Trane SEHJ090-162, SSHJ090-162, SFHJ090-162, SXHJ090-162, SLHJ090-162 Installation and Maintenance Manual
Installation, Operation,
and Maintenance
IntelliPak™ II
Commercial Single-Zone Rooftop Air Conditioners
with CV, VAV, SZVAV, or RR Controls
“F0” and later design sequence
SEHJ090-162 SSHJ090-162
SFHJ090-162 SXHJ090-162
SLHJ090-162
SAFETY WARNING
Only qualified personnel should install and service the equipment. The installation, starting up, and servicing
of heating, ventilating, and air-conditioning equipment can be hazardous and requires specific knowledge and
training. Improperly installed, adjusted or altered equipment by an unqualified person could result in death or
serious injury.When working on the equipment, observe all precautions in the literature and on the tags,
stickers, and labels that are attached to the equipment.
November 2014
RT-SVX24K-EN
Introduction
Read this manual thoroughly before operating or servicing
this unit.
Warnings, Cautions, and Notices
Safety advisories appear throughout this manual as
required.Your personal safety and the proper operation of
this machine depend upon the strict observance of these
precautions.
The three types of advisories are defined as follows:
WARNING
Proper Field Wiring and Grounding
Required!
Failure to follow code could result in death or serious
injury. All field wiring MUST be performed by qualified
personnel. Improperly installed and grounded field
wiring poses FIRE and ELECTROCUTION hazards. To
avoid these hazards, you MUST follow requirements for
field wiring installation and grounding as described in
NEC and your local/state electrical codes.
WARNING
CAUTIONs
NOTICE
Indicates a potentially hazardous
situation which, if not avoided, could
result in death or serious injury.
Indicates a potentially hazardous
situation which, if not avoided, could
result in minor or moderate injury. It
could also be used to alert against
unsafe practices.
Indicates a situation that could result in
equipment or property-damage only
accidents.
Important Environmental Concerns
Scientific research has shown that certain man-made
chemicals can affect the earth’s naturally occurring
stratospheric ozone layer when released to the
atmosphere. In particular, several of the identified
chemicals that may affect the ozone layer are refrigerants
that contain Chlorine, Fluorine and Carbon (CFCs) and
those containing Hydrogen, Chlorine, Fluorine and
Carbon (HCFCs). Not all refrigerants containing these
compounds have the same potential impact to the
environment.Trane advocates the responsible handling of
all refrigerants-including industry replacements for CFCs
such as HCFCs and HFCs.
Important Responsible Refrigerant
Practices
Trane believes that responsible refrigerant practices are
important to the environment, our customers, and the air
conditioning industry. All technicians who handle
refrigerants must be certified.The Federal Clean Air Act
(Section 608) sets forth the requirements for handling,
reclaiming, recovering and recycling of certain
refrigerants and the equipment that is used in these
service procedures. In addition, some states or
municipalities may have additional requirements that
must also be adhered to for responsible management of
refrigerants. Know the applicable laws and follow them.
WARNING
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
Required!
Installing/servicing this unit could result in exposure to
electrical, mechanical and chemical hazards.
• Before installing/servicing this unit, technicians
MUST put on all PPE required for the work being
undertaken (Examples; cut resistant gloves/sleeves,
butyl gloves, safety glasses, hard hat/bump cap, fall
protection, electrical PPE and arc flash clothing).
ALWAYS refer to appropriate Material Safety Data
Sheets (MSDS)/Safety Data Sheets (SDS) and OSHA
guidelines for proper PPE.
• When working with or around hazardous chemicals,
ALWAYS refer to the appropriate MSDS/SDS and
OSHA/GHS (Global Harmonized System of
Classification and Labelling of Chemicals) guidelines
for information on allowable personal exposure
levels, proper respiratory protection and handling
instructions.
• If there is a risk of energized electrical contact, arc, or
flash, technicians MUST put on all PPE in accordance
with OSHA, NFPA 70E, or other country-specific
requirements for arc flash protection, PRIOR to
servicing the unit. NEVER PERFORM ANY
SWITCHING, DISCONNECTING, OR VOLTAGE
TESTING WITHOUT PROPER ELECTRICAL PPE AND
ARC FLASH CLOTHING. ENSURE ELECTRICAL
METERS AND EQUIPMENT ARE PROPERLY RATED
FOR INTENDED VOLTAGE.
Failure to follow instructions could result in death or
serious injury.
About the Manual
Note: This document is customer property and must be
retained by the unit owner for use by maintenance
personnel.
These units are equipped with electronic Unit Control
Modules (UCM). Refer to the “Startup” and “Test Mode”
procedures within this Installation, Operation, and
© 2014Trane All rights reserved RT-SVX24K-EN

Introduction
Maintenance manual and the latest edition of the
appropriate programming manual for Constant Volume
(CV), Rapid Restart (RR), Variable Air Volume (VAV), or
Single Zone Variable Air Volume (SZ VAV) applications
before attempting to operate or service this equipment.
Note: The procedures discussed in this manual should
only be performed by qualified and experienced
HVAC technicians.
Overview of Manual
This booklet describes proper installation, startup,
operation, and maintenance procedures for 90 to 162 ton
rooftop air conditioners designed for CV, RR, VAV, or SZ
VAV applications. By carefully reviewing the information
within this manual and following the instructions, the risk
of improper operation and/or component damage will be
minimized.
Note: One copy of the appropriate service literature ships
inside the control panel of each unit.
It is important that periodic maintenance be performed to
help assure trouble free operation. Should equipment
failure occur, contact a qualified service organization with
qualified, experienced HVAC technicians to properly
diagnose and repair this equipment.
Note: Do Not release refrigerant to the atmosphere!
If adding or removing refrigerant is required, the service
technician must comply with all federal, state, and local
laws.
Copyright
This document and the information in it are the property of
Trane, and may not be used or reproduced in whole or in
part without written permission. Trane reserves the right
to revise this publication at any time, and to make changes
to its content without obligation to notify any person of
such revision or change.
Trademarks
All trademarks referenced in this document are the
trademarks of their respective owners.
Revision History
RT-SVX24K-EN (November 2014)
Updated the IOM with Ultra-Low Leak, AMCA 1A damper
and FDD.These features are Design Specials only.
RT-SVX24K-EN 3

Table of Contents
Introduction ............................. 2
Warnings, Cautions, and Notices ........ 2
Model Number Descriptions .............. 6
Unit Inspection .......................... 9
As soon as the unit arrives at the job site 9
Storage ............................ 9
Unit Clearances ..................... 9
Unit Dimensions and Weight Information 9
General Information .................... 10
Unit Nameplate ...................... 10
Commonly Used Acronyms ............ 10
Unit Description ...................... 10
Constant Volume (CV) and Variable Air
Volume (VAV) Units
................... 13
Constant Volume (CV) Units ........... 17
Variable Air Volume (VAV) Units ........ 17
Single Zone Variable Air Volume (SZVAV)
Only
................................ 20
Unit Clearances ......................... 23
Dimensional Data ....................... 25
Weights ................................ 44
Installation ............................. 47
Roof Curb and Ductwork ............. 47
Field Converting Horizontal Ductwork
(Supply or Return) from Right to
Left Side .......................... 49
Unit Rigging and Placement ........... 51
Air-Cooled and Evaporative Condensers—
Three-Piece Unit Fit Up .............. 54
Air-Cooled and Evaporative Condensers—
Two-Piece Unit Fit Up ............... 58
Complete Tubing and Wiring
Connections as follows: .............. 61
Air-Cooled Tubing Connection ........ 61
Evaporative Condenser Tubing
Connection ........................ 62
Electric Heat Wiring Connection ....... 63
Power and Control Wiring Connections . 63
General Unit Requirements ........... 64
Rigging the Unit .................... 65
Main Electrical Power Requirements ....65
Field Installed Control Wiring ..........65
Requirements for Electric Heat Units ....65
Requirement for Gas Heat .............65
Requirements for Hot Water Heat ......65
Requirements for Steam Heat ..........65
O/A Pressure Sensor and Tubing
Installation .........................65
Condensate Drain Connections ........65
Units with Gas Furnace ...............66
Removing Compressor Assembly
Shipping Hardware ..................66
Removing Supply and Exhaust Fan
Shipping Channels ...................66
Spring Isolators .....................66
Remove Evaporative Condenser Fan
Shipping Brackets ...................66
O/A Sensor and Tubing Installation .....68
Units with Statitrac: ..................68
Evaporative-Cooled Condenser Make-up
Water and Drain Line Installation .......69
Gas Heat Units ......................70
Disconnect Switch w/External Handle . . .78
Electric Heat Units ...................78
Main Unit Power Wiring ..............79
Power Wire Sizing and Protection Devices 81
Field Installed Control Wiring ..........83
Controls using 24 VAC ................83
Controls using DC Analog Input/Outputs .83
Constant Volume System Controls ......84
Variable Air Volume System Controls . . .84
Constant Volume or Variable Air Volume
System Controls .....................84
Single Zone Variable Air Volume & Rapid
Restart System Control ...............85
Emergency Override .................85
Ventilation Override Module (VOM) .....86
Temperature vs. Resistance Coefficient . .87
Installation Checklist .....................95
General Checklist (applies to all units) . . .95
4 RT-SVX24K-EN

Table of Contents
Unit Rigging and Placement (Two-Piece—
addition to General Checklist) ......... 95
Unit Rigging and Placement (Three-piece
unit) (in addition to Two-piece unit rigging
and placement) ..................... 95
Unit Startup ............................ 98
Sequence of Operation ................ 98
Cooling Sequence of Operation ....... 98
Compressor Sequence of Operation . . . 98
Units with Evaporative Condenser
Sequence of Operation .............. 99
Modulating Dehumidification (Hot Gas
Reheat) Sequence of Operation ...... 103
Energy Recovery Sequence of
Operation ........................ 105
Gas Heating Sequence of Operation
Standard ......................... 107
Honeywell Ignition System .......... 107
Modulating Gas Sequence of Operation 108
Electric Heat Sequence of Operation . . 108
Electric Heat—CV, VAV Daytime
Warm-up ......................... 109
VAV Active Occupied Discharge Heating 109
SZVAV Occupied Heating ........... 109
Demand Control Ventilation Sequence
of Operation ...................... 109
Return Fan Sequence of Operation .... 109
Wet Heat Sequence of Operation ..... 110
Unit Startup Check List ............... 110
Voltage Supply and Voltage Imbalance 111
Service Testing—Evaporative Condenser
Components ...................... 115
Verifying Proper Fan Rotation ........ 115
If all of the fans are rotating backwards; 116
If some of the fans are rotating
backwards; ....................... 116
System Airflow Measurements ....... 117
Exhaust Airflow Measurement
(Optional) ........................ 118
TRAQ™ Sensor Airflow Measurement . 119
Performance Data ................... 120
Supply Fan with or without Variable
Frequency Drive ................... 120
Airside Pressure Drop Standard
Evaporator Coil .....................122
Exhaust Fan Performance ............124
Return Fan Performance .............125
Component Static Pressure Drops .....127
Pressure Curves ......................136
(60 Hz) Air-Cooled Condensers ........136
Components .........................145
Standard Unit without Energy Recovery
Wheel ............................145
Standard Unit with Energy Recovery
Wheel ............................148
Energy Recovery Wheel (ERW) ........153
Service and Repair ..................158
Seal Adjustment ....................160
Compressor Startup .................161
Compressor Operational Sounds ......162
Evaporative Condenser Startup .......163
Thermostatic Expansion Valves .......165
Measuring Superheat ...............165
Charging by Subcooling .............165
Standard Ambient Units .............165
Electric, Steam and Hot Water Startup . .166
Gas Furnace Startup ................166
Two Stage Gas Furnace ..............167
Full Modulating Gas Furnace .........169
Final Unit Checkout .................171
Service and Maintenance ...............175
Scroll Compressor Replacement ......183
VFD Programming Parameters ........184
Monthly Maintenance ...............185
Filters .............................185
Air-Cooled Coil Cleaning .............187
Evaporative Condenser Coil Cleaning . .188
Final Process .......................190
Unit Wiring Diagram Number ............192
Warranty and Liability Clause ............198
Commercial Equipment ...............198
Rated 20 Tons and Larger and Related
Accessories
..........................198
RT-SVX24K-EN 5

Model Number Descriptions
SXHJ10540AA715MFDE81D1100A1BA1000AA1A1
1 2 3 4 567 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38
DIGIT 1 — UNIT TYPE
S Self-Contained (Packaged
Rooftop)
DIGIT 2 — UNIT FUNCTION
E DX Cooling, Electric Heat
F DX Cooling, Natural Gas Heat
L DX Cooling, Hot Water Heat
S DX Cooling, Steam Heat
X DX Cooling, No Heat,
Extended Casing
DIGIT3—SYSTEMTYPE
H Single Zone
DIGIT 4 — DEVELOPMENT
SEQUENCE
J Ninth
DIGIT 5, 6, 7 — NOMINAL
CAPACITY
090 90Ton Air-Cooled
105 105Ton Air-Cooled
120 120Ton Air-Cooled
130 130Ton Air-Cooled
150 150Ton Air-Cooled
100 100Ton Evap Condenser
118 118 Ton Evap Condenser
128 128Ton Evap Condenser
140 140Ton Evap Condenser
162 162Ton Evap Condenser
DIGIT 8 — VOLTAGE SELECTION
4 460/60/3 XL
5 575/60/3 XL
C 380/50/3 XL
DIGIT 9 — HEATING CAPACITY
SELECTION
0 No Heat
1 Electric heat 90/56 kW 60/50 Hz
2 Electric heat 140/88 kW 60/50 Hz
3 Electric heat 265/166 kW 60/50 Hz
4 Electric Heat 300/188 kW 60/50 Hz
A Low Gas Heat — 2-stage
B Medium Gas Heat — 2-stage
C High Gas Heat — 2-stage
D Low Gas Heat — Modulating
E Medium Gas Heat — Modulating
F High Gas Heat — Modulating
Steam or Hot Water Heat:
G Low Heat - 1.0" (25mm) Valve
H Low Heat - 1.25" (32mm) Valve
J Low Heat - 1.5" (38mm) Valve
K Low Heat - 2.0" (50mm) Valve
L Low Heat - 2.50" (64mm) Valve
M Low Heat - 3.0" (76mm) Valve
N High Heat - 1.0" (25mm) Valve
P High Heat - 1.25" (32mm) Valve
Q High Heat - 1.5" (38mm) Valve
R High Heat - 2.0" (50mm) Valve
T High Heat - 2.50" (64mm) Valve
U High Heat - 3.0" (76mm) Valve
DIGIT 10, 11 — DESIGN
SEQUENCE
A-ZZ (Factory Assigned) Sequence may
be any letter A to Z, or any digit 1 to 9.
