Page 1

FOREWORD
This wiring diagram manual has been prepared to provide
information on the electrical system of the 1990 TOYOTA
CAMRY.
Applicable models: SV21, 25 series
VZV21 series
For service specifications and repair procedures of the above
models other than those listed in this manual, refer to the
following manuals;
Manual Name Pub. No.
1990 Camry Repair Manual Volume 1
Volume 2
TCCS (3S–FE) Diagnosis Manual
ECT (A140E) Diagnosis Manual
ECT (A540E) Diagnosis Manual
1990 Model New Car Features
All information in this manual is based on the latest product
information at the time of publication. However, specifications
and procedures are subject to change without notice.
RM151U1
RM151U2
DM011U
DM013U
DM014U
NCF059U
TOYOTA MO TOR CORPORATION
Page 2
INTRODUCTION
This manual consists of the following 12 sections:
No.
1 INDEX Index of the contents of this manual.
2 INTRODUCTION Brief explanation of each section.
3
4
5 ABBREVIATIONS Defines the abbreviations used in this manual.
6
HOW TO USE
THIS MANUAL
TROUBLE–
SHOOTING
GLOSSARY OF
TERMS AND
SYMBOLS
Section Description
Instructions on how to use this manual.
Describes the basic inspection procedures for electrical circuits.
Defines the symbols and functions of major parts.
7 RELAY LOCATIONS
8
9
10 INDEX Index of the system circuits.
11
ELECTRICAL
WIRE ROUTING
POWER SOURCE
(POWER–LOAD,
Reference)
SYSTEM CIRCUITS
Shows position of the Electronic Control Unit, Computer, Relays, Junction
Block, etc. This section is closely related to the system circuit.
Describes position of the Parts Connectors, Ground points, etc.
This section is closely related to the system circuit.
Describes power distribution from the power supply to various electrical
loads.
Electrical circuits of each system are shown from the power supply through
ground points. Wiring connections and their positions are shown and
classified by code according to the connection method. (Refer to the
section, “How to use this manual”).
The “System Outline” and “Service Hints” useful for troubleshooting are
also contained in this section.
2
12
GROUND POINTS Shows ground positions of all parts described in this manual.
OVERALL
WIRING DIAGRAM
Provides circuit diagrams showing the circuit connections.
Page 3

HOW TO USE THIS MANUAL
This manual provides information on the electrical circuits installed on vehicles by
dividing them into each system circuit.
The actual wiring of each system circuit is shown from the point where the power source
is received from the battery as far as each ground point. (All circuit diagrams are shown
with the switches in the OFF position.)
When troubleshooting any problem, first understand the operation of the circuit where
the problem was detected (see System Circuit section), the power source supplying
power to that circuit (see Power Source section), and the ground points (see Ground
Points section). See the System Outline to understand the circuit operation.
When the circuit operation is understood, begin troubleshooting of the problem circuit
to isolate the cause. Use Relay Location and Electrical Wire Routing sections to find
each part, junction block and wiring harness connectors, wiring harness and wiring
harness connectors, and ground points of each system circuit. Internal wiring for each
junction block is also provided for better understanding of connection within a junction
block.
Wiring related to each system is indicated in each system circuit by arrows (from
, to ). When o verall connections a re required, see the O verall Wiring Diagram
at the end of this manual.
3
Page 4
HOW TO USE THIS MANUAL
4
Page 5
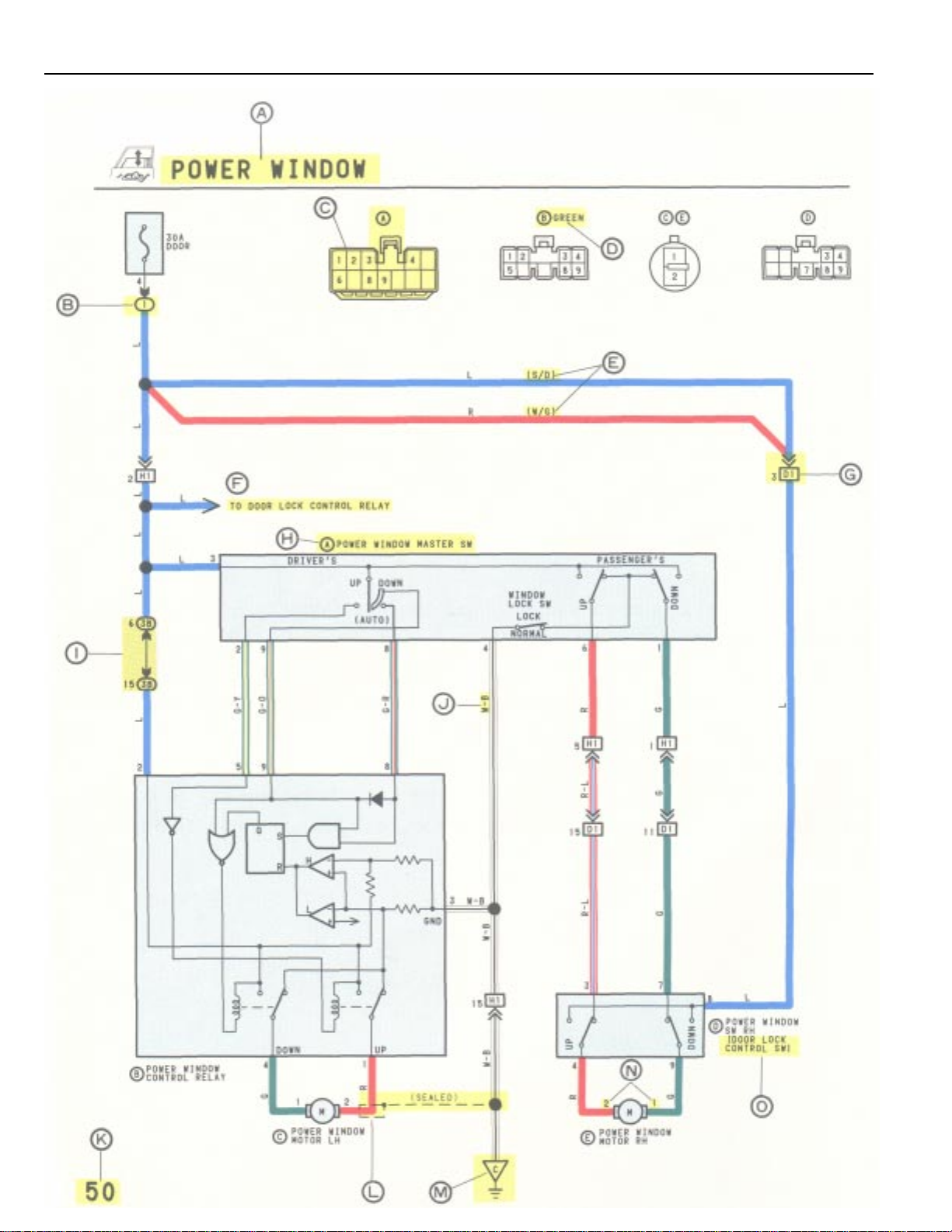
: System Title
A
: Indicates a Relay Block. No shading is used and only
B
C
G
H
the Relay Block No. is shown to distinguish it from the
J/B.
Example: Indicates Relay Block No. 1.
: Indicates the connector to be connected to a part (the
numeral indicates the pin No.)
D
: Connector Color
Connectors not indicated are milky white in color.
E
: ( ) is used to indicate different wiring and connector,
etc. when the vehicle model, engine type, or
specification is different.
F
: Indicates related system.
: Indicates the wiring harness and wiring harness
connector. The wiring harness with male terminal is
shown with arrows ( ).
Outside numerals are pin numbers.
: Represents a part (all parts are shown in sky blue). The
code (e.g. ) is the same as the code used in parts
position.
: Junction Block (The number in the circle is the J/B No.
I
and the connector code is shown beside it). Junction
Blocks are shaded to clearly separate them from other
parts (different junction blocks are shaded differently for
further clarification).
Example:
3B indicates
that it is inside
Junction Block
No. 3.
: Indicates the wiring color.
J
Wire colors are indicated by an alphabetical code.
B = Black L = Blue R = Red
BR = Brown LG = Light Green V = Violet
G = Green O = Orange W = White
GR = Gray P = Pink Y = Yellow
The first letter indicates the basic wire color and the
second letter indicates the color of the stripe.
Example: L – Y
(Blue) (Yellow)
K
: Page No.
: Indicates a sealed wiring harness.
L
M
: Indicates a ground point.
: Indicates the pin number of the connector.
N
The numbering system is different for female and male
connectors.
Example: Numbered in order
The numbering system for the overall wiring diagram is
the same as above.
O
: When 2 parts both use one connector in common, the
parts connector name used in the wire routing section
is shown in square brackets [ ].
from upper left to
lower right
Numbered in order
from upper right to
lower left
5
Page 6
HOW TO USE THIS MANUAL
P
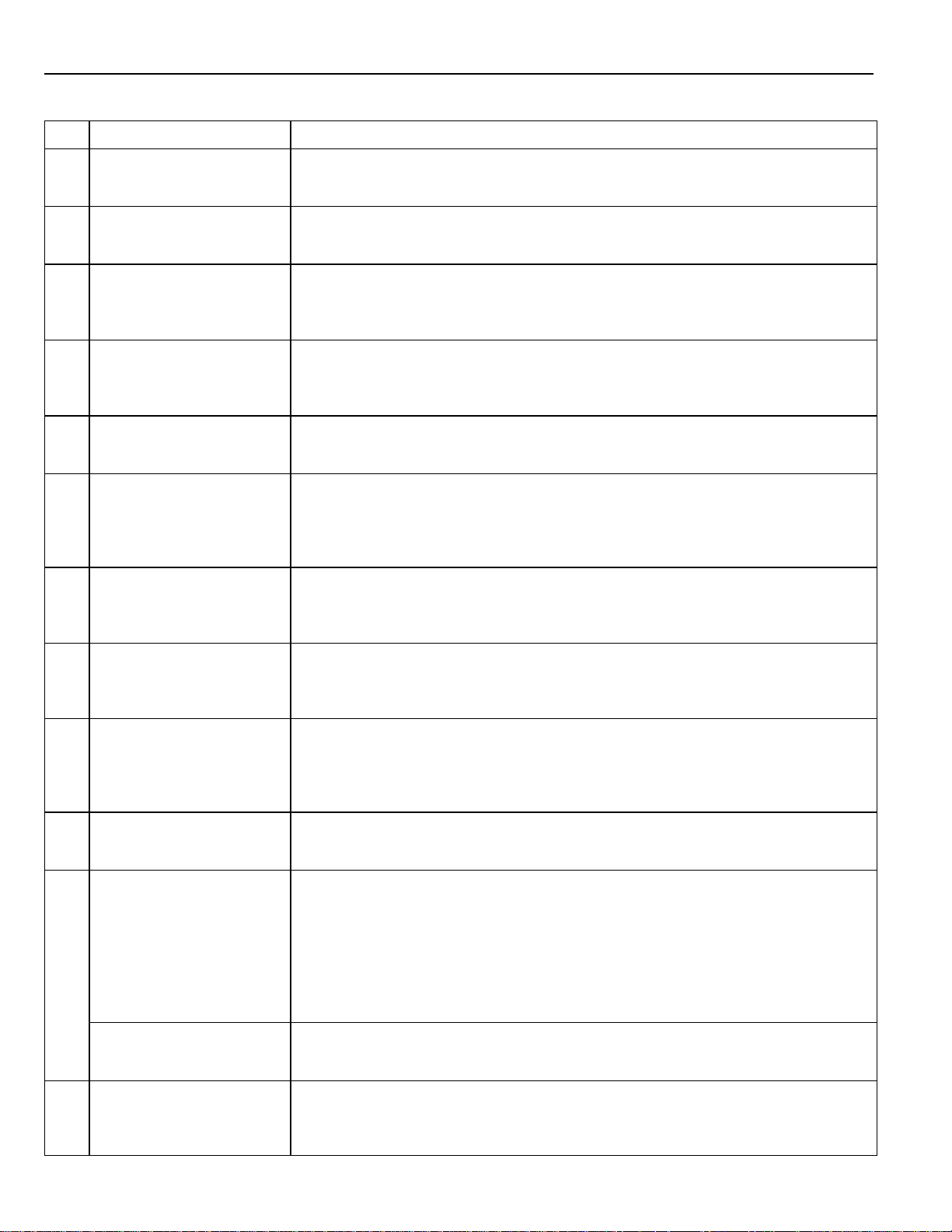
WITH THE IGNITION SW TURNED ON, THE CURRENT FLOWS TO TERMINAL 3 OF THE POWER WINDOW MASTER SW, TERMINAL 2 OF THE POWER WINDOW CONTROL RELAY
AND TERMINAL 8 OF THE POWER WINDOW SW THROUGH THE DOOR FUSE.
1. DRIVER’S WINDOW “MANUAL UP” OPERATION BY MASTER SW
HOLDING MANUAL SW (DRIVER’S) ON “UP” POSITION LOCATED IN POWER WINDOW MASTER SW, THE CURRENT FLOWS TO TERMINAL 5 OF THE POWER WINDOW
CONTROL RELAY THROUGH TERMINAL 3 OF THE MASTER SW TERMINAL 2 TO OPERATE A POWER WINDOW CONTROL RELAY. THUS THE CURRENT INSIDE THE RELAY
FLOWS FROM TERMINAL 2 OF THE RELAY TERMINAL 1 TERMINAL 2 OF THE POWER WINDOW MOTOR TERMINAL 1 TERMINAL 4 OF THE RELAY TERMINAL
3 TO GROUND. THE MOTOR TURNS TO RAISE THE WINDOW. RELEASING THIS SW, THE ROTATION OF MOTOR IS STOPPED AND THE WINDOWS STOP AT DESIRED
POINT.
(FOR THE “MANUAL DOWN” OPERATION, CURRENT FLOWS IN THE REVERSE DIRECTION BECAUSE THE TERMINALS WHERE IT FLOWS ARE CHANGED).
2. DRIVER’S WINDOW “AUTO DOWN” OPERATION BY MASTER SW
ONCE THE “AUTO DOWN” BUTTON OF THE MASTER SW IS PUSHED, THE CURRENT FLOWS TERMINAL 9 OF THE POWER WINDOW CONTROL RELA Y THROUGH TERMINAL
3 OF THE MASTER SW TERMINALS 8 AND 9 TO OPERATE THE RELAY. THUS THE CURRENT INSIDE THE POWER WINDOW CONTROL RELAY FLOWS FROM TERMINAL
2 OF THE RELAY TERMINAL 4 TERMINAL 1 OF THE POWER WINDOW MOTOR TERMINAL 2 TERMINAL 1 OF THE RELAY TERMINAL 3 TO GROUND.
THE MOTOR CONTINUES TO ROTATE, ENABLING THEWINDOW TO DESCEND.
WHEN THE WINDOW DESCENDS TO THE END POSITION, THE CURRENT IS CUT OFF TO RELEASE THE AUTO DOWN FUNCTION BASED ON THE INCREASING CURRENT
BETWEEN TERMINAL 2 OF THE RELAY AND TERMINAL 1 IN RELAY.
3. DRIVER’S WINDOW AUTO DOWN RELEASE OPERATION BY MASTER SW
BY HOLDING THE MANUAL SW (DRIVER’S) IN “UP” POSITION WHILE OPERATING AUTO DOWN. THE CURRENT FROM TERMINAL 3 OF THE MASTER SW PASSING THROUGH
TERMINAL 2 FLOWS TO TERMINAL 5 OF THE RELAY AND RELEASES THE AUTO DOWN FUNCTION IN THE POWER WINDOW CONTROL RELAY . RELEASING THE HAND FROM
SW, STOPS THE WINDOW AND CONTINUING TO TOUCH THE SW, SWITCHES THE FUNCTION TO MANUAL UP OPERATION.
4. PASSENGER’S WINDOW UP OPERATION (MASTER SW) AND WINDOW LOCK SW OPERATION
HOLDING PASSENGER’S WINDOW SW (MASTER SW) ON “UP”, THE CURRENT FLOWS FROM TERMINAL 3 OF THE MASTER SW THROUGH TERMINAL 6 TO TERMINAL 3 OF
THE POWER WINDOW SW (PASSENGER’S) TERMINAL 4 TERMINAL 2 OF THE MOTOR TERMINAL 1 TERMINAL 9 OF THE POWER WINDOW SW TERMINAL
7 TERMINAL 1 OF THE MASTER SW TERMINAL 4 TO GROUND. THE MOTOR RUNS TO RAISE THE WINDOW. RELEASING THIS SW, THE ROTATION OF MOTOR IS
STOPPED AND WINDOW STOPS AT THE DESIRED POINT.
SWITCHING THE WINDOW LOCK SW IN “LOCK” POSITION, THE CIRCUIT IS OPENED AND STOPS THE MOTOR ROTATION.
(FOR THE DOWN OPERATION, CURRENT FLOWS IN THE REVERSE DIRECTION BECAUSE THE TERMINALS WHERE IT FLOWS ARE CHANGED).
5. PASSENGER’S WINDOW DOWN OPERATION (POWER WINDOW SW)
HOLDING POWER WINDOW SW ON “DOWN”, THE CURRENT FLOWS FROM TERMINAL 8 OF THE POWER WINDOW SW TERMINAL 9 TERMINAL 1 OF THE MOTOR
TERMINAL 2 TERMINAL 4 OF THE POWER WINDOW SW TERMINAL 3 TERMINAL 6 OF THE MASTER SW TERMINAL 4 TO GROUND. THE MOTOR RUNS
TO LOWER THE WINDOW.
(FOR THE UP OPERATION, CURRENT FLOWS IN THE REVERSE DIRECTION BECAUSE THE TERMINALS WHERE IT FLOWS ARE CHANGED).
Q
(A) POWER WINDOW MASTER SW
4–GROUND: ALWAYS CONTINUITY
3–GROUND: APPROX. 12 VOLTS WITH IGNITION SW AT ON POSITION
(B) POWER WINDOW CONTROL RELAY
3–GROUND: ALWAYS CONTINUITY
2–GROUND: APPROX. 12 VOLTS WITH IGNITION SW AT ON POSITION
5–GROUND: APPROX. 12 VOLTS WITH IGNITION SW AT ON POSITION AND MASTER SW AT UP POSITION
8–GROUND: APPROX. 12 VOLTS WITH IGNITION SW AT ON POSITION AND MASTER SW AT AUTO DOWN POSITION
9–GROUND: APPROX. 12 VOLTS WITH IGNITION SW AT ON POSITION AND MASTER SW AT DOWN OR AUTO DOWN POSITION
WINDOW LOCK SW
OPEN WITH WINDOW LOCK SW AT LOCK POSITION
SYSTEM OUTLINE
SERVICE HINTS
6
R
S
T
U
V
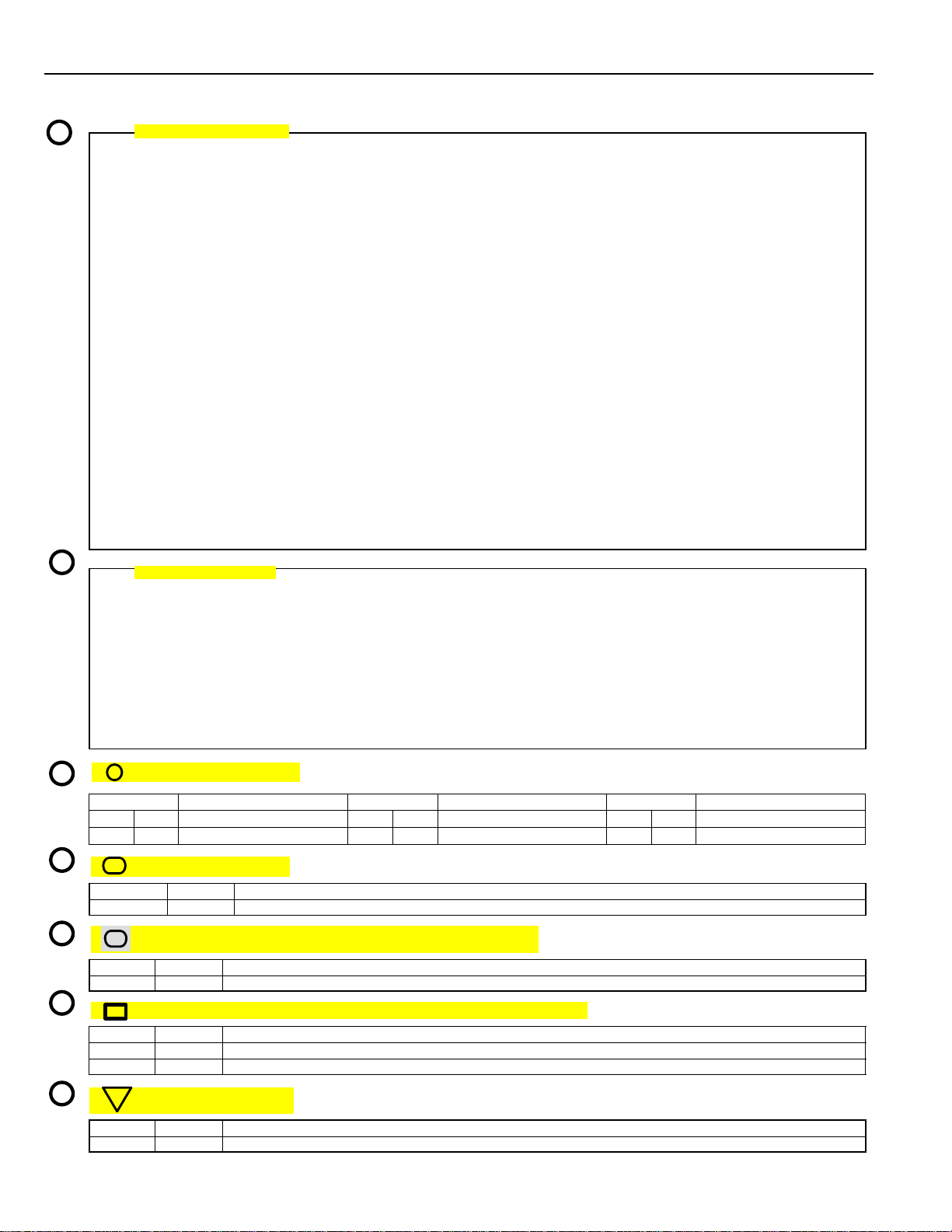
: PARTS LOCATION
CODE SEE PAGE CODE SEE PAGE CODE SEE P AGE
A P4 21 C P5 21 E P6 21
B P2 21 D P3 21
: RELAY BLOCKS
CODE SEE PAGE RELAY BLOCK (RELAY BLOCK LOCATION)
1 16 R/B NO. 1 (INSTRUMENT PANEL LEFT)
: JUNCTION BLOCK AND WIRE HARNESS CONNECTOR
CODE SEE PAGE JUNCTION BLOCK AND WIRE HARNESS (CONNECTOR LOCATION)
3B 14 J/B NO. 3 AND COWL WIRE (INSTRUMENT PANEL LEFT SIDE)
: CONNECTOR JOINING WIRE HARNESS AND WIRE HARNESS
CODE SEE PAGE JOINING WIRE HARNESS AND WIRE HARNESS (CONNECTOR LOCATION)
D1 26 FRONT DOOR RH WIRE AND COWL WIRE (RIGHT KICK PANEL)
H1 26 FRONT DOOR LH WIRE AND COWL WIRE (LEFT KICK PANEL)
: GROUND POINTS
CODE SEE PAGE GROUND POINT LOCATION
C 24 COWL LEFT
Page 7

: Explains the system outline.
P
: Indicates values or explains the function for reference during troubleshooting.
Q
: Indicates the reference page showing the position on the vehicle of the parts in the system circuit.
R
Example: Part A (Power Window Master SW) represents code P4 on page 21 of the manual.
* The letter in the code is from the first letter of the part, and the number indicates its order
in parts starting with that letter.
Example: P
: Indicates the reference page showing the position on the vehicle of Relay Block Connectors in the
S
system circuit.
Example: Connector 1 is described on page 16 of this manual and is installed on the left side of the
instrument panel.
T
: Indicates the reference page showing the position on the vehicle of J/B and Wire Harness in the system
circuit.
Example: Connector 3B connects the Cowl Wire and J/B No. 3. It is described on page 14 of this
manual, and is installed on the instrument panel left side.
U
: Indicates the reference page describing the wiring harness and wiring harness connector (the female
wiring harness is shown first, followed by the male wiring harness).
Example: Connector D1 connects the front door RH wire (female) and cowl wire (male). It is described
on page 26 of this manual, and is installed on the right side kick panel.
V
: Indicates the reference page showing the position of the ground points on the vehicle.
4
Part is 4th in order
Power Window Master SW
Example: Ground point C is described on page 24 of this manual and is installed on the cowl left side.
7
Page 8
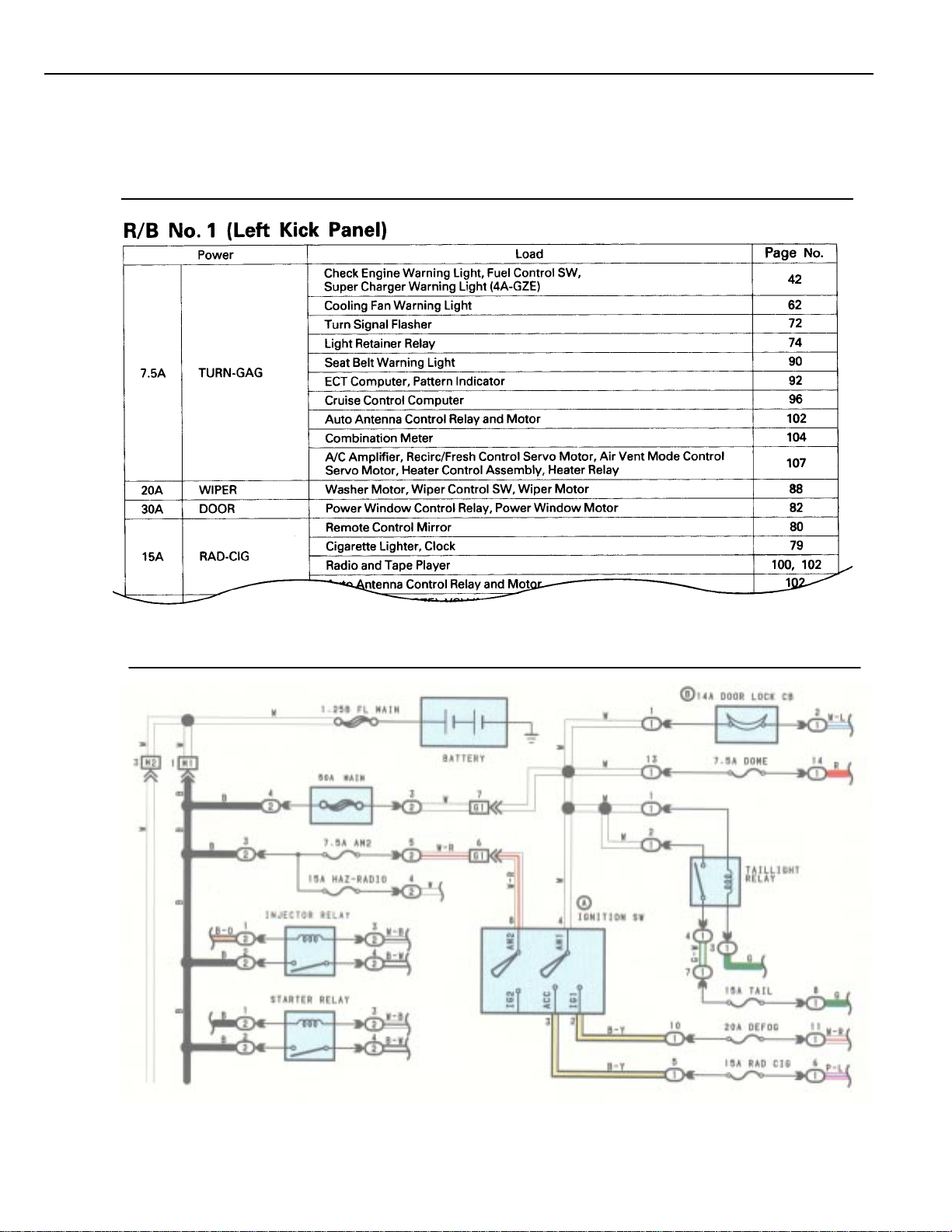
HOW TO USE THIS MANUAL
The Power – Load section, describes which parts each power source (fuses, fusible links, and circuit breakers) transmits
current to. In the Power Source circuit diagram, the conditions when battery power is supplied to each system are explained.
Since all System Circuit diagrams start from the power source, the power source system must be fully understood.
POWER SOURCE (Power–Load, Reference)
POWER SOURCE
8
Page 9
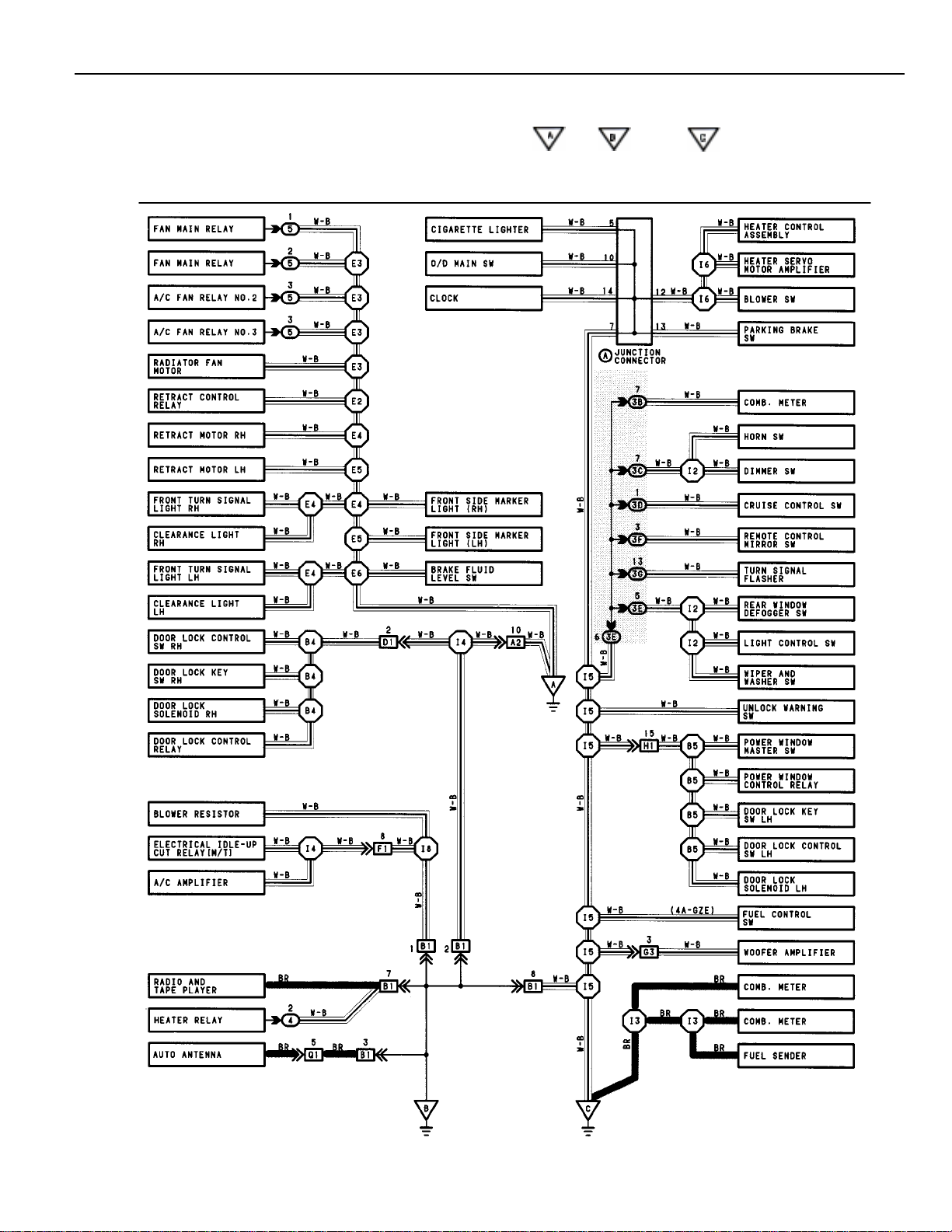
The ground points circuit diagram shows the connections from all major parts to the respective ground points. When
troubleshooting a faulty ground point, checking the system circuits which use a common ground may help you identify the
problem ground quickly. The relationship between ground points ( , , and shown below) can also be
checked this way.
GROUND POINTS
9
Page 10
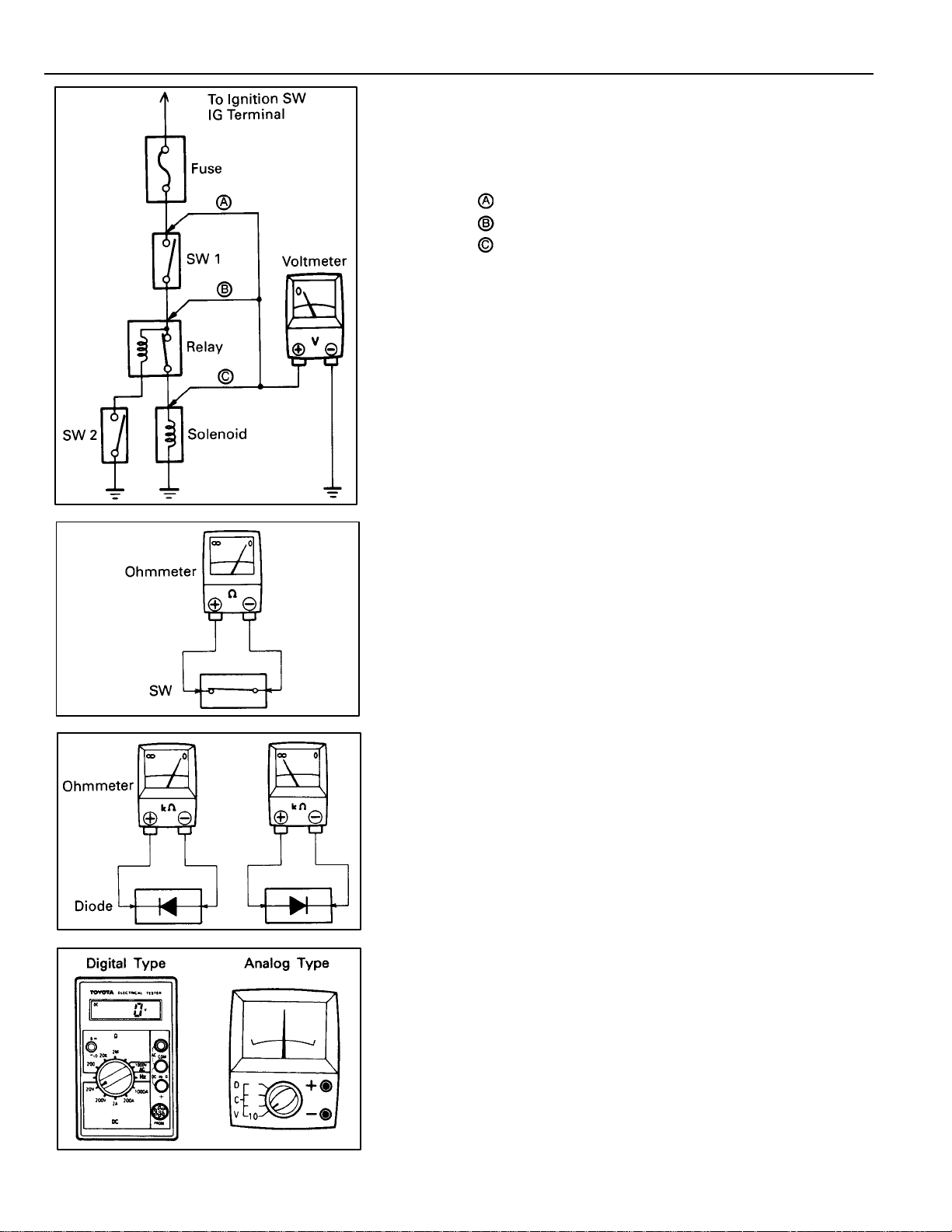
TROUBLESHOOTING
VOLTAGE CHECK
(a) Establish conditions in which voltage is present at the
check point.
Example:
– Ignition SW on
– Ignition SW and SW 1 on
– Ignition SW, SW 1 and Relay on (SW 2 off)
(b) Using a voltmeter, connect the negative lead to a good
ground point or negative battery terminal, and the
positive lead to the connector or component terminal.
This check can be done with a test light instead of a
voltmeter.
CONTINUITY AND RESISTANCE CHECK
(a) Disconnect the battery terminal or wire so there is no
voltage between the check points.
(b) Contact the two leads of an ohmmeter to each of the
check points.
If the circuit has diodes, reverse the two leads and check
again.
When contacting the negative lead to the diode positive side
and the positive lead to the negative side, there should be
continuity.
When contacting the two leads in reverse, there should be no
continuity.
(c) Use a volt/ohmmeter with high impedance (10 kΩ/V
minimum) for troubleshooting of the electrical circuit.
10
Page 11
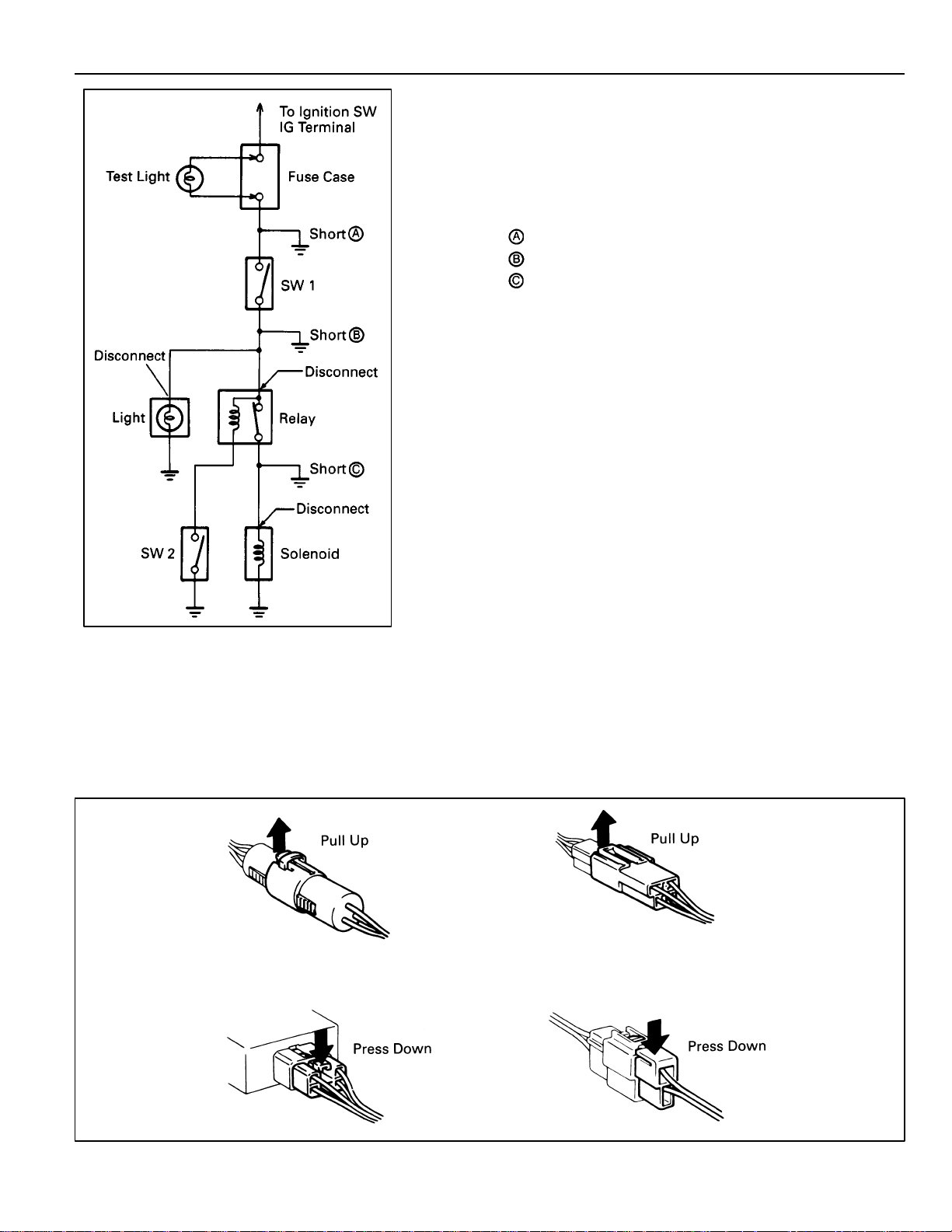
FINDING A SHORT CIRCUIT
(a) Remove the blown fuse and disconnect all loads of the
fuse.
(b) Connect a test light in place of the fuse.
(c) Establish conditions in which the test light comes on.
Example:
– Ignition SW on
– Ignition SW and SW 1 on
– Ignition SW, SW 1 and Relay on (Connect the
Relay) and SW 2 off (or Disconnect SW 2)
(d) Disconnect and reconnect the connectors while
watching the test light.
The short lies between the connector where the test
light stays lit and the connector where the light goes
out.
(e) Find the exact location of the short by lightly shaking
the problem wire along the body.
CAUTION:
Do not open the cover or the case of the ECU and
various computer unless absolutely necessary. (If the
IC terminals are touched, the IC may be destroyed by
static electricity.)
DISCONNECTION OF MALE AND FEMALE
CONNECTORS
To pull apart the connectors, pull on the connector itself, not the
wire harness.
HINT: Check to see what kind of connector you are disconnecting
before pulling apart.
11
Page 12
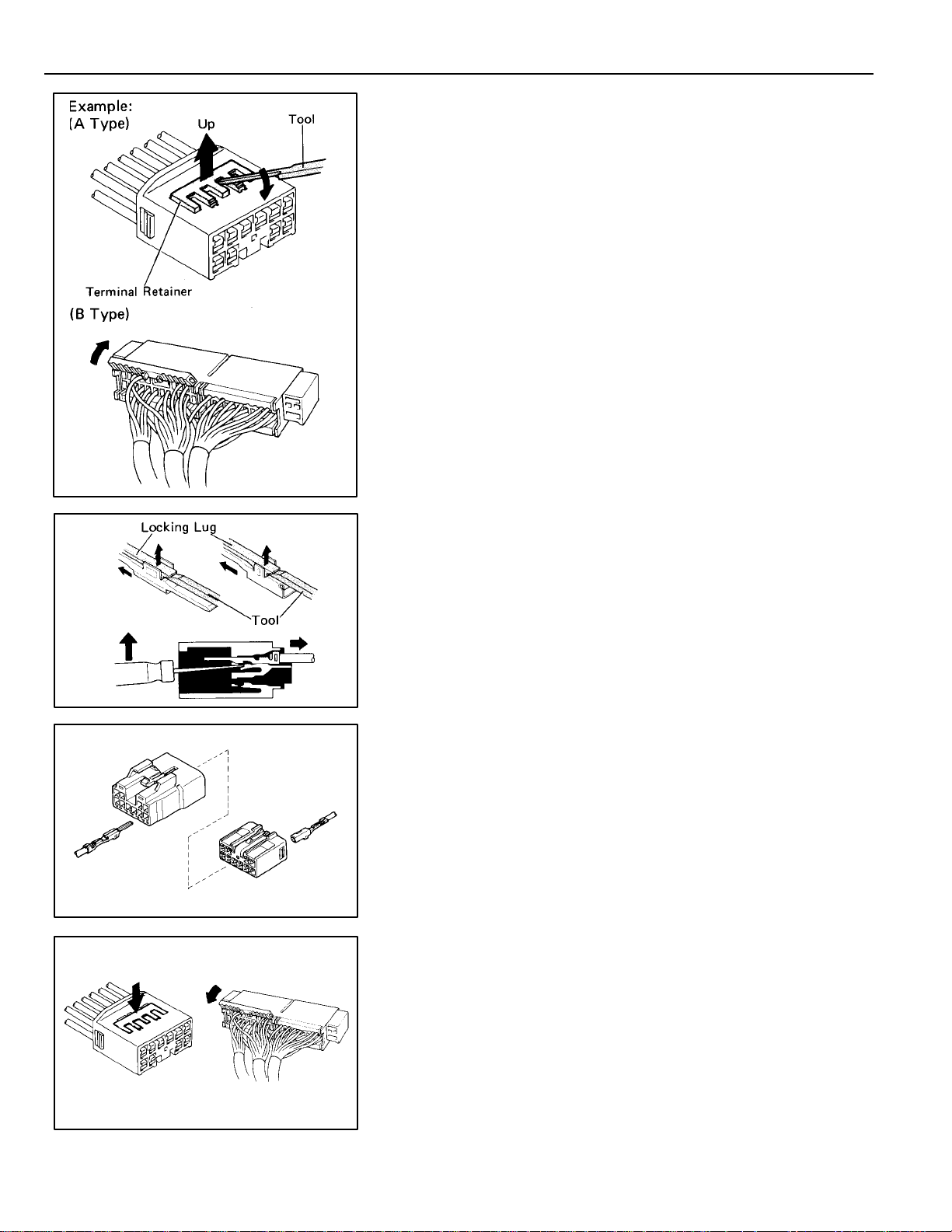
TROUBLESHOOTING
HOW TO REPLACEMENT FOR TERMINAL
(with Terminal Retainer Type)
1. DISCONNECT CONNECTOR
2. DISCONNECT TERMINAL FROM CONNECTOR
(a) “for A type”
Raise the terminal retainer up to the temporally lock
position.
HINT: The needle insertion position varies according
to the connector ’s shape (number of terminals
etc.), so check the position before inserting it.
“for B type”
Open the terminal retainer.
(b) Release the locking lug from terminal and pull the
terminal out from rear.
3. INSTALL TERMINAL TO CONNECTOR
(a) Insert the terminal.
HINT:
1. Make sure the terminal is positioned correctly.
2. Insert the terminal until the locking lug locks firmly.
3. Insert the terminal with terminal retainer in the
temporally lock position.
(b) Push the terminal retainer in to the full lock position.
12
4. CONNECT CONNECTOR
Page 13

