Toro 22300, 22302, 22302TE, 22303, 22303TE Service Manual
...
Commercial Products
Hydraulics
Hydrostatics
Schematics
and Test
Equipment
Part No. 82356SL, Rev. B

Introduction
Turf mowing equipment was very cumbersome and
inefficient when it was first developed back in the
early 1900’s.
Improvements were made through the years of Turf
equipment’s development, but it wasn’t until hydraulics became a part of the design that significant
improvements were made.
Use of hydraulics has increased to form a major
portion of turf product designs. Increases efficiency,
reliability, lowered maintenance costs, safer products and improved operator comfort are all byproducts of the increase in use of hydraulic systems on turf products.
An understanding of hydraulic systems and their
function on a product, is a necessity to properly
service, adjust, troubleshoot or test turf products.
INDEX
1: HYDRAULIC PRINCIPLES, PAGE 2.
OBJECTIVE: To familiarize the technician with the basic fundamentals of hydraulic systems and their
operation.
2: HYDRAULIC SCHEMATICS, PAGE 7.
OBJECTIVE: Improve hydraulic technicians ability to read and comprehend hydraulic schematics, and
apply them to various repair jobs.
3: HYDROSTATIC TRANSMISSIONS, PAGE 14.
OBJECTIVE: Provide technicians with helpful information on the operation and maintenance of
hydrostatic transmissions.
4: HYDRAULIC HOSES AND FITTINGS, PAGE 19.
OBJECTIVE: Review proper hose and fitting service procedures.
5: TEST EQUIPMENT, PAGE 23.
OBJECTIVE: Instruct technicians on the proper test equipment and procedures to effectively and safely
diagnose hydraulic systems.
6: REVIEW QUESTIONS, PAGE 27.
Review Answers
1 - A. 6 - B. 11 - B. 16 - B.
2 - B. 7 - D. 12 - F. 17 - B.
3 - B. 8 - A 13 - A. 18 - D.
4 - A. 9 - C. 14 - A. 19 - D.
5 - B. 10 - B. 15 - C. 20 - B.
1
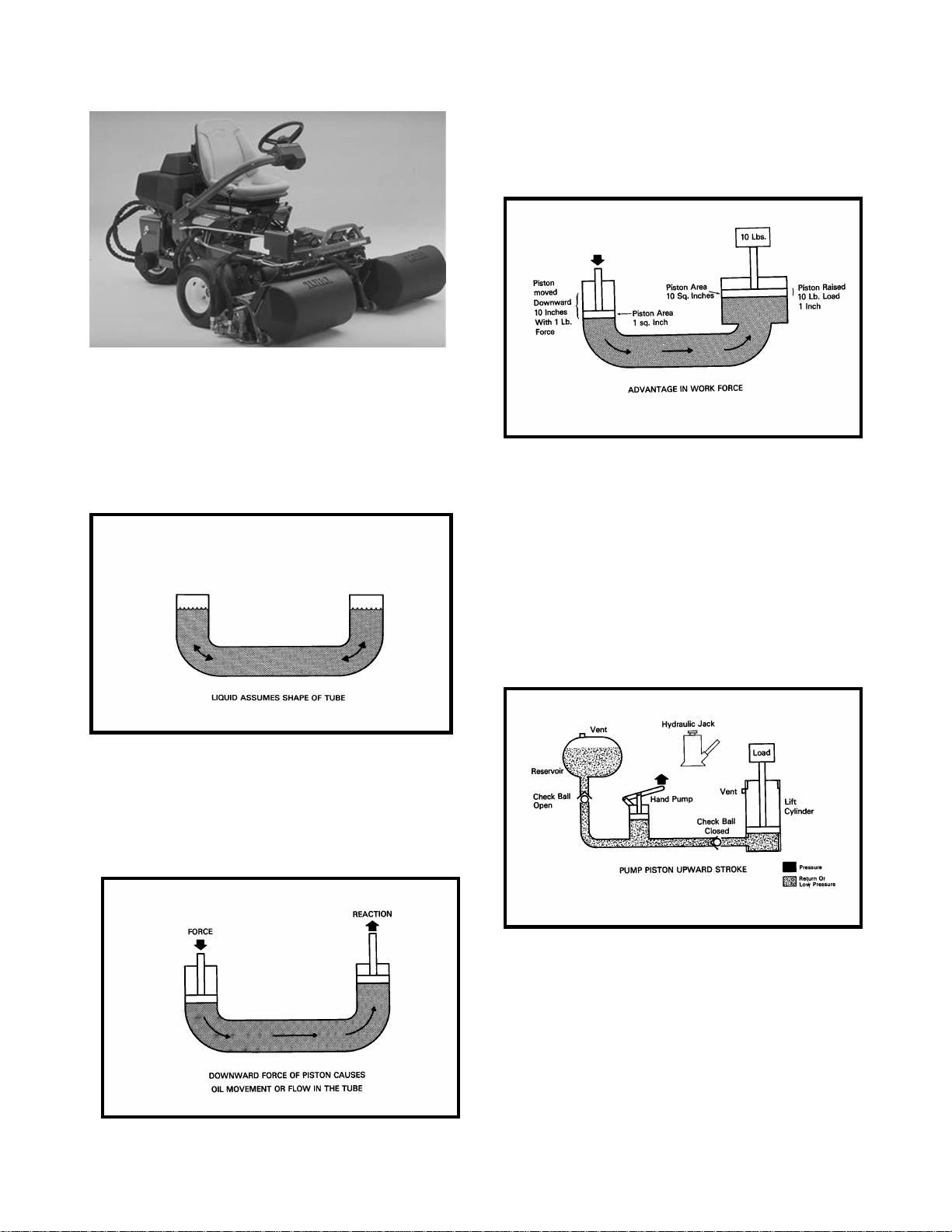
Principles of Hydraulic Circuits and Components
Figure 1
Figure 5
Figure 3
Figure 4
3. By making the containers or cylinders of different
sizes, the mechanical advantage in work force increases (Fig. 4)
Figure 1
A hydraulic circuit, whether it is simple or complex,
uses the following basic hydraulic principles:
1. A liquid can assume any shape and be bidirectional with out affecting its free flow movement
(Fig 2)
Basic Hydraulic Circuits and
Components Used in Turf Equipment.
