Page 1

ONAN TORO POWER PLUS P216V, 18V, 20V ENGINE - VERTICAL
Table of Contents – Page 1 of 2
SAFETY PRECAUT I O NS
GENERAL
PROTECT AGAINST MOVING PARTS
BATTERIES
FUEL SYSTEM
EXHAUST SYSTEM
EXHAUST GAS IS DEADLY!
COOLING SYSTEM
KEEP THE UNIT AND SURROUNDING AREA CLEAN
CAUTION
GENERAL INFORMATION
INTRODUCTION
ENGINE MODEL REFERENCE
SPECIFICATIONS
DIMENSIONS AND CLEARANCES
ASSEMBLY TORQUES
SPECIAL TOOLS
ENGINE TROUBLESHOOTING
OIL SYSTEM
CRANKCASE OIL
OIL FILTER CHANGE
CRANKCASE BREAT HER
PRESSURE LUBRICAT IO N
OIL PUMP
OIL BYPASS CHECK BALL
FUEL SYSTEM
CARBURETOR
CARBURETOR SPEED SETTINGS
CARBURETOR OVERHAUL
REMOVAL
DISASSEMBLY
CLEANING AND REPAIR
REASSEMBLY AN D INSTALLATION
PULSATING-DIAPHRAGM FUEL PUMP
FUEL PUMP TEST PROCEDURE
AIR CLEANER
GOVERNOR SENSITIVIT Y
Page 2

ONAN TORO POWER PLUS P216V, 18V, 20V ENGINE - VERTICAL
Table of Contents – Page 2 of 2
IGNITION AND BATTERY CHARGING
IGNITION SYSTEM DESCRIPTION
IGNITION TIMING
CONTINUITY TEST
IGNITION COIL
SPARK PLUGS
BATTERY INSPECTION
BATTERY JUMP STARTING
FLYWHEEL ALTERNAT OR
ALTERNATOR OUTPUT TEST
STARTING SYSTEM
ELECTRIC STARTER
SERVICE
STARTER REMOVAL
STARTER DISASSEMBLY
STARTER ASSEMBLY
INSPECTION AND TESTING
STARTER MOUNTING
ENGINE DISASSEMBLY
DISASSEMBLY/ASSEMBLY
VALVE SYSTEM
TAPPETS
VALVE FACE AND SEAT GRINDING
FLYWHEEL
GEAR COVER
GOVERNOR CUP
TIMING GEARS
PISTONS AND CONNECTING RODS
CYLINDER BLOCK
CRANKSHAFT
BEARINGS
CRANKSHAFT ENDPLAY
CHECKING CONNECTING ROD BEARING CLEARANCE
OIL SEALS
PISTON ASSEMBLY
INSTALLATION OF PISTON IN CYLINDER
CYLINDER HEADS
Page 3

Service
Manual
P216V,18V,2OV
Toro
Power
Plus
Engine
Tractors
1710
& Riding Mowers
Page 4

Safety
It
is recommended that you read your engine manual and
become thoroughly acquainted with your equipment before
you start the engine.
severe personal injury or death.
severe personal injury or death.
Precautions
This symbol
diate hazards which will result in
This symbol refers
unsafe practice which can result In
if
used warns of imme-
lo
a hazard or
Fuel System
DO NOT
DO NOT smoke or use an open flame
engine or fuel tank. Internal combustion engine fuels are
highly flammable.
Fuel lines must be of steel piping, adequately secured.
and free from leaks. Piping at the engine should be
approved flexible line..
flexible lines as copper will work harden and become
brittle enough to break.
fill
fuel tanks while engine is running.
in
Do
not use copper piping for
the vicinity
of
the
This symbol refers
personal injury or product or properly damage.
Fuels, electrical equipment, batteries, exhaust gases and
moving parts present potential hazards that can result in
serious, personal injury. Take care in following these recommended procedures. All local, state and federal codes should
be consulted and complied with.
Use
of
this engine in aircraft can result in engine failure
and causes serious personal injury or death.
General
Provide appropriate fire extinguishers and install them in
convenient locations. Use an extinguisher rated ABC by
NFPA.
Make sure that all fasteners on the engine are secure and
accurately torqued. Keep guards in position over fans,
driving belts, etc.
If
it is necessary to make adjustments while the engine is
running, use extreme caution when close to hot exhausts,
moving parts. etc.
Protect Against Moving Parts
Do
not wear loose clothing in the vicinity
such as PTO shafts, flywheels, blowers, couplings, fans,
belts, etc.
unsafe practice which
This engine Is not designed or in-
tended for use in any type of aircraft.
lo
a hazard or
can result in
of
moving parts,
Be sure all fuel supplies have a positive shutoff valve.
Exhaust System
Exhaust products
toxic and can cause injury,
applications, especially those within
should be equipped with an exhaust system to discharge
gases to the outside atmosphere.
Do
not use exhaust gases to heat a compartment
Make sure that
Ensure that exhaust manifolds are secure and are not
warped by bolts unevenly torqued.
Gas
Exhaust
Exhaust gases contain carbon monoxide, a poisonous gas
that can cause unconsciousness and death.
and colorless gas formed during combustion
fuels. Symptoms
Dizziness
Headache
Weakness and Sleepiness
If
you experience any
immediately, shut down the unit and do not use until it has
been inspected.
The best protection against carbon monoxide inhalation
proper installation and regular, frequent inspections
complete exhaust system.
or appearance
immediately and have it inspected and repaired at once by a
competent mechanic.
is
of
any internal combustion engine are
or
death if inhaled.
a
confined area,
your
exhaust system
Deadly!
of
carbon monoxide poisoning are:
Vomiting
Muscular Twitching
Throbbing in Temples
of
these symptoms, get out into fresh air
If
of
you notice a change in the sound
exhaust system, shut the unit down
is
free
It
is an odorless
of
hydrocarbon
All
of
engine
leaks.
is
of
the
Keep your hands away from moving parts.
Batteries
Before starting work on the engine, disconnect batteries
of
to prevent inadvertent starting
DO NOT SMOKE while servicing batteries. Lead acid
batteries give
can be ignited by flame, electrical arcing or by smoking.
Verify battery polarity before connecting battery cables.
Connect negative cable last.
off
a highly explosive hydrogen gas which
the engine.
Cooling System
Coolants under pressure have a higher boiling Point than
water.
coolant temperature is above
engine
Keep the Unit and Surrounding Area Clean
Make sure that oily rags are not left on or near the engine.
Remove all unnecessary grease and oil from the unit
Accumulated grease and oil can cause overheating and
subsequent engine damage and present a potential fire
hazard.
DO
NOT open a radiator pressure cap when
212°F
is
running.
(l00°C)
or while
E-6
Page 5

Table
of
Contents
TITLE
General Information
Specifications
Dimensions and Clearances
Assembly Torques and Special Tools
Engine Troubleshooting
Oil System
Fuel
System.
Ignition and Battery Charging
Engine Wiring Diagram.
Starting System..
Engine Disassembly
..........................................................
..................................................
...............................
..........................................
..............................................
...................................
............................
...................
....................................................
................................................
.......................
..................................
....................
............
..........................
PAGE
. l-1
.2-1
.3-1
.4-1
.5-1
.6-1
.7-1
.8-1
.8-7
.9-1
10-1
I
EXHAUST GAS
Exhaust gases from all fuels (including diesel, gasoline, liquid propane, natural
gas) contain carbon monoxide, an odorless and colorless gas. Carbon monoxide
is poisonous and can cause unconsciousness and death. Symptoms of carbon
monoxide poisoning can include:
Dizziness Throbbing in Temples
Nausea Muscular Twitching
Headache Vomiting
Weakness and Sleepiness Inability
IF
YOU
OR
ANYONE ELSE EXPERIENCE ANY OF THESE SYMPTOMS, GET OUT
INTO THE FRESH AIR IMMEDIATELY.
attention. Shut down the unit and do not operate until it has been inspected and
repaired.
Protection against carbon monoxide inhalation includes proper installation,
ventilation and regular, frequent visual and audible inspections of the complete
exhaust system.
IS
DEADLY!
to
Think Coherently
If
symptoms persist, seek medical
I
Page 6