ABBREVIATIONS
ABBREVIATIONS
The following abbreviations are used in this manual.
A/C = Air Conditioner
A.B.S = Anti Lock Brake System
A/T = Automatic Transmission
CB = Circuit Breaker
COMB. = Combination
DIFF. = Differential
ECT = Electronic Controlled Transmission
ECU = Electronic Control Unit
EFI = Electronic Fuel Injection
EGR = Exhaust Gas Recirculation
EX. = Except
FL = Fusible Link
ISC = Idle Speed Control
J/B = Junction Block
LH = Left-Hand
M/T = Manual Transmission
O/D = Overdrive
R/B = Relay Block
RH = Right–Hand
SW = Switch
TCCS = Toyota Computer Controlled System
TEMP. = Temperature
VSV = Vacuum Switching Valve
W/G = Wagon Type
W/ = With
W/O = Without
4WD = Four Wheel Drive
13
Page 14
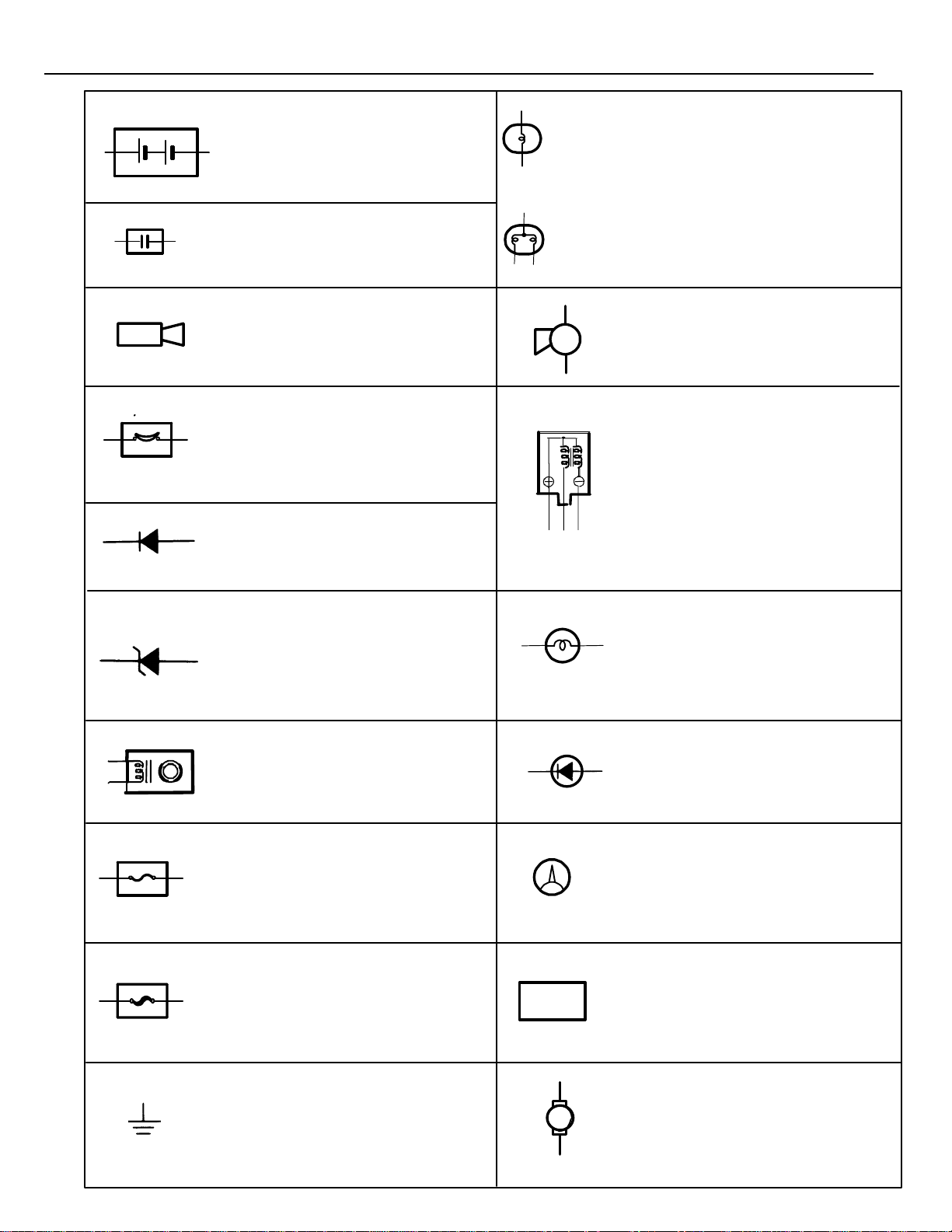
GLOSSARY OF TERMS AND SYMBOLS
BATTERY
Stores chemical energy and
converts it into electrical energy.
Provides DC current for the auto’s
various electrical circuits.
CAPACITOR (Condenser)
A small holding unit for temporary
storage of electrical voltage.
CIGARETTE LIGHTER
An electric resistance heating
element.
CIRCUIT BREAKER
Basically a reusable fuse, a circuit
breaker will heat and open if too
much current flows through it. Some
units automatically reset when cool,
others must be manually reset.
DIODE
A semiconductor which allows
current flow in only one direction.
HEADLIGHTS
1. SINGLE
FILAMENT
2. DOUBLE
FILAMENT
Current flow causes a headlight
filament to heat up and emit light.
A headlight may have either a
single (1) filament or a double (2)
filament.
HORN
An electric device which sounds a
loud audible signal.
IGNITION COIL
Converts low–voltage DC current
into high–voltage ignition current
for firing the spark plugs.
DIODE, ZENER
A diode which allows current flow
in one direction but blocks reverse
flow only up to a specific voltage.
Above that potential, it passes the
excess voltage. This acts as a
simple voltage regulator.
DISTRIBUTOR, IIA
Channels high–voltage current
from the ignition coil to the
individual spark plugs.
FUSE
A thin metal strip which burns
through when too much current
flows through it, thereby stopping
current flow and protecting a
circuit from damage.
FUSIBLE LINK
A heavy–gauge wire placed in
high amperage circuits which
burns through on overloads,
thereby protecting the circuit.
FUEL
LIGHT
Current flow through a filament
causes the filament to heat up
and emit light.
LED (LIGHT EMITTING DIODE)
Upon current flow, these diodes
emit light without producing the
heat of a comparable light.
METER, ANALOG
Current flow activates a magnetic
coil which causes a needle to
move, thereby providing a relative
display against a background
calibration.
METER, DIGITAL
Current flow activates one or
many LED’s, LCD’s, or flourescent
displays, which provide a relative
or digital display.
14
GROUND
The point at which wiring attaches
to the Body, thereby providing a
return path for an electrical circuit;
without a ground, current cannot
flow.
MOTOR
A power unit which converts
M
electrical energy into mechanical
energy, especially rotary motion.
Page 15
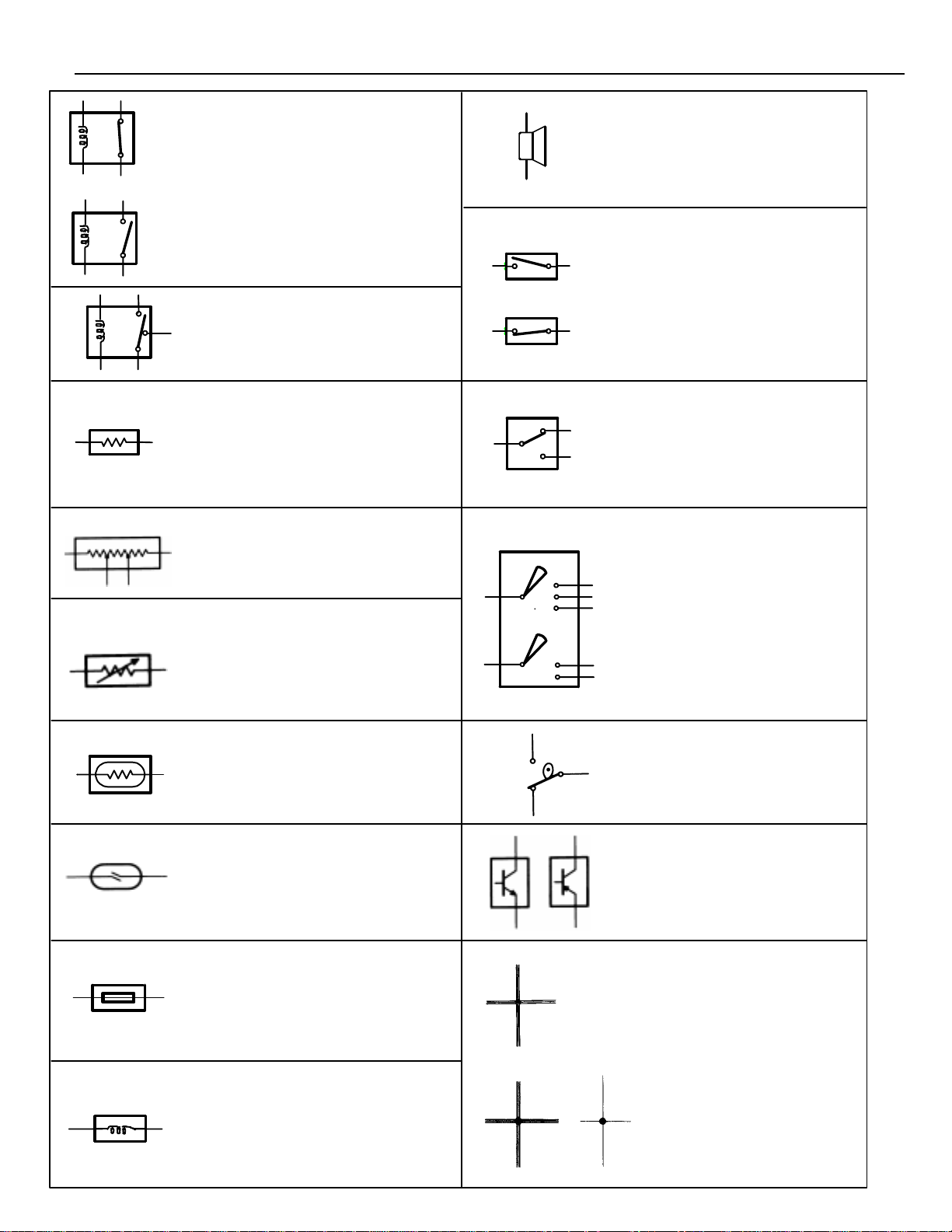
RELAY
1. NORMALLY
CLOSED
2. NORMALLY
OPEN
RELAY, DOUBLE THROW
A relay which passes current
through one set of contacts or the
other.
Basically, an electrically
operated switch which may
be normally closed (1) or
open (2).
Current flow through a
small coil creates a
magnetic field which either
opens or closes an
attached switch.
SPEAKER
An electromechanical device
which creates sound waves from
current flow.
SWITCH, MANUAL
1. NORMALLY
OPEN
2. NORMALLY
CLOSED
Opens and
closes circuits,
thereby
stopping (1) or
allowing (2)
current flow.
RESISTOR
An electrical component with a
fixed resistance, placed in a circuit
to reduce voltage to a specific
value.
RESISTOR, TAPPED
A resistor which supplies two or
more different non–adjustable
resistance values.
RESISTOR, VARIABLE or
RHEOSTAT
A controllable resistor with a
variable rate of resistance.
Also called a potentiometer or
rheostat.
SENSOR (Thermistor)
A resistor which varies its
resistance with temperature.
SENSOR, ANALOG SPEED
Uses magnetic impulses to open
and close a switch to create a
signal for activation of other
components.
SWITCH, DOUBLE THROW
A switch which continuously
passes current through one set
of contacts or the other.
SWITCH,
IGNITION
A key operated switch with
several positions which allow
various circuits. Particularly the
primary ignition circuit, to
become operational.
SWITCH, WIPER PARK
Automatically returns wipers to
the stop position when the wiper
switch is turned off.
TRANSISTOR
A solidstate device typically used
as an electronic relay; stops or
passes current depending on the
applied voltage at “base.”
SHORT PIN
Used to provide an unbroken
connection within a junction block.
SOLENOID
An electromagnetic coil which
forms a magnetic field when
current flows, to move a plunger,
etc.
WIRES
(1) NOT
CONNECTED
(2) SPLICED
Wires are always
drawn as straight
lines on wiring
diagrams. Crossed
wires (1) without a
black dot at the
junction are not
joined;
crossed wires (2)
with a black dot at
the junction are
spliced (joined)
connections.
15
Page 16
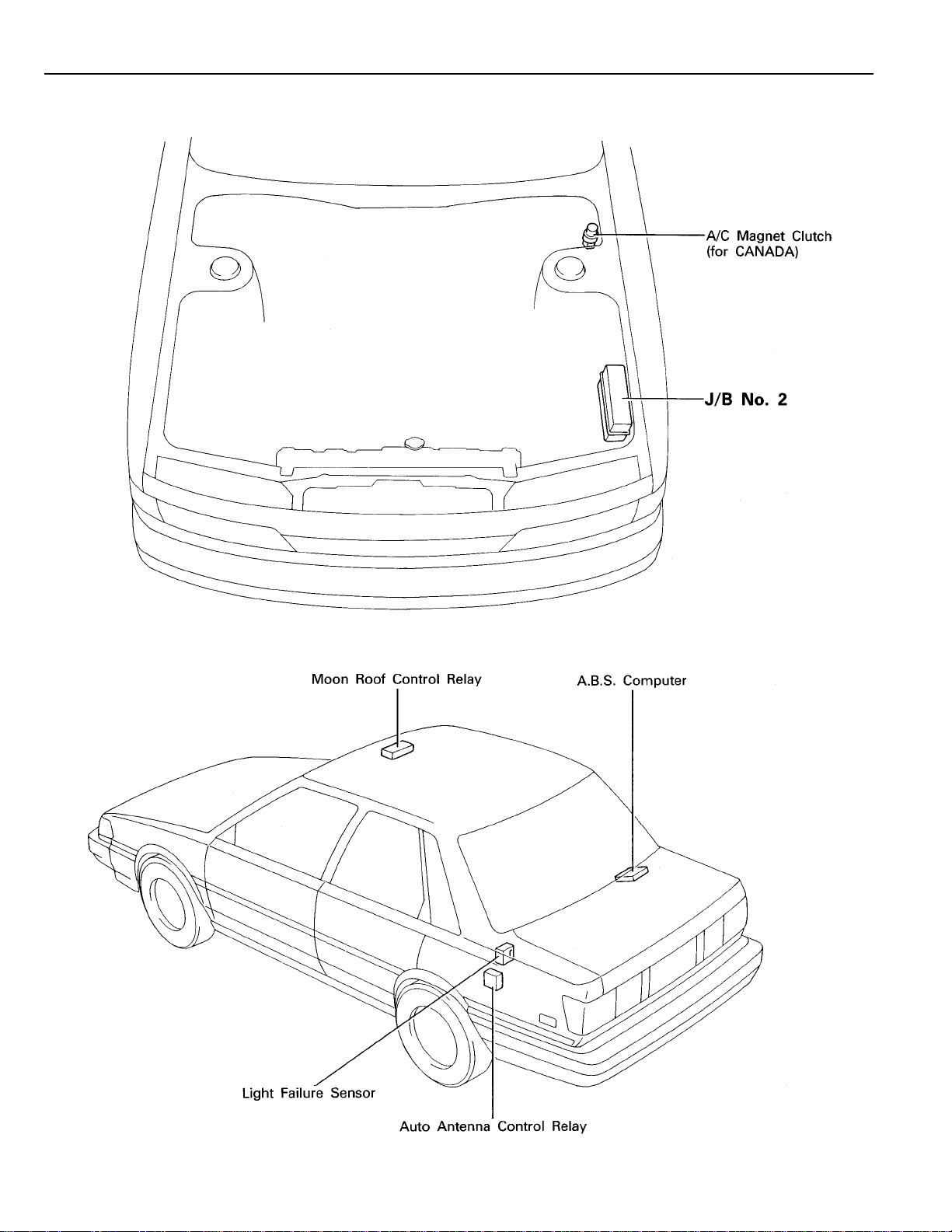
RELAY LOCATIONS
[Engine Compartment]
[Body]
[S/D]
16
Page 17
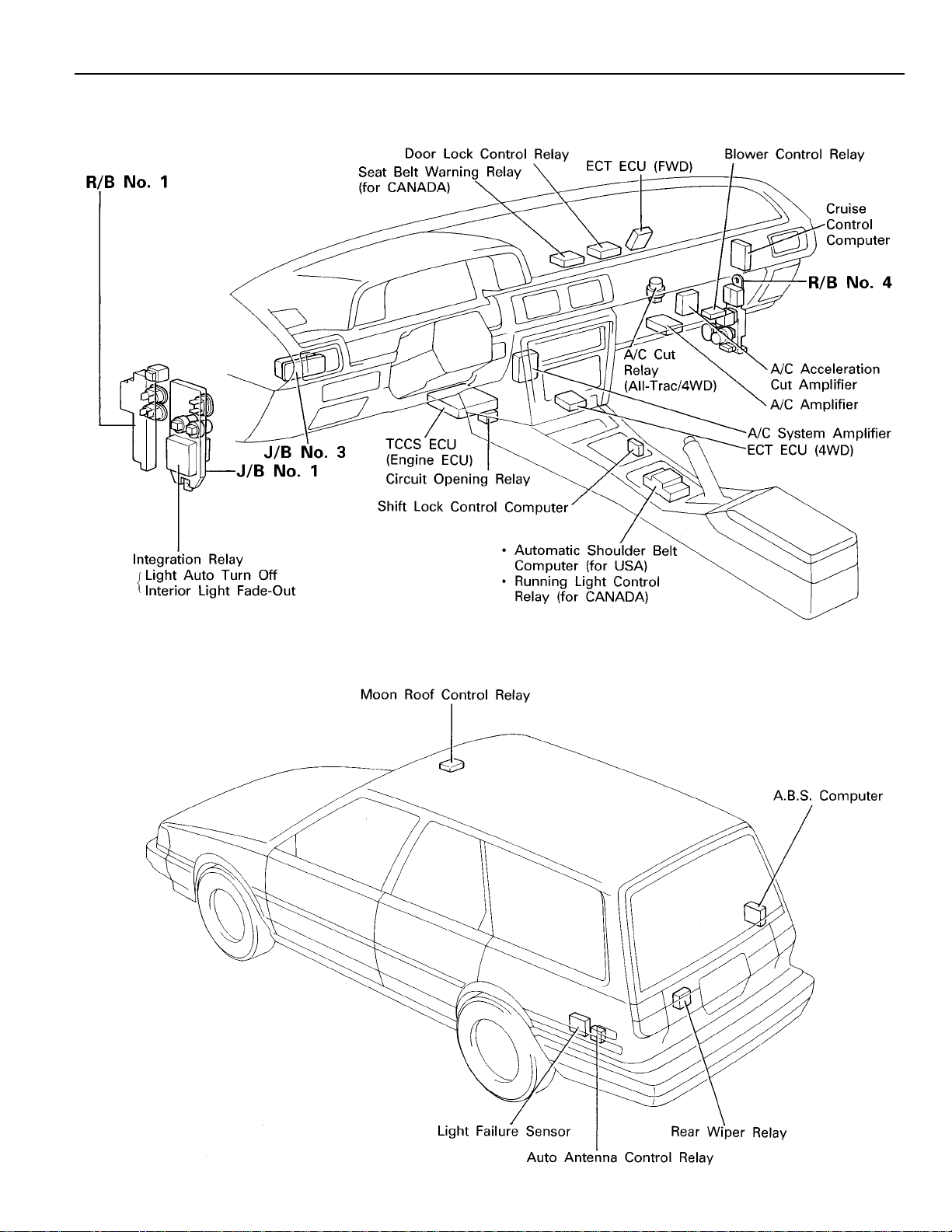
[Instrument Panel]
[Body]
[WAGON]
17
Page 18
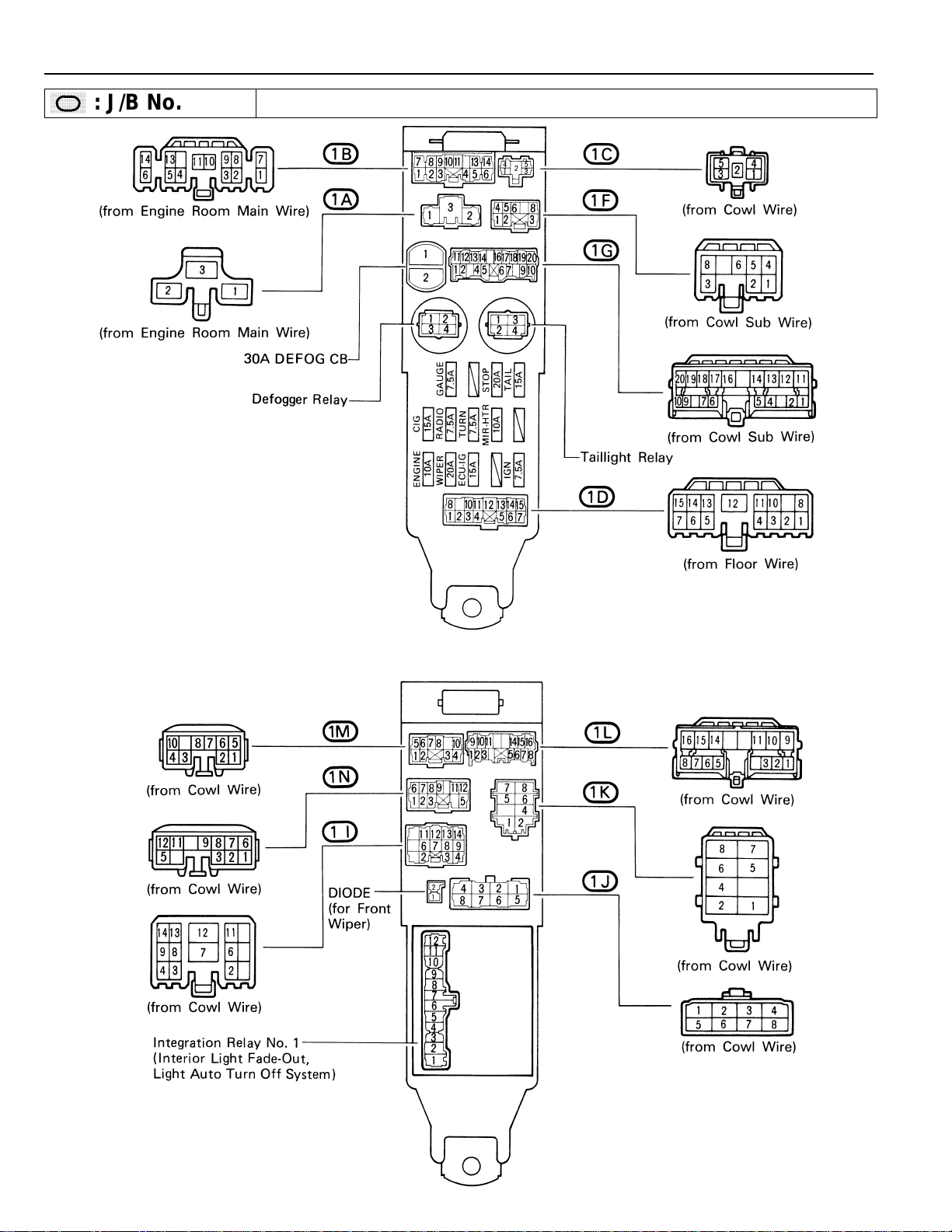
RELAY LOCATIONS
,
,,,
,,
: J/B No. 1 Left Kick Panel
(See Page 17)
18
Page 19
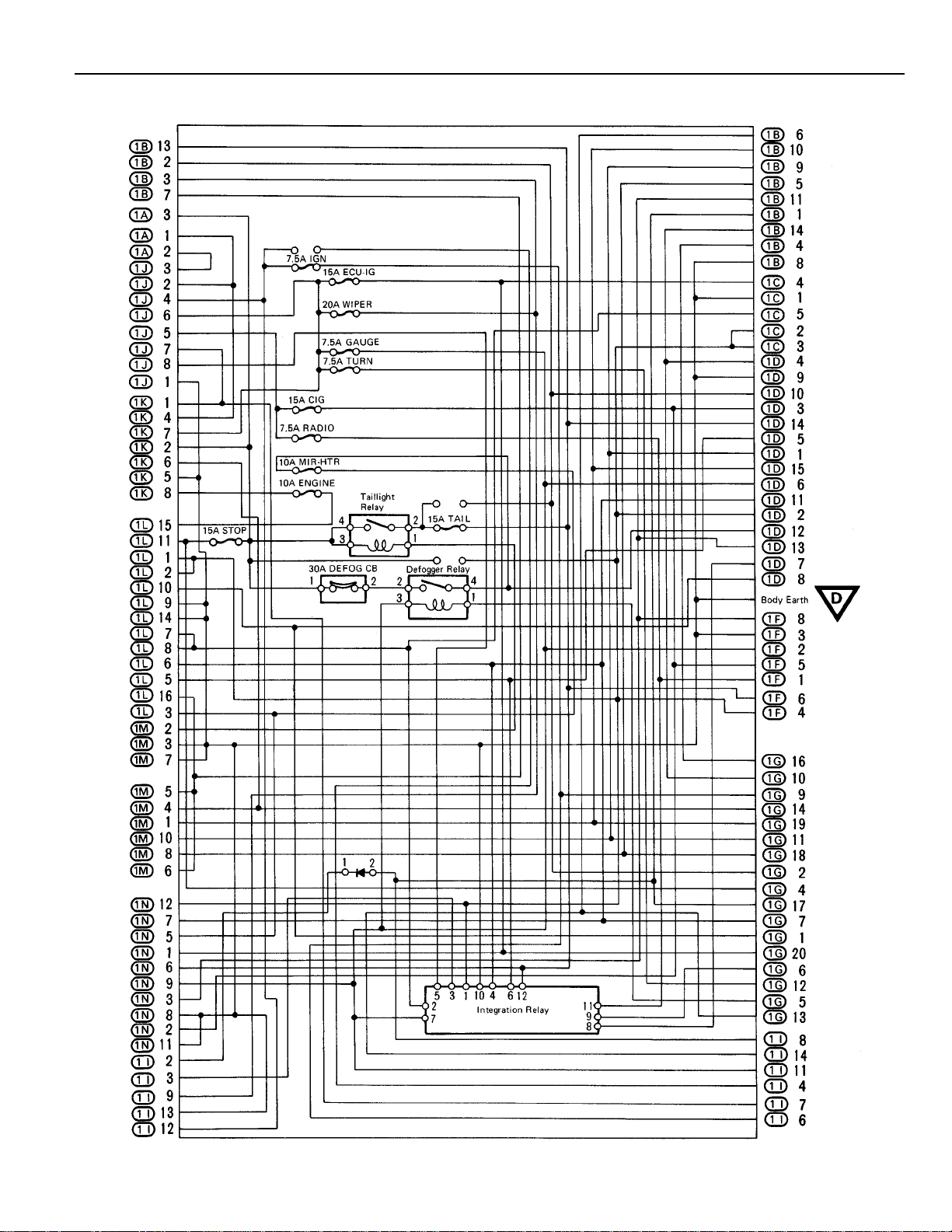
[J/B No. 1 Inner Circuit]
19
Page 20
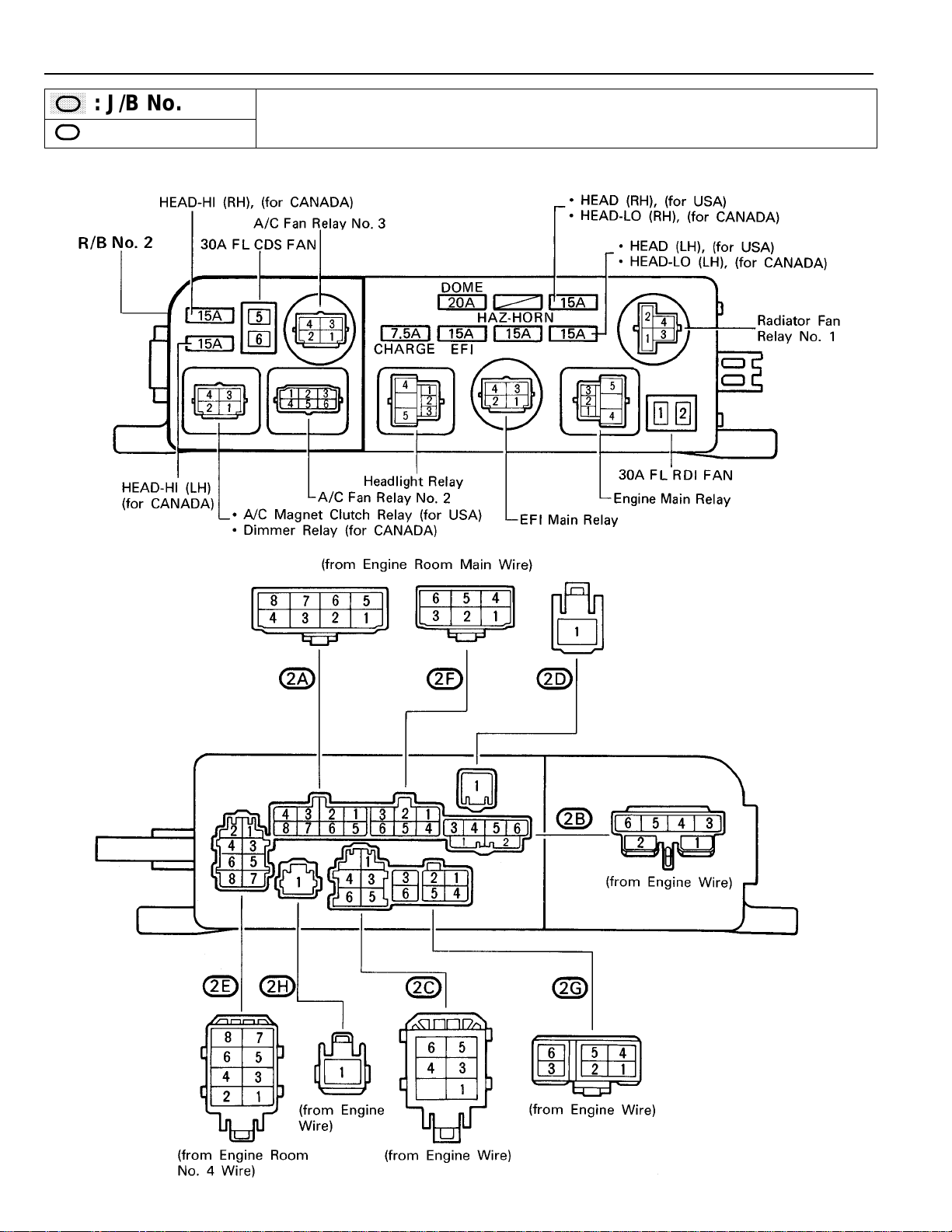
RELAY LOCATIONS
,
,,,
Engi
ft
(S
16)
,,
: J/B No. 2
2
: R/B No. 2
ne Compartment Le
ee Page
20
Page 21
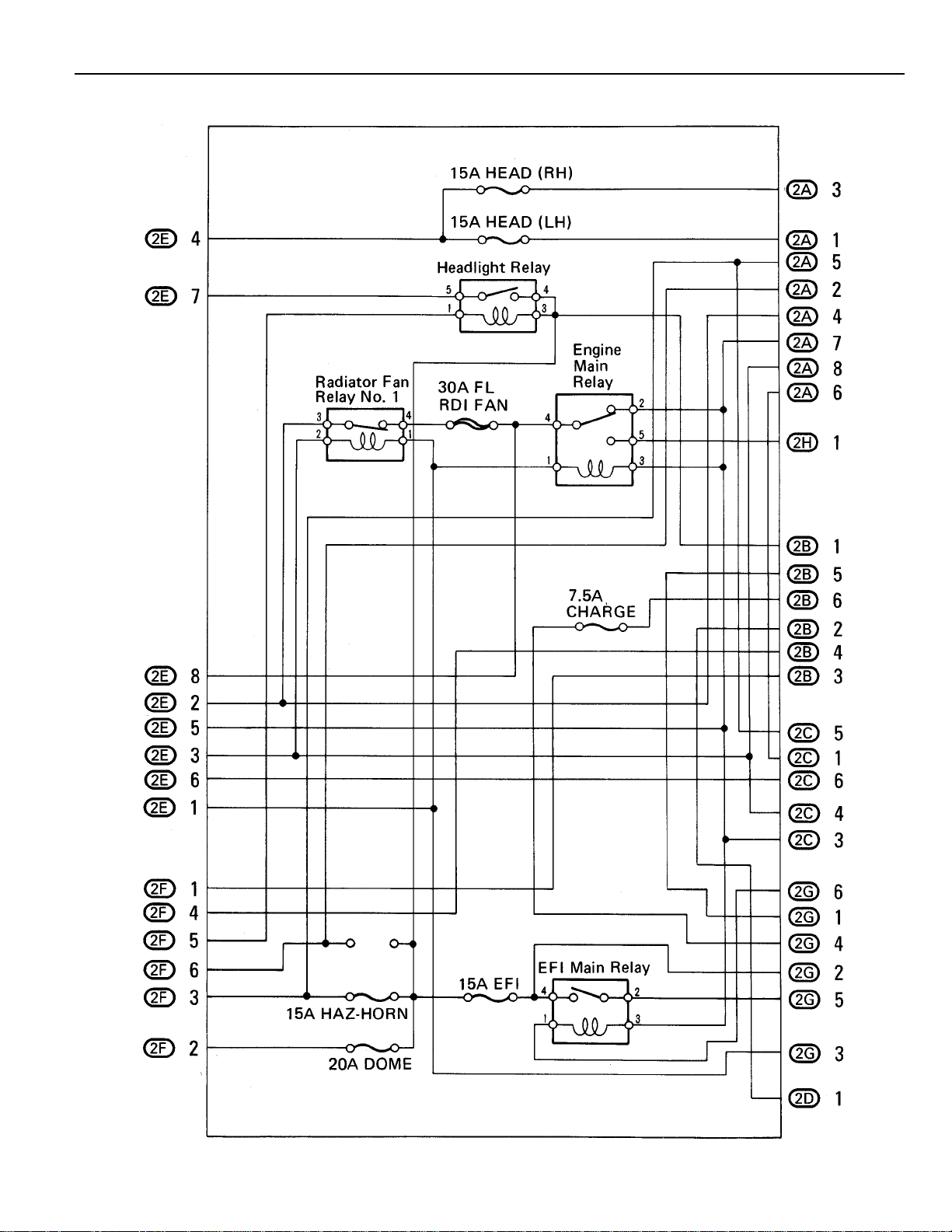
[J/B No. 2 Inner Circuit]
21
Page 22
RELAY LOCATIONS
,
,,,
,,
: J/B No. 3 Instrument Panel Left
(See Page 17)
[J/B No. 3 Inner Circuit]
22
Page 23
1
: R/B No. 1 Left Kick Panel
(See Page 17)
4
: R/B No. 4 Right Kick Panel
(See Page 17)
23
Page 24
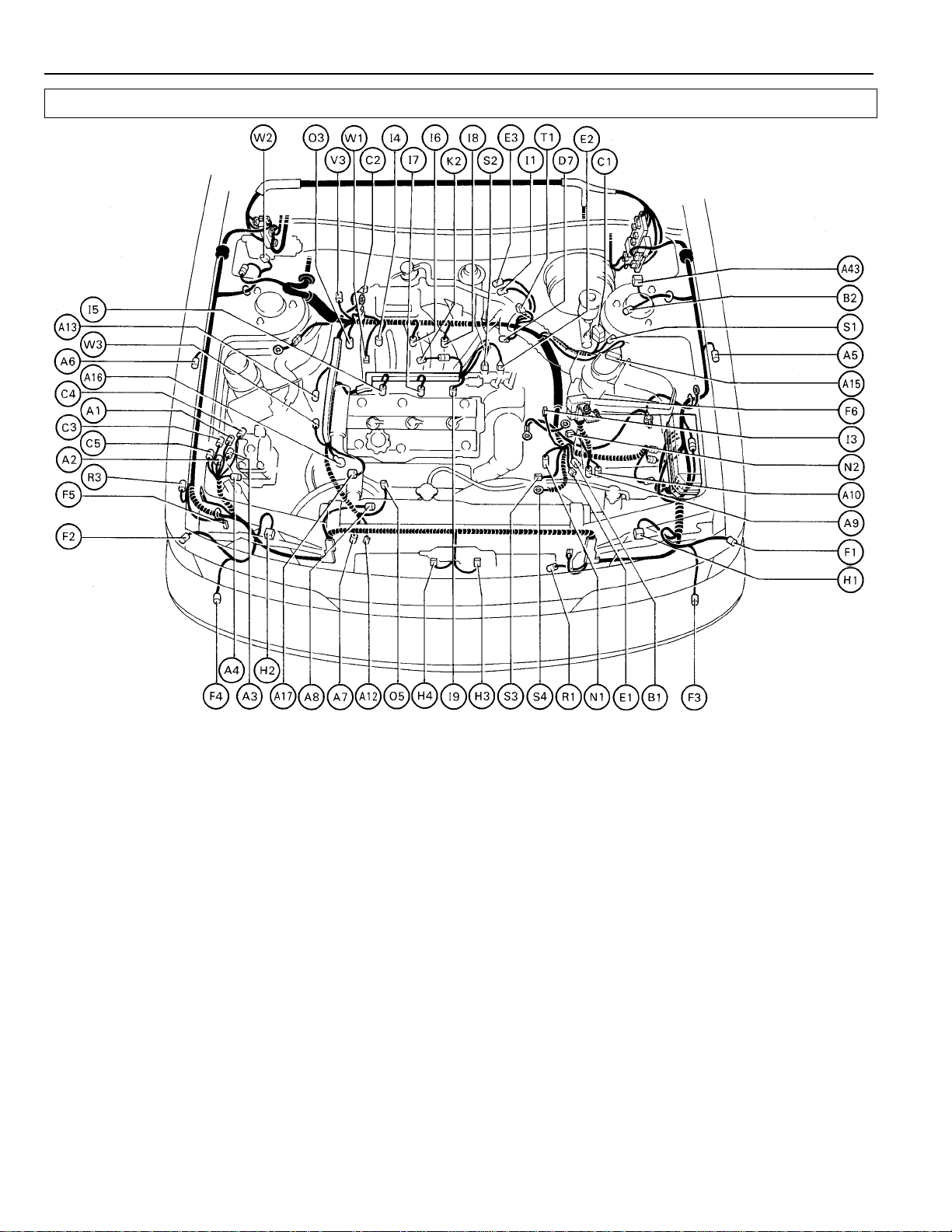
ELECTRICAL WIRING ROUTING
Position of Parts in Engine Compartment
[2VZ–FE]
A 1 A.B.S. Actuator C 4 Cruise Control Vacuum Pump
A 2 A.B.S. Actuator C 5 Cruise Control Vacuum SW
A 3 A.B.S. Actuator
A 4 A.B.S. Check Connector D 1 Diff. Lock Indicator SW
A 5 A.B.S. Speed Sensor Front LH D 2 Diff. Lock Solenoid (3S–FE A/T)
A 6 A.B.S. Speed Sensor Front RH D 3 Diff. Lock Solenoid (for Diff. Lock, 4WD)
A 7 A/C Compressor Sensor D 4 Diff. Lock Solenoid (for Diff. Lock, 4WD)
A 8 A/C Condenser Fan Motor D 5 Diff. Lock Speed Sensor Front (A/T)
A 9 A/C Dual Pressure SW D 6 Diff. Lock Speed Sensor Rear (A/T)
A 10 A/C High Pressure SW (for Radiator Fan) D 7 Distributor (2VZ–FE)
A 11 A/C Idle–Up VSV D 9 Distributor and Ignition Coil (3S–FE)
A 12 A/C A/C Magnet Clutch
A 13 A/C Water Temp. SW (for Radiator Fan, 3S–FE) E 1 ECT Solenoid or O/D Solenoid
A 14 A/C Water Temp. SW (for A/C Cut, 4WD) E 3 EGR Gas Temp. Sensor (for California)
