1
TOSHIBA BiCD Integrated Circuit Silicon Monolithic
Weight:
HZIP25-P-1.00F: 7.7g (typ.)
HZIP25-P-1.00F
TB6600HG
PWM Chopper-Type bipolar
Stepping Motor Driver IC
The TB6600HG is a PWM chopper-type single-chip bipolar sinusoidal
micro-step stepping motor driver.
Forward and reverse rotation control is available with 2-phase,
1-2-phase, W1-2-phase, 2W1-2-phase, and 4W1-2-phase excitation
modes.
2-phase bipolar-type stepping motor can be driven by only clock signal
with low vibration and high efficiency.
Features
• Single-chip bipolar sinusoidal micro-step stepping motor driver
• Ron (upper + lower) = 0.4 Ω (typ.)
• Forward and reverse rotation control available
• Selectable phase drive (1/1, 1/2, 1/4, 1/8, and 1/16 step)
• Output withstand voltage: Vcc = 50 V
• Output current: I
I
• Packages: HZIP25-P-1.00F
• Built-in input pull-down resistance: 100 kΩ (typ.), (only TQ terminal: 70kΩ(typ.))
• Output monitor pins (ALERT): Maximum of I
• Output monitor pins (MO): Maximum of I
• Equipped with reset and enable pins
• Stand by function
• Single power supply
• Built-in thermal shutdown (TSD) circuit
• Built-in under voltage lock out (UVLO) circuit
• Built-in over-current detection (ISD) circuit
OUT
= 5.0 A (absolute maximum ratings, peak)
OUT
= 4.5 A (operating range, maximal value)
= 1 mA
ALERT
= 1 mA
MO
TB6600HG
TB6600HG
2014-01-30
2
Pin Functions
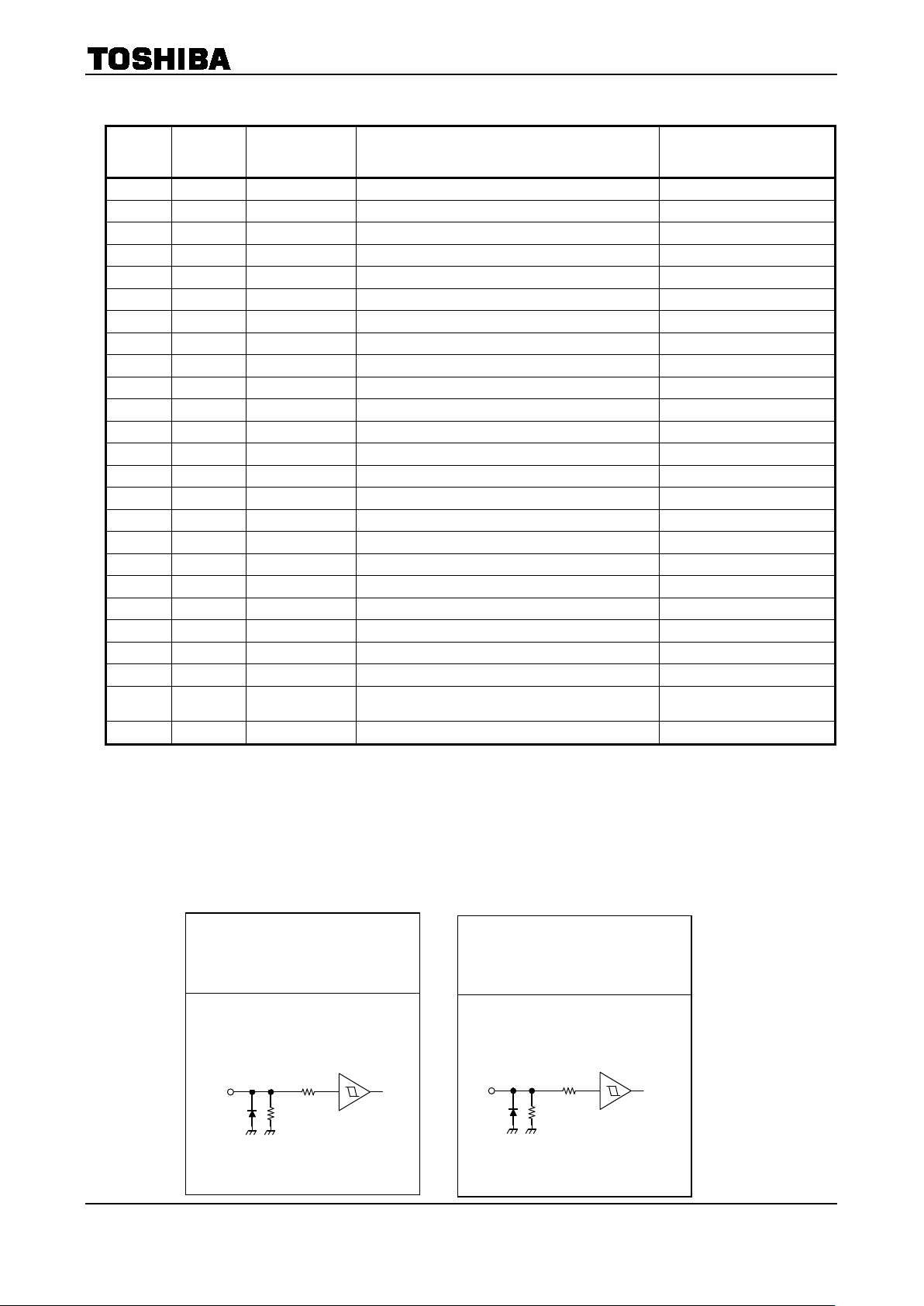
Input pins
100k
VDD 10kΩ
7
TB6600HG
Pin No.
1 Output ALERT TSD / ISD monitor pin Pull-up by external resistance
2 ― SGND Signal ground
3 Input TQ Torque (output current) setting input pin
4 Input Latch/Auto Select a return type for TSD. L: Latch, H: Automatic return
5 Input Vref
6 Input Vcc Power supply
7 Input M1 Excitation mode setting input pin
8 Input M2 Excitation mode setting input pin
9 Input M3 Excitation mode setting input pin
10 Output OUT2B B channel output 2
11 ― NFB B channel output current detection pin
12 Output OUT1B
13 ― PGNDB
14 Output OUT2A
15 ― NFA A channel output current detection pin
16 Output OUT1A
17 ― PGNDA
18 Input ENABLE Enable signal input pin H: Enable, L: All outputs off
19 Input RESET Reset signal input pin L: Initial mode
20 Input Vcc Power supply
21 Input CLK CLK pulse input pin
22 Input CW/CCW Forward/reverse control pin L: CW, H:CCW
23 ― OSC Resistor connection pin for internal oscillation setting
24 Output Vreg Control side connection pin for power capacitor
25 Output MO Electrical angle monitor pin Pull-up by external resistance
I/O Symbol Functional Description Remark
Voltage input for 100% current level
B channel output 1
Power ground
A channel output 2
A channel output 1
Power ground
Connecting capacitor to
SGND
<Terminal circuits>
Input pins
(M1, M2, M3,CLK, CW/CCW,
ENABLE, RESET, Latch/Auto)
(TQ)
10kΩ
Ω
0kΩ
2014-01-30
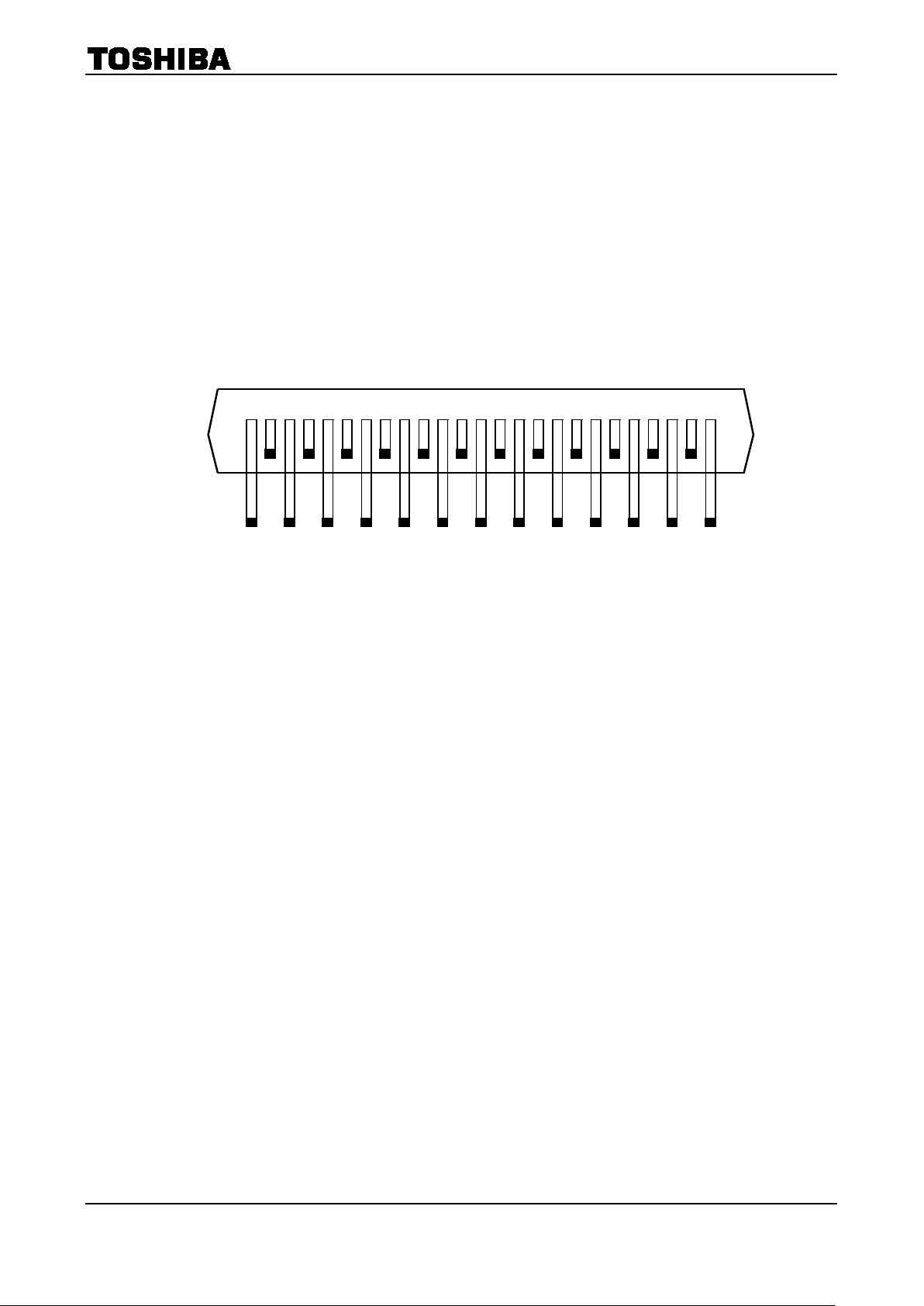
3
(
MO
M1
RESETTQALERT
Vref
PGNDA
CLK
OSC
N
FA
PGNDB
N
FB
M3
23251113151719
21
1618202224
13579
Vcc
CW/CCW
Vreg
2468101214
SGND
Latch/Auto
VccM2OUT2B
OUT1B
OUT2A
OUT1A
ENA BLE
Pin Assignment
Top View)
TB6600HG
2014-01-30

