Page 1

28-Port 10/100/1000Mbps
Gigabit Ethernet
Web Smart Switch
with
2×1000BASE-T, 24×10/100BASE-TX ports
2 optional mini-GBIC ports
User’s Guide
Page 2

Page 3

FCC Warning
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the
regulations for a Class A digital device, pursuant to Part 15 of the
FCC Rules. These limits ar e desig n ed to prov id e r easonab le p ro tectio n
against harmful interference when the equipment is operated in a
commercial environment. This equipment generates, uses, and can
radiate radio frequency energy and, if not installed and used in
accordance with this user’s guide, may cause harmful interference to
radio communications. Operation of this equipment in a residential
area is likely to cause harmful in terf erence, in which case th e user will
be required to correct the interference at his or her own expense.
CE Mark Warning
This is a Class A product. In a domestic environment, this product
may cause radio interference, in which cas e the user may be required
to take adequate m easures.
VCCI Warning
This is a product of VCCI Class A Compliance.
Page 4

UL Warning
a) Elevated Operating Ambient Temperature- If installed in a closed
or multi-unit rack assemb ly, the operating ambient temperature of the
rack environment may be greater than room ambient. Therefore,
consideration should be given to installing the equipment in an
environment compatible with the manufacturer's maximum rated
ambient temperature (Tmra).
b) Reduced Air Flow- Installation of the equipment in a rack should
be such that the amount of air flow required for safe operation of the
equipment is not compromised.
c) Mechanical Loading- mounting of the equipment in the rack
should be such that a hazardous condition is not achieved due to
uneven mechanical loading.
d) Circuit Overloading- Consideration should be given to the
connection of the equipment to the supply circuit and the effect that
overloading of circuits might have on over current protection and
supply wiring. Appropriate consideration of equipment nameplate
ratings should be use d whe n add ress ing this concern.
e) Reliable Earthing- Reliable earthing of rack-mounted equipment
should be maintained. Particular attention should be given to supply
connections other than direct connections to the branch circuit (e.g.,
use of power strips).
Ver. 1.00
Page 5

TABLE OF CONTENT
About This Guide.................................................................................1
Purpose ............................................................................................1
Terms/Usage....................................................................................1
Introduction..........................................................................................3
Gigabit Ethernet Technology...........................................................3
Fast Ethernet Technology................................................................4
Switching Technology .....................................................................5
VLAN (Virtual Local Area Network)..............................................6
Features............................................................................................6
Unpacking and Installation .................................................................. 9
Unpacking........................................................................................9
Installation .......................................................................................9
Rack Mounting ..............................................................................10
Connecting Network Cable............................................................11
AC Power.......................................................................................11
Identifying External Components ......................................................13
Front Panel............ ......................... ......................... ....................... 13
Rear Panel......................................................................................14
Understanding LED Indicators ..........................................................15
Power and System LEDs ...............................................................15
Ports 1~24 10/100M Status LEDs..................................................16
Ports 25~26 Gigabit Status LEDs ..... .............................................16
Ports 27~28 mini-GBIC Status LEDs............................................17
i
Page 6

Configuration.....................................................................................19
Installing the Web Management Utility.........................................19
Discovery List................................................................................20
Monitor List...................................................................................21
Device Setting................................................................................23
Toolbar...........................................................................................24
Configuring the Switch..................................................................25
Login..............................................................................................26
Setup Menu....................................................................................28
Configuring Setup Setting..............................................................28
Port Settings...............................................................................28
VLAN Settings (Virtual Local Area Network)..........................30
Trunk Setting .............................................................................31
Mirror Setting.............................................................................31
Device Status .............................................................................32
Statistic.......................................................................................32
System Setting ...........................................................................34
Trap Setting................................................................................34
Set Password..............................................................................35
Backup Setting...........................................................................36
Reset Setting ..............................................................................37
Logout............................................................................................37
Technical Specifications....................................................................39
ii
Page 7

ABOUT THIS GUIDE
Congratulations on your purchase of the 24+4G-Port
10/100/1000Mbps Gigabit Ethernet Web Smart Switch. This device
integrates 1000Mbps Gigabit Ethernet, 100Mbps Fast Ethernet and
10Mbps Ethernet network capabilities in a highly flexible package.
Purpose
This guide discusses how to install your 24+4G-Port
10/100/1000Mbps Gigabit Ethernet Web Smart Switch.
Terms/Usage
In this guide, th e term “Switch” (first letter upper case) refers to your
24+4G-Port 10/100/1000Mbps Gigabit Ethernet Web Smart Switch,
and “switch” (first letter lower case) refers to other Ethernet switches.
1
Page 8

Page 9

INTRODUCTION
This chapter describes the features of the 24+4G-Port
10/100/1000Mbps Gigabit Ethernet Web Smart Switch and some
background information ab out Ethern et/Fast Eth e rn et/Gig abit Ethe rn et
switching technology.
Gigabit Ethernet Technology
Gigabit Ethernet is an extension of IEEE 802.3 Ethernet utilizing the
same packet structure, format, and support for CSMA/CD protocol,
full duplex, flow control, and management objects, but with a tenfold
increase in theoretica l throughput over 100-Mbps Fast Ethernet and a
hundredfold increase over 10-Mbps Ethernet. Since it is compatible
with all 10-Mbps and 100-Mbps Ethernet environments, Gigabit
Ethernet provides a straightforward upgrade without wasting a
company’s existing investment in hardware, software, and trained
personnel.
The increased speed and extra bandwidth offered by Gig abit Ethernet
is essential to coping with the network bottlenecks that frequently
develop as computers and their busses get faster and more users use
applications that generate more traffic. Upgrading key components,
such as your backbone and servers to Gigabit Ethernet can greatly
improve network response times as well as significantly speed up the
traffic between your subnets.
Gigabit Ethernet enables fast optical fiber connections to support
video conferencing, complex imaging, and similar data-intensive
applications. Likewise, since data transfers occur 10 times faster than
Fast Ethernet, servers outfitted with Gigabit Ethernet NIC’s are able to
perform 10 times the number of operations in the same amount of time.
3
Page 10

