Page 1

THOMSON TG580
Wireless-n Multi-User ADSL2+ Gateway
Setup and User Guide
Page 2

Page 3

THOMSON TG580
Setup and User Guide
Page 4

Copyright
Copyright ©1999-2009 THOMSON. All rights reserved.
Distribution and copying of this document, use and communication of its contents is not permitted without written authorization
from THOMSON. The content of this document is furnished for informational use only, may be subject to change without notice,
and should not be construed as a commitment by THOMSON. THOMSON assumes no responsibility or liability for any errors or
inaccuracies that may appear in this document.
THOMSON Telecom Belgium
Prins Boudewijnlaan, 47
B-2650 Edegem
Belgium
http://www.thomson.net
Trademarks
The following trademarks may be used in this document:
DECT™ is a trademark of ETSI.
Bluetooth® word mark and logos are owned by the Bluetooth SIG, Inc.
Ethernet™ is a trademark of Xerox Corporation.
Wi-Fi®, WMM® and the Wi-Fi logo are registered trademarks of the Wi-Fi Alliance®. Wi-Fi CERTIFIED, Wi-Fi ZONE, Wi-Fi
Protected Access, Wi-Fi Multimedia, Wi-Fi Protected Setup, WPA, WPA2 and their respective logos are trademarks of the
Wi-Fi Alliance®.
UPnP™ is a certification mark of the UPnP™ Implementers Corporation.
DLNA® is a registered trademark, DLNA disc logo is a service mark, and DLNA Certified is a trademark of the Digital Living
Network Alliance. Digital Living Network Alliance is a service mark of the Digital Living Network Alliance.
Microsoft®, MS-DOS®, Windows®, Windows NT® and Windows Vista® are either registered trademarks or trademarks
of Microsoft Corporation in the United States and/or other countries.
Apple® and Mac OS® are registered trademarks of Apple Computer, Incorporated, registered in the United States and
other countries.
UNIX® is a registered trademark of UNIX System Laboratories, Incorporated.
Adobe®, the Adobe logo, Acrobat and Acrobat Reader are trademarks or registered trademarks of Adobe Systems, Incor-
porated, registered in the United States and/or other countries.
Other brands and product names may be trademarks or registered trademarks of their respective holders. All other logos, trademarks and service marks are the property of their respective owners, where marked or not.
Document Information
Status: v1.0 (November 2009)
Reference: E-DOC-CTC-20090507-0002
Short Title: Setup and User Guide TG580 (en)
Page 5

Contents
About this Setup and User Guide ............................................. 1
1 Installation....................................................................................3
1.1 Preliminary Steps............................................................................................ 4
1.2 Installing your Thomson Gateway .................................................................. 5
1.2.1 Manual Installation.................................................................................................................................6
1.3 Adding a New Computer to your Network ..................................................... 7
1.4 Connecting a Computer Using the Ethernet Cable ......................................... 8
2 Thomson Gateway Basics ..........................................................9
2.1 Thomson Gateway LED Behaviour ................................................................ 10
2.1.1 Status LEDs ........................................................................................................................................... 11
2.1.2 WPS Button LED ...................................................................................................................................14
2.2 Thomson Gateway GUI ................................................................................. 15
2.3 Backing Up/Restoring your Configuration .................................................... 16
3 Wireless Access .........................................................................17
3.1 Connecting Your Wireless Client via WPS .................................................... 18
3.2 Connecting Your Wireless Client without WPS ............................................ 20
3.3 Securing Your Wireless Connection.............................................................. 21
3.3.1 Configuring WPA-PSK Encryption ...................................................................................................... 23
3.3.2 Configuring WEP Encryption...............................................................................................................24
4 Thomson Gateway Tools.......................................................... 25
4.1 UPnP ............................................................................................................. 26
4.1.1 Accessing Your Thomson Gateway with UPnP ................................................................................. 27
4.1.2 Managing your Internet connection with UPnP................................................................................. 28
4.1.3 Configuring UPnP on the Thomson Gateway ....................................................................................29
4.1.4 Installing UPnP on Windows XP ......................................................................................................... 30
4.2 Assigning a service (HTTP, FTP,...) to a computer ........................................ 32
4.3 Dynamic DNS ................................................................................................ 34
5 Internet Security ........................................................................ 35
5.1 Firewall.......................................................................................................... 36
E-DOC-CTC-20090507-0002 v1.0
i
Page 6

Contents
5.2 Parental Control ............................................................................................ 37
5.2.1 Adding Rules For The Address Based Filter....................................................................................... 38
6.1 Thomson Gateway ........................................................................................ 41
6.1.1 Information ........................................................................................................................................... 42
6.1.2 Configuration ........................................................................................................................................ 43
6.1.3 Event Logs.............................................................................................................................................49
6.2 Broadband Connection.................................................................................. 50
6.2.1 Broadband Connection ........................................................................................................................ 51
6.2.2 Internet Services...................................................................................................................................53
6.3 Toolbox ......................................................................................................... 56
6.3.1 Remote Access/Assistance .................................................................................................................. 57
6.3.2 Game & Application Sharing...............................................................................................................59
6.3.3 Parental Control....................................................................................................................................65
6.3.4 Firewall .................................................................................................................................................. 67
6.3.5 Intrusion Detection ...............................................................................................................................69
6.3.6 Dynamic DNS........................................................................................................................................ 70
6.3.7 Dynamic Routing ..................................................................................................................................72
6.3.8 User Management................................................................................................................................ 73
6 Thomson Gateway GUI............................................................. 39
6.4 Home Network .............................................................................................. 76
6.4.1 Devices ..................................................................................................................................................77
6.4.2 Interfaces...............................................................................................................................................79
7 Troubleshooting ........................................................................87
7.1 General Thomson Gateway Troubleshooting ................................................ 88
7.1.1 Wired Connection Troubleshooting....................................................................................................89
7.1.2 Wireless Connection Troubleshooting ...............................................................................................90
7.2 Reset to Factory Defaults ............................................................................. 91
ii
E-DOC-CTC-20090507-0002 v1.0
Page 7

