Page 1

User Guide
For TP-Link Omada Access Points
1910012768 REV4.6.0
June 2020
Page 2

CONTENTS
About This User Guide........................................................................................................ 1
Overview ................................................................................................................................. 3
1 Quick Start ....................................................................................................................... 4
1.1 Determine the Management Method .................................................................................................. 5
1.2 Build the Network Topology ................................................................................................................... 6
1.3 Log In to the EAP ........................................................................................................................................ 7
1.3.1 Log In via a Wireless Connection ................................................................................................ 7
1.3.2 Log In via a Wired Connection ...................................................................................................... 9
1.4 Do the Basic Configurations ................................................................................................................11
1.5 Configure and Manage the EAP ..........................................................................................................13
2 Configure the Network .............................................................................................. 14
2.1 Configure the Wireless Parameters ..................................................................................................15
2.1.1 Configure SSIDs .............................................................................................................................. 16
2.1.2 Configure Wireless Advanced Settings ................................................................................. 22
Radio Setting .................................................................................................................................... 22
Load Balance .................................................................................................................................... 24
Airtime Fairness .............................................................................................................................. 24
More Settings .................................................................................................................................. 25
2.2 Configure Portal Authentication ........................................................................................................26
Configure Portal............................................................................................................................................ 27
Configure Free Authentication Policy .................................................................................................. 33
2.3 Configure VLAN ........................................................................................................................................35
2.4 Configure MAC Filtering ........................................................................................................................36
2.5 Configure Scheduler ...............................................................................................................................38
2.6 Configure Band Steering .......................................................................................................................41
2.7 Configure QoS ...........................................................................................................................................43
I
Page 3

2.8 Configure Rogue AP Detection ...........................................................................................................47
Detect Rogue APs and Move the Rogue APs to the Trusted AP List ....................................... 48
Manage the Trusted AP List ..................................................................................................................... 50
3 Monitor the Network ..................................................................................................52
3.1 Monitor the EAP ........................................................................................................................................53
3.2 Monitor the Wireless Parameters ......................................................................................................54
Monitor the SSIDs ........................................................................................................................................ 55
Monitor the Radio Settings ....................................................................................................................... 56
Monitor Radio Traffic .................................................................................................................................. 56
Monitor LAN Traffic ..................................................................................................................................... 57
3.3 Monitor the Clients ..................................................................................................................................58
View Client Information .............................................................................................................................. 59
View Block Client Information ................................................................................................................. 60
4 Manage the EAP ...........................................................................................................61
4.1 Manage the IP Address of the EAP ....................................................................................................62
4.2 Manage System Logs .............................................................................................................................64
View System Logs ....................................................................................................................................... 65
Configure the Way of Receiving Logs .................................................................................................. 65
4.3 Configure Web Server............................................................................................................................67
4.4 Configure Management Access .........................................................................................................68
Configure Access MAC Management .................................................................................................. 68
Configure Management VLAN ................................................................................................................ 69
4.5 Configure LED ...........................................................................................................................................70
4.6 Configure Wi-Fi Control (Only for Certain Devices) ....................................................................70
4.7 Configure PoE Out (Only for Certain Devices) ..............................................................................71
4.8 Configure SSH ...........................................................................................................................................72
4.9 Configure SNMP .......................................................................................................................................73
5 Configure the System ................................................................................................75
II
Page 4

5.1 Configure the User Account ................................................................................................................76
5.2 Controller Settings ..................................................................................................................................77
Enabling Cloud-Based Controller Management ............................................................................... 77
Configuring Controller Inform URL ........................................................................................................ 78
5.3 Configure the System Time..................................................................................................................78
Configure the System Time ..................................................................................................................... 79
Configure Daylight Saving Time ............................................................................................................. 81
5.4 Reboot and Reset the EAP ....................................................................................................................83
5.5 Backup and Restore the Configuration............................................................................................84
5.6 Update the Firmware ..............................................................................................................................84
6 Application Example ..................................................................................................86
6.1 Determine the Network Requirements ............................................................................................87
6.2 Build the Network Topology .................................................................................................................87
6.3 Log in to the EAP ......................................................................................................................................88
6.4 Configure the EAP ...................................................................................................................................89
Configure SSIDs ........................................................................................................................................... 89
Configure Portal Authentication ............................................................................................................. 90
Configure Scheduler ................................................................................................................................... 92
6.5 Test the Network ......................................................................................................................................93
Appendix: Omada App .................................................................................................96
1 Install Omada App on the Mobile Device ........................................................................................97
2 Manage and Monitor your EAP Device .............................................................................................97
III
Page 5

About This User Guide
When using this guide, notice that features available in the EAP may vary by model and software
version. Availability of the EAP may also vary by region or ISP. All images, steps, and descriptions in
this guide are only examples and may not reflect your actual experience.
Some models featured in this guide may be unavailable in your country or region. For local sales
information, visit
The information in this document is subject to change without notice. Every effort has been made
in the preparation of this document to ensure the accuracy of the contents, but all statements,
information, and recommendations in this document do not constitute the warranty of any kind,
express or implied. Users must take full responsibility for their application of any product.
https://www.tp-link.com
.
Conventions
Unless otherwise noted, the introduction in this guide takes EAP245 as an example.
Wireless Speed, Range and Connected Devices Disclaimer
Maximum wireless transmission rates are the physical rates derived from IEEE Standard 802.11
specifications. Range and coverage specifications along with the number of connected devices
were defined according to test results under normal usage conditions. Actual wireless transmission
rate, wireless coverage, and number of connected devices are not guaranteed, and will vary as a
result of 1) environmental factors, including building materials, physical objects and obstacles, 2)
network conditions, including local interference, volume and density of traffic, product location,
network complexity, and network overhead and 3) client limitations, including rated performance,
location, connection quality, and client condition.
MU-MIMO Disclaimer (for EAPs that support MU-MIMO)
MU-MIMO capability requires client devices that also support MU-MIMO.
Seamless Roaming Disclaimer (for EAPs that support Seamless Roaming)
Seamless roaming requires both the access point and client devices to support 802.11k and
802.11v protocols.
Lightning and Electro-Static Discharge Protection Disclaimer (for Outdoor EAPs)
Protection against lightning and electro-static discharge may be achieved through proper product
setup, grounding and cable shielding. Refer to the instruction manual and consult an IT professional
to assist with setting up this product.
1
Page 6

More Info
Some models featured in this guide may be unavailable in your country or region. For local sales
information, visit
For technical support, latest software, and management app, visit
The Quick Installation Guide can be found where you find this guide or inside the package of the
EAP.
The authentication information can be found where you find this guide.
Specifications can be found on the product page at
To ask questions, find answers, and communicate with TP-Link users or engineers, please visit
https://community.tp-link.com
If you have any suggestions or needs on the product guides, welcome to email
techwriter@tp-link.com.cn
https://www.tp-link.com
to join TP-Link Community.
.
.
https://www.tp-link.com/support
https://www.tp-link.com
.
.
2
Page 7

Overview
Omada series products provide wireless coverage solutions for small-medium business and
households. They can either work independently as standalone APs or be centrally managed by
Omada Software Controller, Omada Hardware Controller (OC200/OC300), or Omada Cloud-Based
Controller, providing a flexible, richly-functional but easily configured wireless network for small-
medium business and households.
3
Page 8

1
This chapter introduces how to build a wireless network using the EAPs and how to
complete the basic settings. Follow the steps below:
1.
Determine the Management Method
2. Build the Network Topology
3. Log In to the EAP
4. Configure and Manage the EAP
Quick Start
4
Page 9

1.1 Determine the Management Method
Before building your network, choose a proper method to manage your EAP based on
your actual network situation. The EAP can support two configuration options: Standalone
Mode or Controller Mode.
■ Controller Mode
If you want to configure and manage a large-scale network centrally, which consists
of mass devices such as access points, switches, and gateways, Controller Mode is
recommended. In Controller Mode, the EAP can be centrally configured and monitored via
Omada SDN Controller.
To prepare the EAP for Omada SDN Controller Management, refer to
For detailed instructions about the network topology in such situations and how to use
Omada SDN Controller, refer to the User Guide of Omada SDN Controller. The guide can
be found on the download center of our official website:
https://www.tp-link.com/support/download/
■ Standalone Mode
If you have a relatively small-sized network and only one or just a small number of devices
need to be managed, Standalone Mode is recommended. In Standalone Mode, the EAP
can be singly configured and monitored via the GUI (Graphical User Interface, also called
web interface in this text).
This User Guide introduces how to configure and monitor the EAP in Standalone Mode.
Note:
The GUI is inaccessible while the EAP is managed by a controller. To turn the EAP back to
Standalone Mode and access its GUI, you can forget the EAP on the controller or reset the EAP.
Controller Settings
.
5
Page 10
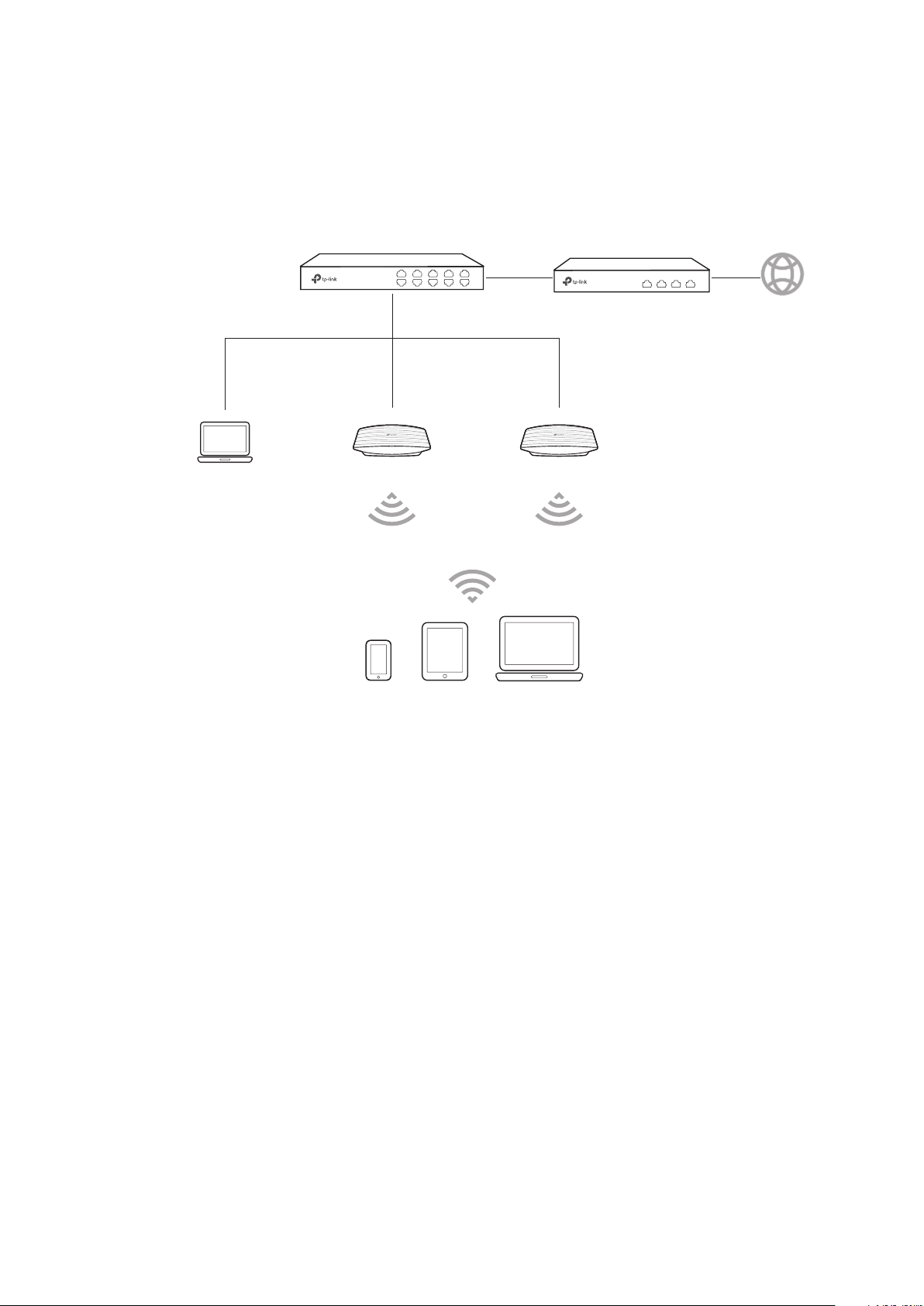
1.2 Build the Network Topology
To manage the EAPs in Standalone mode, refer to the following topology.
IP: 192.168.0.100
Switch
Router (DHCP Server)
LAN: 192.168.0.1
EAPEAPPC
Clients
Internet
• The router is the gateway of the network, and devices in the LAN surf the internet via
the router. At the same time, the router acts as a DHCP server to assign dynamic IP
addresses to the EAPs and clients.
• The Layer 2 switch is connected to the LAN interface of the router.
• The PC and the EAPs are all connected to the Layer 2 switch. Since the PC and the EAPs
are in the same network segment, the PC can log in to the web pages of the EAPs and
manage them.
6
Page 11
1.3 Log In to the EAP
The following sections introduce how to log in to the EAP via a wireless connection and a
wired connection.
1.3.1 Log In via a Wireless Connection
To access the management web page via a wireless connection, you can use either the
domain name or the IP address of the EAP. We recommend you to log in using the domain
name for a wireless connection. In this method, you needn’t know the IP address of the
EAP, but you need to prepare a wireless client device, such as a wireless laptop. Follow the
steps below to log in to the EAP via domain name:
1. Set the wireless client device to get IP settings assigned automatically.
2. Search the default SSID (Network name) using your wireless client device and connect
to the wireless network of the EAP. The default SSID of the EAP is printed on the
product label at the bottom of the device. The dual-band EAP has two default SSIDs
named TP-Link_2.4GHz_XXXXXX and TP-Link_5GHz_XXXXXX on the 2.4GHz band
and 5GHz band, and the single-band EAP has a default SSID named TP-Link_2.4GHz_
XXXXXX on the 2.4GHz band.
7
Page 12
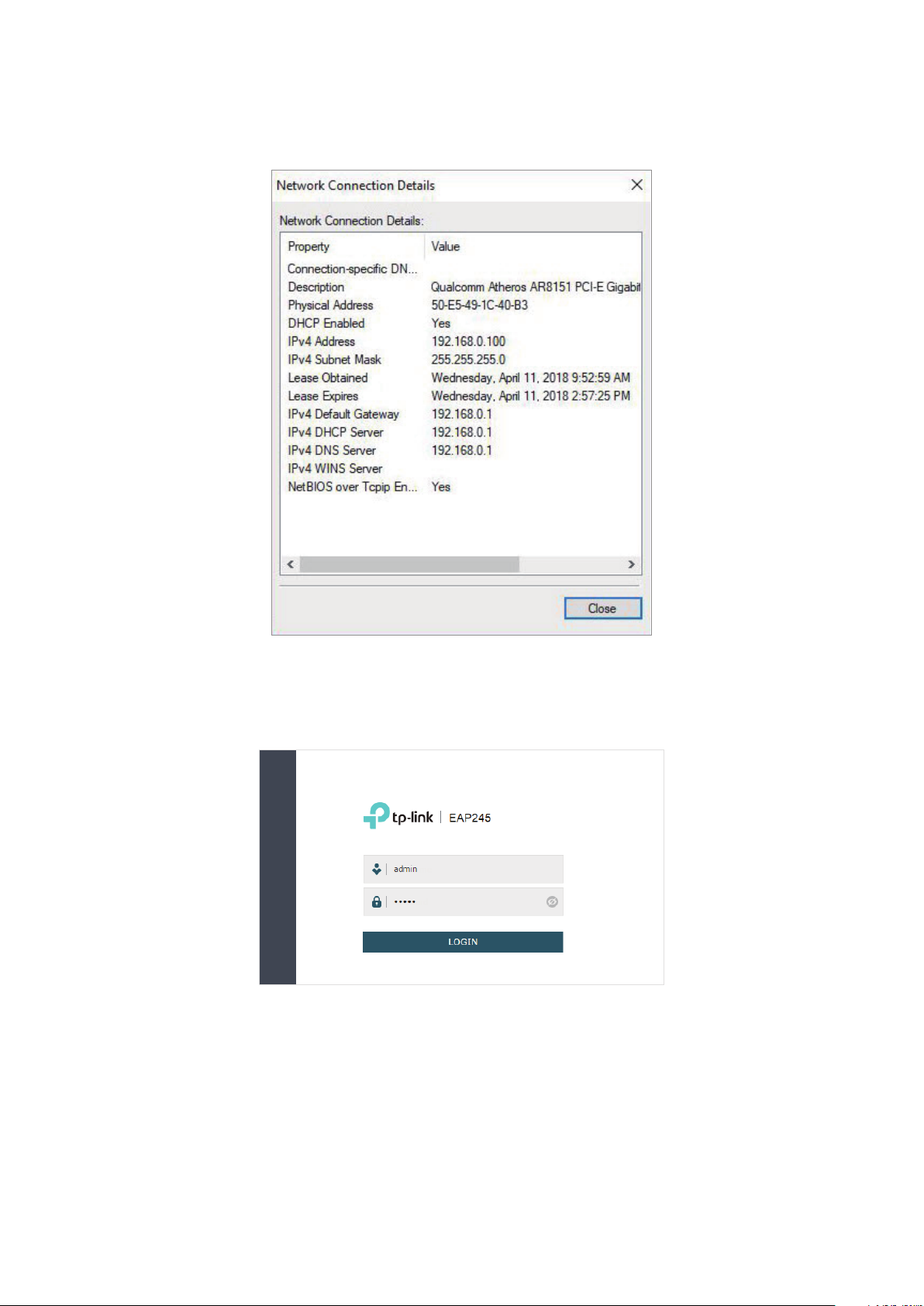
3. Make sure that the wireless client has been assigned the IP address and has got the IP
address of the DNS server and the gateway.
4. Launch a web browser on the client device and enter http://tplinkeap.net in the
address bar to load the login page of the EAP. Use admin for both of the username and
password to log in.
Tips:
To facilitate access to the EAP via a wired device, you can set a static IP address for the EAP and
remember it well or write it down. But make sure that this IP address is not being used in the same
LAN. For detailed instructions about how to set a static IP address for the EAP, refer to
IP Address of the EAP
.
Manage the
8
Page 13

