
PCMCIA
Fax Modem 56K
User Manual

FCC REGULATORY STATEMENTS
FCC Part 68 Registration
This device complies with FCC Part 68 rules, and the use of this
device is subject to the following restrictions:
The FCC has established rules which permit this device to be
directly connected to the telephone network. Standardized jacks
are used for these connections. This equipment should not be used
on party lines or coin phones.
If this device is malfunctioning, it may also be causing harm to
the telephone network; this device should be disconnected until
the source of the problem can be determined and until repair has
been made. If this is not done, the telephone company may
temporarily disconnect service.
The telephone company may make changes in it's facilities,
equipment, operation and procedures; if such changes affect the
compatibility or use of this device, the telephone company is
required to give adequate notice of the situation with the FCC.
If the telephone company requests information on what equipment
is connected to their lines, inform them of:
a. The telephone number to which this unit is connected.
b. The Ringer Equivalence Number (REN).
c. The USOC jack required.
d. The FCC Registration number.
Items (b) and (d) are indicated on the label. The Ringer
Equivalence Number (REN) is used to determine how many
devices can be connected to your telephone line. In most areas, the
sum of the REN's of all the devices on any one line should not
exceed 5.0. If too many devices are attached, they may not ring
properly.
FCC Part 15 Registration
This device complies with Part 15 of FCC rules. Operation is
subject to the following two conditions:
1. This device may not cause harmful interface, and
2. This device must accept any interface received including
interface that may cause undesired operation.
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the
limits for a Class B digital device, pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC
Rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection
against harmful interference in a residential installation. This
equipment generates, uses and can radiate radio frequency energy,

and if not installed and used in accordance with the instructions,
may cause harmful interference to radio communications.
However, there is no guarantee that interference will not occur in a
particular installation. If this equipment does cause harmful
interference to radio or television reception, which can be
determined by turning off and on, the user is encouraged to try to
correct the interference by one or more of the following measures:
(1) Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
(2) Increase the distance between the equipment and receiver.
(3) Connect the equipment into an outlet on a circuit
different from that to which the receiver is connected.
(4) Consult an experienced radio/TV technician for help.
CTR 21 pan-European Certification
This equipment has been approved in accordance with Council
Decision 98/482/EC for pan-European single terminal connection
to the public switched telephone network (PSTN). However, due
to differences between the individual PSTNs provided in different
countries, the approval does not, of itself, give an unconditional
assurance of successful operation on every PSTN network
termination point. In the event of problems, you should contact
your equipment supplier in the first instance.
This device is designed to work with the notified networks in all
EC member states. Nevertheless, some of the network services in
invidual countries might not be supported, but they will not affect
the normal data and fax applications. For example, the metering
charge service in Germany. Besides you may encounter difficulty
of using PULSE dialing function in some of the countries, such as
Nordic countries. This kind of network compatibility is dependent
on the physical and software settings of this device. If the users
are desired to use this device on those networks, they should
contact the vendor or supplier first.

INTRODUCTION
This PCMCIA Fax Modem 56K is a credit-card-size
Type II PC card that complies with the PCMCIA 2.1
standards.
The PCMCIA Fax Modem 56K is Bell, ITU-T
(formerly CCITT) compliant and Hayes AT
command compatible, so that it can be used
worldwide with today’s popular communication
software programs. You will be able to send and
receive faxes to/from any Group 3 compatible fax
machine. Using standard phone lines, the data
communication functions of the modem will enable
you to successfully hook up to the Internet, transmit
E-mail, send and receive information and
communicate with other PCs, Bulletin Board Services
(BBS) or computer networks such as Compuserve
Specifications
Data
:
K56flex, V.90, V.34bis, V.34, V.32bis, V.32,
V.22bis, V.22, and V.21, Bell 212A and Bell
103
Fax
:
V.17, V.29, V.27ter, and V.21 channel 2
Group 3 send and receive facsimile
Error Correction
V.42 and MNP 2-4
Data Compression
V.42bis and MNP 5
Communication software compatible commands
Hayes compatible enhanced "AT" command
set
:
:
:
- 1 -