2. Pascal’s law states that when a confined fluid is
placed under pressure, the pressure is transmitted
equally in all directions and on all faces of the container. This is the principle used to extend the ram
on a hydraulic cylinder (Fig 3)
Although hydraulic circuit layouts may vary significantly in different applications, many of the components are similar in design or function. The principle behind most hydraulic systems is similar to that
of the basic hydraulic jack. Oil from the reservoir is
drawn past a check ball into the piston type pump
during the pistons up-stroke (Fig 5)
2
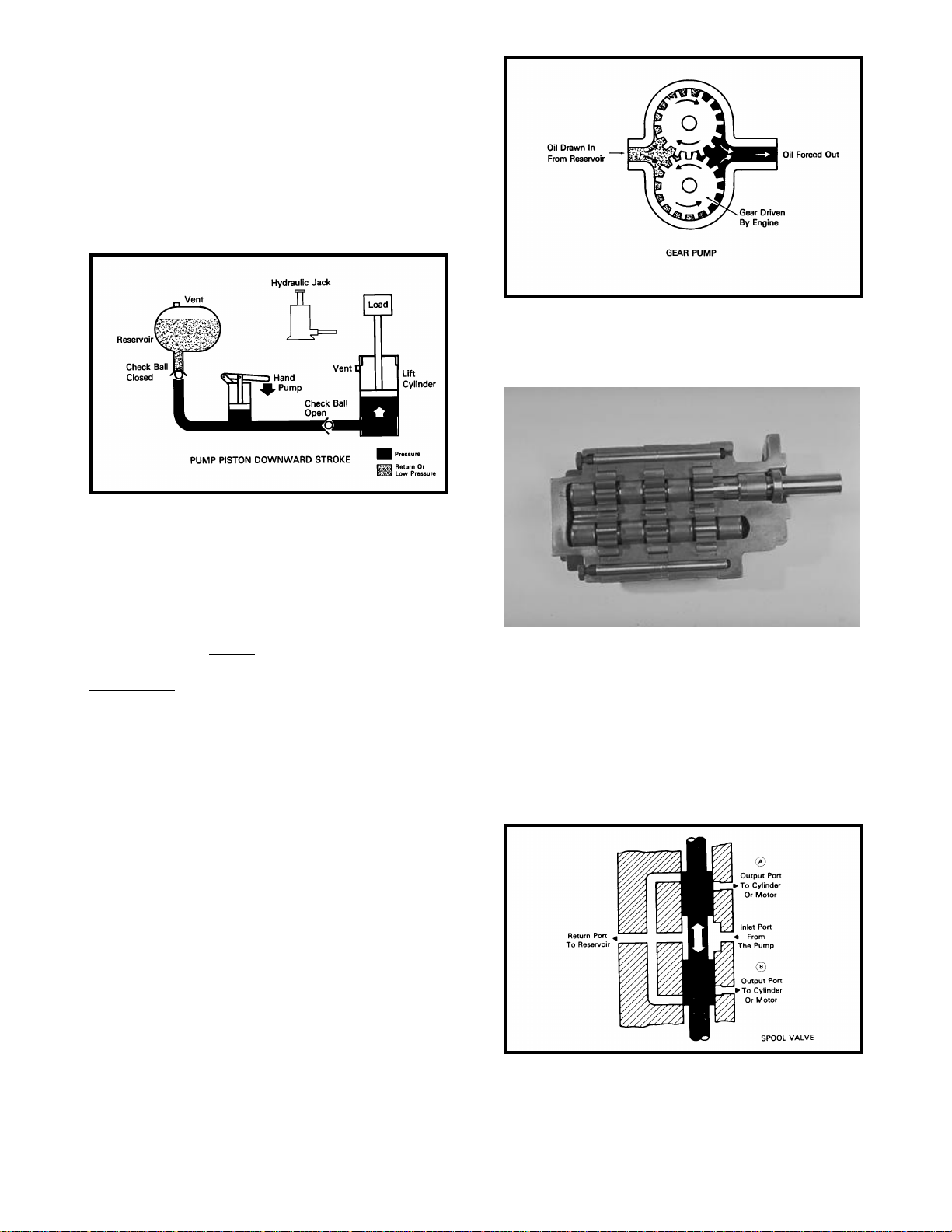
When the piston in the pump is pushed downward,
Figure 6
Figure 7
Figure 9
oil will be directed past a second check ball into the
cylinder. As the pump is actuated up and down, the
incoming oil will cause the cylinder ram to extend.
