Page 1
Installation
Operation
Maintenance
Packaged Heat Pump
3 Through 10 Ton
Model Numbers
WSC036A - WSC120A
WSC036E - WSC060E
February 2009
RT-SVX23D-EN
Page 2
Warnings, Cautions and Notices
Important
Environmental Concerns!
Scientific research has shown that certain man-made chemicals can affect the earth's naturally
occurring stratospheric ozone layer when released to the atmosphere. In particular, several of the
identified chemicals that may affect the ozone layer are refrigerants that contain Chlorine, Fluorine
and Carbon (CFCs) and those containing Hydrogen, Chlorine, Fluorine and Carbon (HCFCs). Not all
refrigerants containing these compounds have the same potential impact to the environment.
Trane advocates the responsible handling of all refrigerants-including industry replacements for
CFCs such as HCFCs and HFCs.
Responsible Refrigerant Practices!
Trane believes that responsible refrigerant practices are important to the environment, our
customers, and the air conditioning industry. All technicians who handle refrigerants must be
certified. The Federal Clean Air Act (Section 608) sets forth the requirements for handling,
reclaiming, recovering and recycling of certain refrigerants and the equipment that is used in these
service procedures. In addition, some states or municipalities may have additional requirements
that must also be adhered to for responsible management of refrigerants. Know the applicable
laws and follow them.
ATTENTION: Warnings, Cautions and Notices appear at appropriate sections throughout
this literature. Read these carefully. Your personal safety and the proper operation of this
machine depend upon the strict observance of these precautions.
WAR NING : Indicates a potentially hazardous situation which, if not avoided, could
result in death or serious injury.
CAUTION: Indicates a potentially hazardous situation which, if not avoided, could
result in minor or moderate injury. It may also be used to alert against unsafe practices.
NOTICE: Indicates a situation that could result in equipment or property-damage only
accidents.
Overview of Manual
Note: One copy of this document ships inside the control panel of each unit and is customer
property. It must be retained by the unit’s maintenance personnel.
This booklet describes proper installation, operation, and maintenance procedures for air cooled
systems. By carefully reviewing the information within this manual and following the instructions,
the risk of improper operation and/or component damage will be minimized.
It is important that periodic maintenance be performed to help assure trouble free operation. A
maintenance schedule is provided at the end of this manual. Should equipment failure occur,
contact a qualified service organization with qualified, experienced HVAC technicians to properly
diagnose and repair this equipment.
Model Number Description
All products are identified by a multiple-character model number that precisely identifies a
particular type of unit. An explanation of the alphanumeric identification code is provided below.
Its use will enable the owner/operator, installing contractors, and service engineers to define the
operation, specific components, and other options for any specific unit.
© 2009 Trane. All rights reserved RT-SVX23D-EN
Page 3

Warnings, Cautions and Notices
When ordering replacement parts or requesting service, be sure to refer to the specific model
number and serial number printed on the unit nameplate.
WARNING
Contains Refrigerant under Pressure!
System contains oil and refrigerant under high pressure. Recover refrigerant to relieve pressure
before opening the system. See unit nameplate for refrigerant type. Do not use non-approved
refrigerants, refrigerant substitutes, or refrigerant additives.
Failure to follow proper procedures or the use of non-approved refrigerants, refrigerant
substitutes, or refrigerant additives could result in death or serious injury or equipment damage.
WARNING
R-410A Refrigerant under Higher Pressure than R-22!
The units (WSC036E-WSC060E) described in this manual use R-410A refrigerant which operates
at higher pressures than R-22 refrigerant. Use ONLY R-410A rated service equipment or
components with this unit. For specific handling concerns with R-410A, please contact your
local Trane representative.
Failure to use R-410A rated service equipment or components could result in equipment
exploding under R-410A high pressures which could result in death, serious injury, or equipment
damage.
WARNING
Hazardous Voltage w/Capacitors!
Disconnect all electric power, including remote disconnects and discharge all motor start/run
capacitors before servicing. Follow proper lockout/tagout procedures to ensure the power
cannot be inadvertently energized. Verify with an appropriate voltmeter that all capacitors have
discharged. Failure to disconnect power and discharge capacitors before servicing could result in
death or serious injury.
WARNING
Harmful Ultraviolet (UV) Lights!
Do not field install ultraviolet lights in the manufacturer air handling equipment for the intended
purpose of improving indoor air quality. High intensity C-band ultraviolet light is known to
severely damage polymer (plastic) materials and poses a personal safety risk to anyone exposed
to the light without proper personal protective equipment (can cause damage to eyes and skin).
Polymer materials commonly found in HVAC equipment that may be susceptible include
insulation on electrical wiring, fan belts, thermal insulation, various fasteners and bushings.
Degradation of these materials could result in serious damage to the equipment. Failure to
follow this recommendation could result in death or serious injury and equipment damage.
The manufacturer accepts no responsibility for the performance or operation of our air handling
equipment in which ultraviolet devices were installed outside of the manufacturer’s factory.
NOTICE
Roof Damage!
System contains oil and refrigerant under high pressure. Roofs should be protected from
exposure to oils and refrigerant in the system. If rooftop is not protected damage to the roof may
occur.
RT-SVX23D-EN 3
Page 4

Table of Contents
Warnings, Cautions and Notices . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
Overview of Manual . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
Model Number Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
General Information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
Unit Nameplate . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
Compressor Nameplate . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
Unit Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
System Input Devices & Functions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
Pre-Installation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
Unit Clearances . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Installation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
General Unit Requirements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
Table 1. Typical Unit Weights & Point Loading Data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Table 2. Typical Unit Weights & Point Loading Data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
Table 3. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
Table 4. AC Conductors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
Table 5. DC Conductors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
Pre-Start . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
Table 6. Temperature versus resistance
(temperature vs. resistance is negative)
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
Start-Up . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
Table 7. Service test guide for component operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
Table 8. Belt tension measurement and deflection ranges . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
Maintenance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 48
Table 9. Sample maintenance log . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 51
Trouble Shooting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 52
Table 10. Cooling (CSP) and heating setpoint (HSP) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 55
Wiring Diagrams . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 58
Limited Warranty . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 59
4 RT-SVX23D-EN
Page 5

Model Number Descriptions
WSC036A3RBA** C000A10001A1
123456789101112,13141516171819202122232425
DIGIT 1 - Unit Function
W = Packaged Heat Pump
DIGIT 2 - Efficiency
S = Standard Efficiency
DIGIT 3 - Airflow
C = Convertible
DIGITS 4,5,6 - Nominal Gross
Cooling Capacity (MBh)
036 = 3 Ton
048 = 4 Ton
060 = 5 Ton
072 = 6 Ton
090 = 7½ Ton
120 = 10 Ton
DIGIT 7 - Major Design Sequence
A= First
E=R410A
DIGIT 8 - Unit Voltage
1 = 208-230/60/1
3 = 208-230/60/3
4 = 460/60/3
W = 575/60/3
DIGIT 9 - Unit Controls
R = ReliaTel™Microprocessor
DIGIT 10 - Electric Heater
0 = No Electric Heater
A = 5 kw (1 phase)
B = 6 kw (3 phase)
D = 10 kw (1 phase)
E = 12 kw (3 phase)
F = 14 kw (1 phase)
G = 18 kw (1 and 3 phase)
J = 23 kw (3 phase)
K = 27 kw (3 phase)
N = 36 kw (3 phase)
P = 54 kw (3 phase)
DIGIT 11 - Minor Design
Sequence
A = First Sequence
DIGITS 12,13 - Service Sequence
Factory Assigned
DIGIT 14 - Fresh Air Selection
0= No Fresh Air
A = Manual Outside Air Damper
0-50%
B = Motorized Outside Air Damper 0-
50%
C = Economizer, Dry Bulb 0-100%
without Barometric Relief
D = Economizer, Dry Bulb 0-100%
withBarometric Relief
E = Economizer, Reference Enthalpy
0-100% without Barometric Relief
F = Economizer, Reference Enthalpy
0-100% with Barometric Relief
G = Economizer, Comparative
Enthalpy 0-100% without
Barometric Relief
H = Economizer, Comparative
Enthalpy 0-100% with Barometric
Relief
DIGIT 15 - Supply Fan/Drive Type/
Motor
0= Standard Drive
1 = Oversized Motor
2 = Optional Belt Drive Motor
DIGIT 16 - Hinged Service
Access/Filters
0 = Standard Panels/Standard Filters
A = Hinged Access Panels/Standard
Filters
B = Standard Panels with 2 inch
MERV 7 pleated filter
C = Hinged Access Panels with 2 inch
MERV 7 pleated filter
D = Standard Panels with 2 inch
MERV 13 pleated filter
E = Hinged Access Panels with 2 inch
MERV 13 pleated filter
DIGIT 17 - Condenser Coil
Protection
0 = Standard Coil
1 = Standard Coil with Hail Guard
2 = Epoxy Coated Condenser Coil
3 = Epoxy Coated Condenser Coil
with Hail Guard
4 = *CompleteCoat Condenser Coil
5 = *CompleteCoat Condenser Coil
and Hail Guard
DIGIT 18 - Through the Base
Provisions
0 = No Through the Base Provisions
A = Through the Base Electric
DIGIT 19 - Disconnect/Circuit
Breaker (3 phase only)
0 = Without Disconnect Switch/Circuit
Breaker
1 = Unit Mounted Non-Fused
Disconnect Switch
2 = Unit Mounted Circuit Breaker
DIGIT 20 - Convenience Outlet
0 = No Convenience Outlet
A = Unpowered Convenience Outlet
B = Powered Convenience Outlet
(3 phase only)
DIGIT 21 - Communications
Options
0 = No Communications Interface
1 = Trane Communications Interface
2 = LonTalk® Communications
Interface
DIGIT 22 - Refrigeration System
Option
0 = Standard Refrigeration System
DIGIT 23 - Refrigeration Controls
0 = No Refrigeration Control
1 = High Pressure Control
2= Frostat
3 = Crankcase Heater
4 = High Pressure Control and Frostat
5 = High Pressure Control and
Crankcase Heater
6 = Frostat and Crankcase Heater
7 = High Pressure Control, Frostat
and Crankcase Heater
DIGIT 24 - Smoke Detector
0= No Smoke Detector
A = Return Air Smoke Detector
B = Supply Air Smoke Detector
C = Supply and Return Air Smoke
Detectors
DIGIT 25 - Monitoring Controls
0 = No Monitoring Control
1 = Clogged Filter Switch
2 = Fan Failure Switch
3 = Discharge Air Sensing Tube
4 = Clogged Filter Switch and Fan Fail
Switch
5 = Clogged Filter Switch and
Discharge
Air Sensing Tube
6 = Fan Fail Switch and Discharge Air
Sensing Tube
7 = Clogged Filter and Fan Fail
Switches and Discharge Air
Sensing Tube
RT-SVX23D-EN 5
Page 6

General Information
Unit Nameplate
A Mylar unit nameplate is located on the unit’s corner support next to the filter access panel. It
includes the unit model number, serial number, electrical characteristics, refrigerant charge, as well
as other pertinent unit data.
Compressor Nameplate
The nameplate for the compressors are located on the side of the compressor.
Unit Description
Before shipment, each unit is leak tested, dehydrated, charged with refrigerant and compressor oil,
and run tested for proper control operation.
The condenser coils are aluminum fin, mechanically bonded to copper tubing.
Direct-drive, vertical discharge condenser fans are provided with built-in thermal overload
protection.
The ReliaTel™ Control Module is a microelectronic control system that is referred to as
“Refrigeration Module” (RTRM). The acronym RTRM is used extensively throughout this
document when referring to the control system network.
These modules through Proportional/Integral control algorithms perform specific unit functions
that governs unit operation in response to; zone temperature, supply air temperature, and/or
humidity conditions depending on the application. The stages of capacity control for these units
is achieved by starting and stopping the compressors.
The RTRM is mounted in the control panel and is factory wired to the respective internal
components. The RTRM receives and interpret information from other unit modules, sensors,
remote panels, and customer binary contacts to satisfy the applicable request for cooling.
Economizer Control Actuator (Optional) ReliaTel™ Control
The ECA monitors the mixed air temperature, return air temperature, minimum position setpoint
(local or remote), power exhaust setpoint, CO2 setpoint, CO2, and ambient dry bulb/enthalpy
sensor or comparative humidity (return air humidity against ambient humidity) sensors, if
selected, to control dampers to an accuracy of +/- 5% of stroke. The actuator is spring returned to
the closed position any time that power is lost to the unit. It is capable of delivering up to 25 inch
pounds of torque and is powered by 24 VAC.
RTCI -- ReliaTel™ Trane Communication Interface (Optional)
This module is used when the application calls for an ICSTM building management type control
system. It allows the control and monitoring of the system through an ICS panel. The module can
be ordered from the factory or ordered as a kit to be field installed. Follow the installation
instruction that ships with each kit when field installation is necessary.
RLCI - ReliaTel™ LonTalk Communication Interface (Optional)
This module is used when the application calls for an ICSTM building management type control
system that is LonTalk. It allows the control and monitoring of the system through an ICS panel.
The module can be ordered from the factory or ordered as a kit to be field installed. Follow the
installation instruction that ships with each kit when field installation is necessary.
6 RT-SVX23D-EN
Page 7

RTOM – ReliaTel™ Options Module (Optional)
The RTOM monitors the supply fan proving, clogged filter, supply air temperature, exhaust fan
setpoint, supply air tempering, Frostat™ and smoke detector. Refer to system input devices and
functions for operation.
System Input Devices & Functions
The RTRM must have a zone sensor or thermostat input in order to operate the rooftop unit. The
flexibility of having several mode capabilities depends upon the type of zone sensor thermostat
selected to interface with the RTRM.
The descriptions of the following basic Input Devices used within the RTRM network are to acquaint
the operator with their function as they interface with the various modules. Refer to the unit’s
electrical schematic for the specific module connections.
The following controls are available from the factory for field installation.
Supply Fan Failure Input (Optional)
The Fan Failure Switch can be connected to sense indoor fan operation:
FFS (Fan Failure Switch) If air flow through the unit is not proven by the differential pressure switch
connected to the RTRM (factory set point 0.07 “ w.c.) within 40 seconds nominally, the RTRM will
shut off all mechanical operations, lock the system out, send a diagnostic to ICS, and the SERVICE
output will flash. The system will remain locked out until a reset is initiated either manually or
through ICS.
General Information
Clogged Filter Switch (Optional)
The unit mounted clogged filter switch monitors the pressure differential across the return air
filters. It is mounted in the filter section and is connected to the RTOM. A diagnostic SERVICE signal
is sent to the remote panel if the pressure differential across the filters is at least 0.5" w.c. The
contacts will automatically open when the pressure differential across the filters decreases to
approximately 0.4" w.c. The clogged filter output is energized when the supply fan is operating and
the clogged filter switch has been closed for at least 2 minutes. The system will continue to operate
regardless of the status of the filter switch.
Note: On units equiped with factory installed MERV 13 filters, a clogged filter switch with different
pressure settings will be installed. This switch will close when the differential pressure is
approximately 0.8' w.c. and open when the differential falls to 0.7" w.c.
Compressor Disable (CPR1/2)
This input incorporates the low pressure control (LPC) of each refrigeration circuit and can be
activated by opening a field supplied contact installed on the LTB.
If this circuit is open before the compressor is started, the compressor will not be allowed to
operate. Anytime this circuit is opened for 1 continuous second during compressor operation, the
compressor for that circuit is immediately turned “Off”. The compressor will not be allowed to
restart for a minimum of 3 minutes should the contacts close.
If four consecutive open conditions occur during the first three minutes of operation, the
compressor for that circuit will be locked out, a diagnostic communicated to the remote panel (if
installed), and a manual reset will be required to restart the compressor.
Low Pressure Control
When the LPC is opened for 1 continuous second, the compressor for that circuit is turned off
immediately. The compressor will not be allowed to restart for a minimum of 3 minutes.
If four consecutive open conditions occur during an active call for cooling, the compressor will be
locked out, a diganostic communicated to ICS™, if applicable, and a manual reset required to
RT-SVX23D-EN 7
Page 8