Fax Service Class 1 commands
Built-in DTE interface
:
DTE speed up to 115,200 bps
16C550 UART interface
System Requirements
A notebook or desktop computer with PCMCIA
type II or III slot.
A telephone line with RJ-11 jack.
A CD-ROM drive.
Windows 95/98/2000/Millennium or Windows
NT pre-installed.
- 2 -
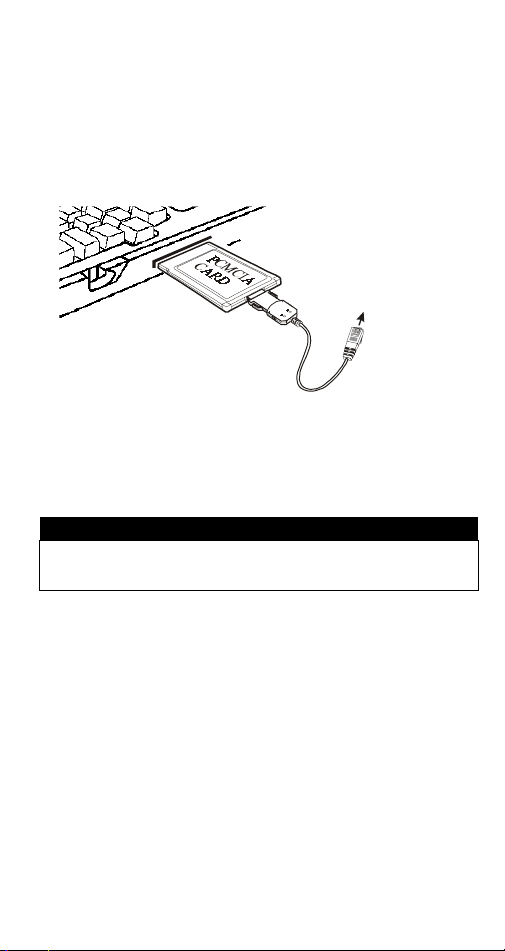
HARDWARE INSTALLATION
1. Locate the PCMCIA slot of your system.
2. Align the PCMCIA FAX MODEM 56K PC Card
toward the PCMCIA slot. Push evenly and
steadily until it is seated.
Notebook
Connects to RJ-11 phone jack
3. Connect the other end of the PC Card cable to
the telephone line outlet.
4. You are now ready to continue the software
installation.
CAUTION
To reduce the risk of fire, use only No. 26 AWG
or larger telecommunication line cord.
1. For Windows NT does not support
“Hot Insert/Remove”, be sure to
complete the hardware installation as
described above before you start
Windows NT and software
installation.
- 3 -
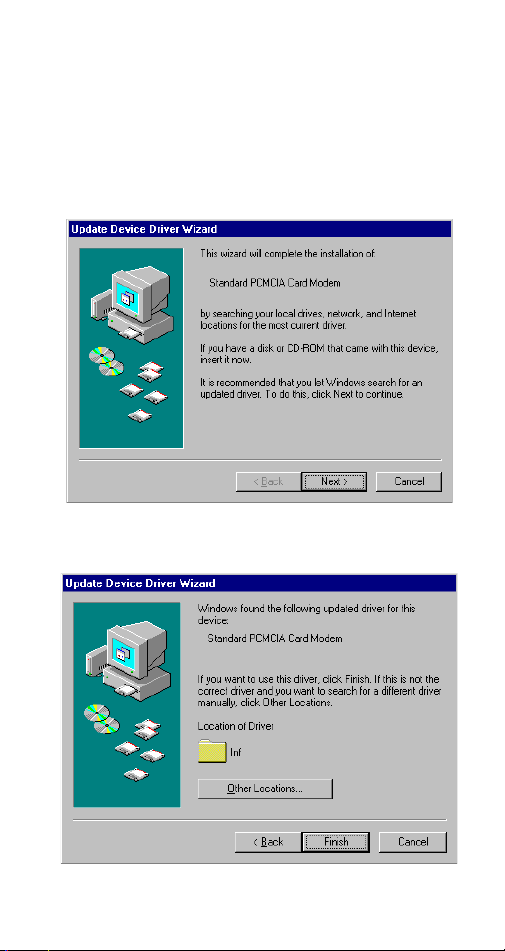
SOFTWARE INSTALLATION
Installation for Windows 95
1. As soon as the PCMCIA Fax Modem 56K PC is
inserted into the PCMCIA slot, Windows
automatically detects the new hardware device
and prompts the following message.
2. Insert the device driver compact disc into your
CD-ROM drive. When the following dialog box
appears, click the
Other Locations
button.
- 4 -
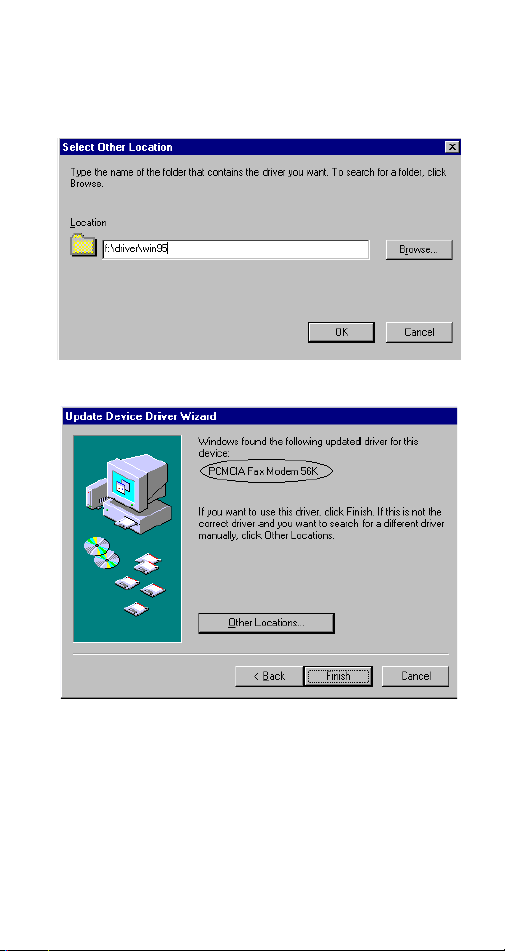
3. Type the CD-ROM drive letter followed by
driver\win95.
Or you may click the
button to select the
driver\win95
Browse
folder in your
CD-ROM drive. Click OK.
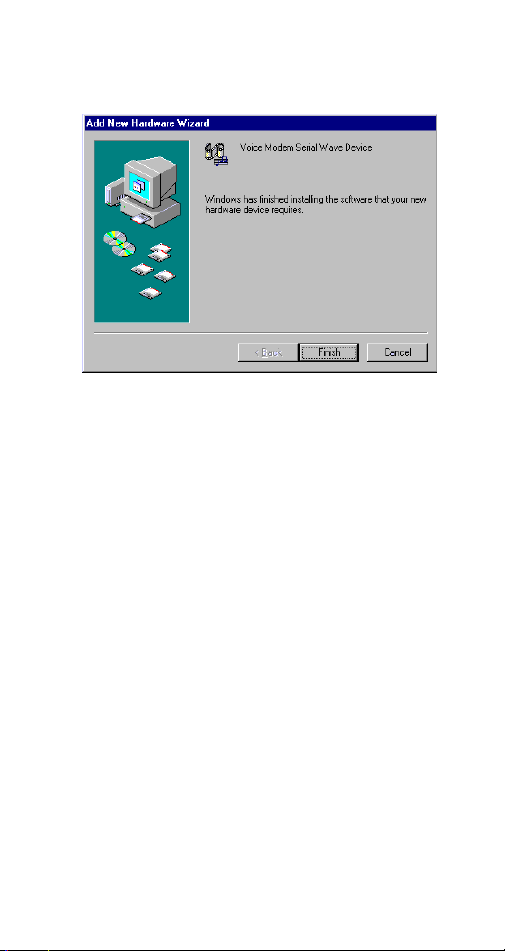
4. When the following figure appears, click
Finish.
The Installation program will continue.
5. When the following figure appears, click OK to
continue.
- 5 -
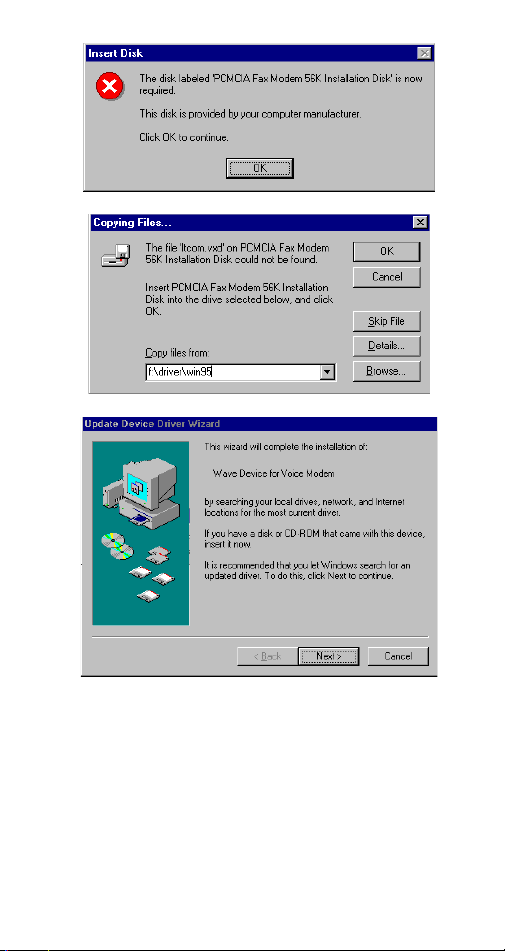
6. Repeat Step 3 as described above.
7. Follow the on-screen instruction to continue.
8. When finished, press
installation.
Remember to restart Windows 95 to
activate the new device.
- 6 -
Finish
to complete the
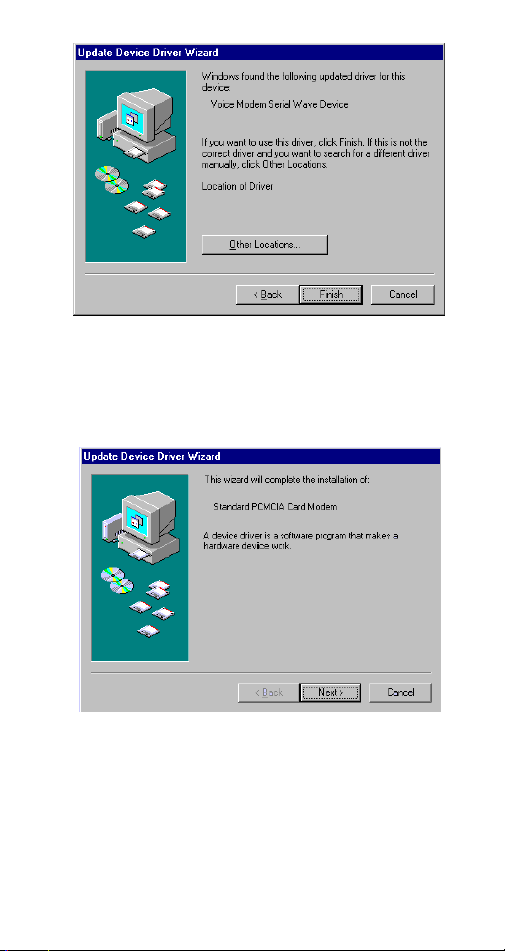
Installation for Windows 98
1. As soon as the PCMCIA Fax Modem 56K PC is
inserted into the PCMCIA slot, Windows
automatically detects the new hardware device
and the following message will be prompted.
2. Insert the device driver compact disc into your
CD-ROM drive. When the following dialog box
appears, click
Next
.
- 7 -
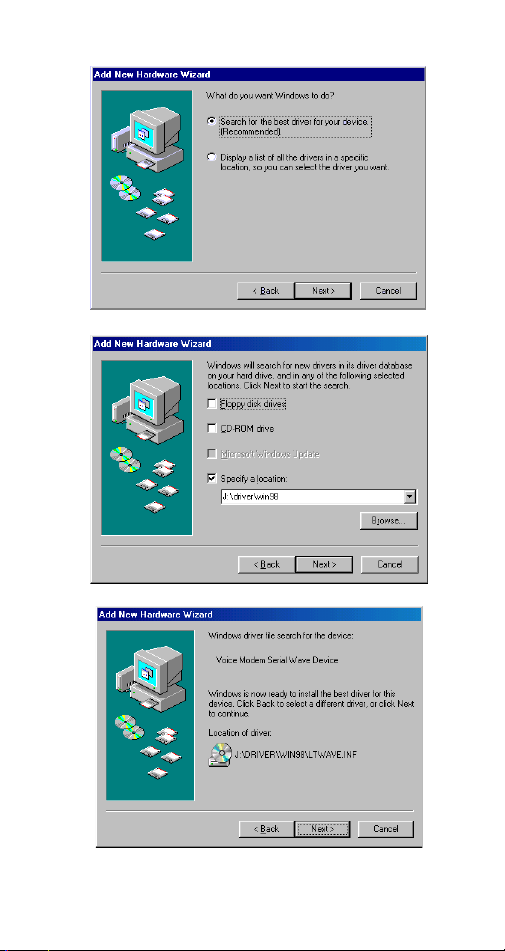
3. Select
Specify a location
when the following
figure appears. Enter the CD-ROM drive letter
followed by
driver\win98
may click the
driver\win98
folder in your CD-ROM drive.
Browse
- 8 -
. Click
button to select the
Next
. Or you
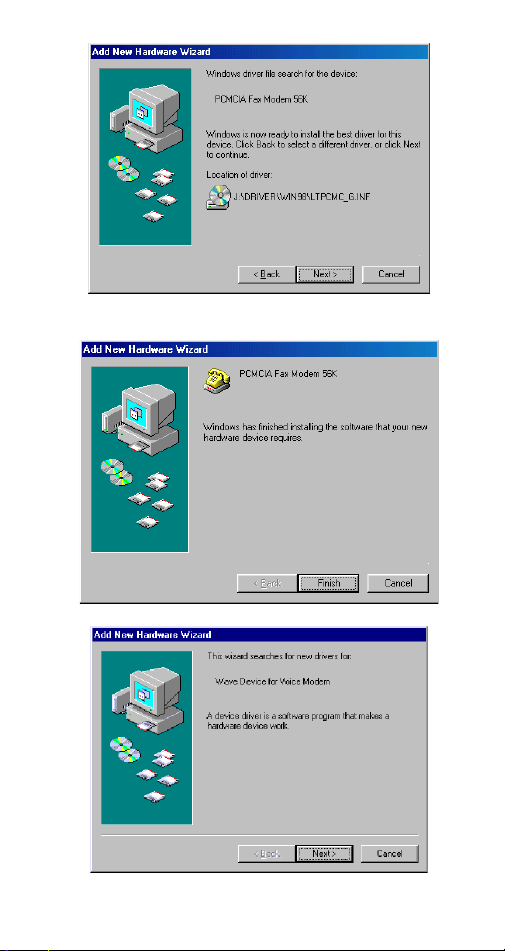
4. When the following figure appears, click
The Installation program will continue.
5. Follow the on-screen instruction to proceed.
- 9 -
Finish.
- 10 -
6. The installation program will proceed
automatically. Click
Finish
to complete the
installation.
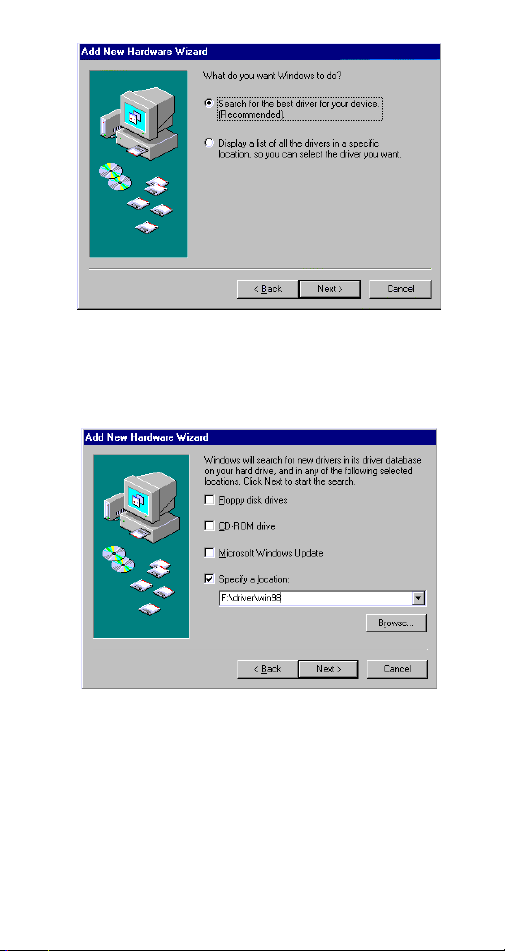
Installation for Windows 2000
If you want to use the Microsoft built-in driver, make
sure to execute
perform the following procedures to update the latest
driver.
1. Once the PCMCIA Fax Modem 56K PC Card is
plugged into your PCMCIA slot, Windows will
prompt you a standard PCMCIA Card Modem
has been installed and ask you if you want to
restart your computer. Select No.
2. Double-click the small icon at the right bottom
on your screen as illustrated below. If the icon
does not appear at all, go to
Control PanelÆ SystemÆHardwareÆDevice
Manager
d:\Driver\Win2000\PAR.exe
My ComputerÆ
. Select
Modems
and skip to Step 4.
. Or
- 11 -