General
Information
INTRODUCTION
This manual deals with specific mechanical and electrical information needed by engine mechanics for
troubleshooting, servicing, repairing, or overhauling the
engine.
Use the separate PARTS MANUAL for parts identification
and for establishing their proper location on assemblies.
The PARTS MANUAL contains detailed exploded views
of each assembly and the individual piece part numbers
and their proper names for ordering replacement parts.
The illustrations and procedures presented in each
section apply
cleaner side of the engine is the front end. Right and left
sides are determined by viewing the engine from the
front. The No.
on the left.
If
a major repair or an overhaul is necessary, a competent
mechanic should either do the job
check the work of the mechanic assigned
ensure that all dimensions, clearances and torque
values are within the specified tolerances.
Use the table
separate engine system sections.
The troubleshooting guide is provided
reference for locating and correcting engine trouble.
The wiring diagram
nents are interconnected.
The disassembly section contains major overhaul
procedures for step by step removal, disassembly,
inspection, repair, and assembly
components.
to
the engines listed on the cover. The air
1
cylinder is on the right,
of
contents for a quick reference
shows
how the electrical compo-
No.
2
cylinder is
or
supervise and
to
the job
as
of
the engine
a quick
to
to
the
Use only Genuine
ensure quality and the best possible repair and overhaul
results. When ordering parts, always use the complete
model and spec number as well
shown on the nameplate.
ENGINE
Identify your model by referring
specification (spec letter) as shown on the unit nameplate. Always use these numbers and the engine serial
number when making reference
How
to
interpret MODEL and SPEC NO.
P
2 16
12
1.
Factory code for general identification of basic
engine series.
2.
Number of cylinders.
3.
BHP rating.
4.
Designation
5.
Engine duty cycle.
6.
Factory code for designated optional equipment,
any.
7.
Specification (spec letter) which advances with
factory production modifications.
Tom
Plower Plus replacement parts to
MODEL
V
3
(G
=
horizontal shaft,
as
the serial number
REFERENCE
to
'the model and
to
your engine.
/
10464
6
V
=
vertical shaft)
A
7
if
INCORRECT SERVICE
PERSONAL INJURY AND/OR EQUIPMENT DAMAGE. SERVICE PERSONNEL
MUST
SERVICE.
BE
QUALIFIED TO PERFORM ELECTRICAL AND/OR MECHANICAL
OR
REPLACEMENTOF PARTS CAN RESULT IN SEVERE
Page 7
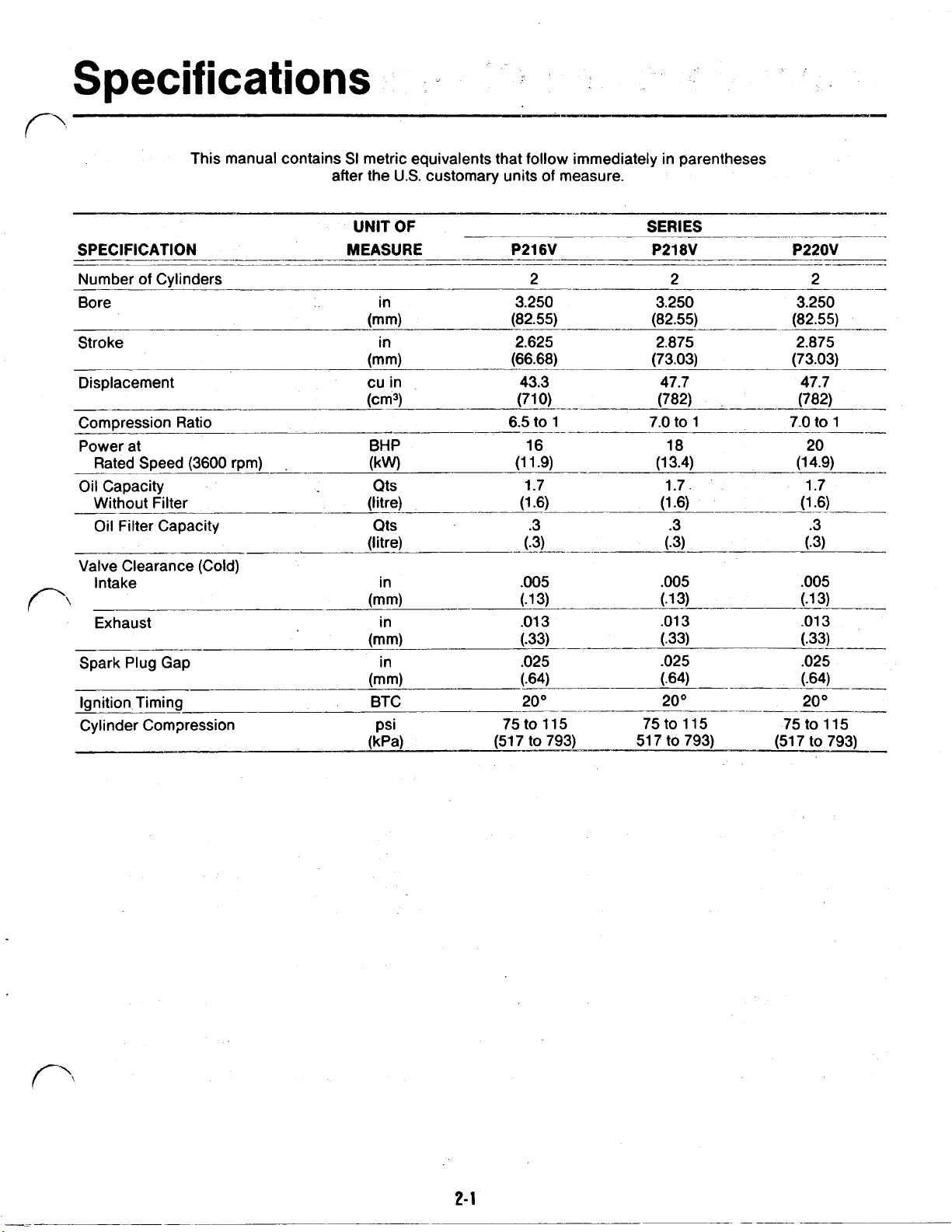
Specifications
.
This manual contains
SPECIFICATION MEASURE P216V P218V P220V
Number
Bore
Stroke
Displacement
Compression Ratio
Power at
Oil Capacity Qts
Valve Clearance (Cold)
of
Cylinders
Rated Speed
Without Filter (litre)
Oil Filter Capacity
Intake in
(3600
rpm)
.
SI
metric equivalents that
U.S.
after the
UNIT OF SERIES
customary units
follow
of
measure.
immediately in parentheses
2
in
(mm)
in
(mm)
CU in
(cm³)
BHP
(kW)
3.250 3.250 3.250
(82.55) (82.55) (82.55)
2.625
(66.68)
43.3
(71
0)
6.5
to
1
16 18 20
(1 1.9) (1 3.4)
(73.03) (73.03)
7.0
1.7 1.7. 1.7
(1 .6)
Qts
(litre)
.3 .3 .3
(.3) (.3) (.3)
.005
2
2
2.875 2.875
47.7 47.7
(782)
to
1
(1
(782)
7.0
(1
4.9)
(1.6)
to
__-
.005 .005
1
Spark Plug Gap
Ignition Timing
Cylinder Compression psi
in
(mm)
BTC
(kPa)
.025
(.64) (.64) (.64)
20°
75
(517
to
to
115 75
793) 51
.025 .025
20° 20
to
7
115
to
793) (517
75
to
to
115
793)
2-
1
Page 8
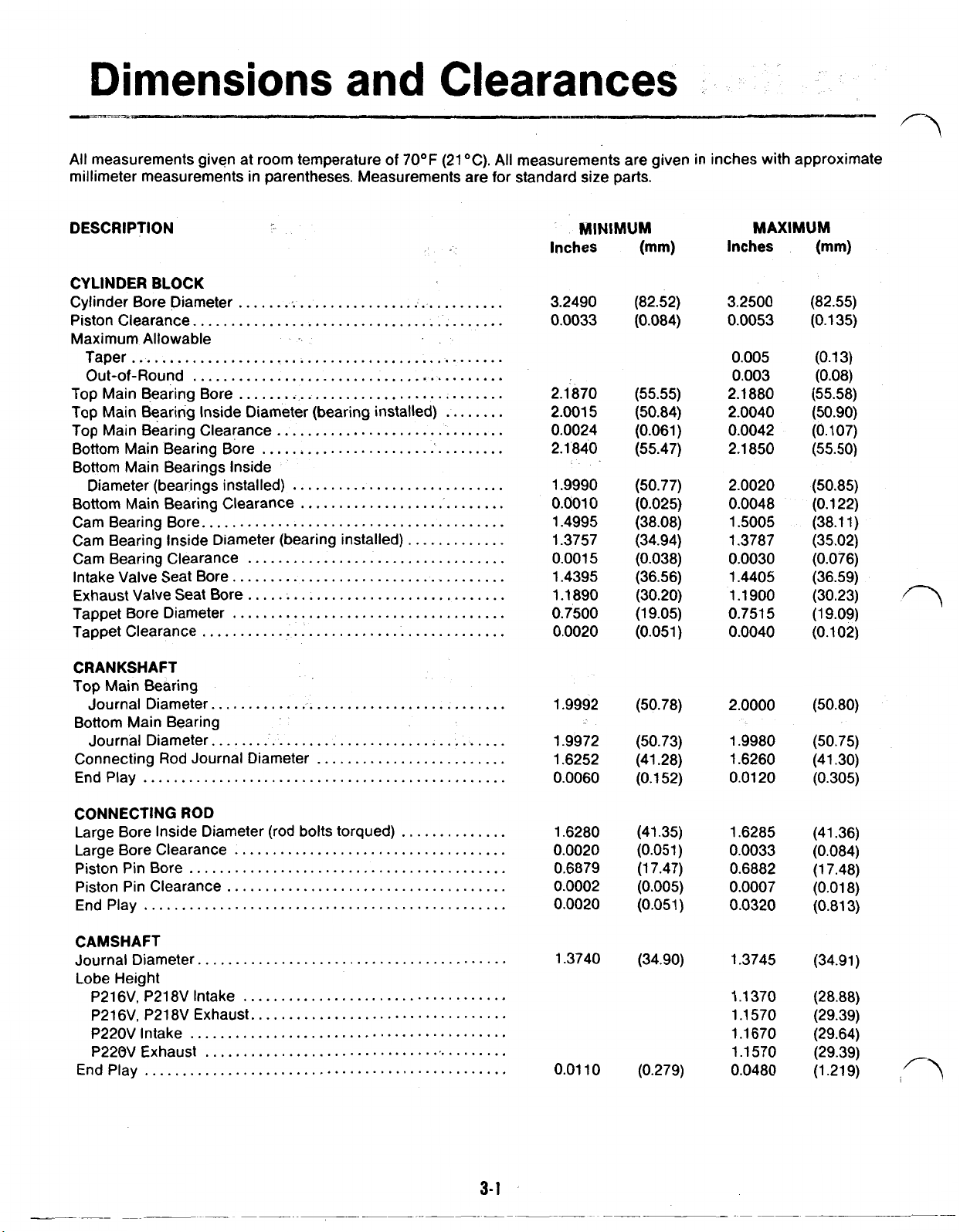
Dimensions
All
measurements given at room temperature
millimeter measurements in parentheses
and
of
.
Measurements are
Clearances
70°F (21 °C)
.
All
measurements are given in inches with approximate
for
standard size parts
.
DESCRIPTION
CYLINDER BLOCK
Cylinder Bore Diameter
Piston Clearance
Maximum Allowable
Taper
Out-of-Round
Top Main Bearing Bore
Top Main Bearing Inside Diameter (bearing installed)
Top Main Bearing Clearance
Bottom Main Bearing Bore
Bottom Main Bearings Inside
Bottom Main Bearing Clearance
Cam Bearing Bore
Cam Bearing Inside Diameter (bearing installed)
Cam Bearing Clearance
Intake Valve Seat Bore
Exhaust Valve Seat Bore
Tappet Bore Diameter
Tappet Clearance
CRANKSHAFT
Top Main Bearing
Bottom Main Bearing
Connecting Rod Journal Diameter
End Play
.................................................
Diameter (bearings installed)
Journal Diameter
Journal Diameter
................................................
....................................
..........................................
.........................................
...................................
..............................
.................................
............................
............................
........................................
.............
..................................
....................................
..................................
....................................
........................................
.......................................
........................................
.........................
........
3.2490
0.0033
2.1 870
2.001
0.0024
2.1 840
1.9990
0.001
1.4995
1.3757
0.001
1.4395
1.1
890
0.7500
0.0020
1.9992 (50.78)
1.9972
1.6252
0.0060
5
0
5
(82.52)
(0.084)
(55.55)
(50.84)
(0.061)
(55.47)
(50.77)
(0.025)
(38.08)
(34.94)
(0.038)
(36.56)
(30.20)
(1 9.05)
(0.051
)
(50.73)
(41.28)
(0.1
52)
MAXIMUM
Inches
3.2500
0.0053
0.005
0.003
2.1 880
2.0040
0.0042
2.1 850
2.0020
0.0048
1
5005
1.3787
0.0030
1.4405
1.1 900
0.751 5
0.0040
2.0000
1.9980
1.6260
0.01 20
(mm)
(82.55)
(0.1
35)
(0.1
3)
(0.08)
(55.58)
(50.90)
(0.1
07)
(55.50)
(50.85)
(0.1
22)
(38.1
1)
(35.02)
(0.076)
(36.59)
(30.23)
(1
9.09)
(0.1 02)
(50.80)
(50.75)
(41.30)
(0.305)
CONNECTING
Large Bore Inside Diameter (rod bolts torqued)
Large Bore Clearance
Piston Pin Bore
Piston Pin Clearance
End Play
CAMSHAFT
Journal Diameter
Lobe Height
P216V. P218V Intake
P216V. P218V Exhaust
P220V Intake
P220V Exhaust
End
Play
ROD
....................................
..........................................
.....................................
................................................
.........................................
...................................
..................................
..........................................
.........................................
................................................
..............
3-
1
1.6280
0.0020
0.6879
0.0002
0.0020
1.3740 (34.90)
0.01
10
(41.35)
(0.051)
(1
7.47)
(0.005)
(0.051)
(0.279)
1.6285
0.0033
0.6882
0.0007
0.0320
1.3745 (34.91)
1.1 370 (28.88)
1.1 570 (29.39)
1.1
670 (29.64)
1.1
570 (29.39)
0.0480 (1.219)
(41.36)
(0.084)
(1
7.48)
(0.01 8)
(0.81
3)
Page 9
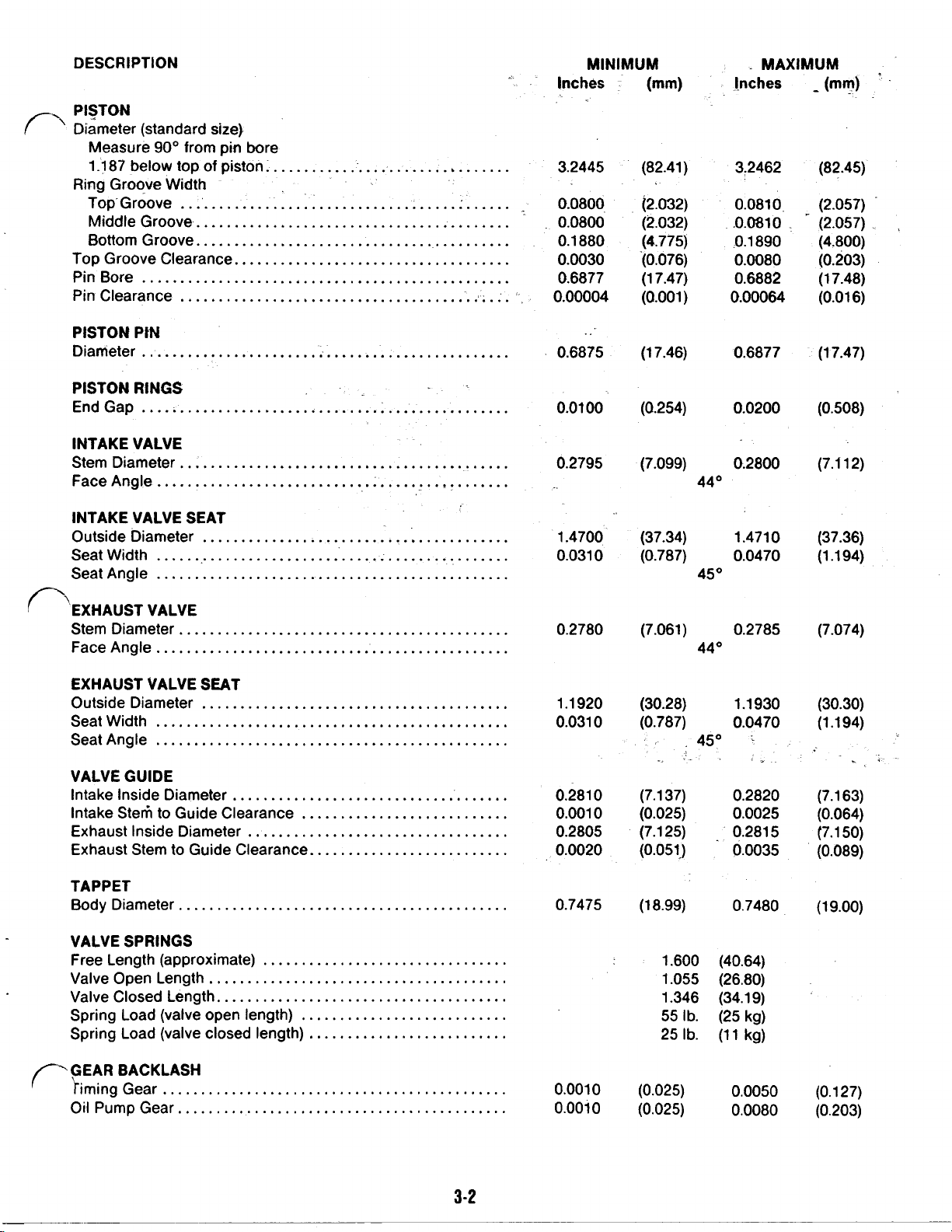
DESCRIPTION
(standard size)
pin
Measure 90° from
1
.187
below
top
Ring Groove Width
Top Groove
Middle Groove.
Bottom Groove.
Top Groove Clearance.
Pin Bore
Pin Clearance
PISTON PIN
Diameter
PISTON RINGS
End Gap
INTAKE VALVE
Stem Diameter
Face Angle
.....................................
................................................
............................................
.......................
..........................................
...........................................
.................................
bore
of
piston.
................................
.......
........................................
.........................................
...................................
........................
...........
MINIMUM
Inches
3.2445
0.0800.
0.0800
0.1 880
0.0030
0.6877
0.00004
0.6875 (1 7.46) 0.6877 (1 7.47)
0.01
00
0.2795 (7.099) 0.2800 (7.1 12)
(mm)
(82.41)
(2.032)
(2.032)
(4.775)
(0.076)
(1 7.47)
(0.001)
(0.254) 0.0200 (0.508)
44
.
MAXIMUM
Inches
3.2462 (82.45)
0
0.081
.0.0810
.0.1890
0.0080
0.6882
0.00064
(mm)
(2.057)
(2.057)
(4.800)
(0.203)
(1 7.48)
(0.01 6)
INTAKE VALVE SEAT
Outside Diameter
Seat Width
Seat Angle
Stem Diameter
Face Angle
EXHAUST VALVE SEAT
Outside Diameter
Seat Width
Seat Angle
VALVE GUIDE
Intake Inside Diameter
Intake Stem to Guide Clearance
Exhaust Inside Diameter
Exhaust Stem to Guide Clearance..
TAPPET
Body Diameter.
VALVE SPRINGS
Free Length (approximate)
Valve Open Length
Valve Closed Length
Spring Load (valve open length)
Spring Load (valve closed length)
...............................................
..............................................
VALVE
..............................................
..............................................
..............................................
........................................
...........................................
........................................
....................................
...........................
..................................
..........................................
................................
.......................................
......................................
...........................
........................
..........................
1.4700 (37.34) 1.471
0.031
0.2780 (7.061) 0.2785 (7.074)
1.1 920
0.031
0.281
0.001
0.2805
0.0020
0.7475 (1 8.99) 0.7480
0
0
0
0
(0.787) 0.0470 (1.1 94)
(30.28)
(0.787)
(7.1 37)
(0.025)
(7.1 25)
(0.051)
1.600
1.055
1.346
55
Ib.
Ib.
25
45°
44
45°
-
1.1 930
0.0470
0.2820
0.0025
0.281
0.0035
(40.64)
(26.80)
(34.1 9)
(25 kg)
(11
kg)
0
5
(37.36)
(30.30)
(1.194)
(7.1 63)
(0.064)
(7.1
50)
(0.089)
(1 9.00)
GEAR BACKLASH
Timing Gear
Oil Pump Gear..
.............................................
.........................................
3-2
0.001
0.001
0
0
(0.025)
(0.025)
0.0050
0.0080
(0.1 27)
(0.203)
Page 10