The lift cylinder will hold its extended position because the check ball is being seated by the pressure against it from the load side of the cylinder.
The cylinder will return to neutral by unseating or
bypassing the check balls, allowing the oil in the
cylinder to return back to the reservoir (Fig.6)
Below is a cutaway view of an actual three section
pump.
Because the pump displacement is usually much
smaller than the cylinder, each stroke of the pump
will move the cylinder a very small amount. If the
cylinder is required to move at a faster rate, the
surface area of the pump piston must be increased
and/or the rate which the pump is actuated must be
increased. OIL FLOW GIVES THE CYLINDER
RAM ITS SPEED OF MOVEMENT AND OIL
PRESSURE CREATES WORK FORCE.
We can improve the efficiency and Increase the
versatility of a basic circuit by adding some sophisticated components and changing the circuit layout. By incorporating a gear pump in place of a
hand piston pump, we increase oil flow to the cylinder which will increase the actuation rate of the
ram.
The most common type of pump is the gear pump
(Fig 7). As the gears in the pump rotate, suction is
created at the inlet port of the pump. The fluid is
drawn in to the pump and is carried in the spaces
between the gear teeth to the discharge port of the
pump. At the discharge side of the pump the gear
teeth mesh together and the oil is discharged from
the pump.
Figure 8
The flow from the pump to the cylinder is controlled
by a sliding spool valve which can be actuated by
an electric solenoid, or a hand or foot operated
lever. The valve shown in Figure 9 is a open center
valve, meaning that the oil flow is returned to the