A 15 Air Flow Meter
A 16 Alternator F 1 Front Clearance and Side Marker Light LH
A 17 Alternator F 2 Front Clearance and Side Marker Light RH
A 43 A/C Magnet Clutch Relay (for CANADA) F 3 Front Turn Signal Light LH
A 44 A/T Fluid Temp. SW F 4 Front Turn Signal Light RH
B 1 Back–Up Light SW (M/T) F 6 Fusible Link Box
B 2 Brake Fluid Level Warning SW
C 1 Check Connector H 2 Headlight RH
C 2 Cold Start Injector H 3 Horn
C 3 Cruise Control Actuator H 4 Horn
or Short Pin (w/o A/C) D 8 Distributor and Ignition Coil (3S–FE)
or Sensor (for Condenser Fan, 2VZ–FE) E 2 EFI Water Temp. Sensor
F 5 Front Washer Motor
H 1 Headlight LH
24
Page 25
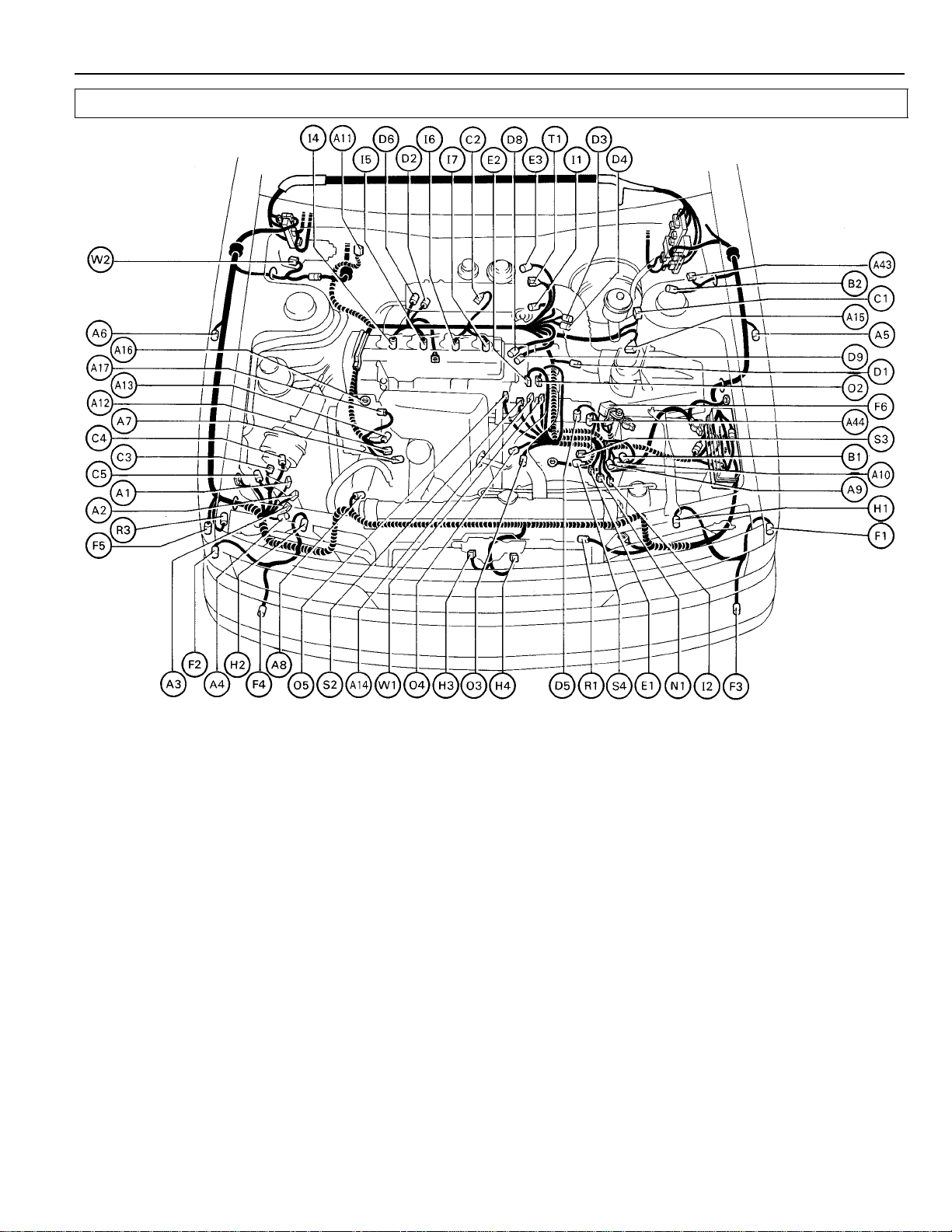
[3S–FE]
Position of Parts in Engine Compartment
I 1 ISC Valve R 1 Radiator Fan Motor
I 2 Igniter (3S–FE) R 3 Rear Washer Motor
I 3 Igniter and Ignition Coil (2VS–FE)
I 4 Injector No. 1 S 1 Short Pin (for Fan Check)
I 5 Injector No. 2 S 2 Start Injector Time SW
I 6 Injector No. 3 S 3 Starter
I 7 Injector No. 4 S 4 Starter
I 8 Injector No. 5
I 9 Injector No. 6 T 1 Throttle Position Sensor
K 2 Knock Sensor (2VZ–FE) V 3 VSV (for Fuel Pressure Up)
N 1 Neutral Start SW and Back–Up Light SW (A/T) W 1 Water Temp. Sender
N 2 Noise Filter (for Ignition System) W 2 Wiper Motor
W 3 Water Temp. Sensor (for Radiator Fan, 2VZ–FE)
O 2 O/D Water Temp. SW
O 3 Oxygen Sensor Main
O 4 Oxygen Sensor Sub (3S–FE)
O 5 Oil Pressure SW
25
Page 26
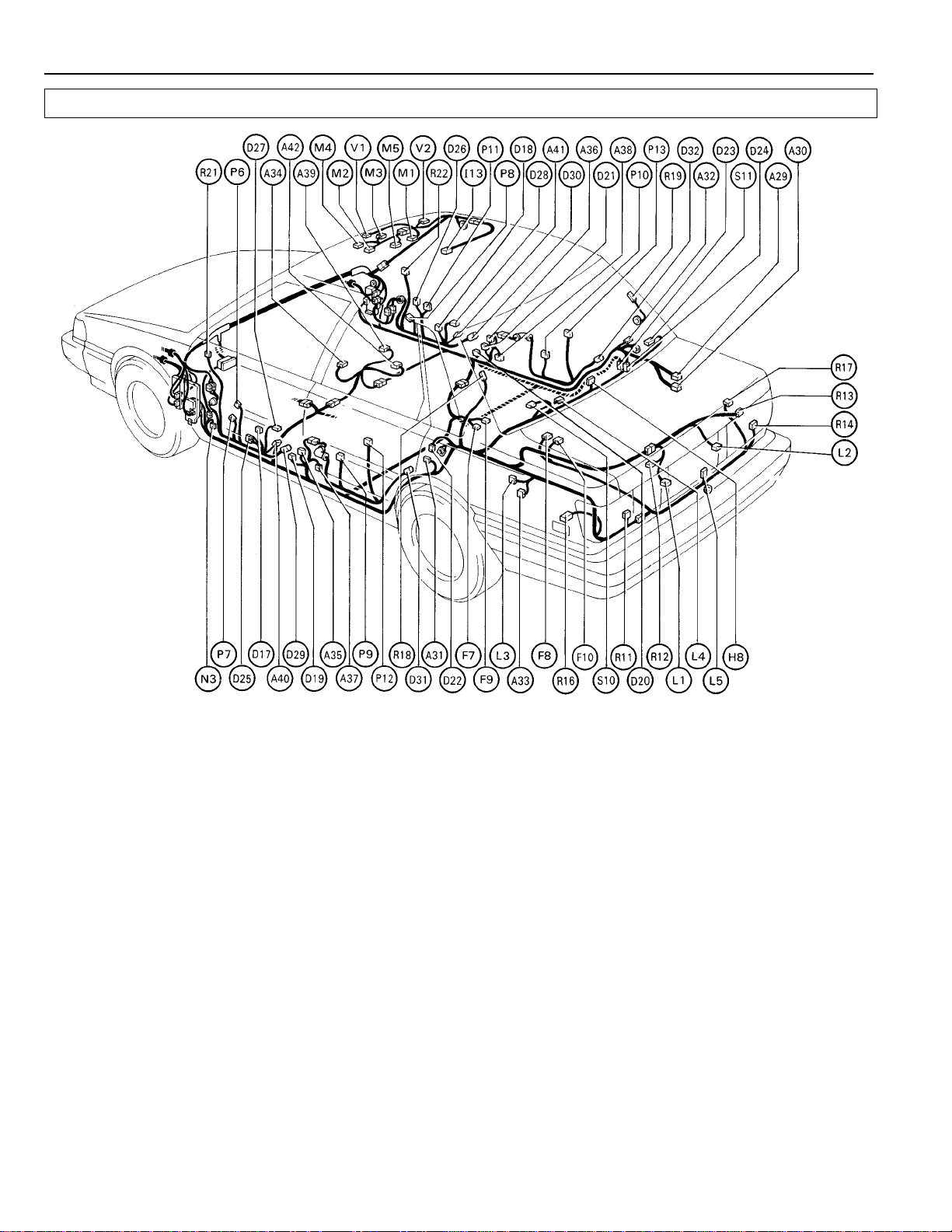
ELECTRICAL WIRING ROUTING
Position of Parts in Body
[SEDAN]
A 29 A.B.S. Computer D 20 Door Courtesy SW Front RH (CANADA)
A 30 A.B.S. Computer D 21 Door Courtesy SW Front RH (USA)
A 31 A.B.S. Speed Sensor Rear LH D 22 Door Courtesy SW Rear LH
A 32 A.B.S. Speed Sensor Rear RH D 23 Door Courtesy SW Rear RH (CANADA)
A 33 Auto Antenna Motor and Control Relay D 24 Door Courtesy SW Rear RH (USA)
A 34 Automatic Shoulder Belt Computer (USA) D 25 Door Key Cylinder Light and Outside handle SW
A 35 Automatic Shoulder Belt Limit SW LH D 26 Door Lock Control SW RH
A 36 Automatic Shoulder Belt Limit SW RH D 27 Door Lock Key SW LH
A 37 Automatic Shoulder Belt Motor LH D 28 Door Lock Key SW RH
A 38 Automatic Shoulder Belt Motor RH D 29 Door Lock Solenoid Front LH
A 39 Automatic Shoulder Belt Release Lever D 30 Door Lock Solenoid Front RH
A 40 Automatic Shoulder Belt SW LH D 32 Door Lock Solenoid Rear RH
A 41 Automatic Shoulder Belt SW RH
A 42 Automatic Shoulder Belt Spool Release SW F 7 Fuel Pump
B 8 Back Door Courtesy SW (W/G) F 9 Fuel Sender
B 9 Back Door Lock Solenoid (W/G) F 10 Fuel Sender (All–Trac/4WD)
D 17 Door Courtesy Light LH H 8 High Mount Stop Light
D 18 Door Courtesy Light RH
D 19 Door Courtesy SW Front LH I 13 Interior Light
Warning Light (USA) D 31 Door Lock Solenoid Rear LH
F 8 Fuel Pump (All–Trac/4WD)
26
Page 27
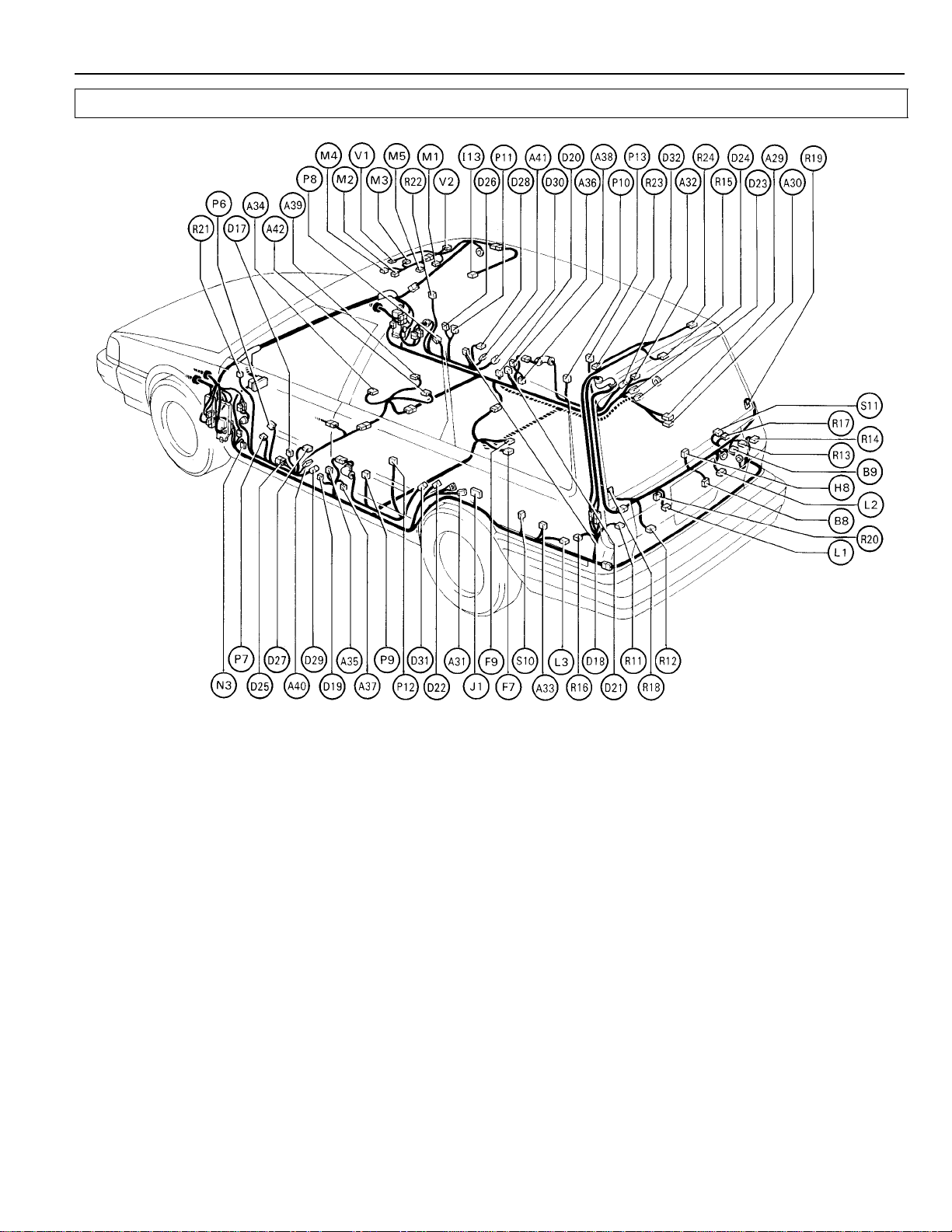
[STA TION WAGON]
Position of Parts in Body
J 1 Junction Connector (W/G) P 12 Power Window SW Rear LH
P 13 Power Window SW Rear RH
L 1 Licence Plate Light LH
L 2 Licence Plate Light RH R 11 Rear Combination Light LH
L 3 Light Failure Sensor R 12 Rear Combination Light LH
L 4 Luggage Compartment Light (S/D) R 13 Rear Combination Light RH
L 5 Luggage Compartment Light SW (S/D) R 14 Rear Combination Light RH
R 15 Rear Interior Light (W/G)
M 1 Map Light (w/o Moon Roof) R 16 Rear Side Marker Light LH
M 2 Moon Roof Control Relay R 17 Rear Side Marker Light RH
M 3 Moon Roof Limit SW R 18 Rear Window Defogger (+)
M 4 Moon Roof Motor R 19 Rear Window Defogger (–)
M 5 Moon Roof SW and/or Map Light R 20 Rear Wiper Motor
R 21 Remote Control Mirror LH
N 3 Noise Filter (Defogger) R 22 Remote Control Mirror RH
R 23 Roof Speaker Rear LH (W/G)
P 6 Power Window Master SW and R 24 Roof Speaker Rear RH (W/G)
Door Lock Control SW LH
P 7 Power Window Motor Front LH S 10 Speaker Rear LH
P 8 Power Window Motor Front RH S 11 Speaker Rear RH
P 9 Power Window Motor Rear LH
P 10 Power Window Motor Rear RH V 1 Vanity Light LH
P 11 Power Window SW Front RH V 2 Vanity Light RH
27
Page 28
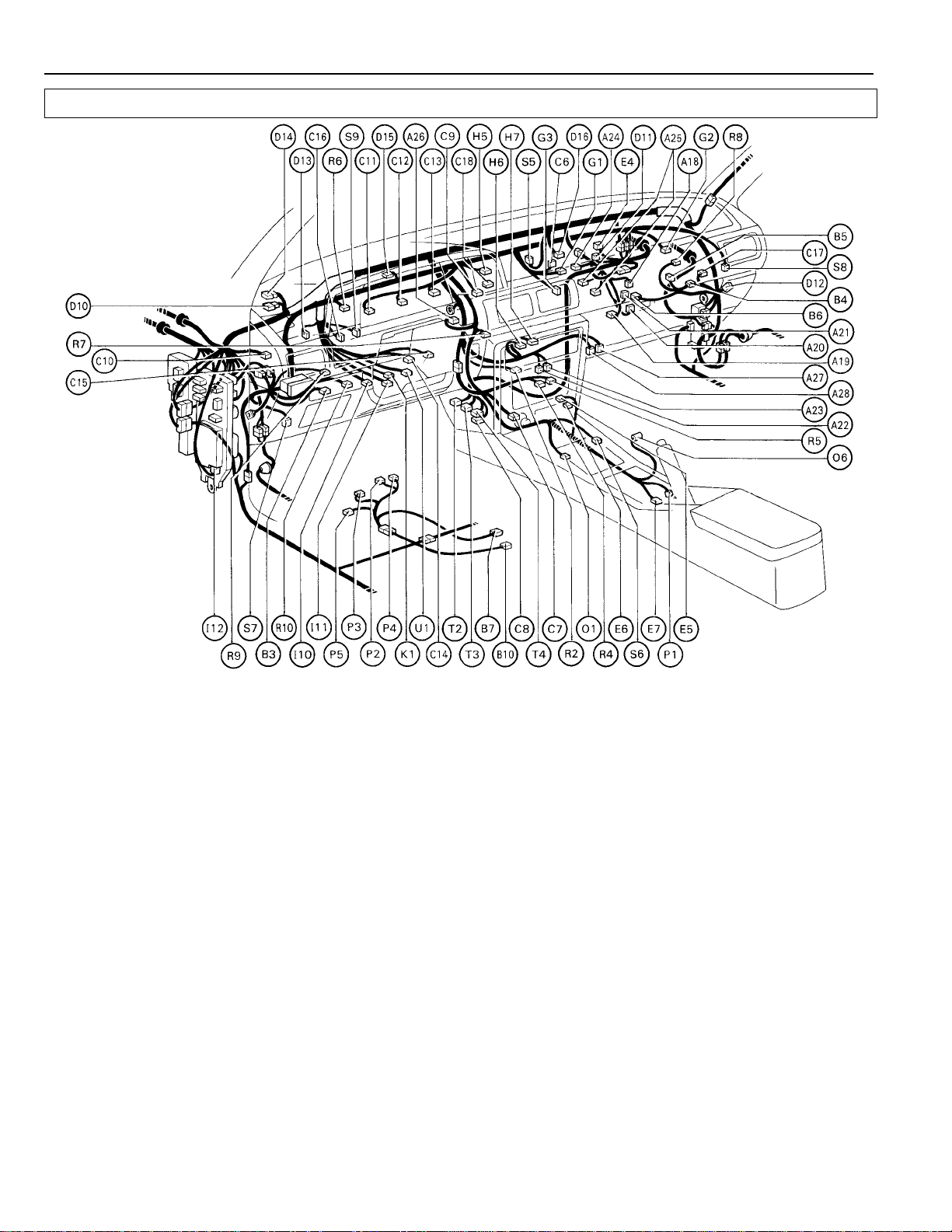
ELECTRICAL WIRING ROUTING
Position of Parts in Instrument Panel
A 18 A/C Acceleration Cut Amplifier C 17 Cruise Control Computer O 1 O/D Main SW and A/T Indicator
A 19 A/C Amplifier (FWD) D 10 Diode (E lect rical Idle–Up Syste m)
A 20 A/C Amplifier (All–Trac/4WD) D 11 Diode (Over Drive System) P 1 Parking Brake SW
A 21 A/C Cut Relay (All–Trac/4WD) or D 12 Diode (for Interior Light System, P 2 Power Seat Motor (Front Vertical)
A 22 A/C System Amplifier (for Heater) w/o Door Lock System) P 5 Power Seat SW
A 23 A/C System Amplifier (for Heater) D 14 Diode (for Front Wiper System)
A 24 A/C Thermistor (3S–FE) D 15 Diode (for Rear Wiper System) R 2 Running Light Control Relay
A 25 A/C Thermistor and Diode (2VZ–FE) D 16 Door Lock Control Relay (for CANADA)
A 26 A/T Indicator (Instrument Panel) R 4 Radio and Tape Player
A 27 Air Mix Control Servo Motor E 4 ECT ECU (FWD) R 5 Radio and Tape Player
A 28 Air V ent Mode Control Servo Motor E 5 ECT ECU (All–Trac/4WD) R 6 Rear Window Defogger SW
B 3 Back Door Lock Control SW (W/G) E 7 ECT Pattern Select SW or Diff. Lock Control SW
B 4 Blower Control Relay (All–Trac/4WD)
B 5 Blower Motor G 1 Glove Box Light R 8 Recirc/Fresh Control Servo Motor
B 6 Blower Resistor G 2 Glove Box Light SW (CANADA) R 9 Remote Control Mirror SW
B 7 Buckle SW (w/ Power Seat) G 3 Glove Box Light SW (USA) R 10 Rheostat
B 10 Buckle SW (w/o Power Seat)
C 6 Center Diff. Lock Indicator Light H 6 Heater Control Assembly S 6 Shift Lock Control Computer
C 7 Cigarette Lighter Blower SW (Lever SW Type) S 8 Speaker Front RH
C 8 Circuit Opening Relay H 7 Heater Control Assembly S 9 Stop Light SW and Cruise Control
C 9 Clock (Push SW Type) or A/C SW and Stop SW
C 10 Clutch Start SW (M/T) Blower SW (Lever SW Type)
C 11 Combination Meter T 2 TCCS ECU (Engine ECU)
C 12 Combination Meter I 10 Ignition Key Cylinder Light T 3 TCCS ECU (Engine ECU)
C 13 Combination Meter I 11 Ignition SW T 4 TCCS ECU (Engine ECU)
C 14 Combination SW I 12 Integration Relay
C 15 Combination SW U 1 Unlock Warning SW
C 16 Cruise Control Clutch SW K 1 Key Interlock Solenoid
(SV) or A/C Condenser Fan C 18 Cruise Control Main SW Light
Control Amplifier (VSV) O 6 OX Sensor Sub (2VZ–FE)
Compressor Control Amplifier w/ Door Lock System) P 3 Power Seat Motor (Rear Vertical)
(2VZ–FE) D 13 Diode (for Interior Light System, P 4 Power Seat Motor (Slide)
E 6 ECT ECU (All–Trac/4WD) R 7 Rear Wiper and Washer SW (W/G)
H 5 Hazard SW S 5 Seat Belt Warning Relay
(All–T rac/4WD) (Push SW Type) or A/C SW and S 7 Speaker Front LH
28
Page 29
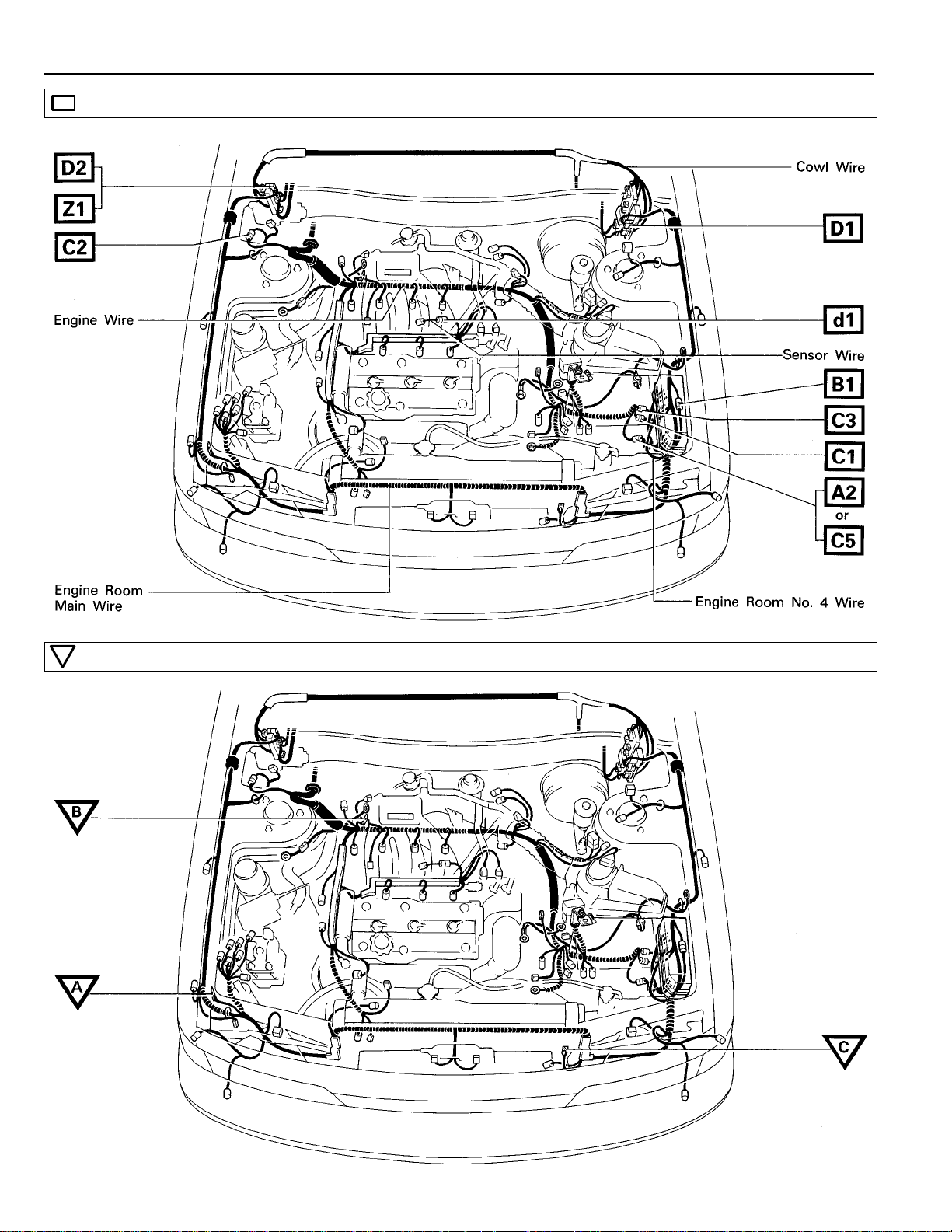
ELECTRICAL WIRING ROUTING
: Location of Connector Joining Wire Harness and Wire Harness
[2VZ–FE]
: Location of Ground Points
[2VZ–FE]
30
Page 30
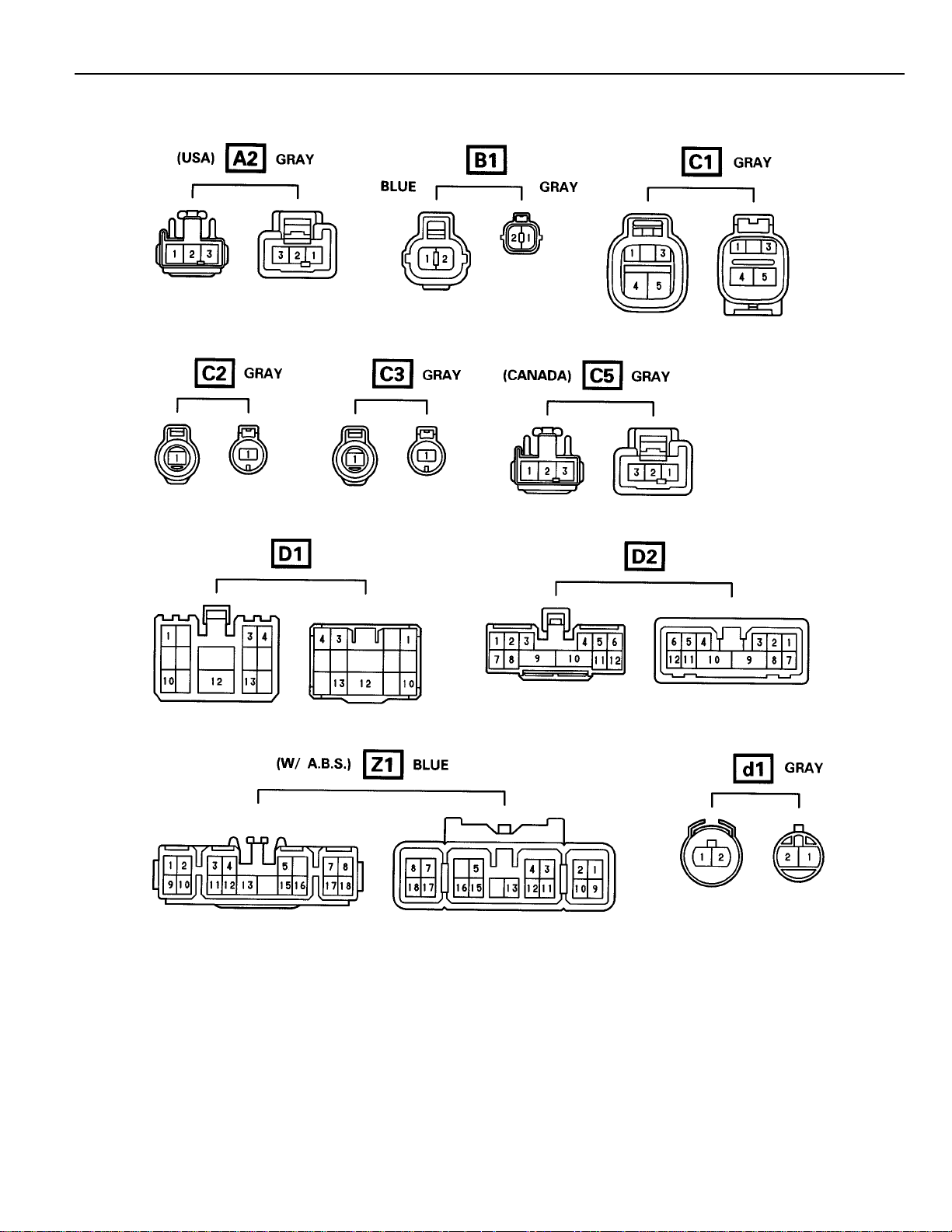
Connector Joining W ire Harness and Wire Harness
31
Page 31