4
Block Diagram
M1
M2
CLK
M3
OSC
1/3
TSD / ISD / UVLO
MO
ALERT
OUT1A
OUT2A
NFA
OUT1B
OUT2B
NFB
Vref
SGND
PGNDB
Current selector
circuit A
3 4 12
15
14
16
6, 20
1
25
24 7 8 9 22
21
19
18
17
2
Current selector
circuit B
11
10
RESET
13
PGNDA
23
5
Latch/Auto TQ
Vcc
Vreg
100%/30%
ENABLE
CW/CCW
Sett ing of Vref
Reg(5V)
Input
circuit
OSC
Input
TQ
L 30%
H 100%
Voltage ratio
Pre
-drive
Pre
-drive
TB6600HG
H-Bridge
driver A
H-Bridge
driver B
2014-01-30

5
Description of Functions
1. Excitation Settings
The excitation mode can be selected from the following eight modes using the M1, M2 and M3 inputs. New
excitation mode starts from the initial mode when M1, M2, or M3 inputs are shifted during motor operation.
In this case, output current waveform may not continue.
TB6600HG
Input
M1 M2 M3
L L L
L L H 1/1 (2-phase excitation, full-step)
L H L
L H H
H L L 1/4 (W1-2 phase excitation)
H L H 1/8 (2W1-2 phase excitation)
H H L 1/16 (4W1-2 phase excitation)
H H H
Note: To change the exciting mode by changing M1, M2, and M3, make sure not to set M1 = M2 = M3 = L or M1 = M2 =
M3 = H.
(Operation of the internal circuit is almost turned off.)
1/2A type (1-2 phase excitation A type)
1/2B type (1-2 phase excitation B type)
(Operation of the internal circuit is almost turned off.)
Mode
(Excitation)
Standby mode
( 0%, 71%, 100% )
( 0%, 100% )
Standby mode
Standby mode
The operation mode moves to the standby mode under the condition M1 = M2 = M3 = L or M1 = M2 = M3
= H.
The power consumption is minimized by turning off all the operations except protecting operation.
In standby mode, output terminal MO is HZ.
Standby mode is released by changing the state of M1=M2=M3=L and M1=M2=M3=H to other state.
Input signal is not accepted for about 200 μs after releasing the standby mode.
2014-01-30
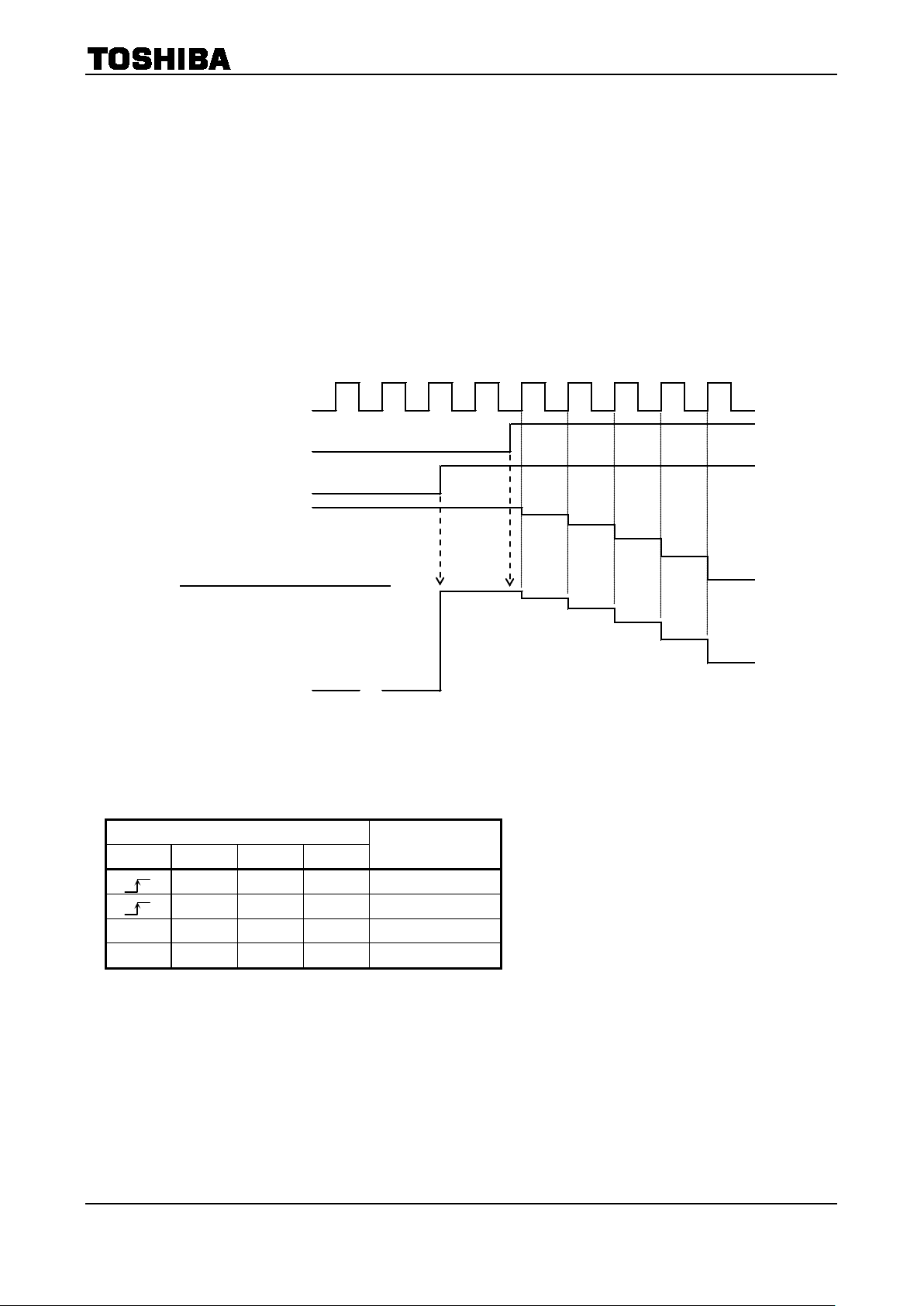
6
2. Function
(例1)
内部電流設定
Z
出力電流(A相)
CLK
RESET
ENABLE
(Example 1)
Internal current set
Output
(*)
(1)To turn on the output, configure the ENABLE pin high. To turn off the output, configure the ENABLE
pin low.
(2) The output changes to the Initial mode shown in the table below when the ENABLE signal goes High
level and the RESET signal goes Low level. (In this mode, the status of the CLK and CW/CCW pins are
irrelevant.)
(3) As shown in the below figure of Example 1, when the ENABLE signal goes Low level, it sets an OFF on
the output. In this mode, the output changes to the initial mode when the RESET signal goes Low level.
Under this condition, the initial mode is output by setting the ENABLE signal High level. And the motor
operates from the initial mode by setting the RESET signal High level.
CLK CW/CCW RESET ENABLE
L H H CW
H H H CCW
X X L H Initial mode
X X X L Z
(phase A )
(*: Output current starts rising at the timing of PWM frequency just after ENABLE pin outputs high.)
current
Input
TB6600HG
Command of the standby has a higher priority
Output mode
than ENABLE. Standby mode can be turned on
and off regardless of the state of ENABLE.
X: Don’t Care
2014-01-30

