Page 1

GAS TRIMMER GUIDE, MODELS 51630, 51603, 51604
Table of Contents – Page 1 of 1
FOREWORD
GENERAL INFORMATION
MAINTENANCE PROCEDURES
AIR CLEANER MAINTENANCE
EXHAUST SYSTEM MAINTENANCE
FLEXIBLE DRIVE SHAFT MAINTENANCE
CARBURETOR ADJUSTMENTS -- MODEL TC-1 500 WITH TILLOTSON
CARBURETOR ADJUSTMENT -- MODELS TC-300, TC-400 WITH WALBRO
TROUBLESHOOTING AND TEST PROCEDURES
DISASSEMBLY, REPAIR, REASSEMBLY INSTRUCTIONS
WALBRO CARBURETOR OPERATION
CUTTER HEAD TROUBLESHOOTING
CLUTCH REPAIR
Page 2
GASOLINE POWERED TRIMMER
&
MAINTENANCE
REPAIR GUIDE
MODEL
NO.
51630
1000001
2000001
2000001 & UP
&
&
UP
UP
COPYRIGHT(C)
The
MINNEAPOLIS, MN
Tor0
ALL
Company
RIGHTS
55420
RESERVED
-
1982
U.S.A.
Form
492-0266
Page 3

FOREWORD'
This Maintenance and Repair Guide will provide you
accomplish the maintenance and repair of gasoline-powered flexible line trimmers powered by
the new
The number of repair procedures for this line of engine;s has been limited for simplicity and
economy The repairs are easy to accomplish. even for operators or mechanics who have
limited experience
Should you require additional information concerning these trimmers.
us Address inquiries to:
General Information
Two-cycle Engine -Theory of Operation
Engine operation
Engine Specifications
Engine Torque Specifications
Maintenance Procedures
Air Cleaner Maintenance
Exhaust system Maintenance
Flexible Drive Shaft Maintenance
Carburetor Adjustments; Model TC-1500 (Tillotson Carburetor)
Carburetor Adjustments; Models TC-300 & TC-400 (Walbro carburetor)
Troubleshooting and Test Procedures
Preliminary Checks:
Testing Cylinder Compression
Compression Test Procedure
Checking For Spark
Checking Fuel Tank
Engine Troubleshooting Chart
Checking Fuel Tank
Checking the Stop Switch
Disassembly. Repair. Reassembly Instructions
Trimmer Engine Removal. Disassembly. Replacement
Starter Rope Replacement
Starter Assembly Replacement
Walbro Carburetor Operation
Walbro Carburetor Servicing
Cutter Head Troubleshooting Chart
Clutch Repair
Automatic Line Feed Repair
line
of the lightweight two-cycle engines manufactured by The Tor0 Company
in
the repair of small two-cycle engines
TABLE
venting
OF
with
complete information necessary to
The Tor0 Company
8111
Lyndale Avenue South
Minneapolis
Attn.. Service Department
CONTENTS
......................................
......................................
MN
we
urge you to write to
55420
PAGE
1-3
1
1
3
3
4-7
4
4
5
5-6
6-7
7-9
7
7
7
8
8
9
8
8
10-18
10
12
13
14
16
17
18
Page 4
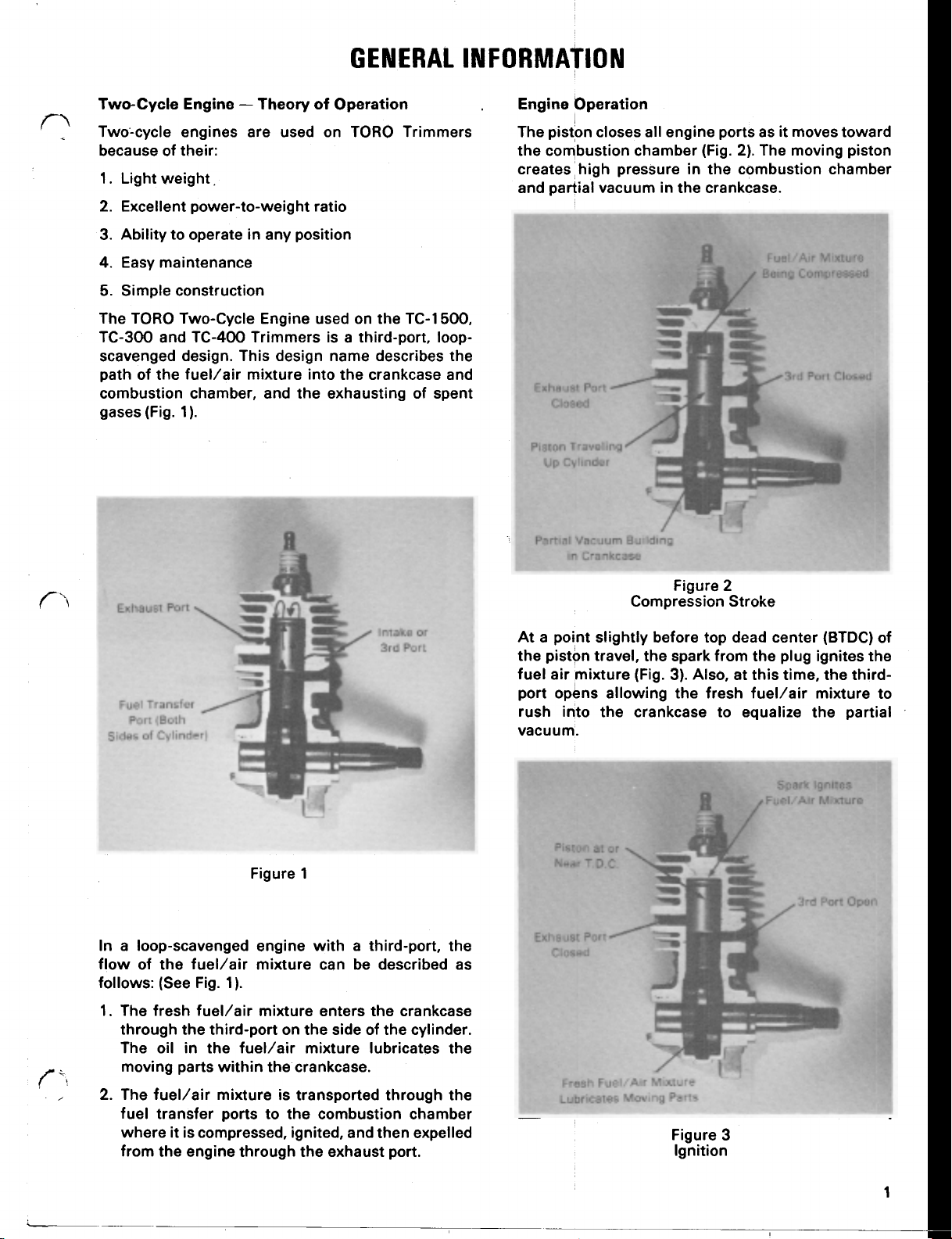
