
TRENDnet User’s Guide
Cover Page

TRENDnet User’s Guide
Contents
Product Overview ........................................................................... 1
Package Contents .......................................................................................................... 1
Features ......................................................................................................................... 1
Product Hardware Features........................................................................................... 2
Application Diagram ...................................................................................................... 4
Basic Router Setup .......................................................................... 5
Creating a Home Network ............................................................................................. 5
Router Installation ......................................................................................................... 6
Connect additional wired devices to your network ..................................................... 11
Wireless Networking and Security ................................................. 12
How to choose the type of security for your wireless network .................................. 12
Secure your wireless network ..................................................................................... 13
Connect wireless devices to your router ..................................................................... 15
Connect wireless devices using WPS ........................................................................... 16
Basic wireless settings ................................................................................................. 18
Steps to improve wireless connectivity ....................................................................... 20
Advanced wireless settings .......................................................................................... 21
Multiple SSID ........................................................................................................... 21
Wireless Schedule ................................................................................................... 22
Wireless Isolation .................................................................................................... 22
Additional Wireless Settings ................................................................................... 23
Wireless Operation Modes .......................................................................................... 24
AP Router Mode ...................................................................................................... 24
AP Only Mode ......................................................................................................... 25
WDS Only Mode & WDS Hybrid Mode .................................................................... 26
Access Control Filters .................................................................... 30
Access control basics ................................................................................................... 30
MAC address filters ................................................................................................. 30
Domain/URL Filters ................................................................................................. 31
Keyword Blocking .................................................................................................... 32
Packet Outbound/Inbound Filter ............................................................................ 32
Advanced Router Setup ................................................................ 35
Access your router management page ........................................................................ 35
Change your router login password ............................................................................ 35
Set your router date and time ..................................................................................... 36
Manually configure your Internet connection ............................................................ 37
Clone a MAC address ................................................................................................... 37
Change your router IP address .................................................................................... 38
Set up the DHCP server on your router ....................................................................... 38
Set up DHCP reservation ............................................................................................. 40
Enable/disable UPnP on your router ........................................................................... 41
Allow/deny VPN connections through your router ..................................................... 41
Additional Security Settings ......................................................................................... 42
Allow/deny multicast streaming.................................................................................. 42
Identify your network on the Internet ........................................................................ 43
Allow remote access to your router management page ............................................. 43
Open a device on your network to the Internet .......................................................... 44
DMZ ......................................................................................................................... 44
Virtual Server .......................................................................................................... 44
Special Applications ................................................................................................ 46
Prioritize traffic using QoS (Quality of Service) ........................................................... 47
Create schedules ......................................................................................................... 48
Table of Contents
© Copyright 2013 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
i

TRENDnet User’s Guide
Using VLANs ................................................................................................................. 49
Add static routes to your router .................................................................................. 50
Enable dynamic routing on your router ...................................................................... 51
Using WoL (Wake on LAN) on your router .................................................................. 51
Router Management Page Structure ............................................. 62
Technical Specifications ................................................................ 63
Troubleshooting ........................................................................... 64
Table of Contents
Appendix ...................................................................................... 65
Setup IPv6 on your router ........................................................................................... 52
Router Maintenance & Monitoring ................................................ 53
Reset your router to factory defaults .......................................................................... 53
Router Default Settings ............................................................................................... 53
Backup and restore your router configuration settings .............................................. 54
Restart your router ...................................................................................................... 56
Check connectivity using the router management page ............................................. 56
Check the router system information .......................................................................... 57
View your router log .................................................................................................... 59
Configure your router log ............................................................................................ 60
Enable SNMP on your router ....................................................................................... 61
Enable TR-069 on your router ..................................................................................... 61
© Copyright 2013 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
ii

TRENDnet User’s Guide
Product Overview
Package Contents
In addition to your router, the package includes:
• Multi-Language Quick Installation Guide
• CD-ROM (User’s Guide)
• Network cable (1.5m / 5ft.)
• RJ-11 telephone cable (1.8m / 5ft.)
• Detachable Antenna
• Power adapter (5V DC, 1.2A)
If any package contents are missing or damaged, please contact the retail store, online
retailer, or reseller/distributor from which the product was purchased.
TEW-718BRM
Features
The N150 Wireless ADSL 2/2+ Modem Router, model TEW-718BRM, provides both a
modem for Internet access and a wireless n network in a single solution. No need to buy
a separate modem and router. This modem supports Internet service providers with
ADSL 2 and ADSL 2+ networks.
Install TEW-718BRM quickly with a step-by-step setup wizard to browse the Internet,
download files, and video chat with the latest in wireless n technology. Connect
computers, game consoles, and media players to the built-in 4-port switch. WMM®
Quality of Service (QoS) technology prioritizes online gaming, Internet calls, and video
streams. One-touch Wi-Fi Protected Setup (WPS) connects WPS peripheral devices at
the touch of a button.
• 4 x 10/100 Mbps Auto-MDIX RJ-45 LAN ports (option to convert port 1 to WAN
port)
• 1 x RJ-11 (telephone) ADSL WAN port (Internet)
• Detachable antenna
• WPS / reset button
• Status LEDs
• Router + Modem or Modem Only (Bridge) modes
• Modem compliant with ADSL, ASDL2, and ADSL2+ standards
• Wireless
o Data rates of up to 150 Mbps, based on IEEE 802.11n*
o Backward compatible with IEEE 802.11 b/g standards
o Create a wireless schedule to automatically turn off wireless when
away
o Broadcast up to 2 SSIDs with different wireless encryption
o Wi-Fi Multimedia (WMM) Quality of Service (QoS) data prioritization
o Advanced wireless encryption up to WPA2-RADIUS
o One touch wireless connection using the WPS button
• Supports up to 8 PVCs
• Support for IPv6: Static, DHCPv6, PPPoE, 6 to 4, and IPv6 in IPv4 Tunnel,
Stateful / Stateless Auto-configuration
• Support for port-based and 802.1Q VLANs (ID range: 1~4094)
• Set device time using Network Time Protocol (NTP) and define schedules for
Wireless, Virtual Server, and Packet Filters
TEW-718BRM
© Copyright 2013 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
1

Port
Ports
TRENDnet User’s Guide
• Smart Quality of Service (QoS) controls to allocate bandwidth to: Gaming, Chat,
VoIP, P2P, Video, and Web Access
• Advance Firewall protection with Network Address Translation (NAT), Stateful
Packet Inspection (SPI), and WAN stealth mode
• Supports Internet Group Multicast Protocol IGMPv1/2/3 proxy and snooping
for multicast applications
• Access Control: Virtual Servers, MAC / IP Packet Filters, URL / Keyword Filters,
Demilitarized Zone (DMZ) host, PPTP / L2TP / IPsec VPN pass through
• Supports static and dynamic RIP v1/2 routing
• Dynamic DNS support
• Universal Plug and Play (UPnP) for auto discovery and support for device
configuration of Internet applications
• Local / remote management via Web browser, upgrade firmware, and backup /
restore configuration
• Supports TR069 remote management (CPE and ACS support)
• Device monitoring using modem and router logs, email alerts, and SNMP v1/2c
support
*Maximum wireless signal rates are referenced from IEEE 802.11 theoretical specifications. Actual
data throughput and coverage will vary depending on interference, network traffic, building
materials and other conditions.
Product Hardware Features
Rear View
2dBi Detachable Antenna
Power
• Power Port – Connect the included power adapter from your modem router
power port and to an available power outlet.
Note: Use only the adapter that came with your router.
• LAN Ports – Connect Network cables (also called network cables) from your
modem router LAN ports to your wired network devices.
• ADSL WAN Port (RJ-11 telephone port) –Connect an RJ-11 telephone cable
from your modem router ADSL WAN port to your telephone jack/DSL line.
• Antenna – The antenna broadcast wireless network signals.
LAN
ADSL
TEW-718BRM
© Copyright 2013 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
2

LED
LED
LED
TEW-718BRM
ADSL
WLAN
LAN 1-4
WPS Button/
Reset Button/
WLAN (On/Off)
• Status LED - This LED indicator is blinking green when your modem router is
ready and working successfully. If this LED indicator is solid green on or off,
your router is not receiving power or ready, or not working properly.
• ADSL WAN (Link/Activity) LED – This LED indicator is blinking green when the
ADSL status of the modem router is ready to establish connection to your ISP.
The LED indicator will turn solid green when the modem router has been
properly configured with the settings provided by your ISP and successful ADSL
connection has been made to your ISP. This LED indicator will be blink while
data is transmitted or received through the ADSL port of your modem router.
• WLAN (Link/Activity) LED – This LED indicator is solid green when the wireless
is “On” and functioning properly on your modem router. This LED indicator will
be blinking while data is transmitted or received by your wireless clients or
wireless network devices connected to your modem router. This LED indicator
will be off when the wireless functionality of your modem router is disabled.
• LAN 1-4 (Link/Activity) LEDs – These LED indicators are solid green when the
LAN ports are successfully connected to your wired network devices (which are
turned on). These LED indicators will blink green while data is transmitted or
received through your modem router’s LAN ports.
• WPS/Reset/WLAN Button – This button has multiple functions depending on
the amount of time it is pushed and released.
o WPS (Wi-Fi Protected Setup) – Push and hold this button for 3
seconds and release to activate WPS. Within 2 minutes, push and hold
the WPS button on your wireless client device. WLAN LED indicator
will blink rapidly to indicate that WPS has been activated.
o Reset – Push and hold this button for 15 seconds and release to reset
your router to its factory defaults. Status LED indicator will blink
rapidly after released to indicate the reset process has started.
o WLAN (On/Off) – Push and hold this button for 10 seconds and release
to disable or enable the wireless functionality of your modem router.
The Status LED will start to blink rapidly and the WLAN LED indicator
will turn off (disabled) or turn on (enabled) to indicate the status of
the wireless functionality of your modem router.
TRENDnet User’s Guide
Front View
Status
© Copyright 2013 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
3

TRENDnet User’s Guide
TEW-718BRM
Application Diagram
The router is installed near the wall telephone jack/DSL line (DSL service supplied by your ISP “Internet Service Provider”) which connects to the Internet. Wireless signals from the router
are broadcasted to wireless clients such as laptops (with wireless capability) thereby providing Internet access.
© Copyright 2013 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
4

TRENDnet User’s Guide
Basic Router Setup
Creating a Home Network
What is a network?
A network is a group of computers or devices that can communicate with each other. A
home network of more than one computer or device also typically includes Internet
access, which requires a router.
A typical home network may include multiple computers, a media player/server, a
printer, a modem, and a router. A large home network may also have a switch,
additional routers, access points, and many Internet-capable media devices such as TVs,
game consoles, and Internet cameras.
• Modem – Connects a computer or router to the Internet or ISP (Internet
Service Provider).
Note: The TEW-718BRM/TEW-718BRM5 is a combination DSL modem and
router, therefore, you do not require a separate DSL modem from your ISP when
setting up this product.
• Router – Connects multiple devices to the Internet.
• Switch –Connect several wired network devices to your home network. Your
router has a built-in network switch (the LAN port 1-4). If you have more wired
network devices than available Network ports on your router, you will need an
additional switch to add more wired connections.
How to set up a home network
1. For a network that includes Internet access, you’ll need:
• Computers/devices with a Network port or wireless networking capabilities.
• A modem and Internet service to your home, provided by your ISP (modem
typically supplied by your ISP).
• A router to connect multiple devices to the Internet.
2. Set up your router. See “How to setup your router” below.
3. To connect additional wired computers or wired network devices to your network,
see “Connect additional wired devices to your network” on page 11.
4. To set up wireless networking on your router, see “Wireless Networking and Security”
on page 12.
How to setup your router
Refer to the Quick Installation Guide or continue to the next section “Router
Installation” on page 6 for more detailed installation instructions.
Where to find more help
In addition to this User’s Guide, you can find help below:
• http://www.trendnet.com/support
(documents, downloads, and FAQs are available from this Web page))
TEW-718BRM
© Copyright 2013 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
5