DIGIT 12 — UNIT
CONFIGURATION SELECTION
1 One-Piece Unit w/o Blank Section
2 One-Piece Unit w/4' Blank Section
3 One-Piece Unit w/8' Blank Section
4 Two-Piece Unit w/o Blank Section
5 Two-Piece Unit w/4' Blank Section
6 Two-Piece Unit w/8' Blank Section
7 Three-Piece unit w/o Blank Section
8 Three-Piece Unit w/4' Blank Section
9 Three-Piece Unit w/8' Blank Section
DIGIT 13 — AIRFLOW DIRECTION
1 Downflow Supply /Upflow Return
2 Downflow Supply / Horiz End Return
3 Downflow Supply / Horiz Right Return
4 Right Side Horiz Supply/Upflow
Return
5 Right Side Horiz Supply / Horizontal
End Return
6 Right Side Horiz Supply / Horizontal
Right Return
DIGIT 14 — SUPPLY FAN
OPTIONS
1 Standard CFM
3 Standard CFM - TEFC Motor(s)
4 Low CFM
6 Low CFM -TEFC Motor(s)
7 = Standard CFM - w/ Motor Shaft
Grounding
9 = Standard CFM -TEFC Motor(s) w/
Shaft Grounding
A = Low CFM - w/ Motor Shaft Grounding
C = Low CFM -TEFC Motor(s) w/ Shaft
Grounding
DIGIT 15 — SUPPLY FAN MOTOR
SELECTION
F15hp
G20Hp
H25Hp
J30Hp
K40Hp
L50Hp
M60Hp
N75Hp
P100Hp
DIGIT 16 — SUPPLY FAN RPM
SELECTION
7700
8800
9900
A 1000
B1100
C 1200
D 1300
E 1400
F 1500
G 1600
H 1700
J 1800
K 1900
L2000
DIGIT 17 — EXHAUST/RETURN
FAN OPTIONS
0 None
1 Std CFM Exhaust Fan
w/o Statitrac CV Only
2 Low CFM Exhaust Fan
w/o Statitrac CV Only
3 Std CFM Exhaust w/o VFD
w/ Statitrac
4 Low CFM Exhaust w/o VFD
w/ Statitrac
5 Std CFM Exhaust w/ VFD w/
Bypass w/ Statitrac
6 Low CFM Exhaust w/ VFD w/
Bypass w/ Statitrac
7 Std CFM Exhaust w/ VFD w/o
Bypass w/ Statitrac
8 Low CFM Exhaust w/ VFD w/o
Bypass w/ Statitrac
A Std CFM Return w/o Statitrac CV
Only
B Low CFM Return w/o Statitrac CV
Only
C Std CFM Return w/ VFD w/
Bypass w/ Statitrac
D Low CFM Return w/ VFD w/
Bypass w/ Statitrac
E Std CFM Return w/ VFD w/o
Bypass w/ Statitrac
F Low CFM Return w/ VFD w/o
Bypass w/ Statitrac
6 RT-SVX24K-EN

Model Number Descriptions
DIGIT 18 — EXHAUST/RETURN
FAN MOTOR SELECTION
0 None
D 7.5 Hp
E10Hp
F15Hp
G20Hp
H25Hp
J30Hp
K40Hp
L50Hp
M60Hp
DIGIT 19 — EXHAUST/RETURN
RPM SELECTION
0 None
3300
4400
5500
6600
7700
8800
9900
A 1000
B1100
C 1200
D 1300
E 1400
DIGIT 20 — SYSTEM CONTROL
SELECTION
1 Constant Volume (CV) (Zone
Temperature Control)
2 CV w/ DischargeTemp Control
4 VAV w/ VFD Supply w/o Bypass
(DischargeTemp Control)
5 VAV w/ VFD Supply w/ Bypass
(DischargeTemp Control)
6 VAV – Single Zone VAV w/VFD w/o
Bypass (Zone Temperature Control)
7 VAV – Single Zone VAV w/VFD w/
Bypass (Zone Temperature Control)
DIGIT 21 — OUTSIDE AIR and
ECONOMIZER OPTION/
CONTROLS
A 0-25% Motorized Damper
B Economizer w/Dry Bulb
C Economizer w/Reference
Enthalpy
D Economizer w/Comparative
Enthalpy
E Econ w/Outside
Air Measure/Dry Bulb
F Econ w/Outside Air Measure/Ref
Enthalpy
G Econ w/Outside Air
Measure/Comp Enthalpy
H Econ w/DCV/Dry Bulb
J Econ w/DCV/Ref Enthalpy
K Econ w/DCV/Comp Enthalpy
1
1
1
DIGIT 22 — DAMPER OPTION
0 Standard
1 Low Leak
2 Ultra Low Leak
U Ultra Low Leak, AMCA 1A, w/ FDD
(Design Special)
DIGIT 23— PRE-EVAPORATOR
COIL FILTER SELECTION
0 Two Inch High Efficiency
Throwaway
1 Two InchThrowaway Rack/Less
Filters
2 90-95% Bag Filters w/Prefilters
3 Bag Filter Rack/Less Filters
4 90-95% Cartridge Filters w/
Prefilters
5 Cartridge Rack/Less Filters
6 90-95% Low Pressure Drop
Cartridge Filters w/ Prefilters
7 Low Pressure Drop Cartridge
Rack/Less Filters
DIGIT 24 — BLANK SECTION
APPLICATION OPTIONS
0 None
A 90-95% Bag w/Prefilters
B 90-95% Low Pressure Drop
Cartridge w/ Prefilters
C 90-95%, Cartridge Filters w/
Prefilters
D 90-95% HighTemp Cartridge
w/ Prefilters
E HEPA w/Prefilters
F HighTemp HEPA w/Prefilters
DIGIT 25 — ENERGY RECOVERY
WHEEL
0 None
1 Low CFM ERW w/ Bypass Defrost
2 Standard CFM ERW w/ Bypass
Defrost
DIGIT 26 — UNIT MOUNTED
POWER CONNECTION
SELECTION
A Terminal Block
B Non-Fused Disconnect
C Non-Fused Disconnect w/
Powered Convenience Outlet
D Circuit Breaker w/ high fault SCCR
E Circuit Breaker w/ high fault SCCR/
Powered Convenience Outlet
DIGIT 27 — CONDENSER COIL
SELECTION
0 Air-Cooled Aluminum
A Evap Condenser
B Evap Condenser w/ Sump Heater
C Evap Condenser w/ Dolphin
WaterCare System
D Evap Condenser w/ Dolphin
WaterCare System & Sump Heater
E Evap Condenser w/ Conductivity
Controller
F Evap Condenser w/ Conductivity
Controller and Sump Heater
J Corrosion Protected Condenser Coil
DIGIT 28 — EVAPORATOR COIL
AND DRAIN PAN
0 Standard Evap Coil w/Galvanized
Drain Pan
A Standard Evap Coil w/ Stainless
Steel Drain Pan
B High Cap Evap Coil w/Galvanized
Drain Pan
C High Cap Evap Coil w/Stainless
Steel Drain Pan
DIGIT 29 — REFRIGERATION
SYSTEM SELECTION A
0 Standard
A Suction Service Valves
B Replaceable Core Liquid Filter
Driers
C Suction Service Valves &
Replaceable Core Liquid Filter
Driers
DIGIT 30 — REFRIGERATION
SYSTEM SELECTION B
0 Standard
1 Hot Gas Reheat
2 Hot Gas By-Pass
3 Hot Gas Reheat2/Hot Gas By-Pass
2
DIGIT 31 — AMBIENT CONTROL
OPTION
0 Standard Ambient
1 Low Ambient
DIGIT 32 — HIGH DUCT TEMP
THERMOSTAT
0 None
1 High Duct TempThermostat
DIGIT 33 — CONTROLS OPTION
0 None
1 Remote Human Interface (RHI) &
Inter-Processor Communication
Bridge (IPCB)
2 IPCB
3 Rapid Restart
1
Requires CO2 Zone Sensor(s)
RT-SVX24K-EN 7
2
Humidity sensor required

Model Number Descriptions
DIGIT 34 — MODULE OPTIONS
0 None
A 0-5 volt Generic Building
Automation System (GBAS)
B 0-10 volt GBAS
C 0-5 volt GBAS and 0-10 volt GBAS
F LonTalk® Communication
Interface (LCI)
D Ventilation Override
G 0-5 volt GBAS volt & Ventilation
Override
H 0-10 volt GBAS & Ventilation
Override
J 0-5 volt GBAS and 0-10 volt GBAS
& Ventilation Override
L LCI & Ventilation Override
M BACnet Communication Interface
(BCI)
N BCI & Ventilation Override
DIGIT 35 — ZONE SENSOR
OPTION
0 None
A Dual Setpoint w/Man/Auto
Changeover — BAYSENS108
B Dual Setpoint w/Man/Auto
Chgovr & Sys Lights —
BAYSENS110
C Room Sensor w/timed Override &
Cancel — BAYSENS073
D Room Sensor w/TO (Timed
Override) & Cancel &
Local Stpt Adj — BAYSENS074
G VAV w/System Lights —
BAYSENS021
L Programmable
Night Setback — BAYSENS119
DIGIT 36 — AGENCY APPROVAL
OPTION
0 None
1 cULus
DIGIT 37 — SERVICE
ENHANCEMENTS
0 Single Side Access Door
A Dual Side Access Door
B Single Side Access Doors/
Marine Lights
C Dual Side Access Doors/
Marine Lights
DIGIT 38 — MISCELLANEOUS
OPTIONS
0 None
1 Belt Guards
2 Burglar Bars
3 Belt Guards/Burglar Bars
Tip: EXAMPLE
Model number
SXHJ10540AA715MFDE81D1100A
1BA1000AA1A1
describes a unit with the following
characteristics:
DX Cooling, No Heat, Extended
Casing, 105Ton nominal capacity,
with 460/3/60 power supply,
3 piece construction with
downflow supply and upflow
return, low CFM fans, a 60 hp
supply fan w/ a 1500 rpm drive, a
10 Hp return fan with VFD, bypass
and statitrac, with CV control, and
economizer w/ comparative
enthalpy, low leak dampers,
2” throwaway rack less filters,
terminal blank connection, Air
Cooled Copper Condenser coil,
high cap evap with galvanized
drain pan, suction service valves,
hot gas reheat, 0-5V GBAS, dual
setpoint with Manual/Auto
Changeover, cULus approval,
Dual side access, and belt guards.
The service digit for each model
number contains 38 digits; all 38
digits must be referenced.
8 RT-SVX24K-EN
Unit Inspection
As soon as the unit arrives at the job site
[ ] Verify that the nameplate data matches the data on
the sales order and bill of lading (including electrical
data).
[ ] Verify that the power supply complies with the unit
nameplate specifications.
[ ] Verify that the power supply complies with the
electric heater specifications on the unit nameplate.
[ ]Visually inspect the exterior of the unit, including the
roof, for signs of shipping damage.
[ ] Check for material shortages. Refer to the
Component Layout and Ship with Location illustration.
Important: If the job site inspection of the unit reveals
damage or material shortages, file a claim
with the carrier immediately. Specify the
type and extent of the damage on the “bill of
lading” before signing.
[ ] Visually inspect the internal components for
shipping damage as soon as possible after delivery
and before it is stored. Do not walk on the sheet metal
base pans.
WARNING
No Step Surface!
Do not walk on the sheet metal drain pan. Walking on
the drain pan could cause the supporting metal to
collapse, resulting in the operator/technician to fall.
Failure to follow this recommendation could result in
death or serious injury.
[ ] If concealed damage is discovered, notify the
carrier's terminal of damage immediately by phone
and by mail. Concealed damage must be reported
within 15 days.
Request an immediate joint inspection of the damage
by the carrier and the consignee. Do not remove
damaged material from the receiving location. Take
photos of the damage, if possible.The owner must
provide reasonable evidence that the damage did not
occur after delivery.
[ ] Remove the protective plastic coverings that
shipped over the compressors.
openings) from the ambient air until the unit is
ready for startup.
Note: Do not use the unit heater for temporary heat
without first completing the startup procedure
detailed under “Unit Startup,” p. 98.
Trane will not assume any responsibility for equipment
damage resulting from condensate accumulation on the
unit electrical and/or mechanical components.
Unit Clearances
Figure 10, p. 23 Table 4, p. 23 illustrates the minimum
operating and service clearances for either a single or
multiple unit installation.These clearances are the
minimum distances necessary for adequate service,
cataloged unit capacity, and peak operating efficiency.
Providing less than the recommended clearances may
result in condenser coil starvation, “short-circulating” of
exhaust and economizer airflows, or recirculation of hot
condenser air.
Unit Dimensions and Weight Information
Description Reference
Air-Cooled Condenser
One-piece unit dimensions Figure 12, p. 25, Table 5, p. 26
Two-piece unit dimensions Figure 12, p. 25, Table 6, p. 27
Three-piece unit dimensions Figure 12, p. 25, Table 8, p. 33
T ypical unit and operation weights Table 12, p. 44
Evaporative Condenser
Two-piece unit dimensions Figure 12, p. 25, Table 7, p. 30
Three-piece unit dimensions Figure 12, p. 25, Table 9, p. 36
Typical unit and operation
(a)Weights shown represent approximate operating weights. Actual
weights are stamped on the unit nameplate.
weights
(a)
Table 12, p. 44
Storage
Take precautions to prevent condensate from forming
inside the unit electrical compartments and motors if:
a. The unit is stored before it is installed; or,
b. The unit is set on the roof curb, and temporary heat
is provided in the building. Isolate all side panel
service entrances and base pan openings (e.g.,
conduit holes, S/A and R/A openings, and flue
RT-SVX24K-EN 9

General Information
Unit Nameplate
One Mylar unit nameplate is located on the outside upper
left corner of the control panel door. It includes the unit
model number, serial number, electrical characteristics,
weight, refrigerant charge, as well as other pertinent unit
data. A small metal nameplate with the Model Number,
Serial Number, and Unit Weight is located just above the
Mylar nameplate, and a third nameplate is located on the
inside of the control panel door.
Compressor Nameplate
The Nameplate for the Scroll Compressor is located on the
compressor lower housing. Max amps is listed on the
nameplate and is the absolute highest amp load on the
compressor at any operating condition (does not include
locked rotor amps or inrush).This value should never be
exceeded.
Commonly Used Acronyms
For convenience, a number of acronyms and
abbreviations are used throughout this manual.These
acronyms are alphabetically listed and defined below.