About this Setup and User Guide
About this Setup and User Guide
Used Symbols
A note provides additional information about a topic.
A caution warns you about potential problems or specific precautions that need to be taken.
Terminology
Generally, the THOMSON TG580 will be referred to as Thomson Gateway in this Setup and User Guide.
Typographical Conventions
Following typographical convention is used throughout this manual:
Sample text indicates a hyperlink to a Web site.
Example: For more information, visit us at www.thomson.net
Sample text indicates an internal cross-reference.
Example: If you want to know more about guide, see “1 Introduction” on page 7.
Sample text indicates an important content-related word.
Example: To enter the network, you must authenticate yourself.
Sample text indicates a GUI element (commands on menus and buttons, dialog box elements, file
names, paths and folders).
Example: On the File menu, click Open to open a file.
.
Documentation and software updates
THOMSON continuously develops new solutions, but is also committed to improving its existing products.
For more information on THOMSON's latest technological innovations, documents and software releases,
visit us at www.thomson.net
.
E-DOC-CTC-20090507-0002 v1.0
1
Page 8

About this Setup and
User Guide
2
E-DOC-CTC-20090507-0002 v1.0
Page 9

1 Installation
1 Installation
Introduction
In a few minutes you will be able to access the Internet using your Thomson Gateway.
This Setup and User Guide will show you how to set up your Thomson Gateway and how to connect your
computer(s) to the Internet.
Main features
As soon as you have completed the installation of your Thomson Gateway you will be able to benefit from all
the services offered by your Thomson Gateway. This Setup and User Guide will focus on the following
features:
Broadband Internet connection.
This chapter describes how to connect your Thomson Gateway to the Internet.
Wired and wireless access to your local network devices.
For more information, see ”1.4 Connecting a Computer Using the Ethernet Cable” on page 8 and
”3 Wireless Access” on page 17.
Internet Security:
For more information, see ”5 Internet Security” on page 35.
Useful networking tools like UPnP, Dynamic DNS and many more.
Before you can start to use these features, we will first setup your Thomson Gateway.
E-DOC-CTC-20090507-0002 v1.0
3
Page 10

1 Installation
1.1 Preliminary Steps
DSL service
The DSL service must be up and running on your telephone line.
If both conventional telephone and DSL service are simultaneously available from the same copper pair, you
will need a central splitter or distributed filters for decoupling DSL and telephone signals.
Public telephone lines carry voltages that can cause electric shock. Only try to set up splitter/
filters that have been designed to be installed by unqualified personnel. For further assistance,
contact your Internet Service Provider.
Computer requirements
If you want to connect your computer using:
The Ethernet cable, make sure that the computer is equipped with an Ethernet Network Interface Card
(NIC).
A wireless connection, you will need a WiFi-certified wireless client adapter for each computer you want
to connect wirelessly.
Internet connection details
You may need the following connection details from your Internet Service Provider (ISP):
Your ISP’s method for connecting to the Internet (for example PPPoE)
The VPI/VCI (for example 8/35)
Your user name and password to connect to the Internet for PPP connections
Your IP settings in case of static configurations
You may have received this information when you subscribed at your Internet Service Provider. You may be
prompted for this information at a given step in the installation procedure.
4
E-DOC-CTC-20090507-0002 v1.0
Page 11

1 Installation
1.2 Installing your Thomson Gateway
Overview
How it works
The Setup and User Guide will first help you to connect your computer to the Thomson Gateway. After this is
done, you can configure your Thomson Gateway using your web browser.
Requirements
Javascript must be enabled on your web browser.
Getting started
Proceed with ”1.2.1 Manual Installation” on page 6.
E-DOC-CTC-20090507-0002 v1.0
5
Page 12

1 Installation
1.2.1 Manual Installation
Procedure
Proceed as follows:
1 Connect the cables
2 Configure the Thomson Gateway
Connect the cables
Proceed as follows:
1 Connect the Thomson Gateway to the DSL line.
2 Connect the power supply.
3 Turn on the Thomson Gateway.
4 Connect your computer to the Thomson Gateway as described in ”1.3 Adding a New Computer to your
Network” on page 7.
Configure the Thomson Gateway
You are now ready to configure your Internet connection and local network.
Proceed as follows:
1 Open your web browser, and browse to http://dsldevice.lan
Gateway (by default: 192.168.1.254).
2 The Thomson Gateway GUI appears. Click the Thomson Gateway menu item on the left-hand side.
3 The Thomson Gateway page appears. In the Pick a task list, click Setup.
4 The Easy Setup wizard appears. This wizard will guide you through the configuration of your Thomson
Gateway.
5 Click Next and follow the instructions.
6 After running the Easy Setup wizard, you are connected to the Internet.
For more information, see ” Setting up your Thomson Gateway” on page 45.
or to the IP address of your Thomson
6
E-DOC-CTC-20090507-0002 v1.0
Page 13

1 Installation
1.3 Adding a New Computer to your Network
Overview
If you want to connect your computer to the Thomson Gateway using:
A Wireless connection, continue with ”3 Wireless Access” on page 17.
An Ethernet cable connection, continue with ”1.4 Connecting a Computer Using the Ethernet Cable” on
page 8.
E-DOC-CTC-20090507-0002 v1.0
7
Page 14

1 Installation
1.4 Connecting a Computer Using the Ethernet Cable
Requirements
Your computer must have a free Ethernet port.
Your computer must be configured to obtain an IP address automatically. This is the default setting.
Ethernet cable
In your package, you will find a cable with yellow connectors. This is the Ethernet cable.
Procedure
Proceed as follows:
1 Connect one end of the Ethernet cable to the yellow Ethernet port(s) of your Thomson Gateway:
2 Connect the other end of the Ethernet cable to your computer.
3 Your computer is now connected to your network. No additional configuration is needed.
8
E-DOC-CTC-20090507-0002 v1.0
Page 15

2 Thomson Gateway Basics
In this chapter
Thomson Gateway LED Behaviour 10
Thomson Gateway GUI 15
Backing Up/Restoring your Configuration 16
2 Thomson Gateway Basics
Topi c Page
E-DOC-CTC-20090507-0002 v1.0
9
Page 16

2 Thomson Gateway
Basics
2.1 Thomson Gateway LED Behaviour
Content
This chapter describes the behaviour of:
Status LEDs
WPS Button LED
10
E-DOC-CTC-20090507-0002 v1.0
Page 17

