Page 1

MONOPACK 2
Manual
Version: 1.04
Jan 29th, 2010
Trinamic Motion Control GmbH & Co KG
Sternstraße 67
D - 20357 Hamburg, Germany
http://www.trinamic.com
Page 2

Monopack 2 Manual V1.04 2
Copyright © 2010, TRINAMIC Motion Control GmbH & Co. KG
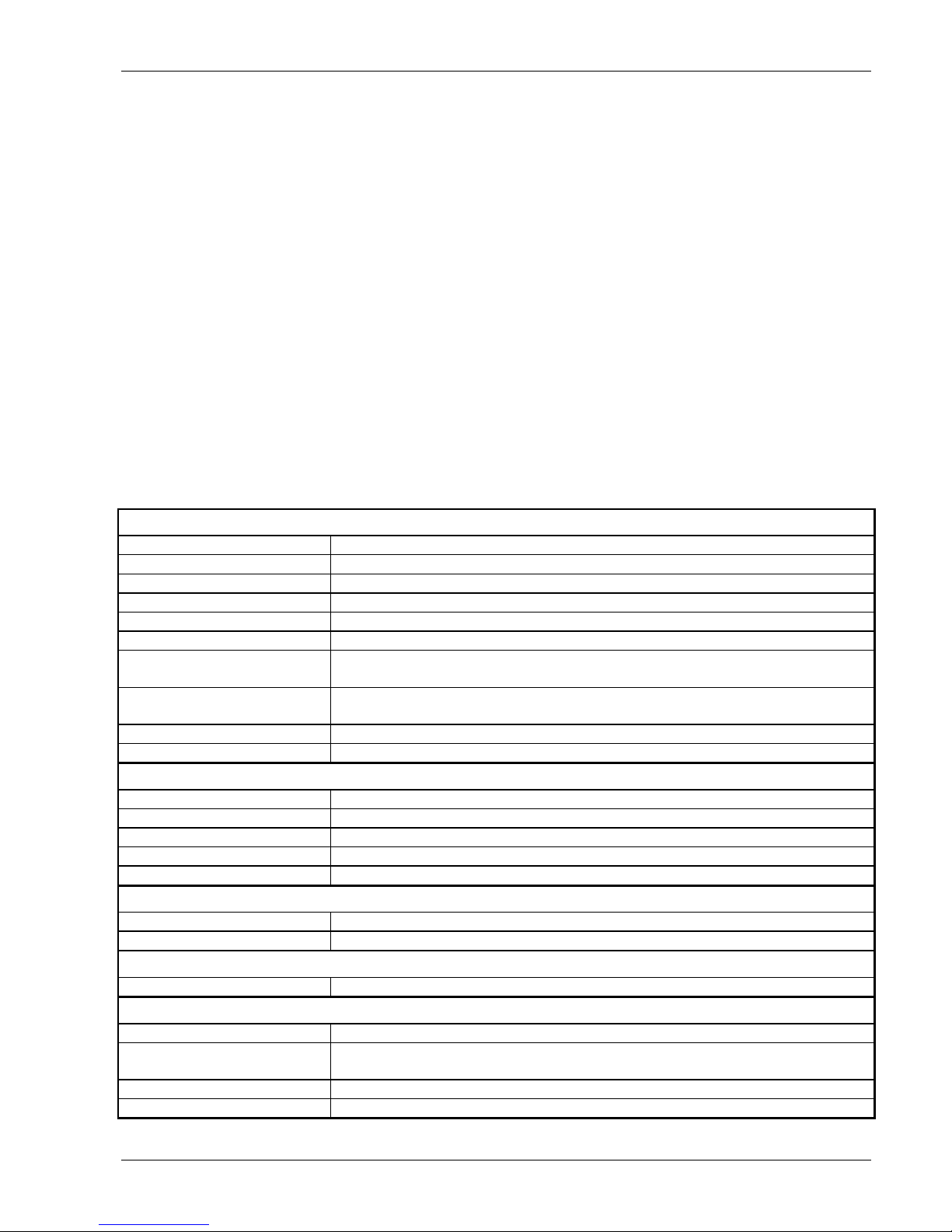
Version
Version
Date
Author
Remarks
1.00
2-Nov-05
OK
Initial version
1.01
18-Aug-06
HC
Added firmware update information
1.01
21-Aug-06
BD
Added Monopack LT frequency incompatibility information
1.02
16-May-2007
HC
Added Mixed Decay information (chapter 4.2.5)
1.03
15-Feb-08
GE
Added V2.0 info
1.04
29-Jan-10
OK
Declaration of Conformity added
Table of Contents
1 Introduction ................................................................................................................................................................... 5
1.1 Brief Description .................................................................................................................................................. 5
1.2 Technical Data ...................................................................................................................................................... 5
2 Connecting the Monopack 2 ..................................................................................................................................... 6
2.1 Pin Assignments .................................................................................................................................................. 6
2.2 Connecting the Motor ........................................................................................................................................ 6
2.3 Stop Switches and Reference Switches........................................................................................................ 7
2.3.1 Linear vs. Circular Drives ........................................................................................................................ 7
2.4 Incremental Encoder .......................................................................................................................................... 7
2.5 Power Supply ....................................................................................................................................................... 7
2.6 The RS232 interface ............................................................................................................................................ 7
2.7 The 25 pin Sub-D Socket ................................................................................................................................... 8
2.7.1 CAN and RS485 Interface ........................................................................................................................ 8
2.7.2 The Step/Direction Interface .................................................................................................................. 8
2.7.3 The Alarm Input ........................................................................................................................................ 8
2.7.4 The Alarm Output ..................................................................................................................................... 8
2.7.5 The Incremental Encoder Output ......................................................................................................... 8
2.7.6 The Stop Switch Outputs ....................................................................................................................... 8
2.8 The Step/Direction input socket...................................................................................................................... 9
2.9 The hexadecimal Switch.................................................................................................................................... 9
2.10 The DIP switches ................................................................................................................................................ 9
3 Controlling the Monopack 2 .................................................................................................................................... 10
3.1 Step/Direction Mode ......................................................................................................................................... 10
3.2 Binary Command Mode ................................................................................................................................... 10
3.2.1 Format of the Data Telegrams............................................................................................................ 10
3.2.2 Unit Addresses ......................................................................................................................................... 10
3.2.3 Parameter Storage .................................................................................................................................. 10
3.3 Monopack LT (ASCII) Command Mode ....................................................................................................... 11
4 Binary Command Reference .................................................................................................................................... 12
4.1 Parameter Storage Control ............................................................................................................................. 12
4.2 Motor Parameters .............................................................................................................................................. 12
4.2.1 Current Limit ($10) .................................................................................................................................. 12
4.2.2 Current Control ($11) ............................................................................................................................. 12
4.2.3 Get Current Control Settings ($53) .................................................................................................... 13
4.2.4 Frequency Range ($12) .......................................................................................................................... 13
4.2.5 Microstep Resolution, Waveform and Mixed Decay ($17) ........................................................... 13
4.3 Driving .................................................................................................................................................................. 14
4.3.1 About the Parameters ........................................................................................................................... 14
4.3.2 Velocity and Maximum Acceleration ($14) ...................................................................................... 14
4.3.3 Bow Value ($63) ...................................................................................................................................... 15
4.3.4 Get Acceleration and Velocity Settings ($52) ................................................................................. 15
Page 3