• AC = Air Cooled Condenser
• BAS = Building automation systems
• BCI = BACnet® Communication Interface module
• CFM = Cubic-feet-per-minute
• CKT. = Circuit
• CLV = Cooling valve (reheat only)
• CV = Constant volume
• CW = Clockwise
• CCW = Counterclockwise
• E/A = Exhaust air
• EC = Evaporative Condenser
• ECEM = Exhaust/comparative enthalpy module
• FDD = Fault Detection and Diagnostic
• RT = Rooftop unit
• O/A = Outside air
• GBAS = Generic building automation system
• HGBP = Hot gas bypass
• MCHE = Microchannel Condenser Coil
• HGRH = Hot gas reheat
• HI = Human Interface
• HVAC = Heating, ventilation and air conditioning
• I/O = Inputs/outputs
• IOM = Installation/operation/ maintenance manual
• IPC = Interprocessor communications
• IPCB = Interprocessor communications bridge
• LCI-I = LonTalk® Communication Interface for
IntelliPak
• LH = Left-hand
• MCM = Multiple compressor module
• MDM = Modulating Dehumidification Module
• MPM = Multipurpose module
• MWU = Morning warm-up
• NSB = Night setback
• O/A = Outside air
• psig = Pounds-per-square-inch, gauge pressure
• PTFE = Polytetrafluoroethylene (Teflon®)
• R/A = Return air
• RAH = Return air humidity
• RH = Right-hand
• RHV = Reheat valve
• RPM = Revolutions-per-minute
• RTM = Rooftop module
• S/A = Supply air
• SCCR = Short circuit current rating
• SCM = Single circuit module
• SZ = Single-zone (unit airflow)
• SZVAV = Single zone variable air volume
• TCI = Tracer communications module
• UCM = Unit control modules
• VAV = Variable air volume
• VCM = Ventilation control module
• VOM = Ventilation override module
• w.c. = Water column
• WCI = Wireless Communication Interface
Unit Description
Available tonnages
Air-Cooled Tonnages
90 100
105 118
120 128
130 140
150 162
EachTrane commercial, single-zone rooftop air
conditioner ships fully assembled from the factory. An
optional roof curb, specifically designed for the S_HJ units
is available fromTrane.The roof curb kit must be field
assembled and installed according to the latest edition of
the roof curb installation manual.
Trane Commercial Rooftop Units are controlled by a
microelectronic control system that consists of a network
of modules and are referred to as Unit Control Modules
(UCM).The acronym UCM is used extensively throughout
this document when referring to the control system
network.These modules through Proportional/Integral
control algorithms perform specific unit functions which
provide the best possible comfort level for the customer.
They are mounted in the control panel and are factory
wired to their respective internal components. They
receive and interpret information from other unit
Evaporative Condenser
Tonnages
10 RT-SVX24K-EN
General Information
modules, sensors, remote panels, and customer binary
contacts to satisfy the applicable request for economizing,
mechanical cooling, heating, and ventilation. Refer to the
following discussion for an explanation of each module
function.
Table 1. Resistance input vs. setpoint temperature
RTM cooling or
heating setpoint
input used as the
source for a ZONE
temp setpoint (°F)
40 40 1084
45 45 992
50 50 899
55 55 796
60 60 695
65 65 597
70 70 500
75 75 403
80 80 305
n/a 85 208
n/a 90 111
RTM cooling
setpoint input
used as the source
for SUPPLY AIR
temp setpoint
cooling (°F)
Resistance (Ohms)
Max.
Tolerance 5%
Table 2. RTM resistance value vs. system operating
mode
Resistance applied to
RTM MODE input
Terminals (Ohms)
Max. Tolerance 5%
2320 Auto Off
4870 Auto Cool
7680 Auto Auto
10770 On Off
13320 On Cool
16130 On Auto
19480 Auto Heat
27930 On Heat
Constant Volume Units
Fan Mode System Mode
Rooftop Module (RTM - Standard on all units)
The rooftop Module (RTM) responds to cooling, heating,
and ventilation requests by energizing the proper unit
components based on information received from other
unit modules, sensors,
remote panels, and customer supplied binary inputs. It
initiates supply fan, exhaust fan, exhaust damper
positioning or variable frequency drive output, and
economizer operation based on
that information.
Compressor Module (MCM - standard on all
units)
The Compressor module, upon receiving a request for
mechanical cooling, energizes the appropriate
compressors and condenser fans. It monitors the
compressor operation through feedback information it
receives from various protection devices.
Human Interface Module (HI - standard on all
units)
The Human Interface module enables the operator to
adjust the operating parameters for the unit using a 16 key
keypad.The 2 line, 40 character LCD screen provides
status information for the various unit functions as well as
menus for the operator to set or modify the operating
parameters.
Heat Module (used on heating units)
The Heat module, upon receiving a request for Heating,
energizes the appropriate heating stages or strokes the
Modulating Heating valve as required.
Ventilation Override Module (VOM - Optional)
The Ventilation Override module initiates specified
functions such as; space pressurization, exhaust, purge,
purge with duct pressure control, and unit off when any
one of the five (5) binary inputs to the module are
activated.The compressors and condenser fans are
disabled during the ventilation operation. If more than one
ventilation sequence is activated, the one with the highest
priority is initiated.
Interprocessor Communications Board (IPCB Optional used with the Optional Remote
Human Interface)
The Interprocessor Communication Board expands
communications from the rooftop unit UCM network to a
Remote Human Interface Panel. DIP switch settings on the
IPCB module for this application should be; Switches 1 and
2“Off”, Switch 3 “On”.
Lontalk®/BACnet® Communication Interface
Module (LCI/BCI - Optional - used on units
with Trane ICS™ or 3rd party Building
Automation Systems)
The LonTalk/BACnet Communication Interface modules
expand communications from the unit UCM network to a
TraneTracer Summit™ or a 3rd party building automation
system and allow external setpoint and configuration
adjustment and monitoring of status and diagnostics.
Exhaust/Comparative Enthalpy Module
(ECEM - Optional used on units with Statitrac
and/or comparative enthalpy options)
The Exhaust/Comparative Enthalpy module receives
information from the return air humidity sensor, the
RT-SVX24K-EN 11
General Information
outside air humidity sensor,and the return air temperature
sensor to utilize the lowest possible humidity level when
considering economizer operation. In addition, it receives
space pressure information which is used to maintain the
space pressure to within the setpoint control band. Refer
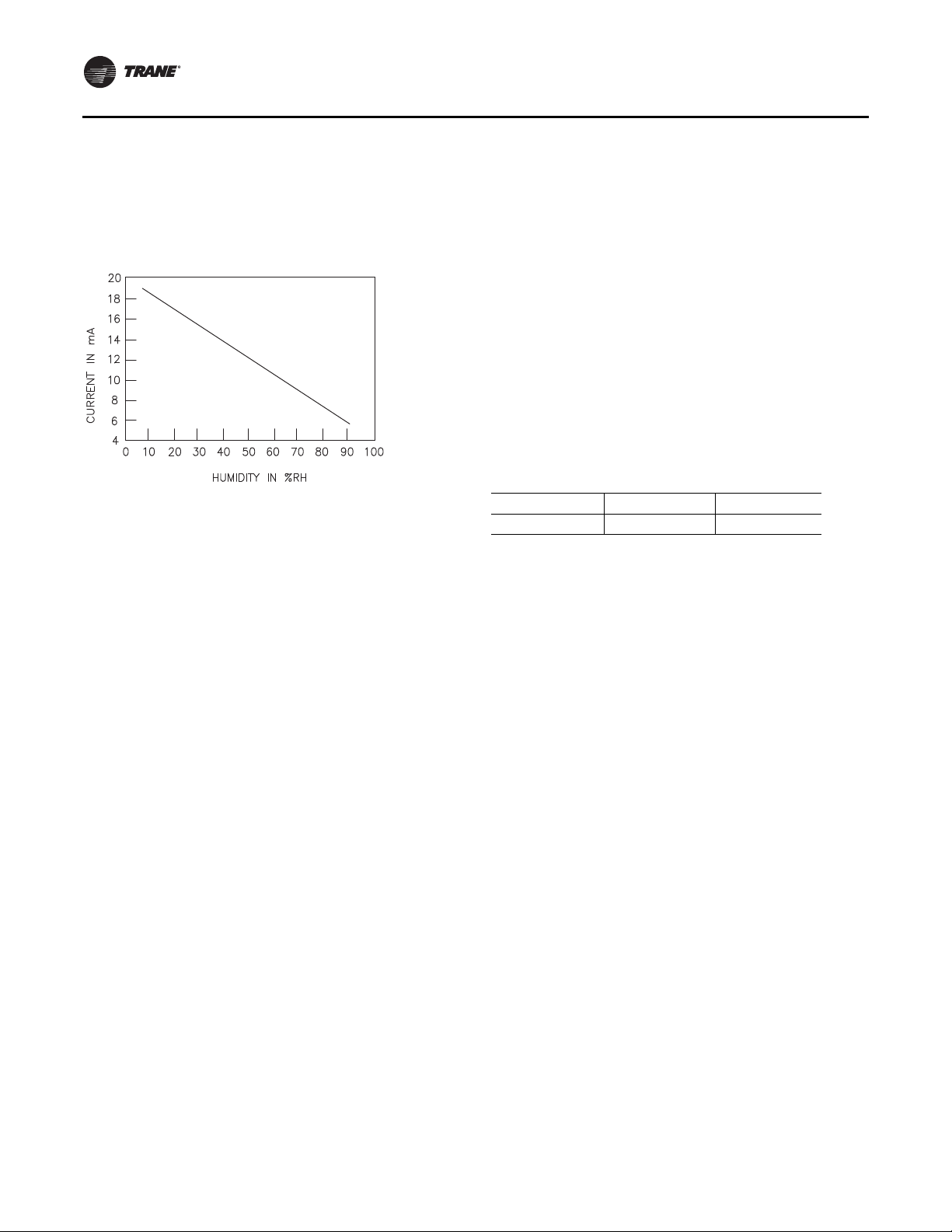
to Figure 1 for the Humidity vs. Voltage input values.
Figure 1. Humidity vs. current
Multi Purpose Module MPM (Optional - used
with Return Fan Control, Energy Recovery, and
Evaporative Condensers)
The MPM supports three optional features.The first of
which is return plenum pressure control by receiving
analog voltage information for measuring return plenum
pressure, calibrating that reading, and providing an output
to control the return fan speed (if variable speed
configured) in response to control algorithm requests.
This module also provides inputs and outputs for control
of all Energy Recovery feature devices including the
energy wheel, exhaust and outdoor air bypass dampers,
and recovery preheat.The liquid line pressure sensor
inputs for both refrigeration circuits are received through
the MPM in support of head pressure control on watercooled condenser units.
Ventilation Control Module (VCM)
The Ventilation Control Module (VCM) is located in the
filter section of the unit and is linked to the unit UCM
network. Using a “velocity pressure” sensing ring located
in the outside air section allows the VCM to monitor and
control the quantity of outside air entering the unit to a
minimum airflow setpoint.
An optional temperature sensor can be connected to the
VCM whichenables it to control a field installed outside air
preheater.An optional CO
VCM to control CO
minimum CFM upward as the CO
increase.
The maximum effective (reset) setpoint value for outside
air entering the unit is limited to the systems operating
CFM.The following table lists the velocity pressure vs.
Input Voltage (see also Figure 6, p. 18.).
Table 3. Minimum outside air setpoint w/VCM and
TRAQ™ sensing
Unit Input Volts CFM
90-162 Tons 0.5 - 4.5 VDC 0 - 46000
The velocity pressure transducer/solenoid assembly is
illustrated below. Refer to the “Units withTRAQ™ Sensor,”
p. 103 for VCM operation.
2
sensor can be connected to the
2
reset.The reset function adjusts the
concentrations
2
Variable Speed Module (VSM - Optional -
Used with Fault Detection and Diagnostics
FDD)
The VSM is used with FDD.The VSM will accept a 0-10Vdc
actuator feedback position signal which will then be used
to determine the state of OutsideAir Damper system.
Modulating Dehumidification Module MDM
(Optional - used with Dehumidification
Control)
The MDM supports specific control inputs and outputs for
Modulating Dehumidification control including
modulating Reheat and Cooling valve control as well as
the Reheat Pumpout Coil Relay output. The Modulating
Dehumidification control algorithm provides control
requests to the MDM to accomplish proper
Dehumidification control.
12 RT-SVX24K-EN
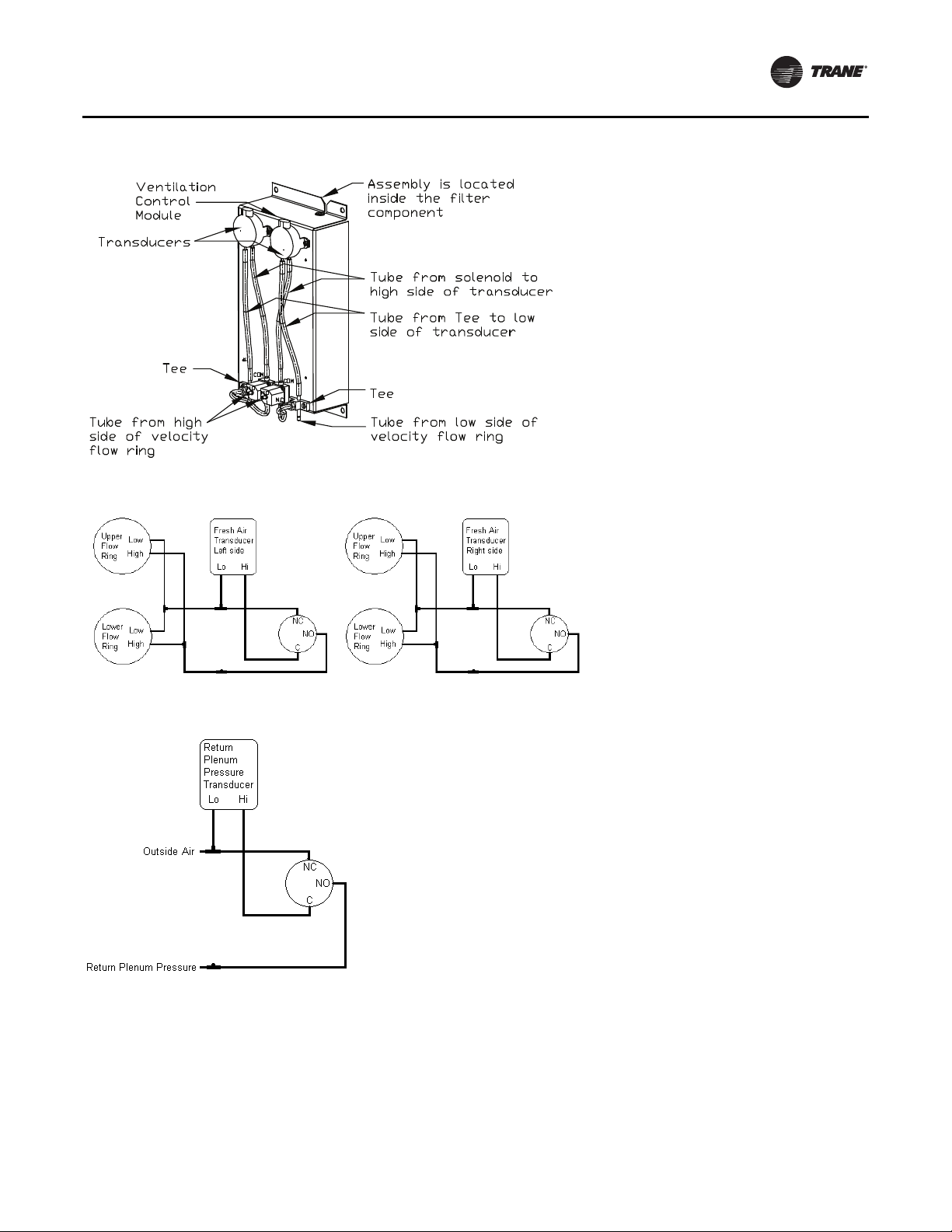
Figure 2. Velocity pressure transducer/solenoid assembly
Figure 3. Outside air tubing schematic
General Information
Figure 4. Return air pressure tubing schematic
Generic Building Automation System Module
(GBAS - Optional used with
non-Trane building control systems)
The Generic Building Automation System (GBAS) module
allows a non-Trane building control system to
communicate with the rooftop unit and accepts external
setpoints in the form of analog inputs for cooling, heating,
supply air pressure, and a binary Input for demand limit.