7
fchop(kHz)
Min
Typ.
Max
30 - 60 - 51 - 40 - 120 - 20
-
3. Initial Mode
When RESET is used, the phase currents are as follows.
Excitation Mode Phase A Current Phase B Current
1/1 (2-phase excitation, full-step) 100% -100%
1/2A type (1-2 phase excitation A type) (0%, 71%, 100%) 100% 0%
1/2B type (1-2 phase excitation B type) (0%, 100%) 100% 0%
1/4 (W1-2 phase excitation) 100% 0%
1/8 (2W1-2 phase excitation)
1/16 (4W1-2 phase excitation)
current direction is defined as follows.
OUT1A → OUT2A: For ward dir ec tion
OUT1B → OUT2B: Forward direction
100% 0%
100% 0%
4. 100% current settings (Current value)
100% current value is determined by Vref inputted from external part and the external resistance for
detecting output current. Vref is doubled 1/3 inside IC.
Io (100%) = (1/3 × Vref) ÷ R
The average current is lower than the calculated value because this IC has the method of peak current
detection.
Pleas use the IC under the conditions as follows;
NF
TB6600HG
0.11Ω ≤ R
≤ 0.5Ω, 0.3V ≤ Vref ≤ 1.95V
NF
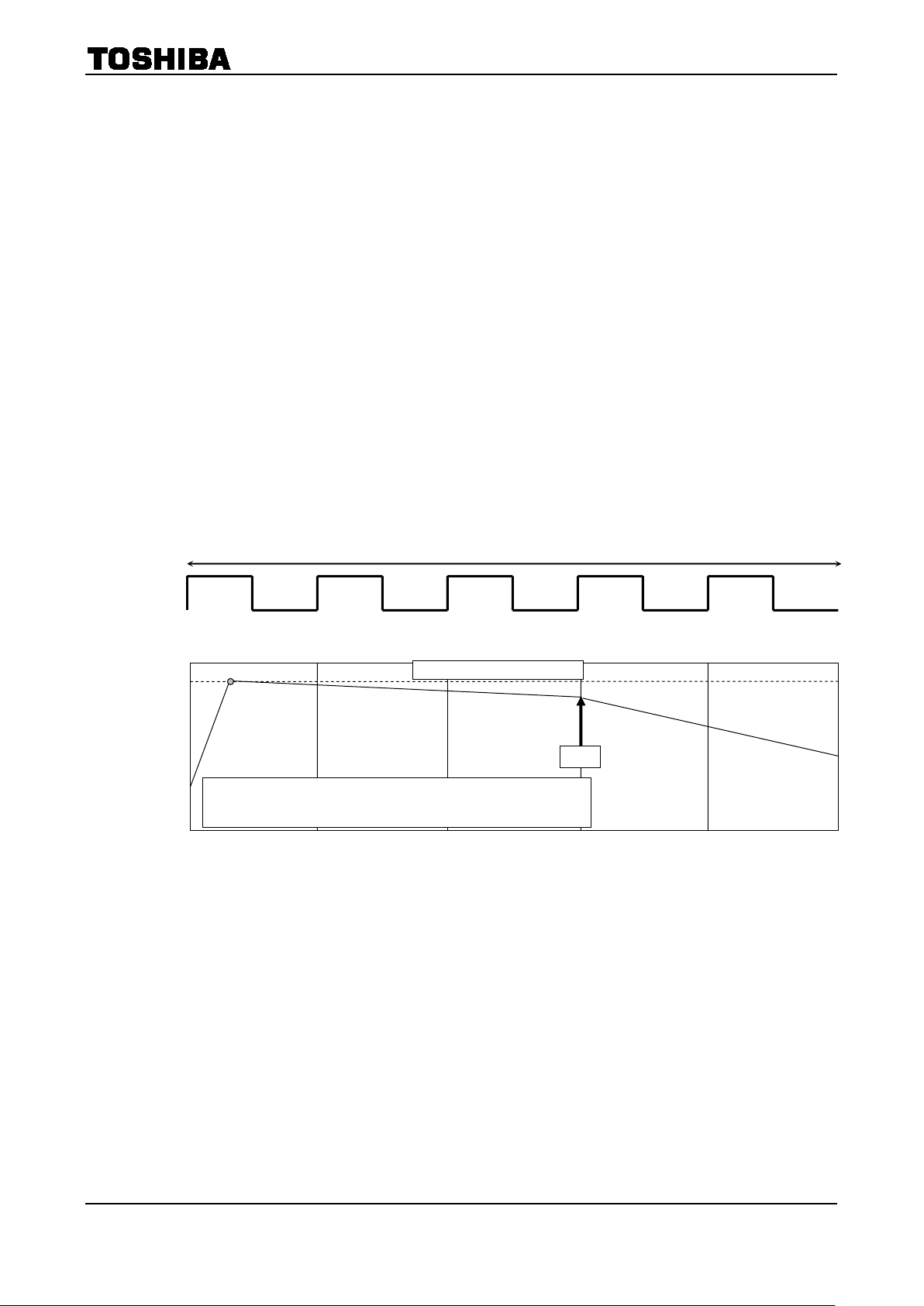
5. OSC
Triangle wave is generated internally by CR oscillation by connecting external resistor to OSC terminal.
Rosc should be from 30kΩ to 120kΩ. The relation of Rosc and fchop is shown in below table and figure. The
values of fchop of the below table are design guarantee values. They are not tested for pre-shipment.
Rosc(kΩ)
2014-01-30
TB6600HG
8
OSC
Interna
Waveform
f
chop
NF
40
fast
Decay
Mode
Charge mode → NF: Predefined current level → Slow mode →
Predefined Current Level
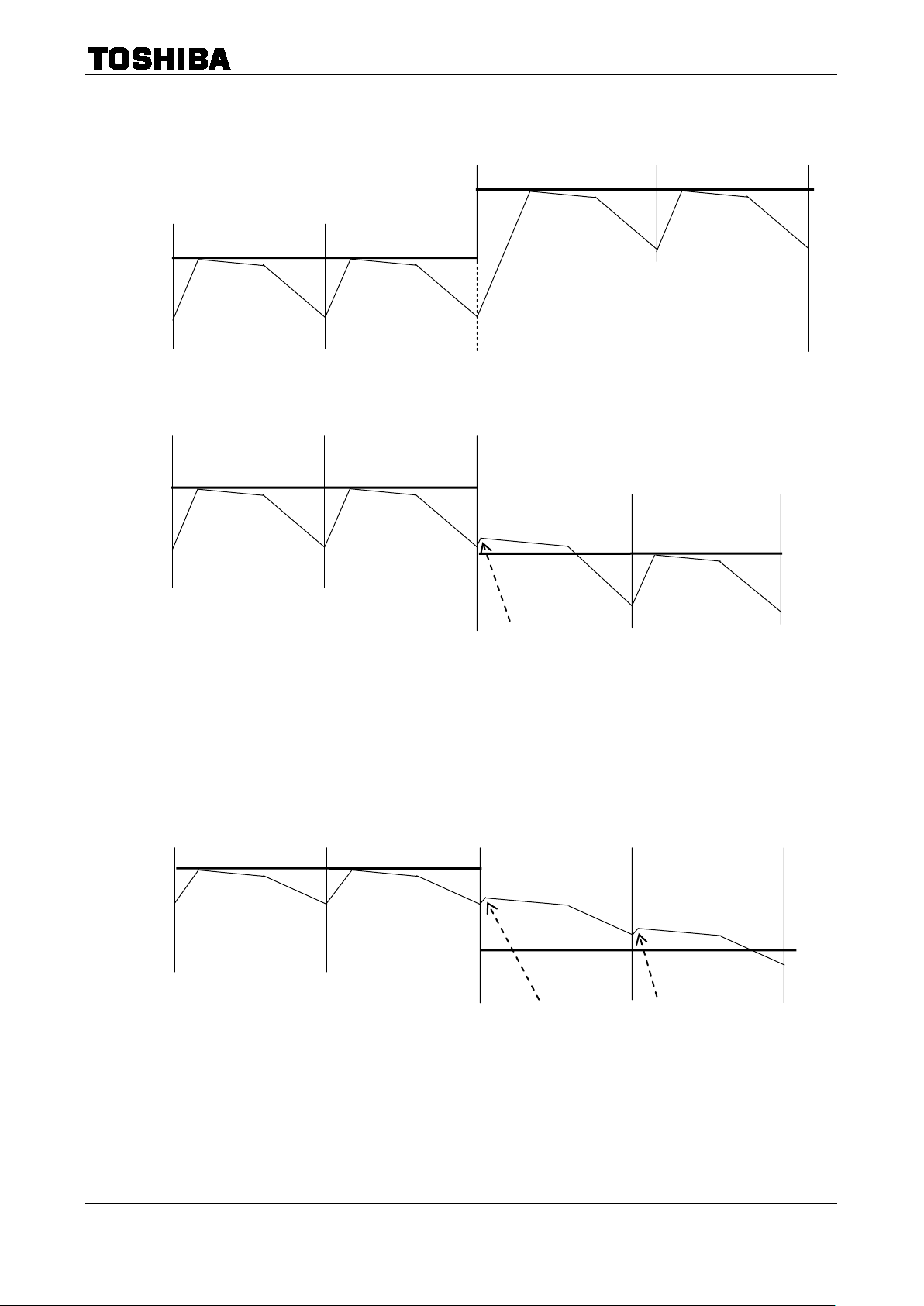
6. Decay Mode
It takes approximately five OSCM cycles for charging-discharging a current in PWM mode. The 40% fast
decay mode is created by inducing decay during the last two cycles in Fast Decay mode.
The ratio 40% of the fast decay mode is always fixed.
The relation between the master clock frequency (fMCLK), the OSCM frequency (fOSCM) and the PWM
frequency (fchop) is shown as follows:
fOSCM = 1/20 ×fMCLK
fchop = 1/100 ×fMCLK
When Rosc=51kΩ, the master clock=4MHz, OSCM=200kHz, the frequency of PWM(fchop)=40kHz.
6-1. Current Waveform and Mixed Decay Mode settings
The period of PWM operation is equal to five periods of OSCM.
The ratio 40% of the fast decay mode is always fixed.
The “NF” refers to the point at which the output current reaches its predefined current level.
MDT means the point of MDT (MIXED DECAY TIMMING) in the below diagram.
M
l
%
MDT(Mixed decay timing) → Fast mode → Current monitoring →
(When predefined current level > Output current) Charge mode
MDT
2014-01-30
9
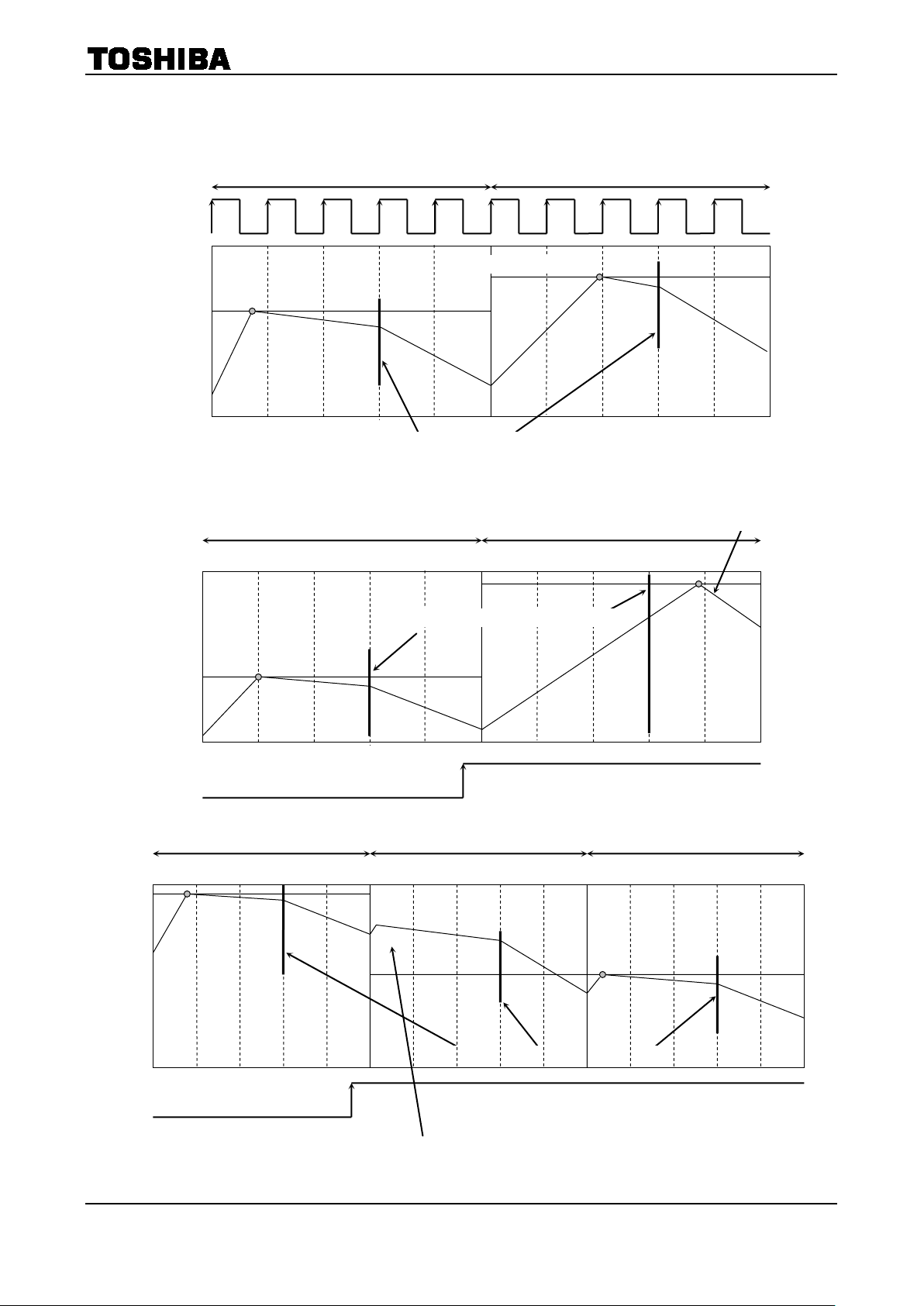
6-2. Effect of Decay Mode
Predefined
Curre
Slow
Slow
Fast
Predefined
Curre
Slow
Charge
Fast
Fast
Fast
Slow
Even if the output current rises above the predefined current at the RNF point, the
Slow
Slow
Charge
Slow
Fast
Slow
Fast
Charge
Predefined
Curre
Predefined
Curre
Fast
Charge
Fast
ned current at the RNF point, the
Slow
Slow
Slow
Slow
Fast
Fast
Charge
Charge
Fast
Charge
Fast
Charge
Predefined
Curre
Predefined
Curre
• Increasing the current (sine wave)
nt Level
TB6600HG
nt Level
• Decreasing the current (In case the current is decreased to the predefined value in a short time because
it decays quickly.)
nt Level
nt Level
Charge
Even if the output current rises abov e the predefi
current control mode is briefly switched to Charge mode for current sensing.
• Decreasing the current (In case it takes a long time to decrease the current to the predefined value
because the current decays slowly.)
nt Level
nt Level
Charge Charge
current control mode is briefly switched to Charge mode for current sensing.
During Mixed Decay and Fast Decay modes, if the predefined current level is less than the output current at
the RNF (current monitoring point), the Charge mode in the next chopping cycle will disappear (though the
current control mode is briefly switched to Charge mode in actual operations for current sensing) and the
current is controlled in Slow and Fast Decay modes (mode switching from Slow Decay mode to Fast Decay
mode at the MDT point).
Note: The above figures are rough illustration of the output current. In actual current waveforms, transient response
curves can be observed.
2014-01-30
10
NF
NF
OS
Internal
waveform
I
OUT
f
chop
f
chop
Predefined
Predefined Current Level
40
Fast
DECAY
MODE
MDT (MIXED DECAY TIMMING) points
NF
40
Fast
DECAY
MODE
I
OUT
f
chop
f
chop
Predefined
Current Level
CLK signal input
Switches to Fast mode after Charge mode
NF
MDT (MIXED DECAY TIMMING) points
NF
NF
I
OUT
f
chop
f
chop
Predefined
CLK signal input
f
chop
MDT (MIXED DECAY TIMMING) points
Predefined Current
Level
40
Fast
DECAY
MODE
t at the
switched to Charge
Predefined
Current Level
6-3. Current Waveforms in Mixed Decay Mode
CM
Current Level
%
• When the NF points come after Mixed Decay Timing points
%
• When the output current value > predefined current level in Mixed Decay mode
Current
Level
%
Even if the output current rises above the predefined curren
RNF point, the current control mode is briefly
mode for current sensing.
TB6600HG
2014-01-30