Assembly
The torque values given in Table 1 have been deter- Tighten all studs, nuts, and capscrews as required to
mined for specific applications. Standard torque values keep them from working loose. Refer to the
must not be used where those listed in Table 1 apply.
The engine assembly torques given here will assure
proper tightness without danger
threads must be clean and lubricated with new engine
oil before torquing.
Torques
of
stripping threads.
All
MANUAL
for
the location of washers and capscrews.
PARTS
DESCRIPTION
Gearcase Cover
Oil Base
Oil Base Cover (inner bolts).
Oil Base Cover (outer bolts).
Oil Cooler
Oil Pump
Hood Support Screws..
Starter Mounting Bolts
Connecting Rod Bolts..
Flywheel Capscrews
Valve Cover.
......................
...............
....................
......................
........
.........
........
............
.......
.
..........
....
....
TABLE
TORQUE
SPECIFICATION
Ft.-Lb. Nm
10-12 14-16
27-29 36-39
19-21 25-28
9-11 12-15
20-24
7-9 10-12
7-9
19-21 25-28
12-14
50-55
3-4 4-5
27-33
10-12
16-19
67-75
1.
DESCRIPTION
Cylinder Head Bolts (cold)
Asbestos Gasket
Graphoil Gasket..
Intake Manifold
Mounting Screws..
Exhaust Manifold
Mounting Screws..
/4"
Other 1
Nuts and Bolts
Other 5/16" Cylinder Block
Nuts and Bolts
Cylinder Block
............
...........
..........
..........
..............
...............
TORQUE
SPECIFICATION
Ft.-Lb. Nm
16-1 8
14-1 6
6-10
9-11
7-9
8-10
22-24
19-22
8-14
12-15
10-12
11-14
Special
The following is a partial list of the special
from Onan. Use Onan tools whenever a repair or
overhaul is required. Refer to the
complete listing of tools available.
Valve Seat Driver
Valve Guide Driver
Oil Seal Guide and Driver
Combination Bearing Remover (Main and Cam)
Combination Bearing Driver (Main and Cam)
Flywheel Puller
Tools
tools
TOOL CATALOG
available
for a
Page 11
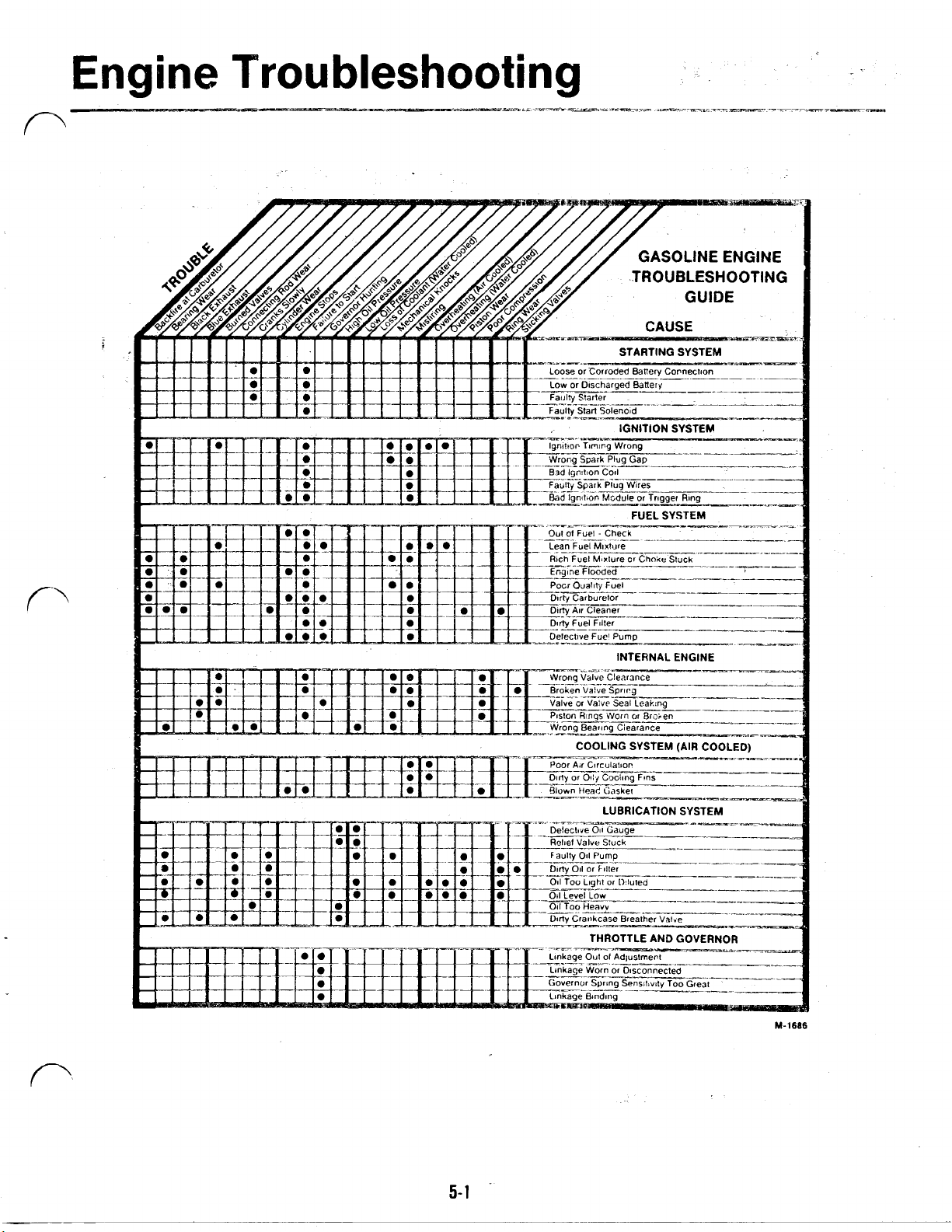
Engine
Troubleshooting
5-
M-1686
1
Page 12
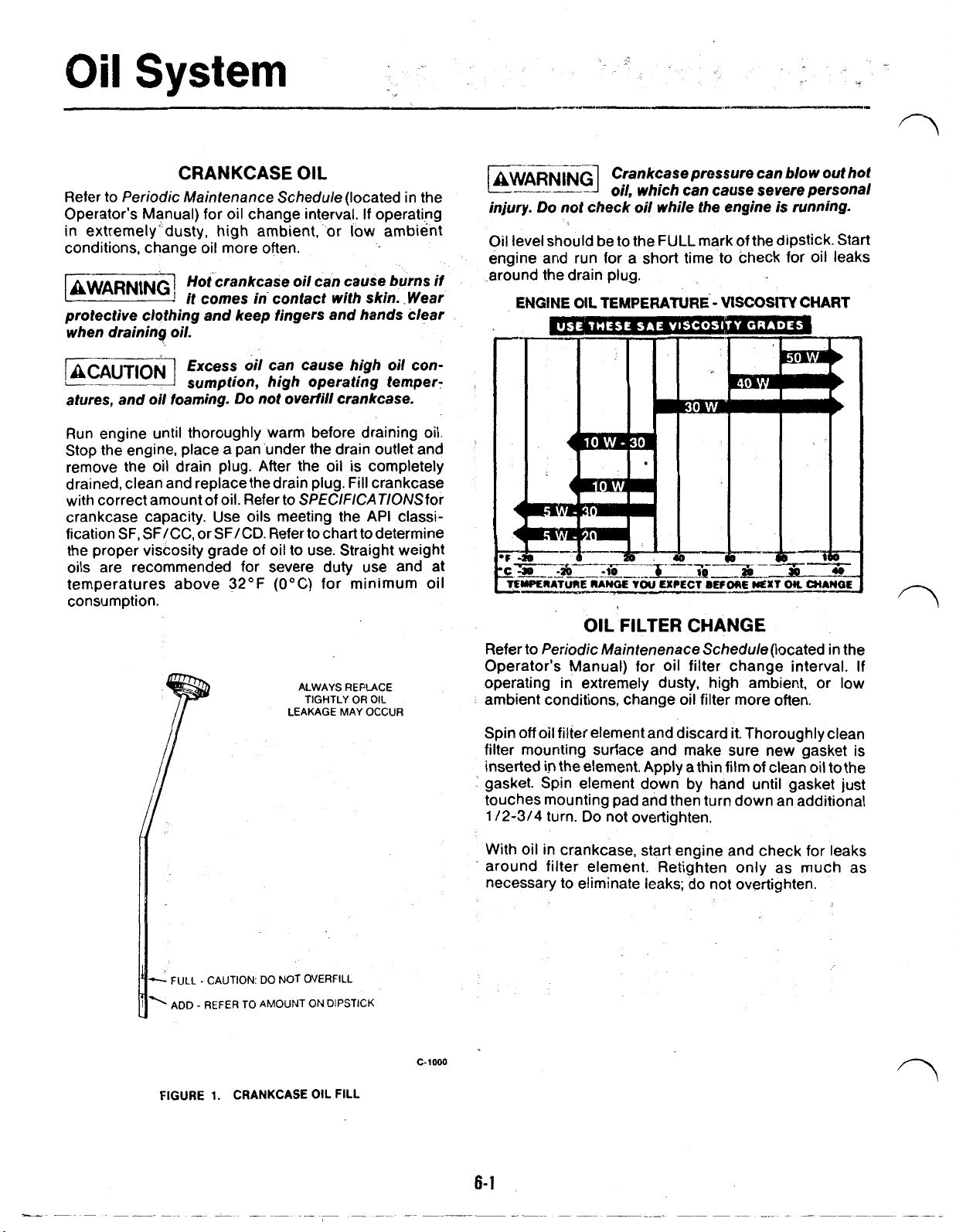
Oil
System
CRANKCASE
Refer
to
Periodic Maintenance Schedule (located in the
Operator's Manual) for oil change interval.
in extremely'-dusty, high ambient, 'or low ambient
conditions, change oil more often.
Hotcrankcase oil can cause burns if
it comes in contact with skin.. Wear
protective clothing and keep fingers and hands clear
when draining oil.
Excess oil can cause high oil consumption, high operating temper-
atures, and oil foaming.
Run engine until thoroughly warm before draining oil.
Stop the engine, place a pan 'under the drain outlet and
remove the
drained, clean and replace the drain plug. Fill crankcase
with correct amount of oil. Refer
crankcase capacity. Use oils meeting the
fication SF, SF/CC, or SF/CD. Refer
the proper viscosity grade of oil
oils are recommended for severe duty use and at
temperatures above 32°F
consumption.
oil
drain plug. After the
Do
OIL
If
operating
not overfill crankcase.
oil
is
completely
to
SPEClFlCATlONS for
API
classi-
to
chart
to
determine
to
use. Straight weight
(0°C)
for minimum oil
Crankcase pressure can blow out hot
oil, which can cause severe personal
Do
injury.
Oil level should be to the FULL mark of the dipstick. Start
engine and run for a short time
around the drain plug.
Refer
Operator's Manual) for oil filter change interval.
operating in extremely dusty, high ambient, or low
ambient conditions, change oil filter more often.
not check oil while the engine
to
ENGINE
to
OIL
TEMPERATURE-
OIL
FILTER
Periodic Maintenenace Schedule (located in the
VISCOSITY
CHANGE
is
running.
check for oil leaks
CHART
If
FIGURE
1.
CRANKCASE
OIL
FILL
C-1000
Spin
off
oil
filter elementand discard it. Thoroughly clean
filter mounting surface and make sure new gasket is
inserted
gasket. Spin element down by hand until gasket just
touches mounting pad and then turn down an additional
112-314
With oil in crankcase, start engine and check for leaks
around filter element. Retighten only as much as
necessary
in
the element. Apply a thin film of clean oil to the
turn. Do not overtighten.
to
eliminate leaks; do not overtighten.
Page 13
CRANKCASEBREATHER
The crankcase breather prevents pressure from building
It
up the crankcase
by removing moisture or gasoline vapors and other
harmful blow-by materials from the crankcase. These
vapors are routed
mixed with incoming air and burned in the combustion
chamber.
high oil consumption, rough idle, reduced engine power,
and
engine.
A
sticky breather valve can cause oil leaks,
a
rapid formation of sludge and varnish within the
Crankcase Breather Service
The crankcase breather does not require servicing.
Replace breather if it’s broken or cracked or
becomes pressurized as evidenced by
seals or excessive oil
also prevents oil contamination
to
the carburetor where they are
if
crankcase
oil
leaks at the
in
the air cleaner housing.
Oil
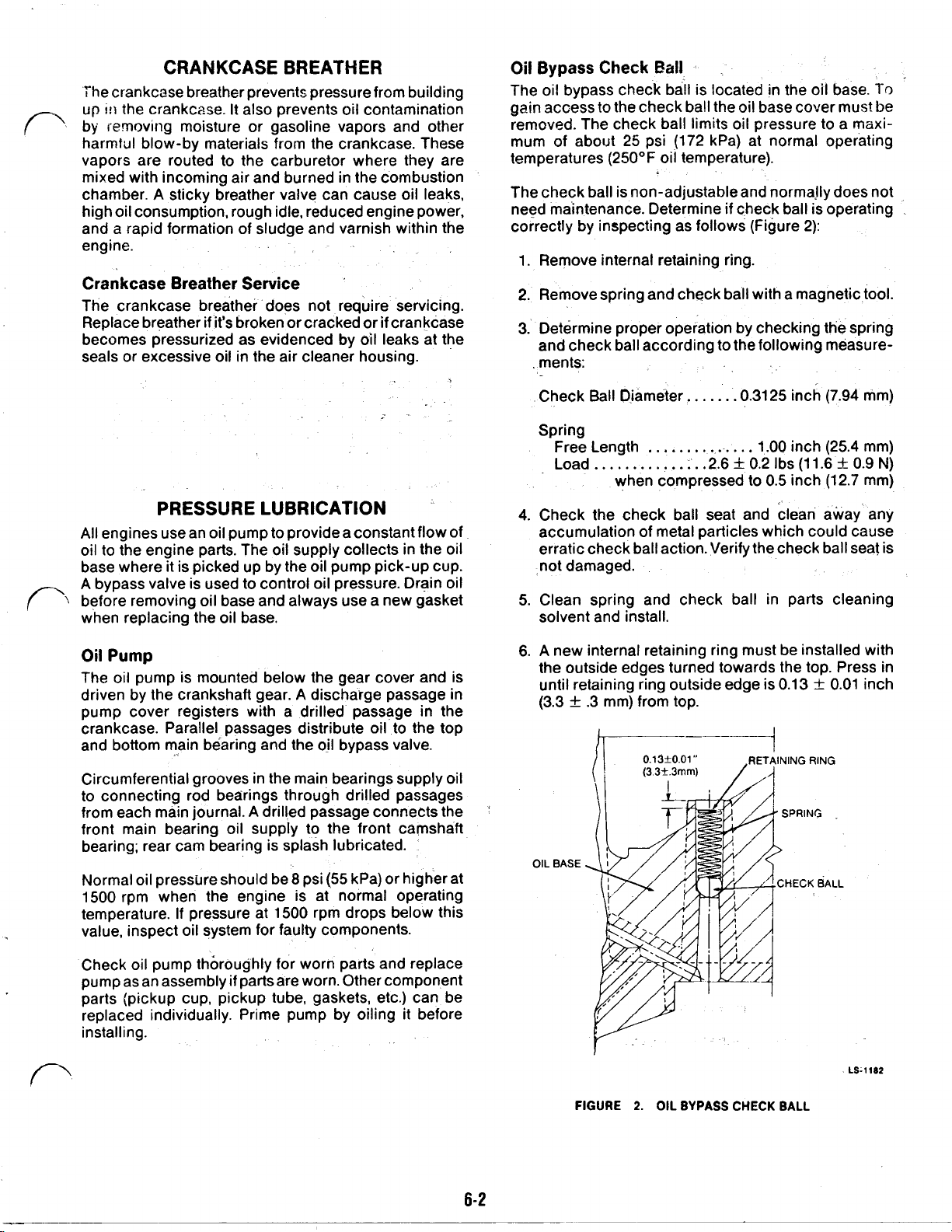
Bypass
The oil bypass check ball is located in the
gain access
removed. The check ball limits oil pressure
mum
temperatures
The check ball is non-adjustable and normally does not
need maintenance. Determine
correctly by inspecting as follows (Figure
1.
Remove internal retaining ring.
2.
Remove spring and check ball with a magnetic
3.
Determine proper operation by checking the spring
and check ball according
ments:
of
Check
to
about
Ball
the check ball the oil base cover must be
25
psi
(172
kPa) at normal operating
(250°F
oil temperature).
if
check ball is operating
to
the following measure-
2):
oil
to
base.
a maxi-
tool.
To
PRESSURE
All
engines use an oil pump
to
the engine parts. The oil supply collects in the oil
oil
base where
A
bypass valve is used
before removing oil base and always use a new gasket
when replacing the oil base.
Oil
Pump
The oil pump is mounted below the gear cover and is
driven by the crankshaft gear.
pump cover registers with a drilled passage
crankcase. Parallel passages distribute oil
and bottom main bearing and the oil bypass valve.
Circumferential grooves in the main bearings supply oil
to
connecting rod bearings through drilled passages
from each main journal.
front main bearing oil supply
bearing; rear cam bearing is splash lubricated.
Normal oil pressure should be
1500
temperature.
value, inspect oil system for faulty components.
it
is picked up by the oil pump pick-up cup.
rpm when the engine is at normal operating
If
pressure at
LUBRICATION
to
provide a constant flow of
to
control oil pressure. Drain oil
A
discharge passage in
to
the top
A
drilled passage connects the
to
the front camshaft
8
psi
(55
kPa) or higher at
1500
rpm drops below this
in
the
Check Ball Diameter.
Spring
Free Length
Load..
4.
Check the check ball seat and clean away- any
accumulation of metal particles which could cause
erratic check ball action. Verify the check ball seat is
not damaged.
5.
Clean spring and check ball in parts cleaning
solvent and install.
6.
A
new internal retaining ring must be installed with
the outside edges turned towards the top. Press in
until retaining ring outside edge is
(3.3 ± .3
OIL
BASE
...............
............
when compressed
mm) from top.
0.13±0.01”
(33±.3mm)
.....
.0.3125
.2.6 ± 0.2
to
RETAINING RING
inch
1.00
inch
Ibs
(11.6
0.5
inch
0.13 ± 0.01
(7.94
(25.4
±
(12.7
mm)
mm)
0.9
mm)
inch
N)
Check oil pump thoroughly for worn parts and replace
pump as an assembly
parts (pickup cup, pickup tube, gaskets, etc.) can be
replaced individually. Prime pump by oiling it before
installing.
if
parts are worn. Other component
6-2
FIGURE
2.
OIL BYPASS
CHECK
LS-1102
BALL
Page 14
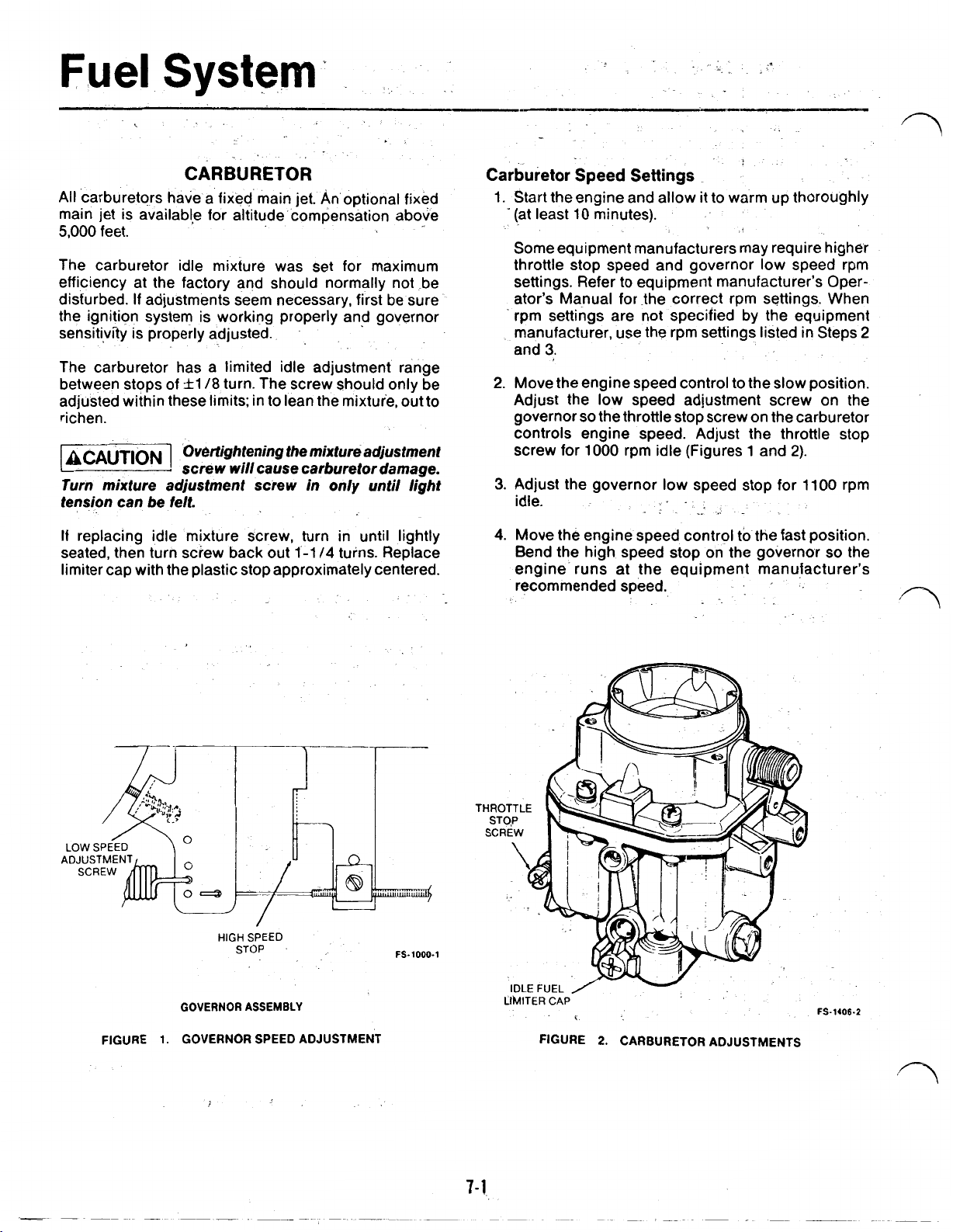
F’uel
System
..
..
_.i
..
.
CARBURETOR
All
carburetors have a fixed’main jet. An’optional fixed
main jet is avai1abI.e for altitude compensation above
5,000
feet.
The carburetor idle mixture was set for maximum
efficiency at the factory and should normally not
disfurbed.
If
adjustments seem necessary, first be sure
the ignition system is working properly and governor
sensitivity is properly adjusted.
The carburetor has a limited idle adjustment range
between stops of
adjusted within these limits; in
fl/8
turn. The screw should only be
to
lean the mixtuie, out
richen.
Overtightening the mixture adjustment
screw
Turn mixture adjustment screw in
will
cause carburetor damage.
only
until light
tension can be felt.
If
replacing idle mixture screw, turn in until lightly
seated, then turn sciew back out 1-1
limiter cap with the plastic
stop
/4
turns. Replace
approximately centered.
be
to
Carburetor
1. Start the engine and allow it
Speed
Settings
to
warm up thoroughly
“(at least 10 minutes).
Someequipment manufacturers may require higher
throttle stop speed and governor low speed rpm
settings. Refer to equipment manufacturer’s Operator’s Manual for .the correct rpm settings. When
.
rpm settings are not specified by
the
equipment
manufacturer, use the rpm settings listed in Steps
and
3.
2.
Move the engine speed control
to
the slow position.
Adjust the low speed adjustment screw on the
governor
so
the throttle stop screw on the carburetor
controls engine speed. Adjust the throttle stop
screw for
3.
Adjust the governor low speed stop for 11
idle.
4.
Move the engine speed control
1000
rpm idle (Figures 1 and
-..
_.
..
to
the fast position.
2).
Bend the high speed stop on the governor
engine. runs at the equipment manufacturer’s
recommended speed.
.-
00
so
2
rpm
the
FIGURE
HIGH
SPEED
STOP
GOVERNOR
1.
GOVERNOR SPEED ADJUSTMENT
ASSEMBLY
FS-1000-1
LIMITER
CAP-
FIGURE
2.
CARBURETOR ADJUSTMENTS
FS-1406.2
Page 15
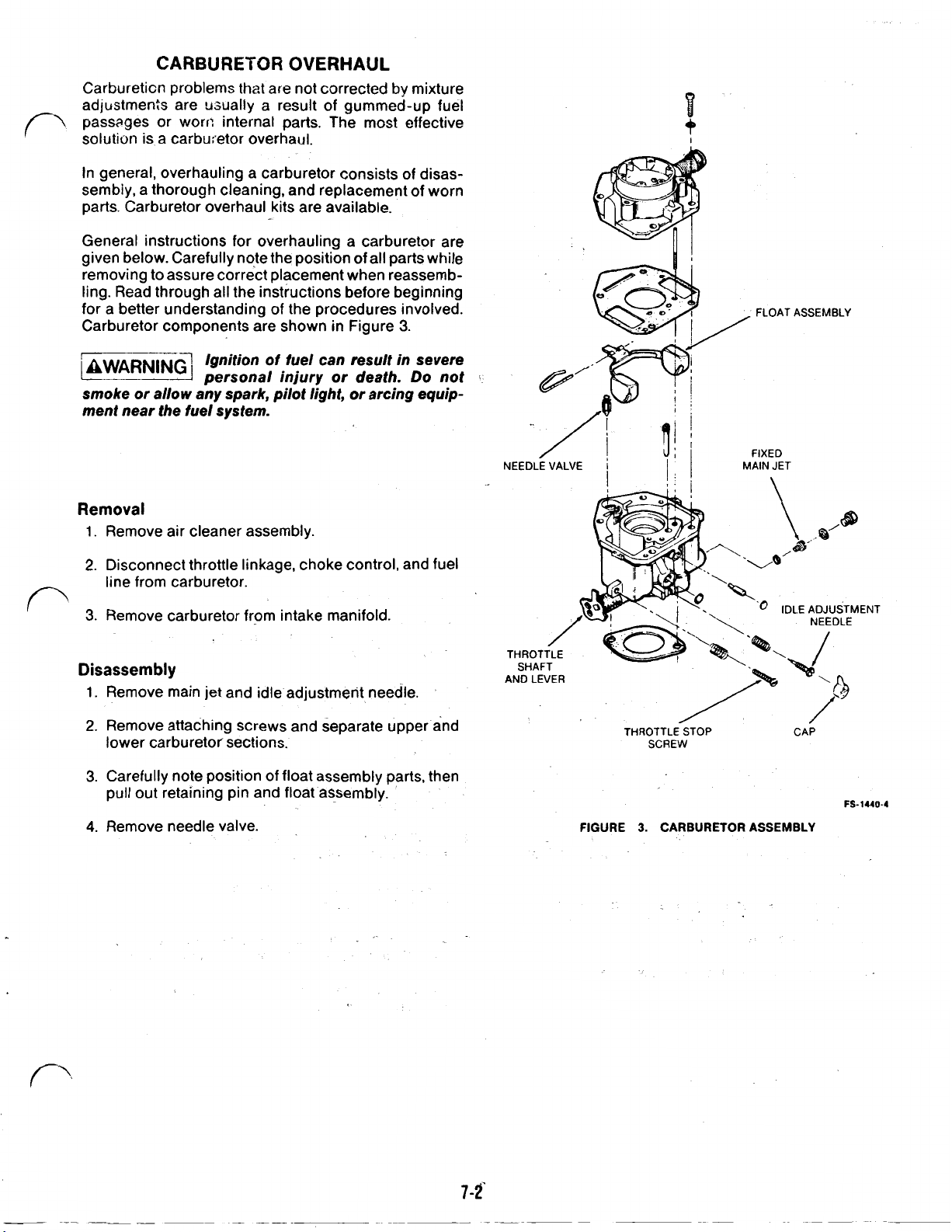
CARBURETOR
Carburetion problems
that
OVERHAUL
are not corrected
by
mixture
adjustments are usually a result of gummed-up fuel
passages or worn internal parts. The most effective
solution is a carburetor overhaul.
In general, overhauling a carburetor consists
of
disassembly, a thorough cleaning, and replacement of worn
parts. Carburetor overhaul kits are available.
General instructions for overhauling a carburetor are
given below. Carefully note the position of all parts while
removing
to
assure correct placement when reassemb-
ling. Read through all the instructions before beginning
for a better understanding of the procedures involved.
Carburetor components are shown in Figure
lgnition of fuel can
result
personal injury or death.
3.
in severe
Do
not
smoke or allow any spark, pilot light, or arcing eguipment near the fuel system.
Removal
1.
Remove air cleaner assembly.
2.
Disconnect throttle linkage, choke control, and fuel
line from carburetor.
3.
Remove carburetor from intake manifold.
ASSEMBLY
IDLE
ADJUSTMENT
NEEDLE
Disassembly
1.
Remove main jet and idle adjustment needle.
2.
Remove attaching screws and separate upper and
lower carburetor sections.
3.
Carefully note position of float assembly parts, then
pull out retaining pin and float assembly.
4.
Remove needle valve.
AND
LEVER
THROTTLE STOP CAP
SCREW
FIGURE
3.
CARBURETOR ASSEMBLY
FS-1440-4
Page 16