Refer to the “Field Installed Control Wiring” section for the
input wiring to the GBAS module and the various desired
setpoints with the corresponding DC voltage inputs for
both VAV, SZVAV, RR and CV applications.
Input Devices and System Functions
The descriptions of the following basic Input Devices used
within the UCM network are to acquaint the operator with
their function as they interface with the various modules.
Refer to the unit electrical schematic for the specific
module connections.
Constant Volume (CV) and
Variable Air Volume (VAV) Units
Supply Air Temperature Sensor
An analog input device used with CV and VAV applications
that monitors the supply air temperature for: supply air
temperature control (VAV), supply air temperature reset
(VAV), supply air temperature low limiting (CV), supply air
tempering (CV/VAV). It is mounted in the supply air
discharge section of the unit and is connected to the RTM.
RT-SVX24K-EN 13

General Information
Return Air Temperature Sensor
An analog input device used with a return humidity sensor
on CV and VAV applications when the comparative
enthalpy option is ordered. It monitors the return air
temperature and compares it to the outdoor temperature
to establish which temperature is best suited to maintain
the cooling requirements. It is mounted in the return air
section and is connected to the ECEM.
Leaving EvaporatorTemperature Sensor
An analog input device used with CV and VAV applications
that monitors the refrigerant temperature inside the
evaporator coil to prevent coil freezing. It is attached to the
suction line near the evaporator coil and is connected to
the MCM. It is factory set for 30°F and has an adjustable
range of 25°F to 35°F.The compressors are staged “Off” as
necessary to prevent icing. After the last compressor stage
has been turned “Off”, the compressors will be allowed to
restart once the evaporator temperature rises 10°F above
the“coil frost cutout temperature” and the minimum three
minute “Off” time has elapsed.
Entering Evaporator Temperature Sensors
Analog input devices used with CV and VAV applications.
This device is used in conjunction with the Leaving
EvaporatorTemperature Sensor to prevent the unit from
running compressors with insufficient charge.
Filter Switch
A binary input device used on CV and VAV applications
that measures the pressure differential across the unit
filters. It is mounted in the filter section and is connected
to the RTM. A diagnostic SERVICE signal is sent to the
remote panel if the pressure differential across the filters
is at least 0.5" w.c.The contacts will automatically open
when the pressure differential across the filters decrease
to 0.4" w.c.The switch differential can be field adjusted
between 0.17" w.c. to 5.0" w.c. ± 0.05" w.c.
Leaving Recovery Exhaust Temp Sensor
Analog input device used on CV andVAV applications with
Energy Recovery option installed. It is used to monitor the
temperature of the leaving air on the Exhaust Fan side of
the energy recovery wheel.This temperature is used to
determine if the temperature of the wheel is too cold as
compared to the Recovery Frost Avoidance Setpoint.The
result is used to determine when to enable energy wheel
frost avoidance functions.
Supply, Exhaust and Return Fan Airflow
Proving Switches
Supply Airflow Proving Switch is a binary input device
used on CV and VAV applications to signal the RTM when
the supply fan is operating. It is located in the supply fan
section of the unit and is connected to the RTM. During a
request for fan operation, if the differential switch is
detected to be open for 40 consecutive seconds;
compressor operation is turned “Off”, heat operation is
turned “Off”, the request for supply fan operation is turned
“Off” and locked out, exhaust dampers (if equipped) are
“closed”, economizer dampers (if equipped) are “closed”,
and a manual reset diagnostic is initiated.
Exhaust/return Airflow Proving Switch is a binary input
device used on all rooftop units equipped with an exhaust
fan. It is located in the exhaust/return fan section of the unit
and is connected to the RTM. During a request for fan
operation, if the differential switch is detected to be open
for 40 consecutive seconds, the economizer is closed to
the minimum position setpoint, the request for exhaust
fan operation is turned “Off” and locked out, and a manual
reset diagnostic is initiated.The fan failure lockout can be
reset at the Human Interface located in the unit control
panel, byTracer, or by cycling the control power to the
RTM Off/On.
Lead-Lag
A selectable mode of operation through the Human
Interface. It alternates the starting between the first
compressor of each refrigeration circuit. Only the
compressor banks will switch, not the order of the
compressors within a bank, providing the fir st compressor
in each circuit had been activated during the same request
for cooling.
Charge Isolation
During the OFF cycle, most of the charge is isolated
between the compressor (internal) discharge check valves
and liquid line solenoid valve.This reduces the OFF cycle
charge migration, and liquid feedback during subsequent
startup.The liquid line solenoid is energized (opened) with
the start of the circuit compressor.
Supply, Exhaust and Return Fan Circuit
Breakers
The supply fan and exhaust fan motors are protected by
circuit breakers or fuses. They will trip and interrupt the
power supply to the motors if the current exceeds the
breaker's “must trip” value.The rooftop module (RTM)
will shut all system functions “Off” when an open fan
proving switch is detected.
Low Pressure Control
Low Pressure Control is accomplished using a binary input
device on CV andVAV applications. LP cutouts are located
on the suction lines near the scroll compressors.The LPC
contacts are designed to close when the suction pressure
exceeds 41 ± 4 psig. If the LP control is open when a
compressor is requested to start, none of the compressors
on that circuit will be allowed to operate.They are locked
out and a manual reset diagnostic is initiated.
The LP cutouts are designed to open if the suction
pressure approaches 22 ± 4 psig. If the LP cutout opens
after a compressor has started, all compressors operating
on that circuit will be turned off immediately and will
14 RT-SVX24K-EN

General Information
remain off for a minimum of three minutes. If the LP cutout
trips four consecutive times during the first three minutes
of operation, the compressors on that circuit will be locked
out and a manual reset diagnostic is initiated.
Saturated Condenser Temperature Sensors
Analog input devices used on CV and VAV applications
mounted inside a temperature well located on a
condenser tube bend.They monitor the saturated
refrigerant temperature inside the condenser coil and are
connected to the MCM. As the saturated refrigerant
temperature varies due to operating conditions, the
condenser fans are cycled “On” or “Off” as required to
maintain acceptable operating pressures.
Head Pressure Control
Accomplished using two saturated refrigerant
temperature sensors on CV and VAV applications. During
a request for compressor operation, when the condensing
temperature rises above the “lower limit” of the
controlband, the Compressor Module (MCM) starts
sequencing condenser fans “On”. If the operating fans can
not bring the condensing temperature to within the
controlband, more fans are turned on. As the saturated
condensing temperature approaches the lower limit of the
controlband, fans are sequenced “Off”.
The minimum “On/Off” time for condenser fan staging is
5.2 seconds. If the system is operating at a given fan stage
below 100% for 30 minutes and the saturated condensing
temperature is above the “efficiency check point” setting,
a fan stage will be added. If the saturated condensing
temperature falls below the “efficiency check point”
setting, the fan control will remain at the present operating
stage. If a fan stage cycles four times within a 10 minute
period, the control switches from controlling to the “lower
limit” to a temperature equal to the “lower limit” minus
the “temporary low limit suppression” setting. It will
utilize this new “low limit” temperature for one hour to
reduce condenser fan short cycling.
For evaporative condensing units, head pressure is
monitored with pressure transducers attached to the
saturated condensing line and converted to a temperature
by the MPM.This temperature is used to control the
variable speed fan and sump pump. When the
temperature rises above the upper limit (120°F) the sump
pump is energized. If the condensing temperature drops
below the lower limit (70°F) the sump pump is deenergized.
High Pressure Limit Controls
High Pressure controls are located on the discharge lines
near the scroll compressors. They are designed to open
when the discharge pressure approaches 650 ± 10 psig.
The controls reset automatically when the discharge
pressure decreases to approximately 550 ± 10 psig.
However, the compressors on that circuit are locked out
and a manual reset diagnostic is initiated after the fourth
occurrence of a high pressure condition.
Outdoor Air Humidity Sensor
An analog input device used on CV and VAV applications
with 100% economizer. It monitors the outdoor humidity
levels for economizer operation. It is mounted in the
outside air intake section and is connected to the RTM.
Return Air Humidity Sensor
An analog input device used on CV and VAV applications
with the comparative enthalpy option. It monitors the
return air humidity level and compares it to the outdoor
humidity level to establish which conditions are best
suited to maintain the cooling requirements. It is mounted
in the return air section and is connected to the ECEM.
Space Humidity Sensor
Analog input device used on CV andVAV applications with
modulating dehumidification option and/or
humidification field installed option. It is used to monitor
the humidity level in the space and compared to
dehumidification and humidification setpoints to maintain
space humidity requirements. It is field mounted in the
space and connected to the RTM.
Status/Annunciator Output
An internal function within the RTM module on CV and
VAV applications that provides:
c. diagnostic and mode status signals to the remote
panel (LEDs) and to the Human Interface
d. control of the binary Alarm output on the RTM
e. control of the binary outputs on the GBAS module
to inform the customer of the operational status
and/or diagnostic conditions
Low Ambient Compressor Lockout
Utilizes an analog input device for CV and VAV
applications. When the system is configured for low
ambient compressor lockout, the compressors are not
allowed to operate if the temperature of the outside air
falls below the lockout setpoint. When the temperature
rises 5°F above the lockout setpoint, the compressors are
allowed to operate.The factory preset is 50°F.
These compressors come equipped with a protection
module that monitors phase loss, phase sequencing and
motor temperature.
Space PressureTransducer
An analog input device used on CV and VAV applications
with the Statitrac option. It modulates the exhaust
dampers to keep the space pressure within the building to
a customer designated controlband. It is mounted on the
bottom support below the return damper blade assembly
and is connected to the ECEM. Field supplied pneumatic
tubing must be connected between the space being
controlled and the transducer assembly.
RT-SVX24K-EN 15

General Information
MorningWarm-Up—Zone Heat
When a system changes from an unoccupied to an
occupied mode, or switches from STOPPED to AUTO, or
power is applied to a unit with the MWU option, the heater
in the unit or external heat will be brought on if the space
temperature is below the MWU setpoint.The heat will
remain on until the temperature reaches the MWU
setpoint.
If the unit is VAV, then the VAV box/unocc relay will
continue to stay in the unoccupied position and the VFD
output will stay at 100% during the MWU mode.When the
MWU setpoint is reached and the heat mode is terminated,
then the VAV box/unocc relay will switch to the occupied
mode and the VFD output will be controlled by the duct
static pressure. During Full Capacity MWU the economizer
damper is held closed for as long as it takes to reach
setpoint. During Cycling Capacity MWU the economizer
damper is allowed to go to minimum position after one
Compressor Motor Winding Thermostats
A thermostat is embedded in the motor windings of each
Scroll compressor. Each thermostat is designed to open if
the motor windings exceed approximately 221°F. The
thermostat will reset automatically when the winding
temperature decreases to approximately 181°F.
Rapid cycling, loss of charge, abnormally high suction
temperatures, or the compressor running backwards
could cause the thermostat to open. During a request for
compressor operation, if the Compressor Module detects
a problem outside of normal parameters, it turns any
operating compressor(s) on that circuit “Off”, locks out all
compressor operation for that circuit, and initiates a
manual reset diagnostic (compressor trip).
These compressors come equipped with a protection
module that monitors phase loss, phase sequencing and
motor temperature.
hour of operation if setpoint has not been reached.
Figure 5. Transducer voltage output vs. pressure input for supply, return and building pressure
-0.75 to 9.0 Iwc Pressure Transducer Voltage Output vs. Pressure Input
4.50
4.00
3.50
3.00
2.50
Volts
2.00
1.50
1.00
0.50
0.00
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
250.2
75
-0.
-0.
7
2
7
2
7
2
0.
1.
1.
2.
2.
7
3.
3.
Pressure (inches w.c.)
5
2
7
4.
4.
5.
Supply Air Temperature Low Limit
Uses the supply air temperature sensor input to modulate
the economizer damper to minimum position in the event
the supply air temperature falls below the occupied
heating setpoint temperature.
Discharge Line Thermostat for Evaporative
Condensers
The first compressor on each circuit is equipped with a
Discharge Line Thermostat. If the temperature of the line
exceeds 210°F the thermostat interrupts the 115V circuit for
the compressors and both of the compressors on that
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
2
7
2
7
2
5.
6.
6.
7
7.
7.
5
2
7
8.
8.
circuit will be de-energized. Once the temperature drops
below 170°F the thermostat will close and allow the
compressor to be energized.
Freezestat
A binary input device used on CV and VAV units with
Hydronic Heat. It is mounted in the heat section and
connected to the Heat Module. If the temperature of the air
leaving the heating coil falls to 40°F, the normally open
contacts on the freezestat closes signalling the Heat
Module and the Rooftop Module (RTM) to:
f. drive the Hydronic Heat Actuator to the full open
position
16 RT-SVX24K-EN

General Information
g. turn the supply fan “Off”
h. closes the outside air damper
i. turns “On” the SERVICE light at the Remote Panel
j. initiates a “Low Temp Limit” diagnostic to the
Human Interface
Compressor Circuit Breakers
The Scroll Compressors are protected by circuit breakers
whichinterrupt the power supply to the compressors if the
current exceeds the breakers “must trip” value. During a
request for compressor operation, if the Compressor
Module detects a problem outside normal parameters, it
turns any operating compressor(s) on that circuit “Off”,
locks out all compressor operation for that circuit, and
initiates a manual reset diagnostic (compressor trip).
Constant Volume (CV) Units
Zone Temperature—Cooling
Relies on input from a sensor located directly in the space,
while a system is in the occupied “Cooling” mode. It
modulates the economizer (if equipped) and/or stages the
mechanical cooling “On and Off” as required to maintain
the zone temperature to within the cooling setpoint
deadband.
