Toyota 7FBE10 Owner's Manual

FOREWORD
This manual covers the service procedures of the TOYOTA ELECTRIC
POWERED FORKLIFT 7FBE10 to 20 series.
Please use these manuals for providing quick, correct servicing of the corresponding forklift models.
This manual deals with the above models as of February 2003. Please understand that disagreement can take place between the descriptions in the manual and actual vehicles due to change in design and specifications. Any
change or modifications thereafter will be informed by Toyota Industrial
Equipment Parts & Service News.

SECTION INDEX
GENERAL 0
BATTERY 1
CHARGER (OPT) 2
CONTROLLER 3
MULTI-DISPLAY FUNCTIONS 4
TROUBLESHOOTING 5
MOTOR 6
DRIVE UNIT & FRONT AXLE 7
REAR AXLE 8
STEERING 9
BRAKE 10
BODY & FRAME 11
MATERIAL HANDLING SYSTEM 12
MAST 13
CYLINDER 14
OIL PUMP 15
OIL CONTROL VALVE 16
SAS FUNCTIONS (OPT) 17
APPENDIX 18
SECTION
NAME
0-1
GENERAL
Page Page
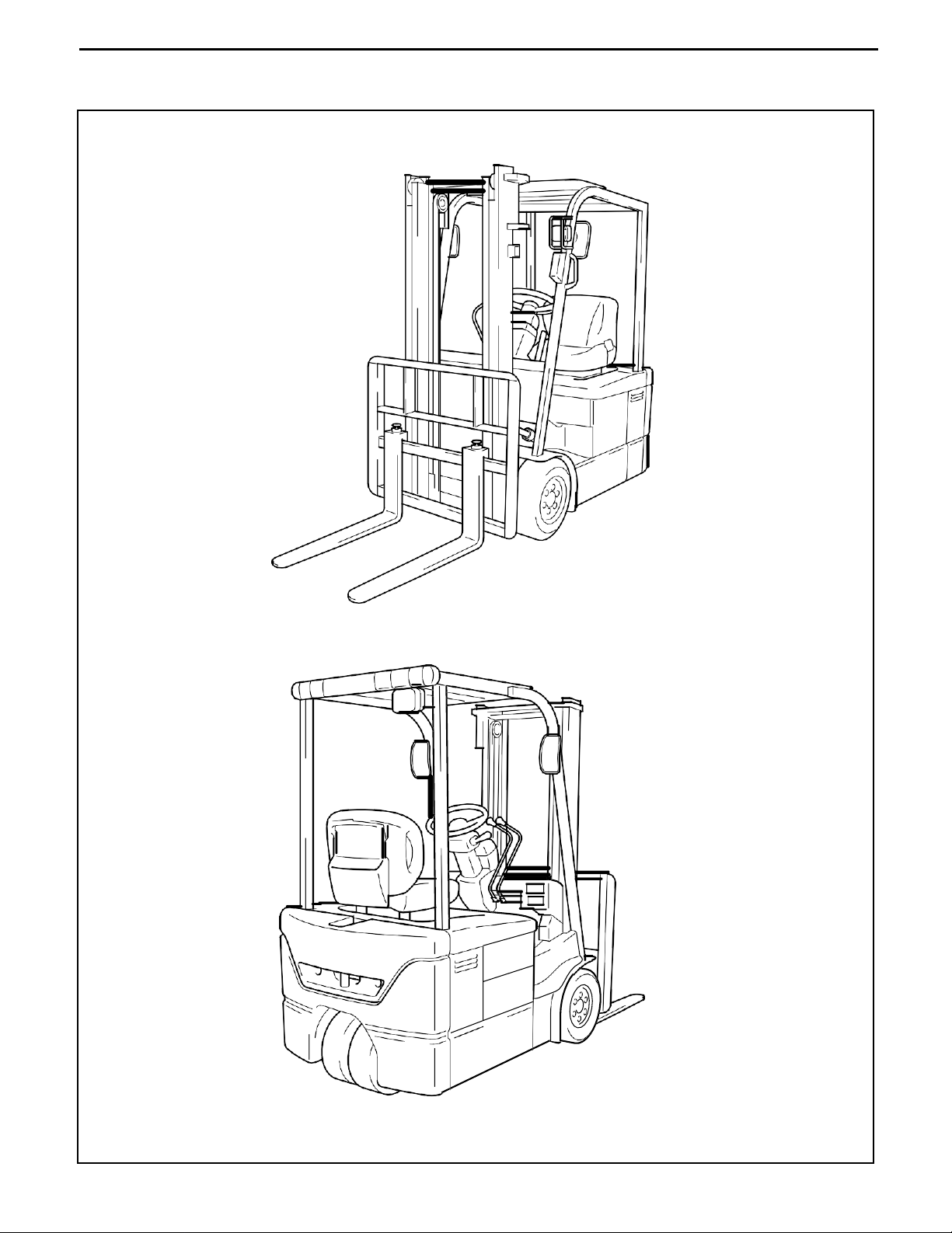
VEHICLE EXTERIOR VIEW........... 0-2 HIGH PRESSURE HOSE FITTING
VEHICLE MODELS ...................... 0-3
TIGHTENING TORQUE ......... .. 0-17
0
FRAME NUMBER .........................
0-3
HOW TO USE THIS MANUAL ......
0-4
EXPLANATION METHOD ..................
0-4
TERMINOLOGY .................................
0-5
ABBREVIATIONS ..............................
0-5
SI UNITS .............................................
0-6
OPERATING TIPS .........................
0-7
GENERAL INSTRUCTIONS ..............
0-7
JACK-UP POINT ................................
0-8
HOISTING THE VEHICLE ..................
0-9
WIRE ROPE SUSPENSION ANGLE
LIST .............................................. 0-10
SAFE LOAD FOR EACH WIRE ROPE
SUSPENSION ANGLE ................. 0-10
MEMBER WEIGHTS ......................... 0-11
TOWING THE VEHICLE ................... 0-11
ELECTRICAL PARTS
INSPECTION .................................
0-12
NOTES ON SAS ...............................
0-14
STANDARD BOLT & NUT
TIGHTENING TORQUE ............0-15
BOLT STRENGTH CLASS
IDENTIFICATION METHOD ......... 0-15
TIGHTENING TORQUE TABLE ....... 0-16
PRECOATED BOLTS ......................... 0-17
RECOMMENDED LUBRICANT
QUANTITY AND TYPES ......... 0-18
LUBRICATION CHART .............. 0-19
PERIODIC MAINTENANCE ....... 0-20
PERIODIC REPLACEMENT OF
PARTS AND LUBRICANTS .... 0-25
0-2
VEHICLE EXTERIOR VIEW

0-3
VEHICLE MODELS
0
FRAME NUMBER
Vehicle model
Drive motor model
Punching format
Punching position
7FBE10
AR09
7FBE13-50011
Punching position
7FBE13
7FBE15
7FBE18-50011
7FBE18
7FBE20
7FBE20-50011
Vehicle model code
Payload (ton)
Vehicle Model
Control method
Voltage (V)
10
1.0
7FBE10
AC microcomputer controller
48
13
1.25
7FBE13
15
1.5
7FBE15
18
1.75
7FBE18
20
2.0
7FBE20
0-4
1 9 5
T = 46.1 to 48.1
(470 to 490)
[34.0 to 35.5]
6
5 7 3
2
1
4
•
Some step numbers may be
omitted in some illustrations.
HOW TO USE THIS MANUAL
EXPLANATION METHOD
1.
Operating procedure
(1)
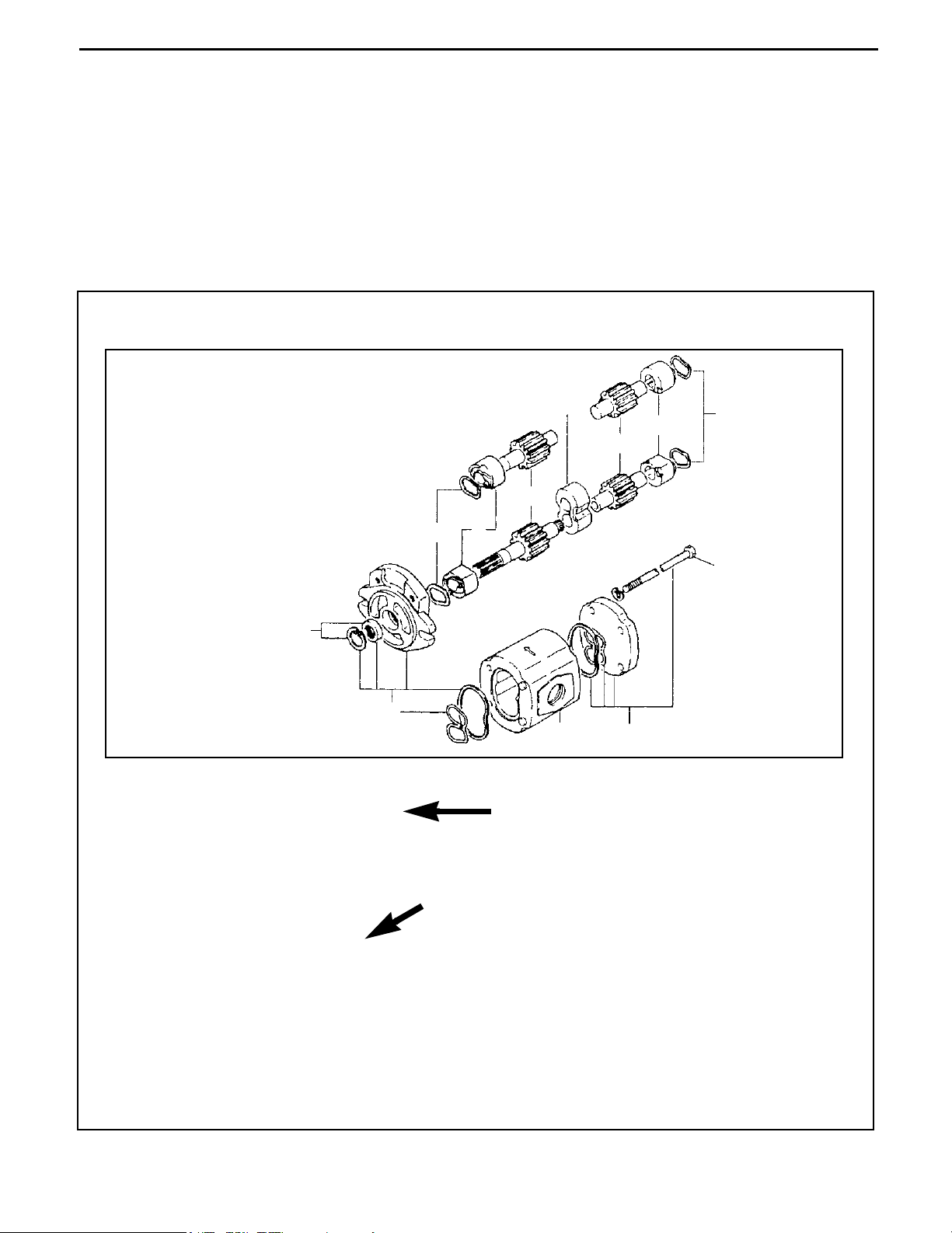
Operating procedures are described using either pattern A or pattern B.
