Total Control MP/16 Operator's Manual
1995 by U.S. Robotics Access Corp.
8100 North McCormick Blvd.
Skokie, IL 60076-2999
All Rights Reserved
OPERATOR’S MANUALOPERATOR’S MANUAL
MP/16 withMP/16 with
SNMP ManagementSNMP Management
TTOTAL OTAL CCONTROLONTROL

U.S. Robotics and the U.S. Robotics logo are registered trademarks of U.S.
Robotics Access Corp. Total Control, MP/16, Courier, and V.Everything are
trademarks of U.S. Robotics Access Corp. Any trademarks, tradenames, service
marks or service names owned or registered by any other company and used in this
manual are the property of their respective companies.

About This Guide
This guide covers the following topics:
Chapter 1. Overview. Provides a brief overview of SNMP
management, useful in helping to define SNMP terms used
throughout the manual.
Chapter 2. Installation. Guides you through all the steps necessary
to prepare the MP/16 for management using SNMP. Also
contains information on cabling and configuring the modems
in the MP/16.
Chapter 3. Using Total Control MIBs. Provides information useful
for managing the MP/16 using MIBs. Intended for those who
are not using Total Control Manager/SNMP (TCM) to manage
the MP/16.
Chapter 4. Special Applications. Use to configure the MP/16
modems for such applications as Cellular and Link Security.
This guide assumes that you will be configuring the MP/16
modems through SNMP management. However, two Appendixes
(C and D) provide information on AT commands, which can be
used to configure the modems if so desired.
We Welcome Your Suggestions
Every effort has been made to provide useful, accurate
information. If you have any comments or suggestions concerning
the documentation of this product, please let us know.
By voicemail: (847) 933-5200
Via the Internet: sysdocs@usr.com


Contents
Chapter 1 Overview......................................................1-1
SNMP Management..........................................1-1
Applications......................................................1-3
Modem Features...............................................1-5
Chapter 2 Installation...................................................2-1
Summary..........................................................2-1
Required Accessories........................................2-2
The Unit............................................................2-3
Placement.........................................................2-5
Power...............................................................2-6
Assigning IP Addresses.....................................2-7
Management Over a LAN...............................2-11
Dial-Up Management......................................2-13
Modem Setup.................................................2-18
Chapter 3 Using Total Control MIBs............................3-1
Command Tables..............................................3-2
Supported MIB II Groups...................................3-4
The Chassis MIB...............................................3-6
The NMC MIB.................................................3-14
The Modem MIB.............................................3-34
The Trap MIB..................................................3-41
Chapter 4 Special Applications...................................4-1
Link Security.....................................................4-2
Cellular.............................................................4-6
MNP10 Parameters.........................................4-10
ETC Parameters.............................................4-13
Result Codes ..................................................4-16
Leased Line....................................................4-22

Appendix A EIA RS-232 Pinouts.................................A-1
RJ45 Pin Assignments......................................A-2
RJ45 to DB-9 and DB-25 Conversions..............A-3
Connecting the MP/16 to Another DCE.............A-4
Minimum Requirements....................................A-4
Appendix B Configuration Menu Guide..................... B-1
The Main Menu................................................B-1
Configuration Menu..........................................B-2
Saving Configuration to Nonvolatile Memory....B-8
Appendix C Using AT Commands............................. C-1
Syntax.............................................................C-1
Sending Commands to the Modem..................C-2
Repeat Last Command.................................... C-3
Issuing Commands While Online.....................C-4
Help/Command Summary Requests................C-5
Viewing Configurations.................................... C-5
Remote Access...............................................C-5
Appendix D AT Command Reference........................ D-1
Basic Command Set........................................ D-1
Ampersand (&) Command Set.........................D-8
Percent Command Set...................................D-16
S-Registers.....................................................D-18
Appendix E Modem Testing........................................E-1
Testing With &T................................................E-1
Testing With Register S16................................E-8
Appendix F Warranty and Regulatory Information....F-1
Limited Warranty..............................................F-1
Service.............................................................F-2
FCC Registration..............................................F-3
Connecting to the Telephone Company............F-3
Radio and Television Interference....................F-3
For Canadian Users..........................................F-4
IC (Industry Canada)........................................F-5
Appendix G Technical Specifications........................ G-1
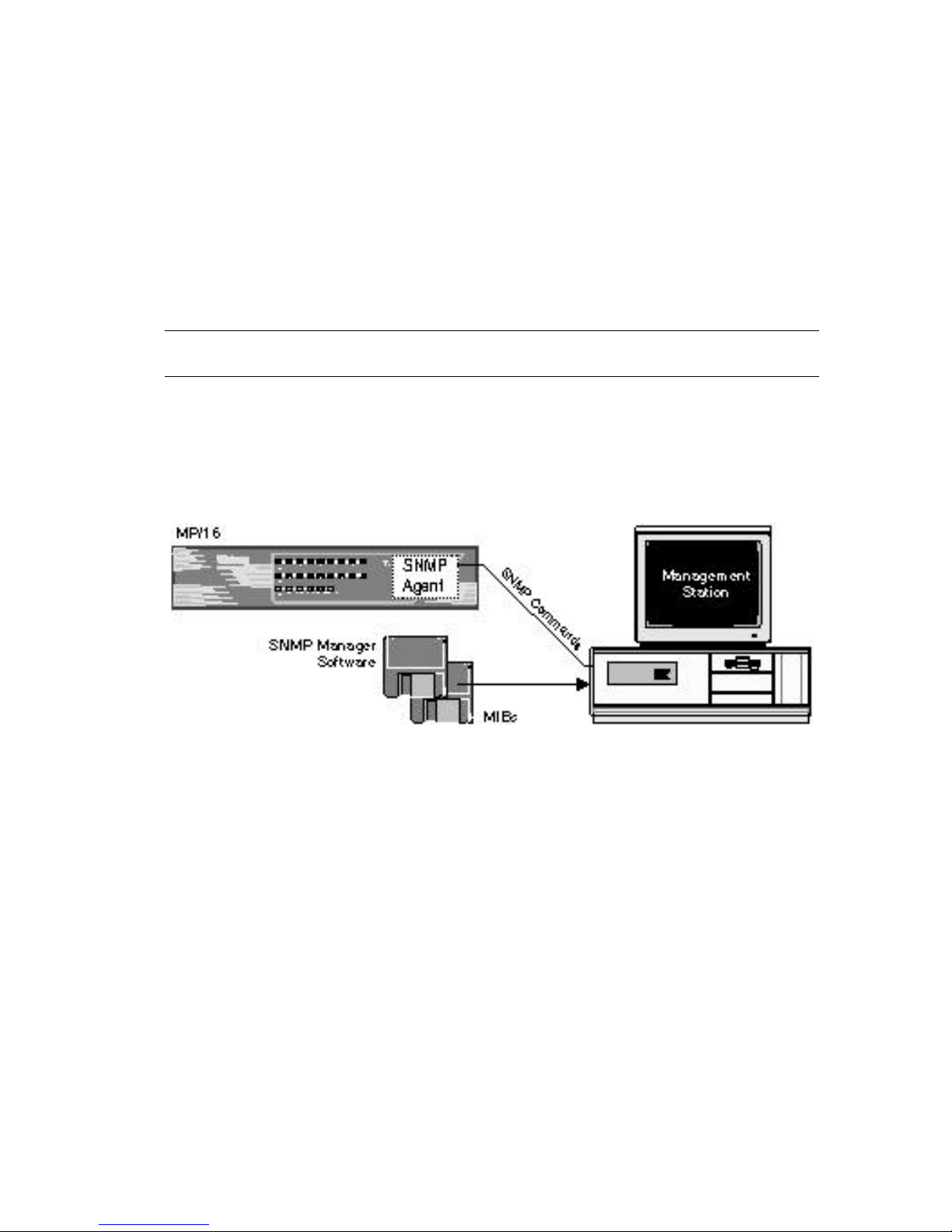
SNMP Management 1-1
Chapter 1 Overview
SNMP Management
The Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) is a widely
supported management protocol that provides remote control and
monitoring of network devices such as the MP/16. The following
figure illustrates the basic components of SNMP management.
Figure 1-1. Basic Components of SNMP Management
SNMP Agent
A special SNMP agent contained in the MP/16 interprets SNMP
commands and relays them to the managed objects in the MP/16.
Management Station
As a network manager, you are responsible for setting up the
Management Station, a PC running SNMP management software
from which you manage the MP/16 and other devices in your
network.
SNMP Management Software
SNMP management software runs on the Management Station
(MS), and serves as a user interface for issuing SNMP commands to
all managed network devices, including the MP/16.