In addition, the phenomenal bandwidth delivered by Gigabit Ethernet
is the most cost-effective method to take advantage of today and
tomorrow’s rapidly improving switching and routing internetworking
technologies. And with expected advances in the coming years in
silicon technology and digital signal processing that will enable
Gigabit Ethernet to eventually operate over unshielded twisted-pair
(UTP) cabling, outfitting your network with a powerful 1000-Mbpscapable backbone/server connection creates a flexible foundation for
the next generation of network technology products.
Fast Ethernet Technology
The growing importance of LANs and the increasing complexity of
desktop computing applications are fueling the need for high
performance networks. A number of high-speed LAN technologies
have been proposed to provide greater bandwidth and improve
client/server response times. Among them, 100BASE-T (Fast
Ethernet) provides a non-disruptive, smooth evolution from the
current 10BASE-T technology. The non-disruptive and smooth
evolution nature, and the dominating potential market base, virtually
guarantees cost-effective and high performance Fast Ethernet
solutions.
100Mbps Fast Ethernet is a standard specified by the IEEE 802.3
LAN committee. It is an extension of the 10Mbps Ethernet standard
with the ability to transmit and receive data at 100Mbps, while
maintaining the CSMA/CD Ethernet protocol. Since the 100Mbps
Fast Ethernet is compatible with all other 10Mbps Ethernet
environments, it provides a straightforward upgrade and takes
advantage of the existing investment in hardware, software, and
personnel training.
4
Page 11

Switching Technology
Another approach to pushing beyond th e limits of Ethernet technolog y
is the development of switching technology. A switch bridges
Ethernet packets at the MAC address level of the Ethernet protocol
transmitting among connected Ethernet or Fast Ethernet LAN
segments.
Switching is a cost-effective way of increasing the total network
capacity available to users on a local area network. A switch increases
capacity and decreases network loading by dividing a local area
network into different segments, which don’t compete with each other
for network transmission capacity.
The switch acts as a high-speed selective bridge between the
individual segments. The switch, without interfering with any other
segments, automatically forwards traffic that needs to go from one
segment to another. By doing this the total network capacity is
multiplied, while still maintaining the same network cabling and
adapter cards.
Switching LAN technology is a marked improvement over the
previous generation of network bridges, which were characterized by
higher latencies. Routers have also been used to segment local area
networks, but the cost of a router, the setup and maintenance required
make routers relatively impractical. Today switches are an ideal
solution to most kinds of local area network congestion problems.
5
Page 12

VLAN (Virtual Local Area Networ k)
A VLAN is a group of end-stations that are not constrained by their
physical location and can communicate as if a common broadcast
domain, a LAN. The primary utility of using VLAN is to reduce
latency and need for routers, using faster switching instead. Other
VLAN utility includes:
Security, Security is increased with the reduction of opportunity in
eavesdropping on a broadcast network because data will be switched
to only those confidential users within the VLAN.
Cost Reduction, VLANs can be used to create multiple broadcast
domains, thus eliminating the need of expensive routers.
Port-based (or port-group) VLAN is the common method of
implementing a VLAN, and is the one supplied in the Switch.
Features
24×10/100Mbps Auto-negotiation Fast Ethernet RJ45 ports
Full/half duplex transfer mode for 10/100Mbps RJ45 port
Full duplex transfer mode for Gigabit port
2×10/100/1000Mbps Auto-negotiation Gigabit RJ45 ports
2×mini-GBIC ports
All RJ45 ports support auto MDI/MDIX, so there is no need to
use cross-over cables or an up-link port
Wire speed reception and transmission
Store-and-Forward switching scheme capability to support rate
adaptation and ensure data integrity
6
Page 13

Up to 4K unicast addresses entities per device, self-learning, and
table aging
768KBytes packet buffer
Supports IEEE 802.3x flow control for full-duplex mode ports
Supports Back-press ure flo w cont rol fo r half-duplex mode ports
Easy setting via Web Mana gement Utility
Standard 19” Rack-mount size
Supports port-base VLAN
Supports port-base QoS
Supports Trunking on 1000BASE-T ports
Supports Port-mirroring
Supports Port-setting for Speed/Disable, Flow control
Easy configuration via WEB Browser
7
Page 14

Page 15

UNPACKING AND INSTALLATION
This chapter provides unpacking and installation information for the
Switch.
Unpacking
Open the shipping cartons of the Switch and carefully unpacks its
contents. The carton should contain the following items:
One 24+4G-Port 10/100/1000Mbps Gigabit Ethernet Web
Smart Switch
Four rubber feet to be used for shock cushioning
Screws and two mounting brackets
If any item is found missing or damaged, please contact your local
reseller for replacement.
One AC power cord, suitable for your area’s electrical power
connections
CD-Rom with Web Management Utility and User’s Guide
Installation
The site where you install the hub stack may greatly affect its
performance. When installing, consider the following pointers:
Install the Switch in a fairly cool and dry place. See Technical
Specifications for the acceptable temperature and humidity operating
ranges.
Install the Switch in a site free from strong electromagnetic field
generators (such as motors), vibration, dust, and direct exposure to
sunlight.
9
Page 16
Leave at least 10cm of space at the front and rear of the hub for
ventilation.
Install the Switch on a sturdy, level surface that can support its weigh t,
or in an EIA standard-size equipment rack. For information on rack
installation, see the next section, Rack Mounting.
When installing the Switch on a leve l surface, attach the rubber feet to
the bottom of each device. The rubber feet cushion the hub and
protect the hub case from scratching.
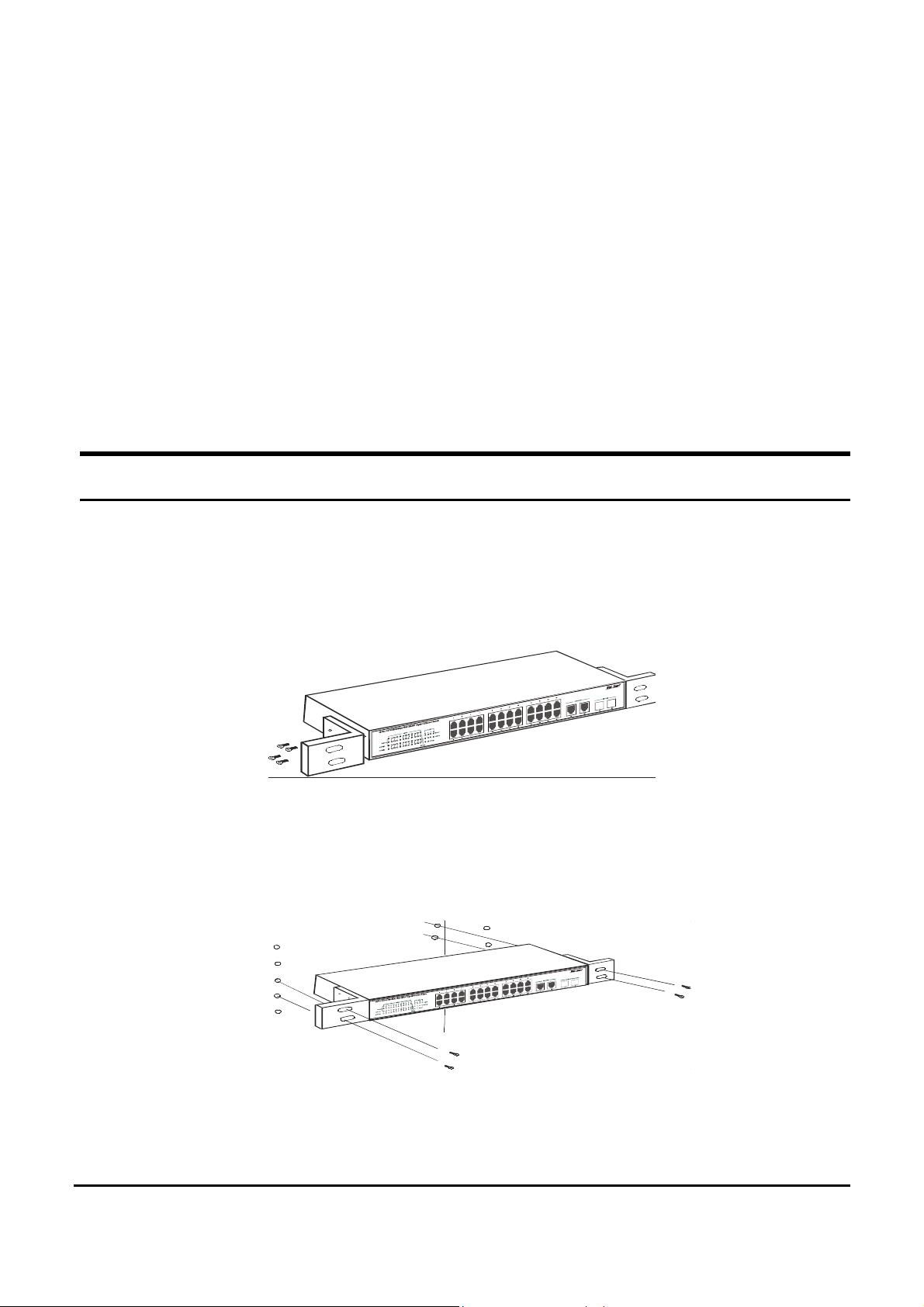
Rack Mounting
The switch can be mounted in an EIA standard-size, 19-inch rack,
which can be placed in a wiring closet with other equipment. Attach
the mounting brackets at the switch’s front panel (one on each side),
and secure them with the provided screws.
Figure 1. Combine the Switch with the provided screws
Then, use screws provided with the equipment rack to mount each
switch in the rack.
Figure 2. Mount the Switch in the rack
10
Page 17