reservoir when the valve is in the neutral position. If
the oil flow is stopped in the neutral position than
the valve is a closed center valve.
3
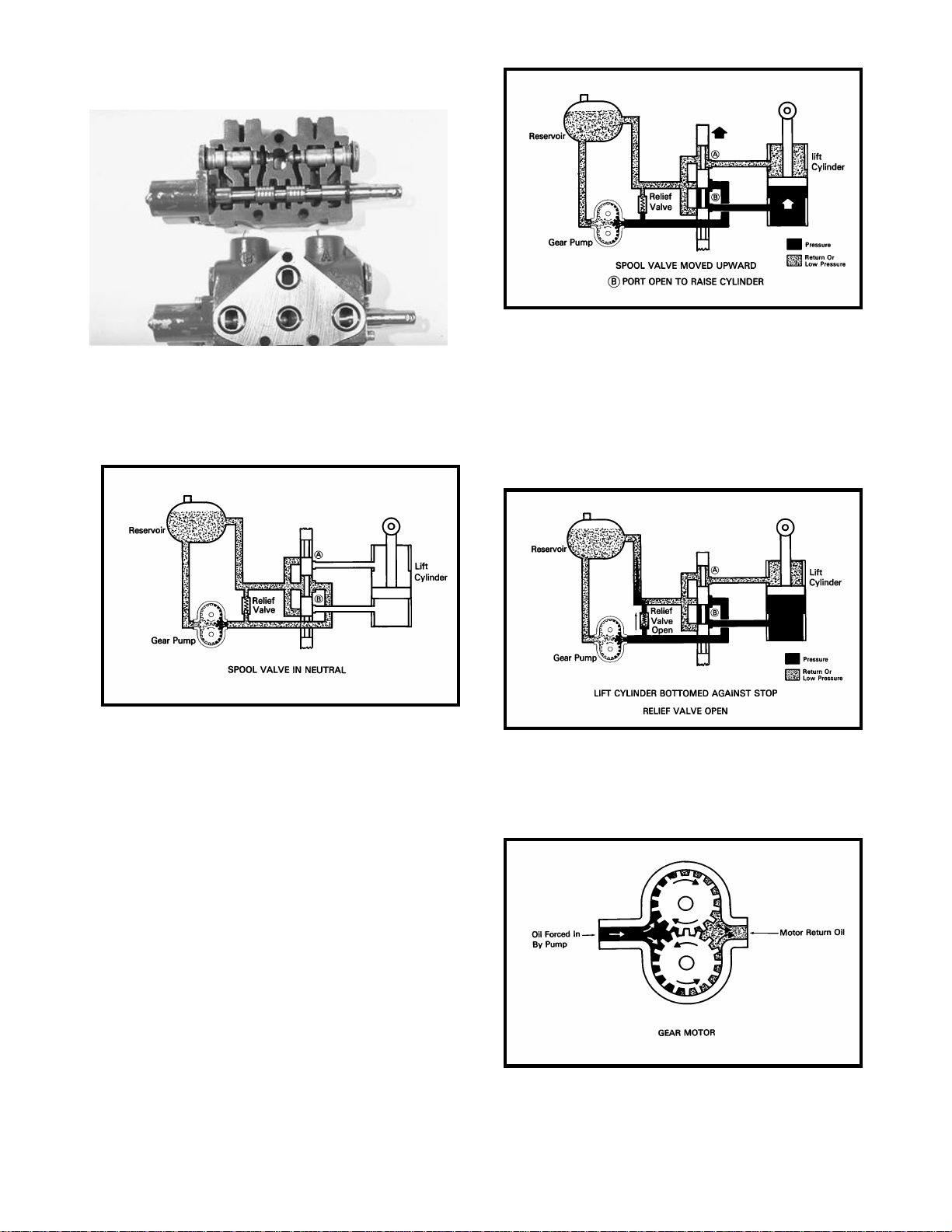
Below is a cutaway of an actual hydraulic control
Figure 12
Figure 11
Figure 13
Figure 14
valve (Fig 10).
Figure 10
Here we see have a spool valve in our simple hydraulic
system, we can see that the valve is in the neutral position and all the flow from the pump is directed back to
the reservoir.
If the spool is moved upward, the oil flow from the
pump is directed through the spool to one end of
the lift cylinder. The oil in the opposite end of the
cylinder is pushed out as the ram extends, and will
pass through the spool and return to the reservoir.(Fig 12).
Since the fluid from a positive displacement pump
must flow continuously whenever the pump is running it must have some where to go if not being
used by the actuators. If the load on the cylinder
becomes too great or if the ram bottoms out, the
flow from the pump will be directed past the relief
valve returning to the reservoir (Fig 13).
Substituting the lift cylinder with a gear motor, we
can now utilize out basic circuit to create rotational
movement to drive attachments (Fig 14).
4
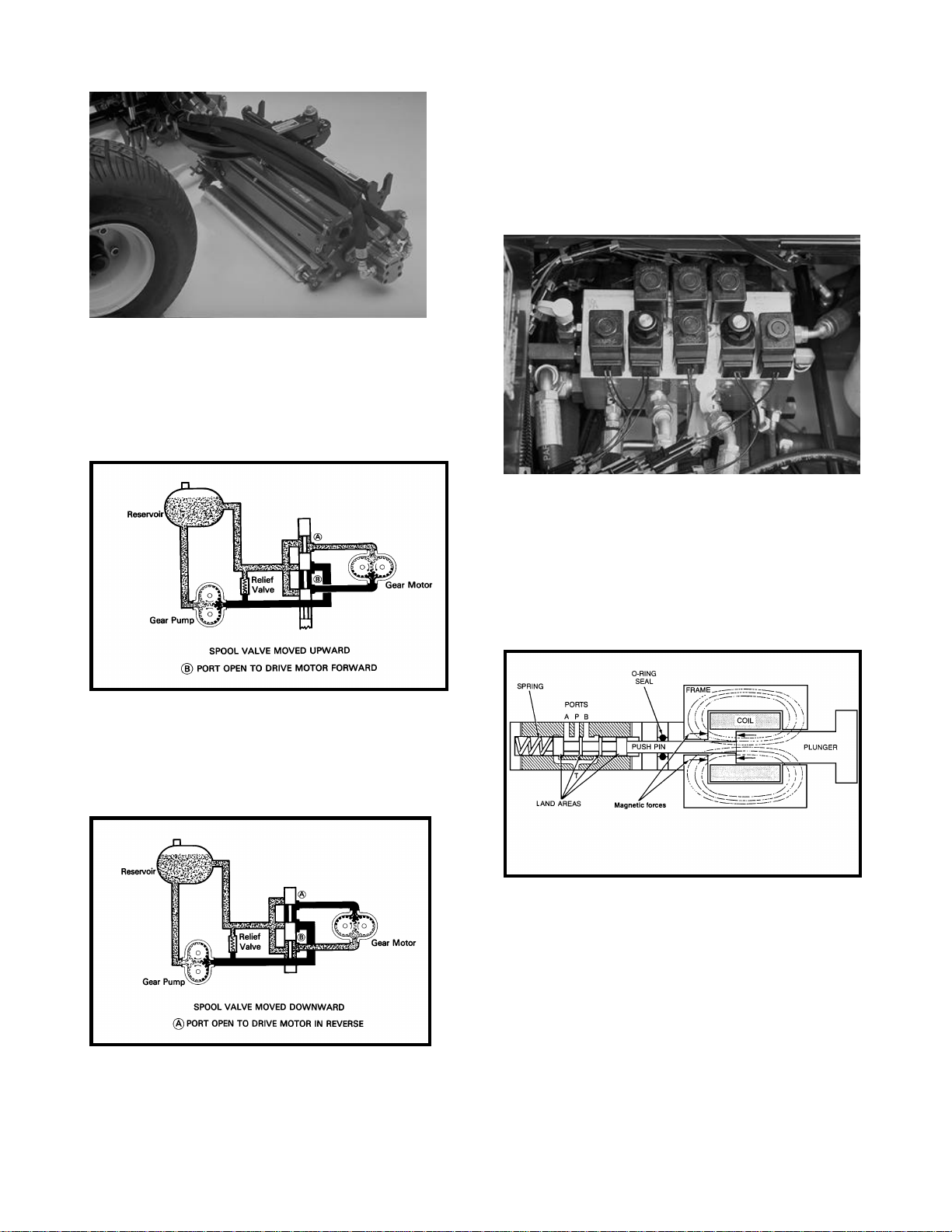
Figure 15 shows a hydraulic reel motor.
Figure 16
Figure 17
Figure 19
Figure 15
Figure 16 illustrates the basic circuit and components necessary to drive the reel cutting units. With
the spool in the upward position, the oil flow is directed through the spool valve to the lower port
driving the motor in the forward direction.
solenoid valves and the internal porting to make
the valve operate (Fig 18). The outer ports on the