GENERAL INFORMATION
Two-cycle
Two-cycle engines are used on TORO Trimmers
because of their:
1.
Light weight.
2.
Excellent power-to-weight ratio
3.
Ability to operate
4. Easy maintenance
5. Simple construction
The
TORO
TC-300 and TC-400 Trimmers is a third-port, loop-
scavenged design. This design name describes the
path
combustion chamber, and the exhausting of spent
gases (Fig.
Engine Theory
in
any position
Two-cycle Engine used on the TC-1500,
of
the fuel/air mixture into the crankcase and
1
of
Operation
Engine Operation
The piston closes all engine ports as
the combustion chamber (Fig.
creates high pressure
and partial vacuum
,
2).
The moving piston
in
the combustion chamber
in
the crankcase.
it
moves toward
st Port
\
transfer
(Both
Cylinder)
Figure
In
a loop-scavenged engine
flow of the fuel/air mixture can be described as
follows: (See Fig.
1.
The fresh fuel/air mixture enters the crankcase
through the third-port on
The oil
moving parts
2.
The fuel/air mixture is transported through the
fuel transfer ports to the combustion chamber
where
from the engine through the exhaust port.
it
1).
in
the fuel/air mixture lubricates the
within
is compressed, ignited, and then expelled
1
with
a third-port, the
the
side of the cylinder.
the crankcase.
Figure
Compression Stroke
At a point slightly before top dead center (BTDC) of
the piston travel, the spark from the plug ignites the
fuel air mixture (Fig.
port opens allowing the fresh fuel/air mixture to
rush into the crankcase to equalize the partial
vacuum.
Piston
at or
T.D
Near
Exhaust
Closed
Lubricates
C.
Port
Fresh Fuel/Air Mixture
Moving
3).
Parts
Figure
Ignition
2
Also, at this time, the third-
Spark
Fuel/Air Mixture
Ignites
I
Open
3
1
Page 5
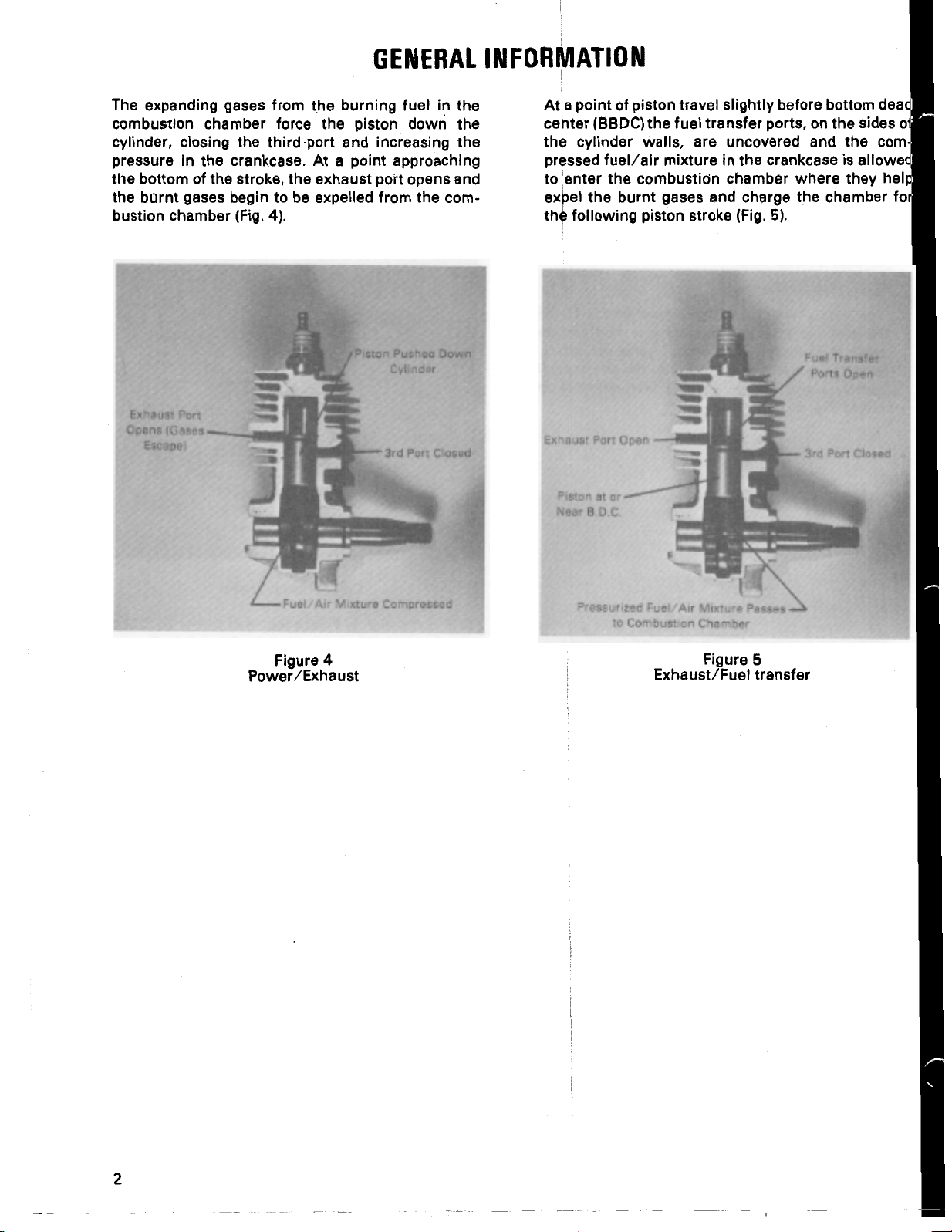
GENERAL
INFORMATION
The
combustion chamber force the piston down the
cylinder, closing the third-port and increasing the
pressure
the bottom of the stroke, the exhaust port opens and
the burnt gases begin to be expelled from the combustion chamber (Fig.
banding gases from the burning fuel
e expanding
in
the crankcase. At a point approaching
4).
in
the
Closed
At a point of piston travel slightly before bottom dead
center
the
pressed fuel/air mixture in the crankcase
to
expel the burnt gases and charge the chamber fa
the
(BBDC)
cylinder walls, are uncovered and the com-
enter
following piston stroke (Fig.
the fuel transfer ports, on the sides
is
allowed
the combustion chamber where they help
5).
c
Mixture Compressed
Figure
Power/Exhaust
4
Exhaust/Fuel transfer
Figure
5
Page 6