Connecting Network Cable
The Switch supports 10Mbps Ethernet or 100Mb ps Fast Ethernet and
it runs both in half and full duplex mode using two pair of Category 5
cable.
The Switch also supports 2-Ports 1000Mbps Gigabit Ethernet that
runs in Auto-negotiation mode and 10Mbps Ethernet or 100Mbps Fast
Ethernet that runs both in half and full duplex mode and 1000Mbps
Gigabit Ethernet runs in full duplex mode using four pair of Category
5 Cable.
These RJ45 ports are Auto-MDI type port. The Switch can auto
transform to MDI-II or MDI-X type, so you can just make an easy
connection that without worrying if you are using a standard or
crossover RJ45 cable.
There are additional 2 ports mini-GBIC slot for optional mini-GBIC
module.
AC Power
The Switch used the AC power supply 100-240V AC, 50-60 Hz. The
power switch is located at the rear of the unit adjacent to the AC
power connector and the system fan. The switch’s p ower supply will
adjust to the local power source automatically and may be turned on
without having any or all LAN segment cables connected.
11
Page 18

Page 19

IDENTIFYING EXTERNAL COMPONENTS
This chapter describes the front panel, rear panel, and LED indicators
of the Switch.
Front Panel
The figure below shows the front panels of the Switch.
28-Port 10/100/1000Mbps Web-SMART Gigabit Ethernet Switch
Link/ACT
POWER
SYSTEM
10/100M
1357 9 11 13 15 17 19 21 23 25 26 27 28
4
810
16 18 20
12 14
2
Gigabit
22 24
100Mbps
100Mbps
Link/ACT
1000Mbps
1000BASE-T
Mini GBIC
Figure 3. Front panel of 24+4G-port Gigabit Ethernet Switch
LED Indicator:
Comprehensive LED indicators display the status of the switch and
the network (see the LED Indicators chapter below).
Fast Ethernet Ports (Port 1~24):
These ports support network speeds of either 10Mbps or 100Mbps,
and can operate in half- and full- duplex transfer modes. These ports
also supports automatic MDI/MDIX crossover detection function
gives true “plug and play” capability, just need to plug-in the network
cable to the hub directly and don’t care if the end node is NIC
(Network Interface Card) or switch and hub.
Gigabit Ethernet Ports (Port 25~26):
The Switch is equipped with two Gigabit twisted pair ports, supported auto
negotiable 10/100/1000Mbps and auto MDI/MDIX crossover detection
function. These two ports can operate in half-duplex mode for 10/100Mbps
and full- duplex mode for 10/100/1000Mbps.
13
Page 20
mini-GBIC Ports (Port 27~28):
The Switch is equipped with two mini-GBIC ports, supported optional
1000BASE-SX/LX mini-GBIC module.
Note: When the port was set to “Forced Mode”, the Auto
MDI/MDIX will be disabled.
Rear Panel
Figure 4. Rear pa nel of the Switch
Power Switch:
This is a switch where you can control to enable or disable the power.
AC Power Connector:
This is a three-pronged connector that supports the power cord. Plug
in the female connector of the provide d power cord in to this conne ctor,
and the male into a power outlet. Supported inp ut voltages range from
100-240V AC at 50-60Hz.
Reset:
The Reset button is to reset all the setting back to the factory default.
Note: Be sure that you recorded the setting of your device, else all
the setting will be erased when pressing the “Reset” button.
14
Page 21
UNDERSTANDING LED INDICATORS
The front panel LEDs provides instant status feedback, and, helps
monitor and troubleshoot when needed.
24-Port 10/100MbpsEthernet Sm art Sw itch
28-Port 10/100/1000Mbps Web-SMART Gigabit Ethernet Switch
POWER
POWER
SYSTEM
SYSTEM
Link/ACT
Link/ACT
10/100M
35791113 15
1
FX
1
2345678910111213141516
2
FDX
4 8 1012141618202224
19
17
23 25 26
21
17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24
100Mbps
Gigabit
27
100Mbps
28
Link/ACT
1000Mbps
Figure 5. LED indicators of the Switc h
Power and System LEDs
POWER: Power Indicator
On : When the Power LED lights on, the Switch is receiving power.
Off : When the Power turns off or the power cord has i mproper connection.
SYSTEM: Management Indicator
Blinking : When the CPU is working, the System LED is blinking.
On/Off : The CPU is not working.
15
Page 22
Ports 1~24 10/100M Status LEDs
Link/ACT: Link/Activity
On : When the Link/ACT LED lights on, the respective port is successfully
connected to an Ethernet network.
Blinking : When the Link/ACT LED is blinking, the port is transmitting or
receiving data on the Ethernet network.
Off : No link.
100Mbps
On : When the 100Mbps LED lights on, the respective port is connected to a
100Mbps Fast Ethernet network.
Off : When the respective port is connected to a 10Mbps Ethernet network
Ports 25~26 Gigabit Status LEDs
Link/ACT: Link/Activity
On : When the Link/ACT LED lights on, the respective port is successfully
connected to an Ethernet network.
Blinking : When the Link/ACT LED is blinking, the port is transmitting or
receiving data on the Ethernet network.
Off : No link.
16
Page 23