TRENDnet User’s Guide
Router Installation
Before you Install
Many Internet Service Providers (ISPs) allow your router to connect to the Internet
without verifying the information fields listed below. Skip this section for now and if
your router cannot connect to the Internet using the standard installation process, come
back to this page and contact your ISP to verify required ISP specification fields listed
below.
General ADSL Parameters
VCI: ____
VPI: ____
MTU: ________
Data Encapsulation (LLC/VCMux) : _________
Schedule Type (UBR/CBR/VBR/GFR): _______
VLAN Tag (If required by your ISP): _________
ADSL Connection Types:
1. Ethernet over ATM (RFC 1483 Bridged) with NAT
• 1a. Obtain IP Address Automatically (Dynamic IP Address)
Host Name (Optional) ______________________
ISP registered Mac Address or Clone MAC address (Optional)___:___:___:___:___:___
• 1b. Fixed IP address (Static IP Address)
WAN IP Address: _____. _____._____._____ (e.g. 215.24.24.129)
WAN Subnet Mask: _____. _____._____._____
WAN Gateway IP Address: _____. _____._____._____
Primary DNS Server Address: _____. _____._____._____
Secondary DNS Server Address: _____. _____._____._____
2. IP over ATM (RFC 1483 Routed)
• 2a. Obtain IP Address Automatically (Dynamic IP Address)
Host Name (Optional) ______________________
ISP registered Mac Address or Clone MAC address (Optional)___:___:___:___:___:___
• 2b . Fixed IP address (Static IP Address)
WAN IP Address: _____. _____._____._____ (e.g. 215.24.24.129)
WAN Subnet Mask: _____. _____._____._____
WAN Gateway IP Address: _____. _____._____._____
Primary DNS Server Address: _____. _____._____._____
Secondary DNS Server Address: _____. _____._____._____
3. PPP over ATM (PPPoE)
• 3a. PPPoE to obtain IP automatically
Account/User Name: _________
Password: ________________
• 3b. PPPoE with a fixed IP address
User Name: _________
Password: ________________
Verify Password: ________________
IP Address: ____. _____._____._____ (e.g. 215.24.24.129)
Primary DNS Server Address: _____. _____._____._____
Secondary DNS Server Address: _____. _____._____._____
4. PPP over Ethernet (PPPoA)
• 4a. PPPoA to obtain IP automatically
Account/User Name: _________
Password: ________________
• 4b. PPPoA with a fixed IP address
User Name: _________
Password: ________________
Verify Password: ________________
IP Address: ____. _____._____._____ (e.g. 215.24.24.129)
Primary DNS Server Address: _____. _____._____._____
Secondary DNS Server Address: _____. _____._____._____
TEW-718BRM
© Copyright 2013 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
6
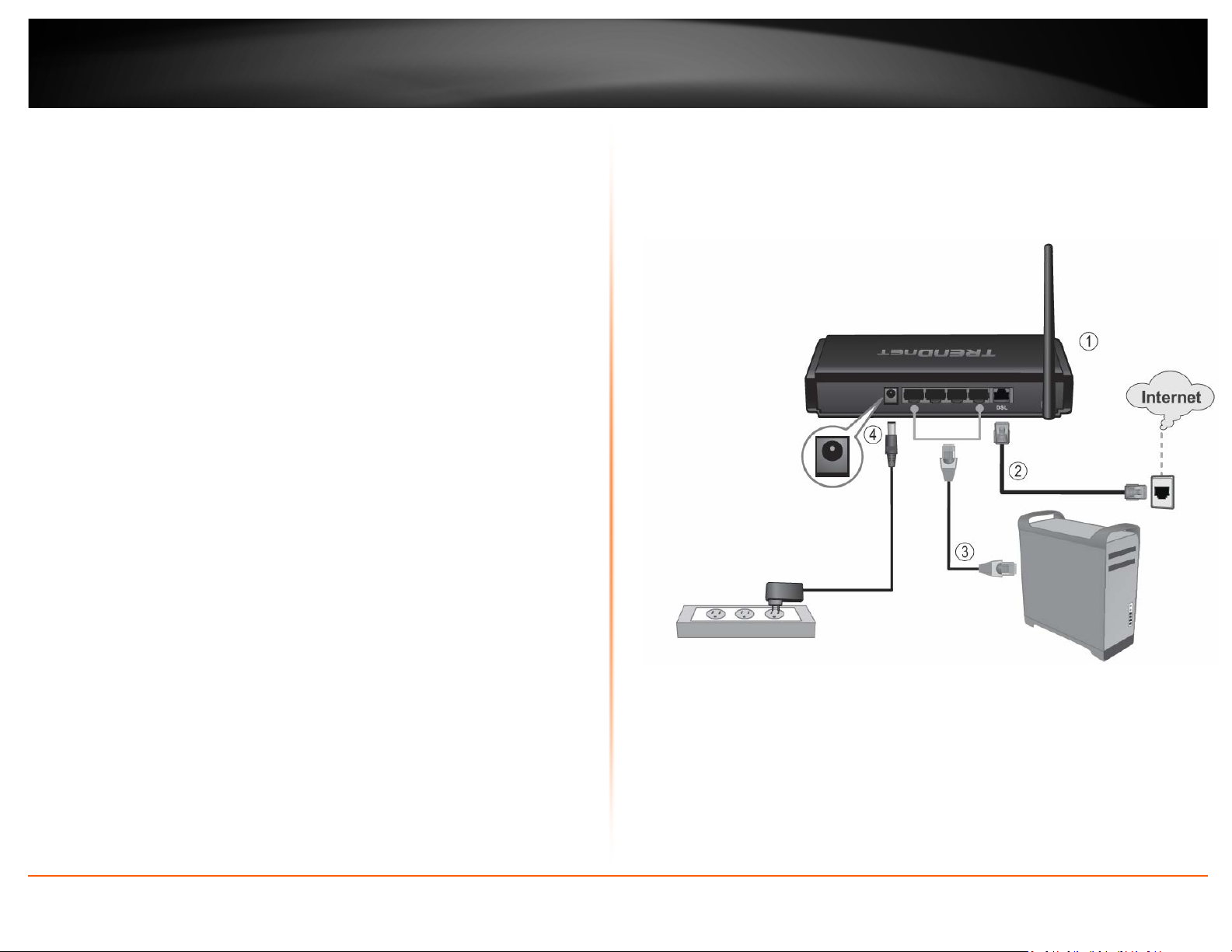
TRENDnet User’s Guide
Hardware Installation
1. Connect the detachable antenna to your modem router.
2. Connect one end of the RJ-11 telephone cable to the modem router ADSL port.
Connect the other end of the RJ-11 telephone cable to the telephone jack/DSL line.
3. Using the Network cable, connect your computer to one of the four LAN ports on the
modem router.
4. Connect the power adapter to the modem router and then to a power outlet.
5. Verify that the status LED indicators on the front of the modem to confirm the device
is fully functional: Status (Green), ADSL (Green), WLAN (Green) and the LAN port
(1,2,3,4) (Green) your computer is connected.
TEW-718BRM
© Copyright 2013 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
7
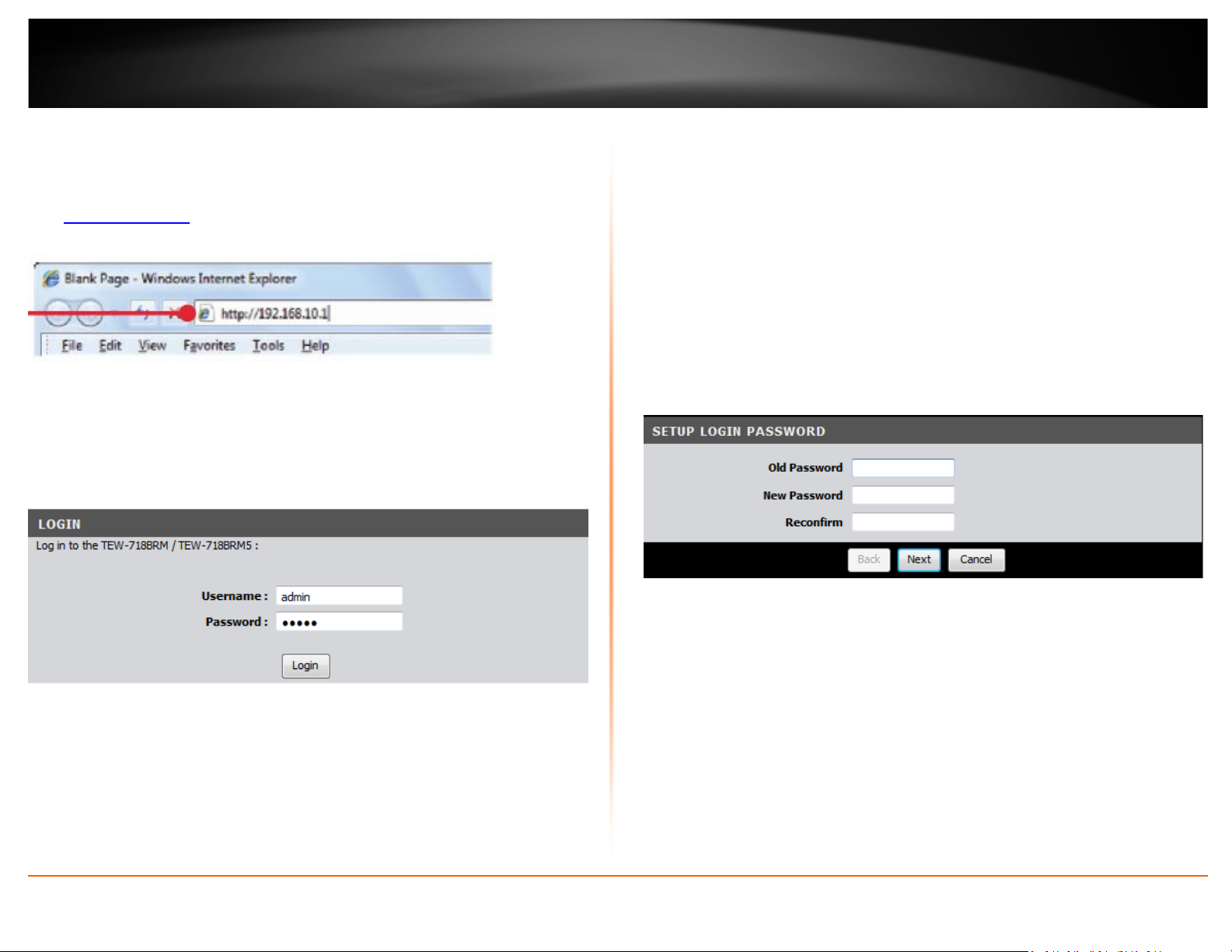
TRENDnet User’s Guide
Setup Wizard
1. Open your web browser (e.g. Internet Explorer, Firefox, Safari, Chrome, or Opera) and
go to http://192.168.10.1
2. Enter the default user name and password and then click Login.
Default User Name: admin
Default Password: admin
. Your router will prompt you for a user name and password.
3. The Setup Wizard will automatically appear. In the “Old Password” field, enter your
current login password (Default: admin). Then, in the “New Password” field enter a new
login password for your modem router and enter it again next to “Reconfirm” to
confirm the new password. This will change the default password required to log into
your modem router. Click Next.
Note: If the Setup Wizard does not automatically appear, click Setup Wizard (the top
button on the left tab).
Note: This is the password to enter your router’s management interface and NOT to
connect to the router wirelessly. Once you change the login password, it will be required
every time you log into your router. Store your router password in a location that you
can reference at a future time. It is strongly recommended to change your modem
router’s default password.
TEW-718BRM
© Copyright 2013 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
8
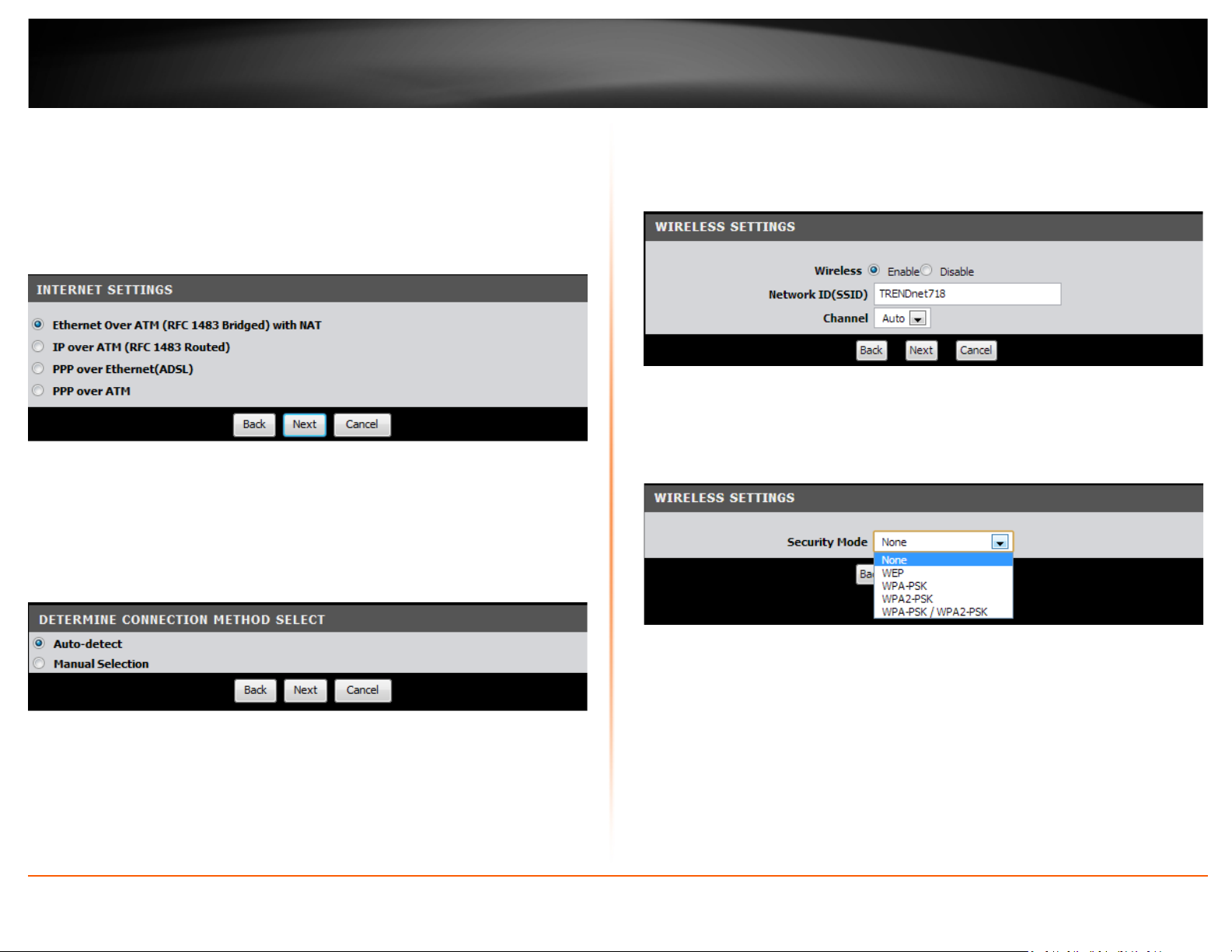
TRENDnet User’s Guide
4. This section determines what method the router will use to interface with your ISP
service. Select the ADSL Internet connection type provided by your ISP and click Next.
Note: It is strongly recommended to contact your ISP to verify all required settings for
one of the options listed on page 6. The options listed on page 6 match the settings
options available to choose from.
5. The Setup Wizard can automatically detect your VPI/VCI and Data Encapsulation
settings of your ADSL connection. Select Auto-detect and click Next.
Note: If you encounter any issues with the Auto-Detect feature on the wizard, you can
click “Skip Scan”, and configure your ADSL connection settings manually.
7. SSID: Enter a unique SSID (Wireless Network Name). Choose something that you
would easily identify when searching for available wireless networks (using laptops,
smart phones, etc.) Click Next.
8. Select the type of wireless security and enter in the key that will be used to access
your wireless network. Click Next.
TEW-718BRM
Note:
1. To protect your network from unauthorized access, it is recommended to enable
6. Depending the ADSL connection type you selected, you may need to enter additional
information such as your PPPoE/PPPoA user name and password information provided
by your ISP static IP . Enter any additional information required by your ISP for your
ADSL connection and click Next.
© Copyright 2013 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
wireless encryption. See “Secure your wireless network” on page 12 for information on
configuring wireless security.
2. Once wireless security is enabled on your router, each wireless device connecting to
your router must be configured with the same wireless security type and key.
9
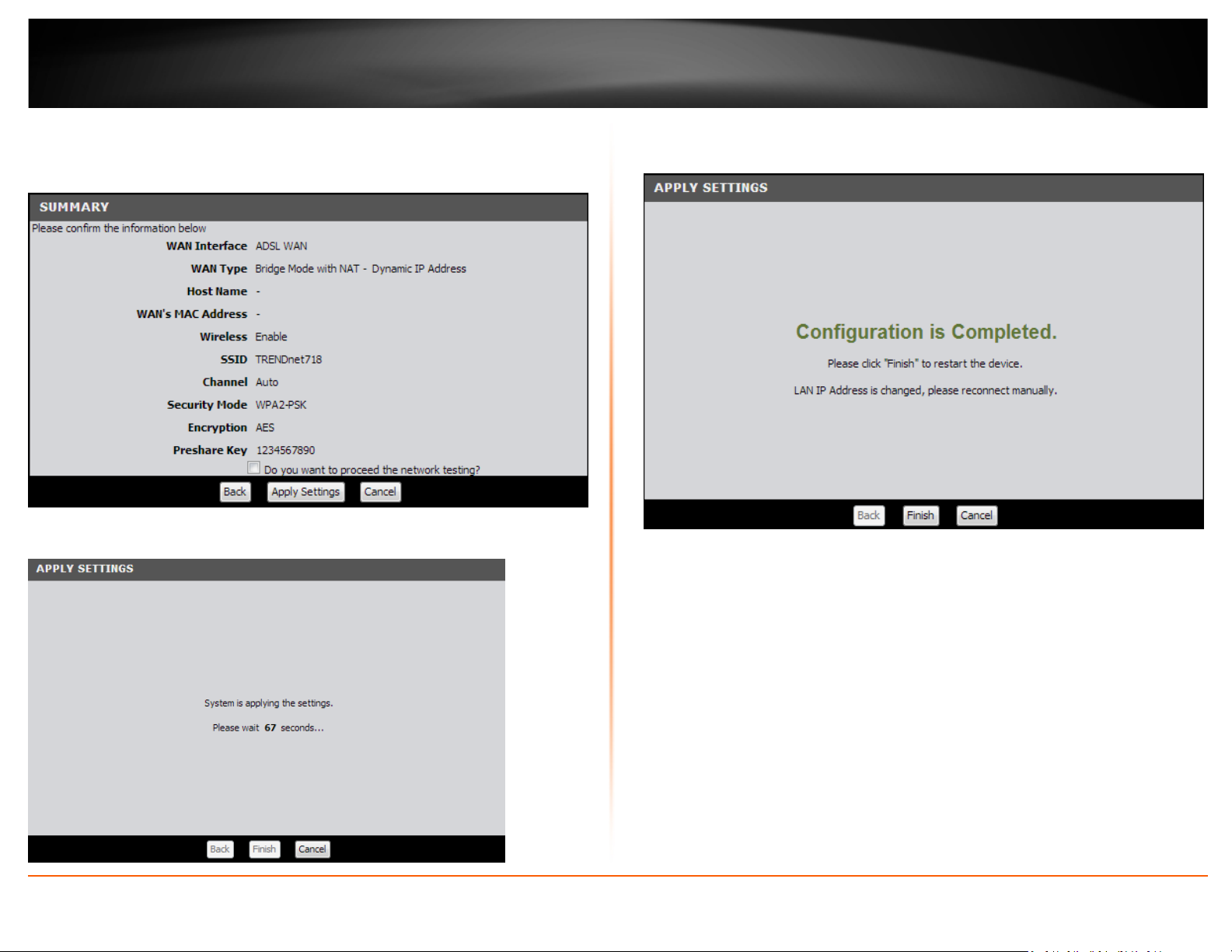
TRENDnet User’s Guide
9. The Summary page will allow you to quickly review the settings you applied in the
Setup Wizard. Click Apply Settings to commit the changes.
10. Wait for your modem router to apply the settings.
11. Click Finish to return to the router management page.
12. Verify you have an Internet connection by opening a Web browser on your
computer.
Note: If you cannot access the Internet, please verify your hardware connections and
LED status and re-run the Setup Wizard to verify you have applied the correct settings.
TEW-718BRM
© Copyright 2013 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
10

TRENDnet User’s Guide
TEW-718BRM
Connect additional wired devices to your network
You can connect additional computers or other network enabled devices to your
network by using Network cables. Connect them to one of the available LAN ports
labeled 1,2,3,4 on your modem router. Check the status of the LED indicators (1, 2, 3, or
4) on the front panel of your router to ensure the physical cable connection from your
computer or device.
Note: If you encounter issues connecting to your network, there may be a problem with
your computer or device network settings. Please ensure that your computer or device
network settings (also called TCP/IP settings) are configured to obtain IP address settings
automatically (also called dynamic IP address or DHCP) and to Obtain DNS Server
address settings automatically.
© Copyright 2013 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
11

