Uniden IGO500, IGO430 Owner's Manual

IGO500
IGO430
In-Car Navigation
For more exciting new products please visit our website:
Australia: www.uniden.com.au
New Zealand: www.uniden.co.nz

Page 2
Thank you for purchasing this Uniden product. Read the Quick Start Guide rst
and start using your device right away. This document is the detailed description of
the navigation software. You can easily discover your device while you are using
it; however, we still recommend that you read this manual to fully understand the
screens and the features of your software.
3 Year Map Updates Subscription* via Redemption
Go to the GPS Navigation web page on www.uniden.com.au for Australia or
www.uniden.co.nz for New Zealand and download the redemption form to claim
your updates subscription.
*Map updates are for Australia and New Zealand and are provided through
www.naviextras.com

Page 3
Table of Contents
What Do I Do First? 6
Make Sure These Items Arrived in the Box 6
Plug it in 7
Hardware Keys 8
How Do I Put It in My Car? 9
Safety considerations 9
Attaching the Windshield Mount 10
Adjusting the Windshield Mount 11
Mount to the Windshield 11
Removing the Windshield Mount 11
1 Warnings and Safety information 12
2 Getting started 13
2.1 Startup screen: the Map and Navigation menu 15
2.2 Buttons and other controls on the screen 16
2.2.1 Using keyboards 18
2.2.2 Beyond single screen tap 19
2.3 Map screen 20
2.3.1 Navigating on the map 20
2.3.2 Position markers 22
2.3.2.1 Vehimarker and Lock-on-Road 22
2.3.2.2 Selected Map location (Cursor) and selected map object 23
2.3.3 Objects on the map 23
2.3.3.1 Streets and roads 23
2.3.3.2 Turn preview and Next street 24
2.3.3.3 Lane information and Signposts 25
2.3.3.4 Junction View 26
2.3.3.5 Motorway exit services 26
2.3.3.6 3D object types 27
2.3.3.7 Elements of the active route 28
2.3.4 Manipulating the map 28
2.3.5 Quick menu 30
2.3.6 Checking the details of the current position (Where Am I?) 34

Page 4
3 Navigating 36
3.1 Selecting the destination of a route 36
3.1.1 Entering an address or part of an address 37
3.1.1.1 Entering an address 37
3.1.1.2 Entering an address starting with the street name 40
3.1.1.3 Entering the midpoint of a street as the destination 42
3.1.1.4 Selecting an intersection as the destination 44
3.1.1.5 Selecting a town/suburb centre as the destination 46
3.1.1.6 Entering an address with a postal code 48
3.1.1.7 Tips on entering addresses quickly 50
3.1.2 Selecting the destination from the Places of Interest 51
3.1.2.1 Quick search for a Place of Interest 52
3.1.2.2 Searching for a Place of Interest using preset categories 53
3.1.2.3 Searching for a Place of Interest by category 56
3.1.2.4 Searching for a Place of Interest by name 60
3.1.2.5 Selecting nearby assistance from ‘Where Am I?’ 63
3.1.3 Selecting a map location as the destination 65
3.1.4 Selecting the destination from your Favourites 66
3.1.5 Selecting the most likely destination (Smart History) 68
3.1.6 Selecting the destination from the History 69
3.1.7 Entering the coordinate of the destination 70
3.1.8 Navigate to a location stored in a photo 71
3.1.9 Building the route from the list of destinations (Create Route) 72
3.2 Viewing the entire route on the map 74
3.3 Checking route parameters and accessing route related functions 74
3.4 Modifying the route 75
3.4.1 Selecting a new destination when already having a route:
New Route, Waypoint of Final Destination 75
3.4.2 Setting a new starting position for the route 76
3.4.3 Editing the list of destinations (Edit Route) 78
3.4.4 Pausing the active route 79
3.4.5 Cancelling the active route 79
3.4.6 Checking route alternatives when planning the route 79
3.4.7 Changing the route planning method (route alternatives) 81
3.4.8 Changing the vehicle used in route planning 82

Page 5
3.4.9 Changing the road types used in route planning 83
3.5 Saving a location as a Favourite destination 84
3.6 Saving a location as an alert point 85
3.7 Editing an alert point 86
3.8 Watching the simulation of the route 87
4 Off-road navigation 89
4.1 Selecting the destination of the route 89
4.2 Navigating in off-road mode 89
5 Reference Guide 91
5.1 Concepts 91
5.1.1 Smart Zoom 91
5.1.2 Daytime and night colour themes 91
5.1.3 Tunnel View 91
5.1.4 Route calculation and recalculation 92
5.1.5 Green routing 95
5.1.6 Road Safety Cameras and Other Proximity Alerts Points 96
5.1.7 Speed limit warning 97
5.1.8 Battery and GPS position quality indicators 98
5.1.9 Trafc information in route planning 99
5.1.9.1 Historical trafc 99
5.2 ‘More’ menu 100
5.3 Settings menu 102
5.3.1 Sound and Warnings 103
5.3.2 Customise Quick menu 107
5.3.3 Route Settings 107
5.3.4 User proles 113
5.3.5 Map Settings 114
5.3.6 Visual guidance settings 116
5.3.7 Display settings 118
5.3.8 Regional settings 118
5.3.9 Trip monitor settings 119
5.3.10 Log Collection settings 119
6 Glossary 121
7 End User Licence Agreement 123
8 Limited One Year Warranty 129

Page 6
What Do I Do First?
Make Sure These Items Arrived in the Box
If anything listed here is missing or damaged, contact your place of purchase
immediately.
IGO500 or IGO430 GPS navigation device
Press and hold the power button at the TOP
of the device to start or resume the navigation
programme.
Owners Manual Quick Start Guide sheet
USB cable DC (car) adapter Windshield Mount (2 part)
Part 1 Part 2