100Mbps
On : When the 100Mbps LED lights on, the respective port is connected to a
100Mbps Fast Ethernet network.
Off : When the respective port is connected to a 10Mbps Ethernet or
1000Mbps Gigabit Ethernet network.
1000Mbps
On : When the 1000Mbps LED lights on, the respective port is connected to a
1000Mbps Gigabit Ethernet network.
Off : When the respective port is connected to a 10Mbps Ethernet or 100Mbps
Fast Ethernet network
Ports 27~28 mini-GBIC Status LEDs
Link/ACT: Link/Activity
On : When the mini-GBIC module is installed and connected to a network,
the Link/ACT LED lights on.
Blinking : When the LED is blinking, the mi ni-GBIC mo dule is receivi ng data on a
network.
Off : No link.
1000Mbps
On : When the 1000Mbps LED lights on, the respective port is connected to a
1000Mbps Gigabit Ethernet network.
Off : When the respective port is disconnected to the network
17
Page 24

Page 25

CONFIGURATION
Through the Web Browser you can configure the Switch such as
VLAN, Trunking, QoS… etc.
With the attached Web Management Utility, you can easily discover
all the Web Management Switch, assign the IP Address , changing the
password and upgrading the new firmware.
Installing the Web Management Utility
The following gives instructions guiding you through the installations
of the Web Manageme nt utility.
1. Insert the Utility CD in the CD-Rom Drive.
2. From the Start menu on the Windows desktop, choose Run.
3. In the Run dialog box, type D:\Web Management
Utility\setup.exe (D:\ depends where your CD-Rom drive is
located) and click OK.
4. Follow the on-screen instru ctions to install the utility.
5. Upon completion, go to Program Files ->
web_management_utility and execute the Web Management
utility. (Figure 6.)
19
Page 26

Figure 6. Web Manage ment Utility
The Web Management Utility was divided into four parts, Discovery
List, Monitor List, Device Setting and Toolbar function, for details
instruction, follow the below section.
Discovery List
This is the list where you can discover all the Web management
devices in the entire network.
By pressing the “Discovery” button, you can list all the Web
Management devi ce s in the discovery list.
Double click or press the “Add to monitor list” button to select a
device from the Discovery List to the Monitor List.
System word definitions in the Disco very List:
20
Page 27

MAC Address: Shows the device MAC Address.
IP Address: Shows the current IP address of the device.
Protocol version: Shows the version of the Utility protocol.
System Name: Shows the appointed device system name.
Location: Shows where the device is located.
Trap IP: Shows the IP where the Trap to be sent.
Product Name: Shows the device product name.
Subnet Mask: Shows the Subnet Mask set of the device.
Gateway: Shows the Gateway set of the device.
Monitor List
All the Web Smart Device in the Monitor List can be monitored; you
can also receive the trap and show the status of the device.
System word definitions in the M oni t or L i st:
S: Shows the system symbol of the Web-Smart device,
represent for device system is not aliv e.
MAC Address: Shows the device MAC Address.
Protocol version: Shows the version of the Utility protocol.
Product Name: Shows the device product name.
System Name: Shows the appointed device system name.
Trap IP: Shows the IP where the Trap to be sent.
Subnet Mask: Shows the Subnet Mask set of the device.
Gateway: Shows the Gateway set of the device.
IP Address: Shows the current IP address of the device.
Location: Shows where the device is located.
21
Page 28

View Trap: The Trap function can receive the events that happen
from the Web Management Switch in the Monitor List.
There is a light indicator behind the “View Trap” button, when the
light indicates in green, it means that there is no trap transmitted, and
else when it indicates in red, it means that there is new trap
transmitted, this is to remind us to view the trap. (Figure 7)
Figure 7.
When the “View Trap” button is clicked, a Trap Information window
will pop out, it will show the trap information including the Symbol,
Time, Device IP and the Event occured. (Figure 8)
The symbol “
” represents the trap signal arise, this symbol will
disappear after you review and click on the event record.
Figure 8.
Note: In order to receive Trap information, switch has to be configured with
Trap IP and Trap Events in Web browser, which are available in the Trap
Setting Menu (see Page 40 for detail).
Add Item: To add a device to the Monitor List manually, enter the IP
Address of the device that you wa nt to monitor.
Delete Item: To delete the device in the Monitor List.
22
Page 29

Device Setting
You can set the device by using the function key in the Device Setting
Dialog box.
Configuration Setting : In this Configuration Setting, you can set the
IP Address, Subnet Mask, Gateway, Set Trap to (Trap IP Address),
System name and Location.
Select the device in the Discovery list or Monitor List and press this
button, then the Conf iguration Setting window will pop out as Figure
9, after filling up the data that you want to cha nge, you must fill up th e
password and press the “Set” to proc ess the data changed immediately.
Figure 9. Configuration Setting
Password Change: You can use this Password Change when you
need to change the password, f ill in the password needed in the dialog
box and press “Set” button to proceed the password change
immediately.
23
Page 30