ENGINE
SPECIFICATIONS
(Model51630) (Model51603)
Genuine TOR0 Two-Cycle Oil or other high quality two-cycle oil, BIA
TC
TC300
32:1
or
unleaded regular leaded
approved
.40
(13.5
TC400
(model 51604)
oz.)
CooIing~Shroud
Carburetor Mounting Screws
Screws
t
Fillotson ModelSP-1A
with
self contained fuel
pump, accelerator pump and filter screen
pump and
Factory adjusted and
Procedures-pp. test run.
filter
screen
Solid state,-capacitive discharge ignition(CD1)
1.29-1.67mm(-051-066 in.)BTDC
.20-.30mm (.008-.012
WalbroWa-120series with
self
contained fuel
Factory adjusted and test run.
Adjusting Procedures
22degrees BTDC
in.)
ENGINE TORQUE SPECIFICATIONS
TORQUE-Kg-cm/Kg-m
.35-41Kg-cm
23-35Kg-cm
29-40Kg-cm-15-35
12-23Kg-cm10-20in-lbs
~.TORQUE-in.-lbs/ft-lbs
30-45in.-lbs.
20-30in-lbs
in.-lbs.
NOTE: Metric Torque Conversions:
inch-pounds X1.152= kilogram-centimeters
foot-pounds
X
.1383
=
kilogram-meters
29-40Kg-cm
23-35kg-cm
25-35in.-lbs.
3
Page 7
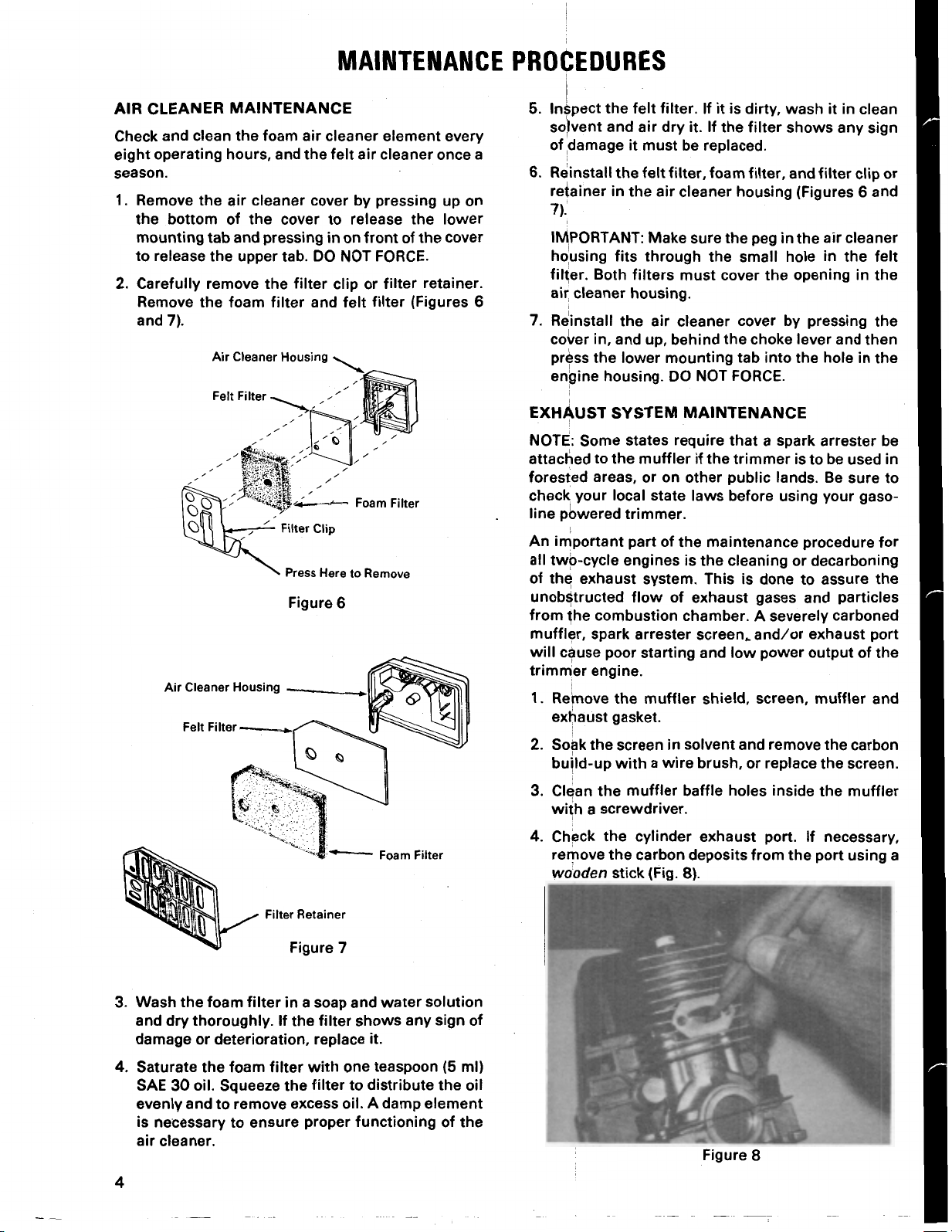
MAINTENANCE PROCEDURES
AIR CLEANER MAINTENANCE
Check and clean the foam air cleaner element every
eight operating hours, and the felt air cleaner once
season.
1.
Remove the air cleaner cover by pressing up on
the bottom of the cover to release the lower
mounting tab and pressing
to release the upper tab.
2.
Carefully remove the filter clip or filter retainer.
Remove the foam filter and felt filter (Figures
and
7).
Air Cleaner Housing
in
on front
DO
NOT FORCE.
of
the cover
a
6
5.
Inspect the felt filter. If
solvent and air dry
of ,damage
6.
Reinstall the felt filter, foam filter, and filter clip or
retainer
it
must be replaced.
in
the air cleaner housing (Figures 6 and
it
is dirty, wash
it.
If the filter shows any sign
it
in
7).'
IMPORTANT: Make sure the peg
housing fits through the small hole
filter. Both filters must cover the opening
air, cleaner housing.
7.
Reinstall the air cleaner cover by pressing the
cover
in,
and up, behind the choke lever and then
press the lower mounting tab into the hole
engine housing.
DO
NOT FORCE.
in
the air cleaner
in
the
clean
felt
in
the
in
the
Air Cleaner Housing
Felt Filter
Press Here to Remove
Figure
6
EXHAUST
NOTE: Some states require that a spark arrester be
attached to the muffler if the trimmer is to be used
forested areas, or on other public lands. Be sure to
check your local state laws before using your gasoline powered trimmer.
An important part of the maintenance procedure for
all
two-cycle engines is the cleaning or decarboning
of
the
unobstructed flow of exhaust gases and particles
from the combustion chamber. A severely carboned
muffler, spark arrester screen. and/or exhaust port
will
cause poor starting and low power output of the
trimm'er engine.
1.
Remove the muffler shield, screen, muffler and
exhaust gasket.
2.
Soak the screen
build-up
3.
Clean the muffler baffle holes inside the muffler
with a screwdriver.
4.
Check the cylinder exhaust port. If necessary,
remove the carbon deposits from the port using a
SYSTEM
exhaust system. This is done to assure the
with
wiiden
stick (Fig.
MAINTENANCE
in
solvent and remove the carbon
a wire brush, or replace the screen.
8).
in
3.
Wash the foam filter
and dry thoroughly. If the filter shows any sign of
damage or deterioration, replace
4.
Saturate the foam filter
SAE
30
oil. Squeeze the filter to distribute the oil
evenly and to remove excess oil. A damp element
is necessary to ensure proper functioning of the
air cleaner.
4
in
a soap and water solution
it.
with
one teaspoon (5ml)
Figure
8
Page 8

