
1

Federal Communication Commission Interference Statement
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class B digital device,
pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection
against harmful interference in a residential installation. This equipment generates uses and can
radiate radio frequency energy and, if not installed and used in accordance with the instructions,
may cause harmful interference to radio communications. However, there is no guarantee that
interference will not occur in a particular installation. If this equipment does cause harmful
interference to radio or television reception, which can be determined by turning the equipment off
and on, the user is encouraged to try to correct the interference by one of the following measures:
- Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
- Increase the separation between the equipment and receiver.
- Connect the equipment into an outlet on a circuit different from that to which the receiver
is connected.
- Consult the dealer or an experienced radio/TV technician for help.
This device complies with Part 15 of the FCC Rules. Operation is subject to the following two
conditions: (1) This device may not cause harmful interference, and (2) this device must accept any
interference received, including interference that may cause undesired operation.
FCC Caution: Any changes or modifications not expressly approved by the party responsible for
compliance could void the user's authority to operate this equipment.
IMPORTANT NOTE:
FCC Radiation Exposure Statement:
This equipment complies with FCC radiation exposure limits set forth for an uncontrolled
environment. This equipment should be installed and operated with minimum distance 20cm
between the radiator & your body.
This transmitter must not be co-located or operating in conjunction with any other antenna or
transmitter.
The availability of some specific channels and/or operational frequency bands are country
dependent and are firmware programmed at the factory to match the intended destination. The
firmware setting is not acc ess i ble by the end user.
Copyright
This publication, including all photographs, illustrations and software, is protected under international
copyright laws, with all rights reserved. Neither this manual, nor any of the material contained herein, may
be reproduced without written consent of the author.
Copyright 2006
Trademark recognition
All product names used in this manual are the properties of their respective owners and are acknowledged.
2

Table of Contents
Getting Started ............................................................................................ 5
Package Contents .................................................................................... 5
Minimum System Requirements .............................................................. 5
Introduction ................................................................................................. 6
Features ................................................................................................... 6
Wireless Performance Considerations ..................................................... 7
Overview ..................................................................................................... 8
Network Diagram ..................................................................................... 8
FronT panel (LEDs): ................................................................................. 8
Rear panel: ............................................................................................... 8
Using the Configuration Menu .................................................................... 9
Network ..................................................................................................... 10
WAN Setting ........................................................................................... 10
LAN Setting ............................................................................................ 12
QoS ........................................................................................................ 14
DHCP Client List .................................................................................... 14
Wireless .................................................................................................... 15
Basic ...................................................................................................... 15
Advanced ............................................................................................... 17
MAC Filter .............................................................................................. 18
Security .................................................................................................. 19
WPS ....................................................................................................... 20
Station List .............................................................................................. 21
Advanced .................................................................................................. 21
DMZ ....................................................................................................... 21
Virtual Server ......................................................................................... 22
Routing ................................................................................................... 23
Access Control ....................................................................................... 24
S pecial Applications ............................................................................... 25
Gaming ................................................................................................... 26
Inbound Filter ......................................................................................... 27
Schedule ................................................................................................ 28
Advance Network ................................................................................... 29
Administrator ............................................................................................. 30
Wizard .................................................................................................... 30
3

Management .......................................................................................... 30
Upload Firmware .................................................................................... 31
Setting Management .............................................................................. 32
Time ....................................................................................................... 32
Status ..................................................................................................... 33
Help........................................................................................................... 34
Network Glossary ..................................................................................... 35
Specifications ............................................................................................ 38
Limited Warranty ....................................................................................... 39
4

Getting Started
Congratulations on purchasing the TEW-639GR! This manual provides information for setting up and
configuring the TEW-639GR. This manual is intended for both home users and professionals.
PACKAGE CON TENTS
TEW-639GR 2.4GHz 300Mbps Wireles s N Gigabit Router
CD-ROM (User’s Guide)
Multi-Language Quick Installation Guide
1 x Network cable
Power Adapter (12V, 1A)
Using a power supply with a different voltage than the one included with your product will cause damage
and void the warranty for this product. If any item is found missing or damaged, please contact your local
reseller for replacement.
MINIMUM SYSTEM REQUIREMENTS
Ethernet-Based Cable or DSL Modem
Computers with Windows, Macintosh, or Linux-based operating systems with an installed Ethernet
adapter and CD-ROM Drive
Internet Explorer Version 6.0 or Netscape Navigator Version 7.0 and Above
5

Introduction
The TEW-639GR 2.4GHz 300Mbps Wireless N Gigabit Router is an high-performance, wireless router that
supports high-speed wireless networking at home, at work or in public places.
Unlike most routers, the TEW-639GR provides data transfers at up to 300Mbps when using 11n connection.
This router is also back compatible with 802.11g or 11b devices. This means that you do not need to
change your entire network to maintain connectivity. You may sacrifice some of 11n’s speed when you mix
11n and 11b/g devices, but you will not lose the ability to communicate when you incorporate the 11n
standard into your 11b/g network. You may choose to slowly change your network by gradually replacing
the 11b/g devices with 11n devices.
FEATURES
4 x 10/100/1000Mbps Auto-MDIX LAN ports
1 x 10/100/1000Mbps WAN port (Internet)
1 x external wireless radio on/off switch (turn off your wireless network when away)
1 x external Wi-Fi Protected Setup (WPS) button
One-touch wireless security setup using the Wi-Fi Protected Setup (WPS) button when connecting to a
WPS adapter
Wireless Distribution System (WDS) support
Compatible with most popular cable/DSL Internet service providers using Dynamic/Static IP, PPPoE,
PPTP and L2TP
High-speed wireless data rates up to 300Mbps using an IEEE 802.11n connection
3 external antennas provide high-speed performance and expansive wireless coverage
Advanced Firewall protection with Network Address Translation (NAT) and Stateful Packet Inspection
(SPI)
Access restriction with Internet Access Control; time scheduling and MAC filtering
Built-in pre-configured virtual servers and Application Level Gateway services for special Internet
applications
Universal Plug and Play (UPnP) for auto discovery and support for device configuration of Internet
applications
Multiple pass-through sessions for popular VPN applications (IPSec, L2TP and PPTP)
WMM quality of service support
Easy setup via Web browser using the latest versions of Internet Explorer, FireFox, Safari, and Chrome
6

WIRELESS PERFORMANCE CONSIDERATIONS
There are a number of factors that can impact the range of wireless devices.
1. Adjust your wireless devices so that the signal is traveling in a straight path, rather than at an angle.
The more material the signal has to pass through the more signal you will lose.
2. Keep the number of obstructions to a minimum. Each obstruction can reduce the range of a wireless
device. Position the wireless devices in a manner that will minimize the amount of obstructions
between them.
3. Building materials can have a large impact on your wireless signal. In an indoor environment, try to
position the wireless devices so that the signal passes through less dense material such as dry wall.
Dense materials like metal, solid wood, glass or even furniture may block or degrade the signal.
4. Antenna orientation can also have a large impact on your wireless signal. Use the wireless adapter’s site
survey tool to determine the best antenna orientation for your wireless devices.
5. Interference from devices that produce RF (radio frequency) noise can also impact your signal. Position
your wireless devices away from anything that generates RF noise, such as microwaves, radios and
baby monitors.
6. Any device operating on the 2.4GHz frequency will cause interference. Devices such as 2.4GHz
cordless phones or other wireless remotes operating on the 2.4GHz frequency can potentially drop the
wireless signal. Although the phone may not be in use, the base can still transmit wireless signal.
Move the phone’s base station as far away as possible from your wireless devices.
If you are still experiencing low or no signal consider repositioning the wireless devices or installing
additional access points. The use of higher gain antennas may also provide the necessary coverage
depending on the environment.
limit the range. Typical ranges vary depending on the types of materials and background RF (radio
frequency) noise in your home or business. The key to maximizing wireless range is to follow these basic
guidelines:
1 Keep the number of walls and ceilings between the TEW-639GR and other network devices to a
minimum - each wall or ceiling can reduce your wireless products range from 3-90 fe et (1-30 meters.)
Position your devices so that the number of walls or ceilings is minimized.
2 Be aware of the direct line between network devices. A wall that is 1.5 feet thick (.5 meters), at a
45-degree angle appears to be almost 3 feet (1 meter) thick. At a 2-degree angle it looks over 42 feet
(14 meters) thick! Position devices so that the signal will travel straight through a wall or ceiling (instead
of at an angle) for better reception.
3 Building Materials can impede the wireless signal - a solid metal door or aluminum studs may have a
negative effect on range. Try to position wireless devices and computers with wireless adapters so that
the signal passes through drywall or open doorways and not other materials.
4 Keep your product away (at least 3-6 feet or 1-2 meters) from electrical devices or appliances that
generate extreme RF noise.
7