valve body are threaded to allow hoses and lines to
be connected to the valve body. Care should be
taken when tightening the hose and line fittings so
the valve is not distorted by over tightening of the
connections. Tighten the line and hose connections
to the correct Flats From Finger Tight (F.F.F.T.)
spec. listed in the service manual.
Figure 18
Actuating the spool to the down position, the flow of
oil from the pump is directed to the opposite port of
the motor. The motor than rotates in the reverse direction (Fig 17).
The electric solenoid valve operates by supplying
electrical current to a coil magnet, the magnetic
field moves a valve spool and this directs the oil.
The thing to remember is that the only difference
between a hydraulic\electric valve, and a regular
hydraulic valve is the way that the spool is moved.
The solenoid valves consist of the valve cartridge
and the solenoid coil (Fig 19). To disassemble the
valve remove the coil assembly and then carefully
unscrew the valve body. The O-rings and seals
should be replaced whenever a valve body is removed or replaced.
Another type of valve system becoming popular in
turf equipment is the electric solenoid type valve
system. The solenoid valve system consists of a
machined valve body. This valve body contains the
5
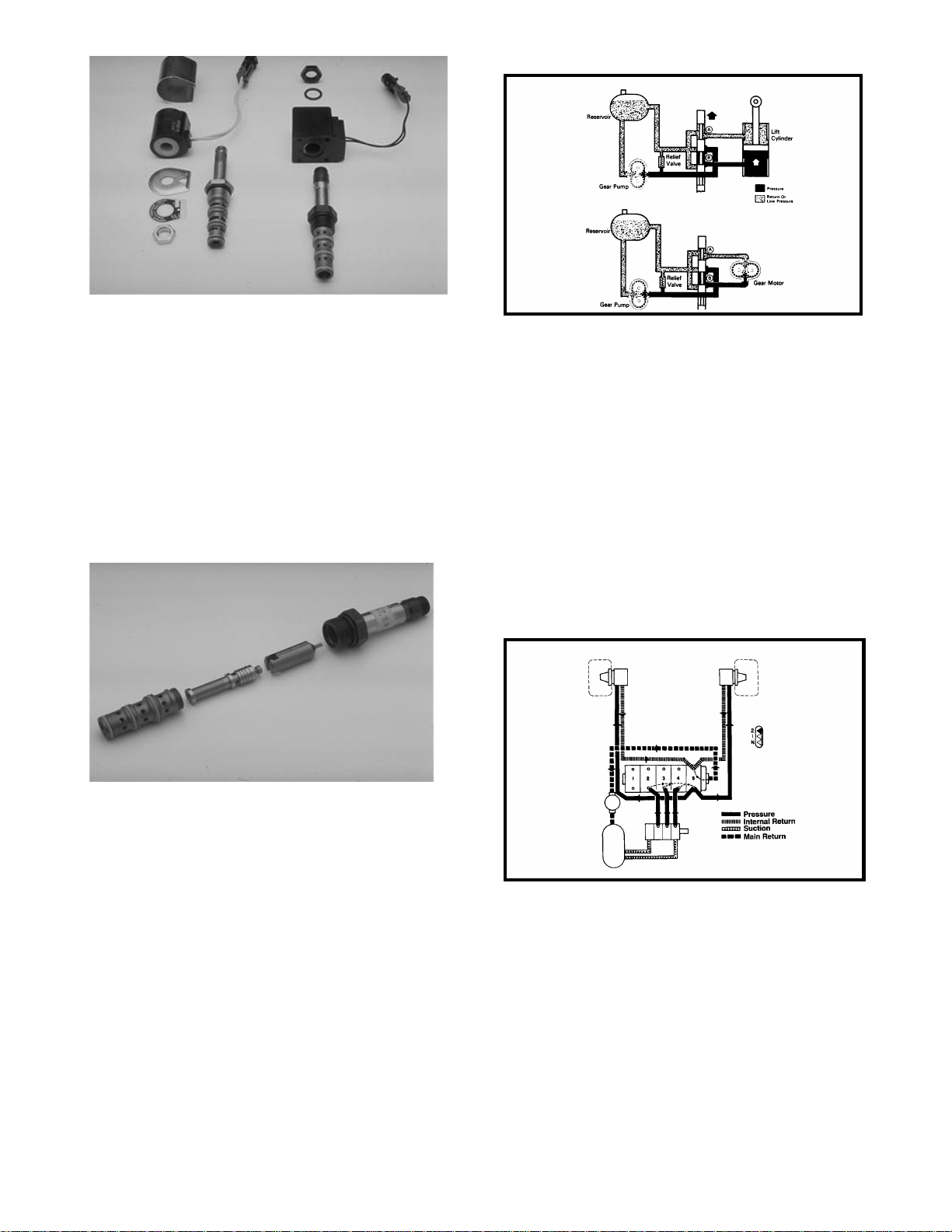
Figure 20
Figure 22
Figure 23
Inside the cartridge valve there is the valve spool,
the armature and the armature spring. The manufacturing tolerances are extremely close and great
care should be used when cleaning this type of
valve. Cartridge valves used in most Toro equipment should not be disassembled. Figure 20 is for
illustrative purposes only. The best way to clean the