1-2 Overview
SNMP Commands
There are three SNMP commands: Get, Set, and GetNext. The
Management Station issues SNMP commands to set parameters or
perform other actions on a managed device.
MIBs
A Management Information Base (MIB) is a list of objects with
variables that pertain to a particular type of device, such as a
modem. MIBs are necessary when sending or receiving SNMP
information between the Management Station and the MP/16. For
example, the Total Control Modem MIB defines an object for each
modem parameter. When you send a command from TCM to
change a modem setting, TCM references the Modem MIB so that
the command can be properly coded, translated by the MP/16
management module, and applied to the modems. Likewise, when
TCM polls the MP/16 for the status of the modems, TCM uses the
Modem MIB to interpret the SNMP information gathered and
display the correct settings and LED status for each modem.
NOTE: Total Control Manager/SNMP (TCM) is a Windows-based
SNMP management software developed by U.S. Robotics
specifically for Total Control products such as the MP/16. It’s
virtual front panel display and configuration windows provide a
user interface that streamlines management functions. TCM
eliminates the need to deal with MIBs when communicating with
U.S. Robotics Total Control devices.
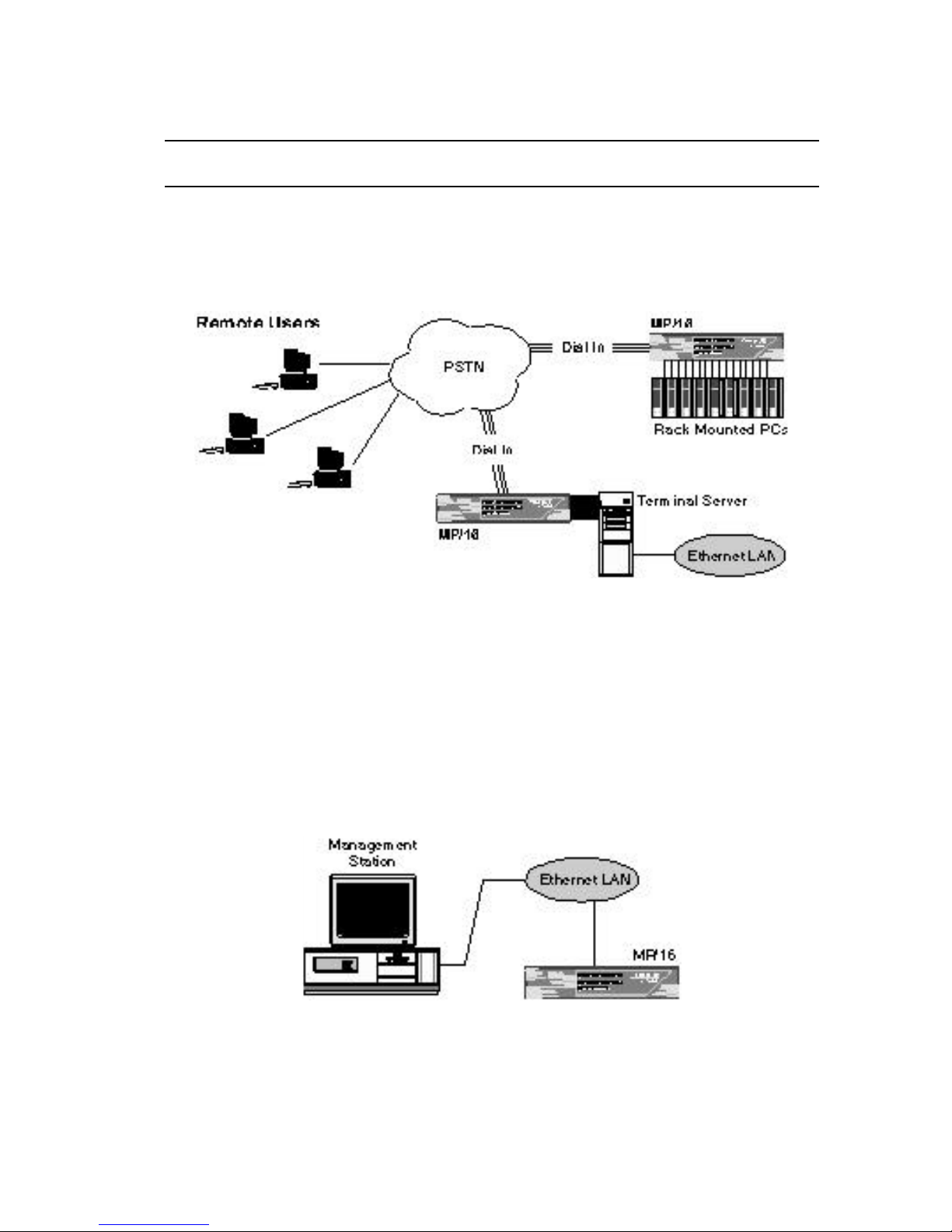
Applications 1-3
Applications
The MP/16 modem pool integrates sixteen modems for dial-up
access to terminal servers, front-end processors, bulletin boards,
email, or other resources.
Figure 1-2. Typical Setups for Dial-up LAN Access
SNMP management allows you to operate the MP/16, monitor line
activity, and perform dial-up accounting from across a LAN or
WAN (dial-up) connection.
Management from a LAN
The LAN port on the MP/16 allows you to establish an SNMP
connection over a LAN.
Figure 1-3. Management Station on the LAN
1-4 Overview
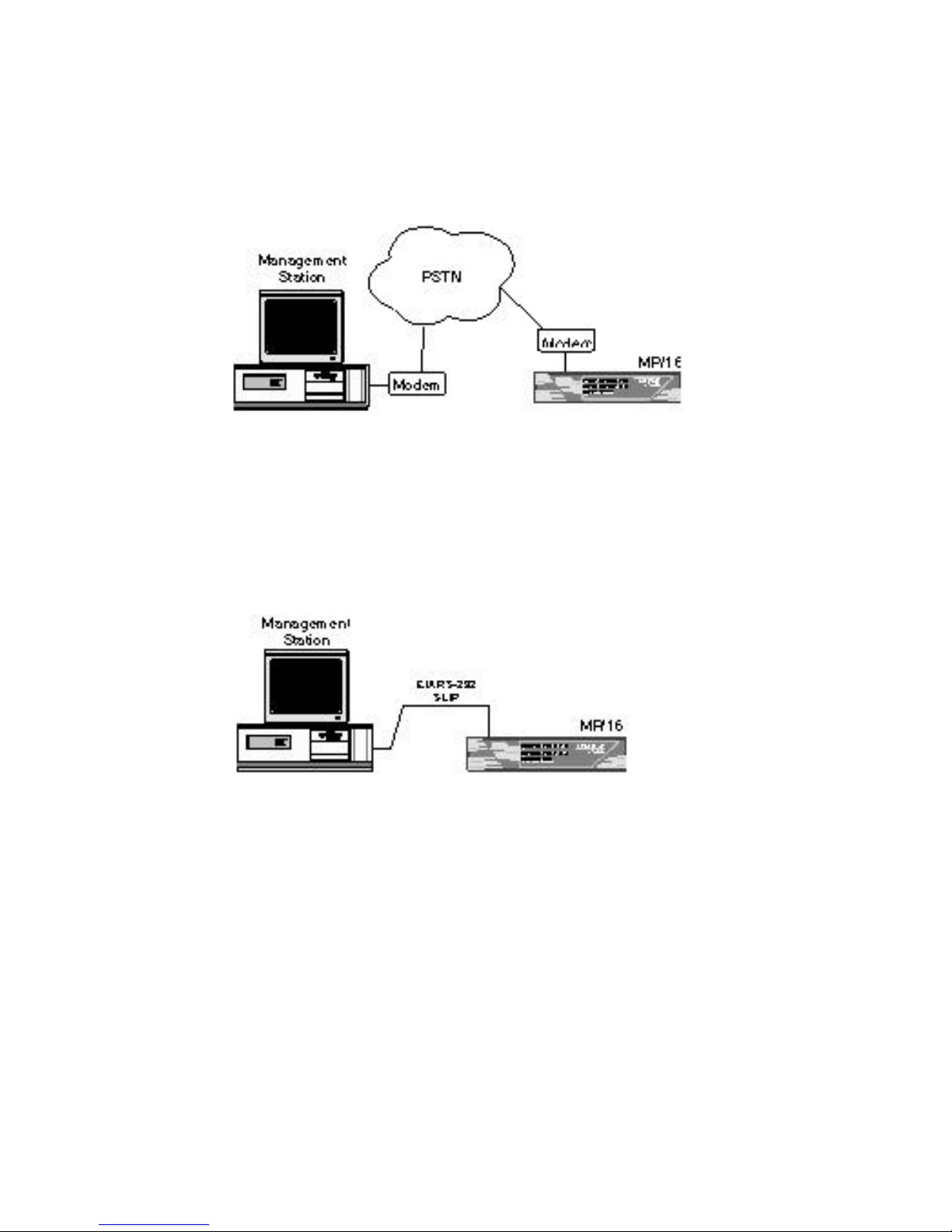
Dial-up Management
The Console port allows SNMP management over dial-up SLIP
connections from Management Stations in remote locations.