NEEDLE
AND SEAT
FLOAT
BEND FLOAT
TANG HERE
TO ADJUST BEND FLOAT ARM
LEVEL
ADJUSTMENT WITH FUEL
HERE TO ADJUST
NO FUEL
When checking (loaf
FIGURE
level
4.
CARBURETOR FLOAT LEVEL ADJUSTMENTS
Cleaning and Repair
1.
Soak all metal components not replaced in carburetor cleaner.
other non-metal parts. Follow the cleaner manufacturer's recommendations.
2.
Clean all carbon from the carburetor bore, especially
where the throttle and choke plates seat. Be careful
not
to
plug the idle or main fuel ports.
3.
Dry out all passages with low pressure air
Avoid using wire or other objects for cleaning which
may increase the size of critical passages.
4.
Check the condition of the adjustment needle;
replace if damaged. Replace float
or
damaged.
5.
Check the choke and throttle shafts for excessive
play in their bore. This condition may necessitate
replacement of the carburetor.
6.
Replace old components with new parts.
Do
not soak non-metal floats
if
loaded with fuel
(35
and
or
PSI).
float
drop,
measure lo float
body,
not
seam.
Reassembly and Installation
1.
Install needle valve, main jet, and float assembly.
Make sure float pivot pin
moves freely without binding.
2.
Turn carburetor on its side and measure float level
(Figure
Measure float drop (the distance from the top of
carburetor body
necessary.
3.
Position gasket on lower carburetor section and
install upper carburetor section.
4.
Install idle adjustment screw, throttle stop screw,
and fixed main jet plug.
5.
Mount carburetor on intake manifold and install
assembly on engine.
6.
Connect governor and throttle linkage, choke
control, and fuel line. Mount air cleaner assembly.
7.
Adjust carburetor and governor according
tions given in this section.
4).
Adjust float level only
is
properly placed and float
'if
necessary.
to
top of float). Adjust only if
to
direc-
Page 17

PULSATING-DIAPHRAGM FUEL PUMP
Pulsating-diaphragm fuel pumps, or pulse pumps, rely
on changes in crankcase vacuum
movement of the pump diaphragm. As the engine's
pistons move outward, a vacuum is created. This
vacuum is transmitted
to pull back and suck fuel into the pump.
pistons move inward, crankcase vacuum is' reduced
and the diaphragm return spring pushes the pump
diaphragm forward, forcing fuel through the pump
outlet.
to
the pump diaphragm causing it
to
create a pulsating
As
the engine's
Ignition fuel can result
severe personal injury or death.
Thoroughly clean up
7.
Remove fuel outlet line from fuel pump.
8.
Connect a pressure gauge
a
piece of fuel hose with clamps.
9.
Start engine and allow
seconds. While holding pressure gauge level with
pump outlet record pressure gauge reading.
any
spilled fuel.
to
to
fuel pump outlet using
idle for at least five
in
Fuel Pump Test Procedure
Before testing, make certain the fuel pump vacuum and
fuel line connections are tight and free of leaks.
1.
Operate engine at an idle for five minutes to ensure
that carburetor is full of fuel.
lgnition of fuel can result in
severe personal injury or death.
Thoroughly clean up any spilled fuel.
2.
Shut engine off and remove fuel inlet line from fuel
pump.
Connect a vacuum gauge to fuel pump inlet using a
3.
piece of fuel hose with clamps.
Start engine and allow
4.
seconds. Record vacuum gauge reading.
Move throttle control
5.
least five seconds and record vacuum gauge
reading.
Shut engine off and remove vacuum gauge hose
6.
from fuel pump inlet. Connect fuel inlet line
pump.
to
idle for at least five
to
high idle position. Wait at
to
fuel
10. Move throttle control to high idle position and allow
engine to run for at least five seconds. While holding
pressure gauge level with pump outlet record
pressure gauge reading.
11.
Shut engine
from fuel pump outlet. Connect fuel outlet line
pump.
Replace the fuel pump
values specified in TABLE 1.
off
and remove pressure gauge hose
if
test readings are not within the
TABLE
1
to
fuel
PULSE PUMP TEST SPEClFICATlONS
ENGINE PUMP INLET PUMP OUTLET
SPEED VACUUM PRESSURE
(Minimum) (Minimum)
Low
Idle
High ldle
2.6
inches 1.7 psi
of mercury
2.6
inches 1.7 psi
of mercury
7-4
Page 18

AIR
CLEANER
A
dirty air cleaner element can cause
engine damage. Ensure air cleaner
element is kept clean and free
Running engine without air cleaner
element will result in engine dam-
age.
Do
not run engine without air cleaner element
installed.
of
excess debris.
Engine is equipped with a paper element. Refer
to
Periodic Maintenance Schedule (located in the Opera-
tor's Manual) for service and replacement intervals.
Service by gently tapping element on a flat surface.
engine is equipped with an element wrapper, refer
to
Periodic Maintenance Schedule for service intervals.
Service element wrapper as follows:
1.
Wash element wrapper in water and detergent
(Figure
a sponge. Allow wrapper
2.
Distribute one tablespoon
5).
Remove excess water by squeezing like
to
dry thoroughly.
of
SAE
30
'engine
oil
evenly around wrapper. Knead into wrapper and
wring out excess oil.
If
ELEMENT
COVER
ELEMENT
BASE
FIGURE
5.
CLEANING ELEMENT WRAPPER
7-5
FIGURE
6.
AIR
CLEANER ASSEMBLY
XFS-1773
Page 19