TRENDnet User’s Guide
Wireless Networking and Security
How to choose the type of security for your wireless network
Setting up wireless security is very important. Leaving your wireless network open and
unsecure could expose your entire network and personal files to outsiders. TRENDnet
recommends reading through this entire section and setting up wireless security on your
new router.
There are a few different wireless security types supported in wireless networking each
having its own characteristics which may be more suitable for your wireless network
taking into consideration compatibility, performance, as well as the security strength
along with using older wireless networking hardware (also called legacy hardware).
It is strongly recommended to enable wireless security to prevent unwanted users from
accessing your network and network resources (personal documents, media, etc.).
In general, it is recommended that you choose the security type with the highest
strength and performance supported by the wireless computers and devices in your
network. Please review the security types to determine which one you should use for
your network.
Wireless Encryption Types
cards(wireless clients), you may have to set your router to WEP to allow the old
adapters to connect to the router. Note: This encryption standard will limit
connection speeds to 54Mbps.
• WPA: This encryption is significantly more robust than the WEP technology.
Much of the older 802.11g hardware was been upgraded (with firmware/driver
upgrades) to support this encryption standard. Total wireless speeds under
this encryption type however are limited to 54Mbps.
• WPA / WPA2: This setting provides the router with the ability to detect
wireless devices using either WPA or WPA2 encryption. Your wireless network
will automatically change the encryption setting based on the first wireless
device connected. For example, if the first wireless client that connects to your
wireless network uses WPA encryption your wireless network will use WPA
encryption. Only when all wireless clients disconnect to the network and a
wireless client with WPA2 encryption connects your wireless network will then
change to WPA2 encryption. NOTE: WPA2 encryption supports 802.11n speeds
and WPA encryption will limit your connection speeds to 54Mbps
• WPA2: This is the most secure wireless encryption available today, similar to
WPA encryption but more robust. This encryption standard also supports the
highest connection speeds. TRENDnet recommends setting your router to this
encryption standard. If you find that one of your wireless network devices does
not support WPA2 encryption, then set your router to either WPA or WPA-Auto
encryption.
TEW-718BRM
• WEP: Legacy encryption method supported by older 802.11b/g hardware. This
is the oldest and least secure type of wireless encryption. It is generally not
recommended to use this encryption standard, however if you have old 802.11
b or 802.11g wireless adapters or computers with old embedded wireless
© Copyright 2013 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Note: Check the specifications of your wireless network adapters and wireless appliances
to verify the highest level of encryption supported.
12
Security Standard
WEP
WPA
WPA2
Standards
IEEE 802.11a/b/g/n
802.11g speeds)
IEEE 802.11a/b/g/n
802.11g speeds)
IEEE 802.11a/b/g/n
Highest
Setting
Up to 54Mbps
Up to 54Mbps
Up to 450Mbps*
Encryption
Strength
Low
Medium
High
Open System or
Different key sizes
TKIP
8-63 characters
AES
8-63 characters
300Mbps, or 450Mbps)
TRENDnet User’s Guide
Below is brief comparison chart of the wireless security types and the recommended
configuration depending on which type you choose for your wireless network.
Compatible
Wireless
Performance
Under This
Additional
Options
(802.11n devices
will operate at
Shared Key,
HEX or ASCII,
(802.11n devices
will operate at
TKIP or AES,
Preshared Key or
RADIUS
TKIP or AES,
Preshared Key or
RADIUS
Secure your wireless network
Setup > Wireless Settings
After you have determined which security type to use for your wireless network (see
“How to choose the security type for your wireless network” on page 12), you can set up
wireless security.
1. Log into your router management page (see “Access your router management page”
on page 35
2. Click on Setup, and click on Wireless Settings.
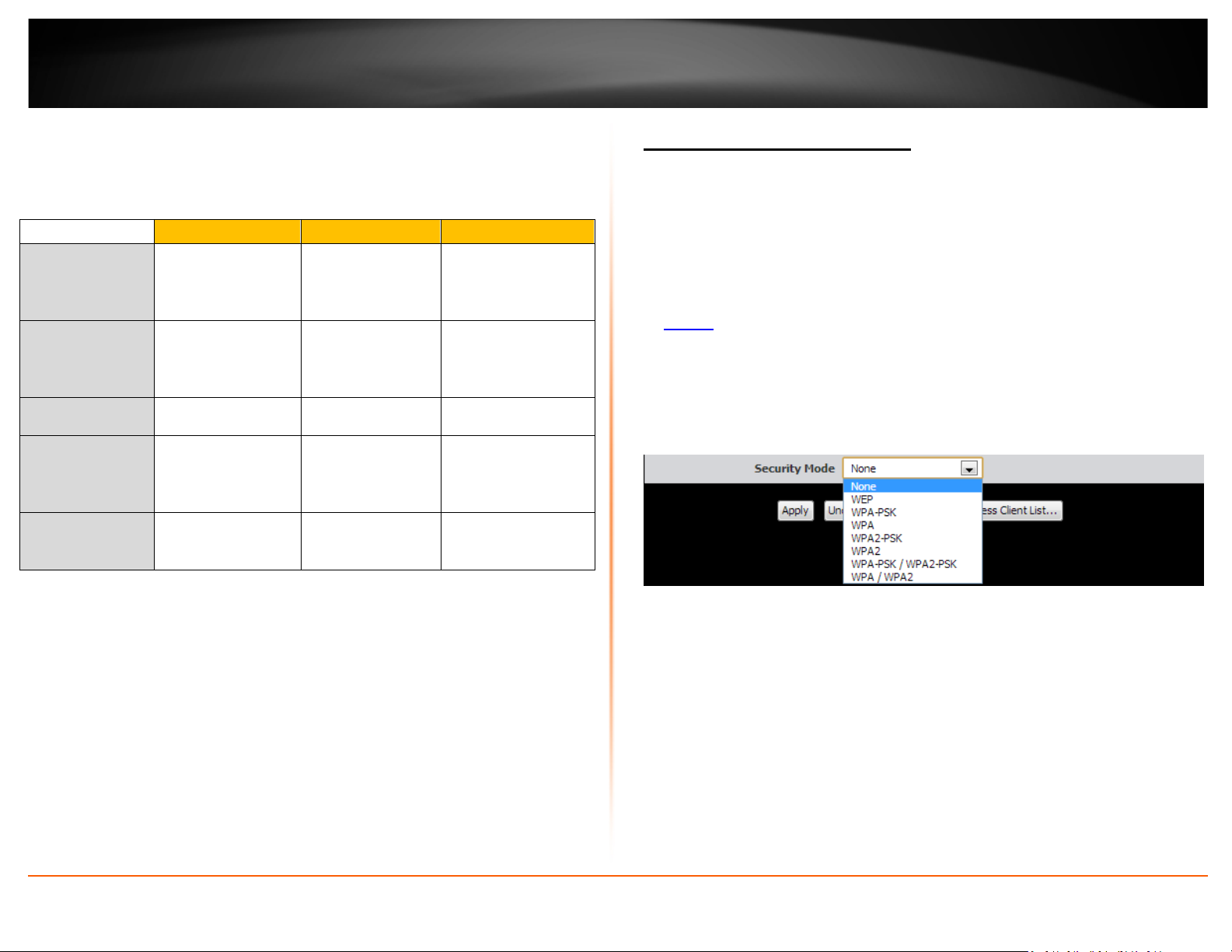
3. Click on the Security Mode drop-down list to select your wireless security type.
).
TEW-718BRM
Recommended
Configuration
*Dependent on the maximum 802.11n data rate supported by the device (150Mbps,
© Copyright 2013 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Open System ASCII
13 characters
Preshared Key
Preshared Key
13
TRENDnet User’s Guide
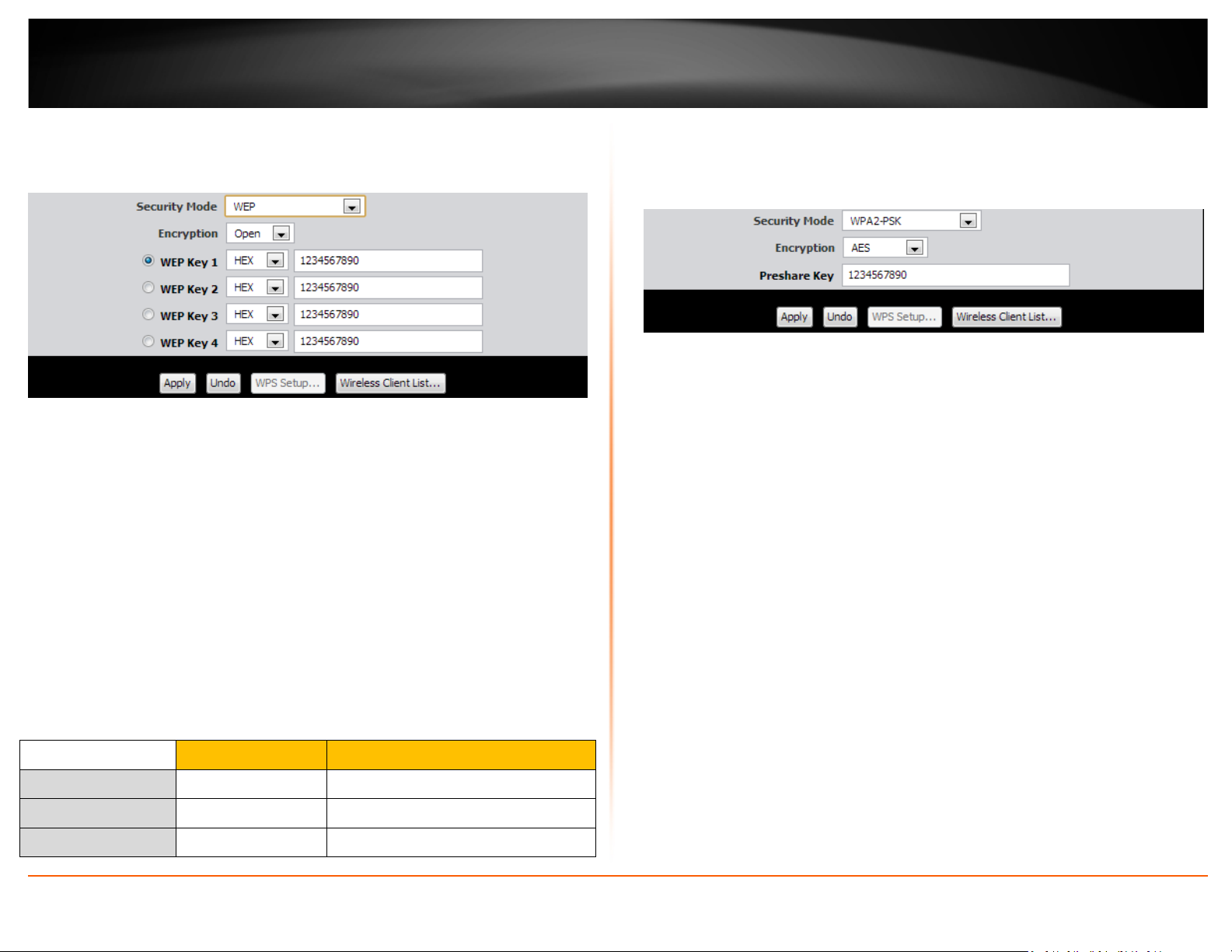
Selecting WEP:
If selecting WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy), please review the WEP settings to configure
and click Apply to save the changes.
• Encryption – Choose Open, Shared, or Auto.
Note: It is recommended to use Open System because it is known to be more secure
than Shared Key.
• WEP Key 1-4
o Choose HEX or ASCII.
Note: It is recommended to use ASCII because of the much larger
character set that can be used to create the key.
o This is where you enter the password or key needed for a computer to
connect to the router wirelessly
o You can define up to 4 passwords or 4 keys. Only one key can be active
at a given time. Most users simply define one key.
o Choose a key index 1, 2, 3, or 4 and enter the key.
o When connecting to the router, the client must match both the
password and the Key number. (e.g. if you have activated Key 2 with a
password of 12345, then the client must select: Key 2 (entering Key 1,
3, or 4 will block the ability to connect) and enter password 12345)
WEP Key Format
Character set 0-9 & A-F, a-f only Alphanumeric (a,b,C,?,*, /,1,2, etc.)
64-bit key length 10 characters 5 characters
128-bit key length 26 characters 13 characters
HEX ASCII
Selecting WPA-PSK, WPA-PSK / WPA2-PSK, or WPA2-PSK (WPA2-PSK recommended):
If selecting WPA-PSK, WPA-PSK / WPA2-PSK, or WPA2-PSK, (Wi-Fi Protected Access
Preshared Key) please review the settings to configure and click Apply to save the
changes.
First, from the Security Mode drop-down list, select WPA-PSK, WPA-PSK / WPA2-PSK,
or WPA2-PSK.
o Select the Encryption type. When selecting WPA-PSK security, it is
recommended to use TKIP.
o When selecting WPA-PSK / WPA2-PSK security, it is recommended to
use AES.
o When selecting WPA2-PSK security, it is recommended to use AES.
Create your Wireless security preshared key (password or key):
• Preshare Key – Enter the preshared key.
o This is the password or key that is used to connect your computer to
this router wirelessly
Note: 8-63 alphanumeric characters (a,b,C,?,*, /,1,2, etc.)
Then from the PSK/EAP row, select either PSK or EAP
• PSK stands for Preshared Key
• EAP stands for Extensive Authentication Protocol, also called Remote
Authentication Dial-In User Service or RADIUS).
Note: EAP requires an external RADIUS server, PSK only requires you to create a
passphrase.
TEW-718BRM
© Copyright 2013 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
14
TRENDnet User’s Guide
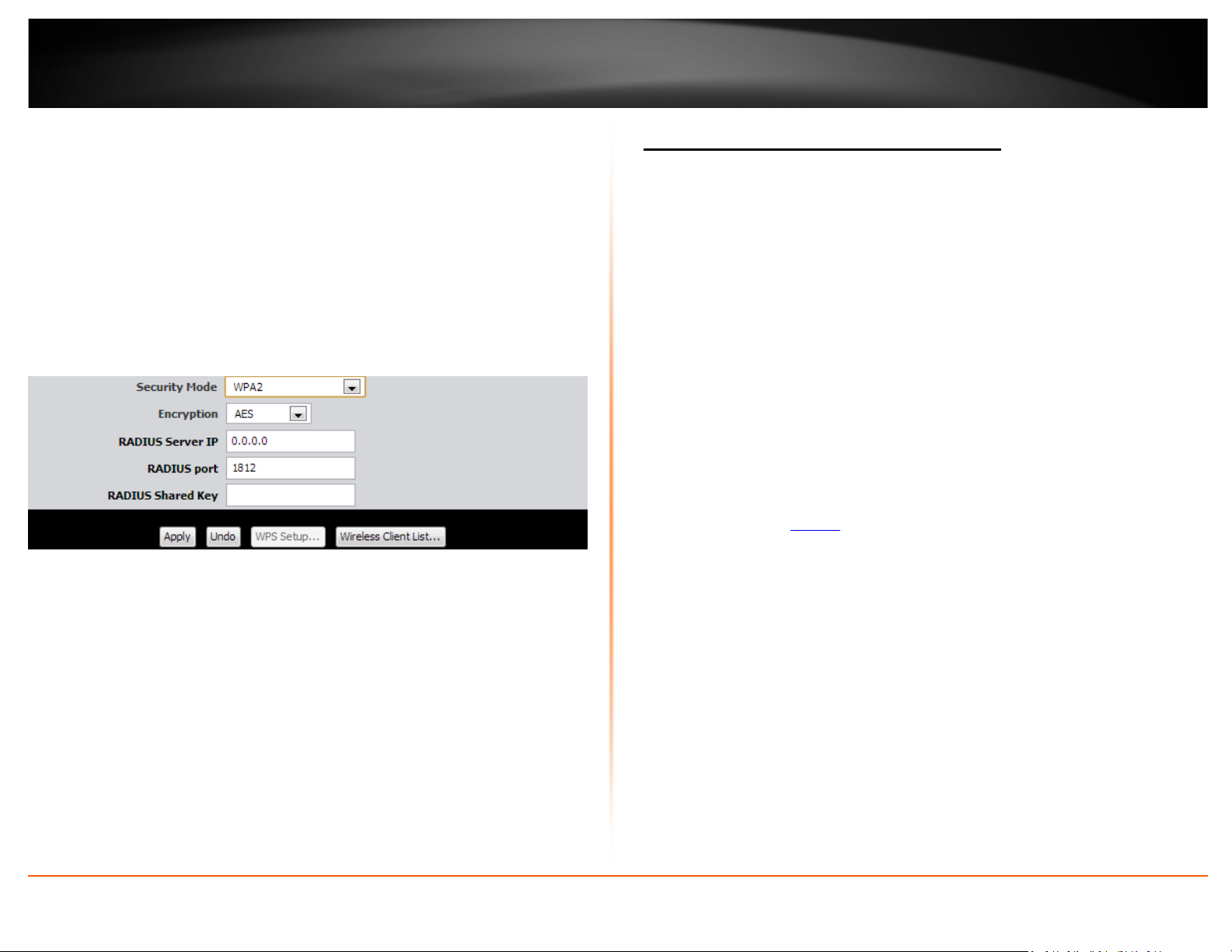
Selecting WPA, WPA / WPA2, or WPA2:
If selecting WPA, WPA / WPA2, or WPA2 (Wi-Fi Protected Access Extensible
Authentication Protocol) please review the settings to configure and click Apply to save
the changes.
EAP (Extensible Authentication Protocol) is also called Remote Authentication Dial-In
User Service or RADIUS.
Select the Encryption Type
o When selecting WPA security, it is recommended to use TKIP.
o When selecting WPA / WPA2 security, it is recommended to use AES.
o When selecting WPA2 security, it is recommended to use AES.
o RADIUS Server IP – Enter the IP address of the RADIUS server. (e.g.
192.168.10.250)
o RADIUS Port – Enter the port your RADIUS server is configured to use
for RADIUS authentication.
Note: It is recommended to use port 1812.
o RADIUS Shared Key – Enter the shared key (or shared secret) used to
authorize your router with your RADIUS server.
Connect wireless devices to your router
A variety of wireless network devices can connect to your wireless network such as:
• Gaming Consoles
• Internet enabled TVs
• Network media players
• Smart Phones
• Wireless Laptop computers
• Wireless IP cameras
Each device may have its own software utility for searching and connecting to available
wireless networks, therefore, you must refer to the User’s Manual/Guide of your
wireless client device to determine how to search and connect to this router’s wireless
network.
See the “Appendix” on page 65
network.
for general information on connecting to a wireless
TEW-718BRM
© Copyright 2013 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
15

TRENDnet User’s Guide
Connect wireless devices using WPS
Setup > Wireless Settings > WPS Setup
WPS (Wi-Fi Protected Setup) is a feature that makes it easy to connect devices to your
wireless network. If your wireless devices support WPS, you can use this feature to
easily add wireless devices to your network.
Note: You will not be able to use WPS if you set the SSID Broadcast setting to Disabled.
There are two methods the WPS feature can easily connect your wireless devices to
your network.
• Push Button Configuration (PBC) method
o RECOMMENDED Hardware Push Button method–with an external
button located physically on your router and on your client device
o WPS Software/Virtual Push Button - located in router management
page
• PIN (Personal Identification Number) Method - located in router management
page
Note: Refer to your wireless device documentation for details on the operation of WPS.
Recommended Hardware Push Button (PBC) Method
Note: it is recommended that a wireless key (passphrase or password) is created before
connecting clients using the PBC method. If no wireless key is defined when connecting
via PBC, the router will automatically create an encryption key that is 64 characters long.
This 64 character key will then have to be used if one has to connect computers to the
router using the traditional connection method.
To add a wireless device to your network, simply push the WPS button on the wireless
device you are connecting(consult client device User’s Guide for length of time), then
push and hold the WPS button located on your router for 3 seconds and release it. The
WLAN LED on your modem router will flash rapidly indicating that the WPS setup
process has been activated. (See “Product Hardware Features” on page 2
For connecting additional WPS supported devices, repeat this process for each
additional device.
PBC (Software/Virtual Push Button)
Setup > Wireless Settings > WPS Setup
In addition to the hardware push button located physically on your router, the router
management page also has push button which is a software or virtual push button you
can click to activate WPS on your router.
1. Log into your router management page (see “Access your router management page”
on page 35
2. Click on Setup and click Wireless Settings, then click on the WPS Setup button at the
bottom of the page.
).
TEW-718BRM
)
© Copyright 2013 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
16
TRENDnet User’s Guide
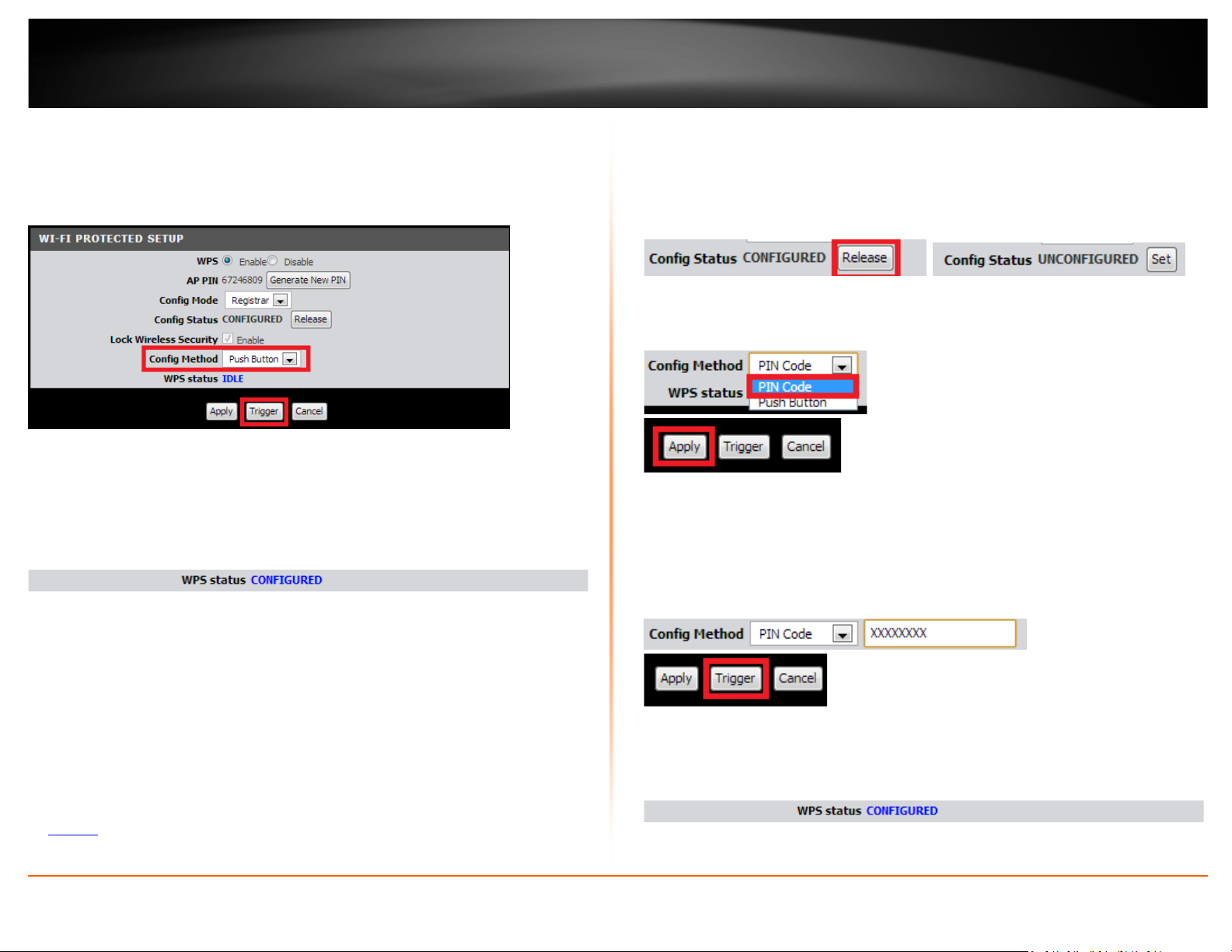
3. To add a wireless device to your network, simply the push the WPS button on the
wireless device (consult wireless device’s User’s Guide for length of time), you are
connecting, then in your router management page, make sure the Config Method is set
to Push Button (default setting) and click on the Trigger button at the bottom of the
page.
4. The WPS Status area will display status messages about the WPS process.
5. The WPS Status area will display “Configured” message to indicate that the wireless
client device successfully connected using WPS.
PIN (Personal Identification Number)
Setup > Wireless Settings > WPS Setup
If your wireless device has WPS PIN (typically an 8-digit code printed on the wireless
device product label or located in the wireless device wireless software utility), you can
use this method.
1. Log into your router management page (see “Access your router management page”
on page 35
).
2. Click on Setup and click Wireless Settings, then click on the WPS Setup button at the
bottom of the page.
3. Next to Config Status, click Release. The status will change to Unconfigured.
4. Click the Config Method drop-down list and select PIN Code. Click Apply.
5. In the empty field, enter the 8-digit WPS PIN of the wireless client device you are
connecting and click Trigger.
Note: You may need to initiate the WPS PIN on your wireless device first when using this
method. Refer to your wireless device documentation for details on the operation of
WPS.
6. The WPS Status area will display “Configured” message to indicate that the wireless
client device successfully connected using WPS.
TEW-718BRM
© Copyright 2013 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
17
TRENDnet User’s Guide
TEW-718BRM
Basic wireless settings
Setup > Wireless Settings
This section outlines available management options under the Wireless Settings tab.
1. Log into your router management page (see “Access your router management page”
on page 35
2. Click on Setup, and click on Wireless Settings.
3. To save changes to this section, click Apply when finished.
).
• Wireless
o Enable turns on the wireless networking on your router (by default it
is enabled).
o Disable turns off wireless networking on your router.
Note: It is recommended to leave the wireless setting to Enable unless you do not
plan on connecting any wireless computers or devices to your network.
• SSID Broadcast
o Enable allows wireless devices to search and discover your wireless
network name (also called SSID) broadcasted by your router.
o Disable turns off the ability for wireless devices to find your network.
It is still possible for wireless devices to be configured to connect to
your wireless network.
Note: Setting this option to Disable, will disable WPS functionality.
• Channel – In North America, this router can broadcast on 1 of 11 Channels (13
in Europe and other countries). Selecting the Auto option enables the router to
automatically select the best Channel for wireless communication. To manually
set the channel on which the router will broadcast, click the drop-down list and
select the desired Channel for wireless communication. The goal is to select the
Channel that is least used by neighboring wireless networks.
• SSID – This acronym stands for Service Set Identifier and is the name of your
wireless network. It differentiates your wireless network from others around
you. By default, the router broadcast TRENDnet718 as the wireless network
name. If you choose to change the SSID, change it to a name that you can easily
remember.
© Copyright 2013 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
• Wireless Mode - Select the appropriate mode for your network.
18
TRENDnet User’s Guide
o B/G/N mixed – Select this mode for the best compatibility. This mode
allows older 802.11b and 802.11g wireless devices to connect to the
router in addition to newer 802.11n devices.
o B/G mixed – This mode only allows devices to connect to the router
using older and slow 802.11b or 802.11g technology and it thereby
reduces the router’s maximum speed to 54Mbps (typically not
recommended).
o N only – This mode only allows newer 802.11n devices to connect to
your router. This mode does ensure the highest speed and security for
your network, however if you have older 802.11g wireless clients, they
will no longer be able to connect to this router.
o G only – This mode only allows devices to connect to the router using
older and slow 802.11g technology (typically not recommended).
o B only – This mode only allows devices to connect to the router using
older and slow 802.11b technology (typically not recommended).
Note: Please check the specifications on your wireless devices for the highest wireless
capability supported first before applying these settings. If you are unsure, it is
recommended that you keep the default setting (B/G/N mixed) for the best
compatibility.
When applying the 802.11 mode setting, please keep in mind the following:
• Wireless devices that support 802.11n are backwards compatible and can
connect wirelessly at 802.11g or 802.11b.
• Connecting at 802.11b or 802.11g will limit the capability of your 802.11n
supported wireless devices from obtaining higher performance and data rates.
• Allowing 802.11b or 802.11g devices to connect to an 802.11n capable wireless
network may degrade the wireless network performance below the higher
performance and data rates of 802.11n.
• Wireless devices that only support 802.11b or 802.11g will not be able to
connect to a wireless network that is set to 802.11n only mode.
• Wireless devices that only support 802.11b will not be able to connect to a
wireless network that is set to 802.11g only mode.
• Bandwidth – This setting only applies to wireless devices connecting at
802.11n. Another term used to describe this parameter is Channel Width.
Select the appropriate channel width for your wireless network.
o 20 MHz – This mode operates using a single 20MHz channel for
wireless devices connecting at 802.11n. This setting may provide more
stability than Auto 20/40 MHz for connectivity in busy wireless
environments where there are several wireless networks in the area.
o Auto 20 MHz/40 MHz – This mode can automatically switch between
using a single 20MHz channel or 40MHz (two 20MHz channels). When
40MHz is active, this mode is capable of providing higher performance
only if the wireless devices support the 40MHz channel width.
Enabling 20/40MHz typically results in substantial performance
increases when connecting to an 802.11n client.
• Wireless Client List – Clicking on the Wireless Client List button at the bottom
of the page will display a list of wireless clients that are currently connected to
your modem router.
TEW-718BRM
© Copyright 2013 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
19