1.3.2 Log In via a Wired Connection
For a wired connection, you can only log in to the EAP via its IP address. In this method,
you need to know the IP address of the EAP first. Follow the steps below to log in via the IP
address of the EAP with a wired client. The method of log in via the IP address wirelessly is
similar.
1. Get the IP address of the EAP. There are two methods.
• Log in to the router which acts as the DHCP server. In the DHCP client list, find the IP
address of your EAP according to its MAC address. The MAC address can be found
at the bottom of the EAP.
• Go to https://www.tp-link.com/download/EAP-Controller.html#EAP_Discovery_Tool
to download EAP Discovery Utility. EAP Discovery Utility is a software that can scan
all EAPs in the same network segment. Install and launch EAP Discovery Utility on the
PC, and find the IP address of the EAP. In the following figure, the IP address of the
EAP is 192.168.0.5.
9
Page 14
2. Launch a web browser and enter 192.168.0.5 in the address bar to load the login page
of the EAP. Use admin for both of the username and password to log in.
Tips:
• Some EAP models only works with certain software version of Discovery Utility. If your Discovery
Utility can’t discover your EAP anyway, try a different software version.
• To facilitate access to the EAP via a wired device, you can set a static IP address for the EAP and
remember it well or write it down. But make sure that this IP address is not being used in the same
LAN. For detailed instructions about how to set a static IP address for the EAP, refer to
the IP Address of the EAP
• The DHCP fallback IP address is 192.168.0.254 by default, which you can use to log in to its
web management page when the DHCP server is not available in your network. Follow the steps
below:
.
Manage
1. Connect the EAP to your computer with an Ethernet Cable.
2. Assign a static IP address 192.168.0.X (X ranges between 2 and 253) together with the subnet
mask 255.255.255.0 to your computer.
3. Open a web browser and enter 192.168.0.254 in the address bar to load the login page of the
E A P.
10
Page 15
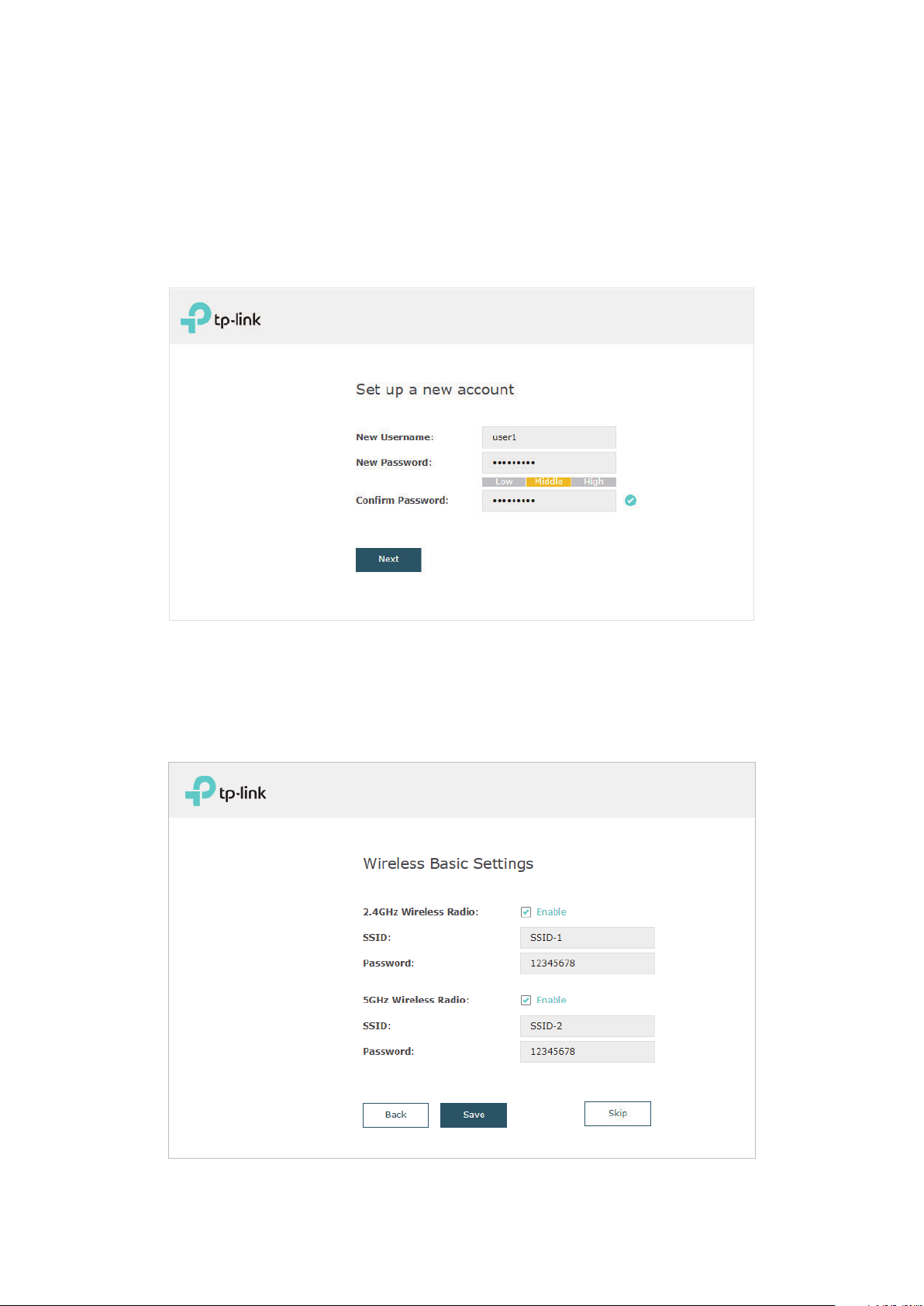
1.4 Do the Basic Configurations
After Logging in to EAP, follow the step-by-step instructions to complete the basic
configurations.
1. In the pop-up window, configure a new username and a new password for your user
account, then click Next.
2. For the dual-band EAP, select at least one radio band between 2.4GHz and 5GHz to
configure the SSID and password. For the single-band EAP, configure the SSID and
password on the 2.4GHz band. Click Save. You can also skip this step and configure
wireless settings later on the management page.
11
Page 16
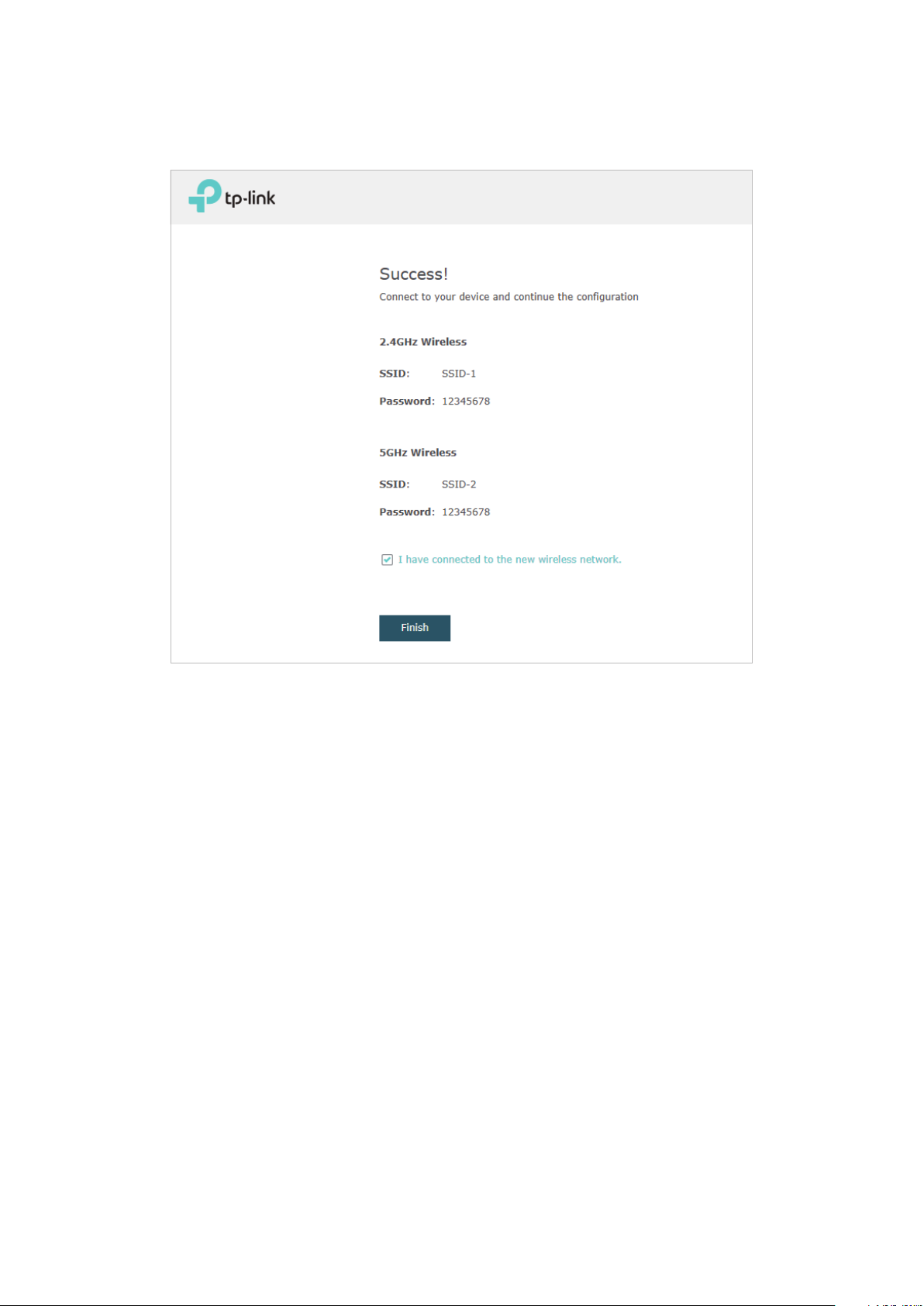
3. The following page will appear. Make sure that your device has connected to the new
wireless network and tick the checkbox. Then click Finish.
Tips:
If needed, you can also create more new SSIDs. For detailed instructions about how to create new
SSIDs, refer to
Configure SSIDs
.
12
Page 17
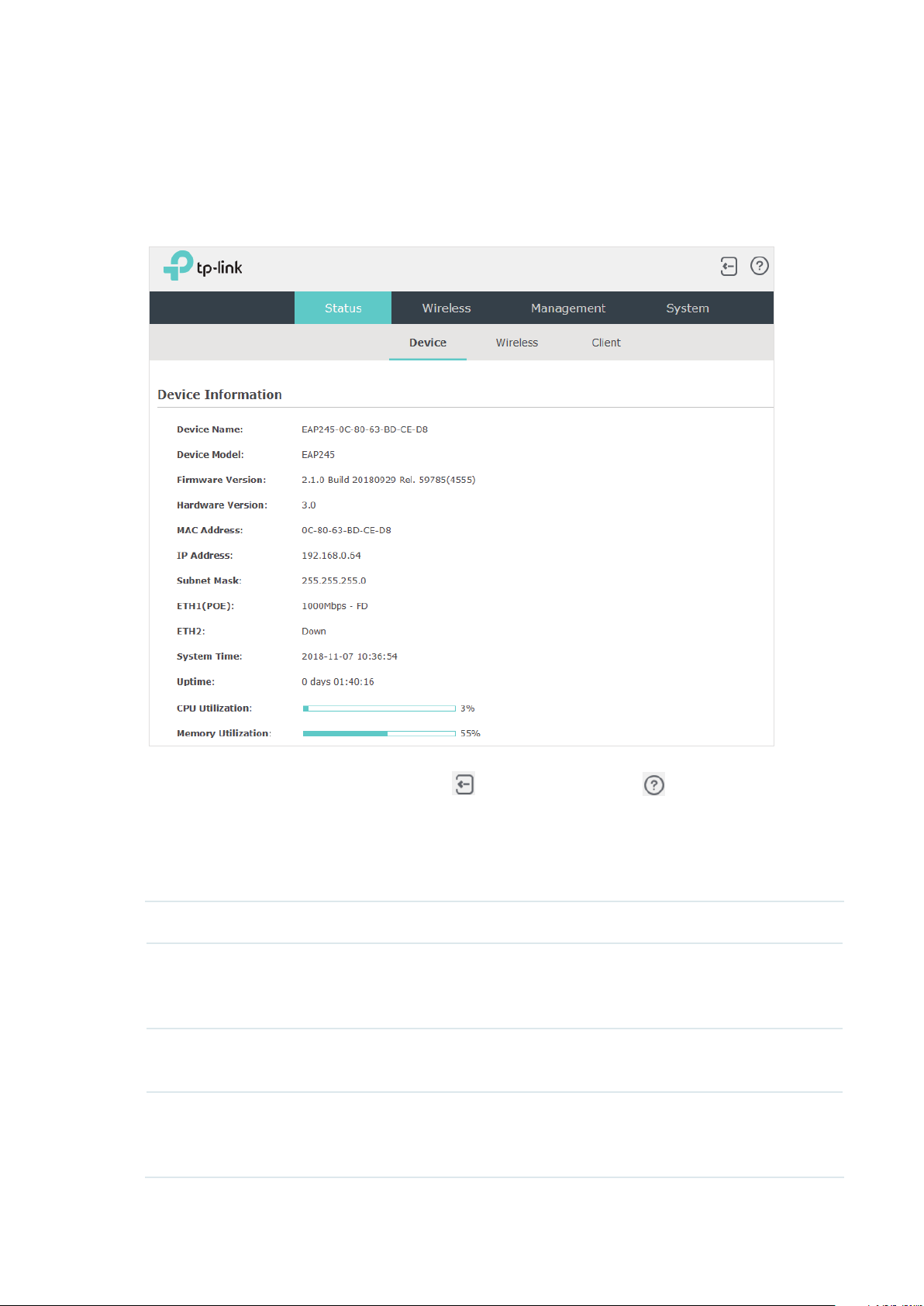
1.5 Configure and Manage the EAP
After all the steps above are completed, the legal wireless clients can enjoy the internet via
the EAP. Additionally, you can configure the advanced functions of the EAP according to
your need, and manage it conveniently on the web page.
On the top of the page, you can click to log out and click to open the technical
support website.
There are four tabs: Status, Wireless, Management and System. The following table
introduces what you can configure under each tab.
Status You can view the information of the EAP, wireless traffic and clients.
Wireless You can configure the wireless parameters and the advanced features, such
as Portal, VLAN, MAC Filtering, Scheduler, Band Steering, QoS and Rogue AP
Detection.
Management You can manage the EAP using the management features, such as System
Logs, Web Server, Management Access, LED Control, SSH and SNMP.
System You can configure the system parameters, including the login account and
the system time. In addition, you can reboot and reset the EAP, backup and
restore the configuration, and upgrade the EAP using the new firmware file.
13
Page 18