Pattern A: Each step of the operation is explained with its own illustration.
Pattern B: The entire operation is indicated by step numbers in one illustration, followed by
cautions, notes, and point operations.
Example of pattern B
DISASSEMBLY · INSPECTION · REASSEMBLY
Tightening torque unit T=N·m(kg·m)[ft·lbf]
Disassembly Procedure
1
Remove the cover. [Point 1]
2
Remove the bushing. [Point 2]
3
Remove the gear.
Point Operations
[POINT 1]
Disassembly:
Operation to be explained
Explanation of operation point with illustration
Make match marks before removing the pump cover
[POINT 2]
Inspection:
Measure the bushing inside diameter.
Limit 19.12 mm
8
0-5
1.
How to read component figures
(1)
The component figures use the illustration in the parts
catalog for the vehicle model. Please refer to the catalog
to check the part name.
2.
Matters omitted from this manual
(Example)
3201
Parts catalog
FIG number
(1)
This manual omits descriptions of the following jobs, but perform them in actual operation:
(a)
Cleaning and washing of removed parts as required
(b)
Visual inspection (partially described)
0
TERMINOLOGY
CAUTION:
Important matters, negligence of which may cause accidents. Be sure to observe them.
NOTE:
Important items, negligence of which may cause accidents, or matters in operating procedure
which require special attention.
Standard: Value showing the allowable range in inspection or adjustment
Limit: The maximum or minimum value allowed in inspection or adjustment.
ABBREVIATIONS
Abbreviation
Meaning
Abbreviation
Meaning
ASSY
Assembly
SAE
Society of Automotive Engineers
(USA)
ATT
Attachment
SAS
System of active stability
LH
Left Hand
SST
Special Service Tool
L/
Less
STD
Standard
OPT
Option
T=
Tightening Torque
O/S
Oversize
T
Number of teeth (T)
PS system
Power Steering
U/S
Undersize
RH
Right Hand
W/
With

0-6
SI UNITS
Meaning of SI
This manual uses SI units. SI represents the International System of Units, which was established to unify
the various systems of units used in the past for smoother international technical communication.
New Units Adopted in SI
Item
New unit
Conventional
unit
Conversion rate*1 (1 [conventional unit] = X [SI
unit])
Force*
2
N (newton)
kgf
1 kgf = 9.80665 N
Torque
*2
(Moment)
N·m
kgf·cm
1 kgf·cm = 9.80665 N·m
Pressure*
2
Pa (pascal)
kgf/cm
2
1 kgf/cm2 = 98.0665 kPa = 0.0980665 MPa
mmHg
1 mmHg = 0.133322 kPa
Revolving speed
rpm
rpm
1 rpm = 1 r/min
Spring con-
N/mm
kgf/mm
1 kgf/mm = 9.80665 N/mm
Volume l
cc
1 cc = 1 ml
Power W
PS system
1 PS = 0.735499 kW
Heat quantity
W·h
cal
1 kcal = 1.16279 W·h
Specific fuel
g/W·h
g/PS·h
1 g/PS·h = 1.3596 g/kW·h
<Reference>
*
1: X represents the value in SI units as converted from 1 [in conventional units], which can be
used as the rate for conversion between conventional and SI units.
*
2: In the past, kilogram [kg] representing mass was often used in place of weight kilogram [kgf],
which should be used as the unit of force.
Conversion between Conventional and SI Units
Equation for conversion
When converting, change the unit of the value in conventional or SI units to the one in the
conversion rate column in the table above before calculation. For example, when converting 100 W
to the value in conventional unit PS, first change it to 0.1 kW and divide by the conversion rate
0.735499.
Value in SI unit = Conversion rate Value in conventional unit
Conversion rate: Figure corresponding
to X in the conversion rate column in
the table above
Value in conventional unit = Value in SI unit Conversion rate

0-7
OPERATING TIPS
GENERAL INSTRUCTIONS
1.
Skillful operation
(1)
Prepare the tools, necessary measuring instruments (circuit tester, megohmmeter, oil pressure
gauge, etc.) and SSTs before starting operation.
(2)
Check the cable color and wiring state before disconnecting any wiring.
(3)
When overhauling functional parts, complicated sections or related mechanisms, arrange the parts
neatly to prevent confusion.
(4)
When disassembling and inspecting a precision part such as the control valve, use clean tools and
operate in a clean location.
(5)
Follow the specified procedures for disassembly, inspection and reassembly.
(6)
Always replace gaskets, packing, O-rings, self-locking nuts and cotter pins with new ones each
time they are disassembled.
(7)
Use genuine Toyota parts for replacement.
(8)
Use specified bolts and nuts and observe the specified tightening torque when reassembling.
(Tighten to the medium value of the specified tightening torque range.) If no tightening torque is
specified, use the value given in the “standard tightening torque table”.
2.
Protection of functional parts (battery operated vehicles)
(1)
Before connecting the battery plug after vehicle inspection or maintenance, thoroughly check each
connector for any connection failure or imperfect connection.
Failure or imperfect connection of connectors related to controllers, especially, may damage
elements inside the controllers.
3.
Defect status check
Do not start disassembly and/or replacement immediately, but first check that disassembly and/or
replacement is necessary for the defect.
4.
Waste fluid disposal
Always use a proper container when draining waste fluid from the vehicle.
Careless discharge of oil, fuel, coolant, oil filter, battery or other harmful substance may adversely
affect human health and the environment. Always collect and sort well, and ask specialized companies
for appropriate disposal.
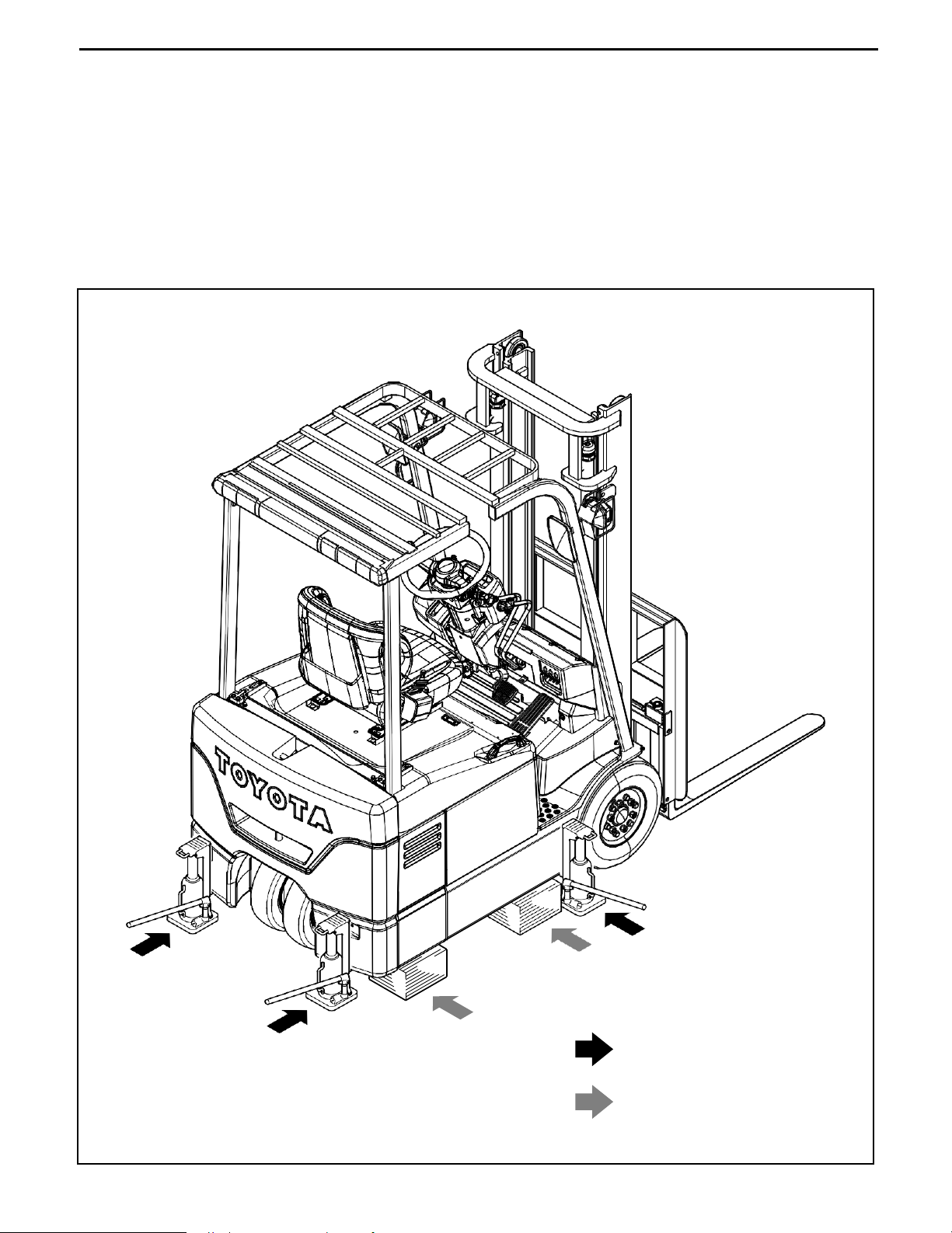
0-8
Jack-up point
JACK-UP POINT
Always observe the following instructions when jacking up the vehicle:
•
When the fork is loaded, unload it and park the vehicle on a flat surface. Be sure to avoid an
inclined or rough surface.
•
Use a jack with ample capacity and jack up the vehicle at the specified jack-up point. Jacking up
at any other point is dangerous.
•
Always support the load of jacked-up vehicle with wooden blocks at specified points.
Supporting the vehicle with the jack only is very dangerous.
•
Never, under any circumstances, put any part of the body (including hands and feet) under the
jacked-up vehicle.