TRENDnet User’s Guide
Steps to improve wireless connectivity
There are a number of factors that can impact the range of wireless devices. Follow
these tips to help improve your wireless connectivity:
1. Keep the number of obstructions to a minimum. Each obstruction can reduce
the range of a wireless device. Position the wireless devices in a manner that
will minimize the amount of obstructions between them.
a. For the widest coverage area, install your router near the center of
your home, and near the ceiling, if possible.
b. Avoid placing the router on or near metal objects (such as file cabinets
and metal furniture), reflective surfaces (such as glass or mirrors), and
masonry walls.
c. Any obstruction can weaken the wireless signal (even non-metallic
objects), so the fewer obstructions between the router and the
wireless device, the better.
d. Place the router in a location away from other electronics, motors,
and fluorescent lighting.
e. Many environmental variables can affect the router’s performance, so
if your wireless signal is weak, place the router in several locations and
test the signal strength to determine the ideal position.
2. Building materials can have a large impact on your wireless signal. In an indoor
environment, try to position the wireless devices so that the signal passes
through less dense material such as dry wall. Dense materials like metal, solid
wood, glass or even furniture may block or degrade the signal.
3. Antenna orientation can also have a large impact on your wireless signal. Use
the wireless adapter’s site survey tool to determine the best antenna
orientation for your wireless devices.
4. Interference from devices that produce RF (radio frequency) noise can also
impact your signal. Position your wireless devices away from anything that
generates RF noise, such as microwaves, radios and baby monitors.
If possible, upgrade wireless network interfaces (such as wireless cards in computers)
from older wireless standards to 802.11n. If a wirelessly networked device uses an older
standard, the performance of the entire wireless network may be slower. If you are still
experiencing low or no signal consider repositioning the wireless devices or installing
additional access points.
TEW-718BRM
© Copyright 2013 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
20

TRENDnet User’s Guide
Advanced wireless settings
Setup > Wireless Settings
The advanced wireless features can provide you with additional options for setting up
your wireless network such as multiple SSID, activate/deactivate wireless according to
schedule, and operation modes such as WDS (Wireless Distribution System) bridging or
wireless bridging.
Multiple SSID
Setup > Wireless Settings
The multiple SSID feature allows you to broadcast up to two additional SSIDs (or
wireless network names). To wireless devices searching for available wireless networks
to connect to, the SSIDs (or wireless network names) will appear as separate and
different wireless networks. Since they appear as separate wireless networks, they are
also referred to as virtual APs (Access Points). Each virtual AP can be configured each
with a different SSID (or wireless network name), security type and additional settings
for wireless devices to connect. You can use the multiple SSID feature to setup guest
wireless accounts with a different security type to keep your primary wireless network
security information private. In addition, the SSIDs can be mapped to a specified VLAN
ID. See the VLAN section for instructions on assigning VLAN IDs to the SSIDs.
1. Log into your router management page (see “Access your router management page”
on page 35
2. Click on Setup, and click on Wireless Settings.
3. Click the AP Number drop-down list to select which SSID settings you would like to
configure.
Note: The primary SSID is AP1 and is enabled by default.
© Copyright 2013 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
).
4. Check the Enable option the selected SSID.
5. Enter the Network ID (SSID) (or wireless network name) to assign to the secondary
SSID.
Note: If enabling the secondary SSID AP2, it is strongly recommended to assign an SSID
that is different from the primary SSID AP1, so it can easily identifiable when searching
for wireless networks.
6. Select Enable to allow wireless devices to search and discover the SSID (or wireless
network name) of the selected SSID. Disable turns off the ability for wireless devices to
find your SSID (or wireless network name) of the selected virtual AP when scanning for
available wireless networks. It is still possible for wireless client devices to be manually
configured to connect to the selected SSID even if the SSID broadcast is disabled.
7. Configure the wireless security for the selected SSID. See “Securing your wireless
network” for details on configuring wireless security.
8. To save changes, click Apply.
Note: If you would like to discard the changes, click Undo before you click Apply.
TEW-718BRM
21

TRENDnet User’s Guide
Wireless Schedule
Setup > Wireless Settings
The wireless scheduling feature allows you to control when the wireless functionality of
your router is enabled and disabled using a predefined time schedule. This can be a
useful security tool to prevent unauthorized access for the duration when the router is
not being used.
Note: Before applying scheduling, please ensure your Time settings are configured
correct and you have defined a schedule. See page 36
page 48 to create a schedule.
1. Log into your router management page (see “Access your router management page”
on page 35
2. Click on Setup, and click on Wireless Settings.
3. Click the Wireless Schedule drop-down list and select the preconfigured time
schedule you would like to assign.
Note: Please note that configuring this setting will apply to both SSIDs and cannot be
configured separately for each SSID.
4. To save changes, click Apply.
Note: If you would like to discard the changes, click Undo before you click Apply.
).
Wireless Isolation
Advanced > Advanced Wireless
Wireless isolation is a security feature that restricts communication between wireless
client devices. In other words, enabling wireless isolation prevents wireless client
devices from communicating or accessing each other when connecting through the
modem router. When wireless isolation is enabled, wireless client devices will still be
able to access the Internet and wired devices while connecting through the modem
router.
to configure Time Settings and see
1. Log into your router management page (see “Access your router management page”
on page 35
2. Click on Advanced, and click on Advanced Wireless.
3. At the bottom under Wireless Isolation, check the Enable checkbox to enable the AP
isolation feature or uncheck the option to disable.
4. To save changes, click Apply.
Note: If you would like to discard the changes, click Undo before you click Apply.
).
TEW-718BRM
© Copyright 2013 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
22

TRENDnet User’s Guide
Additional Wireless Settings
Advanced > Advanced Wireless
These settings are advanced options that can be configured to change advanced
wireless broadcast specifications. It is recommended that these settings remain set to
their default values unless you are knowledgeable about the effects of changing these
values. Changing these settings incorrectly can degrade performance.
1. Log into your router management page (see “Access your router management page”
on page 35
2. Click on Advanced, and click on Advanced Wireless.
).
• Regulatory Domain – The channel region assigned (FCC 1~11 or ETSI 1~13).
This setting cannot be modified and is displayed for informational purposes.
• Beacon Interval – A beacon is a management frame used in wireless networks
that transmitted periodically to announce the presence and provide
information about the router’s wireless network. The interval is the amount
time between each beacon transmission.
Default Value:100 milliseconds (range: 1-1000)
• Transmit Power – The wireless transmit power can be modified to a lower
setting such as 50%, 25%, and 12% if necessary. Lowering the wireless transmit
may help to better stabilize the wireless connectivity and reduce the effects of
wireless interference in areas where there are several 2.4GHz wireless devices.
(Default: 100%)
• RTS Threshold – The Request To Send (RTS) function is part of the networking
protocol. A wireless device that needs to send data will send a RTS before
sending the data in question. The destination wireless device will send a
response called Clear to Send (CTS). The RTS Threshold defines the smallest
data packet size allowed to initiate the RTS/CTS function.
Default Value: 2347 (range: 256-2346)
• Fragmentation – Fragmentation in wireless networks is the process of
breaking down data communications into smaller data packets in order to
improve data efficiency when transferring or receiving data between wireless
devices. The fragmentation threshold defines the maximum size of the data
packets that are broken down.
Default Value: 2346 (range: 1500~2346, even numbers only)
• DTIM Interval – A Delivery Traffic Indication Message (DTIM) is an
informational message that is sent as part of a beacon by an access point (your
wireless router) to a wireless client (wireless device or connecting station) in
sleep mode to provide an alert that data is awaiting delivery. The DTIM Interval
(also called Data Beacon Rate) is the amount of time between DTIM
transmissions included in part of a beacon.
Default Value: 1 (range: 1-255)
• WMM Capable – Wi-Fi Multimedia is a Quality of Service (QoS) feature which
prioritizes audio and video data packets. This feature requires the wireless
device to also support WMM. Click Enable (recommended) or Disable to turn
this feature on or off on your router.
• Tx Rates – The wireless transmission rates can be locked down on the device
for testing/troubleshooting or may even stabilize wireless connectivity if
wireless connectivity issues are encountered. Using the default setting “Best”
will allow the device to automatically the best possible data rate achievable.
(Rates (Mbps): 1 , 2, 5.5, 6, 9, 11, 12, 18, 24, 36, 48, 54, MCS0~MCS23).
TEW-718BRM
© Copyright 2013 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
23

TRENDnet User’s Guide
Wireless Operation Modes
The modem router supports multiple wireless operation modes for different application
purposes. This section will explain each operation mode, the function, and how it is
used.
AP Router Mode
Setup > Wireless Settings
AP (Access Point) Router Mode the default wireless operation mode (recommended
mode) of your modem router. This mode allows the modem router to function as both a
wireless access point and router at the same time. In this mode, wireless client devices
connect to your network, access local network resources (Ex. Shared files/folders on
computer or device connected wired or wireless), and the Internet. All client devices
connected either wired or wireless can all access share and access the Internet at the
same time. When operating in this mode, basic wireless settings such as SSID and
wireless security along with Internet access would need to be configured as covered in
the Initial Setup Wizard on page 8.
1. Log into your router management page (see “Access your router management page”
on page 35
2. Click on Setup, and click on Wireless Settings.
3. Click the Wireless Operation Mode drop-down list and select AP Router Mode.
4. To save changes, click Apply.
Note: If you would like to discard the changes, click Undo before you click Apply.
Note: Please refer to page 18 on configuring your wireless settings and page 12
configuring your wireless security settings.
5. If prompted to reboot in order to apply changes, click Reboot at the bottom of the
page and click OK or Continue to reboot the device.
).
TEW-718BRM
on
© Copyright 2013 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
24

TRENDnet User’s Guide
AP Only Mode
Setup > Wireless Settings
AP (Access Point) Only mode allows the modem router to function as a wireless access
point only. In this mode, wireless client devices connect to your network but will not be
assigned IP addresses automatically and cannot share Internet access. The device needs
to be interconnected from one of the four LAN ports (LAN 1-4) to one of the LAN ports
of another router which is configured for and connected to Internet. In addition, the
router must also be configured to assign IP addresses automatically. Please note that in
the diagram, the additional router can be wired or wireless. It is also recommended that
before using this mode, the modem router LAN IP address should be modified to an
available address within the range of the additional router (ex. 192.168.0.x, 192.168.1.x,
etc.) to ensure you are still able to access it’s router management page after set up.
When enabling this mode, the modem router’s DHCP server will be disabled
automatically.
2. Click on Setup, and click on Wireless Settings.
3. Click the Wireless Operation Mode drop-down list and select AP Only Mode.
4. To save changes, click Apply.
Note: If you would like to discard the changes, click Undo before you click Apply.
5. If prompted to reboot in order to apply changes, click Reboot at the bottom of the
page and click OK or Continue to reboot the device.
6. Finally, connect one of the four LAN ports (LAN 1-4) to one of the LAN ports of your
additional router.
TEW-718BRM
Note: Please configure the modem router first, before connecting to any other routers.
Note: Please refer to page 18 on configuring your wireless settings and page 12
configuring your wireless security settings are configured first before using this mode.
1. Log into your router management page (see “Access your router management page”
on page 35
© Copyright 2013 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
).
on
25

TRENDnet User’s Guide
WDS Only Mode & WDS Hybrid Mode
Setup > Wireless Settings
Wireless bridging using WDS allows the modem router to create a wireless bridge with
other WDS supported wireless routers and access points configured in WDS mode to
bridge groups of network client devices together through a wireless bridge. In WDS
Hybrid Mode, the router will also function in access point mode allowing wireless client
devices such as computers, game consoles, mobile phones, etc. to connect in order to
access network resources from multiple groups of network devices as well as the
Internet, unlike WDS Only which strictly operates in wireless bridge mode only and does
NOT allow wireless client devices to connect.
Note: You can create up to four WDS bridge connections. WDS (Wireless Distribution
System) is not currently standardized and may not connect to different model wireless
routers or access points, therefore, when using WDS, it is recommended to use the same
model and version for wireless bridging.
To understand the difference between WDS Only and WDS Hybrid, please reference
diagrams provided.
Notice that in WDS Only mode, the wireless client devices (Laptop Computers) were
removed as the modem router will not allow wireless client devices to connect in this
mode and strictly operate in wireless bridge mode only.
In WDS Hybrid mode (Recommended), the modem router can operate in wireless bridge
mode and also allow wireless client devices to connect at the same time.
TEW-718BRM
© Copyright 2013 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
26

TRENDnet User’s Guide
Note: Before configuring WDS, please ensure the following first:
1. Make sure different IP addresses are assigned to each WDS supported wireless device
used for bridging. (ex. 192.168.10.1,192.168.10.2, 192.168.10.3) to avoid IP address
conflict. See page 38
2. If you are using more than one WDS supported router or access point, please make
sure the LAN DHCP server is enabled on only one unit and disabled on all others to avoid
IP address conflict. See page 38
3. Assign a specific wireless channel and use the same channel on all WDS supported
wireless devices. See page 18
4. Configure the same wireless security and key on all WDS supported devices. See page
14 for configuring wireless security settings.
To configure WDS bridging between TEW-718BRM / TEW-718BRM5 routers:
1. Log into your router management page (see “Access your router management page”
on page 35
2. Click on Setup, and click on Wireless Settings.
3. Click the Wireless Operation Mode drop-down list and select WDS Hybrid Mode or
WDS Only Mode.
).
for changing the LAN IP address.
for configuring basic wireless settings.
for DHCP server options.
5. Click the Channel drop-down list and select a specific wireless channel.
Note: The wireless channel must be the same on all WDS devices.
6. Configure your wireless security. See page 14
Note: The wireless security must be the same on all WDS devices.
7. Enter the wireless MAC address of the other WDS supported device.
(e.g. 00:11:22:AA:BB:CC)
Note: If the other WDS supported device is discoverable wirelessly, you can use the Scan
Remote AP’s MAC List to scan for the other WDS and copy the wireless MAC address
from the discover list.
8. To save changes, click Apply.
Note: If you would like to discard the changes, click Undo before you click Apply.
on securing your wireless network.
TEW-718BRM
9. If prompted to reboot in order to apply changes, click Reboot at the bottom of the
4. Next to Network ID (SSID), enter the SSID (or wireless network name) of the first
router. (e.g. TRENDnet718_1)
Note: SSID setting does not need to be modified if using WDS only mode.
© Copyright 2013 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
page and click OK or Continue to reboot the device.
27

TRENDnet User’s Guide
For additional TEW-718BRM / TEW-718BRM5 routers, make sure to disable the DHCP
server first on all additional routers and configure the LAN IP address to be different on
each router (e.g 192.168.10.2, 192.168.10.3, 192.168.10.4, etc.). You will connect
devices to the LAN ports 1-4 only on all additional routers and the WAN port is not used.
Then, repeat steps 3-9 for additional TEW-718BRM / TEW-718BRM5 routers you are
bridging.
Lazy Mode – Lazy mode is additional WDS configuration option that helps to simplify
setup on to add additional WDS supported devices. At least one device must be
manually configured with all WDS and remote wireless MAC address. The secondary
WDS device must configure at least the wireless channel and wireless security settings.
Then WDS Lazy Mode can be enabled to learn the wireless MAC address of the manually
configured WDS device automatically and create the wireless bridge.
You can repeat the steps to configure the first modem router and configure the wireless
channel, wireless security, and enable lazy mode for enable additional wireless access
points or routers that create a bridge to the first modem router.
TEW-718BRM
© Copyright 2013 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
28

TRENDnet User’s Guide
Universal Repeater
Setup > Wireless Settings
Universal Repeater mode allows the modem router to function as a wireless extender or
repeat the signal of another wireless access point or router in order to extend or
broaden the signal coverage. The diagram displays the modem router in universal
repeater mode repeating/extending the signal of an existing wireless router in order for
laptop computers to establish better wireless connectivity in an area with weak signal
coverage. When enabling this mode, the modem router’s DHCP server will be disabled
automatically.
1. Log into your router management page (see “Access your router management page”
on page 35).
2. Click on Setup, and click on Wireless Settings.
3. Click the Wireless Operation Mode drop-down list and select Universal Repeater.
5. A list of available wireless networks will appear at the bottom of the page. Click Select
next to the wireless network you would like to repeat. The selected entry will populate
the fields at the top of the page. Enter the wireless network encryption key if necessary.
6. To save changes, click Apply.
Note: If you would like to discard the changes, click Undo before you click Apply.
7. If prompted to reboot in order to apply changes, click Reboot at the bottom of the
page and click OK or Continue to reboot the device.
TEW-718BRM
4. Click the Scan button at the bottom of the page.
© Copyright 2013 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
29

TRENDnet User’s Guide
Access Control Filters
Access control basics
MAC address filters
Advanced > Firewall > MAC Filter
Every network device has a unique, 12-digit MAC (Media Access Control) address. Using
MAC filters, you can allow or deny specific computers and other devices from using this
router’s wired or wireless network.
1. Log into your router management page (see “Access your router management page”
on page 35
2. Click on Advanced, click on Firewall, and click on MAC Filter.
3. Add the MAC addresses to the MAC Table first before applying the MAC filter
function.
Note: MAC filter can be configured to allow access to the listed MAC address and deny
all others unlisted or vice versa. The recommended function is to choose to only allow
access to the MAC addresses listed and deny all others unlisted because it is easier to
determine the MAC addresses of devices in your network then to determine which MAC
addresses you do not want to allow access.
To simplify configuration, click the DHCP clients drop-down list to select and computer
or device that is currently connected to your router. Once you have selected the
computer or device, click the ID drop-down list to select which entry to copy the
selected DHCP client information and click Copy To. You can choose a DHCP client from
the drop down list or you can manually enter the MAC/IP address information.
).
Note: If you are manually entering the MAC/IP address information, refer to your
computer or device documentation to find the MAC address.
4. After the MAC address (e.g. 00:11:22:AA:BB:CC) and IP address (e.g. 192.168.10.101)
information is entered, make sure the Allow option next to the entry to allow network
access for this MAC address.
Note: Any unspecified MAC/IP addresses or entries without the Allow option checked
will be denied network access.
5. Next to MAC Address Control at the top of the page, check the Enable option to
enable MAC filtering. Note: Please add MAC/IP address entries first before enabling.
6. Click Apply at the bottom of the page to save the changes.
Note: If you would like to discard the changes, click Undo before you click Apply.
• Next – Displays the next page to the current page of MAC filtering entries.
• Previous – Displays the previous page to the current page of MAC filtering
entries.
TEW-718BRM
© Copyright 2013 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
30