11
Output Stage Transistor Operation Mode
U1
L1
U2
L2
PGND
OFF
OFF
U1
L1
U2
L2
OFF
ON
Note
PGND
U1
L1
U2
L2
Note
PGND
Note
RNF
Vcc
ON
ON
Charge Mode
Slow Mode
Fast Mode
ON
RNF
Vcc
RNF
Vcc
OFF
OFF
OFF
ON
ON
TB6600HG
OUT1 OUT2
Load
Load
OUT1 OUT2
OUT1 OUT2
Load
Output Stage Transistor Operation Functions
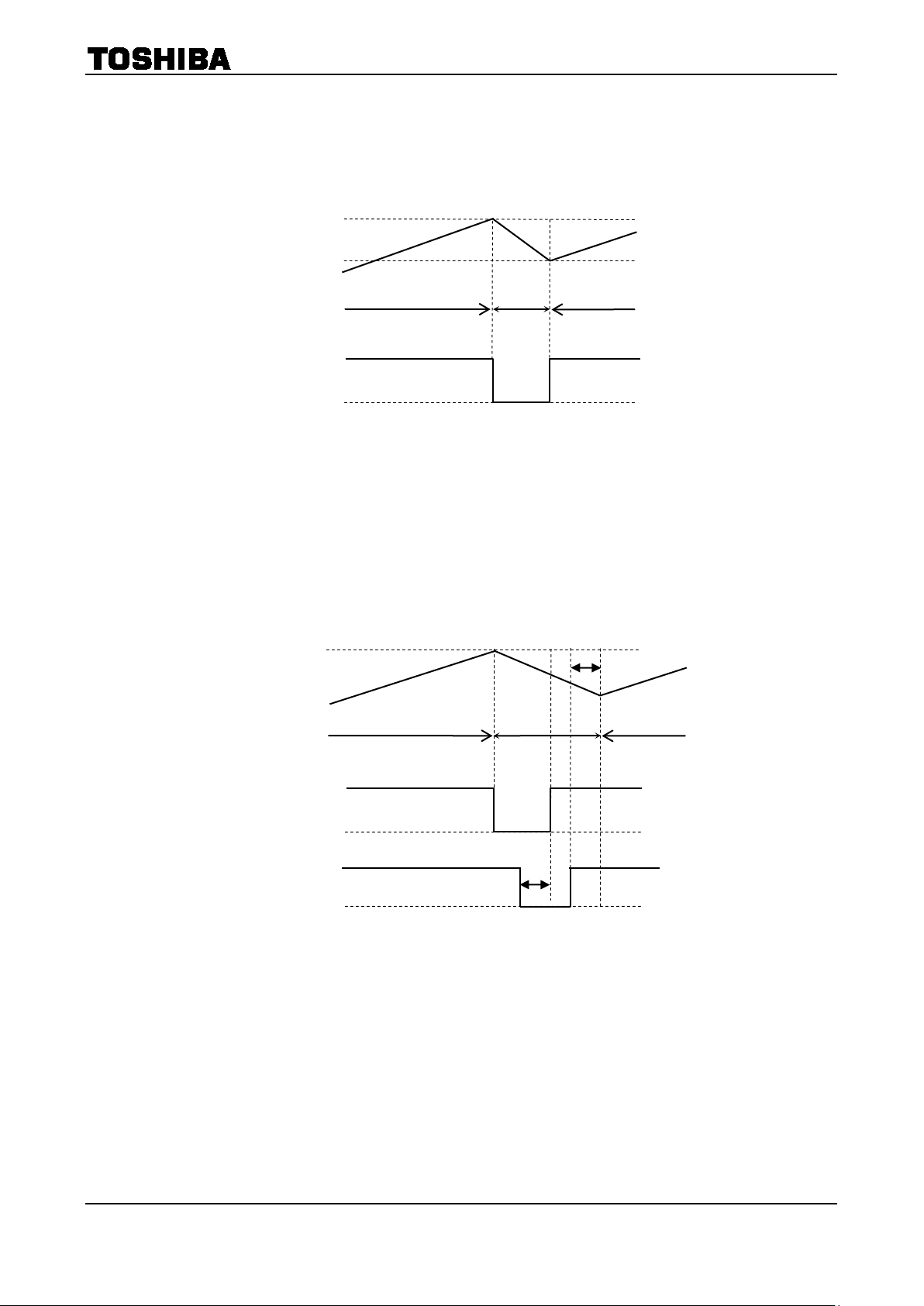
CLK U1 U2 L1 L2
CHARGE ON OFF OFF ON
SLOW OFF OFF ON ON
FAST OFF ON ON OFF
Note: The above chart shows an example of when the current flows as i ndicated b y the arrows in t he above figures .
If the current flows in the opposite direction, refer to the follo wing char t:
CLK U1 U2 L1 L2
CHARGE OFF ON ON OFF
SLOW OFF OFF ON ON
FAST ON OFF OFF ON
Upon transitions of above-mentioned functions, a dead time of about 300 ns (Design guarantee value) is inserted
respectively.
2014-01-30
TB6600HG
12
・
1
90°C (typ.) (Note)
160°C (typ.) (Note)
Junction temperature (Chip temperature)
H
0.3ms or more when Rosc=51k
(*)Output current starts rising at the
timing of PWM frequency just after
ENABLE pin outputs high.
(*)
Thermal Shut-Down circuit (TSD)
(1) Automatic return
TSD = 160°C (typ.) (Note)
TSDhys = 70°C (typ.) (Note)
Junction temperature (Chip temperature)
Automatic return has a temperature hysteresis shown in the above figure.
In case of automatic return, the return timing is adjusted at charge start of fchop after the temperature falls to the
return temperature (90°C (typ.) in the above figure).
The return period after the temperature falls corresponds to one cycle to two cycles of fchop.
(2) Latch type
TSD = 160°C (typ.) (Note)
60°C (typ.) (Note)
Output state
ALERT output
Output state
ALERT output
Output on Output off Output on
H
L
Output on Output off Output on
L
ENABLE input
The operation returns by programming the ENABLE as H → L → H shown in above figure or turning on power
supply and turning on UVLO function. In this time, term of L level of ENABLE should be 0.3ms or more.
To recover the operation, the junction temperature (the chip temperature) should be 90°C or less when ENABLE
input is switched from L to H level. Otherwise, the operation does not recover.
State of internal IC when TSD circuit operates.
The states of the internal IC and outputs, while the shutdown circuit is operating, correspond to the state when
ENABLE is L.
The state after automatic return corresponds to the state when ENABLE is H. Please configure the Reset L to
rotate the motor from the initial state.
H
L
Ω
Note: Pre-shipment testing is not perf or med.
2014-01-30