Wooden block or stand
setting points
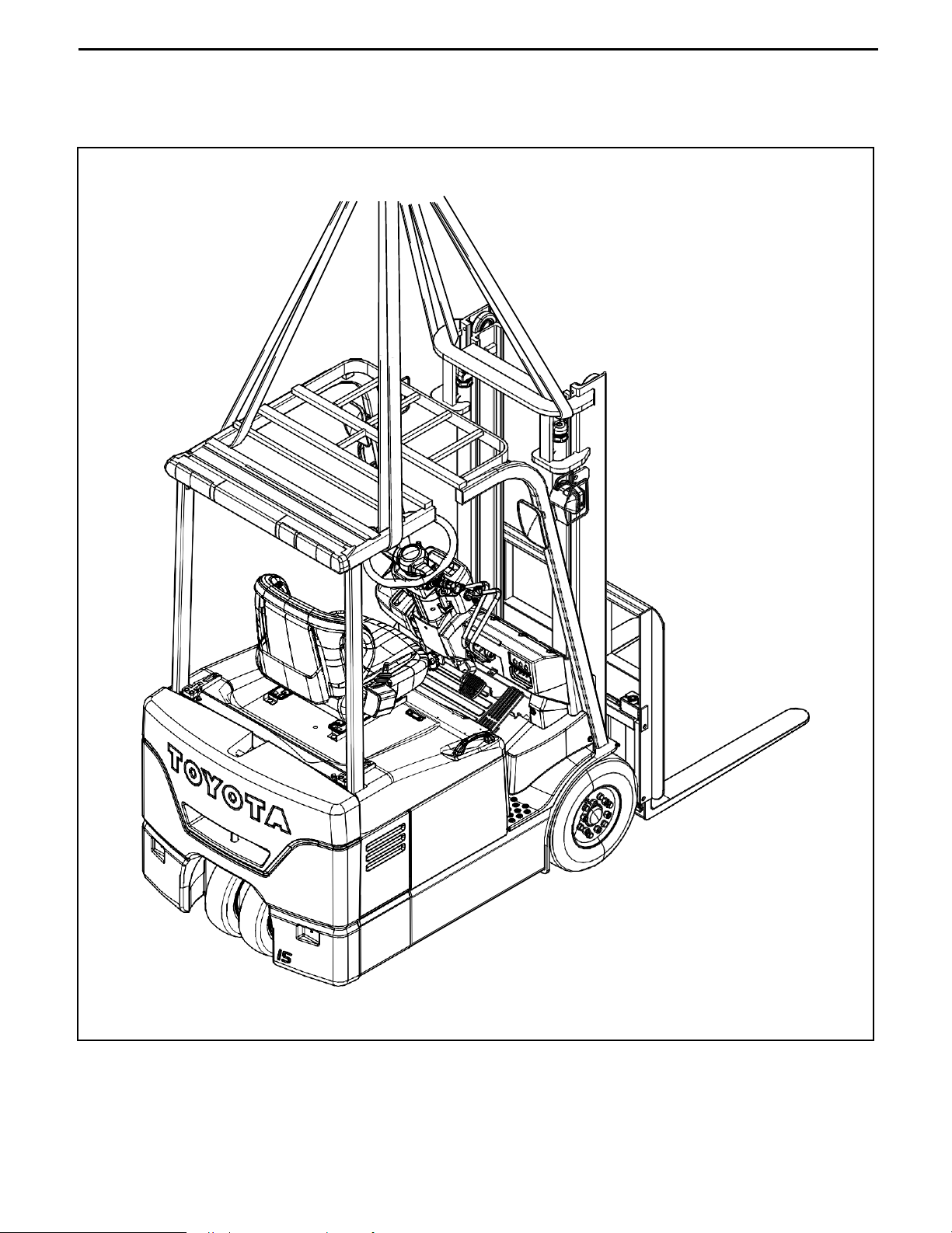
0-9
HOISTING THE VEHICLE
When hoisting the vehicle, always observe the specified hoist attachment section and method. Never hoist
by any other attachment section as it is very dangerous.

0-10
1tf
WIRE ROPE SUSPENSION ANGLE LIST
Suspension
Angle
Tension
Compression
Suspension
method
Suspension
Angle
Tension
Compression
Suspension
method
0
1.00
time
0 time
2t
90
1.41
time
1.00 time
90
2t
30
1.04
time
0.27 time
30
2t
120
2.00
time
1.73 time
120
2t
60
1.16
time
0.58 time
60
2t
SAFE LOAD FOR EACH WIRE ROPE SUSPENSION ANGLE
Unit: N (tf) [lbf]
Rope
diameter
Cutting
load
Single-
rope
Two-rope suspension
four-rope suspension
0
0
30
60
90
0
30
60
90
6 mm
(0.24 in)
21380
(2.18)
[4807]
3040
(0.31)
[683.6]
6080
(0.62)
[1367]
5880
(0.6)
[1323]
5200
(0.53)
[1169]
4310
(0.44)
[970]
12160
(1.24)
[2734]
11770
(1.2)
[2646]
10400
(1.06)
2337
8630
(0.88)
[1940]
8 mm
(0.32 in)
31480
(3.21)
[7078]
4410
(0.45)
[992.3]
8830
(0.9)
[1985]
8530
(0.87)
[1918]
7650
(0.78)
[1720]
6280
(0.64)
[1411]
17650
(1.8)
[3969]
17060
(1.74)
[3937]
15300
(1.56)
[3440]
12550
(1.28)
[2322]
10 mm
(0.4 in)
49230
(5.02)
[11690]
6960
(0.71)
[1565.6]
14020
(1.43)
[3153]
13440
(1.37)
[3021]
11770
(1.2)
[2646]
9810
(1.0)
[2205]
27460
(2.8)
[6174]
26480
(2.7)
[5954]
23540
(2.4)
[5292]
19610
(2.0)
[4410]
12.5 mm
(0.5 in)
76880
(7.84)
[17387]
10980
(1.12)
[2469.5]
21570
(2.2)
[4851]
21280
(2.1)
[4631]
18630
(1.9)
[4190]
14710
(1.5)
[3308]
43150
(4.4)
[9702]
41190
(4.2)
[9261]
37270
(3.8)
[8379]
29420
(3.0)
[6615]
14 mm
(0.56 in)
96400
(9.83)
[21675]
13730
(1.4)
[3087]
27460
(2.8)
[6174]
26480
(2.7)
[5954]
23540
(2.4)
[5292]
18630
(1.9)
[4190]
54920
(5.6)
[12348]
52960
(5.4)
[11907]
47070
(4.8)
[10584]
37270
(3.8)
[8379]

0-11
MEMBER WEIGHTS
Unit: kg (lbs)
Member
Vehicle model
Weight
BATTERY ASSY
See P1-2
Drive motor ASSY
All Models
Approx. 37 (82)
Pump motor ASSY
All Models
Approx. 31 (68)
Front axle ASSY W/ drive motor ASSY
All Models
Approx. 122 (269)
Rear axle ASSY W/ rear axle cylinder ASSY
All Models
Approx. 45 (99)
Counterweight
7FBE10
Approx. 405 (893)
7FBE13
Approx. 598 (1319)
7FBE15
Approx. 697 (1537)
7FBE18
Approx. 853 (1881)
7FBE20
Approx. 1040 (2293)
Mast ASSY W/ lift bracket (W/ lift cylinder, L/ fork,
Lifting height 3000mm, V mast)
7FBE10 to 7FBE18
330 (730)
7FBE20
400 (880)
Vehicle weight
7FBE10
2225 (4906)
7FBE13
2425 (5347)
7FBE15
2685 (5920)
7FBE18
2840 (6262)
7FBE20
3155 (6957)
TOWING THE VEHICLE
Note the cautions below when towing the vehicle.
1.
Lift the rear wheels for towing
2.
The traveling speed when towing must not exceed the
maximum traveling speed of the forklift.
3.
Before starting towing, always set the key switch to OFF
and the direction switch to the neutral position.
4.
Before towing, either remove the fork or take action to
prevent the fork from coming into contact with the
ground due to bouncing.

0-12
ELECTRICAL PARTS INSPECTION
1.
Always disconnect the battery plug before inspecting or servicing electrical parts.
2.
Pay sufficient attention when handling electronic parts.
(1)
Never subject electronic parts, such as computers
and relays, to impact.
(2)
Never expose electronic parts to high temperature or
moisture.
(3)
Do not touch connector terminals, as they may be
deformed or damaged due to static electricity.
3.
Use a circuit tester that matches the object and purpose of measurement.
Analog type: This type is convenient for observing movement during operation and the operating
condition. Measured value is only a reference
Digital type: A fairly accurate reading is possible. However, it is difficult to observe operation or
movement.
(1)
Difference between results of measurement with analog and digital types
The results of measurements using the analog type and the digital type may be different.
Differences between the polarities of the analog type and the digital type are described below.
1)
Analog circuit tester
Example of measurement result
Tester range: k range
Analog type
Forward
Continuity
11 k
Reverse
No continuity
2)
Digital circuit tester
Example of measurement result
Tester range: 2 M range
Digital type
Forward
No continuity
1
Reverse
Continuity
2 M
Forward
Reverse
Forward
Reverse
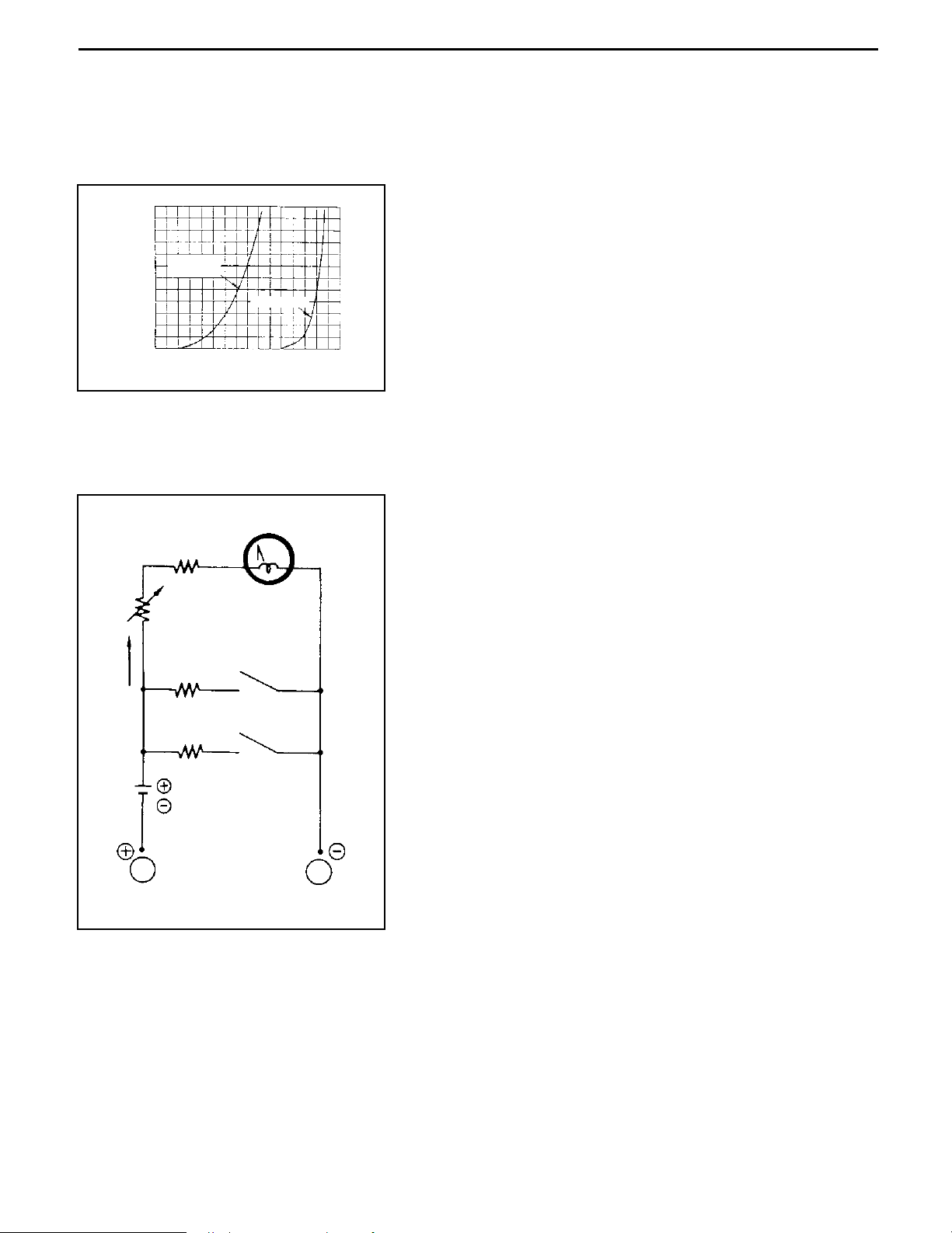
0-13
(2)
Difference in result of measurement with a circuit tester
The circuit tester power supply voltage depends on the tester type. 1.5 V, 3.0 V or 6.0 V is used.