Monopack 2 Manual V1.04 3
Copyright © 2010, TRINAMIC Motion Control GmbH & Co. KG
4.3.5 Get actual Position ($20) ...................................................................................................................... 15
4.3.6 Get actual Acceleration and Velocity ($21) ...................................................................................... 15
4.3.7 Drive a Ramp ($23) ................................................................................................................................. 16
4.3.8 Constant Rotation ($25) ........................................................................................................................ 16
4.3.9 Reset Position ($27) ............................................................................................................................... 16
4.3.10 Soft Stop ($2A) ........................................................................................................................................ 16
4.3.11 Emergency Stop ($2B) ........................................................................................................................... 16
4.4 Stop and Reference Switches ........................................................................................................................ 17
4.4.1 Switch Mode ($54) .................................................................................................................................. 17
4.4.2 Deceleration at Stop Switches ($57) ................................................................................................. 17
4.4.3 Reference Search ($22) .......................................................................................................................... 17
4.4.4 Reference Search Velocity ($16).......................................................................................................... 18
4.4.5 Travel Check Tolerance ($59) ............................................................................................................... 18
4.4.6 Number of Microsteps per Revolution ($15) ................................................................................... 18
4.4.7 Get the State of the Stop Switches ($30) ........................................................................................ 18
4.5 Incremental Encoder ........................................................................................................................................ 19
4.5.1 About Incremental Encoders ............................................................................................................... 19
4.5.2 Encoder Configuration ($70) ................................................................................................................ 19
4.5.3 Encoder Counter ($71) ........................................................................................................................... 20
4.5.4 Encoder Holding Register ($72) .......................................................................................................... 20
4.5.5 Deviation Alarm ($73) ............................................................................................................................ 20
4.5.6 Configure Automatic Position Correction ($58) ............................................................................. 20
4.5.7 PID Controller Configuration ($6A, $6B, $6C, $6D, $6F) .............................................................. 21
4.6 Alarms and Errors ............................................................................................................................................. 22
4.6.1 Alarm Mode ($51) ................................................................................................................................... 22
4.6.2 Reset Alarm Output ($74) ..................................................................................................................... 22
4.7 Other Settings .................................................................................................................................................... 22
4.7.1 Enter Step/Direction Mode ($50) ........................................................................................................ 22
4.7.2 Set CAN receive ID and RS485 ID ($55) ........................................................................................... 22
4.7.3 Set CAN send ID ($56) ........................................................................................................................... 23
4.7.4 Set CAN Baud Rate ($C0) ...................................................................................................................... 23
4.7.5 Get Version Number ($43) .................................................................................................................... 23
4.7.6 Hardware Reset ($CC) ............................................................................................................................ 23
4.8 Factory Default Settings ($DD) ...................................................................................................................... 23
5 Monopack LT Command Reference ....................................................................................................................... 24
5.1 Interface selection ............................................................................................................................................ 24
5.2 Command overview ......................................................................................................................................... 24
5.2.1 Set the pre-divider.................................................................................................................................. 25
5.2.2 Set microstep resolution ...................................................................................................................... 25
5.2.3 Acceleration setting ............................................................................................................................... 25
5.2.4 Bow setting .............................................................................................................................................. 25
5.2.5 Velocity setting ........................................................................................................................................ 25
5.2.6 Direction setting ..................................................................................................................................... 25
5.2.7 Drive with fixed velocity ...................................................................................................................... 25
5.2.8 Soft stop .................................................................................................................................................... 25
5.2.9 Hard stop .................................................................................................................................................. 26
5.2.10 Set target position or relative distance ........................................................................................... 26
5.2.11 Drive to target position ........................................................................................................................ 26
5.2.12 Relative move .......................................................................................................................................... 26
5.2.13 Set motor standby current ................................................................................................................... 26
5.2.14 Set motor run current ........................................................................................................................... 26
5.2.15 Set motor acceleration current ........................................................................................................... 26
5.2.16 Set mixed decay mode ......................................................................................................................... 27
5.2.17 Automatic reference search ................................................................................................................. 27
5.2.18 Find reference switch position ........................................................................................................... 27
5.2.19 Set stop switch mode ........................................................................................................................... 27
5.2.20 Change actual position ......................................................................................................................... 27
5.2.21 Query actual position ............................................................................................................................ 27
Page 4

Monopack 2 Manual V1.04 4
Copyright © 2010, TRINAMIC Motion Control GmbH & Co. KG
5.2.22 Query actual velocity ............................................................................................................................. 28
5.2.23 Query status of stop switches ............................................................................................................ 28
5.2.24 Query TMC453 FIFO filling.................................................................................................................... 28
5.2.25 Step/Direction mode selection ........................................................................................................... 28
5.2.26 Display actual ADC values .................................................................................................................... 28
5.2.27 Write all parameters to the EEPROM ................................................................................................ 28
5.2.28 Enable or disable the EEPROM ............................................................................................................ 28
5.2.29 Choose interface and set RS485 delay ............................................................................................. 28
5.2.30 Set the RS485 address........................................................................................................................... 29
5.3 Help screen ......................................................................................................................................................... 29
5.4 Messages sent by the device ......................................................................................................................... 29
6 The Monopack PC Software ..................................................................................................................................... 30
6.1 Using the Program ............................................................................................................................................ 30
6.2 Firmware update / Reset to factory default .............................................................................................. 30
7 Application Notes ....................................................................................................................................................... 31
7.1 Making a simple RS232 to RS485 Converter ............................................................................................. 31
7.2 Setting the Maximum Current ....................................................................................................................... 31
7.3 Using the “ic485-I” RS232 to RS485 Converter ......................................................................................... 32
7.4 Choosing Plugs for the Monopack ............................................................................................................... 32
8 Declaration of Conformity ....................................................................................................................................... 33
TRINAMIC Motion Control GmbH & Co. KG does not authorize or warrant any of its products for use in life support
systems, without the specific written consent of TRINAMIC Motion Control GmbH & Co. KG.
Life support systems are equipment intended to support or sustain life, and whose failure to perform, when
properly used in accordance with instructions provided, can be reasonably expected to result in personal injury or
death.
Trinamic Motion Control GmbH & Co KG, Germany 2005
All rights reserved. No part of the contents of this book may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any
means without the written permission of the publisher. Information given in this data-sheet is believed to be
accurate and reliable. However no responsibility is assumed for the consequences of its use nor for any
infringement of patents or other rights of third parties which may result from its use. Specifications are subject to
change without notice.
Page 5
Monopack 2 Manual V1.04 5
Copyright © 2010, TRINAMIC Motion Control GmbH & Co. KG
1 Introduction
1.1 Brief Description
The Monopack 2 is an intelligent easy-to-use stepper motor driver for two-phase bipolar stepper motors with up to
5A coil current. It comes in a small and robust housing and provides a high motor power and dynamics. It can be
controlled via CAN bus, an RS485, RS232 or a Step/Direction interface and provides the functionality for either
remote controlled or stand alone applications. Its optional encoder feedback and a number of protection features
makes this drives very dependant and reliable. The Monopack 2 can do up to 406 microsteps and needs a power
supply of 12-48 Volts.
A Windows 95/98/ME/NT/2000/XP based PC software is supplied to explore the possibilities of the Monopack 2. To
use this software, the Monopack just has to be connected to the PC via its RS232 interface.
The Monopack 2 replaces the Trinamic products “Monopack” and “Monopack LT” which have been discontinued. It
is fully compatible with the Monopack and offers most features of the Monopack LT. A DIP switch allows to select
either “Monopack” or “Monopack LT” mode. Also the maximum motor current can be either 2.5A like in the old
Monopack and Monopack LT or, in the extended mode, 5A. This can also be selected by a DIP switch. From version
V2.0 on the Monopack 2 is RoHS conform.
1.2 Technical Data
Features and operational ratings
Ramp profile
S-curve, controlled by a TMC 453
Step type
Microstepping resolution from 1 to 64 or 100.8, 202.125 or 406.5
Power supply
12V - 48 V DC
Motor current
Maximum 5A peak coil current in extended mode or 2.5A in compatible mode
Motor type
Bipolar 2-phase stepper motor
Encoder type
Two channel incremental encoder with optional zero channel and 5V outputs
Inputs
Two stop switches (left and right), one reference switch, one differential alarm
input
Outputs
One differential alarm output, one differential encoder output (channel A, B and
Null)
Temperature range
0-70°C
Dimensions
132mm x 130mm x 45mm (without plugs)
Electrical data of the stop switch, reference switch and encoder inputs
Integrated pull up resistor
10k to internal +5V
Logic level low
0.0V..+1.3V
Logic level high
+3.3V..+5.0V
Continus protection voltage
-8V..+13V
Short time protection voltage
-24V..+24V
Electrical data of the differential inputs:
Common-mode input voltage
-7V to +12V
Differential input voltage
±6V
Electrical data of the differential outputs:
Differential output voltage
1.7V
Interfaces
RS232
9600 or 19200 baud, 8 data bits, 1 stop bit, no parity bit
Rs485
9600 or 19200 baud, 8 data bits, 1 stop bit, no parity bit, 100 Ohms termination
selectable
CAN
CAN 2.0B, 125, 250, 500 kbit/s or 1Mbit/s, 100 Ohms termination selectable
Step-/ Direction
Differential interface
Page 6

Monopack 2 Manual V1.04 6
Copyright © 2010, TRINAMIC Motion Control GmbH & Co. KG
2 Connecting the Monopack 2
2.1 Pin Assignments
The connectors of the Monopack 2 and their pin assignments are shown in Figure 2.1.
Max 45VDC
+ -
Address
CAN/
RS485
8 1
MONOPACK 2
CAN/RS485 Termination
ON = RS485
ON = RS485
ON = CAN
ON = CAN
ON
OFF
ON = Monopack LT mode
ON = Upgrade firmware
OFF= max. 2.5A,
ON=max. 5A
1 13
14 25
CANL/RS485-
CANH/RS485+
EnCHB-
EnCHB+
StopL-
StopL+
AlarmIN-
AlarmIN+
MC1-
MC1+
DIR-
DIR+
GND
EnCHN-
EnCHN+
EnCHA-
EnCHA+
StopR-
StopR+
AlarmOUT-
AlarmOUT+
MC0-
MC0+
STEP-
STEP+
Encoder
+5V A B N GND
SYNC
IN
Stop Switch
R GND L GND
Motor max. 3A
A1 A2 B1 B2
RS232
1 5
6 9
2=TxD
3=RxD
5=GND
+5V
STEP -
STEP+
GND
DIR-
DIR+
Figure 2.1: Connectors and pin assignments
2.2 Connecting the Motor
Connect one phase coil to the “A1” and “A2” connectors and the other phase coil to the “B1 ” and “B2” connectors.
Attention: Do not connect or disconnect the motor while the Monopack 2 is powered on as this could damage the
power drivers!
When using the stop switches, the motor must be connected so that the traveler moves towards the stop switch
connected to the “Stop Switch R” input when the velocity is positive and towards the stop switch connected to
the “Stop Switch L” input when the velocity is negative. Change the polarity of one of the coils if this should not
be the case. Otherwise, some functions of the Monopack 2 can not operate correctly (especially the stop switches
and the reference search algorithm).
Page 7