Page 7
Plug it in
Connect the power adapter to the power connector on the lower left side of
the device.
Plug the other end into your car’s cigarette lighter (or any standard 12VDC -
24VDC outlet).
Only use the power adapter that comes with your device. Any other adapter
might damage the device.
Press and hold the power button at the top of the device to turn it on/off.
Whenever it senses power coming in the LCD screen turns on and the device
resumes from it’s last status. You can turn the LCD screen on/off anytime you
want: just momentarily push the power button.
Page 8
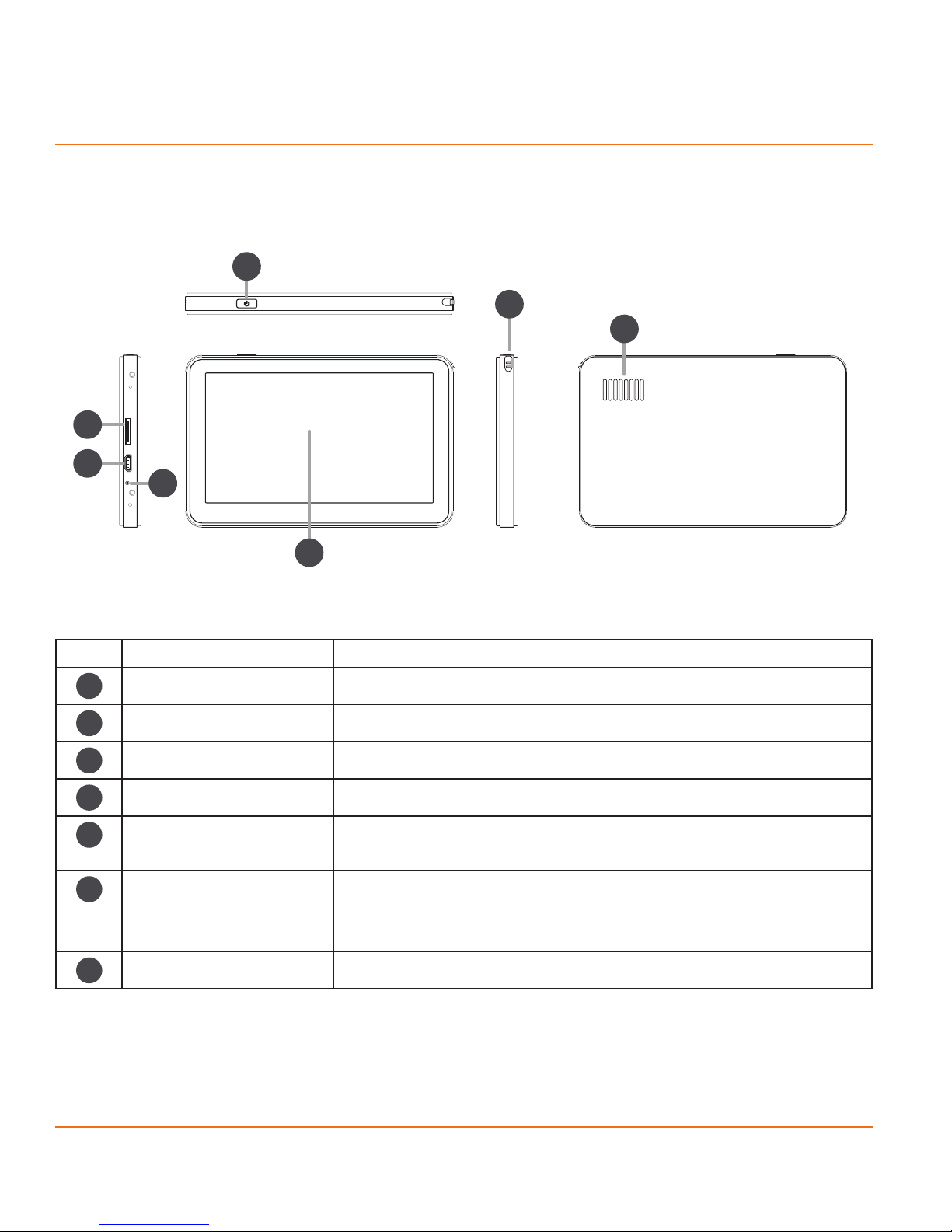
Hardware Keys
IGO500 / IGO430 model
1
3
7
2
4
5
6
Ref Component Description
1
Power Key Power on/off/sleep
2
Touch-pen* Touch-pen
3
Speaker Speaker
4
micro SD card slot micro SD card slot
5
micro USB power/
charge port
Charge the GPS device by connecting the DC
Adaptor (car charger) or USB cable.
6
Reset If the device fails to operate properly, try resetting the
device. Press the reset button by using the touch pen
or a similar tool.
7
LCD Display Screen LCD Display Screen
*IGO500 touch-pen location is shown. IGO430 touch-pen is tted on the
windshield mount.

Page 9
How Do I Put It in My Car?
Safety Considerations
Don’t install any device where it will block your view (including your mirrors!)
while you’re driving.
Keep your attention on the road! Don’t try to operate or focus on any device
while you’re driving. If you have to concentrate on a device, pull off the road
for a few minutes.
It’s a good idea to take valuable items with you when you leave you car—that
includes GPS devices. If you can’t take the device with you, lock it in the glove
compartment or hide it somewhere. And don’t forget to take down the
windshield mount: you don’t want to remind any potential thieves that you
might have some valuable mobile electronics in the car.
Don’t leave the device in direct sunlight for a long period of time or where the
temperature could go above 60º C (140º F).

Page 10
Attaching the Windshield Mount
Assemble the Windshield mount.
1) Loosen the locking collar on part 2.
2) Push the ball joint of Part 1 through the locking collar into part 2.
Insert the bracket hook into
the notches at the bottom of
the device.
Rotate the bracket
up so the head ts
into the gap.
Part 1 Part 2
Locking
collar

Page 11
Suction lock
Locking
collar
Adjusting the Windshield Mount
Mount on the Windshield
Make sure the device does not block your view of the road or your mirrors.
Once you decide where you want the device, hold the suction cup in that position,
then adjust the mount so you have the best view of the device.
1) Press the suction cup at against the windshield.
2) Push the suction lock up (clockwise) until it snaps into place.
3) Adjust the unit & bracket to a nal position. Tighten the locking collar to secure.
4) Gently pull on the mount to make sure it is secure.
If you have trouble getting the suction cup to stick:
Clean the spot with an ammonia-free cleanser.
Dry the spot completely (use a lint-free cloth, if possible).
Make sure the spot is smooth and at (suction cups won’t stick well on a
curved or textured surface).
Removing the Windshield Mount
When you release the suction latch, make sure you’re holding or somehow
supporting the device.
Lift the suction lock and use the plastic pull tab to pull the suction cup off of the glass.
Turn the windshield
mount arm to
a suitable angle for
mounting.

Page 12
1 Warnings and Safety information
The navigation system helps you nd your way to your destination with the built-in
GPS receiver. The software does not transmit your GPS position; others cannot
track you.
If you accept this when rst using the application, it collects usage information
and GPS logs that may be used for improving the application and the quality and
coverage of maps. The data is processed anonymously; no one will be able to
track any personal information. If you change your mind later, you can enable or
disable the log collection in Log Collection settings (page 119).
It is important that you look at the display only when it is safe to do so. If you are
the driver of the vehicle, we recommend that you operate your software before
you start your journey. Plan the route before your departure and stop if you need
to change the route.
You must obey the trafc signs and follow the road geometry. If you deviate from
the recommended route, your software changes the instructions accordingly.
Never place your device where it obstructs the driver’s view, where it is in the
deployment zone of an airbag or where it might cause injuries in an accident.
For more information, consult the End User Licence Agreement (page 123).