The resistance of a semiconductor, such as a diode, varies with the circuit tester power supply
voltage.
The diode characteristics are shown in the figure below.
The resistance values of the same semiconductor measured
with two types of circuit testers having different power supply
voltages are different.
This manual describes the results of measurement with a
circuit tester whose power supply voltage is 3.0 V.
(3)
Difference in measurement result by measurement range (analog type)
In the analog type circuit tester, changing the measurement range switches over the internal circuit
to vary the circuit resistance. Even when the same diode is measured, the measurement result
varies with the measurement range.
Always use the range described in the repair manual for
measurement.
Germanium
diode
Silicon
diode
(V)
0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4 0.5 0.6 0.7 0.8
Forward voltage
4
3
2
1
0
6
5 (mA)
Power source: 1.5V
Range:1
(SW1)
Resistor
Range:10
Resistor
0
Variable resistor
Meter
Resistor
Black
Red
Forward current Current flow

0-14
NOTES ON SAS
1.
For the explanations of SAS functions and operation, also see “New Model Feature 7FBE10 to 20 Pub.
No.PE314”.
2.
See page 17-6 FOR REPAIR WORK of this repair manual before servicing.
3.
If repair or replacement is performed in any section of the vehicle that relates to SAS function, perform
necessary matching to ensure proper SAS function (see page 4-47).
4.
always be sure to operate the vehicle carefully. Be aware of the difference in control features between
with and without SAS.
5.
Many precision valves are used in the SAS oil control valves. When disassembling or replacing
hydraulic parts (valves, piping, etc.), be sure to clean the parts before installation. Periodic change of
the hydraulic oil is also very important.
6.
As the vehicle is equipped with high-precision electronic devices, modification of electrical parts may
cause vehicle failure. Be sure to use genuine Toyota parts for replacement and installation of the
electrical parts (auxiliary equipment, optional parts, etc.).
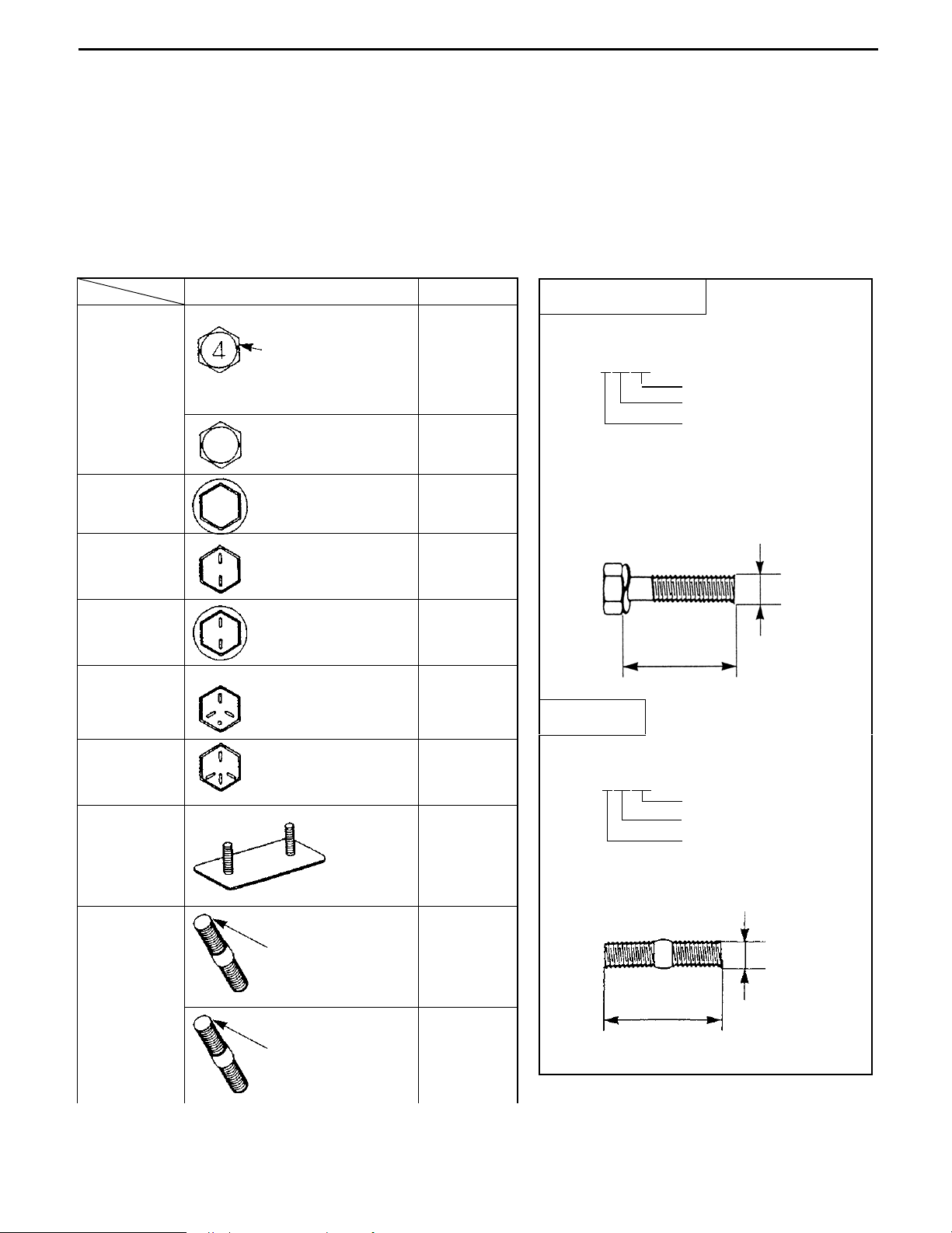
0-15
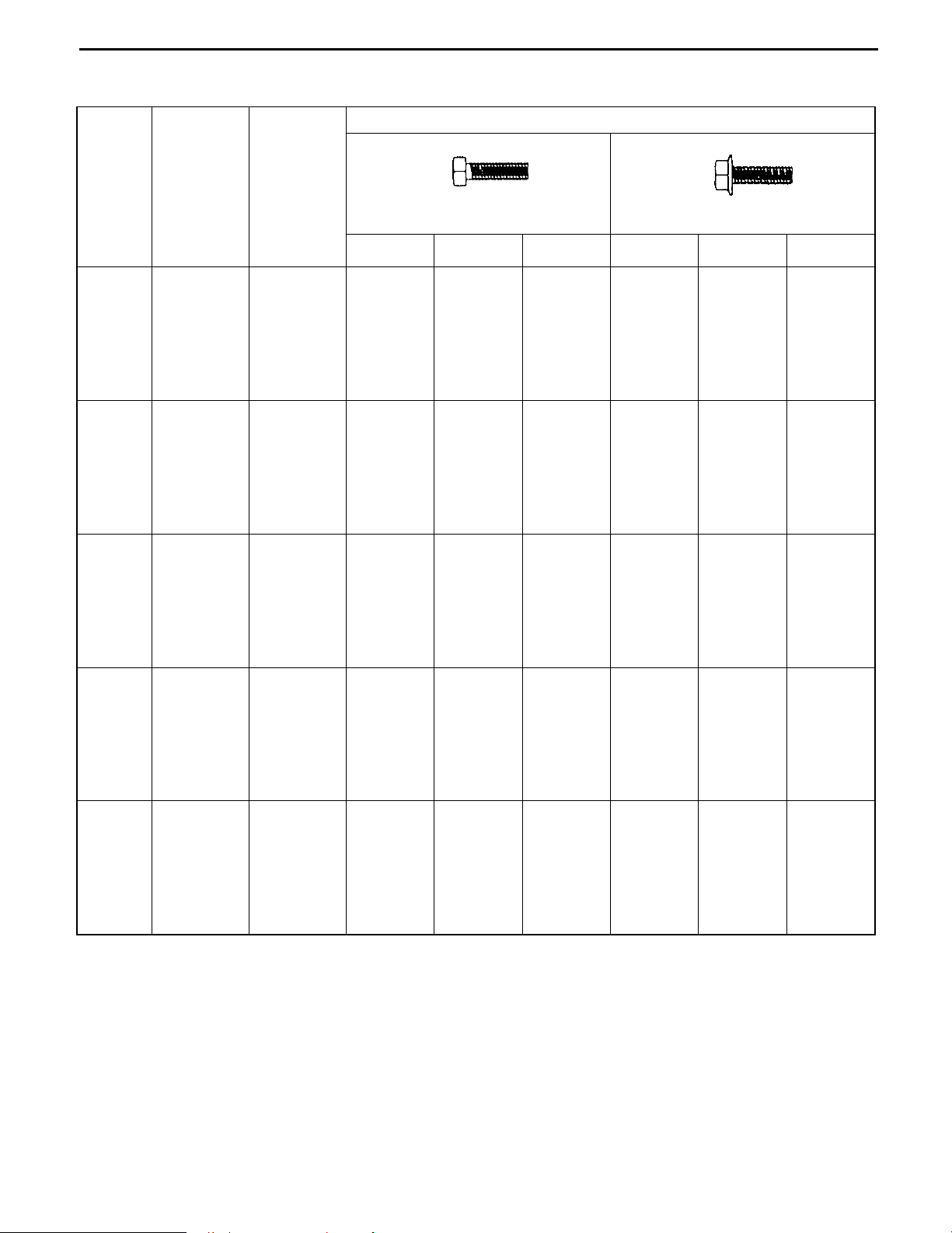
Shape and class
Class
Hexagon
head bolt
Hexagon
bolt
Bolt with raised
or etched
numeral on head
4 = 4T
5 = 5T
6 = 6T
7 = 7T
8 = 8T
(standard)
No mark
4T
Hexagon
flange bolt
No mark
4T
Hexagon
head bolt
(standard)
Bolt with two
raised lines on
head
5T
Hexagon
flange bolt
Bolt with two
raised lines on
head
6T
Hexagon
head bolt
(standard)
Bolt with three
raised lines on
head
7T
Hexagon
head bolt
(standard)
Bolt with four
raised lines on
head
8T
Welded bolt
4T
Stud bolt
No mark
4T
2 mm groove(s)
on one/both
edge(s)
6T
Hexagon head bolt
Part No.
91611-40625
Length (mm)
Nominal diameter (mm)
Class
Nominal diameter
Length
Stud bolt
Part No.