Monopack 2 Manual V1.04 7
Copyright © 2010, TRINAMIC Motion Control GmbH & Co. KG
2.3 Stop Switches and Reference Switches
For stop and reference switches, only openers can be used. The stop and reference switch inputs can be used in
different ways:
Two stop switches and a separate reference switch: Connect the left stop switch to the “Stop Switch L”
input and the right stop switch to the “Stop Switch R” input. Connect the reference switch to the “Ref
IN” input.
One stop switch and a separate reference switch: Connect the stop switch to the desired stop switch
input and the other stop switch input permanently to ground.
Combining the reference switch with one stop switch: Connect one switch to the reference switch
input and to the desired stop switch input, as shown in Figure 2.1. If only one stop switch is to be
used connect the other stop switch input to ground.
2.3.1 Linear vs. Circular Drives
In a linear drive (Figure 2.2), the traveler moves between two end points. It is not necessarily driven by a linear
stepper motor. In most cases, stop switches are used at the end points, and also a reference switch is used for
finding the reference point. The reference switch can also be combined with one of the end switches (as shown in
Figure 2.1).
Right Stop
Switch
Traveller
Left Stop
Switch
Reference
Switch
Negative
Direction
Positive
Direction
Figure 2.2: A linear drive
In a circular drive (Figure 2.3), the traveler moves around. There are no end points, and for that reason there are
also no stop switches. So the stop switch inputs are disabled in circular mode. A reference switch can be used for
finding the reference point.
Traveller
Reference
Switch
Figure 2.3: A circular drive
2.4 Incremental Encoder
Connect the two channels of the incremental encoder to the inputs “A” and “B”. An optional null channel can be
connected to the “N” input. The incremental encoder connector also provides a 5V power supply.
2.5 Power Supply
The voltage should be between 12 and 48 Volts to operate and must not exceed 49V. When using a regulated
power supply, set the current limit higher than the maximum motor current.
2.6 The RS232 interface
The 9-pin Sub-D socket provides the RS232 interface. This interface can be used in
Monopack mode as well as in Monopack LT mode. The pin assignments are as follows:
Pin
Signal name
2
TxD
3
RxD
5
GND
RS232
1 5
6 9
2=TxD
3=RxD
5=GND
Page 8

Monopack 2 Manual V1.04 8
Copyright © 2010, TRINAMIC Motion Control GmbH & Co. KG
2.7 The 25 pin Sub-D Socket
This socket contains the RS485 interface, the CAN interface, the
STEP/DIRECTION interface and the alarm input and output. The signals
of the incremental encoder input and the stop switch inputs are output
here as differential signals. The following subsections describe those
interfaces.
2.7.1 CAN and RS485 Interface
For the CAN and the RS485 interface, the same pins are used. So the
interface which shall be used must be selected via the DIP switches:
To use the CAN interface, set switch 1 and 2 to ON and
switch 3 and 4 to OFF position.
To use the RS485 interface, set switch 1 and 2 to OFF and
switch 3 and 4 to ON position.
The termination of both interfaces (120 Ohms) can be switched on and
off with switch 6. Switch 5 is not used. Attention: Changing between
RS485 and CAN interface requires a hardware reset (by powering off for
a short time).
2.7.2 The Step/Direction Interface
The Step/Direction interface uses differential signals. After powering on, the Monopack is in Step/Direction mode
so that the Step/Direction interface is usable. After getting the first RS485 or CAN command the Monopack leaves
the Step/Direction mode and enters the command mode where the Step/Direction interface can not be used. It is
possible to switch back to Step/Direction mode by a command.
The motor current control inputs MC0 and MC1 also belong to the Step/Direction interface. Using these inputs, the
motor current can be controlled by hardware in three steps (please see also section 4.2.1):
MC0
MC1
Motor current
0 0 1/3 of configured maximum current
1 0 2/3 of configured maximum current
0 1 2/3 of configured maximum current
1 1 Configured maximum current
In contrast to the old Monopack, these motor current settings can also be controlled by software (please see
section 4.2.1). The step and direction inputs are also provided on the Step/Direction input socket. These are
internally connected to the step/direction inputs of the 25-pin socket.
2.7.3 The Alarm Input
The alarm input is a differential input which can be used to stop the motor in case of emergency. To connect a
key to this input, simply connect it between AlarmIN+ and +5V (from the incremental encoder connector) and
connect the AlarmIN- input to ground.
2.7.4 The Alarm Output
This differential output is set high in case of an alarm or error condition. Alarm and error conditions can be
cleared by command $74 (s. 4.6.2).
2.7.5 The Incremental Encoder Output
The incremental encoder outputs (EnchA+/-, EnchB+/-, EnchN+/-) provide the encoder signals from the encoder input
(s. 2.4) converted to differential signals.
2.7.6 The Stop Switch Outputs
The stop switch outputs (StopL+/- and StopR+/-) provide the signals from the stop switch inputs (s. 2.3) converted
to differential signals.
1 13
14 25
CANL/RS485-
CANH/RS485+
EnCHB-
EnCHB+
StopL-
StopL+
AlarmIN-
AlarmIN+
MC1-
MC1+
DIR-
DIR+
GND
EnCHN-
EnCHN+
EnCHA-
EnCHA+
StopR-
StopR+
AlarmOUT-
AlarmOUT+
MC0-
MC0+
STEP-
STEP+
Page 9

Monopack 2 Manual V1.04 9
Copyright © 2010, TRINAMIC Motion Control GmbH & Co. KG
2.8 The Step/Direction input socket
The Step/Direction input socket provides the same differential step/direction inputs as the 25-pin Sub-D socket. It is
electrically identical with those inputs.
2.9 The hexadecimal Switch
This switch is used to set the LSN of the CAN receive identifier and the RS485 address. If the switch is set to zero,
the CAN receive identifier and the RS485 address will be reset to 1 and the CAN send identifier will be reset to 2
(please see also section 3.2.2, 4.7.2 and 4.7.3). The position of the hexadecimal switch is only read after a hardware
reset. So it is required to power off the unit when changing the hexadecimal switch setting.
2.10 The DIP switches
The DIP switches allow selecting the interface that is to be used and the operating mode. They have the following
functions:
Switch
Function
1
OFF: Use RS485 interface; ON: Use CAN interface
2
OFF: Use RS485 interface; ON: Use CAN interface
3
OFF: Use CAN interface; ON: Use RS485 interface
4
OFF: Use CAN interface; ON: Use RS485 interface
5
OFF: Use Monopack 2 (binary) command set (compatible with old Monopack)
ON: Use Monopack LT (ASCII) command set (compatible with old Monopack LT)
6
OFF: normal operation
ON: perform a firmware upgrade
7
OFF: No bus termination
ON: 100 Ohms RS485/CAN bus termination
8
OFF: Maximum current is 2.5A (compatible with Monopack / Monopack LT)
ON: Maximum current is 5.7A
Please note that switches 5 and 6 are only read after a hardware reset. So it is necessary to power off the unit
when changing the settings of switch 5 or 6.
Page 10

Monopack 2 Manual V1.04 10
Copyright © 2010, TRINAMIC Motion Control GmbH & Co. KG
3 Controlling the Monopack 2
3.1 Step/Direction Mode
Right after powering on, the device works as a step/direction power module. After getting the first command via
the RS232 interface, the RS485 interface or the CAN interface, it switches from step/direction mode to command
mode. It is possible to switch back to step/direction mode using command $50.
3.2 Binary Command Mode
The binary command mode is selected when DIP switch #6 is in its “off” position. This mode is compatible with
the old “Monopack”, with some extensions. In the binary command mode the Monopack 2 expects data telegrams
via the RS232 interface, the RS485 interface or the CAN interface. With those interfaces the following parameters
can be used:
RS485 interface
19200 baud
8 data bits, no parity bit, 1 stop
bit
RS232 interface
19200 baud
8 data bits, no parity bit, 1 stop
bit
CAN interface
125, 250, 500 or 1000 kbit/s
Default: 250 kbit/s
3.2.1 Format of the Data Telegrams
Every data telegram consists of one command byte and seven parameter bytes. Unused parameter bytes must be
set to zero. It is not allowed to leave out unused parameter bytes. In RS485 mode, every data telegram is
preceded by an address byte which contains the RS485 address of the unit. In CAN mode the identifier field of the
CAN telegram is used to address the unit. So the format of every Monopack data telegram is as follows:
Address
(in RS485 mode only)
Command
P0
P1
P2
P3
P4
P5
P6
Some commands also send back a data telegram of the same format as answer.
3.2.2 Unit Addresses
In RS485 mode, the LSN of the address can be set by the hexadecimal switch. The MSN can be set using command
$55 (s. 4.7.2).
In CAN mode, the LSN of the CAN receive ID is set by the hexadecimal switch. The rest of the CAN receive ID can
be set using command $55. The CAN send ID is set using command $56 (s. 0).
The CAN baud rate can be set using command $C0 (s. 4.7.4).
If the hexadecimal switch is set to zero the RS485 address and the CAN receive ID will be
reset to 1. The CAN send ID will be reset to 2.
3.2.3 Parameter Storage
Most of the parameters which can be set by the commands can be stored in an EEPROM. This makes it possible
that the Monopack is configured only once and can then be used without having to reconfigure it every time it is
powered on again. In firmware versions prior to 2.05, the EEPROM values are always changed whenever a
parameter changing command is given. From version 2.05 on, this can be controlled, so that parameters can also
be changed temporarily without affecting the values stored in the EEPROM and the parameters can also be read
back. These features are controlled by the P0 byte of the command. Please see section 4.1 for further explanation.
Page 11