ELECTRICAL WIRING ROUTING
: Location of Connector Joining Wire Harness and Wire Harness
[3S–FE]
: Location of Ground Points
[3S–FE]
32
Page 32

Connector Joining W ire Harness and Wire Harness
33
Page 33

ELECTRICAL WIRING ROUTING
: Location of Connector Joining Wire Harness and Wire Harness
: Location of Ground Points
34
Page 34

Connector Joining W ire Harness and Wire Harness
35
Page 35

ELECTRICAL WIRING ROUTING
: Location of Connector Joining Wire Harness and Wire Harness
[SEDAN]
: Location of Ground Points
[SEDAN]
36
Page 36

Connector Joining W ire Harness and Wire Harness
37
Page 37

ELECTRICAL WIRING ROUTING
: Location of Connector Joining Wire Harness and Wire Harness
[STA TION WAGON]
: Location of Ground Points
[STA TION WAGON]
38
Page 38

Connector Joining W ire Harness and Wire Harness
39
Page 39

POWER SOURCE (Power–Load, Reference)
A
IGN
20A
WIPER
20A
STOP
15A
ECU–IG
15A
CIG
J/B No. 1 (Left Kick Panel)
Power Load Page No.
Engine Main Relay 44
7.5
7.5A TURN Turn Signal Flasher 92
7.5A GAUGE
15A TAIL
7.5A RADIO
30A DEFOG CB Rear Window Defogger 146
10A MIR–HTR Engine ECU 67
10A ENGINE IC Regulator 50
Charge Warning Light 50
EFI Main Relay (3S–FE), Engine ECU (2VZ–FE) 52, 124
Radiator Fan Relay No. 1, A/C Fan Relay No. 2 158
Washer Motor , Wiper Motor, Wiper Relay 98
Rear Washer Motor , Rear Wiper Relay, Rear Wiper Motor 100
Engine ECU 52, 124
Light Failure Sensor, Stop Lights, Hi Mount Stop Light 94
Cruise Control Computer 120
ECT ECU (3S–FE) 129
Shift Lock Control Computer 140
A.B.S. Computer 142
Check Engine Warning Light 52
Integration Relay 68
Light Failure Sensor, Rear Lights W arning Light 88, 94
Back–Up Lights 96
Power Main Relay 102, 148
Automatic Shoulder Belt Computer, Automatic Shoulder Belt Release
Lever Warning Light, Seat Belt Warning Light
Seat Belt Warning Light, Seat Belt Warning Relay 118
A/T Indicator, O/D Of f Indicator Light, ECT ECU (3S–FE), Engine ECU (2VZ–FE) 124
O/D Solenoid, O/D Off Indicator Light 134
Diff. Lock Solenoid, Center Diff. Lock Indicator, ECT ECU (A/T) 136
A.B.S. Warning Light 142
Rear Window Defogger SW, Defogger Relay 146
Antenna Motor and Control Relay 150
Combination Meter 154
Heater Relay, Blower Control Relay, A/C System Amplifier,
Recirc/Fresh Control Servo Motor, Heater Control Assembly
Engine ECU 67
Glove Box Light, Combination Meter, Rheostat, ECT Pattern Select SW Light, Rear
Wiper SW Light, Cruise Control Main SW Light, Hazard SW Light, O/D Main SW Light,
Rear Window Defogger SW Light, Cigarette Lighter Light, A/T Indicator Light, Radio
Light, Diff. Lock Control SW Light, Center Diff. Lock Indicator Light, A/C SW Light,
Heater Control SW Light
Front Clearance and Side Marker Lights, Licence Plate Lights,
Rear Side Marker Lights, Light Failure Sensor, Taillights
Clock 139
Cruise Control Main SW, Cruise Control Computer 120
ECT ECU (3S–FE) 129
Shift Lock Control Computer 140
A.B.S. Computer 142
Mirror Motor 112
Clock 139
Shift Lock Control Computer 140
Antenna Motor and Control Relay 150
Radio and Tape Player 152
Clock, Cigarette Lighter 139
Antenna Motor and Control Relay 150
114
158
84
88
40
Page 40

J/B No. 2 (Engine Compartment)
20A
DOME
15A
HAZ–HORN
30A
FL AM2
Power Load Page No.
Integration Relay 68, 76
Map Light, Door Key Cylinder Light, Door Courtesy Light, Rear Interior Light, Ignition Key Cylinder
Light, Interior Light, Vanity Light, Door W arning Light, Luggage Compartment Light
20A DOME
7.5A CHARGE IC Regulator 50
15A HEAD LH Headlight LH (USA) 70
15A HEAD RH Headlight RH (USA) 70
15A HEAD–LO (LH) Headlight LH (CANADA) 72
15A HEAD–LO (RH) Headlight RH (CANADA) 72
15A EFI
30A FL RDI F AN Radiator Fan Motor 158
ECT ECU (3S–FE) 129
Clock 139
Antenna Motor 150
Radio and Tape Player 152
Turn Signal Flasher 92
Horns, Horn Relay 111
Fuel Pump, ISC Valve, Engine ECU, Circuit Opening Relay, Check Connector,
OX Sensor (Main) (2VZ–FE)
Engine ECU 67
Engine ECU (2VZ–FE) 124
R/B No. 1 (Near the J/B No. 1)
Power Window Master SW, Power Window Motor 102
Power Seat Motor 105
30A POWER CB
AUTOMATIC
30A
SHOULDER BELT CB
10A ECU–B
Door Lock Control Relay, Door Lock Solenoid 106
Back Door Lock Solenoid 110
Moon Roof Control Relay 148
Automatic Shoulder Belt Computer, Automatic Shoulder Belt Motor 114
Seat Belt Warning Relay 118
A.B.S. Computer 142
Noise Filter (for Rear Window Defogger) 146
76
52
R/B No. 2 (Engine Compartment)
15A HEAD–HI (RH) Headlight LH (CANADA) 72
15A HEAD–HI (RH) Headlight RH (CANADA) 72
30A FL CDS FAN Condenser Fan Motor, A/C Condenser Fan Control Amplifier (2VZ–FE) 158
R/B No. 4 (Right Kick Panel)
Heater Control Assembly, A/C SW, A/C Amplifier, Magnet Clutch Relay, A/C Magnet Clutch, A/C
10A A/C
40A HEATER CB Blower Motor 158
Idle–Up VSV (3S–FE), A/C Acceleration Cut Amplifier (3S–FE), A/C Fan Relay No. 3 (3S–FE), A/C
Cut Relay (ALL–TRAC/4WD), Engine ECU (3S–FE), A/C Condenser Fan Control Amplifier
(2VZ–FE), Compressor Control Amplifier (2VZ–FE)
Fusible Link Box (Near the Battery)
IGN Fuse 44
Noise Filter (2VZ–FE) 46
Igniter, Ignition Coil and Distributor (3S–FE) 46, 59
Injector 52
40A FL MAIN Headlight Relay 44, 68, 70
44, 68, 72,
80A ALT
Taillight Relay
FL 0.5G 46
Alternator 50
Fusible Links (Near the Battery)
Automatic Shoulder Belt CB, Power CB 44
FL 0.5G
FL 1.0Y A.B.S. Actuator 142
Starter, Starter Relay, Start Injector Time SW, Cold Start Injector 46
IC Regulator 50
158
84, 88
41
Page 41

POWER SOURCE
40A MAIN
G
W
2B
1
W
FUSIBLE
A
LINK BOX
2
3
W
2B
FL 1. 0Y
2
2B
TO A. B. S
ACTUATOR
W–L
80A ALT
30A AM2
456
W
W
W
C21
WW
D210
W–R
2B4
4
2F
FL 0. 5G
W
W–R
BATTERY
1
2F
34
TAILLIGHT
W
12
1
2D
2
1A
1J3
3
W
1A
W
1K2
1A1
R–B
RELAY
15A TAIL
20A STOP
30A DEFOG CB
10A ECU–B
12
1
R
1
4
)
5
2E7
ANADA
C
(
W
2
1
324
2
R–B
2H1
51
2
43
2E8
L
3
HEADLIGHT
RELAY
1
W
(
)
USA
2
R–B
2E4
30A HEATER CB
21
44
3
B–O
2G
ENGINE
MAIN RELAY
7
2A
30A FL RDI FAN
30A FL CDS FAN
56
22
15A EFI
20A DOME
15A HAZ–HORN
4
2E
R–L
DIMMER
RELAY
22
R–L
4
C1
15A HEAD–LH
15A
15A HEAD–HI(LH
12
2
12
15A HEAD–HI(RH
15A HEAD–LO(LH
15A HEAD–LO(RH
B
W–B
W
HEAD–RH
13
D1
)
)
)
)
1
1
7. 5A GAUGE
1
2
15A ECU–IG
7. 5A TURN
20A WIPER
10A ENGINE
7. 5A RADIO
15A CIG
7. 5A IGN
30A AUTOMATIC
SHOULDER BELT CB
2
30A POWER CB
1
L–W
1
W–L
1
ACC
P–L
1J21K4
W
48
AM1
237
IG1
B–Y
W
W
IGNITION SW
K7
1
B–Y
W
W
B
8
1K
L
W–R
IG2 AM2
B–O
6
1I
W–B
C
B–O
1J41J5 1J6
44
Page 42

18
COWL WIRE AND J/B NO. 1 (LEFT KICK PANEL)
SERVICE HINTS
TAILLIGHT RELAY
2–4 : CLOSED WITH LIGHT CONTROL SW AT TAIL OR HEAD POSITION
CLOSED WITH ENGINE RUNNING
ENGINE MAIN RELAY
CHANGED WITH IGNITION SW AT ON OR ST POSITION
HEADLIGHT RELAY
4–5 : CLOSED WITH LIGHT CONTROL SW AT HEAD POSITION OR DIMMER SW AT FLASH POSITION
CLOSED WITH ENGINE RUNNING
(B)
IGNITION SW
4–3 : CLOSED WITH IGNITION KEY AT ACC OR ON POSITION
8–7, 4–2 : CLOSED WITH IGNITION KEY AT ON OR ST POSITION
DIMMER RELA Y
CHANGED FROM HEAD (LO) TO HEAD (HI) WITH DIMMER SW AT FLASH POSITION OR WITH HEADLIGHT RELAY ON AND
DIMMER SW AT HIGH POSITION
: PARTS LOCATION
CODE SEE PAGE CODE SEE P AGE CODE SEE PAGE
A F6 24 (2VZ–FE), 25 (3S–FE) B I11 28
: RELAY BLOCKS
CODE SEE PAGE RELAY BLOCKS (RELAY BLOCK LOCATION)
1 23 R/B NO. 1 (LEFT KICK PANEL)
2 20 R/B NO. 2 (ENGINE COMPARTMENT LEFT)
4 23 R/B NO. 4 (RIGHT KICK PANEL)
: JUNCTION BLOCK AND WIRE HARNESS CONNECTOR
CODE SEE PAGE JUNCTION BLOCK AND WIRE HARNESS (CONNECTOR LOCATION)
1A 18 ENGINE ROOM MAIN WIRE AND J/B NO. 1 (LEFT KICK PANEL)
1I
1J
18 COWL WIRE AND J/B NO. 1 (LEFT KICK PANEL)
1K
2A 20 ENGINE ROOM MAIN WIRE AND J/B NO. 2 (ENGINE COMPARTMENT LEFT)
2B 20 ENGINE WIRE AND J/B NO. 2 (ENGINE COMPARTMENT LEFT)
2D 20 ENGINE ROOM MAIN WIRE AND J/B NO. 2 (ENGINE COMPARTMENT LEFT)
2E 20 ENGINE ROOM NO. 4 WIRE AND J/B NO. 2 (ENGINE COMPAR TMENT LEFT)
2F 20 ENGINE ROOM MAIN WIRE AND J/B NO. 2 (ENGINE COMPARTMENT LEFT)
2G
20 ENGINE WIRE AND J/B NO. 2 (ENGINE COMPARTMENT LEFT)
2H
: CONNECTOR JOINING WIRE HARNESS AND WIRE HARNESS
CODE SEE PAGE JOINING WIRE HARNESS AND WIRE HARNESS (CONNECTOR LOCATION)
30 (2VZ–FE)
C1
C2
D1
D2
32 (3S–FE)
30 (2VZ–FE)
32 (3S–FE)
30 (2VZ–FE)
32 (3S–FE)
30 (2VZ–FE)
32 (3S–FE)
ENGINE ROOM MAIN WIRE AND ENGINE WIRE (NEAR J/B NO. 2)
ENGINE ROOM MAIN WIRE AND ENGINE WIRE (NEAR WIPER MOTOR)
ENGINE ROOM WIRE AND COWL WIRE (LEFT KICK PANEL)
ENGINE ROOM WIRE AND COWL WIRE (RIGHT KICK PANEL)
: GROUND POINTS
CODE SEE PAGE GROUND POINTS LOCATION
30 (2VZ–FE)
C
32 (3S–FE)
RADIATOR LEFT
4
A
BLACK
2
56
B
2
BLACK
34
78
45
Page 43
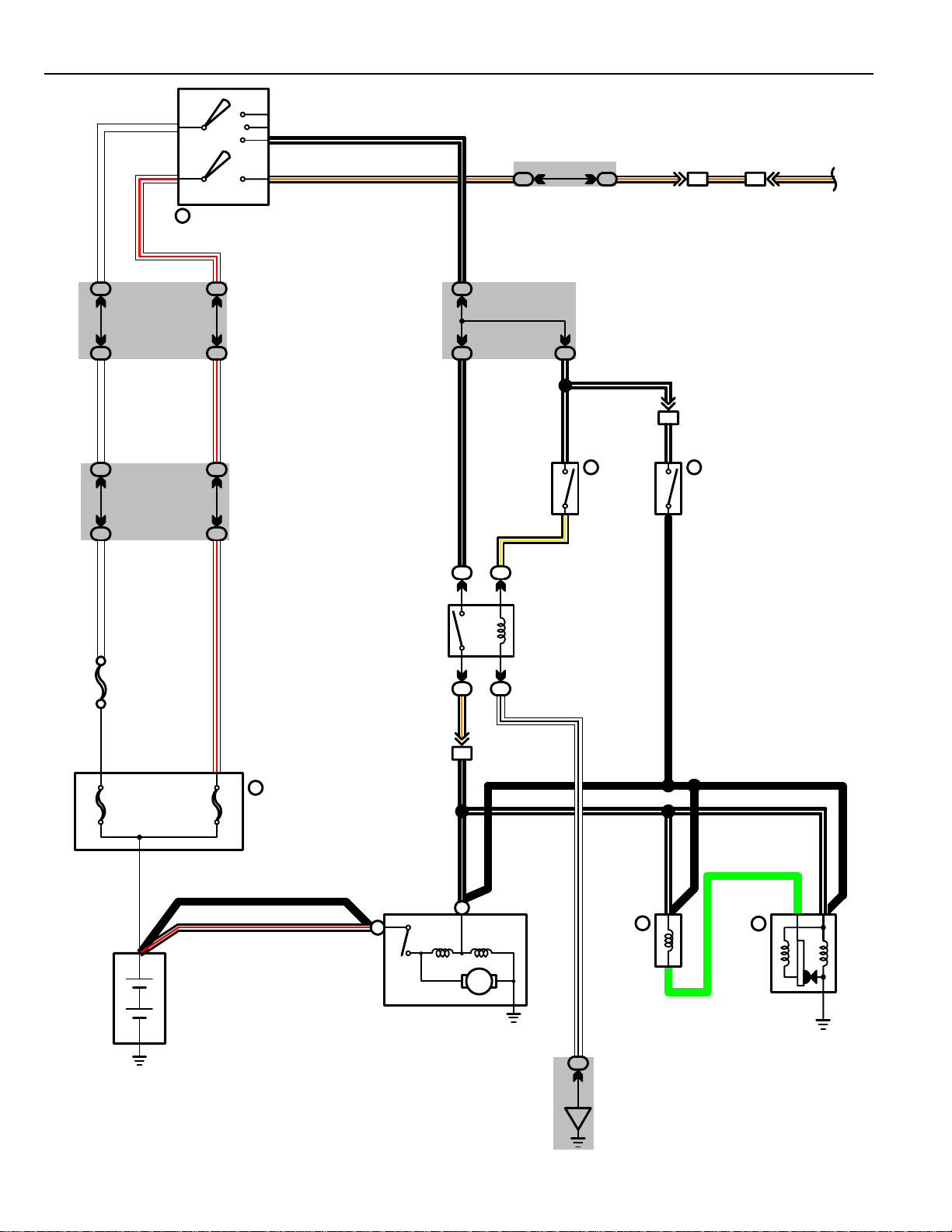
STARTING AND IGNITION SYSTEMS
AM1
4
AM2
8
A
W
W–R
1A11A2
W
2F12F4
2B32B4
IGNITION SW
W–R
ACC
IG1
ST1
IG2
B–W
1
K112
B–W
2
32
12
D1
D
NEUTRAL
START SW
(
)
A/T
B–Y
4
1J
B–O
7
B–W
1J71J21J3
1K11I7
)
B–W
M/T
(
B–W
1
12
1I
B–W
(
A/T
)
M/T
(
C
CLUTCH
START SW
(
)
M/T
)
5
B–OB–OB–O
B–O
C1
11
W
FL O. 5G
5
80A ALT
2
B
BATTERY
W–R
4
B
FUSIBLE
LINK BOX
30A AM2
(
W/ ALL–TRAC/ 4WD
(
B–R
FWD
)
1
)
E
STARTER
12
43
11
B–O
K114
B–W
)
(
1
B–W B–W
M/T
B
B–W
F
M
STARTER
RELAY
(
)
M/T
W–B
(
A/T
(
M/T
B
)
)
)
)
M/T
A/T
(
(
B
B–W
2
GH
COLD
START
INJECTO R
1
(
B
(
G
START
INJECTOR
TIME
SW
A/T
M/T
)
)
12
STASTJ
46
W–B
1N11
D
Page 44

B–O
B–O
(
3S–FE)B–O
DISTRIBUTOR
I
G2 G– NE
G1
1324
R
Y
B
)
2VZ–FE
(
B–O
1
J
IGNITER
432
L
W–R
SEALED
B
W–G
)
2VZ–FE
(
B–O
1
2
W–B
K
NOISE
FILTER
)
3S–FE
(
IGNITION COIL AND
DISTRIBUTOR
B–O
21
MM
DISTRIBUTOR
G1 G– NE
NNN
231
R
W
B
W–L
IGNITER
416
W–R
SEALED
B–O
53
O
W
B
BR
114132320
G–G2 NE IGF IGT
G1
TCCS ECU
L
TO A/C AMPLIFIER
TO TACHOMETER
W–B
B
B
B
BR
B
341 58
PPP PQ
G–G1 NE IGF IGT
TCCS ECU
TO A/C AMPLIFIER
TO TACHOMETER
B
B
47
Page 45

STARTING AND IGNITION SYSTEM
COWL WIRE AND J/B NO. 1 (LEFT KICK PANEL)
SERVICE HINTS
(A) IGNITION SW
4–1 : CLOSED WITH IGNITION SW AT ST POSITION
8–7 : CLOSED WITH IGNITION SW AT ON OR ST POSITION
(C) CLUTCH START SW
2–1 : CLOSED WITH CLUTCH PEDAL FULLY DEPRESSED
STARTER RELAY
(1) 2–(1) 4 : CLOSED WITH CLUTCH START SW ON AND IGNITION SW A T ST POSITION
STARTER
POINTS CLOSED WITH CLUTCH STAR T SW ON AND IGNITION SW AT ST POSITION
(D) NEUTRAL START SW (A/T)
2–3 : CLOSED WITH A/T SHIFT LEVER IN P OR N POSITION
(G) COLD START INJECTOR
2–1 : VOLT WHILE START INJECTOR TIME SW IS CLOSED AND STARTER CRANKING
(H) START INJECTOR TIME SW
POINTS OPEN ABOVE 35°C (95°F)
2–1 : APPROX. 20–40 Ω BELOW 30°C (86°F)
2–1 : APPROX. 40–60 Ω ABOVE 40°C (104°F)
2–GROUND : APPROX. 20–80 Ω
: PARTS LOCA TION
CODE SEE PAGE CODE SEE P AGE CODE SEE PAGE
A I11 28 G C2 24 (2VZ–FE), 25 (3S–FE) M D8 25
B F6 24 (2VZ–FE), 25 (3S–FE) H S2 24 (2VZ–FE), 25 (3S–FE) N D9 25
C C10 28 I D7 24 O I2 25
D N1 24 (2VZ–FE), 25 (3S–FE) J I3 24 P T3 28
E S4 24 (2VZ–FE), 25 (3S–FE) K N2 24 Q T4 28
F S3 24 (2VZ–FE), 25 (3S–FE) L T4 28
: JUNCTION BLOCK AND WIRE HARNESS CONNECTOR
CODE SEE PAGE JUNCTION BLOCK AND WIRE HARNESS (CONNECTOR LOCATION)
1A 18 ENGINE ROOM MAIN WIRE AND J/B NO. 1 (LEFT KICK PANEL)
1I 18
1J 18
1K 18
2B 20 ENGINE WIRE AND J/B NO. 2 (ENGINE COMPARTMENT LEFT)
2F 20 ENGINE ROOM MAIN WIRE AND J/B NO. 2 (ENGINE COMPARTMENT LEFT)
COWL WIRE AND J/B NO. 1 (LEFT KICK PANEL)
: CONNECTOR JOINING WIRE HARNESS AND WIRE HARNESS
CODE SEE PAGE JOINING WIRE HARNESS AND WIRE HARNESS (CONNECTOR LOCATION)
30 (2VZ–FE)
C1
32 (3S–FE)
30 (2VZ–FE)
D1
32 (3S–FE)
K1 34 ENGINE WIRE AND COWL WIRE (BEHIND GLOVE BOX)
ENGINE ROOM MAIN WIRE AND ENGINE WIRE (NEAR J/B NO. 2)
ENGINE ROOM WIRE AND COWL WIRE (LEFT KICK PANEL)
: GROUND POINTS
CODE SEE PAGE GROUND POINTS LOCATION
30 (2VZ–FE)
B
32 (3S–FE)
D 34 J/B NO. 1 SET BOLT
INTAKE MANIFOLD
48
Page 46
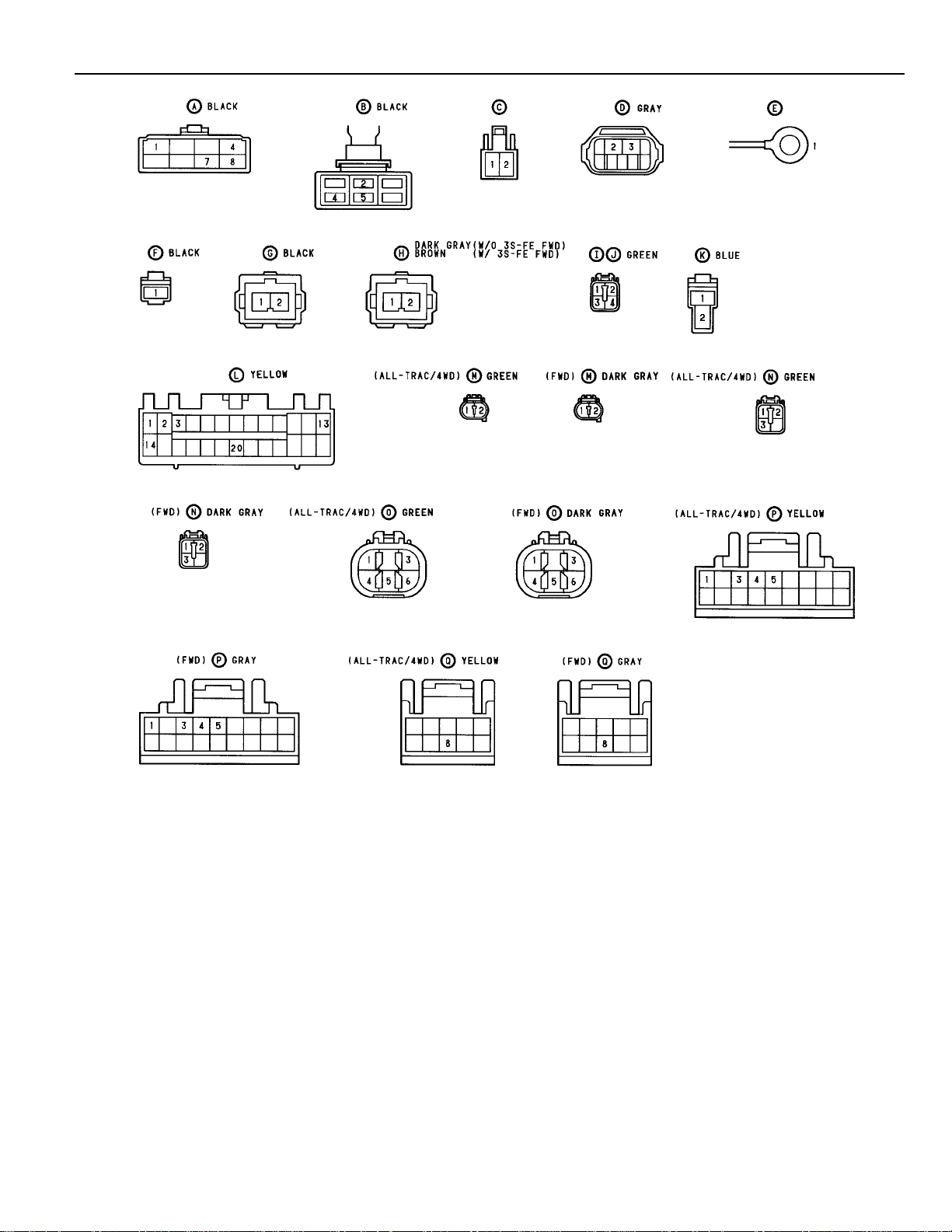
49
Page 47

CHARGING SYSTEM
W
W
6
2B
7. 5A
IGN
1G9
B–O
F26
W
W
3
B
CHARGE
WARNING
LIGHT
[COMB. METER]
8
YB–O
FL 0. 5G
(
L115
EX. 3S–FE FWD
(
L415
A
5
3S–FE FWD
)
)
7. 5A
CHARGE
2G4
Y
10A
ENGINE
1L15
B–YB–Y
D110
Y
C11
B–Y
Y
W
32 11
CCC D
IG L S B
W
W
W
ALTERNATOR
50
80A ALT
2
FUSIBLE LINK BOX
BATTERY
Y
IC REGULATOR
Page 48