92132-40614
Length (mm)
Nominal diameter (mm)
Class
Nominal diameter
Length
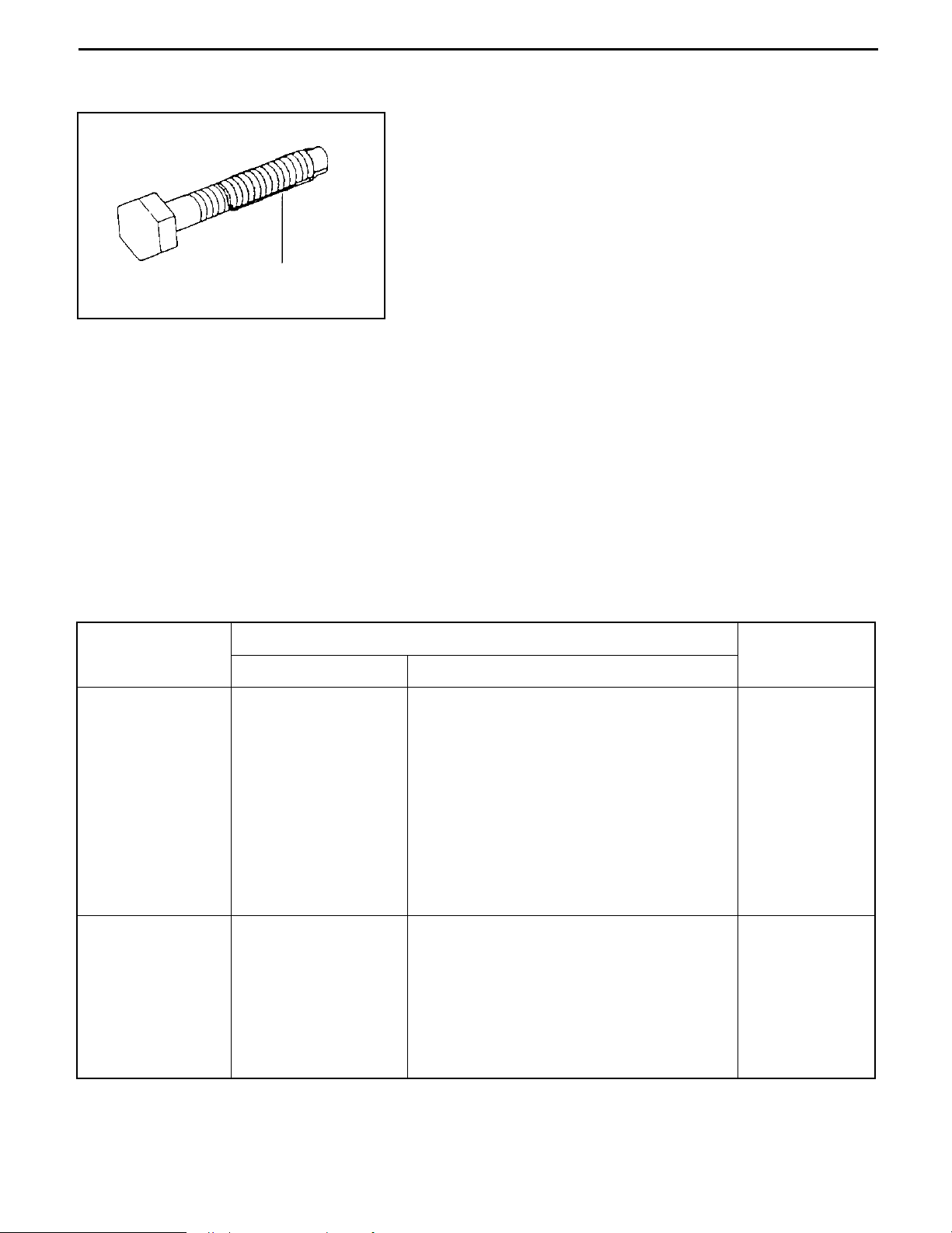
STANDARD BOLT & NUT TIGHTENING TORQUE
Tightening torque of standard bolts and nuts are not indicated throughout the manual.
Use the charts and table below to judge the standard tightening torque.
1.
Find the class of the bolt strength on the table below and then find the bolt tightening torque on the
tightening torque table.
2.
The nut tightening torque can be judged from its corresponding bolt type.
BOLT STRENGTH CLASS IDENTIFICATION METHOD
Identification by bolt shape Identification by part No.
0-16
TIGHTENING TORQUE TABLE
Class
Nominal
diameter
mm
Pitch
mm
Standard tightening torque
Hexagon
head bolt
Hexagon
flange bolt
N·m
kgf·cm
ft·lbf
N·m
kgf·cm
ft·lbf
6 1.0
5.4
55
48in·lbf
5.9
60
52in·lbf
8 1.25
13
130 9
14
145
10
4T
10
12
1.25
1.25
25
47
260
480
19
35
28
53
290
540
21
39
14
1.5
75
760
55
83
850
61
16
1.5
113
1150
83
⎯ ⎯ ⎯
6 1.0
6.4
65
56in·lbf
7.5
75
65in·lbf
8 1.25
16
160
12
18
175
13
5T
10
12
1.25
1.25
32
59
330
600
24
43
36
65
360
670
26
48 14
1.5
91
930
67
100
1050
76
16
1.5
137
1400
101
157
1600
116
6 1.0
7.8
80
69in·lbf
8.8
90
78in·lbf
8 1.25
19
195
14
21
215
16
6T
10
12
1.25
1.25
38
72
400
730
29
53
43
79
440
810
32
59 14
1.5
110
1100
80
123
1250
90
16
1.5
170
1750
127
191
1950
141
6 1.0
11
110 8
12
120 9 8 1.25
25
260
19
28
290
21
7T
10
12
1.25
1.25
52
95
530
970
38
70
58
103
590
1050
43
76
14
1.5
147
1500
108
167
1700
123
16
1.5
226
2300
166
⎯ ⎯ ⎯
6 1.0
12
125 9
14
145 9 8 1.25
29
300
22
32
330
24
8T
10
12
1.25
1.25
61
108
620
1100
45
80
68
123
690
1250
50
90
14
1.5
172
1750
127
196
2000
145
16
1.5
265
2700
195
299
3050
221
0-17
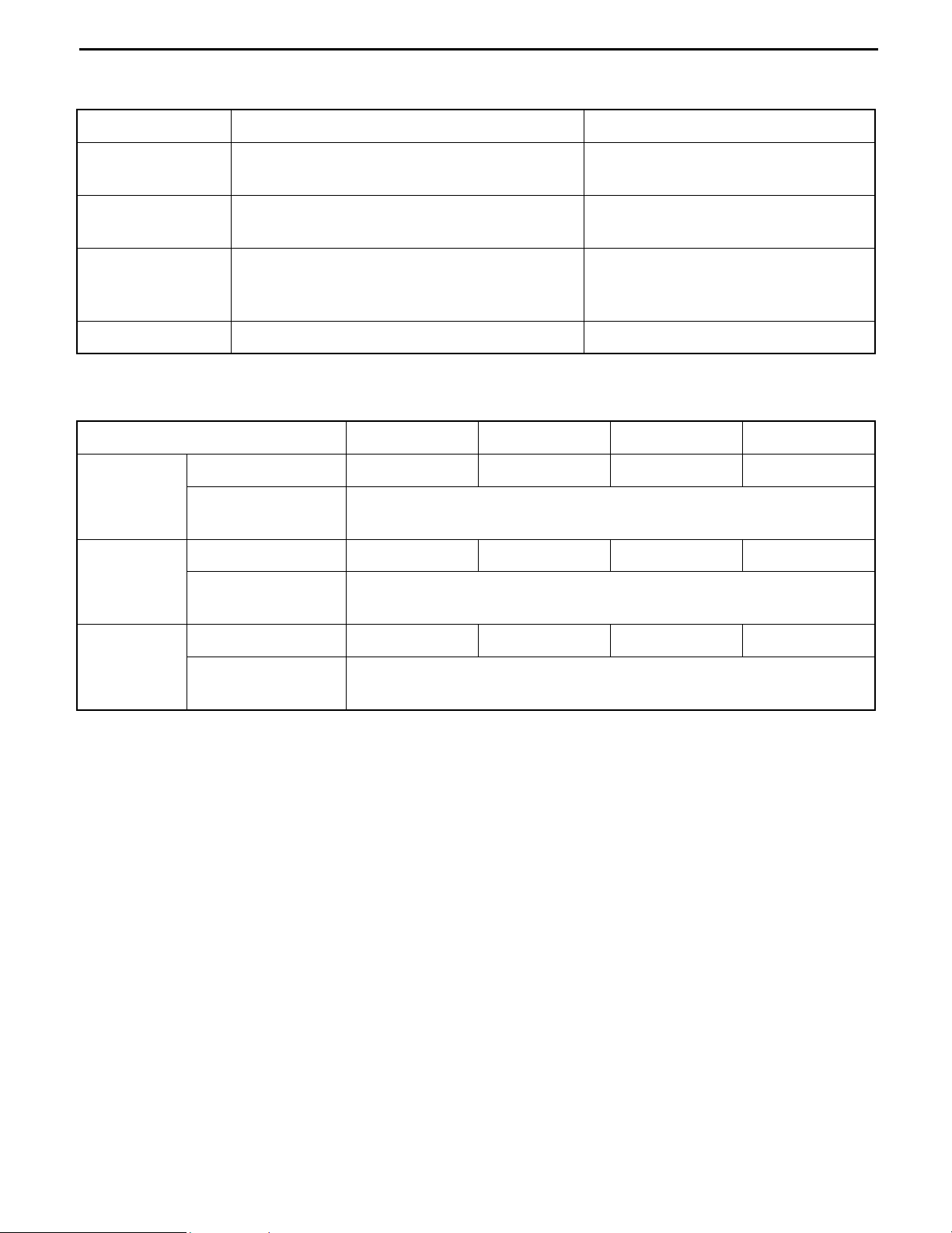
PRECOATED BOLTS
1.
Do not replace or restore a precoated bolt as it is in the
following cases:
(1)
After it has been removed.
(2)
When it has been moved by tightness check, etc.
(loosened or tightened)
NOTE:
For torque check, tighten the bolt at the lower limit of the
allowable tightening torque range; if the bolt moves,
retighten it according to the steps below.
2.
How to reuse precoated bolts
(1)
Wash the bolt and threaded hole.
(The threaded hole must be washed even when
replacing the bolt with a new one)
(2)
Completely dry the washed parts by blowing with air.
(3)
Apply a specified seal lock agent to the threaded
portion of the bolt.
HIGH PRESSURE HOSE FITTING TIGHTENING TORQUE
1.
When connecting a high pressure hose, wipe the hose fitting and corresponding nipple contact
surfaces with a clean cloth to remove foreign matter and dirt. Also check that there are no dents or
other damage on the contact surfaces before installation.
2.
When connecting the high pressure hose, hold the hose to align the fitting with the nipple and tighten
the fitting.
3.
The maximum tightening torque must not exceed twice the standard tightening torque.