Monopack 2 Manual V1.04 11
Copyright © 2010, TRINAMIC Motion Control GmbH & Co. KG
3.3 Monopack LT (ASCII) Command Mode
The Monopak LT compatible command mode is selected when DIP switch #6 is in its “on” position. This command
set is compatible with the old “Monopack LT” command set. In LT mode, the communication with the Monopack 2
can either take place via the RS232 interface or via the RS485 interface. The CAN interface can not be used in LT
mode. The baud rate is 9600 bps.
Attention: The Monopack 2 uses a higher clock frequency than the Monopack LT. Thus the velocity and
acceleration settings do not give identical results. To be compatible with the settings required by the
Monopack LT, please multiply your velocity and acceleration settings by 0.691.
Page 12

Monopack 2 Manual V1.04 12
Copyright © 2010, TRINAMIC Motion Control GmbH & Co. KG
4 Binary Command Reference
In the description of the commands, hexadecimal values are marked with a leading “$” sign. Numbers which
occupy more than one byte are stored with least significant byte first and are marked with a “#” sign.
To get used to the binary command set we recommend to start with the Monopack Control Panel software. Please
refer to chapter 6.
4.1 Parameter Storage Control
As described in section 3.2.3 it can be controlled whether parameters are to be stored in the EERPOM or not, and
parameters can also be read back. This is done using the P0 parameter. The meaning of this parameter is as
follows:
P0 byte
Function
0
Set value and store the new value in the
EEPROM
1
Set value, but do not alter the EEPROM
2
Read the value from the EEPROM
3
Read the actual value
Whenever a parameter is read, a data telegram of the same format as the command is sent back.
4.2 Motor Parameters
4.2.1 Current Limit ($10)
Set the absolute maximum current. This command is new on the Monopack 2. On the old Monopack, the absolute
maximum current could only be set using the MC0 and MC1 input. On the Monopack 2 this is also possible, but it
is now better to use this command. The absolute maximum motor current also depends on the setting of DIP
switch #8.
CMD
$10
P0
Parameter storage control (s. 4.1)
P1
Current limit
0: Selected by MC0 and MC1 inputs
1: 0.8A when DIP switch #8 is OFF and 4.15A when switch #8 is ON
2: 1.6A when DIP switch #8 is OFF and 5.0A when switch #8 is ON
3: 2.5A when DIP switch #8 is OFF and 5.7A when switch #8 if ON
4.2.2 Current Control ($11)
Set up the motor current control. The current is separately controlled for the standby phase (v=0), the acceleration
phase and the constant velocity phase. All three values with this command have a range of 0..255, where 255
means 100% of the selected absolute maximum current. Please see also section 4.2.1 for selecting the absolute
maximum current.
CMD
$11
P0
Parameter storage control (s. 4.1)
P1
Standby current (motor standing still) (0..255)
P2
Active current (motor rotating with constant velocity)
(0..255)
P3
Acceleration phase current (0..255)
Page 13

Monopack 2 Manual V1.04 13
Copyright © 2010, TRINAMIC Motion Control GmbH & Co. KG
4.2.3 Get Current Control Settings ($53)
Get the current control settings from the internal EEPROM (as set up using command $11).
CMD
$53
P0
0 Answer
CMD
$53
P0
0
P1
Standby current
P2
Active current
P3
Acceleration current
4.2.4 Frequency Range ($12)
Set the frequency range for all ramp operations. The following formula defines the microstep frequency. Fclk is the
clock frequency of the device, which is 16MHz.
f
clkstep
vff
15
2
CMD
$12
P0
Parameter storage control (s. 4.1)
P1
pre-divider value (f) (0..15)
4.2.5 Microstep Resolution, Waveform and Mixed Decay ($17)
This command allows setting the microstep resolution and the waveform which is used to generate the
microsteps.
The number of microsteps can either be set between 1 and 64 or to 65, 66 or 67. Setting it to 65, 66 or 67 results
in the following numbers of microsteps:
Parameter
Resolution
65
100.8
66
202.125
67
406.5
The second parameter controls the waveform. It is a sine wave when set to zero, a triangular wave when set to
-1.0 and a trapezoid wave when set to +1.0. Please note that the waveform can only be set when the microstep
resolution is set to a value between 1 and 64. If other microstep resolutions are used, the waveform parameter
will be ignored and a sine wave will be used.
CMD
$17
P0
Parameter storage control (s. 4.1)
P1
Microstep resolution (1..64 or 65, 66, 67)
P2
Waveform (-1..+1)*127 (signed byte)
(-127 (0x81) means –1.0, +127 (0x7F) means +1.0)
P5
0: Mixed Decay disabled
1: Mixed Decay enabled
The mixed decay setting especially at rotation velocities in the range of a few 10 steps per seconds to several 100
steps per second improves motor behavior (less resonance). However, the actual performance depends on the
motor and mechanics. For supply voltages above 24V and for low inductivity motors, best microstep behavior is
reached when mixed decay setting is continuously on.
Page 14

Monopack 2 Manual V1.04 14
Copyright © 2010, TRINAMIC Motion Control GmbH & Co. KG
The figure above shows differences in chopper cycles with fast and slow decay. Fast decay is better at high
velocities, while slow decay shows better performances at low velocities. With the mixed decay feature activated
the modes will be switched automatically for best motor performances. Mixed decay should be switched off in
standstill to avoid possible chirping noise.
4.3 Driving
4.3.1 About the Parameters
Driving is controlled by the bow, acceleration, velocity and pre-divider parameters. See section 4.2.4 for calculating
the step frequency for a given velocity. When driving linear ramps by using command $25 (s. 4.3.8), the microstep
acceleration rate can be calculated as follows:
f
clk
afa
224
2
2max
f
clk
is 16MHz
f is the pre-divider setting (s. 4.2.4)
amax is the acceleration setting (to be set up using command $14)
Command $23 (s. 4.3.7) uses S-shaped ramps. With these ramps, the bow parameter is used: a high bow value
increases the positioning speed, while a low bow value smoothens the acceleration ramp. The duration of the
bow phase can be calculated as follows (compare to the acceleration and velocity formula):
)2/(1max/256
15 f
clkbow
fbowat
Attention: The following limitations apply: Do not set the bow higher than about 20 times the acceleration, and
do not set the acceleration higher than about 20 times the minimum required velocity value.
4.3.2 Velocity and Maximum Acceleration ($14)
Set the acceleration and the maximum velocity.
CMD
$14
P0
Parameter storage control (s. 4.1)
P1,P2
Maximum Acceleration (1..8191) #
P3,P4
Maximum Velocity (1..8191) #
Page 15

Monopack 2 Manual V1.04 15
Copyright © 2010, TRINAMIC Motion Control GmbH & Co. KG
4.3.3 Bow Value ($63)
Set the bow value for the ramp generation. This value must not be set to zero.
CMD
$63
P0
Parameter storage control (s. 4.1)
P1,P2
Bow (1..8191)#
4.3.4 Get Acceleration and Velocity Settings ($52)
Get the acceleration and velocity settings from the internal EEPROM.
CMD
$52
P0
0
Answer
CMD
$52
P0 0 P1,P2
Maximum Acceleration #
P3,P4
Reference Search Velocity #
P5,P6
Maximum Velocity #
4.3.5 Get actual Position ($20)
Get the actual position of the motor.
CMD
$20
P0
0
Answer
CMD
$20
P0
0
P1 – P4
Actual position (signed 24 bit)#
4.3.6 Get actual Acceleration and Velocity ($21)
Get the actual acceleration and velocity of the motor and if a reference search is just being executed. Please note
that during a reference search or an automatic position correction, the returned acceleration and velocity values
are invalid.
CMD
$21
P0
0
Answer
CMD
$21
P0 0 P1,P2
Velocity (signed 12 bit)#
P3,P4
Acceleration (signed 12 bit)#
P5
0 – reference search not active
1 – reference search active (acc./vel. values are invalid!)
P6
0 – automatic correction not active
1 – automatic correction active (acc./vel. values are
invalid!)
Page 16