2 Thomson Gateway Basics
2.1.1 Status LEDs
Introduction
On the front panel of your Thomson Gateway, you can find a number of status LEDs, indicating the state of
the device during normal operation.
Following LEDs are available on your Thomson Gateway:
LED Name
Power LED
Broadband LED
Internet LED
Wireless LED
Ethernet LED
WPS LED
E-DOC-CTC-20090507-0002 v1.0
11
Page 18

2 Thomson Gateway
Power LED
Colour State Description
Green Solid on Power on, normal operation
Red Solid on Power on, self-test failed, indicating device malfunction
Amber Blinking Bootloader active (during upgrade)
Off Power off
Broadband LED
Colour State Description
Green Blinking Pending DSL line synchronisation or No DSL line
Solid on DSL line synchronised
Basics
Internet LED
Colour State Description
Green Blinking Internet activity
Solid on Internet connectivity, no activity
Red Solid on Internet connection setup failed
Off No Internet connection
Wireless LED
Colour State Description
Green Blinking Wireless activity, WPA(2) encryption
Solid on No wireless activity, WPA(2) encryption
Amber Blinking Wireless activity, WEP encryption
Solid on No wireless activity, WEP encryption
Red Blinking Wireless activity, no security
Solid on No wireless activity, no security
12
Red/green Toggling Wireless client registration phase
Off WLAN disabled
E-DOC-CTC-20090507-0002 v1.0
Page 19

2 Thomson Gateway Basics
Ethernet LED
Colour State Description
Green Solid on Ethernet connection, no activity
Blinking Ethernet activity
Off No Ethernet connection
E-DOC-CTC-20090507-0002 v1.0
13
Page 20
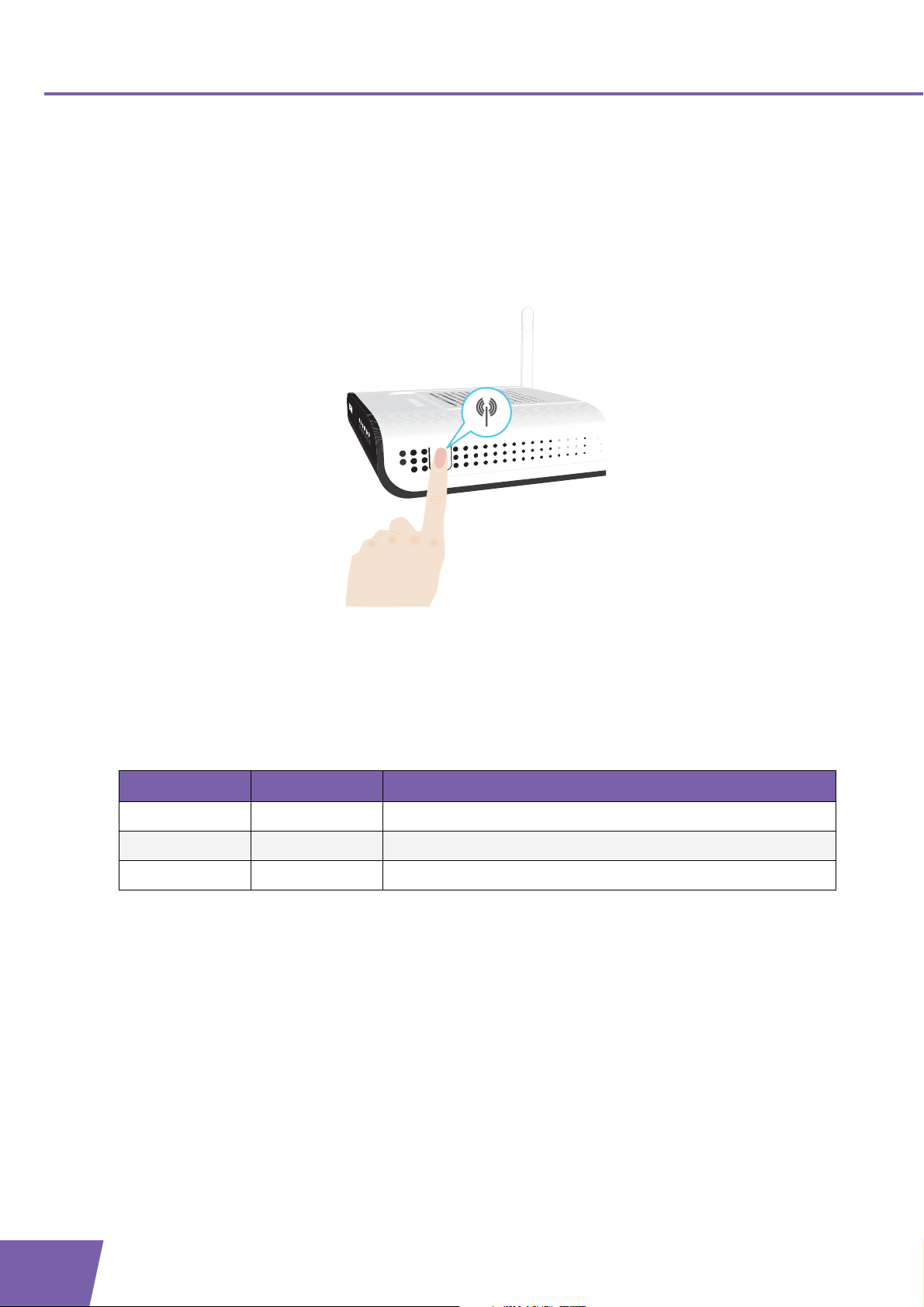
2 Thomson Gateway
2.1.2 WPS Button LED
Introduction
The WPS button allows you to add new wireless clients to your network.
Basics
For more information, see Connecting Your Wireless Client via WPS.
WPS LED
Colour State Description
Green Solid On Client successfully registered via WPS
Amber Blinking WPS registration ongoing
Red Blinking Error occurred
14
E-DOC-CTC-20090507-0002 v1.0
Page 21
2 Thomson Gateway Basics
2.2 Thomson Gateway GUI
Introduction
The Thomson Gateway Graphical User Interface (GUI) allows you to configure your Thomson Gateway using
your web browser.
Requirements
Javascript must be enabled on your browser. For more information, consult the help of your Internet
browser.
Accessing the Thomson Gateway Web Interface
Proceed as follows:
1 Open your web browser.
2 Browse to http://dsldevice.lan
3 If you have protected your Thomson Gateway with a user name and password, the Thomson Gateway
will prompt you to enter these. Enter your user name and password and click OK.
4 The Thomson Gateway GUI appears. For more information, see ”6 Thomson Gateway GUI” on page 39.
or the IP address of your Thomson Gateway (by default: 192.168.1.254).
If your computer runs Windows Vista or Windows XP, you can also access the Thomson Gateway GUI using
the Internet Gateway Device icon. For more information, see ”4.1 UPnP” on page 26.
E-DOC-CTC-20090507-0002 v1.0
15
Page 22