TB6600HG
13
Latch/Auto is an input pin for determining the return method of TSD.
If Latch/Auto pin outputs low, TSD function returns by either of turning on power supply again or programming
the ENABLE as H → L → H.
If Latch/Auto pin outputs high, it returns automatically.
In standby mode, TSD function returns automatically regardless of the state of the Latch/Auto pin.
When power supply voltage Vcc is less than 8V, TSD function cannot operate regardless of the state of the
Latch/Auto pin.
2014-01-30

14
ISD (Over current detection)
・
DMOS
Power transistor current
6.5A (typ.)
Dead band
1
Output on Output off Output on
(*)Output current starts rising at the
timing of PWM frequency just after
EN
H
0.3ms or more when Rosc=51k
(*)
Current that flows through output power MOSFETs are monitored individually. If over-current is detected
in at least one of the eight output power MOSFETs, all output power MOSFETs are turned off then this
status is kept until ENABLE signal is input. In this time, term of L level of ENABLE should be 0.3ms or
more.
Masking term of 1μs or more (typ. when Rosc=51kΩ) (Note) should be provided in order to protect detection
error by noise. ISD does not work during the masking term.
Over c urrent detection value ISD=6.5 A (Note)
TB6600HG
ABLE pin outputs high.
Output state
ALERT output
μs or more(typ.)
L
ENABLE input
The operation returns by programming the ENABLE as H → L → H shown in above figure or turning
on power supply and turning on UVLO function.
State of internal IC when ISD circuit operates.
The states of the internal IC and outputs, while the over current detection circuit is operating, correspond to the
state when ENABLE is L.
The state after automatic return corresponds to the state when ENABLE is H. Please configure the Reset L to
rotate the motor from the initial state.
H
L
Note: Pre-shipment testing is not performed.
Ω
Return method of ISD
ISD function returns by either of turning on power supply again or programming the ENABLE as H → L → H
regardless of the state of the Latch/Auto pin.
In standby mode, ISD function cannot operate.
When power supply voltage Vcc is less than 8V, ISD function cannot operate.
2014-01-30

TB6600HG
15
・
Under Voltage Lock Out (UVLO) circuit
Outputs are shutoff by operating at 5.5 V (Typ.) of Vcc or less.
It has a hysteresis of 0.5 V (Typ.) and returns to output when Vcc reaches 6.0 V (Typ.). The following values are
design guarantee values.
State of internal IC when UVLO circuit operates.
The states of the internal IC and outputs correspond to the state in the ENABLE mode and the initial mode at
the same time.
After a return, it can start from the initial mode.
When Vcc falls to around 5.5 V and UVLO operates, output turns off.
It recovers automatically from the initial mode when both Vcc rise to around 6.0 V or more. The following
values are design guarantee values.
2014-01-30

TB6600HG
16
up resistance)
ALERT output
ALERT terminal outputs low in detecting either TSD or ISD.
ALERT terminal is connected to power supply externally via pull-up resistance.
V
Applied voltage to pull-up resistance is up to 5.5 V. And conducted current is up to 1 mA.
It is recommended to gain 5 V by connecting the external pull-up resistance to Vreg pin.
MO output
MO turns on at the predetermined state and output low.
MO terminal is connected to power supply externally via pull-up resistance.
V
Applied voltage to pull-up resistance is up to 5.5 V. And conducted current is up to 1 mA.
It is rec ommended to gain 5 V by connecting the external pull-up resistance to Vreg pin.
Voltage pull-up of MO and ALERT pins
・It is recommended to pull-up voltage to Vreg pin.
・In case of pull-up to except 5 V (for instance, 3.3 V etc.), it is recommended to use other power supply (ex. 3.3 V)
while Vcc output between the operation range. When Vcc decreases lower than the operation range and Vreg
decreases from 5 V to 0 V under the condition that other power supply is used to pull-up voltage, the current
continues to conduct from other power supply to the IC inside through the diode shown in the figure. Though this
phenomenon does not cause destruction and malfunction of the IC, please consider the set design not to continue
such a state for a long time.
・As for the pull-up resistance for MO and ALERT pins, please select large resistance enough for the conducting
current so as not to exceed the standard value of 1 mA.
Please use the resistance of 30 kΩ or more in case of applying 5 V, and 20 kΩ or more in case of applying 3.3 V.
= 0.5 V (max.) at 1 mA
ALERT
TSD ISD ALERT
Under TSD detection Under ISD detection
Normal Under ISD detection
Under TSD detection
Normal Normal Z
= 0.5 V (max.) at 1 mA
MO
State MO
Initial Low
Not initial Z
Normal
Low
(To pull-
(To Vreg in the IC)
2014-01-30

17
Sequence and current level in each excitation mode
CLK
100
(%)
0 −100
t0
t1
t2
t7
t8
t4
t5
t6
IA
100
(%)
0
−100
IB
MO
CLK
100
(%)
0
−100
t0
t1
t2
t3
t7
t8
t4
t5
t6
IA
100
(%)
0
−100
IB
MO
It operates from the initial state after the excitation mode is switched.
1/1-step Excitation Mo de (M1: L, M2: L, M3: H, CW Mo d e )
TB6600HG
t3
1/1-step Excitation Mo de (M1: L, M2: L, M3: H, CCW Mo d e)
2014-01-30