Page 13
2 Getting started
The software is optimised for in-car or pedestrian use. There is no need to use a
stylus. You can use it easily by tapping the screen buttons and the map with your
ngertips.
When using the navigation software for the rst time, an initial setup process starts
automatically. Do as follows:
1. Read the End User Licence Agreement. Tap
to continue.
2. You are now asked whether you allow the software to collect usage
information and GPS logs that may be used for improving the application
and the quality and coverage of maps. Tap
to allow the
anonymous statistics or
to disable this function. Later you can
turn them on or off individually in Log Collection settings (page 119)
3. Please take a moment to initially set up your new device to your preferences.
Later on you can run this conguration wizard, or change these (and some
more) settings under the More / settings menu. Tap
to continue.
Page 14
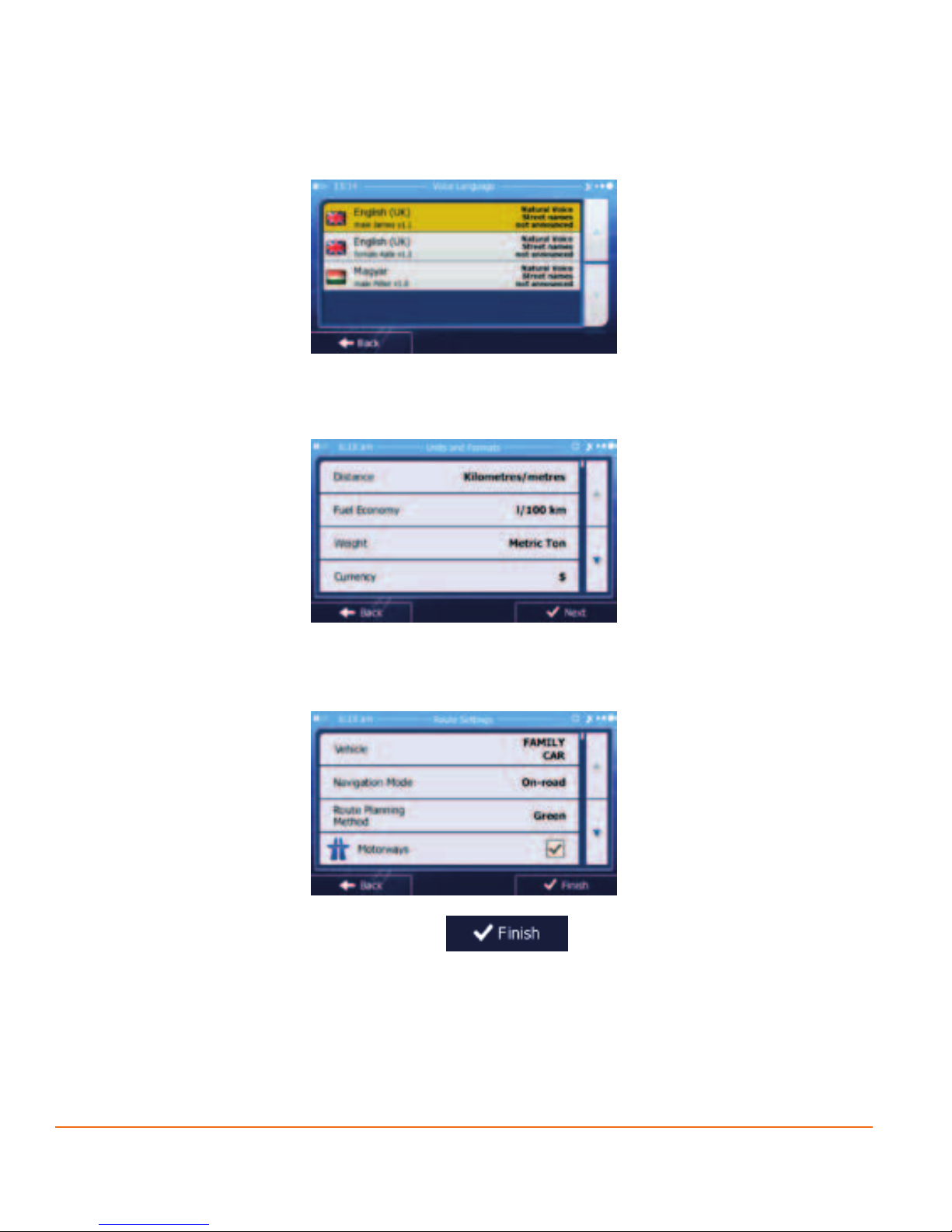
4. Select the language and speaker used for voice guidance messages. Later
you can change it in Regional settings (page 118).
5. If needed, modify the time format and unit settings. Later you can
change them in Regional settings (page 118).
6. If needed, modify the default route planning options. Later you can change
them in Route settings (page 106).
7. The initial setup is now complete. Tap to continue. The Conguration
wizard can be restarted later from the Settings menu (page 102).
Page 15
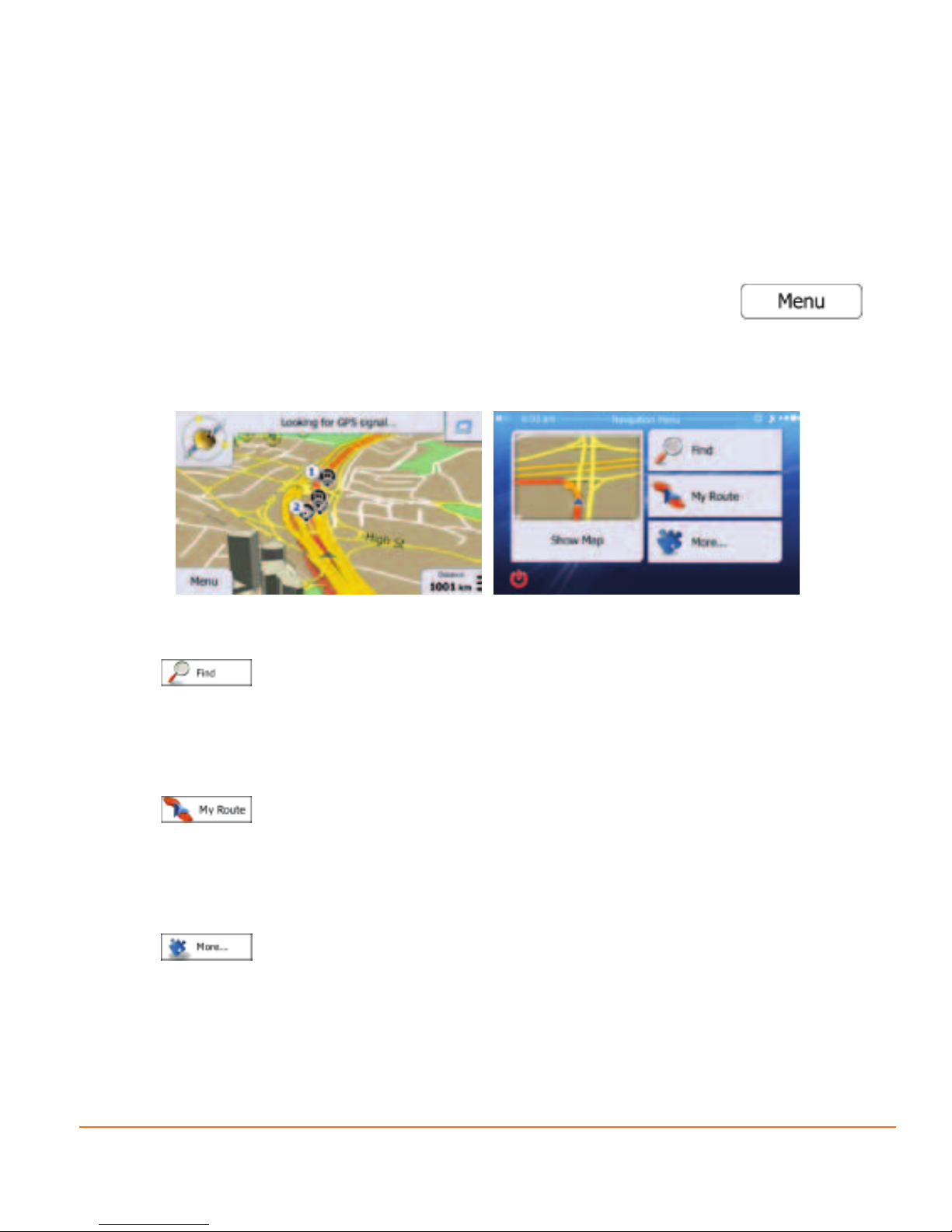
After the initial setup, the Map screen appears and the device looks for GPS
signal. A view of the sky is required to lock onto GPS. For the initial start this may
take a few minutes. you can start using the software. This is the screen you see
every time navigation starts.
2.1 Startup screen: the Map and Navigation menu
The software starts with the map screen. For rst time users touch to
open the Navigation menu.
From the Navigation menu you can reach all parts of the software.
You have the following options:
• Tap
to select your destination by entering an address or selecting a
place of interest, a location on the map or one of your Favourite destinations.
You can also look up your recent destinations from the Smart History, enter a
coordinate or use the location saved in a photo.
• Tap
to display the route parameters and the route in its full length on
the map. You can also perform route-related actions such as cancelling your
route, picking route alternatives, simulating navigation or adding the
destination to your Favourites.
• Tap
to customise the way the navigation software works, watch the
Tutorial, simuate demo routes, or to run some additional applications.
Page 16
• Tap to start navigating on the map. The button itself is a miniature
live map that shows your current position, the recommended route and the
surrounding map area. Tap the button to enlarge the map to the full screen.
• Tap
to stop navigation and exit the software.
2.2 Buttons and other controls on the screen
When you are using the software, you usually tap buttons on the touch screen.
You only need to conrm selections or changes if the application needs to restart,
it needs to perform a major reconguration, or you are about to lose some of your
data or settings. Otherwise, the software saves your selections and applies the
new settings without conrmation as soon as you use the controls.