2
This chapter introduces how to configure the network parameters and the advanced
features of the EAP, including:
• Configure the Wireless Parameters
• Configure Portal Authentication
• Configure VLAN
• Configure MAC Filtering
• Configure Scheduler
• Configure Band Steering
• Configure QoS
Congure the Network
• Configure Rogue AP Detection
14
Page 19
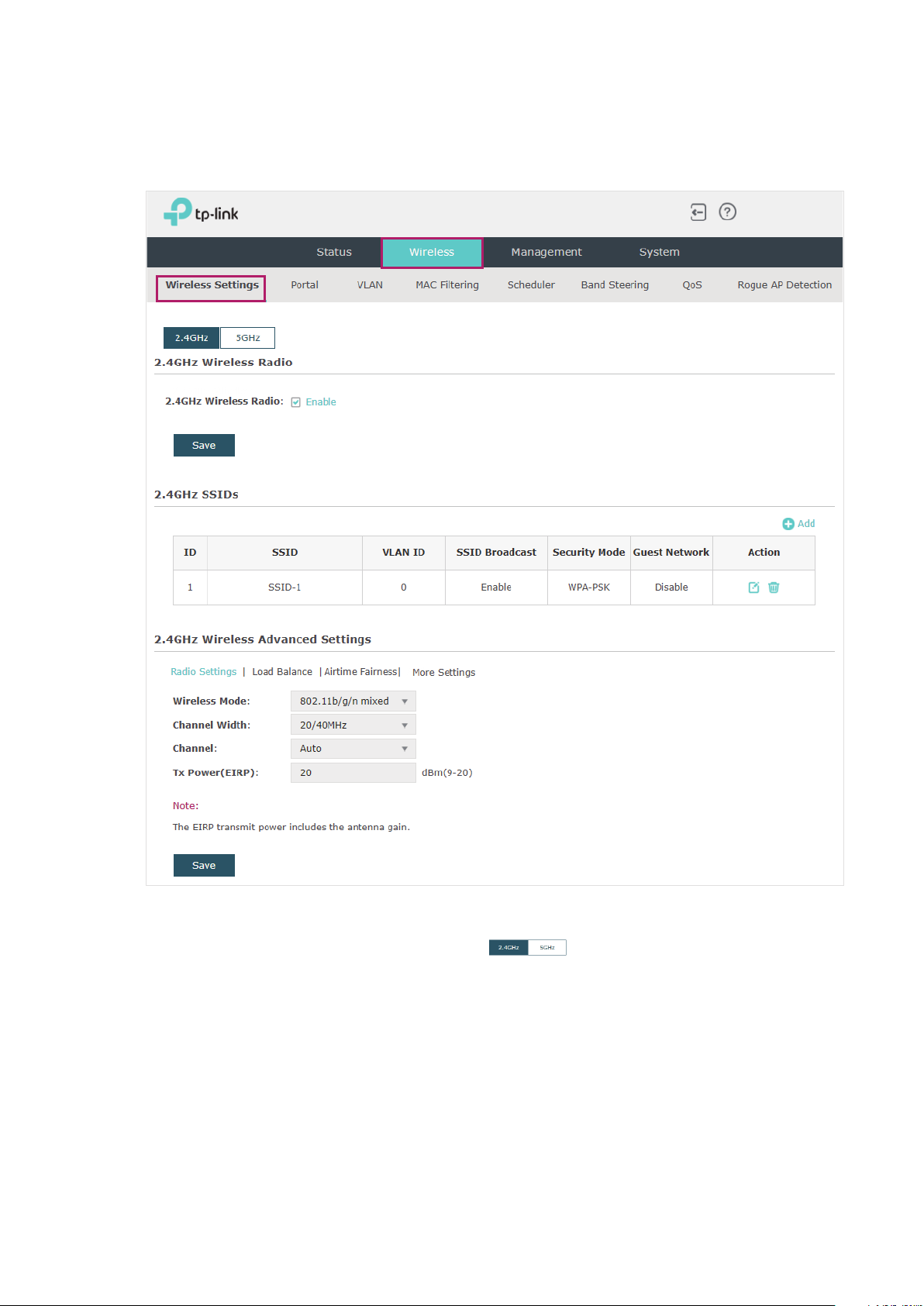
2.1 Configure the Wireless Parameters
To configure the wireless parameters, go to the Wireless > Wireless Settings page.
For a dual-band EAP, there are two bands: 2.4GHz and 5GHz. The wireless parameters are
separately set on each band. You can click to select a band and configure the
wireless parameters on this band.
15
Page 20
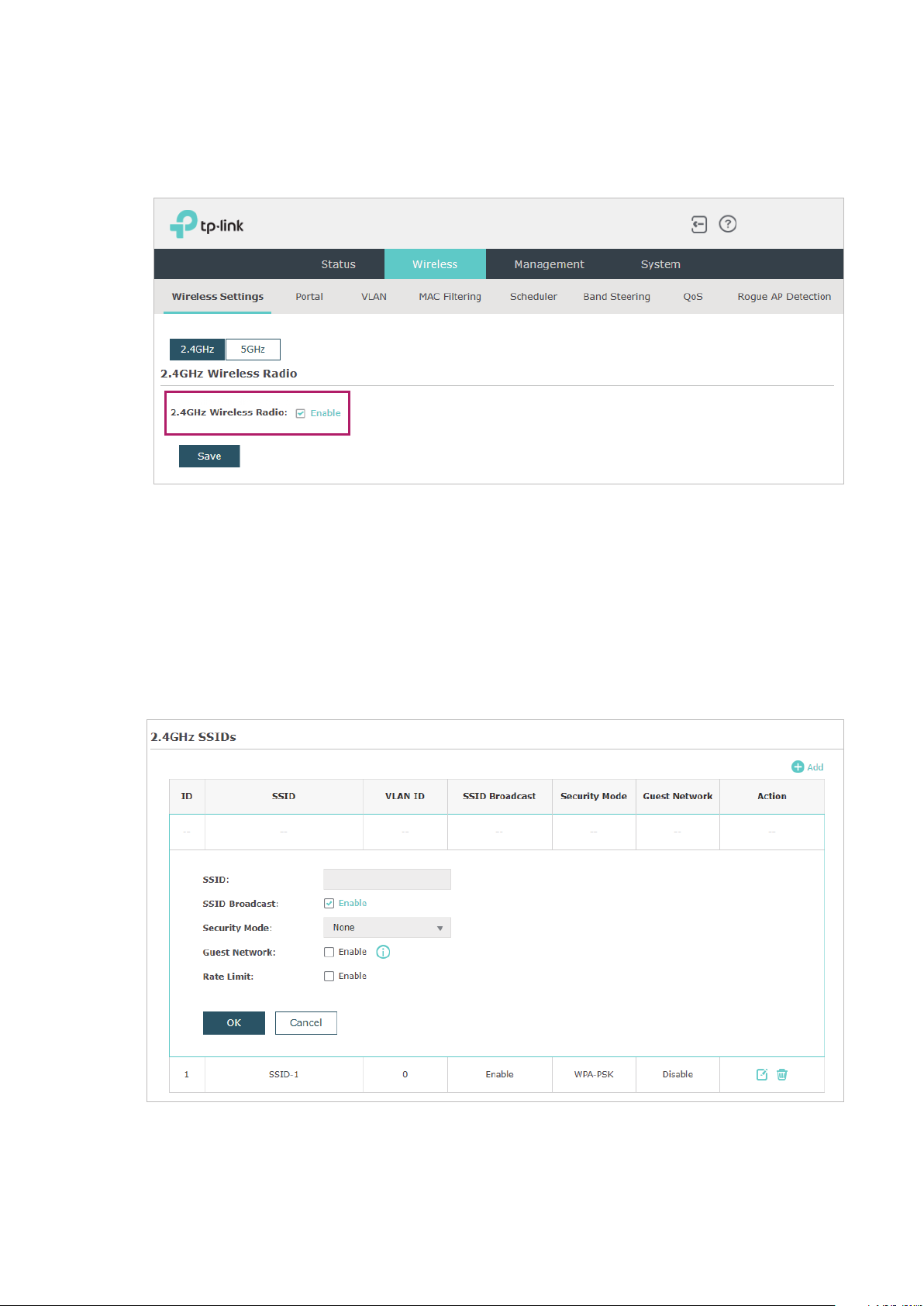
Before configuring the wireless parameters on each band, check the box to enable 2.4GHz
or 5GHz Wireless Radio. Only when this option is enabled will the wireless radio on 2.4GHz
or 5GHz band works.
Demonstrated with 2.4GHz, the following sections introduce these contents:
SSIDs
and
Configure Wireless Advanced Settings
2.1.1 Configure SSIDs
SSID (Service Set Identifier) is used as an identifier for a wireless LAN, and is commonly
called as the “network name“. Clients can find and access the wireless network through
the SSID. For one EAP, you can build up to eight SSIDs per frequency band.
Configure
.
16
Page 21
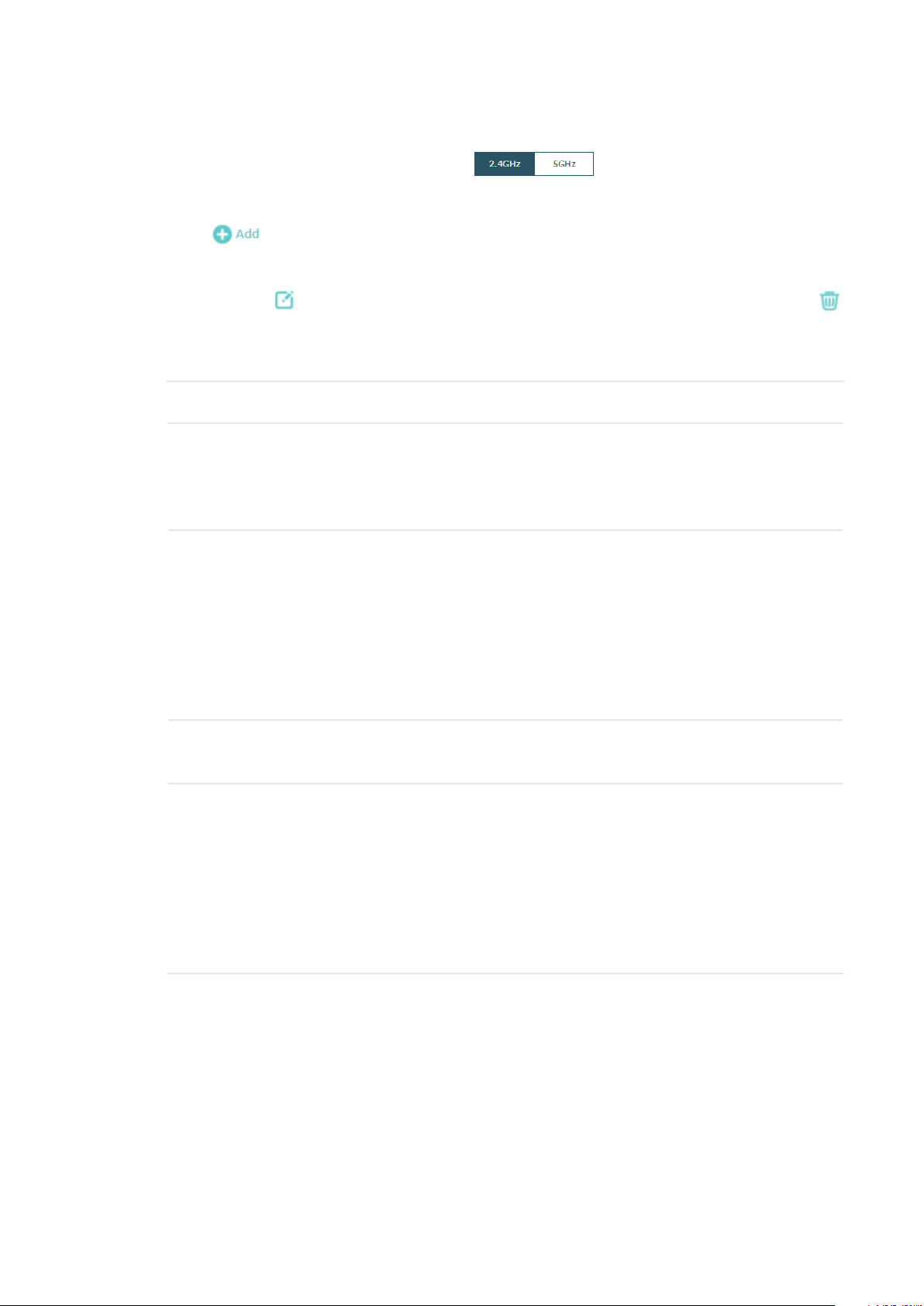
Follow the steps below to create an SSID on the EAP:
1. If your EAP is a dual-band device, click to choose a frequency band on
which the new SSID will be created.
2. Click to add a new SSID on the chosen band.
Tips:
You can also click to edit the specific SSID which already exists in the list. And you can click
to delete the SSID in the list.
3. Configure the following required parameters for this SSID:
SSID Specify a name for the wireless network.
SSID Broadcast With the option enabled, EAP will broadcast the SSID to the nearby
hosts, so that those hosts can find the wireless network identified by
this SSID. If this option is disabled, users must enter the SSID manually
to connect to the EAP.
Security Mode Select the security mode of the wireless network. There are four
options:
None
: Clients can access the wireless network without authentication.
WEP/WPA-Enterprise/WPA-Personal
authentication before accessing the wireless network. For network
security, we recommend that you encrypt your wireless network. The
following sections will introduce how to configure these security modes.
Guest Network With this option enabled, guest network will block clients from reaching
any private IP subnet.
Rate Limit With this option enabled, the download and upload rate of each client
which connects to the SSID will be limited to balance bandwidth usage.
You can limit the download and upload rate for some specific clients by
configuring rate limit in client list, refer to
more details.
Note that the download and upload rate will be limited to the smaller
value if you set the limit value both in SSID and client configuration.
: Clients need to pass the
View Client Information
4. Click OK to create the SSID.
Following is the detailed instructions about how to configure
WEP, WPA-Enterprise
to get
and
WPA-Personal
.
• WEP
WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy) is a traditional encryption method. It has been proved
that WEP has security flaws and can easily be cracked, so WEP cannot provide effective
17
Page 22
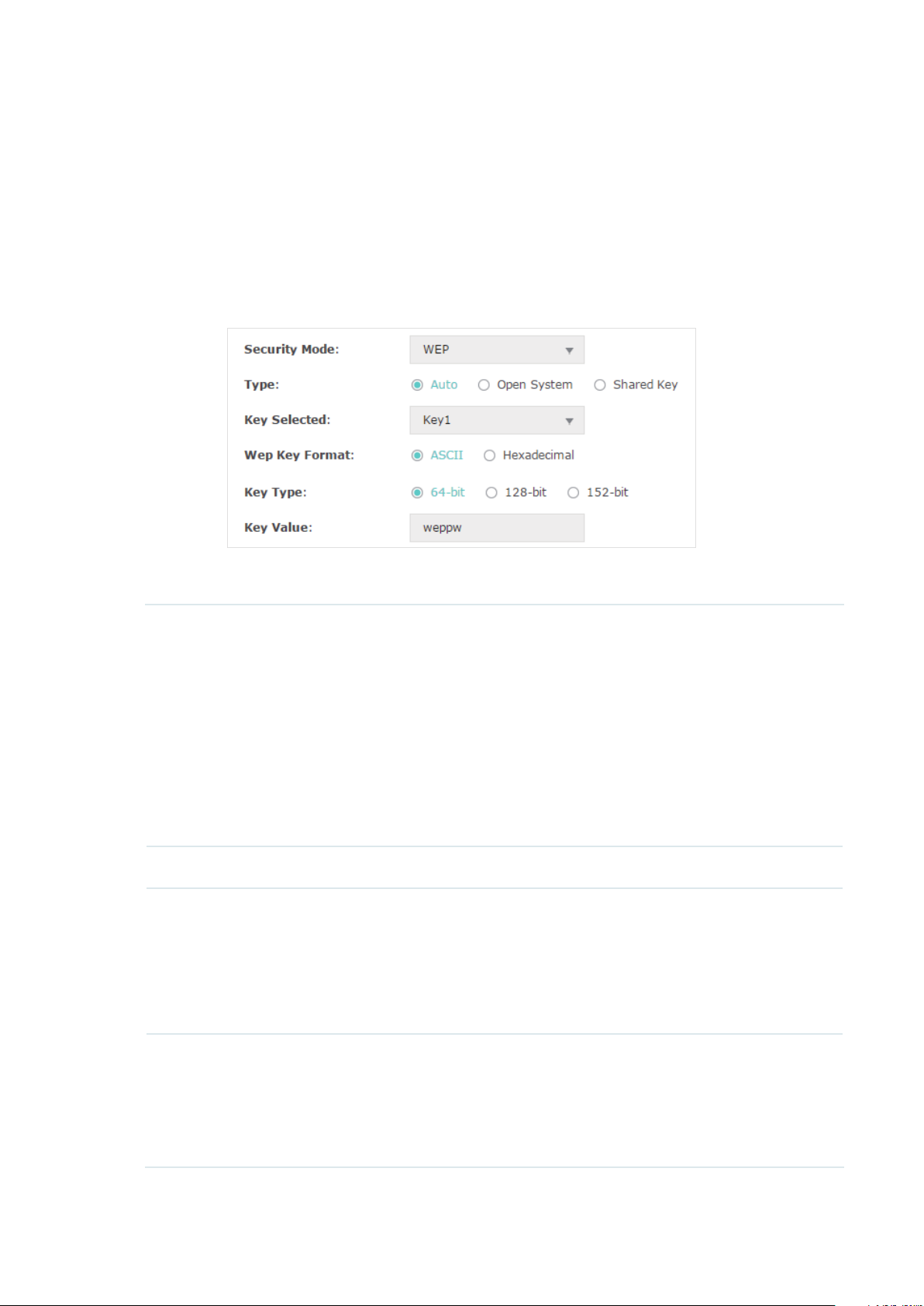
protection for wireless networks. Since WPA-Personal and WPA-Enterprise are much
safer than WEP, we recommend that you choose WPA-Personal or WPA-Enterprise if your
clients also support them.
Note:
WEP is not supported in 802.11n mode or 802.11ac mode. If WEP is applied in 802.11n, 802.11 ac
or 802.11n/ac mixed mode, the clients may not be able to access the wireless network. If WEP is
applied in 802.11b/g/n mode (2.4GHz) or 802.11a/n (5GHz), the EAP may work at a low transmission
rate.
The following table detailedly introduces how to configure each item:
Type Select the authentication type for WEP.
Auto: The EAP can select Open System or Shared Key automatically based
on the wireless capability and request of the clients.
Open System: Clients can pass the authentication and associate with
the wireless network without password. However, correct password is
necessary for data transmission.
Shared Key: Clients have to input the correct password to pass the
authentication, otherwise the clients cannot associate with the wireless
network or transmit data.
Key Selected Select one key to specify. You can configure four keys at most.
WEP Key Format Select ASCII or Hexadecimal as the WEP key format.
ASCII: With this format selected, the WEP key can be any combination of
keyboard characters of the specified length.
Hexadecimal: With this format selected, the WEP key can be any
combination of hexadecimal digits (0-9, a-f, A-F) with the specified length.
Key Type Select the WEP key length for encryption.
64Bit: Enter 10 hexadecimal digits or 5 ASCII characters.
128Bit: Enter 26 hexadecimal digits or 13 ASCII characters.
152Bit: Enter 32 hexadecimal digits or 16 ASCII characters.
18
Page 23
Key Value Enter the WEP keys. The length and valid characters are determined by the
key format and key type.
• WPA-Enterprise
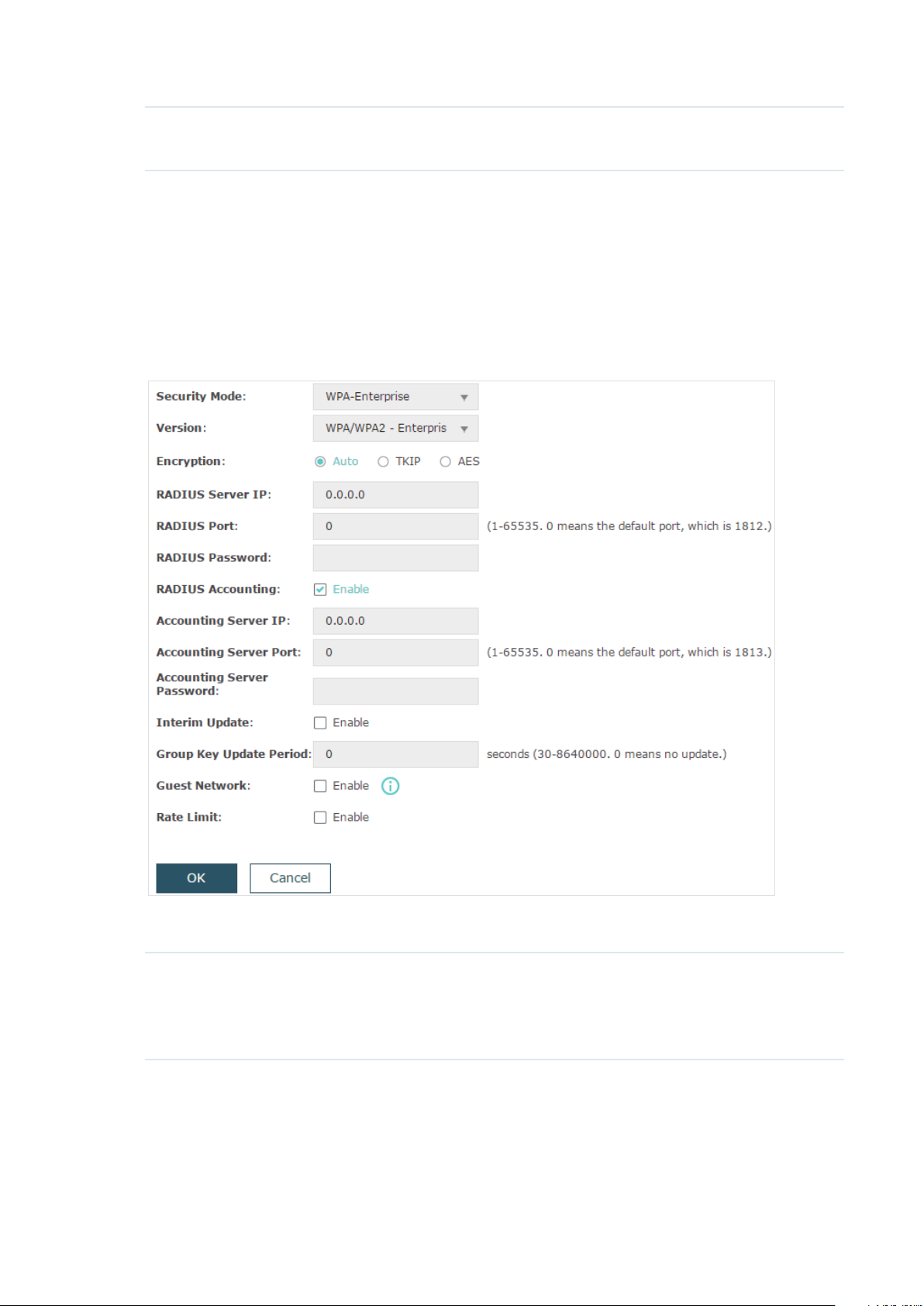
WPA-Enterprise (Wi-Fi Protected Access-Enterprise) is a safer encryption method
compared with WEP and WPA-Personal. It requires a RADIUS server to authenticate the
clients via 802.1X and EAP (Extensible Authentication Protocol). WPA-Enterprise can
generate different passwords for different clients, which ensures higher network security.
But it also costs more to maintain the network, so it is more suitable for business networks.
The following table introduces how to configure each item:
Version Select the version of WPA-Enterprise according to your needs. If you
select WPA/WPA2-Enterprise, the EAP automatically decides whether
to use WPA-Enterprise or WPA2-Enterprise during the authentication
process.
19
Page 24