Overview
NETWORK DIAGRAM
FRONT PANEL (LEDS):
• PWR
• WAN
• LAN1
• LAN2
• LAN3
• LAN4
• Wireless
• WPS
REAR PANEL:
• DC-IN
• RESET
• WAN
• LAN1
• LAN2
• LAN3
• LAN4
8
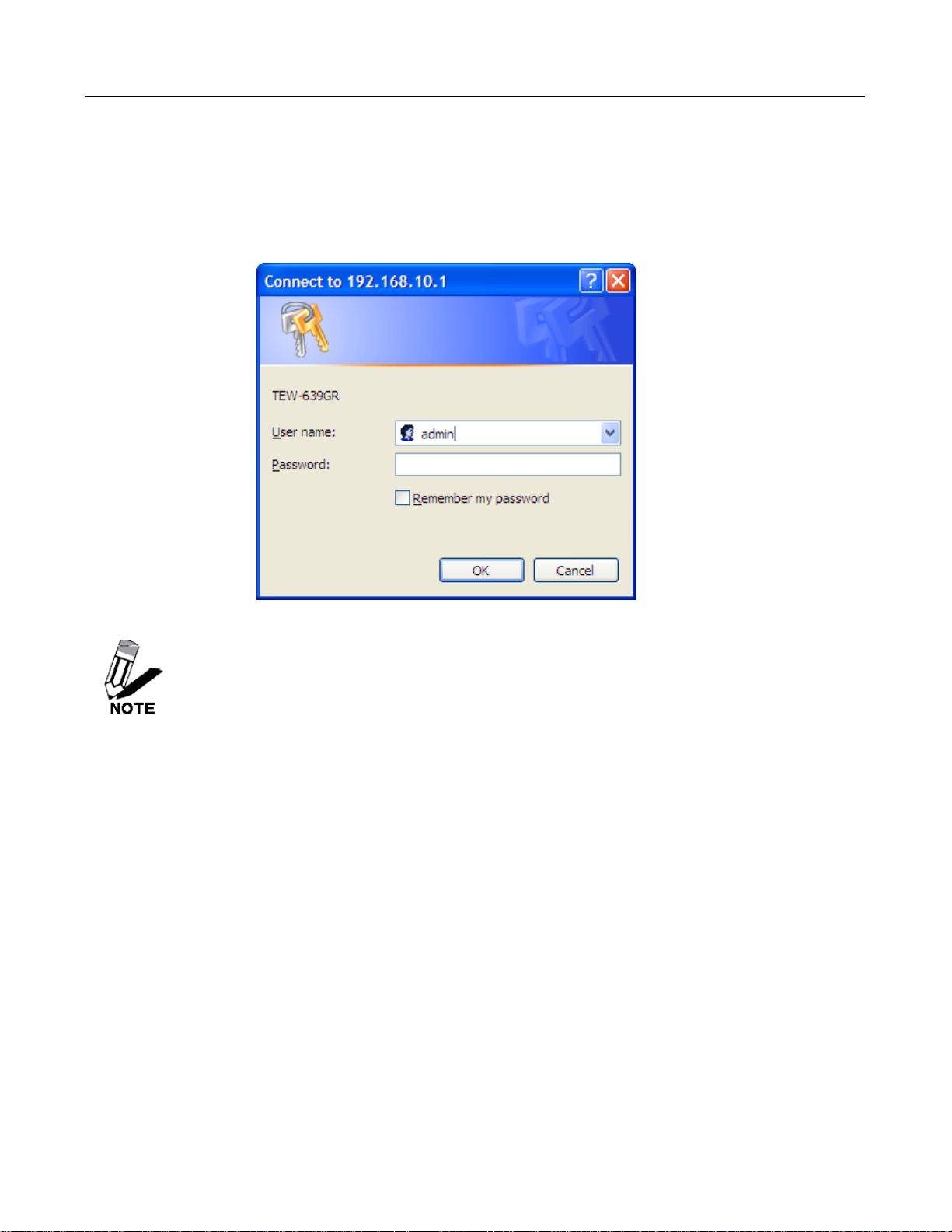
Using the C onfiguration Menu
Whenever you want to configure your TEW-639GR, you can access the Configuration Menu through
your PC by opening the Web-browser and typing in the IP Address of the TEW-639GR. The
TEW-639GR’s default IP Address is http://192.168.10.1
• Open the Web browser.
• Type in the IP Address of the Router (http://192.168.10.1 )
If you have changed the default IP Address assigned to the TEW-639GR, make sure to
enter the correct IP Address.
• Select admin in the User Name field.
• Default password is admin.
• Click OK.
9
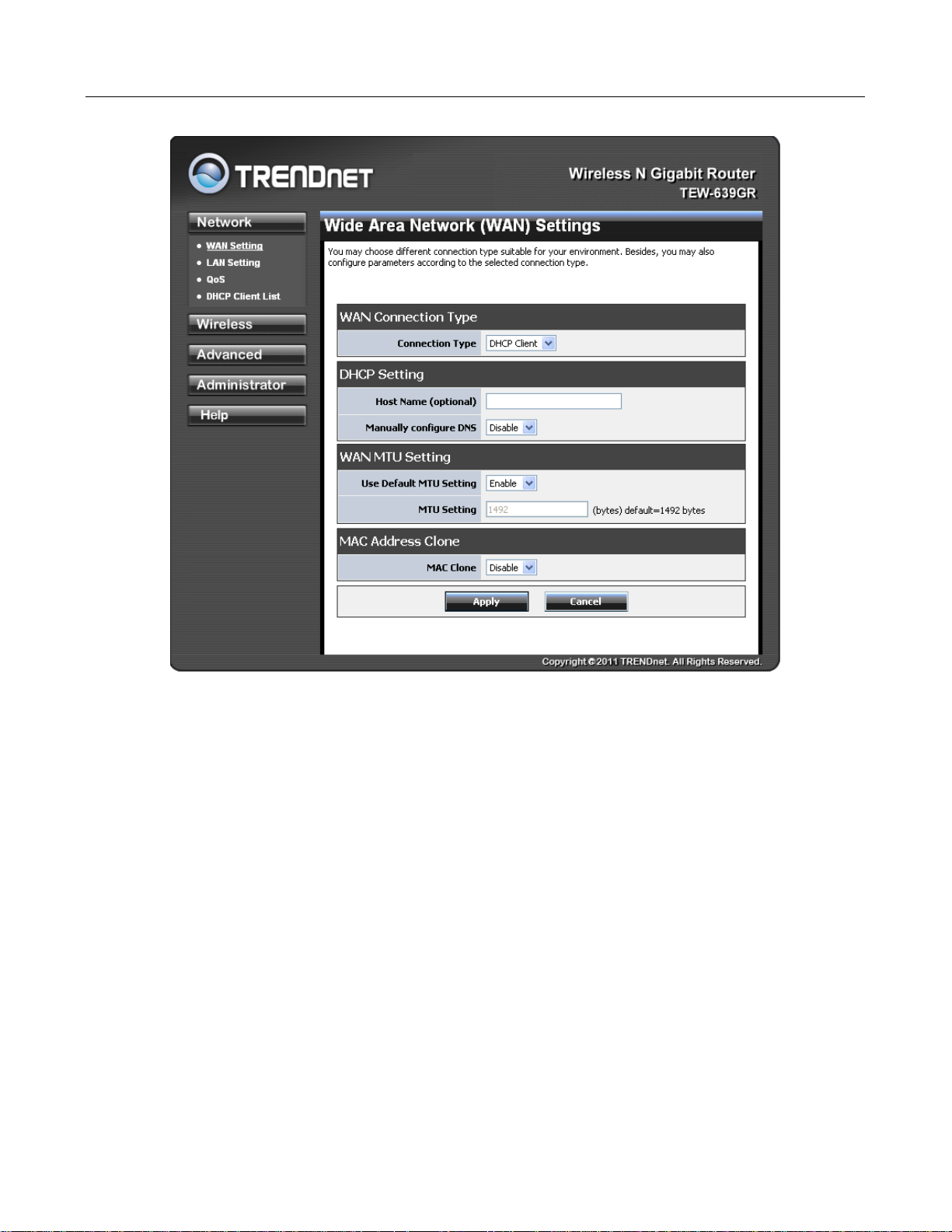
Network
WAN SETTING
WAN Connection Type: There are several connection types to choose from: Static IP, DHCP,
PPPoE, PPTP, L2TP, and Russia PPTP. If you are unsure of your connection method, please contact
your Internet Service Provider.
Static: Used when your ISP provides you a set IP address that does not change. The IP information is
manually entered in your IP configuration settings. You must enter the IP address, Subnet Mask,
Gateway, Primary DNS Server, and Secondary DNS Server. Your ISP provides you with all of this
information.
DHCP: A method of connection where the ISP assigns your IP address when your router requests one
from the ISP's server.
Host Name: Some ISP' s may check your computer's Host Name. The Host Name identifies your
system to the ISP's server.
PPPoE: Select this option if your ISP requires you to use a PPPoE (Point to Point Protocol over
Ethernet) connection. DSL providers typically use this option. This method of connection requires you
to enter a Username and Password (provided by your Internet Service Provider) to gain access to
the Internet.
Reconnect Mode: Typically PPPoE connections are not always on. The router allows you to set the
reconnection mode. The settings are:
Always on: A connection to the Internet is always maintained.
On demand: A connection to the Internet is made as needed.
Manual: You have to open up the Web-based management interface and click the Connect button
manually any time that you wish to connect to the Internet.
10