Zone Temperature—Heating
Relies on input from a sensor located directly in the space,
while a system is in the occupied “Heating” mode or an
unoccupied period, to stage the heat “on and off” or to
modulate the heating valve (hydronic heat only) as
required to maintain the zone temperature to within the
heating setpoint deadband.The supply fan will be
requested to operate any time there is a request for heat.
On gas heat units, the fan will continue to run for 60
seconds after the furnace is turned off.
Supply Air Tempering
On CV units equipped with staged gas heat, if the supply
air temperature falls 10°F below the occupied heating
setpoint temperature while the heater is “Off”, the first
stage of heat will be turned “On”.The heater is turned “Off”
when the supply air temperature reaches 10°F above the
occupied heating setpoint temperature.
Variable Air Volume (VAV) Units
Occupied Cooling—Supply Air Temperature
When a VAV unit is in the occupied mode, the supply air
temperature will be controlled to the customer specified
supply air cooling setpoint by modulating the economizer
and/or staging the mechanical cooling “On and Off” as
required.The changeover relay contacts must be open, or
BAS command set to auto or cool, for the cooling to
operate.
DaytimeWarm-up
On VAV units equipped with heat, if the zone temperature
falls below the daytime warm-up initiate temperature
during the occupied mode, the system will switch to full
airflow. During this mode, theVAV box/unocc relay will be
energized (this is to signal the VAV boxes to go to 100%).
After theVAV box max stroke time has elapsed (factory set
at 6 minutes), the VFD output will be set to 100%.The
airflow will be at 100% and the heat will be turned on to
control to the occupied heating setpoint.
When the zone temperature reaches the daytime warm-up
termination setpoint, the heat will be turned off, the relay
will be de-energized, releasing the VAV boxes, the VFD
output will go back to duct static pressure control and the
unit will return to discharge air control. If the occ zone
heating setpoint is less than the DWU terminate setpoint,
the heat will turn off when the occ zone heat setpoint is
reached, but it will stay in DWU mode and cycle the heat
to maintain setpoint.
Unoccupied Heating—Zone Temperature
When aVAV unit is equipped with gas, electric, or hydronic
heat and is in the unoccupied mode, the zone temperature
will be controlled to within the customer specified setpoint
deadband. During an unoccupied mode for aVAV unit, the
VAV box/unocc relay will be in the unoccupied position
and theVFD output will be at 100%.This means that if there
is a call for heat (or cool) and the supply fan comes on, it
will be at full airflow and the VAV boxes in the space will
need to be 100% open as signaled by the VAV box/unocc
relay.
Supply Air Tempering
On VAV units equipped with “Modulating Heat”,ifthe
supply air temperature falls 10°F below the supply air
temperature setpoint, the heat will modulate to maintain
the supply air temperature to within the low end of the
setpoint deadband.
Occupied Heating—Supply Air Temperature
When a VAV unit is equipped with “Modulating Heat”, and
the system is in an occupied mode, and the field supplied
changeover relay contacts have closed or per a BAS
command, the supply air temperature will be controlled to
the customer specified supply air heating setpoint. It will
remain in the heating status until the changeover relay
contacts are opened or BAS has released the heat
command.
RT-SVX24K-EN 17
Supply Duct Static Pressure Control
(Occupied)
The RTM relies on input from the duct pressure transducer
when a unit is equipped with aVariable Frequency Drive to
set the supply fan speed to maintain the supply duct static
pressure to within the static pressure setpoint deadband.
The transducer compares supply duct pressure to ambient
pressure. Refer to Figure 43, p. 67.
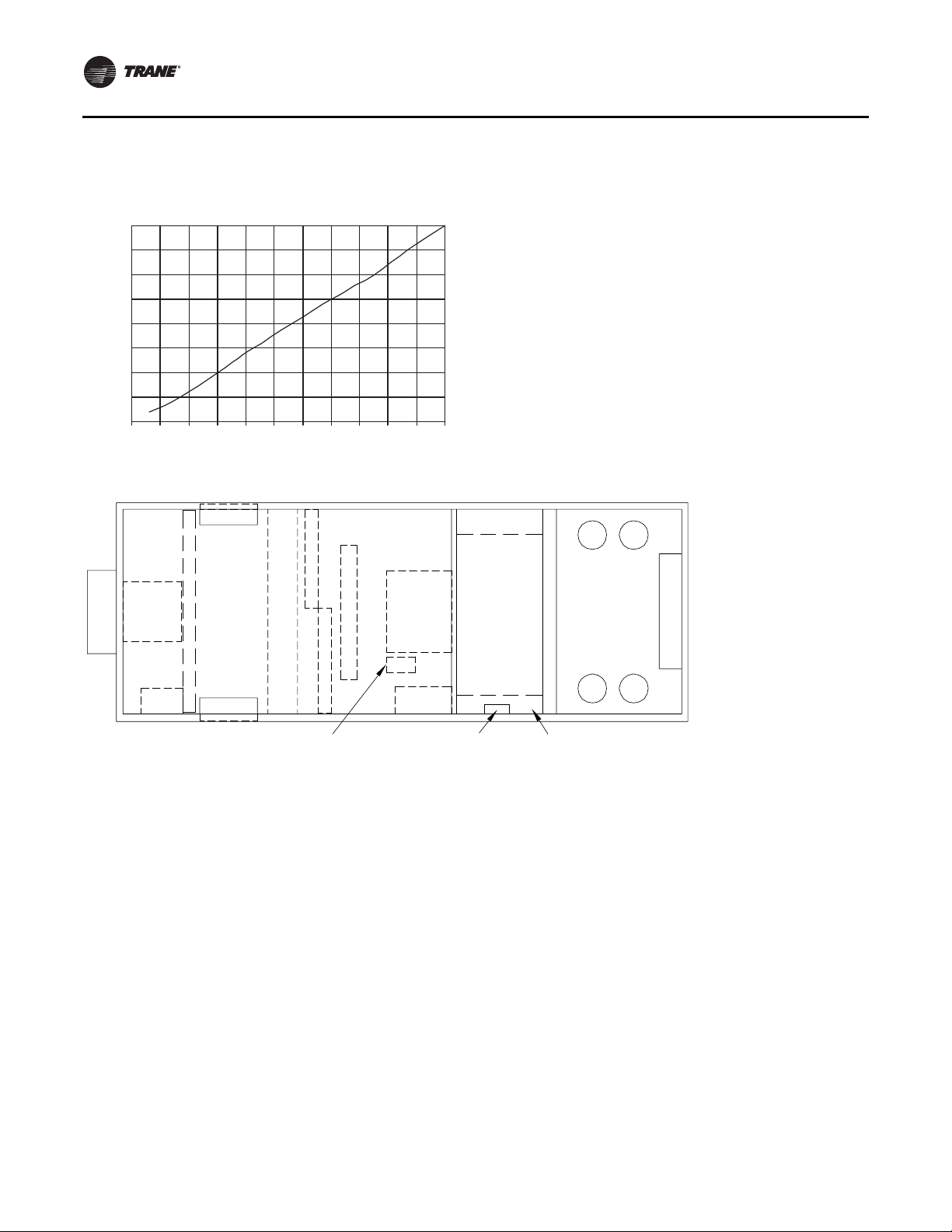
General Information
Figure 6. Transducer voltage output vs. pressure input
with VCM and TRAQ™ sensing
4.0
3.5
3.0
2.5
2.0
Volts
1.5
1.0
0.5
0.0
Transducer Voltage Output vs. Pressure I nput
-0.5 0.0 0.5 1.0 1.5 2.0 2.5 3.0 3.5 4.0 4.5 5.0
Pre ssu re (inche s w.c.)
Figure 7. Unit component layout and “ship with” locations
Outside Air
Dampers
Evap Coil
Return/
Exhaust
Hood
Exhaust Damper
Fan
Return Air Dampers
Filter Section
Reheat Coil Option
Evap Coil
Supply Fan
Space Temperature Averaging
Space temperature averaging for Constant Volume
applications is accomplished by wiring a number of
remote sensors in a series/parallel circuit.
The fewest number of sensors required to accomplish
space temperature averaging is four.The Space
Temperature Averaging with Multiple Sensors figure
illustrates a single sensor circuit (Single Zone), four
sensors wired in a series/parallel circuit (Four Zone), nine
sensors wired in a series/parallel circuit (Nine Zone). Any
number squared, is the number of remote sensors
required.
Wiring termination will depend on the type of remote
panel or control configuration for the system. Refer to the
wiring diagrams that shipped with the unit.
Condenser
Heating
Section
Fans
Compressor
Section
Controls
Variable
Frquency
Drive (VFD)
Outside Air
Dampers
Outside Air
Static Kit and
sensors
Variable
Frquency
Drive (VFD)
Flue Vent
Access
Hot Water/Steam
Hydronic Connection
18 RT-SVX24K-EN
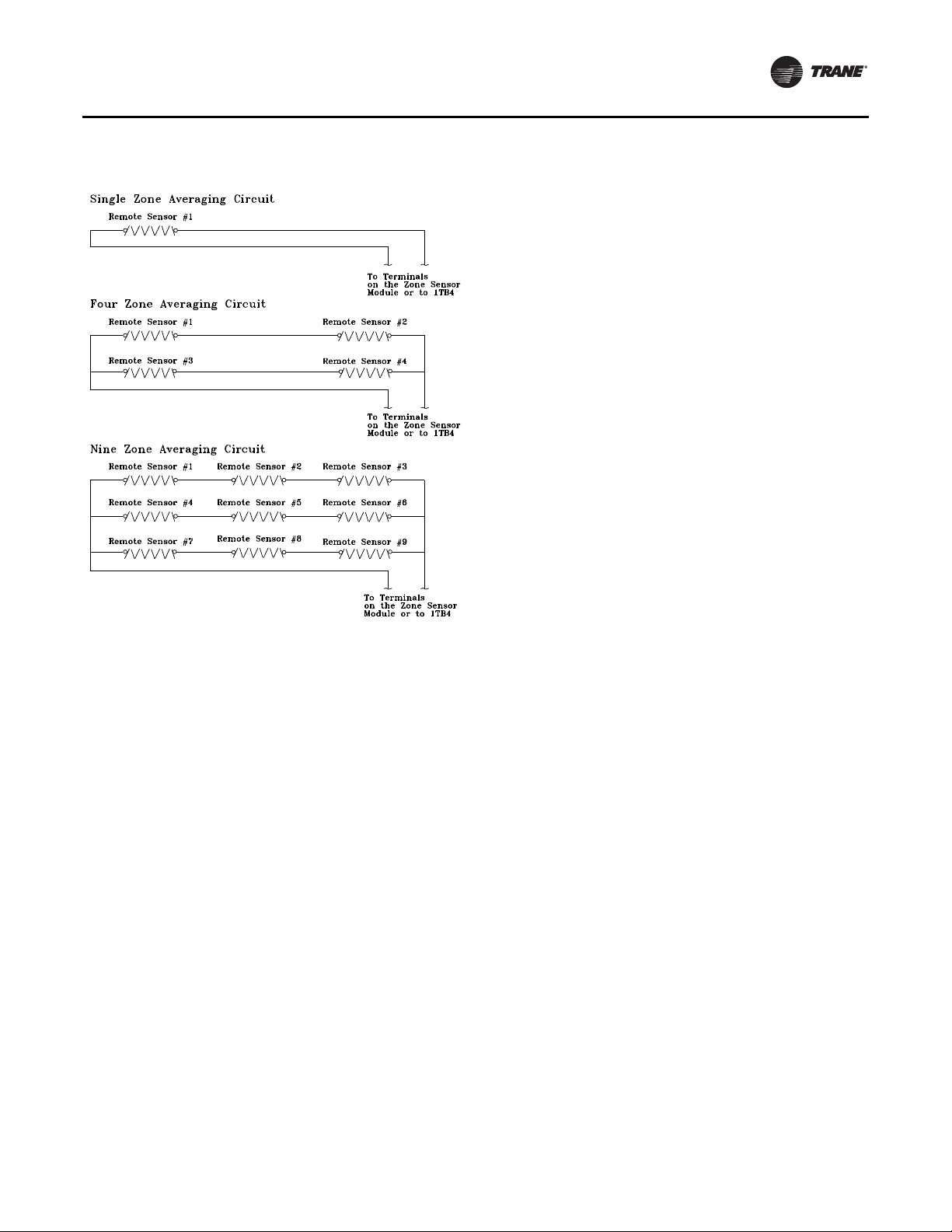
Figure 8. Space temperature averaging with multiple
sensors
General Information
Unit Control Modules
Unit control modules are microelectronic circuit boards
designed to perform specific unit functions.The control
modules, through proportional/integral control
algorithms, provide the best possible comfort level for the
customer.They are mounted in the control panel and are
factory wired to their respective internal components.
The control modules receive and interpret information
from other unit modules, sensors, remote panels, and
customer binary contacts to satisfy the applicable request
for economizing, mechanical cooling, heating, and
ventilation. Figure 9 illustrates the typical location of each
designated module.