Encryption Select the Encryption type. Note that some encryption type is only
available under certain circumstances.
Auto: The default setting is Auto and the EAP will select TKIP or AES
automatically based on the client device’s request.
TKIP: Temporal Key Integrity Protocol. TKIP is not supported in
802.11n mode, 802.11ac mode or 802.11n/ac mixed mode. If TKIP is
applied in 802.11n, 802.11 ac or 802.11n/ac mixed mode, the clients
may not be able to access the wireless network. If TKIP is applied in
11b/g/n mode (2.4GHz) or 11a/n mode(5GHz), the device may work at
a low transmission rate.
AES: Advanced Encryption Standard. It is securer than TKIP.
RADIUS Server IP Enter the IP address of the RADIUS Server.
RADIUS Port Enter the port number of the RADIUS Server.
RADIUS Password Enter the shared secret key of the RADIUS server.
RADIUS Accounting Enable or disable RADIUS accounting feature.
Accounting Server IP Enter the IP address of the accounting server.
Accounting Server
Enter the port number of the accounting server.
Port
Accounting Server
Enter the shared secret key of the accounting server.
Password
Interim Update With this option enabled, you can specify the duration between
accounting information updates. By default, the function is disabled.
Enter the appropriate duration between updates for EAPs in Interim
Update Interval.
Interim Update
Interval
Group Key Update
Period
With Interim Update enabled, specify the appropriate duration
between updates for EAPs. The default duration is 600 seconds.
Specify an update period of the encryption key. The update period
instructs how often the EAP should change the encryption key. 0
means that the encryption key does not change at anytime.
20
Page 25
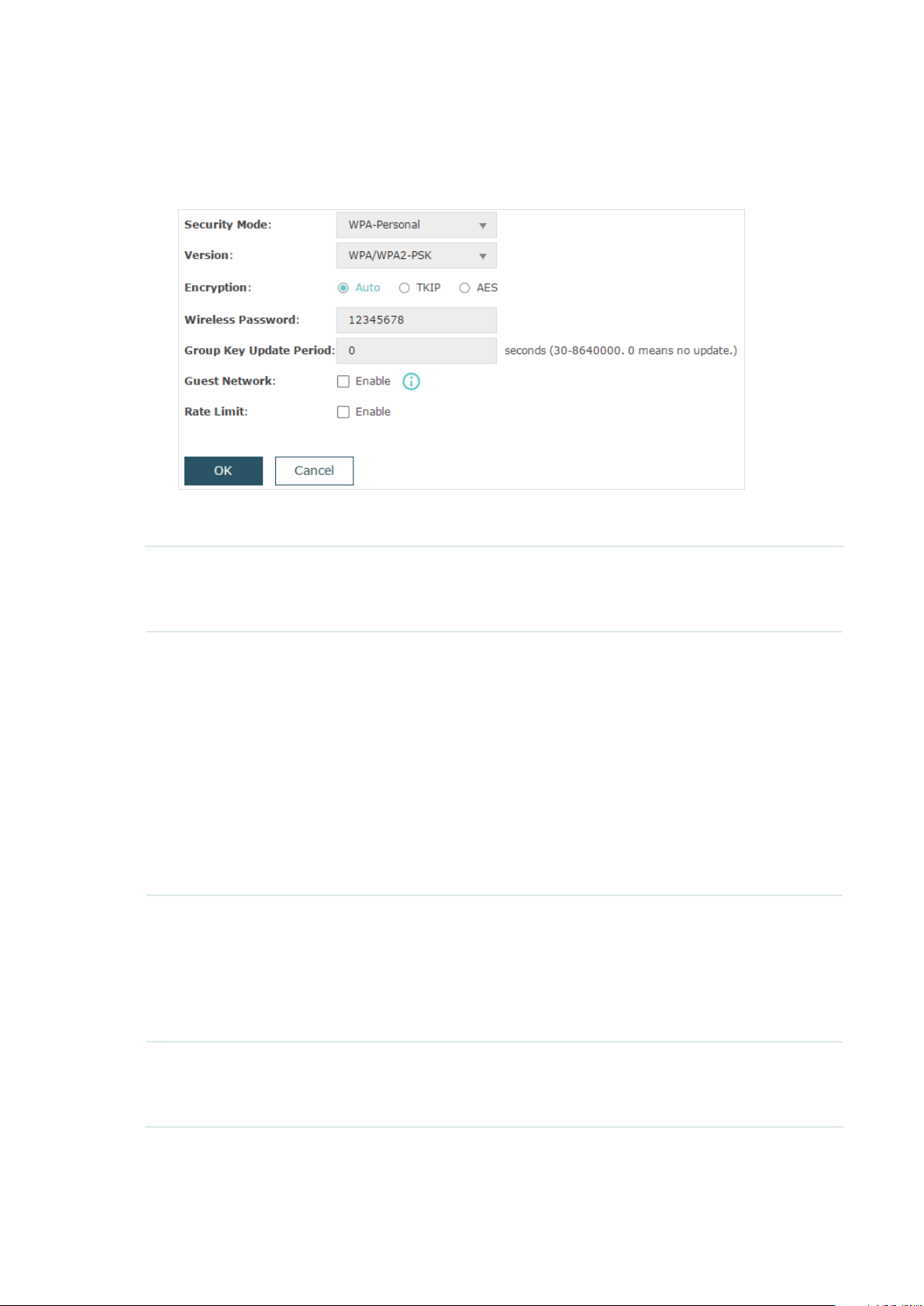
• WPA-Personal
WPA-Personal is based on a pre-shared key. It is characterized by high safety and simple
settings, so it is mostly used by common households and small businesses.
The following table introduces how to configure each item:
Version Select the version of WPA-Personal according to your needs. If you select
WPA/WPA2-PSK, the EAP automatically decides whether to use WPA-PSK
or WPA2-PSK during the authentication process.
Encryption Select the Encryption type. Note that some encryption type is only available
under certain circumstances.
Auto: The default setting is Auto and the EAP will select TKIP or AES
automatically based on the client device’s request.
TKIP: Temporal Key Integrity Protocol. TKIP is not supported in 802.11n
mode, 802.11ac mode or 802.11n/ac mixed mode. If TKIP is applied in
802.11n, 802.11 ac or 802.11n/ac mixed mode, the clients may not be able
to access the wireless network. If TKIP is applied in 11b/g/n mode (2.4GHz)
or 11a/n mode(5GHz), the device may work at a low transmission rate.
AES: Advanced Encryption Standard. It is securer than TKIP.
Wireless
Password
Group Key
Update Period
Configure the wireless password with ASCII or Hexadecimal characters.
• For ASCII, the length should be between 8 and 63 and the valid characters
contain numbers, letters (case-sensitive) and common punctuations.
• For Hexadecimal, the length should be between 8 and 64, and the valid
characters contain: 0-9, a-f, A-F.
Specify an update period of the encryption key. The update period instructs
how often the EAP should change the encryption key. 0 means that the
encryption key does not change at anytime.
21
Page 26
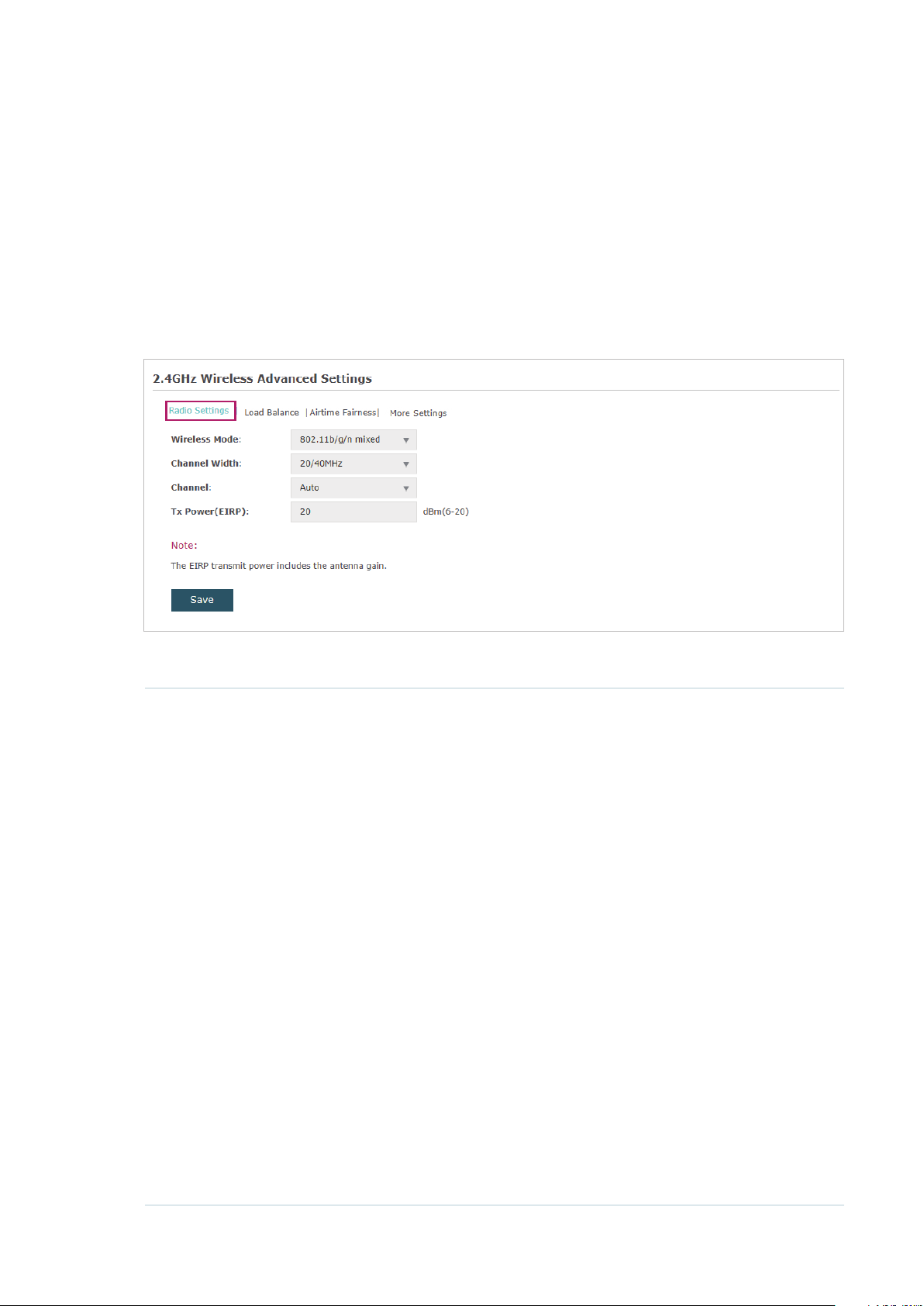
2.1.2 Configure Wireless Advanced Settings
Proper wireless parameters can improve the performance of your wireless network.
This section introduces how to configure the advanced wireless parameters of the EAP,
including
Radio Setting, Load Balance, Airtime Fairness
and
More Settings
.
Radio Setting
Radio settings directly control the behavior of the radio in the EAP and its interaction with
the physical medium; that is, how and what type of signal the EAP emits.
Select the frequency band (2.4GHz/5GHz) and configure the following parameters.
Wireless Mode Select the IEEE 802.11 mode the radio uses.
• For 2.4GHz:
802.11b/g/n/ax mixed: All of 802.11b, 802.11g, 802.11n, and 802.11ax
clients operating in the 2.4GHz frequency can connect to the EAP. Note
that 802.11ax is only available for certain devices.
802.11b/g/n mixed: All of 802.11b, 802.11g, and 802.11n clients operating
in the 2.4GHz frequency can connect to the EAP.
802.11b/g mixed: Both 802.11b and 802.11g clients can connect to the
EAP.
802.11n only: Only 802.11n clients can connect to the EAP.
• For 5GHz:
802.11a/n/ac/ax mixed: All of 802.11a, 802.11n, 802.11ac, and 802.11ax
clients operating in the 5GHz frequency can connect to the EAP. Note that
802.11ax is only available for certain devices.
802.11a/n/ac mixed: All of 802.11a, 802.11n, and 802.11ac clients
operating in the 5GHz frequency can connect to the EAP.
802.11n/ac mixed: Both 802.11n clients and 802.11ac clients operating in
the 5GHz frequency can connect to the EAP.
802.11ac only: Only 802.11ac clients can connect to the EAP.
22
Page 27
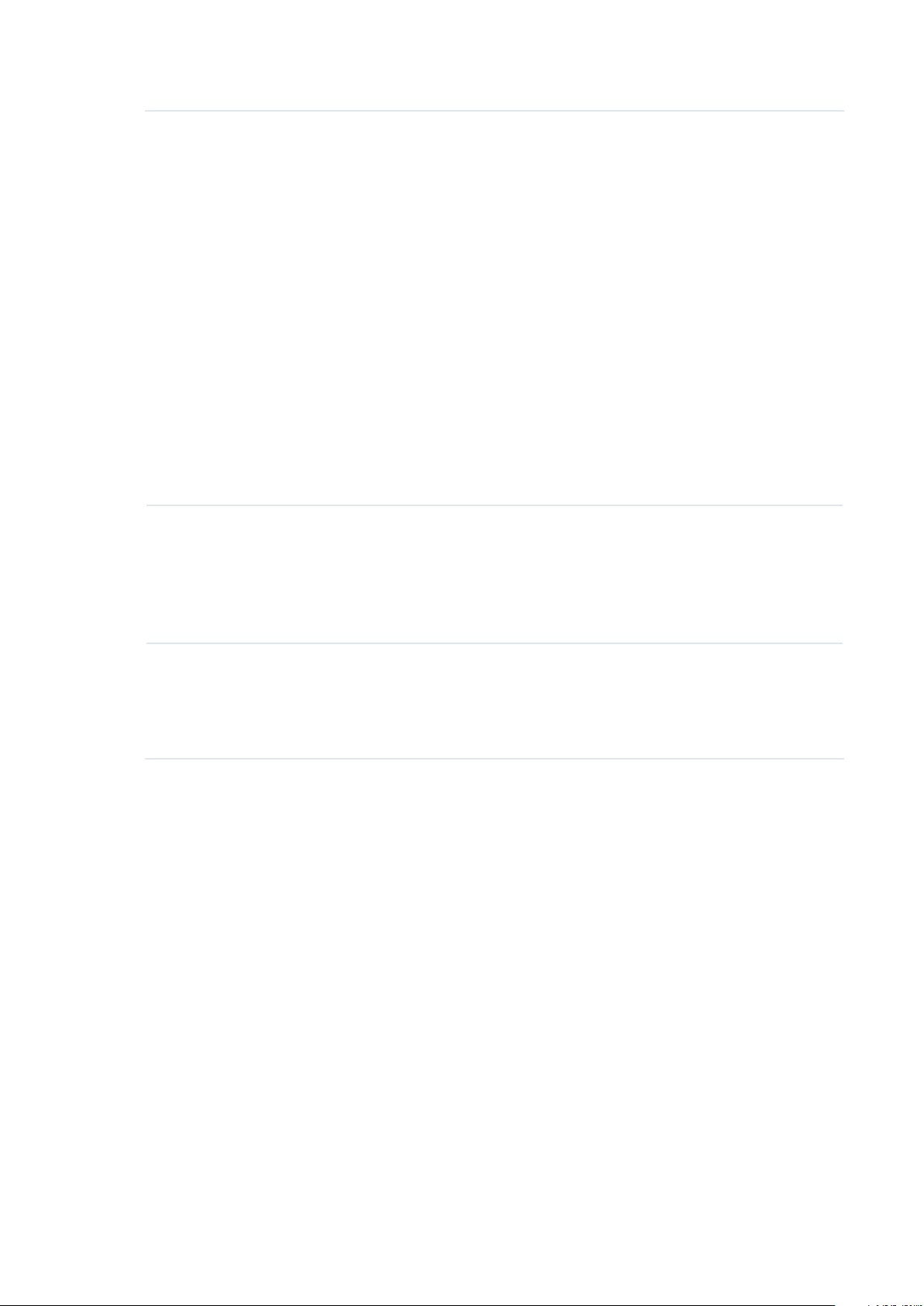
Channel Width Select the channel width of the EAP. The available options differ among
different EAPs.
For some EAPs, available options include 20MHz, 40MHz and 20/40MHz.
For other EAPs, available options include 20MHz, 40MHz, 80MHz and
20/40/80MHz.
When the radio mode includes 802.11n, we recommend you set the channel
bandwidth to 20/40 MHz or 20/40/80MHz to improve the transmission
speed. However, you may choose a lower bandwidth due to the following
reasons:
• To increase the available number of channels within the limited total
bandwidth.
• To avoid interference from overlapping channels occupied by other
devices in the environment.
• Lower bandwidth can concentrate higher transmit power, increasing
stability of wireless links over long distances.
Channel Limit Check the box to enable the Channel Limit function. With this function