Maximum Idle Time: Time interval the machine can be idle before the PPPoE connection is
disconnected. The Maximum Idle Time value is only used for the "On demand" and "Manual"
reconnect modes.
L2TP: L2TP (Layer Two Tunneling Protocol) uses a virtual private network to connect to your ISP.
This method of connection requires you to enter a Username and Password (provided by your Internet
Service Provider) to gain access to the Internet.
L2TP Server IP Address: The ISP provides this parameter, if necessary. The value may be the same
as the Gateway IP Address.
Reconnect Mode: Typically PPPoE connections are not always on. The router allows you to set the
reconnection mode. The settings are:
Always on: A connection to the Internet is always maintained.
On demand: A connection to the Internet is made as needed.
Manual: You have to open up the Web-based management interface and click the Connect button
manually any time that you wish to connect to the Internet.
Maximum Idle Time: Time interval the machine can be idle before the PPPoE connection is
disconnected. The Maximum Idle Time value is only used for the "On demand" and "Manual"
reconnect modes.
WAN Interface IP Type
Static: If your ISP has assigned a fixed IP address, select this option. The ISP provides the values for
the following fields for WAN Interface IP Setting: IP Address, Subnet Mask , Default Gateway.
Dynamic: If the ISP's servers assign the router's IP addressing upon establishing a connection, select
this option.
PPTP: PPTP (Point to Point Tunneling Protocol) uses a virtual private network to connect to your ISP.
This method of connection is primarily used in Europe. This method of connection requires you to
enter a Username and Password (provided by your Internet Service Provider) to gain access to the
Internet.
PPTP Server IP Address: The ISP provides this parameter, if necessary. The value may be the same
as the Gateway IP Address.
Reconnect Mode: Typically PPPoE connections are not always on. The router allows you to set the
reconnection mode. The settings are:
Always on: A connection to the Internet is always maintained.
On demand: A connection to the Internet is made as needed.
Manual: You have to open up the Web-based management interface and click the Connect button
manually any time that you wish to connect to the Internet.
Maximum Idle Time: Time interval the machine can be idle before the PPPoE connection is
disconnected. The Maximum Idle Time value is only used for the "On demand" and "Manual"
reconnect modes.
WAN Interface IP Type
Static: If your ISP has assigned a fixed IP address, select this option. The ISP provides the values for
the following fields for WAN Interface IP Setting: IP Address, Subnet Mask , Default Gateway, and
optional for DNS Server
Dynamic: If the ISP's servers assign the router's IP addressing upon establishing a connection, select
this option.
Russia PPTP: The Russia PPTP can configure IP address on the WAN interface and establish PPTP
to get IP address, subnet mask, default gateway and DNS for ANOTHER logical IP interface on WAN
port. So the physical WAN port will have 2 logical IP interfaces and can communicate with internal
ISP’s network resources and also communicate with Internet through PPTP tunnel. It is specified by
Russia Cobrina ISP, user can configure it the same as the normal PPTP and PPTP server IP Address
can use the domain name string.
WAN MTU Setting: The Maximum Transmission Unit (MTU) is a parameter that determines the
largest packet size (in bytes) that the router will send to the WAN. If LAN devices send larger packets,
the router will break them into smaller packets. Ideally, you should set this to match the MTU of the
connection to your ISP. Typical values are 1500 bytes for an Ethernet connection and 1492 bytes for a
PPPoE connection. If the router's MTU is set too high, packets will be fragmented downstream. If the
11
router's MTU is set too low, the router will fragment packets unnecessarily and in extreme cases may
be unable to establish some connections. In either case, network performance can suffer. t modes.
MAC Address Clone: Each networking device has it's own unique MAC address defined by the
hardware manufacturer. Some ISP's may check your computer's MAC address. Some ISP's record
the MAC address of the network adapter in the computer or router used to initially connect to their
service. The ISP will then only grant Internet access to requests from a computer or router with this
particular MAC address. This router has a different MAC address than the computer or router that
initially connected to the ISP. If you need to change the MAC address of the rounter's WAN-side
Ethernet interface, either type in an alternate MAC address (for example, the MAC address of the
router initially connected to the ISP) or copy the MAC address of a PC. To copy the MAC address of
the computer that initially connected to the ISP, connect to the router using that computer and click the
Clone Your PC's MAC Address button. The WAN interface will then use the MAC address of the
network adapter in your computer.
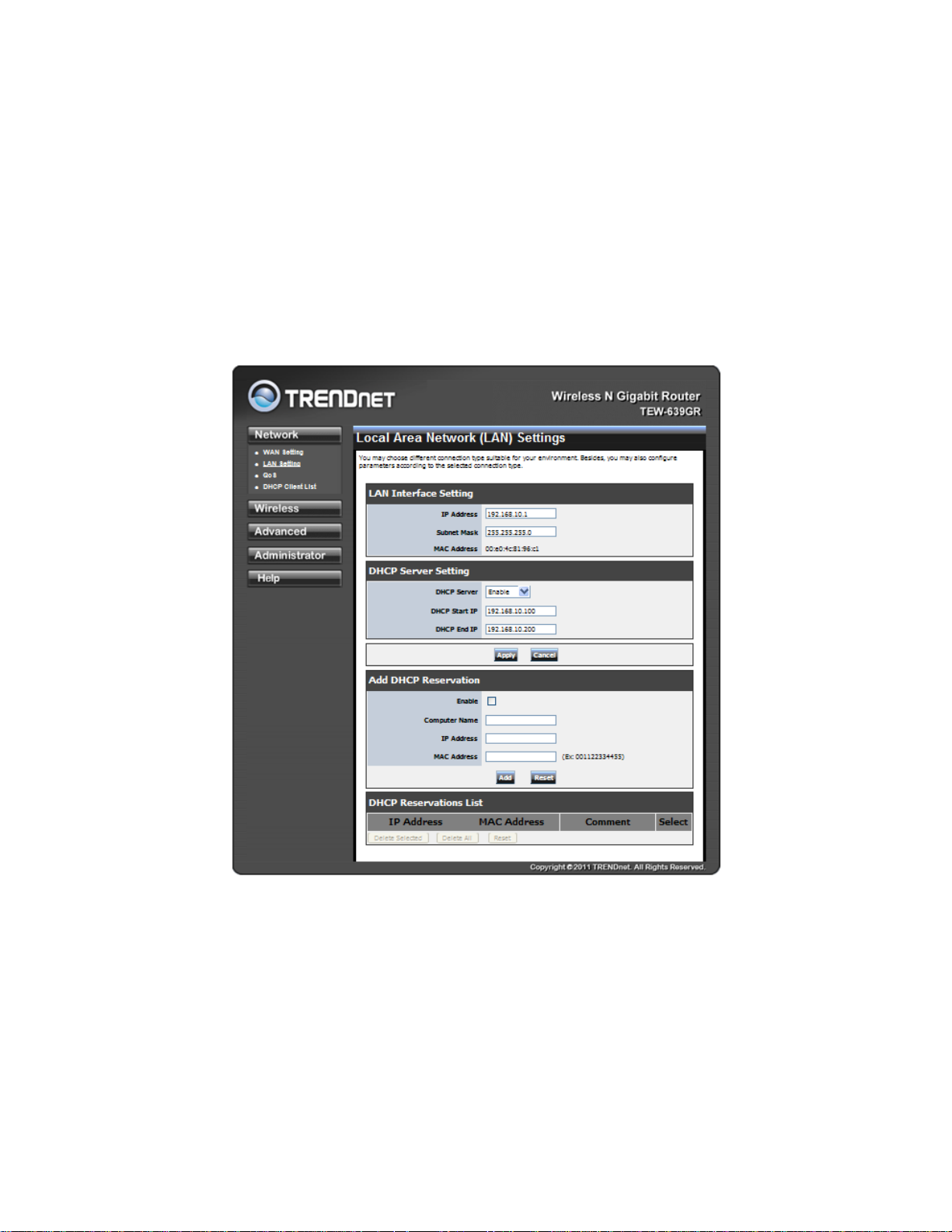
LAN SETTING
IP Address: The IP address of the this device on the local area network. Assign any unused IP
address in the range of IP addresses available for the LAN.
Subnet Mask: The subnet mask of the local area network.
DHCP Server Settings: DHCP stands for Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol. The DHCP section is
where you configure the built-in DHCP Server to assign IP addresses to the computers and other
devices on your local area network (LAN).
Enable DHCP Server: Once your router is properly configured and this option is enabled, the DHCP
Server will manage the IP addresses and other network configuration information for computers and
other devices connected to your Local Area Network. There is no need for you to do this yourself.
The computers (and other devices) connected to your LAN also need to have their TCP/IP
configuration set to "DHCP" or "Obtain an IP address automatically". When you set Enable DHCP
Server, the following options are displayed.
12