Figure 10. Password Change
Firmware Upgrade: When the device has a new function, there will
be a new firmware to update the device, use this function to update.
Figure 11.
Web Access: Double click the device in the Monitor List or select a
device in the Monitor List and press this “Web Access” button to
access the device in Web browser.
Toolbar
The toolbar in the Web Management Utility have four main tabs, File,
View, Options and Help.
In the “File TAB”, there are Monitor S av e, Mon itor S av e As , Mon ito r
Load and Exit.
24
Page 31

Monitor Save: To record the setting of the Monitor List to the
default, when you open the Web Management Utility next time, it
will auto load the default r ecorded setting.
Monitor Save As: To record the setting of the Monitor List in
appointed filename and file path.
Monitor Load: To manually load the settin g f ile of the Monitor List.
Exit: To exit the Web Management Utility.
In the “View TAB”, there are view log and clear log function, this
function will help you to show trap setting.
View Log: To show the event of the Web Management Utility and
the device.
Clear Log: to clear the log.
In the “Option TAB”, there are Refresh Time function, this function
helps you to refresh the time of monitoring the device. Choose 15 secs,
30 secs, 1 min, 2 min and 5 min to select the time of monitoring.
In the “Help TAB”, there is About function, it will show out the
version of the Web Management Utility.
Configuring the Switch
The 24+4G-Port 10/100/1000Mbps Gigabit Ethernet Web Smart
Switch has a Web GUI interface for smart switch configuration. The
Switch can be configured through the Web Browser. A network
administrator can manage, control and monitor the switch from the
local LAN. This section indicates how to configure the Switch to
enable its smart functions including:
25
Page 32

Port Setting (Speed/Disable, Duplex mode, Flow Control and
Port base QoS)
Virtual LAN Group setting (VLAN)
Trunking
Port Mirroring
System Setting
Device status and Statistic
Login
Before you configure this device, note that when the Web Smart
Switch is configured through an Ethernet connection, make sure the
manager PC must be set on same the IP network. For ex ample, wh en
the default network address of the default IP address of the Web Smart
Switch is 192.168.0.1, then the manager PC should be set at
192.168.0.x (where x is a number between 2 and 254), and the default
subnet mask is 255.255.255.0.
Open Internet Explorer 5.0 or above Web b rowser.
Enter IP address http://192.168.0.1
setting) to the address location.
Figure 12.
(the factory-default IP address
26
Page 33
Or through the Web Management Utility, you do not need to
remember the IP Address, select the device shown in the Monitor List
of the Web Management Utility to settle the device on the Web
Browser.
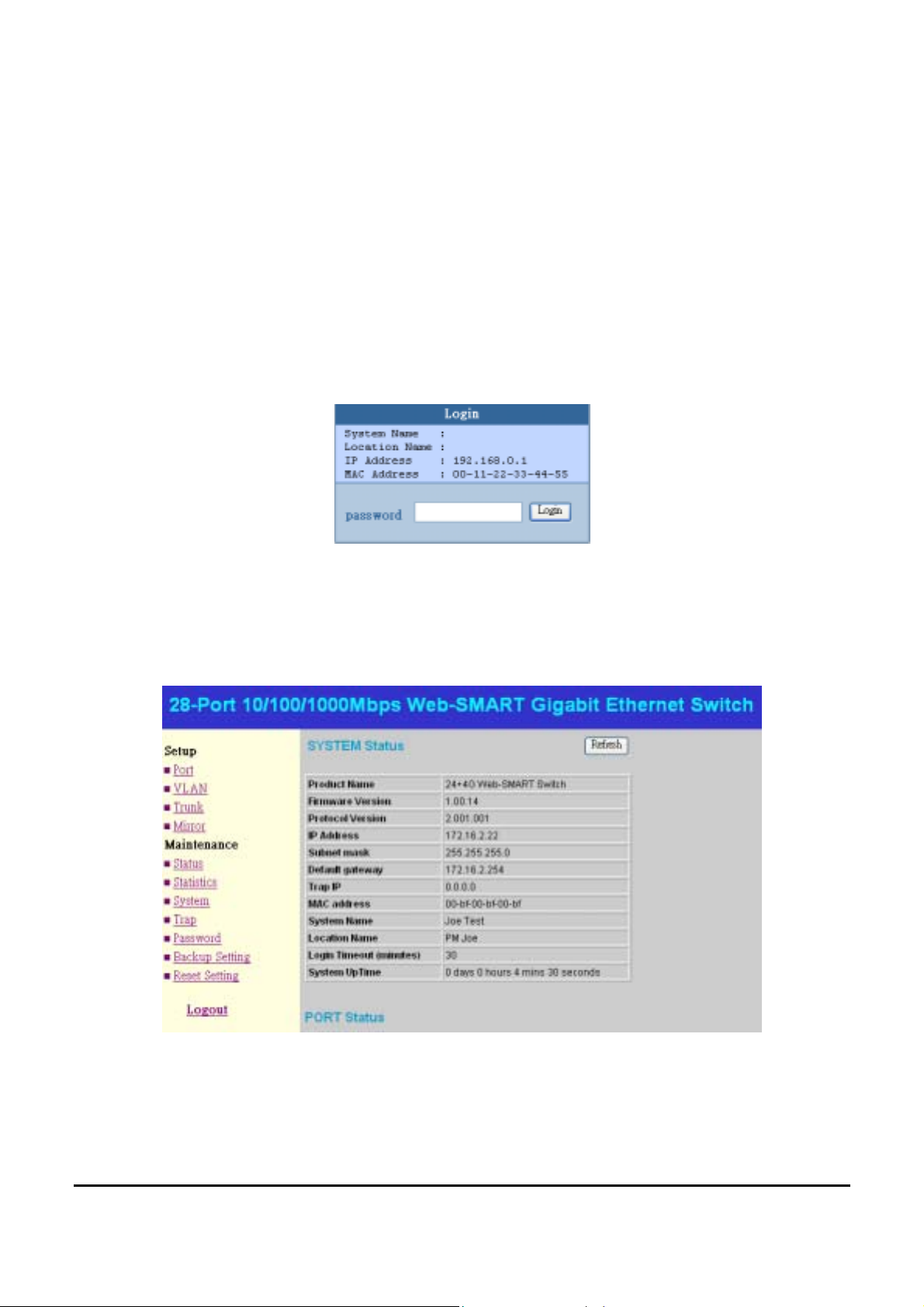
When the following dialog page appears, remain enter the default
password "admin" and press Login to enter the main configuration
window.
Figure 13.
After entering the password, the main page comes up, the screen will
display the device status.
Figure 14. Device Status
27
Page 34