18
1/2-step Excitation Mode (A type) (M1: L, M2: H, M3: L, CW Mode)
CLK
100
(%)
0 −100
t0
t1
t2
t3
t7
t8
t4
t5
t6
71 −71
IA
100
(%)
0
−100
71
−71
IB
MO
CLK
100
(%)
0
−100
t0
t1
t2
t3
t7
t8
t4
t5
t6
71
−71
IA
100
(%)
0
−100
71
−71
IB
MO
It operates from the initial state after the excitation mode is switched.
TB6600HG
1/2-step Excitation Mode (A type) (M1: L, M2: H, M3: L, CCW Mode)
2014-01-30

19
1/2-step Excitation Mo de (B type) (M1: L, M2: H, M3: H, CW Mode)
CLK
100
(%)
0 −100
t0
t1
t2
t3
t7
t8
t4
t5
t6
IA
100
(%)
0
−100
IB
MO
CLK
100
(%)
0
−100
t0
t1
t2
t3
t7
t8
t4
t5
t6
IA
100
(%)
0
−100
71
−71
IB
MO
It operates from the initial state after the excitation mode is switched.
TB6600HG
1/2-step Excitation Mo de (B type) (M1: L, M2: H, M3: H, CCW Mode)
2014-01-30

20
1/4-step Excitation Mode (M1: H, M2: L, M3: L, CW Mode)
CLK
100
(%)
0
−100
t0
t1
t2
t3
t7
t8
t4
t5
t6
71
−71
IA
IB
t9
t10
t11
t15
t16
t12
t13
t
14
38 −38
92
92
100
(%)
0
100
71
71
38
−38
92
−92
MO
It operates from the initial state after the excitation mode is switched.
CLK
100
(%)
0
100
t0
t1
t2
t3
t7
t8
t4
t5
t6
71
71
IA
IB
t9
t10
t11
t15
t16
t12
t13
t
14
38
−38
92
−92
100
(%)
0
−100
71
−71
38
−38
92
−92
MO
−
TB6600HG
−
−
1/4-step Excitation Mode (M1: H, M 2: L, M3: L, CCW Mode)
−
−
2014-01-30
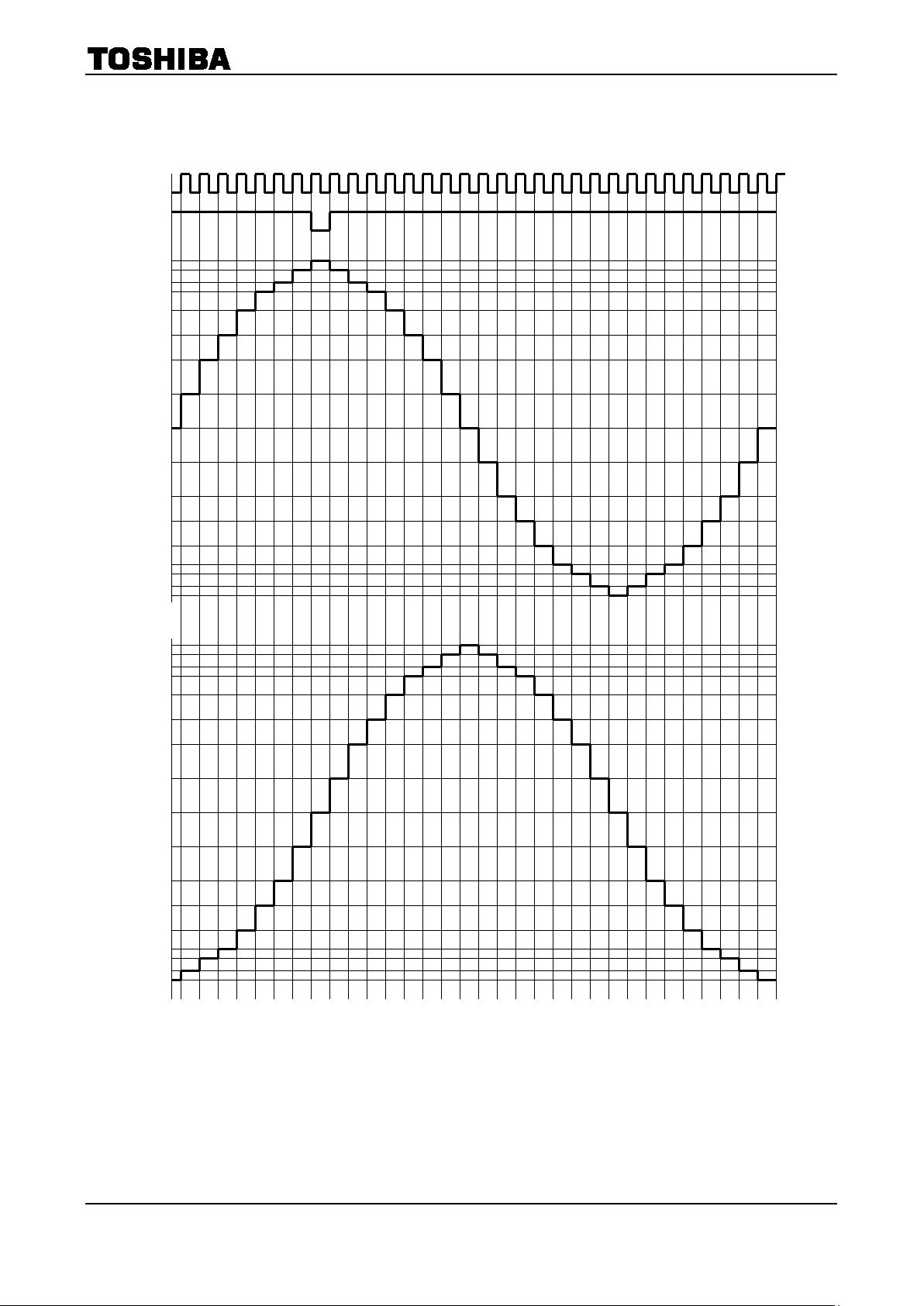
21
1/8-Step Excitation Mode (M1: H, M 2: L, M3: H, CW Mode)
IA
IB
It operates from the initial state after the excitation mode is switched.
MO
38
CLK
t0
t1
t2
t3
t7
t8
t4
t5
t12
t13
t6
100
(%)
98
92
83
71
56
38
20
0 −20
38
56 −71
−92 −98
−100
100
(%)
98
92
83
71
56
20
0
20 −38
56
71 −98 −100
t9
t10
t11
t14
t17
t18
t15
t16
t19
t20
t21
t22
t27
t28
t24
t25
t29
t30
t31
t32
t23
t26
−83
−83
−92
−
−
TB6600HG
−
−
−
2014-01-30

22
1/8-Step Excitation Mode (M1: H, M2: L, M3: H, CCW Mode)
It operates from the initial state after the excitation mode is switched.
MO
38
83
−92
−83
71
CLK
100
(%)
98
92
83
71
56
38
20
0
−20
38
−56 −92
−98
100
100
(%)
98
92
83
71
56
20 0 −20
−38
56
−71 −98
100
t0
t1
t2
t3
t7
t8
t4
t5
t12
t13
t6
t9
t10
t11
t14
t17
t18
t15
t16
t19
t20
t21
t22
t27
t28
t24
t25
t29
t30
t31
t32
t23
t26
IA
IB
−
−
TB6600HG
−
−
−
−
2014-01-30

TB6600HG
23
−100
−98 0 −96
−88
−92
−77
−71
−56
−63
−47
−38
−29
−20
−10
−83
10
20
29
38
47
56
63
71
77
83
88
92
96
98
100
[%]
CLK
IA
IB
It operates from the initial state after the excitation mode is switched.
MO
1/16-step Excitatio n M o de (M1: H, M2: H, M3: L, CW Mo d e)
t0・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・t64
2014-01-30

TB6600HG
24
−100
−98 0 −96
−88
−92
−77
−71
−56
−63
−47
−38
−29
−20
−10
−83
10
20
29
38
47
56
63
71
77
83
88
92
96
98
100
[%]
CLK
IA
IB
MO
It operates from the initial state after the excitation mode is switched.
1/16-step Excitatio n M o de (M1: H, M2: H, M3: L, CCW Mode)
t0・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・t64
2014-01-30

25
Current level
Current level (1/16, 1/8, 1/4, 1/2, 1/1 )
θ16 --- 100.0 ---
θ15 95.5 99.5 100.0
θ14 94.1 98.1 100.0
θ13 91.7 95.7 99.7
θ12 88.4 92.4 96.4
θ11 84.2 88.2 92.2
θ10 79.1 83.1 87.1
θ9 73.3 77.3 81.3
θ8 66.7 70.7 74.7
θ7 59.4 63.4 67.4
θ6 51.6 55.6 59.6
θ5 43.1 47.1 51.1
θ4 34.3 38.3 42.3
θ3 25.0 29.0 33.0
θ2 15.5 19.5 23.5
θ1 5.8 9.8 13.8
θ0 --- 0.0 ---
%
Max.
Unit
1/16,
1/8, 1/4,
1/2, 1/1
Min.
Typ.
2-phase, 1-2-phase, W1-2-phase, 2W1-2-phase, 4W1-2-phase excitation (unit: %)
TB6600HG
2014-01-30