SERVICE HINTS
ALTERNATOR
(C) 1–GROUND : 13.9–15.1 VOLTS WITH ENGINE RUNNING AT 2000 RPM AND 25°C (77°F)
13.5–14.3 VOL TS WITH ENGINE RUNNING AT 2000 RPM AND 115°C (239°F)
(C) 2–GROUND : 0–4 VOLTS WITH IGNITION SW AT ON POSITION AND ENGINE NOT RUNNING
: PARTS LOCA TION
CODE SEE PAGE CODE SEE P AGE CODE SEE PAGE
A F6 24 (2VZ–FE), 25 (3S–FE) C A17 24 (2VZ–FE), 25 (3S–FE)
B C11 28 D A16 24 (2VZ–FE), 25 (3S–FE)
: JUNCTION BLOCK AND WIRE HARNESS CONNECTOR
CODE SEE PAGE JUNCTION BLOCK AND WIRE HARNESS (CONNECTOR LOCATION)
1G 18 COWL SUB WIRE AND J/B NO. 1 (LEFT KICK PANEL)
1L 18 COWL WIRE AND J/B NO. 1 (LEFT KICK PANEL)
2B
2G
20 ENGINE WIRE AND J/B NO. 2 (ENGINE COMPARTMENT LEFT)
: CONNECTOR JOINING WIRE HARNESS AND WIRE HARNESS
CODE SEE PAGE JOINING WIRE HARNESS AND WIRE HARNESS (CONNECTOR LOCATION)
30 (2VZ–FE)
C1
32 (3S–FE)
30 (2VZ–FE)
D1
32 (3S–FE)
F2 34 INSTRUMENT PANEL WIRE AND COWL SUB WIRE (LEFT KICK PANEL)
L1 34 ENGINE WIRE AND INSTRUMENT PANEL WIRE (BEHIND GLOVE BOX)
ENGINE ROOM MAIN WIRE AND ENGINE WIRE (NEAR J/B NO. 2)
ENGINE ROOM WIRE AND COWL WIRE (LEFT KICK PANEL)
ABLACK
2
5
38
BLACKBCD
1
1
23
51
Page 49

ENGINE CONTROL (3S–FE)
SYSTEM OUTLINE
THE TCCS SYSTEM UTILIZES A MICROCOMPUTER AND MAINTAINS OVERALL CONTROL OF THE E/G, T/M, ETC. AN OUTLINE OF ENGINE CONTROL IS
GIVEN HERE.
1. INPUT SIGNALS
(1) WATER TEMP. SIGNAL SYSTEM
THE WATER TEMP. SENSOR DETECTS THE E/G COOLANT TEMP. AND HAS A BUILT–IN THERMISTOR WITH A RESISTANCE WHICH VARIES
ACCORDING TO THE WATER TEMP. THUS THE WATER TEMP. IS INPUT IN THE FORM OF A CONTROL SIGNAL TO TERMINAL THW OF THE TCCS
ECU.
(2) INTAKE AIR TEMP. SIGNAL SYSTEM
THE INTAKE AIR TEMP. SENSOR IS INSTALLED INSIDE THE AIR FLOW METER AND DETECTS THE INTAKE AIR TEMP., WHICH IS INPUT AS A
CONTROL SIGNAL TO TERMINAL THA OF THE ECU.
(3) OX SENSOR SIGNAL SYSTEM
THE OXYGEN DENSITY IN THE EXHAUST EMISSIONS IS DETECTED AND INPUT AS A CONTROL SIGNAL TO TERMINAL OX1 OF THE ECU.
(4) RPM SIGNAL SYSTEM
CRANKSHAFT POSITION IS DETECTED BY THE PICK–UP COIL INSTALLED INSIDE THE DISTRIBUTOR. CRANKSHAFT POSITION IS INPUT AS A
CONTROL SIGNAL TO TERMINAL G1 OF THE ECU, AND RPM IS INPUT TO TERMINAL NE FROM THE IGNITER.
(5) THROTTLE SIGNAL SYSTEM
THE THROTTLE POSITION SENSOR DETECTS THE THROTTLE VALVE OPENING ANGLE, WHICH IS INPUT AS A CONTROL SIGNAL TO
TERMINAL VTA (W/ECT), PSW (W/O ECT) OF THE ECU, OR WHEN THE VALVE IS FULLY CLOSED, TO TERMINAL IDL.
(6) VEHICLE SPEED SIGNAL SYSTEM
THE SPEED SENSOR, INSTALLED INSIDE THE COMBINATION METER, DETECTS THE VEHICLE SPEED AND INPUTS A CONTROL SIGNAL TO
TERMINAL SPD OF THE ECU.
(7) A/C SW SIGNAL SYSTEM
THE OPERATING VOLTAGE OF THE A/C MAGNET CLUTCH IS DETECTED AND INPUT IN THE FORM OF A CONTROL SIGNAL TO TERMINAL A/C
OF THE ECU.
(8) BATTERY SIGNAL SYSTEM
VOLTAGE IS CONSTANTLY APPLIED TO TERMINAL BATT OF THE ECU. WHEN THE IGNITION SW IS TURNED TO ON, VOLTAGE FOR ECU
OPERATION IS APPLIED VIA THE EFI MAIN RELAY TO TERMINALS +B AND +B1 OF THE ECU.
(9) INTAKE AIR VOLUME SIGNAL SYSTEM
INTAKE AIR VOLUME IS DETECTED BY THE POTENTIOMETER INSTALLED INSIDE THE AIR FLOW METER AND IS INPUT AS A CONTROL SIGNAL
TO TERMINAL VS OF THE ECU. INSIDE THE AIR FLOW METER THERE IS ALSO A SW FOR FUEL PUMP OPERATION, AND WHEN THE
MEASURING PLATE OPENS (AIR INTAKE OCCURS), THIS SW TURNS ON AND CURRENT FLOWS TO THE FUEL PUMP TO OPERATE IT.
(10) STOP LIGHT SW SIGNAL SYSTEM
THE STOP LIGHT SW IS USED TO DETECT WHETHER OR NOT THE VEHICLE IS BRAKING AND THE INFORMATION IS INPUT AS A CONTROL
SIGNAL TO TERMINAL STP OF THE ECU.
(11) STA SIGNAL SYSTEM
TO CONFIRM THAT THE E/G IS CRANKING, THE VOLTAGE APPLIED TO THE STARTER MOTOR DURING CRANKING IS DETECTED AND IS INPUT
AS A CONTROL SIGNAL TO TERMINAL STA OF THE ECU.
(12) NEUTRAL START SW SIGNAL SYSTEM
THE NEUTRAL START SW DETECTS WHETHER THE SHIFT POSITION IS IN NEUTRAL OR NOT, AND INPUTS A CONTROL SIGNAL TO TERMINAL
NSW OF THE ECU.
(13) ELECTRICAL IDLE–UP SYSTEM
THE SIGNAL WHEN SYSTEMS SUCH AS THE REAR WINDOW DEFOGGER, HEADLIGHTS, ETC. WHICH CAUSE A HIGH ELECTRICAL BURDEN ARE
ON IS INPUT TO TERMINAL ELS AS A CONTROL SIGNAL.
2. CONTROL SYSTEM
* EFI (ELECTRONIC FUEL INJECTION) SYSTEM
THE EFI SYSTEM MONITORS THE ENGINE CONDITIONS THROUGH THE SIGNALS EACH SENSOR (INPUT SIGNALS [1] TO [12]) INPUTS TO THE ECU.
BASED ON THIS DATA AND THE PROGRAM MEMORIZED IN THE ECU, THE MOST APPROPRIATE FUEL INJECTION TIMING IS DECIDED AND
CURRENT IS OUTPUT TO TERMINALS #10 AND #20 OF THE ECU, CAUSING THE INJECTORS TO OPERATE (TO INJECT FUEL). IT IS THIS SYSTEM
WHICH, THROUGH THE WORK OF THE ECU, FINELY CONTROLS FUEL INJECTION IN RESPONSE TO DRIVING CONDITIONS.
* ESA (ELECTRONIC SPARK ADVANCE) SYSTEM
THE ESA SYSTEM MONITORS THE ENGINE CONDITIONS USING THE SIGNALS (INPUT SIGNALS [1, 3, 4, 6, 7, 9, 11]) INPUT TO THE ECU FROM EACH
SENSOR. BASED ON THIS DATA AND THE PROGRAM MEMORIZED IN THE ECU, THE MOST APPROPRIATE IGNITION TIMING IS DECIDED AND
CURRENT IS OUTPUT TO TERMINAL IGT OF THE ECU. THIS OUTPUT CONTROLS THE IGNITER TO PRODUCE THE MOST APPROPRIATE IGNITION
TIMING FOR THE DRIVING CONDITIONS.
* ISC (IDLE SPEED CONTROL) SYSTEM
THE ISC SYSTEM (ROTARY SOLENOID TYPE) INCREASES THE RPM AND PROVIDES IDLING STABILITY FOR FAST IDLE–UP WHEN THE E/G IS COLD
AND WHEN THE IDLE SPEED HAS DROPPED DUE TO ELECTRICAL LOAD, ETC. THE ECU EVALUATES THE SIGNALS FROM EACH SENSOR (INPUT
SIGNALS [1, 4, TO 8, 11, 12, 13,]), OUTPUTS CURRENT TO TERMINALS ISC1 AND ISC2, AND CONTROLS THE ISC VALVE.
3. DIAGNOSIS SYSTEM
WITH THE DIAGNOSIS SYSTEM, WHEN THERE IS A MALFUNCTION IN THE ECU SIGNAL SYSTEM, THE MALFUNCTIONING SYSTEM IS RECORDED IN
THE MEMORY. THE MALFUNCTIONING SYSTEM CAN THEN BE FOUND BY READING THE DISPLAY (CODE) OF THE CHECK ENGINE WARNING LIGHT.
4. FAIL–SAFE SYSTEM
WHEN A MALFUNCTION OCCURS IN ANY SYSTEM, IF THERE IS A POSSIBILITY OF ENGINE TROUBLE BEING CAUSED BY CONTINUED CONTROL
BASED ON THE SIGNALS FROM THAT SYSTEM. THE FAIL–SAFE SYSTEM EITHER CONTROLS THE SYSTEM BY USING DATA (STANDARD VALUES)
RECORDED IN THE ECU MEMORY OR ELSE ST OPS THE ENGINE.
52
Page 50

SERVICE HINTS
(B) (C) (D) (E) INJECTOR
1–2 : APPROX 13.8 Ω
EFI MAIN RELA Y
2–4 : CLOSED WITH IGNITION SW AT ON OR ST POSITION
(H)
CIRCUIT OPENING RELAY
1–2 : CLOSED WITH STARTER RUNNING OR MEASURING PLATE (AIR FLOW METER) OPEN
AIR FLOW METER
(Q)
1–2 : CLOSED WITH STARTER RUNNING MEASURING PLATE OPEN
5–6 : 200–600 Ω (MEASURING PLATE FULLY CLOSED) 20–1200 Ω (MEASURING PLATE FULLY OPEN)
5–4 : 200–400 Ω
5–7 : 10–20 KΩ (–20°C, –4°F)
4–7 KΩ (0°C, 32°F)
2–3 KΩ (20°C, 68°F)
0.9–1.3 KΩ (40°C, 104°F)
THROTTLE POSITION SENSOR
(R)
TCCS ECU (ELECTRONIC CONTROLLED UNIT)
RESISTANCE AT COMPUTER
0.4–0.7 KΩ (60°C, 140°F)
(T) 2–4, : 0.2–0.8 KΩ WITH CLEARANCE BETWEEN LEVER AND
(S) 3–2 STOP SCREW 0 MM (0 IN)
(T) 3–4, : 2.3 KΩ OR LESS WITH CLEARANCE BETWEEN LEVER AND
(S) 1–2 STOP SCREW 0.5 MM (0.020 IN)
(T) 2–4, (S) 3–2 : 3.3–10 KΩ WITH THROTTLE VALVE FULLY OPEN
(T) 1–(T) 4 : 3–7 KΩ
Ω WITH 0.7 MM (0.028 IN)
EFI WATER TEMP. SENSOR
1–2 : 10–20 KΩ (–20°C, –4°F)
4–7 KΩ (0°C, 32°F)
2–3 KΩ (20°C, 68°F)
0.9–1.3 KΩ (40°C, 104°F)
0.4–0.7 KΩ (60°C, 140°F)
0.2–0.4 KΩ (80°C, 176°F)
VOLTAGES AT ECU CONNECTORS
(M) 2–(O) 7:10–14 VOLTS (ALWAYS)
(M) 1,8–(O) 7:10–14 VOLTS (IGNITION SW ON)
(N) 6–(O) 7:8–14 VOLTS (IGNITION SW ON AND THROTTLE VALVE OPEN)
(M) 5–(N) 14 : 4–6 VOLTS (IGNITION SW ON)
(M) 4–(N) 14 : 4–5 VOLTS (IGNITION SW ON AND MEASURING PLATE FULLY CLOSED)
(M) 3–(N) 14 : 1–3 VOLTS (IGNITION SW ON AND INTAKE AIR TEMP. 20°C, 68°F)
(N) 10–(N) 14 : 0.1–1.0 VOLTS (IGNITION SW ON AND COOLANT TEMP. 80°C, 176°F)
(O) 3–(O) 7:6–14 VOLTS (ENGINE CRANKING)
(N)9, 18–(O)7: 9–14 VOLTS (IGNITION SW ON)
(O) 8–(O) 7:0.7–1.0 VOLTS (IDLING)
(N) 7–(O) 7:0.5 OR LESS (IGNITION SW ON AND CHECK CONNECTOR T–E1 SHORT)
(N) 15–(O) 7:8–14 VOLTS (IGNITION SW ON AND A/C SW ON)
(N) 8–(O) 7:8–14 VOLTS (NO TROUBLE (”CHECK” ENGINE WARNING LIGHT OFF) AND ENGINE RUNNING)
(N)11–(N)14 : 0.1–1.0 VOLTS (IGNITION SW ON AND THROTTLE VALVE FULLY CLOSED)
(N) 11–(O) 7:4–5 VOLTS (IGNITION SW ON AND THROTTLE VALVE FULLY CLOSED)
(N) 6–(N) 14 : 8–14 VOLTS (IGNITION SW ON AND THROTTLE VALVE OPEN)
(O) 4–(O) 5:9–14 VOLTS (IGNITION SW ON)
(O) 9–(O) 10 : 4–5 VOLTS (IGNITION SW ON AND THROTTLE
(N) 16–(O) 7 : VALVE FULLY CLOSED)
(DISCONNECT WIRING CONNECTOR)
(N) 6–(N) 14 : Ω (THROTTLE VALVE OPEN) LESS THAN 2.3 KΩ (THROTTLE VALVE FULLY CLOSED)
(N) 11–(N) 14 : 3.3–10 KΩ (THROTTLE VALVE FULLY OPEN) 0.2–0.8 KΩ (THROTTLE VALVE FULLY CLOSED)
(N) 6–(O) 7:
(N) 11–(O) 7:0 Ω (THROTTLE VAL VE FULLY OPEN)
(M) 4–(N) 14 : 20–400 Ω (MEASURING PLATE FULLY CLOSED) 20–3000 Ω (MEASURING PLATE FULLY OPEN)
(M) 3–(N) 14 : 2–3 KΩ (INTAKE AIR TEMP. 20°C, 68°F)
(N) 10–(N) 14 : 0.2–0.4 KΩ (COOLANT TEMP. 80°C, 176°F)
(N) 3–(N) 4:140–180 Ω
0.02–0.5 VOLTS (IGNITION SW ON AND MEASURING PLATE FULLY OPEN)
2–4 VOLTS (IDLING)
: 10–14 VOLTS (IGNITION SW ON AND CHECK CONNECTOR T–E1 NOT SHORT)
10–14 VOLTS (IGNITION SW ON AND THROTTLE VALVE FULL Y OPEN)
Ω (THROTTLE VALVE FULLY OPEN) 0 Ω (THROTTLE VALVE FULLY CLOSED)
Ω (THROTTLE VALVE FULLY CLOSED)
53
Page 51

ENGINE CONTROL (3S–FE)
B–O B–O
A
IGNITION
SW
IG2
71
1J41J7
D112
B–O B–O B–O
C15
B–O
2
BC DE
NO. 2
1
Y
B–O
2
NO. 4
1
Y
Y B–O
ST1
B–W
1
1K
1I71I12
F
)
B–Y(M/T
)
)
B–OW
2
NO. 3
1
B–W(A/T
B–W
)
M/T
(
1
CLUTCH
START SW
(
M/T
2
B–O
B–O
B–O
2
NO. 1
1
W
WW
W
B–W(M/T
STARTER
RELAY
INJECTOR
Y
)
)
M/T
(
B–W
11
12
43
11
B–O
W–B
B–W
B–W(M/T
A
7. 5
IGN
1I6
B–O
D113 C14
)
A/T
(
B–W
K17
B–O
B–W
K114
B–WB
2
)
A/T
(
NEUTRAL
START SW
3
G
)
M/T
)
(
A/T
(
B–W
)
B–O
2G6
14
B
32
2A72C32G5
)
)
M/T
(
A/T
(
B
W–B
B–W
W–B
CK I
15A
EFI
2
2G
EFI
MAIN
RELAY
W–R
23
W–B
146
L–B
L44
L14
L–BL–BL–B
H17
V310
W–B
TO COLD START
INJECTOR
START INJECTOR
TIME SW
)
)
M/T
(
A/T
(
B
B–W
W–R
)
)
A/T
M/T
(
B–W
(
B
H
CIRCUIT
OPENING
RELAY
G
W–B
L–B
)
)
FWD
(
ALL–TRAC/4WD
(
I
FUEL
PUMP
12
M
B(A/T
B–W(M/T
(
ALL–TRAC/4WD
W–B
)
)
W–L
W–RW–R
G
W–B
L–B
W
Y
B–WB–W
)
)
W–B
FWD
(
54
Page 52

B–O
B–O
20A
STOP
W–L
FROMELECTRICAL
Y–BY–B
Y–L
VS
FROM
ECT ECU
L–B
Y–G
Y–R
W–B
BR
7564
E2
THA
2
Y–R
L–R
G–B
G
R
GBR
2
EFI WATER
TEMP. SENSOR
1
W–R
W–RW–R
W–R
8
10 5 4 12 10 6 14 12 7
L46
L16
2
3
W–L
12 146137 9 11 8 16
(
)
FWD
(
ALL–TRAC/4WD
P
SPEED SENSOR
[COMB. METER]
TO CRUISE
CONTROL
COMPUTER
Y–B
K11K14
Y–B
)
G
W–B
L–B
W–R
W
Y
B–W(M/T
B–W
L–R
L–R
VC
FC E
1
Q
AIR FLOWMETER
)
B(A/T
)
1L11 1F2
IDLE–UP DIODE
G–RG–WG–W
J
1
STOP LIGHT
SW
3
K110
PSW
11311
L
)
)
W/ ECT
(
W/O ECT
(
B–R
B–R
BR
312
TSTST
2
1
T
THROTTLE
POSITION SENSOR
BRBRBR
L
S
34
7. 5A
GAUGE
F13
YY
J/B NO.3
TO ECT ECU
L
(
W/ ECT
BR
(
W/ ECT
(
W/O ECT
9
3B
NM
)
12
)
)
CHECK ENGINE
[COMB. METER]
6
R–L G–R
K
TCCS ECU
(
W/O ECT
U
)
CHECK
CONNECTOR
V
EGR GAS
TEMP. SENSOR
BRBR
9
L
TTHGE2IDLVTATHWTHAE21VSVCSPD
L–B
Y–G
BR
Y–G
36 4
E1 T
FP +B
81
L–B
W–R
AMPLIFIER
VF
R–W W
R–W
W–R
B(A/T
B–W
)
)
FWD
ALL–TRAC/4WD
(
(
R–L
W
BR
)
SEALED
(
W
Y
)
)
TO A/C
G–W
11
R–L
OX2
J15
J311
L–B
ACTWSTPELSL3L2L1ECTBATT+B1+B
OX1
9
B–W(M/T
L414
L114
G–R
W–B W–B V–Y V–Y
E
55
Page 53

ENGINE CONTROL (3S–FE)
56
Page 54
: PARTS LOCATION
CODE SEE PAGE CODE SEE P AGE CODE SEE PAGE
A I11 28 K C13 28 V C1 25
B I5 25 L C11 28 W D8 25
C I7 25 M T2 28 X D9 25
D I4 25 N T3 28 Y I2 25
E I6 25 O T4 28 Z O3 25
F C10 28 P C13 28 a I1 25
G N1 25 Q A15 25 b O4 25
H C8 28 R E2 25
I F7 26 (S/D), 27 (STATION W/G) S T1 25 (W/ECT)
I F8 26 (S/D ALL–TRAC/4WD) T T1 25 (W/O ECT)
J S9 28 U E3 25
: RELAY BLOCKS
CODE SEE PAGE RELAY BLOCKS (RELAY BLOCK LOCATION)
1 23 R/B NO. 1 (LEFT KICK PANEL)
: JUNCTION BLOCK AND WIRE HARNESS CONNECTOR
CODE SEE PAGE JUNCTION BLOCK AND WIRE HARNESS (CONNECTOR LOCATION)
1F 18 COWL SUB WIRE AND J/B NO. 1 (LEFT KICK PANEL)
1I
1J
18 COWL WIRE AND J/B NO. 1 (LEFT KICK PANEL)
1K
1L
2A 20 ENGINE ROOM MAIN WIRE AND J/B NO. 2 (ENGINE COMPARTMENT LEFT)
2C 20 ENGINE WIRE AND J/B NO. 2 (ENGINE COMPARTMENT LEFT)
2E 20 ENGINE ROOM NO. 4 WIRE AND J/B NO. 2 (ENGINE COMPAR TMENT LEFT)
2G 20 ENGINE WIRE AND J/B NO. 2 (ENGINE COMPARTMENT LEFT)
3B 22 INSTRUMENT PANEL WIRE AND J/B NO. 3 (INSTRUMENT PANEL LEFT)
: CONNECTOR JOINING WIRE HARNESS AND WIRE HARNESS
CODE SEE PAGE JOINING WIRE HARNESS AND WIRE HARNESS (CONNECTOR LOCATION)
C1 32 ENGINE ROOM MAIN WIRE AND ENGINE WIRE (NEAR J/B NO. 2)
D1 32 ENGINE ROOM WIRE AND COWL WIRE (LEFT KICK PANEL)
F1 34 INSTRUMENT PANEL WIRE AND COWL SUB WIRE (LEFT KICK PANEL)
H1 34 FLOOR NO. 1 WIRE AND INSTRUMENT PANEL WIRE (LEFT KICK PANEL)
J1
34 ENGINE WIRE AND A/C WIRE (BEHIND GLOVE BOX)
J3
K1 34 ENGINE WIRE AND COWL WIRE (BEHIND GLOVE BOX)
L1
34 ENGINE WIRE AND INSTRUMENT PANEL WIRE (BEHIND GLOVE BOX)
L4
V3 36 FLOOR NO. 1 WIRE AND LUGGAGE ROOM NO. 1 WIRE (ALL–TRAC/4WD, BACK PANEL LEFT)
: GROUND POINTS
CODE SEE PAGE GROUND POINTS LOCATION
B 32 INTAKE MANIFOLD
C 32 RADIATOR LEFT
E 34 LEFT KICK PANEL
36 (S/D)
I
38 (STATION W/G)
K 36 (S/D) BACK PANEL CENTER (ALL–TRAC/4WD)
LEFT REAR FENDER
57
Page 55

ENGINE CONTROL (3S–FE)
58
Page 56

ENGINE CONTROL (2VZ–FE)
SYSTEM OUTLINE
THE TCCS SYSTEM UTILIZES A MICROCOMPUTER AND MAINTAINS OVERALL CONTROL OF THE E/G, T/M, ETC. AN OUTLINE OF ENGINE CONTROL IS
GIVEN HERE.
1. INPUT SIGNALS
(1) WATER TEMP. SIGNAL SYSTEM
THE WATE R TEMP. SENSOR DETECTS THE E/G COOLANT TEMP. AND HAS A BUILT–IN THERMISTOR WITH A RESISTANCE WHICH VARIES ACCORDING
TO THE WATER TEMP. THUS THE WATER TEMP. IS INPUT IN THE FORM OF A CONTROL SIGNAL TO TERMINAL THW OF THE TCCS ECU.
(2) INTAKE AIR TEMP. SIGNAL SYSTEM
THE INTAKE AIR TEMP. SENSOR IS INSTALLED INSIDE THE AIR FLOW METER AND DETECTS THE INTAKE AIR TEMP., WHICH IS INPUT AS A
CONTROL SIGNAL TO TERMINAL THA OF THE ECU.
(3) OXYGEN SENSOR SIGNAL SYSTEM
THE OXYGEN DENSITY IN THE EXHAUST. EMISSIONS IS DETECTED AND INPUT AS A CONTROL SIGNAL TO TERMINAL OX1 OF THE ECU. TO
MAINTAIN STABLE DETECTION PERFORMANCE BY THE OXYGEN SENSOR, A HEATER IS USED FOR WARMING THE SENSOR. THE HEATER IS
ALSO CONTROLLED BY THE ECU (HT).
(4) RPM SIGNAL SYSTEM
CRANKSHAFT POSITION AND E/G RPM ARE DETECTED BY THE PICK–UP COIL INSTALLED INSIDE THE DISTRIBUTOR. CRANKSHAFT POSITION
IS INPUT AS A CONTROL SIGNAL TO TERMINALS G1 AND G2, OF THE ECU, AND RPM IS INPUT TO TERMINAL NE.
(5) THROTTLE SIGNAL SYSTEM
THE THROTTLE POSITION SENSOR DETECTS THE THROTTLE VALVE OPENING ANGLE, WHICH IS INPUT AS A CONTROL SIGNAL TO TERMINAL
VTA OF THE ECU, OR WHEN THE VALVE IS FULLY CLOSED, TO TERMINAL IDL.
(6) VEHICLE SPEED SIGNAL SYSTEM
THE SPEED SENSOR, INSTALLED INSIDE THE COMBINATION METER, DETECTS THE VEHICLE SPEED AND INPUTS A CONTROL SIGNAL TO
TERMINAL SP1 OF THE ECU.
(7) NEUTRAL START SW SIGNAL SYSTEM (A/T)
THE NEUTRAL START SW DETECTS WHETHER THE SHIFT POSITION IS IN NEUTRAL OR NOT, AND INPUTS A CONTROL SIGNAL TO TERMINAL
NSW OF THE ECU.
(8) A/C SW SIGNAL SYSTEM
THE OPERATING VOLTAGE OF THE A/C MAGNET CLUTCH IS DETECTED AND INPUT IN THE FORM OF A CONTROL SIGNAL TO TERMINAL A/C OF
THE ECU.
(9) BATTERY SIGNAL SYSTEM
VOLTAGE IS CONSTANTLY APPLIED TO TERMINAL BATT OF THE ECU. WHEN THE IGNITION SW IS TURNED TO ON, VOLTAGE FOR ECU
OPERATION IS APPLIED VIA THE EFI MAIN RELAY TO TERMINALS +B AND +B1 OF THE ECU. ALSO, CURRENT FLOWS VIA THE IGN FUSE TO
TERMINAL IGSW OF THE ECU.
(10) INTAKE AIR VOLUME SIGNAL SYSTEM
INTAKE AIR VOLUME IS DETECTED BY THE POTENTIOMETER INSTALLED INSIDE THE AIR FLOW METER AND IS INPUT AS A CONTROL SIGNAL
TO TERMINAL VS OF THE ECU. INSIDE THE AIR FLOW METER THERE IS ALSO A SW FOR FUEL PUMP OPERATION, AND WHEN THE MEASURING
PLATE OPENS (AIR INTAKE OCCURS), THIS SW TURNS ON AND CURRENT FLOWS TO THE FUEL PUMP TO OPERATE IT.
(11) STA SIGNAL SYSTEM
TO CONFIRM THAT THE E/G IS CRANKING, THE VOLTAGE APPLIED TO THE STARTER MOTOR DURING CRANKING IS DETECTED AND IS INPUT
AS A CONTROL SIGNAL TO TERMINAL STA OF THE ECU.
(12) ENGINE KNOCK SIGNAL SYSTEM
ENGINE KNOCKING IS DETECTED BY THE KNOCK SENSOR AND INPUT AS A CONTROL SIGNAL TO TERMINAL KNK OF THE ECU.
2. CONTROL SYSTEM
* EFI (ELECTRONIC FUEL INJECTION) SYSTEM
THE EFI SYSTEM MONITORS THE ENGINE CONDITIONS THROUGH THE SIGNALS EACH SENSOR (INPUT SIGNALS [1] TO [11]) INPUTS TO THE ECU.
BASED ON THIS DATA AND THE PROGRAM MEMORIZED IN THE ECU, THE MOST APPROPRIATE FUEL INJECTION TIMING IS DECIDED AND
CURRENT IS OUTPUT TO TERMINALS #10, #20 AND #30 OF THE ECU. CAUSING THE INJECTORS TO OPERATE (TO INJECT FUEL). IT IS THIS SYSTE M
WHICH, THROUGH THE WORK OF THE ECU, FINELY CONTROLS FUEL INJECTION IN RESPONSE TO DRIVING CONDITIONS.
* ESA (ELECTRONIC SPARK ADVANCE) SYSTEM
THE ESA SYSTEM MONITORS THE ENGINE CONDITIONS USING THE SIGNALS (INPUT SIGNALS [1, 3, 4, 5, 6, 8, 10, 11, 12]) INPUT TO THE ECU FROM
EACH SENSOR. BASED ON THIS DATA AND THE PROGRAM MEMORIZED IN THE ECU, THE MOST APPROPRIATE IGNITION TIMING IS DECIDED AND
CURRENT IS OUTPUT TO TERMINAL IGT OF THE ECU.
THIS OUTPUT CONTROLS THE IGNITER TO PRODUCE THE MOST APPROPRIATE IGNITION TIMING FOR THE DRIVING CONDITIONS.
* OXYGEN SENSOR HEATER CONTROL SYSTEM
THE OXYGEN SENSOR HEATER CONTROL SYSTEM TURNS THE HEATER TO ON WHEN THE INTAKE AIR VOLUME IS LOW (TEMP. OF EXHAUST EMISSIONS
LOW), AND WARMS UP THE OXYGEN SENSOR TO IMPROVE DETECTION PERFORMANCE OF THE SENSOR. THE ECU EVALUATES THE SIGNALS FROM
EACH SENSOR (INPUT SIGNALS [1, 4, 9, 10, 11]), CURRENT IS OUTPUT TO TERMINAL HT AND CONTROLS THE HEATER.
* ISC (IDLE SPEED CONTROL) SYSTEM
THE ISC SYSTEM (STEP MOTOR TYPE) INCREASES THE RPM AND PROVIDES IDLING STABILITY FOR FAST IDLE–UP WHEN THE E/G IS COLD AND
WHEN THE IDLE SPEED HAS DROPPED DUE TO ELECTRICAL LOAD, ETC. THE ECU EVALUATES THE SIGNALS FROM EACH SENSOR (INPUT
SIGNALS [1, 4 TO 8, 11]), OUTPUTS CURRENT TO TERMINALS ISC1 ISC2, ISC3 AND ISC4, AND CONTROLS THE ISC VALVE.
* FUEL PRESSURE–UP SYSTEM
THE FUEL PRESSURE UP SYSTEM CAUSES THE VSV (FOR FUEL PRESSURE UP) TO COME ON FOR HIGH TEMP. STARTS AND IMMEDIATELY AFTER
STARTING IN ORDER TO INCREASE THE FUEL PRESSURE, IMPROVE STARTABILITY AT HIGH TEMPERATURES AND PROVIDE STABLE IDLING. THE
ECU EVALUA TES THE INPUT SIGNALS FROM EACH SENSOR (1, 2, 4 AND 12), OUTPUTS CURRENT TO TERMINAL FPU AND CONTROLS THE VSV.
59
Page 57

ENGINE CONTROL (2VZ–FE)
3. DIAGNOSIS SYSTEM
WITH THE DIAGNOSIS SYSTEM, WHEN THERE IS A MALFUNCTIONING IN THE ECU SIGNAL SYSTEM, THE MALFUNCTION SYSTEM IS
RECORDED IN THE MEMORY. THE MALFUNCTIONING SYSTEM CAN THEN BE FOUND BY READING THE DISPLAY (CODE) OF THE
CHECK ENGINE WARNING LIGHT.
4. FAIL–SAFE SYSTEM
WHEN A MALFUNCTION OCCURS IN ANY SYSTEM, IF THERE IS A POSSIBILITY OF ENGINE TROUBLE BEING CAUSED BY
CONTINUED CONTROL BASED ON THE SIGNALS FROM THAT SYSTEM, THE FAIL–SAFE SYSTEM EITHER CONTROLS THE SYSTEM
BY USING DATA (ST ANDARD VALUES) RECORDED IN THE ECU MEMORY OR ELSE STOPS THE ENGINE.
SERVICE HINTS
(C) (D) (E) (F) (G) (H) INJECTOR
1–2 : APPROX. 13.8
(I)
NEUTRAL START SW (A/T)
2–3 : CLOSED WITH A/T SHIFT LEVER IN P OR N POSITION
EFI MAIN RELA Y
4–2 : CLOSED WITH IGNITION SW AT ON OR ST POSITION
(J)
CIRCUIT OPENING RELAY
2–1 : CLOSED WITH STARTER RUNNING OR MEASURING PLATE (AIR FLOW METER) OPEN
AIR FLOW METER
(T)
2–1: CLOSED WITH STARTER RUNNING OR MEASURING PLATE OPEN
5–6: 200–600 (MEASURING PLATE FULLY CLOSED)
20–1200 (MEASURING PLATE FULLY OPEN)
5–4: 200–400
5–7: 10–20 K (–20°C, –4°F)
4–7 K (0°C, 32°F)
2–3 K (20°C, 68°F)
0.9–1.3 K (40°C, 104°F)
0.4–0.7 K (60°C, 140°F)
(U) EFI WATER TEMP. SENSOR
2–1 : 10–20 K (–20°C, –4°F)
4–7 K (0
2–3 K (20
0.9–1.3 K (40
0.4–0.7 K (60
0.2–0.4 K (80
(Y) THROTTLE POSITION SENSOR
2–4 : 0.3–6.3 K WITH CLEARANCE BETWEEN LEVER AND STOP SCREW 0 MM (0 IN.)
3–4 : LESS THAN 2.3 K WITH CLERANCE BETWEEN LEVER AND STOP SCREW 0.30 MM (0.0118 IN.)
Ω WITH CLEARANCE BETWEEN LEVER AND STOP SCREW 0.70 MM (0.0276 IN.)
2–4 : 3.5–10.3 K WITH THROTTLE VALVE FULYY OPEN
1–4 : 4.25–8.25 K
(Z)
EGR GAS TEMP. SENSOR
1–2 : 69.40–88.50 K (50°C, 122°F)
11.89–14.37 K (100
2.79–3.59 K (150
(c)
OXYGEN SENSOR
1–2 : APPROX. 5.1–6.3
°C, 32°F)
°C, 68°F)
°C, 104°F)
°C, 140°F)
°C, 176°F)
°C, 212°F)
°C, 302°F)
60
Page 58