enabled, the wireless frequency 5150MHz~5350MHz will be disabled. This
function can influence the available options in Channel.
This feature is only available on certain devices. To check whether your
device supports this feature, refer to the actual web interface.
Channel Select the channel used by the EAP. For example, 1/2412MHz means that
the channel is 1 and the frequency is 2412MHz.
By default, the channel is automatically selected, and we recommend that
you keep the default setting.
23
Page 28
Tx Power (EIRP) Specify the transmit power value.
If this value is set to be larger than the maximum transmit power that is
allowed by the local regulation, the regulated maximum transmit power will
be applied in the actual situation.
Note:
In most cases, it is unnecessary to use the maximum transmit power.
Specifying a larger transmit power than needed may cause interference to
the neighborhood. Also it consumes more power and reduces longevity of
the device.
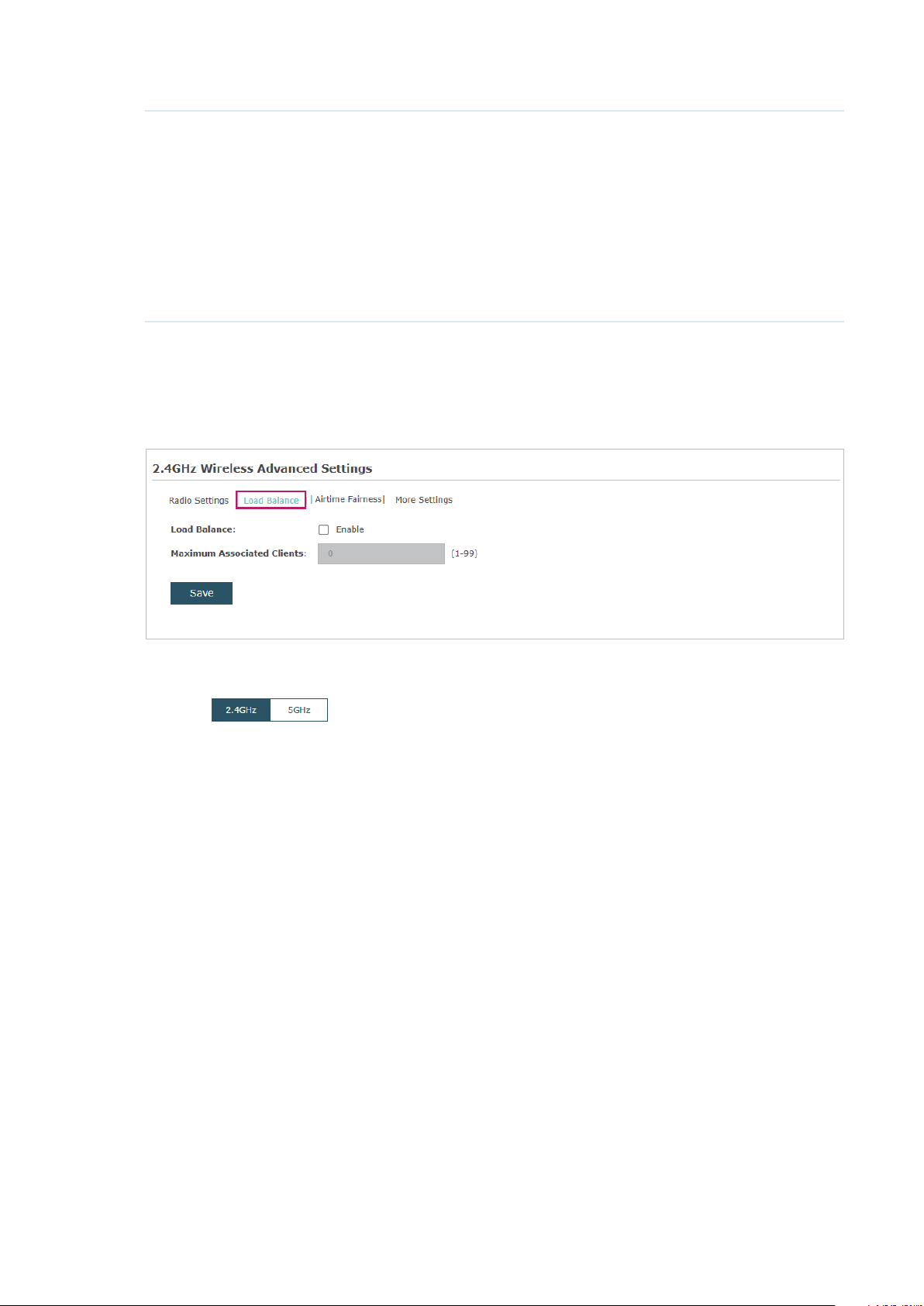
Load Balance
With the Load Balance feature, you can limit the maximum number of clients who can
access the EAP. In this way, you can achieve rational use of network resources.
Follow the steps below to configure Load Balance:
1. Click to choose a frequency band on which the load balance feature will
take effect.
2. Check the box to enable Load Balance.
3. Specify the maximum number of clients who can connect to the EAP at the same time.
While the number of connected clients has reached the limit and there are more clients
requesting to access the network, the EAP will disconnect those with weaker signals.
4. Click Save.
Airtime Fairness
Note:
Airtime Fairness is only available on certain devices. To check whether your device supports this
feature, refer to the actual web interface.
With Airtime Fairness enabled, each client connected to the EAP can get the same amount
of time to transmit data, avoiding low-data-rate clients to occupy too much network
bandwidth.
24
Page 29
Compared with the relatively new client devices, some legacy client devices support
slower wireless rate. If they communicate with the same EAP, the slower clients take more
time to transmit and receive data compared with the faster clients. As a result, the overall
wireless throughput of the network decreases.
Therefore we recommend you check the box to enable this function under multi-
rate wireless networks. In this way, the faster clients can get more time for the data
transmission and the network overall throughput can be improved.
Note:
With Airtime Fairness enabled, 50 wireless clients at most can connect to the EAP in 2.4GHz band.
More Settings
Proper wireless parameters can improve the network’s stability, reliability and
communication efficiency. The advanced wireless parameters consist of Beacon Interval,
DTIM Period, RTS Threshold, and Fragmentation Threshold.
The following table introduces how to configure each item:
Beacon Interval Beacons are transmitted periodically by the EAP to announce the presence
of a wireless network for the clients. Beacon Interval determines the time
interval of the beacons sent by the EAP.
You can specify a value between 40 and 100ms. The default is 100ms.
25
Page 30
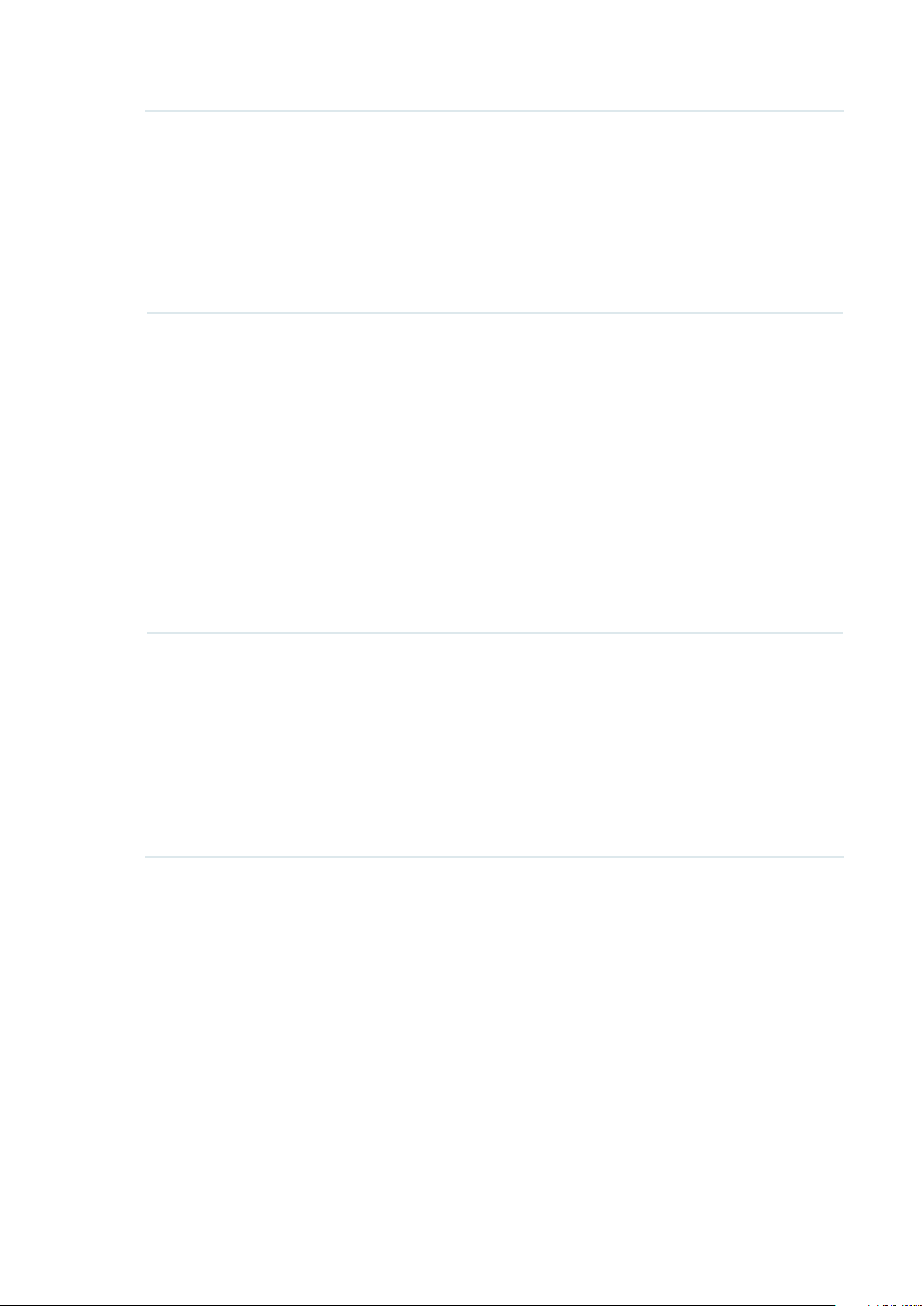
DTIM Period The DTIM (Delivery Traffic Indication Message) is contained in some
Beacon frames. It indicates whether the EAP has buffered data for client
devices. The DTIM Period indicates how often the clients served by this
EAP should check for buffered data still on the EAP awaiting pickup.
You can specify the value between 1-255 Beacon Intervals. The default
value is 1, indicating that clients check for buffered data at every beacon.
An excessive DTIM interval may reduce the performance of multicast
applications, so we recommend you keep the default value.
RTS Threshold RTS/CTS (Request to Send/Clear to Send) is used to improve the data
transmission efficiency of the network with hidden nodes, especially when
there are lots of large packets to be transmitted.
When the size of a data packet is larger than the RTS Threshold, the RTS/
CTS mechanism will be activated. With this mechanism activated, before
sending a data packet, the client will send an RTS packet to the EAP to
request data transmitting. And then the EAP will send CTS packet to inform
other clients to delay their data transmitting. In this way, packet collisions
can be avoided.
For a busy network with hidden nodes, a low threshold value will help
reduce interference and packet collisions. But for a not-so-busy network, a
too low threshold value will cause bandwidth wasting and reduce the data
throughput. The recommended and default value is 2347 bytes.
Fragmentation
Threshold
The fragmentation function can limit the size of packets transmitted over
the network. If the size of a packet exceeds the Fragmentation Threshold,
the fragmentation function is activated and the packet will be fragmented
into several packets.
Fragmentation helps improve network performance if properly configured.
However, a too low fragmentation threshold may result in poor wireless
performance caused by the extra work of dividing up and reassembling
of frames and increased message traffic. The recommended and default
value is 2346 bytes.
2.2 Configure Portal Authentication
Portal authentication provides authentication service to the clients that only need
temporary access to the wireless network, such as the customers in a restaurant or in a
supermarket. To access the network, these clients need to enter the authentication login
page and use the correct login information to pass the authentication. In addition, you can
customize the authentication login page and specify a URL which the authenticated clients
will be redirected to.
In this module, you can also configure Free Authentication Policy, which allows the specific
clients to access the specific network resources without authentication.
26
Page 31