Monopack 2 Manual V1.04 16
Copyright © 2010, TRINAMIC Motion Control GmbH & Co. KG
4.3.7 Drive a Ramp ($23)
Drive an S-shaped ramp to the given position. The maximum acceleration, maximum velocity and bow settings (s.
4.3.1, 4.3.3) are used. If this command is given while a ramp is active, it will be queued and executed after the
currently active ramp has terminated.
CMD
$23
P0
0
P1 – P4
Position (32 bit signed long) # (-8388608..+16777215)
4.3.8 Constant Rotation ($25)
Constant rotation of the motor using the given velocity. The maximum acceleration setting (s. 4.3.1) is used to
accelerate or to decelerate the motor.
CMD
$25
P0
P1,P2
Velocity (-8191..8191)#
4.3.9 Reset Position ($27)
Set the position counter and the encoder counter to zero. If the PID controller is switched on you will have to
turn it off before using this command (s. 4.5.7, command $6F).
CMD
$27
P0
0
4.3.10 Soft Stop ($2A)
Terminate a ramp and stop the motor softly. The maximum acceleration (s. 4.3.1) parameter is used to decelerate
the motor.
CMD
$2A
P0
0
4.3.11 Emergency Stop ($2B)
Stop the motor immediately. This command has the same functionality as setting the external alarm input high.
CMD
$2B
P0
0
Page 17

Monopack 2 Manual V1.04 17
Copyright © 2010, TRINAMIC Motion Control GmbH & Co. KG
4.4 Stop and Reference Switches
4.4.1 Switch Mode ($54)
P2 defines if the reference switch is also used as an end switch. The switch must be connected to both the
reference input and to one stop switch input then (P3 defines if the left or the right stop switch input is used for
this purpose). If the reference switch is not used as a stop switch connect it to the reference input only.
P3 defines the direction of the calibration. Either the left or the right stop switch will be used for calibration
purposes.
P4 defines the movement mode. In circular mode, only the reference switch (connected to the reference input) is
used and the stop switch inputs are disabled. Also, P2 is ignored in circular mode. In linear mode, the end switch
inputs are enabled and P2 is used (please see also section 2.3.1).
P6 enables the travel check function together with command $59 (travel check tolerance, 4.4.5). In this function the
reference switch is also used as a travel check switch. If the travel check switch is found at a position out of the
travel check tolerance, the alarm output will be set high.
CMD
$54
P0
Parameter storage control (s. 4.1)
P1
0 Reserved; always set to zero
P2
0/1 0: separate reference and stop switches
1: stop switch also used as reference switch
P3
0/1 0: use left stop switch for calibration
1: use right stop switch for calibration
P4
0/1 0: circular movement 1: linear movement
P5
0 Reserved; always set to zero
P6
0/1 0:travel check disabled
1: use the reference switch also as a travel check switch (see also
4.4.5)
4.4.2 Deceleration at Stop Switches ($57)
Set the deceleration which is used to decelerate the velocity to zero when a stop switch is reached. If this value is
set to zero, a hard stop will be used (the motor stops abruptly when a stop switch is reached). If set to a value
other than zero, a soft stop will be used.
CMD
$57
P0
Parameter storage control (s. 4.1)
P1,P2
Deceleration (0..8191)#
4.4.3 Reference Search ($22)
This command starts a reference search. During the reference search also other commands can be given and they
are processed. Especially use the command $21 to see if the reference search has already finished. Any driving
command will abort the reference search.
Attention: The motor has to be connected correctly to make this command work correctly (s. 2.2)!
The behavior of the reference search depends on the switch mode setting (command $54, s. 4.4.1) and is as
follows:
Circular mode: The reference switch (connected to the reference switch input) is searched at first from one
and then form the other side. The zero position is then set to the middle of the reference switch.
Linear mode:
Reference switch is also end switch: A move into the reference switch and then out of the reference
switch is executed. The zero position is then set to the beginning of the switch.
Separate reference switch and end switch: First, the left or the right stop switch (as configured) is
searched. After that, the reference switch is searched at first from one, then from the other side. The
zero position is then set to the middle of the reference switch.
Page 18

Monopack 2 Manual V1.04 18
Copyright © 2010, TRINAMIC Motion Control GmbH & Co. KG
CMD
$22
P0
0
4.4.4 Reference Search Velocity ($16)
Set the velocity which is used for reference searches.
CMD
$16
P0
Parameter storage control (s. 4.1)
P1,P2
Velocity (1..8191) #
4.4.5 Travel Check Tolerance ($59)
Set the tolerance of the travel check (see also command $54, section 4.4.1). The travel checking can be enabled or
disabled using command $54. If the travel check (reference switch) is found out of the travel check tolerance the
alarm output will be set high.
CMD
$59
P0
Parameter storage control (s. 4.1)
P1
Tolerance
4.4.6 Number of Microsteps per Revolution ($15)
Set the number of microsteps per revolution. This is needed for travel checking in the circular movement mode.
The number of microsteps per revolution can be calculated from the number of full steps per revolution multiplied
by the number of microsteps set using command $17 (s. 4.2.5).
CMD
$15
P0
Parameter storage control (s. 4.1)
P1,P2,P3,P4
Microsteps per revolution (max. 16777215)#
4.4.7 Get the State of the Stop Switches ($30)
This command reads out the actual state of the stop and reference switch inputs of the Monopack.
CMD
$30
P0
0
Answer
CMD
$30
P0 0 P1
State of left stop switch input (0 or 1)
P2
State of right stop switch input (0 or 1)
P3
State of reference switch input (0 or 1)
Page 19

Monopack 2 Manual V1.04 19
Copyright © 2010, TRINAMIC Motion Control GmbH & Co. KG
4.5 Incremental Encoder
4.5.1 About Incremental Encoders
Using an incremental encoder allows exact position control, as it feeds back the steps of the motor into the
Monopack. The Monopack can then detect deviations and can also try to correct such deviations automatically (see
sections 4.5.5 and 4.5.6). If this does not solve the problems, a PID controller can also be used for highly exact
positioning, but the deviation detection and the automatic position correction after a deviation has occurred are
much easier to use than the PID controller.
The resolution of the encoder (pulses per revolution) must match the resolution of the motor to make deviation
detection and automatic position correction function correctly. If the resolutions do not match, they can be
adapted by changing one or more of the following parameters:
Microstep resolution: This parameter changes the resolution of the motor and can be set using
command $17 (see section 4.2.5).
Encoder pre-divider: This can be used if the resolution of the encoder is higher than the resolution of
the motor. When for example the pre-divider is set to 4, only every 4th pulse of the encoder will be
used to increment or decrement the encoder counter register.
Encoder multiplier: This can be used if the resolution of the encoder is lower than the resolution of
the motor. When for example the multiplier is set to 5, every encoder pulse will increment or
decrement the encoder counter register by 5.
The encoder pre-divider and multiplier are set up using command $70. To find the right combination of the
parameters you can just let the motor run for example 10000 steps (using command $23 (s. 4.3.7), with deviation
detection and automatic position correction switched off) and then watch the encoder counter register (using
command $71). Before doing that, use command $27 (s. 4.3.9) to set all position registers to zero.
4.5.2 Encoder Configuration ($70)
Configure the behavior of the incremental encoder input.
CMD
$70
P0
Parameter storage control (s. 4.1)
P1
Encoder configuration. See the table below for an
explanation of the configuration bits.
P2
Encoder pre-divider (0..255)
P3,P4
Maximum deviation between ramp position and
encoder position counter (11 Bit unsigned #)
P5
Encoder multiplier (0..255). (Available since
firmware version 2.09.)
Explanation of the encoder configuration bits:
Bit
Description
0
Polarity of the encoder N input (1=positive, 0=negative)
1
The next N signal clears the encoder counter register when
set 2 Reserved. Always set to zero.
3
Reserved. Always set to zero.
4
Set this bit to copy the actual ramp position to the encoder
counter register. The bit will be reset automatically.
5
Reserved. Always set to zero.
6
Direction of the encoder signals. 1: A->B, 0: B->A
Page 20

Monopack 2 Manual V1.04 20
Copyright © 2010, TRINAMIC Motion Control GmbH & Co. KG
4.5.3 Encoder Counter ($71)
Get the value of the incremental encoder counter register.
CMD
$71
Answer
CMD
$71
P1
0
P2,P3,P4
Encoder counter value (signed 24 bit #)
4.5.4 Encoder Holding Register ($72)
This command has been removed in version 2.09 of the Monopack firmware.
4.5.5 Deviation Alarm ($73)
Enables or disables the deviation alarm. This alarm occurs when the maximum deviation is exceeded. The alarm
output will then be set high. Set the maximum deviation using command $70. The motor can also be stopped
immediately or softly when the alarm occurs. Furthermore, the automatic position correction (see 4.5.6) can be
started n/200 sec (n=1..65535) after a deviation has been detected. In this case, the alarm output will only be set
when the maximum number of retries for automatic position correction has been exceeded. The maximum
deviation has to be set up using command $70 (s. 4.5.1) first. The automatic position correction has to be set up
using command $58 (s. 4.5.6).
CMD
$73
P0
Parameter storage control (s. 4.1)
P1
0: disable deviation alarm
1: enable deviation alarm
P2
0: do not stop when deviation alarm occurs
1: soft stop when deviation alarm occurs
2: hard stop when deviation alarm occurs
P3,P4
0: no automatic position correction after
deviation
1-65535: start automatic position correction n/200
sec after a deviation has been detected (available
since firmware V2.09)
4.5.6 Configure Automatic Position Correction ($58)
Configure if an automatic position correction shall be done at the end of each ramp or when a deviation has been
detected. Automatic position correction can only be used in conjunction with an incremental encoder which has to
be configured correctly first.
When this function is turned on, the Monopack checks if the position counter of the incremental encoder matches
the desired end position at the end of every ramp (since firmware V2.09, the tolerance value defines a tolerance
window around the end position). If this is not the case, the Monopack will try to correct the position of the
motor using the reference search velocity. The maximum number of retries after each ramp can also be configured.
The alarm output will be set high and the position correction will be aborted if this number is exceeded.
This function is an easy to use alternative to the PID controller.
CMD
$58
P0
Parameter storage control (s. 4.1)
P1
0: automatic correction turned off
1-255: maximum number of retries for position
correction after each ramp.
P3,P4
end position tolerance (16 bit unsigned #)
(available since firmware V2.09)
Page 21