GOVERNOR
These engines are adapted
of speed settings
between minimum and maximum by moving the throttle
lever until the desired speed is reached.
Check Governor arm, spring, linkage, and throttle shaft
for a binding condition or excessive wear at connecting
points.
act slowly and regulation to be poor. Excessive wear will
cause a hunting condition and regulation to-be erratic.
Work the governor arm back and forth several times by
hand while the engine is idling to check for above
conditions.
A
binding condition will cause the governor to
is
desired. Engine speed
SENSITIVITY
for use
where a wide range
is
controlled
The governor linkage should be set
(Figure
1.
2.
If
settings. Adjust
7):
The governor spring should be placed in the second
hole from the end in the governor control arm. The
governor spring should be placed in the third hole
away from pivot in the governor arm. Moving spring
away from pivot will decrease sensitivity, moving
the spring closer will increase sensitivity
The governor control rod
middle hole of the governor arm.
adjustments were made, recheck the carburetor rpm
if
necessary.
should
up
as
follows
be placed in the
FIGURE
7.
GOVERNOR
7-6
FS-1791
LINKAGE
Page 20

Ignition and Battery Charging
IGNITION SYSTEM DESCRIPTION
This engine is equipped 'with 'an electronic battery
ignition system. Both spark plugs fire, simultaneously,
thus the need for a distributor is eliminated. The
electronic ignition module is located on the engine gear
cover below the flywheel. The module receives a timing
signal from magnets within the trigger ring which rotates
with the engine crankshaft (Figure
ignition is suspected of malfunctioning, proceed as
follows:
TRIGGER
RING
IGNITION
MODULE
FIGURE
1.
Check all electrical connections to be sure they are
clean and tight.
wiring is intact, go
2.
Refer
proper resistance.
step
trical shock.
or wires while ignition is on.
1.
IGNITION MODULE AND TRIGGER RING
If
all connections are good and
to
step
to
IGNITION COIL section to test coil for
If
coil checks out good, go
3.
The electronic ignition produces
current which can cause elec-
Do
not touch electrical components
2.
1).
If
the electronic.
\
ES-1670
to
Accidental starting of the engine
can result in severe personal
injury or death. Remove spark plugs before
proceeding.
Ignition of cylinder gases can
cause severe personal injury.
Ground spark tester away from spark plug hole.
3.
Pull spark plug wires
off
spark plugs and remove
spark plugs. Connect an approved spark tester to
each of the spark plug wires and ground them away
from spark plug hole. Turn key on and crank engine
over for
5
seconds while watching for spark.
If
spark occurs regularly, the problem is not in the
ignition system.
attach any lead or jumper with power (such as
to
coil negative terminal.
4.
Connect a jumper lead directly from the positive
battery terminal to the positive
If
no spark occurs, go to step
Incorrect wiring can cause elec-
tronic ignition damage.
Do
4.
not
B+)
(+)
coil terminal
(smaller diameter of the two threaded posts). Crank
engine over while watching for spark.
If
spark
occurs, the problem is in the low oil pressure cut out
switch (if equipped) or related wiring, the lubricating
system (low oil pressure), or in the other circuitry
bringing voltage to the coil.
,.step
5.
5.
Connect positive side of voltmeter to negative
If
no spark occurs, go to
coil terminal (larger diameter of the two threaded
posts) and negative side of voltmeter to engine
ground. Turn key on and rotate flywheel slowly by
hand while observing voltmeter. Voltage should
switch between battery voltage and
revolution.
If
voltage does not switch properly,
1-1.5
for each
replace ignition module.
Incorrect wiring can cause electronic ignition damage.
attach any lead
.to coil negative
6.
Install spark plugs and wires.
or jumper with power (such as
terminal.
being replaced, be sure
new ignition module to positive
black lead from module
If
ignition module is
to
connect red lead from
(+)
terminal of coil,
to
negative
(-)
terminal of
Do
B+)
coil.
a
(-)
not
Page 21

IGNITION TIMING
The' ignition timing is preset at the factory and is not
adjustable. For troubleshooting purposes,
to
make an approximate check of the ignition timing
using reference marks on the blower housing and a
chaff screen bolt (Figure 2). This check can be performed
by a continuity test.
it
is possible
4. Rotate the flywheel slowly by hand in the clockwise
direction until the voltmeter reading switches from
approximately
1
volt to battery voltage. At this point,
one of the chaff screen bolts should lie between the
two timing marks on the blower housing. To recheck
timing, the flywheel must be rotated another
complete revolution
in
the clockwise direction.
Moving the flywheel back and forth across the
reference timing mark will not activate the electronic
ignition control.
5.
Install spark plugs and wires.
IGNITION COIL
To-test primary and secondary windings within the
ignition coil first make sure the ignition power is off and
coil is at room temperature of
1.
Use a Simpson 260
70°F
VOM
or equivalent.
(21
°C).
FIGURE
Continuity
1.
Pull spark plug wires off spark plugs and remove
Test
2.
IGNITION
TIMING
MARKS
spark plugs.
Accidental starting of the engine
can result in severe personal
injury or death. Remove spark plugs before
proceeding.
2. Turn ignition on.
3. Connect a voltmeter between the negative
terminal (larger diameter of the two threaded posts)
and a good engine ground.
(-)
M-1675
coil
2. Place a black lead on negative
red lead
to
positive
(+)
(-)
coil terminal and
coil terminal. Primary
resistance should read between 2.90-3.60 ohms.
3. Change resistance setting on ohmmeter. Place
ohmmeter leads inside of spark plug cable holes
(Figure 3). Secondary resistance should read
between 14,500-19,800 ohms.
4.
If
either of the above resistances are not within
specification, replace coil.
OHMMETER
The electronic ignition produces
current which can cause elec-
trical shock.
Do
not touch electrical components
or wires while ignition
is
on.
8-2
FIGURE
3.
COIL
TEST
Page 22

SPARK PLUGS
Check or replace spark plugs as recommended in the
Periodic Maintenance Schedule (located in Operator's
Manual). Replace spark plugs that show signs of fouling
or electrode erosion.
BATTERY INSPECTION
Keep the battery
terminals
clean and tight. Push the
cable terminal down flush with or slightly below the top
of the battery post (Figure
5).
After making connections,
coat the terminals with a light application of petroleum
jelly or grease to retard corrosion.
Poor contact at the battery cable connections is often a
source of trouble. Make sure battery cables are in good
condition and that contacting surfaces are clean and
tightly connected.
Do
not reverse battery leads. Use
recommended battery tools when disconnecting leads
to avoid mechanical battery damage.
Ignition
can result in severe personal injury.
Do
not smoke or allow any ignition source near the
of
explosive battery gases
battery.
Check battery cells with a hydrometer (Figure
4).
Specific gravity reading should be between 1.260 and
1.290 at
If
one or more cells are low on water, add distilled water
77°F
(25°C).
and recharge. Keep the battery case clean and dry. An
accumulation of moisture or dirt will accelerate discharge and battery failure.
SPECIFIC
GRAVITY
READING
SHOULD
at
77°F
BE
(25°C)
BATTERY
FIGURE
Occasionally,
5.
BATTERY
BATTERY
it
may be necessary to jump start (charge)
JUMP
a weak battery using a charged booster battery.
POST
CABLETERMINAL
CABLE
CONNECTION
STARTING
If
jump
starting is necessary, the following procedure is recommended
to
prevent starter damage, battery damage, and
personal injuries.
1.
Disconnect engine load.
2.
Use a battery of the same voltage
(1
2V) as is used
with your engine.
FIGURE
4.
SPECIFIC GRAVITY TEST
Attach one end of the positive booster cable (red) to
3.
the positive
(+)
terminal
of
the booster battery.
Attach the other end of the positive cable to the
positive
(+)
terminal of your engine battery.
Electrical arcing can cause severe personal injury. Do not allow
positive and negative cable ends to touch.
4.
Attach one end
to negative
of
the negative booster cable (black)
(-)
terminal
of
booster battery., Attach
other end of negative cable to a solid chassis
ground on your engine.
8-3
Page 23

5.
Jump starting in any other manner may result in
to-the
damage
battery or the electrical system.
Overcranking the engine can
I
minutes tor starter to cool
30
than
seconds.
cause starter damage. Allow
if
engaged for longer
Jump starting
a
battery incor-
rectly can cause battery to
explode, resulting in severe personal injury
death.
Do
not smoke or allow any ignition source
near the battery, and do not jump start a frozen
battery.
6.
Turn ignition switch to
ON
to start engine.
STATOR
5
or
This unit
FLYWHEEL
is
equipped with a permanent magnet flywheel
ALTERNATOR
alternator and solid-state voltage regulator-rectifier
(Figure
6).
As
with all solid-state electrical units, pre-
cautions are necessary when servicing.
._
Reversing positive and negative bat-
tery connections or allowing engine
to run without being connected to the alternator will
result in engine electrical system damage.
Do
not
switch battery connections or allow engine to run
without being connected to the alternator.
Weak ignition spark or a discharged battery indicates
trouble in the charging system. Before testing the
engine's charging system, always check the battery for
serviceability.
VOLTAGE REGULATOR
20
AMP
VOLTAGE REGULATOR CONNECTIONS
FIGURE
MOUNTED BEHIND
BLOWER WHEEL
TOSTARTERORBATTERY
ES-1333-1
6.
FLYWHEEL ALTERNATOR SYSTEM
REGULATOR MUST BE GROUNDED
THROUGH MOUNTING BOLTS
CAUTION:
ES-1332
8-4
Page 24

Keep these points
flywheel alternator:
1.
Be sure engine is being run long enough and fast
enough to recharge battery after each start. Charging
system tests require a full charged battery. Alternator
output is reduced
Also, power required for accessories reduces power
available to recharge battery.
2.
The regulator-rectifier has built in protection against
open circuits or short circuits on the alternator
output (B+) terminal. Either condition will cause the
regulator-rectifier to shut off and appear as
functioning. Prior to checking the regulator-rectifier,
check all wiring between the regulator-rectifier
terminal and the battery positive
assure it is free of open circuits, resistances or short
circuits. Also,
it may have insufficient power to "turn on" the
regulator-rectifier.
Be sure regulator-rectifier plug (connector) is in-
3.
serted properly. Plug must bottom in receptacle; this
eliminates any resistance due
Keep clean and tight.
Make. sure alternator stator leads are not shorted
4.
together.
Be sure regulator-rectifier has a good ground
5.
connection. Mating surface for mounting must be
clean and fasteners tightened properly.
6.
Never reverse the battery leads.
When the engine is running between
observe the panel ammeter
connect a test ammeter).
proceed with the
in
mind when testing or servicing the
in
direct proportion to engine rpm.
if
it is not
(+)
terminal to
if
the battery is extremely discharged
to
a poor connection.
1800
to
2600
(if
not already equipped,
If
no charging is evident,
Alternator Output
Test.
B+
rpm,
ALTERNATOR OUTPUT TEST
as
Use a volt-ohmmeter, such
testing the charging system.
1.
Check battery voltage with unit not running.
within specifications (Table
proceeding to step
2.
With the engine-running, check the battery terminal
voltage (regulator output) using a DC voltmeter.
Voltage output should be within the values specified
in Table
replace regulator-rectifier assembly.
less than specified, proceed to step
3.
Examine all wires for loose, corroded, broken connections, short circuits, etc. Check fuses. Repair as
needed to assure complete circuits from regulatorrectifier
and from battery negative
rectifier case.
engine running, proceed to
4.
Disconnect plug from regulator-rectifier and test
the AC voltage at the plug with engine running.
voltage reads more or less than specified in Table
proceed to step
DC voltage is
5.
Use the
open
Disconnect plug from the regulator-rectifier. Connect one ohmmeter test lead to a stator wire,
connect the other test lead to ground. Reading
should show an open (no continuity).
stator must be replaced.
tinuity conned one ohmmeter lead to each wire
coming from the stator. Refer to Table 1 for resistance specifications.
replace stator.
specified and windings are not shorted or open, low
AC voltage may be due to
blower wheel assembly must be replaced.
1.
If
B+
terminal to battery positive
Rx1
scale on the ohmmeter for detecting an
or
ground in the stator (unit not running).
2.
voltage is greater than specified,
If
battery voltage remains low with
5.
If
low,
replace regulator-rectifier.
If
stator resistance readings are as
the Simpson
1)
charge battery before
(-)
terminal to regulator-
step
4.
AC voltage is as specified but
If
reading shows no con-
If
resistance is not as specified,
loss
of magnetism.
270,
If
voltage is
3.
(+)
If
terminal
it doesn't,
when
If
not
If
AC
If
so,
1,
8-5
Page 25

TABLE
1.
TESTING
20
AND
35
AMPERE SYSTEMS
PROCEDURE
20
AMP
35
AMP
r
BATTERY REGULATOR
12
to
13 VDC 13.6
12
to
13
VDC
to
14.7
BASIC
VD
TEST
Refer
to
Alternator
STATOR
RESISTANCE
to
Refer
0.10
0.06
Alternator
Output Test
to
0.19
to
0.10
Ohms
Ohms
Page 26

TYPICAL
WIRING DIAGRAM
IGNITION
SWITCH
WITH
OIL
B+
ACCESSORIES
START
PRESSURE
SWITCH
BYPASS
SWITCH
OIL
PRESSURE
FOR
FOR
SHUTDOWN
:
CONDENSER
OIL
PRESSURE
SWITCH N
CONTROL
ES-1667
These typical wiring diagrams show the basic wiring necessary for operation of the engine. Your engine may
differ in circuitry and features depending on how the
equipment
manufacturer chose
to
configure the final
product
Page 27

Starting
System
ELECTRIC STARTER
Normally the starter will require little or no service other
than possible brush replacement. However,
accident or misuse, the starter requires service or
overhaul, the following will provide the information
necessary to perform this service.
if
through
1.
Remove both battery cables from battery. Disconnect ground cable first.
2.
Disconnect battery cable and electrical lead wires
from starter.
3.
Remove starter motor.
Service
When starting engine, note starter motor action. The
pinion gear should mesh quickly with flywheel ring gear
and spin engine. Once engine starts and solenoid
opens, the starter should disengage and stop.
cranks engine slow,
components. Failure to crank is normally caused by low
battery charge, defective battery cables, corroded or
\
poor connections, or low temperatures.
these variables, starter continues to crank slowly, starter
must be removed and repaired.
or
not at all, check start circuit
If
If
starter
after checking
Starter Removal
Accidental starting
result in severe personal injury
death. Disconnect the negative battery cable and spark
plug wires while servicing engine, controls,
ciated equipment.
of
the engine can
or
asso-
SOLENOID
or
Starter Disassembly
1.
Remove
solenoid (Figure
2.
Remove the two solenoid mounting screws and
remove solenoid.
3.
Scribe a mark across frame and rear bracket
in assembly. Remove the
4.
Remove rear bracket and frame assembly.
5.
Carefully remove armature and lever from front
bracket. Note direction of lever and retainer.
6.
Remove the two brush mounting screws, and remove the rear bracket.
7.
Remove brush holder assembly from the frame by
pulling the brushes out.
“M”
terminal nut and wire lead from
8).
two
through bolts.
THROUGH
to
aid
SOLENOID
BUSHING
FIGURE
1.
STARTER
9-
1
COVER
BRUSH
ES-1665-01
MOTOR
Page 28

8.
Push stopper toward pinion and remove snap ring
(Figure
9.
Remove stopper and overrunning clutch from
2).
armature shaft.
FIGURE
3.
INSTALLING STOPPER
CLUTCH
ES-1194
FIGURE
2.
REMOVING OVERRUNNING CLUTCH
10 Inspect starter for damaged or worn parts.
11.
Repair or replace all damaged or worn parts as
needed.
Starter
1.
2.
Assembly
Install seal in nose housing. Install overrunning
clutch
on
the armature shaft.
Slide stopper on the armature shaft. Position snap
ring in groove in armature shaft.
3.
Pull stopper all the way over snap ring (Figure
may be necessary to tap snap ring into groove with a
punch while maintaining tension on stopper.
4.
Lubrication: When starter motor
is
assembled apply
grease to each of the following points (Recom-
PS
No.
mended grade: Multemp
2):
Armature shaft spline
Both bushings (Both ends of armature)
Stopper on armature shaft
Pinion gear
Sliding portion of lever
ES-1622
3).
It
5.
Fit overrunning clutch into lever, and install with
armature in the front bracket.
6.
Install lever retainer and spacer. Position frame
assembly over armature on the front bracket.
7.
install brush holder assembly. Position brushes in
brush holder. Make certain positive lead wires are
not grounded.
8.
Install washers, as required, on the rear end of
armature shaft to obtain an armature shaft thrust
gap of
washers are required
9.
Install rear bracket. Secure brush holder to rear
0.002
Retaining
Brush
Through
Table
Bolts
to
0.02
inch
(0.05
if
rear bracket is replaced.
1.
Starter Assembly Torques
Screws
to
0.5
mm). New
bracket with two machine screws.
9-2
Page 29