DHCP IP Address Range: These two IP values (Start and End) define a range of IP addresses that
the DHCP Server uses when assigning addresses to computers and devices on your Local Area
Network. Any addresses that are outside of this range are not managed by the DHCP Server; these
could, therefore, be used for manually configured devices or devices that cannot use DHCP to obtain
network address details automatically.
It is possible for a computer or device that is manually configured to have an address that does reside
within this range. In this case the address should be reserved, so that the DHCP Server knows that
this specific address can only be used by a specific computer or device.
Your router, by default, has a static IP address of 192.168.10.1. This means that addresses
192.168.10.2 to 192.168.10.254 can be made available for allocation by the DHCP Server.
Subnet Mask: The subnet mask of the local area network.
Gateway: The IP address of the router on the local area network. For example, 192.168.10.1.
DHCP Lease Time: The amount of time that a computer may have an IP address before it is required
to renew the lease. The lease functions just as a lease on an apartment would. The initial lease
designates the amount of time before the lease expires. If the tenant wishes to retain the address
when the lease is expired then a new lease is established. If the lease expires and the address is no
longer needed than another tenant may use the address.
Add/Edit DHCP Reservation: This option lets you reserve IP addresses, and assign the same IP
address to the network device with the specified MAC address any time it requests an IP address.
This is almost the same as when a device has a static IP address except that the device must still
request an IP address from the router. The router will provide the device the same IP address every
time. DHCP Reservations are helpful for server computers on the local network that are hosting
applications such as Web and FTP. Servers on your network should either use a static IP address or
use this option.
Computer Name: You can assign a name for each computer that is given a reserved IP address. This
may help you keep track of which computers are assigned this way. Example: Game S erver.
IP Address: The LAN address that you want to reserve.
MAC Address: To input the MAC address of your system, enter it in manually or connect to the
router's Web-Management interface from the system and click the Copy Your PC's MAC Address
button. A MAC address is usually located on a sticker on the bottom of a network device. The MAC
address is comprised of twelve digits. Each pair of hexadecimal digits are usually separated by
dashes or colons such as 00-0D-88-11-22-33 or 00:0D:88:11:22:33. If your network device is a
computer and the network card is already located inside the computer, you can connect to the router
from the computer and click the Copy Your PC's MAC Address button to enter the MAC address.
Clear Re-initialize this area of the screen, discarding any changes you have made.
DHCP Reservations List: This shows clients that you have specified to reserve DHCP addresses.
Click the Enable checkbox at the left to directly activate or de-activate the entry. An entry can be
changed by clicking the Edit icon or can be deleted by clicking the Delete icon. When you click the Edit
icon, the item is highlighted, and the "Edit DHCP Reservation" section is activated for editing.
13

QOS
QoS (Quality-of-Service): QoS involves prioritization of network traffic. QoS can be targeted at a
network interface, toward a given server or router's performance, or in terms of specific applications.
DHCP CLIENT LIST
In this section you can see the connected LAN devices are currently receiving an IP addresses.
14

Wireless
BASIC
Wireless Mode: If all of the wireless devices you want to connect with this router can connect in the
same transmission mode, you can improve performance slightly by choosing the appropriate wireless
mode. If you have some devices that use a different transmission mode, choose the appropriate
wireless mode. The TE W-639GR supports 2.4GHz wireless networks. There are many different
configuration options available to choose from. Use the drop down list to select the wireless mode.
Note: One wireless mode can be selected can select at any one time. This means that you can only
select one of the operating frequencies at a time.
Wireless Mode options
2.4GHz 802.11b/g mixed mode - This wireless mode works in the 2.4GHz frequency range and will
allow both wireless b and wireless g client to connect and access the TEW-639GR at 11Mbps for
wireless b, at 54Mbps for wireless g and share access at the same time. Although the wireless b/g
operates in the 2.4GHz frequency, it will allow the use of other 2.4GHz client devices (Wireless n/g @
54Mbps) to connect and access at the same time.
2.4GHz 802.11 n only – This wireless mode works in the 2.4GHz frequency range and will only allow
the use of wireless n client devices to connect and access the TEW-639GR up to 300Mbps*. Although
the wireless n operates in the 2.4GHz frequency, this mode will only permit wireless n client devices to
work and will exclude any other wireless mode and devices that are not wireless n only.
2.4 GHz 802.11b/g/n mixed mode - This wireless mode works in the 2.4GHz frequency range and
will only allow the use of wireless g client devices to connect and access the TEW-639GR at 11Mbps
15

for wireless b, 54Mbps for wireless g and up to 300Mbps* for wireless n and share access at the same
time. Although the wireless b/g/n operates in the same 2.4GHz frequency, it will allow the use of other
2.4GHz client devices (Wireless b/g/n) to connect and access at the same time.
*
Maximum wireless signal rates are referenced from IEEE 802.11 theoretical specifications. Actual data throughput and
coverage will vary depending on interference, network traffic, building materials and other conditions.
Wireless Network Name (SSID): When you are browsing for available wireless networks, this is the
name that will appear in the list (unless Visibility Status is set to Invisible, see below). This name is
also referred to as the SSID. For security purposes, it is highly recommended to change from the
pre-configured network name. Add up to three additional SSIDs to create virtual wireless networks
from one wireless Router Access Point device.
Add Additional Wireless Network Name (SSID): To add additional wireless Network Names simply
add the name to the Multiple SSID field and click on apply at the bottom of the page. When finished,
go to the Security section in this Users Guide for wireless security configuration.
Frequency (Channel): A wireless network uses specific channels in the wireless spectrum to handle
communication between clients. Some channels in your area may have interference from other
electronic devices. Choose the clearest channel to help optimize the performance and coverage of
your wireless network.
Wireless Distribution System (WDS): When WDS is enabled, this access point functions as a
wireless repeater and is able to wirelessly communicate with other APs via WDS links. A WDS link is
bidirectional; so this AP must know the MAC Address (creates the WDS link) of the other AP, and the
other AP must have a WDS link back to this AP. Make sure the APs are configured with same channel.
(Note that WDS security is incompatible with mixed mode, like WPAPSK+WPA2PSK mixed, WEP AUTO and
802.1x, both feature cannot be used at the same time).
Configuring WDS with TEW-639GR: Enable the option for WDS and input the MAC Address of the
wireless device that also supports WDS in to the blank fields. You can add up to four additional
devices in the spaces provided. Click on apply at the bottom of the page, to apply your setting
changes. Enable the security seeing in security page, each WDS APs need to use same security
setting.
(Note: WDS supports wireless g/n modes. The use multiple Access Point will reduces the overall
network throughput to ½ the TEW-639GR.
HT Physical Mode: In HT (High Throughput) Physical mode setting allow for control of the 802.11n
wireless environment.
Channel BandWidth: Set channel width of wireless radio.
20 Channel Width = 20 MHz
20/40 Channel Width = Enables both 20/40 MHz
16

ADVANCED
Beacon Interval: Beacons are packets sent by a wireless router to synchronize wireless devices.
Specify a Beacon Period value between 20 and 1000. The default value is set to 100 milliseconds.
Fragmentation Threshold: Wireless frames can be divided into smaller units (fragments) to improve
performance in the presence of RF interference and at the limits of RF coverage. Fragmentation will
occur when frame size in bytes is greater than the Fragmentation Threshold. This setting should
remain at its default value of 2346 bytes. Setting the Fragmentation value too low may result in poor
performance.
RTS Threshold: When an excessive number of wireless packet collisions are occurring, wireless
performance can be improved by using the RTS/CTS (Request to Send/Clear to Send) handshake
protocol. The wireless transmitter will begin to send RTS frames (and wait for CTS) when data frame
size in bytes is greater than the RTS Threshold. This setting should remain at its default value of 2346
bytes.
Short Preamble: Using a short (400ns) guard interval can increase throughput. However, it can also
increase error rate in some installations, due to increased sensitivity to radio-frequency reflections.
Select the option that works best for your installation.
IAPP(Inter-Access Point Protocol): IEEE 802.11F or Inter-Access Point Protocol is a
recommendation that describes an optional extension to IEEE 802.11 that provides wireless
access-point communications among multivendor systems.
Protection: These protection mechanisms ensure that a STA that is a potential interferer defers any
transmission for a known period of time. These mechanisms are used to ensure that non-ERP STAs
do not interfere with frame exchanges using ERP PPDUs between ERP STAs and that non-HT STAs
do not interfere with frame exchanges using HT PPDUs between HT STAs, thereby allowing non-ERP
and/or non-HT STAs to coexist with ERP and/or HT STAs.
Pkt_Aggregate: Increase efficiency by aggregating multiple packets of application data into a single
transmission frame. In this way, 802.11n networks can send multiple data packets with the fixed
overhead cost of just a single frame.
17