Figure 1-4. Dial-up Management
Direct Management
A local SLIP connection can be made by connecting the
Management Station to the MP/16’s Console port using a standard,
EIA RS-232 connection.
Figure 1-5. Direct SLIP

Modem Features 1-5
Modem Features
33.6 Kbps Connections
In addition to supporting normal connect speeds under V.34, V.FC,
V.32 terbo, V.32 bis and older ITU-T standards, the modems in the
MP/16 can connect at 31.2 Kbps and 33.6 Kbps when connecting
with other U.S. Robotics modems with 33.6 Kbps capability.
Custom Power-on/Reset Defaults
Custom configurations can be stored as power-on/reset defaults in
the modem’s Non-Volatile Random Access Memory (NVRAM).
Software Upgrades
Flash ROM make the modems software upgradable.
Fax Capability
Supports Class 1 or Class 2.0 facsimile software and the V.17 fax
protocol.
Link Security
Link Security prevents unauthorized access at the modem level—
before allowing any type of network connection.
Optional Cellular
If you purchased the MP/16 with cellular, the modems can answer
calls across cellular links using ETC and MNP10.

1-6 Overview

Summary 2-1
Chapter 2 Installation
Summary
1 Check to make sure you have all the required accessories
(page 2-2).
2 Familiarize yourself with the location of the connectors and
DIP switches on the unit’s back panel and the function of the
LEDs on the front panel (pages 2-3 –2-4).
3 Place the unit on a desktop or in a rack (page 2-4).
4 Plug the unit into a power source (page 2-6).
5 Assign IP addresses to the MP/16 (pages 2-7–2-10).
6 Setup the MP/16 for either LAN (pages 2-11–2-12) or dial-up
SLIP management (pages 2-13–2-17)
7 Connect the modems to your Data Terminal Equipement (DTE)
and analog phone source (page 2-18) and set the modem DIP
Switches (pages 2-19–2-20).
8 Set up your Management Station. Be sure to compile the MIBs
on the disk that came with the MP/16 into your SNMP
management software. See your SNMP management software
guide. If you are using Total Control Manager/SMP (TCM) to
manage the MP/16, you will not need this disk, as these MIBs
are included with the software. See the TCM
Installation/Configuration Roadmap for instructions on
compiling the MIBs.

2-2 Installation
Required Accessories
The Total Control MP/16 comes with the following materials:
♦ Power cord
♦ 16 analog phone cords
♦ One RJ45-to-DB-25 serial cable
♦ One null mo dem adapter
♦ Four rubber feet for placing the unit on a desktop.
♦ Two metal flanges and four screws for rack mounting the unit.
♦ One 3.5" floppy diskette containing the Total Control MP/16
Enterprise Specific MIBs
In addition to the provided hardware, you must have the following
to successfully install the Total Control MP/16:
♦ A PC running terminal emulator software.
♦ A good, working knowledge of TCP/IP and an addressing
strategy for your network. Your addressing strategy should
take into account the size of the network, the number of
physical networks, expected growth, and maintenance.
♦ EIA RS-232 serial cables to attach the modem ports to the
router, terminal adapter or other Data Terminal Equipment
(DTE).
If your equipment does not provide an RJ45 interface, consider
the purchase of one of three kinds of U.S. Robotics cable kits.
The following kits are available. Ask your distributor for
ordering information.