RT-SVX24K-EN 19
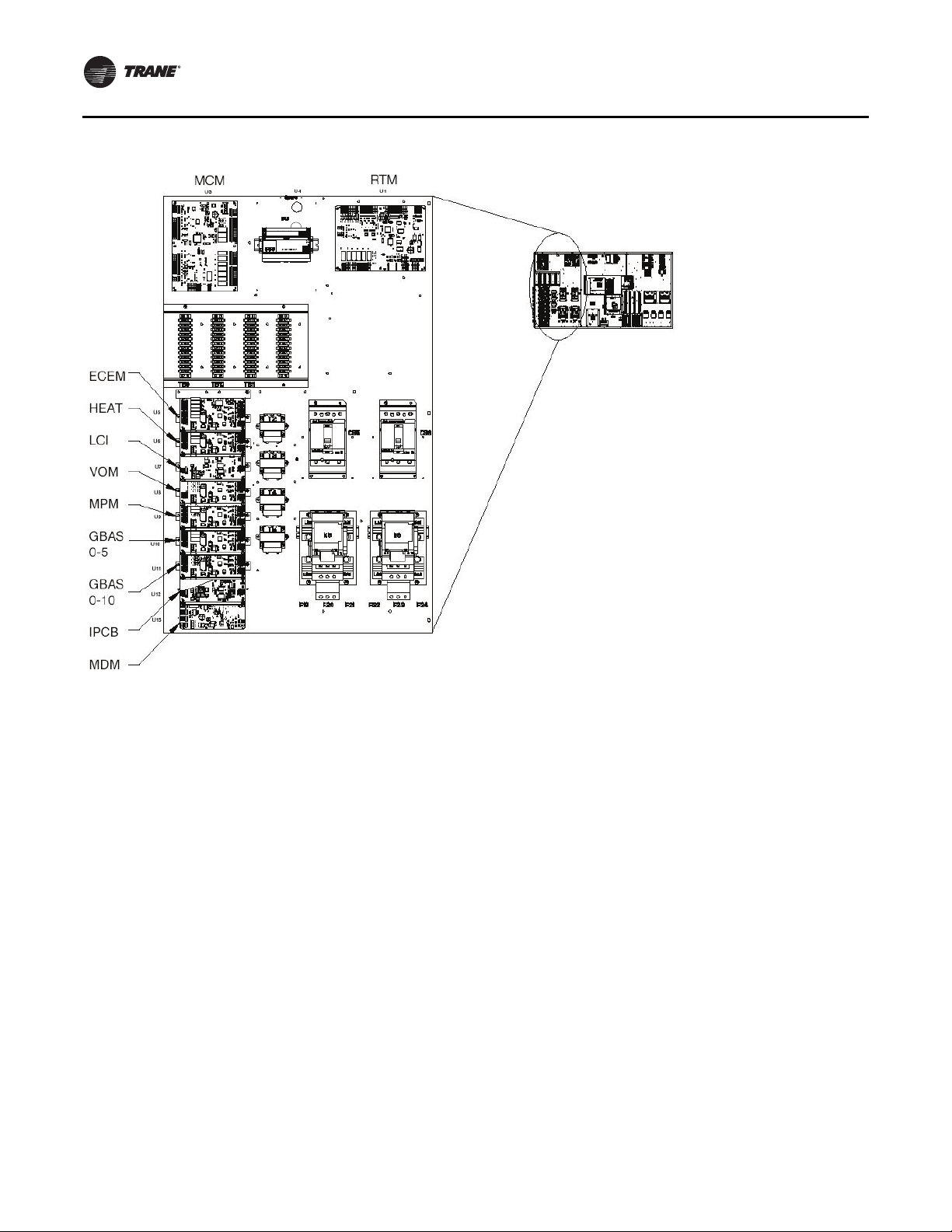
General Information
Figure 9. Control module locations
BCI
Single Zone Variable Air Volume (SZVAV) Only
The IntelliPak controls platform will support Single Zone
VAV as an optional unit control type in order to meet
ASHRAE 90.1. The basic control will be a hybrid VAV/CV
configured unit that provides discharge temperature
control to a varying discharge air temperature target
setpoint based on the space temperature and/or humidity
conditions. Concurrently, the unit will control and optimize
the supply fan speed to maintain the zone temperature to
a zone temperature setpoint.
Supply Fan Output Control
Units configured for Single Zone VAV control will utilize
the same supply fan output control scheme as on
traditional VAV units except the VFD signal will be based
on zone heating and cooling demand instead of the supply
air pressure.
VFD Control
Single Zone VAV units will be equipped with a VFDcontrolled supply fan which will be controlled via a 010VDC signal from the Rooftop Module (RTM). With the
RTM supply fan output energized and the RTM VFD output
at 0VDC, the fan speed output is 37% (22Hz) from the VFD
by default; and at 10VDC the fan speed output is 100%
(60Hz).The control scales the 0-10VDC VFD output from
the RTM linearly to control between the 37-100% range.
The VFD will modulate the supply fan motor speed,
accelerating or decelerating as required to maintain the
zone temperature to the zone temperature setpoint.When
subjected to high ambient return conditions the VFD will
reduce its output frequency to maintain operation. Bypass
control is offered to provide full nominal airflow in the
event of drive failure.
Ventilation Control
Units configured for Single Zone VAV control will require
special handling of the OA Damper Minimum Position
control in order to compensate for the non-linearity of
airflow associated with the variable supply fan speed and
damper combinations. Units configured for TRAQ with or
without DCV will operate identically to traditional units
with no control changes.
Space Pressure Control
For units configured with Space Pressure Control with or
without Statitrac, the new schemes implemented for
economizer minimum position handling require changes
to the existing Space Pressure Control scheme in order to
20 RT-SVX24K-EN

General Information
prevent over/under pressurization.The overall scheme
will remain very similar to VAV units with Space Pressure
Control with the exception of the dynamic Exhaust Enable
Setpoint.
For SZVAV an Exhaust Enable Setpoint must be selected
during the 100% Fan Speed Command. Once selected, the
difference between the Exhaust Enable Setpoint and
Design OA Damper Minimum Position at 100% Fan Speed
Command will be calculated.The difference calculated will
be used as an offset and added to the Active Building
Design OA Minimum PositionTarget in order to calculate
the dynamic Exhaust EnableTarget, which will be used
throughout the Supply Fan Speed/OA Damper Position
range.
The Exhaust EnableTarget could be above or below the
Active Building Design OA Minimum PositionTarget
Setpoint, based on the Active Exhaust Enable Setpoint
being set above or below the Building Design Minimum
Position at 100% Fan Speed Command. Note that an
Exhaust Enable Setpoint of 0% will result in the same effect
on Exhaust Fan control as on VAV applications with and
without Statitrac.
Occupied Cooling Operation
For normal cooling operation, cooling capacity will be
staged or modulated in order to meet the calculated
discharge air target setpoint. If the current active cooling
capacity is controlling the discharge air within the
deadband, no additional cooling capacity change will be
requested. As the Discharge Air Temperature rises above
the deadband, the algorithm will request additional
capacity as required (additional compressors or
economizer).As the Discharge AirTemperature falls below
the deadband, the algorithm will request a reduction in
active capacity.
Default Economizer Operation
By default, the unit will be setup to optimize the minimum
supply fan speed capability during Economizer Only
operation. If the economizer is able to meet the demand
alone, due to desirable ambient conditions, the supply fan
speed will be allowed to increase above the minimum
prior to utilizing mechanical cooling if discharge air
setpoint falls below the discharge air Lower Limit
(Cooling) setpoint.
Unoccupied Mode
In Unoccupied mode the unit will utilize setback setpoints,
0% Minimum OA Damper position, and Auto Fan Mode
operation as on normal CV units.The Supply Fan speed,
and cooling and modulating types of heat, will be
controlled to the discharge air target setpoint as is done
during occupied periods.The Supply fan speed during
staged heat control will be forced to 100% as on normal CV
units.
Occupied Heating Operation
Occupied heating operation has two separate control
sequences; staged and modulated. All staged heating
types will drive the supply fan to maximum flow and stage
heating to control to the Zone Heating Setpoint. For units
with Hydronic and Gas heat, modulated SZVAV Heating.
On an initial call for heating, the supply fan will drive to the
minimum heating airflow.
On an additional call for heating, the heat will control in
order to meet the calculated discharge air target setpoint.
As the load in the zone continues to request heat
operation, the supply fan will ramp-up while the control
maintains the heating discharge air temperature. Heating
can be configured for either the energy saving SZVAV
Heating solution as described above, or the traditional,
less efficient CV Heating solution.
Compressor (DX) Cooling
Compressor control and protection schemes will function
identical to that of a traditional unit. Normal compressor
proving and disable input monitoring will remain in effect
as well as normal 3-minute minimum on, off, and interstage timers. Also, all existing head pressure control
schemes will be in effect.
Cooling Sequence
If the control determines that there is a need for active
cooling capacity in order to meet the calculated discharge
air target setpoint, once supply fan proving has been
made, the unit will begin to stage compressors
accordingly. Note that the compressor staging order will
be based on unit configuration and compressor lead/lag
status.
Once the discharge air target setpoint calculation has
reached the Minimum Setpoint and compressors are
being utilized to meet the demand, as the discharge air
target setpoint value continues to calculate lower the
algorithm will begin to ramp the supply fan speed up
toward 100%. Note that the supply fan speed will remain
at the compressor stage’s associated minimum value (as
described below) until the discharge air target setpoint
value is calculated below the discharge air temperature
Minimum Setpoint (limited discharge air target setpoint).
As the cooling load in the zone decreases the zone cooling
algorithm will reduce the speed of the fan down to
minimum per compressor stage and control the
compressors accordingly. As the compressors begin to
de-energize, the supply fan speed will fall back to the
Cooling Stage’s associated minimum fan speed, but not
below. As the load in the zone continues to drop, cooling
capacity will be reduced in order to maintain the discharge
air within the ± ½ discharge air target deadband.
Fault Detection and Diagnostics
Fault Detection of the Outdoor Air Damper will be
evaluated based on the commanded position of the
damper compared to the feedback position of the damper.
RT-SVX24K-EN 21

General Information
The damper is commanded to a position based on a 2-10
VDC signal. If the Damper position is outside of ±10% of the
commanded position, a diagnostic is generated.
Unit Not Economizing when it should be:
The Unit is operating in Cooling Mode, Economizing is
enabled and/or Mechanical Cooling is enabled. If the
Commanded Economizer Position is greater than Current
Economizer Feedback Position + 10% for 5 continuous
minutes, Unit Not Economizing when it should be
diagnostic is generated.
Unit Economizing when it should not be:
The unit is operating in Cooling Mode, Economizing is
enabled and or Mechanical Cooling is enabled. If the
commanded Economizer Position is less than the current
Economizer Feedback Position - 10% for 5 continuous
minutes, Unit Economizing When it should not be
diagnostic is generated.
Outdoor Air Damper Not Modulating
The unit is operating in Ventilation Only Mode - not
attempting to Economize and the Commanded Damper
Position is greater than the Current Damper Feedback
Position + 10% for 5 continuous minutes, Outdoor Air
Damper Not Modulating diagnostic is generated.
Excessive Outdoor Air
The unit is operating in Ventilation Only Mode - not
attempting to Economize and the Commanded Damper
Position is less than the Current Damper Feedback Position
- 10% for 5 continuous minutes. Excessive Outdoor Air
diagnostic is generated.
To changethe Economizer Control Function to dry bulb, go
to the Configuration Menu on the Human Interface Module
and set Comparative Enthalpy to "Not Installed".This
allows the user to select dry bulb under the Economizer
Control Function which is a Submenu of the Setup Menu.
For additional instructions please see the Programming
andTroubleshooting Guide.
22 RT-SVX24K-EN
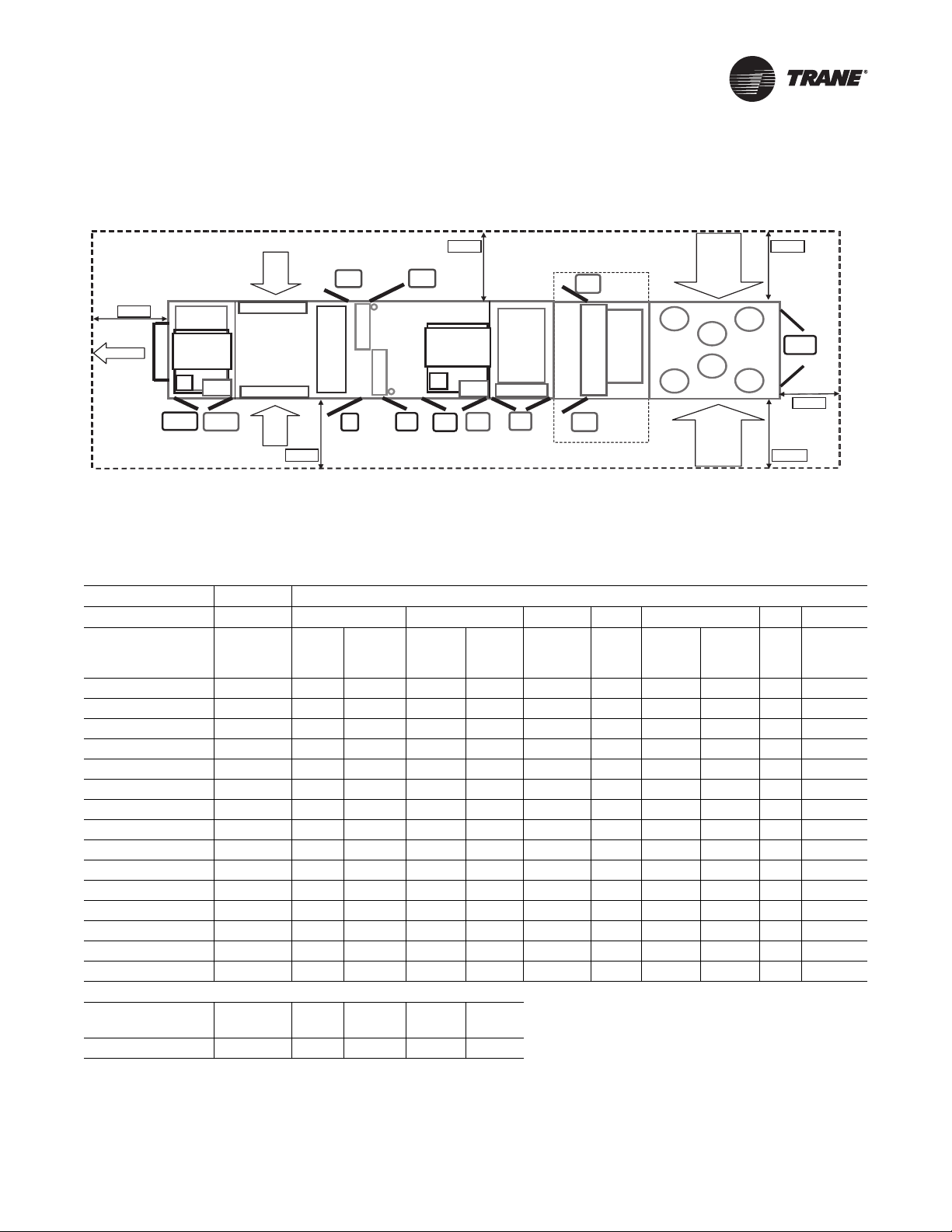
Unit Clearances
(F)
(R)
(
(
)
e
Filters
(a)
AH R
Fltr
Fltr
Std StdStd
Evp
OptionOption
VFD
Evp
Sup
Sup
VFD
Mtr
Std
Figure 10. Minimum required clearance
Outside
Exh
Exhaust
VFD
As Req.
Outsid
Air
AH L
Rtn/Exh
Mtr
Rtn/Exh
VFD
Left Side
(a)Unit drawing is representative only and may not accurately depict all models.
Table 4. Minimum required clearance
Unit Option Selection (Door Swing Ft. and In.)
Standard VFD Two-side Access
Heat
Heat
L&R
As Req. As Req.
Blank Section
Fnl
Fltr
As Req.
Final
Filter
Fnl
Fltr
As Req.