WLAN Partition: When this option is enabled, there is barrier between communications among
wireless stations connecting to this device.
STBC: Space Time Block Coding that is a transmitter diversity technique of spreading the transmit
signal over multiple antennas to improve reception.
Channel BandWidth: Set channel width of wireless radio.
20 Channel Width = 20 MHz
20/40 Channel Width = Enables both 20/40 MHz
RF Output Power: Switch the strength of RF transmit power with percentage.
MAC FILTER
Wireless MAC Filtering: Choose the type of MAC filtering needed.
Turn MAC Filtering Disable: When "Disable" is selected, MAC addresses are not used to control
network access.
Add MAC Filtering Rule: Use this section to add MAC addresses to the list below.
MAC Address: Enter the MAC address of a computer that you want to control with MAC filtering.
Computers that have obtained an IP address from the router's DHCP server will be in the DHCP Client
List. Select a device from the drop down menu.
The rule of thumb: In mixed mode, multicast key has to be TKIP, but unicast key can be different per
stations. In WPA or WPA2 only mode, unicast and multicast key can be only AES for WPA2, and TKIP
for WPA. (AES means the unicast and multicast key are all AES. TKIP/AES means multicast
is TKIP. But unicast can be AES or TKIP, which depends on the peer.)
18

SECURITY
Security Mode: Unless one of these encryption modes is selected, wireless transmissions to and
from your wireless network can be easily intercepted and interpreted by unauthorized users.
WEP: A method of encrypting data for wireless communication intended to provide the same level of
privacy as a wired network. WEP is not as secure as WPA encryption. To gain access to a WEP
network, you must know the key. The key is a string of characters that you create. When using WEP,
you must determine the level of encryption. The type of encryption determines the key length. 128-bit
encryption requires a longer key than 64-bit encryption. Keys are defined by entering in a string in
HEX (hexadecimal - using characters 0-9, A-F) or ASCII (American Standard Code for Information
Interchange - alphanumeric characters) format. ASCII format is provided so you can enter a string that
is easier to remember. The ASCII string is converted to HEX for use over the network. Four keys can
be defined so that you can change keys easily. A default key is selected for use on the network.
WPA-Personal and WPA-Enterprise: Both of these options select some variant of Wi-Fi Protected
Access (WPA) -- security standards published by the Wi-Fi Alliance. The WPA Mode further refines
the variant that the router should employ.
WPA Mode: WPA is the older standard; select this option if the clients that will be used with the router
only support the older standard. WPA2 is the newer implementation of the stronger IEEE 802.11i
security standard. With the "WPA2" option, the router tries WPA2 first, but falls back to WPA if the
client only supports WPA. With the "WPA2 Only" option, the router associates only with clients that
also support WPA2 security.
Cipher Type: The encryption algorithm used to secure the data communication. TKIP (Temporal Key
Integrity Protocol) provides per-packet key generation and is based on WEP. AES (Advanced
Encryption Standard) is a very secure block based encryption. With the "TKIP and AES" option, the
router negotiates the cipher type with the client, and uses AES when available.
Group Key Update Interval: The amount of time before the group key used for broadcast and
multicast data is changed.
WPA-Personal: This option uses Wi-Fi Protected Access with a Pre-Shared Key (PSK).
Pre-Shared Key: The key is entered as a pass-phrase of up to 63 alphanumeric characters in ASCII
(American Standard Code for Information Interchange) format at both ends of the wireless connection.
It cannot be shorter than eight characters, although for proper security it needs to be of ample length
and should not be a commonly known phrase. This phrase is used to generate session keys that are
unique for each wireless client.
19

WPA-Enterprise: This option works with a RADIUS Server to authenticate wireless clients. Wireless
clients should have established the necessary credentials before attempting to authenticate to the
Server through this Gateway. Furthermore, it may be necessary to configure the RADIUS Server to
allow this Gateway to authenticate users.
Authentication Timeout: Amount of time before a client will be required to re-authenticate.
RADIUS Server IP Address: The IP address of the authentication server.
RADIUS Server Port: The port number used to connect to the authentication server.
RADIUS Server Shared Secret: A pass-phrase that must match with the authentication server.
WPA/WPA2 mixed environment: For those WPA2 stations, they will use AES for unicast. For those
WPA stations, they will use TKIP for unicast. But for multicast all WPA and WPA2 stations have to use
the same key, and that will be TKIP, because WPA station only knows about TKIP, WPA2 is new
standard, so it is defined to backward support TKIP on multicast.
WPS
Enable: Enable the WPS feature.
Lock Wireless Security Settings: Locking the wireless security settings prevents the settings from
being changed by any new external registrar using its PIN. Devices can still be added to the wireless
network using WPS.
PIN Settings: A PIN is a unique number that can be used to add the router to an existing network or
to create a new network. The default PIN may be printed on the bottom of the router. For extra
security, a new PIN can be generated. You can restore the default PIN at any time. Only the
Administrator ("admin" account) can change or reset the PIN.
Current PIN: Shows the current value of the router's PIN.
Reset To WPS Default: Restore the default PIN of the router.
Generate New PIN: Create a random number that is a valid PIN. This becomes the router's PIN. You
can then copy this PIN to the user interface of the registrar.
PBC Settings:
router without entering/remember any encryption keys. The user can use the PBC method by
pressing the WPS button on the side of the router or select the PBC option under
Wireless/WPS set tings page and hit Apply .
The push button method can be used to allow wireless clients to connect to the
20

STATION LIST
All the wireless clients connecting to the router will be shown here, you could monitor your
network and prevent any unauthorized wireless connection easily.
Advanced
DMZ
DMZ Setting: DMZ means "Demilitarized Zone." If an application has trouble working from behind the
router, you can expose one computer to the Internet and run the application on that computer.
When a LAN host is configured as a DMZ host, it becomes the destination for all incoming packets
that do not match some other incoming session or rule. If any other ingress rule is in place, that will be
used instead of sending packets to the DMZ host; so, an active session, virtual server, active port
trigger, or port forwarding rule will take priority over sending a packet to the DMZ host. (The DMZ
policy resembles a default port forwarding rule that forwards every port that is not specifically sent
anywhere else.) The router provides only limited firewall protection for the DMZ host. The router does
not forward a TCP packet that does not match an active DMZ session, unless it is a connection
establishment packet (SYN). Except for this limited protection, the DMZ host is effectively "outside the
firewall". Anyone considering using a DMZ host should also consider running a firewall on that DMZ
host system to provide additional protection.
21

Packets received by the DMZ host have their IP addresses translated from the WAN-side IP address
of the router to the LAN-side IP address of the DMZ host. However, port numbers are not translated;
so applications on the DMZ host can depend on specific port numbers.
The DMZ capability is just one of several means for allowing incoming requests that might appear
unsolicited to the NAT. In general, the DMZ host should be used only if there are no other alternatives,
because it is much more exposed to cyberattacks than any other system on the LAN. Thought should
be given to using other configurations instead: a virtual server, a port forwarding rule, or a port trigger.
Virtual servers open one port for incoming sessions bound for a specific application (and also allow
port redirection and the use of ALGs).
Port forwarding is rather like a selective DMZ, where incoming traffic targeted at one or more ports is
forwarded to a specific LAN host (thereby not exposing as many ports as a DMZ host). Port triggering
is a special form of port forwarding, which is activated by outgoing traffic, and for which ports are only
forwarded while the trigger is active.
Few applications truly require the use of the DMZ host. Following are examples of when a
DMZ host might be required:
‧ A host needs to support several applications that might use overlapping ingress ports such that two
port forwarding rules cannot be used because they would potentially be in conflict.
‧ To handle incoming connections that use a protocol other than ICMP, TCP, UDP, and IGMP (also
GRE and ESP, when these protocols are enabled by the PPTP and IPSec
Enable DMZ: Putting a computer in the DMZ may expose that computer to a variety of security risks.
Use of this option is only recommended as a last resort.
DMZ IP Address: Specify the LAN IP address of the LAN computer that you want to have unrestricted
Internet communication.
VIRTUAL SERVER
Enable: Specifies whether the entry will be active or inactive.
Name: Assign a meaningful name to the virtual server, for example Web Server. Several well-known
types of virtual server are available from the "Application Name" drop-down list. Selecting one of these
entries fills some of the remaining parameters with standard values for that type of server.
IP Address: The IP address of the system on your internal network that will provide the virtual service,
for example 192.168.10.50. You can select a computer from the list of DHCP clients in the "Computer
Name" drop-down menu, or you can manually enter the IP address of the server computer.
22