Setup Menu
When the main page appears, find the Setup menu in the left side of
the screen (Figure 15). Click on the setup item that you want to
configure. There are eleven options: Port Settings, VLAN Settings,
Trunk Setting, Mirror Setting, Device Status, Statistic, System Settings,
Trap Setting, Password Setting, Backup Setting and Reset Setting as
shown in the Main Menu screen.
Figure 15. Setup menu
Configuring Setup Setting
Find that there are four items, including Port Settings, VLAN Settings,
Trunk Settings and Mirror Settings in Setup menu.
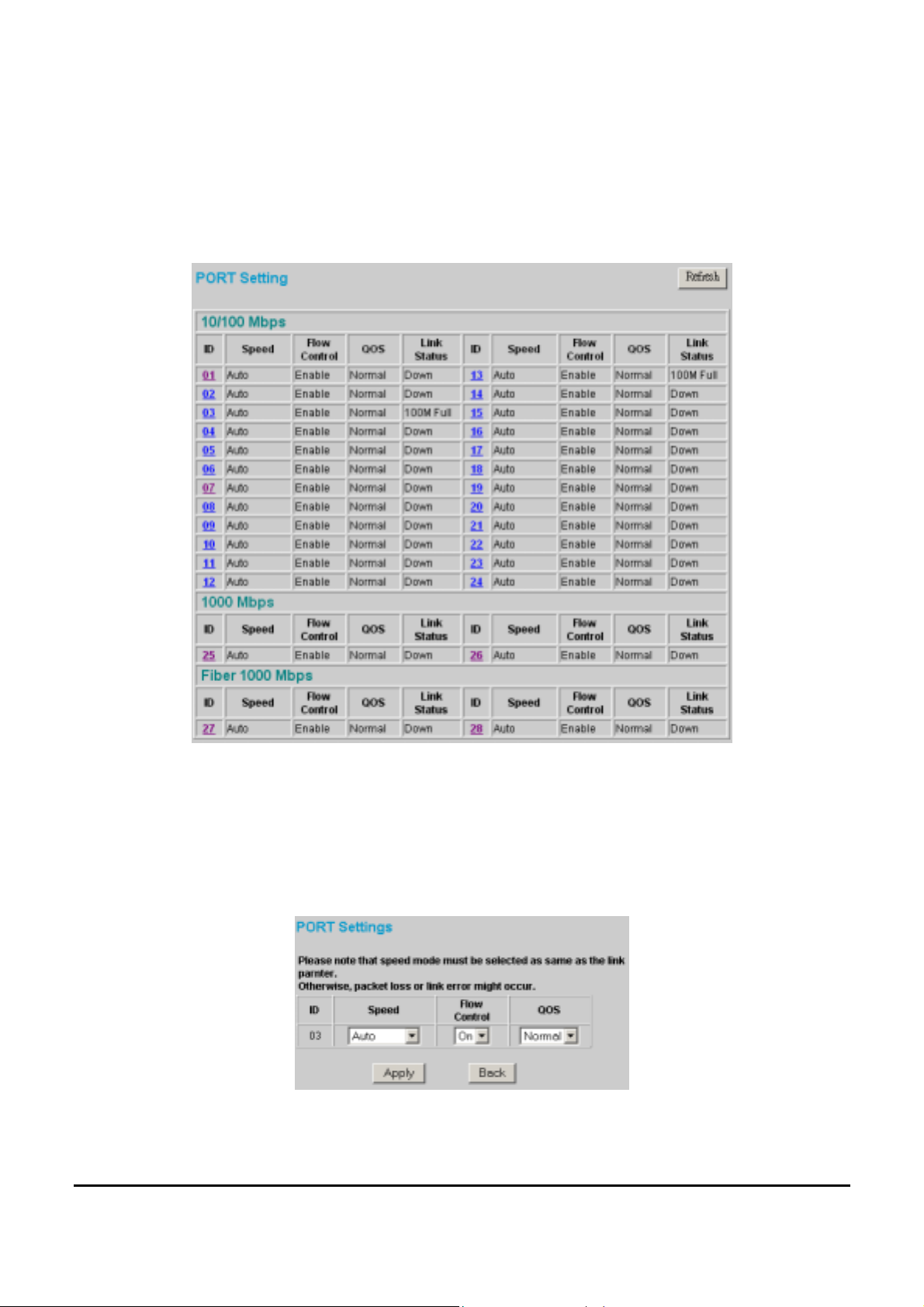
Port Settings
In Port Settings menu (Figure 16), this page will show each port’s
status, press the ID parameter to set each port’s Speed, Flow Control,
QoS priority and Link Status. When you need to renew the posted
information, press the “Refresh” button.
28
Page 35
The Link Status in the screen will show the connection speed and
duplex mode; else this dialog box will show down when the port is
disconnected.
Figure 16. Port Configuration
To change the port setting, click on the ID parameter to enter to the
selected port to configure its Speed/Disable, Flow control and QoS
setting.
Figure 17.
29
Page 36