2 Thomson Gateway
Basics
2.3 Backing Up/Restoring your Configuration
Introduction
Once you have configured your Thomson Gateway to your needs, it may be a good idea to backup your
configuration for later use. This way you can always return to your working configuration in case of
problems.
Backing up your configuration
Proceed as follows:
1 Browse to the Thomson Gateway GUI.
2 On the Thomson Gateway menu, click Configuration.
3 In the Pick a task list, click Save or Restore Configuration.
4 Under Backup current configuration, click Backup Configuration Now.
5 The Thomson Gateway prompts you to save your file.
6 Save your file to a location of your choice.
Restoring your configuration
Proceed as follows:
1 Browse to the Thomson Gateway GUI.
2 On the Thomson Gateway menu, click Configuration.
3 In the Pick a task list, click Save or Restore Configuration.
4 Under Restore saved configuration, click Browse.
5 Browse to your backup file and open it.
These files usually use .bin as extension.
6 The Thomson Gateway restores your configuration.
16
E-DOC-CTC-20090507-0002 v1.0
Page 23

3 Wireless Access
3 Wireless Access
Introduction
With the built-in wireless access point you are no longer need a cable connection between your computer
and your Internet gateway.
What you need to set up a wireless network
To set up a wireless network, you need the following components:
A Wireless Access Point
A Wireless client
Wireless Access Point
You can consider the wireless access point as the heart of your wireless network. The wireless access point:
Connects different wireless devices with each other.
Secures the data sent over wireless connection.
The Thomson Gateway comes with an integrated wireless access point. The only thing you need is a wireless
client.
Other devices like media players and smartphones may also have a built-in wireless client. Check
the documentation of your device for more information.
Wireless client
The wireless client allows you to connect a device, typically a computer, to a wireless access point. Both builtin and external (for example via USB) are available.
Check the documentation of your computer if you are not sure if your computer is equipped with a wireless
client.
Configuring your wireless clients
Before you can start surfing the internet with a wireless connection, you must first connect your wireless
client to your wireless access point: the Thomson Gateway.
For more information, see ”3.1 Connecting Your Wireless Client via WPS” on page 18 and ”3.2 Connecting
Your Wireless Client without WPS” on page 20.
Secure your wireless connection!
Because you no longer need a physical connection, everyone who is within the range of your Thomson
Gateway can access your network. If you do not protect your wireless network, the following could happen:
People can use your connection to access the Internet.
Hackers can use your connection to commit computer crimes.
You can easily prevent this by securing your wireless connection. For more information, see ”3.3 Securing
Your Wireless Connection” on page 21.
E-DOC-CTC-20090507-0002 v1.0
17
Page 24

3 Wireless Access
3.1 Connecting Your Wireless Client via WPS
WPS
Wi-Fi Protected Setup (WPS) allows you to add new wireless clients to your network in a swift and easy way,
without the need to enter all of your wireless settings (SSID, encryption,...).
Requirements
Your wireless client must supports WPS. Check the documentation of your wireless client for this.
Your Thomson Gateway must use WPA(2)-PSK encryption (default encryption) or no encryption. WPS
with WEP encryption is not possible.
Procedure
Proceed as follows:
1 Shortly press the WPS button on the Thomson Gateway:
18
2 The WPS button LED starts blinking orange. This indicates that the Thomson Gateway is now searching
for wireless clients that are in registration mode. You now have two minutes to start WPS on your
wireless client.
3 Start WPS on your wireless client.
The WPS button LED is solid green
This indicates that you have successfully registered your wireless client. You are now connected to the
Thomson Gateway network.
The WPS button LED is blinking red
This indicates that the Thomson Gateway could not find your wireless client.
E-DOC-CTC-20090507-0002 v1.0
Page 25

3 Wireless Access
Make sure that the WLAN LED is blinking amber when you start WPS on your wireless client. If you still have
trouble connecting to the Thomson Gateway, try connecting your wireless client without WPS. For more
information, see ”3.2 Connecting Your Wireless Client without WPS” on page 20.
Troubleshooting
If you are having trouble connecting your wireless client via WPS, try to configure it manually. For more
information, see ”3.2 Connecting Your Wireless Client without WPS” on page 20.
E-DOC-CTC-20090507-0002 v1.0
19
Page 26

3 Wireless Access
3.2 Connecting Your Wireless Client without WPS
Before you start
Before you can connect a computer to your wireless network you need to know which Network Name (SSID)
and wireless encryption your Thomson Gateway is using.
What Network Name (SSID) is the Thomson Gateway using?
If you did not change the SSID manually, your Thomson Gateway uses the SSID that is printed on the bottom
panel label of your Thomson Gateway.
What wireless security is the Thomson Gateway using?
You have not yet configured your Thomson Gateway
In this case, no encryption is used.
You have already configured your Thomson Gateway
If you have configured the wireless security settings through the Thomson Gateway GUI, the encryption key/
passphrase is the one you typed in the the Encryption Key textbox.
Forgot your wireless settings?
If you have changed the wireless settings manually and you can’t remember your settings, try one of the
following:
If one of your computers is already connected to your network:
1 Browse to the Thomson Gateway GUI on a computer that is already connected to your network.
2 On the Home Network menu, click Wireless.
3 In the upper-right corner, click Details.
4 Under:
Configuration, you can find the network name (SSID).
Security, you can find the encryption.
If none of your computers is connected to your network, connect a computer using a wired connection and
follow the procedure above to find out what your wireless settings are.
Another option is to reset your Thomson Gateway and configure it all over again. For more information, see
”7.2 Reset to Factory Defaults” on page 91.
Procedure
Configure your computer with the same wireless settings as your Thomson Gateway. For more information,
consult the help of your wireless client.
20
E-DOC-CTC-20090507-0002 v1.0
Page 27

