Page 1
Product features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2
Installation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3
Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .7
Cable Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . .8
Troubleshooting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .9
Technical Specifications . . . . . . . . .10
Contact Us . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .11
Compliance Information . . . . . . . . .12
*Typical maximum cable distance. Actual distance is dependent upon the physical
characteristics of th network.
Part Number Port One - Copper
10/100Base-T(x)
Port Two Copper
10/100Base-T(x)
Port Three - Copper
10/100Base-T(x)
CBFTF1010-130 RJ-45 100 M
(328 ft*)
RJ-45 100 M
(328 ft*)
RJ-45 100 M
(328 ft*)
User’s Guide
CBFTF1010-130 10/100 Fault-Tolerant Redundant
Link Protector
• 10/100 Base-T(x) to 10/100 Base-T(x)
Ethernet/Fast Ethernet
• Three RJ-45 Ports
The CBFTF1010-130 is a fault-tolerant redundant link protector that provides redundant
paths for fast Ethernet devices. It has three RJ-45 ports. As a redundant link protector,
typically, the main port connects to a critical 10/100 fast Ethernet device. The primary
port and the backup port connect to two different switch ports or two different ports on
separate switches. When the unit powers up, it checks the primary port for a link signal; if
the signal is present, the main and primary ports connect and the signal from the backup
port is then disabled. Any device connected to the backup port will not detect a signal at
this time. However, if the device does not detect a signal on the primary port, then the
main port and backup port connect.
Optional functionality controlled via DIP switches enable changing the transceiver from
fault-tolerant mode to switch mode.
Page 2

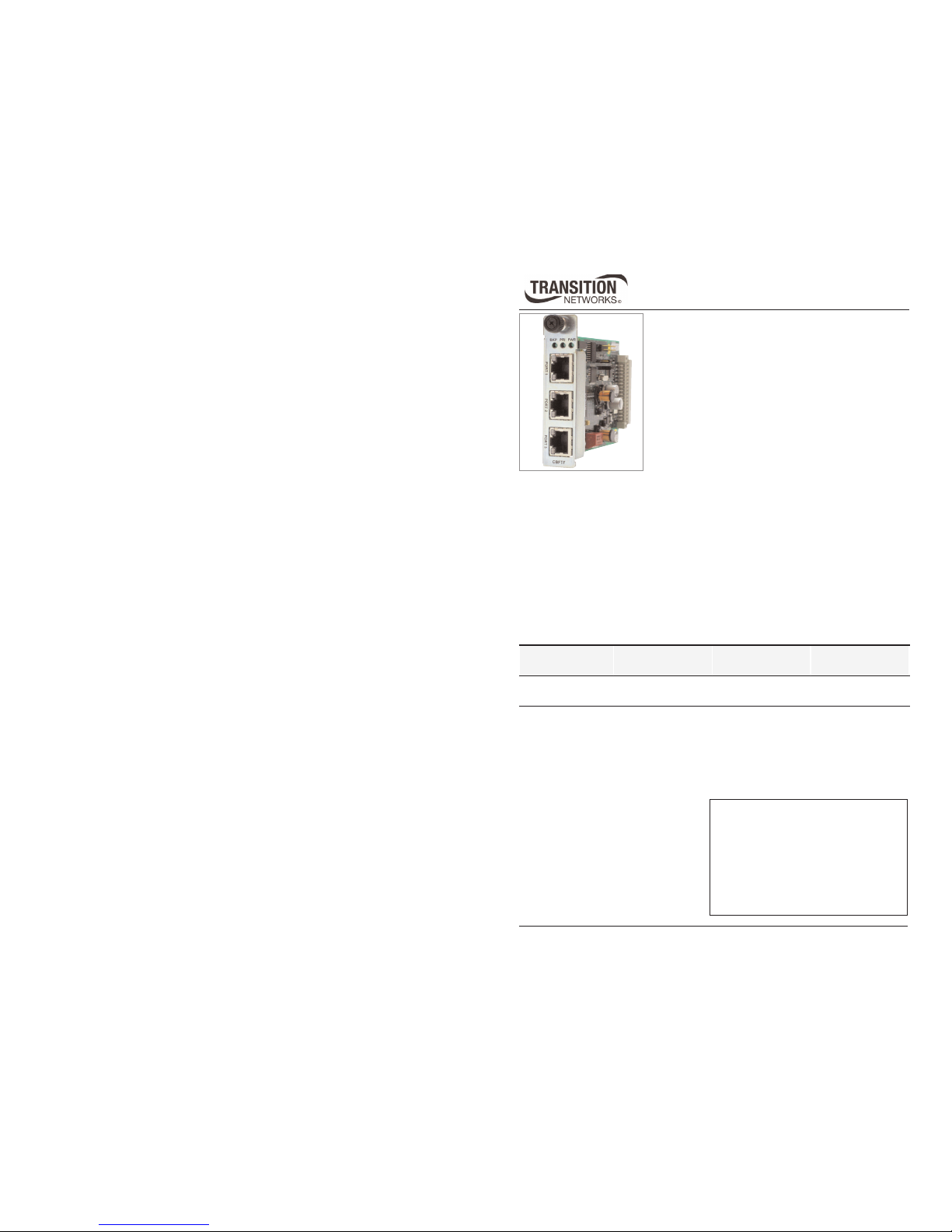
Product Features
Front panel
The CBFTF1010-130 bridging media converter has three RJ-45 10/100Base-TX
ports. See illustration below
Auto-Negotiation (selectable)
The Auto-Negotiation feature automatically configures the bridging media
converter to achieve the best possible mode of operation over a link. The bridging
media converter broadcasts its speed (10 Mbps or 100 Mbps) and duplex
capabilities (full or half) to the other devices and negotiates the best mode of
operation. Auto-Negotiation allows quick and easy installation because the optimal
link is established automatically—no user intervention required.
In a scenario where the media converter is linked to a non-negotiating device,
disable Auto-Negotiation. In this instance, the mode of operation will drop to the
least common denominator between the two devices (e.g., 10 Mbps, half-duplex).
Disabling this feature allows forcing the connection to the desired speed and duplex
mode.
Data transfer rate (selectable)
10Base-T data transfer rate: 10 Mbps Ethernet.
100Base-TX data transfer rate: 100 Mbps Ethernet.