26
Absolute Maximum Ratings (Ta = 25° C)
Characteristic Symbol Rating Unit
TB6600HG
Power supply voltage Vcc
I
Output current (per one phase)
Drain current (ALERT, MO)
O
(PEAK)
I
(ALERT)
I
(MO)
Input voltage V
IN
50 V
5.0 A
1 mA
6
V
3.2 (Note 1)
Power dissipation P
Operating temperature T
Storage temperature T
opr
stg
D
40 (Note 2)
-30 to 85 °C
-55 to 150 °C
W
Note 1: Ta = 25°C, No heatsink
Note 2: Ta = 25°C, with infinite heatsink.
The absolute maximum ratings of a semiconduct or device are a set of ratings that must not be exceeded, even for a
moment. Do not exceed any of these ratings.
Exceeding the rating (s) may cause the device breakd own, damage or deterioration, and ma y result injury by explosion
or combustion.
Please use the IC within the specifie d operating ranges.
Operating Range (Ta = −30~85°C)
Characteristic Symbol Test Condition Min Typ. Max Unit
Power supply voltage Vcc
Output current I
Input voltage
Clock frequency in logical part f
Chopping frequency f
OUT
V
V
ref
CLK
chop
IN
― 0.3 ― 1.95 V
See page 7.
― 8.0 ―
42
V
― ― ― 4.5 A
― 0 ― 5.5
V
― ― ― 200 kHz
20 40 60 kHz
Note: Two Vcc terminals should be programmed the same voltage.
The maximum current of the operating range can not be necessarily conducted depending on various
conditions because output current is limited by the power dissipation P
.
D
Make sure to avoid using the IC in the condition that would cause the temperature to exceed Tj (avg.)
=107°C.
The power supply voltage of 42 V and t he out put c urrent of 4. 5 A are the maximum values of operating range.
Please design the circuit with enough derat ing within t his r ange b y cons ide r ing the power supply variation, the
external resistance, and the electrical charact eristic s of the IC. I n case of exceeding the p ower suppl y voltage
of 42 V and the output current of 4.5 A, the IC will not operate normally.
2014-01-30

TB6600HG
27
step mode)
Electrical Characteristics (Ta = 25°C
, Vcc = 24 V)
Characteristic Symbol Test Condition Min Typ. Max Unit
Input voltage
High V
Low V
IN (H)
IN (L)
M1, M2, M3, CW/CCW, CLK,
RESET, ENABLE, Latch/Auto, TQ
2.0 ― 5.5
-0.2 ― 0.8
V
Input hysteresis voltage VH ― 400 ― mV
M1, M2, M3, CW/CCW, CLK,
― 50 75
μA
Input current
I
IN (H)
RESET, ENABLE, Latch/Auto
VIN = 5.0 V
TQ, VIN = 5.0 V ― 70 105
M1, M2, M3, CW/CCW, CLK,
I
IN (L)
RESET, ENABLE, Latch/Auto, TQ
V
= 0 V
IN
― ― 1
Output open,
Icc
RESET: H, ENABLE: H、
1
M1:L, M2:L, M3:H (1/1-
― 4.2 7
CLK:L
Vcc supply current
Icc
Output open,
RESET: L, ENABLE: L
2
M1:L, M2:L, M3:H (1/1-step mode)
mA
― 3.6 7
CLK:L
Icc
Current limit
Vref input
circuit
voltage
Input current I
Divider ratio V
Minimum CLK pulse width
Output residual voltage
V
NF
IN(Vref)
/V
ref
tw
CLKH
tw
CLKL
V
OL
VOL ALERT
Internal constant voltage Vreg
Chopping frequency f
chop
Standby mode (M1:L, M2:L, M3:L) ― 1.8 4
3
Vref = 3.0 V(Note 1), TQ=H 0.9 1.0 1.1 V
Vref = 3.0 V(Note 1)
Maximum current: 100%, TQ=H ― 3
NF
CLK 2.2 ― ― μs
MO
= 1 mA ― ― 0.5 V
I
OL
External capacitor = 0.1 μF
(in standby mode)
― ―
1 μA
― ―
4.5 5.0 5.5 V
Rosc=51kΩ 28 40 52 kHz
Note 1: Though Vref of the test condition for pre-shipment is 3.0V, make sure to configure Vref within the operating
range which is written in page 26 in driving the motor.
Electrical Characteristics (Ta = 25°C, Vcc = 24 V)
Characteristic Symbol Test Condition Min Typ. Max Unit
Output ON resistor Ron U + Ron
Output transistor switching characteristics
Output leakage
current
Upper side
Lower side I
t
t
ILH
LL
L
r
f
I
= 4 A ― 0.4 0.6 Ω
OUT
VNF = 0 V, Output: Open
Vcc = 50 V
― 50 ―
― 500 ―
― ― 5
― ― 5
2014-01-30
ns
μA

28
Timing Waveforms and Names
CLK
Vcc
GND
tr
tf
10%
90%
90%
10%
CLKH
tw
CLKH
tw
CLKL
OUT1B, OUT2B
tw
Figure 1 Timing Waveforms and Nam es
OUT1A, OUT2A,
TB6600HG
Figure 2 Timing Waveforms and Names
2014-01-30

29
Power Dissipation
②
TB6600HG
TB6600HG
PD – Ta
80
60
(W)
D
①
40
20
Power dissipation P
③
0
25 0
① Infinite heatsink
Rθj-c = 1°C/W
② HEATSINK (RθHS = 3.5°C/W)
Rθj-c + RθHS = 4.5°C/W
③ IC only
Rθj-a = 39°C/W
75
50
Ambient temperature Ta ( °C)
100
125
150
2014-01-30

TB6600HG
30
(例2)
Z
出力電流(A相)
CLK
RESET
ENABLE
内部電流設定
(例1)
内部電流設定
Z
出力電流(A相)
CLK
RESET
ENABLE
(Example 1)
Internal current set
Output current
(Example
Internal current set
Output current
(*:Output current starts rising at the timing of PWM frequency just after ENABLE pin outputs high.)
(*)
(*)
1. How to Turn on the Power
In applying Vcc or shutdown, ENABLE should be Low.
See Example 1(ENABLE = High → RESET = High) and Example 2(RESET = High → ENABLE = High)
as follows. In example 1, a motor can start driving from the initial mode.
(1) CLK: Current step proceeds to the ne xt m ode with respect to every rising edge of CLK.
(2) ENABLE: It is in Hi-Z state in low level. It is output in high level.
RESET: It is in the initial mode (Phase A=100% and Phase B=0%) in l ow level.
①ENABLE=Low and RESET=Low: Hi-Z. Internal current setting is in initial mode.
②ENABLE=Low and RESET=High: Hi-Z. Internal current setting proceeds by internal counter.
③ENABLE=High and RESET=Low: O utput in the initial mode (Phase A=100% and Phase B=0%).
④ENABLE=High and RESET=High: O utput at the value which is determined by the internal counter.
<Recommended control input sequence>
(Phase A)
2)
(Phase A)
2014-01-30

31
Application Circuit
24V
M1
M2
CW/CCW
CLK
ENABLE
M3
OSC
TSD/ISD/UVLO
MO
ALERT
Vcc
OUT1A
OUT2A
NFA
OUT1B
OUT2B
NFB
Vref
Current selector
circuit A
Current selector
circuit B
MCU
0.2
0.2
24V
RESET
PGNDA
PGNDB
Latch/Auto
Vreg
51kΩ
TQ
100%/
30%
0.1μF 47μF
fuse
0.1μF
Control
logic
1/3
OSC
Reg (5V)
SGND
Pre
-drive
Pre
-drive
TB6600HG
H-Bridge
driver A
Ω
H-Bridge
driver B
Ω
Note 1: Capacitors for the power supply lines should be connected as close to the IC as possible.
Note 2: C ur rent detecting resistances (R
NFA and RNFB) should be connected as close to the IC as possible.
Note 3: Pa y at tention for wire layout of PCB not t o all ow GND line to have large common impeda nce.
Note 4: External capacitor connecting to Vreg should be 0.1μF. Pay attention for the wire between this
capacitor and Vreg terminal and the wire between this capacitor and SGN D not to be influenc ed b y
noise.
Note 5: The IC may not operate normally whe n large common impedance is exist ed in GND line or the IC is
easily influenced by noise. For exampl e, if the IC operates continuously for a long t ime under the
circumstance of large current and high voltage, the number of clock signals inputted to CLK
terminal and that of steps of output curr ent wavef orm may n ot proportion al. And so, the IC ma y not
operate normally. To avoid this malfunction, make sure t o conduct Note.1 to Note.4 and evaluate
the IC enough before using the IC.
2014-01-30

32
Package Dimensions
Unit:
.
Note
TB6600HG
Weight: 7.7 g (typ.)
mm
Note:These dimensions are measured from the surface of the heat sink
2014-01-30