cartridge valve is to submerge the valve in clean
mineral sprits and use a probe to push the internal
spool in and out 20 to 30 times to flush out the
contamination. Mineral sprits does not affect the Oring material.
Figure 23 shows the actual hydraulic circuit for a
Greensmaster 3000. This circuit and components
are used to drive the unit in the No.1 traction position. When the engine is started, the pump draws
oil from the reservoir through the suction lines. Oil
from the No.4 section of the pump passes through
the fitting in the No.4 spool valve into the valve.
The traction lever, when located in the No.1 position, moves the spool so oil is directed to flow into
the No.5 metering valve section. When the traction
pedal is pushed forward oil flows out the lines at the
rear of the metering valve section to each motor to
drive the motors. Low pressure oil returns through
the valve and the main return line, through the filter
to the reservoir.
Figure 21
Understanding the basic hydraulic systems and
components can be of great value when troubleshooting and testing hydraulic equipment. Most hydraulic systems will be similar to one of these two
basic systems (Fig 22).
The more sophisticated a hydraulic system becomes, the greater the importance of separating
the system into individual circuits when diagnosing
a hydraulic problem.
6
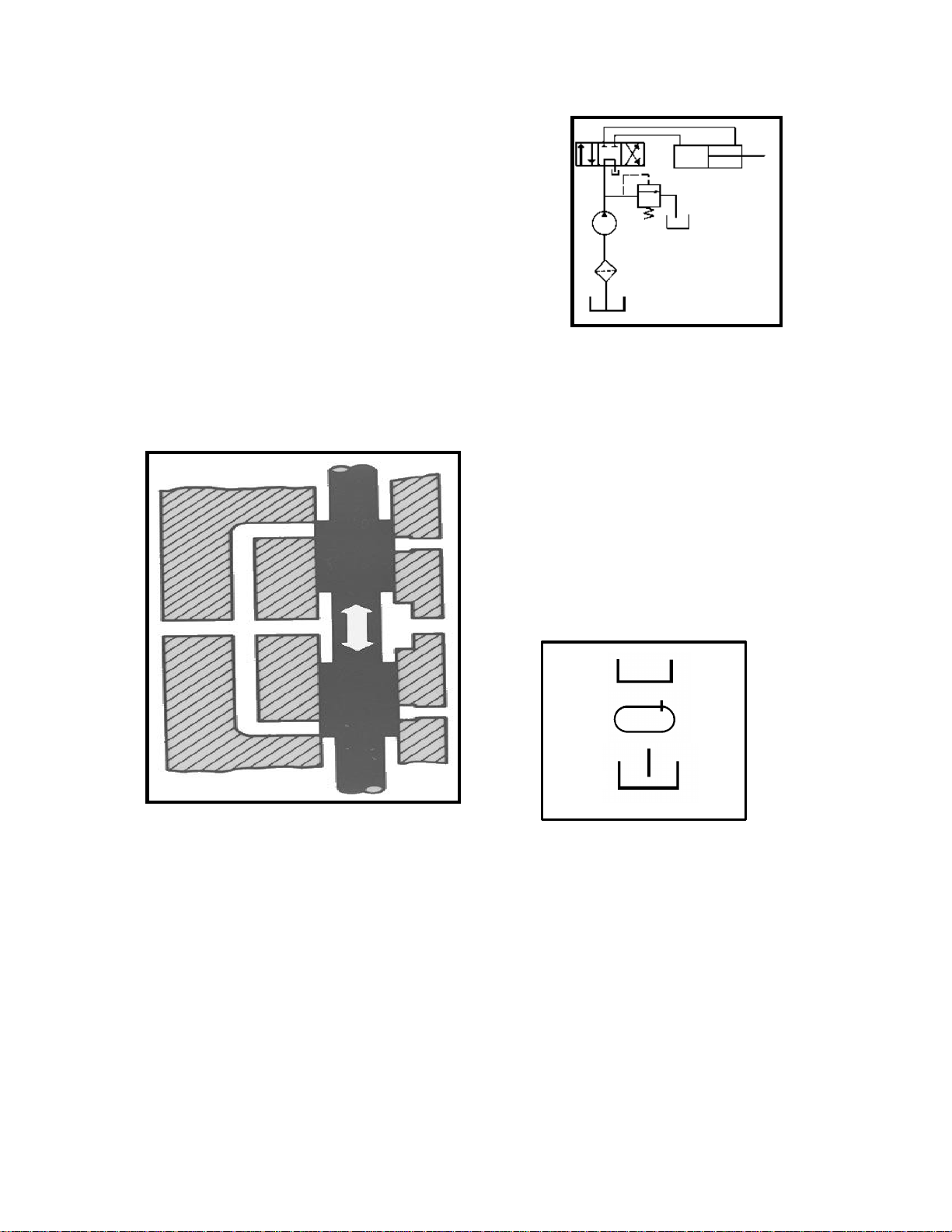
Introduction To Hydraulic Schematics
A
B
Accurate diagrams of hydraulic circuits are essential to the technician who must repair it. The diagram shows how the components will interact. It
shows the technician how it works, what each component should be doing and where the oil should be
going, so that he can diagnose and repair the system.