Condenser
Condenser
Cond R
Cond L
Ctrl Box
L&R
CBox
Std
Door Location Availability 90-118 120-162
Return/
Exhaust Supply Heat Reheat 90-118 120-162
Final
Filter
Energy
Recovery
Exhaust/Ret Motor Std 2' 2" 2' 2" * * * * * * *
Exhaust/Ret VFD As Req. * * 2' 2" * * * * * *
(a)
ERW Fltr
(L & R) (F) Option * * * * * * * * * 2' 2"
ERW Fltr(a) (L & R) (R) Option * * * * * * * * * 2' 2"
Filter (Front) Std 2' 8" 2' 8" * * * * * * *
Filter (Rear) Option * * * * * * 2' 2" 2' 8" *
Evap (Front) Std 2' 2" 2' 2" * * * * * * *
Evap (Rear) Std 2' 8" * * * * * * * *
or Evap (Rear) Option * * * * * 2' 2 * 2' 2" *
Supply Motor Std 2' 8" 2' 8" * * * * * * *
Supply VFD As Req. * * * 2' 2" * * * * *
Heat (Left & Right) As Req. * * * * 2' 2" * * * *
Final Filter (Front) As Req. * * * * * * * * 2' 2"
Final Filter (Rear) As Req. * * * * * * * * 2' 2"
Control Box (L & R) Std 3' 2" 3' 2" * * * * * * *
Minimum Required Clearance (Ft.)
Control
AH_L AH_R Exh Cond_L Cond_R
Box
8' 8' 8' 8' 8' 6'
(a)See Unit Dimensions for Energy Recovery Wheel location.
RT-SVX24K-EN 23
Unit Clearances
Figure 11. Multiple unit placement
Minimum distance between units must be 16’!
Outdoor
Air Intake
Exhaust
Air
Outdoor
Air Intake
Exhaust
Air
Notes:
1. Stagger units to minimize span deflection which deters sound
transmission and to maximize proper diffusion of the exhaust air
before it reaches the adjacent unit outside air intake.
2. Cooling tower should be 5 feet above or 20 feet away from the outside
air intake. For additional information, see 2007 ASHRAE Handbook:
HVAC Applications, page 44.4.
Outdoor
Air Intake
Outdoor
Air Intake
Outdoor
Air Intake
Exhaust
Air
Outdoor
Air Intake
24 RT-SVX24K-EN
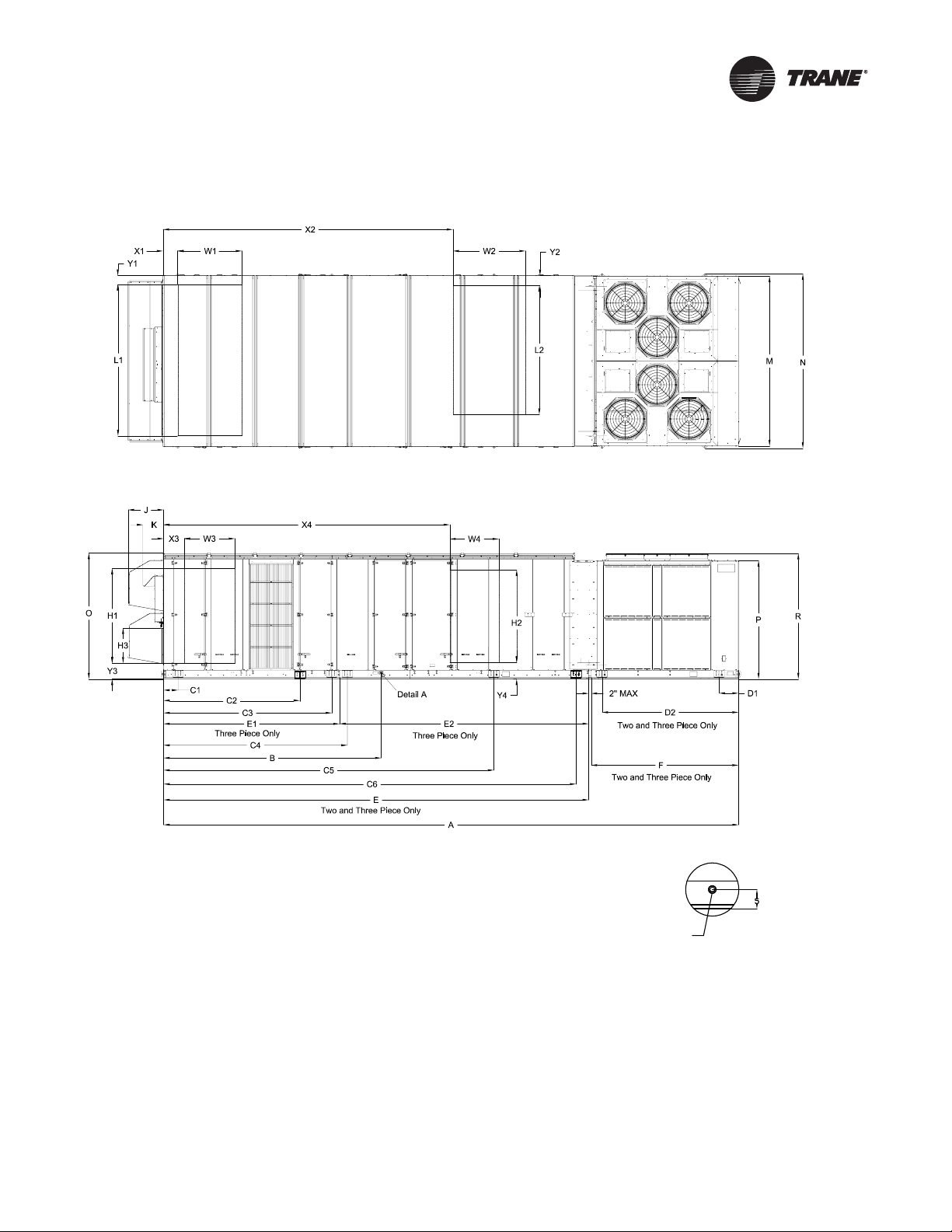
Dimensional Data
Figure 12. Unit Top/Front View
Detail A
1-1/4 NPT. DRAIN
2X TYP. LEFT & RIGHT SIDES OF UNIT
RT-SVX24K-EN 25
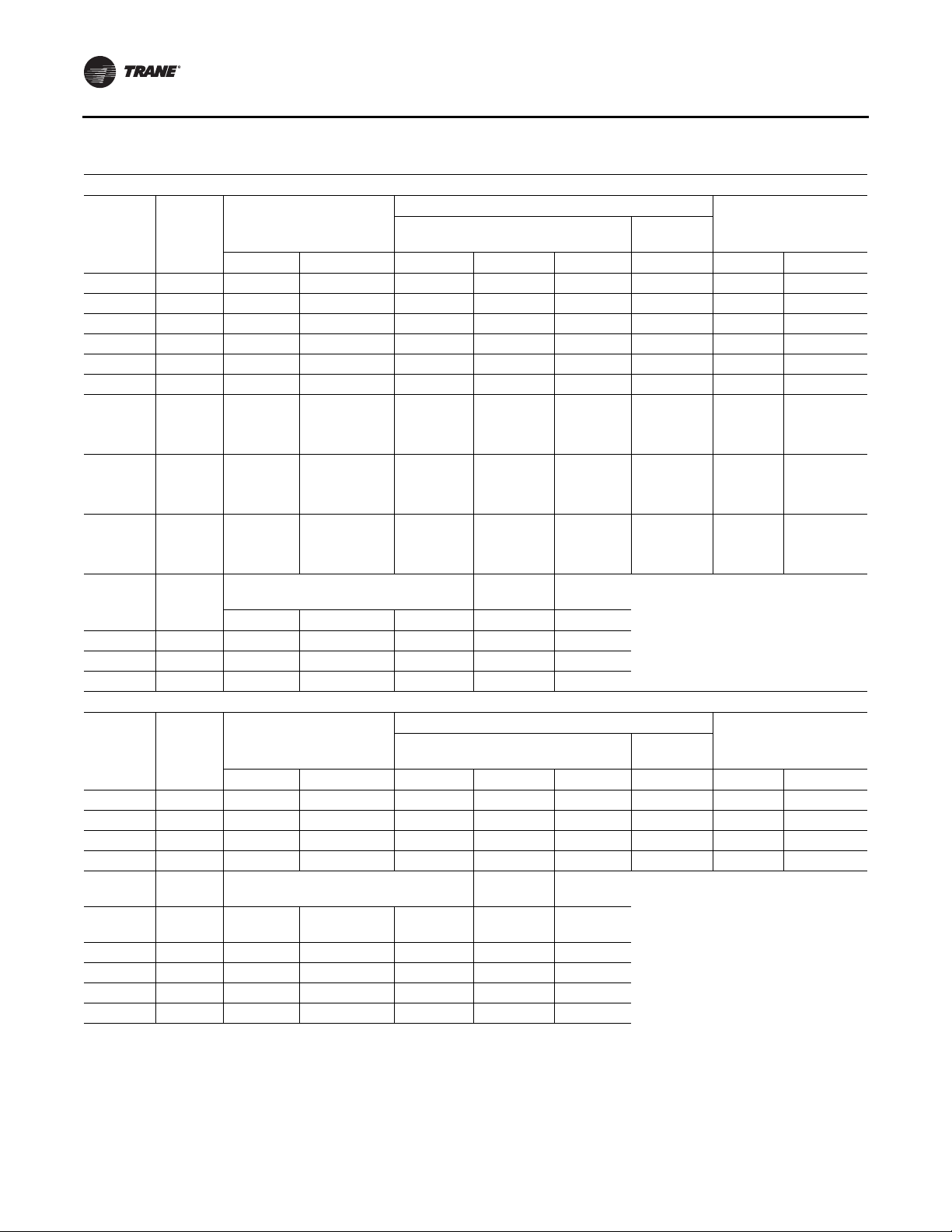
Dimensional Data
Table 5. Unit dimensions (in.)—one-piece unit air-cooled
ONE-PIECE Dimensions without Energy Recovery Wheel (ERW)
Lifting Lug Locations
Tonnage
90 None 437 3/16 159 15/16 66 252 14/16 N/A 27 11/16 139 13/16 143 8/16
90 4 ft 485 6/16 159 15/16 66 252 14/16 N/A 54 2/16 139 13/16 143 8/16
90 8 ft 533 9/16 159 15/16 66 252 14/16 N/A 54 2/16 139 13/16 143 8/16
105 None 455 3/16 159 15/16 66 252 14/16 N/A 27 11/16 139 13/16 143 8/16
105 4 ft 503 6/16 159 15/16 66 252 14/16 N/A 54 2/16 139 13/16 143 8/16
105 8 ft 551 9/16 159 15/16 66 252 14/16 N/A 54 2/16 139 13/16 143 8/16
120-150 (All
Units Except
High Heat
Gas Models)
120-150 (All
Units Except
High Heat
Gas Models)
120-150
(High Heat
Gas Models
Only)
Section
None 528 15/16 197 1/16 66 269 6/16 N/A 63 2/16 139 13/16 143 8/16
4 ft 577 2/16 197 1/16 66 269 6/16 N/A 63 2/16 139 13/16 143 8/16
None 540 15/16 197 1/16 66 269 6/16 N/A 63 2/16 139 13/16 143 8/16
Blank
Unit Dimensions
A B C1 C2 C3 D1 M N
Exhaust
Tonnage
90-150 None 103 12/16 97 9/16 103 7/16 29 3/16 17
90-150 4 ft 103 12/16 97 9/16 103 7/16 29 3/16 17
90-150 8 ft 103 12/16 97 9/16 103 7/16 29 3/16 17
Section
OPRJK
Blank
Unit Height Return Fan
Fan
ONE-PIECE Dimensions with Energy Recovery Wheel
Lifting Lug Locations
Tonnage
90 None 533 9/16 256 5/16 66 201 1/16 349 4/16 27 11/16 139 13/16 143 8/16
90 4 ft 581 13/16 256 5/16 66 201 1/16 349 4/16 54 2/16 139 13/16 143 8/16
105 None 551 9/16 256 5/16 66 201 1/16 349 4/16 27 11/16 139 13/16 143 8/16
105 4 ft 599 13/16 256 5/16 66 201 1/16 349 4/16 54 2/16 139 13/16 143 8/16
Section
Blank
Unit Dimensions
A B C1 C2 C3 D1 M N
Exhaust
Unit Height Return Fan
Fan
Blank
Tonnage
90 None 103 12/16 97 9/16 103 7/16 N/A 17
90 4 ft 103 12/16 97 9/16 103 7/16 N/A 17
105 None 103 12/16 97 9/16 103 7/16 N/A 17
105 4 ft 103 12/16 97 9/16 103 7/16 N/A 17
Section O P R J K
Condenser
Side
Condenser
Side
Unit WidthAir Handler Side
Unit WidthAir Handler Side
26 RT-SVX24K-EN
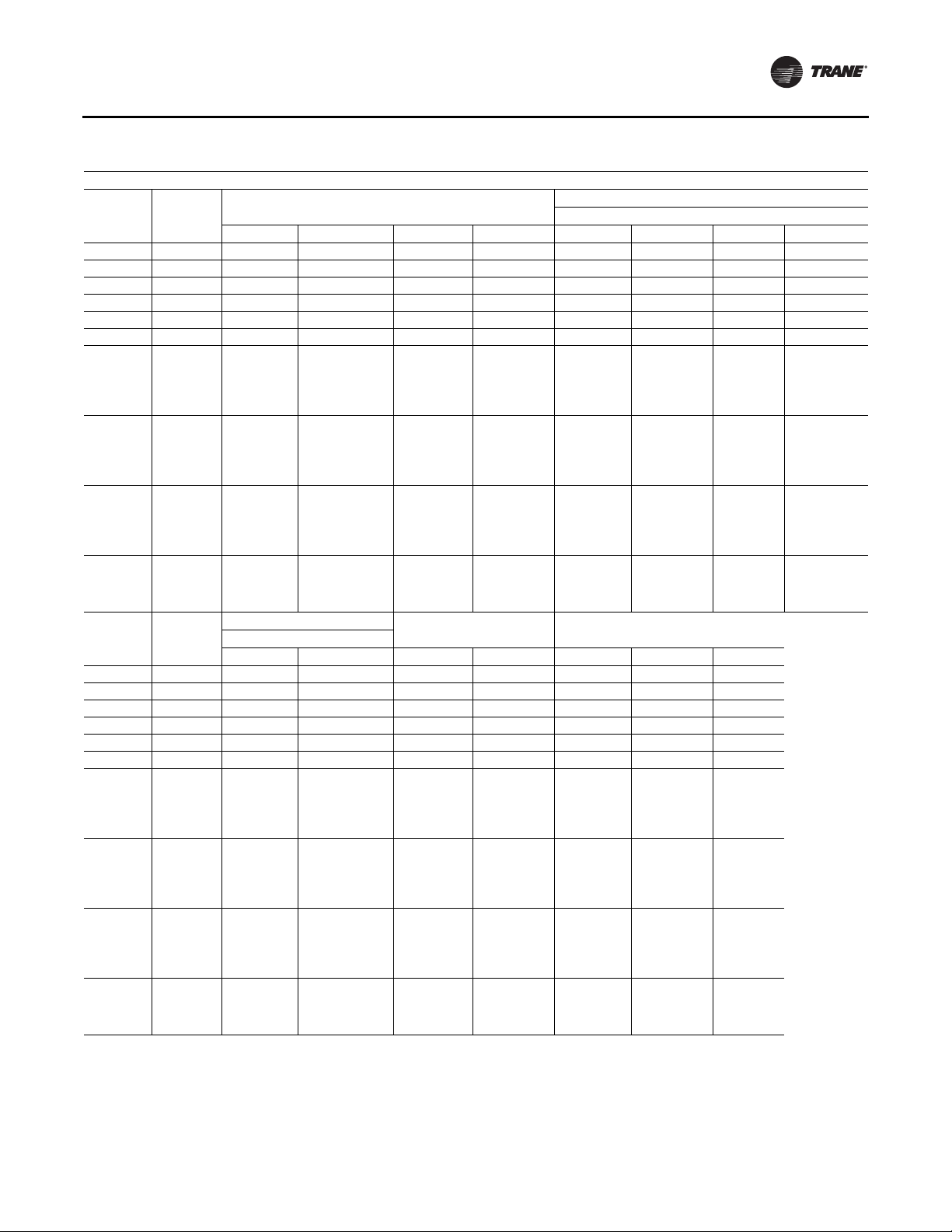
Dimensional Data
Table 6. Unit dimensions (In.)—two-piece unit air-cooled
TWO-PIECE Dimensions without Energy Recovery Wheel (ERW)
Lifting Lug Locations
Tonnage
90 None 454 4/16 159 15/16 330 14/16 121 6/16 66 252 14/16 N/A N/A
90 4 ft 502 7/16 159 15/16 379 1/16 121 6/16 66 252 14/16 368 6/16 N/A
90 8 ft 550 11/16 159 15/16 427 4/16 121 6/16 66 252 14/16 416 10/16 N/A
105 None 472 4/16 159 15/16 330 14/16 139 6/16 66 252 14/16 N/A N/A
105 4 ft 520 7/16 159 15/16 379 1/16 139 6/16 66 252 14/16 368 6/16 N/A
105 8 ft 568 11/16 159 15/16 427 4/16 139 6/16 66 252 14/16 416 10/16 N/A
120-150
(All Units
Except High
Heat Gas
Models)
120-150
(All Units
Except High
Heat Gas
Models)
120-150
(All Units
Except High
Heat Gas
Models)
120-150
(High Heat
Gas Models
Only)
Section
None 546 197 1/16 395 10/16 148 6/16 66 269 6/16 384 15/16 N/A
4 ft 594 4/16 197 1/16 443 13/16 148 6/16 66 269 6/16 433 2/16 N/A
8 ft 642 7/16 197 1/16 492 1/16 148 6/16 66 269 6/16 481 6/16 N/A
None 558 197 1/16 407 10/16 148 6/16 66 269 6/16 396 15/16 N/A
A B E F C1 C2 C3 C4
Blank
Unit Dimensions
Lug Locations
Blank
Tonnage
90 None 16 112 7/16 139 13/16 143 8/16 103 12/16 97 9/16 103 7/16
90 4 ft 16 112 7/16 139 13/16 143 8/16 103 12/16 97 9/16 103 7/16
90 8 ft 16 112 7/16 139 13/16 143 8/16 103 12/16 97 9/16 103 7/16
105 None 16 130 7/16 139 13/16 143 8/16 103 12/16 97 9/16 103 7/16
105 4 ft 16 130 7/16 139 13/16 143 8/16 103 12/16 97 9/16 103 7/16