IMPORTANT: WHEN REMOVING CARBON DEPOSITS, CLOSE THE PORT WITH THE PISTON
TO PREVENT LOOSE CARBON DEPOSITS FROM
FALLING INTO THE CYLINDER. TAKE CARE NOT
TO SCRATCH THE PISTON. DO NOT USE A
METAL TOOL SUCH AS A SCREWDRIVER.
5. Reassemble
exhaust gasket.
the muffler components. Use a fresh
FLEXIBLE DRIVE SHAFT MAINTENANCE
The flexible drive shaft has been lubricated at the
factory. After approximately
tion, the shaft should be removed from its housing
and its entire surface coated
,purpose, lithium-base grease. To remove the shaft,
loosen the lower handle and slide
engine assembly to expose the clamp. Loosen the
clamp and separate the upper and lower tube assemblies. The shaft
from the lower tube (Fig.
will
every 40 hours
with
a
then be able to be pulled
of opera-
No.2
it
toward the
general
9).
Figure 10
CAUTION:
RUNNING
CARBURETOR CAN BE PERFORMED.
TO GUARD AGAINST POSSIBLE PERSONAL INJURY, KEEP HANDS, FEET AND
FACE AWAY FROM MOVING PARTS.
2. Start
mately 3-5 minutes.
when the engine is cold. Be sure to perform the
carburetor adjustments while
wh
SO
the engine and let
to the average outdoor temperature at
the trimmer
THE ENGINE MUST BE
FINAL ADJUSTMENTS OF THE
it
warm up for approxi-
Do not adjust the carburetor
in
an area that is
will
be used.
Figure 9
CARBURETOR ADJUSTMENTS MODEL
TC-1500 WITH TILLOTSON CARBURETOR
The carburetor has been adjusted at the factory, but
an adjustment may be required to compensate for
differences
Tillotson carburetor used on the TC-1500 is not
serviceable. If carburetion difficulties cannot be
corrected by adjustment, the carburetor must be
replaced.
IMPORTANT: The correct amount of line must be fed
from the trimmer spool before adjusting the car-
buretor to ensure that the engine is adjusted for
operation while under load..
1. Remove
bottom of cover
and pressing
tab. DO NOT FORCE (Fig. 10).
in
fuel, temperature and altitude. The
air cleaner cover by pressing up
to
release lower mounting tab
in
on front of cover to release upper
on
CAUTION;
ORS WITHOUT ADEQUATE VENTILA-
EXHAUST
AN
I
COULD BE DEADLY
NO
poi
Hig
If the engine
setting is lost, set both screws
to
"5%".
number settings are rich. (Fig. 11).
DO NOT RUN THE TRIMMER
FUMES
will
Low number settings are lean.
Figure 11
ARE
IF
INHALED.
not start or if the refer-
POISONOUS
so
the arrows
5
Page 9