Protocol: Select the protocol used by the service. The common choices -- UDP, TCP, and both UDP
and TCP -- can be selected from the drop-down menu. To specify any other protocol, select "Other"
from the list, then enter the corresponding protocol number (as assigned by the IANA) in the Protocol
box.
Private Port: The port that will be used on your internal network.
Public Port: The port that will be accessed from the Internet.
Schedule: Select a schedule for when the service will be enabled. If you do not see the schedule you
need in the list of schedules.
Clear: Re-initialize this area of the screen, discarding any changes you have made.
ROUTING
Add/Edit Route: Adds a new route to the IP routing table or edits an existing route.
Destination IP: The IP address of packets that will take this route.
Gateway:Specifies the next hop to be taken if this route is used. A gateway of 0.0.0.0 implies there is
no next hop, and the IP address matched is directly connected to the router on the interface specified:
LAN or WAN.
Metric: The route metric is a value from 1 to 16 that indicates the cost of using this route. A value of 1
is the lowest cost, and 15 is the highest cost. A value of 16 indicates that the route is not reachable
from this router. When trying to reach a particular destination, computers on your network will select
the best route, ignoring unreachable routes.
Interface: Specifies the interface -- LAN or WAN -- that the IP packet must use to transit out of the
router, when this route is used.
Clear: Re-initialize this area of the screen, discarding any changes you have made.
Routes List: The section shows the current routing table entries. Certain required routes are
predefined and cannot be changed. Routes that you add can be changed by clicking the Edit icon or
can be deleted by clicking the Delete icon. When you click the Edit icon, the item is highlighted, and
the "Edit Route" section is activated for editing. Click the Enable checkbox at the left to directly
activate or de-activate the entry.
23

ACCESS CONTROL
Enable: By default, the Access Control feature is disabled. If you need Access Control, check this
option.
Note: When Access Control is disabled, every device on the LAN has unrestricted access to the
Internet. However, if you enable Access Control, Internet access is restricted for those devices that
have an Access Control Policy configured for them. All other devices have unrestricted access to the
Internet.
ALG
24

ALG (Application level gateway): It allows customized NAT traversal filters to be plugged into the
gateway to support address and port translation for certain application layer "control/data" protocols
such as FTP, SIP, RTSP, file transfer in IM applications etc. In order for these protocols to work
through NAT or a firewall, either the application has to know about an address/port number
combination that allows incoming packets, or the NAT has to monitor the control traffic and open up
port mappings (firewall pinhole) dynamically as required. Legitimate application data can thus be
passed through the security checks of the firewall or NAT that would have otherwise restricted the
traffic for not meeting its limited filter criteria.
SPECIAL APPLICATIONS
Add/Edit Port Trigger Rule
Enable: Specifies whether the entry will be active or inactive.
Name: Enter a name for the Special Application Rule, for example Game App, whic h will h elp you
identify the rule in the future. Alternatively, you can select from the Application list of common
applications.
Protocol: Select the protocol used by the service. The common choices -- UDP, TCP, and both UDP
and TCP -- can be selected from the drop-down menu.
Trigger Port: Enter the outgoing port range used by your application (for example 6500-6700).
Schedule: Select a schedule for when this rule is in effect.
Clear: Re-initialize this area of the screen, discarding any changes you have made.
Port Trigger Rule List: This is a list of the defined application rules. Click the Enable checkbox at the
left to directly activate or de-activate the entry. An entry can be changed by clicking the Edit icon or
can be deleted by clicking the Delete icon.
25

GAMING
Add/Edit Port Range Rule: Use this section to add a Port Range Rule to the following list or to edit a
rule already in the list.
Rule Enable: Specifies whether the entry will be active or inactive.
Rule Name: Give the rule a name that is meaningful to you, for example Game Server. You can also
select from a list of popular games, and many of the remaining configuration values will be filled in
accordingly. However, you should check whether the port values have changed since this list was
created, and you must fill in the IP address field.
IP Address: Enter the local network IP address of the system hosting the server, for example
192.168.10.50. You can select a computer from the list of DHCP clients in the "Computer Name"
drop-down menu, or you can manually enter the IP address of the server computer.
TCP Ports to Open: Enter the TCP ports to open (for example 6159-6180, 99).
UDP Ports to Open: Enter the UDP ports to open (for example 6159-6180, 99).
Inbound Filter: Select a filter that controls access as needed for this rule.
Schedule: Select a schedule for the times when this rule is in effect.
Clear: Re-initialize this area of the screen, discarding any changes you have made.
Port Range Rule List: This is a list of the defined Port Range Rules. Click the Enable checkbox at the
left to directly activate or de-activate the entry. An entry can be changed by clicking the Edit icon or
can be deleted by clicking the Delete icon. When you click the Edit icon, the item is highlighted, and
the "Edit Port Forwarding Rule" section is activated for editing.
26

INBOUND FILTE R
Add/Edit Inbound Filter Rule: Here you can add entries to the Inbound Filter Rules List below, or
edit existing entries.
Name: Enter a name for the rule that is meaningful to you.
Action: The rule can either Allow or Deny messages.
Remote IP Range: Define the ranges of Internet addresses this rule applies to. For a single IP
address, enter the same address in both the Start and End boxes. Up to eight ranges can be entered.
The Enable checkbox allows you to turn on or off specific entries in the list of ranges.
Clear: Re-initialize this area of the screen, discarding any changes you have made.
Inbound Filter Rules List:The section lists the current Inbound Filter Rules. An entry can be changed
by clicking the Edit icon or can be deleted by clicking the Delete icon. When you click the Edit icon, the
item is highlighted, and the "Edit Inbound Filter Rule" section is activated for editing.
In addition to the filters listed here, two predefined filters are available wherever inbound filters can be
applied:
Allow All: Permit any WAN user to access the related capability.
Deny All: Prevent all WAN users from accessing the related capability. (LAN users are not affected by
Inbound Filter Rules.)
27

SCHEDULE
Add/Edit Schedule Rule: In this section you can add entries to the Schedule Rules List below or edit
existing entries.
Name: Give the schedule a name that is meaningful to you, such as "Weekday rule".
Day(s): Place a checkmark in the boxes for the desired days or select the All Week radio button to
select all seven days of the week.
All Day - 24 hrs: Select this option if you want this schedule in effect all day for the selected day(s).
Start Time: If you don't use the All Day option, then you enter the time here. The start time is entered
in two fields. The first box is for the hour and the second box is for the minute. Email events are
normally triggered only by the start time. End Time
The end time is entered in the same format as the start time. The hour in the first box and the minutes
in the second box. The end time is used for most other rules, but is not normally used for email events.
Clear: Re-initialize this area of the screen, discarding any changes you have made.
Schedule Rules List: This section shows the currently defined Schedule Rules. An entry can be
changed by clicking the Edit icon or can be deleted by clicking the Delete icon. When you click the Edit
icon, the item is highlighted, and the "Edit Schedule Rule" section is activated for editing.
28

ADVANCE NETWORK
UPNP: UPnP is short for Universal Plug and Play that is a networking architecture that provides
compatibility among networking equipment, software, and peripherals. UPnP-enabled Router will only
work with other UPnP devices/software. If user does not want to use the UPnP functionality, select
“Disabled” to disable it.
WAN Ping Respond: Enable this option to allow WAN pint responses from your router.
29

Administrator
WIZARD
Follow “Internet Connection Setup Wizard” or “Wireless Security Setup Wizard” to get your
Internet connection up and running.
MANAGEMENT
30

Admin Password: Enter a password for the user "admin", who will have full access to the Web-based
management interface.
Device Name: The name of the router can be changed here.
Enable Dynamic DNS: Enable this option only if you have purchased your own domain name and
registered with a dynamic DNS service provider. The following parameters are displayed when the
option is enabled.
Dynamic DNS Provider: Select a dynamic DNS service provider from the pull-down list.
Host Name: Enter your host name, fully qualified; for example: myhost.mydomain.net.
Account: Enter the account provided by your service provider. If the Dynamic DNS provider supplies
only a key, enter that key in all three fields.
Password: Enter the password provided by your service provider. If the Dynamic DNS provider
supplies only a key, enter that key in all three fields.
UPLOAD FIRMWARE
Once you have a firmware update on your computer, use this option to browse for the file and then
upload the information into the router.
31

SETTING MANAGEMENT
Export Settings: This option allows you to export and then save the router's configuration to a file on
your computer. Be sure to save the configuration before performing a firmware upgrade.
Import Settings: Use this option to restore previously saved router configuration settings.
Load Factory Defaults: This option restores all configuration settings back to the settings that were in
effect at the time the router was shipped from the factory. Any settings that have not been saved will
be lost. If you want to save your router configuration settings, use the Export Settings option above.
System Reboot: This restarts the router. It is useful for restarting when you are not near the device.
TIME
Time Configuration
Current Router Time:Displays the time currently maintained by the router. If this is not correct, use
the following options to configure the time correctly.
Time Zone: Select your local time zone from pull down menu.
Automatic Time Configuration
32