TB6600HG
33
Notes on Contents
1. Block Diagrams
Some of the functional blocks, circuits, or constants in the block diagram may be omitted or simplified for
explanatory purposes.
2. Equivalent Circuits
The equivalent circuit diagrams may be simplified or some parts of them may be omitted for explanatory
purposes.
3. Timing Charts
Timing charts may be simplified for explanatory purposes.
4. Application Circuits
The application circuits shown in this document are provided for reference purposes only. Thorough evaluation
is required, especially at the mass production design stage.
Toshiba does not grant any license to any industrial property rights by providing these examples of application
circuits.
5. Test Circuits
Components in the test circuits are used only to obtain and confirm the device characteristics. These components
and circuits are not guaranteed to prevent malfunction or failure from occurring in the application equipment.
IC Usage Considerations
Notes on handling of ICs
[1] The absolute maximum ratings of a semiconductor device are a set of ratings that must not be exceeded, even
for a moment. Do not exceed any of these ratings.
Exceeding the rating(s) may cause the device breakdown, damage or deterioration, and may result injury by
explosion or combustion.
[2] Use an appropriate power supply fuse to ensure that a large current does not continuously flow in case of over
current and/or IC failure. The IC will fully break down when used under conditions that exceed its absolute
maximum ratings, when the wiring is routed improperly or when an abnormal pulse noise occurs from the
wiring or load, causing a large current to continuously flow and the breakdown can lead smoke or ignition. To
minimize the effects of the flow of a large current in case of breakdown, appropriate settings, such as fuse
capacity, fusing time and insertion circuit location, are required.
[3] If your design includes an inductive load such as a motor coil, incorporate a protection circuit into the design to
prevent device malfunction or breakdown caused by the current resulting from the inrush current at power ON
or the negative current resulting from the back electromotive force at power OFF. IC breakdown may cause
injury, smoke or ignition.
Use a stable power supply with ICs with built-in protection functions. If the power supply is unstable, the
protection function may not operate, causing IC breakdown. IC breakdown may cause injury, smoke or ignition.
[4] Do not insert devices in the wrong orientation or incorrectly.
Make sure that the positive and negative terminals of power supplies are connected properly.
Otherwise, the current or power consumption may exceed the absolute maximum rating, and exceeding the
rating(s) may cause the device breakdown, damage or deterioration, and may result injury by explosion or
combustion.
In addition, do not use any device that is applied the current with inserting in the wrong orientation or
incorrectly even just one time.
2014-01-30

TB6600HG
34
Points to remember on handling of ICs
(1) Over current Detection Circuit
Over current detection circuits (referred to as current limiter circuits) do not necessarily protect ICs under all
circumstances. If the over current detection circuits operate against the over current, clear the over current
status immediately.
Depending on the method of use and usage conditions, such as exceeding absolute maximum ratings can cause
the over current detection circuit to not operate properly or IC breakdown before operation. In addition,
depending on the method of use and usage conditions, if over current continues to flow for a long time after
operation, the IC may generate heat resulting in breakdown.
(2) Thermal Shutdown Circuit
Thermal shutdown circuits do not necessarily protect ICs under all circumstances. If the thermal shutdown
circuits operate against the over temperature, clear the heat generation status immediately.
Depending on the method of use and usage conditions, such as exceeding absolute maximum ratings can cause
the thermal shutdown circuit to not operate properly or IC breakdown before operation.
(3) Heat Radiation Design
In using an IC with large current flow such as power amp, regulator or driver, please design the device so that
heat is appropriately radiated, not to exceed the specified junction temperature (T
These ICs generate heat even during normal use. An inadequate IC heat radiation design can lead to decrease
in IC life, deterioration of IC characteristics or IC breakdown. In addition, please design the device taking into
considerate the effect of IC heat radiation with peripheral components.
(4) Back-EMF
When a motor rotates in the reverse direction, stops or slows down abruptly, a current flow back to the motor’s
power supply due to the effect of back-EMF. If the current sink capability of the power supply is small, the
device’s motor power supply and output pins might be exposed to conditions beyond absolute maximum ratings.
To avoid this problem, take the effect of back-EMF into consideration in system design.
(5) Short-circuiting between outputs, air contamination faults, faults due to improper grounding, short-circuiting
between contiguous pins
Utmost care is necessary in the design of the power supply lines, GND lines, and output lines since the IC may
be destroyed by short-circuiting between outputs, air contamination faults, or faults due to improper grounding,
or by short-circuiting between contiguous pins. They may destroy not only the IC but also peripheral parts and
may contribute to injuries for users. Over current may continue to flow in the IC because of this destruction
and cause smoke or ignition of the IC. Expect the volume of this over current and add an appropriate power
supply fuse in order to minimize the effects of the over current. Capacity of the fuse, fusing time, and the
inserting position in the circuit should be configured suitably.
) at any time and condition.
j
2014-01-30

TB6600HG
35
RESTRICTIONS ON PRODUCT USE
• Toshiba Corporation, and its subsidiaries and affiliates (collectively "TOSHIBA"), reserve the right to make changes to the information
in this document, and related hardware, software and systems (collectively "Product") without notice.
• This document and any information herein may not be reproduced without prior written permission from TOSHIBA. Even with
TOSHIBA's written permission, reproduction is permissible only if reproduction is without alteration/omission.
• Though TOSHIBA works continually to improve Product's quality and reliability, Product can malfunction or fail. Customers are
responsible for complying with safety standards and for providing adequate designs and safeguards for their hardware, software and
systems which minimize risk and avoid situations in which a malfunction or failure of Product could cause loss of human life, bodily
injury or damage to property, including data loss or corruption. Before customers use the Product, create designs including the
Product, or incorporate the Product into their own applications, customers must also refer to and comply with (a) the latest versions of
all relevant TOSHIBA information, including without limitation, this document, the specifications, the data sheets and application notes
for Product and the precautions and conditions set forth in the "TOSHIBA Semiconductor Reliability Handbook" and (b) the
instructions for the application with which the Product will be used with or for. Customers are solely responsible for all aspects of their
own product design or applications, including but not limited to (a) determining the appropriateness of the use of this Product in such
design or applications; (b) evaluating and determining the applicability of any information contained in this document, or in charts,
diagrams, programs, algorithms, sample application circuits, or any other referenced documents; and (c) validating all operating
parameters for such designs and applications. TOSHIBA ASSUMES NO LIABILITY FOR CUSTOMERS' PRODUCT DESIGN OR
APPLICATIONS.
• PRODUCT IS NEITHER INTENDED NOR WARRANTED FOR USE IN EQUIPMENTS OR SYSTEMS THAT REQUIRE
EXTRAORDINARILY HIGH LEVELS OF QUALITY AND/OR RELIABILITY, AND/OR A MALFUNCTION OR FAILURE OF WHICH
MAY CAUSE LOSS OF HUMAN LIFE, BODILY INJURY, SERIOUS PROPERTY DAMAGE AND/OR SERIOUS PUBLIC IMPACT
("UNINTENDED USE"). Except for specific applications as expressly stated in this document, Unintended Use includes, without
limitation, equipment used in nuclear facilities, equipment used in the aerospace industry, medical equipment, equipment used for
automobiles, trains, ships and other transportation, traffic signaling equipment, equipment used to control combustions or explosions,
safety devices, elevators and escalators, devices related to electric power, and equipment used in finance-related fields. IF YOU USE
PRODUCT FOR UNINTENDED USE, TOSHIBA ASSUMES NO LIABILITY FOR PRODUCT. For details, please contact your
TOSHIBA sales representative.
• Do not disassemble, analyze, reverse-engineer, alter, modify, translate or copy Product, whether in whole or in part.
• Product shall not be used for or incorporated into any products or systems whose manufacture, use, or sale is prohibited under any
applicable laws or regulations.
• The information contained herein is presented only as guidance for Product use. No responsibility is assumed by TOSHIBA for any
infringement of patents or any other intellectual property rights of third parties that may result from the use of Product. No license to
any intellectual property right is granted by this document, whether express or implied, by estoppel or otherwise.
• ABSENT A WRITTEN SIGNED AGREEMENT, EXCEPT AS PROVIDED IN THE RELEVANT TERMS AND CONDITIONS OF SALE
FOR PRODUCT, AND TO THE MAXIMUM EXTENT ALLOWABLE BY LAW, TOSHIBA (1) ASSUMES NO LIABILITY
WHATSOEVER, INCLUDING WITHOUT LIMITATION, INDIRECT, CONSEQUENTIAL, SPECIAL, OR INCIDENTAL DAMAGES OR
LOSS, INCLUDING WITHOUT LIMITATION, LOSS OF PROFITS, LOSS OF OPPORTUNITIES, BUSINESS INTERRUPTION AND
LOSS OF DATA , A ND (2) DISCLAIMS ANY AND ALL EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTIES AND CONDITIONS RELATED TO
SALE, USE OF PRODUCT, OR INFORMATION, INCLUDING WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS
FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE, ACCURACY OF INFORMATION, OR NONINFRINGEMENT.
• Do not use or otherwise make available Product or related software or technology for any military purposes, including without
limitation, for the design, development, use, stockpiling or manufacturing of nuclear, chemical, or biological weapons or missile
technology products (mass destruction weapons). Product and related software and technology may be controlled under the
applicable export laws and regulations including, without limitation, the Japanese Foreign Exchange and Foreign Trade Law and the
U.S. Export Administration Regulations. Export and re-export of Product or related software or technology are strictly prohibited
except in compliance with all applicable export laws and regulations.
• Please contact your TOSHIBA sales representative for details as to environmental matters such as the RoHS compatibility of Product.
Please use Product in compliance with all applicable laws and regulations that regulate the inclusion or use of controlled substances,
including without limitation, the EU RoHS Directive. TOSHIBA ASSUMES NO LIABILITY FOR DAMAGES OR LOSSES
OCCURRING AS A RESUL T OF NONCOMPLIANCE WITH APPLICABLE LAWS AND REGULATIONS.
2014-01-30

 Loading...
Loading...