MAINTENANCE
3.
Adjust Idle First: With engine idling, rotate the
Low Speed Screw (L) for the leanest fuel mixture
that allows stable idle, and acceleration without
hesitation.
4.
If
necessary, idle speed can be increased by
turning the idle stop screw clockwise (Fig.
12).
PROCEDURES
2.
Low
Speed Screw
by gently rotating
resistance is felt. Next, rotate the screw
turns counterclockwise.
3.
Idle Screw (Fig.
it
clockwise until the screw contacts the throttle
lever After contact is made, continue turning
screw
11/2-21/2
(L)
(Fig.
13)
it
clockwise until a light seating
13)
Close
additional turns.
Close the screw
the screw by rotating
1 1/4-1 1/2
Figure
5.
Hold the throttle trigger at the maximum speed
position and adjust the High Speed Screw (H) for
maximum engine speed.
6.
Recheck the idle adjustment.
CARBURETOR ADJUSTMENT MODELS TC-
300,
TC-400 WITH WALBRO CARBURETOR
IMPORTANT: Do not close the carburetor adjusting
screws too tightly as damage to the screws and seats
may result. Also, the correct amount of line must be
fed from the trimmer spool before adjusting the
carburetor to ensure that the engine is adjusted for
operation while under load.
1.
High Speed Screw (H) (Fig.
by gently rotating
resistance is felt. Next, rotate the screw one turn
counterclockwise.
it
12
13)
Close the screw
clockwise until a light seating
Figure
NOTE: Although these settings are approximate,
the should be able to be started. Further
adjustments of the carburetor may be necessary
to obtain the best performance for your area.
Steps
carburetor.
turn the screws
the 'engine to respond to the change.
4-6
should be followed to fine tune the
When making these adjustments,
1/8
of a turn at a time and wait for
13
6
Page 10

MAINTENANCE PROCEDURES
4. Start
the
engine and
mately
when the engine is cold. The adjustments should
be made
will
sary, re-adjust the idle speed to keep the engine
from stalling
3000-4500 on the TC300)
3-5
minutes. Do not adjust the carburetor
at
the temperatures
be used. Allow the engine to idle. If neces-
(3000-3500
CAUTION:
INDOORS WITHOUT ADEQUATE VENTILA-
TION. EXHAUST FUMES ARE POISONOUS
AND COULD BE DEADLY
let
it
warm up for approxi-
that
the trimmer
RPM on the TC400,
DO NOT RUN THE TRIMMER
IF
INHALED.
TROUBLESHOOTING AND
TEST PROCEDURES
Generally, all gasoline-powered products require
some form of service or repair during their lifetime.
The amount of time and expense involved
ing a product can be greatly impacted by the amount
of time required to initially determine the cause of
the difficulty. Therefore,
these preliminary checks before proceeding to secondary troubleshooting procedures.
Preliminary Checks
1. Check for ignition:
a. Check the start/stop switch position
it
is recommended to make
in
repair-
5.
With' the engine idling, slowly turn the low speed
screw
the engine begins to slow down. Now turn
screw counterclockwise and again note the position when the engine speed is reduced. Set the
screw at a point midway between these two
positions.
6.
Hold
procedure to set the high speed screw.
7.
Re-check the idle adjustment.
8.
Install
parts within the engine. This test
cylinder, piston, or ring and generally determine
whether
replaced,.
Compression
1.
Install the compression gauge into
hole. :IMPORTANT: Be certain that no more than
1/2”
damage to the piston may result (Fig. 14).
clockwise and note the position
the
throttle wide open and follow the same
the
air cleaner cover.
will
the engine is sound or if
Test
Procedure
of
the gauge is threaded into the cylinder as
at
indicate a worn
it
should be
the
spark plug
which
the
a
2.
Check the spark plug: (refer to specifications.
Page
3)
a.
To ensure
b. For damage to the insulator
c. For excessive carbon or burnt electrodes
d. For the correct gap
e.
Check for spark (refer to page
3. Check
a. Check the choke position
4. Check the air cleaner: (refer to page
5.
Check cylinder compression (refer to page
Testing
A compression test of the engine can provide vital
information on the general condition of the working
the
b. Check the condition of the fuel, for freshness,
cleanliness, and proper mixture
a. For loose or damaged mounting screws
b. For dirty filter elements
c. For excessive oil
Cylinder Compression
the
correct type
fuel supply:
in
8)
4)
the foam element
7)
Figure 14
Compression testing
2.
Pull
the
starter rope several times to obtain the
highest possible compression reading.
3. If the compression reading is below
kPa),
cylinder,
suspected If
block /should be installed.
piston, or ring damage should be
so
damaged, a
new
100
psi
engine
(689
short-
7
Page 11

TROUBLESHOOTING AND
TEST PROCEDURES
Checking for Spark
1. Pull off the spark plug cap and remove
Plug.
2.
Inspect the spark plug for wear, carbon deposits
and damage. Replace
or fouled.
3.
Check for the correct spark plug gap and adjust if
necessary to
outer electrode.
NOTE:
could crack the insulator.
4.
Attach a spark or ignition tester as shown
Figures 15 or
5.
While maintaining the plug
the starter-rope and observe for spark.
.020-.024
Do
not pry against inner electrode. This
16.
CAUTION:
ERE
GASOLINE HAS BEEN SPILLED
MABLE VAPORS MAY EXIST. A
NOTE: The spark may be difficult to see
or other brightly illuminated areas.
6.
If no spark is seen, refer to the troubleshooting
chart on page
9.
the
plug if damaged, burnt
in
(5.6
DO
NOT TEST FOR SPARK
mm) by bending
in
this position, pull
the
FIRE
in
daylight
spark
OR
in
Checking Fuel Tank Venting
The fuel tank cap vent allows air into the tank as fuel
is consumed. If this vent is blocked
the engine will eventually stall.
1. Remove the fuel tank cap and inspect the vent. If
the
cap is contaminated with dirt particles, the
vent may need to be replaced.
2.
The cap can be disassembled by prying up the
insert with a flat screwdriver. Care should be
used to prevent damage to
valve (Fig- 17).
Figure 17
3.
Remove the valve, squeeze the valve to close
release
be visible through the valve. If light can be seen,
the~valve should be cleaned or replaced.
4.
With the insert removed, hold the cap up to
light. Light should be visible through a small hole
at
the'
it,
and hold
the center of the cap. if
hole
should be cleaned.
it
up to a light. No light should
with
dust or dirt,
the
insert and the
no
light can be seen,
it,
Checking fuel tank
a
a
Figure 15
Spark
Toro P/N 41-7890
Alternate type spark tester
tester
Figure
16
1.
Visually inspect the bottom of
or other contaminants.
2.
If dirt, water, or other contaminants are present,
the
;tank should be flushed with a small amount of
fuel, and refilled with fresh fuel.
I
the
fuel tank for dirt
Checking the Stop Switch
The “off” switch used on the
400
Gas
Trimmers has one set of contact points.
When the switch is in the "off" position, the contacts
are closed, grounding the coil current to the engine.
A continuity tester or ohmmeter is used to check for
continuity Note: If
should, be adjusted to a low setting. Attach the two
tester (leads to the two switch leads. Continuity
should be evident with the switch in the "off"
position.
continuity If continuity is intermittent or not evident,
the switch is defective or a short has developed in
the
replaced.
In
the "on" position there should be no
wiring and the switch and harness should be
an
ohmmeter is used .the dial
Toro
1500.
300,
and
Page 12