Full-Duplex network (selectable)
In a full-duplex network, maximum cable lengths are determined by the type of
cables used. The 512-Bit Rule does not apply in a full-duplex network.
Half-Duplex network (selectable) (512-Bit Rule)
In a half-duplex network, the maximum cable lengths are determined by the round
trip delay limitations of each fast Ethernet collision domain. (A collision domain is
the longest path between any two terminal devices, e.g., terminal, switch, or router.)
The 512-Bit Rule determines the maximum length of cable permitted by calculating
the round-trip delay in bit times (BT) of a particular collision domain. If the result is
less than or equal to 512 BT, the path is good.
AutoCross™
When the AutoCross feature is activated, it allows either straight-through MDI or
crossover MDI-X cables to be used when connecting to 10Base-T or 100Base-TX
devices. AutoCross determines the characteristics of the connection and
automatically configures the unit to link up, regardless if the cable configuration is
MDI or MDI-X. This feature is ON permanently.
2
Port 1 Port 3
BLK PRI PWR
CBFTF
Port 2
CBFTF1010-130
Technical Support: 1.800.466.4526. Press "2" -- International: 1.408.744.2751
Installation
Note: Wear a grounding strap when removing the circuit board from its anti-static
bag.
Jumpers
The two, 3-pin headers located on the inner surface of the board are used to select
“hardware” and “software” modes, and “redundancy.” See photo below.
• Hardware Mode: DIP switches control the function of the board. You can view
status only via the Web or Focal Point interface.
• Software Mode: Software controls the function of the board. The DIP switches do
not function in software mode.
• Redundancy: automatically switches data transfer responsibilities to the seconday
port if the primary port fails.
3
CBFTF1010-130
techsupport@transition.com -- Click the “Transition Now” link for live Web chat.
Product features -- continued
Redundancy (selectable)
With redundancy enable and the primary port fails, the converter automatically
switches data transfer responsibilities to the backup port without disrupting
network traffic. After the primary port's failure is resolved, the converter
automatically switches data transfer responsibilities back to the primary port.
Parallel detection
Parallel detection is the method used to link when an auto negotiating port detects
a link partner that is in forced mode and therefore cannot participate in the auto
negotiating process. Parallel Detection does not provide the ability to detect half
versus full duplex mode
Per the IEEE method, an auto negotiating port that detects a forced link partner
should drop to the detected speed (10Mbs or 100Mbs) and default to half duplex
The xBFTF-130 allows bypassing the IEEE method by setting the parallel
detection default mode to half or full duplex via DIP switch 3 or through the
duplex setting via WEB and Focal Point interfaces.