Speed/Disable:
This setting has six modes—100M Full, 100M Half , 10M Full, 10M
Half, Auto and Disable —for speed or port disable selections.
Flow Control:
This setting determines whether or not the Switch will be handling
flow control. Set FlowCtrl to Enable for avoiding data transfer
overflow. Or it sets to Disable; there is either no flow control or other
hardware/software management.
When the port is set to forced mode, then the flow control will
automatically set to Disable.
QoS:
In some ports that need to have a high priority to manage the data
transfer, QoS should be change. Set the port’s QoS to high to
determine the port will always transfer their data first.
VLAN Settings (Virtual Local Area Network)
Group individual ports into a small “Virtual” network of their own to
be independent of the other ports. To add a VLAN group, press “Add
Group” button, the new VLAN configuration window will pop out,
you can fill in the description in order to describe this VLAN Group,
check on the port to be a member to this VLAN Group, and press
“Apply” button to execute the setting.
Figure 19. VLAN Group Settings
30
Page 37
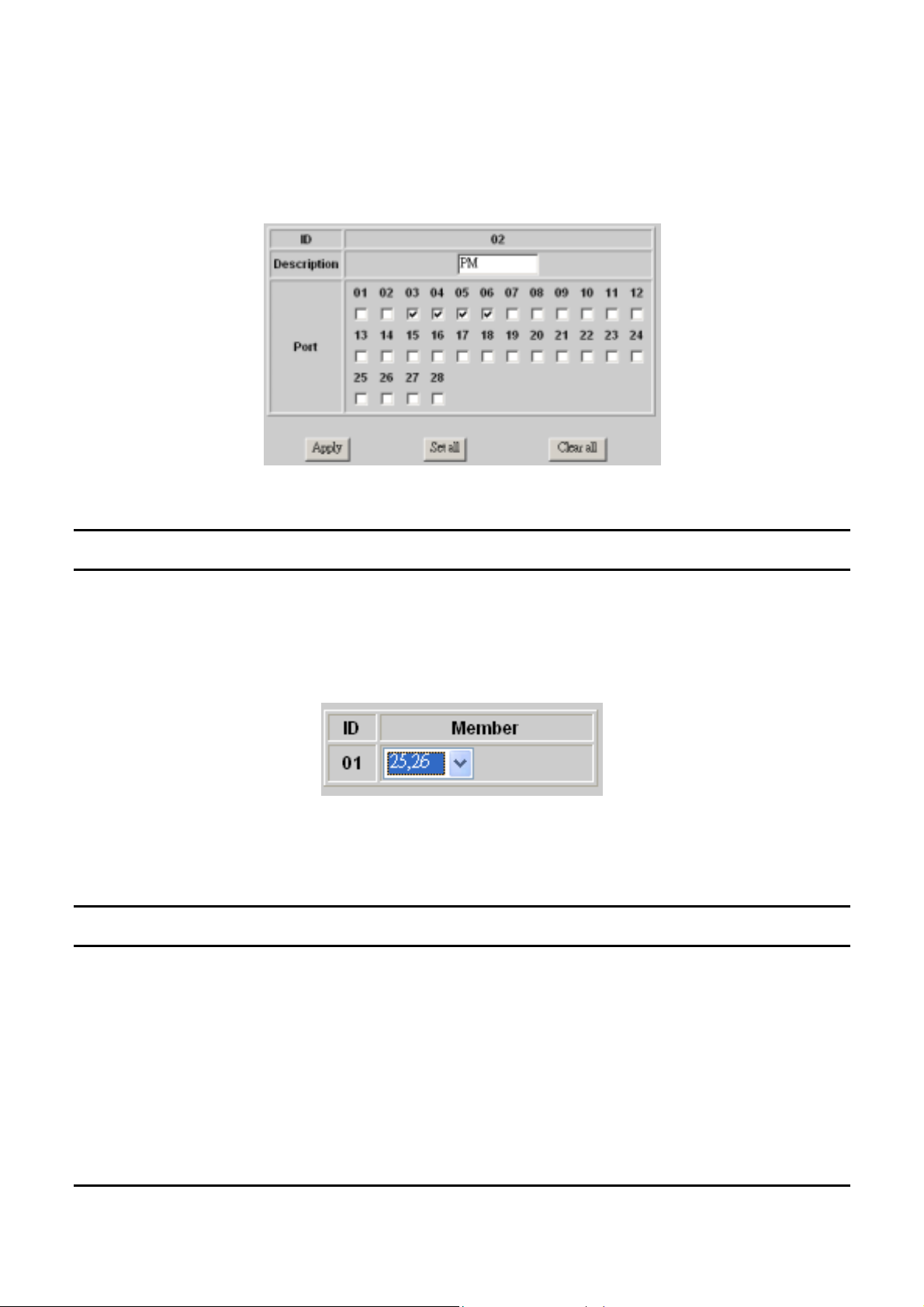
Once you want to modify the VLAN Group, check on the ID
parameter, the ID VLAN configuration window will pop out.
Figure 20. VLAN Settings
Trunk Setting
The Trunk function enables to cascade two devices with a double
times bandwidth (up to 4000Mbps in full duplex mode).
There is only one selection for the trunk setting , port 25 and port 26,
or select “disable” for closing this function.
Figure 21. Trunk Settings
Be sure that the selected tru nk setting port must connect to the device
with a same VLAN group.
Mirror Setting
Port Mirroring is a method of monitoring network traffic that forwards
a copy of each incoming and/or outgoing packet from one port of a
network switch to another port where the packet can be studied. It
enables the manager to keep close track of switch performance and
alter it if necessary.
31
Page 38

Configuring the port mirroring by assigning a source port from which
to copy all packets and a sniffer port where those packets will be sent.
The selection of the sniffer mode is as follow:
TX (transmit) mode: this mode w ill duplicate the data transmit from
the source port and forward to the sniffer port.
RX (receive) mode: this mode will duplicate the data that se nd to the
source and forward to the sniffer port.
Both (transmit and receive) mode: this mode will duplicate bo th the
data transmit from and data that send to the source port, then it will
forward to the sniffer port.
Figure 22.
Device Status
Click on the “Status” to present the device status on this screen, it will
show the System Status, Port Status, VLAN Status, Trunk Status and
Mirror Status..
Press “Refresh” when you need to renew the posted information.
Statistic
The Statistic Menu screen will show the status of each port packet
count.
32
Page 39
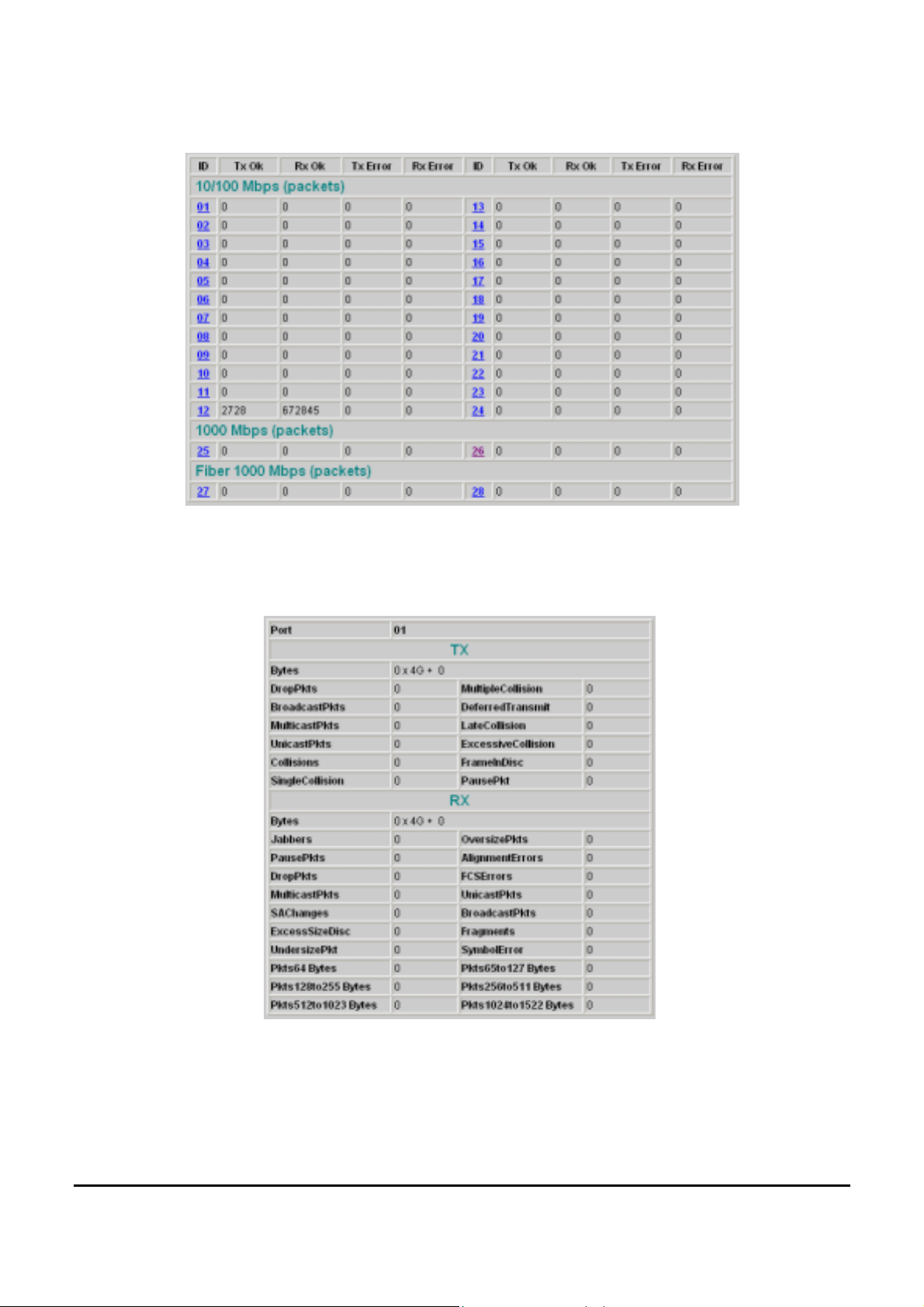
Figure 23. Statistic
For Detail packet information, click on the ID parameter as Figure 24.
Figure 24.
33
Page 40