Enable NTP Server: Select this option if you want to synchronize the router's clock to a Network Time
Server over the Internet. If you are using schedules or logs, this is the best way to ensure that the
schedules and logs are kept accurate. Note that, even when NTP Server is enabled, you must still
choose a time zone and set the daylight saving parameters.
NTP Server Used: Select a Network Time Server for synchronization. You can type in the address of
a time server or select one from the list. If you have trouble using one server, select another.
Set the Date and Time Manually: If you do not have the NTP Server option in effect, you can either
manually set the time for your router here.
STATUS
This page displays the device’s current status.
33

Help
Help section provides web-based explanations on each configurable field.
34

Network Glossar y
Access Point - A device that allows wireless-equipped computers and other devices to
communicate with a wired network. also used to expand the range of a wireless network.
Ad-hoc - A group of wireless devices communicating directly with each other (peer-to-peer)
without the use of
an access point.
AES (Advanced Encrypt ion S ta ndard) - A security method that uses symmetric 128-bit block
data encryption.
Bandwidth - The transmission capacity of a given device or network.
Bit - A binary digit.
Boot - To start a device and cause it to start executing instructions.
Broadband - An always-on, fast Internet connection.
Browser - An application program that provides a way to look at and interact with all the
information on the World Wide Web.
Cable Modem - A device that connects a computer to the cable television network, which in
turn connects to the Internet.
Daisy Chain - A method used to connect devices in a series, one after the other.
DDNS (Dynamic Domain Name System) - Allows the hosting of a website, FTP server, or
e-mail server with a fixed domain name (e.g., www.xyz.com) and a dynamic IP address.
Default Gateway - A device that forwards Internet traffic from your local area network.
DHCP (Dynamic Host Config ur ati on Pr otocol) - A networking protocol that allows
administrators to assign temporary IP addresses to network computers by “leasing” an IP
address to a user for a limited amount o f time , instead of assigning permanent IP addresses.
DMZ (Demilitarized Zone) - Removes the Router's firewall protection from one PC, allowing it
to be “seen” from the Internet.
DNS (Domain Name Server) - The IP address of your ISP's server, which translates the
names of websites into IP addresses.
Domain - A specific name for a network of computers.
Download - To receive a file transmitted over a network.
DSL (Digital Subscriber Line) - An always-on broadband connection over traditional phone
lines.
Dynamic IP Address - A temporary IP address assigned by a DHCP server.
EAP (Extensible Authentication Protocol) - A general authe nti cat ion protocol used to control
network access.
Many specific authentication methods work within this framework.
Encryption - Encoding data transmitted in a network.
Ethernet - IEEE standard network protocol that specifies how data is placed on and retrieved
from a common transmission medium.
Firewall - A set of related programs located at a network gateway server that protects the
resources of a network from users fro m oth er networks.
Firmware - The programming code that runs a networking device.
FTP (File Transfer Protocol) - A protocol used to transfer files over a TCP/IP network.
Full Duplex - The ability of a networking device to receive and transmit data simultaneously.
35

Gateway - A device that interconnects networks with different, incompatible communications
protocols.
Half Duplex - Data transmission that can occur in two directions over a single line, but only
one direction at a time.
HTTP (HyperText Transport Protocol) - The communications protocol used to connect to
servers on the World Wide Web.
Infrastructure - A wireless network that is bridged to a wired network via an access point.
IP (Internet Protocol) - A protocol used to send data over a network
IP Address - The address used to identify a computer or device on a network.
IPCONFIG - A Windows 2000 and XP utility that displays the IP address for a particular
networking device.
IPSec (Internet Protocol Security) - A VPN protocol used to implement secure exchange of
packets at the IP layer.
ISP (Internet Service Provider) - A company that provides access to the Internet.
LAN - The computers and networking products that make up your local network.
MAC (Media Access Control) Address - The unique address that a manufacturer assigns to
each networking devi ce.
Mbps (MegaBits Per Second) - One million bits per second; a unit of measurement for data
transmission.
NAT (Network Address Translation) - NAT technology trans lat es IP a ddr ess es o f a local ar e a
network to a different IP address for the Internet.
Packet - A unit of data sent over a network.
Passphrase - Used much like a password, a passphrase simplifies the WEP encryption
process by automatically generating the WEP encryption keys for Linksys products.
Ping (Packet Internet Groper) - An Internet utility used to determine whether a particular IP
address is online.
POP3 (Post Office Protocol 3) - A standard mail server commonly used on the Internet.
Port - The connection point on a computer or networking device used for plugging in cables or
adapters.
Power over Ethernet (PoE) - A technology enabling an Ethernet network cable to deliver both
data and power.
PPPoE (Point to Point Protocol over Ethernet) - A type of broadband connection that provides
authentication
(username and password) in addition to data transport.
PPTP (Point-to-Point Tunn el i ng Protocol) - A VPN protocol that allows the Point to Point
Protocol (PPP) to be tunneled through an IP network. This protocol is also used as a type of
broadband connection in Europe.
RADIUS (Remote Authentication Dial-In User Service) - A protocol that uses an
authentication server to control network access.
RJ-45 (Registered Jack-45) - An Ethernet connector that holds up to eight wires.
Roaming - The ability to take a wireless device from one access point's range to another
without losing the connection.
Router - A networking dev ice that connects multiple networks together.
36

Server - Any computer whose function in a network is to provide user access to files, printing,
communications, and other services.
SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol) - The standard e-mail protocol on the Internet.
SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol) - A widely used network monitoring and
control protocol.
SPI (Stateful Packet Inspection) Firewall - A technology that inspects incoming packets of
information before all o wing them to enter the network .
SSID (Service Set IDentifier) - Wireless network's name.
Static IP Address - A fixed assigned address to a computer or device that is connected to a
network.
Static Routing - Forwarding data in a network via a fixed path.
Subnet Mask - An addr ess code that determines the size of the network.
Switch - 1. A data switch that connects computing devices to host computers, allowing a large
number of devices to share a limited number of ports. 2. A device for making, breaking, or
changing the connections in an electrical circuit.
TCP (Transmission Control Protocol) - A network protocol for transmitting data that requires
acknowledgement fr o m the reci pient of data sent.
TCP/IP (Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol) - A set of instructions PCs use to
communicate over a network.
Telnet - A user command and TCP/IP protocol used for accessing remote PCs.
TFTP (Trivial File Transfer Protocol) - A version of the TCP/IP FTP protocol that has no
directory or password capability.
Throughput - T he am o unt o f data moved successfully from one node to another in a given
time period.
TKIP (Temporal Key Integrity Protocol) - a wireless encryption protocol that provides dynamic
encryption keys for each packet transmitted.
Topology - The physical layout of a network.
TX Rate - Transmission R ate.
Upgrade - To replace existing software or firmware with a newer version.
Upload - To transmit a file ov er a netw or k .
URL (Uniform Resource Locator) - The address of a file located on the Internet.
VPN (Virtual Private Network) - A security measure to protect data as it leaves one network
and goes to another over the Internet.
WAN (Wide Area Network)- The Internet.
WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy) - A method of encrypting network data transmitted on a
wireless network for
greater security.
WLAN (Wireless Local Area Network) - A group of computers and associated devices that
communicate with each other wirelessly.
WPA (Wi-Fi Protected Access) - a wireless security protocol using TKIP (Temporal Key
Integrity Protocol) encryption, which can be used in conjunction with a RADIUS server.
37