To configure portal authentication, go to the Wireless > Portal page.
Configure Portal
Three portal authentication types are available:
and
External RADIUS Server
authentication type.
. The following sections introduce how to configure each
27
No Authentication, Local Password
Page 32

• No Authentication
With this authentication type configured, clients can pass the authentication and access
the network without providing any login information. They only need to accept the term of
use on the authentication page.
Follow the steps below to configure No Authentication as the portal authentication type:
1. Select the SSID on which the portal will take effect.
2. Select No Authentication as the authentication type.
3. Configure the relevant parameters as the following table shows:
Authentication
Timeout
Specify the value of authentication timeout.
A client’s authentication will expire after the authentication timeout and
the client needs to log in to the authentication page again to access the
network.
Options include 1 Hour, 8 Hours, 24 Hours, 7 Days, and Custom. With
Custom selected, you can customize the time in days, hours, and minutes.
28
Page 33

Redirect With this function configured, the newly authenticated client will be
redirected to the specific URL.
Redirect URL With Redirect enabled, you also need to enter the URL in this field. The
newly authenticated client will be redirected to this URL.
Portal
Customization
Configure the authentication page. Local Web Portal is the only available
option in this authentication type. Enter the title and term of use in the two
boxes.
The EAP uses its built-in web server to provide this authentication page for
clients. To pass the authentication, clients only need to check the box of I
accept the Term of Use and click the Login button.
4. Click Save.
• Local Password
With this authentication type configured, clients are required to provide the correct
password to pass the authentication.
29
Page 34

Follow the steps below to configure Local Password as the portal authentication type:
1. Select the SSID on which the portal will take effect.
2. Select Local Password as the authentication type.
3. Configure the relevant parameters as the following table shows:
Password Specify a password for authentication.
Authentication
Timeout
Redirect With this function configured, the newly authenticated client will be
Redirect URL With Redirect enabled, you also need to enter the URL in this field. The
Portal
Customization
Specify the value of authentication timeout.
A client’s authentication will expire after the authentication timeout and
the client needs to log in to the authentication page again to access the
network.
Options include 1 Hour, 8 Hours, 24 Hours, 7 Days, and Custom. With
Custom selected, you can customize the time in days, hours, and minutes.
redirected to the specific URL.
newly authenticated client will be redirected to this URL.
Configure the authentication page. Local Web Portal is the only available
option is this authentication type. Enter the title and term of use in the two
boxes.
The EAP uses its built-in web server to provide this authentication page
for clients. To pass the authentication, clients need to provide the correct
password in the Password field, check the box of I accept the Term of Use
and click the Login button.
4. Click Save.
30
Page 35

• External RADIUS Server
If you have a RADIUS server on the network to authenticate the clients, you can select
External Radius Server. Clients need to provide the correct login information to pass the
authentication.
31
Page 36

Follow the steps below to configure External Radius Server as the portal authentication
type:
1. Select the SSID on which the portal will take effect.
2. Build a RADIUS server on the network and make sure that it is reachable by the EAP.
3. Go to the Portal configuration page on the EAP. Select External Radius Server as the
authentication type.
3. Configure the relevant parameters as the following table shows:
RADIUS Server IP Enter the IP address of RADIUS server.
RADIUS Port Enter the port of the RADIUS server.
RADIUS Password Enter the password of the RADIUS server.
NAS ID Configure a Network Access Server Identifier (NAS ID) using 1
to 64 characters on the portal. The NAS ID is sent to the RADIUS
server by the EAP through an authentication request packet. With
the NAS ID which classifies users to different groups, the RADIUS
server can send a customized authentication response.
RADIUS Accounting Enable or disable RADIUS accounting feature.
Accounting Server IP Enter the IP address of the accounting server.
Accounting Server Port Enter the port number of the accounting server.
Accounting Server
Passsword
Interim Update With this option enabled, you can specify the duration between
Interim Interval With Interim Update enabled, specify the appropriate duration
Authentication Timeout Specify the value of authentication timeout.
Enter the shared secret key of the accounting server.
accounting information updates. By default, the function is
disabled.
Enter the appropriate duration between updates for EAPs in
Interim Update Interval.
between updates for EAPs. The default duration is 600 seconds.
A client’s authentication will expire after the authentication
timeout and the client needs to log in to the authentication page
again to access the network.
Options include 1 Hour, 8 Hours, 24 Hours, 7 Days, and Custom.
With Custom selected, you can customize the time in days, hours,
and minutes.
32
Page 37

Redirect With this function configured, the newly authenticated client will
be redirected to the specific URL.
Redirect URL With Redirect enabled, you also need to enter the URL in this
field. The newly authenticated client will be redirected to this URL.
Portal Customization Configure the authentication page. There are two options: Local
Web Portal and External Web Portal.
• Local Web Portal
Enter the title and term of use in the two boxes. The EAP uses its
built-in web server to provide this authentication page for clients.
To pass the authentication, clients need to provide the correct
username and password in the Username and Password fields,
check the box of I accept the Term of Use and click the Login
button.
• External Web Portal
With External Web Portal configured, the authentication page
will be provided by the web portal server built on the network.
To configure External Web Portal, you need to complete the
following configurations:
1. Build an external web portal server on your network and make
sure that it is reachable by the EAP.
2. On this configuration page, enter the URL of the authentication
page provided by the external portal server.
3. Add the external web portal server to the Free Authentication
Policy list. In this way, clients can access the web portal server
before authenticated. For details about how to configure Free
Authentication Policy, refer to
Policy
.
Configure Free Authentication
4. Click Save.
Configure Free Authentication Policy
Free Authentication Policy allows some specific clients to access the specific network
resources without authentication. For example, you can set a free authentication policy
to allow clients to visit the external web portal server before authenticated. In this way,
33
Page 38

the clients can visit the login page provided by the web portal server and then pass the
subsequent authentication process.
Follow the steps below to add free authentication policy.
1. In the Free Authentication Policy section, click to load the following page.
2. Configure the following parameters. When all the configured conditions are met, the
client can access the network without authentication.
Policy Name Specify a name for the policy.
Source IP Range Specify an IP range with the subnet and mask length. The clients in this
IP range can access the network without authentication.
Leaving the field empty means that clients with any IP address can
access the specific resources.
Destination IP
Range
Source MAC
Address
Specify an IP range with the subnet and mask length. The devices in
this IP range can be accessed by the clients without authentication.
Leaving the field empty means that all devices in the LAN can be
accessed by the specific clients.
Specify the MAC address of the client, who can access the specific
resources without authentication.
Leaving the field empty means that clients with any MAC address can
access the specific resources.
34
Page 39

Destination Port Specify the port number of the service. When using this service, the
clients can access the specific resources without authentication.
Leaving the field empty means that clients can access the specific
resources no matter what service they are using.
Status Check the box to enable the policy.
Tips:
When External Web Portal is configured in the portal configuration, you should set the IP address
and subnet mask of the external web server as the Destination IP Range. As for Source IP Range,
Source MAC Address and Destination Port, you can simply keep them as empty or configure them
according to your actual needs.
3. Click OK to add the policy.
2.3 Configure VLAN
Wireless VLAN is used to set VLANs for the wireless networks. With this feature, the EAP
can work together with the switches supporting 802.1Q VLAN. Traffic from the clients
in different wireless networks is added with different VLAN tags according to the VLAN
settings of the wireless networks. Then the wireless clients in different VLANs cannot
directly communicate with each other. Note that the traffic from the wired clients will not
be added with VLAN tags.
To configure VLAN for the wireless network, go to the Wireless > VLAN page.
Follow the steps below to configure VLAN on this page.
1. Select the specific SSID in the list to configure the VLAN.
2. In the VLAN column and select Enable to enable the VLAN function on the SSID.
35
Page 40

3. Specify the VLAN ID for the wireless network in the VLAN ID column. Every VLAN ID
represents a different VLAN. It supports maximum 8 VLANs per frequency band. The
VLAN ID range is 0 to 4094. 0 is used to disable VLAN tagging.
4. Click Save.
2.4 Configure MAC Filtering
MAC Filtering is used to allow or block the clients with specific MAC addresses to access
the network. With this feature you can effectively control clients’ access to the wireless
network according to your needs.
To configure MAC Filtering, go to the Wireless > MAC Filtering page.
36
Page 41

Follow the steps below to configure MAC Filtering on this page:
1. In the Settings section, check the box to enable MAC Filtering, and click Save.
2. In the Station MAC Group section, click and the following page will
appear.
1 ) Click and specify a name for the MAC group to be created. Click OK.
You can create up to eight MAC groups.
2 ) Select a MAC group in the group list (the color of the selected one will change to
blue). Click to add group members to the MAC group. Specify
37
Page 42

the MAC address of the host and click OK. In the same way, you can add more MAC
addresses to the selected MAC group.
3. In the MAC Filtering Association section, configure the filtering rule. For each SSID, you
can select a MAC group in the MAC Group Name column and select the filtering rule
(Allow/Deny) in the Action column. Click Save.
For example, the following configuration means that the hosts in Group 2 are denied to
access the SSID SSID-1 on the 2.4GHz band and allowed to access the SSID SSID-2 on
the 5GHz band.
2.5 Configure Scheduler
With the Scheduler feature, the EAP or its wireless network can automatically turn on or
off at the time you set. For example, you can schedule the radio to operate only during the
office working time to reduce power consumption.
38
Page 43

To configure Scheduler, go to the Wireless > Scheduler page.
Follow the steps below to configure Scheduler on this page:
1. In the Settings section, check the box to enable Scheduler and select the Association
Mode. There are two modes: Associated with SSID (the scheduler profile will be applied
to the specific SSID) and Associated with AP (the profile will be applied to all SSIDs on
the EAP). Then click Save.
39
Page 44

2. In the Scheduler Profile Configuration section, click and the following
page will appear.
1 ) Click and specify a name for the prole to be created. Click OK. You
can create up to eight proles.
2 ) Select a profile in the list (the color of the selected one will change to blue). Click
to add time range items to the prole. Specify the Day, Start Time and
End Time of the time range, and click OK.
Tips:
You can add up to eight time range items for one profile. If there are several time range items in one
profile, the time range of this profile is the sum of all of these time ranges.
40
Page 45

3. In the Scheduler Association section, configure the scheduler rule. There are two
association modes:
sections introduce how to configure each mode.
■ Association with SSID
If you select Association with SSID in step 1, the Scheduler Association table will
display all the SSIDs on the EAP. For each SSID, you can select a profile in the Profile
Name column and select the scheduler rule (Radio On/Radio Off) in the Action column.
Then click Save.
For example, the following configuration means that during the time range defined in
Profile2, the radio of SSID SSID-1 is on and the radio of SSID SSID-2 is off.
Association with SSID
and
Association with AP
. The following
■ Association with AP
If you select Association with AP in step 1, the Scheduler Association table will display
the name and MAC address of the EAP. Select a profile in the Profile Name column and
select the scheduler rule (Radio On/Radio Off) in the Action column. Then click Save.
For example, the following configuration means that during the time range defined in
Profile2, the radio of all SSIDs on the EAP is on.
2.6 Configure Band Steering
A client device that is capable of communicating on both the 2.4GHz and 5GHz frequency
bands will typically connect to the 2.4GHz band. However, if too many client devices
are connected to an EAP on the 2.4GHz band, the efficiency of communication will be
41
Page 46

diminished. Band Steering can steer dual-band clients to the 5GHz frequency band which
supports higher transmission rates and more client devices, and thus to greatly improve
the network quality.
Note:
Only the dual-band EAP products support Band Steering.
To configure Band Steering, go to the Wireless > Band Steering page.
Follow the steps below to configure Band Steering on this page:
1. Check the box to enable Band Steering function.
2. Configure the following parameters to balance the clients on both frequency bands:
42
Page 47

Connection
Threshold/Difference
Threshold
Max Failures If a client repeatedly attempts to associate with the EAP on the
Connection Threshold defines the maximum number of clients
connected to the 5GHz band. The value of Connection Threshold
is from 2 to 40, and the default is 20.
Difference Threshold defines the maximum difference between
the number of clients on the 5GHz band and 2.4GHz band. The
value of Difference Threshold is from 1 to 8, and the default is 4.
When the following two conditions are both met, the EAP prefer to
refuse the connection request on 5GHz band and no longer steer
other clients to the 5GHz band:
1.The number of clients on the 5GHz band reaches the Connection
Threshold value.
2.The difference between the number of clients on the 2.4GHz
band and 5GHz band reaches the Difference Threshold value.
5GHz band and the number of rejections reaches the value of Max
Failures, the EAP will accept the request.
The value is from 0 to 100, and the default is 10.
3. Click Save.
2.7 Configure QoS
Quality of service (QoS) is used to optimize the throughput and performance of the EAP
when handling differentiated wireless traffic, such as Voice-over-IP (VoIP), other types of
audio, video, streaming media, and traditional IP data.
In QoS configuration, you should set parameters on the transmission queues for
different types of wireless traffic and specify minimum and maximum wait time for data
transmission. In normal use, we recommend that you keep the default values.
43
Page 48

To configure QoS, go to the Wireless > QoS page.
Follow the steps below to configure QoS on this page:
1. Click to choose a frequency band to be configured.
2. Check the box to enable Wi-Fi Multimedia (WMM). With WMM enabled, the EAP uses
the QoS function to guarantee the high priority of the transmission of audio and video
packets.
44
Page 49

Note:
If 802.11n only mode is selected in 2.4GHz (or 802.11n only, 802.11ac only, or 802.11 n/ac mixed
mode selected in 5GHz), the WMM should be enabled. If WMM is disabled, the 802.11n only mode
cannot be selected in 2.4GHz (or 802.11n only, 802.11ac only, or 802.11 n/ac mixed mode in 5GHz).
3. In the AP EDCA Parameters section, configure the AP EDCA ((Enhanced Distributed
Channel Access) parameters. AP EDCA parameters affect traffic flowing from the EAP
to the client station. The following table detailedly explains these parameters.
The following table detailedly explains these parameters:
Queue Displays the transmission queue. By default, the priority from high to
low is Data 0, Data 1, Data 2, and Data 3. The priority may be changed if
you reset the EDCA parameters.
Data 0 (Voice): Highest priority queue, minimum delay. Timesensitive
data such as VoIP and streaming media are automatically sent to this
queue.
Data 1 (Video): High priority queue, minimum delay. Time-sensitive
video data is automatically sent to this queue.
Data 2 (Best Effort): Medium priority queue, medium throughput and
delay. Most traditional IP data is sent to this queue.
Data 3 (Background): Lowest priority queue, high throughput. Bulk data
that requires maximum throughput and is not time-sensitive is sent to
this queue (FTP data, for example).
Arbitration Inter-
Frame Space
Minimum
Contention
Window
A wait time for data frames. The wait time is measured in slots. Valid
values are from 0 to 15.
A list to the algorithm that determines the initial random backoff wait
time (window) for retry of a transmission.
This value cannot be higher than the value of Maximum Contention
Window.
45
Page 50

Maximum
Contention
Window
Maximum Burst Maximum Burst specifies the maximum burst length allowed for
The upper limit (in milliseconds) for the doubling of the random backoff
value. This doubling continues until either the data frame is sent or the
Maximum Contention Window size is reached.
This value must be higher than the value of Minimum Contention
Window.
packet bursts on the wireless network. A packet burst is a collection of
multiple frames transmitted without header information. The decreased
overhead results in higher throughput and better performance.
4. In the Station EDCA Parameters section, configure the station EDCA (Enhanced
Distributed Channel Access) parameters. Station EDCA parameters affect traffic
flowing from the client station to the EAP.
The following table detailedly explains these parameters:
Queue Displays the transmission queue. By default, the priority from high to
low is Data 0, Data 1, Data 2, and Data 3. The priority may be changed if
you reset the EDCA parameters.
Data 0 (Voice): Highest priority queue, minimum delay. Timesensitive
data such as VoIP and streaming media are automatically sent to this
queue.
Data 1 (Video): High priority queue, minimum delay. Time-sensitive
video data is automatically sent to this queue.
Data 2 (Best Effort): Medium priority queue, medium throughput and
delay. Most traditional IP data is sent to this queue.
Data 3 (Background): Lowest priority queue, high throughput. Bulk data
that requires maximum throughput and is not time-sensitive is sent to
this queue (FTP data, for example).
Arbitration Inter-
Frame Space
A wait time for data frames. The wait time is measured in slots. Valid
values are from 0 to 15.
46
Page 51

Minimum
Contention
Window
A list to the algorithm that determines the initial random backoff wait
time (window) for retry of a transmission.
This value cannot be higher than the value of Maximum Contention
Window.
Maximum
Contention
Window
TXOP Limit The TXOP Limit is a station EDCA parameter and only applies to traffic
The upper limit (in milliseconds) for the doubling of the random backoff
value. This doubling continues until either the data frame is sent or the
Maximum Contention Window size is reached.
This value must be higher than the value of Minimum Contention
Window.
flowing from the client station to the EAP.
The Transmission Opportunity (TXOP) is an interval of time, in
milliseconds, when a WME (Wireless Multimedia Extensions) client
station has the right to initiate transmissions onto the wireless medium
(WM) towards the EAP. The valid values are multiples of 32 between 0
and 8192.
5. Choose whether to enable the following two options according to your need.
The following table detailedly explains these options:
No Acknowledgment With this option enabled, the EAP would not acknowledge frames
with QosNoAck. No Acknowledgment is recommended if VoIP
phones access the network through the EAP.
Unscheduled
Automatic Power Save
Delivery
As a power management method, it can greatly improve the
energy-saving capacity of clients.
6. Click Save.
2.8 Configure Rogue AP Detection
A Rogue AP is an access point that is installed on a secure network without explicit
authorization from the network administrator. With Rogue AP Detection, the EAP can scan
all channels to detect the nearby APs and display the detected APs in the Detected Rogue
AP list. If the specific AP is known as safe, you can move it to the Trusted APs list. Also, you
can backup and import the Trusted AP list as needed.
47
Page 52