The Unit 2-3
U.S. Robotics Cable Kits
DB-25 Kit. Contains eight RJ45 cables with RJ45-to-DB-25
adapters. For use with EIA-standard 25-pin DTE
interfaces.
DB-9 Kit. Contains eight RJ45 cables with RJ45-to-DB-9
adapters. For use with EIA-standard 9-pin DTE interfaces.
Cisco Kit. Contains one 8-to-1 cable for Cisco Systems 2500
Series Access Products.
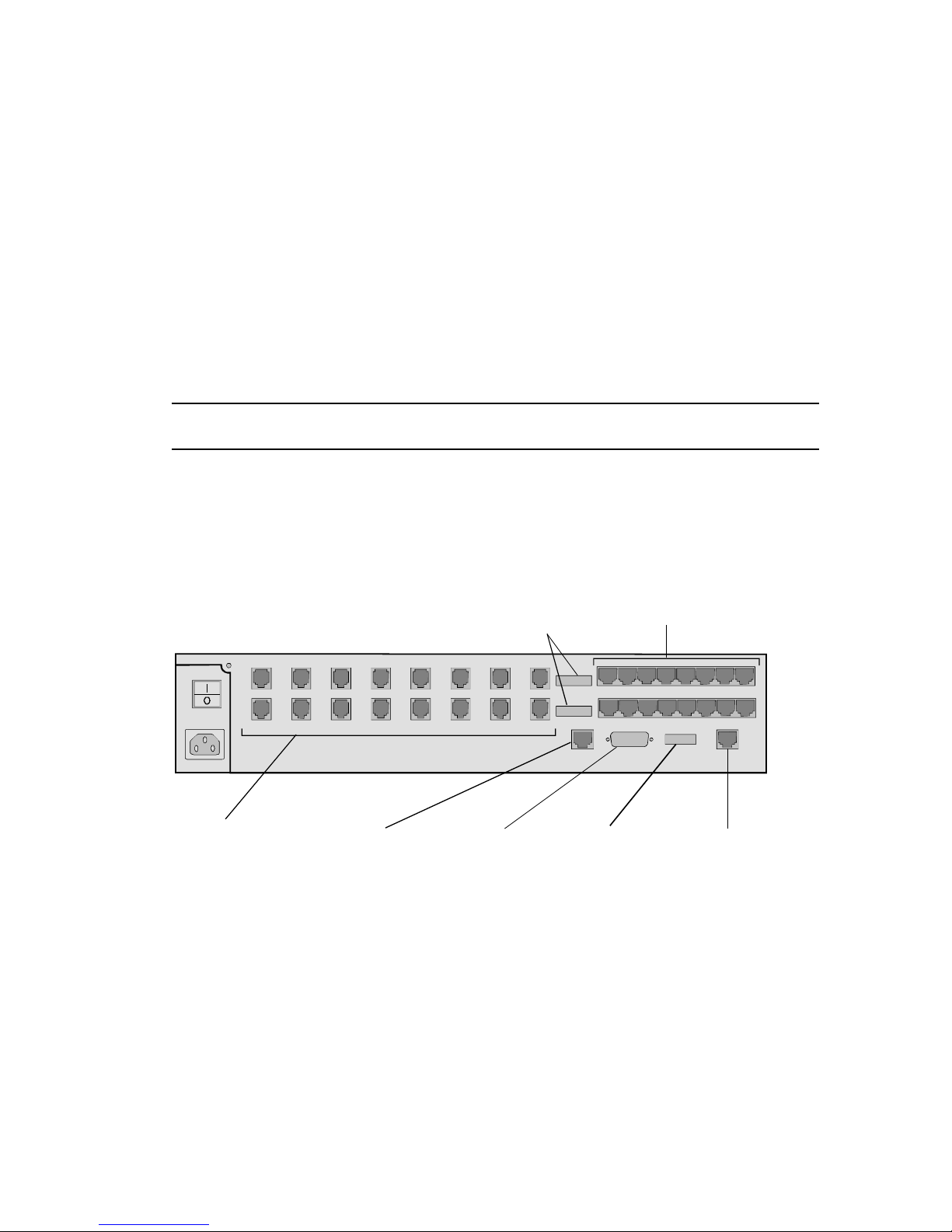
The Unit
Back Panel
1 2 3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10 11 12 13 14 15 16
RJ11 Telco Jacks
Modems 1-16
Sixteen telephone
cords are provided
10base T
Ethernet
Connector
For SNMP
management
only
10base 5
Ethernet
Connector
For SNMP
management
only
Console Port
DIP Switches
Console Port
DIP Switch 3
OFF for configuration
ON for direct SLIP or
Dial-up (WAN)
management
EIA RS-232 Serial Ports
Modems 1-16
Connect to DTE
Serial cables are not
provided
Modem
DIP Switches
First set controls
modems 1-8
Second set controls
modems 9-16
Figure 2-1. MP/16 Back Panel
2-4 Installation
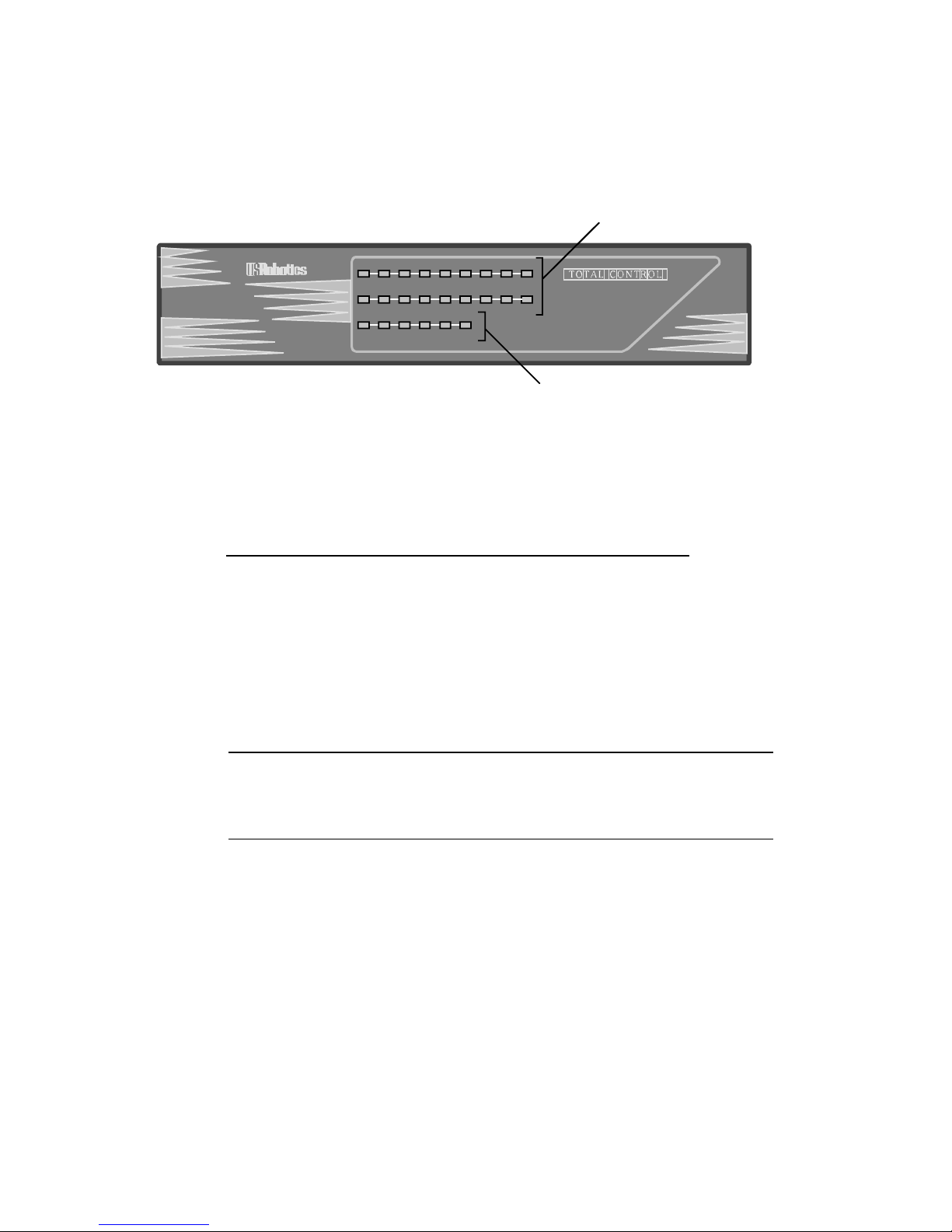
Front Panel
TM
MP/16 V.34
with SNMP Management
16
RUN/
FAIL
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
RUN/
FAIL
9
10
11
12
13 14
15
RUN/
FAIL
STATUS LAN TX LAN RX WAN TX WAN RX
Management LEDs
Modem LEDs
Figure 2-2. MP/16 Front Panel
Modem LEDs
Colors LEDs
Run/Fail Modems 1-16
Off off idle
Green power on online
Orange — dialing
Flashing green — testing/SDL
Red critical failure critical failure
Management LEDs
LED Color Status
RUN/Fail Solid Green Normal
Solid Red Critical SNMP agent failure
Flashing Green Testing/SDL
Flashing Green/Red Non-critical failure
STATUS Solid Green Normal
Solid Red Critical MP/16 failure
LAN TX Green Transmitting on LAN port
LAN RX Green Recieving on LAN port
Orange Rate of incoming ethernet data
(heavy traffic) exceeds processing
capability of system
Red Rate of incoming Ethernet data
(heavy traffic) exceeds memory
resources of system
WAN TX Green Transmitting on WAN port
WAN RX Green Recieving on WAN port
Placement 2-5
Placement
The MP/16 must be placed in a location with access to the
following:
♦ A standard grounded 115V AC wall socket or power supply
♦ Analog phone lines
♦ The router, terminal adapter, or other DTE to which you will
connect the modem EIA RS-232 ports
♦ An Ethernet LAN segment, if you plan to manage the MP/16
from a LAN. An isolated LAN segment is recommended
Placing the MP/16 on a Desktop
Stick the rubber feet (included) into the four recesses on the bottom
of the unit and place on a flat, hard surface. This leaves room
below for adequate ventilation.
CAUTION:
! Use the rubber feet to provide ventilation under the unit.
! Do not block the fan on the side of the unit.
! Do not stack MP/16s more than 8 units high.
Mounting in a Rack
1 Attach the provided flanges to the sides of the MP/16 using the
four screws that came with them.
Figure 2-3. Attaching the Flanges
2-6 Installation
2 Use four of the bolts and anchors that came with your rack to
bolt the flanges to the front vertical railing. Begin by inserting
and tightening the bottom two bolts, then the top two.
! Leave room above and below for adequate ventilation.
Use fan trays if necessary.
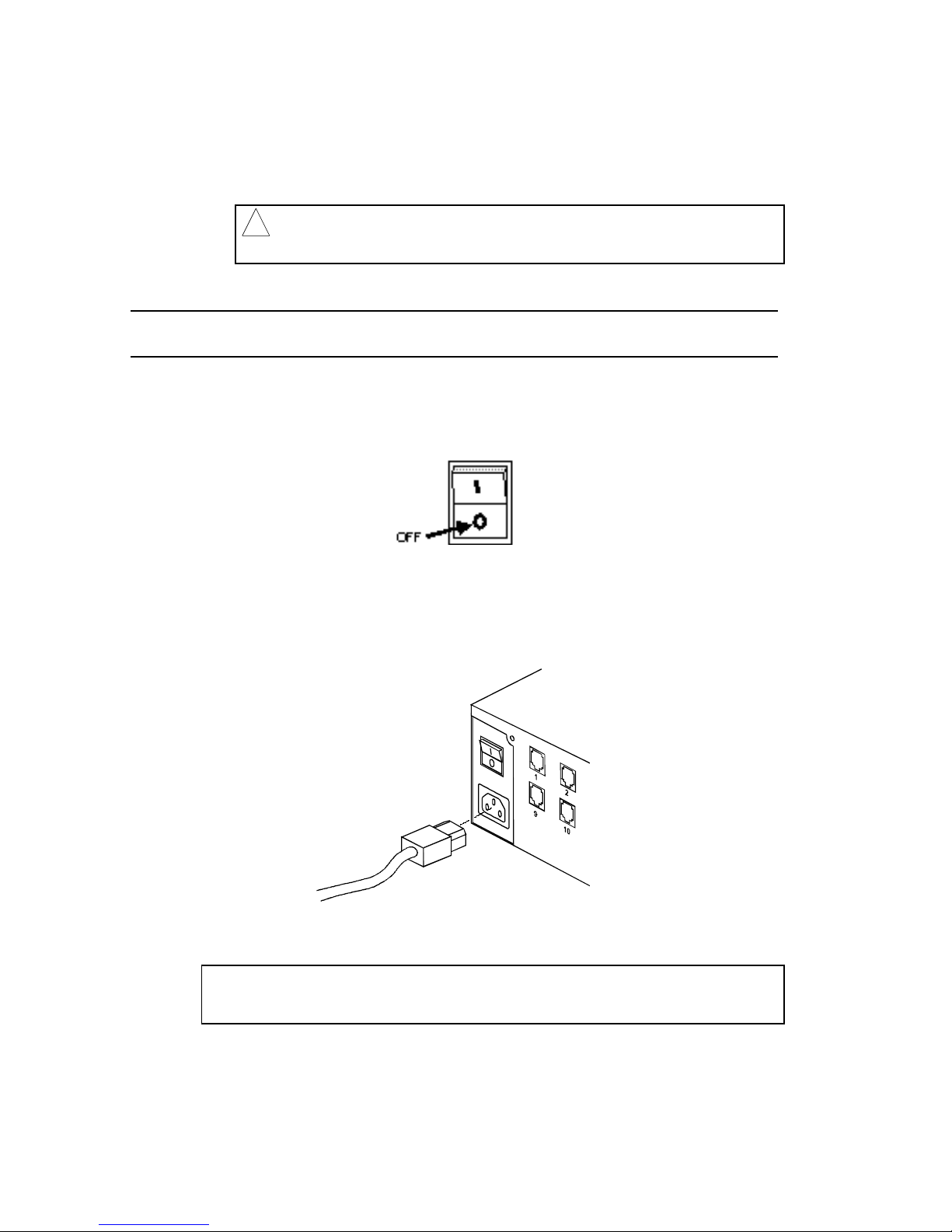
Power
Be sure the power switch on the MP/16 is turned OFF before
plugging in the power cable.