105 8 ft 16 130 7/16 139 13/16 143 8/16 103 12/16 97 9/16 103 7/16
120-150
(All Units
Except High
Heat Gas
Models)
120-150
(All Units
Except High
Heat Gas
Models)
120-150
(All Units
Except High
Heat Gas
Models)
120-150
(High Heat
Gas Models
Only)
Continued on next page
Section
None 16 139 7/16 139 13/16 143 8/16 103 12/16 97 9/16 103 7/16
4 ft 16 139 7/16 139 13/16 143 8/16 103 12/16 97 9/16 103 7/16
8 ft 16 139 7/16 139 13/16 143 8/16 103 12/16 97 9/16 103 7/16
None 16 139 7/16 139 13/16 143 8/16 103 12/16 97 9/16 103 7/16
D1 D2 M N O P R
Unit Width Unit HeightCondenser Side
Air Handler Side
RT-SVX24K-EN 27
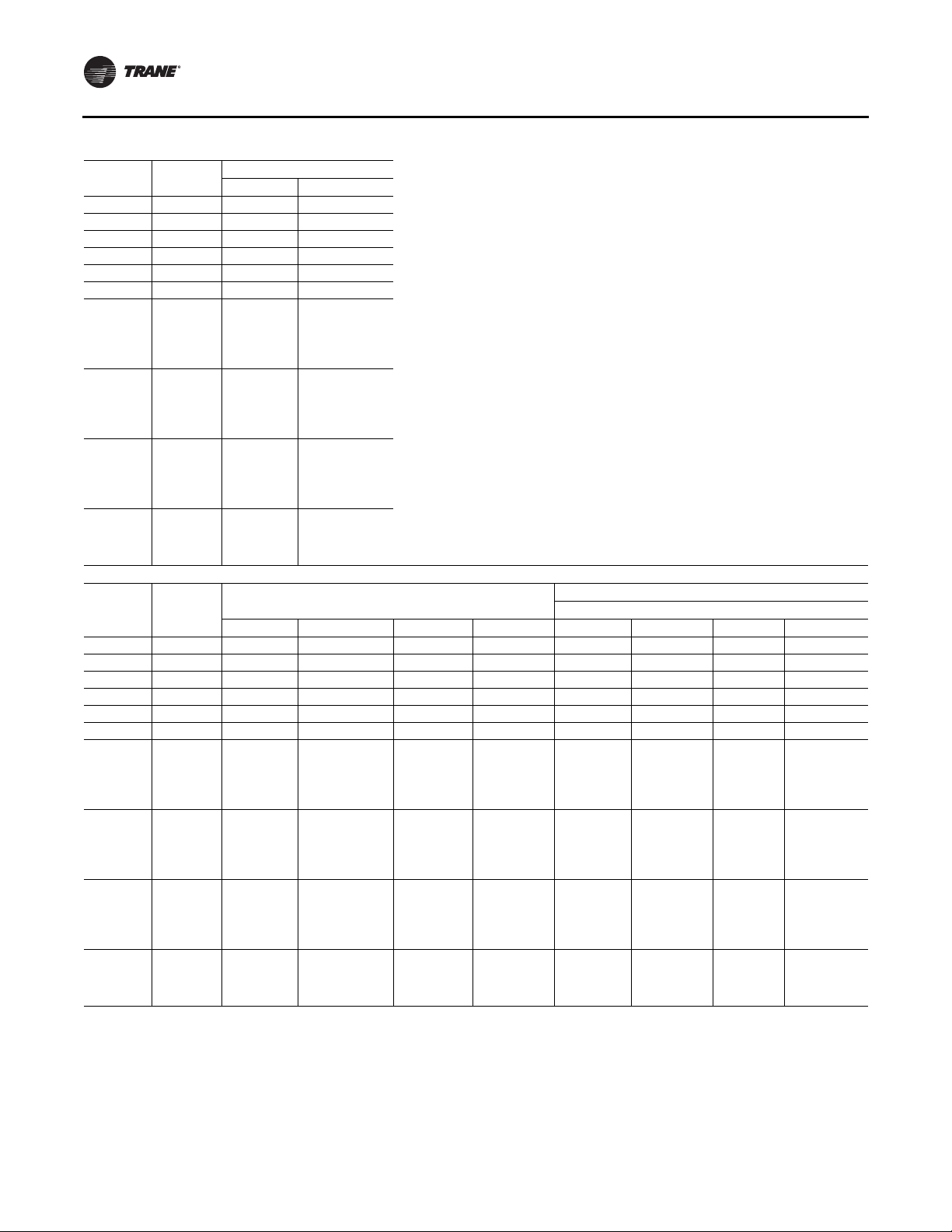
Dimensional Data
Table 6. Unit dimensions (In.)—two-piece unit air-cooled (continued)
Tonnage
90 None 29 3/16 17
90 4 ft 29 3/16 17
90 8 ft 29 3/16 17
105 None 29 3/16 17
105 4 ft 29 3/16 17
105 8 ft 29 3/16 17
120-150
(All Units
Except High
Heat Gas
Models)
120-150
(All Units
Except High
Heat Gas
Models)
120-150
(All Units
Except High
Heat Gas
Models)
120-150
(High Heat
Gas Models
Only)
Section
None 29 3/16 17
None 29 3/16 17
Blank
Blank
Tonnage
90 None 550 11/16 256 5/16 427 5/16 121 6/16 66 201 1/16 349 4/16 N/A
90 4 ft 598 14/16 256 5/16 475 8/16 121 6/16 66 201 1/16 349 4/16 464 13/16
90 8 ft 647 2/16 256 5/16 523 12/16 121 6/16 66 201 1/16 349 4/16 513
105 None 568 11/16 256 5/16 427 5/16 139 6/16 66 201 1/16 349 4/16 N/A
105 4 ft 616 14/16 256 5/16 475 8/16 139 6/16 66 201 1/16 349 4/16 464 13/16
105 8 ft 665 2/16 256 5/16 523 12/16 139 6/16 66 201 1/16 349 4/16 513
120-150
(All Units
Except High
Heat Gas
Models)
120-150
(All Units
Except High
Heat Gas
Models)
120-150
(All Units
Except High
Heat Gas
Models)
120-150
(High Heat
Gas Models
Only)
Continued on next page
Section
None 642 7/16 293 8/16 492 1/16 148 6/16 66 238 5/16 365 5/16 480 14/16
4 ft 690 10/16 293 8/16 540 4/16 148 6/16 66 238 5/16 365 5/16 529 2/16
8 ft 738 14/16 293 8/16 588 8/16 148 6/16 66 238 5/16 365 5/16 577 5/16
None 654 7/16 293 8/16 504 1/16 148 6/16 66 238 5/16 365 5/16 492 14/16
Return Fan Exhaust Fan
JK
4 ft 29 3/16 17
8 ft 29 3/16 17
TWO-PIECE Dimensions with Energy Recovery Wheel (ERW)
Unit Dimensions
A B E F C1 C2 C3 C4
Lifting Lug Locations
Air Handler Side
28 RT-SVX24K-EN
Table 6. Unit dimensions (In.)—two-piece unit air-cooled (continued)
Lug Locations
Blank
Tonnage
90 None 16 112 7/16 139 13/16 143 8/16 103 12/16 97 9/16 103 7/16
90 4 ft 16 112 7/16 139 13/16 143 8/16 103 12/16 97 9/16 103 7/16
90 8 ft 16 112 7/16 139 13/16 143 8/16 103 12/16 97 9/16 103 7/16
105 None 16 130 7/16 139 13/16 143 8/16 103 12/16 97 9/16 103 7/16
105 4 ft 16 130 7/16 139 13/16 143 8/16 103 12/16 97 9/16 103 7/16
105 8 ft 16 130 7/16 139 13/16 143 8/16 103 12/16 97 9/16 103 7/16
120-150
(All Units
Except High
Heat Gas
Models)
120-150
(All Units
Except High
Heat Gas
Models)
120-150
(All Units
Except High
Heat Gas
Models)
120-150
(High Heat
Gas Models
Only)
Section
None 16 139 7/16 139 13/16 143 8/16 103 12/16 97 9/16 103 7/16
4 ft 16 139 7/16 139 13/16 143 8/16 103 12/16 97 9/16 103 7/16
8 ft 16 139 7/16 139 13/16 143 8/16 103 12/16 97 9/16 103 7/16
None 16 139 7/16 139 13/16 143 8/16 103 12/16 97 9/16 103 7/16
Blank
Tonnage
90 None N/A 17
90 4 ft N/A 17
90 8 ft N/A 17
105 None N/A 17
105 4 ft N/A 17
105 8 ft N/A 17
120-150
(All Units
Except High
Heat Gas
Models)
120-150
(All Units
Except High
Heat Gas
Models)
120-150
(All Units
Except High
Heat Gas
Models)
120-150
(High Heat
Gas Models
Only)
Section
None N/A 17
4 ft N/A 17
8 ft N/A 17
None N/A 17
D1 D2 M N O P R
Return Fan Exhaust Fan
JK
Unit WidthCondenser Side Unit Height
Dimensional Data
RT-SVX24K-EN 29
Dimensional Data
Table 7. Unit dimensions (in.)—two-piece unit evaporative condenser
TWO-PIECE Dimensions without Energy Recovery Wheel (ERW)
Lifting Lug Locations
Tonnage
100-118 None 475 8/16 159 15/16 330 14/16 142 10/16 66 252 14/16 N/A N/A
100-118 4 ft 523 12/16 159 15/16 379 1/16 142 10/16 66 252 14/16 368 6/16 N/A
100-118 8 ft 571 15/16 159 15/16 427 5/16 142 10/16 66 252 14/16 416 10/16 N/A
128-162
(All Units
Except High
Heat Gas
Models)
128-162
(All Units
Except High
Heat Gas
Models)
128-162
(All Units
Except High
Heat Gas
Models)
128-162
(High Heat
Gas Models
Only)
Section
None 540 5/16 197 1/16 395 10/16 142 10/16 66 269 6/16 384 15/16 N/A
4 ft 588 8/16 197 1/16 443 14/16 142 10/16 66 269 6/16 433 2/16 N/A
8 ft 636 11/16 197 1/16 492 1/16 142 10/16 66 269 6/16 481 6/16 N/A
None 552 5/16 197 1/16 407 10/16 142 10/16 66 269 6/16 396 15/16 N/A
A B E F C1 C2 C3 C4
Blank
Unit Dimensions
Lug Locations
Tonnage
100-118 None 16 133 11/16 139 13/16 143 8/16 103 12/16 97 9/16 102 12/16
100-118 4 ft 16 133 11/16 139 13/16 143 8/16 103 12/16 97 9/16 102 12/16
100-118 8 ft 16 133 11/16 139 13/16 143 8/16 103 12/16 97 9/16 102 12/16
128-162
(All Units
Except High
Heat Gas
Models)
128-162
(All Units
Except High
Heat Gas
Models)
128-162
(All Units
Except High
Heat Gas
Models)
128-162
(High Heat
Gas Models
Only)
Continued on next page
Section
None 16 133 11/16 139 13/16 143 8/16 103 12/16 97 9/16 102 12/16
4 ft 16 133 11/16 139 13/16 143 8/16 103 12/16 97 9/16 102 12/16
8 ft 16 133 11/16 139 13/16 143 8/16 103 12/16 97 9/16 102 12/16
None 16 133 11/16 139 13/16 143 8/16 103 12/16 97 9/16 102 12/16
Blank
Condenser Side Unit Width Unit Height
D1 D2 M N O P R
Air Handler Side
30 RT-SVX24K-EN
 Loading...
Loading...