3. Click
Properties
.
4. Select the
Driver…
button.
Driver
tab. Click the
- 12 -
Update
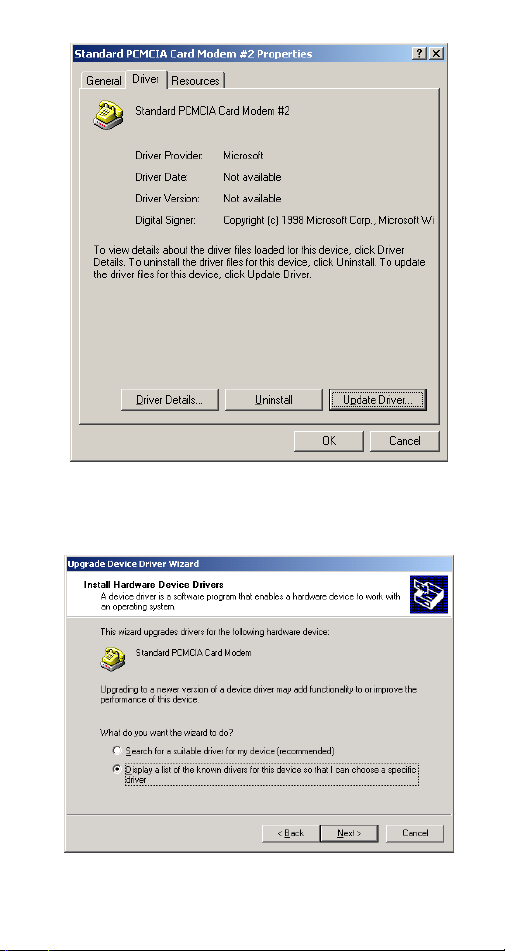
5. Click
6. Select
Next
to continue.
Display a list of the known drivers for
this device so that I can choose a specific
driver
as illustrated below. And click
- 13 -
Next
.
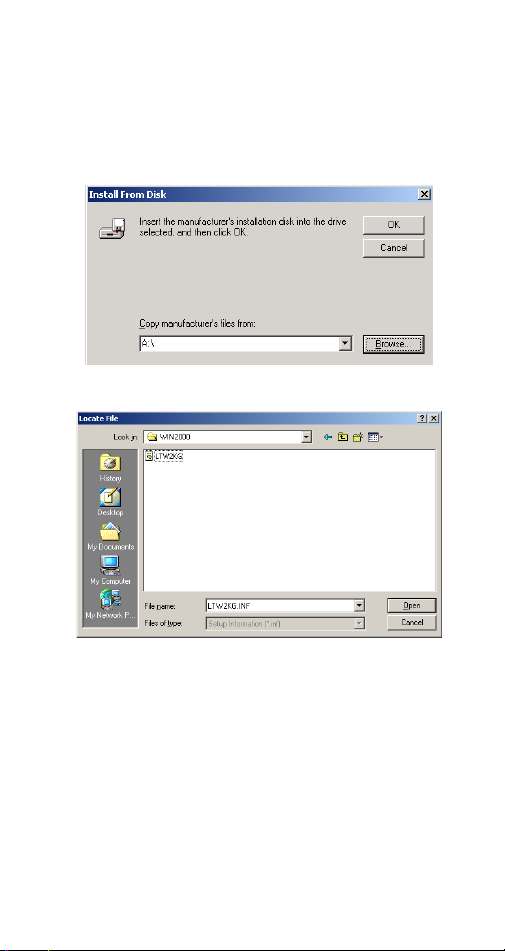
7. Click
Driver Wizard
Have Disk
dialog appears.
when the
Update Device
8. Load the CD that contains the device driver has
into your CD drive. Click
Browse
and direct the
proper file location with the disk drive followed
Driver\Win2000\LTW2KG
by
.
9. Select
LTW2KG
, and click
Open
. Follow the
on-screen instructions to proceed.
10. When the following figure appears, click
- 14 -
Next
.