TCCS ECU (ELECTRONIC CONTROLLED UNIT)
VOLTAGE AT ECU WIRING CONNECTORS
(P) 2, 4, 12, 13–(R) 24 : 10–14 VOLTS (IGNITION SW ON)
(P) 1–(R) 24 : 10–14 VOLTS
(Q) 1–(Q) 9:4–6 VOLTS (IGNITION SW ON)
(Q) 12–(Q) 9:4–6 VOLTS (IGNITION SW ON AND THROTTLE VALVE OPEN)
(Q) 11–(Q) 9:0.1–1.0 VOLTS (IGNITION SW ON AND THROTTLE VALVE FULLY CLOSED)
(P) 11–(R) 24 : 6–14 VOLTS (CRANKING)
(R) 11, 12, 25–(R) 13, 26 : 9–14 VOLTS (IGNITION SW ON)
(P) 5–(R) 24 : 8–14 VOLTS (NO TROUBLE AND ENGINE RUNNING)
(R) 20–(R) 24 : 0.7–1.0 VOLTS (IGNITION SW ON)
(R) 4, 5, 6, 7–(R) 24 : 9–14 VOLTS (IGNITION SW ON)
(Q) 2–(Q) 9:4–5 VOLTS (IGNITION SW ON AND MEASURING PLATE FULLY CLOSED)
(Q) 3–(Q) 9:1–3 VOLTS (IGNITION SW ON AND INTAKE AIR TEMP. 20°C, 68°F)
(Q) 4–(Q) 9:0.1–1.0 VOLTS (IGNITION SW ON AND COOLANT TEMP. 80°C, 176°F)
(P) 10–(R) 24 : 8–14 VOLTS (IGNITION SW ON AND A/C SWITCH ON)
(R) 22–(R) 24 : 4–6 VOLTS (IGNITION SW ON AND HEATER BLOWER SW ON)
(Q) 15–(R) 24 : 10–14 VOLTS (IGNITION SW ON AND CHECK CONNECTOR T–E1 NOT SHORT)
(Q) 22–(R) 24 : 0 VOLTS (IGNITION SW ON AND SHIFT POSITION P OR N RANGE)
(Q) 13–(R) 24 : 10–14 VOLTS (STOP LIGHT SW ON)
4–5 VOLTS (IGNITION SW ON AND THRTTLE VALVE FULLY OPEN)
0.02–0.08 VOLTS (IGNITION SW ON AND MEASURING PLATE FULLY OPEN)
2–4 VOLTS (IDLING)
: 0.3–1.0 VOLTS (3000 RPM)
0 VOLTS (IGNITION SW ON AND CHECK CONNECTOR T–E1 SHORT)
10–14 VOLTS (IGNITION SW ON AND SHIFT POSITION EX. P OR N RANGE)
RESISTANCE AT ECU WIRING COECTORS
(DISCONNECT WIRING CONNECTOR)
(Q) 12–(Q) 9:
(Q) 11–(Q) 9:3.5–10.3 KΩ (THROTTLE VALVE FULLY OPEN)
(Q) 1–(Q) 9:200–400 Ω
(Q) 3–(Q) 9:2–3 KΩ (INTAKE AIR TEMP. 20°C, 68°F)
(Q) 4–(Q) 9:0.2–0.4 KΩ (COOLANT TEMP. 80°C, 176°F)
(R) 2, 15–(R)14 : 140–180 KΩ
(R) 1–(R) 14 : 140–180 KΩ
(Q) 2–(Q) 9:200–600 KΩ (MEASURING PLATE FULLY CLOSED)
(R) 4, 5, 6, 7–(P) 12 : 10–30 Ω
Ω (THROTTLE VALVE FULLY OPEN)
0 OR 2300 Ω (THROTTLE VALVE FULLY CLOSED)
0.3–6.3 KΩ (THROTTLE VALVE FULLY CLOSED)
20–1200 KΩ (MEASURING PLATE FULLY OPEN)
61
Page 59

ENGINE CONTROL (2VZ–FE)
A
7. 5A
IGNITIONSW
IG2
B–OB–OB–OB–O
1J41J7
D112
C15
B–OB–O
ST1
17
B–W
1I71I12
B–W
1
2
1
1K
B–W(A/T
)
M/T
(
B
CLUTCH
START SW
(
)
M/T
B–O
B–Y
)
B–W(M/T
)
)
M/T
(
B–W
B–W
11
12
STARTER
RELAY
34
11
W–B
B–O
K112
IGN
1I6
B–O
D113 C14
B
B–O
2G6
14
32
2A72C32G5
)
)
M/T
(
A/T
(
B
W–B
B–W
W–B
15A
EFI
B–Y
EFI
MAIN
RELAY
2
2G
TO COLD START
INJECTOR
START INJECTOR
TIME SW
)
)
M/T
(
A/T
(
B
B–W
W–R
W–R
)
)
M/T
(
A/T
(
B
B–W
32
J
CIRCUIT
OPENING
RELAY
B–O
W–L
B–O
B–Y
W–RW–R
B–O
CDE FGH
1
NO. 5
2
GR
B–O B–O B–O B–O
1
NO. 4
2
GR
B–O
1
NO. 2
2
Y
B–O
1
INJECTION
2
Y
B–O
1
NO. 3
2
W
GR
B–OW
1
NO. 1
2
W
Y
)
A/T
(
NO. 6
B–W
146
B–W
K114
B–WB
I
2
)
A/T
(
NEUTRAL
START SW
)
M/T
(
B–W
3
)
A/T
(
)
B–W(M/T
W–B
CI
L–B
W–B
L–B
L14
H17
FUEL
PUMP
L–B L–B
12
)
B(A/T
)
B–W(M/T
L–B
M
W–B
G–R
K
W–B
W–B
L–B
W
Y
GR
B–WB–W
62
Page 60

B–O B–O
7. 5A
GAUGE
W–L
B–O
B–Y
W–R
W–R
B–Y
W–R
W–R
TCCS ECU
STA NSW A/C OD1 OD2 R N L 2 SP1 VC VS THA THW
11 22 10 21 20 3 16 14 15 9 1 2 3 4
12 13 4 2 1 5 13 7
M–REL IGSW BATT
Y–B
B–G
J33K11L17L15L117 L118 L120 L16
W–L
B–O
G–O
1F2
F13
YY
J/B
NO. 3
3B9
CHECK ENGINE
[COMB. METER]
CHK
6
R–B
L–W
69
LM
P Q
R
Y–L
14
G–RR–L
L1
GR
O
V–Y
20A
STOP
1L11
(
N
1
W/ CRUISE CONTROL
(
O
1
W/O CRUISE CONTROL
STOP LIGHT
SW
(
N
3
W/ CRUISE CONTROL
(
O
2
W/O CRUISE CONTROL
G–W G–R
K110 L13
G–W
)
)
)
)
L–R
TO
L–R
L–R
PBKW+B1+B
PATTERNSELECT SW
U
G
2
)
A/T
(
B
B–W
B–W
BR
Y
E2
THA
EFC
2
1
EFI WATER TEMP.
SENSOR
BR
L–R
L–B
W–R
W
Y
GR
Y–B
L–W
)
M/T
(
B–W
B–W
G–R
W–B
L–B
W–R
W
Y
GR
TO
A/C AMPLIFIER
TO CRUISE
CONTROL
COMPUTER
R–B
G–O
TOO/DMAINSW
TO BACK UP LIGHT
R
TO A/T
INDICATOR
O
Y–L
V–Y
S
2
SPEED SENSOR
[COMB. METER]
3
W–B
L–W L–W
1
T
AIR FLOW METER
Y–R
L–R
4657
VS
VC
W–B
E
63
Page 61
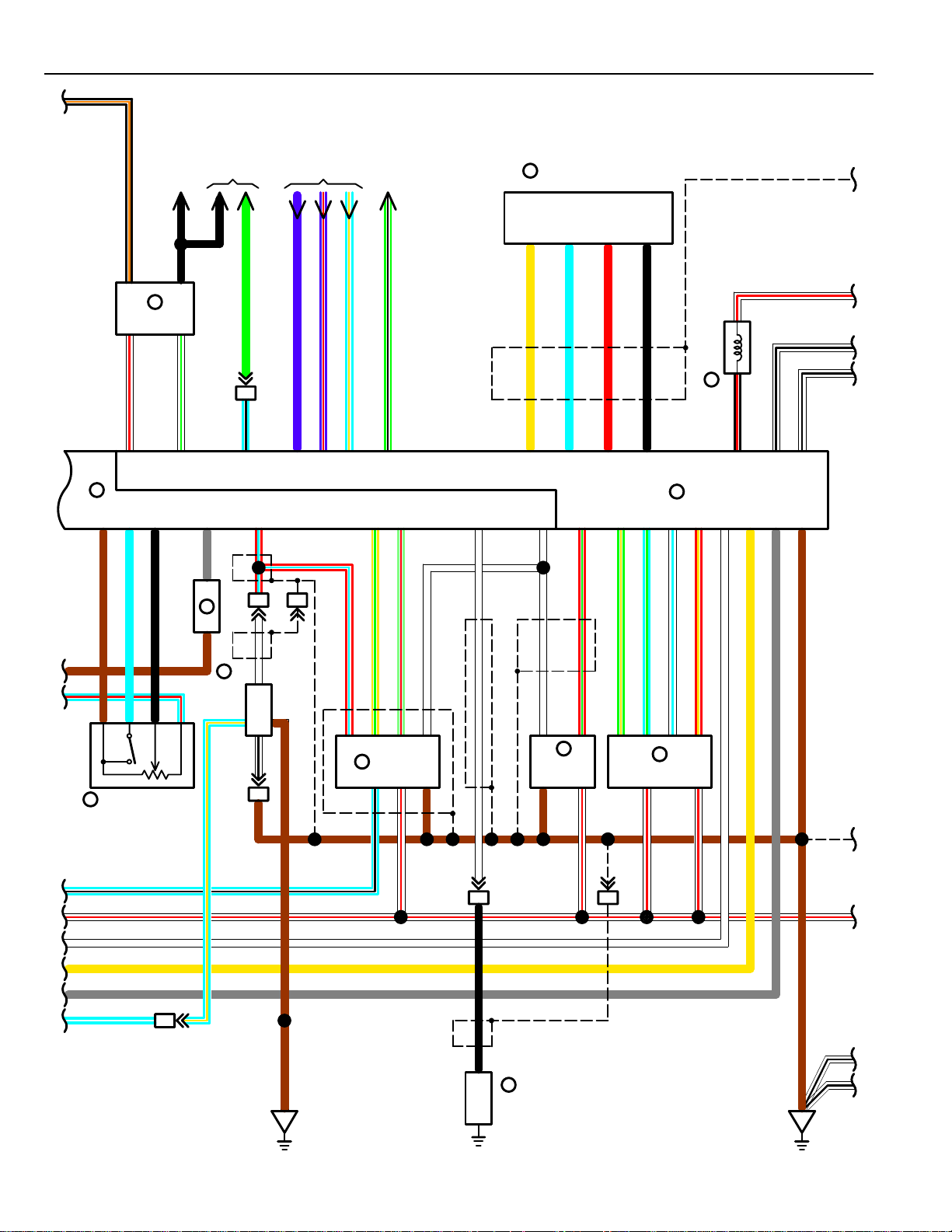
ENGINE CONTROL (2VZ–FE)
B–O
TO TACHO
METER
TO A/C
AMPLIFIER
FROM
ECT SOLENOID
(
TO STARTER
INJECTOR
W DISTRIBUTOR
SEALED
)
B
V
IGNITER
B
B
R–L
L22L24
W
3
4
W–B
L112
V
V–R
)
SEALED
(
G
J310
W–G
10
)
CALIFORNIA
EGR GAS TEMP. SENSOR
(
4321
GR
1
Z
2
BR
OXYGEN
SENSOR
(
SUB
a
)
L–B
12
B–O
12
43
W–R
TCCS ECU
320 2219181710
IGFIGT ACTS1S2SLSTJ
Q
E2 IDL VTA THG OX2 T VF
12 11 5 6 5 7 4 12 24
9
L
BR
BR
L–R
THROTTLE
Y
POSITION SENSOR
G2 NE G1 G–
4123
L–Y
G–B
L
Y
2 1 15 14
KNK OX1 HT ISC2
8614815
)
R–L
Y–G
158134 3 1 1643
OX2 TE1 VF OX
CHECK
b
CONNECTOR
FP +B E1
BR
W
LG–R
BR
SEALED
(
)
SEALED
(
BR
)
SEALED
(
W
OXYGEN
SENSOR
(
MAIN
BR
R–GW–R
c
)
24381
B
R
ISC3
L–G
G–Y
d
ISC VALVE
25
ISC1
W–L
BR
R
ISC4
R–Y
)
2
FUEL
(
VSV
PRESSURE UP
X
1
B–R
W–B
13 26
9
#10 #20 #30 E1
11 25
Y
W
GR
W–R
W–B
E02E01FPUG–G1NEG2
64
L–B
W–R
W
Y
GR
L–W
L–Y
1
L2
W–B
BR
E
L–B
W–R
W
W–R W–R W–R
(
)
SEALED
B
1
e
KNOCK
SENSOR
W–R
d11d12
W–R
W–R
W
Y
GR
BR BR BR
W–B
W–B
B
Page 62
AB J
FCEDHGBLACK GRAY DARK GRAY
I
GRAY
W–R
W–B
W–B
(
SEALED
14 15 16
12
DARK GRAY DARK GRAY
6
20 21
1
2
456
1
)
1234 678 1011
14 15
7
K
DARK GRAY BROWN
12
NO P Q
1
3
512
17 18
1
2
RTU
DARK GRAY BLACK DARK GREEN
9
2019 22
12
23 6
13
24
25 26
SL
12345 91011
12
13
23
M
9
12345678
22
712
123
46
15131211109
14
W–R
W–B
W–B
V
DARK GRAY
12
34
aDARKGRAY
12
34
cWDARKGRAY
12
34
13
6
89
b
DARK GRAY
4
11
12
BLUE
Y
1234
d
123
456
BLACK
GRAY
Z
12
eXGREEN
1
DARK GRAY
65
Page 63

ENGINE CONTROL (2VZ–FE)
: PARTS LOCATION
CODE SEE PAGE CODE SEE P AGE CODE SEE PAGE
A I11 28 L C13 28 W D7 24
B C10 28 M C11 28 X V3 24
C I8 24 N S9 28 Y T1 24
D I7 24 O S9 28 Z E3 24
E I5 24 P T2 28 a O6 28
F I6 24 Q T3 28 b C1 24
G I4 24 R T4 28 c O3 24
H I9 24 S C13 28 d I1 24
I N1 24 T A15 24 e K2 24
J C8 28 U E2 24
K F7 26 (S/D), 27 (STATION W/G) V I3 24
: RELAY BLOCKS
CODE SEE PAGE RELAY BLOCKS (RELAY BLOCK LOCATION)
1 23 R/B NO. 1 (LEFT KICK PANEL)
: JUNCTION BLOCK AND WIRE HARNESS CONNECTOR
CODE SEE PAGE JUNCTION BLOCK AND WIRE HARNESS (CONNECTOR LOCATION)
1F 18 COWL SUB WIRE AND J/B NO. 1 (LEFT KICK PANEL)
1I
1J
18 COWL WIRE AND J/B NO. 1 (LEFT KICK PANEL)
1K
1L
2A 20 ENGINE ROOM MAIN WIRE AND J/B NO. 2 (ENGINE COMPARTMENT LEFT)
2C
20 ENGINE WIRE AND J/B NO. 2 (ENGINE COMPARTMENT LEFT)
2G
3B 22 INSTRUMENT PANEL WIRE AND J/B NO. 3 (INSTRUMENT PANEL LEFT)
: CONNECTOR JOINING WIRE HARNESS AND WIRE HARNESS
CODE SEE PAGE JOINING WIRE HARNESS AND WIRE HARNESS (CONNECTOR LOCATION)
C1 30 ENGINE ROOM MAIN WIRE AND ENGINE WIRE (NEAR J/B NO. 2)
D1 30 ENGINE ROOM WIRE AND COWL WIRE (LEFT KICK PANEL)
F1 34 INSTRUMENT PANEL WIRE AND COWL SUB WIRE (LEFT KICK PANEL)
H1 34 FLOOR NO. 1 WIRE AND INSTRUMENT PANEL WIRE (LEFT KICK PANEL)
J3 34 ENGINE WIRE AND A/C WIRE (BEHIND GLOVE BOX)
K1 34 ENGINE WIRE AND COWL WIRE (BEHIND GLOVE BOX)
L1
34 ENGINE WIRE AND INSTRUMENT PANEL WIRE (BEHIND GLOVE BOX)
L2
d1 30 SENSOR WIRE AND ENGINE WIRE (ABOVE THE ENGINE HEAD COVER)
: GROUND POINTS
CODE SEE PAGE GROUND POINTS LOCATION
B 30 INTAKE MANIFOLD
C 30 RADIATOR LEFT
E 34 LEFT KICK PANEL
36 (S/D)
I
38 (STATION W/G)
LEFT REAR FENDER
66
Page 64

ELECTRICAL IDLE–UP SYSTEM
15A
TAIL
1N61L32G2
G
13
ADIODE
10A
MIR–
HTR
2
G–BGB
K14
BB
92
+B +B1 ISC2 ISC1 E1
BBCC D
81189 7
W–R
W–RW–R
TCCS ECU
G–B
AB
ORANGE DARK GRAY
15A
EFI
W–L
BATTELS
Y
BR
213
(
12
89
)
BC
FWD
(
FWD
(
ALL–TRAC/4WD
DARK GRAY DARK GRAY
)
DARK GRAY DARK GRAY
12
89
9
18
)
(
ALL–TRAC/4WD
(
ALL–TRAC/4WD
)
9
18
)
DC
7
213
+B ISC2 ISC1
ISC VALVE
E
B
(
)
DE
DARK GRAY YELLOW
FWD
123
7
SERVICE HINTS
(A) DIODE (ELECTRICAL IDLE–UP)
1–GROUND : APPROX 12 VOLTS WITH LIGHT CONTROL SW AT TAIL OR HEAD POSITION
: PARTS LOCA TION
CODE SEE PAGE CODE SEE P AGE CODE SEE PAGE
A D10 28 C T3 28 E I1 25
B T2 28 D T4 28
: JUNCTION BLOCK AND WIRE HARNESS CONNECTOR
CODE SEE PAGE JUNCTION BLOCK AND WIRE HARNESS (CONNECTOR LOCATION)
1L
18 COWL WIRE AND J/B NO. 1 (LEFT KICK PANEL)
1N
2G 20 ENGINE WIRE AND J/B NO. 2 (ENGINE COMPARTMENT LEFT)
: CONNECTOR JOINING WIRE HARNESS AND WIRE HARNESS
CODE SEE PAGE JOINING WIRE HARNESS AND WIRE HARNESS (CONNECTOR LOCATION)
K1 34 ENGINE WIRE AND COWL WIRE (BEHIND GLOVE BOX)
: GROUND POINTS
CODE SEE PAGE GROUND POINTS LOCATION
32 INTAKE MANIFOLD
B
67
Page 65

LIGHT AUTO TURN OFF
2B1 1A3
G
G
R–G
(
CANADA
34
15
2F5
R–Y
1B7
1M5
)
)
USA
R–W
(
)
32
HEADLIGHT
RELAY
20A
DOME
2F2
L–YL–Y
1B14
W
2D2B1
2
W
1D4
1D2
1
)
1
ATION RELAY
J/B NO.
INTEGR
(
7. 5A
GAUGE
7
S
Q
R
R
Q
S
34
TAILLIGHT
RELAY
12
1M2
G–R
(
)
CANADA
)
LG
USA
(
E
35
TAIL H–LP
TH
RUNNING
LIGHT RELAY
24
LG R–W
(
)(
CANADA
AA
CANADA
80A ALT
2
FUSIBLE LINK
BOX
W
B
BATTERY
G
65
40A MAIN
DOOR
COURTESY
SW
(
FRONT LH
6
1D5
R
1
C
)
0
1
D
[COMB. SW]
OFF
TAIL
LIGHT
CONTROL
SW
HEAD
D
AA14
G
R–G
213
11
BR
1M3
68
Page 66

SYSTEM OUTLINE
WITH THE IGNITION SW TURNED ON, THE CURRENT FLOWS TO TERMINAL 7 OF THE INTEGRATION RELA Y THROUGH GAUGE FUSE.
VOLTAGE IS APPLIED AT ALL TIMES TO TERMINAL A 2 OF THE INTEGRATION RELAY THROUGH THE TAILLIGHT RELAY COIL, AND TO
TERMINAL A 3 THROUGH THE HEADLIGHT RELAY COIL.
1. NORMAL LIGHTING OPERATION
<TURN TAILLIGHT ON>
WITH LIGHT CONTROL SW TURNED TO TAILLIGHT POSITION, A SIGNAL IS INPUT INTO TERMINAL A 1 OF THE INTEGRATION RELAY.
ACCORDING TO THIS SIGNAL, THE CURRENT FLOWING T O TERMINAL A 2 OF THE RELAY FLOWS FROM TERMINAL A 1 → TERMINAL
2 OF THE LIGHT CONTROL SW → TERMINAL 11 → TO GROUND AND TAILLIGHT RELAY CAUSES TAILLIGHT TO TURN ON.
<TURN HEADLIGHT ON>
WITH LIGHT CONTROL SW TURNED TO HEADLIGHT POSITION, A SIGNAL IS INPUT INTO TERMINALS A 1 AND A 4 OF THE
INTEGRATION RELAY. ACCORDING TO THIS SIGNAL, THE CURRENT FLOWING TO TERMINAL A 3 OF THE RELAY FLOWS TO
TERMINAL A 4 → TERMINAL 13 OF THE LIGHT CONTROL SW → TERMINAL 11 → TO GROUND IN THE HEADLIGHT CIRCUIT, AND
CAUSES T AILLIGHT AND HEADLIGHT RELAY TO TURN THE LIGHT ON. THE TAILLIGHT CIRCUIT IS SAME AS ABOVE.
2. LIGHT AUTO TURN OFF OPERATION
WITH LIGHTS ON AND IGNITION SW TURNED OFF (INPUT SIGNAL GOES TO TERMINAL 7 OF THE RELAY), WHEN DOOR ON DRIVER’S
SIDE IS OPENED (INPUT SIGNAL GOES TO TERMINAL 6 OF THE RELAY), THE RELAY OPERATES AND THE CURRENT IS CUT OFF
WHICH FLOWS FROM TERMINAL A 2 OF THE RELAY TO TERMINAL A 1 IN TAILLIGHT CIRCUIT AND FROM TERMINAL A 3 TO
TERMINAL A 4 IN HEADLIGHT CIRCUIT. AS A RESULT, ALL LIGHTS ARE TURNED OFF AUTOMATICALLY .
SERVICE HINTS
INTEGRA TION RELAY
7–GROUND : APPROX. 12 VOLTS WITH IGNITION SW AT ON POSITION
1–GROUND : ALWAYS APPROX. 12 VOLTS
6–GROUND : CONTINUITY WITH DRIVER’S DOOR OPEN
10–GROUND : ALWAYS CONTINUITY
(A) 3–GROUND : APPROX. 12 VOLTS WITH LIGHT CONTROL SW AT OFF OR TAIL POSITION
(A) 2–GROUND : APPROX. 12 VOLTS WITH LIGHT CONTROL SW AT OFF POSITION
(A) 4–GROUND : CONTINUITY WITH LIGHT CONTROL SW AT HEAD POSITION
(A) 1–GROUND : CONTINUITY WITH LIGHT CONTROL SW AT TAIL OR HEAD POSITION
: PARTS LOCA TION
CODE SEE PAGE CODE SEE P AGE CODE SEE PAGE
A I12 28 C D19 26 (S/D), 27 (STATION W/G) E R2 28 (CANADA)
B F6 24 (2VZ–FE), 25 (3S–FE) D C14 28
: JUNCTION BLOCK AND WIRE HARNESS CONNECTOR
CODE SEE PAGE JUNCTION BLOCK AND WIRE HARNESS (CONNECTOR LOCATION)
1A
18 ENGINE ROOM MAIN WIRE AND J/B NO. 1 (LEFT KICK PANEL)
1B
1D 18 FLOOR WIRE AND J/B NO. 1 (LEFT KICK PANEL)
1M 18 COWL WIRE AND J/B NO. 1 (LEFT KICK PANEL)
2B 20 ENGINE WIRE AND J/B NO. 2 (ENGINE COMPARTMENT LEFT)
2D
20 ENGINE ROOM MAIN WIRE AND J/B NO. 2 (ENGINE COMPARTMENT LEFT)
2F
: GROUND POINTS
CODE SEE PAGE GROUND POINTS LOCATION
D 34 J/B NO. 1 SET BOLT
AB
1234
BLACK
2
56
CD
BLUE
1
2
BLACK
11 13
E
4325
69
Page 67

HEADLIGHTS (USA)
2B1
34
HEADLIGHT
RELAY
15
G
6
A
FUSIBLE
LINK
BOX
40A MAIN
2
BATTERY
2F52E7
R–Y
1B7
1M 1M56
R–W
)
3
)
J/B NO.1
(
4
INTEGRATION
RELAY
B
W/O INTEGRATION RELAY
(
R–G
R–G
W
R–Y
R–W R–W
1M
8
R–L
2E4
LH RH
12
5
R–L
1B
15A
HEAD LH
2A 2A13
R
3
HEADLIGHTS
R–L
R–W
DC
12
15A
HEAD RH
R–Y
3
R–L
R–W
E
[COMB. SW]
LIGHT
CONTROL
DIMMER
SW
SW
OFF
TAIL
HEAD
LOW
HIGH
FLASH
D11
R–W
R–G
13 14 12 3
11 9
BR
1M 1M 1F373
R–Y
W–B
R–L
W–B W–B
1G18
R–LR–L
F210
4
F
HIGH BEAM INDICATOR
LIGHT[COMB. METER]
2
W–B
3B3
J/B NO. 3
8
F1
70
D
Page 68

SERVICE HINTS
HEADLIGHT RELAY
4–5 : CLOSED WITH LIGHT CONTROL SW AT HEAD POSITION OR DIMMER SW AT FLASH POSITION
LIGHT AUTO TURN OFF OPERATION
PLEASE REFER TO THE LIGHT AUTO TURN OFF SYSTEM (SEE PAGE 69)
: PARTS LOCA TION
CODE SEE PAGE CODE SEE P AGE CODE SEE PAGE
A F6 24 (2VZ–FE), 25 (3S–FE) C H1 24 (2VZ–FE), 25 (3S–FE) E C14 28
B I12 28 D H2 24 (2VZ–FE), 25 (3S–FE) F C12 28
: JUNCTION BLOCK AND WIRE HARNESS CONNECTOR
CODE SEE PAGE JUNCTION BLOCK AND WIRE HARNESS (CONNECTOR LOCATION)
1B 18 ENGINE ROOM MAIN WIRE AND J/B NO. 1 (LEFT KICK PANEL)
1F
1G
1M 18 COWL WIRE AND J/B NO. 1 (LEFT KICK PANEL)
18 COWL SUB WIRE AND J/B NO. 1 (LEFT KICK PANEL)
2A 20 ENGINE ROOM MAIN WIRE AND J/B NO. 2 (ENGINE COMPARTMENT LEFT)
2B 20 ENGINE WIRE AND J/B NO. 2 (ENGINE COMPARTMENT LEFT)
2E 20 ENGINE ROOM NO. 4 WIRE AND J/B NO. 2 (ENGINE CMPAR TMENT LEFT)
2F 20 ENGINE ROOM MAIN WIRE AND J/B NO. 2 (ENGINE COMPARTMENT LEFT)
3B 22 INSTRUMENT PANEL WIRE AND J/B NO. 3 (INSTRUMENT PANEL LEFT)
: CONNECTOR JOINING WIRE HARNESS AND WIRE HARNESS
CODE SEE PAGE JOINING WIRE HARNESS AND WIRE HARNESS (CONNECTOR LOCATION)
30 (2VZ–FE)
D1
32 (3S–FE)
F1
34 INSTRUMENT PANEL WIRE AND COWL SUB WIRE (LEFT KICK PANEL)
F2
FLOOR WIRE AND J/B NO. 1 (LEFT KICK PANEL)
: GROUND POINTS
CODE SEE PAGE GROUND POINTS LOCATION
D 34 J/B NO. 1 SET BOLT
BLACKAB EC D BLACK
34
2
6
123
3
911121314
F
24
71
Page 69

HEADLIGHTS (CANADA)
G
G
W
R–B
1
1
65
40A FL MAIN
FUSIBLE LINK
BOX
2
A
B
2D1
2B2
WW
R–G
80A FL ALT
C
[COMB. SW]
LIGHT
CONTROL
SW
DIMMER
SW
INTEGRATION RELAY
4
1
G
OFF
TAIL
HEAD
LOW
HIGH
FLASH
11 9
3
2
132 1412 1362 1 12
R–W
LG
R–G
(
W/O INTEGRATION
)
RELAY
G
(
W/O INTEGRATION
)
RELAY
R–W
R–B
7. 5A
GAUGE
10A
ECU–B
2
1N9
R–L
4
1
R
72
BATTERY
BR
D RUNNING LIGHTS
CONTROL RELAY
W–B
1F31M71M3
D
10
W–B
W–B
45
H
Page 70

G
W
W
R–L
R–L
R–B
2
1K
T
AILLIGHT
R
ELAY
1A3
43
12
1M2
TO
TAILLIGHT
G–R
HEADLIGHT
RELAY
2B1
43
15
2F52E7
R–Y
1B7
1M5
R–G
W
D11
R–W
2
1
324
2
R–B
DIMMER
RELAY
15A
2
R–B
2E4
)
LH
(
HEAD–LO
2A12A3
22
2
)
RH
(
15A
HEAD–LO
11
15A
HEAD–HI
(LH)
22
22
R–B
15A
HEAD–HI
(RH)
R–G
W–B
3514
1G18
F210
4
78
G
Y
W–B
8
F1
W–B
2
W–B R–L R–L
3
3B
5
1B
E
HIGH BEAM INDICATOR
LIGHT[COMB. METER]
NO. 3
J/B
R
R–G
FF
LH
33
W–B
R–W
R–G
2121
RHHEADLIGHT
W–B W–B
TO CLOCK
FROM TERMINAL” L”
OF ALTERNATOR
C
73
Page 71

HEADLIGHTS (CANADA)
SYSTEM OUTLINE
CURRENT FROM THE BATTERY IS ALWAYS FLOWING FROM FL ALT → TAILLIGHT RELAY (COIL SIDE) → TERMINAL 3 OF RUNNING
LIGHT CONTROL RELAY, FL MAIN → HEADLIGHT RELAY (COIL SIDE) → TERMINAL 5 OF RUNNING LIGHT CONTROL RELAY, AND FL
ALT → ECU–B FUSE → TERMINAL 12 OF RUNNING LIGHT CONTROL RELA Y.
WHEN THE IGNITION SW IS TURNED ON, THE CURRENT FLOWING THROUGH THE GAUGE FUSE FLOWS TO TERMINAL 1 OF THE
RUNNING LIGHT CONTROL RELAY.
1. DAYTIME RUNNING LIGHT OPERATION
WHEN THE ENGINE IS STARTED, VOLTAGE IS PRODUCED AT TERMINAL L OF THE ALTERNATOR AND WHEN VOLTAGE IS APPLIED
TO TERMINAL 8 OF THE RUNNING LIGHT CONTROL RELAY, THE RUNNING LIGHT CONTROL RELAY OPERATES AND CURRENT
FLOWS FROM THE TAILLIGHT RELAY (POINT SIDE) → TAIL FUSE → TAIL, LICENSE, SIDE MARKER AND FRONT CLEARANCE LIGHTS
→ GROUND, AND FROM HEADLIGHT RELAY (POINT SIDE) → TERMINAL 1 OF DIMMER RELAY → TERMINAL 4 HEAD FUSES (LOW
SIDE) → HEADLIGHTS → GROUND.
ACCORDINGLY, EVEN IF THE LIGHT CONTROL SW IS IN OFF POSITION, EACH LIGHT MENTIONED HERE LIGHTS UP. THIS SYSTEM
OPERATES UNTIL THE IGNITION SW IS TURNED OFF.
2. TAILLIGHT OPERATION
WHEN THE LIGHT CONTROL SW IS TURNED TO THE TAILLIGHT POSITION, CURRENT FLOWING TO THE TAILLIGHT RELAY (COIL
SIDE) ALWAYS FLOWS TO TERMINAL 3 OF RUNNING LIGHT CONTROL RELAY → TERMINAL 2 → TERMINAL 2 OF INTEGRATION
RELAY → TERMINAL 1 → TERMINAL 2 OF LIGHT CONTROL SW (COMB. SW) → TERMINAL 11 → GROUND, TURNING THE TAILLIGHT
RELAY ON.
THIS CAUSES THE CURRENT FLOWING TO THE TAILLIGHT RELAY (POINT SIDE) TO FLOW FROM THE TAILLIGHT RELAY → TAIL FUSE
→ TAIL, LICENSE, SIDE MARKER AND FRONT CLEARANCE LIGHTS → GROUND, CAUSING THE TAILLIGHTS TO LIGHT UP.
AT THIS TIME, THE CURRENT FLOWING TO THE ECU–B FUSE FLOWS FROM TERMINAL 12 OF THE RUNNING LIGHT CONTROL
RELA Y TO TERMINAL 7, PROVIDING POWER FOR ILLUMINATION OF THE CLOCK.
3. HEADLIGHT OPERATION
WHEN THE LIGHT CONTROL SW IS TURNED TO HEADLIGHT POSITION AND THE DIMMER SW TO LOW SIDE, THE CURRENT
FLOWING TO THE HEADLIGHT RELAY (COIL SIDE) FLOWS TO TERMINAL 5 OF THE RUNNING LIGHT CONTROL RELAY → TERMINAL 4
→ TERMINAL 3 OF INTEGRATION RELAY → TERMINAL 4 → TERMINAL 13 OF LIGHT CONTROL SW (COMB. SW) → TERMINAL 11 →
GROUND, TURNING THE HEADLIGHT RELAY ON.
THIS CAUSES THE CURRENT FLOWING TO THE HEADLIGHT RELAY (POINT SIDE) TO FLOW FROM THE HEADLIGHT RELAY →
TERMINAL 1 OF DIMMER RELAY TERMINAL 4 → HEAD LH (LO), RH (LO) FUSE → HEADLIGHTS (LOW) → GROUND, SO THE
HEADLIGHTS (LOW) LIGHT UP.
WHEN THE DIMMER SW IS SWITCHED TO THE HIGH SIDE, CURRENT FLOWS FROM TERMINAL 1 OF DIMMER RELAY → TERMINAL 3
→ TERMINAL 14 OF RUNNING LIGHT CONTROL RELAY → TERMINAL 13 → TERMINAL 12 OF DIMMER SW → TERMINAL 9 → GROUND,
TURNING THE DIMMER RELAY ON.
THIS CAUSES THE CURRENT FLOWING TO TERMINAL 1 OF THE DIMMER RELAY TO FLOW FROM TERMINAL 2 OF DIMMER RELAY →
HEAD LH (HI), RH (HI) HEADLIGHTS (HIGH) → GROUND, CAUSING THE HEADLIGHTS (HIGH) TO LIGHT UP.
WHEN THE DIMMER SW IS TURNED TO FLASH POSITION, CURRENT FLOWS FROM TERMINAL 5 AND 14 OF THE RUNNING LIGHT
CONTROL RELAY → TERMINAL 6 → TERMINAL 14 OF DIMMER SW (COMB. SW) → TERMINAL 9 → GROUND, SO THAT THE
HEADLIGHT RELAY AND DIMMER RELAY ARE ACTIVATED IN THAT ORDER AND THE HEADLIGHTS CHANGE TO FLASHING MODE.
WHEN THE HEADLIGHTS ARE LIGHTED UP (WITH THE EXCEPTION OF FLASHING MODE), THE TAILLIGHTS ARE LIGHTED UP AS
DESCRIBED IN PART 2 EARLIER.
SERVICE HINTS
TAILLIGHT RELAY
2–4 : CLOSED WITH LIGHT CONTROL SW AT TAIL OR HEAD POSITION
HEADLIGHT RELAY
DIMMER RELA Y
CHANGED FROM HEAD (LO) TO HEAD (HI) WITH DIMMER SW AT FLASH POSITION OR WITH HEADLIGHT RELAY ON AND
DIMMER SW AT HIGH POSITION
CLOSED WITH ENGINE RUNNING
4–5 : CLOSED WITH LIGHT CONTROL SW AT HEAD POSITION OR DIMMER SW AT FLASH POSITION
CLOSED WITH ENGINE RUNNING
74
Page 72