The supplied power cable plugs into the back of the MP/16 and
connects to any standard, grounded 110v, 60Hz AC electrical
outlet.
Figure 2-4. Power Cord
NOTE: You may want to install a line noise filter/surge protector
between the power source and the MP/16.

Assigning IP Addresses 2-7
Assigning IP Addresses
NOTE: This section assumes that you have an addressing
strategy for your network and have already chosen an IP address
and subnet mask for the MP/16.
Default Addresses
The MP/16 Management ports (LAN and Console) are configured
to default to the following Class C IP addresses. We recommend
changing these defaults to fit your network IP addressing scheme.
Table 2-1. Default IP Addresses
Port Default IP Address
LAN Port 192.77.203.193
WAN (Console) Port 192.77.203.65
Subnet Mask 255.255.255.192
Gateway 192.77.203.126
Accessing the Configuration User
Interface (UI)
The MP/16’s Configuration User Interface (UI) allows you to
change IP address information. To access the Configuration UI,
you need the following:
♦ An RJ45-to-DB-25 serial cable (provided)
♦ A null modem adapter (provided)
♦ A PC running a TTY terminal emulator (or communications
program in terminal mode) to act as the configuration console

2-8 Installation
Follow these steps:
1 Make certain that the unit is powered off.
2 Set Console DIP switches. The Console DIP switches are
located to the immediate left of the Console port. (See figure
2-5 below).
Console
DIP Switches
Figure 2-5. Location of Console DIP Switches
♦ DIP switch 3 must be is in the UP (OFF) position.
♦ Use DIP switches 1 and 2 to set the Console port speed to
the highest rate supported by your PC and communication
software (if unsure, leave at 9600 or set it to 19.2K).
The following table reflects the table labeled SPEED
printed on the back of the MP/16.
Table 2-2. Console Port Speed
Switch 1 Switch 2 Speed
OFF OFF 9600
OFF ON 19.2K
ON OFF 38.4K
ON ON 57.6K
Assigning IP Addresses 2-9
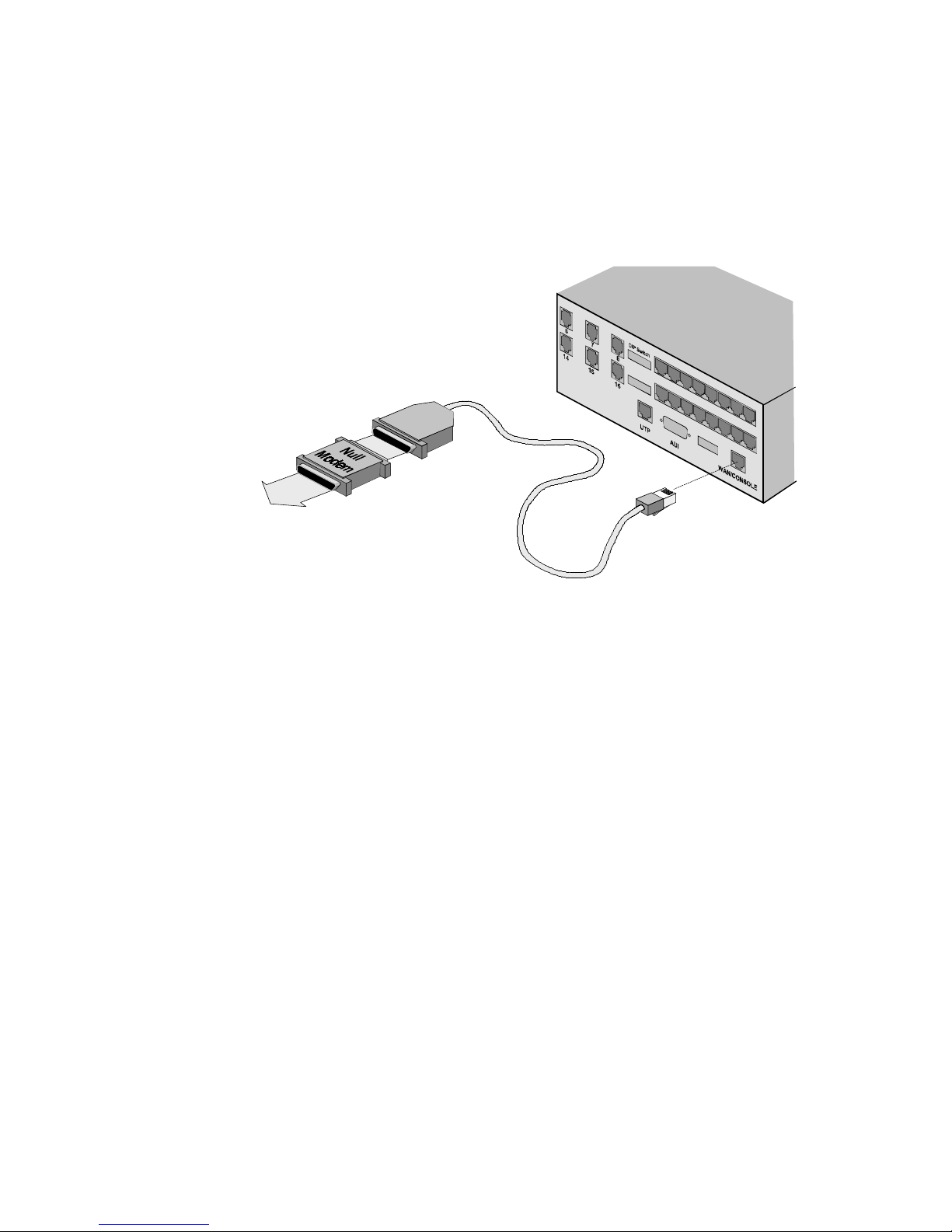
3 Connect the configuration console to the MP/16. Use the
provided RJ45-to-DB-25 serial cable with the provided null
modem adapter (see Figure 2-6 below) to connect the MP/16
Console port to a serial port on the PC or terminal you are
using as the configuration console.
To PC or
Terminal
Figure 2-6. Connecting to the Console Port
4 Power on the MP/16. The Run/Fail LED on the bottom row of
LEDs flashes while the MP/16 runs its self-diagnostic. After
the MP/16 has finished booting, the Run/Fail light should be
solid green.
5 Power on the configuration console. Run the terminal
emulator (or communications program in terminal mode). It
must be set to the same port speed that you set the Console port to in
step 2. It must also be set for hardware flow control (CTS/RTS)
with a data format of 8-N-1.
6 Press Return. Press Return from the configuration console.
The User Interface (UI) Main Menu should appear. If the UI
Main menu does not appear, check the following:
♦ The port speed setting in your communications software
must match the port speed on the MP/16 (set in step 2).
♦ Your communications software must be set for hardware
flow control (CTS/RTS) and a data format of 8-N-1.

2-10 Installation
♦ The null modem adapter must be attached to the serial
cable and plugged into a COM port on the configuration
console.
♦ The communications softwa re must be set for the COM
port that the MP/16 is connected to.
The User Interface
After you have established a successful connection, the UI Main
menu should appear on the configuration terminal screen.
1 Type “1” at the Main menu prompt and press Enter to bring up
the Configuration menu.
2 Change the default IP addresses, subnet mask, and any other
management parameters. If necessary, refer to Appendix B,
Management Configuration Menu Guide.
3 IMPORTANT! Save settings to NVRAM. After completing all
IP address assignments, select Save Configuration to Non-Volatile
Memory (7) from the Configuration menu to save the settings to
the MP/16’s NVRAM. Make sure that Console DIP Switch 4 is
in the UP (OFF) position so that the MP/16 boots from the
NVRAM configuration.