11. When Windows prompt you to continue the
installation. Select
Yes
- 15 -
.

12. Remember to restart your computer to activate
this new device.
Installation for Windows Millennium
If you want to use the Microsoft built-in driver, make
sure to execute
perform the following procedures to update the latest
driver.
1. Once the PCMCIA Fax Modem 56K PC Card is
plugged into the PCMCIA slot of your system,
Windows will automatically detect the Lucent
Win Modem.
d:\Driver\WinME\PAR.exe
- 16 -
. Or

2. To update WDM Communication Device driver,
right-click
My ComputerÆÆÆÆPropertiesÆÆÆÆDevice
Manager.
3. Click
WDM Modem Enumerator
- 17 -
to expand.

4. Load the device driver into the CD-ROM drive
of your system. Click
PropertiesÆÆÆÆDriverÆÆÆÆUpdate Driver.
5. Select
(Advanced)
6. Select
click
Specify the location of the driver
and click
Next.
Display a list of all the drivers…
Next.
- 18 -
and

7. Click the
Have Disk…
button. Click
select the CD-ROM drive where you put the
device driver. (for example: D:\) Enter the CDROM driver letter followed by Driver\WinME.
Browse
to
8. Click
Next.
- 19 -

9. Click
Next
to proceed.
10. Click OK to finish the installation.
- 20 -

11. Go back to step 2. Click
Modem
to expand.
12. Load the device driver into the CD-ROM drive
of your system. Click
PropertiesÆÆÆÆDriverÆÆÆÆUpdate Driver.
- 21 -

13. Select
(Advanced)
Specify the location of the driver
and click
Next.
14. Select
click
Display a list of all the drivers…
Next.
- 22 -
and

15. Click the
Have Disk…
button. Click
select the CD-ROM drive where you put the
device driver. (for example: D:\) Enter the CDROM driver letter followed by Driver\WinME.
Browse
to
16. Click
Next.
- 23 -