TRENDnet User’s Guide
Domain/URL Filters
Advanced > Firewall > URL Filter
You may want to allow or block computers or devices on your network access to specific
websites (e.g. www.trendnet.com
Locators).
1. Log into your router management page (see “Access your router management page”
on page 35
2. Click on Advanced, click on Firewall, and click on URL Filter.
3. Next to URL Filter, check the Enable option to enable URL filtering.
4. In the entry list, choose an entry and under URL, enter the URL or domain name (e.g.
www.trendnet.com
).
) you would like to block access.
, etc.), also called domains or URLs (Uniform Resource
5. Click Apply at the bottom of the page to save the changes.
Note: If you would like to discard the changes, click Undo before you click Apply.
Additional URL filter options:
Log DNS Query – Checking the Enable optin will log all URL or domain queries in the
router log.
Privilege IP Addresses Range – Enter the IP address range (use last IP address number
only such as 192.168.10.101-192.168.10.110) to exclude from Domain/URL filtering. IP
addresses included in the range will not be blocked from accessing any of the URLs
specified.
TEW-718BRM
• Drop – Checking the option will drop or block access to the specific URL or
domain.
• Log – Checking the option will log the access requests to the specific URL or
domain in the router log. Note: Checking the Log option only will not block
access. You will need to check the Drop option to block access.
• Enable – Check the enable option to enable the URL/domain filter.
© Copyright 2013 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
31

TRENDnet User’s Guide
Keyword Blocking
Advanced > Firewall > Keyword Blocking
You may want to allow or block computers or devices on your network access to web
content with specific keywords instead of complete URL to generally allow or block
computers or devices access to websites that may contain the keyword in the URL or on
the web page.
1. Log into your router management page (see “Access your router management page”
on page 35
2. Click on Advanced, click on Firewall, and click on Keyword Blocking.
3. Next to Keyword Blocking, check the Enable option to enable URL filtering.
4. In the entry list, choose an entry and under keyword, enter the keyword you would
like to block access and check the Enable option.
5. Click Apply at the bottom of the page to save the changes.
Note: If you would like to discard the changes, click Undo before you click Apply.
).
Packet Outbound/Inbound Filter
Advanced > Packet Filter
You may want specify inbound or outbound access control to allow/deny sources (or
Internet IP addresses) to your network from the Internet or from computers or devices
on your network to the Internet. Firewall rules may allow for more granular control of
specific inbound and outbound access between your network and the Internet. It is
recommended that these settings remain set to default unless you are knowledgeable
about the effects of changing the firewall rule configuration. It is possible to have
undesirable functionality from your router if these settings are improperly modified.
1. Log into your router management page (see “Access your router management page”
on page 35
2. Click on Advanced and click on Packet Filter.
Outbound Packet Filter
You may want apply outbound packet filters to allow or deny access of specific traffic
from computers or devices on your local network to the Internet.
To configure outbound packet filters:
Next to Outbound Packet Filter, check the Enable option to enable outbound filtering.
).
• Select Allow all to pass except those match the following rules to allow all
traffic and deny only the filters specified in the list.
• Select Deny all to pass except those match the following rules to deny all
traffic and allow only the filter specified in the list.
TEW-718BRM
© Copyright 2013 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
32

TRENDnet User’s Guide
Review the outbound packet filter settings.
• Source IP – Enter the source IP address or computer/device IP address on your
local network to apply the filter. (e.g. 192.168.10.101)
• Destination IP : Ports – Enter the destination IP address of the
computer/device located on the Internet and port number to apply the filter.
To specify all port numbers, do not specify any value for Ports field. For specific
port numbers, enter a port number or range within the range of 1-65535 (e.g.
21 or 21-30) in the Ports field.
Note: Typically, you can specify 0.0.0.0 for any destination IP address located on
the Internet or enter the specific IP address. (e.g. 10.10.10.200)
• Protocol – Select the protocol type to filter. TCP, UDP, or you can select Both
to choose both protocol types.
• Enable – Check the option to enable the filter.
• Use rule# - Click the drop-down list to select a pre-defined schedule. The filter
will only be active during the time period defined in the pre-defined schedule.
Note: Before applying scheduling, please ensure your Time settings are configured
correct and you have defined a schedule. See page 36
page 48 to create a schedule.
Click Apply at the bottom of the page to save the changes.
Note: If you would like to discard the changes, click Undo before you click Apply.
Clicking MAC Level will bring you to the MAC Filter configuration page. See MAC Filter
section.
Inbound Packet Filter
You may want apply inbound packet filters to allow or deny access of specific traffic
from the Internet to computers or devices on your local network.
to configure Time Settings and see
To configure inbound packet filters:
Click Inbound Filter at the bottom of the outbound packet filter page.
Next to Inbound Packet Filter, check the Enable option to enable inbound filtering.
• Select Allow all to pass except those match the following rules to allow all
traffic and deny only the filters specified in the list.
• Select Deny all to pass except those match the following rules to deny all
traffic and allow only the filter specified in the list.
Review the inbound packet filter settings.
• Source IP – Enter the source IP address or computer/device IP address on your
located on the Internet to apply the filter. (e.g. 192.168.10.101)
Note: Typically, you can specify 0.0.0.0 for any source IP address located on the
Internet or enter the specific IP address. (e.g. 10.10.10.200)
• Destination IP : Ports – Enter the destination IP address of the
computer/device located on your local network and port number to apply the
filter. To specify all port numbers, do not specify any value for Ports field. For
TEW-718BRM
© Copyright 2013 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
33

TRENDnet User’s Guide
specific port numbers, enter a port number or range within the range of 165535 (e.g. 21 or 21-30) in the Ports field.
• Protocol – Select the protocol type to filter. TCP, UDP, or you can select Both
to choose both protocol types.
• Enable – Check the option to enable the filter.
• Use rule# - Click the drop-down list to select a pre-defined schedule. The filter
will only be active during the time period defined in the pre-defined schedule.
• Note: Before applying scheduling, please ensure your Time settings are
configured correct and you have defined a schedule. See page 36
Time Settings and see page 48 to create a schedule.
Click Apply at the bottom of the page to save the changes.
Note: If you would like to discard the changes, click Undo before you click Apply.
Clicking MAC Level will bring you to the MAC Filter configuration page. See MAC Filter
section.
to configure
TEW-718BRM
© Copyright 2013 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
34

TRENDnet User’s Guide
Advanced Router Setup
Access your router management page
Note: Your router management page http://192.168.10.1 is accessed through the use of
your Internet web browser (e.g. Internet Explorer, Firefox, Chrome, Safari, Opera) and
will be referenced frequently in this User’s Guide.
1. Open your web browser (e.g. Internet Explorer, Firefox, Safari, Chrome, or Opera) and
go to http://192.168.10.1
2. Enter the default user name and password and then click Login.
Default User Name: admin
Default Password: admin
. Your router will prompt you for a user name and password.
Change your router login password
Maintenance > Password
1. Log into your router management page (see “Access your router management page”
on page 35
2. Click on Maintenance, and click on Password.
3. In the Old Password field, enter the current password (default: admin). New
Password field, enter the new password and in the New Password field, and in the
Reconfirm field, retype the new password again to confirm.
4. Click Apply at the bottom of the page to save the changes.
Note: If you would like to discard the changes, click Undo before you click Apply.
).
TEW-718BRM
Note: If you change the router login password, you will need to access the router
management page using the User Name “admin” and the new password instead of the
At the bottom left panel, under Language, click the drop-down list to select your
preferred language.
© Copyright 2013 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
default password “admin”.
35

TRENDnet User’s Guide
Set your router date and time
Setup > Time and Date
1. Log into your router management page (see “Access your router management page”
on page 35
2. Click on Setup, and click on Time and Date.
3. Next to Time Zone, click the drop-down list to select your time zone.
4. You can choose one of the following options to set the System Time:
Note: If you do not choose Manual or Auto, choose one of the predefined time servers in
the list.
).
• Time Server (RFC-868) - Next to Auto-Synchronization, check the Enable
option and click the drop-down list and select on one of the options to
configure your time server. You can choose Auto to set the router to
automatically select a predefined time server or Manual to manually enter a
time server (e.g. pool.ntp.org) that is not listed.
Click Apply at the bottom of the page to save the changes, then click Sync with
Time Server and wait for a status result.
Note: If you would like to discard the changes, click Undo before you click
Apply.
OR
• Sync with your computer time - Click Sync with my PC (Date & Time of your
computer) and wait for a status result, then click Apply to save the changes.
TEW-718BRM
Check the Daylight saving time option and configure Start and End of your
daylight savings duration.
© Copyright 2013 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
36

TRENDnet User’s Guide
Manually configure your Internet connection
Setup > Internet Setup
1. Log into your router management page (see “Access your router management page”
on page 35
2. Click on Setup, and click on Internet Setup.
3. In the WAN Interface drop-down list, select which interface to use.
4. In the WAN Type drop-down list, select the type of Internet connection provided by
your ISP (Internet Service Provider).
5. Complete the fields required by your ISP and the optional settings only if required.
6. Click Apply at the bottom of the page to save the changes.
Note: If you would like to discard the changes, click Undo before you click Apply.
Note: If you are unsure which Internet connection type you are using, please contact
your ISP (Internet Service Provider).
7. If prompted to reboot in order to apply changes, click OK or Continue to reboot the
device.
).
• ADSL WAN (Default) – Standard setting for use with ADSL ISPs. Internet
connectivity will be established through the RJ-11 (telephone jack) of the
modem router. PVCs (Private Virtual Circuits) are used to manage and provide
Internet connectivity through ADSL. By default PVC0 is active and used for your
primary ADSL connection.
• Ethernet WAN (Optional) - Converts LAN port 1 to a WAN port Ethernet
interface and disables the use of the RJ-11 port. The Ethernet WAN type does
not require PVC configuration.
Clone a MAC address
Setup > Internet Setup
On any home network, each network device has a unique MAC (Media Access Control)
address. Some ISPs register the MAC address of the device (usually a router or a
computer) connected directly to the modem. If your computer MAC address is already
registered with your ISP and to prevent the re-provisioning and registration process of a
new MAC address with your ISP, then you can clone the address (assign the registered
MAC address of your previous device to your new router). If you want to use the MAC
address from the previous device (computer or old router that directly connected to the
modem, you should first determine the MAC address of the device or computer and
manually enter it into your router using the clone MAC address feature.
Note: For many ISPs that provide dynamic IP addresses automatically, typically, the
stored MAC address in the modem is reset each time you restart the modem. If you are
installing this router for the first time, turn your modem before connecting the router to
your modem. To clear your modem stored MAC address, typically the procedure is to
disconnect power from the modem for approximately one minute, then reconnect the
power. For more details on this procedure, refer to your modem’s User Guide/Manual or
contact your ISP.
1. Log into your router management page (see “Access your router management page”
on page 35
2. Click on Setup, and click on Internet Setup.
3. Next to ISP registered MAC Address, click Clone to clone your computer’s MAC
address or manually enter the 12-digit MAC address of your old router.
(e.g. 00:11:22:AA:BB:CC)
4. Click either Clone MAC Address to clone the MAC address of the computer you are
currently using or manually enter the 12-digit MAC address of your old router.
5. Click Apply at the bottom of the page to save the changes.
).
Note: If you would like to discard the changes, click Undo before you click Apply.
TEW-718BRM
© Copyright 2013 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
37

TRENDnet User’s Guide
Change your router IP address
Setup > Local Network
In most cases, you do not need to change your router IP address settings. Typically, the
router IP address settings only needs to be changed, if you plan to use another router in
your network with the same IP address settings, if you are connecting your router to an
existing network that is already using the IP address settings your router is using, or if
you are experiencing problems establishing VPN connections to your office network
through your router.
Note: If you are not encountering any issues or are not faced with one of the cases
described above or similar, it is recommended to keep your router IP address settings as
default.
Default Router IP Address: 192.168.10.1
Default Router Network: 192.168.10.0 / 255.255.255.0
1. Log into your router management page (see “Access your router management page”
on page 35
2. Click on Setup, and click on Local Network.
3. Next to LAN IP Address and Subnet Mask, enter the router IP address settings.
).
• LAN IP Address – Enter the new router IP address.
(e.g. 192.168.200.1)
• Subnet Mask – Click the Subnet Mask drop-down list to select a mask.
(e.g. 255.255.255.0)
Note: The DHCP address range will change automatically to your new router IP
address settings so you do not have to change the DHCP address range manually to
match your new router IP address settings.
4. To save changes, click Apply.
Note: You will need to access your router management page using your new router IP
address to access the router management page. (e.g. Instead of using the default
http://192.168.10.1
your new router IP address http://(new.router.ipaddress.here) to access your router
management page.
using your new router IP address will use the following format using
Set up the DHCP server on your router
Setup > Local Network
Your router can be used as a DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) server to
automatically assign an IP address to each computer or device on your network. The
DHCP server is enabled by default on your router. If you already have a DHCP server on
your network, or if you do not want to use your router as a DHCP server, you can disable
this setting. It is recommended to leave this setting enabled.
1. Log into your router management page (see “Access your router management page”
on page 35
2. Click on Setup, and click on Local Network.
3. Review the DHCP Server settings.
).
TEW-718BRM
© Copyright 2013 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
38

TRENDnet User’s Guide
• DHCP Server – Enable or Disable the DHCP server.
• IP Pool Starting Address – Changes the starting address for the DHCP server
range. (e.g. 192.168.10.20)
• IP Pool Starting Address – Changes the last address for the DHCP server range.
(e.g. 192.168.10.30)
Note: The Start IP and End IP specify the range of IP addresses to automatically
assign to computers or devices on your network.
• Lease Time – Specifies the DHCP client lease time in seconds.
• Domain Name (Optional) – Specifies a domain name to assign to computers or
devices. (e.g. trendnet.com)
• DHCP Server Relay – If you have an external DHCP server and do not want to
use the router’s built-in DHCP server. To enable this setting, click Enable.
• DHCP Server IP – If DHCP Server Relay is enabled, enter the IP address of your
external DHCP server to relay DHCP requests.
Note: The DHCP lease time is the amount of time a computer or device can keep an
IP address assigned by the DHCP server. When the lease time expires, the computer
or device will renew the IP address lease with the DHCP server, otherwise, if there is
no attempt to renew the lease, the DHCP server will reallocate the IP address to be
assigned to another computer or device.
4. To save changes, click Apply.
Note: Clicking the More… option will allow you to configure additional parameters for
your DHCP server on your router to assign to computers or devices on your network.
Clients List – If you click Clients List, you can view the list of active lease entries for
computers or devices that have been assigned IP addresses automatically from the
DHCP server on your router.
The DHCP Clients List will allow you to select multiple clients and assign DHCP
reservation by selecting and clicking Fixed Mapping.
• Delete – Deletes the selected DHCP client device from the DHCP Clients List
table.
• Back – (At the bottom of the page) Returns you to the main DHCP server
configuration page.
• Refresh –(At the bottom of the page) Refreshes the DHCP Clients List.
TEW-718BRM
© Copyright 2013 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
39

TRENDnet User’s Guide
Set up DHCP reservation
Setup > Local Network > Fixed Mapping
DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) reservation (also called Static DHCP) allows
your router to assign a fixed IP address from the DHCP server IP address range to a
specific device on your network. Assigning a fixed IP address can allow you to easily
keep track of the IP addresses used on your network by your computers or devices for
future reference or configuration such as virtual server (also called port forwarding, see
“Virtual Server” on page 44
“Special Applications” on page 46).
1. Log into your router management page (see “Access your router management page”
on page 35
2. Click on Setup, click on Local Network
4. You can choose one of the following options to add a DHCP reservation:
).
• Select an existing DHCP client from drop-down menu - If the device or
computer are adding is already connected to your router and is assigned an IP
address automatically from the DHCP server on your router, click the DHCP
clients drop-down menu and select computer or device. Then click the ID drop-
down menu and select the ID you would like to assign the DHCP client and click
Copy to.
The DHCP client will be copied to the ID you selected in the list. Check the
Enable option next to the entry.
) or special applications (also called port triggering, see
Click Apply at the bottom of the page to save the changes.
Note: If you would like to discard the changes, click Undo before you click
Apply. If you click Back, this will return you to the main DHCP Server page.
OR
Enter the DHCP reservation manually – Select one of the empty/available IDs
in the list and next to the ID # click on MAC Address and enter the MAC
address (e.g. 00:11:22:AA:BB:CC) of the computer or device for which you are
creating the reservation. Then click on the IP Address field and enter the IP
address (e.g. 192.168.10.101) to assign for the reservation and check the
Enable option.
Note: You cannot assign IP addresses outside of the DHCP range. The IP address
is required to be within the DHCP IP address range (IP Pool Starting Address &
IP Pool Starting Address) in the main DHCP Server page.
Click Apply at the bottom of the page to save the changes.
Note: If you would like to discard the changes, click Undo before you click
Apply. If you click Back, this will return you to the main DHCP Server page.
TEW-718BRM
© Copyright 2013 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
40

TRENDnet User’s Guide
Enable/disable UPnP on your router
Advanced > UPnP
UPnP (Universal Plug and Play) allows devices connected to a network to discover each
other and automatically open the connections or services for specific applications (e.g.
instant messenger, online gaming applications, etc.) UPnP is enabled on your router by
default to allow specific applications required by your computers or devices to allow
connections through your router as they are needed.
1. Log into your router management page (see “Access your router management page”
on page 35
2. Click on Advanced, and click on UPnP.
3. Next to UPnP, click Enabled or Disabled to turn the feature on or off on your router.
Note: It is recommended to leave this setting enabled, otherwise, you may encounter
issues with applications that utilize UPnP in order allow the required communication
between your computers or devices and the Internet.
4. Click Apply at the bottom of the page to save the changes.
Note: If you would like to discard the changes, click Undo before you click Apply.
).
Allow/deny VPN connections through your router
Advanced > Firewall > Others
A Virtual Private Network (VPN) is a network that uses a public network, such as the
Internet, to provide secure communications between a remote computer or network
and another network. Some offices often provide VPN access to their networks to
enable employees to work from their remote office/home office, or while traveling.
If your office or place of work has allowed and authorized access for you to access their
network through VPN, the default VPN settings in your router have been configured to
pass through the most common types of VPN protocols, which typically do not require
any additional configuration changes.
1. Log into your router management page (see “Access your router management page”
on page 35
2. Click on Advanced, click on Firewall, and click on Others.
3. Next to Disable PPTP, Disable L2TP, or Disable IPsec check Enable to turn off the VPN
passthrough feature for the specific VPN protocol.
Note: It is recommended to leave these settings unchecked to ensure VPN passthrough
capability is enabled on your router.
4. Click Apply at the bottom of the page to save the changes.
Note: If you would like to discard the changes, click Undo before you click Apply.
).
TEW-718BRM
© Copyright 2013 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
41

TRENDnet User’s Guide
Additional Security Settings
Advanced > Firewall > Others
To provide additional security, your router offers DoS (Denial of Service) detection, SPI
mode, WAN stealth mode to further prevent network attacks. You may want to enable
these features for additional network security.
1. Log into your router management page (see “Access your router management page”
on page 35
2. Click on Advanced, click on Firewall, and click on Others.
3. Review the additional security settings.
).
• Discard PING from WAN Side – Check this option to prevent your router from
responding to ping or ICMP (Internet Control Message Protocol) requests from
the Internet.
• DoS Attack Detection – Check this option to enable DoS (Denial of Service)
detection. If DoS attacks are detected, information can be found in the device
logs. Please note that this is detection only, not prevention.
• SPI mode – Check this option to enable the router to record packet sessions
through the router and ensure that incoming and outgoing packets are valid.
• Keep WAN in stealth mode – Check this option to prevent your router from
responding to port scans from the Internet.
4. Click Apply at the bottom of the page to save the changes.
Note: If you would like to discard the changes, click Undo before you click Apply.
Allow/deny multicast streaming
Setup > Internet Setup
In some cases, applications require multicast communication (also called IP multicast
which is the delivery of information to a specific group of computers or devices in a
single transmission) typically used in media streaming applications. Multicast streaming
is disabled by default on your router to deny applications that require multicast
communication through your router.
1. Log into your router management page (see “Access your router management page”
on page 35
2. Click on Setup, and click on Internet Setup
3. Under your Internet connection settings, next to Multicast, click the drop-down menu
and select the IGMP multicast version protocol you would like to enable.
4. Click Apply at the bottom of the page to save the changes.
Note: If you would like to discard the changes, click Undo before you click Save.
).
• Auto – Automatically detects which IGMP multicast version to use.
• IGMP v1 – Specifies to use IGMP protocol version 1 for multicast traffic.
• IGMP v2 – Specifies to use IGMP protocol version 2 for multicast traffic.
• IGMP v3 – Specifies to use IGMP protocol version 3 for multicast traffic.
• IGMP Snooping – Enabling IGMP snooping supports helps to passthrough
multicast streams and traffic more effectively and prevents the network from
being flooded by multicast traffic. It is recommended to enable this setting if
enabling IGMP multicast support.
TEW-718BRM
© Copyright 2013 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
42