Remote Configuration
Optionally,configuration can be performed from a remote location
by attaching a modem to the Console port to which you dial in
from a remote configuration console. Follow the same basic
procedure for local configuration, but use the following guidelines:
♦ Set the modem’s port speed to match the MP/16’s Console
port speed. For U.S. Robotics modems, attach a PC running
communications software to the modem’s serial port, set the
software for the right speed, and send the modem an AT
command. The modem matches its port speed to the rate at
which the AT command is sent.
♦ Connect the modem to the MP/16 Console port, but do NOT
use the null modem adapter.
♦ Dial into the modem from the remote configuration console
using a communications program in terminal mode.
Management Over a LAN 2-11
Additional Configuration Options
In addition to setting the IP addresses and subnet mask, the
Configuration UI allows you to do the following:
♦ View Local Ethernet MAC Address. The MP/16 has a unique
MAC address burned in at the factory. This address cannot be
changed.
♦ Set Local SNMP Community Strings , which determines the
level of access for the MP/16 from a Management Station. The
default Community strings are “public” for read-only and
“private” for read-write.
♦ Re-initialize Authorized Access List . This clears the authorized
access list as set in Total Control Manager/SNMP (TCM),
granting access to all users.
NOTE: If you are using TCM/SNMP, these options may be set at
a later time through the TCM interface.
Management Over a LAN
Two types of Ethernet connectors on the back of the MP/16 (AUI
and UTP) allow SNMP management over a LAN. The LAN IP
address and subnet mask are assigned through the MP/16 User
Interface (UI) as explained in the previous section.
NOTE: We suggest the MP/16 be on an isolated LAN segment
that does not receive Medium Access Control (MAC) layer
broadcasts. This will prevent the MP/16 from expending too
much time on nonproductive traffic and allow it to concentrate its
resources on other, real-time management functions.
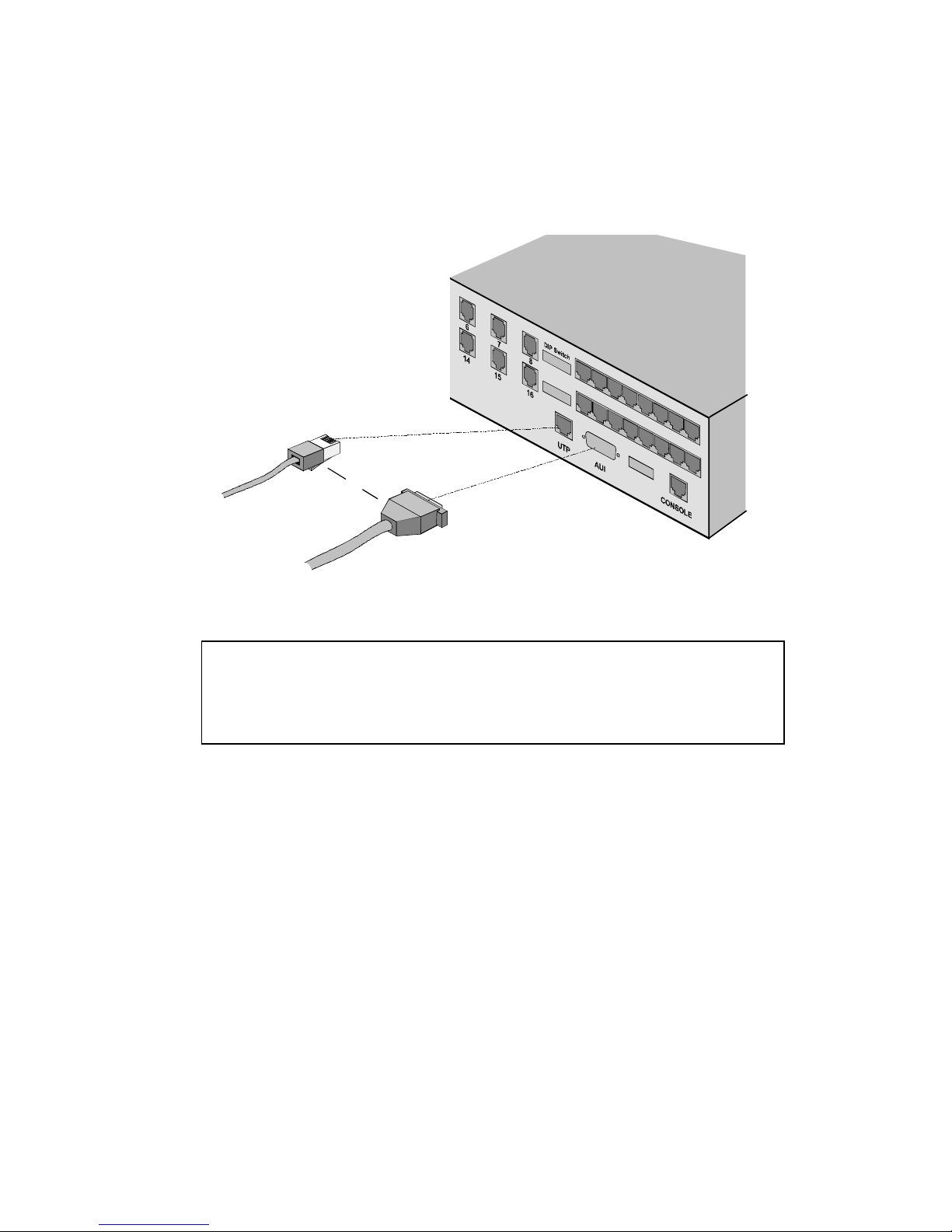
2-12 Installation
Plug the thick net (10Base5) or twisted pair (10BaseT) network
cable into the appropriate socket on the MP/16. The MP/16
automatically detects which type of network cable you are using
when you power it on.
or
Twisted Pair
(10BaseT)
Thicknet
(10Base5)
Figure 2-7. Cabling to a LAN
NOTE: If there is no Ethernet cable attached to the MP/16 when
you power it on, the MP/16 defaults to the AUI port. If you later
decide to connect to the UTP port, you must reset the MP/16 by
powering it off.
ThinNet Installations
If you want to connect the MP/16 to “thin Ethernet” coaxial cable,
you will need a Multiple Access Unit (MAU) to convert from one
of the existing connectors.

Dial-Up Management 2-13
Dial-Up Management
The Console port on the back of the MP/16 allows you to manage
it using a dial-up SLIP (WAN) connection. The Console port must
be assigned a WAN IP address and subnet mask. If you have not
already done so, follow the steps for assigning IP addresses earlier
in this chapter before continuing.
To set up the MP/16 for dial-up management, you will need the
following:
♦ A modem. We suggest using a separ ate, external modem. For
instructions on using one of the modems in the MP/16, see
Using an MP/16 Modem for Dial-up Management at the end of
this section.
♦ A female DB-25 or DB-9 to RJ45 cable, such as the ones that
come with the optional U.S. Robotics serial cable kit.
♦ A terminal or PC, running communications software to
configure the modem.