10. Install and tighten the two through capscrews.
11. Install solenoid plunger in lever. Secure solenoid
to
front bracket with two machine screws.
12. Install wire lead
to
the terminal
“M”
on solenoid.
13. After assembly, adjust pinion clearance. Pinion
0.08
inch
(0.5
to
clearance should be 0.02 to
if
not, check as follows (Figure
4):
2.0 mm);
A. Connect starter to a battery. Close switch. This
will shift pinion into cranking position.
B.
Push pinion back by hand and measure pinion
clearance.
If
clearance does not fall within the
specified limits, adjust by adding or removing
shims located between solenoid and front
bracket. Adding shims decreases clearance;
removing shims increases clearance. Shims are
included with replacement solenoid.
COMMUTATOR
BARS
FIGURE
Testing Armature
5.
TESTING ARMATURE FOR GROUNDS
for
an
Open
Circuit:
Using an
ohmmeter, check for continuity between the commutator
segments.
If
there
is
no continuity (high resistance), the
segments are open and armature must be replaced.
PINION
FIGURE
SWITCH
BATTERY
12V
.4.
PINION CLEARANCE ADJUSTMENT
PINION
FRONT
CLEARANCE
ES-1623
Inspection and Testing
Inspect the starter components for mechanical defects
for
before testing
Testing Armature
core and the end of each commutator bar with a pair
ohmmeter leads (Figure
indicates a grounded armature. Replace grounded
armature.
grounds or shorts.
for
Grounds: Touch armature shaft or
5).
A
low ohmmeter reading
Of
Testing Armature
locating shorts in the armature (Figure
for
a
Short
Circuit:
Use a growler for
6).
Place armature
in growler and hold a thin steel blade (e.g. hacksaw
blade) parallel to the core and just above it while slowly
rotating armature in growler.
to
cause the blade
vibrate and be attracted
A
shorted armature will
to
the core.
If
armature is shorted, replace with a new one.
BLADE
GROWLER
ES-1002
FIGURE
6.
TESTING ARMATURE FOR
SHORT
CIRCUITS
9-3
Page 30

Commutator Inspection:
colored, clean with number
paper. Blow grit
out
If commutator is scored, rough, or worn, turn it down
If
commutator is dirty or dis-
00
to
000
commutator
of armature after cleaning.
in
lathe.
Field Coil: Use an ohmmeter
between brushes.
If
there is no continuity, the field coil is
open and must be replaced. With field coil mounted
to
check for continuity
in
the frame, check for continuity between the field coil and
frame. Replace frame assembly if there is continuity.
a
Overrunning Clutch: lnspect pinion and spline teeth for
or
wear
If
gear also. Rotate pinion.
damage.
pinion gear is worn or damaged, inspect flywheel ring
It
should turn free when turned
in one direction, and lock when turned in the opposite
direction.
damage.
Cleaning
cleaning solution
Do
not clean overrunning clutch
overrunning
will
clutch
result
in
in
starter
in
liquid
liquid
cleaning solutions.
Brushes: Clean around brushes and holders, wiping
all brush dust and
.4528
inch
(1
dirt.
If
brushes are worn shorter than
1.5
mm) replace them (Figure
WEAR
LIMIT
FIGURE
7.
BRUSH
WEAR
7).
LIMIT FIGURE
off
ES-1193
Solenoid: Push solenoid plunger
in
and release it. The
plunger should return to its original position. While
holding plunger all the way
between terminals
“M”
and “B”.
replace the solenoid (Figure
in,
check for continuity
If
there is no continuity,
8).
After replacing solenoid
check pinion clearance.
8.
TERMINAL
SOLENOID TERMINALS
“B”
ES-1345
Check for shorts between positive side of brush holder
and brush holder base.
If
there is continuity, replace
holder assembly. Check for free movement of brushes.
All
brushes should move freely
in
the brush holders.
Bushings:
either the front or rear bushing
show
If
of wear or damage, replace them. Bushing and rear
bracket are replaced as an assembly. Check armature
shaft thrust gap
if
rear bracket is replaced.
Remove front bushing by tapping bushing from inside
with a
7/16
inch tap.
Do
not remove cap from front
bracket. Thread capscrew, same size as tap, into
bushing. Using a slide hammer remove bushing from
front bracket. Press new bushing into front bracket. Use
care not
to
distort inside diameter of bushing.
9-4
signs
Page 31

Brush Replacement:
Cut old positive brush from pigtail
at the brush. Be Careful not to damage field coil. Clean
1/4
to
3/8
inch
(6.5
to
9.5
mm) of brush end of pigtail
with sandpaper or emery cloth. (Figure
9).
Starter
Mounting
Before installing starter motor, make sure the starter
mounting surface on the engine base is clean and free
of
oil.
To
install starter use the following procedure. The
starter pinion gear lash does not require adjustment.
1.
Install starter motor and torque mounting capscrews
to
that specified in
ASSEMBLY
TORQUES.
PIGTAIL
STILL
ATTACHED
TO
FIELD
COIL
SMALL
FIGURE
CHAMFER
9.
BRUSH
REPLACEMENT
(approx.
SOLDER
MUST
EXTEND
BRUSH
LARGE
REPLACEMENT
SURFACE
CHAMFER
BRUSH
CLEAN
1/4
to
NOT
BEYOND
3/8
inch)
Push prepared end of pigtail lead into hole in replacement brush from the small chamfered side. Solder pigtail
lead to replacement brush on the large chamfered side,
using
50/50
tin/lead, rosin core solder and a standard
240/325 Watt soldering iron. Use a file to remove any
excess solder that may extend beyond brush surface.
2.
Connect battery cable and wires to starter. Connect
battery cables to battery. Connect ground cable last.
Materialprotruding from soldered side
surface of brush can cause equipment
damage.
Do
not use excessive solder or heat and file
any excess material from brush surface.
9-5
Page 32

Engine
Disassembly
DISASSEMBLY/ASSEMBLY
When complete engine disassembly is necessary, first
remove all complete assemblies. Individual assemblies
such as fuel pump and carburetor can be disassembled
and repaired at another time.
Suggested Disassembly Order
1. Drain engine oil.
2. Disconnect all exhaust and electrical lines.
3. Removeengine from its mountingsand place upright
in a suitable work area.
per side provides a suitable fixture to hold the
engine and prevent damage
oil
4. Remove
blower housings, etc.
5.
Remove flywheel.
6.
Remove ignition trigger and gear cover, being
careful
7.
Remove crank gear, using a gear puller and ring.
8.
Remove all accessories such as oil filter, starter,
intake manifold, fuel lines, spark plugs, etc.
9.
Remove oil pump and cylinder heads.
10. Remove valves, springs, lifters, etc.
11. Remove camshaft and gear assembly.
12. Remove oil cooler.
13. Set engine on its back to remove oil base cover, oil
pickup cup and oil pickup tube.
14. Remove connecting rods and pistons.
15. Remove oil base casting, crankshaft
and lower bearing.
Keep all parts in their respective orders. Keep valve
assemblies together. Return rod caps to their respective
pistons. Analyze the reasons for parts failure.
fill
to
protect oil seal from keyway damage.
Suggested Assembly Procedure
Engine assembly is normally the reverse
assembly procedure, observing proper clearances and
torques. Use a torque wrench
Coat the internal engine parts with oil as they are
assembled. After the internal engine parts are assem-
bled, the engine should turn over by hand freely. Use
only genuine Onan parts and special
reassembling your engine.
1. Use proper bearing driver to install top main bearing
after coating
2. Insert lower main bearings in oil base casting.
it
A 2 x
4 wood frame 10 inches
to
the crankshaft.
tube, and all housings, shrouds,
of
the dis-
to
assure proper tightness.
tools
when
with a light film of oil.
3. Insert crankshaft, oil base casting, and crankshaft
gear.
4. Install pistons and connecting rods.
5.
Install oil pickup tube with its spring, oil pickup cup,
and oil base cover.
6.
Install oil cooler.
7.
Install camshaft and gear assembly; align crank
gear mak with cam gear mark.
8.
Install valve assemblies, oil pump, oil cooler, and
cylinder heads.
9.
Install all accessories such as oil filter, starter fuel
lines and spark plugs.
10. Install gear cover with oil seal, trigger ring, and
flywheel..
11. Check valve clearance.
12. Install all housings, shrouds, intake manifold, and oil
fill tube. Always use a new oil
reinstalling the oil fill tube.
13. Fill engine oil.
fill
tube seal when
Operation
Start engine and check oil pressure. Run for approximately 15 minutes 'to bring engine
temperatures. Check for oil leaks, fuel leaks, and exhaust
leaks. Adjust carburetor and governor for speed and
sensitivity.
to
operating
Testing Compression
The compression tester
condition of valves, pistons,-piston rings and cylinders.
To check compression:
1. Run the engine until thoroughly warm.
2. Stop engine and remove spark plugs.
3. Remove air cleaner and place throttle and choke
the wide open position.
4.
Insert the compression gauge in one spark plug
hole.
5.
Crank the engine and note the reading.
to
Refer
There may be variations due to equipment, temperature,
atmospheric conditions and altitude. These pressures
are for a warm engine at cranking speed (about 300
rpm).
SPECIFICATIONS
is
used to determine the
in
for compression pressures.
Page 33

Tappet
Adjustment
The engine is equipped with adjustable valve tappets.
The valve tappet clearance should be checked and
Schedule
as specified in the
(located
in
the Operator’s Manual). Adjust the
Periodic Maintenance
valve clearance only when engine is at ambient temperature. Proceed as follows:
1.
Remove ignition key
2.
Remove all parts necessary
to
prevent accidental starting.
to
gain access to valve
tappets.
3.
Remove spark plugs
engine over
4.
Rotate crankshaft
by
to
ease the task of turning the
hand.
in
a clockwise direction until the
right intake valve (viewed from carburetor end)
opens and closes. Continue turning the crankshaft
until the flywheel timing mark is lined up with the
governor shaft on the gear cover. This should place
the right piston
(#1)
at the top
of
its compression
stroke. Verify that the left intake and exhaust valves
are closed and there is no pressure on the valve
lifters.
5.
The correct feeler gauge for the valve adjustment
(see SPEClFlCATIONS) should pass freely between
valve cap and tappet; a
gauge should not (Figure
6.
To correct valve clearance, use a
end wrench
to
turn the adjusting screw
0.002
inch (0.05 mm) thicker
1).
7/16
inch open
to
obtain the
correct clearance. The screw is self-locking and
will stay where
it
is set.
A
9/16
inch
(14
mm) open
end wrench is required to hold the tappet while
turning the adjusting screw.
7.
To adjust valves on the left hand cylinder, turn
engine one complete revolution and again line up
the flywheel timing mark with the governor shaft on
the gear cover. Then follow adjustment procedure
given for right hand cylinder.
8.
Replace all parts removed in Step
screws securely. Torque valve cover bolts
2.
Tighten all
to
speci-
fied torque.
VALVE
A
properly functioning valve system is essential for good
engine performance.
valve design as shown in Figure
SYSTEM
All
engines utilize an L-head type
1.
Access
to
the valve
system can be obtained by removing the cylinder heads
and the valve covers.
be used
A
to
remove valves from the cylinder block.
valve stem seal
This seal must be replaced each time the valve
A
valve spring compressor must
is
used on the intake valve guides.
is
removed.
Place valves, springs, retainers, and tappets in a rack as
they are removed from cylinder block
so
they can
be
identified and reinstalled in their original locations.
Discard old valve stem seals and replace with new ones
during assembly.
Use the following procedures
to
inspect and service the
valve system.
Inspection
Clean carbon from the valves, valve seats, valve guides,
and cylinder block.
Valves:
warpage, out-of-round, and carbon deposits.
Burning and pitting are caused by the valve failing
seat tightly. This condition is often caused by hard
carbon particles on the seat.
valve springs, insufficient tappet clearance. warpage,
and misalignment.
Check the valve face for evidence of burning,
to
It
may also be due
to
weak
VALVE
SEAT
INSERT
VALVE
FIGURE
STEM
1.
SEAL
INTAKE
VALVE
VALVE
CLEARANCE
\
ASSEMBLY
VALVE
ADJUSTING
SCREW
CLEARANCE
VT-1000
VT-1034
Page 34

Warpage occurs chiefly in the upper stem due to its
exposure to intense heat. Out-of-round wear follows
when the seat is pounded by a valve whose head is not
in line with the stem and guide. If a valve face is burned
or warped, or
Too
much clearance in the intake guide admits air and
if
the stem is worn, install a new valve.
oil into the combustion chamber, upsetting carburetion,
increasing oil consumption, and making heavy carbon
deposits. Carbon reduces heat dissipation. Clean metal
is a good heat conductor but carbon insulates and
retains heat. This increases combustion chamber temper-
atures which causes warping and burning.
Unburned carbon residue gums valve stems and causes
them
to
stick in the guide. Deposits of hard carbon with
sharp points projecting become white hot and-cause
pre-ignition and pinging.
Refinish valves that are slightly pitted or burned on an
accurate valve grinder.
If
valves are badly pitted or have
a thin margin when refacing, replace them.
Driving out old valve guides can cause
guide and tappet bore damage.
Do
not strike guide or tappet bores with driver during
removal.
Valve Guide Installation:
Run a small polishing rod
covered with crocus cloth through valve guide holes to
clean out carbon and other foreign materials. Place a
new gasket on the intake valve guide, and coat the outer
edge of each new guide with oil. Place guide in cylinder
block and press
(8.7
mm) from valve box side
method of installation is shown in Figure
in
until guide protrudes
of
block. A suggested
ROD
3.
11
/32
inch
VT-1020
FIGURE
Stems and Guides:
guides for wear (Figure
2.
VALVE STEM AND VALVE GUIDE INSPECTION
Always check valve stems and
2).
Use a hole gauge to measure
the valve guide. When clearance with stem exceeds that
specified in
DlMENSlONS AND CLEARANCES
replace
either valve or guide or both, as may be necessary.
Always regrind seat to make concentric with the newly
installed guide.
Worn valve stem guides can be replaced from inside the
valve chamber (a seal is provided behind the intake
valve guides only). The smaller diameter of the tapered
valve guides must face toward the valve head. Tappets
are also replaceable from the valve chamber after first
removing the valve assemblies.
Valve Guide Removal:
Before removing valve guides,
use an electric drill with a wire brush to remove carbon
and other foreign material from top surface of guides.
Failure
to
to
perform this operation may result in damage
the
guide bores. Drive the guides out with a hammer
and valve guide drive.
VALVE
GUIDE
NUT
5/16-18 HEX
(2
REQUIRED)
5/16-18
FIGURE
3.
VALVE GUIDE INSTALLATION
Valve Stem Seals (intake only): Do
NUT
THREADED
ROD
not reuse valve stem
VT-1023
seals. Each time the valves are removed from cylinder
block, a new seal must be used when valve is reinstalled.
Removing a valve after installing valve
stem seal can cause seal damage.
not allow valve stem groove to come in contact
Do
with
valve stem seal after installation.
10-3
Page 35