General Information
restart tyhe compressor. On dual compressor units only the affected compressor circuit is locked
out.
High Pressure Control (Optional — Standard on R-410A models)
The high pressure controls are wired in series between the compressor outputs on the RTRM and
the compressor contactor coils. If the high pressure control switch opens, the RTRM senses a lack
of current while calling for cooling and locks the compressor out.
If four consecutive open conditions occur during an active call for cooling, the compressor will be
locked out, a diganostic communicated to ICS™, if applicable, and a manual reset required to
restart tyhe compressor. On dual compressor units only the affected compressor circuit is locked
out.
Power Exhaust Control (Optional)
The power exhaust fan is started whenever the position of the economizer dampers meets or
exceed the power exhaust setpoint when the indoor fan is on.
The setpoint panel is located in the return air section and is factory set at 25%.
Lead/Lag Control (Dual Circuit Only)
Lead/Lag is a selectable input located on the RTRM. The RTRM is configured from the factory with
the Lead/Lag control disabled. To activate the Lead/Lag function, simply cut the wire connected to
J3-8 at the RTRM. When it is activated, each time the designated lead compressor is shut off due
to the load being satisfied, the lead compressor or refrigeration circuit switches. When the RTRM
is powered up, i.e. after a power failure, the control will default to the number one circuit
compressor.
Zone Sensor Module (ZSM) (BAYSENS107*)
This electronic sensor features three system switch settings ( Heat, Cool, and Off) and two fan
settings (On and Auto). It is a manual changeover control with single setpoint. (Cooling Setpoint
Only)
Zone Sensor Module (ZSM) (BAYSENS109*)
This electronic sensor features four system switch settings (Heat, Cool, Auto, and Off) and two fan
settings (On and Auto). It is a manual or auto changeover control with dual setpoint capability. It
can be used with a remote zone temperature sensor BAYSENS077*.
Programmable Zone Sensor - BAYSENS119*
This 7 day programmable sensor features 2, 3 or 4 periods for Occupied or Unoccupied
programming per day. If the power is interrupted, the program is retained in permanent memory.
If power is off for an extended period of time, only the clock and day may have to be reset.
The Zone Sensor allows selection of 2, 3 or 4 system modes (Heat, Cool, Auto, and Off), two fan
modes (On and Auto). It has dual temperature selection with programmable start time capability.
The occupied cooling set point ranges between 45 and 98 degrees Fahrenheit. The heating set point
ranges between 43 and 96 degrees Fahrenheit.
A liquid crystal display (LCD) displays zone temperature, temperature set points, day of the week,
time, and operational mode symbols.
The Option Menu is used to enable or disable applicable functions, i.e.; Morning Warm-up,
Economizer minimum position override during unoccupied status, Fahrenheit or Centigrade,
Supply air tempering, Remote zone temperature sensor, 12/24 hour time display, Smart fan, and
Computed recovery.
During an occupied period, an auxiliary relay rated for 1.25 amps @ 30 volts AC with one set of
single pole double throw contacts is activated. Electronic Timeclock (BAYCLCK001A).
8 RT-SVX23D-EN
Page 9

General Information
Status Inputs (4 Wires Optional). The ZSM can be wired to receive four (4) operating status signals
from the RTRM (HEAT, COOL, SYSTEM “ON”, SER-VICE). Four (4) wires from the RTRM should be
connected to the appropriate terminals (7, 8, 9 & 10) on the ZSM.
Remote Zone Sensor (BAYSENS073*)
This electronic sensor features remote zone sensing and timed override with override cancellation.
It is used with a Trane Integrated ComfortTM building management system.
Remote Zone Sensor (BAYSENS074*)
This electronic sensor features single setpoint capability and timed override with override
cancellation. It is used with a Trane Integrated ComfortTM building management system.
Remote Zone Sensor (BAYSENS016A)
This bullet type temperature sensor can be used for; outside air (ambient) sensing, return air
temperature sensing, supply air temperature sensing, remote temperature sensing (uncovered.
Wiring procedures vary according to the particular application and equipment involved. Refer to
the unit’s wiring diagrams for proper connections.
Remote Zone Sensor (BAYSENS077*)
This electronic sensor can be used with BAYSENS106*, 108*, 110*, 119* Remote Panels. When this
sensor is wired to a BAYSENS119* Remote Panel, wiring must be 18 AWG Shielded Twisted Pair
(Belden 8760 or equivalent). Refer to the specific Remote Panel for wiring details.
High Temperature Sensor (BAYFRST001A)
This sensor connects to the RTRM Emergency Stop Input located on the LTB and provides high limit
“shutdown” of the unit and requires a manual reset. The sensor is used to detect high temperatures
due to fire in the air conditioning or ventilation ducts. The sensor is designed to mount directly to
the sheet metal duct. Each kit contains two sensors. The return air duct sensor (X1310004001) is
set to open at 135°F. The supply air duct sensor (X1310004002) is set to open at 240°F. The control
can be reset after the temperature has been lowered approximately 25°F below the cutout setpoint.
Evaporator Frost Control
This input incorporates the Frostat™ control (FOS) located on the indoor coil and can be activated
by closing a field supplied contact installed in parallel with the FOS.
If this circuit is open before the compressor is started, the compressor will not be allowed to
operate. Anytime this circuit is opened for 1 continuous second during compressor operation, the
compressor for that circuit is immediately turned “Off”. The compressor will not be allowed to
restart for a minimum of 3 minutes should the FOS close.
Smoke Detector Sensor (Optional)
This sensor is only applicable on units equipped with a RTOM. It provides high limit “shutdown”
of the unit and requires a manual reset. The sensor is used to detect smoke due to fire in the air
conditioning or ventilation ducts.
Note: Important! The supply and return air smoke detectors are designed to shut off the unit if
smoke is sensed in the supply air stream or return air stream. This function is performed
by sampling the airflow entering the unit at the return air opening. Follow the instructions
provided below to assure that the airflow through the unit is sufficient for adequate
sampling. Failure to follow these instructions will prevent the smoke detectors from
performing it's design function.
Note: Important! Airflow through the unit is affected by the amount of dirt and debris
accumulated on the indoor coil and filters. To insure that airflow through the unit is
adequate for proper sampling by the return air smoke detector, complete adherence to the
maintenance procedures, including recommended intervals between filter changes, and
coil cleaning is required.
RT-SVX23D-EN 9
Page 10

General Information
Note: Important! Periodic checks and maintenance procedures must be performed on the smoke
In order for the supply air smoke detector or return air smoke detector to properly sense smoke
in the supply air stream or return air stream, the air velocity entering the smoke detector unit must
be between 500 and 4000 feet per minute. Equipment covered in this manual will develop an
airflow velocity that falls within these limits over the entire airflow range specified in the evaporator
fan performance tables.
There are certain models, however, if operated at low airflow, will not develop an airflow velocity
that falls within the required 500 to 4000 feet per minute range. For these models, the design airflow
shall be greater than or equal to 1000 feet per minute MINIMUM.
Phase Monitor
This sensor monitors voltage between the 3 conductors of the 3 phase power supply. Two LED
lights are provided. The green light indicates that a balanced 3 phase supply circuit is properly
connected. The red light indicates that unit operation has been prevented. There are two conditions
that will prevent unit operation.The power supply circuit is not balanced with the proper phase
sequence of L1,L2,L3 for the 3 conductors of a 3 phase circuit. The line to line voltage is not between
180 volts and 633 volts.
detector to insure that it will function properly. For detailed instructions concerning these
checks and procedures, refer to the appropriate section(s) of the smoke detector Installation
and Maintenance Instructions provided with the literature package for this unit.
10 RT-SVX23D-EN
Page 11

Pre-Installation
Unit Inspection
As soon as the unit arrives at the job site
• Verify that the nameplate data matches the data on the sales order and bill of lading (including
electrical data).
• Verify that the power supply complies with the unit nameplate specifications.
• Visually inspect the exterior of the unit, including the roof, for signs of shipping damage.
WARNING
Fiberglass Wool !
Product contains fiberglass wool. Disturbing the insulation in this product during installation,
maintenance or repair will expose you to airborne particles of glass wool fibers and ceramic
fibers known to the state of California to cause cancer through inhalation. Glass wool fibers may
also cause respiratory, skin or eye irritation.
Precautionary Measures
Avoid breathing fiberglass dust.
Use a NIOSH approved dust/mist respirator.
Avoid contact with the skin or eyes. Wear long-sleeved, loose-fitting clothing, gloves, and eye
protection.
Storage
Wash clothes separately from other clothing: rinse washer thoroughly.
Operations such as sawing, blowing, tear-out, and spraying may generate fiber concentrations
requiring additional respiratory protection. Use the appropriate NIOSH approved respiration in
these situations.
First Aid Measures
Eye Contact - Flush eyes with water to remove dust. If symptoms persist, seek medical
attention.
Skin Contact - Wash affected areas gently with soap and warm water after handling.
If the job site inspection of the unit reveals damage or material shortages, file a claim with the
carrier immediately. Specify the type and extent of the damage on the “bill of lading” before
signing.
• Visually inspect the internal components for shipping damage as soon as possible after
delivery and before it is stored. Do not walk on the sheet metal base pans.
• If concealed damage is discovered, notify the carrier’s terminal of damage immediately by
phone and by mail. Concealed damage must be reported within 15 days.
• Request an immediate joint inspection of the damage by the carrier and the consignee. Do not
remove damaged material from the receiving location. Take photos of the damage, if possible.
The owner must provide reasonable evidence that the damage did not occur after delivery.
• Notify the appropriate sales representative before installing or repairing a damaged unit.
Take precautions to prevent condensate from forming inside the unit’s electrical compartments and
motors if:
• the unit is stored before it is installed; or,
RT-SVX23D-EN 11
Page 12

Pre-Installation
Unit Clearances
• the unit is set on the roof curb, and temporary heat is provided in the building. Isolate all side
panel service entrances and base pan openings (e.g., conduit holes, S/A and R/A openings, and
flue openings) from the ambient air until the unit is ready for start-up.
Note: Do not use the unit’s heater for temporary heat without first completing the start-up
procedure detailed under “Starting the Unit”.
The manufacturer will not assume any responsibility for equipment damage resulting from
condensate accumulation on the unit’s electrical and/or mechanical components.
Figure 1, p. 13 illustrates the minimum operating and service clearances for either a single or
multiple unit installation. These clearances are the minimum distances necessary to assure
adequate serviceability, cataloged unit capacity, and peak operating efficiency.
Providing less than the recommended clearances may result in condenser coil starvation, “shortcircuiting” of exhaust and economizer airflows, or recirculation of hot condenser air.
12 RT-SVX23D-EN
Page 13

Unit Clearances
033A THROUGH 063A UNITS033A THROUGH 063A UNITS
036A THROUGH 060A UNITS036A THROUGH 060A UNITS
THC036E UNITSTHC036E UNITS
072A THROUGH 120A UNITS072A THROUGH 120A UNITS
TSC072E THROUGH TSC120E UNITSTSC072E THROUGH TSC120E UNITS
THC048E AND THC060E UNITSTHC048E AND THC060E UNITS
Figure 1. Typical Installation Clearances for Single & Multiple Unit Applications
RT-SVX23D-EN 13
Page 14

Unit Clearances
Figure 2. Unit Dimensional Data WSC036A, WSC048A, WSC060A
Figure 3. Unit Dimensional Data WSC036E, WSC048E
14 RT-SVX23D-EN
Page 15
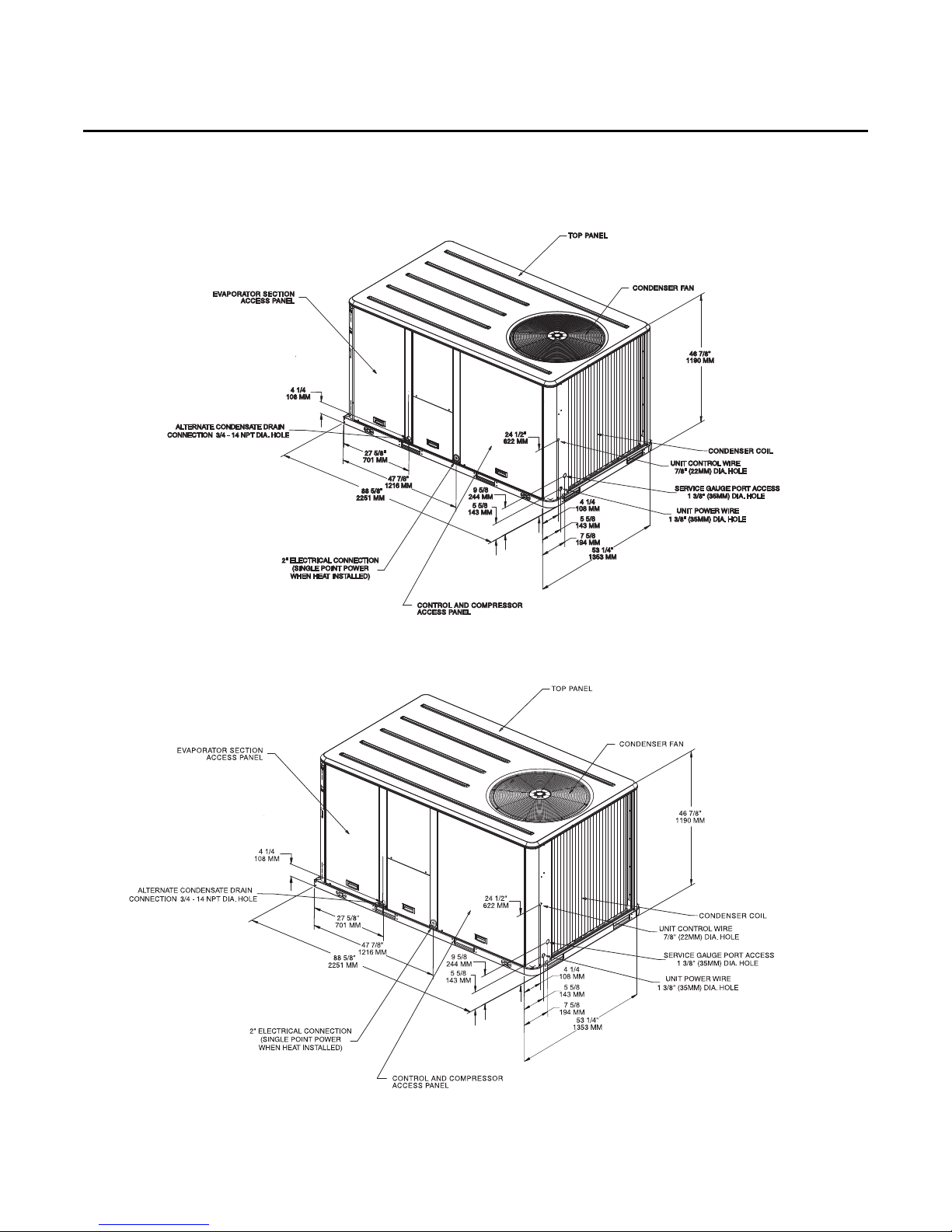
Figure 4. Unit Dimensional Data WSC072A, WSC090A, WSC060E
Unit Clearances
Figure 5. Unit Dimensional Data WSC120A
RT-SVX23D-EN 15
Page 16
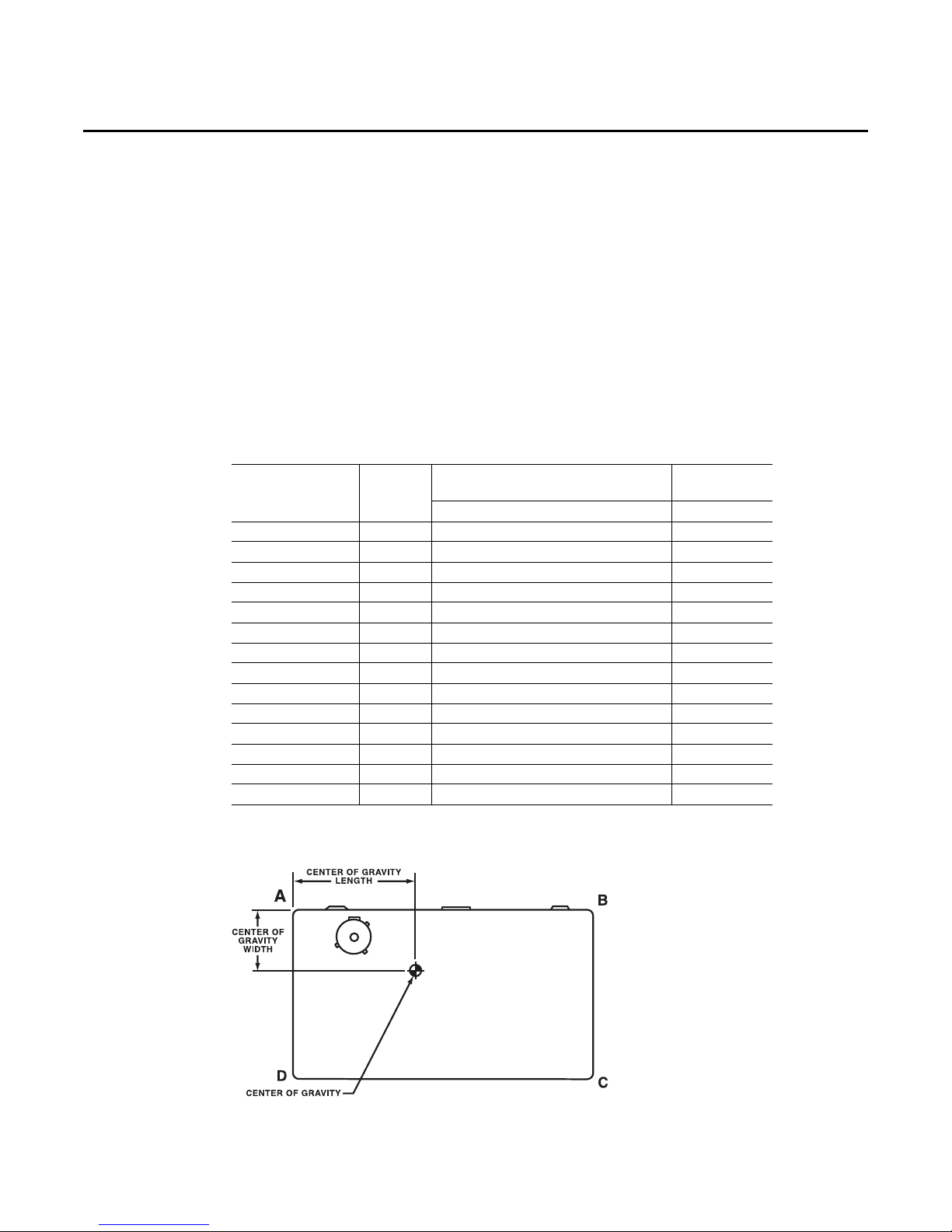
Unit Clearances
WARNING
Heavy Objects!
Do not use cables (chains or slings) except as shown. Each of the cables (chains or slings) used
to lift the unit must be capable of supporting the entire weight of the unit. Lifting cables (chains
or slings) may not be of the same length. Adjust as necessary for even unit lift. Other lifting
arrangements may cause equipment or property-only damage. Failure to properly lift unit may
result in death or serious injury. See details below.
WARNING
Improper Unit Lift!
Test lift unit approximately 24 inches to verify proper center of gravity lift point. To avoid
dropping of unit, reposition lifting point if unit is not level. Failure to properly lift unit could
result in death or serious injury or possible equipment or property-only damage.
Table 1. Typical Unit Weights & Point Loading Data
Net
Unit Model
WSC036A(1,3,4,W)* 442 138 110 88 105 31 19
WSC036E(1,3,4,W)* 514 177 107 113 117 29 20
WSC048A1* 474 151 114 95 114 31 19
WSC048A(3,4,W)* 474 151 114 95 114 31 19
WSC048E(1,3,4,W)* 525 181 109 115 119 29 20
WSC060A(1,3,4,W)* 492 160 118 97 117 31 19
WSC060E(1,3,4,W)* 682 228 177 114 163 38 24
WSC060(A,B)(D,T)* 532 170 128 107 127 31 19
WSC072A(3,4,W)* 724 243 184 128 170 38 22
WSC072(A,B)(D,T)* 812 269 206 146 191 38 22
WSC090A(3,4,W)* 763 249 200 137 177 39 22
WSC090(A,B)(D,T)* 834 282 210 147 195 38 22
WSC120A(3,4,W)* 941 320 243 162 215 38 21
WSC120AT* 981 330 253 172 225 38 21
Weight
(lbs)
A B C D Length Width
Corner Wt. (lbs)
Center of
Gravity (In.)
Figure 6. Corner weights
16 RT-SVX23D-EN
Page 17