TROUBLESHOOTING SHOOTING
AND
TEST PROCEDURES
Page 13

DISASSEMBLY,
REPAIR,
REASSEMBLY
Trimmer Engine Removal, Disassembly,
Replacement
1.
Drain the gas from the trimmer gas tank and
remove the spark plug high tension wire.
2.
Remove the air cleaner cover by pressing up on
the bottom of the cover to release the lower
mounting tab, and pressing
cover to release the upper tab.
3.
With the trimmer on its left side, remove the
nine Phillips head screws which attach the case
halves together. NOTE: A service fixture, plans
for which are described
Service Bulletin No.81-05, is very useful for
supporting the trimmer for disassembly and
reassembly.
4.
Remove the right hand case half by lifting
the left hand case half. The case half may
appear to be stuck to the engine due to the fit of
the rubber engine isolation mounts between the
case and the engine backing plate. NOTE: When
reassembling, install the rubber isolation
mounts
engine backing plate.
5.
Remove the engine housing tube and recoil
starter assembly by tipping the engine to the
rear and lifting the tube and starter from the left
hand case half.
6.
IMPORTANT: Note how the fuel line, throttle
lever, throttle link, spring, switch, and wiring
harness are routed and attached (Fig.
Mounting
Engine
in
the case halves rather than on the
Block
in
on the front of the
in
Gasoline Trimmer
it
18).
from
INSTRUCTIONS
8.
Remove the throttle and switch, assemblies and
Iift, the engine from the Left Hand Case.
I
9. Remove
clip.
10, Remove the carburetor by removing the Phillips
head screws which pass through the spit back/
choke assembly and carburetor.
11.
Remove the cooling shroud halves by removing
the three screws which attach the shroud to the
backing plate, and gently prying open the latch
next to the spark plug wire. NOTE: The TC300
and TC400 have a single piece cooling shroud.
12. Remove the flywheel by retaining the starter
cup
and removing the flywheel
Use
separate the flywheel from the crankshaft taper.
The two holes cast into the flywheel should be
tapped
long capscrews used to apply pressure against
the: crankshaft end
flywheel and crankshaft
CAPTION: DO NOT attempt to pry the flywheel
from the crankshaft or tap on the crankshaft end
to loosen the flywheel. The crankshaft is made
up of three parts,
pressed onto the crankpin. Prying or striking the
crankshaft can result
replacement of the short block.
13. Remove the CDI (Ignition) Module by removing
the' two screws which attach the laminations to
the' cylinder assembly.
14.
Remove the backing plate assembly by removing
the three bolts and two Phillips head screws
which pass through the backing plate and back-
ing'plate stress plate into the cylinder assembly.
the air cleaner elements and retaining
with
the starter cup wrench P/N45-1390)
nut
(Fig. 24, p. 17).
the handle of the starter cup wrench to
with
a
l/4"-20
tap, and two 1/4”-20 x 3/4”
until
the seat between the
is
loosened.
with
the crankshaft ends being
in
damage that
will
require
Figure 18
7.
Remove the gas line from the carburetor inlet by
compressing and sliding the fuel line clamp up
onto the fuel line and twisting and pulling
fuel line.
10
on
the
NOTE (TC1500 only): The intake gasket is sealed
with
a light coating of gasket sealant, and the
backing plate may appear to be stuck to the
cylinder assembly.
15. Remove the crankcase pad by squeezing the end
of the crankcase pad clip
through the hole
16. Remove the heat shield and muffler by removing
the' two hex socket capscrews and the Phillips
head screw to the heat shield tab. The
then be removed by removing the Phillips head
w
that fastens
in
so
that
it
can be passed
the crankcase.
tab
it
to the cylinder assembly.
can
Page 14