Valve
Spring:
ends, distortion; and tension.
Check valve springs for cracks, worn
If
spring ends are worn,
check valve spring retainer for wear. Check for spring
distortion by placing spring on a flat surface next
square. Measure height of spring and rotate
square edge
0.06
inch
to
measure distortion.
(1.5
mm) replace spring. Check spring tension
If
distortion exceeds
it
against
to
a
at the installed height for both the valve open and closed
position using an accurate valve spring tester. Replace
any valve spring that is weak, cracked, worn, or distorted.
Valve Seat Removal:
deposits from valve
Remove carbon and combustion
seat.
Select proper puller size
determined by inside diameter of valve seat. On some
pullers use a new seat as a guide
(Figure
4).
Puller jaws must expand into cylinder block
to
adjust puller depth
at the point where bottom of valve seat insert rests on
cylinder block. Position puller on valve seat and tighten
hex nut. Clamp cylinder block
slide hammer
blow
with the slide hammer.
to
puller. Tighten hex nut between each
to
a solid bench. Attach
Valve Rotators:
Free rotating valves are used for intake
and exhaust. While in the open position, the valves must
rotate freely.
Valve Seats:
Inspect valve seat inserts.
If
seats are in
serviceable condition clean seat up by using either a
seat cutter
or
seat grinder.
If
seats are loose, cracked
or
severely pitted, new ones must be installed. Remove
valve seat inserts using a valve seat removal
seat insert bores in cylinder block are damaged
so
that a press fit cannot be obtained when installing
tool.
If
or
valve
worn
new standard size valve seat inserts, the bores must be
machined for an oversize seat.
USE
NEW
VALVE
SEAT
ADJUST
PULLER DEPTH
TO
VALVE
VALVE
INSERT
(USE
CHECK
FOR
BURRS
INSERTING
SEAT
DRIVER
PROPER
THIS
SURFACE
BEFORE
TOOL)
SEAT
PULLER
FIGURE
4.
JAWS
VALVE SEAT REMOVAL
C-1104
VT-1025
FIGURE
Valve Seat Installation:
5.
INSERTING NEW VALVE SEAT
After the old seat has been
removed, clean out any carbon or metal burrs from the
seat insert recess. Use a valve seat insert driver and
hammer
seat insert in
to
install the insert (Figure
so
the insert enters the recess evenly.
5).
Drive the valve
Make certain that the valve seat insert rests solidly on
the bottom
of
the recess all the way around its
circumference.
To
assure a tight valve seat fit and eliminate the danger
of seat loosening in the bore, valve seat must be staked.
Use Onan valve seat staker
Insert valve seat staker into valve seat or guide in
cylinder block. Using a lead hammer, strike the staking
tool a sharp blow
place.
It
will be necessary
to
wedge new valve seat securely in
only.
to
refinish valve seat inserts
before installing valves.
10-4
Page 36

TAPPETS
Very little wear takes place on tappet diameters
tappet bores.
If
the clearance between tappet and bore
in cylinder block exceeds specifications, replace the
tappet. Oversize tappets are available.
Inspect the tappet faces which contact camshaft lobes
for roughness, scuffing,
worn tappets.
If
tappets are worn, inspect camshaft for
or
concave wear. Replace any
wear.
or
in
VALVE FACE AND SEAT GRINDING
Before installing new valves
inspect valve seats for proper valve seating. If used
valves are reinstalled, the valve stems should be cleaned
and valve faces ground
Refinish valve seats
valves and seats, remove all evidence of pitting and
grooving.
If
end of valve stem is pitted
clean it up on the refacer wheel.
usually enough
to
square stem and remove any pits
burrs. The valve guide should be thoroughly cleaned.
valve guide is worn,
or
parts must be replaced.
By grinding the valve face and seat at slightly different
angles, a fine line of contact on face and seat is
obtained, eliminating the need
faces. The one degree difference
the interference angle (Figure
greater than that of the valve face. This assures contact
at the maximum diameter on valve seat seating surface.
or
previously used valves,
to
their specified angles of
to
a
45°
angle. When refacing
or
worn, true it and
A
very light grind is
44°.
valve is warped, the necessary
to
lap the seating sur-
in
angles is defined as
6).
The seat angle is
or
If
around the whole valve face, keep grinding until complete face is ground clean. Be sure the correct valve
face angle is maintained. When valve head is warped, a
knife edge will be ground (Figure
head due
removed
to
the large amount
to
completely reface valve. Heavy valve heads
7)
on part
of
metal that must be
or
all of the
are required for strength and good heat dissipation.
Knife edges lead
to
due
heat localizing on the edge.
to
breakage, burning, and pre-ignition
Replace any valve that cannot be entirely refaced while
keeping a good valve margin (Figure
worn,
or
damaged in any way. The amount of grinding
necessary
worn
to
true a valve indicate whether valve head is
or
warped.
WARPED
VALVE WITH
KNIFE
EDGE
GOOD
MARGIN
FIGURE
7.
VALVE
HEAD
KNIFE
INCH
MARGIN
7)
or
EDGE
MINIMUM
(.E
MM)
is
warped,
M-1184
FIGURE
Refinish valve faces
machine. The
grinding. Check
removed.
check
to
If
see
6.
VALVE INTERFERENCE ANGLE
to
first
cut from valve face must be a light
if
there is an unevenness of metal being
only part of valve's face has been touched,
if
valve is properly seated in machine
valve is warped, worn,
a
44°
angle on a valve refacing
or
distorted. When cut is even
VT-1021
or
if
When new valve seats are installed,
or
previously used
seats reground, refinishing must be done with a valve
seat grinder used according
to
the manufacturer's
directions.
Valve seats should be ground .with a
and the width of the seat band should be
3/64
inch
(0.8
to
1.2
mm) wide. Grind only enough
45
degree stone
1/32
inch
assure proper seating.
Place each valve in its proper location. Check each
valve for a tight seat. Make several marks at regular
intervals across the valve face using machinist's bluing.
Observe
if
the marks rub off uniformly when the valve is
rotated part of a turn against the seat. The valve seat
should contact the valve face evenly
line
of
contact should
be
at the center of the valve face.
at
ail points. The
10-5
to
to
Page 37

FLYWHEEL
Removing the flywheel is a relatively simple process, but
the following procedure must be followed
damage
1.
to
the gear case and possible injury to the
Turn the flywheel mounting screw outward about
two turns.
Incorrect flywheel removal can
result in severe personal injury.
Do
not remove flywheel screw completely when
using flywheel puller.
2.
Install a flywheel puller on the flywheel (Figure
FLYWHEEL
to
avoid
8).
GEAR
COVER
After removing the mounting screws, tap the gear cover
gently with a
soft
faced hammer to loosen
it.
When installing the gear cover, make sure the pin in the
gear cover engages the nylon lined (smooth) hole in the
governor cup. Turn the governor cup
so
the nylon lined,
hole is at the three o'clock position. Use a small amount
of
grease to assist
in
holding governor cup
in
position.
The smooth side of the governor yoke must ride against
the governor cup. Turn the governor arm and shaft
clockwise as far as possible and hold in this position
until the gear cover is installed flush against the
crankcase.
seal (Figure
Be
careful not to damage the gear cover oil
9).
FLYWHEEL
MOUNTING
FIGURE
3.
Turn the puller bolts in, alternately, until the wheel
8.
FLYWHEEL PULLER
SCREW
snaps loose on the shaft.
Improper flywheel removal can
cause gear case damage.
use any tools to pry against gear cover when
removing flywheel.
4.
Unscrew the puller from the flywheel, remove the
flywheel mounting screw and washer and pull the
flywheel off the shaft. Take care not to drop the
wheel.
A
bent or broken fin will destroy the balance.
CS-1000
Do
not
ROTATE
CUP
SO
INTO
THE
HOLE
BUSHING
ROLL
GOVERNOR
ROLL
PIN
METAL
LINED
OR
PLASTIC
IN
THE
FIGURE
FITS
CUP
I
PIN
GOVERNOR
9.
GEAR COVER ASSEMBLY
GOVERNOR
GOVERNOR
YOKE
OIL
CUP
GOVERNOR
IF
FEELER
ENTER
FALLEN
(Smooth
Toward
SEAL
WILL
HOLE
OUT
SHAFT
SHAFT
Side
Cup)
Page 38

IS
PROPERLY
ASSEMBLED
DIMENSION SHOWN
ON
DRAWING
BE
AS
THE
WILL
INDICATED
GOVERNOR
GOVERNOR
CUP
FLYBALL
5
BALL
GOVERNOR
FLYBALL LOCATIONS
10
BALL
GOVERNOR
CS-1238
GOVERNOR
FIGURE
CUP
10.
GOVERNOR CUP DETAILS
With the gear cover removed, the governor cup can be
taken
off
after removing the snap ring from the camshaft
center pin. Catch the flyballs while sliding the cup
(Figure
10).
Replace with a new part any flyball which is grooved
has a flat spot; the ball spacer
if
its arms are worn
otherwise damaged; the gear/spacer assembly
on gear hub, and the governor cup
grooved
spinning
or
rough. The governor cup must be a free-
fit
on the camshaft center pin,
if
the race surface is
but
without any
if
loose
off
or
or
excessive play.
When installing the governor cup, tilt the engine
gear is up, put the flyballs in place (Figure
10),
so
the
and
install the cup and snap ring on the center pin.
The camshaft center pin extends out
3/4
inch
(19
mm)
from the end of the camshaft. This distance provides an
in-and-out travel distance of 7/32 inch
(5.6
mm) for the
governor cup, as illustrated. Hold the cup against the
flyballs when measuring. The camshaft center pin
cannot be pulled outward
If
the center pin extends out
the flyballs properly.
(5.6
mm), the engine will race, especially at no load.
or
removed without damage.
too
far, the cup will not hold
If
the distance is less than 7/32“
Remove the center pin and press in a new pin.
TIMING
If
replacement of either the crankshaft gear
GEARS
or
the
camshaft gear becomes necessary, always install both
gears new.
The camshaft and gear must be replaced as an assembly.
Before removing the camshaft and gear assembly,
remove the cylinder head and valve assemblies.
To remove the crankshaft gear, first remove the snap
ring and retainer washer, then attach the gear pulling
ring using two
No.
10-32 screws (Figure
11).
Tighten
the screws alternately until both are tight. Attach a gear
puller to the puller ring and proceed to remove the gear.
Each liming gear is stamped with
gear teeth must mesh
so
“O”
near the edge. The
that these marks exactly
coincide when the gears are installed in the engine.
When installing the camshaft gear and shaft assembly,
be sure the thrust washer
is
properly in place behind the
camshaft gear. Then install the crankshaft retaining
washer and lock ring.
Page 39

FIGURE
CRANKSHAFT
'GEAR
INSTALLING
GEARS
11.
TIMING GEAR REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION
VT-1029-01
4.
Turn the crankshaft until the piston is at the bottom
of
its
stroke and remove the connecting rod nuts. Lift
from
the rod bearing cap
the rod and push the rod
and piston assembly out through the top
cylinder using
hammer handle.
Do
not scratch the
a
crankpin and cylinder wall when removing the
piston and rod..
5.
Mark each piston and
returned
to
their respective cylinders after overhaul.
rod
assembly
so
they can be
Keep connecting rod bearing caps with their
respective rods.
6.
Remove the piston rings from the piston with a
13).
piston ring spreader (Figure
Remove the piston
pin retainer and push the piston pin out.
of
the
PISTONS
AND
CONNECTING
RODS
Observe the following procedure when removing pistons
and connecting rods from the engine.
1.
Drain oil.
2.
Remove the cylinder head and oil cooler from the
engine.
3.
Remove the ridge from the top
of
each cylinder with
a ridge reamer before attempting piston removal
(Figure
12).
Improper piston removal can
cause piston damage. Use ridge
reamer
to
remove cylinder ridge before removing
piston.
FIGURE
7.
Remove dirt and deposits from the piston surfaces
13.
REMOVING PISTON RINGS
with an approved cleaning solvent. Clean the piston
ring grooves with a groove cleaner or the end of a
piston ring filed
must be taken
to
a sharp point (Figure
not
to
remove metal from the groove
14).
sides.
Care
FIGURE
12.
REMOVING RIDGE
FROM
CYLINDER
10-8
Improper piston cleaning can
'cause piston damage.
use
a caustic cleaning solvent or
cleaning pistons.
8.
Clean the connecting rods
passages with compressed air.
in
solvent.
wire
Blow
Do
brush
out
not
for
all
Page 40

FIGURE
15.
CHECKING RING SIDE CLEARANCE
Measuring Pistons:
FIGURE
14.
PISTON
GROOVE
CLEANING
Inspection
Follow the procedures given below when inspecting
pistons and connecting rods.
Piston Inspection:
1.
Inspect the pistons
lands, skirts and pin bosses. Check for wear at
the ring lands using a new ring and feeler gauge
(Figure
15).
Replace the piston when the
side clearance of the top compression ring
reaches that specified in
CLEARANCES.
2.
Replace pistons showing signs of scuffing,
scoring, worn ring lands, fractures
from preignition. Excessive piston wear near the
edge of the
top
for
fractures at the ring
DIMENSIONS AND
or
damage
ring land indicates preignition.
Refer'
determine where
to
DIMENSIONS AND CLEARANCES
to
measure piston to be sure the
total clearance follows specifications.
to
Page 41

Measuring Piston Rings:
1.
Install the
the piston and push the ring
piston
ring in the cylinder bore. Invert
to
the end of ring
travel, about halfway into the bore, which trues
the ring end gap. Check the gap with a feeler
gauge (Figure
2.
The practice of filing ring ends to increase the
end gap is not recommended.
16).
If
the ring end gap
does not meet specifications, check for the correct set of rings and the correct bore size.
cylinder bore that
size will reduce the end gap
is
0.001
inch
(0.03
0.003
mm) under
inch
mm).
A
(0.08
CYLINDER
BLOCK
The cylinder block is the main support for all other basic
engine parts. Crankshaft and camshaft are supported by
the block, assuring alignment of the crankshaft and
cylinder bores.
Cleaning
After removing pistons, crankshaft, cylinder heads, etc..
inspect block for cracks and wear.
serviceable, prepare
1.
Scrape all old gasket material
it
for cleaning as follows:
oil by-pass to allow cleaning solution
If
block
from
block. Remove
to
contact
is
still
inside of oil passages.
2.
Remove grease and scale from cylinder block by
agitating in a bath of commercial cleaning solution
or hot soapy washing solution.
3.
Rinse block in clean hot water
to
remove- cleaning
solution.
Inspection
When rebuilding the engine, thoroughly inspect block
for any condition that would make
This inspection must be made after all parts have been
removed and block has been thoroughly cleaned and
dried.
it
unfit for further use.
FIGURE
Connecting Rod Inspection:
16.
POSITIONING OF PISTON RING
AND MEASURING OF END GAP
Replace connecting rod bolts and nuts that have
damaged threads. Replace connecting rods that
have deep nicks, signs of fractures, scored bores, or
bores with dimensions which exceed that specified
DIMENSIONS AND CLEARANCES.
in
1.
Make a thorough check for cracks. Minute cracks
may be detected by coating the suspected area with
a mixture of
25
percent kerosene and
75
percent
light motor oil. Wipe the part dry and immediately
apply a coating of zinc oxide (white lead) dissolved
in
wood alcohol.
If
cracks are present, the white
coating will become discolored at the defective
area. Always replace a cracked cylinder block.
2.
Inspect
all
machined surfaces and threaded holes.
Carefully remove any nicks or burrs from machined
surfaces. Clean
out
tapped holes and clean up any
damaged threads.
3.
Check top of block for flatness with a straight edge
and a feeler gauge.
Cylinder Bore Inspection:
Inspect cylinder bores for
scuffing, scratches, wear, and scoring. If cylinder bores
are scuffed, scratched, worn, or scored, they must be
rebored and hone3 for the next oversize piston.
When the appearance of cylinder bores is good and
there are no scuff marks, check cylinder bore for wear or
out of roundness as follows:
1.
Check cylinder bore for taper, out of round, and
wear with a cylinder bore gauge, telescopic gauge.
or inside micrometer. These measurements should
be taken at four places: top and bottom of piston ring
to
travel, parallel and perpendicular
shaft (Figure
17).
axis of crank-
10-10
Page 42