17. Click
Next
to proceed.
18. Click
Finish
to complete the installation.
- 24 -

19. To verify if the PCMCIA Fax Modem 56K exists
in your system, go to
PCMCIA Fax Modem 56K
Device Manager.
PCMCIA Fax
and
Modem 56K WDM Modem Enumerator
should be found. If not, contact your dealer for
technical support.
Installation for Windows NT
1. Before you start Windows NT, make sure the
PCMCIA Fax Modem 56K PC Card has been
properly inserted into the free PCMCIA slot of
your computer.
2. Load the device driver compact disk in the CD-
ROM drive.
3. Start Windows NT.
4. Go to
5. Click the CD-ROM drive. Click the
My Computer
driver\winnt
.
folder. Or you may click the
- 25 -

Browse
the
6. Double-click
button to select the CD-ROM drive and
driver\winnt
folder.
setup.exe
. The installation program
will proceed automatically.
Note: If Softex or Card Wizard was already installed
in your system, Windows will appear message for PC
Card malfunctioning. Ignore this message and install
the WinNT driver. Remember to reboot after the
installation.
- 26 -

CHECKING COUNTRY/REGION
Please perform the following steps to check the
country/region setting of the modem before you use
the Internal Fax Modem 56K. For best performance,
make sure that the Country/region is set to the country
that you are using the modem in, eg.
America.
United States of
Windows 95/98/98SE/Millennium
1. Go to
Start→→→→Settings→→→→Control Panel→→→→Modems.
2. When the
appears, click the
Modems Properties
Dialing Properties
dialog box
button.
3. When the following dialog box appears, specify
the country/region that you are in and click
- 27 -
OK.

Windows 2000
1. Go to
Start→→→→Settings→→→→Control Panel→→→→Modems.
2. When the
box appears, click the
Phone And Modem Options
Edit
button.
- 28 -
dialog
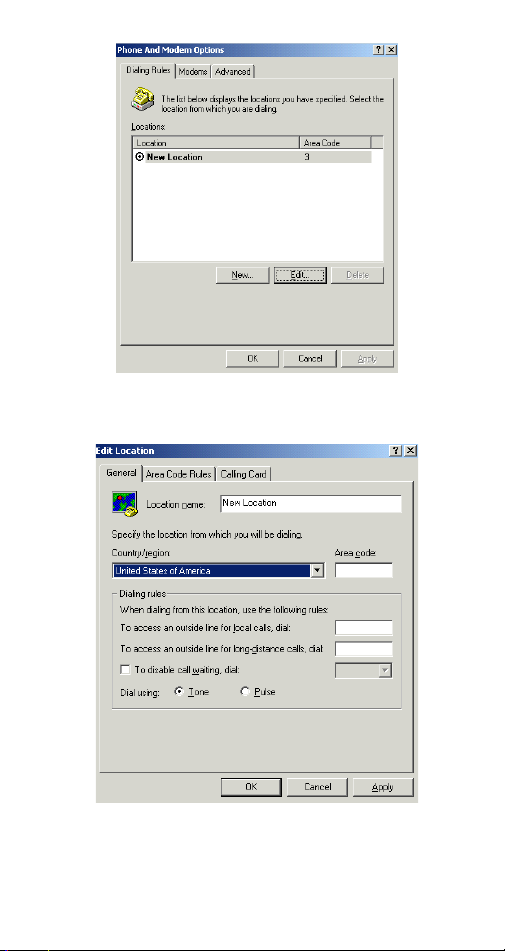
3. When the following dialog box appears, specify
the country/region that you are in and click
OK.
Windows NT4.0
1. Go to
- 29 -

Start→→→→Settings→→→→Control Panel→→→→Modems.
2. When the
appears, click the
Modems Properties
Dialing Properties
dialog box
button.
3. When the following dialog box appears, specify
the country/region that you are in and click
OK.
- 30 -

Setup Diagnostics (for Windows 95/98)
You can perform the following steps to check if your
PCMCIA FAX MODEM 56K is well installed.
1. Go to the
Control Panel
2. When the
appears, select the
Start
menu. Point to
. Double-click
Modems Properties
Diagnostics
3. Select the COM port whichever is installed
PCMCIA Fax Modem 56K
Settings
Modems
.
dialog box
tab.
and click OK.
. Click
- 31 -

4. If the screen does not at all include the PCMCIA
Fax Modem 56K, stop the diagnostics
procedures, and skip to the following section
Uninstall
titled “
”.
5. For Windows 95/98, if the information shown
below can be found on the screen, it means the
modem is well installed. Click OK to exit.
- 32 -

UNINSTALL (FOR WIINDOWS 95/98)
If for some reason, you have to uninstall the driver of
PCMCIA Fax Modem 56K after installation, perform
the following steps.
1. Go to
2. Select the CD-ROM drive whichever contains
3. Choose and double-click the
4. Click
My Computer
.
the PCMCIA Fax Modem 56K device driver.
in95, win98
w
or
winnt
folder depending on the system you are working
on.
Ltremove.exe
. The PCMCIA Fax/Modem
56K device driver will automatically removed.
- 33 -

APPLICATIONS
To use the PCMCIA Fax/Modem 56K for data
communication, for example, to send/receive faxes or
to get onto the Internet, you may use any application
software that you are familiar with. Or you may also
choose to use the bundled application software that
comes with the PCMCIA Fax/Modem 56K. The
following are examples for sending faxes and going
to the Internet.
Using BitWare to Send a Fax
1. Be sure BitWare has been successfully installed
in your system.
2. Go to the
click the Cheyenne BitWare icon. When the
opening screen appears, click the
Cheyenne BitWare
program. Double-
Setup
icon.
3. Select
appears.
4. When the Modem Setup dialog box appears,
press Auto Detect and click OK to continue. The
Modem
when the
- 34 -
Setup
dialog box

BitWare Fax Driver is then successfully
installed. Click
Close
to finish the setup.
5. Print the file you want to fax to file and set the
printer to BitWare Fax Driver as shown below.
6. Click
Start
when the following dialog box
appears. The fax will then be sent.
Internet Access
1. Go to
2. Select
3. Double-click
My Computer
Dial-Up Networking
.
.
Make a New Connection
dialogue box appears for you to name the new
connection and select the device. Name the new
connection appropriately and click
- 35 -
Next
, a
.