2-14 Installation
Use the following steps to set up the MP/16 for dial-up
management:
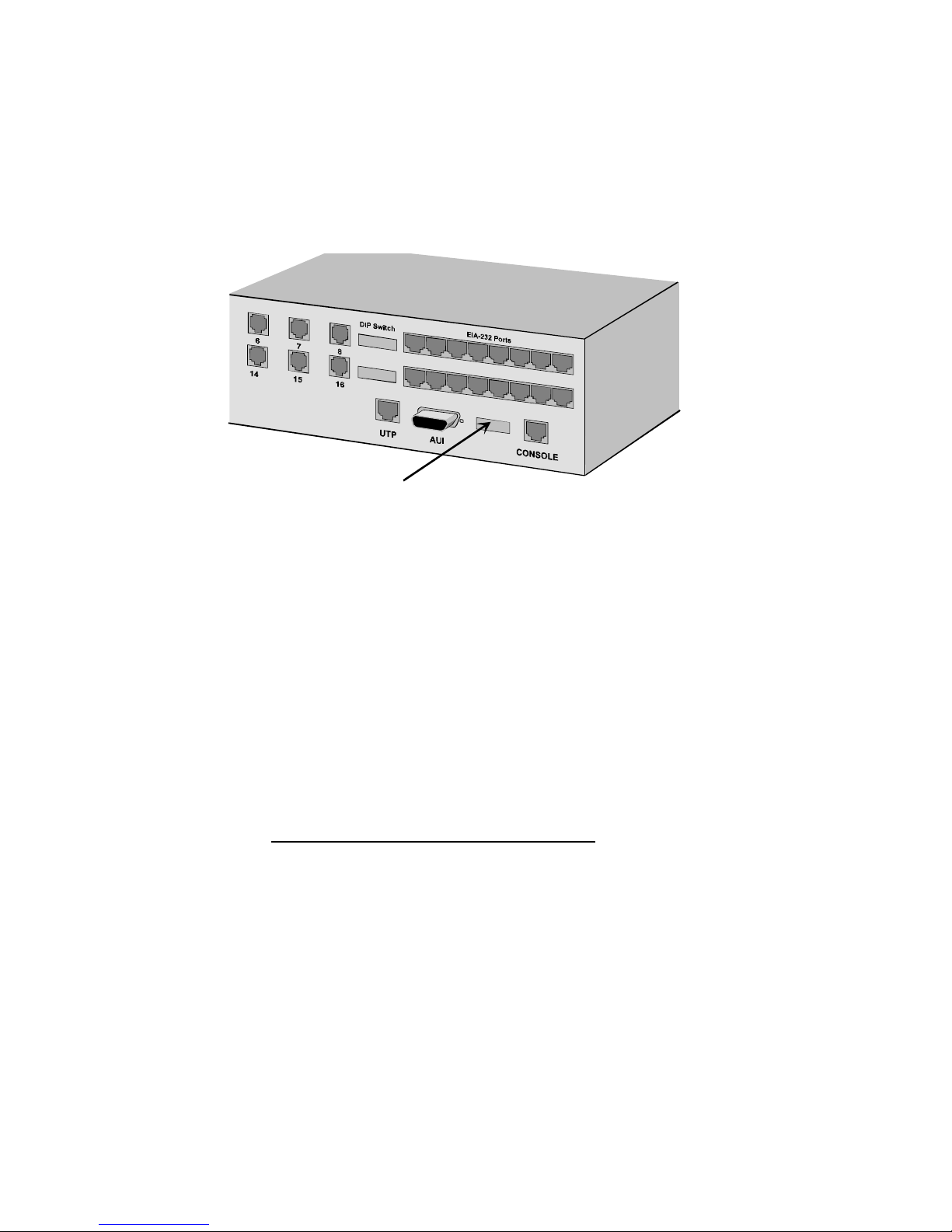
1 Set Console port DIP switches. The Console port DIP
switches are located to the immediate left of the Console port.
Console
DIP Switches
Figure 2-8. Location of Console port DIP Switches
♦ Set DIP switch 3 to the DOWN (ON) position. This
configures the Console port for management.
♦ Use DIP switches 1 and 2 to set the Console port speed to
the highest speed supported by the modem. For U.S.
Robotics High Speed modems, set the port speed at 57.6K.
The following table reflects the table labeled SPEED
printed on the back of the MP/16.
Table 2-3. Console Port Speed
Switch 1 Switch 2 Speed
OFF OFF 9600
OFF ON 19.2K
ON OFF 38.4K
ON ON 57.6K

Dial-Up Management 2-15
2 Configure the modem. Connect a PC running a
communications program or terminal emulator to the modem.
a IMPORTANT: Set the communications software or
terminal emulator to the same serial port rate at which you
set the Console port in step 1.
b Configure the modem with the following settings:
Setting
Command
(for USR modems)
Auto Answer DIP Switch 5 OFF
Functional DTR DIP Switch 1 OFF/&D2
CTS flow control &H1
Fixed DTE rate &B1**
RTS flow control &R2
DSR override &S0
ITU-T answer sequence B0
Command mode local echo off DIP Switch 4 ON/E0
Online echo off F1
Suppress result codes DIP Switch 3 OFF/Q1
** U.S. Robotics modems fix their serial ports to match the rate at which AT
commands are sent to them across the serial port.
c If you are using a U.S. Robotics modem or your modem
contains NVRAM, you’ll probably want to save these
settings to the modem’s NVRAM so you don’t have to reenter them every time you power on the modem.
For U.S. Robotics modems, use the following command:
AT&W
Make sure that the modem is set to load settings from
NVRAM when powered on (DIP Switch 10 OFF).
2-16 Installation
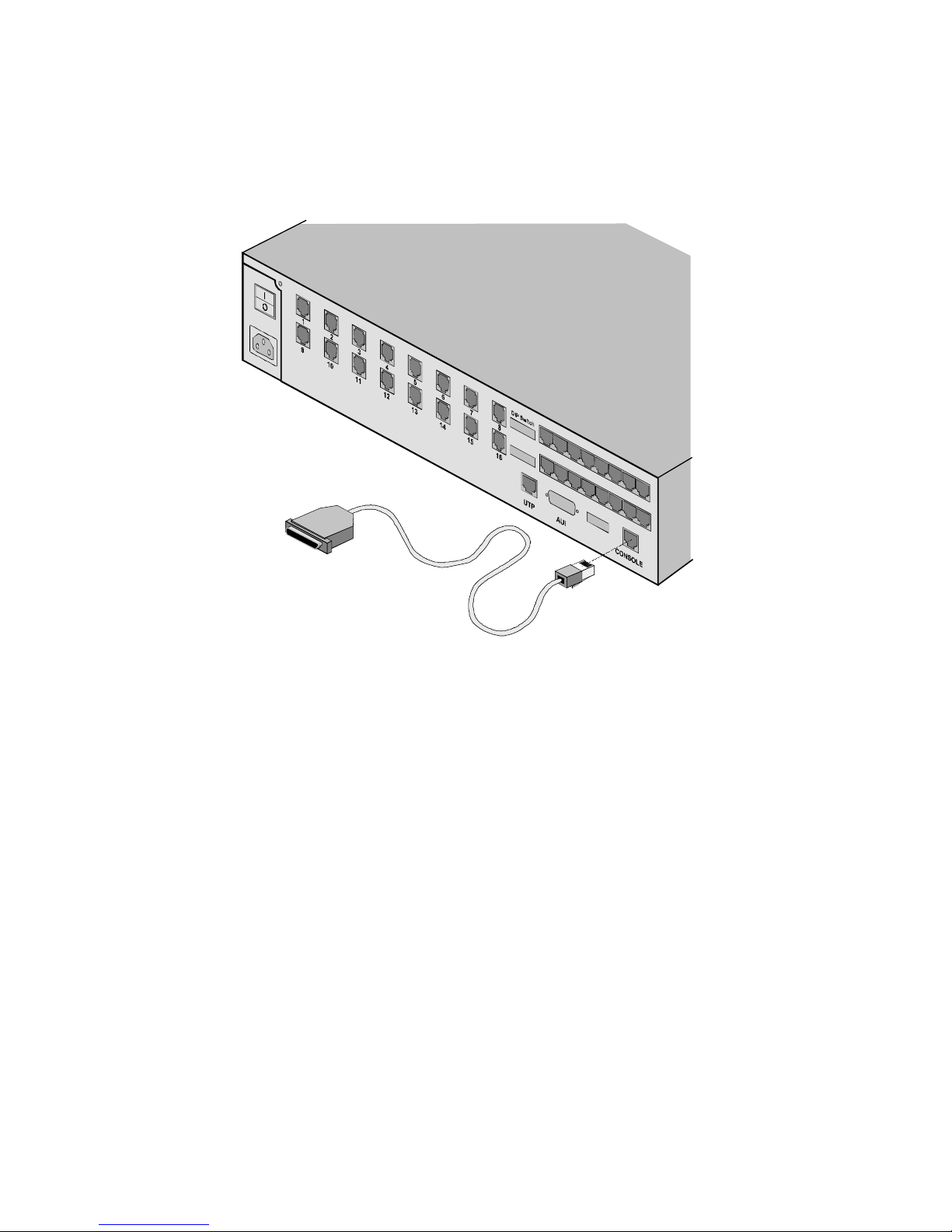
3 Connect the modem to the MP/16 Console port. Use the RJ45-
to-DB-25/DB-9 serial cable to connect the modem to the
MP/16 Console port as pictured below:
To external modem
Dial into modem from
configuration console
Figure 2-9. WAN connection using an external modem
Using an MP/16 Modem for Dial-up
Management
Use the same steps for setup as you would if you were using a
separate modem, with the following guidelines:
♦ In Step 2, Configuring the modem, don’t use the modem DIP
switches to configure the MP/16 modem if these settings are
going to conflict with those required to connect the other seven
modems to your DTE. Instead, use the equivalent AT
commands. AT commands that share functionality with DIP
switches can NOT be saved to the modem’s NVRAM.
However, once a management session is established, you can
use the Auto Configuration feature to save these setting in the
MP/16’s management NVRAM.