TRENDnet User’s Guide
Identify your network on the Internet
Advanced > Dynamic DNS
Since most ISPs constantly change your home IP address, providing access to devices on
your home or small office Local Area Network (such as IP Cameras) from the Internet
requires setting up a Dynamic DNS service and entering the parameters into this
management area. Dynamic DNS services allow your router to confirm its location to the
given Dynamic DNS service, thereby providing the Dynamic DNS service with the ability
to provide a virtual fixed IP address for your network. This means that even though your
ISP is always changing your IP address, the Dynamic DNS service will be able to identify
your network using a fixed address—one that can be used to view home IP Camera and
other devices on your local area network.
Note: First, you will need to sign up for one of the DDNS service providers listed in the
Server Address drop-down list.
1. Sign up for one of the DDNS available service providers list under Server Address.
(e.g. dyndns.com, no-ip.com, etc.)
2. Log into your router management page (see “Access your router management page”
on page 35
3. Click on Advanced and click on Dynamic DNS.
4. Next to DDNS, click Enable.
your information in the fields.
6. To save changes, click Apply.
).
5. In the Server Address drop-down list, select the provider you selected, and enter
• Host Name: Personal URL provided to you by your Dynamic DNS service
provider (e.g. www.trendnet.dyndns.biz)
• User Name / E-mail: The user name needed to log in to your Dynamic DNS
service account
• Password/Key: This is the password to gain access to Dynamic DNS service
(NOT your router or wireless network password) for which you have signed up
to.
Allow remote access to your router management page
Maintenance > Remote Management
You may want to make changes to your router from a remote location such at your
office or another location while away from your home.
1. Log into your router management page (see “Access your router management page”
on page 35
2. Click on Maintenance, and click on Remote Management.
3. Under the HTTP section, click Enabled.
4. To save changes, click Apply.
This section also provides the option to configure the idle timeout period before
automatically logging you out of the router management page. Next to Administrator
Time-out, you can enter the idle timeout in seconds before automatically logging you
out of the router management page.
).
• Host – It is recommended to leave this setting as 0.0.0.0 / 0, to allow remote
access from anywhere on the Internet.
Note: You can enter a specific IP subnet of Internet IP addresses or specific
Internet IP address (ex. 10.10.10.10 / 32) that is allowed to access your router
management page, all others will be denied.
• Port– It is recommended to leave this setting as 8080.
Note: If you have configured port 8080 for another configuration section such
as virtual server or special application, please change the port to use.
(Recommended port range 1024-65534)
TEW-718BRM
© Copyright 2013 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
43

TRENDnet User’s Guide
Open a device on your network to the Internet
This router can provide access to devices on your local area network to the Internet
using the Virtual Server, Special Application, method (DMZ NOT recommended).
DMZ
Advanced > Firewall > DMZ
You may want to expose a specific computer or device on your network to the Internet
to allow anyone to access it. Your router includes the DMZ (Demilitarized Zone) feature
that makes all the ports and services available on the WAN/Internet side of the router
and forwards them to a single IP address (computer or network device) on your
network. The DMZ feature is an easy way of allowing access from the Internet however,
it is a very insecure technology and will open local area network to greater threats from
Internet attacks.
It is strongly recommended to use Virtual Server (also called port forwarding, see
“Virtual Server” on page 35
the Internet.
1. Make sure to configure your computer or network device to use a static IP address or
you can use the DHCP reservation feature (see “Set up DHCP reservation” on page 53).
2. Log into your router management page (see “Access your router management page”
on page 35
3. Click on Advanced, click on Firewall, and click on DMZ.
4. Next to IP Address of DMZ Host, enter the IP address you assigned to the computer
or network device to expose to the Internet and check Enable.
).
) to allow access to your computers or network devices from
Virtual Server
Advanced > NAT > Virtual Server
Virtual Server (also called port forwarding) allows you to define specific ports (used or
required by a specific application) and forward them to a single IP address (a computer
or device) on your network. Using this feature is more secure compared to using DMZ
(see “DMZ” on page 44
used by an application. An example would be forwarding a port to an network/IP
camera (typically on TRENDnet IP cameras use HTTP TCP port 80 for remote access web
requests) on your network for to allow remote access to it.
Since most ISPs constantly change your home IP address, to be able to access the Virtual
Server port(s) from the Internet it is recommended to setup Dynamic DNS service (See
DynDNS section).
1. Log into your router management page (see “Access your router management page”
on page 35
2. Click on Advanced, click on NAT, and click on Virtual Server.
To simplify configuration, there is a list of commonly used pre-defined virtual server
entries to modify by clicking the Well known services drop-down list, otherwise, you
can choose to manually add a new virtual server.
).
) in which DMZ forwards all ports instead of only specific ports
TEW-718BRM
5. To save changes, click Apply.
Note: If using ADSL WAN with multiple PVCs, click the DMZ Mode drop-down list to
select Multi Mode which will allow you which PVC to assign the DMZ Host.
© Copyright 2013 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
44

TRENDnet User’s Guide
3. Review the virtual server settings.
• Service Ports – Enter the port number required by your device. This will be the
same port number used to access the device from the Internet and will include
both TCP and UDP protocols.
Note: Please refer to the device documentation to determine which ports and
protocols are required.
• Server IP – Enter the IP address of the device to forward the port. (e.g.
192.168.10.101).
Note: You should assign a static IP address to the device or use DHCP
reservation to ensure the IP address of the device does not change.
• Enable – Checking the Enable option turns on the virtual server.
• Schedule - Click the drop-down list assign a pre-defined schedule when the
virtual server is activated or inactive.
Note: To define a schedule, see the “Create schedules” section.
4. To save changes, click Apply.
Note: If using ADSL WAN with multiple PVCs, click the Virtual Server Mode drop-down
list to select MultiMode which will allow you which PVC to assign the Virtual Server.
Example: To forward TCP port 80 to your IP camera
1. Make sure to configure your network/IP camera to use a static IP address or you can
use the DHCP reservation feature (see “Set up DHCP reservation” on page 53).
Note: You may need to reference your camera documentation on configuring a static IP
address.
2. Log into your router management page (see “Access your router management page”
on page 35
3. Click on Advanced, click on NAT, and click on Virtual Server.
4. In the Well known services drop-down list, select the pre-defined virtual server entry
named WEB (80). In the ID drop-down list, select 1. Click Copy to.
5. ID 1 fields will be populated with the selected pre-defined virtual server entry.
6. Under Server IP, enter the IP address assigned to the camera. (e.g. 192.168.10.101)
).
TEW-718BRM
7. To save changes, click Apply.
© Copyright 2013 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
45

TRENDnet User’s Guide
Special Applications
Advanced > NAT > Special AP
Special applications (also called port triggering) is typically used for online gaming
applications or communication applications that require a range of ports or several
ports to be dynamically opened on request to a device on your network. The router will
wait for a request on a specific port or range of ports (or trigger port/port range) from a
device on your network and once a request is detected by your router, the router will
forward a single port or multiple ports (or incoming port/port range) to the device on
your network. This feature is not typically used as most devices and routers currently
use UPnP (Universal Plug and Play) to automatically configure your router to allow
access for applications. See “Enable/disable UPnP on your router” on page 41
Note: Please refer to the device documentation to determine if your device supports
UPnP first, before configuring this feature.
1. Log into your router management page (see “Access your router management page”
on page 35
2. Click on Advanced, click on NAT, and click on Special AP.
To simplify configuration, there is a list of commonly used pre-defined special
application entries to modify by clicking the Popular applications drop-down list,
otherwise, you can choose to manually add a new special application.
).
3. Review the special application settings.
• Trigger – Port or port range requested by the device.
(e.g. 2000-2001 or 2000)
Note: Please refer to the device documentation to determine which ports are
.
Note: Please refer to the device documentation to determine which ports are required.
4. To save changes, click Apply.
required.
• Incoming Ports – Port(s) forwarded to the device.
(e.g. 2000-2038,2069,2081,2200-2210)
Note: Please refer to the device documentation to determine which ports are
required.
• Enable – Checking the Enable option turns on the special application.
TEW-718BRM
© Copyright 2013 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
46

TRENDnet User’s Guide
Prioritize traffic using QoS (Quality of Service)
Configuration > Advanced Setting > Quality of Service
You may want to prioritize outbound traffic for specific computers or devices on your
network to have higher priority.
1. Log into your router management page (see “Access your router management page”
on page 35
2. Click on Advanced, and click on Quality of Service.
3. Click the QoS drop-down list and select the Enable option.
4. The WAN Interface allows you to select a specific PVC to assign QoS if using ADSL
WAN and multiple PVCs with your ISP. The default setting is PVC0.
5. Enter the approximated upload (Upstream) and download (Downstream) speeds in
kbps provided by your ISP.
).
Management feature, the modem router can automatically determine the
traffic priority based on the selected categories to prioritize.
• User-Defined QoS – This QoS mode is recommended for advanced users only is
provided only to allow the option to provide more granular control of the
modem router QoS settings.
To configure Smart-QoS:
1. For the QoS Mode, select Smart-QoS.
2. Check the categories you would like to assign priority and enter the percentage.
OR enable Flexible Bandwidth Management and check which categories you would
like to prioritize.
TEW-718BRM
6. Choose the QoS Mode.
• Smart-QoS (Recommended) – This mode allows for easy QoS configuration
based on simply selecting pre-defined application categories. You can manually
assign a percentage to assign for each category or using the Flexible Bandwidth
© Copyright 2013 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
3. To save changes, click Apply.
47

TRENDnet User’s Guide
Create schedules
Maintenance > Time Schedule
For additional security control, your router allows you to create schedules to specify a
time period when a feature on your router should be activated and deactivated. Before
you use the scheduling feature on your router, ensure that your router system time is
configured correctly. See page 36
Note: You can apply a predefined schedule to the following features:
• Wireless
• Virtual Server
• Packet Filters
• QoS
Create a schedule to define the days/time period when a feature should be active or
inactive:
1. Log into your router management page (see “Access your router management page”
on page 35
2. Click on Maintenance, and click on Time Schedule.
3. Next to Schedule, check the Enable option.
4. Click Apply at the bottom of the page.
5. Next to a schedule entry, click Add New.
).
6. Next to Name of Rule #, enter a name for the schedule.
7. Next to Policy, select the type of policy.
Note: This setting will determine how the schedule function should operate the feature it
is applied.
to configure the system time.
• Deactivate – Choosing this policy type will activate or enable the feature during
the day/time schedule specified and deactivate or disable the feature anytime
other day/times outside of the specified schedule.
• Activate – Choosing this policy type will deactivate or disable the feature
during the day/time schedule specified and activate or enable the feature
anytime other day/times outside of the specified schedule.
8. Next to one of the entries, click Week Day and choose the day you would like to apply
the schedule. In the Start Time (hh:mm) field, enter the start time. (e.g. 05:00) and in
the End Time (hh:mm) field, enter the end time. (e.g.15:00).
Time Range: 00:00 (12:00AM) - 23:59 (11:59PM)
Note: Under Week Day, you can choose every day to apply the schedule to every day of
the week.
9. To save changes, click Apply.
10. Apply the schedule to one of the applicable features (Wireless, Virtual Server, Packet
Filters, or QoS) in the drop-down list option Use Rule#.
TEW-718BRM
© Copyright 2013 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
48

TRENDnet User’s Guide
Using VLANs
Advanced > VLAN
You may want set up VLANs (Virtual Local Area Networks) to separate your network into
groups in order to isolate/restrict network traffic, reduce the congestion of traffic in one
large network, or expand the physical boundaries of one local LAN network. The
primary applications of VLAN and this device would be IPTV applications where ISP can
bridge the WAN and one or more LAN ports together to improve IPTV service
compatibility and performance from the ISP or separating wireless network access
based on SSID and assigned VLAN mapping.
Note: This device does not support Inter-VLAN Layer 3 routing (does not support multiple
IP interfaces). This device only supports Layer 2 based VLAN where traffic can be
forwarded based on PVID (Port VLAN ID) and VID (VLAN ID) tags or identifiers. You would
require an additional network router or Layer 3 device that supports inter-VLAN routing.
Note: Configuring this feature assumes that you have some general networking
knowledge.
1. Log into your router management page (see “Access your router management page”
on page 35
2. Click on Advanced, and click on VLAN.
3. Under VID columns, enter the VID settings. (Range: 1~4094)
Note: The default VID is 1 which is the primary LAN IP interface setting. Initially, all ports
and SSIDs are assigned VID 1 which puts all interfaces in the same LAN network. It
strongly recommended to keep at least one wired LAN port in VID 1 for management
purposes. If VID 1 is removed, the router management page will no longer be accessible
through the LAN IP address.
).
4. Check the Tx TAG options for the selected interfaces to add the VID tag information
to incoming and outgoing traffic.
5. To save changes, click Apply.
Note: In addition, the WAN VLAN interface settings can be configured by clicking WAN
VLAN Settings button at the bottom of the page.
Below is an example diagram of two separate networks created using 2 VLANs assigned
to each SSID and LAN port 1 and 2 communicating independently.
TEW-718BRM
© Copyright 2013 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
49

TRENDnet User’s Guide
Add static routes to your router
Advanced > Static Route
You may want set up your router to route computers or devices on your network to
other local networks through other routers. Generally, different networks can be
determined by the IP addressing assigned to those networks. Generally speaking and for
the case of an example, your network may have 192.168.10.x IP addressing and another
network may have 192.168.20.x IP addressing and because the IP addressing of these
two networks are different, they are separate networks. In order to communicate
between the two separate networks, static routing needs to be configured. Below is an
example diagram where routing is needed for devices and computers on your network
to access the other network.
Note: Configuring this feature assumes that you have some general networking
knowledge.
1. Log into your router management page (see “Access your router management page”
on page 35
2. Click on Advanced, and click on Static Route.
3. Next to Static Routing, check the Enable option to enable static routing.
3. Review the static route settings.
4. To save changes, click Apply.
).
• Destination – Enter the IP network address of the destination network for the
route.
(e.g. 192.168.20.0)
• Subnet Mask – Enter the subnet mask of the destination network for the route.
(e.g. 255.255.255.0)
• Gateway – Enter the gateway to the destination network for the route.
(e.g. 192.168.10.2)
• Hop – Enter the number of hops (routers) required to reach the destination
network. The hop count range that can be specified is 0-99.
• Enable – Check the option to enable the route and uncheck the option to
disable the route.
TEW-718BRM
© Copyright 2013 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
50

TRENDnet User’s Guide
Enable dynamic routing on your router
Advanced > RIP Settings
You may want to setup your router to route computers or devices on your network to
other local networks through other routers. If other routers support dynamic routing
such as RIP (Routing Information Protocol), you can enable this feature on your router
to automatically learn the required routes to reach those networks. It is required that
the same dynamic routing protocol and version is also enabled on the other routers in
order your router and the other routers to exchange information about the network.
Note: Configuring this feature assumes that you have some general networking
knowledge.
1. Log into your router management page (see “Access your router management page”
on page 35
2. Click on Configuration at the top of the page, click on Advanced Setting, and click on
Routing.
3. Select the appropriate dynamic routing protocol and version communicate with other
routers.
4. To save changes, click Apply.
).
• Disabled – Disable sending and receiving or exchange of routing information
dynamically between your router and other routers.
• RIPv1 - Enables sending and receiving or exchange of routing information
dynamically between your router and other routers to build routes to your
network and other networks using the RIP version 1 protocol.
• RIPv2 – Enables sending and receiving routing information dynamically
between your router and other routers to build routes to your network and
other networks using the RIP version 2 protocolRIP 1 - Receive routing
information from other routers using the RIP version 1 protocol.
Using WoL (Wake on LAN) on your router
Maintenance > Ping
You may want to use your router to power on devices remotely using WoL (Wake on
LAN). In order for this feature to work, the computer or device should support WoL and
this feature should be enabled and configured properly. Please refer to your computer
or device User’s Guide/Manual for instructions on using WoL.
1. Log into your router management page (see “Access your router management page”
on page 35
2. Click on Maintenance, and click on Ping.
3. Next to MAC Address for Wake-on-LAN, enter the MAC address of the device with
WoL enabled and configured. (e.g. 00:11:22:AA:BB:CC) click Wake up to send WoL
messages to the MAC Address specified.
4. To save changes, click Apply.
).
TEW-718BRM
© Copyright 2013 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
51

TRENDnet User’s Guide
Setup IPv6 on your router
Setup > IPv6
IPv6 (Internet Protocol Version 6) was developed to be the successor protocol to well
known and widely used protocol IPv4 (Internet Protocol Version 4) for network
addressing. The new addressing protocol is designed to minimize processing overhead
by routers, significantly increase the available IP address space, provide integrated
security, and open the possibility of more extensions and options. ISP have already
transition their networks to accommodate IPv6 and are starting to offer IPv6 services.
Note: The router offers native IPv6 as well as IPv4 to IPv6 transitional connection types.
1. Log into your router management page (see “Access your router management page”
on page 35
2. Click on Setup, and click on IPv6.
3. Next to IPv6, select the Enable option to enable IPv6.
WAN IPv6 Address Settings
4. Click the Connection Type drop-down list to select the connection provided by your
ISP (Internet Service Provider).
).
7. If prompted to reboot in order to apply changes, click OK or Continue to reboot the
device.
Note: When configuring PPPoE, the IPv6 Dual Stack option is available under Setup >
Internet Setup in the PPPoE connection settings.
LAN IPv6 Address Settings
8. Enter your LAN IPv6 address.
• LAN IPv6 Address – Enter the router LAN IPv6 address.
9. Configure your IPv6 Autoconfiguration (LAN IPv6 DHCP server) settings.
TEW-718BRM
5. Complete the fields required by your ISP and the optional settings only if required.
6. Click Apply at the bottom of the page to save the changes.
Note: If you would like to discard the changes, click Undo before you click Apply.
Note: If you are unsure which Internet connection type you are using, please contact
your ISP (Internet Service Provider).
© Copyright 2013 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
10. Click Apply at the bottom of the page to save the changes.
Note: If you would like to discard the changes, click Undo before you click Apply.
52

TRENDnet User’s Guide
Router Maintenance & Monitoring
Reset your router to factory defaults
Maintenance > Configuration Backup/Restore
You may want to reset your router to factory defaults if you are encountering difficulties
with your router and have attempted all other troubleshooting. Before you reset your
router to defaults, if possible, you should backup your router configuration first, see
“Backup and restore your router configuration settings” on page 54
There are two methods that can be used to reset your router to factory defaults.
• Reset Button – Located on the front panel of your router, see “Product
Hardware Features” on page 2
difficulties with accessing your router management page.
OR
• Router Management Page
1. Log into your router management page (see “Access your router management page”
on page 35
2. Click on Maintenance, and click on Configuration Backup/Restore.
3. Under Restore Factory Default, click Restore. When prompted to confirm this action,
click OK.
).
.
. Use this method if you are encountering
Router Default Settings
Administrator User Name admin
Administrator Password admin
Router IP Address 192.168.10.1
Router Subnet Mask 255.255.255.0
DHCP Server IP Range 192.168.10.101-192.168.199
Wireless Enabled
SSID (wireless network name) TRENDnet718
Wireless Security Disabled
802.11 Mode 2.4GHz 802.11b/g/n mixed mode
Channel Auto Channel
TEW-718BRM
© Copyright 2013 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
53