Nominal diameter
of screw
Tightening torque standard N·m (kgf·cm) [ft·lbf]
Inside diameter
of hose
mm (in)
Standard
Tightening range
7/16-20UNF
25 (50) [18.1]
24 to 26 (240 to 270) [17.4 to 19.5]
6 (0.24)
9/16-18UNF
49 (500) [36.2]
47 to 52 (480 to 530) [34.7 to 38.3]
9 (0.35)
3/4-16UNF
59 (600) [43.4]
56 to 62 (570 to 630) [41.2 to 45.6]
12 (0.47)
7/8-14UNF
59 (600) [43.4]
56 to 62 (570 to 630) [41.2 to 45.6]
12 (0.47)
7/8-14UNF
78 (800) [57.9]
74 to 82 (740 to 840) [53.5 to 60.8]
15 (0.59)
1•1/16-12UNF
118 (1200) [86.8]
112 to 123 (1140 to 1250) [82.5 to 90.4]
19 (0.75)
1•5/16-12UNF
137 (1400) [101.3]
130 to 144 (1330 to 1470) [96.2 to 106.4]
25 (0.98)
PF1/4
25 (250) [18.1]
24 to 26 (240 to 270) [17.4 to 19.5]
6 (0.24)
PF3/8
49 (500) [36.2]
47 to 52 (480 to 530) [34.7 to 38.3]
9 (0.35)
PF1/2
59 (600) [43.4]
56 to 62 (570 to 630) [41.2 to 45.6]
12 (0.47)
PF3/4
118 (1200) [86.8]
112 to 123 (1140 to 1250) [82.5 to 90.4]
19 (0.75)
PF1
137 (1400) [101.3]
130 to 144 (1330 to 1470) [96.2 to 106.4]
25 (0.98)
Seal lock agent
0-18
RECOMMENDED LUBRICANT QUANTITY AND TYPES
Application
Type
Capacity
Drive unit
Castle hypoid gear oil W
(API GL-4, SAE 75W-80)
Approx. 0.4 l (0.11 US gal)
(Until purring out from the filler port)
Hydraulic oil
STD: Castle hydraulic oil (ISO VG32)
Cold storage vehicle: Mobil Aero HFE
See “Hydraulic oil level by lifting
height” below
Chassis parts
MP grease
Chassis grease special
Esso beacon 325
Appropriate amount
Battery
Distilled water
Appropriate amount
Hydraulic oil level by lifting height
Unit:l (US gal)
Lifting height
V mast
SV mast
FV Mast
FSV Mast
To 3000mm
(118 in)
Capacity
14 (3.70)
14 (3.70)
17 (4.49)
⎯
Hydraulic oil level
in the tank
12.4 (3.27)
To 4000mm
(157.5 in)
Capacity
15 (3.96)
15 (3.96)
19 (5.01)
16 (4.22)
Hydraulic oil level
in the tank
14.2 (3.75)
To 6000mm
(236 in)
Capacity
18 (4.75)
⎯ ⎯
19 (5.01)
Hydraulic oil level
in the tank
17.2 (4.54)
0-19
I
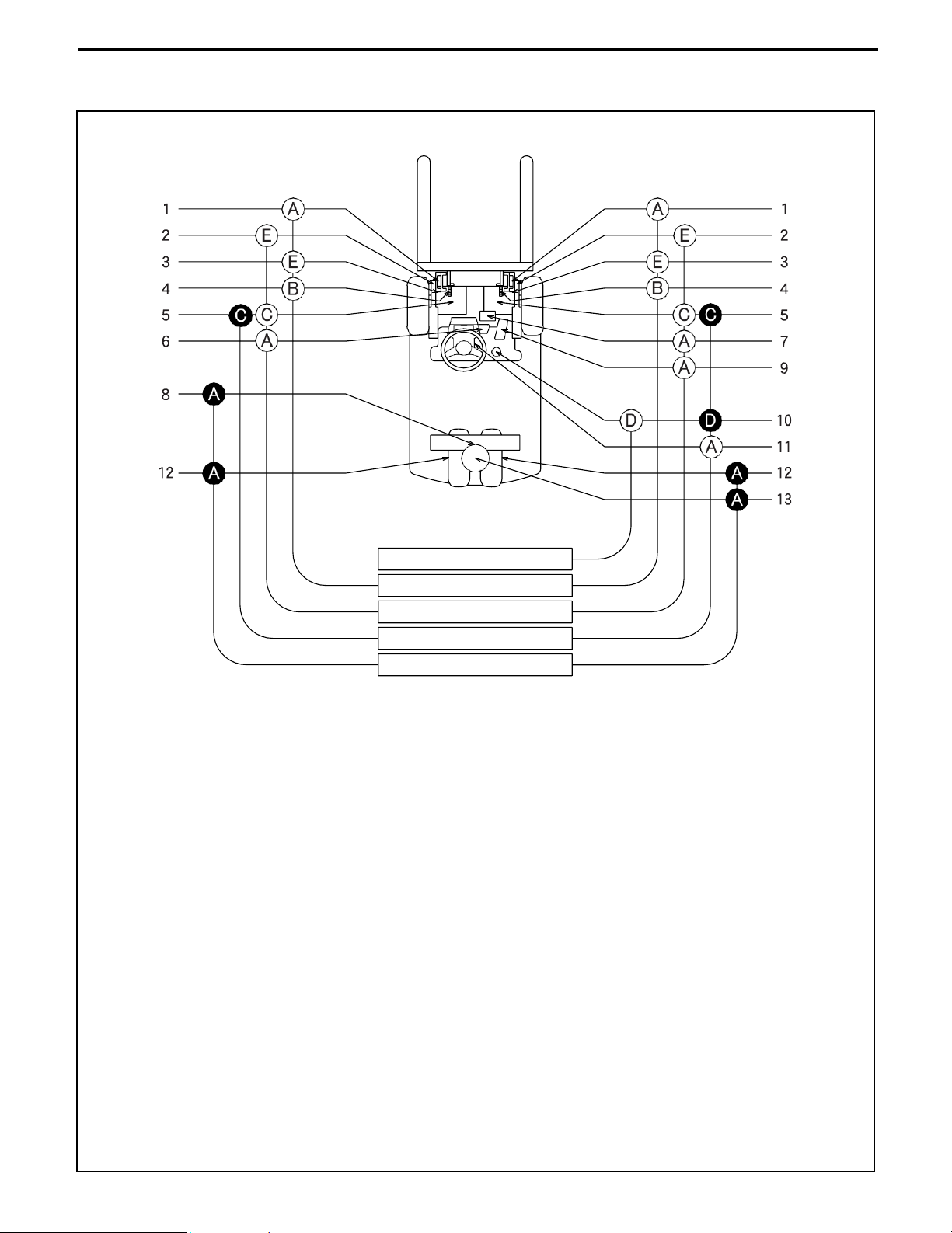
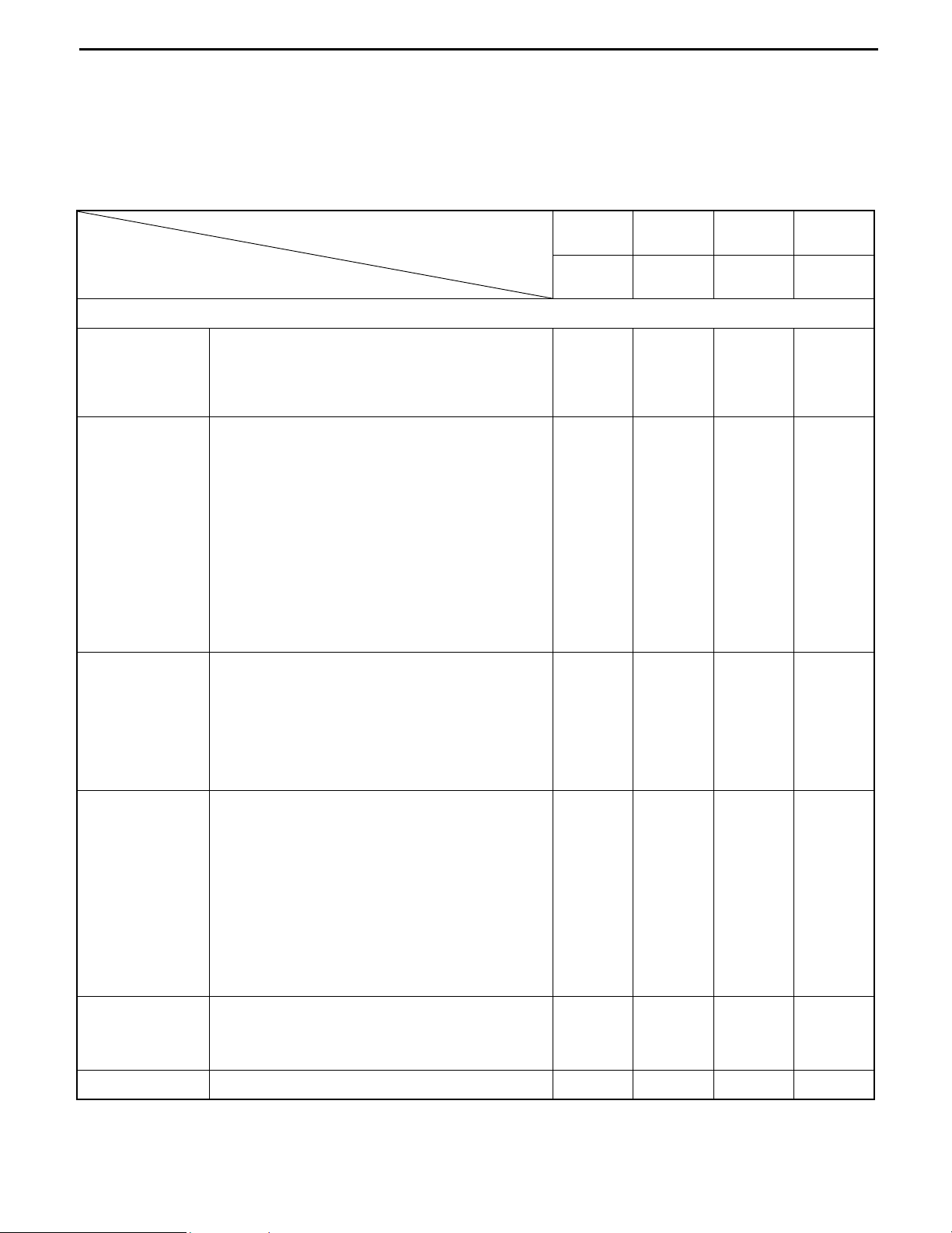
LUBRICATION CHART
: Inspection and addition I. Inspection every 8 hours (daily)
: Replacement II. Inspection every 40 hours (weekly)
A: MP grease III. Inspection every 170 hours (monthly)
B: Motor oil IV. Inspection every 1000 hours (6 monthly)
C: Gear oil (SAE 75W-80) V. Inspection 2000 hours (annual)
D: Hydraulic oil (ISO VG32)
E: Chassis grease special
1.
Mast strip 8. Steering rack and pinion gear
2.
Tilt cylinder front pin 9. Accelerator link
3.
Mast support bushing 10. Oil tank
4.
Lift chain 11. Tilt steering lock device
5.
Drive unit 12. Rear wheel bearing
6.
Brake link 13. Rear axle bearing
7.