Type Example Description How to use it
Button
Tap it to initiate a
function, to open a
new screen, or to set
a parameter.
Tap it once.
Button
with
value
Some buttons display
the current value of
a eld or setting. Tap
the button to change
the value. After the
change, the new
value is shown on
the button.
Tap it once.
Icon
Shows status
information.
Some icons also
function as a
button. Tap them
once.
Page 17
List
When you need to
select from several
options, they appear
in a list.
Grab the list
anywhere and slide
your nger up or
down. Depending
on the speed of the
sliding, the list will
scroll fast or slow,
only a bit or till the
end. Alternatively,
move between
pages with the
and
buttons and tap the
value that you want.
Slider
When a feature can
be set to different
values in a range,
the software shows
an indicator on a
gauge that displays
and sets the value.
• Drag the handle to
move the slider to
its new position.
• Tap the slider
where you want the
handle to appear;
the thumb jumps
there.
Radio
Button
When there are only
a few choices, radio
buttons may be used
instead of lists. Only
one value can be
selected.
Tap one of the
buttons to select a
new value.
Switch
When there are
only two choices, a
checkmark shows
whether the feature
is enabled.
Tap it to turn the
switch on or off.
Page 18
Virtual
keyboard
Alphabetic and
alphanumeric
keyboards to enter
text and numbers.
Each key is a touch
screen button.
2.2.1 Using keyboards
You only need to enter letters or numbers when you cannot avoid it. You can type
with your ngertips on the full-screen keyboards and you can switch between
various keyboard layouts, for example English, Greek or numerical.
Task Details
Switching to another keyboard
layout, for example from an English
keyboard to a Greek keyboard
Tep the
button and select the
new keyboard layout from the list.
Correcting your entry on the
keyboard
Tap
to remove the unneeded
character(s).
Tap and hold the button to delete several
characters or the entire input string.
Entering a space, for example
between a rst name and a family
name or in multi-word street
names
Tap the
button at the bottom centre
of the screen.
Entering upper and lower
case letters
When entering a text, the rst character
appears in upper case while the rest of
the text is in lower case. Tap
to enter
an upper case letter or tap twice to turn
on Caps Lock. Tap again and lower case
letters return.
Page 19
Entering numbers and symbols
Tap
to switch to a keyboard offering
numeric and symbol characters.
Finalising the keyboard entry
(accepting the suggested search
result)
Tap
.
Finalising the keyboard entry
(opening the list of search results)
Tap
.
Finalising the keyboard entry
(saving your input)
Tap
.
Cancelling the keyboard entry
(returning to the previous screen)
Tap
.
2.2.2 Beyond single screen tap
You usually need to tap the screen only once. However, some useful features can
be accessed with combined touch screen tapping. Those are the following:
Action Details
Tapping and
holding the
screen
Tap and keep pressing the following buttons to reach extra functions:
• Tap and hold
on list and menu screens: the Map
screen appears.
• Tap and hold any of the
, , , , and
buttons on the Map screen: you can rotate, tilt or scale the map
continuously.
• Tap and hold
on keyboard screens: you can delete
several characters quickly.
• Tap and hold
or in long lists: you can scroll pages
continuously.