Monopack 2 Manual V1.04 21
Copyright © 2010, TRINAMIC Motion Control GmbH & Co. KG
4.5.7 PID Controller Configuration ($6A, $6B, $6C, $6D, $6F)
The following commands ($6A, $6B, $6C, $6D, $6F) are to be used for setting up the PID controller configuration
registers of the TMC453. Please see the TMC453 manual for further explanation of the PID controller registers.
CMD
$6A
P0
Parameter storage control (s. 4.1)
P1,P2
Pid_control register
P3,P4
Pid_vcalc_factor register
CMD
$6B
P0
Parameter storage control (s. 4.1)
P1
Pid_pcof register
P2
Pid_p_range register
P3
Pid_icof register
P4
Pid_i_range register
P5
Pid_dcof register
P6
Pid_d_range register
CMD
$6C
P0
Parameter storage control (s. 4.1)
P1
Pid_clip_p register
P2
Pid_clip_i register
P3
Pid_clip_d register
CMD
$6D
P0
Parameter storage control (s. 4.1)
P1
Pid_clip_int_sum register
P2
Pid_clip_int_input register
P3,P4
Pid_clip_sum register
CMD
$6F
P0
0
P1
0:turn off the PID controller
1:turn on the PID controller
Page 22

Monopack 2 Manual V1.04 22
Copyright © 2010, TRINAMIC Motion Control GmbH & Co. KG
4.6 Alarms and Errors
4.6.1 Alarm Mode ($51)
Set up the alarm mode. The alarm mode determines if the motor is to be powered off when an external alarm
(alarm input set high) or a driver error occurs. The motor can be powered on again by resetting the alarm using
command $74 (s. 4.6.2).
CMD
$51
P0
Parameter storage control (s. 4.1)
P1
0: only stop motor in case of external alarm
1: stop and power off in case of external alarm
P2
0: do not stop motor in case of driver error
1: stop and power off in case of driver error
4.6.2 Reset Alarm Output ($74)
Reset the alarm output and return the alarm reason as answer.
CMD
$74
P0
0
Answer
CMD
$74
P0
0
P1
Driver error (0=no/1=yes) (short circuit, overload, etc.)
P2
Deviation error (0=no/1=yes) (s. 4.5.5)
P3
External alarm input (0=no/1=yes)
P4
Travel check tolerance error (0=no/1=yes) (s. 4.4.5)
P5
Position correction error (0=no/1=yes) (s. 4.5.6)
4.7 Other Settings
4.7.1 Enter Step/Direction Mode ($50)
This command can be used to switch the Monopack back to step-/direction mode (e.g. after changing parameters
or resetting an alarm).
CMD
$50
P0
0
P1
0: step/direction mode
1: command mode (any other command will also
switch to command mode)
4.7.2 Set CAN receive ID and RS485 ID ($55)
Set the CAN identifier which will be used for receiving data from the CAN bus and the RS485 address. Please note
that the LSN of the CAN receive ID and the LSN of the RS485 address are set by the hexadecimal switch and not by
command. Please see also section 3.2.2 and 2.8.
CMD
$55
P0
Parameter storage control (s. 4.1)
P1 – P4
32 bit unsigned long ID # (only 11 bits are used)
Page 23

Monopack 2 Manual V1.04 23
Copyright © 2010, TRINAMIC Motion Control GmbH & Co. KG
4.7.3 Set CAN send ID ($56)
Set the CAN identifier which will be used for sending data on the CAN bus. Please see also section 3.2.2 and 2.8.
CMD
$56
P0
Parameter storage control (s. 4.1)
P1-P4
32 bit unsigned long ID # (only 11 bits are used)
4.7.4 Set CAN Baud Rate ($C0)
Change the baud rate of the CAN interface. After executing this command, a hardware reset is required to make
the change take effect.
CMD
$C0
P0
0
P1
1: 125 kBit/s
2: 250 kBit/s
3: 500 kBit/s
4: 1 Mbit/s
4.7.5 Get Version Number ($43)
Get the firmware version number and the reset flag. The reset flag is 1 if a reset occurred before the last $43
command was given.
CMD
$43
P0
0
Answer
CMD
$43
P0
Firmware revision (decimal 203 means V2.03)
P1
Reset Flag: 1 after a reset
P2
Not used
P3, P4
Temperature (16 bit #) (units: TBD)
On the old Monopack this command also returned the serial number of the device. This is no longer supported on
the Monopack 2. Instead, the Monopack 2 returns the actual temperature of the device.
4.7.6 Hardware Reset ($CC)
Reset the microcontroller of the MONOPACK so that all parameters are re-read from the EEPROM. This command
can be used to make parameter changes which need a hardware reset take effect.
CMD
$CC
P0
0
4.8 Factory Default Settings ($DD)
Set all parameters which are stored in the EEPROM (including the CAN and RS485 addresses and the CAN baud
rate) to their factory default settings. After executing this command, a hardware reset has to be issued to make all
the changes take effect.
CMD
$DD
P0
0
P1
Must be $31
P2
Must be $41
Page 24

Monopack 2 Manual V1.04 24
Copyright © 2010, TRINAMIC Motion Control GmbH & Co. KG
5 Monopack LT Command Reference
When the DIP switch #5 is in its “ON” position, the ASCII command set of the former Monopack LT will be used.
This chapter provides a reference of the Monopack LT command set. The commands can simply be entered using a
terminal program, for example HyperTerminal.
5.1 Interface selection
In LT mode, the Monopack 2 can either communicate via RS232 or via RS485 interface. The default interface is the
RS232 interface. To use the RS485 interface it must be selected by using the Y command. This setting can then be
stored in the EEPROM to make it the default setting after next power-on.
5.2 Command overview
The table given here is an overview of all possible commands. Every command is described in detail in the
following sections. Commands without parameters do not need to be terminated by a CR. They are executed as
soon as they are entered. Commands with parameters must be terminated with a CR. The value must follow the
command letter without any additional spaces. The command will be executed as soon as the CR has been sent.
Some commands also send back one or more messages. Each message is terminated by a CR and LF.
Command
Short description
See section
A<value>
Set acceleration (<value>=1..8191)
5.2.3
B<value>
Set bow (<value>=1..8191)
5.2.4
C<value>
Select Step/Direction mode (<value>= 0 or 2)
5.2.25
D
Driver with constant velocity
5.2.7
d
Display voltage and temperature
5.2.26
E
Enable / disable EEPROM
5.2.28
F
Set operating frequency range
5.2.1
f
Query FIFO filling
5.2.24
G
Automatic reference search
5.2.17
H
Soft stop
5.2.8
I
Set standby current
5.2.13
J
Set constant speed current
5.2.14
K
Set acceleration current
5.2.15
M<value>
Set stop switch mode (<value>=0..2)
5.2.19
N
Find reference switch closing position
5.2.18
O
Find reference switch opening position
5.2.18
P<value>
Change position counter
5.2.20
p
Query actual position
5.2.21
Q
Mixed decay setting
5.2.16
R
Relative move
5.2.12
S
Set target position, relative distance or reference switch offset
5.2.10
s
Query stop and reference switches
5.2.23
T
Move to target position
5.2.11
U<value>
Set microstep resolution
5.2.2
V<value>
Set velocity (<value>=1..8191)
5.2.5
v
Query actual velocity
5.2.22
W
Write settings to EEPROM
5.2.27
X
Hard stop
5.2.9
Y<value>
Choose interface and set RS485 delay (<value>=0..9)
5.2.29
Z<value>
Set RS485 address (<value>=33..255)
5.2.30
+
Set direction CW
5.2.6
-
Set direction CCW
5.2.6
Page 25