Oil control valve lever pin
V
IV
III
II
0-20
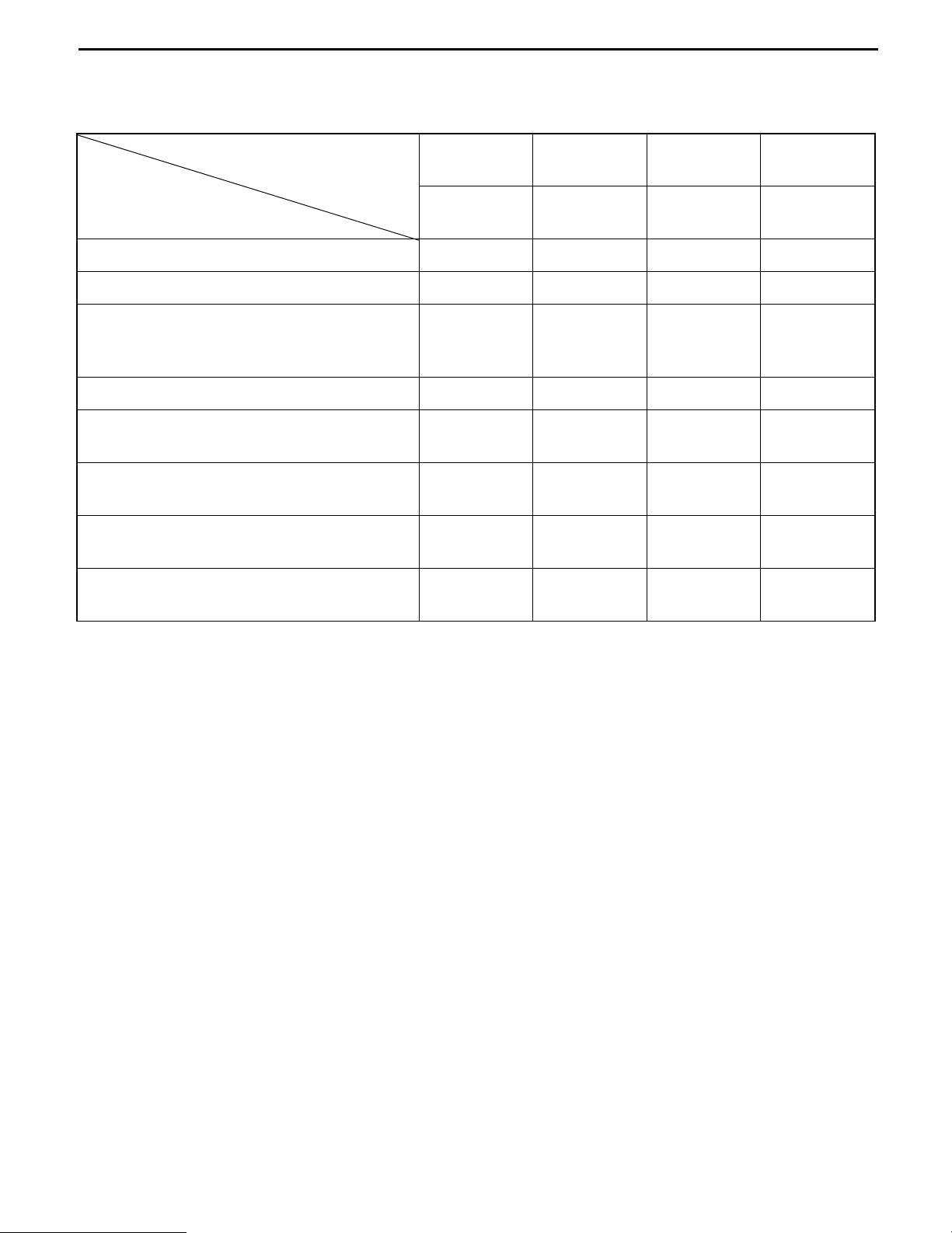
PERIODIC MAINTENANCE
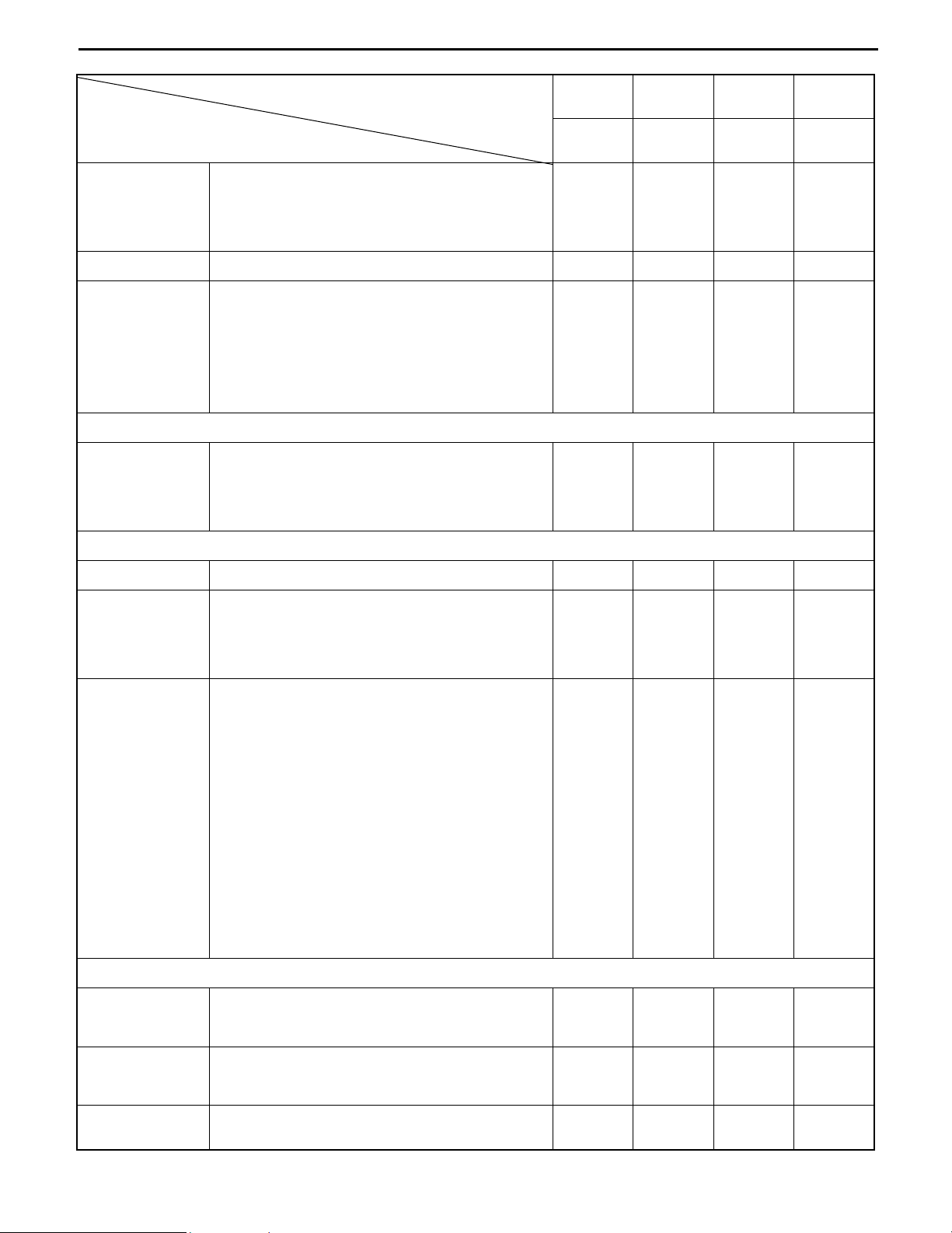
INSPECTION METHOD
I: Inspection · Repair or Replacement if required
M: Measurement · Repair or Adjustment if required
T: Retightening C: Cleaning L: Lubrication
*: For new vehicle *1: Flaw detector
Item
Inspection timing
Every
month
Every 3
months
Every 6
months
Every 12
months
Every
170 hours
Every
500 hours
Every
1000 hours
Every
2000 hours
ELECTRICAL SYSTEM
Motor
Rotation sound abnormality
Looseness in the connecting parts
Insulation resistance
I
T
M
Charging level (Display)
I
Electrolyte level
I
Electrolyte specific gravity
M
Battery
Looseness in the connecting parts
Abnormality in the upper portion of the
battery and/or the case
I
I
Insulation resistance
M
Voltage measurement of each battery cell
after charging
M
Charger
Timer function (Timer test)
Looseness in the connecting parts
HVR function voltage measurement
Operating condition of the magnetic switch,
contact contamination, roughness
I
T
M
I
Contact looseness, damage, abrasion
I
Operating condition, contamination and
abrasion of the auxiliary contact
I
Magnet switch
Mounting condition of the arc shooter
Operating condition and timing
I
I
Looseness of the coil installation locations
I
Mounting condition and looseness of the
main circuit lead wire
I
Micro switch
Operating condition and timing
Damage and looseness of installation
locations
I
I
Direction lever
Operating condition, damage
I
0-21
Item
Inspection timing
Every
month
Every 3
months
Every 6
months
Every 12
months
Every
170 hours
Every
500 hours
Every
1000 hours
Every
2000 hours
Controller
Operating condition
Interior contamination, damage
Motor input voltage
I
C
M
Fuses
Looseness of the installation locations
I
Wiring
(incl. charging
cable)
Harness deterioration, damage and
looseness of the clamp
Looseness of the connections, taping
condition
Connecting condition and damage of the
battery connector
I
I
I
POWER TRANSMISSION SYSTEM
Drive unit
Oil leak
Oil level
Bolt or nut looseness
I
I
T
DRIVE SYSTEM
Front axle
Damage and deformation
I
Rear axle
Damage and deformation
Looseness of rear axle bearing
Abnormal noise of rear axle bearing
I
I
I
Tire pressure
M
I
M
I
T
I
I
I
Tire crack, damage and abnormal wear
Tire tread depth
Metal piece, stone and other foreign matter
Wheels
on tire
Loosening of wheel nut and bolt
Rim, side ring and disc wheel damage
Looseness and abnormal noise of front
wheel bearing
Looseness and abnormal noise of rear
wheel bearing
STEERING SYSTEM
Steering wheel
Play, loosening, looseness
Function
I
I
Steering valve
Oil leak
Looseness of the installation locations
I
T
Wheels for
steering
Turning angle to left and right
I

0-22
Item
Inspection timing
Every
month
Every 3
months
Every 6
months
Every 12
months
Every
170 hours
Every
500 hours
Every
1000 hours
Every
2000 hours
Power steering
Oil leak
Looseness of the installation locations
Damage of power steering hose
I
I
I
BRAKING SYSTEM
Brake pedal
Reserve
Braking performance
M
I
Parking brake
Operating force and pull margin
Braking performance
I
I
Rod and cable
Looseness and damage
Operating condition
I
I
Clearance between disc and pad
M
Wear of sliding portion and pad
I
Disc brake
Disc wear and damage
Looseness of the disc installation locations
I
I
Operating condition
I
Return spring fatigue
I
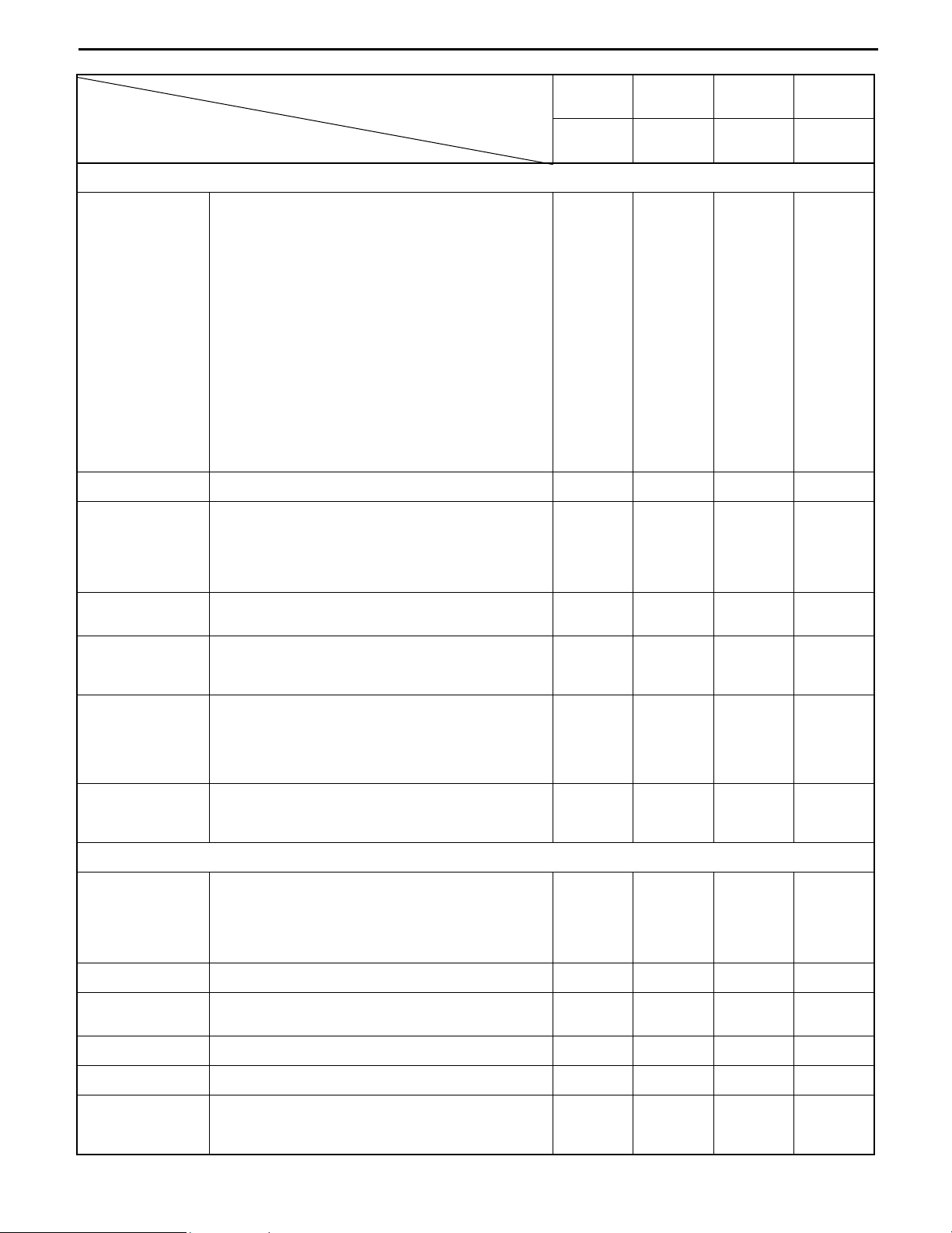
MATERIAL HANDLING SYSTEM
Fork
Damage or wear of fork or stopper pin
Fork deformation and wear