4. Enter the area code and phone number of your
Internet Service Provider (ISP). Follow the onscreen instruction to proceed.
5. When finished, from the
Dial-Up Networking
window right-click your newly created
connection. Select
Types
tab, enter the proper selections as shown
Properties
. On the
Server
below and click OK to finish the settings.
.
6. You are now ready to connect to the Internet.
- 36 -

TROUBLE SHOOTING
This chapter provides information on the most
commom problems, the possible causes, and the
solutions.
The modem does not respond to AT commands.
Conflict of COMx: port setting with another device.
Change the COMx: port of the PCMCIA Fax Modem
56K to a free port. Be sure to update your software
COMx: port setting as well.
The modem does not execute the command line.
Make sure you are typing 'AT' at the beginning of
command line.
Make sure the modem is not in Data Mode. type +++
if necessary.
Make sure your software is set to the same COMx:
port as the modem is.
The modem does not give a response after an AT
command was executed.
The echo and/or responses may be turned off by the
ATE0Q1 commands.
Use AT&V to check that.
Use ATE1Q0 then Enter to change them back.
Make sure the modem is in Command Mode rather
than in Data Mode when you type the AT command.
The modem gives an 'ERROR' response after an AT
command was executed.
Make sure you did not type an invalid command.
Make sure your command line is 40 characters or less
in length.
The modem goes off-hook and disables the telephone
line.
The modem may be set to auto-answer mode when it
rings.
- 37 -

Type ATS0=0, then Enter at the command line to
disable the auto-answer mode.
The modem does not auto-answer the phone.
Make sure the software is configured to auto-answer
the phone.
Type ATS0=n then press Enter. The n stands for the
number of rings the modem will answer on.
The software does not control the modem properly or
can not detect the modem.
Make sure the software has been set up correctly.
Check the initialization and dial strings.
Some TSRs (programs that stay in memory after they
are loaded) may conflict with the communications
software.
Restart your computer without loading any TSRs.
The characters on the screen are doubled.
Both the modem and the software have the echo
feature turned on at the same time.
Turn off the software echo feature off.
The remote modem is echoing your typed characters.
Type ATE1 then Enter at the command line. Then turn
off the software echo feature.
No text appears on the screen when in data mode.
The remote modem is not echoing your typed
characters.
Type ATE0 then press Enter at the command line.
Then turn the software echo feature on.
Your software may not be set to use Full Duplex or the
remote modem may not be set to use Full Duplex
either.
C:The remote modem may be waiting for you to type a
command before it will reply with text.
No text appears on the screen when in command
mode.
- 38 -

If you can't see the characters you are typing, then
type ATE1 then press Enter.
The modem does not dial a phone number after you
execute the AT dial command.
If you are using touch tone dialing on a phone line that
requires pulses, then it may not work.
Use ATDT in place of ATDP.
When your communications software tells the modem
to dial, it does not.
Make sure the software dialing prefix is ATDT.
Make sure the software and modem are set to the
same COMx: port.
The modem may not have hung up the phone line
since the last call.
Change to command mode and type ATH then
press Enter.
When dialing another modem, you receive a
'CONNECT' response, but nothing else.
The remote modem may be waiting for you to type a
command. Or try to press Enter for logging on to the
remote site.
The modem speaker does not make any sound when
you're connecting to another modem.
The software may have the speaker disabled.
Change the setting in your software or use the ATMn
command to turn the speaker on.
The modem disconnects (looses the connection) in the
middle of use.
The remote modem may have locked up.
The telephone switch may have disconnected your
call.
Your software may have turned off the DTR signal.
The modem does not connect with another modem.
- 39 -

There may be a problem with the remote modem if
you do not hear the high pitched tone from the remote
modem.
Occasionally, the modem gives a burst of errors.
The telephone line may be noisy or bad.
Hang up the call and try to connect again for getting a
better telephone line.
If there are other telephones on the same line that
your modem is using, someone may have picked up a
telephone on that extension.
Your telephone line may have the call waiting feature.
Try adding '*70,' to your ATDT dialing command line. If
it doesn’t help, ask your telephone company how to
disable it temporarily.
The modem gets errors in transmitted data randomly.
Try to use V.42 or MNP1-4 if possible.
Connect the modems at a slower baud rate.
After you download a file, it was not stored on your
disk drive.
If both modems are using MNP or V.42 protocol, then
the flow control may not be enabled.
Configure your software to use RTS/CTS flow control.
That will cause your computer to pause long enough
for the file to be stored to disk.
The text on the screen is not legible.
Your software settings may not match the settings on
the remote site.
Make sure your data bits, stop bits, and parity settings
match the settings that the other computer is using.
The two most common settings are: 8 data bits, None
parity, and 1 stop bit (8,N,1) or 7 data bits, Even
parity, and 1 stop bit (7,E,1).
If the telephone line is very noisy, you may see
corrupted data on your screen.
- 40 -

Due to poor telephone line conditions, the modem
may have fallen back to a slower communication
speed. You may need to change the baud rate setting
in your software to match this slower speed. To return
the modem to the higher speed, disconnect the link
and re-establish again.
When using V.42bis or MNP5, some features are
disabled.
You may be using a non-streaming protocol, like
Xmodem or Ymodem to transfer files. Those are fine
unless you are using V.42bis or MNP5
When using V.42bis or MNP5, you should use a
streaming transfer protocol like Ymodem-G or
Zmodem.
Configure your software to use hardware flow control
(RTS/CTS ON).
When the modem is connecting to another modem, it
reports a higher connect baud rate that it is really
using.
The modem defaults to report the modem-to-computer
baud rate when it responds with CONNECT.
Go to command mode with your communication
program (like Telix) and type ATW2, then press Enter.
This tells the modem to report the modem-to-modem
baud rate instead.
- 41 -
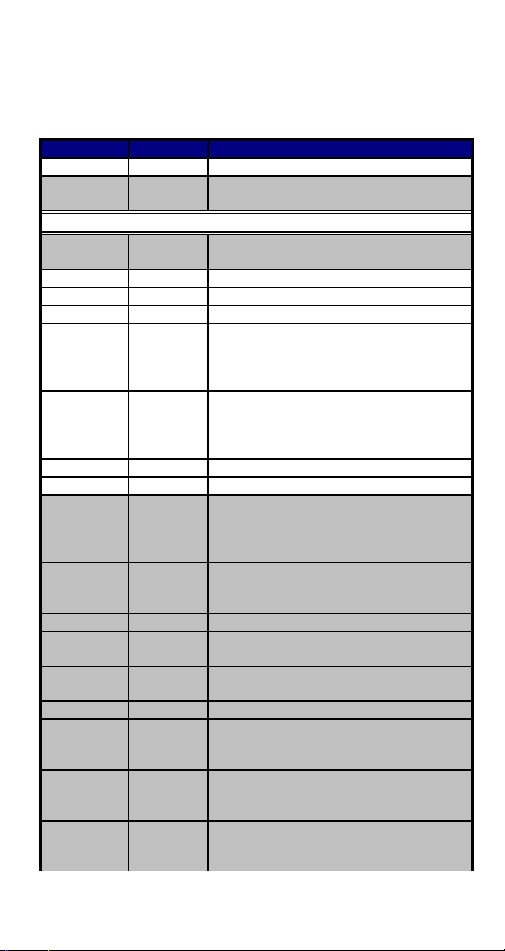
APPENDIX A: AT COMMAND
Basic AT Command Set
Command Options Function & Description
A/ Re-execute the last command string
<any key> Terminate the current connection attempt
All the following commands require an “AT” prefix
A Go off-hook and attempt to establish a
Bn Line modulation options
B0 Select V.22 mode for 1200 bps connection
B1 * Select Bell 212A for 1200 bps connection
B2 Select V.23 1200 bps for receiving, 75 bps
B3 Select V.23 75 bps for receiving, 1200 bps
B15 Select V.21 for 300 bps connection
B16 Select Bell 103 for 300 bps connection
Dn Dial command, beginning the dialing
L Re-dial last number. Should be the first
P Pulse dial.
R Reverse dial. Originate call in answer mode
S=n Dial the phone number stored in NVRAM
T DTMF tone dial.
W Wait for second dial tone. The modem
, Pause. Cause the modem to pause for a
! Hook Flash (for call transfer). Cause the
when entered in handshaking state
connection without waiting for a ring
for transmitting in originate mode; 75 bps
for receiving and 1200 bps for transmitting
in answer mode
for transmitting in originate mode; 1200
bps for receiving and 75 bps for
transmitting in answer mode
sequence. The string “n” (telephone
number and modifiers) listed as follows is
entered after the “D” command
character following ATD, ignored
otherwise
(go on-line in answer mode)
at location “n” (n=0, 1, 2, 3)
waits for the second dial tone before
processing the dial string
time before processing the next character in
the dial string (specified by S8 register)
modem to go on-hook for 0.5 second then
return to off-hook
- 42 -