: PARTS LOCATION
18
COWL WIRE AND J/B NO. 1 (LEFT KICK PANEL)
CODE SEE PAGE CODE SEE P AGE CODE SEE PAGE
A F6 24 (2VZ–FE), 25 (3S–FE) D R23 28 F H2 24 (2VZ–FE), 25 (3S–FE)
B I12 28 E C12 28
C C14 28 F H1 24 (2VZ–FE), 25 (3S–FE)
: RELAY BLOCKS
CODE SEE PAGE RELAY BLOCKS (RELAY BLOCK LOCATION)
1 23 R/B NO. 1 (LEFT KICK PANEL)
2 20 R/B NO. 2 (ENGINE COMPARTMENT LEFT)
4 23 R/B NO. 4 (RIGHT KICK PANEL)
: JUNCTION BLOCK AND WIRE HARNESS CONNECTOR
CODE SEE PAGE JUNCTION BLOCK AND WIRE HARNESS (CONNECTOR LOCATION)
1A
18 ENGINE ROOM MAIN WIRE AND J/B NO. 1 (LEFT KICK PANEL)
1B
1F
1G
1M
18 COWL SUB WIRE AND J/B NO. 1 (LEFT KICK PANEL)
1K
18 COWL WIRE AND J/B NO. 1 (LEFT KICK PANEL)
1N
2A 20 ENGINE ROOM MAIN WIRE AND J/B NO. 2 (ENGINE COMPARTMENT LEFT)
2B 20 ENGINE WIRE AND J/B NO. 2 (ENGINE COMPARTMENT LEFT)
2D 20 ENGINE ROOM MAIN WIRE AND J/B NO. 2 (ENGINE COMPARTMENT LEFT)
2E 20 ENGINE ROOM NO. 4 WIRE AND J/B NO. 2 (ENGINE COMPAR TMENT LEFT)
2F 20 ENGINE ROOM MAIN WIRE AND J/B NO. 2 (ENGINE COMPARTMENT LEFT)
3B 22 INSTRUMENT PANEL WIRE AND J/B NO. 3 (INSTRUMENT PANEL LEFT)
: CONNECTOR JOINING WIRE HARNESS AND WIRE HARNESS
CODE SEE PAGE JOINING WIRE HARNESS AND WIRE HARNESS (CONNECTOR LOCATION)
30 (2VZ–FE)
D1
32 (3S–FE)
F1
34 INSTRUMENT PANEL WIRE AND COWL SUB WIRE (LEFT KICK PANEL)
F2
ENGINE ROOM WIRE AND COWL WIRE (LEFT KICK PANEL)
: GROUND POINTS
CODE SEE PAGE GROUND POINTS LOCATION
30 (2VZ–FE)
C
32 (3S–FE)
D 34 J/B NO. 1 SET BOLT
H 34 R/B NO. 4 SET BOLT
RADIATOR LEFT
75
Page 73

INTERIOR LIGHTS (w/ DOOR LOCK)
1C21F4
L–Y
M13
3
P1
R
111
4
W–B
)
W/ MOON ROOF
MAP LIGHT
(
ABC D
R–G
R–G R–G
R–G
1
2
W–B
)
W/O MOON ROOF
MAP LIGHT
(
R–G
LH
R–G
RH
VANITY LIGHT
L–Y
L–Y L–Y
M11
b11
BB
2
)
ON
DOOR
OFF
W/ MOON ROOF
INTERIOR LIGHT
(
1
M12
1C5
(
DELUX
)
)
L–Y
R–B
USA
(
CANADA
(
F25
R
2
)
ON
DOOR
OFF
W/O MOON ROOF
INTERIOR LIGHT
(
1
FE
R–W
1G7
)
7
8
DOOR WARNING LIGHT
[COMB. MERER]
R L–Y
G
F211b12
R
(LE)
P11M16
)
W/ MOON ROOF
(
W–B
G
)
W/O MOON ROOF
(
W–B
)
LE
(
1
INTEGRATION RELAY
(
)
J/B NO. 1
10
H
OUT SIDE
HANDLE SW
1
1C
5
W–B W–B
1K
D
2
E2
2
3
R–W R–W B–W B–W
E213
R–B
2
(LE)
4
6
1D51I3
R
)
11
DOOR COURTESY
SW FRONTLH
I
)
USA
(
CANADA
(
R–G
G–Y
)
DELUX
(
1L61L5
R–W
1
J
DIODE
2
76
Page 74

RR–G
)
LE
(
2
1
IGNITION KEY
CYLINDER LIGHT
KL
)
LE
(
1
2
DOOR KEY
CYLINDER LIGHT
1N12 1D21D41B14 2F2
L–YL–Y
E29O12X15
RR
1
MN
LH
2
R–W
L–YL–Y
DOOR
COURTESY
LIGHT
(LE)
L–Y
L–Y L–Y
L–Y
R
1
RH
2
R–W
L–Y
1
)
STATION W/G
REAR INTERIOR LIGHT
(
2
O
R–W
)
S/D
(
)
STATION W/G
(
1
2
R–W L–Y
)
S/D
(
LAGGAGE
COMPARTMENT
LIGHT
P
20A
D0ME
E24E21O15X14
G–R
1L71L81L6
FROMDOOR LOCK
CONTROL RELAY
Q
R–B
J
R–Y
R–Y
N14
R–Y
1
DOOR COURTESY
SW FRONT RH
DIODE
21
R–W
(
)
DELUX
)
)
R–W
W/ A. B. S
(
W/OA.B.S
(
R–W
(LE)
(
V32
S/D ALL–TRAC/4WD
(
S/D FWD
LAGGAGE
COMPARTMENT
UT
)
)
S/D
(
LIGHT SW
V22
R–W
R–W
11
1D
1N7
R–W
REAR
RH
R–W R–W
(
)
W/G
R–W
R–W
N17
)
R–W
USA W/O A. B. S.
(
11
DOOR COURTESY
SW
R–W
)
R
EX. USA W/O A. B. S.
(
R–W
SR
REAR
LH
R–WR–W
W16
R–W
Y16
R–WW–B
21
1
)
STATION W/G
BACK DOOR
COURTESY SW
(
L
)
77
Page 75

INTERIOR LIGHTS (w/ DOOR LOCK)
SERVICE HINTS
INTEGRA TION RELA Y NO. 1 (J/B NO. 1)
(1G) 7–GROUND : APPROX. 12 VOLTS WITH DOOR CLOSED
20A DOME FUSE : ALWAYS 12 VOLTS
(1I) 3–GROUND : APPROX. 12 VOLTS WITH DRIVER’S DOOR
(1L) 7–GROUND : APPROX. 12 VOLTS WITH DOOR CLOSED
(H) OUTSIDE HANDLE SW (DRIVER’S DOOR)
1–3 : CLOSED WITH DRIVER’S DOOR OUTSIDE HANL HOLD UP
(I) (Q) (R) (S) DOOR COURTESY SW
1–GROUND : CLOSED WITH DOOR OPEN
(T) BACK DOOR COURTESY SW (W/G)
2–GROUND : CLOSED WITH BACK DOOR OPEN
(U) LUGGAGE COMPARTMENT LIGHT SW
1–GROUND : CLOSED WITH LUGGAGE COMPARTMENT DOOR OPEN
: PARTS LOCATION
CODE SEE PAGE CODE SEE P AGE CODE SEE PAGE
A M5 26 (S/D), 27 (STATION W/G) I D17 26 (S/D), 27 (STATION W/G) Q D18 26 (S/D), 27 (STATION W/G)
B M1 26 (S/D), 27 (STATION W/G) J D12 28 Q D19 26 (S/D), 27 (STATION W/G)
C V1 26 (S/D), 27 (STATION W/G) K I10 28 R D21 26 (S/D), 27 (STATION W/G)
D V2 26 (S/D), 27 (STATION W/G) L D23 26 (S/D), 27 (STATION W/G) R D22 26 (S/D), 27 (STATION W/G)
E I13 26 (S/D), 27 (STATION W/G) M D15 26 (S/D), 27 (STATION W/G) S D20 26 (S/D), 27 (STATION W/G)
F I13 26 (S/D), 27 (STATION W/G) N D16 26 (S/D), 27 (STATION W/G) T B8 27
G C11 28 O R15 27 U L5 26
H D23 26 (S/D), 27 (STATION W/G) P L4 26
: JUNCTION BLOCK AND WIRE HARNESS CONNECTOR
0 VOLT WITH ANY DOOR OPEN
OUTSIDE HANDLE HOLD UP
0 VOLT WITH ANY DOOR OPEN
0 VOLT → 12 VOLTS WITHIN 8.5 SECONDS AFTER DOOR CLOSED
OR AFTER DRIVER’S DOOR OUTSIDE HANDEL HOLD UP
CODE SEE PAGE JUNCTION BLOCK AND WIRE HARNESS (CONNECTOR LOCATION)
1B 18 ENGINE ROOM MAIN WIRE AND J/B NO. 1 (LEFT KICK PANEL)
1C 18 COWL WIRE AND J/B NO. 1 (LEFT KICK PANEL)
1D 18 FLOOR WIRE AND J/B NO. 1 (LEFT KICK PANEL)
1F
18 COWL SUB WIRE AND J/B NO. 1 (LEFT KICK PANEL)
1G
1I
1K
18 COWL WIRE AND J/B NO. 1 (LEFT KICK PANEL)
1L
1N
2F 20 ENGINE ROOM MAIN WIRE AND J/B NO. 2 (ENGINE COMPARTMENT LEFT)
: CONNECTOR JOINING WIRE HARNESS AND WIRE HARNESS
CODE SEE PAGE JOINING WIRE HARNESS AND WIRE HARNESS (CONNECTOR LOCATION)
E2 34 FRONT DOOR LH WIRE AND COWL WIRE (LEFT KICK PANEL)
F2 34 INSTRUMENT PANEL WIRE AND COWL SUB WIRE (LEFT KICK PANEL)
M1 34 COWL WIRE AND ROOF WIRE (INSTRUMENT PANEL RIGHT)
N1 34 FLOOR NO. 2 WIRE AND COWL WIRE (RIGHT KICK PANEL)
O1 34 FRONT DOOR RH WIRE AND COWL WIRE (RIGHT KICK PANEL)
36 (S/D)
P1
38 (STATION W/G)
V2 36 FLOOR NO. 1 WIRE AND LUGGAGE ROOM NO. 1 WIRE (BACK PANEL LEFT)
V3 36 FLOOR NO. 1 WIRE AND LUGGAGE ROOM NO. 1 WIRE (BACK PANEL LEFT)
W1 38 BACK DOOR NO. 1 WIRE AND FLOOR NO. 1 WIRE (BACK PANEL LEFT)
X1 38 LUGGAGE ROOM NO. 3 WIRE AND FLOOR NO. 1 WIRE (BACK PANEL LEFT)
Y1 38 BACK DOOR NO. 1 WIRE AND BACK DOOR NO. 2 WIRE (BACK DOOR LEFT)
36 (S/D)
b1
38 (STATION W/G)
ROOF NO. 2 WIRE AND ROOF WIRE (W/ MOON ROOF, ROOF RIGHT)
INTERIOR LIGHT WIRE AND ROOF WIRE (W/ MOON ROOF, ROOF RIGHT)
78
Page 76

: GROUND POINTS
CODE SEE PAGE GROUND POINTS LOCATION
D 34
G
L 38
36 (S/D)
38 (STATION W/G)
J/B NO. 1 SET BOLT
ROOF RIGHT (W/ MOON ROOM)
BACK DOOR RIGHT
79
Page 77

INTERIOR LIGHTS (w/o DOOR LOCK)
1C21F4
L–Y
M13
3
P1
R
111
4
ABC D
W–B
P11M16
R–G R–G
)
W/ MOON ROOF
MAP LIGHT
(
R–G
1
2
W–B
)
W/O MOON ROOF
MAP LIGHT
(
R–G
LH
R–G
RH
VANITY LIGHT
10
L–Y
L–Y L–Y
M11
b11
BB
2
)
DOOR
W/ MOON ROOF
INTERIOR LIGHT
(
1
M12
R–W B–W B–W
1C51G7
INTEGRATION RELAY
(
)
J/B NO. 1
ON
OFF
)
)
L–Y
R–B
U. S. A.
CANADA
(
(
F25
R
2
)
ON
OFF
DOOR
W/O MOON ROOF
INTERIOR LIGHT
(
1
FE
R–W
(
DELUX
(LE)
3
7
8
DOOR WARNING LIGHT
[COMB. METER]
RL–Y
G
F211b12
R
)
412
6
(LE)
80
)
W/ MOON ROOF
(
W–B
G
)
W/O MOON ROOF
(
W–B
R–W
E213
R–B
H
OUT SIDE
HANDLE SW
2
1
1C
5
W–B W–B
1K
D
2
E2
1D51I3
R
11
DOOR COURTESY
SW FRONT LH
I
Page 78
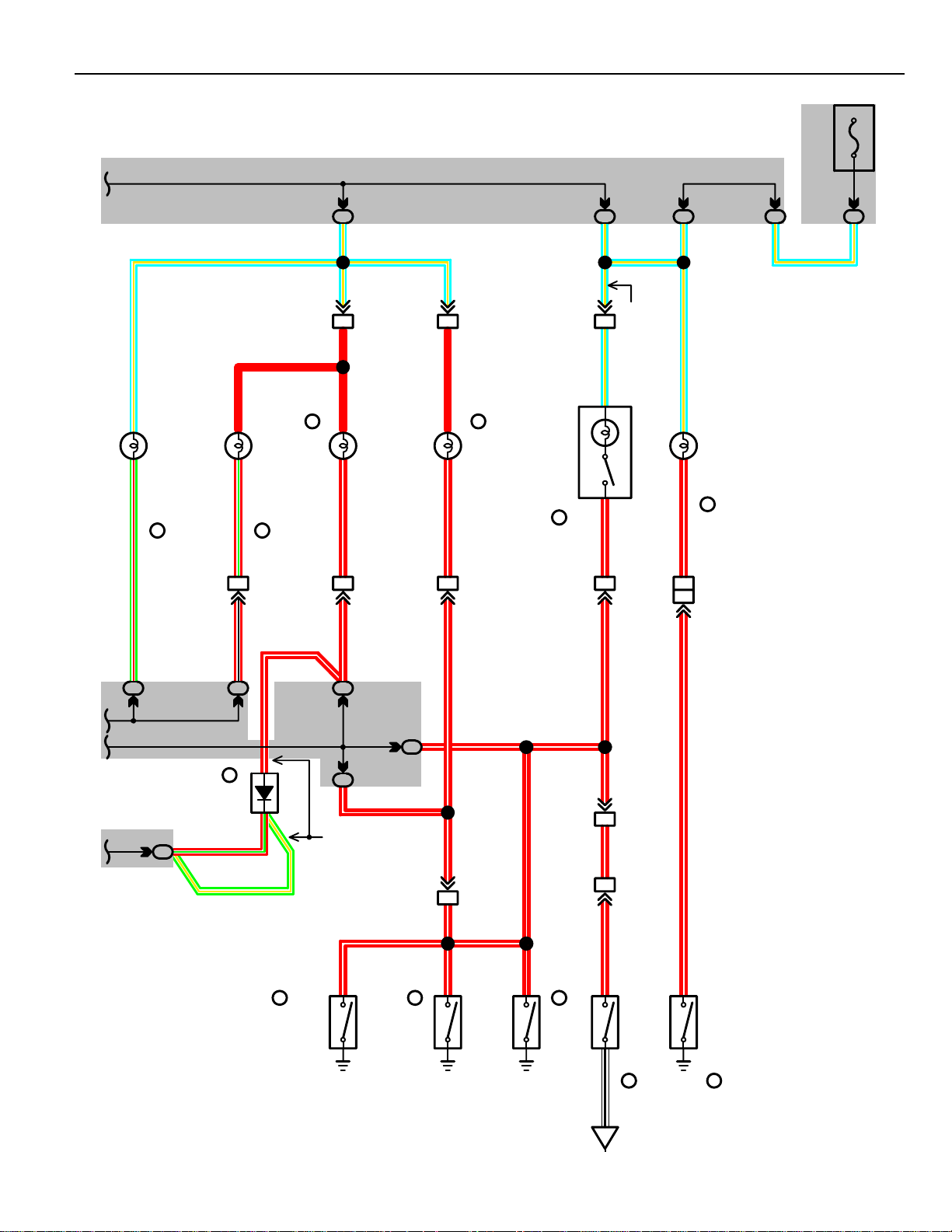
20A
D0ME
RR–G
)
LE
(
2
1
IGNITION KEY
CYLINDER LIGHT
JK
G–R
)
LE
(
1
2
DOOR KEY
CYLINDER LIGHT
E24E21O15X14
R–B
1N12 1D21D41B14
L–YL–Y
L–Y
E29O12X15
RR
R
LM
1
2
R–W
R–W
DOOR
COURTESY
LIGHT
LH
1
RH
2
R–W
L–Y
1
)
STATION W/G
REAR INTERIOR LIGHT
(
2
N
R–W
L–Y
L–Y L–YL–YL–Y
)
S/D
(
)
STATION W/G
(
1
2
R–W L–Y
V32
V22
)
S/D
(
LAGGAGE
COMPARTMENT
LIGHT
O
(
S/D ALL–TRAC/4WD
(
)
S/D FWD
2F2
)
1L71L8
5
1L
(
1
P
DIODE
2
R–G
)
USA
G–Y
(
CANADA
DOOR COURTESY
SW FRONT RH
(
W/G
SRQ
R–W
)
R–WR–W
W16
R–W
Y16
R–WW–B
)
STATION W/G
(
BACK DOOR
COURTESY
SW
)
S/D
(
LAGGAGE
COMPARTMENT
LIGHT SW
UT
1L6
R–W
11
1D
7
1N
R–W
(
W/O INTEGRATION
)
RELAY
)
R–W R–W
111121
REAR
RH
R–W R–W
R–W
)
USA
R–W
(
N17
)
R–W
USA
(
(
CANADA
R–W
DOOR COURTESY SW
R–W
)
R–W
REAR
LH
L
81
Page 79

INTERIOR LIGHTS (w/o DOOR LOCK)
SERVICE HINTSSERVICE HINTS
INTEGRA TION RELA Y NO. 1 (J/B NO. 1)
(1G) 7–GROUND : APPROX. 12 VOLTS WITH DOOR CLOSED
20A DOME FUSE : ALWAYS 12 VOLTS
(1I) 3–GROUND : APPROX. 12 VOLTS WITH DRIVER’S DOOR
(1L) 7–GROUND : APPROX. 12 VOLTS WITH DOOR CLOSED
(H) OUTSIDE HANDLE SW (DRIVER’S DOOR)
1–3 : CLOSED WITH DRIVER’S DOOR OUTSIDE HANL HOLD UP
(I) (Q) (R) (S) DOOR COURTESY SW
1–GROUND : CLOSED WITH DOOR OPEN
(T) BACK DOOR COURTESY SW (W/G)
2–GROUND : CLOSED WITH BACK DOOR OPEN
(U) LUGGAGE COMPARTMENT LIGHT SW
1–GROUND : CLOSED WITH LUGGAGE COMPARTMENT DOOR OPEN
: PARTS LOCATION
CODE SEE PAGE CODE SEE P AGE CODE SEE PAGE
A M5 26 (S/D), 27 (STATION W/G) I D19 26 (S/D), 27 (STATION W/G) Q D20 26 (S/D), 27 (STATION W/G)
B M1 26 (S/D), 27 (STATION W/G) J I10 28 Q D21 26 (S/D), 27 (STATION W/G)
C V1 26 (S/D), 27 (STATION W/G) K D25 26 (S/D), 27 (STATION W/G) R D23 26 (S/D), 27 (STATION W/G)
D V2 26 (S/D), 27 (STATION W/G) L D17 26 (S/D), 27 (STATION W/G) R D24 26 (S/D), 27 (STATION W/G)
E I13 26 (S/D), 27 (STATION W/G) M D18 26 (S/D), 27 (STATION W/G) S D22 26 (S/D), 27 (STATION W/G)
F I13 26 (S/D), 27 (STATION W/G) N R15 27 T B8 27
G C11 28 O L4 26 U L5 26
H D25 26 (S/D), 27 (STATION W/G) P D13 28
: JUNCTION BLOCK AND WIRE HARNESS CONNECTOR
0 VOLT WITH ANY DOOR OPEN
OUTSIDE HANDLE HOLD UP
0 VOLT WITH ANY DOOR OPEN
0 VOLT → 12 VOLTS WITHIN 8.5 SECONDS AFTER DOOR CLOSED
OR AFTER DRIVER’S DOOR OUTSIDE HANDEL HOLD UP
CODE SEE PAGE JUNCTION BLOCK AND WIRE HARNESS (CONNECTOR LOCATION)
1B 18 ENGINE ROOM MAIN WIRE AND J/B NO. 1 (LEFT KICK PANEL)
1C 18 COWL WIRE AND J/B NO. 1 (LEFT KICK PANEL)
1D 18 FLOOR WIRE AND J/B NO. 1 (LEFT KICK PANEL)
1F
18 COWL SUB WIRE AND J/B NO. 1 (LEFT KICK PANEL)
1G
1I
1K
18 COWL WIRE AND J/B NO. 1 (LEFT KICK PANEL)
1L
1N
2F 20 ENGINE ROOM MAIN WIRE AND J/B NO. 2 (ENGINE COMPARTMENT LEFT)
: CONNECTOR JOINING WIRE HARNESS AND WIRE HARNESS
CODE SEE PAGE JOINING WIRE HARNESS AND WIRE HARNESS (CONNECTOR LOCATION)
E2 34 FRONT DOOR LH WIRE AND COWL WIRE (LEFT KICK PANEL)
F2 34 INSTRUMENT PANEL WIRE AND COWL SUB WIRE (LEFT KICK PANEL)
M1 34 COWL WIRE AND ROOF WIRE (INSTRUMENT PANEL RIGHT)
N1 34 FLOOR NO. 2 WIRE AND COWL WIRE (RIGHT KICK PANEL)
O1 34 FRONT DOOR RH WIRE AND COWL WIRE (RIGHT KICK PANEL)
36 (S/D)
P1
38 (STATION W/G)
V2 36 FLOOR NO. 1 WIRE AND LUGGAGE ROOM NO. 1 WIRE (BACK PANEL LEFT)
V3 36 FLOOR NO. 1 WIRE AND LUGGAGE ROOM NO. 1 WIRE (BACK PANEL LEFT)
W1 38 BACK DOOR NO. 1 WIRE AND FLOOR NO. 1 WIRE (BACK PANEL LEFT)
X1 38 LUGGAGE ROOM NO. 3 WIRE AND FLOOR NO. 1 WIRE (BACK PANEL LEFT)
Y1 38 BACK DOOR NO. 1 WIRE AND BACK DOOR NO. 2 WIRE (BACK DOOR LEFT)
36 (S/D)
b1
38 (STATION W/G)
ROOF NO. 2 WIRE AND ROOF WIRE (W/ MOON ROOF, ROOF RIGHT)
INTERIOR LIGHT WIRE AND ROOF WIRE (W/ MOON ROOF, ROOF LIGHT)
82
Page 80

: GROUND POINTS
CODE SEE PAGE GROUND POINTS LOCATION
D 34
G
L 38
36 (S/D)
38 (STATION W/G)
J/B NO. 1 SET BOLT
ROOF RIGHT (W/ MOON ROOM)
BACK DOOR RIGHT
83
Page 81

ILLUMINATION
TAILLIGHT
RELAY
34
15A
TAIL
12
1A31M2
LG
2D1
2B2
WW
A
52
80A FL ALT
FUSIBLE LINK BOX
2
B
INTEGRATION
RELAY
(
)
J/B NO. 1
G
)
3A14 3B63A13 3D8
G
W/O INTEGRATION RELAY
D
(
2 23
GLOVEBOX
LIGHT
1 11
1
G
G
G–W
E
1
1F6
F11
GG
G
6
1N
J/B NO 3
.
G
G
GH
)
ANALOG
COMB. METER
(
B
GG
G
ECT PATTERN
SELECT SW
B
BATTERY
C
[COMB. SW]
LIGHT
CONTROL
SW
OFF
TAIL
HEAD
GLOVE BOX
LIGHT SW
W–B
2
W–B
3A13A2
J/B NO. 3
8
F1
W–B
1
23
W–B
RHEOSTATF
B
3B43D11
3A12
2
11
BR
1M3
3
1F
D
84
Page 82

G G
J/B NO.3
3C93C23B73D23A53C83D13A63D9
G
)
W/G
IJ K MNOL
(
1
4
REAR WIPER SW
B–W
3C11 3C33B53D43A11 3C10 3C43A43D12
G
2
6
CRUISE CONTROL
MAIN SW
B
G
2
1
HAZARD SW
B
G
2
4
O/DMAINSW
B
REAR WINDOW
G
1
4
DEFOGGER SW
B
J/B NO.3
G
3
1
CIGARETTE
LIGHTER
B
GB–R
)
6
9
INSTRUMENT PANEL
A/T INDICATOR
(
G
PQ10
RADIO
5
W–G
G
RS
2
3
DIFF. LOCK
CONTROLSW
B
G
1
2
CENTER DIFF. LOCK
INDICATORLIGHT
B
85
Page 83

ILLUMINATION
AB C
BLACK BLACK
12
G
(
)
LEVER SW TYPE A/C
(
)
)
G
T
16
U
4
T
5
U
3
HEATER CONTROL
SW
G
PUSH SW TYPE A/C
LEVER SW TYPE A/C
(
(
V
1
A/C SW
4
USA
2
5
)(
DDE
GRAY
12
GH
12
12
46
CANADA
12
)
12
KMJBLUE
12
13
2
11
F
1
23
I
1
4
L
BLUE
2
4
N
1
3
B–W
B–W
OPQ
I15
9
B–R
3D10
(
RR
W/ ECT
J/B NO. 3
2
3
6
)(
2
3
T
5
16
W/O ECT
)
BLUE BLUE
10
S
12
U
34
5
V
12
46
86
Page 84

SERVICE HINTS
TAILLIGHT RELAY
2–4 : CLOSED WITH LIGHT CONTROL SW AT TAIL OR HEAD POSITION (LIGHT AUTO TURN OFF SYSTEM OFF)
CLOSED WITH ENGINE RUNNING
(B) INTEGRATION RELAY
PLEASE REFFER TO LIGHT AUTO TURN OFF SYSTEM (SEE PAGE 69)
RHEOSTAT
(F) 1–2, : APPROX. 12 VOLTS WITH RHEOSTAT FULLY TURNED COUNTERCLOCKWISE AND 0 VOLTS WITH FULLY
TURNED CLOCK WISE
: PARTS LOCA TION
CODE SEE PAGE CODE SEE P AGE CODE SEE PAGE
A F6 24 (2VZ–FE), 25 (3S–FE) H E5 28 P R5 28
B I12 28 I R7 28 Q R4 28
C C14 28 J C18 28 R R7 28
D G1 28 K H5 28 S C6 28
E G2 28 (CANADA) L O1 28 T H6 28
E G3 28 (USA) M R6 28 U H7 28
F R10 28 N C7 28 V H6 28
G C11 28 O A26 28
: JUNCTION BLOCK AND WIRE HARNESS CONNECTOR
CODE SEE PAGE JUNCTION BLOCK AND WIRE HARNESS (CONNECTOR LOCATION)
1A 18 ENGINE ROOM MAIN WIRE AND J/B NO. 1 (LEFT KICK PANEL)
1F 18 COWL SUB WIRE AND J/B NO. 1 (LEFT KICK PANEL)
1M
18 COWL WIRE AND J/B NO. 1 (LEFT KICK PANEL)
1N
2B 20 ENGINE WIRE AND J/B NO. 2 (ENGINE COMPARTMENT LEFT)
2D 20 ENGINE ROOM MAIN WIRE AND J/B NO. 2 (ENGINE COMPARTMENT LEFT)
3A
3B
22 INSTRUMENT PANEL WIRE AND J/B NO. 3 (INSTRUMENT PANEL LEFT)
3C
3D
: CONNECTOR JOINING WIRE HARNESS AND WIRE HARNESS
CODE SEE PAGE JOINING WIRE HARNESS AND WIRE HARNESS (CONNECTOR LOCATION)
F1 34 INSTRUMENT PANEL WIRE AND COWL SUB WIRE (LEFT KICK PANEL)
I1 34 COWL WIRE AND INSTRUMENT PANEL WIRE (INSTRUMENT PANEL CENTER)
: GROUND POINTS
CODE SEE PAGE GROUND POINTS LOCATION
D 34 J/B NO. 1 SET BOLT
87
Page 85

TAILLIGHTS
34
(
W/ LIGHT FAILURE SENSOR
(
W/O LIGHT FAILURE SENSOR
)
)
1A31M2
W
2D1
2B2
W
)
A
5
G
80A FL ALT
FUSIBLE LINK BOX
2
BATTERY
W/O INTEGRATION RELAY
(
D
[COMB. SW]
LIGHT
(
3
TAIL
T
2
LG
OFF
TAIL
CONTROL
SW
HEAD
TAILLIGHT
RELAY
G–R
)
CANADA
B
RUNNING
LIGHTS
RELAY
)
W/ INTEGRATION
RELAY
(
C
INTEGRATION
RELAY
(
)
J/B NO. 1
11
12
)
LG
USA
(
2
1
GG
2
7. 5A
E
GAUG
2
1F
1D6
)
G
USA
(
)
E
Y
W/O INTEGRATION RELAY
(
G
LIGHT FAILURE
2310
SENSOR
94
LG
W–B
LG
3
YY
F1
9
3B
R–L
6
10
REAR LIGHT
WARNINGLIGHT
[COMB. METER]
Y–G
F
H116
Y–G
LG
G
LG LG
)
)
G
S/D
S/D
(
(
LG
G
LG
V36
V21
U14
G
J/B
NO. 3
G
GG
G
(
S/D ALL–TRAC/4WD
(
)
S/D FWD
(
ALL–TRAC/4WD
LG
LG–R(FW–D
G
15
TAIL
1D14
G
G
G
(
STATION W/G
(
STATION W/G
)
)
13
1B
1
V1
)
)
G
G
G
)
LG–R
88
BR
1M3
(
GI JLK
5
H
1
LH RH
4
H
4
W–B
W–B
D
I
3
W–B
U1
W–B W–B
115
4
W–B
(
)
S/D
)
S/D
(
STATION W/G
TAILLIGHTS
[REAR COMB.
LIGHTS]
(
)
S/D
(
STATION W/G
W–B
)
4
)
W–B
1
KJIG
4
L
4
W–BW–B
W–B
Page 86
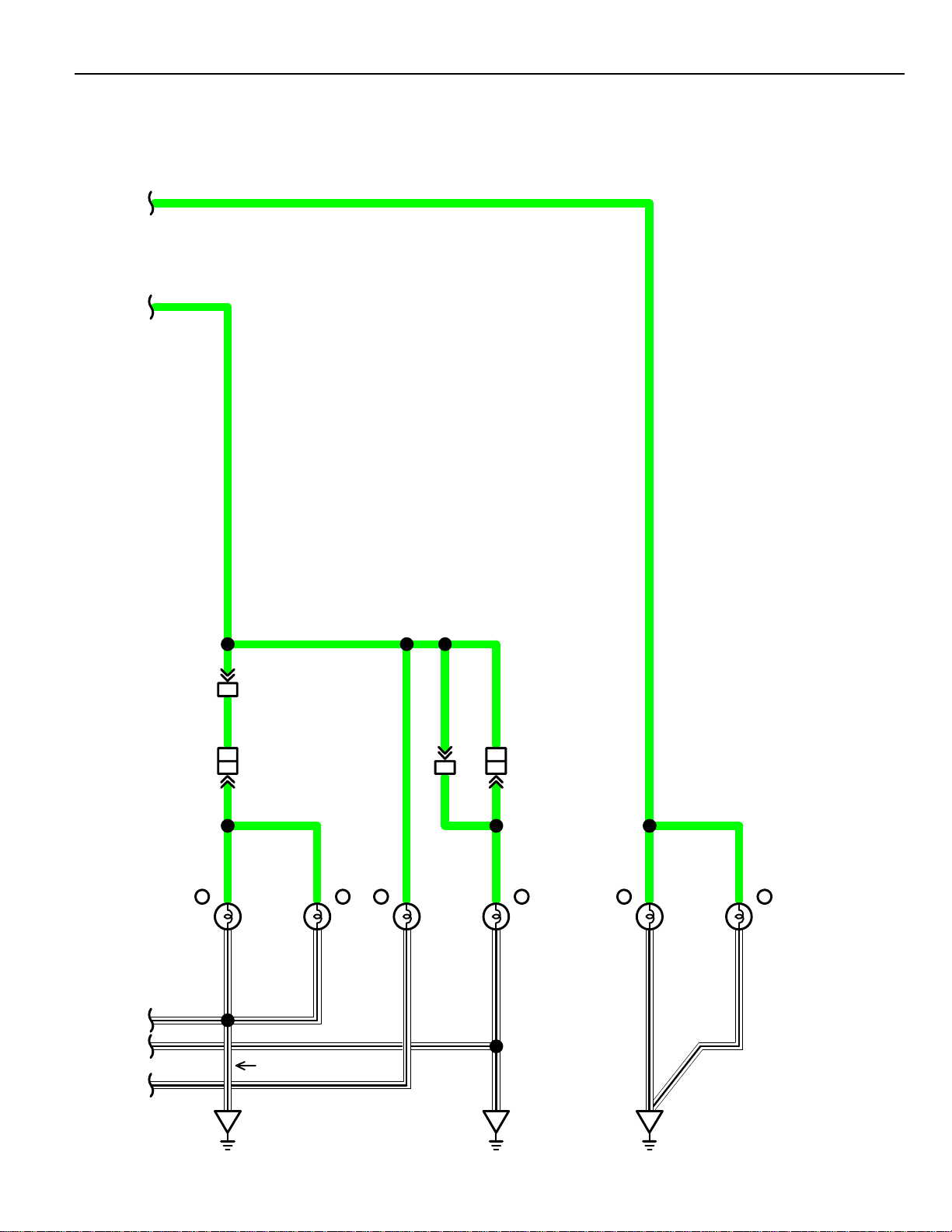
G
G
G
G
W15
(
)
U16
S/D
(
STATION W/G
GGG
2
MNOPQR
LH LH LHRH RH RH
(
W–B
S/D
W–B
W–B
LICENCE
PLATE
LIGHTS
1
W–B
)
W–B
(
STATION W/G
)
G
2
1
W–B
)
G
)
G
G
V11Y15
G
G
2
REAR
SIDE
MARKER
LIGHTS
1
W–B
W–B
G
STATION W/G
(
(
V35
S/D ALL–TRAC/4WD
(
S/D FWD
)
V25
G
G
2
1
W–B
W–B
G
)
G
G
1
2
W–B
FRONT
CLEARANCE
AND
SIDE
MARKER
LIGHTS
G
1
2
W–B
LKC
89
Page 87

TAILLIGHTS
SYSTEM OUTLINE
WHEN THE LIGHT CONTROL SW IS TURNED TO TAIL OR HEAD POSITION, THE CURRENT FLOWS TO TERMINAL 10 OF THE LIGHT
FAILURE SENSOR THROUGH THE TAIL FUSE.
WHEN THE IGNITION SW IS TURNED ON, THE CURRENT FLOWS FROM THE GAUGE FUSE TO TERMINAL 2 OF THE LIGHT FAILURE
SENSOR AND THROUGH THE REAR LIGHT WARNING LIGHT TO TERMINAL 3 OF THE LIGHT FAILURE SENSOR.
T AIL LIGHT DISCONNECTION WARNING
WITH THE IGNITION SW ON AND THE LIGHT CONTROL SW TURNED TO TAIL OR HEAD POSITION, IF THE TAILLIGHT CIRCUIT IS
OPEN, THE LIGHT FAILURE SENSOR DETECTS THE FAILURE BY THE CHANGE IN CURRENT FLOWING FROM TERMINAL 10 OF THE
LIGHT FAILURE SENSOR TO TERMINAL 4, AND THE WARNING CIRCUIT OF THE LIGHT FAILURE SENSOR IS ACTIVATED.
AS A RESULT, THE CURRENT FLOWS FROM TERMINAL 3 OF THE LIGHT FAILURE SENSOR → TERMINAL 9 → GROUND AND TURNS
THE REAR LIGHT WARNING LIGHT ON, WHICH REMAINS ON UNTIL THE LIGHT CONTROL SW IS TURNED OFF.
SERVICE HINTS
TAILLIGHT RELAY
2–4 : CLOSED WITH LIGHT CONTROL SW AT TAIL OR HEAD POSITION (INTEGRATION RELAY ON)
CLOSED WITH ENGINE RUNNING
(C) INTEGRATION RELAY
PLEASE REFER TO LIGHT AUTO TURN OFF SYSTEM (SEE PAGE 69)
(E) LIGHT FAILURE SENSOR
(DISCONNECT THE FAILURE SENSOR AND INSPECT THE CONNECTOR)
10–GROUND : APPROX. 12 VOLTS WITH LIGHT CONTROL SW AT TAIL OR HEAD POSITION
3–GROUND : APPROX. 12 VOLTS WITH ENGINE RUNNING
2–GROUND : APPROX. 12 VOLTS WITH IGNITION SW ON
9–GROUND : CONTINUITY
4–GROUND : CONTINUITY
: PARTS LOCA TION
CODE SEE PAGE CODE SEE P AGE CODE SEE PAGE
A F6 24 (2VZ–FE), 25 (3S–FE) G R11 26 M L1 26 (S/D), 27 (STATION W/G)
B R2 28 (CANADA) H R11 27 N L2 26 (S/D), 27 (STATION W/G)
C I12 28 I R12 26 O R16 26 (S/D), 27 (STATION W/G)
D C14 28 J R13 26 P R17 26 (S/D), 27 (STATION W/G)
E L3 26 (S/D), 27 (STA TION W/G) K R14 26 Q F1 24 (2VZ–FE), 25 (3S–FE)
F C13 28 L R14 27 R F2 24 (2VZ–FE), 25 (3S–FE)
: JUNCTION BLOCK AND WIRE HARNESS CONNECTOR
CODE SEE PAGE JUNCTION BLOCK AND WIRE HARNESS (CONNECTOR LOCATION)
1A
18 ENGINE ROOM MAIN WIRE AND J/B NO. 1 (LEFT KICK PANEL)
1B
1D 18 FLOOR WIRE AND J/B NO. 1 (LEFT KICK PANEL)
1F 18 COWL SUB WIRE AND J/B NO. 1 (LEFT KICK PANEL)
1M 18 COWL WIRE AND J/B NO. 1 (LEFT KICK PANEL)
2B 20 ENGINE WIRE AND J/B NO. 2 (ENGINE COMPARTMENT LEFT)
2D 20 ENGINE ROOM MAIN WIRE AND J/B NO. 2 (ENGINE COMPARTMENT LEFT)
3B 22 INSTRUMENT PANEL WIRE AND J/B NO. 3 (INSTRUMENT PANEL LEFT)
: CONNECTOR JOINING WIRE HARNESS AND WIRE HARNESS
CODE SEE PAGE JOINING WIRE HARNESS AND WIRE HARNESS (CONNECTOR LOCATION)
F1 34 INSTRUMENT PANEL WIRE AND COWL SUB WIRE (LEFT KICK PANEL)
H1 34 FLOOR NO. 1 WIRE AND INSTRUMENT PANEL WIRE (LEFT KICK PANEL)
U1 36 FLOOR NO. 1 WIRE AND LUGGAGE ROOM NO. 2 WIRE (LUGGAGE COMPARTMENT DOOR)
V1 38 LUGGAGE ROOM NO. 1 WIRE AND FLOOR NO. 1 WIRE (BACK PANEL LEFT)
V2
36 FLOOR NO. 1 WIRE AND LUGGAGE ROOM NO. 1 WIRE (BACK PANEL LEFT)
V3
W1 38 BACK DOOR NO. 1 WIRE AND FLOOR NO. 1 WIRE (BACK PANEL LEFT)
Y1 38 BACK DOOR NO. 1 WIRE AND BACK DOOR NO. 2 WIRE (BACK DOOR LEFT)
90
Page 88