Specifications
Hardware
WAN
1 x 10/100/1000Mbps Auto-MDIX port (Internet)
LAN
4 x 10/100/1000Mbps Auto-MDIX port
Wireless On/Off
Switch
On/Off Power
Switch
WPS Button
Wi-Fi Protected Setup (WPS) automated wireless connection push button
Reset Button
Reset button to Factory Default
Connection Type
Dynamic IP, Static (fixed) IP, PPPoE, PPTP, L2TP
3K configurable NAT entries; restricted NAPT
NetMeeting, SIP
WDS
Enable/disable Wireless Distribution System support
UPnP
UPnP IGD 1.0 compliant
DMZ
DMZ host, 24 configurab le Virtual Servers and Game Servers
DNS
Static or WAN assigned DNS servers; 4 verified services for DDNS
Internet Access
Control
Time based Internet access; port range/service filtering; Internet domain restriction; 32
user defined schedules, 2 4 MAC address filter entries
LED Indicator
Power, LAN1~LAN4, WAN, WLAN, WPS
Power Sw it ch
On/Off power switch
Power Adapter
12V DC, 1A external power adapter
Power
Consumption
Dimension (L x W x
H)
Weight
350g (0.8 lb)
Temperature
Operation: 0°~ 40°C (32°F~ 104°F); Storage: -20°~ 60°C (-4°F~140 °F)
Humidity
Max. 90% (non-condensing)
Certifications
CE, FCC
Wireless
Frequency
Antenna
Modulation
Receiving
Channels
Wired: IEEE 802.3 (10Base-T), IEEE 802.3u (100Base-TX) and IEEE 802.3ab
Standards
NAT Firewall
(1000BaseT)
Wireless: IEEE 802.11b, IEEE 802.11g, IEEE 802.11n
Turn on/off wireless LAN
Electrical power on/off switch
IP ranges, port ranges and schedule
Port triggering for 24 special applications
ALG support (enable/disable support) –RTP/RTSP, AOL, FTP, ICMP, WMP/MMS,
779mA
150 x 163 x 26 mm (5.9 x 6.4 x 1.0 in)
2.412 ~ 2.472 GHz
3 x 4dBi fixed dipole antenna
DBPSK/DQPSK/CCK/OFDM (BPSK/QPSK/16-QAM/64-QAM)
802.11b: up to 11Mbps
Data Rate
Security
Output Power
Sensitivity
802.
11g: up to 54Mbps
802.11n: up to 300Mbps
WEP(HEX/ASCII): 64/128-b
WPA(AES/TKIP): WP A/ WP A2-Radius, WPA-PSK/WPA2-PSK
802.11b:
802.11g: 23dBm (typical)
802.11n: 26dBm (typical)
802.11b: -84dBm (typical) @ 11Mbps
802.11g: -72d
802.11n: -65dBm (typical) @ 300Mbps
1~ 11 (FCC), 1~13 (ETSI)
19dBm (typical)
Bm (typical) @ 54 Mbps
it
38

Limited Warranty
TRENDnet warrants its products against defects in material and workmanship, under normal
use and service, for the following lengt hs of time fr om the date of purchase.
TEW-639GR – 3 Years Warranty
AC/DC Power Adapter, Cooling Fan, and Power Supply carry 1 year warranty.
If a product does not operate as warranted during the applicable warranty period, TRENDnet
shall reserve the right, at its expense, to repair or replace the defective product or part and
deliver an equivalent product or part to the customer. The repair/replacement unit’s warranty
continues from the original date of purchase. All products that are replaced become the
property of TRENDnet. Replacement products may be new or reconditioned. TRENDnet does
not issue refunds or credit. Please contact the point-of-purchase for their return policies.
TRENDnet shall not be responsible for any software, firmware, information, or memory data of
customer contained in, stored on, or integrated with any products returned to TRENDnet
pursuant to any warranty.
There are no user serviceable parts inside the product. Do not remove or attempt to service
the product by any unauthorized service center. This warranty is voided if (i) the product has
been modified or repaired by any unauthorized service center, (ii) the product was subject to
accident, abuse, or improper use (iii) the product was subject to conditions more severe than
those specified in the manual.
Warranty service may be obtained by contacting TRENDnet within the applicable warranty
period and providing a copy of the dated proof of the purchase. Upon proper submission of
required documentation a Return Material Authorization (RMA) number will be issued. An
RMA number is required in order to initiate warranty service support for all TRENDnet
products. Products that are sent to TRENDnet for RMA service must have the RMA number
marked on the outside of return packages and sent to TRENDnet prepaid, insured and
packaged appropriately for safe shipment. Customers shipping from outside of the USA and
Canada are responsible for return shipping fees. Customers shipping from outside of the USA
are responsible for custom charges, including but not limited to, duty, tax, and other fees.
WARRANTIES EXCLUSIVE: IF THE TRENDNET PRODUCT DOES NOT OPERATE AS
WARRANTED ABOVE, THE CUSTOMER’S SOLE REMEDY SHALL BE, AT TRENDNET’S
OPTION, REPAIR OR REPLACE. THE FOREGOING WARRANTIES AND REMEDIES ARE
EXCLUSIVE AND ARE IN LIEU OF ALL OTHER WARRANTIES, EXPRESSED OR IMPLIED,
EITHER IN FACT OR BY OPERATION OF LAW, STATUTORY OR OTHERWISE, INCLUDING
WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE.
TRENDNET NEITHER ASSUMES NOR AUTHORIZES ANY OTHER PERSON TO ASSUME FOR
IT ANY OTHER LIABILITY IN CONNECTION WITH THE SALE, INSTALLATION
MAINTENANCE OR USE OF TRENDNET’S PRODUCTS.
TRENDNET SHALL NOT BE LIABLE UNDER THIS WARRANTY IF ITS TESTING AND
EXAMINATION DISCLOSE THAT THE ALLEGED DEFECT IN THE PRODUCT DOES NOT
EXIST OR WAS CAUSED BY CUSTOMER’S OR ANY THIRD PERSON’S MISUSE, NEGLECT,
IMPROPER INSTALLATION OR TESTING, UNAUTHORIZED ATTEMPTS TO REPAIR OR
39

MODIFY, OR ANY OTHER CAUSE BEYOND THE RANGE OF THE INTENDED USE, OR BY
ACCIDENT, FIRE, LIGHTNING, OR OTHER HAZARD.
LIMITATION OF LIABILITY: TO THE FULL EXTENT ALLOWED BY LAW TRENDNET ALSO
EXCLUDES FOR ITSELF AND ITS SUPPLIERS ANY LIAB ILITY, WHETHER BASED IN
CONTRACT OR TORT (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE), FOR INCIDENTAL, CONSEQUENTIAL,
INDIRECT, SPECIAL, OR PUNITIVE DAMAGES OF ANY KIND, OR FOR LOSS OF REVENUE
OR PROFITS, LOSS OF BUSINESS, LOSS OF INFORMATION OR DATE, OR OTHER
FINANCIAL LOSS ARISING OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SALE, INSTALLATION,
MAINTENANCE, USE, PERFORMANCE, FAILURE, OR INTERRUPTION OF THE
POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGES, AND LIM ITS ITS LIABILITY TO REPAIR,
REPLACEMENT, OR REFUND OF THE PURCHASE PRICE PAID, AT TRENDNET’S OPTION.
THIS DISCLAIMER OF LIABILITY FOR DAMAGES WILL NOT BE AFFECTED IF ANY
REMEDY PROVIDED HEREIN SHALL FAIL OF ITS ESSENTIAL PURPOSE.
Governing Law: This Limited Warranty shall be governed by the laws of the state of California.
Some TRENDnet products include software code written by third party developers. These codes are
subject to the GNU General Public License ("GPL") or GNU Lesser General Public License ("LGPL").
Go to http://www.trendnet.com/gpl
or http://www.trendnet.com Download section and look for the
desired TRENDnet product to access to the GPL Code or LGPL Code. These codes are distributed
WITHOUT WARRANTY and are subject to the copyrights of the developers. TRENDnet does not
provide technical support for these codes. Please go to
http://www. gnu.org/licenses/gpl.txt or
http://www. gnu.org/licenses/lgpl.txt for specific terms of each license.
REPAIR OR MODIFY, OR ANY OTHER CAUSE BEYOND THE RANGE OF THE INTENDED
USE, OR BY ACCIDENT, FIRE, LIGHTNING, OR OTHER HAZARD.
LIMITATION OF LIABILITY: TO THE FULL EXTENT ALLOWED BY LAW TRENDNET ALSO
EXCLUDES FOR ITSELF AND ITS SUPPLIERS ANY LIABILITY, WHETHER BASED IN
CONTRACT OR TORT (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE), FOR INCIDENTAL, CONSEQUENTIAL,
INDIRECT, SPECIAL, OR PUNITIVE DAMAGES OF ANY KIND, OR FOR LOSS OF
REVENUE OR PROFITS, LOSS OF BUSINESS, LOSS OF INFORMATION OR DATE, OR
OTHER FINANCIAL LOSS ARISING OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SALE,
INSTALLATION, MAINTENANCE, USE, PERFORMANCE, FAILURE, OR INTERRUPTION
OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGES, AND LIMITS ITS LIABILITY TO REPAIR,
REPLACEMENT, OR REFUND OF THE PURCHASE PRICE P AID, AT TRENDNET’S
OPTION. THIS DISCLAIMER OF LIABILITY FOR DAMAGES WILL NOT BE AFFECTED IF
ANY REMEDY PROVIDED HEREIN SHALL FAIL OF ITS ESSENTIAL PURPOSE.
Governing Law: This Limited Warranty shall be governed by the laws of the state of California.
Some TRENDnet products include software code written by third party developers. These
codes are subject to the GNU General Public License ("GPL") or GNU Lesser General Public
License ("LGPL").
Go to http://www.trendnet.com/gpl or http://www.trendnet.com Download section and look for
the desired TRENDnet product to access to the GPL Code or LGPL Code. These codes are
distributed WITHOUT WARRANTY and are subject to the copyrights of the developers.
TRENDnet does not provide technical support for these codes. Please go to
http://www.gnu.org/licenses/gpl.txt or http://www.gnu.org/licenses/lgpl.txt for specific terms of
each license.
40

41
 Loading...
Loading...