Table 2. Typical Unit Weights & Point Loading Data
Net Weight
Accessory 3-5 Tons 6-10 Tons
Economizer 26 36
Barometric Relief 7 10
Powered Exhaust - 80
Motorized Outside Air Damper 20 30
Manual Outside Air Damper 16 26
Roof Curb 70 115
Oversized Motor 5 8
Belt Drive Motor 38 -
Smoke Detector, Return 7 7
Smoke Detector, Supply 5 5
Coil Guards 12 20
Hinged Doors 10 12
Powered Convenience Outlet 38 38
Through the Base Electrical 8 13
Electric Heaters 15 30
Unit Mounted Circuit Breaker 5 5
Unit Mounted Disconnect 5 5
1. Weights for options not listed are < 5 lbs.
2. Net weight should be added to unit weight when ordering factoryinstalled accessories.
Unit Clearances
Figure 7. Rigging and Center-of-Gravity Data
RT-SVX23D-EN 17
Page 18
Installation
Foundation
Ductwork
Horizontal Units
If the unit is installed at ground level, elevate it above the snow line. Provide concrete footings at
each support location with a “full perimeter” support structure or a slab foundation for support.
Refer to Table 1 , p . 16 for the unit’s operating and point loading weights when constructing a
footing foundation.
If anchoring is required, anchor the unit to the slab using hold down bolts or isolators. Isolators
should be installed to minimize the transmission of vibrations into the building.
For rooftop applications, ensure the roof is strong enough to support the combined unit and
support structural weight. Refer to Tab l e 1 , p. 16 for the unit operating weights. If anchoring is
required, anchor the unit to the roof with hold-down bolts or isolators. Check with a roofing
contractor for proper waterproofing.
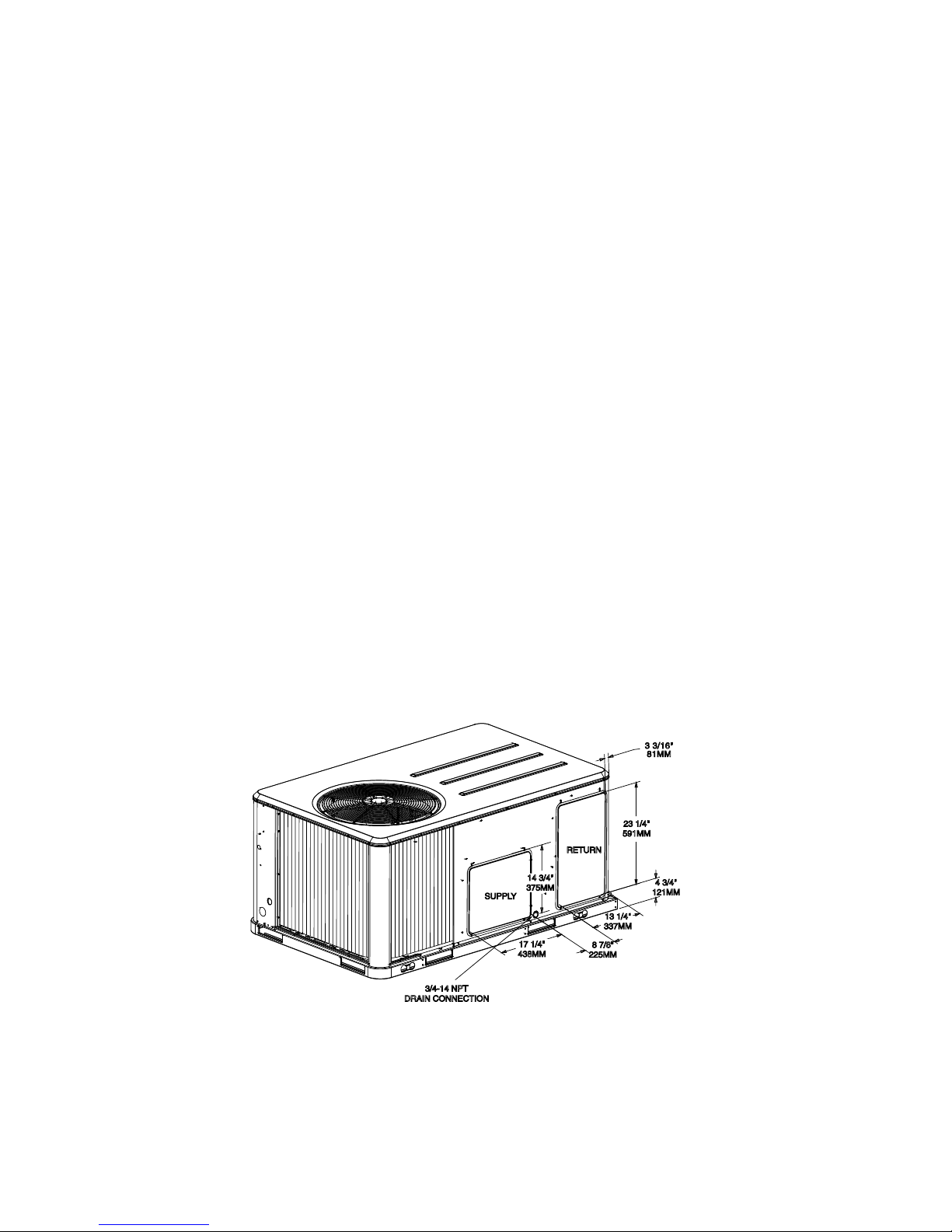
Figure 8, p. 18 and Figure 10, p. 19 illustrate the supply and return air openings as viewed form the
rear of the unit.
Elbows with turning vanes or splitters are recommended to minimize air noise due to turbulence
and to reduce static pressure.
When attaching the ductwork to the unit, provide a water- tight flexible connector at the unit to
prevent operating sounds from transmitting through the ductwork.
All outdoor ductwork between the unit and the structure should be weather proofed after
installation is completed.
Figure 8. WSC036A-WSC060A, WSC036E, WSC048E Horizontal Unit Supply & Return Air
Openings
18 RT-SVX23D-EN
Page 19
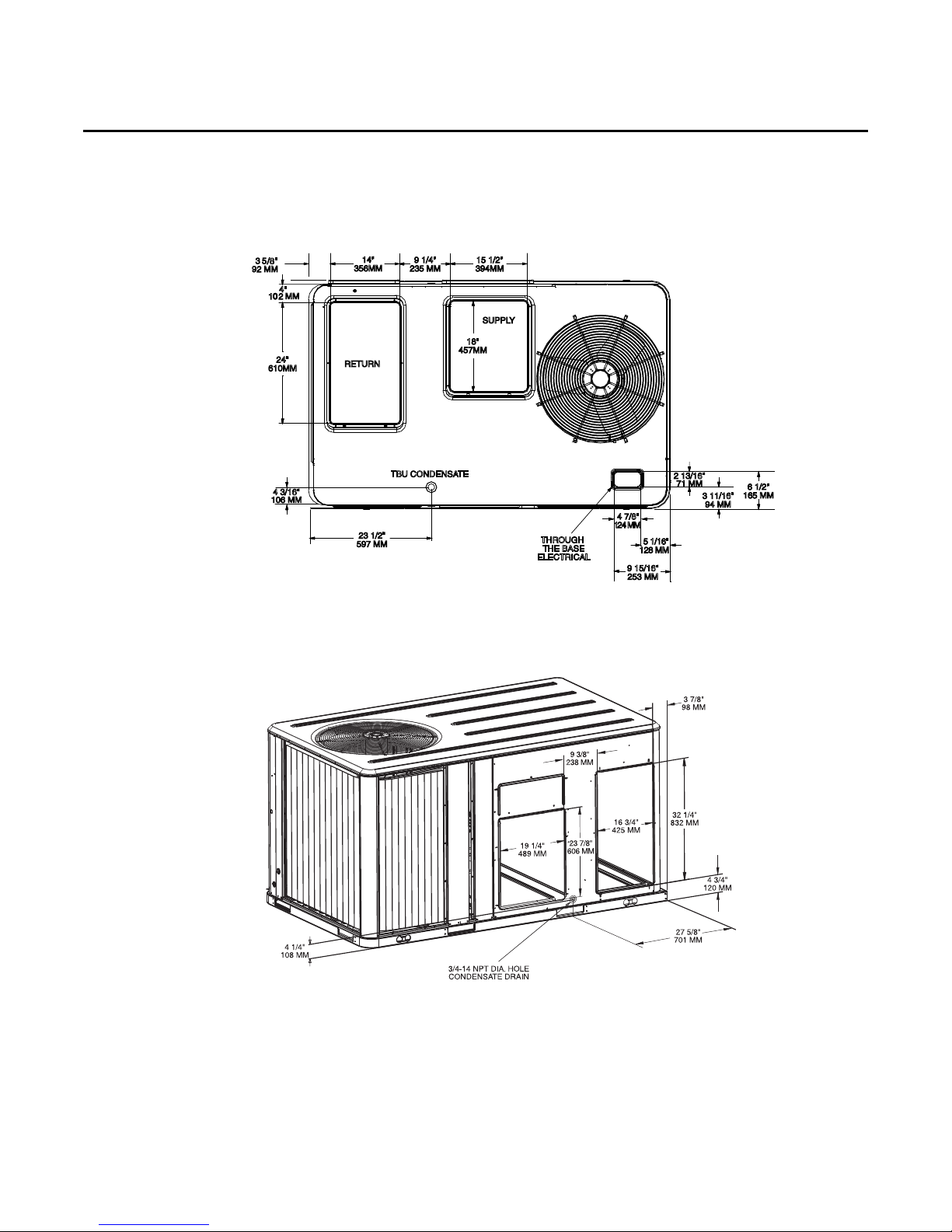
Installation
Figure 9. WSC036A-WSC060A, WSC036E, WSC048E Downflow Unit Supply & Return Air
Openings
Figure 10. WSC072A-WSC120A, WSC060E Horizontal Unit Supply & Return Air Openings
Return
Supply
RT-SVX23D-EN 19
Page 20
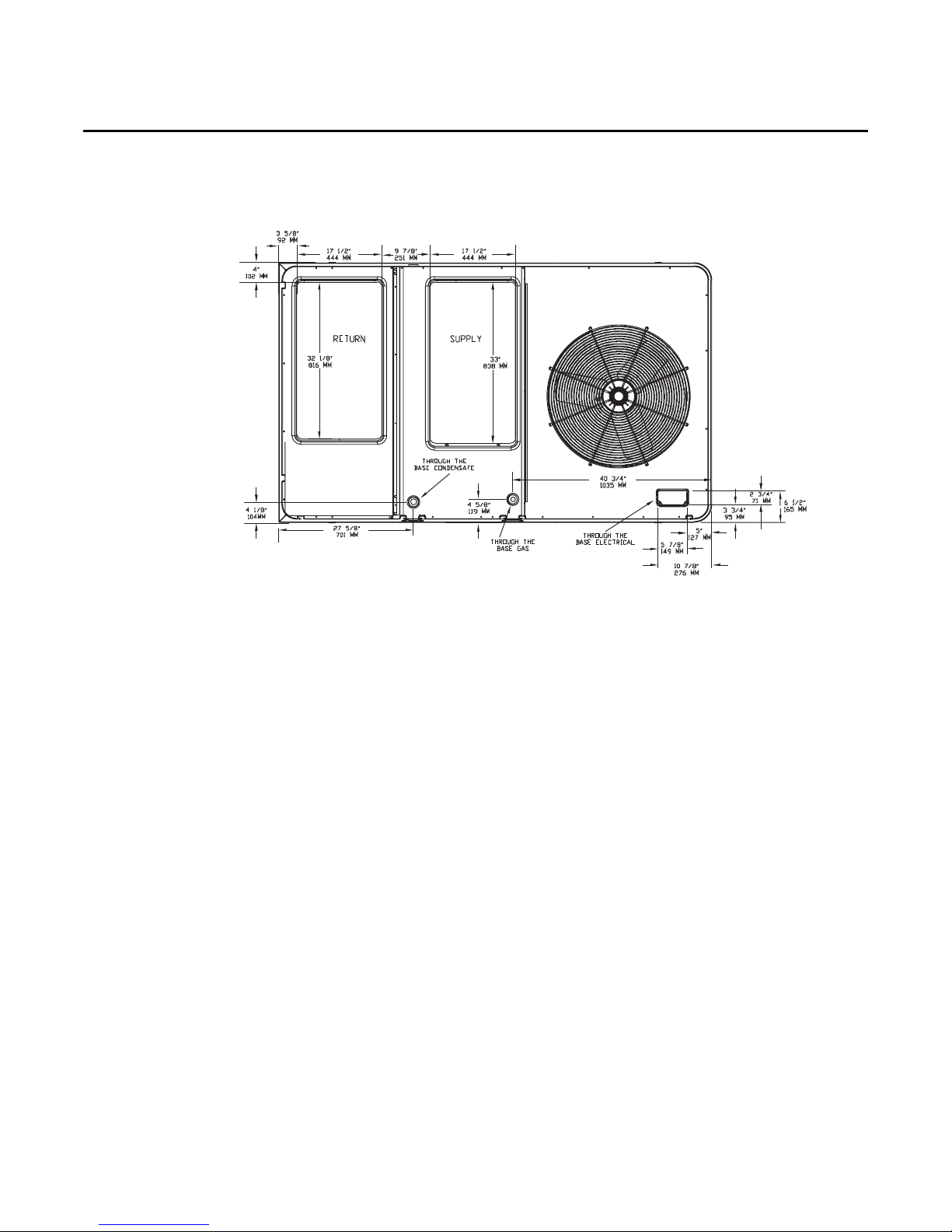
Installation
Figure 11. WSC072A-WSC120A, WSC060E Horizontal Unit Supply & Return Air Openings
Roof Curb
DownflowThe roof curbs for these units consists of a “full perimeter” enclosure to support the unit.
Before installing any roof curb, verify;
1. That it is the correct curb for the unit,
2. That it includes the necessary gaskets and hardware,
3. That the purposed installation location provides the required clearance for proper operation.
4. Insure that the curb is level and square. The top surface of the curb must be true to assure an
adequate curb-to-unit seal.
WARNING
Combustible Materials!
Maintain proper clearance between the unit heat exchanger, vent surfaces and combustible
materials. Refer to unit nameplate and installation instructions for proper clearances. Improper
clearances could result in a fire hazard. Failure to maintain proper clearances could result in
death or serious injury or property damage.
5. Verify that appropriate materials were used in the construction of roof and ductwork.
Combustible materials should not be used in the construction of ductwork or roof curb that is
in close proximity to heater elements or any hot surface. Any combustible material on the inside
of the unit base should be removed and replaced with appropriate material.
Step-by-step curb assembly and installation instructions ship with each accessory roof curb kit.
Follow the instructions carefully to assure proper fit-up when the unit is set into place.
Note: To assure proper condensate flow during operation, the unit (and curb) must be level.
If the unit is elevated, a field constructed catwalk around the unit is strongly recommended to
provide easy access for unit maintenance and service.
20 RT-SVX23D-EN
Page 21