3 Wireless Access
3.3 Securing Your Wireless Connection
Introduction
By using encryption, communication between the wireless clients and your Thomson Gateway is protected
by a passphrase. Only clients which use the correct network name (SSID) and passphrase can connect to your
network.
Encryption methods
During the years a number of encryption types have been developed. The list below gives you an overview of
the supported encryption types ordered by security level, you will find the highest level of security at the top
of the list:
WPA-PSK Encryption:
The wireless data is being encrypted with a user-defined key. Wireless clients must be configured with
this key before they can connect to the Thomson Gateway.
WEP Encryption:
The first encryption type used for wireless connections. Like WPA-PSK it uses a user-defined key, but WEP
has been proven to have some security issues. We strongly recommend you to use WPA-PSK instead.
WPA-PSK versions
The Thomson Gateway supports the following WPA-PSK versions:
WPA2 (also referred to as WPA2-PSK):
WPA2 is the most secure version, but not all wireless clients already support it. Before you select this
version, make sure all of your wireless clients support it.
WPA+WPA2:
If not all of your wireless clients support WPA2 or you are not sure if they support WPA2, we recommend
you to choose WPA+WPA2. Wireless clients that support WPA2 will use WPA2, the others will use WPA.
WPA:
If none of your wireless clients support WPA2 choose this option.
If you want to configure WPA2 on the built-in wireless utility of Windows XP Service Pack 2 (SP2),
you first have to:
Upgrade your Windows XP to Service Pack 3.
- or -
Install the following update: http://support.microsoft.com/kb/917021.
Which encryption method should I use?
We strongly recommend you to use WPA+WPA2.
Although the Thomson Gateway allows you to use WEP or no security, it is not recommended to use these
settings. Only use WEP if you have wireless clients that don’t support a higher encryption level.
Configuring the wireless encryption
Proceed as follows:
1 Open the Thomson Gateway GUI.
2 On the left menu, click Home Network.
E-DOC-CTC-20090507-0002 v1.0
21
Page 28

3 Wireless Access
3 Under Wireless, click your access point.
Your access point will be listed in the following format: “WLAN:<Network Name> (<Actual
Speed>)”. For example, WLAN: Thomson83C7C7 (54Mbps).
4 The Wireless Access Point page appears.
5 In the Location bar, click Configure.
6 Under Security, you can change the Encryption. If you want to use:
WPA-PSK Encryption, continue with ”3.3.1 Configuring WPA-PSK Encryption” on page 23.
WEP Encryption, continue with ”3.3.2 Configuring WEP Encryption” on page 24.
22
E-DOC-CTC-20090507-0002 v1.0
Page 29

3 Wireless Access
3.3.1 Configuring WPA-PSK Encryption
Procedure
Continuing from ” Configuring the wireless encryption” on page 21:
1 Select Use WPA-PSK Encryption.
2 In the WPA-PSK Encryption Key box, type a pass phrase (also known as Pre-shared key) of your choice.
The pass phrase must consist of 8 to 63 alphanumeric characters or 8 to 64 hexadecimal characters
(characters from 0 to 9 and from A to F).
3 In the WPA-PSK Version list, click the WPA-version of your choice. Following options are available:
WPA2:
WPA2 is the most secure version, but not all wireless clients already support it. Before you select this
version, make sure all of your wireless clients support it.
WPA+WPA2:
If not all of your wireless clients support WPA2 or you are not sure if they support WPA2, we
recommend you to choose WPA+WPA2. Wireless clients that support WPA2 will use WPA2, the
others will use WPA.
WPA:
If none of your wireless clients support WPA2 choose this option.
If you want to configure WPA2 on the built-in wireless utility of Windows XP Service Pack 2
(SP2), you first have to:
Upgrade your Windows XP to Service Pack 3.
- or -
Install the following update: http://support.microsoft.com/kb/917021
4 Click Apply.
5 Configure your wireless client(s) with the same settings.
.
E-DOC-CTC-20090507-0002 v1.0
23
Page 30

3 Wireless Access
3.3.2 Configuring WEP Encryption
Warning
Although the Thomson Gateway allows you to use WEP or no security, it is not recommended to use these
settings. Only use WEP if you have wireless clients that don’t support a higher encryption level.
Procedure
Continuing from ” Configuring the wireless encryption” on page 21:
1 Select Use WEP Encryption
2 In the WEP Key Length list, click the desired key length (a higher key length offers higher security).
3 In the Encryption key box, type a Network key of your choice. If you are using:
A 64-bit key:
Type 10 hexadecimal characters (characters from 0 to 9 and from A to F) or 5 alphanumeric
characters.
A 128-bit key:
Type 26 hexadecimal characters (characters from 0 to 9 and from A to F) or 13 alphanumeric
characters.
4 Click Apply.
5 Configure your wireless client(s) with the same settings.
24
E-DOC-CTC-20090507-0002 v1.0
Page 31

4 Thomson Gateway Tools
4 Thomson Gateway Tools
In this chapter
In this chapter we will take a closer look at following features:
Topi c Page
UPnP 26
Assigning a service (HTTP, FTP,...) to a computer 32
Dynamic DNS 34
Feature availability
Depending on the configuration offered by your Internet Service Provider (ISP), some features may not be
available on your Thomson Gateway. For more information, contact your ISP.
E-DOC-CTC-20090507-0002 v1.0
25
Page 32