Page 20
Gestures
(drag&drop)
You need to drag and drop the screen only in cases like:
• Moving the handle on a slider.
• Scrolling the list: grab the list anywhere and slide your nger up
or down. Depending on the speed of the sliding, the list will scroll
fast or slow, only a bit or till the end.
• Moving the map in map browsing mode: grab the map, and
move it in the desired direction.
2.3 Map screen
2.3.1 Navigating on the map
The Map screen is the most frequently used screen of the software.
A small live map is displayed on the Navigation menu, as a part of the
button.
To enlarge this small map and open the Map screen, tap .
The map is displayed in black and white when there is no GPS position:
This map shows the current position (the Vehimarker, a blue arrow by default), the
recommended route (an orange line), and the surrounding map area.
When there is no GPS position, the Vehimarker is transparent. It shows your last
known position.
You see coloured dots circling around a satellite symbol in the top left corner. The
more green dots you see, the closer you are to get the valid GPS position.
Page 21
When GPS position is available, the Vehimarker is displayed in full colour, now
showing your current position.
There are screen buttons and data elds on the screen to help you navigate.
During navigation, the screen shows route information.
By default, only one data eld is displayed in the bottom right corner. Tap this eld
to see all route data elds.
Tap any of the data elds to suppress others and display only the selected one.
The data elds are different when you are navigating an active route and when
you have no specied destination (the orange line is not displayed).
Default data elds when cruising without a destination (tap and hold any of the
elds to change its value):
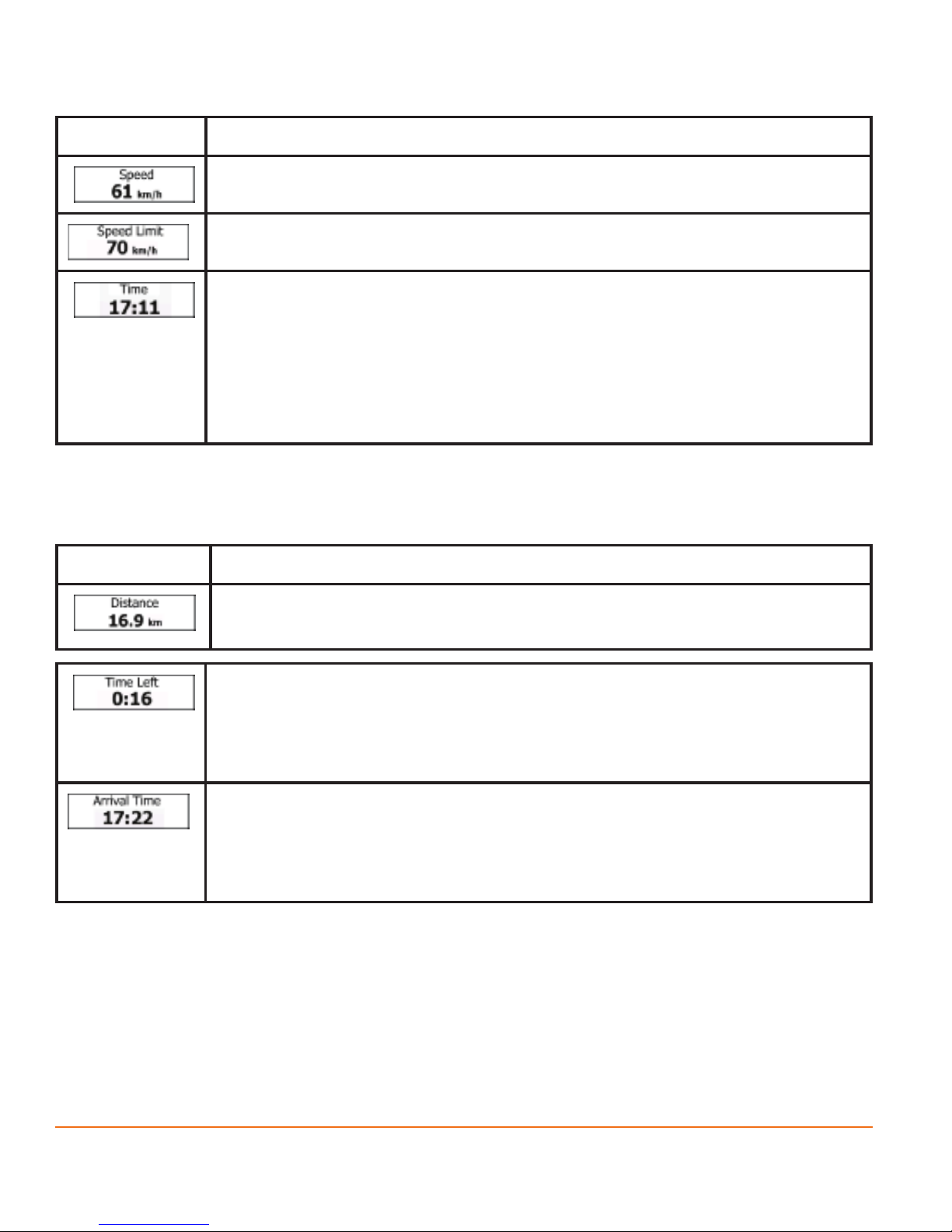
Page 22
Field Description
Shows your current speed given by the GPS receiver.
Shows the speed limit of the current road if the map contains it.
Shows the current time corrected with time zone offset. The
accurate time comes from the GPS satellites, and the time zone
information comes from the map or it can be set manually in
Regional settings.
(The current time is always displayed in the top left corner of the
high level menu screens.)
Default data elds when navigating a route (tap and hold any of the elds to
change its value):
Field Description
Shows the distance you need to travel on the route before
reaching your nal destination.
Shows the time needed to reach the nal destination of the route
based on information available for the remaining segments of the
route. Historical trafc data or trafc patterns are also taken into
account whenever such information exists.
Shows the estimated arrival time at the nal destination of the
route based on information available for the remaining segments
of the route. Historical trafc data or trafc patterns are also
taken into account whenever such information exists.
2.3.2 Position markers
2.3.2.1 Vehimarker and Lock-on-Road
When your GPS position is available, the software marks your current position
with the Vehimarker. By default, this marker is a blue arrow, but you can change
this icon in Settings.