Rigging
Installation
Recommendations for installing the Supply Air and Return Air ductwork joining the roof curb are
included in the curb instruction booklet. Curb ductwork must be fabricated and installed by the
installing contractor before the unit is set into place.
Note: For sound consideration, cut only the holes in the roof deck for the ductwork penetrations.
Do not cut out the entire roof deck within the curb perimeter.
If a Curb Accessory Kit is not used:
a. The ductwork can be attached directly to the factory-provided flanges around the unit’s
supply and return air openings. Be sure to use flexible duct connections at the unit.
b. For “built-up” curbs supplied by others, gaskets must be installed around the curb perimeter
flange and the supply and return air opening flanges.
A Rigging illustration and Center-of-Gravity dimensional data table is shown in Figure 7, p. 17. Refer
to the typical unit operating weights table before proceeding.
1. Remove all drill screws fastening wood protection to metal baserail. Remove all screws
securing wooden protection to wooden top crate.
2. Remove Wooden Top Crate.
WARNING
Heavy Objects!
Do not use cables (chains or slings) except as shown. Each of the cables (chains or slings) used
to lift the unit must be capable of supporting the entire weight of the unit. Lifting cables (chains
or slings) may not be of the same length. Adjust as necessary for even unit lift. Other lifting
arrangements may cause equipment or property-only damage. Failure to properly lift unit may
result in death or serious injury.
WARNING
Improper Unit Lift!
Test lift unit approximately 24 inches to verify proper center of gravity lift point. To avoid
dropping of unit, reposition lifting point if unit is not level. Failure to properly lift unit could
result in death or serious injury or possible equipment or property-only damage.
3. Rig the unit as shown in Figure 7, p. 17. Attach adequate strength lifting slings to all four lifting
brackets in the unit base rail. Do not use cables, chains, or slings except as shown.
4. Install a lifting bar, as shown in Figure 7, p. 17, to protect the unit and to facilitate a uniform lift.
The minimum distance between the lifting hook and the top of the unit should be 7 feet.
5. Test-lift the unit to ensure it is properly rigged and balanced, make any necessary rigging
adjustments.
RT-SVX23D-EN 21
Page 22

Installation
6. Lift the unit enough to allow the removal of two Fork Lift brackets and hardware. Remove the
two Fork Lift brackets, two metal runners and three wooden boards as shown in the following
Figure.
Figure 12. Fork lift pockets
7. Downflow units; align the base rail of the unit with the curb rail while lowering the unit onto
the curb. Make sure that the gasket on the curb is not damaged while positioning the unit.
General Unit Requirements
• The checklist listed below is a summary of the steps required to successfully install a
commercial unit. This checklist is intended to acquaint the installing personnel with what is
required in the installation process. It does not replace the detailed instructions called out in the
applicable sections of this manual.
• Check the unit for shipping damage and material shortage; file a freight claim and notify
appropriate sales representative.
• Verify correct model, options and voltage from unit nameplate.
• Verify that the installation location of the unit will provide the required clearance for proper
operation.
• Assemble and install the roof curb (if applicable). Refer to the latest edition of the curb installers
guide that ships with each curb kit.
• Fabricate and install ductwork; secure ductwork to curb.
• Rigging the unit.
• Set the unit onto the curb; check for levelness.
• Ensure unit-to-curb seal is tight and without buckles or cracks.
• Install and connect a condensate drain line to the evaporator drain connection.
Factory Installed Economizer
• Ensure the economizer has been pulled out into the operating position. Refer to the economizer
installers guide for proper position and setup.
• Install all access panels.
Temperature Limit Switch Usage for Electric Heat Units
Units are factory shipped in the downflow discharge confriguration but can be field converted to
a horizontal discharge confriguration. Some, but not all units require a different TC0-A limit switch,
which is wire tied near the terminal block in the heater compartment if horizontal discharge
confriguration is used.
22 RT-SVX23D-EN
Page 23

Horizontal Discharge Conversion WSC036A-WSC060A, WSC036E, WSC048E
RTV Sealant
• Supplies Needed by Installer for Conversion: 3 oz. tube of High Temperature RTV sealant.
(500°F/260°C: Similar to Dow Corning 736)
Note: Failure to use recommended sealant could result in unit performance loss.
If a unit is to be converted to a Horizontal discharge, the following conversion must be performed:
1. Remove RETURN and SUPPLY duct covers.
2. Locate supply cover. Apply ¼ in. (6mm.) continuous bead of 500°F RTV sealant to the flange as
shown.
Figure 13.
Installation
3. Position SUPPLY DUCT COVER as shown, rotate 90 degrees to allow entrance into supply
opening.
Note: If unit is equipped with Discharge Air Sensing option refer to the following figure for proper
tube positioning based on unit tonnage.
Figure 14.
4. Slide SUPPLY DUCT COVER into duct openings until inward edge of duct cover engages with
the 2 retaining clips on the duct flanges. Secure the outward edge of each duct cover with 2
screws.
RT-SVX23D-EN 23
Page 24

Installation
Supply duct cover with
RTV installed
Supply Duct Cover
Screw into 4
dimples on top
edge
Figure 15.
5. Slide RETURN DUCT COVER (insulation side up) into supply opening until inward edge of duct
cover engages with the 2 retaining clips on the duct flange. Secure out-ward edge of the duct
cover with two screws.
Note: Certain unit/electric heater combinations require a limit switch change out for horizontal
airflow applications. Refer to the following instructions to determine if this process is
required for the unit undergoing installation.
6. After completing installation of the duct covers for horizontal discharge, proceed to TCO-1
instructions.
Horizontal Discharge Conversion WSC072A - WSC120A, WSC060E
• Supplies Needed by Installer for Conversion: 3 oz. tube of high Temperature RTV sealant.
(500°F/260°C : Similar to Dow Corning 736)
Note: Failure to use recommended sealant could result in unit performance loss.
If a unit is to be converted to a Horizontal discharge, the following conversion must be performed:
1. Remove RETURN and SUPPLY duct covers.
2. Place SUPPLY DUCT COVER over downflow return opening. (insulation side down)
3. Using self-drilling screws, (or screws removed from duct cover), screw through dimples to
attach Duct Cover to base.
Figure 16.
24 RT-SVX23D-EN
Page 25

Installation
RTV Sealant
Insulation side
down
Supply duct cover
Insulation side up
Return duct
cover
4. On original RETURN DUCT COVER, apply ¼” (6mm.) continuous bead of 500°F RTV sealant
around flange (opposite insulation side), as shown.
Figure 17.
5. Slide RETURN DUCT COVER (insulation side up) into supply opening until inward edge of duct
cover engages with the 2 retaining clips on the duct flange. Secure outward edge of the duct
cover with two screws.
Figure 18.
Note: If Unit is equipped with Return Air Smoke Detector, refer to field conversion instructions for
horizontal discharge before installing return air duct.
Note: Certain unit/electric heater combinations require a limit switch change out for horizontal
airflow applications. Refer to the following instructions to determine if this process is
required for the unit undergoing installation.
6. After completing installation of the duct covers for horizontal discharge, proceed to TCO-A
instructions.
TCO-A Instructions:
If the unit being installed is listed in the following table and is equipped with the corresponding
model number of factory installed electric heater package in the table, the limit control TCO-A must
be replaced with the extra limit control shipped in the heater compartment. Replace TCO-A
following the instructions in steps 1through 3 below. If the unit being installed does not have a
factory installed electric heater package or is equipped with a factory installed electric heater model
that does not correspond to any in this table, skip steps1 through 3 and go on to next step in the
installation process.
RT-SVX23D-EN 25
Page 26

Installation
Table 3.
Unit Model Number Electric Heater Model Number
WSC072A4, 090A4 BAYHTRS427A, 436A
WSC072AW, 090AW BAYHTRSW27, W36
WSC120A4 BAYHTRT454A
WSC120AW BAYHTRTW54A
1. Remove the heater section access panel and open the electric heater dead front panel.
2. TCO-A is the limit control located in the central part of the heater mounting plate and that is
located on the bottom of the two heater element assemblies. To replace this device, first
remove the two wires connected to the terminals. Next, remove the two screws which secure
it to the heater element mounting plate. Once TCO-A has been removed form the heater
element mounting plate, discard this device.
3. Obtain the replacement TCO-A which is secured by a wire tie near the electric heater terminal
block in the heater compartment . Attach it to the heater element mounting plate with the two
screws that were removed in step 8 above. Connect the two wires that were un-hooked in step
8 to the terminals on the new TCO-A. Refer to the heater package wiring diagram to assure that
the wiring is connected properly.
4. Close the electric heater dead front panel and replace heat section access panel.
Return Air Smoke Detector
The factory installed Return Air Smoke Detector is installed in the Downflow discharge position.
No additional field setup is required.
If a unit is to be converted to Horizontal discharge, the following conversion must be performed:
1. If the unit has an economizer, it must be pulled out in the operating position.
2. Remove the 3 screws from the mounting brackets. Refer to Downflow View for screw locations.
Figure 19. Downflow View
26 RT-SVX23D-EN
Page 27

Installation
3. Lift the tube and bracket from the downflow duct opening. Rotate the tube and bracket
assembly 180° degrees ensuring that the holes on the copper sensing tube face away from the
unit and face the return air ductwork. Refer to Horizontal View.
Note: Check to insure that the flexible tubing lies flat on the base pan surface.
4. Slide the top bracket down the copper sensing tube, insert the tab on the left side into the slot
on the indoor coil blockoff and secure the right side of the bracket with one of the 3 screws
removed in step 2. Refer to Horizontal View.
5. Using the remaining 2 screws removed in step 2, secure the bottom bracket. Refer to Horizontal
View.
Figure 20. Horizontal View
Main Electrical Power Requirements
• Verify that the power supply complies with the unit nameplate specifications.
• Inspect all control panel components; tighten any loose connections.
• Connect properly sized and protected power supply wiring to a field-supplied/installed
disconnect switch and to the main power terminal block (HTB1) in the unit control panel.
• Install proper grounding wires to an earth ground.
Note: All field-installed wiring must comply with NEC and applicable local codes.
Electric Heat Requirements
• Verify that the power supply com plies with the electric heater specifications on the unit and
heater nameplate.
• Inspect the heater junction box and control panel; tighten any loose connections.
• Check electric heat circuits for continuity.
Low Voltage Wiring (AC & DC) Requirements
• Install the zone thermostat, with or without switching subbase.
RT-SVX23D-EN 27
Page 28

Installation
• Connect properly sized control wiring to the proper termination points between the zone
thermostat and the unit control panel.
Condensate Drain Configuration
An evaporator condensate drain connection is provided on each unit. Refer to Figure 4 for the
appropriate drain location.
The condensate drain pan is factory installed to drain condensate to the back side of the unit. See
Figure 8, p. 18 and Figure 10, p. 19. It can be converted to drain condensate out the front side of the
unit or through the base.
To convert drain condensate out the front of unit:
1. Remove evaporator access panel and supply air access panels.
2. Remove the support panel that the condensate drain pan exits through.
3. Slide the condensate drain pan out of the unit and rotate 180°.
4. Slide the condensate drain pan back into the unit, align the drain with the grommeted opening
in the rear support panel and push until the coupling is seated in the grommet.
5. Replace the front support panel by aligning the panel with tabs in the raceway. Align the
condensate drain pan support in the grommeted hole as the panel is put in place.
6. Replace evaporator access panel and supply air access panels.
To convert drain condensate through the base of unit:
1. Remove evaporator access panel and supply air access panels.
2. Remove the support panel that the condensate drain pan exits through.
3. Slide the condensate drain pan out of the unit.
4. Place on a level surface in the position it was removed from the unit.
5. Remove the plug knockout in the bottom of the drainpan to convert it to through the base
drainage.
6. Plug the original condensate drain opening with a field supplied 3/4" NPT plug.
7. Slide the condensate drain pan back into the unit, align the drain support with the grommeted
opening in the rear support panel and push until the support is seated in the grommet.
8. Replace the front support panel by aligning the panel with tabs in the raceway. Align the
plugged condensate drain pan coupling in the grommeted hole as the panel is put in place.
9. Replace evaporator access panel and supply air access panels.
A condensate trap must be installed at the unit due to the drain connection being on the “negative
pressure” side of the fan. Install the P-Trap using the guidelines in Figure 21, p. 29.
A condensate drain line must be connected to the P-Trap. Pitch the drain lines at least 1/2 inch for
every 10 feet of horizontal run to assure proper condensate flow. Do not allow the horizontal run
to sag causing a possible double-trap condition which could result in condensate backup due to “air
lock”.
28 RT-SVX23D-EN
Page 29