Figure
19
REASSEMBLY
DISASSEMBLY, REPAIR,
INSTRUCTIONS
Page 15

Starter Rope Replacement
1.
Follow steps 1-5 of Trimmer & Engine Disas-
sembly/Assembly Instructions. NOTE: Do not
remove the Recoil Starter Assembly from the
Upper Shaft Housing Tube.
2.
Remove the damaged rope from the pulley.
3. Knot one end of the replacement rope. Align
cut-out sections of the Drum and the metal
Ratchet Cover. Feed the un-knotted end of the
rope through the clearance hole and into the rope
groove
in
the Drum (Figure
20).
the
the
end of the rope remaining through the
guide slot
bushing and handle.
5.
IMPORTANT: Check the starter for proper assembly
by
extending the starter rope full length. With
the rope extended,
to be rotated an additional
direction but not more
6.
To reassemble reverse steps
Instructions (page
Starter Assembly Replacement.
1.
Follow steps
2.
Remove the Recoil Starter Assembly from the
Upper Shaft Housing Tube. Retain
passing a bar through the holes
the Recoil Starter Assembly to remove.
in
the retainer. Install
the
starter pulley must be able
than
IO).
1-5
of
Trimmer & Engine Disas-
Instructions.
the
1/2
turn in a clockwise
1 1/2
turns.
1-5
in Disassembly
the
tube by
in
the tube. Twist
rope
Figure
4.
a.
TC 1500, TC300, TC400
Wind the rope clockwise onto the drum, slipp-
ing the rope under the four retainer tabs (do
not wind the drum) until the handle is within
inches from the Drum. Continue by rotating
the Drum and sliding the rope under the retainer tabs until the rope extends through the
widest gap between the rope retainer tabs.
Install the rope bushing and handle.
b. TC400 (step 4a or 4b
upon the style of the starter drum)
Wind
the
rope clockwise onto the drum, slip-
ping
the
rope between the retainer and the
drum until 2 inches of rope remains. Thread
20
will
apply depending
2
3. Press
the Recoil Starter Assembly which are retained
4. IMPORTANT: Check the starter for proper as-
5.
the
replacement Recoil Starter Assembly
into: the Upper Shaft Housing Tube. The slots
by the Trimmer case halves must be in line with
the locating holes in
between rope retainer tabs on the Starter must
be rotated
the tube. NOTE: Press only on the end of the
Recoil Starter Assembly.
sembly by extending the starter rope full length.
With the rope extended, the starter pulley must
be able to be rotated and
clockwise direction. If the Starter Drum stops
rotating before the rope is extended full length,
remove one wrap of the Starter Rope by sliding
from under the rope retainer tabs and repeat test
procedure. If more than
wrap one more turn on the starter.
To reassemble reverse steps
Instructions)page
180°
the
tube, and the widest gap
from the Pole Clamp slot cut
additional 1/2 turn
1 1/2
turns are possible,
1-5
in
Disassembly
10).
in
in
in
a
it
Page 16

DISASSEMBLY, REPAIR,
REASSEMBLY INSTRUCTIONS
WALBRO CARBURETOR OPERATION
1.
Engine Impulse: Actuates Fuel Pump Diaphragm with
alternating pressure-vacuum pulses.
2.
Fuel Pump Diaphragm: Fluctuates
impulse. Transfers fuel through Fuel Pump Valves.
3.
Fuel Inlet: Fuel drawn from tank.
4.
Inlet Valve: Responds to Fuel Pump Diaphgram. Opens
during vacuum pulse. Closes during pressure pulse.
5.
Outlet Valve: Closes during vacuum pulse. Opens during
pressure pulse.
6.
Filter Screen: Filters fuel on route to Metering Chamber.
7.
Inlet Needle Valve: Lifts off seat to allow fuel entry into
Metering Chamber.
8.
Throttle Valve: Regulates engine speed
mary. Second, and Third Idle holes, then Nozzle for fuel
delivery.
9.
Primary Idle Hole: Only fuel source to engine at Idle
position.
10.
Second Idle Hole: Allows additional fuel flow on acceleration.
11.
Third Idle Hole: Increases fuel flow at Part Throttle.
12.
Idle Needle: Adjust for fuel richness to 3 Idle holes.
in
response to engine
as
it
exposes Pri-
Alternate fuel pump system
modate internal pulse and/or external fuel
source.
13.
Idle take-Off: Fuel entry for Idle holes.
14.
Idle Port: Fuel reservoir for Idle holes.
15.
Atmospheric Vent: Allows air pressure against Metering
Diaphragm.
16.
Circuit Plate: Meters fuel from Metering Chamber to Low
Speed and High Speed Circuits.
17.
Metering Diaphragm: Drawn up by vacuum to activate
Metering Lever.
18.
Metering Lever: Lifts Inlet Needle
19.
Metering Lever Spring: Transmits force to Metering Lever.
Closes
Needle Valve as Metering Chamber fills.
20.
Metering Chamber: Fuel reservoir, feeds to Idle and Nozzle
off
seat.
to
accom-
circuits.
21.
Nozzle Check Valve: Engine vacuum draws Valve open.
22,
Nozzle Well: Fuel is drawn
high speed
23.
Hi Speed Needle: Adjusts for fuel richness at high speeds.
24.
Nozzle Increases fuel discharge for high speeds.
25.
Venturi: Increases air velocity at Nozzle, creating a suction
to draw fuel into Throttle Bore.
in
from Metering Chamber at
13
Page 17

DISASSEMBLY, REPAIR,
Metering Lever
Inlet Needle
Fuel Inlet Screen
Fuel Pump Diaphragm
REASSEMBLY
WALBRO CARBURETOR
V
INSTRUCTIONS
SERVICING
-Metering Diaphragm Cover
-Metering Diaphragm Assembly
Metering Diaphragm Gasket
Circuit Plate Assembly
Circuit Check Valve
Circuit Plate Gasket
Throttle Valve Screw
Throttle Valve
,Idle Needle
Hi Speed Needle
Throttle Shaft Assembly
Fuel Pump Gasket
Idle
Fuel Pump Cover
Figure
Carburetor Disassembly (Refer
1. Remove the fuel pump cover screw and pump
cover.
2.
Remove the fuel pump diaphragm and fuel pump and foreign matter.
gasket.
3.
Inspect the diaphragm for flatness and continu- lever components including lever, pin, needle
ity. The diaphragm should have
flapper valves should be flat and free ,from
curling.
4.
Blow through the external pulse hole on the
body casting to insure that there are no
structions.
5.
Blow through the internal fuel hole on the body
casting to insure that there are no obstructions.
6.
Remove and discard the filter screen.
7.
Remove the four screws and metering dia- operation of the throttle valve and lever.
phragm plate.
to
Fig.
22):
no
holes. The valve and spring.
ob-
22
8.
Remove the metering diaphragm and gasket.
9.
Inspect the metering diaphragm for holes, dirt
10. Remove the metering lever screw and metering
11. Remove the circuit plate screw with the diaphragm and gasket.
12. Remove the high and low speed adjustment
needle
13. Thoroughly inspect and clean the carburetor,
especially all small orifices and openings, using
a solvent wash and an air gun.
!
14. Dry the carburetor with air and inspect the
Adjust Screw
14
Page 18