(Shunt in Default Position)
Letter "H" = Hardware
J4 (3-Pin Header)
J2 (3-Pin Header)
Letter "S" = Software
Letter "R" = Redundant
Shunt in Redundant Position
(Default)
Page 3
Installation -- continued
DIP switch settings
Four (4) DIP switches, see illustration below.
• SW 1: Auto-Negotiation
• SW 2: Speed
• SW 3: Duplex
• SW 4: Redundancy
4
CBFTF1010-130
Tech Support: 1-800-260-1312 International: 00-1-952-941-7600, 24 hours
1342
Up
1342
Down
1342
Down
1342
Up
When Auto-Negotiation is enabled (switch #1 UP), the bridging media
converter advertises all rate and mode capabilities to the network:
100Mb/s full duplex, 100Mb/s half-duplex, 10Mb/s full duplex, and
10Mb/s half duplex.
Note: Switch “2” does not function when switch “#1” is in the UP position (Auto-
Negotiation enabled).
When auto-negotiation is disabled (switch #1 DOWN), the bridging
media converter does not advertise rate and mode capabilities to the
network.
100Base-TX data transfer rate (switch #2 UP), 100 Mbps fast Ethernet.
10Base-TX data transfer rate (switch #2 DOWN), 10 Mbps fast Ethernet.
Note: See the diagrams below and use a very small flatblade screwdriver or similar
tool to set the DIP switch.
1234
Side View
4 DIP Switches
5
CBFTF1010-130
techsupport@transition.com -- Click the “Transition Now” link for live Web chat.
Fully Inserted and Secured Card
Chassis Slot Screw Hole
Inserting Redundant Link
Protector Card
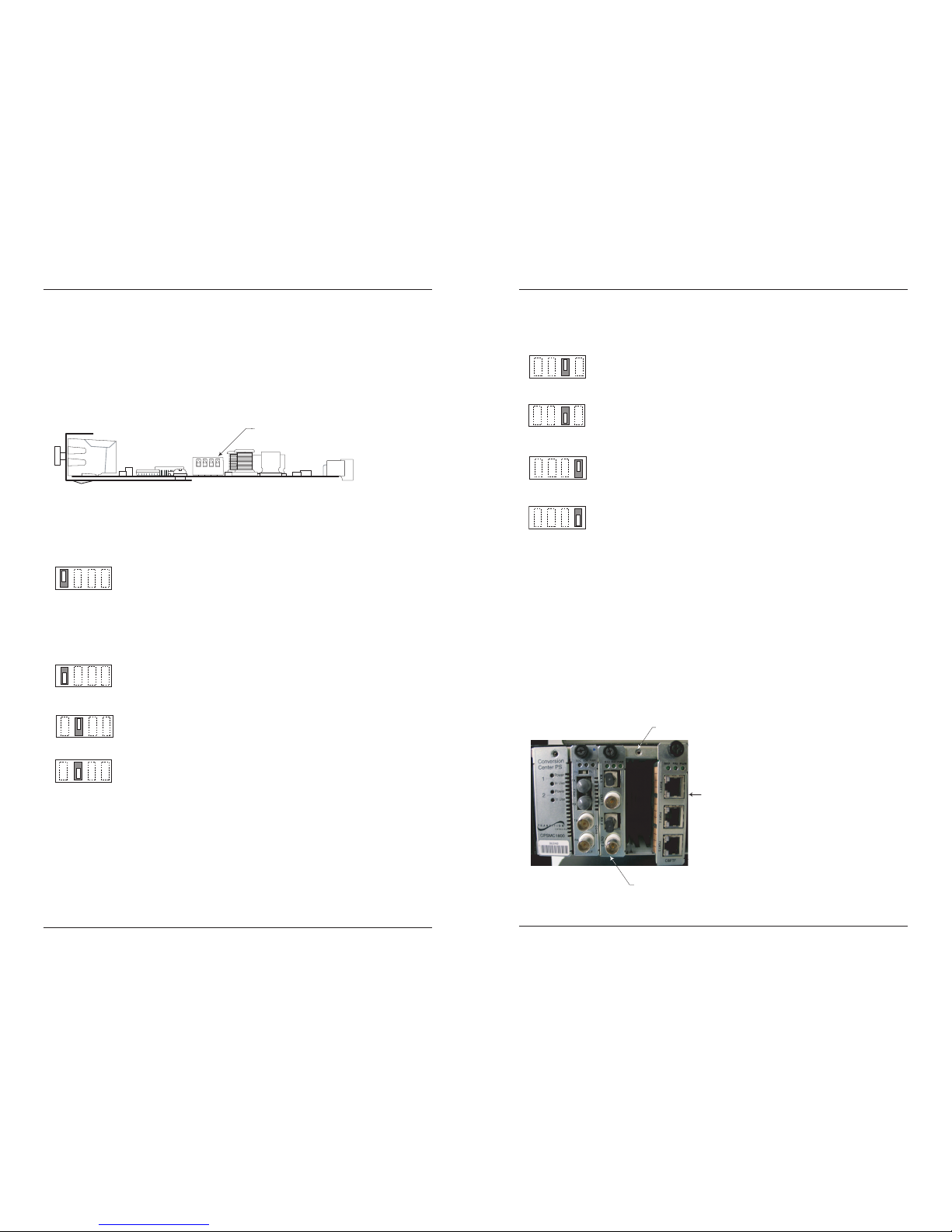
Installing the transceiver in the Point System chassis
To insert the redundant link protector card, do the following:
1. Wearing a ground strap, slide the card into an available slot in the Point System
chassis. See photo below.
