The factory defaults and other available jumper
selections are presented below:
OPTD3 option board status LEDs
Table 43. OPTD3 I/O terminals
Ter mi na l Technical information
1
2 TxD Transmit data
3 RxD Receive data
4
5 GND Ground isolated
6 +9V +9V isolated
7
8
9
Table 44.
LED Meaning
Green (LED 1) Receiving data
Red (LED 2) Transmitting data
Jumper block X3:
ConnectorconnectiontoGND
Connected to GND
th ro ug h RC f il ter
Connected
directly to GND
7293.emf
Page 81

Descriptions of VACON® option boards vacon • 79
Local contacts: http://drives.danfoss.com/danfoss-drives/local-contacts/
3
3.3.4 OPTD6
I/O terminals on OPTD6
Jumper selections
There are two jumper blocks on the OPTD6 board. The factory defaults and other available jumper
selections are presented below:
Note! This figure presents the layout of D6 board version F or later. See Chapter
Jumper selections below.
Description:
Monitor Bus adapter board for VACON
®
NXP. Interface to fast monitor bus
used by the NCDrive PC tool.
Allowed slots: B, D, E.
Type ID: 17462
Termi nal s: One screw terminal block (M3)
Jumpers: 2; X3, X4.
Board parameters: None
Table 45. OPTD6 I/O terminals
Ter mi na l Technical information
21 CAN_L Monitor Bus negative data
22 CAN_H Monitor Bus positive data
23 CAN_GND Monitor Bus ground
7294.emf
Page 82

3
vacon • 80 Descriptions of VACON® option boards
Local contacts: http://drives.danfoss.com/danfoss-drives/local-contacts/
Figure 30. Jumper selections for OPTD6, up to version E.
Figure 31. X3 jumper selections for OPTD6, version F and later.
NOTE! Position C can be used with 3- or 4-wire can cable to interconnect isolated CAN ground
levels in the network. It is recommended to connect the cable shield to the grounding clamp of the
drive.
See more details of the alternatives on page 76.
Jumper block X3:
CAN grounding
Connected to shield Not connected to shield
Jumper block X4:
CAN termination
Terminated N ot terminated
= Factory default
7295.emf
Jumper block X3:
CAN grounding
ABC
A: Connected to
g
round
B: Connected to ground via LC filter
C: Connected to CAN isolated ground
Not assembled: No connection
7296.emf
Page 83

VACON® Option Boards – operational details vacon • 81
Local contacts: http://drives.danfoss.com/danfoss-drives/local-contacts/
4
4. VACON
®
OPTION BOARDS – OPERATIONAL DETAILS
Table 46. VACON® option boards, types A and B
Board
type
Slots
allowed
6)
ID DI DO
AI
(mA/V)
AI (mA),
isol.
AO
(mA/V)
AO
(mA),
isol.
RO
(no/nc)
RO
(no)
+10V
ref
TI
+24V/
EXT
+24V
42240
VAC
DI
(Enc.
10-
24V)
DI (Enc.
RS-422)
Out +5/
+15V/
+24V
Out
+15/
+24V
Pt-100
Basic boards
OPTA_
OPTA1 A 16689 6 1 2 1 1 2
OPTA2 B 16690 2
OPTA3 B 16691 1 1 1
OPTA4
4)
C 16692 31
OPTA5
4)
C 16693 31
OPTA7 C 16695 2 61
OPTA8 A 16696 6 1
2
1)
1
1)
1
1)
2
OPTA9
3)
A 16697 6 1 2 1 1 2
OPTAE
4)
A 16709 2 3
OPTAL A 16716 1
2
8)
2
9)
6
OPTAN A 16718 6
2
10)
2
10)
1
11)
1
I/O expander boards
OPTB_
OPTB1 BCDE 16945
6
5)65)
OPTB2 BCDE 16946 1 1 1
OPTB4 BCDE 16948
1
2)
2
2)
1
OPTB5 BCDE 16949 3
OPTB8 BCDE 16952 3
OPTB9 BCDE 16953 1 5
OPTBB C
16962
16963
2
OPTBH BCDE 16968
Page 84

4
vacon • 82 VACON® Option Boards – operational details
Local contacts: http://drives.danfoss.com/danfoss-drives/local-contacts/
Tab l e 4 7. VA CON® option boards, type D
Adapter boards
NXOPTD_
OPTD1 DE 17457 System Bus adapter board: 2 x fiber optic pairs
OPTD2
7)
(B)DE 17458 System Bus adapter board: 1 x fiber optic pair & CAN bus adapter (galvanically decoupled)
OPTD3 DE 17459 RS232 adapter card (galvanically decoupled)
OPTD6 BDE 17462 MonitorBus adapter board (galvanically decoupled)
Explanations:
1)
Analogue inputs AI1 and AI2, analogue output AO1 and voltage reference +10Vref galvanically decoupled (all these in same potential)
2)
Analogue input AI1 and analogue outputs AO1 and AO2 galvanically decoupled from each other and
other electronics
3)
Similar to OPTA1 only with bigger terminals for 2.5mm
2
wires
4) Special application required for use in NXS
5) Bidirectional terminals
6)
In case of several optional slots, the bold slot letter indicates the factory default slot (NOTE: not applicable if several boards with the same default slot are installed)
7)
If the board is placed in slot B the SystemBus is not available; only the Monitor Bus can be used.
Remove jumpers X5 and X6.
8) AI1 0-10V, AI2 -10V...+10V
9) AO1 mA, AO2 V
10) 2 (mA/V), incl. -10…+10V
11) Also -10V ref
Page 85

VACON® Option Boards – operational details vacon • 83
Local contacts: http://drives.danfoss.com/danfoss-drives/local-contacts/
4
Table 48. All in One applications and supported VACON® NX option boards
NXS, NXP NXL
Board type
Basic boards
OPTA_
Basic
NXFIFF01
Standard
NXFIFF02
Local-
Remote
NXFIFF03
Multi-step
speed
NXFIFF04
PID
NXFIFF05
Multi-
purpose
NXFIFF06
PFC
NXFIFF07
Multi-control
OPTA1
••
••••6)•
6)
OPTA2
••
••••6)•
6)
OPTA3
•
••••6)•
6)
OPTA4
OPTA5 (NXP only)
OPTA7 (NXP only) ▲ ▲ ▲ ▲ ▲ ▲ ▲
OPTA8
••
••••6)•
6)
OPTA9
••
••••6)•
6)
OPTAE (NXP only)
OPTAL
••
•••••
I/O expander boards
OPTB_
OPTB1
•
6)
•
6)
OPTB2
•
6)
•
6)
*
OPTB4
••••
•
6)
•
6)
*
OPTB5
•
6)
•
6)
*
OPTB8
•
••
OPTB9,
•
6)
•
6)
Adapter boards
OPTD_
OPTD1
(NXP only)
OPTD2
7)
(NXP only)
OPTD3
•••••••
OPTD6
7)
(NXP only)
•
= Used with this application (NXS, NXP) 6) =
Digital inputs, digital outputs, analogue inputs and analogue outputs
can be programmed
= Used with this application (NXP) 7) =
This board is supported by specified applications if program NC
Sys-
Drive is used
▲
= Used with special applications only
*)
= Used with this application (NXL)
Page 86

Document ID:
DPD00884B
Rev. B
Sales code: DOC-IOboards+DLUK
Vacon Ltd
Member of the Danfoss Group
Runsorintie 7
65380 Vaasa
Finland
www.danfoss.com
 Loading...
Loading...