CIRCUIT DIAGRAMS
There are two types of circuit diagrams.
A: Cutaway Circuit Diagrams show the internal
construction of the components as well as the oil
flow paths. By using colors, shades or various patterns in the lines and passages, they are able to
show many different conditions of pressure and
flow (Fig 1).
1. Schematic symbol systems
A: I.S.O = International Standards Organization.
B: A.N.S.I. = American National Standards Institute
C: A.S.A = American Standards Association
D: J.I.C. = Joint Industry Conference
A combination of these symbols are shown in this
manual. There are difference between the systems
but there is enough similarity so that if you understand the symbols in this manual you will be able to
interpret other symbols as well.
Figure 2
Figure 1
B: Schematic Circuit Diagrams are usually
preferred for troubleshooting because of their ability
to show current and potential system functions. A
schematic diagram is made up of consistent
geometric symbols for the components and their
controls and connections (Fig 2).
2. Hydraulic reservoirs
C
Figure 3
Reservoirs (Fig 3) are pictured as either an open
square meaning it is a vented reservoir, or a closed
reservoir meaning that it is a pressurized reservoir.
Every system reservoir has at least two lines connected to it, and some have many more. Often the
components that are connected to it are spread all
over the schematic. Rather than having a lot of
confusing lines all over the schematic, it is customary to draw individual reservoir symbols close to
the component. Similar to the ground symbol in
some wiring schematics. The reservoir is usually
the only component to be pictured more than once.