2. Push the card all the way into the slot (should snap in).
3. Push in and turn the screw clockwise to secure the card to the chassis frame.
1342
Down
1342
Down
1342
Up
1342
Up
Full duplex (switch #3 UP with auto-negotiation disabled ). Also when
Parallel detection occurs (auto-negotiation enabled only), the device
will be forced to full duplex.
Half duplex (switch #3 DOWN with auto-negotiation disabled ). Also
when Parallel detection occurs (auto-negotiation enabled only), the
device will be forced to half duplex.
Redundancy enabled switch #4 UP (with J2 shunt in the “R” position)
Redundancy enabled switch #4 DOWN (with J2 shunt in the “R”
position). See notes below
Note: With redundancy turned OFF ), the primary and secondary port LEDs will turn
OFF; therefore, returning these ports to normal functionality.
Note: The functionality for each switch setting applies to all ports simultaneously.
Note: With the shunt removed from header J2, the switch is set to redundant mode.
Installation -- continued
Setting DIP switches -- continued
Page 4

6
CBFTF1010-130
Tech Support: 1-800-260-1312 International: 00-1-952-941-7600, 24 hours
Installation -- continued
RJ-45 cable pin assignments
Installing the RJ-45 cable
1 Locate or build an IEEE 802.3 compliant 10Base-T or 100Base-TX cables, with
male RJ-45 connectors installed onto both ends.
2. Connect the RJ-45 connector at one end of the cable to the RJ-45 port on the
bridging media converter as shown below.
3. Connect the RJ-45 connector at the other end of the cable to the RJ-45 port on the
other device (switch, workstation, etc.) as shown below.
Note: The MDI (straight-through) cable or the MDI-X (crossover) cable connection
is configured automatically, according to network conditions.
RJ-45 Port
Transceiver
RJ-45 Port
Switch,Workstati on, etc.
12345678
Pair 1
Pai r 2
RJ-45 10Base-T
7
CBFTF1010-130
techsupport@transition.com -- Click the “Transition Now” link for live Web chat.
Pr imary
Po wer
Link/Act/SPD
(Qty 3)
Duple
x
(Qty 3)
Fr ont View
Port 2
Port 3Port 1
(Secondary)
Backup
Card LEDs
Power (PWR): LED ON indicates chassis is powering the board
Primary: ON when the primary port is in use
Backup (Secondary): ON when the secondary port is in use
TP port LEDs
LINK/ACT/SPD: Green (ON) for 100 Mbps and Link/Act; Flashing when
transmitting data; Orange for 10Mbps
Duplex (DPX): Green (ON) for full duplex; OFF for half duplex
Operation
Status LEDs
There are three (3) LEDs on the converter chassis front panel and two (2) on each
TP port.
Page 5

CBFTF1010-130
Tech Support: 1-800-260-1312 International: 00-1-952-941-7600, 24 hours
8
Cable Specifications
Copper cable (10Base-T/100Base-TX)
Ensure that the correct cable type is installed to support the highest speed and mode of
operation. Though category 3 cable is adequate for a 10Base-T installation, category 5
cable is recommended, since category 3 cable DOES NOT support 100Base-TX.