TRENDnet User’s Guide
Backup and restore your router configuration settings
Maintenance > Configuration Backup/Restore
You may have added many customized settings to your router and in the case that you
need to reset your router to default, all your customized settings would be lost and
would require you to manually reconfigure all of your router settings instead of simply
restoring from a backed up router configuration file.
To backup your router configuration:
1. Log into your router management page (see “Access your router management page”
on page 35
2. Click on Maintenance, and click on Configuration Backup/Restore.
3. Click Backup Settings.
3. Depending on your web browser settings, you may be prompted to save a file (specify
the location) or the file may be downloaded automatically to the web browser settings
default download folder. (Default Filename: config.bin)
4. Save the configuration file to location on your computer.
).
To restore your router configuration:
1. Log into your router management page (see “Access your router management page”
on page 35
2. Click on Maintenance, and click on Configuration Backup/Restore.
3. Under Restore Settings, next to Load Settings, depending on your web browser, click
on Browse or Choose File.
A separate file navigation window should open.
4. Navigate to the location of the router configuration file to restore.
(Default Filename: config.bin).
5. Select the router configuration file to restore and click Restore Settings.
(Default Filename: config.bin). If prompted, click Yes or OK.
6. Wait for the router to restore settings.
).
TEW-718BRM
© Copyright 2013 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
54

TRENDnet User’s Guide
Upgrade your router firmware
Maintenance > FW Upgrade
TRENDnet may periodically release firmware upgrades that may add features or fix
problems associated with your TRENDnet router model and version. To check if there is
a firmware upgrade available for your device, please check your TRENDnet model and
version using the link. http://www.trendnet.com/downloads/
In addition, it is also important to verify if the latest firmware version is newer than the
one your router is currently running. To identify the firmware that is currently loaded on
your router, log in to the router, and check the version located at the top right of the
router management page. If there is a newer version available, also review the release
notes to check if there were any new features you may want or if any problems were
fixed that you may have been experiencing.
1. If a firmware upgrade is available, download the firmware to your computer.
2. Unzip the file to a folder on your computer.
Please note the following:
• Do not interrupt the firmware upgrade process. Do not turn off the device or
press the Reset button during the upgrade.
• If you are upgrade the firmware using a laptop computer, ensure that the
laptop is connected to a power source or ensure that the battery is fully
charged.
• Disable sleep mode on your computer as this may interrupt the firmware
upgrade process.
• Do not upgrade the firmware using a wireless connection, only using a wired
network connection.
• Any interruptions during the firmware upgrade process may permanently
damage your router.
1. Log into your router management page (see “Access your router management page”
on page 35
Note: You can check your router’s current firmware version at the top right of the page.
2. Click on Maintenance, and click on FW Upgrade.
Note: This page also displays the current firmware version of your router.
3. Depending on your web browser, next to Upgrade Firmware, click Browse or Choose
File.
5. Navigate to the folder on your computer where the unzipped firmware file (.bin) is
located and select it.
6. Click Upgrade to start the firmware upgrade process. If prompted, click yes or OK.
).
TEW-718BRM
© Copyright 2013 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
55

TRENDnet User’s Guide
Restart your router
Maintenance > Reboot Device
You may want to restart your router if you are encountering difficulties with your router
and have attempted all other troubleshooting.
There are two methods that can be used to restart your router.
• Turn the router off disconnect the power adapter from the rear panel of your
router for 10 seconds and reconnect the power adapter, see “Product
Hardware Features” on page 2
Use this method if you are encountering difficulties with accessing your router
management page. This is also known as a hard reboot or power cycle.
OR
• Router Management Page – This is also known as a soft reboot or restart.
1. Log into your router management page (see “Access your router management page”
on page 35
2. Click on Maintenance, and click on Reboot Device. If prompted, click yes or OK.
3. Click Reboot to restart the router. If prompted, click yes or OK.
).
Check connectivity using the router management page
Maintenance > Ping
For troubleshooting purposes, you may want to check your router connectivity using the
ping (also known as a network connectivity test) test tool on your router management
page.
1. Log into your router management page (see “Access your router management page”
.
on page 35
2. Click on Maintenance, and click on Ping.
3. Next to Domain Name or IP address for Ping Test, enter in the IP address (e.g.
192.168.10.101) or host name (e.g. www.trendnet.com) to test and click Ping.
4. You will receive a success or fail result message of the address you entered providing
a basic indicating of the router’s connectivity to the Internet or devices that are
connected to your network.
5. You will receive a success or fail result message of the address you entered providing
a basic indicating of the router’s connectivity to the Internet or devices that are
connected to your network. Click Back to bring you back to the Ping Test page.
6. Click Apply at the bottom of the page to save the domain name or IP address.
Note: In addition, you can run an ADSL diagnostic connectivity test under Maintenance >
Diagnostics.
).
TEW-718BRM
© Copyright 2013 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
56

TRENDnet User’s Guide
Check the router system information
Status
You may want to check the system information of your router such as WAN (Internet)
connectivity, wireless and wired network settings, and router MAC address information.
1. Log into your router management page (see “Access your router management page”
on page 35
2. Click on Status.
3. Review the device information.
IPv4 System Status WAN (Internet) Information
).
• MAC Address – The current MAC address used by your router’s ADSL WAN port
or interface configuration.
• Connection Type – The current connection type configured ADSL or Ethernet.
• IP Address – The current IPv4 address assigned to your router WAN port or
interface configuration.
• Subnet Mask - The current IPv4 subnet mask assigned to your router WAN port
or interface configuration.
• Gateway – The current gateway IPv4 address assigned to your router WAN
port or interface configuration.
• Domain Name Server – The current DNS address(es) assigned to your router
port or interface configuration.
• Connection Time – Displays the current WAN (Internet) connection status and
the duration that the connection has been established. When using DHCP
Client (or Dynamic IP address) Internet connection type, you will provide the
option to Release and Renew your IP address settings.
Other Internet connection types such as PPPoE will provide the option to
Connect and Disconnect.
IPv6 System Status WAN (Internet) Information
• WAN Link-Local Address – When IPv6 is enabled, displays the current WAN
Link Local Address used by your router’s ADSL WAN port or interface
configuration.
• Global IPv6 Address – When IPv6 is enabled, displays the current Global IPv6
Address used by your router.
• LAN IPv6 Link-Local Address – When IPv6 is enabled, displays the current LAN
IPv6 Link-Local Address used by your router’s LAN port or interface
configuration.
• Link Status – When IPv6 is enabled, displays the IPv6 link status.
TEW-718BRM
© Copyright 2013 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
57

TRENDnet User’s Guide
Wireless Status Information
• MAC Address – The current MAC address of your router’s wireless or interface
configuration.
• Wireless Operation Mode – Displays the current wireless operation mode
configuration of your router.
• Wireless mode – Displays if the router wireless interface is currently enabled or
disabled.
• SSID – Displays the current wireless network name assigned to your router.
• Channel – Displays the current wireless channel your router is operating.
• Security – Displays the current wireless security configured on your router.
Wired LAN Status Information
Packet Statistics Information
The table displays the amount of octets, unicast, and multicast packets sent and
received on your router’s WAN (Internet), LAN, and WLAN interfaces.
Clicking Refresh at the bottom of the page will refresh the information on the status
page.
Clicking View Log will bring you to log page (Maintenance > Syslog > Web Log). See the
“View your router log” section.
Clicking Clients List will bring you to the DHCP Clients List (Setup > Local Network >
Clients List). See “Set up the DHCP server on you router” section.
The router will also display the current TCP/UDP sessions. To view the current sessions,
click NAT Status.
TEW-718BRM
The router will display details ADSL Modem Status information. To view the modem
status information, click ADSL Modem Status.
• MAC Address – The current MAC address of your router’s wired LAN or
interface configuration.
• IP Address - Displays your router’s current IP address.
• Subnet Mask – Displays your router’s current subnet mask.
• DHCP Server - Display your router’s DHCP server status, enabled or disabled.
© Copyright 2013 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
The router system time, uptime, and CPU/Memory load info are displayed the bottom.
58

TRENDnet User’s Guide
View your router log
Maintenance > Syslog > Web Log
Your router log can be used to obtain activity information on the functionality of your
router or for troubleshooting purposes.
1. Log into your router management page (see “Access your router management page”
on page 35
2. Click on Maintenance, and click on Web Log.
3. Review the device log information.
).
• Time – Displays the time of the log entry. If the time is inaccurate, make sure to
set the router date and time correctly. (See “Set your router date and time” on
page 36
• Log – Displays the log message.
)
Router Log Navigation
• First Page – Displays the first page of the log.
• Last Page – Displays the last page of the log.
• Previous Page – Display the log page previous to the current. The Page: 1/1 will
display the current page.
• Next Page – Displays the log page next to the current.
• Clear Log - Clears all logging
• Refresh - The Page: 1/1 will display the current page.
• Download – Download the log file to a local text file on your local hard drive.
TEW-718BRM
© Copyright 2013 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
59

TRENDnet User’s Guide
Configure your router log
Maintenance > Syslog
You may want send your router log to your e-mail address or to an external log server
(also known as Syslog server) so you can check it periodically while away from home.
You may also want to only see specific categories of logging.
Send router logs to an external log server
Maintenance > Syslog > Syslogd
1. Log into your router management page (see “Access your router management page”
on page 35
2. Click on Maintenance, click on Syslogd.
3. Next to Syslog Server, enter the IP address of the external log server to send router
logging and check Enable.
4. To save changes, click Apply.
Send router logs to your e-mail address
Maintenance > Syslog > Email Alert
1. Log into your router management page (see “Access your router management page”
on page 35
2. Click on Maintenance, click on Email Alert.
).
).
3. Review the e-mail log settings.
• Setting of Email alert – Check the option to enable email alert.
• SMTP Server : port – Enter the IP address (e.g. 10.10.10.10) or domain name
(e.g. mail.trendnet.com) of your e-mail server. Enter the port used by your email service. (e.g. Default SMTP Server Port: 25)
• SMTP Username – Enter your account user name for your e-mail service.
• SMTP Password – Enter your password for your e-mail service.
• E-mail addresses – Enter the e-mail addresses to send the log file. (e.g.
user1@trendnet.com,user2@trendnet.com
• E-mail subject – Enter the email subject to briefly describe the purpose of the
email. (e.g. router log file)
4. To save changes, click Apply.
5. Click Email Log Now to send an e-mail of the current router log using your email alert
settings.
)
TEW-718BRM
© Copyright 2013 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
60

TRENDnet User’s Guide
Enable SNMP on your router
Advanced > SNMP
SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol) is a network management protocol used
to monitor (read) and/or manage (write) multiple network devices on a network. This
preconfigured external SNMP server.
1. Log into your router management page (see “Access your router management page”
on page 35
2. Click on Advanced and click on SNMP.
3. Review the options for SNMP.
).
• IP 1-4 – Enter up to four IP addresses of external SNMP servers. (e.g.
192.168.10.250)
• SNMP Version – Select the correct SNMP version to match the SNMP version of
your external SNMP server(s), V1 or V2c.
• WAN Access IP Address – You can specify a single IP address from the Internet
to allow to connect your router using SNMP. (optional)
Note: When allowing Remote SNMP access, leaving this setting blank will allow
access from any IP address from the Internet. It is recommended to specify an IP
address if allowing Remote SNMP access.
Enable TR-069 on your router
Maintenance > TR069 Setting
TR-069 is a network management protocol used to remote manage multiple network
devices on a network typically by ISPs (Internet Service Providers). TR069 usually used
in conjunction with ACS (Auto Configuration Servers) server managed by your ISP.
1. Log into your router management page (see “Access your router management page”
on page 35
2. Click on Maintenance and click on TR069 Setting.
3. Please consult your ISP for the required TR069 settings for remote management.
).
TEW-718BRM
• Enable SNMP – Check the Local option to allow SNMP access on the router
wired LAN and wireless interfaces. Check the Remote option to allow SNMP
access on the router WAN (Internet) interface.
• Get Community – Enter the community name to match the settings with the
external SNMP server. This community will have SNMP read access only.
• Set Community – Enter the community name to match the settings with the
external SNMP server. This community will have SNMP write access.
© Copyright 2013 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
.
61

TRENDnet User’s Guide
Router Management Page Structure
Setup Wizard
• Change Login Password
• Setup ADSL Internet Settings
• Auto Detect VPI/VCI & Encapsulation settings
• Setup Basic Wireless Settings
• Setup Wireless Security
Setup
Advanced
• Internet Setup
• Wireless Settings
o Wireless Operation Modes
o Wireless Security
• Local Settings
• Time and Date
• IPv6
• Advanced Wireless
• RIP Settings
• NAT
o Virtual Server
o Special Application
• Firewall
o MAC Filter
o URL Filter
o Keyword Blocking
o DMZ
o Others
• Packet Filter
• Static Route
• Dynamic DNS
• VLAN
• Quality of Service (QoS)
• UPnP
• SNMP
Maintenance
• Password
• Remote Management
• TR069 Setting
• Syslog
• Time Schedule
• Firmware (FW) Upgrade
• Configuration Backup/Restore
o System Information
o Web Log (Internal)
o Syslog (External)
o Email Alert
o Reset to Factory Default
• Ping
o Ping Test Tool
o Wake-on-LAN (WoL)
• Diagnostics (ADSL Connectivity Test)
• Reboot Device
Status
• IPv4 System Status
• IPv6 System Status
• Wireless Status
• LAN Status
• Statistics Information
• ADSL Modem Status
• NAT Sessions
Logout
• Logout of router management page
TEW-718BRM
© Copyright 2013 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
62

Output: 5V DC, 1.2A external power adapter
TRENDnet User’s Guide
TEW-718BRM
Technical Specifications
Hardware
IEEE 802.3, IEEE 802.3u, IEEE 802.1Q, IEEE 802.1p, IEEE 802.11b, IEEE
802.11g, based on IEEE 802.11n technology
Standards
WAN (ADSL Line Interface) 1 x RJ-11 port (telephone)
LAN
Reset / WPS / WLAN On & Off
Button
ATM & PPP Protocols / Modes
Firewall
Schedules Define schedules for wireless, virtual server, packet filters, and QoS
Network Protocols/Features
Quality of Service
Management / Monitoring
LED Indicators Status, ADSL, WLAN, LAN1~LAN4
Power Adapter Input: 100~240V AC, 50~60Hz, 0.2A
Complies with ADSL standards:
-ANSI T1.413 Issue2, G.992.1 (G.dmt, Annex A), G.992.2 (G.lite)
Complies with ADSL2 standard: G.992.3 (G.dmt.bis, Annex L)
Complies with ADSL2+ standard: G.992.5 (G.dmt.bis+, Annex M)
4 x 10/100 Mbps Auto-MDIX RJ-45 ports (option to convert port 1 to WAN
port)
Reset: Reset to factory defaults (Hold for 15 sec.)
WPS: Activates Wi-Fi Protected Setup (WPS) (Hold for 3 sec.)
WLAN On / Off: Enables or disables wireless radio (Hold for 10 sec.)
VC and LLC multiplexing (Up to 8 PVCs), Ethernet over ATM (RFC 1483
Bridged) with NAT, RFC 1483 bridged, IP over ATM (RFC 1483 Routed), PPP
over ATM (RFC2364), PPP over Ethernet (RFC2516), ATM Traffic QoS (UBR,
CBR, VBR, GFR)
NAT, SPI, DMZ host, virtual servers, MAC / IP filters, URL / keyword filters,
deny WAN ping requests, and WAN stealth mode
IGMP v1/2/3 proxy and snooping , Static and dynamic routing RIP v1/2,
UPnP, DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) server/relay, Dynamic
DNS (DynDNS.com, No-IP.com, TZO.com, and dhs.org), NTP (Network Time
Protocol), PPTP / L2TP / IPsec VPN pass through, IPv6: Static, DHCPv6,
PPPoE, 6 to 4, and IPv6 in IPv4 Tunnel, Stateful / Stateless autoconfiguration
Smart-QoS (simple) or manually defined QoS ToS / CoS (Type of service /
Class of service) based on IP, TCP/UDP port, MAC, DSCP (Differentiated
Services Code Point), and WMM
Local / remote configuration, upgrade firmware, backup / restore
configuration via web browser, TR-069 remote management, DoS (Denial of
Service) detection, internal system log, Syslog, email alert, SNMP v1/v2c,
ping test tool, and Wake-on-LAN (WoL), NAT Status log, Client List log, Web
log, Modem log
Power Consumption 5 watts (max)
Dimension (L x W x H) 189 x 118 x 33 mm (7.4 x 4.6 x 1.3 in.)
Weight 221.1 g (7.8 oz)
Temperature
Humidity Max. 95% (non-condensing)
Certifications CE, FCC
Wireless
Frequency 2.4 ~2.483GHz band
Modulation DBPSK / DQPSK / CCK / OFDM (BPSK / QPSK / 16-QAM / 64-QAM)
Modes
SSID
Antenna 1 x 2 dBi detachable dipole antenna
Data Rate
Security
Output Power
Receiving Sensitivity
Channels 1~ 11 (FCC), 1~13 (ETSI)
Operation: 0° ~ 40°C (32°F ~ 104°F)
Storage: -10° ~ 70°C (14°F ~ 158°F)
Access Point Router, Access Point Only, WDS Hybrid, WDS Only, Universal
Repeater
Broadcast up to 2 SSIDs each with different wireless encryption with support
for VLAN mapping
802.11b: up to 11 Mbps
802.11g: up to 54 Mbps
802.11n: up to 150 Mbps
WEP (HEX/ASCII): 64/128-bit
WPA (AES/TKIP): WPA / WPA2-RADIUS, WPA-PSK / WPA2-PSK
802.11b: 17 dBm (typical)
802.11g: 14 dBm (typical)
802.11n: 14 dBm (typical)
802.11b: -91 dBm (typical) @ 11 Mbps
802.11g: -91 dBm (typical) @ 54 Mbps
802.11n: -87 dBm (typical) @ 150 Mbps
*Maximum wireless signal rates are referenced from IEEE 802.11 theoretical specifications. Actual
data throughput and coverage will vary depending on interference, network traffic, building
materials and other conditions.
© Copyright 2013 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
63

TRENDnet User’s Guide
Troubleshooting
Q: I typed http://192.168.10.1 in my Internet Browser Address Bar, but an error
message says “The page cannot be displayed.” How can I access the router
management page?
Answer:
1. Check your hardware settings again. See “Router Installation” on page 2.
2. Make sure the LAN and WLAN lights are lit.
3. Make sure your network adapter TCP/IP settings are set to Obtain an IP address
automatically or DHCP (see the steps below).
4. Make sure your computer is connected to one of the router’s LAN ports
5. Press on the factory reset button for 15 seconds, the release.
Windows 7
a. Go into the Control Panel, click Network and Sharing Center.
b. Click Change Adapter Settings, right-click the Local Area Connection icon.
c. Then click Properties and click Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4).
d. Then click Obtain an IP address automatically and click OK.
Windows Vista
a. Go into the Control Panel, click Network and Internet.
b. Click Manage Network Connections, right-click the Local Area Connection
icon and click Properties.
c. Click Internet Protocol Version (TCP/IPv4) and then click Properties.
d. Then click Obtain an IP address automatically and click OK.
Windows XP/2000
a. Go into the Control Panel, double-click the Network Connections icon
b. Right-click the Local Area Connection icon and the click Properties.
c. Click Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) and click Properties.
d. Then click Obtain an IP address automatically and click OK.
Note: If you are experiencing difficulties, please contact your computer or operating
system manufacturer for assistance.
Q: I am not sure what type of Internet Account Type I have for my Cable/DSL
connection. How do I find out?
Answer:
Contact your Internet Service Provider (ISP) for the correct information.
Q: The Wizard does not appear when I access the router. What should I do?
Answer:
1. Click on Setup Wizard on the left hand side.
2. Near the top of the browser, “Pop-up blocked” message may appear. Right click on
the message and select Always Allow Pop-ups from This Site.
3. Disable your browser's pop up blocker.
Q: I went through the Wizard, but I cannot get onto the Internet. What should I do?
Answer:
1. Verify that you can get onto the Internet with a direct connection into your ADSL
modem from your ISP (meaning, plug your computer directly to the modem and verify
that your single computer (without the help of the router) can access the Internet).
2. Power cycle your modem router. Unplug the power to the modem router. Wait 30
seconds, and then reconnect the power to the modem router. Wait for the modem
router to fully boot up, then try to re-access the Internet .
3. Contact your ISP and verify all the information that you have in regards to your
Internet connection settings is correct.
Q: I cannot connect wirelessly to the router. What should I do?
Answer:
1. Double check that the WLAN light on the router is lit.
2. Power cycle the router. Unplug the power to the router. Wait 15 seconds, then plug
the power back in to the router.
3. Contact the manufacturer of your wireless network adapter and make sure the
wireless network adapter is configured with the proper SSID. The preset SSID is
TRENDnet(model_number).
4. To verify whether or not wireless is enabled, login to the router management page,
click on Wireless.
5. Please see “Steps to improve wireless connectivity” on page 19
have wireless connectivity problems.
TEW-718BRM
if you continue to
© Copyright 2013 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
64