Filter Installation
Installation
Figure 21. Condensate Trap Installation
Each unit ships with filters installed. The quantity of filters is determined by unit size. Access to the
filters is obtained by removing the indoor fan access panel. To modify the 3, 4 or 5 ton unit’s filter
rack to accept two inch filters, remove the L-shaped angle attachment screws and rotate the angles
90 degrees.
Reinstall the screws and insert new filters. Refer to the unit Service Facts (shipped with each unit)
for filter requirements.
Note: Do not operate the unit without filters.
Field Installed Power Wiring
An overall dimensional layout for the field installed wiring entrance into the unit is illustrated in
“Unit Clearances,” p. 13. To insure that the unit’s supply power wiring is properly sized and
installed, follow the guidelines outlined below.
Note: All field installed wiring must conform to NEC guidelines as well as State and Local codes.
Verify that the power supply available is compatible with the unit’s nameplate ratings. The available
supply power must be within 10% of the rated voltage stamped on the nameplate. Use only copper
conductors to connect the power supply to the unit.
NOTICE
Use Copper Conductors Only!
Unit terminals are not designed to accept other types of conductors. Failure to use copper
conductors may result in equipment damage.
Note: If the unit is not equipped with an optional factory installed nonfused disconnect switch or
circuit breaker, a field supplied disconnect switch must be installed at or near the unit in
accordance with the National Electrical Code (NEC latest edition).
Main Unit Power Standard Wiring
1. Location of the applicable electrical service entrance is illustrated in “Unit Clearances,” p. 13.
Complete the unit’s power wiring connections at Compressor Contactor # 1 (CC1) inside the unit
control panel. Refer to the customer connection diagram that is shipped with the unit for
specific termination points.
RT-SVX23D-EN 29
Page 30

Installation
2. Provide proper grounding for the unit in accordance with local and national codes.
Main Unit Power Optional TBUE Wiring (Through the Base Electrical Option)
1. Location of the applicable electrical service is illustrated below. Refer to the customer
connection diagram that is shipped with the unit for specific termination points. The
termination points, depending on the customer option selected would be a factory mounted
nonfused disconnect switch (UDC) or circuit breaker (UCB). If neither a factory mounted
nonfused disconnect switch (UDC) or circuit breaker (UCB) was factory mounted, field wiring
connections should be terminated in the control box at Compressor Contactor # 1 (CC1).
2. Provide proper grounding for the unit in accordance with local and national codes.
Note: Black Gasket is shipped from the factory and is located in the literature Shi p Wi th ba g in th e
control box. Apply Black Gasket around conduit plate on all 4 sides after installation to
prevent air leakage from the building entering the electrical enclosures.
Note: Seal between wiring and conduit with Black Gasket or weather proof sealer to prevent air
leakage from the building entering the electrical enclosures. Also seal around conduit and
wiring at all roof and curb penetrations.
Figure 22.
Field Installed Control Wiring
An overall layout of the various control options available with the required number of conductors
for each control device is illustrated in Figure 28, p. 36.
Note: All field wiring must conform to NEC guidelines as well as state and local codes.
30 RT-SVX23D-EN
Page 31

Control Power Transformer
WARNING
Hazardous Voltage!
Disconnect all electric power, including remote disconnects before servicing. Follow proper
lockout/tagout procedures to ensure the power can not be inadvertently energized. Failure to
disconnect power before servicing could result in death or serious injury.
The 24 volt control power transformers are to be used only with the accessories called out in this
manual. Transformers rated greater than 50 VA are equipped with internal circuit breakers. If a
circuit breaker trips, turn “Off” all power to the unit before attempting to reset it.
Failure to disconnect power before servicing can cause severe personal injury or death.
The transformer is located in the control panel. The circuit breaker is located on the left side of the
transformer and can be reset by pressing in on the black reset button.
Controls using 24 VAC
Before installing any connecting wiring, refer to“Unit Clearances,” p. 13 for the electrical access
locations provided on the unit and Table 4, p. 31 for AC conductor sizing guidelines, and;
a. Use copper conductors unless otherwise specified.
b. Ensure that the AC control wiring between the controls and the unit’s termination point does
not exceed three (3) ohms/conductor for the length of the run.
Note: Resistance in excess of 3 ohms per conductor may cause component failure due to
insufficient AC voltage supply.
c. Be sure to check all loads and conductors for grounds, shorts, and mis-wiring.
d. Do not run the AC low voltage wiring in the same conduit with the high voltage power wiring.
e. Route low voltage wiring per illustrations on Figure 25, p. 33.
Installation
Table 4. AC Conductors
Distance from Unit to Control RecommendedWire Size
000 - 460 feet
000 - 140 m
461 - 732 feet
141 - 223 m
733 - 1000 feet
224 - 305 m
18 gauge
.75 mm
16 gauge
1.3 mm
14 gauge
2.0 mm
2
2
2
Controls using DC Analog Input/Outputs (Standard Low Voltage Multiconductor Wire)
Before installing any connecting wiring between the unit and components utilizing a DC analog
input\output signal, refer to “Unit Clearances,” p. 13 for the electrical access locations provided on
the unit.
1. Table 5, p. 32 lists the conductor sizing guidelines that must be followed when interconnecting
the DC binary output devices and the system components utilizing a DC analog input\output
signal to the unit.
Note: Resistance in excess of 2.5 ohms per conductor can cause deviations in the accuracy of the
controls.
RT-SVX23D-EN 31
Page 32

Installation
2. Ensure that the wiring between controls and the unit’s termination point does not exceed two
and a half (2.5) ohms/conductor for the length of the run.
3. Do not run the electrical wires transporting DC signals in or around conduit housing high
voltage wires.
4. Route low voltage wiring per illustrations on Figure 25, p. 33.
Table 5. DC Conductors
Distance from Unit to Control Recommended Wire Size
0 - 150 feet
0 - 45.7 m
151 - 240 feet
46 - 73.1 m
241 -385 feet
73.5 - 117.3 m
386 - 610 feet
117.7 - 185.9 m
611 - 970 feet
186.2 - 295.7 m
22 gauge
.33 mm
20 gauge
.50 mm
18 gauge
.75 mm
16 gauge
1.3 mm
14 gauge
2.0 mm
2
2
2
2
2
Figure 23. ReliaTel conventional thermostat field wiring diagram
RTRM
32 RT-SVX23D-EN
Page 33

Figure 24. ReliaTel refrigeration module
Installation
Figure 25. Customer control low voltage routing
RT-SVX23D-EN 33
Page 34

Installation
More than 5 HVAC units
5 or fewer HVAC units
Smoke Detector - (ReliaTel™ only) Customer Low Voltage Wiring-
When interlocking System Sensor smoke detectors together, all of the detectors must be powered
from the same power supply. If multiple smoke detectors are required, all detectors must be
disconnected from the HVAC unit power supply and connected together from another single
source supply.
Note: Do not interconnect smoke detectors together that have separate power supplies. Do not
exceed ten smoke detectors on one power supply.
Note: Multiple System Sensor smoke detectors are connected together using terminals 1 and 12
on each detector.
If you have supply and return smoke detectors in all HVAC units, you can connect a maximum of
5 HVAC units (10 detectors) up to one power supply. See the following field wiring example below.
If you have more than 5 HVAC units, you can connect all the supplies together on one power supply
(up to 10 HVAC units), and all the returns together (up to 10 HVAC units) on another power supply.
See the following field wiring example below.
Figure 26. Smoke detector field wiring examples
34 RT-SVX23D-EN
Page 35

Pre-Start
Space Temperature Averaging (ReliaTel™ only)
Space temperature averaging is accomplished by wiring a number of remote sensors in a series/
parallel circuit.
Using the BAYSENS016* or BAYSENS077*, at least four sensors are required to accomplish space
temperature averaging. Example #1 illustrates two series circuits with two sensors in each circuit
wired in parallel. The square of any number of remote sensors is required. Example #2 illustrates
three sensors squared in a series/parallel circuit. Using BAYSENS077*, two sensors are required
to accomplish space temperature averaging. Example #3 illustrates the circuit required for this
sensor. Table 4 lists the temperature versus resistance coefficient for all sensors.
Figure 27. Space temperature averaging
RT-SVX23D-EN 35
Page 36

BAYSENS119*
ASYSTAT777*
Zone Sensor
BAYSENS077*
ASYSTAT111*
BAYSENS107*
BAYSENS073*
Zone Sensor
BAYSENS077*
ASYSTAT111*
BAYSENS109*
BAYSENS074*
Zone Sensor
BAYSENS119*
ASYSTAT777*
BAYSENS109*
Pre-Start
Figure 28. Typical field wiring diagrams for optional controls
36 RT-SVX23D-EN
Page 37

Table 6. Temperature versus resistance (temperature vs. resistance is negative)
Temperature
Degrees F° Degrees C°
-20° -28.9° 170.1 K - Ohms
-15° -26.1° 143.5 K - Ohms
-10° -23.3° 121.4 K - Ohms
-5° -20.6° 103.0 K - Ohms
0° -17.8° 87.56 K - Ohms
5° -15.0° 74.65 K - Ohms
10° -12.2° 63.80 K - Ohms
15° -9.4° 54.66 K - Ohms
20° -6.7° 46.94 K - Ohms
25° -3.8° 40.40 K - Ohms
30° -1.1° 34.85 K - Ohms
35° 1.7° 30.18 K - Ohms
40° 4.4° 26.22 K - Ohms
45° 7.2° 22.85 K - Ohms
50° 10.0° 19.96 K - Ohms
55° 12.8° 17.47 K - Ohms
60° 15.6° 15.33 K - Ohms
65° 18.3° 13.49 K - Ohms
70° 21.1° 11.89 K - Ohms
75° 23.9° 10.50 K - Ohms
80° 26.7° 9.297 K - Ohms
85° 29.4° 8.247 K - Ohms
90° 32.2° 7.330 K - Ohms
95° 35.0° 6.528 K - Ohms
100° 37.8° 5.824 K - Ohms
Nominal
Resistance
Pre-Start
Use the checklist provided below in conjunction with the “General Unit Requirements” checklist to
ensure that the unit is properly installed and ready for operation.
WARNING
Hazardous Voltage!
Disconnect all electric power, including remote disconnects before servicing. Follow proper
lockout/tagout procedures to ensure the power can not be inadvertently energized. Failure to
disconnect power before servicing could result in death or serious injury.
Failure to disconnect power before servicing can cause severe personal injury or death.
• Check all electrical connections for tightness and “point of termination” accuracy.
• Verify that the condenser airflow will be unobstructed.
• Verify that the condenser fan and indoor blower turn freely without rubbing and are properly
tightened on the shafts.
• Check the supply fan belts for proper tension and the fan bearings for sufficient lubrication. If
the belts require adjustment, or if the bearings need lubricating, refer to the maintenance
section of this manual for instructions.
• Verify that a condensate trap is installed and the piping is properly sized and pitched.
RT-SVX23D-EN 37
Page 38

Pre-Start
• Verify that the correct size and number of filters are in place.
• Inspect the interior of the unit for tools and debris and install all panels in preparation for
Voltage Imbalance
Three phase electrical power to the unit must meet stringent requirements for the unit to operate
properly. Measure each leg (phase-to-phase) of the power supply. Each reading must fall within the
utilization range stamped on the unit nameplate. If any of the readings do not fall within the proper
tolerances, notify the power company to correct this situation before operating the unit.
Excessive three phase voltage imbalance between phases will cause motors to overheat and
eventually fail. The maximum allowable voltage imbalance is 2%. Measure and record the voltage
between phases 1, 2, and 3 and calculate the amount of imbalance as follows:
% Voltage Imbalance = 100 X AV - VD where;
AV (Aver age Volt age ) Vo lt 1 + Vol t 2 + Volt 3
V1, V2, V3 = Line Voltage Readings
VD = Line Voltage reading that deviates the farthest from the average voltage.
Example: If the voltage readings of the supply power measured 221, 230, and 227, the average volts
would be:
221 + 230 + 227
starting the unit.
3
AV
3
= 226 Avg.
VD (reading farthest from average) = 221
The percentage of Imbalance equals:
100 X 226 - 221
226
= 2.2%
The 2.2% imbalance in this example exceeds the maximum allowable imbalance of 2.0%. This
much imbalance between phases can equal as much as a 20% current imbalance with a resulting
increase in motor winding temperatures that will decrease motor life. If the voltage imbalance is
over 2%, notify the proper agencies to correct the voltage problem before operating this
equipment.
Electrical Phasing (Three Phase Motors)
The compressor motor(s) and the supply fan motor are internally connected for the proper rotation
when the incoming power supply is phased as A, B, C.
Proper electrical supply phasing can be quickly determined and corrected before starting the unit
by using an instrument such as an Associated Research Model 45 Phase Sequence Indicator and
following the steps below:
• Turn the field supplied disconnect switch that provides power to the main power terminal block
or to the “Line” side of the optional factory mounted disconnect switch to the “Off” position.
• Connect the phase sequence indicator leads to the terminal block or to the “Line” side of the
optional factory mounted disconnect switch as follows;
Black (phase A) to L1
Red (phase B) to L2
38 RT-SVX23D-EN
Page 39

Pre-Start
Yellow (phase C) toL3
• Close the field supplied main power disconnect switch or circuit protector switch that provides
the supply power to the unit.
WARNING
Live Electrical Components!
During installation, testing, servicing and troubleshooting of this product, it may be necessary
to work with live electrical components. Have a qualified licensed electrician or other individual
who has been properly trained in handling live electrical components perform these tasks.
Failure to follow all electrical safety precautions when exposed to live electrical components
could result in death or serious injury.
To prevent injury or death from electrocution, it is the responsibility of the technician to
recognize this hazard and use extreme care when performing service procedures with the
electrical power energized.
• Observe the ABC and CBA phase indicator lights on the face of the sequencer. The ABC
indicator light will glow if the phase is ABC. If the CBA indicator light glows, open the disconnect
switch or circuit protection switch and reverse any two power wires.
• Restore the main electrical power and recheck the phasing. If the phasing is correct, open the
disconnect switch or circuit protection switch and remove the phase sequence indicator.
Compressor Crankcase Heaters
(Optional - standard in WSC048E3, 4, W & WSC060E units)
Each compressor can be equipped with a crankcase heater. The proper operation of the crankcase
heater is important to maintain an elevated compressor oil temperature during the “Off” cycle to
reduce oil foaming during compressor starts. Oil foaming occurs when refrigerant condenses in
the compressor and mixes with the oil. In lower ambient conditions, refrigerant migration to the
compressor could increase.
When the compressor starts, the sudden reduction in crankcase pressure causes the liquid
refrigerant to boil rapidly causing the oil to foam. This condition could damage compressor
bearings due to reduced lubrication and could cause compressor mechanical failures.
Before starting the unit in the “Cooling” mode, set the system switch to the “Off” position and turn
the main power disconnect to the “On” position and allow the crankcase heater to operate a
minimum of 8 hours.
Before closing the main power disconnect switch, insure that the “System” selection switch is in
the “Off” position and the “Fan” selection switch is in the “Auto” position.
Close the main power disconnect switch and the unit mounted disconnect switch, if applicable.
WARNING
Live Electrical Components!
During installation, testing, servicing and troubleshooting of this product, it may be necessary
to work with live electrical components. Have a qualified licensed electrician or other individual
who has been properly trained in handling live electrical components perform these tasks.
Failure to follow all electrical safety precautions when exposed to live electrical components
could result in death or serious injury.
To prevent injury or death from electrocution, it is the responsibility of the technician to
recognize this hazard and use extreme care when performing service procedures with the
electrical power energized.
RT-SVX23D-EN 39
Page 40

Pre-Start
Test Modes
Upon power initialization, the RTRM performs self-diagnostic checks to insure that all internal
controls are functional. It also checks the configuration parameters against the components
connected to the system. The Liteport LED located on th e RT RM module is t urn ed “On” with in one
second of power-up if internal operation is okay.
Use one of the following “Test” procedure to bypass some time delays and to start the unit at the
control panel. Each step of unit operation can be activated individually by temporarily shorting
across the “Test” terminals for two to three seconds. The Liteport LED located on the RTRM module
will blink when the test mode has been initiated.
The unit can be left in any “Test” step for up to one hour before it will automatically terminate, or
it can be terminated by opening the main power disconnect switch. Once the test mode has been
terminated, the Liteport LED will glow continuously and the unit will revert to the “System” control.
There are three methods in which the “Test” mode can be cycled at LTB-Test 1 and LTB-Test 2.
1. Step Test Mode - This method initiates the different components of the unit, one at a time, by
temporarily shorting across the two test terminals for two to three seconds.
For the initial start-up of the unit, this method allows the technician to cycle a component “On”
and have up to one hour to complete the check.
2. Resistance Test Mode - This method can be used for start-up providing a decade box for variable
resistance outputs is available. This method initiates the different components of the unit, one
at a time, when a specific resistance value is placed across the two test terminals. The unit will
remain in the specific test mode for approximately one hour even though the resistance is left
on the test terminals.
3. Auto Test Mode - This method is not recommended for start-up due to the short timing between
individual component steps. This method initiates the different components of the unit, one at
a time, when a jumper is installed across the test terminals. The unit will start the first test step
and change to the next step every 30 seconds. At the end of the test mode, control of the unit
will automatically revert to the applied “System” control method.
For unit test steps, test modes, and step resistance values to cycle the various components, refer
to Table 7, p . 4 1 .
ReliaTel Controls
Upon power initialization, the RTRM performs self-diagnostic checks to insure that all internal
controls are functional. It also checks the configuration parameters against the components
connected to the system. The Liteport LED located on th e RT RM module is t urn ed “On” with in one
second of power-up if internal operation is okay.
Use one of the following “Test” procedure to bypass some time delays and to start the unit at the
control panel. Each step of unit operation can be activated individually by temporarily shorting
across the “Test” terminals for two to three seconds. The Liteport LED located on the RTRM module
will blink when the test mode has been initiated. The unit can be left in any “Test” step for up to
one hour before it will automatically terminate, or it can be terminated by opening the main power
disconnect switch. Once the test mode has been terminated, the Liteport LED will glow
continuously and the unit will revert to the “System” control.
40 RT-SVX23D-EN
Page 41