System Setting
The System Setting includes the System name, Location name, Login
Timeout, IP Address, Subnet Mask and Gateway. Through the Web
Management Utility, you can easily recognize the device by using the
System Name and the Location Name.
The Login Timeout is to s et the idle time-out for security issue, when
there is no action when running the Web Smart Utility and the time is
up, you must re-login to Web Smart Utility before you set the Utility.
Fill up the IP Address, Subnet Mask and Gateway for the device.
Figure 25.
Trap Setti ng
The Trap Setting enables the device to monitor the Trap through the
Web Management Utility, set the Trap IP Address of the manager
where the trap to be sent.
Figure 26. Trap Setting
34
Page 41

System Events: Monitoring the system’s trap.
Device Bootup: a trap when booting up the system.
Illegal Login: a trap when there is using a wrong password login,
and it will record from where the IP to be login.
Fiber Port Events: Monitori ng the Fiber port status.
Link Up/Link Down: a trap when there is linking status happens in
fiber port.
Abnormal* Receive Error: a trap when there are receive data
error in fiber port.
Abnormal* Transmit Error: a trap when there are transmit data
error in fiber port.
Copper Port Events: Monitoring the copper port status.
Abnormal* Receive Error: a trap when there are receive data
error in copper port.
Abnormal* Transmit Error: a trap when there are transmit data
error in copper port.
Abnormal*: 50 error packet count within 10 seconds.
Set Password
Password is the invaluable tool for the manager to secure Web
Management Switch, use this function to change the password.
If you forget the password, press the “Reset” button in the rear panel
of the Switch, the current setting includes VLAN, Port Setting… etc.
will be lost and the Switch will restore to the default setting.
35
Page 42

Figure 27. Set Password
Backup Setting
The backup tools help you to backup the current setting of the Switch.
Once you need to backup the setting, press the “Backup” button to
save the setting.
To restore a current setting file to the device, you must specify the
backup file and press “Restore” button to proceed the setting of the
recorded file.
Figure 28. Back u p Se tting
Note: when restoring a recorded file, the current password will not be erased.
36
Page 43

Reset Setting
The Factory Reset button helps you to reset the device back to the
default setting from the factory. Be aware that the entire configuration
will be reset, the IP address of the device will be set to default setting
192.168.0.1.
Figure 29. Reset Setting
Logout
When press this function, the web configuration will go back to first
Login page.
Figure 30. L ogout
37
Page 44

Page 45

TECHNICAL SPECIFICATIONS
General
Standards IEEE 802.3 10BASE-T Ethernet
IEEE 802.3u 100BASE-TX Fast Ethernet
IEEE 802.3ab 1000BASE-T Gigabit Ethernet
IEEE 802.3x Full Duplex Flow Control
Protocol CSMA/CD
Data Transfer Rate Ethernet: 10Mbps (half duplex), 20Mbps (full-duplex)
Fast Ethernet: 100Mbps (half duplex), 200Mbps (full-duplex)
Gigabit Ethernet: 2000Mbps (full-duplex)
Topology Star
Network Cables 10BASET: 2-pair UTP Cat. 3, 4, 5; up to 100m
100BASE-TX: 2-pair UTP Cat. 5; up to 100m
1000BASE-T: 4-pair UTP Cat. 5; up to 100m
Fiber module: mini-GBIC Fiber module
Number of Ports 24 × 10/100Mbps Auto-MDIX RJ45 ports
2 × 10/100/1000Mbps Auto-MDIX RJ45 ports
2 × mini-GBIC fiber slot
Physical and Environmental
AC inputs 100-240V AC, 50-60 Hz internal universal power supply
Power Consumption 19Watts (Max)
Temperature
Humidity Operating: 10% ~ 90%, Storage: 5% ~ 90%
Dimensions 440 x 200 x 44 mm (W x H x D)
EMI: FCC Class A, CE Mark Class A, VCCI Class A
Safety: cUL(UL60950), CB(IEC60950)
Operating: 0° ~ 40° C, Storage: -10° ~ 70° C
39
Page 46

Performance
Transmits Method: Store-and-forward
Filtering Address
Table:
Packet
Filtering/Forwarding
Rate:
MAC Address
Learning:
Transmits Method: Store-and-forward
RAM Buffer: 768K bytes per devic e
4K entries per device
10Mbps Ethernet: 14,880/pps
100Mbps Fast Ethernet: 148,800/pps
1000Mbps Gigabit Ethernet: 1,488,00 0/pps
Automatic update
40
 Loading...
Loading...