Page 23
The exact location of the Vehimarker depends on the vehicle type used for route
calculation. The vehicle type can be selected in Route settings (page 107).
• If you choose pedestrian: The Vehimarker is at your exact GPS position. The
direction of the icon shows your current heading.
• In all other cases: The Vehimarker may not show your exact GPS position
and heading. If roads are near, it is aligned to the nearest road to suppress
GPS position errors, and the direction of the icon is aligned to the direction of
the road.
2.3.2.2 Selected map location (Cursor) and selected map object
You can mark a map location in the following ways:
• Tap the map when navigating,
• Tap the map when you are asked to conrm the destination at the end of a
search, or
• Tap the map in Find on Map (page 65)
When a map location is selected, the Cursor appears at the selected point on the
map. The Cursor is displayed with a radiating red dot (
) to make it visible at
all zoom levels.
The location of the Cursor can be used as the destination of the route, you can
search for Places around it, or you can save this location as one of your Favourite
destinations.
You can also select some of the objects on the map. If you tap the map at the icon
of a Place of Interest or an alert point, the object will be selected (you see a red
circling border around the object), and you can get information about this object or
use it as a route point.
2.3.3 Objects on the map
2.3.3.1 Streets and roads
The software shows the streets in a way that is similar to how the paper road
maps show them. Their width and colours correspond to their importance: you can
easily tell a motorway from a small street.
Page 24
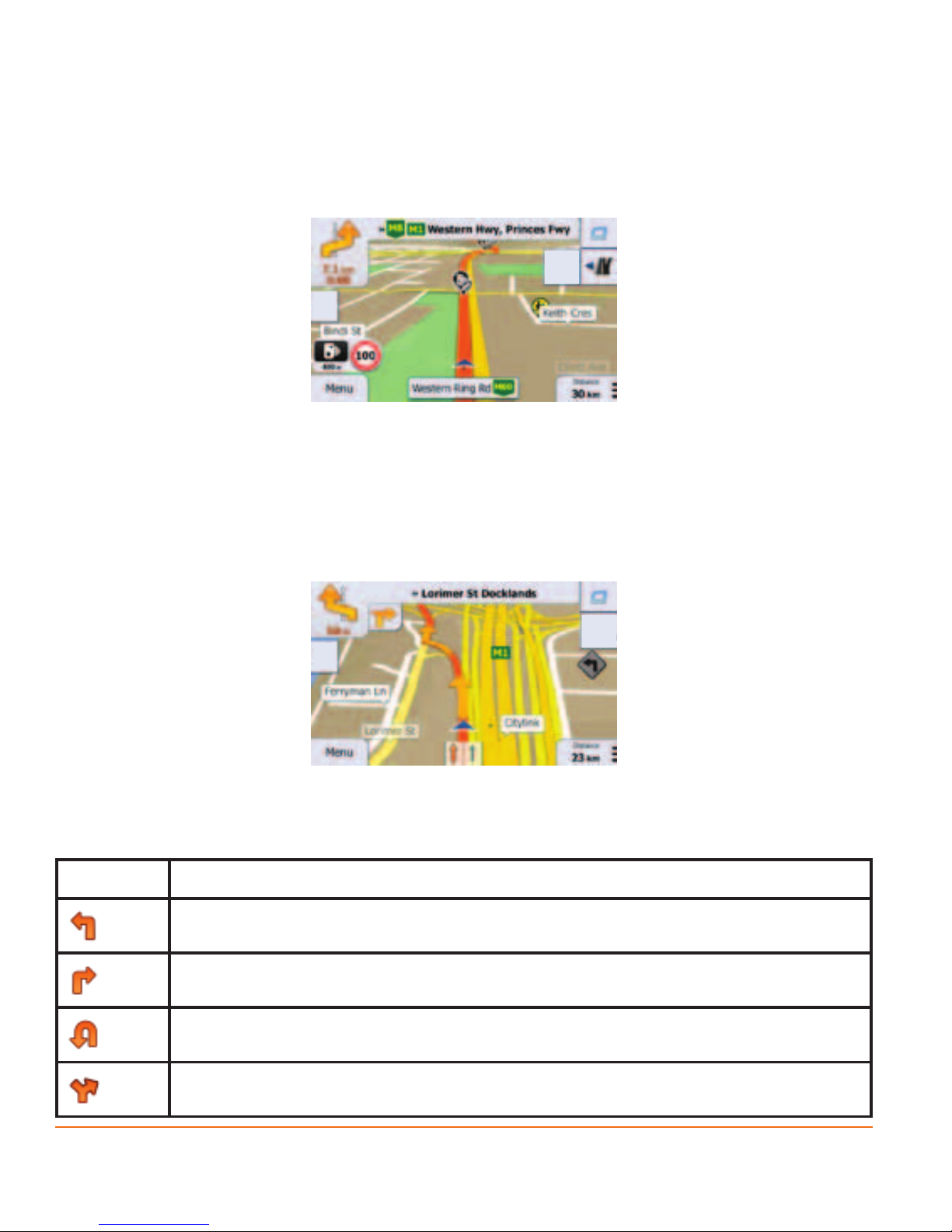
2.3.3.2 Turn preview and Next street
When navigating a route, the top section of the Map screen shows information
about the next route event (manoeuvre) and the next street or the next city/town.
There is a eld in the top left corner that displays the next manoeuvre. Both the
type of the event (turn, roundabout, exiting motorway, etc.) and its distance from
the current position is displayed.
A smaller icon shows the type of the second next manoeuvre if it is near the rst
one. Otherwise, only the next manoeuvre is displayed.
Most of these icons are very intuitive. The following table lists some of the
frequently shown route events. The same symbols are used in both elds:
Icon Description
Turn left.
Turn right.
Turn back.
Bear right.