@ Wait for 5 seconds of silence after dialing
; Return to command state after dialing a
En AT command echo options
E0 Echo disabled
E1 * Echo enabled
Hn Switch-hook control
H0 * Modem goes on-hook
H1 Modem goes off-hook
Mn Speaker control
M0 Speaker always off
M1 * Speaker on until carrier present
M2 Speaker always on
M3 Speaker off during dialing and on until
Nn Select negotiate handshake
N0 When originating or answering, handshake
N1 * When originating or answering, start
On Go on-line
O0 Return modem to a previously esta blished
O1 Begin a retrain sequence, then return to on-
O3 Issue a rate re-negotiation, then return to
P Enable pulse dialing
Qn Result code display options
Q0 * Result code enabled
Q1 Result code disabled
T Enable tone dialing
Vn Result code form
V0 Display result code in numeric form (see
V1 * Display result code in verbose (text) form
Wn Select extended result code options
W0 CONNECT result code reports DTE speed.
W1 CONNECT result code reports DTE speed.
number
number without disconnecting the call
carrier present
only at the communication rate specified by
S37 register and “ATBn” and no fallback
handshaking only at the communication
standard specified by S37 register and
“ATBn” During ha ndshake, fallback to a
lower speed may occur.
state (return to data mode).
line state.
on-line state.
also the result code options table)
Disable protocol result codes.
(see also the “Result Code Options Table”)
- 43 -

W2 * CONNECT result code reports DCE speed.
Xn Select result codes/call progress options
X0 Display CONNECT or “1” for all speeds.
X1 Display connect message and the modem’s
X2 Display connect message and the modem’s
X3 Display connect message and the modem’s
X4 * Display connect message and the modem’s
X5 Same as X4.
X6 Same as X4.
X7 Display CONNECT or “1” for all speeds.
Zn Recall stored profile
Z0 Reset and recall user profile 0. Either Z0 or
* Manufacturer default
Enable protocol result codes.
Enable protocol result codes.
Ignore dial tone and busy tone detection.
data rate, and an indication of the modem’s
error correction and data compression.
Ignore dial tone and busy tone detection.
data rate, and an indication of the modem’s
error correction and data compression.
Check dial tone before proceeding dialing,
ignore busy tone detection.
data rate, and an indication of the modem’s
error correction and data compression.
Ignore dial tone before proceeding dialing,
check busy tone after making dialing.
data rate, and an indication of the modem’s
error correction and data compression.
Check dial tone and busy tone.
Check dial tone and busy tone.
Z1 restores the same single profile.
Extended “AT&” (Ampersand) Command Set
Command Options Function & Description
&Cn Data carrier detect option
&Dn Data Terminal Ready (DTR) option.
&C0 State of carrier from remote modem is
ignored. DCD circuit is always on
&C1 * DCD turns on when the remote modem’s
carrier signal is detected, and off when the
carrier signal is not detected.
&D0 DTR ignored
&D1 Go to command mode on on-to-off DTR
transition
&D2 * Hang up and go to command mode on on-
- 44 -

to-off DTR transition. Auto-answer is
&D3 Hang up and reset from user profile 0 on the
&F Recall factory default setting as active
&Gn V.22bis guard tone option
&G0 * No guard tone
&G1 550 Hz guard tone
&G2 1800 Hz guard tone
&Kn Set local flow control
&K0 Disable flow control
&K3 * Enable bi-directional ha rdware flow c ontrol
&K4 Enable bi-directional software flow control
&Pn Pulse dialing make/break ratio selection
&P0 Make=39%, Break=61%, international
&P1 Make=33%, Break=67%, international
&Qn Async communications mode options
&Q0 Async mode, buffered (same as “AT\N0”)
&Q5 * Error control mode, buffered (same as
&Q8 MNP error control mode. If an MNP error
&Q9 V.42 or MNP error control mode. If neither
&Sn Data Set Ready (DSR) option
&S0 * DSR always on
&S1 DSR on during handshake and on-line, off
&Tn Self-test commands
&T0 Terminate any test in progress
&T1 Local analog loopback test
&T3 Local digital loopback (LDL) test
&T6 Remote digital loopback test, in normal
disable d if DTR is low
on-to-off DTR transition
configuration
(CTS/RTS)
(XON/XOFF)
version (Default)
Make=33%, Break=67% for use in 20 pps,
Japanese version
version
Make=33%, Break=67% for use in 10 pps,
Japanese version (Default)
“AT\N3”)
control protocol is not established, the
modem will fallback according to the
current setting in S36 register.
error control protocol is established, the
modem will fallback according to the
current setting in S36 register.
in test mode or idle mode
mode
- 45 -

&V View active file and stored phone numbers
&W Store active configuration into the modem’s
&Zn=x Store telephone number
* Manufacturer default
NVRAM
n=0 to 3
x=<string> see also the dial modifier
in ”ATDn” command
The max. number of digits per string is 40.
Extended “AT\” (Back Slash) Command Set
Command Options Function & Description
\Jn Constant DTE speed option
\Nn Error control mode options
\Qn Local flow control options
\Tn Set inactive timer (for buffer mode only)
\Vn Protocol result codes
\J0 * DCE and DTE rates are independent
\J1 Force the DTE interface speed to the DCE
connection rate (line speed) after on-line
\N0 Buffered mode, no error control (flow
control is allowed).
\N1 Direct mode, no error control (no flow
control is allowed).
\N2 MNP reliable mode. If MNP 2-4 error
control e stablishment fails, the modem
disconnects.
\N3 * V.42, MNP or buffer mode. The modem
attempts to connect in V.42 mode. If this
fails, the modem attempts to connect in
MNP mode. If this fails, the modem
connects in buffer mode.
\N4 V.42 or disconnect. The modem attempts
to connect in V.42 mode. If this fails, the
call will be disconnected.
\Q0 Disable flow control (same as “AT&K0”)
\Q1 XON/XOFF software flow control (same
as “AT&K4”)
\Q3 * RTS/CTS hardware flow control (same as
“AT&K3”)
n=0 * Disable inactive timer
n=1 - 255 Enable inactive timer. Length in minutes
\V0 Disable protocol result code appended to
DCE speed
\V1 * Enable protocol result code appended to
- 46 -