Note:
The Rogue AP Detection feature is only used for collecting information of the nearby wireless
network and does not impact the detected APs, no matter what operations you have executed in
this feature.
To configure Rogue AP Detection, go to the Wireless > Rogue AP Detection page.
Detect Rogue APs and Move the Rogue APs to the Trusted AP List
Follow the steps below to detect the nearby APs and move the trusted ones to the Trusted
AP list.
1. In the Settings section, check the box to enable Rogue AP Detection. Click Save.
48
Page 53

2. In the Detected Rogue AP List section, click .
3. Wait for a few seconds without any operation. After detection is finished, the detected
APs will be displayed in the list.
The following table introduces the displayed information of the APs:
MAC Displays the MAC address of the AP.
SSID Displays the SSID of the AP.
Band Displays the frequency band the AP is working on.
Channel Displays the channel the AP is using.
Security Displays whether the security mode is enabled on the AP.
Beacon Interval Displays the Beacon Interval value of the EAP.
Beacon frames are sent periodically by the AP to announce to
the stations the presence of a wireless network. Beacon Interval
determines the time interval of the beacon frames sent by the AP
device.
Signal Displays the signal strength of the AP.
4. To move the specific AP to the Trusted AP list, click in the Action column. For
example, we move the first two APs in the above Detected Rogue AP list to the Trusted
AP list.
49
Page 54

5. View the trusted APs in the Trusted AP List section. To move the specific AP back to
the Rogue AP list, you can click in the Action column.
Manage the Trusted AP List
You can download the trusted AP list from your local host to the EAP or backup the current
Trusted AP list to your local host.
• Download the Trusted AP List From the Host
You can import a trusted AP list which records the MAC addresses of the trusted APs. The
AP whose MAC address is in the list will not be detected as a rogue AP.
Follow the steps below to import a trusted AP list to the EAP:
1. Acquire the trusted AP list. There are two ways:
• Backup the list from a EAP. For details, refer to
Host
.
• Manually create a trusted AP list. Create a txt. file, input the MAC addresses of the
trusted APs in the format XX:XX:XX:XX:XX:XX and use the Space key to separate each
MAC address. Save the file as a cfg file.
2. On this page, check the box to choose Download (PC to AP).
3. Click and select the trusted AP list from your local host.
4. Select the file management mode. Two modes are available: Replace and Merge.
Replace means that the current trusted AP list will be replaced by the one you import.
Merge means that the APs in the imported list will be added to the current list with the
original APs remained.
Backup the Trusted AP List to the
50
Page 55

5. Click Save to import the trusted AP list.
• Backup the Trusted AP List to the Host
You can backup the current trusted AP list and save the backup file to the local host.
Follow the steps below to backup the current trusted AP list:
1. On this page, check the box to choose Backup (AP to PC).
2. Click Save and the current trusted AP list will be downloaded to your local host as a cfg
file.
51
Page 56

3
This chapter introduces how to monitor the running status and statistics of the wireless
network, including:
• Monitor the EAP
• Monitor the Wireless Parameters
• Monitor the Clients
Monitor the Network
52
Page 57

3.1 Monitor the EAP
To monitor the EAP information, go to the Status > Device page.
The following device information is displayed:
Device Name Displays the name of the EAP. The name consists of the product model
followed with the MAC address of the EAP by default.
Device Model Displays the product model of the EAP.
Firmware Version Displays the current firmware version the EAP. To update the firmware,
you can refer to
Hardware Version Displays the hardware version the EAP.
MAC Address Displays the MAC address of the EAP.
IP Address Displays the IP address of the EAP.
Subnet Mask Displays the subnet mask of the EAP.
System Time Displays the current system time. To configure the system time, you can
refer to
Uptime Displays how long the EAP has been working since it starts up.
Configure the System Time
Update the Firmware
.
.
53
Page 58

CPU Utilization Displays the CPU occupancy. If this value is too high, the EAP may work
abnormally.
Memory Utilization Displays the memory occupancy.
3.2 Monitor the Wireless Parameters
You can view the wireless parameters of the EAP, including SSID lists, radio settings, radio
traffic and LAN traffic.
Tips:
To change the wireless parameters, you can refer to
To monitor the wireless parameters, go to the Status > Wireless page.
Configure the Wireless Parameters
.
54
Page 59

Monitor the SSIDs
You can monitor the SSID information of the EAP.
The following table introduces the displayed information of the SSID:
SSID Name Displays the SSID name.
Clients Displays the number of clients currently connected to the SSID.
Band Displays the frequency band the SSID is currently using.
Security Displays the security mode of the SSID.
Portal Displays whether portal function is enabled on the SSID.
VLAN ID Displays the VLAN ID of the SSID.
Guest Network Display guest network is enabled on the SSID.
Down (Byte) Displays the total download traffic since the SSID starts working.
Up (Byte) Displays the total upload traffic since the SSID starts working.
55
Page 60

Monitor the Radio Settings
You can monitor the radio settings of the EAP. For a dual-band EAP, there are two bands:
2.4GHz and 5GHz. You can click to select a band to view. The following figure posted in the
introduction takes 2.4GHz as an example.
The following table introduces the displayed information of the EAP.
2.4GHz/5GHz
Wireless Radio
Channel Frequency Displays the channel and frequency which are currently used by the
Channel Width Displays the channel width which is currently used by the EAP.
IEEE802.11 Mode Displays the IEEE802.11 protocol currently used by the EAP.
Max TX Rate Displays the maximum physical rate of the EAP.
Tx Power Displays the transmit power of the EAP.
Displays whether wireless function is enabled on the radio band.
EAP.
Monitor Radio Traffic
You can monitor the radio traffic of the EAP. For a dual-band EAP, there are two bands:
2.4GHz and 5GHz. You can click to select a band to view. The following figure posted in the
introduction takes 2.4GHz as an example.
56
Page 61

The following traffic information of the radio is displayed:
Rx Packets Displays the total number of the received packets on the 2.4GHz/5GHz
band since the EAP starts up.
Tx Packets Displays the total number of the sent packets on the 2.4GHz/5GHz band
since the EAP starts up.
Rx Bytes Displays the total received traffic on the 2.4GHz/5GHz band since the EAP
starts up.
Tx Bytes Displays the total sent traffic on the 2.4GHz/5GHz band since the EAP starts
up.
Rx Dropped
Packets
Tx Dropped
Packets
Rx Errors Displays the total number of error packets which are received on the
Tx Errors Displays the total number of error packets which are sent on the
Displays the total number of the dropped packets which are received on
the 2.4GHz/5GHz band since the EAP starts up.
Displays the total number of the dropped packets which are sent on the
2.4GHz/5GHz band since the EAP starts up.
2.4GHz/5GHz band since the EAP starts up.
2.4GHz/5GHz band since the EAP starts up.
Monitor LAN Traffic
You can view the LAN traffic of EAP.
The following traffic information of the LAN is displayed:
Rx Packets Displays the total number of received packets in the LAN since the EAP
starts up.
Tx Packets Displays the total number of sent packets in the LAN since the EAP starts
up.
Rx Bytes Displays the total received traffic in the LAN since the EAP starts up.
Tx Bytes Displays the total sent traffic in the LAN since the EAP starts up.
57
Page 62

Rx Dropped
Packets
Displays the total number of the dropped packets which are received by the
EAP since it starts up.
Tx Dropped
Packets
Rx Errors Displays the total number of the received error packets since the EAP
Tx Errors Displays the total number of the sent error packets since the EAP starts up.
Displays the total number of the dropped packets which are sent by the
EAP since it starts up.
starts up.
3.3 Monitor the Clients
You can monitor the information of the clients connected to the EAP.
To monitor the client information, go to the Status > Client page.
58
Page 63

View Client Information
There are two types of clients: users and portal authenticated guests. Users are the clients
that connect to the SSID with portal authentication disabled. Guests are the clients that
connect to the SSID with portal authentication enabled.
Click the to select the client types to view the information of the EAP. The
following figure posted in the introduction takes user as an example.
The following client information is displayed:
Hostname Displays the hostname of the user.
IP Address Displays the IP address of the user.
MAC Address Displays the MAC address of the user.
Band Displays the frequency band the user is working on.
SSID Displays the SSID the user is connecting to.
Active Time Displays how long the user has been connected to the SSID.
Up (Byte) Displays the user’s total uploaded traffic to the EAP since the last
connection.
Down (Byte) Displays the user’s total downloaded traffic from the EAP since the last
connection.
RSSI (dBm) Displays the RSSI(Received Signal Strength Indication) of the user.
Rate (Mbps) Displays the wireless transmission rate of the user.
59
Page 64

You can execute the corresponding operation to the EAP by clicking an icon in the Action
column.
Click the icon to configure the rate limit of the client to balance
bandwidth usage. Enter the download limit and upload limit and click
OK.
You can limit the download and upload rate for each clients by which
connect to specific SSIDs when configuring SSIDs, refer to
SSIDs
Note that the download and upload rate will be limited to the smaller
value if you set the limit value both in SSID and client configuration.
Click the icon to block the access of the client to the network.
to get more details.
Configure
View Block Client Information
You can view the information of the clients that have been blocked and resume the client’s
access.
The following information of the blocked client is displayed:
Hostname Displays the hostname of the user.
MAC Address Displays the MAC address of the user.
Up (Byte) Displays the user’s total uploaded traffic to the EAP since the last
connection.
Down (Byte) Displays the user’s total downloaded traffic from the EAP since the last
connection.
Action
You can click the to resume the client's access to the internet.
60
Page 65

4
The EAP provides powerful functions of device management and maintenance. This
chapter introduces how to manage the EAP, including:
• Manage the IP Address of the EAP
• Manage System Logs
• Configure Web Server
• Configure Management Access
• Configure LED
• Configure Wi-Fi Control (Only for Certain Devices)
• Configure PoE Out (Only for Certain Devices)
Manage the EAP
• Configure SSH
• Configure SNMP
61
Page 66

4.1 Manage the IP Address of the EAP
The IP address of the EAP can be a dynamic IP address assigned by the DHCP server or
a static IP address manually specified by yourself. By default, the EAP gets a dynamic IP
address from the DHCP server. You can also specify a static IP address according to your
needs.
Tips:
For detailed introduction about how to find the dynamic IP address of the EAP, refer to
Wired Connection
To configure the IP address of the EAP, go to the Management > Network page.
.
Log In via a
Follow the steps below to configure the IP address of the EAP:
1. Choose your desired IP address mode: Dynamic or Static.
2. Configure the related parameters according to your selection.
62
Page 67

• Dynamic
If you choose Dynamic as the IP address mode, make sure that there is a reachable
DHCP server on your network and the DHCP sever is properly configured to assign IP
address and the other network parameters to the EAP.
For network stability, you can also configure the fallback IP parameters for the EAP:
Fallback IP With the fallback IP configured, if the EAP fails to get an IP
address from a DHCP server within 10 seconds, the fallback
IP will work as the IP address of the EAP. After that, however,
the EAP will keep trying to obtain an IP address from the DHCP
server until it succeeds.
DHCP Fallback IP Specify a fallback IP address for the EAP. Make sure that this IP
address is not being used by any other device in the same LAN.
The default DHCP fallback IP is 192.168.0.254.
DHCP Fallback IP MASK Specify the network mask of the fallback IP. The default DHCP
fallback IP mask is 255.255.255.0.
DHCP Fallback Gateway Specify the network gateway.
• Static
If you choose Static as the IP address mode, you need to manually specify an IP
address and the related network parameters for the EAP. Make sure that the specified
IP address is not being used by any other device in the same LAN.
63
Page 68

Configure the IP address and network parameters as the following table shows:
IP Address Specify a static IP address for the EAP.
IP Mask Specify the network mask.
Gateway Specify the network gateway.
Primary DNS Specify the primary DNS server.
Secondary DNS Specify the secondary DNS server. (Optional)
3. Click Save.
4.2 Manage System Logs
System logs record information about hardware, software as well as system issues and
monitors system events. With the help of system log, you can get informed of system
running status and detect the reasons for failure.
To manage system logs, go to the Management > System Log page.
On this page, you can view the system logs and configure the way of receiving system
logs.
64
Page 69

View System Logs
In the Log section, you can click to refresh the logs and view them in the table.
Configure the Way of Receiving Logs
In the Log Settings section, you can configure the ways of receiving system logs.
Follow the steps below to configure this feature:
1. Check the corresponding box to enable one or more ways of receiving system logs,
and configure the related parameters. Two ways are available:
■ Auto Mail
If Auto Mail is configured, system logs will be sent to a specified mailbox. Check the box
to enable the feature and configure the related parameters.
Note:
SSL encryption is not currently supported.
Auto Mail
and
Server
.
65
Page 70

The following table introduces how to configure these parameters:
From Enter the sender’s E-mail address.
To Enter the receiver’s E-mail address.
SMTP Server Enter the IP address of the sender’s SMTP server.
Note:
At present, the domain name of SMTP server is not supported in
this field.
Enable
Authentication
Time Mode Select Time Mode: Fixed Time or Period Time.
Fixed Time If you select Fixed Time, specify a fixed time to send the system log
Period Time If you select Period Time, specify a period time to regularly send the
If the sender’s mailbox is configured with You can check the box to
enable mail server authentication. Enter the sender’s username and
password.
Fixed Time means that the system logs will be sent at the specific time
every day. Period Time means that the system logs will be sent at the
specific time interval.
mails. For example, 08:30 indicates that the mail will be sent at 8:30 am
everyday.
system log mail. For example, 6 indicates that the mail will be sent every
six hours.
■ Server
If Server is configured, system logs will be sent to the specified system log server, and
you can use the syslog software to view the logs on the server.
Enable this feature and enter the IP address and port of the system log server.
System Log Server IP Enter the IP address of the server.
System Log Server Port Enter the port of the server.
More Client Detail Log With the option enabled, the logs of clients will be sent to the
server.
2. Click Save.
66
Page 71

4.3 Configure Web Server
With the web server, you can log in to the management web page of the EAP. You can
configure the web server parameters of the EAP according to your needs.
To configure Web Server, go to the Management > Web Server page.
Follow the steps below to configure Web Server:
1. Refer to the following table to configure the parameters:
Secure Server Port Designate a secure server port for web server in HTTPS mode. By
default the port is 443.
Server Port Designate a server port for web server in HTTP mode. By default the
port is 80.
Session Timeout Set the session timeout. If you do nothing with the web page within
the timeout, the system will log out automatically. You can log in again
if you want to go back to web page.
Layer-3
Accessibility
With this feature enabled, devices from a different subnet can access
Omada managed devices via the management web page. With this
feature disabled, only the devices in the same subnet can access
Omada managed devices via the management web page.
2. Click Save.
67
Page 72

4.4 Configure Management Access
By default, all hosts in the LAN can log in to the management web page of the EAP with the
correct username and password. To control the hosts’ access to the web page of the EAP,
you can specify the MAC addresses and management VLAN of the hosts that are allowed
to access the web page.
To configure Management Access, go to the Management > Management Access page.
Configure Access MAC Management
Only the hosts with the specific MAC addresses are allowed to access the web page, and
other hosts without MAC addresses specified are not allowed to access the web page.
68
Page 73

Follow the steps below to configure Management Access on this page:
1. Check the box to enable MAC Authentication.
2. Specify one or more MAC addresses in the MAC1/MAC2/MAC3/MAC4 fields. Up to
four MAC addresses can be added.
3. Click Save.
Tips:
• You can click to quickly add the MAC address of your current logged-in host, .
• Verify the MAC addresses carefully. Once the settings are saved, only the hosts in the MAC
address list can access the web page of the EAP.
• If you cannot log in to the web page after saving the wrong configuration, you can reset the EAP to
the factory defaults and use the default username and password (both admin) to log in.
Configure Management VLAN
Management VLAN provides a safer method to manage the EAP. With Management VLAN
enabled, only the hosts in the Management VLAN can access the web page of the EAP.
Since most hosts cannot process VLAN TAGs, you can connect the management host to
the network via a switch, and set up correct VLAN settings for the switches on the network
to ensure the communication between the host and the EAP in the Management VLAN.
Follow the steps below to configure Management VLAN on this page:
1. Check the box to enable Management VLAN.
2. Specify the VLAN ID of the management VLAN. Only the hosts in the Management
VLAN can log in to the EAP via the Ethernet port.
3. Click Save.
69
Page 74

4.5 Configure LED
You can turn on or off the LED light of the EAP and flash the LED to locate your device.
To configure LED, go to the Management > LED Control page.
Check the box to turn on or turn off the LED light of the EAP, and click Save. To flash the
LED, click Locate. Then the LED will flash for 10 minutes or until the locate button is clicked
again.
4.6 Configure Wi-Fi Control
Note:
Wi-Fi Control is only available on certain devices. To check whether your device supports this
feature, refer to the actual web interface. If Wi-Fi Control is available, there is Management > Wi-Fi
Control in the menu structure.
(Only for Certain Devices)
70
Page 75