4 Thomson Gateway
4.1 UPnP
Introduction
UPnP is designed to automate the installation and configuration of a (small) network as much as possible.
This means that UPnP-capable devices can join and leave a network without any effort of a network
administrator.
Supported Operating Systems
Following operating systems support UPnP:
Windows Vista
Windows XP
If your computer is running Windows XP, you first have to install the UPnP component. For more
information, see ”4.1.4 Installing UPnP on Windows XP” on page 30.
Tools
UPnP and the Thomson Gateway
With UPnP you can:
Access the Thomson Gateway GUI without opening your web browser. For more information, see
Accessing Your Thomson Gateway with UPnP.
Connect/disconnect without having to open the Thomson Gateway GUI.
For more information, see Managing your Internet connection with UPnP.
Automatic port configuration for UPnP-enabled games and applications. You do not have to create port to
run services on a computer. If the application is UPnP-enabled, UPnP will create these entries
automatically. For more information, see Assigning a service (HTTP, FTP,...) to a computer.
26
E-DOC-CTC-20090507-0002 v1.0
Page 33

4 Thomson Gateway Tools
4.1.1 Accessing Your Thomson Gateway with UPnP
Windows Vista
If your computer runs Windows Vista:
1 On the Windows Start menu, click Network.
2 The Network window appears:
3 Right-click your Thomson Gateway (displayed as THOMSON TGXXX) and click View device web page.
4 The Thomson Gateway GUI appears.
Windows XP
If your computer runs Windows XP:
1 Go to My Network Places.
2 The My Network Places window appears:
3 Double-click your Thomson Gateway (displayed as THOMSON TGXXX).
4 The Thomson Gateway GUI appears.
E-DOC-CTC-20090507-0002 v1.0
27
Page 34

4 Thomson Gateway
Tools
4.1.2 Managing your Internet connection with UPnP
Windows Vista
If your computer runs Windows Vista:
1 On the Windows Start menu, click Network.
2 The Network window appears:
3 Right-click your Thomson Gateway (displayed as THOMSON TGXXX).
4 If you are currently:
Connected to the Internet, click Disable to disconnect from the Internet.
Not connected to the Internet, click Enable to connect to the Internet.
Windows XP
If your computer runs Windows XP:
1 On the Windows Start menu, click (Settings >) Control Panel.
2 The Control Panel window appears.
Click (Network and Internet Connections) > Internet Connections.
3 The Network Connections window appears;
28
4 If you right-click the Internet Connection icon, you can connect/disconnect your connection to the
Internet.
E-DOC-CTC-20090507-0002 v1.0
Page 35

4 Thomson Gateway Tools
4.1.3 Configuring UPnP on the Thomson Gateway
Introduction
On the Thomson Gateway GUI you can:
Enable/Disable UPnP
Enable/Disable UPnP
Proceed as follows:
1 Browse to the Thomson Gateway GUI.
2 On the Toolbox menu, click Game & Application Sharing.
3 Under Universal Plug and Play:
Select the Use UPnP check box, to enable UPnP.
Clear the Use UPnP check box, to disable UPnP.
4 Click Apply.
E-DOC-CTC-20090507-0002 v1.0
29
Page 36

4 Thomson Gateway
Tools
4.1.4 Installing UPnP on Windows XP
Adding UPnP
If you are running Microsoft Windows XP, it is recommended to add the UPnP component to your system.
Proceed as follows:
1 In the Start menu, click (Settings >) Control Panel.
2 The Control Panel window appears.
Click Add or Remove Programs.
3 The Add or Remove Programs window appears.
Click Add/Remove Windows Components.
4 The Windows Components Wizard appears:
In the Components list, select Networking Services and click Details
5 The Networking Services window appears:
Select Universal Plug and Play or UPnP User Interface and click OK.
6 Click Next to start the installation and follow the instructions in the Windows Components Wizard.
You may need your Windows installation CD during the installation.
7 At the end of the procedure the Wizard informs you that the installation was successful. Click Finish to
quit.
30
E-DOC-CTC-20090507-0002 v1.0
Page 37

4 Thomson Gateway Tools
Adding IGD Discovery and Control
Your Windows XP system is able to discover and control Internet Gateway Devices (IGD) like the Thomson
Gateway on your local network. Therefore, it is recommended to add the IGD Discovery and Control client to
your system.
Proceed as follows:
1 On the Windows taskbar, click Start.
2 Select (Settings >) Control Panel > Add or Remove Programs.
3 In the Add or Remove Programs window, click Add/Remove Windows Components.
4 The Windows Components Wizard appears:
Select Networking Services in the Components list and click Details.
5 The Networking Services window appears:
Select Internet Gateway Device Discovery and Control Client and click OK.
6 Click Next to start the installation and follow the instructions in the Windows Components Wizard.
You may need your Windows installation CD during the installation.
7 At the end of the procedure, the Wizard informs you that the installation was successful. Click Finish to
quit.
E-DOC-CTC-20090507-0002 v1.0
31
Page 38

4 Thomson Gateway
Internet
Tools
4.2 Assigning a service (HTTP, FTP,...) to a computer
Introduction
The Thomson Gateway allows you to use one internet connection for multiple computers. This means that all
your computers share one public IP address, as if only one computer is connected to the outside world.
Problem
When the Thomson Gateway receives an incoming message, the Thomson Gateway has to decide to which
computer he will have to send this message.
If the incoming message is a response to an outgoing message originating from one of your computers, the
Thomson Gateway sends the incoming message to this computer.
If your are running a server or an application that acts as a server (for example a HTTP server, internet game),
the initial message will come from the internet and the Thomson Gateway has to decide to which computer
he should forward the incoming message.
?
Internet
In the latter case, the Thomson Gateway cannot decide all along the service related to the message is not
assigned to one computer.
Solution
To avoid this problem you can:
Enable UPnP.
Assign a game or application to a local networking device.
32
E-DOC-CTC-20090507-0002 v1.0
Page 39

4 Thomson Gateway Tools
UPnP
UPnP is a technology that enables seamless operation of a wide range of games and messaging applications.
Your computer will use UPnP to communicate to the Thomson Gateway which services are running on the
computer.
For example, when you start a UPnP-enabled application on your computer, it will automatically creat the
necessary port mappings to this computer.
For more information on UPnP, see ”4.1 UPnP” on page 26.
Assign a game or application to a local networking device
If you assign a game or application to a local networking device, you will basically tell the Thomson Gateway
that if it receives requests for a specific game or application, it has to forward these messages to a specific
computer.
Proceed as follows to do so:
1 Browse to the Thomson Gateway GUI.
2 On the Toolbox menu, click Game & Application Sharing.
3 In the Pick a task list, click Assign a game or application to a local network device.
4 In the Game or application list, click the service you want to run on the computer. For example, HTTP
Server (World Wide Web).
If the service is not available in the list, click Create a new game or application in the Pick a task
list. For more information, click Help on the Thomson Gateway GUI.
5 In the Device list, select the computer to which you want to assign the service. Your computer will be
listed with its computer name.
The computer must be connected to the network and up and running.
It may be advised to assign “Always use the same address” or to configure the computer with
a static IP!
6 All incoming request for the selected service will now be directed to the selected device. The Thomson
Gateway automatically configures the firewall to allow this service.
E-DOC-CTC-20090507-0002 v1.0
33
Page 40