TRENDnet User’s Guide
Appendix
How to find your IP address?
Note: Please note that although the following procedures provided to follow for your
operating system on configuring your network settings can be used as general
guidelines, however, it is strongly recommended that you consult your computer or
operating system manufacturer directly for assistance on the proper procedure for
configuring network settings.
Command Prompt Method
Windows 2000/XP/Vista/7
1. On your keyboard, press Windows Logo+R keys simultaneously to bring up the Run
dialog box.
2. In the dialog box, type cmd to bring up the command prompt.
3. In the command prompt, type ipconfig /alto display your IP address settings.
MAC OS X
1. Navigate to your Applications folder and open Utilities.
2. Double-click on Terminal to launch the command prompt.
3. In the command prompt, type ipconfiggetifaddr<en0 or en1>to display the wired or
wireless IP address settings.
Note: en0 is typically the wired Network and en1 is typically the wireless Airport
interface.
Graphical Method
MAC OS 10.6/10.5
1. From the Apple menu, select System Preferences.
2. In System Preferences, from the View menu, select Network.
3. In the Network preference window, click a network port (e.g., Network, AirPort,
modem). If you are connected, you'll see your IP address settings under "Status:"
MAC OS 10.4
1. From the Apple menu, select Location, and then Network Preferences.
2. In the Network Preference window, next to "Show:", select Network Status. You'll see
your network status and your IP address settings displayed.
Note: If you are experiencing difficulties, please contact your computer or operating
system manufacturer for assistance.
How to configure your network settings to obtain an IP address automatically or use
DHCP?
Note: Please note that although the following procedures provided to follow for your
operating system on configuring your network settings can be used as general
guidelines, however, it is strongly recommended that you consult your computer or
operating system manufacturer directly for assistance on the proper procedure for
configuring network settings.
Windows 7
a. Go into the Control Panel, click Network and Sharing Center.
b. Click Change Adapter Settings, right-click the Local Area Connection icon.
c. Then click Properties and click Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4).
d. Then click Obtain an IP address automatically and click OK.
Windows Vista
a. Go into the Control Panel, click Network and Internet.
b. Click Manage Network Connections, right-click the Local Area Connection
icon and click Properties.
c. Click Internet Protocol Version (TCP/IPv4) and then click Properties.
d. Then click Obtain an IP address automatically and click OK.
Windows XP/2000
a. Go into the Control Panel, double-click the Network Connections icon
b. Right-click the Local Area Connection icon and the click Properties.
c. Click Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) and click Properties.
d. Then click Obtain an IP address automatically and click OK.
MAC OS 10.4/10.5/10.6
a. From the Apple, drop-down list, select System Preferences.
b. Click the Network icon.
c. From the Location drop-down list, select Automatic.
d. Select and view your Network connection.
In MAC OS 10.4, from the Show drop-down list, select Built-in
Network and select the TCP/IP tab.
In MAC OS 10.5/10.6, in the left column, select Network.
e. Configure TCP/IP to use DHCP.
TEW-718BRM
© Copyright 2013 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
65

TRENDnet User’s Guide
In MAC 10.4, from the Configure IPv4, drop-down list, select Using
DHCP and click the Apply Now button.
In MAC 10.5, from the Configure drop-down list, select Using DHCP
and click the Apply button.
In MAC 10.6, from the Configure drop-down list, select Using DHCP
and click the Apply button.
f. Restart your computer.
Note: If you are experiencing difficulties, please contact your computer or operating
system manufacturer for assistance.
How to find your MAC address?
In Windows 2000/XP/Vista/7,
Your computer MAC addresses are also displayed in this window, however, you can type
getmac –v to display the MAC addresses only.
In MAC OS 10.4,
1. Apple Menu > System Preferences > Network
2. From the Show menu, select Built-in Network.
3. On the Network tab, the Network ID is your MAC Address.
In MAC OS 10.5/10.6,
1. Apple Menu > System Preferences > Network
2. Select Network from the list on the left.
3. Click the Advanced button.
3. On the Network tab, the Network ID is your MAC Address.
How to connect to a wireless network using the built-in Windows utility?
Note: Please note that although the following procedures provided to follow for your
operating system on configuring your network settings can be used as general
guidelines, however, it is strongly recommended that you consult your computer or
operating system manufacturer directly for assistance on the proper procedure for
connecting to a wireless network using the built-in utility.
Windows 7
1. Open Connect to a Network by clicking the network icon (
area.
2. In the list of available wireless networks, click the wireless network you would like to
connect to, then click Connect.
4. You may be prompted to enter a security key in order to connect to the network.
5. Enter in the security key corresponding to the wireless network, and click OK.
Windows Vista
1. Open Connect to a Network by clicking the Start Button.
2. In the Show list, click Wireless.
3. In the list of available wireless networks, click the wireless network you would like to
connect to, then click Connect.
4. You may be prompted to enter a security key in order to connect to the network.
5. Enter in the security key corresponding to the wireless network, and click OK.
Windows XP
1. Right-click the network icon in the notification area, then click View Available
Wireless Networks.
2. In Connect to a Network, under Available Networks, click the wireless network you
would like to connect to.
3. You may be prompted to enter a security key in order to connect to the network.
4. Enter in the security key corresponding to the wireless network, and click Connect.
TEW-718BRM
or ) in the notification
and then click Connect To.
© Copyright 2013 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
66

TRENDnet User’s Guide
Federal Communication Commission Interference Statement
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class B digital
device, pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are designed to provide
reasonable protection against harmful interference in a residential installation. This
equipment generates, uses and can radiate radio frequency energy and, if not installed
and used in accordance with the instructions, may cause harmful interference to radio
communications. However, there is no guarantee that interference will not occur in a
particular installation. If this equipment does cause harmful interference to radio or
television reception, which can be determined by turning the equipment off and on, the
user is encouraged to try to correct the interference by one of the following measures:
• Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
• Increase the separation between the equipment and receiver.
• Connect the equipment into an outlet on a circuit different from that to which
the receiver is connected.
• Consult the dealer or an experienced radio/TV technician for help.
FCC Caution: Any changes or modifications not expressly approved by the party
responsible for compliance could void the user's authority to operate this equipment.
This device complies with Part 15 of the FCC Rules. Operation is subject to the following
two conditions: (1) This device may not cause harmful interference, and (2) this device
must accept any interference received, including interference that may cause undesired
operation.
IMPORTANT NOTE:
FCC Radiation Exposure Statement:
This equipment complies with FCC radiation exposure limits set forth for an
uncontrolled environment. This equipment should be installed and operated with
minimum distance 20cm between the radiator & your body.
This transmitter must not be co-located or operating in conjunction with any other
antenna or transmitter.
The availability of some specific channels and/or operational frequency bands are
country dependent and are firmware programmed at the factory to match the intended
destination. The firmware setting is not accessible by the end user.
RoHS
This product is RoHS compliant.
Europe – EU Declaration of Conformity
This device complies with the essential requirements of the R&TTE Directive 1999/5/EC.
The following test methods have been applied in order to prove presumption of
conformity with the essential requirements of the R&TTE Directive 1999/5/EC:
EN60950-1: 2006 + A11 : 2009 + A1 : 2010 + A12 : 2011
Safety of Information Technology Equipment
EN 50385: 2002
Product standard to demonstrate the compliance of radio base stations and fixed
terminal stations for wireless telecommunication systems with the basic restrictions or
the reference levels related to human exposure to radio frequency electromagnetic
fields (110MHz - 40 GHz) - General public
EN 300 328 V1.7.1 (2006-10)
Electromagnetic compatibility and Radio spectrum Matters (ERM); Wideband
transmission systems; Data transmission equipment operating in the 2,4 GHz ISM band
and using wide band modulation techniques; Harmonized EN covering essential
requirements under article 3.2 of the R&TTE Directive
EN 301 489-1 V1.9.2 (2011-09)
Electromagnetic compatibility and Radio Spectrum Matters (ERM); ElectroMagnetic
Compatibility (EMC) standard for radio equipment and services; Part 1: Common
technical requirements
EN 301 489-17 V2.1.1 (2009-05)
Electromagnetic compatibility and Radio spectrum Matters (ERM); ElectroMagnetic
Compatibility (EMC) standard for radio equipment and services; Part 17: Specific
conditions for 2,4 GHz wideband transmission systems and 5 GHz high performance
RLAN equipment
This device is a 2.4 GHz wideband transmission system (transceiver), intended for use in
all EU member states and EFTA countries, except in France and Italy where restrictive
use applies.
In Italy the end-user should apply for a license at the national spectrum authorities in
order to obtain authorization to use the device for setting up outdoor radio links and/or
for supplying public access to telecommunications and/or network services.
This device may not be used for setting up outdoor radio links in France and in some
areas the RF output power may be limited to 10 mW EIRP in the frequency range of
2454 – 2483.5 MHz. For detailed information the end-user should contact the national
spectrum authority in France.
TEW-718BRM
© Copyright 2013 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
67

Lietuvių
Šiuo TRENDnet deklaruoja, kad šis TEW-718BRM / TEW-718BRM5
[Lithuanian]
atitinka esminius reikalavimus ir kitas 1999/5/EB Direktyvos
TRENDnet User’s Guide
TEW-718BRM
Česky [Czech]
Dansk [Danish]
Deutsch
[German]
Eesti [Estonian]
English
Español
[Spanish]
Ελληνική
[Greek]
Français
[French]
Italiano[Italian]
Latviski
[Latvian]
TRENDnet tímto prohlašuje, že tento TEW-718BRM / TEW-
718BRM5 je ve shodě se základními požadavky a dalšími
příslušnými ustanoveními směrnice 1999/5/ES.
Undertegnede TRENDnet erklærer herved, at følgende udstyr
TEW-718BRM / TEW-718BRM5 overholder de væsentlige krav og
øvrige relevante krav i direktiv 1999/5/EF.
Hiermit erklärt TRENDnet, dass sich das Gerät TEW-718BRM /
TEW-718BRM5 in Übereinstimmung mit den grundlegenden
Anforderungen und den übrigen einschlägigen Bestimmungen
der Richtlinie 1999/5/EG befindet.
Käesolevaga kinnitab TRENDnet seadme TEW-718BRM / TEW718BRM5 vastavust direktiivi 1999/5/EÜ põhinõuetele ja
nimetatud direktiivist tulenevatele teistele asjakohastele sätetele.
Hereby, TRENDnet, declares that this TEW-718BRM / TEW718BRM5 is in compliance with the essential requirements and
other relevant provisions of Directive 1999/5/EC.
Por medio de la presente TRENDnet declara que el TEW-718BRM
/ TEW-718BRM5 cumple con los requisitos esenciales y
cualesquiera otras disposiciones aplicables o exigibles de la
Directiva 1999/5/CE.
ΜΕ ΤΗΝ ΠΑΡΟΥΣΑTRENDnet ΔΗΛΩΝΕΙ ΟΤΙ TEW-718BRM / TEW718BRM5ΣΥΜΜΟΡΦΩΝΕΤΑΙ ΠΡΟΣ ΤΙΣ ΟΥΣΙΩΔΕΙΣ ΑΠΑΙΤΗΣΕΙΣ ΚΑΙ
ΤΙΣ ΛΟΙΠΕΣ ΣΧΕΤΙΚΕΣ ΔΙΑΤΑΞΕΙΣ ΤΗΣ ΟΔΗΓΙΑΣ 1999/5/ΕΚ.
Par la présente TRENDnet déclare que l'appareil TEW-718BRM /
TEW-718BRM5 est conforme aux exigences essentielles et aux
autres dispositions pertinentes de la directive 1999/5/CE.
Con la presente TRENDnet dichiara che questo TEW-718BRM /
TEW-718BRM5 è conforme ai requisiti essenziali ed alle altre
disposizioni pertinenti stabilite dalla direttiva 1999/5/CE.
AršoTRENDnetdeklarē, ka TEW-718BRM / TEW-718BRM5
atbilstDirektīvas 1999/5/EK būtiskajāmprasībām un citiemar to
saistītajiemnoteikumiem.
Nederlands
[Dutch]
Malti [Maltese]
Magyar
[Hungarian]
Polski [Polish]
Português
[Portuguese]
Slovensko
[Slovenian]
Slovensky
[Slovak]
Suomi [Finnish]
Svenska
[Swedish]
nuostatas.
Hierbij verklaart TRENDnet dat het toestel TEW-718BRM / TEW718BRM5 in overeenstemming is met de essentiële eisen en de
andere relevante bepalingen van richtlijn 1999/5/EG.
Hawnhekk, TRENDnet, jiddikjara li dan TEW-718BRM / TEW718BRM5 jikkonforma mal-ħtiġijiet essenzjali u ma provvedimenti
oħrajn relevanti li hemm fid-Dirrettiva 1999/5/EC.
Alulírott, TRENDnet nyilatkozom, hogy a TEW-718BRM / TEW718BRM5 megfelel a vonatkozó alapvetõ követelményeknek és az
1999/5/EC irányelv egyéb elõírásainak.
Niniejszym TRENDnet oświadcza, że TEW-718BRM / TEW718BRM5 jest zgodny z zasadniczymi wymogami oraz pozostałymi
stosownymi postanowieniami Dyrektywy 1999/5/EC.
TRENDnet declara que este TEW-718BRM / TEW-718BRM5 está
conforme com os requisitos essenciais e outras disposições da
Directiva 1999/5/CE.
TRENDnet izjavlja, da je ta TEW-718BRM / TEW-718BRM5 v
skladu z bistvenimi zahtevami in ostalimi relevantnimi določili
direktive 1999/5/ES.
TRENDnettýmtovyhlasuje, že TEW-718BRM / TEW718BRM5spĺňazákladnépožiadavky a
všetkypríslušnéustanoveniaSmernice 1999/5/ES.
TRENDnet vakuuttaa täten että TEW-718BRM / TEW-718BRM5
tyyppinen laite on direktiivin 1999/5/EY oleellisten vaatimusten ja
sitä koskevien direktiivin muiden ehtojen mukainen.
Härmed intygar TRENDnet att denna TEW-718BRM / TEW718BRM5 står I överensstämmelse med de väsentliga
egenskapskrav och övriga relevanta bestämmelser som framgår
av direktiv 1999/5/EG.
© Copyright 2013 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
68

TRENDnet User’s Guide
Limited Warranty
TRENDnet warrants its products against defects in material and workmanship, under
normal use and service, for the following lengths of time from the date of purchase.
TEW-718BRM – 3 Years Warranty
AC/DC Power Adapter, Cooling Fan, and Power Supply carry 1 year warranty.
If a product does not operate as warranted during the applicable warranty period,
TRENDnet shall reserve the right, at its expense, to repair or replace the defective
product or part and deliver an equivalent product or part to the customer. The
repair/replacement unit’s warranty continues from the original date of purchase. All
products that are replaced become the property of TRENDnet. Replacement products
may be new or reconditioned. TRENDnet does not issue refunds or credit. Please
contact the point-of-purchase for their return policies.
TRENDnet shall not be responsible for any software, firmware, information, or memory
data of customer contained in, stored on, or integrated with any products returned to
TRENDnet pursuant to any warranty.
There are no user serviceable parts inside the product. Do not remove or attempt to
service the product by any unauthorized service center. This warranty is voided if (i) the
product has been modified or repaired by any unauthorized service center, (ii) the
product was subject to accident, abuse, or improper use (iii) the product was subject to
conditions more severe than those specified in the manual.
Warranty service may be obtained by contacting TRENDnet within the applicable
warranty period and providing a copy of the dated proof of the purchase. Upon proper
submission of required documentation a Return Material Authorization (RMA) number
will be issued. An RMA number is required in order to initiate warranty service support
for all TRENDnet products. Products that are sent to TRENDnet for RMA service must
have the RMA number marked on the outside of return packages and sent to TRENDnet
prepaid, insured and packaged appropriately for safe shipment. Customers shipping
from outside of the USA and Canada are responsible for return shipping fees. Customers
shipping from outside of the USA are responsible for custom charges, including but not
limited to, duty, tax, and other fees.
WARRANTIES EXCLUSIVE: IF THE TRENDNET PRODUCT DOES NOT OPERATE AS
WARRANTED ABOVE, THE CUSTOMER’S SOLE REMEDY SHALL BE, AT TRENDNET’S
OPTION, REPAIR OR REPLACE. THE FOREGOING WARRANTIES AND REMEDIES ARE
EXCLUSIVE AND ARE IN LIEU OF ALL OTHER WARRANTIES, EXPRESSED OR IMPLIED,
EITHER IN FACT OR BY OPERATION OF LAW, STATUTORY OR OTHERWISE, INCLUDING
© Copyright 2013 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE.
TRENDNET NEITHER ASSUMES NOR AUTHORIZES ANY OTHER PERSON TO ASSUME FOR
IT ANY OTHER LIABILITY IN CONNECTION WITH THE SALE, INSTALLATION MAINTENANCE
OR USE OF TRENDNET’S PRODUCTS.
TRENDNET SHALL NOT BE LIABLE UNDER THIS WARRANTY IF ITS TESTING AND
EXAMINATION DISCLOSE THAT THE ALLEGED DEFECT IN THE PRODUCT DOES NOT EXIST
OR WAS CAUSED BY CUSTOMER’S OR ANY THIRD PERSON’S MISUSE, NEGLECT,
IMPROPER INSTALLATION OR TESTING, UNAUTHORIZED ATTEMPTS TO REPAIR OR
MODIFY, OR ANY OTHER CAUSE BEYOND THE RANGE OF THE INTENDED USE, OR BY
ACCIDENT, FIRE, LIGHTNING, OR OTHER HAZARD.
LIMITATION OF LIABILITY: TO THE FULL EXTENT ALLOWED BY LAW TRENDNET ALSO
EXCLUDES FOR ITSELF AND ITS SUPPLIERS ANY LIABILITY, WHETHER BASED IN
CONTRACT OR TORT (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE), FOR INCIDENTAL, CONSEQUENTIAL,
INDIRECT, SPECIAL, OR PUNITIVE DAMAGES OF ANY KIND, OR FOR LOSS OF REVENUE OR
PROFITS, LOSS OF BUSINESS, LOSS OF INFORMATION OR DATE, OR OTHER FINANCIAL
LOSS ARISING OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SALE, INSTALLATION,
MAINTENANCE, USE, PERFORMANCE, FAILURE, OR INTERRUPTION OF THE POSSIBILITY
OF SUCH DAMAGES, AND LIMITS ITS LIABILITY TO REPAIR, REPLACEMENT, OR REFUND
OF THE PURCHASE PRICE PAID, AT TRENDNET’S OPTION. THIS DISCLAIMER OF LIABILITY
FOR DAMAGES WILL NOT BE AFFECTED IF ANY REMEDY PROVIDED HEREIN SHALL FAIL
OF ITS ESSENTIAL PURPOSE.
Governing Law: This Limited Warranty shall be governed by the laws of the state of
California.
Some TRENDnet products include software code written by third party developers.
These codes are subject to the GNU General Public License ("GPL") or GNU Lesser
General Public License ("LGPL").
Go to http://www.trendnet.com/gpl or http://www.trendnet.com
and look for the desired TRENDnet product to access to the GPL Code or LGPL Code.
These codes are distributed WITHOUT WARRANTY and are subject to the copyrights of
the developers. TRENDnet does not provide technical support for these codes. Please go
http://www.gnu.org/licenses/gpl.txt or http://www.gnu.org/licenses/lgpl.txt for
to
specific terms of each license.
PWP05202009v2 2012/11/6
Limited Warranty
Download section
69

 Loading...
Loading...