Monopack 2 Manual V1.04 25
Copyright © 2010, TRINAMIC Motion Control GmbH & Co. KG
5.2.1 Set the pre-divider
Command: F<value>
The command “F” sets the pre-divider and thus the operation frequency range of the motor. It must be followed
by a value between 0 and 15. This command can only be used when the motor is standing!
Example: F9 sets the pre-divider to 9.
5.2.2 Set microstep resolution
Command: U<value>
The “U” command sets the microstep resolution. It must be followed by the value 0, 1, 2 or 3, where 0 means 25
microsteps, 1 means 50 microsteps, 2 means 32 microsteps and 3 means 64 microsteps. Do not use this command
while the motor is moving!
Example: U3 sets the microstep resolution to 64 microsteps.
5.2.3 Acceleration setting
Command: A<value>
The command “A” sets the acceleration and deceleration of the motor. It must be followed by a value between 1
and 8191. Do not set this value to 0.
Please see section 4.3.1 for the calculation of the actual motor acceleration and bow setting.
Example: A250 sets the acceleration to 250.
5.2.4 Bow setting
Command: B<value>
This command sets the bow value of the S-shaped ramp. It must be followed by a vlaue between 1 and 8191. Do
not set this value to 0.
Example: B10 sets the bow value to 10.
5.2.5 Velocity setting
Command: V<value>
The command “V” sets the maximum velocity of the motor. It must be followed by a value between 1 and 8191.
Please see section 4.2.4 for the calculation of the actual motor velocity.
Example: V2000 sets the velocity to 2000.
Attention: The Monopack 2 uses a higher clock frequency than the Monopack LT. Thus the velocity and
acceleration settings do not give identical results. To be compatible with the settings required by the
Monopack LT, please multiply your velocity and acceleration settings by 0.691.
5.2.6 Direction setting
Command: + or –
The commands “+” and “-“ select the direction in which the motor will be running. Entering “+” selects clockwise
rotation (the position counter will be incremented when the motor is moving), and entering “-“ selects counter
clockwise rotation (the position counter will be decremented when the motor is moving).
5.2.7 Drive with fixed velocity
Command: D
The command “D” accelerates (or decelerates) the motor to the velocity that has been set by a previous “V”
command. After the command has been sent, the message “<v_old> to <v_new>” will be sent back, where
“v_old” is replaced by the actual velocity value and “v_new” by the new velocity value.
5.2.8 Soft stop
Command: H
Page 26

Monopack 2 Manual V1.04 26
Copyright © 2010, TRINAMIC Motion Control GmbH & Co. KG
This command stops the motor. The acceleration value that has been set by a previous “A” command will be used
for the deceleration ramp. The message “<v_act> to 0” (with <v_act> replaced by the actual velocity) will be
sent back after the command has been entered.
5.2.9 Hard stop
Command: X
Entering the “X” command stops the motor immediately, without any deceleration ramp. The message “Motor
stop” will be sent back after the command has been entered. Be careful when driving at high speeds as a hard
stop can cause a voltage overshoot on the power supply then.
5.2.10 Set target position or relative distance
Command: S<value>
The command “S” is used to set the target position for the “T” command or the relative distance for the “R”
command. It must be followed by a value between –8388608 and 16777215.
Example: S50000
5.2.11 Drive to target position
Command: T
After entering the command “T” the motor drives to the target position that has been set by the last “S” command,
using the velocity, acceleration, bow and direction that have been set by the last commands. Please be sure that
you have set the direction appropriately, i.e. when the actual position is lower than the new position the direction
should be set to “+”, and when the actual position is higher than the target position the direction should be set to
“-“. Otherwise the motor will run until the position counter wraps around.
The Monopack 2 sends back the message “to <pos_targ>” (with <pos_targ> = target position) after the
command has been entered.
The motor must be standing before this command is entered.
5.2.12 Relative move
Command: R
This command makes the motor drive a number of microsteps into the actual direction. The number of microsteps
to drive can be set using the “S” command, and the direction can be set using the “+” or “-“ command.
Acceleration, velocity and bow can also be set by the appropriate commands.
After entering this command the message “<pos_act> to <pos_targ>” (with <pos_act> = actual position and
<pos_targ> = new position) will be sent back.
The motor must be standing before this command is entered.
5.2.13 Set motor standby current
Command: I<value>
This command sets the maximum motor current that is used when the motor is standing. It must be followed by
a value between 0 and 255, where 0 means 0% and 255 means 100% of the absolute maximum current (2.5A when
DIP switch #8 is off, 5.7A when DIP switch #8 is on).
5.2.14 Set motor run current
Command: K<value>
The “K” command sets the motor current that is used when the motor is running at constant velocity. It must be
followed by a value between 0 and 255, where 0 means 0% and 255 means 100% of the absolute maximum
current (2.5A when DIP switch #8 is off, 5.7A when DIP switch #8 is on).
5.2.15 Set motor acceleration current
Command: J<value>
The “J” command sets the motor current that is used when the motor is accelerating or decelerating. It must be
followed by a value between 0 and 255, where 0 means 0% and 255 means 100% of the absolute maximum
current (2.5A when DIP switch #8 is off, 5.7A when DIP switch #8 is on).
Page 27

Monopack 2 Manual V1.04 27
Copyright © 2010, TRINAMIC Motion Control GmbH & Co. KG
5.2.16 Set mixed decay mode
Command: Q0 or Q1
The command “Q” command turns mixed decay on or off. Q0 turns off mixed decay, and Q1 turns on mixed decay.
This command is new on the Monopack 2.
5.2.17 Automatic reference search
Command: G
Entering this command starts an automatic reference search. A reference point offset can be specified by a
previous “S” command (use “S0” for no reference point offset). The reference switch must be connected between
the reference switch input and ground as a normally closed switch. During the reference search, the following
messages will be sent back:
“>0 to <v>” right after the command has been entered (with <v>= maximum velocity).
“>n=<pos_1>” when the reference switch is open (where <pos_1> is the microstep position where the
switch opened).
“<v> to <-v>” when the motor turns back into the opposite direction (with <v>= maximum velocity).
“>n=<pos_2>” when the switch is closed again (where <pos_2> is the microstep position where the
switch closed).
“<-v> to 0” when the motor being decelerated.
“>OK” at the end of the automatic reference search.
The velocity, bow, acceleration and direction can be set by the appropriate commands (V, B, A, +, -) before starting
the reference search.
5.2.18 Find reference switch position
Commands: N and O
These two commands can be used to find the reference switch manually. Normally there is no need to use them,
instead use the “G” command.
Entering the “N” command makes the motor run. When the switch gets closed, the microstep position of this point
will be sent back (message “n= <position>”). The motor will not be stopped automatically (use the “H” or “X”
command to do this).
Entering the “O” command also makes the motor run. When the switch gets opened, the microstep position of this
point will be sent back (message “n= <position>”). The motor will not be stopped automatically (use the “H” or
“X” command to do this).
5.2.19 Set stop switch mode
Command: M<value>
This command sets the stop switch mode. The value can be one of the following numbers:
0 for no stop switches.
1 for hard stop when a stop switch opens.
2 for soft stop if the motor is in velocity mode (“D” command) and hard stop if the motor is in positioning
mode (“T” or “R” command) when the stop switch opens.
Example: M2
5.2.20 Change actual position
Command: P<value>
This command changes the actual position, without moving the motor. It must be followed by a value between 8388608 and 16777215. The motor must be standing before using this command.
Example: P-50000
5.2.21 Query actual position
Command: p
After entering this command the actual position will be sent back as a message of the form “p=<position>”,
where <position> is the actual position of the motor.
Page 28

Monopack 2 Manual V1.04 28
Copyright © 2010, TRINAMIC Motion Control GmbH & Co. KG
5.2.22 Query actual velocity
Command: v
The “v” command queries the actual velocity and sends this value back. The velocity is sent back in the form
“v=<velocity>”, where <velocity> is the actual velocity of the motor.
5.2.23 Query status of stop switches
Command: s
The “s” command queries the actual status of the stop switches and the reference switch. The status is sent back
in the form “s=<value>”, where bit 0 represents the status of the left stop switch, bit 1 represents the status of
the right stop switch and bit 2 represents the status of the reference switch.
5.2.24 Query TMC453 FIFO filling
Command: f
This command queries the actual number of entries in the TMC453 command FIFO.
5.2.25 Step/Direction mode selection
Command: C0 or C2
Entering the command “C0” selects the normal command mode, and entering “C2” selects the step/direction mode.
5.2.26 Display actual ADC values
Command: d
Entering the command “d” displays the actual ADC values that represent the actual temperature in the pack and
the actual supply voltage. After the command has been sent, the message “TEMP = <t> VOLT = <v>” will be
sent back.
5.2.27 Write all parameters to the EEPROM
Command: W
After this command has been entered all parameters are stored in the EEPROM of the Monopack 2. When the
EEPROM is enabled these values will be used as the power on default values. The message “Write EE” will be
sent back to confirm that the parameters have been stored. Do not use this command too often, as writing to the
EEPROM more than 100000 times may damage the EEPROM.
5.2.28 Enable or disable the EEPROM
Command: E
This command enables or disables the parameters that are stored in the EEPROM. After the EEPROM has been
enabled, the message “Enable EE” will be sent. When the EEPROM has been disabled, the message “Disable
EE” will be sent.
If the EEPROM is enabled all parameter values that are stored in the EEPROM will be used as default values at
power on. If the EEPROM is disabled the factory default values will be used at power on.
5.2.29 Choose interface and set RS485 delay
Command: Y<value>
The interface that is to be used and also the RS485 delay can be set by the “Y” command. This command must be
followed by a value between 0 and 9. The values have the following meanings:
Value
Meaning
0
Use RS232 interface, normal mode (default setting)
1
Use RS232 interface without echo
2..9
Use RS485 interface, where 2 means minimum delay and
9 means maximum delay.
Page 29