2.
Record measurements taken a? top and bottom of
piston travel as follows:
A.
Measure and record as
diameter (parallel
to
“A”
the cylinder bore
crankshaft) near the top of
cylinder bore.
Measure and record as
B.
“B”
cylinder bore
diameter (parallel to crankshaft) at the bottom of
piston travel.
Measure and record
C.
as
“C”
cylinder bore
diameter (perpendicular to crankshaft) near the
top of cylinder bore.
TOP
END
OF
CYLINDER
RING
WEAR
AREA
Measure and record as
D.
“D”
cylinder bore
diameter (perpendicular to crankshaft) at the
bottom of piston travel.
Reading
E.
reading
“A”
subtracted from reading
“C”
subtracted from reading
“B”
“D”
and
indi-
cates cylinder taper.
If
cylinder taper exceeds that specified in
DIMENSIONS AND CLEARANCES
hone cylinder
F.
Reading
reading
to
the next oversize.
“A”
compared to reading
“B’
compared to reading
whether or not cylinder is out of round.
round exceeds that specified in
AND CLEARANCES
the cylinders must be
rebore and
“C”
and
“D”
indicate
If
out of
DIMENSIONS
rebored and honed to the next oversize.
Reboring the Cylinder
Rebore and hone engine whenever cylinder bore is
worn, damaged, out of round, or
exceeds specifications.
A
worn cylinder bore should be
resized to the smallest standard oversize diameter at
which it will clean up. The final finish and borediameters
should then be obtained by honing. Final bore diameter
should equal the standard diameter added to the
oversize.
if
cylinder taper
Improper boring will
result
in engine
damage. Boring must be done
qualified mechanics.
After boring to the correct oversize cylinder bore
dimension piston and ring clearance should be
appropriate. There is no need to adjust or
“fit”
pistons
and rings.
When reboring cylinders, take the following pre-
cautions:
1.
Make sure cutting tool is properly ground before
using it.
2.
Be sure top of engine block is smooth and deposit
free.
by
FIGURE
17.
METHODS
OF
A
CYLINDER BORE
OF
MEASURING THE DIAMETER
10-1
1
Page 43

3.
Clean base of boring bar before
bar
is set up.
Deposits under boring bar will cause it to tilt and the
cylinder will be distorted after boring.
4.
Make an initial rough cut, followed by a finish cut.
Then hone cylinder bore to the specified oversize.
Honing Cylinders (Using Precision
Refer
to
hone manufacturer's recommended grit site to
produce specified surface finish of
Hones)
20
to
40
RMS.
Too
rough of a finish will wear out the rings and too smooth
of a finish can retard piston ring seating:
1. Position block solidly for either vertical
or
horizontal
honing. Use either a drill press or heavy-duty drill
which operates at approximately
2.
Follow hone manufacturer's instructions for the use
250
to
450
rpm.
of oil or lubricant on stones. Do not use lubricants
with a dry hone.
3.
Insert hone in bore and adjust stones to fit snugly to
the narrowest section. When adjusted correctly, the
hone should not shake or chatter in cylinder bore,
but will drag freely up and down when hone is not
running.
Deglazing Cylinder Bores
Deglaze the cylinder bores
and
no
wear or out of round beyond specifications
before installing new rings. Deglazing gives a fine finish.
but does not enlarge cylinder diameter,
pistons with new rings may still be used.
The reason for deglazing a cylinder is to provide cavities
to hold oil during piston ring break-in.
1.
Wipe cylinder bores with a clean cloth which has
been dipped in clean, light engine oil.
2.
Use a brush type deglazing tool with coated bristle
tips to produce a crosshatch pattern in the cylinder
bore.
3.
Use a slow speed drill to drive the deglazing tool.
Move deglazing tool up and down in cylinder (10 to
12 complete strokes) rapidly enough
crosshatch pattern (Figure 18).
if
there are no scuff marks
so
the original
to
obtain a
4.
Connect drill
to
hone and start drill. Feel out bore for
high spots, which cause an increased drag on
stones. Move hone up and down in bore with short
overlapping strokes about
40
times per minute.
Usually bottom of cylinder must be worked out first
As
because it is smaller.
cylinder takes a uniform
diameter, move hone up and down all the way
through cylinder bore.
5.
Check diameter of the cylinder regularly during
honing.
A
dial bore gauge is the easiest method but
a telescoping gauge can be used. Check size at
places in bore: measure twice at top, middle and
bottom at 90-degree angles.
6.
Crosshatch formed by the stones should form an
included angle of
by moving the rotating hone
down in cylinder bore about
7.
Clean cylinder bores thoroughly with soap, water
and clean rags.
23
degrees. This can be achieved
(250
to
450
rpm) up and
40
times per minute.
A
clean white rag should not
become soiled on wall after cleaning is complete.
Do not use a solvent
or
gasoline since they wash oil
from the walls but leave the metal particles.
8. Dry crankcase and coat
it
with oil.
six
PRODUCECROSSHATCHSCRATCHES
FOR
FAST
RING SEATING
FIGURE
use gasoline, solvents, or commercial cleaners to
clean cylinder bores.
4.
Clean cylinder bore thoroughly with soap, water
18.
CROSSHATCHING
Improper cylinder cleaning will
result in engine damage.
AVOID
THIS
FINISH
Do
and clean rags. Continue cleaning until a clean
white rag shows no discoloring when wiped through
cylinder bore.
not
Page 44

CRANKSHAFT
Clean crankshaft thoroughly and inspect journals for
scoring, chipping, cracking, or signs of overheating.
.If
crankshaft has overheated, is scored, or excessively
worn, reconditioning or replacement will be required.
Examine bearing journals for cracks
if
overheating has
occurred.
Measure crankshaft main bearing and connecting rod
journals at several places on their diameter to check for
roundness and taper.
The only recommended method of reconditioning the
crankshaft is regrinding, as required to accommodate
undersize bearings. Metalizing of bearing journals is not
recommended.
If
regrinding
of
crankshaft journals is necessary, the
work should be done by a reputable machine shop that
has suitable equipment
to
handle precision work of this
type. Undersize main bearings and connecting rods are
available.
Whenever making major repairs on the engine, always
inspect the drilled passages
them
to
remove any foreign material and to assure
of
the crankshaft. Clean
proper lubrication of the connecting rods.
BEARINGS
With camshaft and crankshaft removed, measure all
bearing journal diameters. Measure inside diameter of
bearings. Refer
determine
to
DIMENSIONS AND CLEARANCES
if
measurements are within specifications.
to
ALIGN HOLE
WITH
IN
BEARING BORE OUTSIDE
IN
HOLE
BEARING
TOP
BEARING
BOTTOM
FIGURE
CAMSHAFT
\
CAMSHAFT
19.
CAMSHAFT
BEARING
PRESS
I
BEARING
BEARING IN
(1
2.7
mm)
OUTSIDE
BEARINGS
OF
OF
BLOCK
BLOCK
CT-1094
Visually inspect bearings and journals. Replace any
bearing that
is
scored, chipped, pitted or worn beyond
specifications.
Camshaft Bearings
Replacement camshaft bearings are precision type
which do not require line reaming
installation. Use a press or a suitable driver
bearings. Support casting to avoid distortion and to
avoid damaging the bearing bore during removal and
installation.
Clean. outside of bearing and bearing bore in the block.
Before installing bearings use Locktite
on outside diameter of bearing. Use a combination
bearing driver
to
install bearings.
Place the top camshaft bearing on the crankcase over
the bearing bore with the lubricating hole lined up with
the hole in block (Figure
19).
Be sure to
straight. Press in the top bearing flush with the outside
end of the bearing bore. Lubricating hole in the bearing
must be aligned with the hole in the block after
installation.
or
line boring after
to
remove
Bearing
start
the bearing
Mount
Press in the bottom camshaft bearing to the dimension
shown (Figure
19).
Lubricate bearing surfaces with oil
after installing.
Crankshaft
Bearings
New crankshaft main bearings are precision type which
do not require line reaming or line boring after
installation. Use a press or a suitable driver to remove
bearings. Support casting to avoid distortion and to
avoid damaging the bearing bore during removal and
installation.
Inspect the top and bottom main bearing lock pins for
damage. Replace
if
necessary,
Before installing main bearings expand bearing bores
by placing the casting in an oven heated
(94ºC).
Cool
the precision bearings
to
to
200°F
shrink them
if
possible.
10-1
3
Page 45

TOP
MAIN
BEARING
BORE
The bottom main bearing consists of two bearings. Use
of
a combination driver and lubricate the outside
bearings with
dimension shown (Figure
must line up
1
/8"
diameter pin can be inserted into hole. Lubricate
SAE
30
oil before installing them to the
21).
Oil holes in the bearings
with
those drilled in the engine block
the
so
a
main bearings lightly with oil after installation.
ALIGN
BEARING
NOTCHES
FIGURE
WITH
REPLACEMENT
TOP
MAIN
BEARING
20.
TOP MAIN BEARING INSTALLATION
Replacement top main bearing has the thrust washer
attached to the bearing.
Do
not add an additional thrust
washer to this.
Breathing vapor from towelette and
prolonged contact with skin can be
harmful. Use
only
in
we//
ventilated area and avoid
prolonged contact with skin.
Before installing the top main bearing use the towelette
included with the bearing kit to clean the outside
bearing and bearing bore in the block. Allow three
of
the
to
four minutes to dry. Apply Locktite from the small tube to
the mating surfaces of the bearing and the bearing bore.
Align the lock pin and oil holes in the bearing with the
lock pins and oil holes in the bearing bore (Figure
20).
Use a combination driver and install the bearing flush
with the block. The oil holes must be at least half open
after installation. Wipe
off
excess Locktite around the
bearing. Allow at least one hour at room temperature for
hardening.
OIL
BASE/BEARlNG
,005''
(0.127mm)
Place the thrust washer on the oil base
so
the notches fit
over the lock pins and the grooves are facing away from
the oil base (Figure
oil base. insert crankshaft into
oil
base on engine block.
moved
off
lock pins before tightening oil base or
22).
Place a new oil base gasket on
top
main bearing. Install
Be
sure thrust washer has not
lock
pins will be damaged.
OIL
BASE
FIGURE
Tighten
ASSEMBLY
22.
CRANKSHAFT
!-
the
oil base
TORQUES
the crankshaft endplay (Figure
that specified
in
endplay exceeds limits remove
between the. thrust washer and
A
THRUST
WASHER
GROOVES
OIL
BASE THRUST WASHER AND
SHIM
ENDPLAY
to
the torque recommended in
AND SPECIAL TOOLS.
23)
and compare
DIMENSIONS AND CLEARANCES.
oil
base and add shim(s)
oil
base. Install oil base,
Check
it
with
LS-1186
making sure; the thrust washer and shim(s) notches line
up with the lock pins. Torque oil base and check
endplay.
If
FIGURE
21.
BOTTOM MAIN BEARING INSTALLATION
LS-1183
10-14
MEASURE
HERE
EN
FIGURE
BLOCK
23.
CRANKSHAFT ENDPLAY
CT-1095
Page 46

CHECKING CONNECTING
ROD
BEARING OIL SEALS
CLEARANCE WITH PLASTIGAUGE
1.
Make certain that
so
they are installed in their original positions. Using
a
clean dry cloth, thoroughly clean all oil from
crankshaft journal and connecting rod.
2.
Place a piece of correct size Plastigauge in the
bearing cap the full width of the journal surface and
about
1/4
inch
Rotate the crankshaft about
3.
dead center and reinstall the-bearing cap; tighten
rod bolts
to
TORQUES
crankshaft.
Remove bearing cap. The flattened Plastigauge will
4.
be found adhering
crankshaft.
Compare flattened Plastigauge with thegraduations
5.
on Plastigauge envelope
The number within the matching graduation on the
envelope indicates total clearance in millimeters or
thousandths of an inch.
all
parts are marked or identified
(6.35
mm)
off
center (Figure
30
degrees from bottom
the torque specified in
AND SPECIAL TOOLS.
to
either the bearing cap or
to
determine clearance.
ASSEMBLY
Do
not turn the
24).
The gear cover and oil base have
replace the oil seals. Drive
oil
seals out from the inside,
being careful not to damage the
to
be removed to
oil
base and gear cover
surfaces.
Before installing oil seals
fill
the space between lips with
a multi-purpose grease.
Clean old sealing compound
off
of gear cover
oil
seal
mounting surface before installing new oil seal. Install
the gear cover oil seal to the dimension shown (Figure
Use a seal expander when installing oil base
oil
25).
seal to
prevent damage to oil seal. Install, oil seal flush with
outside
OIL
of
oil base (Figure
SEAL
21)
MOUNTING
OF
I
GEAR
FACE
COVER
FIGURE
24.
MEASURING BEARING CLEARANCE
A
GEAR
COVER
FIGURE
I
GEAR
COVER
OIL
25.
GEAR COVER OIL SEAL
THIS
SHOULD
OLD SEALING COMPOUND
BEFORE
SEAL
GEAR
BE
INSTALLING
COVER
SURFACE
CLEANED OF
SEAL
ALL
LS-1163
Page 47

1. Lubricate all parts with engine oil.
2. Position piston on its respective rod and install the
b pin.
3. Install the rings on the pistons starting with the oil
control ring (Figure 26). Use a piston ring spreader
to prevent twisting or excessive expansion of the
ring Compression rings have a dot or the word
“top” on one side of the ring to indicate which side
faces the top of the piston. Unmarked piston rings
can be installed either way. The oil control ring has
an expander; install the expander first and then
close until the expander ends butt. The joint should
be 180 degrees from the gap of that ring.
PISTON ASSEMBLY
4. Tap the piston down into the bore with the handle
end of a hammer until the connecting rod is seated
on the journal (Figure 27). Install the bearing cap on
the rod.
5. Install one fastener and tighten to 5 ft-lbs (7 Nm).
Repeat this for the other fastener. Tighten both
fasteners down to the torque specified in ASSEMBLY
TORQUES.
OIL HOLE* OR
TOWARD
T
COMPRESSION
FIGURE 26. PISTON RINGS
RINGS
CT-1047
INSTALLATION OF PISTON IN CYLINDER
1. Turn the crankshaft to position the number one rod
bearing journal at the bottom of its stroke.
* OIL HOLE NOT USED, LATER PRODUCTION
CONNECTING ROD
CT-1048
2. Lubricate the number one piston assembly and
inside of the cylinder. Compress the rings with a ring
compressor (Figure 27).
3. Position the piston and rod assembly in the cylinder
block. Oil squirt hole of connecting rod must face
camshaft.
FIGURE 27. INSTALLING PISTON AND CONNECTING ROD
6. Install the remaining piston and rod in the same
manner. Crank the engine over by hand to see that
all bearings are free.
7. Install the oil cooler with a new gasket.
8. Install the cylinder heads. See Cylinder Headsection
for torques and torquing procedure.
9. Replace oil and break in engine.
lo-16
Page 48

CYLINDER
HEADS
3.
Use new head gaskets and clean both :he heads
Remove the cylinder heads for carbon cleaning and and the cylinder block thoroughly where the
gasket change at intervals specified in the Periodic gaskets rest.
Maintenance Schedule (located
Manual).
1.
Use a
1/2
inch
(13
mm) socket wrench
cylinder head bolts or nuts. Lift heads
Torquing or removing cylinder
heads when hot (above
[37°
C])
will result in head damage. Allow heads to
cool to below
100°
F
(37°
removing.
2.
After removing heads, clean out all carbon deposits.
Be
careful not to damage the outer sealing edges
where gaskets
fit.
The heads are made of aluminum
in
the Operator's
off.
C)
before torquing
to
remove
100°F
or
Cylinder Head Installation
1.
Place a head gasket on the cylinder block and align
the holes in the gasket with the holes in the cylinder
block. While holding the gasket against the cylinder
head, carefully install the cylinder
engine.
not attempt
to
slide the head
Do
through the gasket without the cylinder block behind
it
or the gasket may tear.
Follow the head torque sequence shown in Figure
2.
28. Tighten all bolts
(14
Nm),
then
TORQUES.
Recheck all head bolts for correct
to
5
ft-lbs
to
the torque specified in
torque.
(7
Nm), then
head
ASSEMBLY
10
and can be damaged by careless handling.
on the
bolts
ft-lbs
NO.
1
CYLINDER
FIGURE
28.
CYLINDER HEAD TORQUE SEQUENCE
10-1
7
NO.
2
CYLINDER
C-1002
Page 49

Right at home.
Product
shown herein
Wheel
right
designs
notice
Tractors & Riding
Mowers
information and specifications are
as
of the time of printing.
Horse
Products,
to
change product specifications,
and
and
without
Inc. reserves the
standard
equipment without
incurring obligation.
PRINTED
IN
U.S.A.
1089
PART
NUMBER 810713R1
 Loading...
Loading...