Start-Up
Table 7. Service test guide for component operation
Test Step Mode Fan
1FanOn
Minimum
Ventilation
2
3 Cool Stage 1 On
4 (Note 3) Cool Stage 2 On
5 (Note 3) Reheat On Minimum On On Off Off 33K
6 (Note 3) Heat Stage 1 On Minimum Off Off On Off 10K
7 (Note 3) Heat Stage 2 On Minimum Off Off On On 15K
Notes:
1. The condenser fans will operate any time a compressor is "On“ providing the outdoor air temperatures are within the operating values.
2. The exhaust fan will turn on anytime the economizer damper position is equal to or greater than the exhaust fan setpoint.
3. Steps for optional accessories and non-applicable modes in unit will be skipped.
Economizer Test
Open
On Selectable Off Off Off Off
On Open Off Off Off Off 3.3K
Verifying Proper Air Flow (Units with Two Speed Direct Drive Indoor Fan)
Much of the systems performance and reliability is closely associated with, and dependent upon
having the proper airflow supplied both to the space that is being conditioned and across the
evaporator coil.
The indoor fan motor is factory wired to operate on low speed in the cooling and heating mode.
It can be rewired for high speed operation should the application require it. Refer to the wiring
diagram that shipped in the unit.
The indoor fan motors are specifically designed to operate within the BHP parameters listed in the
fan performance tables of the unit Service Facts. By understanding that these motors will safely
work within these conditions, before an oversized motor is required, will allow the air distribution
system to be set up properly and diagnostics enhanced should a problem occur.
When verifying direct drive fan performance, the tables must be used somewhat differently than
those of belt driven fans. Fan performance diagnostics can be easily recognized when these tables
are used correctly.
Before starting the SERVICE TEST, set the minimum position setpoint for the economizer to 0
percent using the setpoint potentiometer located on the Economizer Control (ECA), if applicable.
Econ (Note
2) Comp1 Comp 2 Heat 1Heat 2Ohms
Minimum
Position
Setpoint 0%
Minimum
Position
Minimum
Position
Off Off Off Off 2.2K
On (Note 1) Off Off Off 4.7K
On (Note 1) On Off Off 6.8K
ReliaTel Control
Using the Service Test Guide in Ta bl e 7 , momentarily jump across the Test 1 & Test 2 terminals on
LTB1 one time to start the Minimum Ventilation Test.
With the fan operating properly, determine the total system external static pressure (inches w.c.)
by;
1. Measuring the supply and return duct static pressure,
2. Using the accessory pressure drop table in the Service Facts, calculate the total static pressure
drop for all of the accessories installed on the unit; i.e., curb, economizer, etc.
Note: Static pressure is based on desired CFM and may not be actual static pressure.
RT-SVX23D-EN 41
Page 42

Start-Up
3. Add the total accessory static pressure drop (step 2) to the duct external static pressure (step
1). The sum of these two values represents the total system external static pressure.
4. Measure the amperage at the supply fan contactor and compare it with the full load amp (FLA)
rating stamped on the motor nameplate.
a. Calculate the theoretical BHP.
Actual Motor Amps X Motor HP
Motor Nameplate Amps
b. Using the fan performance tables in the unit Service Facts, plot the total external static
pressure (step 3) and the BHP (step 4a) to obtain the operating CFM.
c. When plotted, if the two values can not be interpolated correspondingly, the static pressure
will most likely be the least accurate measurement. Because of the direct drive motor
operation, the RPM performance is relatively constant making the operating current a very
reliable diagnostic tool.
Example: W_D060 single phase, low speed.
Actual Motor Amp (5.25) = .99%
Motor Nameplate Amps (5.3)
0.99 X Motor HP (0.6) = .59 BHP
The actual external static pressure is approximately 0.45" w.c., airflow equals 2100 CFM.
If the static pressure reading was higher, motor current would have to be lower proportionately to
get an accurate CFM measurement in direct drive applications.
5. If the required CFM is too low, (external static pressure is high causing motor HP output to be
below table value),
a. Relieve supply and/or return duct static.
b. Change indoor fan speed to "High" and repeat steps 1 through 4.
6. If the required CFM is too high, (external static pressure is low causing motor HP output to be
above table value), increase supply and/or return duct static.
7. To stop the SERVICE TEST, turn the main power disconnect switch to the "Off" position or
proceed to the next component start-up procedure.
Verifying Proper Air Flow (Units with Belt Drive Indoor Fan)
Much of the systems performance and reliability is closely associated with, and dependent upon
having the proper airflow supplied both to the space that is being conditioned and across the
evaporator coil.
The indoor fan speed is changed by opening or closing the adjustable motor sheave.
Before starting the SERVICE TEST, set the minimum position setpoint for the economizer to 0
percent using the setpoint potentiometer located on the Economizer Control
(ECA), if applicable.
ReliaTel Control
Using the Service Test Guide in Ta bl e 7 , momentarily jump across the Test 1 & Test 2 terminals on
LTB1 one time to start the Minimum Ventilation Test.
Once the supply fan has started, check for proper rotation. The direction of rotation is indicated by
an arrow on the fan housing.
With the fan operating properly, determine the total system airflow (CFM) by;
1. Measuring the actual RPM,
42 RT-SVX23D-EN
Page 43

Start-Up
2. Measure the amperage at the supply fan contactor and compare it with the full load amp (FLA)
rating stamped on the motor nameplate.
a. a. Calculate the theoretical BHP
Actual Motor Amps X Motor HP
Motor Nameplate Amps
b. Using the fan performance tables in the unit Service Facts, plot the actual RPM (step 1) and
the BHP (step 2a) to obtain the operating CFM.
3. If the required CFM is too low, (external static pressure is high causing motor HP output to be
below table value),
a. Relieve supply and/or return duct static.
b. Change indoor fan speed and repeat steps 1 and 2.
• To Increase Fan RPM; Loosen the pulley adjustment set screw and turn sheave clockwise.
• To Decrease Fan RPM; Loosen the pulley adjustment set screw and turn sheave
counterclockwise.
• If the required CFM is too high, (external static pressure is low causing motor HP output to be
above table value), change indoor fan speed and repeat steps 1 and 2.
• To stop the SERVICE TEST, turn the main power disconnect switch to the "Off" position or
proceed to the next component start-up procedure.
Verifying Proper Air Flow (Units with 5-Tap Direct Drive Indoor Fan)
Much of the systems performance and reliability is closely associated with, and dependent upon
having the proper airflow supplied both to the space that is being conditioned and across the
evaporator coil.
The indoor fan motor is factory wired to operate on speed tap 1 in the cooling and heating mode
for electric/electric units. For Gas/Electric units, the motor is factory wired to operate on speed tap
1 during cooling. For 3 & 4 ton Gas/Electric units operating in heat mode, the minimum setting is
Tap 4. For these units, a separate tap terminal is provided to change speeds automatically between
heating and cooling. The motor can be rewired for different speed settings should the application
require it. Refer to the wiring diagram that shipped in the unit and the unit fan performance tables
in the Service Facts.
The indoor fan motors are specifically designed to operate within the BHP parameters listed in the
fan performance tables of the unit Service Facts.
When verifying direct drive fan performance, the tables must be used somewhat differently than
those of belt driven fans. Fan performance diagnostics can be easily recognized when these tables
are used correctly.
Before starting the SERVICE TEST, set the minimum position setpoint for the economizer to 0
percent using the setpoint potentiometer located on the Economizer Control (ECA), if applicable.
ReliaTel Control
Using the Service Test Guide in Table 5, momentarily jump across the Test 1 & Test 2 terminals on
LTB1 one time to start the Minimum Ventilation Test.
With the fan operating properly, determine the total system external static pressure (inches w.c.)
by the following method:
1. Measure the supply and return duct static pressure and sum the resulting absolute values,
2. Use the accessory pressure drop table in the Service Facts, to calculate the total static pressure
drop for all of the accessories installed on the unit; i.e., curb, economizer, etc.
Note: Accessory static pressure drop is based on desired CFM and may not be actual static
pressure drop.
RT-SVX23D-EN 43
Page 44

Start-Up
3. Add the total accessory static pressure drop (step 2) to the duct external static pressure (step
1). The sum of these two values represents the total system external static pressure.
Using the Fan Performance Tables in the Service Facts, look up the selected speed tap setting and
match the measured ESP to determine the approximate CFM.
If the required CFM is too low, (external static pressure is high) do one or both of the following and
repeat procedure:
• Relieve supply and/or return duct static.
• Change indoor fan speed tap to a higher value
If the required CFM is too high, (external static pressure is low), do one or both of the following and
repeat procedure:
• Increase supply and/or return duct static.
• Change indoor fan speed tap to a lower value.
Note: Minimum setting for units with Gas or Electric Heat is 320 CFM per Ton. For 3 & 4 Ton Gas
Heat units operating in heating mode the heat speed set cannot be lower than Speed Set 4.
4. To stop the SERVICE TEST, turn the main power disconnect switch to the "Off" position or
proceed to the next component start-up procedure.
Return Air Smoke Detector
The return air smoke detector is designed to shut off the unit if smoke is sensed in the return air
stream. Sampling the airflow entering the unit at the return air opening performs this function.
In order for the smoke detector to properly sense smoke in the return air stream, the air velocity
entering the unit must be between 500 and 4000 feet per minute. Equipment covered in this manual
will develop an airflow velocity that falls within these limits over the entire airflow range specified
in the evaporator fan performance tables.
There are certain models however, if operated at low airflow, will not develop an airflow velocity
that falls within the required 500 to 4000 feet per minute range. For these models, the design airflow
shall be greater than or equal to the minimum CFM specified in the table provided below. Failure
to follow these instructions will prevent the smoke detector from performing its design function.
Economizer Start-Up ReliaTel Control
WARNING
Rotating Components!
During installation, testing, servicing and troubleshooting of this product it may be necessary to
measure the speed of rotating components. Have a qualified or licensed service individual who
has been properly trained in handling exposed rotating components, perform these tasks.
Failure to follow all safety precautions when exposed to rotating components could result in
death or serious injury.
Using the Service Test Guide in Ta bl e 7 , momentarily jump across the Test 1 & Test 2 terminals on
LTB1 one time to start the Minimum Ventilation Test.
1. Set the minimum position setpoint for the economizer to the required percentage of minimum
ventilation using the setpoint potentiometer located on the Economizer Control (ECA).
The economizer will drive to its minimum position setpoint, exhaust fans (if applicable) may
start at random, and the supply fan will start when the SERVICE TEST is initiated.
The Exhaust Fan will start anytime the economizer damper position is equal to or greater than
the exhaust fan setpoint.
2. Verify that the dampers stroked to the minimum position.
3. ReliaTel Control
44 RT-SVX23D-EN
Page 45

Momentarily jump across the Test 1 & Test 2 terminals on LTB1 one additional time if continuing
from previous component start-up or until the desired start-up component Test is started.
4. Verify that the dampers stroked to the full open position.
5. To stop the SERVICE TEST, turn the main power disconnect switch to the “Off” position or
proceed to the next component start-up procedure.
Compressor Start-Up
Using the Service Test Guide in Ta bl e 7 , continue the SERVICE TEST start-up procedure for each
compressor circuit.
1. Attach a set of service gauges onto the suction and discharge gauge ports for each circuit. Refer
to the refrigerant circuit illustration in the Service Facts.
2. Momentarily jump across the Test 1 & Test 2 terminals on LTB one additional time if continuing
from previous component start-up or until the desired start-up component Test is started.
Scroll Compressors
a. Once each compressor has started, verify that the rotation is correct. If a scroll compressor
b. If the electrical phasing is correct, before condemning a compressor, interchange any two
3. After the compressor and condenser fan have started and operated for approximately 30
minutes, observe the operating pressures. Compare the operating pressures to the operating
pressure curve in the Service Facts.
4. Check system superheat. Follow the instruction listed on the superheat charging curve in the
Service Facts.
Superheat should be within ±5 F of the superheat chart value.
5. Repeat steps 1 through 4 for each refrigerant circuit.
6. To stop the SERVICE TEST, turn the main power disconnect switch to the “Off” position or
proceed to the next component start-up procedure.
Start-Up
is rotating backwards, it will not pump and a loud rattling sound can be observed.
leads (at the compressor Terminal block) to check the internal phasing. If the compressor
runs backward for an extended period (15 to 30 minutes), the motor winding can overheat
and cause the motor winding thermostat to open.
Heating Start-Up
Using the Service Test Guide in Ta bl e 7 , continue the SERVICE TEST start-up procedure for each
compressor circuit.
1. Clamp an amp meter around one of 1st stage heater power wires at the heater contactor.
2. Momentarily jump across the Test 1 & Test 2 terminals on LTB one additional time if continuing
from previous component start-up or until the desired start-up component Test is started.
3. Verify that the heater stage is operating properly.
4. Clamp an amp meter around one of 2nd stage heater power wires at the heater contactor (if
applicable).
5. Momentarily jump across the Test 1 & Test 2 terminals on LTB one additional time if continuing
from previous component start-up or until the desired start-up component Test is started.
6. Verify that the heater stage is operating properly.
7. To stop the SERVICE TEST, turn the main power disconnect switch to the “Off” position or
proceed to the next component start-up procedure.
RT-SVX23D-EN 45
Page 46

Start-Up
Final System Setup
After completing all of the pre-start and start-up procedures outlined in the previous sections (i.e.,
operating the unit in each of its Modes through all available stages of cooling & heating), perform
these final checks before leaving the unit:
• Program the Night Setback (NSB) panel (if applicable) for proper unoccupied operation. Refer
to the programming instructions for the specific panel.
• Verify that the Remote panel “System” selection switch, “Fan” selection switch, and “Zone
Temperature” settings for automatic operation are correct.
• Inspect the unit for misplaced tools, hardware, and debris.
• Verify that all exterior panels including the control panel doors and condenser grilles are
secured in place.
• Close the main disconnect switch or circuit protector switch that provides the supply power to
the unit’s terminal block or the unit mounted disconnect switch.
Make sure all personnel are standing clear of the unit before proceeding. The system components
will start when the power is applied.
Fan Belt Adjustment - Belt Drive Units
WARNING
Live Electrical Components!
During installation, testing, servicing and troubleshooting of this product, it may be necessary
to work with live electrical components. Have a qualified licensed electrician or other individual
who has been properly trained in handling live electrical components perform these tasks.
Failure to follow all electrical safety precautions when exposed to live electrical components
could result in death or serious injury.
WARNING
Rotating Components!
Disconnect all electric power, including remote disconnects before servicing. Follow proper
lockout/tagout procedures to ensure the power can not be inadvertently energized. Failure to
disconnect power before servicing could result in death or serious injury.
The fan belts must be inspected periodically to assure proper unit operation.
Replacement is necessary if the belts appear frayed or worn. Units with dual belts require a
matched set of belts to ensure equal belt length.
When removing or installing the new belts, do not stretch them over the sheaves. Loosen the belts
using the belt tension adjustment bolts on the motor mounting base.
Once the new belts are installed, using a Browning or Gates tension gauge (or equivalent)
illustrated in Figure 29; adjust the belt tension as follows;
1. To determine the appropriate belt deflection;
a. Measure the center-to-center shaft distance (in inches) between the fan and motor sheaves.
b. Divide the distance measured in Step 1a by 64; the resulting value represents the amount
of belt deflection that corresponds to the proper belt tension.
2. Set the large O-ring on the belt tension gauge at the deflection value determined in Step 1b.
3. Set the small O-ring at zero on the force scale of the gauge plunger.
4. Place the large end of the gauge at the center of the belt span; then depress the gauge plunger
until the large O-ring is even with the top of the next belt or even with a straightedge placed
across the fan and motor sheaves. Refer to Figure 29
46 RT-SVX23D-EN
Page 47