DISASSEMBLY,
REPAIR,
REASSEMBLY
Carburetor Re-Assembly
1.
Install a new filter screen
hollow tube or tool of approximately
diameter. NOTE: The screen must be pushed
far enough to be below the fuel inlet hole.
2.
Inspect the circuit plate for flatness and correct if
necessary.
3.
Inspect the new circuit plate diaphragm and
gasket for flatness. Install the circuit plate, circuit
diaphragm and circuit plate gasket with
phragm in contact with the plate
contact with body casting.
pressure on the circuit plate screw
warp the circuit plate.
4.
Install the metering lever components and adjust
the metering lever to be flush
the circuit plate, Fig.
23.
with
any appropriate
,300
and
gasket in
Use only moderate
so
as not to
with
the surface of
INSTRU'CTIONS
5.
Install the high and low speed needles and set at
inch
in
dia-
approximately 1 and
low speed letters are indicated on the side of the
carburetor casting. The high speed needle is the
long needle and the low speed needle is the short
needle.
6.
Install the metering diaphragm and related components as follows: Install the gasket over the
locator pins on the casting. Next, install the
metering diaphragm over the locator pins on the
casting. (The metering plate pin must be
tact
with
metering diaphragm cover
vent hole
the throttle valve.
7.
With
cover
with the body casting
gasket in contact with the fuel pump cover.
extension on the cover should be located on the
same side as the throttle lever.
in
the large single screw, install the fuel pump
with
1/4
turns open. The high and
in
con-
the metering lever.) Next, install the
with
four screws. The
the cover should be located opposite
the
fuel pump diaphragm in contact
and
with
the
fuel pump
The
Figure
23
8.
Visually inspect the carburetor and tighten all
screws.
15
Page 19

of
Difficulty
TROUBLESHOOTING AND
TEST PROCEDURES
CUTTER HEAD TROUBLESHOOTING
Reduced cutting
ability
Cutting line fails
to
advance
Cutting line pulls
back into drum
tangles)
spool
Line
to turn
Clutch fails to
engage
Clutch fails
disengage at idle
speed
fails
to
(or
RPM
RPM
too
low
too high
Binding
Not seated
engine
cutting unit
Not seated in
engine
cutting unit
in
or
or
I
Bearing seized
Cutting line Clutch slipping
too short,
won't index
Driver broken,'
line swelled
from moisture,
dirty, line
tangled
Cutting line not
indexed often
enough
to engine shut
Off
Driver
broken
Unbalanced
cutting unit,
bearings worn,
dirt
accumulation
or
or
I
prior
drum
Bearing grease
on clutch drum
Power
shaft
snap ring out
groove (some
models), clutch
spring broken
Incorrect
assembly
Incorrect
assembly
of
I
16
Page 20

i
DISASSEMBLY,
REASSEMBLY
CLUTCH
INSTRUCTIONS
REPAIR
REPAIR,
The clutch consists of two assemblies: (Fig. 24):
A. The upper housing containing the upper power
shaft, ball bearing, oil shield, clutch spacer,
clutch assembly and
B.
The lower bearing housing and clutch drum
which is threaded to the lower housing shaft.
NOTE: The oil shield was not used
production of the TC-400 clutch assembly. Also,
the upper power shaft
changed to a machined shaft
The two shafts are interchangeable. The oil
shield may be added to existing clutch assemblies using the upper shaft
ring.
Disassembly
1.
Remove the cutter head
2.
Remove the clutch housing from the trimmer
tube by loosening the housing clamp bolt.
3.
Remove the six screws securing the upper and
lower sections of the clutch housing. Separate
the two sections by gently prying them apart.
4.
The clutch assembly (shoes and springs) can be
removed
1390
holes
the opposite end of the power shaft
&
Assembly
with
the multipurpose tool P/N #45-
(Fig 25). Align the pins on the tool
in
the clutch assembly. While supporting
with
the snap ring was
with
with
instructions
or
line feed assembly.
in
early
a shoulder.
the machined
with
the
with
a piece
of
3/16
inch square key stock, turn the clutch
assembly counterclockwise. The spacer, oil shield
and power shaft can now be removed.
Clutch
Wrench
Multipurpose tool (P/N 45-1
NOTE; When reassembling the clutch shoe and
spring assembly, be sure
"off" is toward you. The wide flange on the
spacer must be against the clutch shoe and
spring assembly.
5.
Remove the three screws
The bearing fits loosely and can be pushed out by
gently tapping the bearing from the top or clamp
end
of
the housing.
6.
The shaft and bearings
ing are not serviceable as individual components
and must be replaced as an assembly.
Figure 25
that
in
in
the lower clutch hous-
390)
the side marked
the bearing retainer.
17
Page 21

DISASSEMBLY, REPAIR,
REASSEMBLY
AUTOMATIC
1.
Drain the gasoline from the fuel tank and remove
the high tension wire from the spark plug.
2. Insert a medium flat screw driver in one of the
two window slots in the
spool will snap off. (Fig. 26). NOTE: Use as wide
screw driver as
damage the cap.
will
spool
fit
in
the slot
Figure 26
hub and twist. The
so
as not to
INSTRUCTIONS
LINE
a
FEED
3.
Hold
core counterclockwise. The driver
with
4.
Remove the washer and compression spring and
slide the drum off the power shaft.
5.
Clean the debris from the inside and outside of
the
the, power shaft.
6. Replace any worn or broken parts.
7.
Reassemble the trimmer head in the reverse
order. Be certain that the roll pin on the power
shaft is seated
8.
The spool and spool core are keyed. They must be
properly aligned when putting the spool back on.
Thread the end of the line through the eyelet.
Plate the spool on the keyed core and push in
place until you hear
REPAIR
the drum securely, and unscrew the spool
it.
drum
and remove any debris wrapped around
in
the slot in the drum.
it
click.
will
turn off
18
 Loading...
Loading...