Page 25
Turn sharp left.
Keep left.
Continue straight in the intersection.
Go left on the roundabout, 3rd exit (next manoeuvre).
Enter roundabout (second next manouvre).
Enter motorway.
Exit motorway.
Board ferry.
Leave ferry.
Approaching a waypoint.
Approaching the destination.
2.3.3.3 Lane information and Signposts
When navigating on multilane roads, it is important to take the appropriate lane in
order to follow the recommended route. If lane information is available in the map
data, the software displays the lanes and their directions using small arrows at the
bottom of the map. Highlighted arrows represent the lanes you need to take.
Where there is additional information available, signposts substitute arrows.
Signposts are displayed at the top of the map. The colour and style of the signposts
are similar to the real ones you can see above road or by the roadside. They show
the available destinations and the number of the road the lane leads to.
All signposts look similar when cruising (when there is no recommended route).
When navigating a route, only that signpost is displayed in vivid colours that points
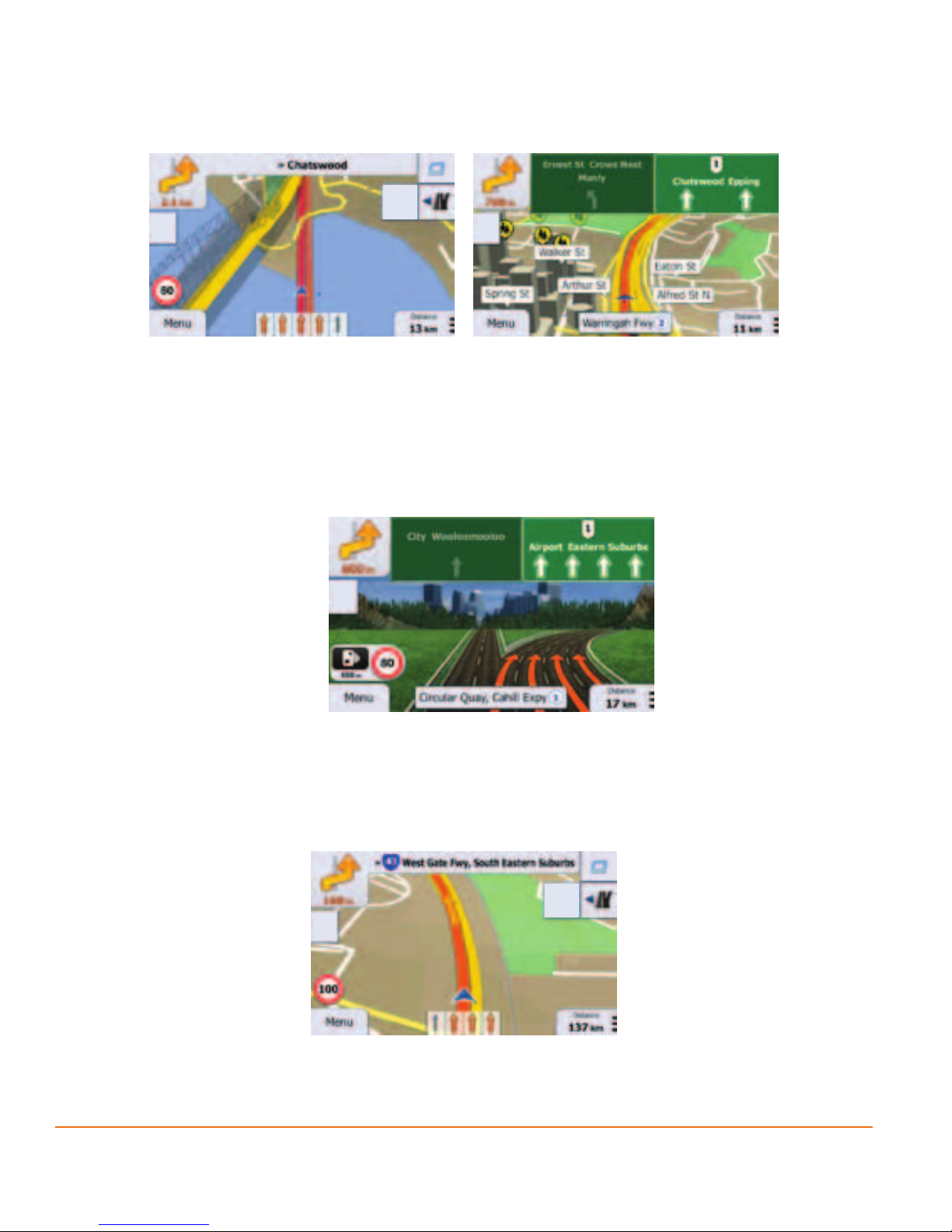
Page 26
to the lane(s) to be taken; all others are darker.
2.3.3.4 Junction view
If you are approaching a motorway exit or a complex intersection and the needed
information exists, the map is replaced with a 3D view of the junction. The lanes
you need to take are displayed with arrows. Signposts can also be present if
information is available.
2.3.3.5 Motorway exit services
You may need a petrol station or a restaurant during your journey. This feature
displays a new button on the map when you are driving on motorways.
Tap this button to open a panel with the details of the next few exits or service stations.
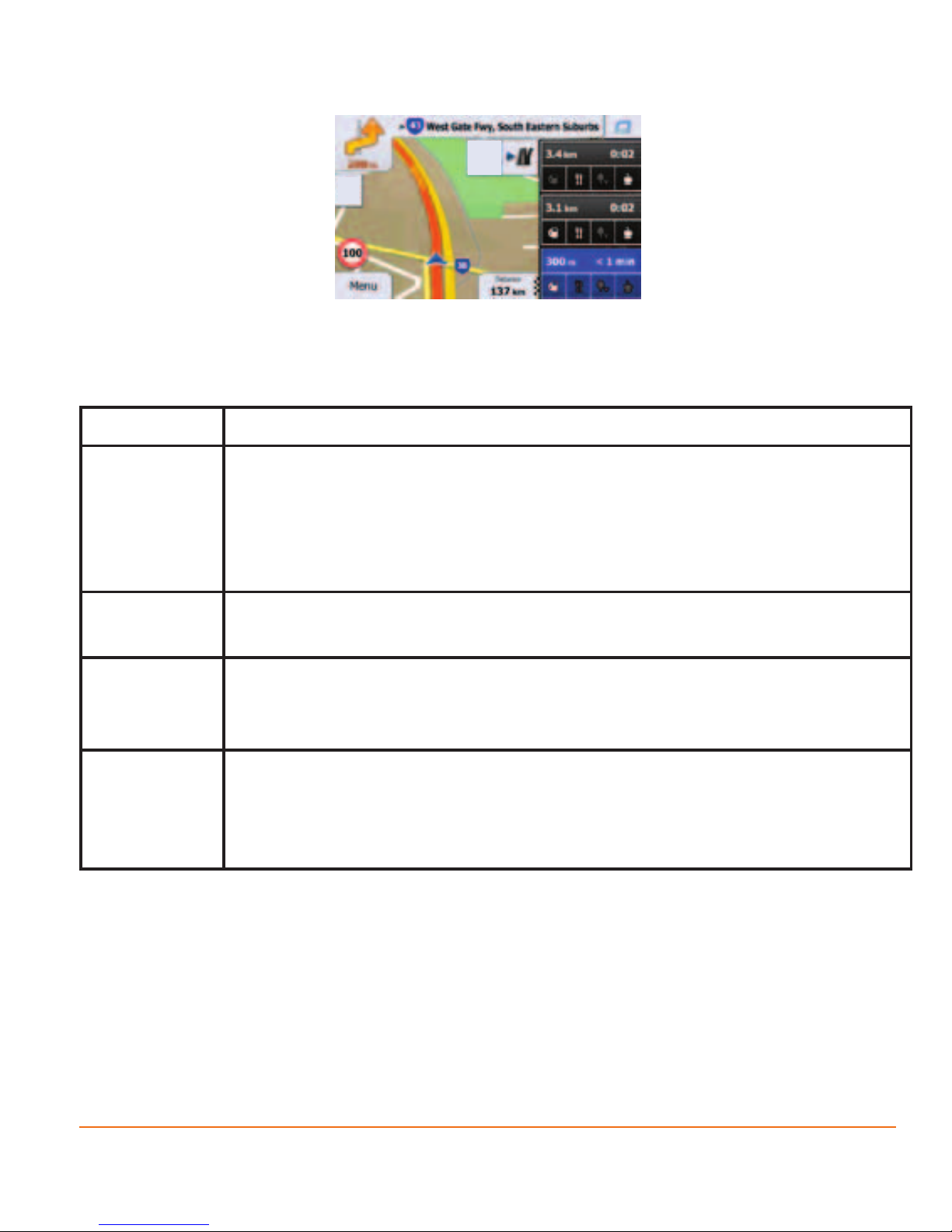
Page 27
2.3.3.6 3D object types
Your software supports the following 3D object types:
Type Description
3D terrain 3D terrain map data shows changes in terrain, elevations or
depressions in the land when you view the map in 2D, and use it to
plot the route map in 3D when you navigate. Hills and mountains
are shown in the background of the 3D map, and illustrated by
colour and shading on the 2D map.
Elevated
roads
Complex intersections and vertically isolated roads (such as
overpasses or bridges) are displayed in 3D.
3D
landmarks
Landmarks are 3D artistic or block representations of prominent or
well-known objects.
3D
buildings
(optional
data)
3D block representation of full city building data containing actual
building size and position on the map.
Page 28
2.3.3.7 Elements of the active route
Your software shows the route in the following way:
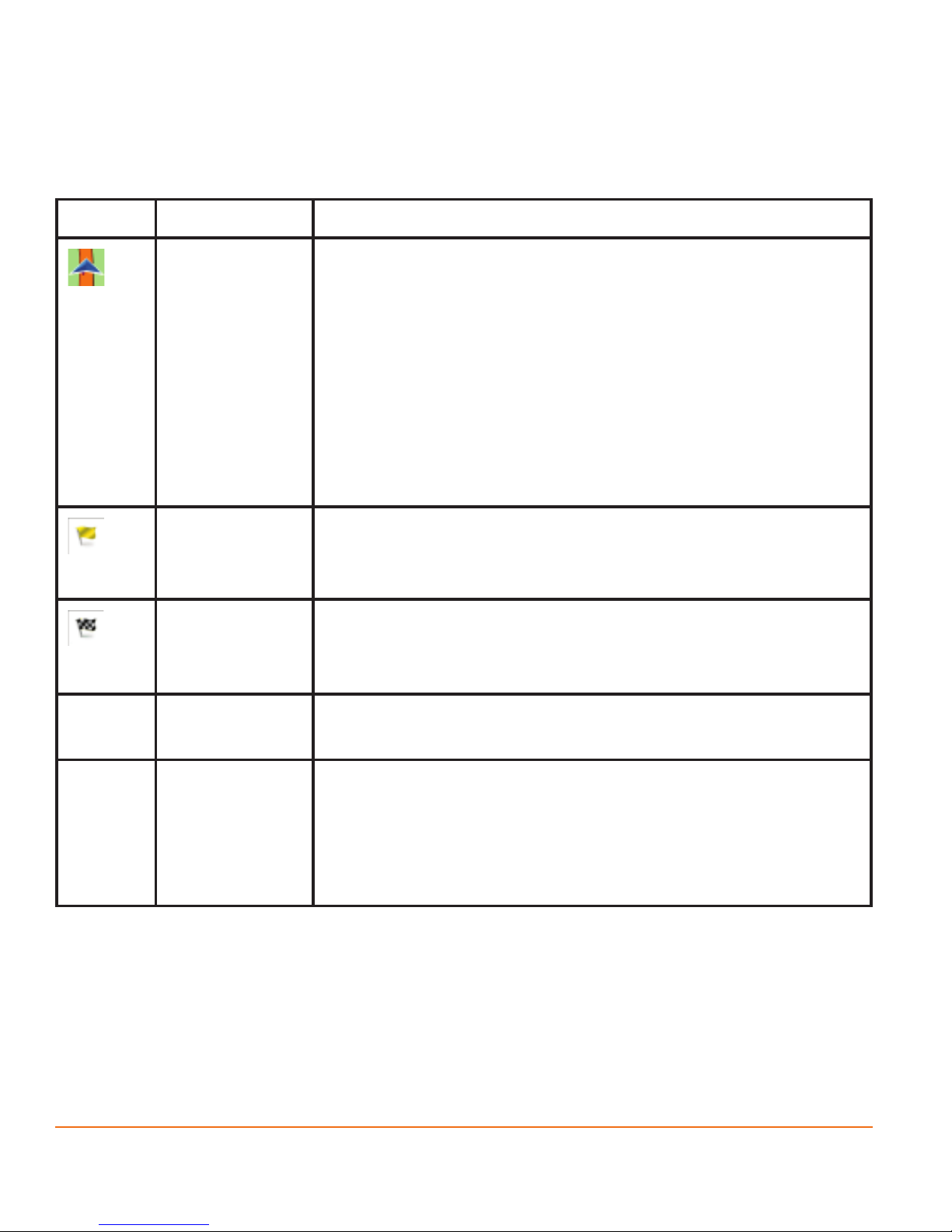
Symbol Name Description
Current GPS
position and
Start point
Your current position displayed on the map.
• In pedestrian mode it is the exact GPS position.
• If a vehicle is selected for route calculation and
roads are near, the symbol is snapped onto the
nearest road.
Normally if GPS position is available, the route starts from
the current position. If there is no valid GPS position, your
software uses the last known position as the start point.
Waypoint
(intermediate
destination)
An intermediate destination of the route before