Start-Up
5. Remove the belt tension gauge. The small O-ring now indicates a number other than zero on
the plunger’s force scale. This number represents the force (in pounds) required to give the
needed deflection.
6. Compare the “force” scale reading (Step 5) with the appropriate “force” value listed in Ta ble 8 .
If the “force” reading is outside the range, readjust the belt tension.
Note: Actual belt deflection “force” must not exceed the maximum “force” value shown in
7. Recheck the belt tension at least twice during the first 2 to 3 days of operation. Belt tension may
decrease until the new belts are “run in”.
Figure 29. Belt tension gauge
Table 8. Belt tension measurement and deflection ranges
Deflection Force (Lbs.)
Belts
Cross
Section
A
B
Small P.D
Range
3.0 - 3.6 3 4 1/2 3 7/8 5 1/2 3 1/4 4
3.8 - 4.8 3 1/2 5 4 1/2 6 1/4 3 3/4 4 3/4
5.0 - 7.0 4 5 1/2 5 6 7/8 4 1/4 5 1/4
3.4 - 4.2 4 5 1/2 5 3/4 8 4 1/2 5 1/2
4.4 - 5.6 5 1/8 7 1/8 6 1/2 9 1/8 5 3/4 7 1/4
5.8 - 8.8 6 3/8 8 3/4 7 3/8 10 1/8 7 8 3/4
Super Gripbelts Gripnotch
Min. Max. Min. Max. Min. Max
RT-SVX23D-EN 47
Steel Cable
Gripbelts
Page 48

Maintenance
Monthly Maintenance
Before completing the following checks, turn the unit OFF and lock the main power disconnect
switch open.
WARNING
Rotating Components!
Disconnect all electric power, including remote disconnects before servicing. Follow proper
lockout/tagout procedures to ensure the power can not be inadvertently energized. Failure to
disconnect power before servicing could result in death or serious injury.
Failure to disconnect power before servicing can cause severe personal injury or death.
Filters
• Inspect the return air filters. Clean or replace them if necessary. Refer to the unit Service Facts
for filter information.
Return Air Smoke Detector Maintenance
Airflow through the unit is affected by the amount of dirt and debris accumulated on the indoor coil
and filters. To insure that airflow through the unit is adequate for proper sampling by the return
air smoke detector, complete adherence to the maintenance procedures, including recommended
intervals between filter changes, and coil cleaning is required.
Periodic checks and maintenance procedures must be performed on the smoke detector to insure
that it will function properly. For detailed instructions concerning these checks and procedures,
refer to the appropriate section(s) of the smoke detector Installation and Maintenance Instructions
provided with the literature package for this unit.
Cooling Season
• Check the unit’s drain pans and condensate piping to ensure that there are no blockages.
• Inspect the evaporator and condenser coils for dirt, bent fins, etc. If the coils appear dirty, clean
them according to the instructions described in “Coil Cleaning” later in this section.
• Manually rotate the condenser fan(s) to ensure free movement and check motor bearings for
wear. Verify that all of the fan mounting hardware is tight.
• Inspect the F/A-R/A damper hinges and pins to ensure that all moving parts are securely
mounted. Keep the blades clean as necessary.
• Verify that all damper linkages move freely; lubricate with white grease, if necessary.
• Check supply fan motor bearings; repair or replace the motor as necessary.
• Check the fan shaft bearings for wear. Replace the bearings as necessary.
• Check the supply fan belt. If the belt is frayed or worn, replace it. Refer to the “Fan Belt
Adjustment” section for belt replacement and adjustments.
• Verify that all wire terminal connections are tight.
• Remove any corrosion present on the exterior surfaces of the unit and repaint these areas.
• Generally inspect the unit for unusual conditions (e.g., loose access panels, leaking piping
connections, etc.).
• Make sure that all retaining screws are reinstalled in the unit access panels once these checks
are complete.
• With the unit running, check and record the: ambient temperature; compressor suction and
discharge pressures (each circuit); superheat (each circuit);
48 RT-SVX23D-EN
Page 49

Heating Season
Coil Cleaning
Maintenance
Record this data on an “operator’s maintenance log” like the one shown in Tab l e 9 . If the operating
pressures indicate a refrigerant shortage, measure the system superheat. For guidelines, refer to
the “Compressor Start-Up” section.
Note: Do Not release refrigerant to the atmosphere! If adding or removing refrigerant is required,
the service technician must comply with all federal, state and local laws.
• Inspect the unit’s air filters. If necessary, clean or replace them.
• Check supply fan motor bearings; repair or replace the motor as necessary.
• Inspect both the main unit control panel and heat section control box for loose electrical
components and terminal connections, as well as damaged wire insulation. Make any
necessary repairs.
• Verify that the electric heat system operates properly.
Regular coil maintenance, including annual cleaning, enhances the unit’s operating efficiency by
minimizing: compressor head pressure and amperage draw; evaporator water carryover; fan brake
horsepower, due to increase static pressure losses; airflow reduction.
At least once each year, or more often if the unit is located in a “dirty” environment, clean the
evaporator and condenser coils using the instructions outlined below. Be sure to follow these
instructions as closely as possible to avoid damaging the coils.
Note: For units equipped with hail guards follow removal procedure listed below.
Hail Guard Removal
Figure 30. Slide-style and ball-style latches
HAIL GUARD
• Unlatch hail guards.
• Pull the top of the hail guard outward until the fastener studs are free of the retaining nuts.
• Lift the hail guard from the lower retaining bracket and set aside.
To clean refrigerant coils, use a soft brush and a sprayer (either a garden pump-up type or a highpressure sprayer). A high-quality detergent is also required; suggested brands include “SPREX
A.C.”, “OAKITE 161”, “OAKITE 166” and “COILOX”. If the detergent selected is strongly alkaline (ph
value exceeds 8.5), add an inhibitor.
RT-SVX23D-EN 49
Page 50

Maintenance
WARNING
Hazardous Chemicals!
Coil cleaning agents can be either acidic or highly alkaline. Handle chemical carefully. Proper
handling should include goggles or face shield, chemical resistant gloves, boots, apron or suit as
required. For personal safety refer to the cleaning agent manufacturer’s Materials Safety Data
Sheet and follow all recommended safe handling practices. Failure to follow all safety
instructions could result in death or serious injury.
1. Remove enough panels from the unit to gain access to the coil.
2. Protect all electrical devices such as motors and controllers from any over spray.
3. Straighten any bent coil fins with a fin comb.
4. Mix the detergent with water according to the manufacturer’s instructions. If desired, heat the
solution to 150°F maximum to improve its cleansing capability.
WARNING
Hazardous Pressures!
Coils contain refrigerant under pressure. When cleaning coils, maintain coil cleaning solution
temperature under 150°F to avoid excessive pressure in the coil. Failure to follow these safety
precautions could result in coil bursting, which could result in death or serious injury.
Do not heat the detergent-and-water solution above 150°F. Hot liquids sprayed on the exterior of
the coil will raise the coil’s internal pressure and may cause it to burst. Failure to follow proper
procedures can result in personal illness or injury or severe equipment damage.
5. Pour the cleaning solution into the sprayer. If a high-pressure sprayer is used:
a. do not allow sprayer pressure to exceed 600 psi.
b. the minimum nozzle spray angle is 15 degrees.
c. maintain a minimum clearance of 6" between the sprayer nozzle and the coil.
d. spray the solution perpendicular (at 90 degrees) to the coil face.
6. Spray the leaving-airflow side of the coil first; then spray the opposite side of the coil. Allow the
cleaning solution to stand on the coil for five minutes.
7. Rinse both sides of the coil with cool, clean water.
8. Inspect both sides of the coil; if it still appears to be dirty, repeat Steps 6 and 7.
9. Reinstall all of the components and panels removed in Step 1 and any protective covers
installed in step 2.
Note: For units equipped with hail guards follow reinstallation procedure listed below.
Hail Guard Reinstallation
To reinstall the hail guard, locate the bottom of the hail guard in the lower bracket and secure it to
the upper unit bracket with the attached fasteners.
Note: Secure hail guard latches.
50 RT-SVX23D-EN
Page 51

Final Process
For future reference, you may find it helpful to record the unit data requested below in the blanks
provided.
Complete Model Number
_________________________________________________________________________
Unit Serial Number
_________________________________________________________________________
Wiring Diagram Numbers (from unit control panel)
_________________________________________________________________________
Schematics
_________________________________________________________________________
Connections
_________________________________________________________________________
Table 9. Sample maintenance log
Refrigerant Circuit #1 Refrigerant Circuit #2
Suct.
Press.
Psig/
kPa
Date
Current
Ambient
Temp. F/C
Compr.
Oil Level
- ok
- low
- ok
- low
- ok
- low
- ok\
- low
- ok
- low
- ok
- low
- ok
- low
- ok
- low
- ok
- low
- ok
- low
- ok
- low
Disch.
Press.
Psig/
kPa
Liquid
Press.
Psig/
kPa
Super
-heat
F/C
Subcool.
F/C
Compr.
Oil
Level
- ok
- low
- ok
- low
- ok
- low
-- ok
- low
- ok
- low
- ok
- low
- ok
- low
- ok
- low
- ok
- low
- ok
- low
- ok
- low
Suct.
Press.
Psig/kPa
Disch.
Press.
Psig/
kPa
Maintenance
Liquid
Press.
Psig/
kPa
Superheat
F/C
Subcool.
F/C
RT-SVX23D-EN 51
Page 52

Trouble Shooting
The RTRM has the ability to provide the service personnel with some unit diagnostics and system
status information.
Before turning the main power disconnect switch “Off”, follow the steps below to check the ReliaTel
Refrigeration Module (RTRM). All diagnostics & system status information stored in the RTRM will
be lost when the main power is turned “Off”.
WARNING
Live Electrical Components!
During installation, testing, servicing and troubleshooting of this product, it may be necessary
to work with live electrical components. Have a qualified licensed electrician or other individual
who has been properly trained in handling live electrical components perform these tasks.
Failure to follow all electrical safety precautions when exposed to live electrical components
could result in death or serious injury.
To prevent injury or death from electrocution, it is the responsibility of the technician to
recognize this hazard and use extreme care when performing service procedures with the
electrical power energized.
1. Verify that the Liteport LED on the RTRM is burning continuously. If the LED is lit, go to Step 3.
2. If the LED is not lit, verify that 24 VAC is presence between J1-1 and J1-2. If 24 VAC is present,
proceed to Step 3. If 24 VAC is not present, check the unit main power supply, check transformer
(TNS1). Proceed to Step 3 if necessary.
3. Utilizing “Method 1” or “Method 2” in the “System Status Diagnostic” section, check the
following:
•System status
• Heating status
• Cooling status
If a System failure is indicated, proceed to Step 4. If no failures are indicated, proceed to Step 5.
4. If a System failure is indicated, recheck Steps 1 and 2. If the LED is not lit in Step 1, and 24 VAC
is present in Step 2, the RTRM has failed. Replace the RTRM.
5. If no failures are indicated, use one of the TEST mode procedures described in the “Unit StartUp” section to start the unit. This procedure will allow you to check all of the RTRM outputs,
and all of the external controls (relays, contactors, etc.) that the RTRM outputs energize, for each
respective mode. Proceed to Step 6.
6. Step the system through all of the available modes, and verify operation of all outputs, controls,
and modes. If a problem in operation is noted in any mode, you may leave the system in that
mode for up to one hour while troubleshooting. Refer to the sequence of operations for each
mode, to assist in verifying proper operation. Make the necessary repairs and proceed to Steps
7 and 8.
7. If no abnormal operating conditions appear in the test mode, exit the test mode by turning the
power “Off” at the main power disconnect switch.
8. Refer to the individual component test procedures if other microelectronic components are
suspect.
System Status Checkout Procedure
“System Status” is checked by using one of the following two methods:
52 RT-SVX23D-EN
Page 53

Method 1
Trouble Shooting
If the Zone Sensor Module (ZSM) is equipped with a remote panel with LED status indication, you
can check the unit within the space. If the ZSM does not have LED’s, use Method 2. BAYSENS110*,
BAYSENS109*, BAYSENS119*, & BAYSENS023A all have the remote panel indication feature. The
LED descriptions are listed below.
LED 1 (System)
“On” during normal operation.
“Off” if a system failure occurs or the LED fails.
“Flashing” indicates test mode.
LED 2 (Heat)
“On” when the heat cycle is operating.
“Off” when the heat cycle terminates or the LED fails.
“Flashing” indicates a heating failure.
LED 3 (Cool)
“On” when the cooling cycle is operating.
“Off” when the cooling cycle terminates or the LED fails.
“Flashing” indicates a cooling failure.
LED 4 (Service)
“On” indicates a clogged filter.
“Off” during normal operation.
“Flashing” indicates an evaporator fan failure
Below is the complete listing of failure indication causes.
System failure
Check the voltage between terminals 6 and 9 on J6, it should read approximately 32 VDC. If no
voltage is present, a System failure has occurred. Refer to Step 4 in the previous section for the
recommended troubleshooting procedure.
Cooling Failure
1. Cooling and heating set point (slide pot) on the zone sensor has failed. Refer to the “Zone
Sensor Test Procedure” section.
2. Zone temperature thermistor ZTEMP on ZTS failed. Refer to the “Zone Sensor Test Procedure”
section.
3. CC1 or CC2 24 VAC control circuit has opened, check CC1 & CC2 coils, and any of the controls
below that apply to the unit (HPC1, HPC2).
4. LPC1 has opened during the 3 minute minimum “on time” during 4 consecutive compressor
starts, check LPC1 or LPC2 by testing voltage between the J1-8 & J3-2 terminals on the RTRM
and ground. If 24 VAC is present, the LPC’s has not tripped. If no voltage is present, LPC’s has
tripped.
Service Failure
1. If the supply fan proving switch has closed, the unit will not operate (when connected to RTOM),
check the fan motor, belts, and proving switch.
2. Clogged filter switch has closed, check the filters.
RT-SVX23D-EN 53
Page 54

Trouble Shooting
Method 2
Simultaneous Heat and Cool Failure
1. Emergency Stop is activated.
The second method for determining system status is done by checking voltage readings at the
RTRM (J6). The system indication descriptions and the approximate voltages are listed below.
System Failure
Measure the voltage between terminals J6-9 & J6-6.
Normal Operation = approximately 32 VDC
System Failure = less than 1 VDC, approximately 0.75 VDC
Test Mode = voltage alternates between 32 VDC & 0.75 VDC
Heat Failure
Measure the voltage between terminals J6-7 & J6-6.
Heat Operating = approximately 32 VDC
Heat Off = less than 1 VDC, approximately 0.75 VDC
Heating Failure = voltage alternates between 32 VDC & 0.75 VDC
Cool Failure
Measure the voltage between terminals J6-8 & J6-6.
Cool Operating = approximately 32 VDC
Cool Off = less than 1 VDC, approximately 0.75 VDC
Cooling Failure = voltage alternates between 32 VDC & 0.75 VDC
Service Failure
Measure the voltage between terminals J6-10 & J6-6.
Clogged Filter = Approximately 32 VDC.
Normal = Less than 1 VDC, approximately 0.75 VDC Fan Failure = voltage alternates between 32
VDC & 0.75 VDC.
To use LED’s for quick status information at the unit, purchase a BAYSENS110* ZSM and connect
wires with alligator clamps to terminals 6 through 10. Connected each respective terminal wire (6
through 10) from the Zone Sensor to the unit J6 terminals 6 through 10.
Note: If the system is equipped with a programmable zone sensor, BAYSENS119* the LED
indicators will not function while the BAYSENS110* is connected.
Resetting Cooling and Heating Lockouts
Cooling Failures and Heating Lockouts are reset in an identical manner. Method 1 explains resetting
the system from the space; Method 2 explains resetting the system at the unit.
Note: Before resetting Cooling Failures and Heating Lockouts check the Failure Status Diagnostics
by the methods previously explained. Diagnostics will be lost when the power to the unit
is disconnected.
Method 1
To reset the system from the space, turn the “Mode” selection switch at the zone sensor to the “Off”
position. After approximately 30 seconds, turn the “Mode” selection switch to the desired mode,
i.e. Heat, Cool or Auto.
54 RT-SVX23D-EN
Page 55