* Manufacturer default
DCE speed
Extended “AT%” (Percent) Command Set
Command Options Function & Description
%B View numbers in blacklist. If blacklisting is
%Cn Data compression control
%C0 No data compression
%C1 * V.42bis/MNP 5 data compression enabled.
* Manufacturer default
in effect, this command displays the
numbers for which the last call attempted in
the past two hours failed. The ERROR
result code appears in the countries that do
not require blacklisting.
Extended “AT-” (Dash) Command Set
Command Options Function & Description
-Cn Data calling tone options
-V90=<n> command to enable/disable .90 and change
• Manufacturer default
-C0 * Disable data calling tone
-C1 Enable data calling tone (the freq. is 1,300
Hz with a cadence of 0.5 sec. ON and 2
sec. OFF)
downstream rate
-V90=0 disable V.90
-V90=1 enable V.90 Auto Rate (default value)
-V90=X controls the downstream rate
-V90? Shows the current value
-V90=? Shows the range [0-21]
Possible Values of V.90
“AT-V90=X” Downstream Rate
0 V.90 disabled
1 Auto Rate (default)
2 28000 kbit/s
3 29333 kbit/s
4 30666 kbit/s
5 32000 kbit/s
6 33333 kbit/s
7 34666 kbit/s
- 47 -

8 36000 kbit/s
9 37333 kbit/s
10 38666 kbit/s
11 40000 kbit/s
12 41333 kbit/s
13 42666 kbit/s
14 44000 kbit/s
15 45333 kbit/s
16 46666 kbit/s
17 48000 kbit/s
18 49333 kbit/s
19 50666 kbit/s
20 52000 kbit/s
21 53333 kbit/s
- 48 -

APPENDIX B: S-REGISTERS
S-Registers, “ATSn=x”
RegisterDec. Function & Description Default
S0= 0 - 255 Set the number of the rings required
S1= 0 - 255 Count the incoming rings and s tore the
S2= 0 - 255 S2 holds the decimal value of the ASCII
S3= 0 - 127 Hold the decimal value of the Carriage
S4= 0 - 127 Hold the decimal value of the character
S5= 0 - 32,
127
S6= Set the length of time, in seconds, that
2 - 65 For inte rnationa l version 003
S7= Set the time, in seconds, that the modem
before the modem automatically
answers
a call. Set “S0=0” to disable autoanswer mode
value to this register. The value of this
register is incremented with each ring. If
no rings occur over an 8 sec. interval,
this register is cleared. User can read
but should not change this value
character used as the escape character.
The default value (043) corresponds to
an ASCII character “+”. A value of 128
to 255 disables the escape process, i.e.,
no escape character will be re cognized
Return <CR> character used as the
command line and result code
terminator. Pertain to asynchronous
operation only
recognized as a line feed.The line feed
control character is output after the
carriage return control character if
verbose result code are used.
Hold the decimal value of the character
recognized as a backspace. The modem
will not recognize the backspace
character if this register is set to a value
greater than 32
the modem must wait (minimum 2
seconds even if the value is less than 2)
after going off-hook before dialing the
first digit of the telephone number
must wait before hanging up because
carrier is not detected
- 49 -
000
000
043
013
010
008

1 - 255 For international version 050
35 - 59 For Japanese version 050
S8= 0 - 65 Set the time, in seconds, that the modem
must pause when the “,” dial modifier is
encountered in the dial string
S10= 1 - 255 Set the length of time, in tenths of a
second, that the modem waits before
hanging up after a loss of carrier
S11= 50 - 150 DTMF duration and inter digit delay.
Set the duration and spacing, in miniseconds, in DTM F touch tine dialing
S12= 0 - 255 Define the maximum period, in 2-
hundredths of a sec ond, allowed
between consecutive asynchronous
escape character “+” (plus) for the
escape sequence to be considered valid
S28= 0 - 255 V.34 modulation en-/disabler
0: disabled
1- 255: enabled
S30= 0 - 90 Inactivity timer. Set the length of time,
in minutes, that the modem counts when
there is no data flow in or out the DTE
serial port. A connection is disengaged
when the counter reaches the preset
value. Set S30 =0 to disable the
inactivity timer.
For buffer mode only.
S37= Desired DCE speed (line speed) 000
0 Maximum modem s pe ed
2 Attempt 1200/75 bps connection
3 Attempt to a 300 bps connection
5 Attempt to a 1200 bps connection
6 Attempt to a 2400 bps connection
7 Attempt to a 4800 bps connection
8 Attempt to a 7200 bps connection
9 Attempt to a 9600 bps connection
10 Attempt to a 12000 bps connection
11 Attempt to a 14400 bps connection
12 Attempt to a 16800 bps connection
13 Attempt to a 19200 bps connection
14 Attempt to a 21600 bps connection
15 Attempt to a 24000 bps connection
16 Attempt to a 26400 bps connection
17 Attempt to a 28800 bps connection
18 Attempt to a 31200 bps connection
19 Attempt to a 33600 bps connection
S38= 56K Dial Line Rate Options. Set the 000
002
020
144
050
001
000
- 50 -

max. 56K downstream speed that the
modem attempts to connect
0 56K disabled
1 56K enabled, auto-speed selection, max.
modem speed
2 32000 bps
3 34000 bps
4 36000 bps
5 38000 bps
6 40000 bps
7 42000 bps
8 44000 bps
9 46000 bps
10 48000 bps
11 50000 bps
12 52000 bps
13 54000 bps
14 56000 bps
S48= 7, 128 LAPM error control and feature
negotiation.
S48=7 Negotiation enabled
S48=128 Negotiation disabled. Force
immediate fallback options
specified in S36
S36=0 or 2, and S48=7
LAPM or hang up
S36=0 or 2 and S48= 128
Don’t use
S36=1 or 3, and S48=7
LAPM or async
S36=1 or 3, and S48=128
Async
S36=4 or 6, and S48=7
LAPM, MNP or hang up
S36=4 or 6, and S48=128
MNP or hang up
S36=5 or 7, and S48=7
LAPM, MNP or async
S36=5 or 7, and S48=128
MNP or hang up
S91= 6 - 15 Transmitting power level adjustment
(Japanese version only)
Range: -6 dBm to -15 dBm
Default: -15 dBm
010
- 51 -
 Loading...
Loading...