reaching the nal destination.
Destination
(end point)
The last point of the route.
Route colour The route always stands out with its colour on the
map, both in daytime and in night colour mode.
Streets and
roads that
are excluded
from the
navigation
You can choose whether you want to use or avoid
certain road types (page 107). However, when your
software cannot avoid such roads, the route will
include them and it will show them in a colour that is
different from the route colour.
2.3.4 Manipulating the map
Tap the map anywhere to browse it during navigation. The map stops following
the current position (the Vehimarker, a blue arrow by default, is not locked in a x
position on the screen any more) and control buttons appear to help you modify
the map view.
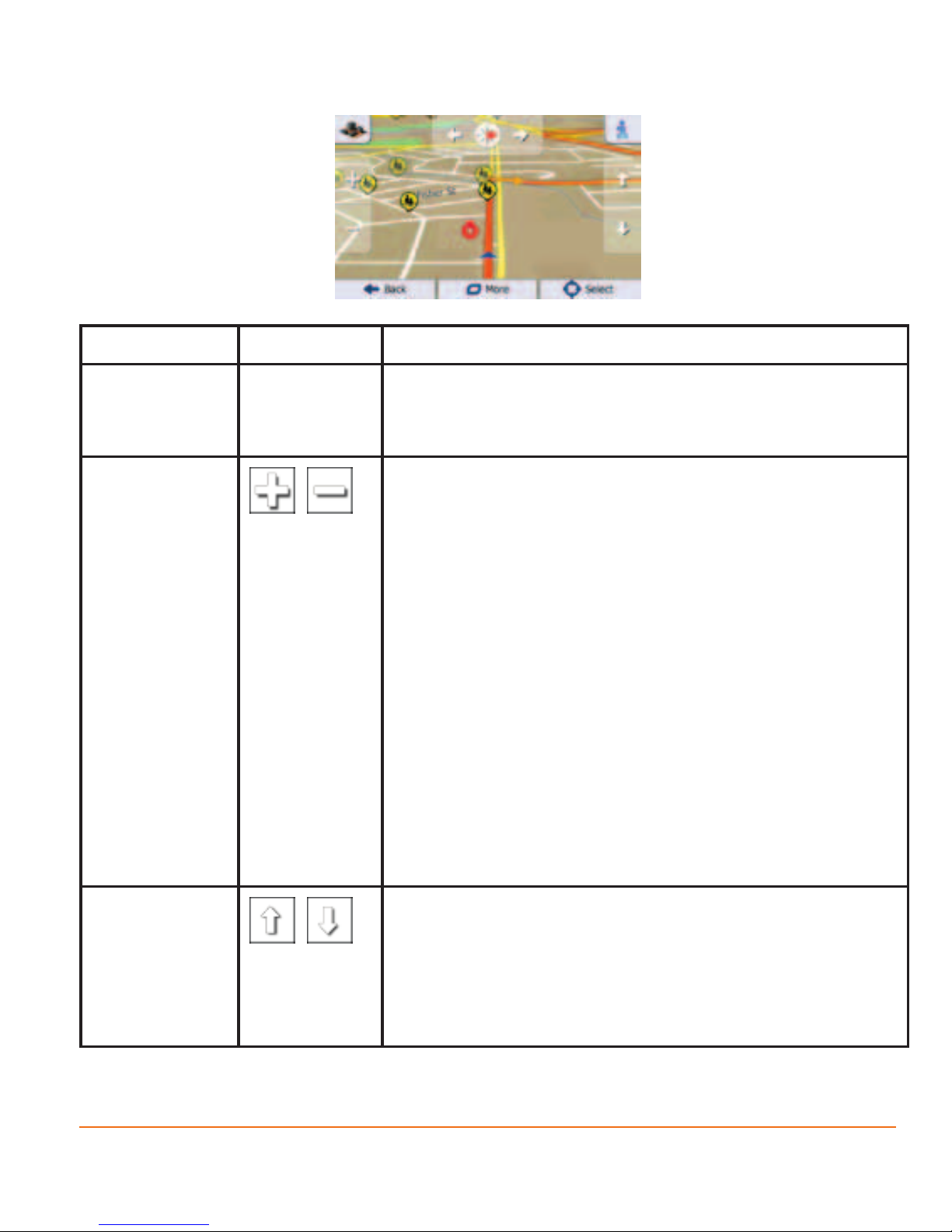
Page 29
Action Button(s) Description
Moving the
map with
drag&drop
No buttons You can move the map in any direction: tap and
hold the map, and move your nger towards the
direction you want to move the map.
Zooming in
and out
,
Changes how much of the map is displayed on the
screen.
Your software uses high-quality vector maps that
let you examine the map at various zoom levels,
always with optimised content. It always displays
street names and other text with the same font
size, never upside-down, and you only see the
streets and objects that you need.
Map scaling has a limit in 3D map view mode. If
you zoom out further, the map switches to 2D view
mode.
Tap the button once to modify the view in large
steps, or tap and hold the button to modify it
continuously and smoothly.
Tilting up and
down
,
Changes the vertical view angle of the map in 3D
mode.
Tap the button once to modify the view in large
steps, or tap and hold the button to modify it
continuously and smoothly.
Page 30
Rotating left
and right
,
Changes the horizontal view angle of the map.
Tap the button once to modify the view in large
steps, or tap and hold the button to modify it
continuously and smoothly.
2D or 3D
view
,
Tap this button to switch between the 3D
perspective and 2D top-down map view modes.
Compass in
2D map view
mode
,
The direction of the compass shows North. Tap the
button to switch to North-up view, then tap again to
rotate the map in the previous direction.
Compass in
3D map view
mode
,
The direction of the compass shows North. Tap the
button to switch to North-up view, then tap again to
rotate the map in the previous direction.
Location
information
Tap this button to open a new screen with
information about the selected map point, the
Cursor.
Return to
normal
navigation
Tap this button to move the map back to follow the
current GPS position. Automatic map rotation is
also re-enabled.
The map manipulation buttons disappear and
navigation continues.
Additional
options
Tap this button to open a list of additional features
like saving the Cursor as a Favourite destination,
or searching for Places around the Cursor.
Select
destination
Tap this button to select the Cursor as a new
destination. The route is automatically calculated.
2.3.5 Quick menu
The Quick menu is a selection of controls that are frequently needed during
navigation. It can be opened directly from the Map screen by tapping
.
 Loading...
Loading...