Trouble Shooting
Method 2
To reset the system at the unit, cycle the unit power by turning the disconnect switch “Off” and then
“On”.
Lockouts can be cleared through the building management system. Refer to the building
management system instructions for more information.
Zone Temperature Sensor (ZTS) Service Indicator
The ZSM SERVICE LED is a generic indicator, that will signal the closing of a Normally Open switch
at any time, providing the Indoor Motor (IDM) is operating. This indicator is usually used to indicate
a clogged filter, or an air side fan failure.
The RTRM will ignore the closing of this Normally Open switch for 2 (±1) minutes. This helps
prevent nuisance SERVICE LED indications. The exception is the LED will flash 40 seconds after the
fan is turned “On” if the Fan Proving Switch is not made.
Clogged Filter Switch
This LED will remain lit the entire time that the Normally Open switch is closed. The LED will be
turned off immediately after resetting the switch (to the Normally Open position), or any time that
the IDM is turned “Off”.
If the switch remains closed, and the IDM is turned “On”, the SERVICE LED will be turned “On” again
after the 2 (±1) minute ignore delay.
This LED being turned “On”, will have no other affect on unit operation. It is an indicator only.
Fan Failure Switch
When the “Fan Failure” switch is wired to the RTOM, the LED will remain flashing the entire time
the fan proving switch is closed, indicating a fan failure, and it will shut the unit operations down.
Zone Temperature Sensor (ZTS) Test
Note: These procedures are not for programmable or digital models and are conducted with the
Zone Sensor Module electrically removed from the system.
Test 1 Zone Temperature Thermistor (ZTEMP)
This component is tested by measuring the resistance between terminals 1 and 2 on the Zone
Temperature Sensor. Below are some typical indoor temperatures, and corresponding resistive
values.
Test 2 Cooling Set Point (CSP) and Heating Set Point (HSP)
Table 10. Cooling (CSP) and heating setpoint (HSP)
Zone Temperature
50 F° 10.0 C° 19.9 K-Ohms 889 Ohms
55 F° 12.8 C° 17.47 K-Ohms 812 Ohms
60 F° 15.6 C° 15.3 K-Ohms 695 Ohms
65 F° 18.3 C° 13.49 K-Ohms 597 Ohms
70 F° 21.1 C° 11.9 K-Ohms 500 Ohms
75 F° 23.9 C° 10.50 K-Ohms 403 Ohms
80 F° 26.7 C° 9.3 K-Ohms 305 Ohms
85 F° 29.4 C° 8.25 K-Ohms 208 Ohms
90 F° 32.2 C° 7.3 K-Ohms 110 Ohms
Nominal ZTEMP
Resistance
Nominal CSP or
HSP Resistance
The resistance of these potentiometers are measured between the following ZSM terminals. Refer
to the chart above for approximate resistances at the given setpoints.
RT-SVX23D-EN 55
Page 56

Trouble Shooting
Cool SP = Terminals 2 and 3
Range = 100 to 900 Ohms approximate
Heat SP = Terminals 2 and 5
Range = 100 to 900 Ohms approximate
Test 3 System Mode and Fan Selection
The combined resistance of the Mode selection switch and the Fan selection switch can be
measured between terminals 2 and 4 on the Zone Sensor. The possible switch combinations are
listed below with their corresponding resistance values.
Test 4 LED Indicator Test, (SYS ON, HEAT, COOL & SERVICE)
Method 1
Testing the LED using a meter with diode test function. Test both forward and reverse bias. Forward
bias should measure a voltage drop of 1.5 to 2.5 volts, depending on your meter. Reverse bias will
show an Over Load, or open circuit indication if LED is functional.
Method 2
Testing the LED with an analog Ohmmeter. Connect Ohmmeter across LED in one direction, then
reverse the leads for the opposite direction. The LED should have at least 100 times more resistance
in reverse direction, as compared with the forward direction. If high resistance in both directions,
LED is open. If low in both directions, LED is shorted.
Method 3
To test LED’s with ZSM connected to unit, test voltages at LED terminals on ZSM. A measurement
of 32 VDC, across an unlit LED, means the LED has failed.
Note: Measurements should be made from LED common (ZSM terminal 6 to respective LED
terminal). Refer to the Zone Sensor Module (ZSM) Terminal Identification table at the
beginning of this section.
Programmable & Digital Zone Sensor Test
Testing serial communication voltage
1. Verify 24 VAC is present between terminals J6-14 & J6-11.
2. Disconnect wires from J6-11 and J6-12. Measure the voltage between J6-11 and J6-12, should
be about 32 VDC.
3. Reconnect wires to terminals J6-11 and J6-12. Measure voltage again between J6-11 and J6-12,
voltage should flash high and low every 0.5 seconds. The voltage on the low end will measure
about 19 VDC, while the voltage on the high end will measure from approximately 24 to 38 VDC.
4. Verify all modes of operation, by running the unit through all of the steps in the “Test Modes”
section discussed in “Unit Start-Up”.
5. After verifying proper unit operation, exit the test mode. Turn the fan on continuously at the
ZSM, by pressing the button with the fan symbol. If the fan comes on and runs continuously,
the ZSM is good. If you are not able to turn the fan on, the ZSM is defective.
ReliaTel Refrigeration Module (RTRM) Default Chart
If the RTCI loses input from the building management system, the RTRM will control in the default
mode after approximately 15 minutes. If the RTRM loses the Heating and Cooling setpoint input,
the RTRM will control in the default mode instantaneously. The temperature sensing thermistor in
the Zone Sensor Module is the only component required for the “Default Mode” to operate.
56 RT-SVX23D-EN
Page 57

Unit Operation without a Zone Sensor
This procedure is for temporary operation only. The economizer and condenser fan cycling
functions are disabled.
1. Open and Lock the unit disconnect switch.
2. Remove the Outside Air Sensor (OAS) from the condenser section of unit.
3. Use two (2) wire nuts, to individually cap the wires.
4. Locate the RTRM (J6). Connect two (2) wires to terminals J6-1 and 2.
5. Connect the sensor (OAS) using two wire nuts to the two (2) field supplied wires that were
connected to terminals 1 and 2 on J6.
Unit Economizer Control (ECA) Troubleshooting ReliaTel Control
Verify Economizer Status by Economizer Actuator (ECA) LED indicator:
OFF: No Power or Failure
ON: Normal, OK to Economize
Slow Flash: Normal, Not OK to Economize
Fast Flash - 1/2 Second On / 2 Seconds Off:
Error Code:
Communications Failure
Pulse Flash: 2 Seconds On / 1/2 Second Off:
Error Code:
1 Flash: Actuator Fault
2 Flashes: CO2 Sensor
3 Flashes: RA Humidity Sensor
4 Flashes: RA Temp Sensor
5 Flashes: OA Quality Sensor
6 Flashes: OA Humidity Sensor
7 Flashes: OA Temp Sensor
8 Flashes: MA Temp Sensor
9 Flashes: RAM Fault
10 Flashes: ROM Fault
11 Flashes: EEPROM F
Trouble Shooting
RT-SVX23D-EN 57
Page 58

Wiring Diagrams
Note: For easier access, published unit wiring diagrams (individual, separate diagrams for unitary
product lines) will become available via e-Library instead of through wiring manuals after
2007 . For diagrams prior to 2008 please refer to wiring diagram book W_C-SVE001B-EN for
heat pump units.
Drawing
number Description
4366-1008 Power Schematic - 230v/60hz/1ph 2 - 5 Ton Heat Pump / Standard Drive Motor
4366-1021 Power Schematic - 230v/60hz/3ph 2 - 5 Ton Heat Pump / Direct Drive
4366-1014 Power Schematic - 230v/60hz/3ph 2 - 7.5 Ton Heat Pump / Belt Drive Motor
4366-1036 Power Schematic - 230v/60hz/3ph 10 Ton Heat Pump / Belt Drive Motor
4366-1024 Power Schematic - 2 - 5 Ton Heat Pump / Standard Drive Motor
4366-1010 Power Schematic - 460-575v/60hz/3ph 2 - 7.5 Ton Heat Pump / Belt Drive Motor
4366-1035 Power Schematic - 460-575v/60hz/3ph 10 Ton Heat Pump / Belt Drive Motor
4366-1510 Connection Diagram - 230v/60hz/1ph 2 - 5 Ton Heat Pump
4366-1511 Connection Diagram - 208-230,460,575v/60hz/3ph 2 - 5 Ton Heat Pump / Direct Drive
4366-1512 Connection Diagram - 208-230,460,575v/60hz/3ph 2 - 5 Ton Heat Pump / Belt Drive
4366-1542 Connection Diagram - 208-230,460,575v/60hz/3ph 6 - 7.5 Ton Heat Pump / Belt Drive
4366-1535 Connection Diagram - 208-230,460,575v/60hz/3ph 10 Ton Heat Pump / Belt Drive
4366-1007 Control Schematic - 2 - 7.5 Ton Heat Pump
4366-1043 Control Schematic - 10 Ton Heat Pump
4366-1099 Novar Schematic - 2024
4366-1047 Novar Schematic - 3051
4366-1031 Through The Base Utilities Schematic
4366-1003 CO2 / Ventilation Override Schematics
4366-1091 5.0 KW - 208-240v/60hz/1ph BAYHTRR105A
4366-1092 10.0 KW - 208-240v/60hz/1ph BAYHTRR110A
4366-1093 13.8 KW - 208-240v/60hz/1ph BAYHTRR114A
4366-1098 17.6 KW - 208-240v/60hz/1ph BAYHTRR118A
4366-1096 6.0 KW - 208-600v/60hz/3ph BAYHTRR306A, BAYHTRR406A, BAYHTRRW06A
4366-1084 9.0 & 18.0 KW - 208-240v/60hz/3ph BAYHTRS309A, BAYHTRS318A
4366-1094 12.0 & 17.4 KW - 208-240v/60hz/3ph BAYHTRR312A, BAYHTRR318A
4366-1095 23.0 KW - 208-240v/60hz/3ph BAYHTRR323A
4366-1089 27.0 & 36.0 KW - 208-240v/60hz/3ph BAYHTRS327A, BAYHTRS336A
4366-1086 54.0 KW - 208-240v/60hz/3ph BAYHTRT354A
4366-1097
4366-1087
4366-1089
4366-1090 54.0 KW - 480-600v/60hz/3ph BAYHTRT454A, BAYHTRTW54A
9.0 & 18 KW - 480-600v/60hz/3ph BAYHTRS409A, BAYHTRSW09A, BAYHTRS418A, BAYHTRT418A, BAYHTRSW18A,
BAYHTRTW18A
12.0, 17.4 & 23.0 KW - 480-600v/60hz/3ph BAYHTRR412A, BAYHTRR418A, BAYHTRR423A, BAYHTRRW12A, BAYHTRRW18A,
BAYHTRRW23A
27.0 & 36.0 KW - 480-600v/60hz/3ph BAYHTRS427A, BAYHTRT427A, BAYHTRSW27A, BAYHTRTW27A, BAYHTRS436A,
BAYHTRT436A, BAYHTRSW36A, BAYHTRTW36A
58 RT-SVX23D-EN
Page 59

Limited Warranty
Heat Pump WCC, WCD, WCH, WCM and WSC (Parts Only)
Models Less Than 20 Tons for Residential Use*
This limited warranty is extended by Trane Inc., to the original purchaser and to any succeeding
owner of thereal property to which the Heat Pump is originally affixed, and applies to products
purchased and retained for use within the U.S.A. and Canada.
If any part of your Heat Pump fails because of a manufacturing defect within five years from the
date of the original purchase, Warrantor will furnish without charge the required replacement part.
Any local transportation, related service labor, diagnosis calls, refrigerant and related items are not
included.
If the sealed motor-compressor fails because of a manufacturing defect within five years from the
date of original purchase, Warrantor will furnish without charge the required replacement
compressor. Any local transportation, related service labor, diagnosis calls, refrigerant and related
items are not included.
This limited warranty does not cover failure of your Heat Pump if it is damaged while in your
possession, failure attributable or caused by unreasonable use of the Heat Pump and/or failure to
properly maintain the Heat Pump as set forth in the Use and Care manual.
This limited warranty applies to product installed on or after 10/1/2001 where product is
manufactured after 1/1/2000. This limited warranty is not retroactive to any installations prior to 10/
1/2001 or on product produced prior to 2000.
THE LIMITED WARRANTY AND LIABILITY SET FORTH HEREIN ARE IN LIEU OF ALL OTHER
WARRANTIES AND LIABILITIES, WHETHER IN CONTRACT OR IN NEGLIGENCE, EXPRESS OR
IMPLIED, IN LAW OR IN FACT, INCLUDING IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND
FITNESS FOR PARTICULAR USE, AND IN NO EVENT SHALL WARRANTOR BE LIABLE FOR ANY
INCIDENTAL OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES.
Some states do not allow limitations on how long an implied limited warranty lasts or do not allow
the exclusion or limitation of incidental or consequential damages, so the above limitation or
exclusion may not apply to you.
This limited warranty gives you specific legal rights, and you may also have other rights which vary
from state to state. Parts will be provided by our factory organization through an authorized service
organization in your area listed in the yellow pages. If you wish further help or information
concerning this limited warranty, contact:
Trane.
2701 Wilma Rudolph Blvd.
Clarksville, TN 37040-1008
Attention: Manager, Product Service
GW-611-4001
* This limited warranty is for residential usage of this equipment and not applicable when this
equipment is used for a commercial application. A commercial use is any application where the end
purchaser uses the product for other than personal, family or household purposes.
RT-SVX23D-EN 59
Page 60

Limited Warranty
Heat Pump WCZ, WCY, WCX, WCC, WCD, WCH, WCM, WCP and WSC (Parts Only)
Models Less Than 20 Tons for Commercial Use*
This warranty is extended by Trane Inc., to the original purchaser and to any succeeding owner of
the real property to which the Heat Pump is originally affixed, and applies to products purchased
and retained for use within the U.S.A. and Canada. There is no warranty against corrosion, erosion
or deterioration.
If any part of your Heat Pump fails because of a manufacturing defect within one year from the date
of the original purchase, Warrantor will furnish without charge the required replacement part.
In addition, if the sealed motor-compressor fails because of a manufacturing defect within the
second through fifth year from the date of original purchase, Warrantor will furnish without charge
the required replacement compressor. Warrantor’s obligations and liabilities under this warranty
are limited to furnishing F.O.B. Warrantor factory or warehouse replacement parts for Warrantor’s
products covered under this warranty. Warrantor shall not be obligated to pay for the cost of lost
refrigerant. No liability shall attach to Warrantor until products have been paid for and then liability
shall be limited solely to the purchase price of the equipment under warranty shown to be
defective.
THE WARRANTY AND LIABILITY SET FORTH HEREIN ARE IN LIEU OF ALL OTHER WARRANTIES
AND LIABILITIES, WHETHER IN CONTRACT OR IN NEGLIGENCE, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, IN LAW
OR IN FACT, INCLUDING IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR
PARTICULAR USE, AND IN NO EVENT SHALL WARRANTOR BE LIABLE FOR ANY INCIDENTAL OR
CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES.
Some states do not allow limitations on how long an implied warranty lasts or do not allow the
exclusion or limitation of incidental or consequential damages, so the above limitation or exclusion
may not apply to you. This warranty gives you specific legal rights, and you may also have other
rights which vary from state to state.
Trane.
2701 Wilma Rudolph Blvd.
Clarksville, TN 37040-1008
Attention: Manager, Product Service
GW-604-4800
* This warranty is for commercial usage of said equipment and not applicable when the equipment
is used for a residential application. Commercial use is any application where the end purchaser
uses the product for other than personal, family or household purposes.
60 RT-SVX23D-EN
Page 61

Page 62

Page 63

Page 64

Literature Order Number RT-SVX23D-EN
Date February 2009
Supersedes RT-SVX23D-EN (December 2008)
The manufacturer has a policy of continuous product and product data improvement and reserves
the right to change design and specifications without notice.
 Loading...
Loading...