4 Thomson Gateway
4.3 Dynamic DNS
Introduction
The dynamic DNS service allows you to assign a fixed DNS host name (for example john.dyndns.org) to a
broadband connection even if this connection is using a dynamically assigned IP address. As soon as the
device gets a new IP address, the dynamic DNS server updates its entry to the new IP address.
What you need
Before you can configure dynamic DNS, you first have to create an account at a dynamic DNS service
provider. For example:
www.dyndns.org
www.no-ip.com
www.dtdns.com
Tools
Procedure
Proceed as follows:
1 Browse to the Thomson Gateway GUI.
2 On the Toolbox menu, click Dynamic DNS.
3 On the Location bar, click Configure.
4 Select the Enabled check box.
5 Type the user name and password of your Dynamic DNS service account in the corresponding fields.
6 In the Service list, click the name of your Dynamic DNS service provider.
7 In the Host box, type the host name that you got from the Dynamic DNS service provider (for example
mywebpage.dyndns.org).
8 Click Apply.
34
E-DOC-CTC-20090507-0002 v1.0
Page 41

5 Internet Security
Overview
The Thomson Gateway offers you various options to secure your network:
Topi c Page
Firewall 36
Parental Control 37
5 Internet Security
E-DOC-CTC-20090507-0002 v1.0
35
Page 42

5 Internet Security
5.1 Firewall
Changing the security level
Proceed as follows:
1 Browse to the Thomson Gateway GUI.
2 On the Toolbox menu, click Firewall.
3 The Firewall page appears. In the upper-right corner, click Configure.
4 A list with security settings with a brief description is displayed.
5 Select the security level of your choice and click Apply.
36
E-DOC-CTC-20090507-0002 v1.0
Page 43

5 Internet Security
5.2 Parental Control
Introduction
The Thomson Gateway allows you to deny access to specific web sites.
Access Denied page
When a user tries to access a page that is being blocked, the following page is displayed:
Address-based filtering
With address-based filtering (or URL-filtering) you can block web sites based on their address (for example
www.porn.com).
Proceed as follows:
1 Browse to the Thomson Gateway GUI.
2 On the Toolbox menu, click Parental Control.
3 On the Location bar, click Configure.
4 Make sure that the Use Address Based Filter check box is selected.
5 In the Action for Unknown Sites, select:
Allow as the default rule if you want to allow access to all web sites and manually specify which web
sites may not be accessed.
Block as the default rule if you want to deny access to all web sites and manually specify a number of
web sites that may be accessed.
6 Click Apply.
7 If you want to make exceptions for specific web sites, add the necessary rules in the address-based filter.
For more information, see ”5.2.1 Adding Rules For The Address Based Filter” .
E-DOC-CTC-20090507-0002 v1.0
37
Page 44

5 Internet Security
5.2.1 Adding Rules For The Address Based Filter
Options
With the address based filter you can:
Deny access to a specific Web site
Allow access to a specific Web site
Deny access to a specific Web site
Proceed as follows:
1 Browse to the Thomson Gateway GUI.
2 On the Toolbox menu, click Web Site Filtering.
3 Make sure the Use Address Based Filter check box is selected.
4 Type the URL of the Web site you want to block (for example “mail.provider.com”) in the Web Site box.
5 In the Action list, click Block.
6 Click Add.
Allow access to a specific Web site
Proceed as follows:
1 Browse to the Thomson Gateway GUI.
2 On the Toolbox menu, click Web Site Filtering.
3 Make sure the Use Address Based Filter check box is selected.
4 Type the URL of the Web site you want to allow (for example “netbanking.bank.com”) in the Web Site
box.
5 Click Allow in the Action list.
6 Click Add.
38
E-DOC-CTC-20090507-0002 v1.0
Page 45