Certain devices have an LED/Wi-Fi button on the front panel. With Wi-Fi Control enabled,
you can press the button to turn on or off both of the Wi-Fi and LED at the same time.
To configure Wi-Fi Control, go to the Management > Wi-Fi Control page.
Check the box to enable Wi-Fi Control and click Save.
Note:
You can enable Wi-Fi Control only when the option LED ON/OFF is enabled.
4.7 Configure PoE Out
Note:
PoE Out is only available on certain devices. To check whether your device supports this feature,
refer to the actual web interface. If PoE Out is available, there is Management > PoE Out in the menu
structure.
Certain devices have a PoE OUT port that can transmit data and supply power to the client
simultaneously. You can also disable PoE Out to make the port transmit data only.
To configure PoE Out, go to the Management > PoE Out page.
(Only for Certain Devices)
71
Page 76

Check the box to enable PoE Out and click Save.
4.8 Configure SSH
If you want to remotely log in to the EAP via SSH, you can deploy an SSH server on your
network and configure the SSH feature on the EAP.
To configure SSH, go to the Management > SSH page.
Follow the steps below to configure SSH on this page:
1. Refer to the following table to configure the parameters:
Server Port Designate a server port for SSH. By default the port is 22.
Layer-3
Accessibility
SSH Login Enable or disable SSH Login globally.
With this feature enabled, devices from a different subnet can access
Omada managed devices via SSH. With this feature disabled, only the
devices in the same subnet can access Omada managed devices via
SSH.
2. Click Save.
72
Page 77

4.9 Configure SNMP
The EAP can be configured as an SNMP agent and work together with the SNMP manager.
Once the EAP has become an SNMP agent, it is able to receive and process request
messages from the SNMP manager. At present, the EAP supports SNMP v1 and v2c.
To configure the EAP as an SNMP agent, go to the Management > SNMP page.
Follow the steps below to complete the configuration on this page:
1. Check the box to enable SNMP Agent.
2. Refer to the following table to configure the required parameters:
SysContact Enter the textual identification of the contact person for this managed
node.
SysName Enter an administratively-assigned name for this managed node.
SysLocation Enter the physical location of this managed node.
Get Community Community refers to a host group aiming at network management.
Get Community only has the read-only right of the device’s SNMP
information. The community name can be considered a group password.
The default setting is public.
Get Source Defines the IP address (for example, 10.10.10.1) for management
systems that can serve as Get Community to read the SNMP information
of this device. The default is 0.0.0.0, which means all hosts can read the
SNMP information of this device.
73
Page 78

Set Community Set Community has the read and write right of the device’s SNMP
information. Enter the community name that allows read/write access to
the device’s SNMP information. The community name can be considered
a group password. The default setting is private.
Set Source Defines the IP address (for example, 10.10.10.1) for management
systems that can serve as Set Community to read and write the SNMP
information of this device. The default is 0.0.0.0, which means all hosts
can read and write the SNMP information of this device.
3. Click Save.
Note:
Defining community can allow management systems in the same community to communicate
with the SNMP Agent. The community name can be seen as the shared password of the network
hosts group. Thus, for the security, we recommend that modify the default community name before
enabling the SNMP Agent service. If the field of community is blank, the SNMP Agent will not
respond to any community name.
74
Page 79

5
This chapter introduces how to configure the system of the EAP, including:
• Configure the User Account
• Controller Settings
• Configure the System Time
• Reboot and Reset the EAP
• Backup and Restore the Configuration
• Update the Firmware
Congure the System
75
Page 80

5.1 Configure the User Account
Every EAP has a user account, which is used to log in to the management page of the EAP.
When you start the EAP at the first time, the username and password of the user account
are both admin. After the first login, the system will require you to set a new username and
a new password for the user account. And then you can use the new user account to log in
to the EAP. Also, you can change your user account as needed.
Tips:
Please remember your user account well. If you forget it, reset the EAP to the factory defaults and
log in with the default user account (username and password are both admin).
To configure the user account, go to System > User Account page.
Follow the steps below to change your user account on this page:
1. Enter the old username and old password of your user account.
2. Specify a new username and a new password for your user account. The system
will automatically detect the strength of your entered password. For security, we
recommend that you set a password with high strength.
3. Retype the new password.
4. Click Save.
76
Page 81

5.2 Controller Settings
To make your controller adopt your EAP, make sure the EAP can be discovered by the
controller. Controller Settings enable your EAP to be discovered in either of the following
scenarios.
• If you are using Omada Cloud-Based Controller,
Management
• If your EAP and controller are located in the same network, LAN and VLAN, the controller
can discover and adopt the EAP without any controller settings. Otherwise, you need to
inform the EAP of the controller’s URL/IP address, and one possible way is to
Controller Inform URL
For details about the whole procedure, refer to the User Guide of Omada SDN
Controller. The guide can be found on the download center of our official website:
https://www.tp-link.com/support/download/
.
.
Enable Cloud-Based Controller
Configure
Enable Cloud-Based Controller Management
Go to the System > Controller Settings page. In the Cloud- Based Controller Management
section, enable Cloud-Based Controller Management and click Save. After you add the
77
Page 82

EAP to your Omada Cloud-Based Controller, you can check the connection status on this
page.
78
Page 83

Configure Controller Inform URL
Go to the System > Controller Settings page. In the Controller Inform URL section, inform
the EAP of the controller’s URL/IP address, and click Save. Then the EAP make contact
with the controller so that the controller can discover the EAP.
5.3 Configure the System Time
System time is the standard time for Scheduler and other time-based functions. The EAP
supports the basic system time settings and the Daylight Saving Time (DST) feature.
79
Page 84

To configure the system time, go to the System > Time Settings page.
The following two sections introduce how to configure the basic system time settings and
the Daylight Saving Time feature.
Configure the System Time
In the Time Settings section, you can configure the system time. There are three methods
to set the system time:
NTP Server
, and
Synchronize the System Time with PC’s Clock
Set the System Time Manually, Acquire the System Time From an
.
Determine the way of setting the system time and follow the steps below to complete the
configurations:
80
Page 85

• Set the System Time Manually
To set the system time manually, follow the steps below:
1. Configure the following three options on the page: Time Zone, Date and Time.
Time Zone Select your time zone from the drop-down list. Here GMT means
Greenwich Mean Time.
Date Specify the current date in the format MM/DD/YYYY. MM means month,
DD means day and YYYY means year.
For example: 06/01/2017.
Time Specify the current time in the format HH/MM/SS. HH means hour, MM
means minute and SS means second.
It uses 24-hour system time. For example: 14:36:21.
2. Click Save.
Note:
The system time set manually will be lost after the EAP is rebooted.
• Acquire the System Time From an NTP Server
To get the system time from an NTP server, follow the steps below:
1. Build an NTP server on your network and make sure that it is reachable by the EAP. Or
you can simply find an NTP server on the internet and get its IP address.
Note:
If you use an NTP server on the internet, make sure that the gateway address is set correctly on the
EAP. Otherwise, the EAP cannot get the system time from the NTP server successfully. To set the
gateway address, refer to
Configure the Wireless Parameters
2. Specify the NTP server for the EAP. If you have two NTP servers, you can set one of
them as the primary NTP server, and the other as the secondary NTP server. Once the
primary NTP server is down, the EAP can get the system time from the secondary NTP
server.
Primary NTP
Server
Enter the IP address of the primary NTP server.
Note:
If you have only one NTP server on your network, enter the IP
address of the NTP server in this field.
.
Secondary NTP
Server
Enter the IP address of the secondary NTP server.
3. Click the button and the acquired system time will be displayed in the Date
and
Time fields.
81
Page 86

4. Click Save.
• Synchronize the System Time with PC’s Clock
To synchronize the system time with the clock of your currently logged-in host,
follow the steps below:
1. Click the button and the synchronized system time will be displayed
in the Date and Time fields.
2. Click Save.
Note:
The system time synchronized with PC’s clock will be lost after the EAP is rebooted.
Configure Daylight Saving Time
Daylight saving time is the practice of advancing clocks during summer months so that
evening daylight lasts longer, while sacrificing normal sunrise times. The EAP provides
daylight saving time configuration.
Follow the steps below to configure daylight saving time:
1. Check the box to enable Daylight Saving.
2. Select the mode of daylight saving time. Three modes are available: Predefined Mode,
Recurring Mode and Date Mode.
3. Configure the related parameters of the selected mode.
■ Predefined Mode
If you select Predefined Mode, choose your region from the drop-down list and the EAP
will use the predefined daylight saving time of the selected region.
82
Page 87

There are four regions provided: USA, European, Austrilia and New Zealand. The
following table introduces the predefined daylight saving time of each region.
USA From 2: 00 a.m. on the Second Sunday in March to 2:00 a.m. on the First
Sunday in November.
European From 1: 00 a.m. on the Last Sunday in March to 1:00 a.m. on the Last
Sunday in October.
Australia From 2:00 a.m. on the First Sunday in October to 3:00 a.m. on the First
Sunday in April.
New Zealand From 2: 00 a.m. on the Last Sunday in September to 3:00 a.m. on the
First Sunday in April.
■ Recurring Mode
If you select Recurring Mode, manually specify a cycle time range for the daylight saving
time of the EAP. This configuration will be used every year.
The following table introduces how to configure the cycle time range.
Time Offset Specify the time to set the clock forward by.
Start Specify the start time of daylight saving time. The interval between the
start time and end time should be more than 1 day and less than 1 year
(365 days).
End Specify the end time of daylight saving time. The interval between the
start time and end time should be more than 1 day and less than 1 year
(365 days).
83
Page 88

■ Date Mode
If you select Date Mode, manually specify an absolute time range for the daylight saving
time of the EAP. This configuration will be used only once.
The following table introduces how to configure the absolute time range.
Time Offset Specify the time to set the clock forward by.
Start Specify the start time of daylight saving time. The interval between the
start time and end time should be more than 1 day and less than 1 year
(365 days).
End Specify the end time of daylight saving time. The interval between the
start time and end time should be more than 1 day and less than 1 year
(365 days).
4. Click Save.
5.4 Reboot and Reset the EAP
You can reboot and reset the EAP according to your need.
To reboot and reset the EAP, go to the System > Reboot&Reset page.
• To reboot the EAP, click the button , and the EAP will be rebooted automatically.
Please wait without any operation.
84
Page 89

• To reset the EAP, click the button , and the EAP will be reset to the factory
defaults automatically. Please wait without any operation.
Note:
After reset, all the current configuration of the EAP will be lost. We recommend that you check
whether you have any configuration that needs to be backed up before resetting the EAP.
5.5 Backup and Restore the Configuration
You can save the current configuration of the EAP as a backup file and save the file to
your host. And if needed, you can use the backup file to restore the configuration. We
recommend that you backup the configuration before resetting or upgrading the EAP.
To backup and restore the configuration, go to the System > Backup&Restore page.
• To backup the configuration, click the button in the Backup section, and the
backup file will be saved to the host automatically.
• To restore the configuration, click the button in the Restore section and
choose the backup file from the host. Then click the button to restore the
configuration.
5.6 Update the Firmware
We occasionally provide the firmware update files for the EAP products on our official
website. To get new functions of the EAP, you can check our official website and download
the update files to update the firmware of your EAP.
85
Page 90

To update the firmware, go to the System > Firmware Update page.
Follow the steps below to update the firmware of your EAP:
1. Go to our website
https://www.tp-link.com
and search your EAP model. Download the
proper firmware file on the support page of the EAP.
2. Click the button , locate and choose the correct firmware file from your host.
3. Click the button to update the firmware of the EAP. After updated, the EAP will
be rebooted automatically.
Note:
The update process takes several minutes. To avoid damage to the EAP, please wait without any
operation until the update is finished.
86
Page 91

6
This chapter provides an application example about how to establish and manage a EAP
wireless network:
A restaurant wants to provide the wireless internet access for the employees and guests.
The restaurant now has a router, a switch, a dual-band EAP and a computer. Follow the
steps below to establish the wireless network:
1. Determine the Network Requirements
2. Build the Network Topology
3. Log in to the EAP
4. Configure the EAP
5. Test the Network
Application Example
87
Page 92

6.1 Determine the Network Requirements
Management Host
Before starting to build the network, we need to first analyze and determine the network
requirements. In this restaurant example, the network requirements are as follows:
• On both 2.4GHz and 5GHz bands, there are two SSIDs needed: one for the restaurant
employees and one for the guests.
• In order to advertise the restaurant, the Portal feature needs to be configured on the
SSIDs for the guests. In this way, the guests who have passed the portal authentication
will be redirected to the restaurant’s official website http://www.restaurant1.com.
• The employees of the restaurant can use the correct password to access the internet
and do not need to pass the portal authentication. For security, the SSIDs for the
employees should be encrypted with WPA2-PSK.
• To reduce power consumption, the Scheduler feature needs to be configured. The radio
should operate only during the working time (9:00 am to 22:00 pm).
6.2 Build the Network Topology
Build the network topology as the following figure shows.
Switch
EAP
• The router is the gateway of the network and acts as a DHCP server to assign dynamic
IP addresses to the management host, EAP and clients. The LAN IP of the router is
192.168.88.1/24.
• Connect the switch to the LAN port of the router.
• Connect the management host and the EAP to the switch. The IP address mode of
Router (DHCP Server)
LAN: 192.168.88.1
Internet
the management host and EAP is dynamic, which means that they will get dynamic IP
addresses from the router.
Tips:
If the router has more than one LAN port, we can also respectively connect the management host
and the EAP to the LAN ports of the router.
88
Page 93

6.3 Log in to the EAP
After building the network topology, follow the steps below to log in to the web page of the
EAP:
1. On the management host, launch the web browser and enter “192.168.88.1” in the
address bar. Then log in to the router and find the IP address of the EAP. As the
following figure shows, the IP address of the EAP is 192.168.88.101.
2. Enter “192.168.88.101” in the address bar to load the login page of the EAP. Type the
default username and password (both admin) in the two fields and click LOGIN.
3. In the pop-up window, specify a new username and a new password for the user
account. Click Next.
89
Page 94

6.4 Configure the EAP
To achieve the network requirements in this application example, we need to
SSIDs, Configure Portal Authentication
and
Configure Scheduler
.
Configure
Configure SSIDs
1. After Logging in to EAP, follow the step-by-step instructions to complete the basic
configurations of creating SSIDs. Configure the SSID as “employee_2.4GHz” and
“employee_5GHz”, specify the Password as “restaurant123abc“. Click Save.
2. Go to the Wireless > Wireless Settings page. Create SSIDs for guests on 2.4GHz. Click
to add a new SSID.
90
Page 95

3. The following page will appear. Configure this SSID as “guest_2.4GHz“, keep the
Security Mode as “None” and check the box to enable the Portal feature for this SSID.
Click OK.
4. Click to enter the configuration page for the 5GHz band. Similarly to
the configurations for the 2.4GHz band, configure another SSID for the guests on the
5GHz band.
Configure Portal Authentication
Follow the steps below to configure portal authentication:
1. Go to the Wireless > Portal page.
91
Page 96

2. Configure the portal feature as the following figure shows.
1 ) Select the SSIDs for the guests on which the portal will take eect.
2 ) Select the Authentication Type as “Local Password” and specify the Password as
“restaurant123”.
3 ) Configure Authentication Timeout. Here we customize the timeout as 2 hours. It
means that guests will be logged out after they have been authenticated for 2 hours.
To continue to use the internet service, these guests need to enter the password to
pass the portal authentication once again.
4 ) Check the box to enable Redirect, and enter the website of the restaurant: http://
www.restaurant1.com.
92
Page 97

5 ) Congure the authentication page. Specify the title and the term of use. To access
the internet, guests need to enter the correct password in the Password field,
accept the Term of Use, and click the Login button.
3. Click Save.
Configure Scheduler
Follow the steps below to schedule the radio to operate only during the working time (9:00
am to 22:00 pm).
1. Go to the Wireless > Scheduler page.
2. In the Settings section, check the box to enable Scheduler, and select the Association
Mode as “Associated with AP“. Click Save.
3. In the Scheduler Profile Configuration section, click .
1 ) The following page will appear. Click and specify the prole name as
“worktime”. Click OK.
93
Page 98

2 ) Choose the newly added prole “worktime”, and click . Then the item
configuraiton page will appear. Specify the time range as everyday 9:00 to 22:00.
Click OK.
4. In the Scheduler Association section, select “worktime“ in the Profile Name column
and select “Radio On” in the Action column. Click Save.
6.5 Test the Network
To ensure that the employees and guests can surf the internet via the wireless network,
we can use a client device, such as a telephone, to test whether the SSIDs are working
normally.
• To test the SSIDs for the employees, follow the steps below:
1 ) Enable the Wi-Fi feature of the client device.
2 ) Choose the SSID “employee_2.4GHz“ or “employee_5GHz“ among the detected
SSIDs.
3 ) Enter the password “restaurant123abc“ to join the wireless network.
4 ) Check whether internet websites can be visited successfully.
94
Page 99

• To test the SSIDs for the guests, follow the steps below:
1 ) Enable the Wi-Fi feature of the client device.
2 ) Choose the SSID “guest_2.4GHz“ or “guest_5GHz“ among the detected SSIDs.
3 ) The default web browser on the device will pop up and the authentication page will
appear. Enter the password “restaurant123”, check the box to accept the term of
use, and click the LOGIN button.
Tips:
Generally, the web browser pops up automatically. But if the web browser does not pop up, we
can manually launch the web browser and visit any http website. Then the authentication page will
appear.
95
Page 100

4 ) If the network is working normally, we will be redirected to the website of the
restaurant: http://www.restaurant1.com.
96
 Loading...
Loading...