Category 3: (minimum requirement for 10 Mbps operation)
Gauge: 24 to 22 AWG
Attenuation: 11.5 dB/100m @ 5-10 MHz
Maximum cable distance: 100 meters
Category 5: (minimum requirement for 100 Mbps operation)
Gauge: 24 to 22 AWG
Attenuation: 22.0 dB/100m @ 100 MHz
Maximum cable distance: 100 meters
• Straight-through (MDI) or crossover (MDI-X) cable may be used.
• Shielded (STP) or unshielded (UTP) twisted-pair cable may be used.
• Pins 1/2 and 3/6 are the two active pairs in an Ethernet network.
• Use only dedicated wire pairs for the active pins:
(e.g., blue/white & white/blue, orange/white & white/orange, etc.)
• Do not use flat or silver satin wire.
10Base-T and the Ethernet collision domain:
• Refer to the 5-Segment Rule before installing half-duplex 10Base-T
cable.
• Installing full-duplex twisted-pair cable avoids collision domain
considerations—maximum distance 100 meters.
100Base-TX and the Fast Ethernet collision domain:
• Refer to the 512-Bit Rule before installing half-duplex 100Base-TX cable.
• Installing full-duplex twisted-pair cable avoids collision domain
considerations—maximum distance 100 meters.
Note: A Fast Ethernet collision domain can have only “1” Class “I” repeater or “2”
Class “II” repeaters.
Crossover Cable
1
2
3
6
Straight-Through Cable
Twisted Pair #1
Twisted Pair #1
Twisted Pair #2
Twisted Pair #2
1
2
3
6
1
2
3
6
1
2
3
6
9
CBFTF1010-130
techsupport@transition.com -- Click the “Transition Now” link for live Web chat.
Troubleshooting
If the CBFTF1010-130 fails or initially does not power up and function properly, ask the
following questions and take the suggested corrective actions.
1. Is the power LED on the bridging media converter ON?
NO:
a. Is the chassis plugged into AC power?
b. Is the card fully inserted into the chassis?
c. Contact Technical Support: 1.800.466.4526, then press "2."
YES: Go to step 2.
2. Is there an active (connected to an output source) RJ-45 cable inserted into the
bridging media converter main port?
NO:
a. Insert an RJ-45 cable into the bridging media converter main port.
b. Insert the other cable end into an active device.
YES: Go to step 3.
3. Is the link/active LED on the main port lit (ON)?
NO:
a. Check that the RJ-45 cable is properly inserted into the bridging media
converter main port.
b. Check that the other cable end is inserted into an active device.
c. Check the cable for damage.
d. Contact Technical Support .
YES: Go to step 4.
4. Is there an RJ-45 cable inserted into the primary port on the bridging media
converter?
NO:
a. Insert the RJ-45 cable into the bridging media converter primary port.
b. Insert the other end of the cable into the input of an active device.
YES: Go to step 5.
5. Is the primary LED on the chassis lit (ON)?
NO:
a. Check that the RJ-45 cable is properly inserted into the primary port.
b. Check that the other end of the cable is properly inserted into an active
device.
c. Check the cable for damage.
d. Contact Technical Support.
YES: Go to step 6.
Page 6

10
CBFTF1010-130
Technical Support: 1.800.466.4526. Press "2" -- International: 1.408.744.2751
Troubleshooting -- continued
6. Is there an RJ-45 cable inserted into the secondary port on the bridging media
converter?
NO:
a. Insert the RJ-45 cable into the bridging media converter secondary port.
b. Insert the other end of the cable into the input of the an active device.
YES: Go to step 7.
7. Is the secondary LED on the board lit (ON)?
NO:
a. Check that the RJ-45 cable is properly inserted into the secondary port.
b. Check that the other end of the cable is properly inserted into an active
device.
c. Check the cable for damage.
c. Contact technical support.
8. YES: Contact technical support: 1.800.466.4526, then press "2."
Technical specifications
Standards: IEEE 802.3™ 2000
Regulatory: Emissions: EN55022 Class A; Immunity: EN55024
Safety compliance: CE Mark
Data Rate: 10 Mbps, 100 Mbps
Dimensions: 0.86”W x 5.0”D x 3.4”H
(22 mm x 127 mm x 86 mm)
Shipping weight: 1 lb. approximately
Power consumption: 2.4 watts
Power supply: Powered by chassis
Operating temp: 0°C to 50°C (32°F to 140°F )
Switching time: <189 ms (primary to secondary)
Storage temp: -20°C to +85°C (-4°F to 185°F)
Humidity: 5% to 95%, non-condensing
Altitude: 0 – 10,000 feet
Warranty: Lifetime
11
CBFTF1010-130
techsupport@transition.com -- Click the “Transition Now” link for live Web chat.