Monopack 2 Manual V1.04 29
Copyright © 2010, TRINAMIC Motion Control GmbH & Co. KG
So if the RS485 interface is to be used, first enter a Y9 command in an RS232 session and then store this setting
to the EEPROM using the “W” command and enable the EEPROM using the “E” command. After cycling the power
the Monopack 2 is in RS485 mode. Now try to use an Y command with a value lower than 9 to make RS485 faster.
5.2.30 Set the RS485 address
Command: Z<value>
The RS485 address of the Monopack 2 can be set using the “Z” command. This command must be followed by a
value between 33 and 255 which is the ASCII code of the RS485 address letter to be used. The address setting
must be stored in the EEPROM using the “W” command.
5.3 Help screen
Entering the command “?” shows a help screen. This help screen displays all possible commands and the values of
all possible settings. It also show the actual settings of all values.
5.4 Messages sent by the device
When using the RS232 interface the Monopack 2 after power on firsts sends a message containing the firmware
revision. With the Monopack 2 this is at least V1.3 (the old Monopack LT had firmware revision 1.2).
Monopack Lite V1.3 (C) TRINAMIC Motion Control GmbH & Co KG 2005
In certain error conditions the Monopack 2 also sends a message:
Overload! The current is too high (possible short circuit of the outputs).
Overtemperature! The temperature in the pack is too high.
Undervoltage! The supply voltage is too low (below 12V).
Page 30

Monopack 2 Manual V1.04 30
Copyright © 2010, TRINAMIC Motion Control GmbH & Co. KG
6 The Monopack PC Software
The Monopack PC software is provided to explore and configure the Monopack using its RS485 interface. To use
this software, an RS485 adapter is needed to connect the Monopack to a RS232 (COM) port of a PC. The PC
software uses the RTS line of the PC’s RS232 port to control the data direction of the RS485 adapter. The software
needs at least Windows 95 or a later version to run. To install the software, just copy the file “MonoControl.exe”
from the Monopack software disk to the hard disk of your PC. Simply double click the “MonoControl.exe” file to run
the program.
6.1 Using the Program
After starting the program, its main window
(Figure 6.1) is displayed. First, select the
interface the Monopack is connected to in the
“Interface” section and enter its RS485 address
in the “Unit Address” section. Then click the
“Open” button to open the connection.
All Monopack commands described in this
manual can be found on the “Parameters (1)”,
“Parameters (2)”, “PID”, “Get” and “Other” pages.
To use a command, first click on the appropriate
radio button in the “Command” section. With
Parameter and PID commands, select if the
values are to be changed or to be read out in
the “Modifier” section. Then, fill in the necessary
parameters in the “Parameter” section and after
that, click the “Send Command” button in the
“Command Bytes” section. The command will
then be sent to the Monopack. The command
and its parameter bytes are also displayed in
the “Command Bytes” section of the main
window.
For commands which send back an answer, the
answer is displayed in the corresponding
“Parameter” or “Last Answer” section.
Figure 6.1: The Monopack PC Software
6.2 Firmware update / Reset to factory default
To update the Monopack2 to the actual firmware follow following procedure:
1. Switch off the Monopack and connect it to PC
2. Set DIP-Switch 6 to ON, refer to 2.1
3. Energize Monopack2
4. Start program MONOpack2.exe and press “Update Firmware” in tab MPII
5. Update: Start the update by selecting the new firmware file “MPII-V___.hex”
a. If the update process is interrupted start again (the bootloader is not overwritten)
Reset: Reset the module by clicking “Clear EEPROM”.
6. When the update / reset process is successful switch off the MONOpack2 and set back DIP-Switch 6.
7. The Monopack2 is ready to use.
Note: The program MONOpack2.exe can be found at TechLibCD and at www.trinamic.com, where the newest
firmware version is also provided.
Page 31

Monopack 2 Manual V1.04 31
Copyright © 2010, TRINAMIC Motion Control GmbH & Co. KG
7 Application Notes
7.1 Making a simple RS232 to RS485 Converter
The following drawing shows how to make a simple passive RS232 to RS485 converter. Please note that this
simple converter is not intended for use with long cables or more than one Monopack connected to it. It is only
provided for testing purposes. It might not work with some notebook computers. It also does not work with
Windows 95, Windows 98 or Windows ME.
Please also note that just for controlling a single Monopack 2 with a PC, an RS485 is no longer needed. Instead,
the RS232 interface of the Monopack 2 can be used to connect it directly to the RS232 interface of a PC.
1N4148
LED red
BC547B
1N4148
470R
TxD
RxD
RTS (+=send)
GND
1k
1k
RS485 -
RS485+
GND
2
3
5
7 15
1
14
RS232 RS485Converter (passive)
Figure 7.1: A simple passive RS232 to RS485 converter
The RS485 data direction of this simple converter is controlled by the RTS signal of the PC’s RS232 interface. The
pin numbers on the RS232 side are for use with a 9 pin Sub-D plug. The pin numbers on the RS485 side are the
appropriate pin numbers of the Monopack 25 pin Sub-D socket.
7.2 Setting the Maximum Current
On the old Monopack it was necessary to set the maximum current by hardware, as shown in Figure 2.1. As
mentioned in chapter 4.2.1, this is no longer necessary with the Monopack 2 (but still possible). The maximum
current can now be controlled by software.
AlarmOut- (Pin 8)
AlarmOut+ (Pin 9)
MC0+ (Pin 11)
MC1+ (Pin 23)
GND (Pin 1)
MC0- (Pin 10)
MC1- (Pin 22)
1N4148 or similar
Figure 7.2: Setting the MC0/1 inputs to 1 (possible, but no longer necessary)
This circuit will set both MC inputs to 1. The pin numbers given in the drawing are the pin numbers of the 25-pin
Sub-D socket. Leave out the connections to MC1+ and MC1- if only MC0 is to be set to 1. However, with the
Monopack 2 this setting is not necessary any more, since a software setting is also possible.
Page 32

Monopack 2 Manual V1.04 32
Copyright © 2010, TRINAMIC Motion Control GmbH & Co. KG
7.3 Using the “ic485-I” RS232 to RS485 Converter
The “ic485-lp-1f” RS232 to RS485 converter is an easy to use RS485 converter which can be powered either by the
RS232 interface of the PC or by an external power supply. The data direction can be controlled by the RTS line of
the PC’s RS232 interface. To use this converter, connect it and set up its switches as shown in Figure 7.3. Connect
it to the PC using a standard RS232 cable (not a null modem cable) and a 9-to-25-pin adapter.
4 3 2 1
14
15
(Monopack 25-pin
Sub-D socket)
T-RTS
R-ON
T-RTS
R-/RTS
T-ON/R-ON
DCE
SIM
DTE
MON
Converter
To PC (RS232)
Figure 7.3: Connecting the RS485 converter
The converter can be ordered at Conrad Elektronik, Order No. 981290-80.
7.4 Choosing Plugs for the Monopack
Normally, the Monopack is shipped with all plugs needed. These plugs are manufactured by Weidmüller, Phoenix,
Ria and Wieland. Spare plugs can for example be ordered at RS Components (www.rs-components.com) with the
following order numbers:
Plug
RS Components Order Number
2-way (Weidmüller)
403-875
4-way (Weidmüller)
403-897
5-way (Weidmüller)
209-7040
Page 33

Monopack 2 Manual V1.04 33
Copyright © 2010, TRINAMIC Motion Control GmbH & Co. KG
8 Declaration of Conformity
Declaration of Conformity
for
MONOpack 2
1-Axis stepper motor controller / driver with encoder interface
Manufacturer
TRINAMIC Motion Control GmbH & Co. KG
Sternstraße 67
D – 20357 Hamburg
Germany
www.trinamic.com
Statement of Conformity
Based on test results using applicable standards, the product is CE compliant and meets the European and national
guidelines.
Sample tests have been accomplished by an accredited test labor (EMV Services GmbH & Co. KG, Schloßstraße 6-12,
D-21079 Hamburg, Germany).
Applied Standards:
EN 61000-6-4 (2002) Generic emission standard; part 2: industrial environment
EN 61000-6-2 (2002) Generic immunity standard; part 2: industrial environment
EN 61000-4-2 (2001) Immunity of electrostatic discharge
EN 61000-4-3 (2003) Immunity of radiated, radio frequency electromagnetic field
EN 61000-4-6 (2003) Immunity of conducted disturbances, induced by radio frequency fields
This conformity is indicated by the symbol , i.e. "Conformité Européenne".
Page 34

Monopack 2 Manual V1.04 34
Copyright © 2010, TRINAMIC Motion Control GmbH & Co. KG
 Loading...
Loading...