Cracks at fork root and welded part of tooth
I
I
I
*1
Deformation and damage of each part and
crack at welded part
I
Wear and damage of roller
I
Mast and
lift bracket
Mast and lift bracket looseness
Wear and damage of mast support bushing
I
I
Wear and damage of roller pin
I
Wear and damage of mast strip
I
Chain lubrication
I
Chain and
Deformation, damage and slackness of
chain
I
chain wheel
Abnormality of chain anchor bolt
I
Wear, damage and revolution of chain
wheel
I
Various
attachments
Abnormality and installation condition of
each part
I
0-23
Item
Inspection timing
Every
month
Every 3
months
Every 6
months
Every 12
months
Every
170 hours
Every
500 hours
Every
1000 hours
Every
2000 hours
HYDRAULIC SYSTEM
Looseness, deformation and damage of rod
I
I
M
I
I
T
M
I
and rod end
Cylinder operation
Natural drop and natural forward tilt
Oil leak and damage
Cylinder
Wear and damage of pin and cylinder
bearing
Loosening and damage of cylinder
mounting
Lifting speed
Uneven movement
Oil pump
Oil leak and abnormal sound
I
Oil level and contamination
I
C
Hydraulic oil
tank
Oil leak I
Tank and oil strainer cleaning
Hydraulic oil
filter
Filter clogging
C
Control lever
Loose linkage
Operation
I
I
Oil leak I
M
Oil control
valve
Safety valve function
I
Relief pressure measurement
Hydraulic hose
Oil leakage, deformation and damage
I
T
and piping
Looseness
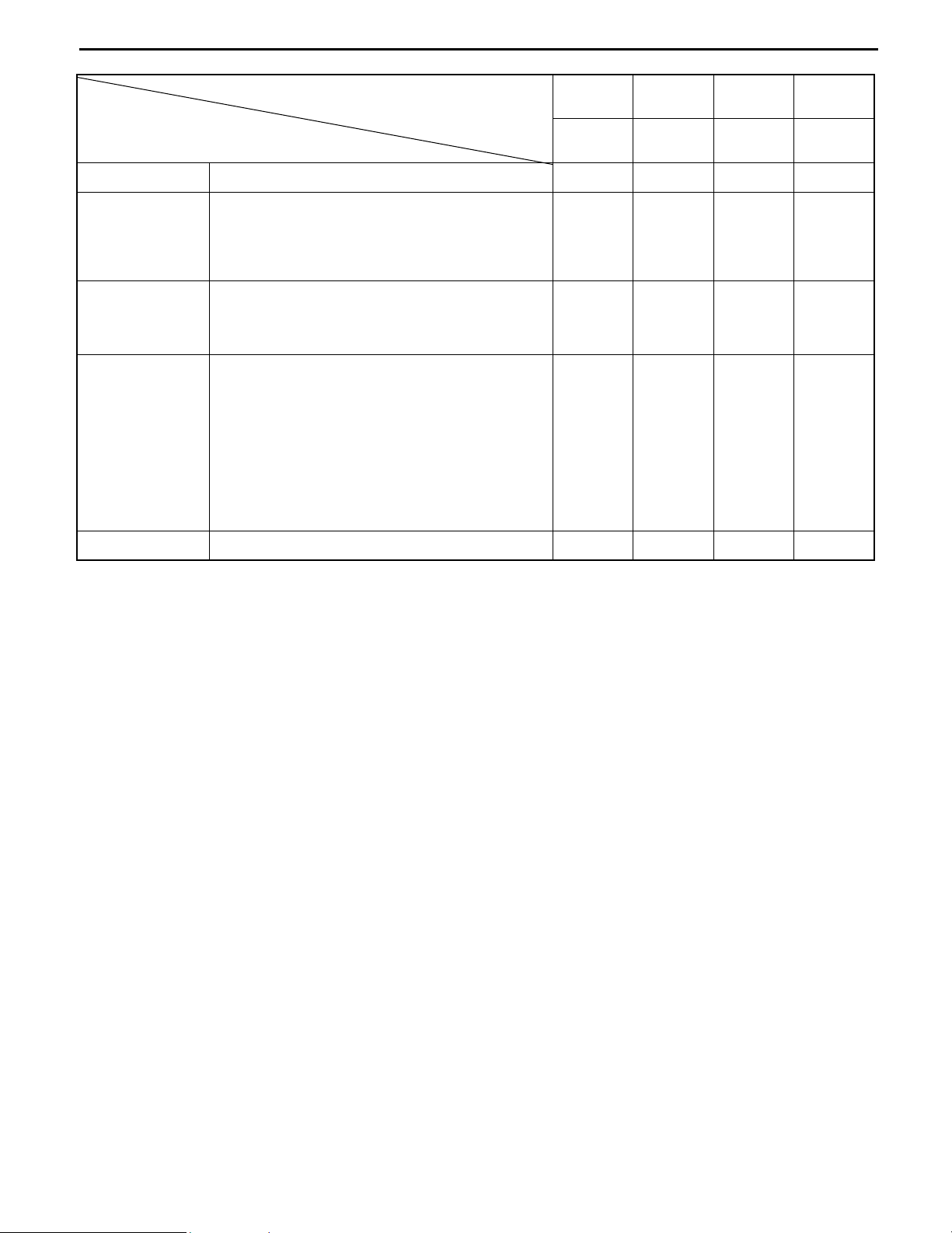
SAFETY DEVICES, ETC.
Looseness of the installation locations
T
I
I
Head guard
and backrest
Deformation, crack and damage
Crack at welded portion
Lighting system
Function and installation condition
I
Direction
indicator
Function and installation condition
I
Horn
Function and installation condition
I
Backup buzzer
Function and installation condition
I
Rear view
Rear reflection status
I
mirror
Dirt, damage
I
0-24
Item
Inspection timing
Every
month
Every 3
months
Every 6
months
Every 12
months
Every
170 hours
Every
500 hours
Every
1000 hours
Every
2000 hours
Instruments
Operation
I
Loosening and damage of mounting
I
Seat
Seatbelt damage and function
I
Deadman seat operation
I
Body
Damage and cracks in frame, cross members, etc.
Bolts and nuts looseness
I
T
Functions
I
Loosening and damage at sensor mounting
portion
I
SAS
Damage, deformation, oil leakage and loosened installation of functional parts
I
Loosening and damage of wire harnesses
I
Rusting and corrosion of load sensor
I
Others
Grease up
L
0-25
PERIODIC REPLACEMENT OF PARTS AND LUBRICANTS
●
: Replacement
Replacement cycle
Item
Every
month
Every
3 months
Every
6 months
Every
12 months
Every
170 hours
Every
500 hours
Every
1000 hours
Every
2000 hours
Drive unit gear oil
●
Hydraulic oil
●
Hydraulic oil filter
●
New
vehicle initial
replacement
●
Rear wheel bearing grease
●
Power steering hose
●
Every
2 years
Power steering rubber parts
●
Every
2 years
Hydraulic hose
●
Every
2 years
Lift chain
●
Every
3 years

0-26
1-1
BATTERY
BATTERY COMPARTMENT AND
Page
REQUIRED WEIGHT ........................................... 1-2
SERVICE STANDARDS. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-3 1
DISPLAY ..................................................................... 1-3
TROUBLESHOOTING ............................................ 1-4
BATTERY ASSY ..................................................... 1-5
REMOVAL · INSTALLATION ............................................... 1-5
INSPECTION .................................................................... 1-6
REPLACING BATTERY PLUG TERMINAL ..................... 1-9
 Loading...
Loading...