Contact Us
Technical support
Technical support is available at techsupport@transition.com
• US and Canada: 1-800-260-1312 (24 hours)
• International: 00-1-952-941-7600 (24 hours)
Transition now
Chat live via the Web with Transition Networks Technical Support. Log onto
www.transition.com and click the Transition Now link.
Web-based seminar
Transition networks provides seminars via live, web-based training. Log onto
www.transition.com and click the Learning Center link.
Email
Ask a question anytime by sending an email to our technical support staff:
techsupport@transition.com
Address
Transition Networks
6475 City West Parkway
Minneapolis, MN 55344, U.S.A.
Telephone: 952-941-7600,
Toll free: 800-526-9267
Fax: 952-941-2322
Declaration of Conformity
Name of Mfg: Transition Networks, 6475 City West Parkway,
Minneapolis, MN 55344 U.S.A.
Model: CBFTF1010-130 Bridging Media Converter
Part Number: CBFTF1010-130
Regulation: EMC Directive 89/336/EEC
Purpose: To declare that the CBFTF1010-130 to which this declaration
refers is in conformity with the following standards:
CISPR 22:1997+A1:2000; EN 55022:1998+A1:2000 Class A; FCC Part 15 Subpart B;
21CFR subpart J
I, the undersigned, hereby declare that the equipment specified above conforms to the above Directive(s)
and Standard(s).
October, 2006
Stephen Anderson, Vice-President of Engineering Date
Page 7

12
CBFTF1010-130
Trademark notice
All registered trademarks and trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
Copyright restrictions
© 2004-2005 Transition Networks. All rights reserved. No part of this work may be reproduced or
used in any form or by any means—graphic, electronic or mechanical—without written permission
from Transition Networks.
Printed in the U.S.A. 33350.A
Compliance Information
CSA Certified
CISPR22/EN55022 Class A + EN55024
CE Mark
FCC regulations
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a class A digital device,
pursuant to part 15 of the FCC rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection
against harmful interference when the equipment is operated in a commercial environment. This
equipment generates, uses, and can radiate radio frequency energy and, if not installed and used in
accordance with the instruction manual, may cause harmful interference to radio communications.
Operation of this equipment in a residential area is likely to cause harmful interference, in which
case the user will be required to correct the interference at the user’s own expense.
Canadian Regulations
This digital apparatus does not exceed the Class A limits for radio noise for digital apparatus set out
on the radio interference regulations of the Canadian Department of Communications.
Le présent appareil numérique n'émet pas de bruits radioélectriques dépassant les limites
applicables aux appareils numériques de la class A prescrites dans le Règlement sur le brouillage
radioélectrique édicté par le ministère des Communications du Canada.
European Regulations
WARNING: This is a Class A product. In a domestic environment this product may cause radio
interference in which case the user may be required to take adequate measures.
Achtung ! Dieses ist ein Gerät der Funkstörgrenzwertklasse A. In Wohnbereichen können bei
Betrieb dieses Gerätes Rundfunkstörungen auftreten. In diesem Fäll ist der Benutzer für
Gegenmaßnahmen verantwortlich.
Attention ! Ceci est un produit de Classe A. Dans un environment domestique, ce produit risque de
créer des interférences radioélectriques, il appartiendra alors à l'utilsateur de prende les measures
spécifiques appropriées.
In accordance with European Union Directive 2002/96/EC of the European Parliament
and of the Council of 27 January 2003, Transition Networks will accept post usage
returns of this product for proper disposal. The contact information for this activity can
be found in the 'Contact Us' portion of this document.
CAUTION: RJ connectors are NOT INTENDED FOR CONNECTION TO THE
PUBLIC TELEPHONE NETWORK. Failure to observe this caution could result
in damage to the public telephone network.
Der Anschluss dieses Gerätes an ein öffentlickes Telekommunikationsnetz in den EG-Mitgliedstaaten
verstösst gegen die jeweligen einzelstaatlichen Gesetze zur Anwendung der Richtlinie 91/263/EWG zur
Angleichung der Rechtsvorschriften der Mitgliedstaaten über Telekommunikationsendeinrichtungen
einschliesslich der gegenseitigen Anerkennung ihrer Konformität.
 Loading...
Loading...