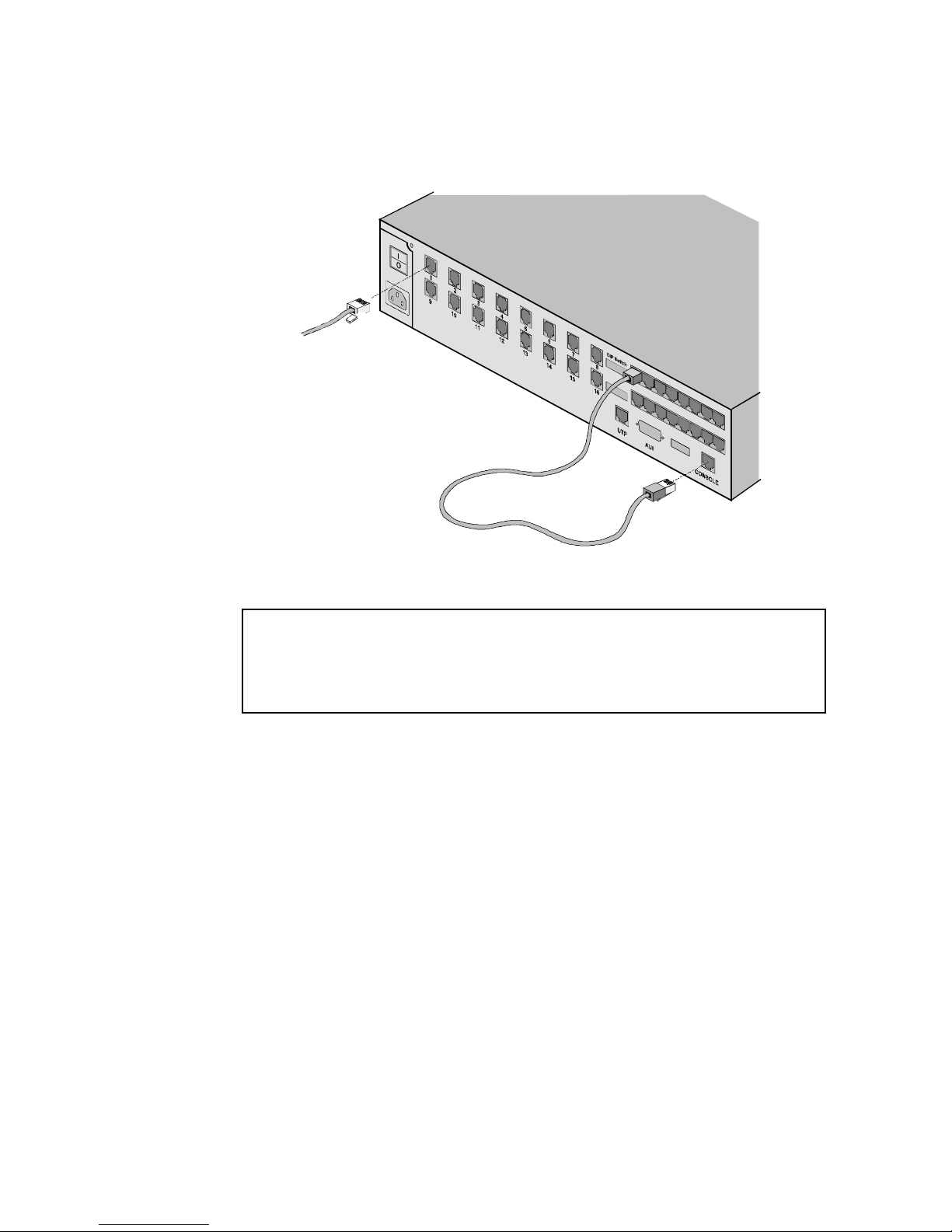
Dial-Up Management 2-17
♦ In Step 3, cable the MP/16 modem to the Console port using a
standard RJ45-to-RJ45 cable. The following diagram illustrates
this setup:
RJ11 Plug
to TELCO
Figure 2-10. Using an MP/16 Modem for Dial-up Management
NOTE: If you use one of the modems in the MP/16 to dial in to
the MP/16, you will NOT be able to perform future upgrades to
the modems in the MP/16 through TCM without onsite
intervention.
2-18 Installation
Modem Setup
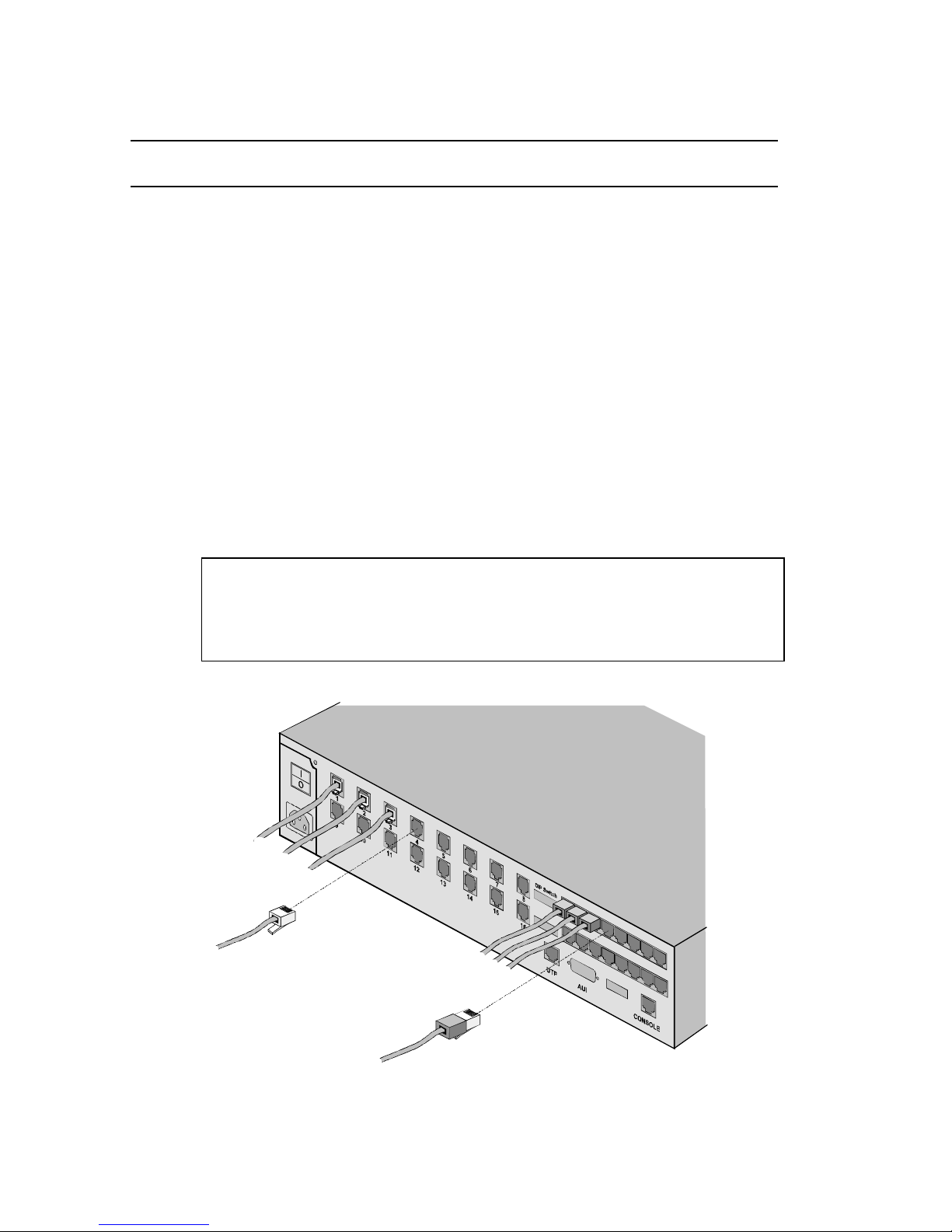
Connecting to the Telephone Company
Plug the provided RJ11 telephone cords into RJ11 jacks the back of
the MP/16. The jacks are labeled 1-16 and marked Telco. Connect
the other end of the cables to your analog phone lines.
Connecting to Your DTE
The RJ45 serial ports for the modems in the MP/16 conform to the
EIA RS-232 standard for Data Communication Equipment (DCE)
devices. Standard RJ45 cables may be used to connect the modems
to any RJ45 Data Terminal Equipment (DTE) interface also in
conformance with the RJ45 EIA-232 standard.
NOTE: Not all equipment provides standard DTE EIA RS-232
interfaces. For RJ45 pin assignments, RJ-to-DB and DCE-to-DCE
pinout conversions, and other information useful for building
custom cables, see Appendix A.
RJ11 Plug
to TELCO
RJ45 Plug
to DTE
Figure 2-10. Cabling the Modems
 Loading...
Loading...