7
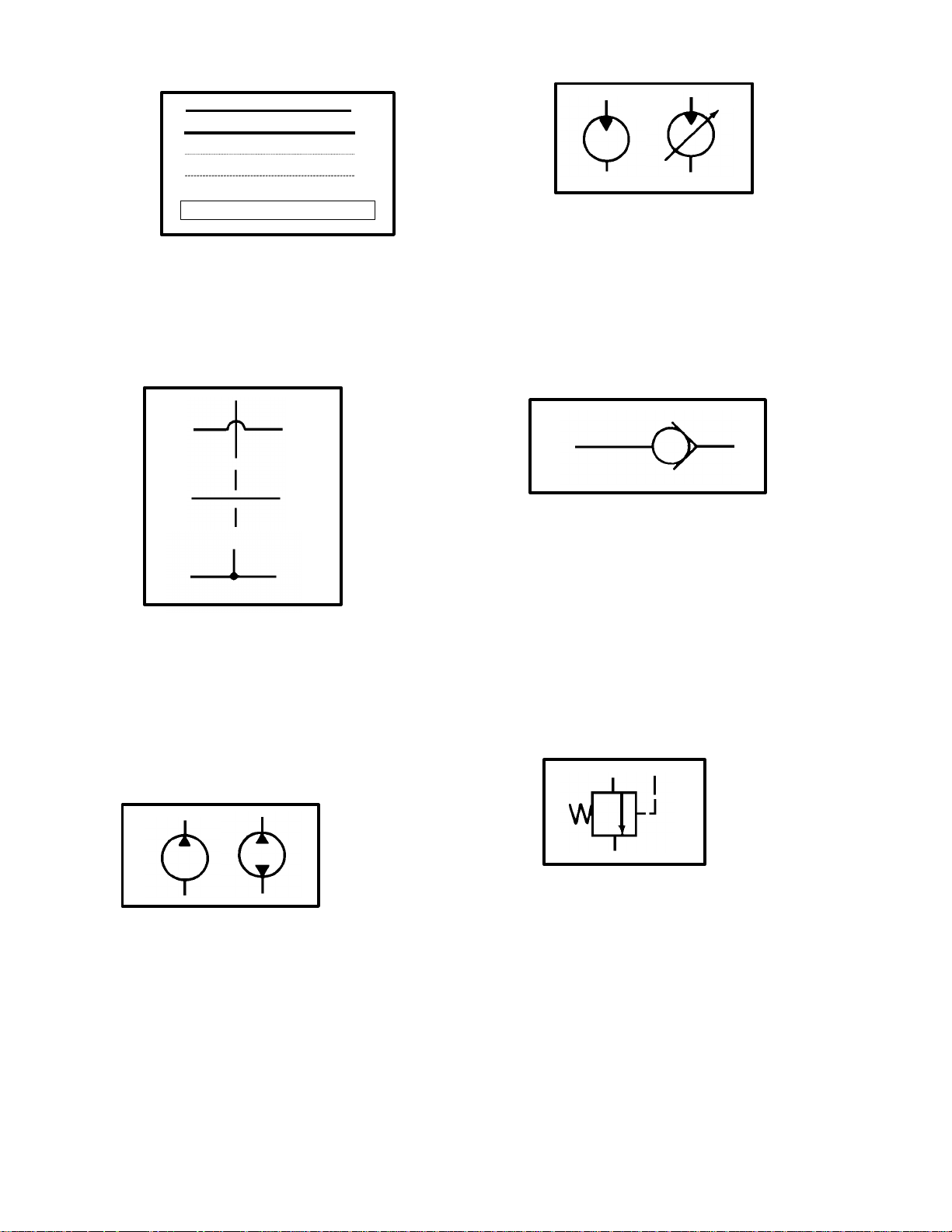
3. Lines
5. Hydraulic motors
LINES
Figure 4
A hydraulic line, tube, hose or any conductor that
carries the liquid between components is shown as
a line. Some lines have arrows to show direction of
oil flow, and lines may be shown as dashed lines to
show certain types of oil flow.
Figure 5
There are lines that cross other lines (Fig 5) but are
not connected, there are several ways to show lines
that are not connected. Lines that are connected
are shown with a dot or sometime just as two lines
crossing. If the schematic shows a specific symbol
to show lines that are not connected then anything
else is connected.
Figure 7
Hydraulic motor symbols (Fig 7) are circles with triangles, but opposite of a hydraulic pump, the triangle points inward to show the oil flows in to the
motor. One triangle is used for a non-reversible
motor and two triangles are used for a reversible
motor. An arrow through a motor shows that it is a
variable speed motor.
6. Check valves
Figure 8
A check valve (Fig 8) is shown as a ball in a V
seat. When oil pressure is applied to the left side of
the ball, the ball is forced into the V and no oil can
flow. When oil pressure is applied to the right side
of the ball, the ball moves away from the seat and
oil can flow past it. A by-pass check is a one way
valve with a spring on the ball end of the symbol.
This shows that pressurized oil must overcome the
spring pressure before the ball will unseat.
7. Relief valves
4. Hydraulic pumps
Figure 6
There are many basic pump designs. (Fig 6) A simple fixed displacement pump is shown as a circle
with a triangle that is pointing outward. The triangle
points in the direction that the oil will flow. If the
pump is reversible or is designed to pump in either
direction, it will have two triangles in it and they will
point opposite of each other indicating that oil may
flow in both directions.
Figure 9
A relief valve (Fig 9) is shown as a normally closed
valve with one port connected to the pressure line
and the other line connected to the reservoir. The
flow direction arrow points away from the pressure
line and toward the reservoir. When pressure in the
system overcomes the valve spring, pressure is directed through the valve to the reservoir.
8
 Loading...
Loading...