: GROUND POINTS
CODE SEE PAGE GROUND POINTS LOCATION
30 (2VZ–FE)
C
32 (3S–FE)
D 34 J/B NO. 1 SET BOLT
36 (S/D)
I
38 (STATION W/G)
36 (S/D)
K
38 (STATION W/G)
L 38 DECK RIGHT
RADIATOR LEFT
LEFT REAR FENDER
BACK PANEL CENTER
91
Page 89

TURN SIGNAL AND HAZARD W ARNING LIGHTS
7. 5A
TURN
1G12
LL
F24
A
HAZARD SW
HAZARD TURN
TURNSIGNAL
FLASHER
3
1
W–B
1L14
OFF
ON
79 5 6 518
(
I1
USA)4
(
CANADA)15
2
1
REAR LH[REAR
1
1
3
3
4
COMB. LIGHT]
4
I1
G–R G–R
6
G–W
1K
1M10 1G11 1G19 1M1
1D11B91B10 1D15
G–B G–B
(
)
C
S/D
(
D
STATION W/G
(
)
C
S/D
(
D
STATION W/G
W–B
10 8
)(
G–L
G–W
EX. USA S/D STD
(
F217
)
G–W
G–W
CANADA
1G14
1M
)
)
)
G–B
USA S/D STD
)(
G–B
USA
(
4
F218 F22
G–B
G–B
3
FRONT LH
2
W–B
7
F2
W
G–Y
G–Y
G–Y
G–Y
FE
3
FRONT RH
2
W–B
W
(
USA
G–W
(
CANADA
G–Y
G–B
G–W
G–B
G–Y
G–Y
G–Y G–Y
G–Y
V34V2
)
)
TURNSIGNAL SW
B
[COMB. SW]
(
STATION W/G
5
V1
6
)
)
S/D FWD
(
S/D ALL–TRAC/4WD
(
1G
16
G–Y
REAR RH[REAR
G–Y
G
3
H
3
G
4
COMB. LIGHT]
H
4
W–B
4
1B
RH
LH
G–Y
G–B
)
(
)
S/D
(
STATION W/G
(
)
S/D
(
STATION W/G
15A
HAZ–HORN
2F3
W
G–B
31
)
)
G–W
LH RH
G–Y
2
W–B
3B3
J/B
NO. 3
INDICATOR
LIGHTS
[COMB. METER]
W–B
I
F18
W–B
1F3
92
D
ICAK
D
Page 90

18
COWL WIRE AND J/B NO. 1 (LEFT KICK PANEL)
SERVICE HINTS
TURN SIGNAL FLASHER
2–GROUND : APPROX. 12 VOLTS WITH IGNITION SW ON OR HAZARD SW ON
1–GROUND : CHANGES FROM 12 TO 0 VOLT WITH IGNITION SW ON AND TURN SIGNAL SW LEFT OR RIGHT,
OR WITH HAZARD SW ON
3–GROUND : ALWAYS CONTINUITY
: PARTS LOCA TION
CODE SEE PAGE CODE SEE P AGE CODE SEE PAGE
A H5 28 D R11 27 G R14 26
B C14 28 E F3 24 (2VZ–FE), 25 (3S–FE) H R14 27
C R11 26 F F4 24 (2VZ–FE), 25 (3S–FE) I C12 28
: RELAY BLOCKS
CODE SEE PAGE RELAY BLOCKS (RELAY BLOCK LOCATION)
1 23 R/B NO. 1 (LEFT KICK PANEL)
: JUNCTION BLOCK AND WIRE HARNESS CONNECTOR
CODE SEE PAGE JUNCTION BLOCK AND WIRE HARNESS (CONNECTOR LOCATION)
1B 18 ENGINE ROOM MAIN WIRE AND J/B NO. 1 (LEFT KICK PANEL)
1D 18 FLOOR WIRE AND J/B NO. 1 (LEFT KICK PANEL)
1F
1G
1M
18 COWL SUB WIRE AND J/B NO. 1 (LEFT KICK PANEL)
1K
1L
18 COWL WIRE AND J/B NO. 1 (LEFT KICK PANEL)
2F 20 ENGINE ROOM MAIN WIRE AND J/B NO. 2 (ENGINE COMPARTMENT LEFT)
3B 22 INSTRUMENT PANEL WIRE AND J/B NO. 3 (INSTRUMENT PANEL LEFT)
: CONNECTOR JOINING WIRE HARNESS AND WIRE HARNESS
CODE SEE PAGE JOINING WIRE HARNESS AND WIRE HARNESS (CONNECTOR LOCATION)
F1 34 INSTRUMENT PANEL WIRE AND COWL SUB WIRE (LEFT KICK PANEL)
F2 34 INSTRUMENT PANEL WIRE AND COWL SUB WIRE (LEFT KICK PANEL)
I1 34 COWL WIRE AND INSTRUMENT PANEL WIRE (INSTRUMENT PANEL CENTER)
V1 38 LUGGAGE ROOM NO. 1 WIRE AND FLOOR NO. 1 WIRE (BACK PANEL LEFT)
V2 36
V3 36
FLOOR NO. 1 WIRE AND LUGGAGE ROOM NO. 1 WIRE (BACK PANEL LEFT)
: GROUND POINTS
CODE SEE PAGE GROUND POINTS LOCATION
30 (2VS–FE)
A
32 (3S–FE)
30 (2VS–FE)
C
32 (3S–FE)
D 34 J/B NO. 1 SET BOLT
36 (S/D)
I
38 (STATION W/G)
36 (S/D) BACK PANEL CENTER
K
38 (STATION W/G) DECK RIGHT
A GCFEGRAY
I
123
RIGHT FENDER
RADIATOR LEFT
LEFT REAR FENDER
B
1
8
55678910 34
HDBLACK
3
4
23
93
Page 91

STOP LIGHTS
(
W/ LIGHT FAILURE SENSOR
(
W/O LIGHT FAILURE SENSOR
)
)
20A
STOP
1L11 1D6
G–RG–WG–W
(
A
1
W/ CRUISE CONTROL
(
1
B
W/O CRUISE CONTROL
STOP LIGHT
SW
(
3
A
W/ CRUISE CONTROL
(
B2
W/O CRUISE CONTROL
1L10
1D8
723
G–W
G–W
)
)
)
)
D
LIGHT FAILURE SENSOR
HOLD
CIRCUIT
1 9
G–R
G–W G–W
7. 5A
GAUGE
2
1F
YY
YY
G–W
3
F1
J/B
NO. 3
3B9
6
10
REAR LIGHT
WARNING LIGHT
[COMB. METER]
C
H114
Y–G Y–G R–L
W–B
)
G–R
G–W
(
S/D ALL–
TRAC/4WD
(
S/D FWD
V31
)
)
G–R
EF HJI
2
G
2
LH RH
G
4
W–B
KILI
G–R
G–W
(
V14U12V23
STATION W/G
G–R
G–R
(
222
S/D
(
STATION W/G
STOP LIGHTS
[REAR COMB.
LIGHT]
(
S/D
(
STATION W/G
W–B
G–R
)
G–R
)
)
)
)
)
G–W
S/D
S/D
(
(
G–R
HFE
444
W–B
U13
W–B
G–RG–R
G–W
G–R
2
I
4
J
4
W–B
W–B
4
W1
(
STATION W/G
G–R
)
(
Y14
STATION W/G
G–R
2
HIGH MOUNT
STOP LIGHT
1
)
W–B
STATION W/G
(
W–B
G–W
(
S/D)W–B
)
K
W–B
W–B
94
Page 92

SYSTEM OUTLINE
CURRENT IS APPLIED AT ALL TIMES THROUGH A STOP FUSE TO TERMINAL 1 OF THE STOP LIGHT SW.
WHEN THE IGNITION SW IS TURNED ON, CURRENT FLOWS FROM THE GAUGE FUSE TO TERMINAL 2 OF THE LIGHT FAILURE
SENSOR AND THROUGH THE REAR LIGHT WARNING LIGHT TO TERMINAL 3 OF THE LIGHT FAILURE SENSOR.
STOP LIGHT DISCONNECTION WARNING
WHEN THE IGNITION SW IS TURNED ON AND THE BRAKE PEDAL IS PRESSED (STOP LIGHT SW ON), IF THE STOP LIGHT CIRCUIT IS
OPEN, THE CURRENT FLOWING FROM TERMINAL 7 OF THE LIGHT FAILURE SENSOR TO TERMINAL 1 CHANGES, SO THE LIGHT
FAILURE SENSOR DETECTS THE DISCONNECTION AND THE WARNING CIRCUIT OF THE LIGHT FAILURE SENSOR IS ACTIVATED.
AS A RESULT, THE CURRENT FLOWS FROM TERMINAL 3 OF THE LIGHT FAILURE SENSOR → TERMINAL 9 → GROUND AND TURNS
THE REAR LIGHT WARNING LIGHT ON. BY PRESSING THE BRAKE PEDAL, THE CURRENT FLOWING TO TERMINAL 2 OF THE LIGHT
FAILURE SENSOR KEEPS THE WARNING CIRCUIT ON HOLD AND THE WARNING LIGHT ON UNTIL THE IGNITION SW TURNED OFF.
SERVICE HINTS
STOP LIGHT SW
(A) 1–(A) 3 : CLOSED WITH BRAKE PEDAL DEPRESSED (W/ CRUISE CONTROL)
(B) 1–(B) 2 : CLOSED WITH BRAKE PEDAL DEPRESSED (W/O CRUISE CONTROL)
(D) LIGHT FAILURE SENSOR
1, 7–GROUND : APPROX. 12 VOLTS WITH ST OP LIGHT SW ON
2, 3–GROUND : APPROX. 12 VOLTS WITH IGNITION SW ON
9–GROUND : ALWAYS CONTINUITY
: PARTS LOCA TION
CODE SEE PAGE CODE SEE P AGE CODE SEE PAGE
A S9 28 E R11 26 I R14 26
B S9 28 F R12 26 J R14 27
C C13 28 G R11 27 K H8 26 (S/D), 27 (STATION W/G)
D L3 26 (S/D), 27 (STATION W/G) H R13 26
: JUNCTION BLOCK AND WIRE HARNESS CONNECTOR
CODE SEE PAGE JUNCTION BLOCK AND WIRE HARNESS (CONNECTOR LOCATION)
1D 18 FLOOR WIRE AND J/B NO. 1 (LEFT KICK PANEL)
1F 18 COWL SUB WIRE AND J/B NO. 1 (LEFT KICK PANEL)
1L 18 COWL WIRE AND J/B NO. 1 (LEFT KICK PANEL)
3B 22 INSTRUMENT PANEL WIRE AND J/B NO. 3 (INSTRUMENT PANEL LEFT)
: CONNECTOR JOINING WIRE HARNESS AND WIRE HARNESS
CODE SEE PAGE JOINING WIRE HARNESS AND WIRE HARNESS (CONNECTOR LOCATION)
F1 34 INSTRUMENT PANEL WIRE AND COWL SUB WIRE (LEFT KICK PANEL)
H1 34 FLOOR NO. 1 WIRE AND INSTRUMENT PANEL WIRE (LEFT KICK PANEL)
U1 36 FLOOR NO. 1 WIRE AND LUGGAGE ROOM NO. 2 WIRE (LUGGAGE COMPARTMENT DOOR)
V1 38 LUGGAGE ROOM NO. 1 WIRE AND FLOOR NO. 1 WIRE (BACK PANEL LEFT)
V2 36
V3 36
W1 38 BACK DOOR NO. 1 WIRE AND FLOOR NO. 1 WIRE (BACK PANEL LEFT)
Y1 38 BACK DOOR NO. 1 WIRE AND BACK DOOR NO. 2 WIRE (BACK DOOR LEFT)
FLOOR NO. 1 WIRE AND LUGGAGE ROOM NO. 1 WIRE (BACK PANEL LEFT)
: GROUND POINTS
CODE SEE PAGE GROUND POINTS LOCATION
36 (S/D)
I
38 (STATION W/G)
36 (S/D) BACK PANEL CENTER
K
38 (STATION W/G) DECK RIGHT
L 38 BACK DOOR RIGHT
LEFT REAR FENDER
AB C
1
3
2
4
1
2
KFH GJ
2
4
12
BROWN
610
DIE
12 3
79
2
4
95
Page 93
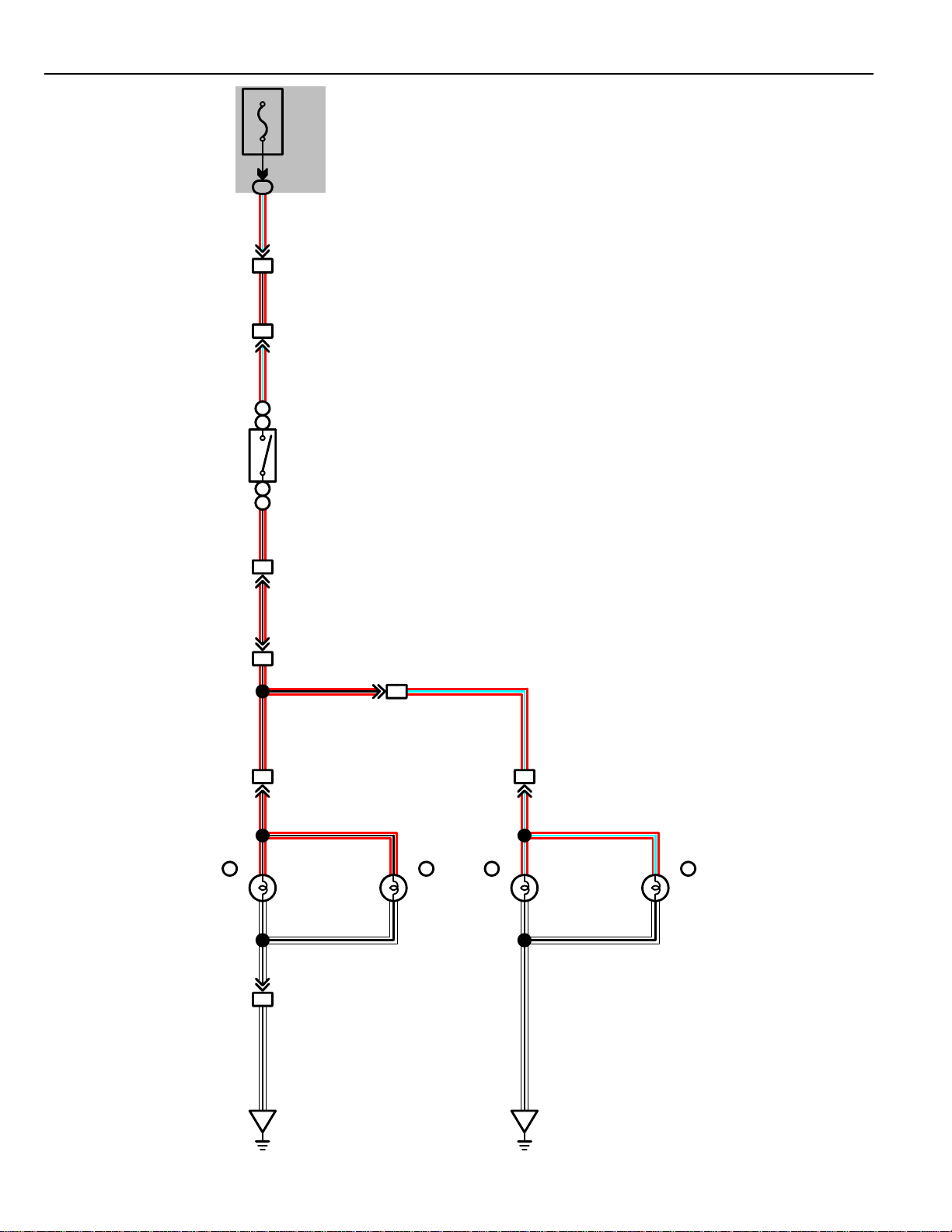
BACK–UP LIGHTS
7. 5A
GAUGE
1I11
R–LR–BR–L
D14
C13
6
A
(
)
A/T
(
)
2
B
M/T
BACK–UP
LIGHT SW
(
)
5
A/T
A
(
)
1
M/T
B
L15
R–B R–B
H112
R–B
R–B
(
STATION W/G
)
S/D
(
R–B
3311
CDEF
BACK–UP LIGHT
[REAR COMB.
LIGHT]
4444
W–B
U13
)
R–B
W–B W–B
1
W1
R–L
Y11U11
R–L
R–L
BACK–UP LIGHT
W–B
[REAR COMB.
LIGHT]
RH
RHLH
LH
96
W–B
I
W–B
L
Page 94

SERVICE HINTS
BACK–UP LIGHT SW
(A) 5–6. (B) 1–2 : CLOSED WITH SHIFT LEVER IN R POSITION
: PARTS LOCA TION
CODE SEE PAGE CODE SEE P AGE CODE SEE PAGE
A N1 24 (2VZ–FE), 25 (3S–FE) C R12 26 (S/D), 27 (STATION W/G) E R12 26 (S/D), 27 (STATION W/G)
B B1 24 (2VZ–FE), 25 (3S–FE) D R13 26 (S/D), 27 (STATION W/G) F R13 26 (S/D), 27 (STATION W/G)
: JUNCTION BLOCK AND WIRE HARNESS CONNECTOR
CODE SEE PAGE JUNCTION BLOCK AND WIRE HARNESS (CONNECTOR LOCATION)
1I 18 COWL WIRE AND J/B NO. 1 (LEFT KICK PANEL)
: CONNECTOR JOINING WIRE HARNESS AND WIRE HARNESS
CODE SEE PAGE JOINING WIRE HARNESS AND WIRE HARNESS (CONNECTOR LOCATION)
30 (2VS–FE)
C1
32 (3S–FE)
30 (2VS–FE)
D1
32 (3S–FE)
H1 34 FLOOR NO. 1 WIRE AND INSTRUMENT PANEL WIRE (LEFT KICK PANEL)
L1 34 ENGINE WIRE AND INSTRUMENT PANEL WIRE (BEHIND GLOVE BOX)
U1 36 FLOOR NO. 1 WIRE AND LUGGAGE ROOM NO. 2 WIRE (LUGGAGE COMPARTMENT DOOR)
W1 38 BACK DOOR NO. 1 WIRE AND FLOOR NO. 1 WIRE (BACK PANEL LEFT)
Y1 38 BACK DOOR NO. 1 WIRE AND BACK DOOR NO. 2 WIRE (BACK DOOR LEFT)
ENGINE ROOM MAIN WIRE AND ENGINE WIRE (NEAR J/B NO. 2)
ENGINE ROOM WIRE AND COWL WIRE (LEFT KICK PANEL)
: GROUND POINTS
CODE SEE PAGE GROUND POINTS LOCATION
I 36 LEFT REAR FENDER
L 38 BACK DOOR RIGHT
(
)(
A/T
56
M/T
)
GRAY
2
1
DCFEABGRAY
1
34
4
97
Page 95

FRONT WIPER AND WASHER
20A
WIPER
A
WIPER AND WASHER
[COMB. SW]
OFF
INT
LOW/MIST
SW(W/ WIPER RELAY
HIGH
WASHER
)
WIPER RELAY
L–R
2
B
FRONT
M
WASHER
MOTOR
1
L–W
1B1I1
DIODE
L–W
(
W/O REAR WIPER
8
16
W–B
LG
21
C
DIODE
(
FOR FRONT
WIPER
2
L–W
)
W/ REAR WIPER
(
)
)
3
1B
1I9
L
L
L
4
L–Y
7
L–B
13
L–O
L
18
W–B
1I13
L–O
D26D25D23D24
L–O
1243
+2 +1 B +S
L–B
L–B
M
L
L
L–Y
L–Y
98
D
WIPER MOTOR
D
Page 96

SYSTEM OUTLINE
WITH THE IGNITION SW TURNED ON, THE CURRENT FLOWS TO TERMINAL 18 OF THE WIPER AND WASHER SW, TERMINAL 2 OF
THE WASHER MOTOR AND TERMINAL 4 OF THE WIPER MOTOR THROUGH THE WIPER FUSE.
1. LOW SPEED POSITION
WITH WIPER SW TURNED TO LOW POSITION, THE CURRENT FLOWS FROM TERMINAL 18 OF THE WIPER AND WASHER SW →
TERMINAL 7 → TERMINAL 2 OF THE WIPER MOTOR → WIPER MOTOR → TO GROUND AND CAUSES TO THE WIPER MOTOR TO RUN
AT LOW SPEED.
2. HIGH SPEED POSITION
WITH WIPER SW TURNED TO HIGH POSITION, THE CURRENT FLOWS FROM TERMINAL 18 OF THE WIPER AND WASHER SW →
TERMINAL 13 → TERMINAL 1 OF THE WIPER MOTOR → WIPER MOTOR → TO GROUND AND CAUSES TO THE WIPER MOTOR TO
RUN AT HIGH SPEED.
3. INT POSITION (W/ INT SW)
WITH WIPER SW TURNED TO INT POSITION, THE RELAY OPERATES AND THE CURRENT WHICH IS CONNECTED BY RELAY
FUNCTION FLOWS FROM TERMINAL 18 OF THE WIPER AND WASHER SW → TERMINAL 16 → TO GROUND. THIS FLOW OF CURRENT
OPERATES THE INTERMITTENT CIRCUIT AND THE CURRENT FLOWS FROM TERMINAL 18 OF THE WIPER AND WASHER SW →
TERMINAL 7 → TERMINAL 2 OF THE WIPER MOTOR → TO GROUND AND THE WIPER FUNCTIONS.
THE INTERMITTENT OPERATION IS CONTROLLED BY A CONDENSER’S CHARGED AND DISCHARGED FUNCTION INSTALLED IN
RELAY AND THE INTERMITTENT TIME IS CONTROLLED BY A TIME CONTROL SW TO CHANGE THE CHARGING TIME OF THE
CONDENSER.
4. WASHER CONTINUOUS OPERATION (W/ INT CONTROL)
WITH WASHER SW TURNED TO ON, THE CURRENT FLOWS FROM TERMINAL 2 OF THE WASHER MOTOR → TERMINAL 1 →
TERMINAL 8 OF THE WIPER AND WASHER SW → TERMINAL 16 → TO GROUND AND CAUSES TO THE WASHER MOTOR TO RUN AND
WINDOW WASHER TO JET. THIS CAUSES THE CURRENT TO FLOW TO WASHER CONTINUOUS OPERATION CIRCUIT (W/ INT SW) IN
TERMINAL 18 OF THE WIPER AND WASHER SW → TERMINAL 7 → TERMINAL 2 OF THE WIPER MOTOR → TO GROUND AND THE
WIPER FUNCTION.
SERVICE HINTS
(A) WIPER AND WASHER SW
16–GROUND : ALWAYS CONTINUITY
18–GROUND : APPROX. 12 VOLTS WITH IGNITION SW AT ON POSITION
7–GROUND : APPROX. 12 VOLTS WITH WIPER AND WASHER SW AT LOW POSITION
4–GROUND : APPROX. 12 VOLTS WITH IGNITION SW ON UNLESS WIPER MOTOR AT STOP POSITION
13–GROUND : APPROX. 12 VOLTS WITH WIPER AND WASHER SW AT HIGH POSITION
(D) WIPER MOTOR
3–4 : CLOSED UNLESS WIPER MOTOR A T STOP POSITION
APPROX. 12 VOLTS EVERY 4 SECONDS INTERMITTENTLY WITH WIPER SW AT INT POSITION
: PARTS LOCA TION
CODE SEE PAGE CODE SEE P AGE CODE SEE PAGE
A C15 28 C D14 28
B F5 24 (2VZ–FE), 25 (3S–FE) D W2 24 (2VZ–FE), 25 (3S–FE)
: JUNCTION BLOCK AND WIRE HARNESS CONNECTOR
CODE SEE PAGE JUNCTION BLOCK AND WIRE HARNESS (CONNECTOR LOCATION)
1B 18 ENGINE ROOM MAIN WIRE AND J/B NO. 1 (LEFT KICK PANEL)
1I 18 COWL WIRE AND J/B NO. 1 (LEFT KICK PANEL)
: CONNECTOR JOINING WIRE HARNESS AND WIRE HARNESS
CODE SEE PAGE JOINING WIRE HARNESS AND WIRE HARNESS (CONNECTOR LOCATION)
30 (2VZ–FE)
D2
32 (3S–FE)
ENGINE ROOM MAIN WIRE AND COWL WIRE (RIGHT KICK PANEL)
: GROUND POINTS
CODE SEE PAGE GROUND POINTS LOCATION
D 34 J/B NO. 1 SET BOLT
ABBLACK
478
13 16
18
21
12
DGRAYCBLACKGRAY
12
34
99
Page 97

REAR WIPER AND WASHER
20A
WIPER
1B31I9
L–RL–B
L
2
REARWASHER
M
MOTOR
1
A
REARWIPER AND WASHER SW
B
WASHER2
INT
OFF
WASHER1
57 8
L–BL–B
A
GRAY
12
B
578
LG–B
CGRAY
LG–BLG–B
G113
LLL
W31
Y31 Y34Y36F28
D DD
REAR WIPER RELAY
1
1B6
1G13
DIODE
(
FORREARWIPER
L–R
2
C
)
1
LG
H11H17
W34
LG–B
LG–B
L–B L–B
W36
L–BL–B
321
64
21
W–B
W–B
D
123
3C16
J/B
NO. 3
W–BW–B
100
IC
23 5
L+B
S
M
REAR WIPER
MOTOR
F18
1F3
D
Page 98

SYSTEM OUTLINE
WHEN THE IGNITION SW IS TURNED ON, CURRENT FLOWS THROUGH THE WIPER FUSE TO TERMINAL 1 OF THE REAR WIPER
RELA Y, TERMINAL +B OF THE REAR WIPER MOTOR AND TERMINAL 2 OF THE REAR WASHER MOTOR.
1. REAR WIPER OPERATION
WHEN THE IGNITION SW IS ON AND THE REAR WIPER AND WASHER SW IS TURNED TO THE INT POSITION, THE CURRENT
FLOWING TO TERMINAL 1 OF THE REAR WIPER RELAY FLOWS TO TERMINAL 4 OF RELAY → TERMINAL 7 OF REAR WIPER AND
WASHER SW → TERMINAL 8 → GROUND, CAUSING THE RELAY INTERMITTENT CIRCUIT TO OPERATE SO THAT THE CURRENT
FLOWING TO TERMINAL 1 OF THE RELAY FLOWS TO TERMINAL 3 → TERMINAL L OF REAR WIPER MOTOR → GROUND. THIS
CAUSES THE WIPER MOTOR T O OPERATE THE WIPER.
2. WASHER OPERATION (WIPER OFF)
WHEN THE WASHER SW IS PUSHED WITH THE IGNITION SW ON AND THE WIPER OFF, THE CURRENT FLOWING TO TERMINAL 2 OF
THE REAR WASHER MOTOR FLOWS TO TERMINAL 1 OF THE MOTOR → TERMINAL 5 OF REAR WIPER AND WASHER SW →
TERMINAL 8 → GROUND, AND THE WASHER SPRAYS ONLY WHILE THE SW IS PUSHED. THIS CURRENT FLOW CAUSES THE
CURRENT FLOWING TO TERMINAL 1 OF REAR WIPER RELAY TO FLOW TO TERMINAL 6 → TERMINAL 5 OF WIPER AND WASHER SW
→ TERMINAL 8 → GROUND, CAUSING THE CONTINUOUS OPERATION CIRCUIT OF THE RELAY TO OPERATE. ACCORDINGLY, THE
CURRENT FLOWING TO TERMINAL 1 OF THE RELAY FLOWS TO TERMINAL 3 OF RELAY → TERMINAL L OF WIPER MOTOR →
GROUND, CAUSING THE WIPER TO OPERA TE CONTINUOUSLY. THE WIPER CONTINUES TO OPERATE FOR APPROX. 3 SECS. AFTER
THE WASHER SW IS TURNED OFF.
3. WASHER OPERATION (WIPER ON)
WHEN THE WIPER AND WASHER SW IS PUSHED MORE STRONGLY DURING WIPER OPERATION, THE CURRENT FLOWING TO
TERMINAL 2 OF THE WASHER MOTOR FLOWS TO TERMINAL 1 → TERMINAL 5 OF WIPER AND WASHER SW → TERMINAL 8 →
GROUND, SO THE WASHER SPRAYS ONLY WHILE THE SW IS PRESSED. THIS CURRENT FLOW CAUSES THE CURRENT FLOWING
TO TERMINAL 1 OF RELAY TO FLOW TO TERMINAL 6 → TERMINAL 5 OF WIPER AND WASHER SW → TERMINAL 8 → GROUND,
CAUSING THE CONTINUOUS OPERATION SWITCH OF THE RELAY TO OPERATE. THE CURRENT FLOWING TO TERMINAL 1 OF RELAY
THEN FLOWS TO TERMINAL 3 OF RELAY → TERMINAL L OF WIPER MOTOR → GROUND, CAUSING THE WIPER TO OPERATE
CONTINUOUSLY. THE WIPER CONTINUES TO OPERATE FOR APPROX. 3 SECS. AFTER THE WASHER SW IS TURNED OFF.
SERVICE HINTS
(A) REAR WASHER MOTOR
2–GROUND : APPROX. 12 VOLTS WITH IGNITION SW AT ON POSITION
1–GROUND : CONTINUITY WITH WASHER SW TURNED ON
REAR WIPER RELAY
1–GROUND : APPROX. 12 VOLTS WITH IGNITION SW AT ON POSITION
5–GROUND : ALWAYS CONTINUITY
1–3 : POINTS CHANGES EVERY 12 SECONDS INTERMITTENTLY WITH IGNTION SW ON AND WIPER SW AT INT POSITION
: PARTS LOCA TION
CODE SEE PAGE CODE SEE P AGE CODE SEE PAGE
A R3 24 (2VZ–FE), 25 (3S–FE) C D15 28
B R7 28 D R20 27
: JUNCTION BLOCK AND WIRE HARNESS CONNECTOR
CODE SEE PAGE JUNCTION BLOCK AND WIRE HARNESS (CONNECTOR LOCATION)
1B 18 ENGINE ROOM MAIN WIRE AND J/B NO. 1 (LEFT KICK PANEL)
1F
1G
3C 22 INSTRUMENT PANEL WIRE AND J/B NO. 3 (INSTRUMENT PANEL LEFT)
18 COWL SUB WIRE AND J/B NO. 1 (LEFT KICK PANEL)
1I 18 COWL WIRE AND J/B NO. 1 (LEFT KICK PANEL)
: CONNECTOR JOINING WIRE HARNESS AND WIRE HARNESS
CODE SEE PAGE JOINING WIRE HARNESS AND WIRE HARNESS (CONNECTOR LOCATION)
F1
34 INSTRUMENT PANEL WIRE AND COWL SUB WIRE (LEFT KICK PANEL)
F2
G1 34 FLOOR NO. 1 WIRE AND COWL WIRE (LEFT KICK PANEL)
H1 34 FLOOR NO. 1 WIRE AND INSTRUMENT PANEL WIRE (LEFT KICK PANEL)
W3 38 BACK DOOR NO. 1 WIRE AND FLOOR NO. 1 WIRE (BACK PANEL LEFT)
Y3 38 BACK DOOR NO. 1 WIRE AND BACK DOOR NO. 2 WIRE (BACK DOOR LEFT)
: GROUND POINTS
CODE SEE PAGE GROUND POINTS LOCATION
D 34 J/B NO. 1 SET BOLT
101
Page 99

POWER WINDOWS
W–B
A
POWER WINDOW MASTER SW
+
–
7. 5A
GAUGE
1I11
R–L
11
12
34
11
30A
POWER
CB
1
1
W–L
POWER MAIN
RELAY
LL
E110
7
UP
L
L
8
FRONT LH FRONT RH
DOWN
UP
L
DOWN
+
–
LOCK
NORMAL
1
W–B
W–B
1L9
5
1K
D
2 6 13 12
W–B
R
W–B
E22
W–B
R
BD
21
M
FRONT LH
G
L
O24O22O23
L
52 3
UP
POWER WINDOW
SW
14
G
POWER WINDOW MOTORS
G
G–W
E15E16
G–W G–L
FRONT RH
21
FRONT RH
5
R–LR–LR–L
C
DOWN
R
M
L
102
Page 100

SERVICE HINTS
(A) POWER WINDOW MASTER SW
7, 8–GROUND: APPROX. 12 VOLTS WITH IGNITION SW AT ON POSITION
2–GROUND : ALWAYS CONTINUITY
6–GROUND : APPROX. 12 VOLTS WITH IGNITION SW ON AND MASTER SW
(DRIVER’S WINDOW) UP
13–GROUND : APPROX. 12 VOLTS WITH IGNITION SW ON AND MASTER SW
(DRIVER’S WINDOW) DOWN OR DOWN HOLD
WINDOW LOCK SW
OPEN WITH WINDOW LOCK SW AT LOCK POSITION
A
621
7 8 9 10 11 12 14513
CGE
HBDF
1
2
12
345
L
REAR LH REAR RH
UP
10 14119
E13E14E28E23
DOWN
R–Y
UP
G–B
R–B
12345
DOEN
L
G–Y G–Y
L
LL
G15
S15S11
L L
POWER WINDOW
SW
G13G14
G–Y
G–B
35 1
UP
REAR LH REAR RH
42 42
G
2 21 1
REAR LH REAR RH
R–Y
L
N11N111
R–Y
S14T15
R–B
E G
DOWN
F
M
R
POWER WINDOW MOTORS
L
POWER WINDOW
SW
G–B
LLL
G–B
T11T14
G–B
35 1
UP
G
R–B
N15
R–BR–B
DOWN
H
M
R
103
 Loading...
Loading...