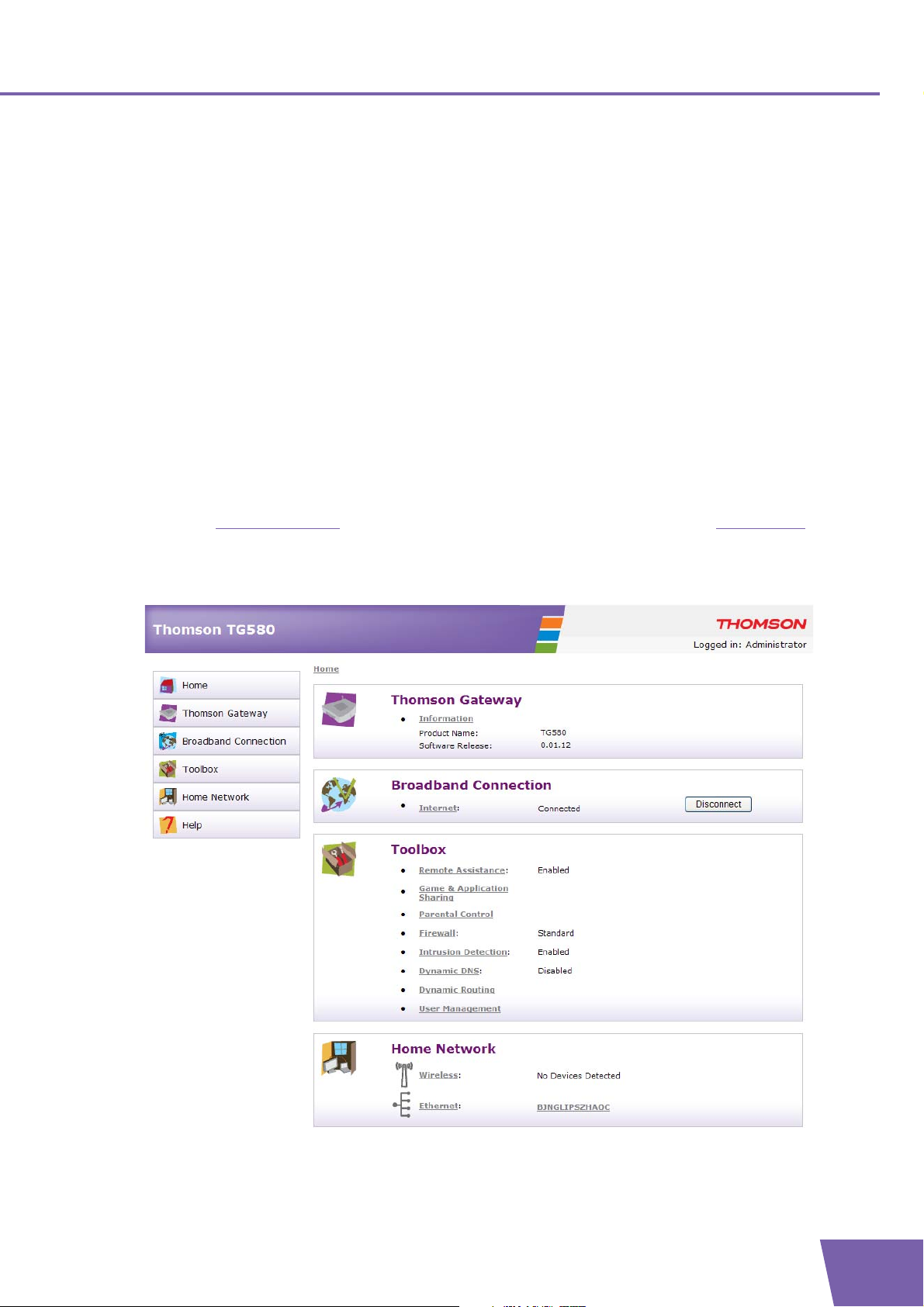
6 Thomson Gateway GUI
6
3
4
5
1
2
6 Thomson Gateway GUI
Introduction
The Thomson Gateway comes with an integrated configuration web interface, commonly referred to as the
Graphical User Interface (GUI).
It allows you to configure your Thomson Gateway simply by using a web browser from any local computer
connected to the Thomson Gateway.
Requirements
Before you can access the Thomson Gateway web pages:
Javascript must be enabled on your web browser. For more information, consult the help of your Internet
browser.
Your computer must be configured to obtain an IP address automatically. This is the default setting.
Components
You can find the following components on the Thomson Gateway GUI:
Label Description
1 Menu
2 Location bar
3 Login section
4 Notification Area
5 Content pane
6 Tasks
E-DOC-CTC-20090507-0002 v1.0
39
Page 46

6 Thomson Gateway
Menu
The menu consists of the following menu items:
Home:
Allows you to go back to the home page.
Thomson Gateway:
Provides basic information on the Thomson Gateway.
Broadband Connection:
Allows you to view/configure your broadband connections.
Toolbox:
Allows you to assign games or applications to a device and secure your Internet connection.
Home Network:
Allows you to manage your local network.
Help:
Allows you to view context-related help information.
Location bar
The location bar allows you to:
View your current position in the Thomson Gateway GUI.
Depending on the page you are on, view the following buttons:
Overview to view a summary of the current status or configuration.
Details to view more detailed information on the current status or configuration.
Configure to change the current settings.
GUI
Login section
In this section, you can see the current user name.
Notification Area
The notification area is used to display:
Error messages, indicated by a red traffic light.
Warnings, indicated by an orange traffic light.
Information, indicated by a green traffic light.
If none of these events occurs, the notification area will not be shown.
Content pane
The content pane displays the information and configurable items of the selected topic.
Tas ks
To allow a quick configuration of your Thomson Gateway, some pages may offer you a number of related
tasks in the Pick a task list. These tasks will guide you to the page where you can perform the selected task.
40
E-DOC-CTC-20090507-0002 v1.0
Page 47

6 Thomson Gateway GUI
6.1 Thomson Gateway
The Thomson Gateway page
The Thomson Gateway page gives you an overview of some basic product information and configuration
parameters of your Thomson Gateway.
The Thomson Gateway menu
In the Thomson Gateway menu, you can find the following items:
Click... To...
Information View some system information on your Thomson Gateway.
Configuration View some configuration information on your Thomson Gateway.
Event Logs View the last events recorded on your Thomson Gateway.
Tas ks
On the Thomson Gateway page you can carry out following tasks:
Setting up your Thomson Gateway.
Restarting your Thomson Gateway.
Returning to Factory Default Settings.
Viewing Event Logs.
Checking connectivity to the Internet.
E-DOC-CTC-20090507-0002 v1.0
41
Page 48

6 Thomson Gateway
6.1.1 Information
Introduction
On the System Information page, you can find some important system information of your Thomson
Gateway. You may need this when contacting your help desk.
This page lists the Thomson Gateway’s:
Product Name
Software Release
Boot Loader Version
ADSL Modem Code Version
HW Version
Serial Number
GUI
Restarting your Thomson Gateway
Proceed as follows:
1 In the Pick a task list, click Restart.
2 The Thomson Gateway prompts you to confirm your choice, click Yes, Restart my Thomson Gateway.
3 The Thomson Gateway restarts and returns to the Home page.
42
E-DOC-CTC-20090507-0002 v1.0
Page 49

6 Thomson Gateway GUI
6.1.2 Configuration
Overview
The System Configuration Overview page displays basic configuration information.
Details
The System Configuration Details page displays all of the available configuration information.
E-DOC-CTC-20090507-0002 v1.0
43
Page 50

6 Thomson Gateway
Configure
The System Configuration Configure page allows you to change your current configuration.
GUI
This page consists of the following sections:
Service Configuration:
Click Configuration Wizard to edit the service settings of your Thomson Gateway. The Easy Setup wizard
will be launched. For more information, see ” Setting up your Thomson Gateway” on page 45
Time Configuration:
Select Auto-configuration if you want the Thomson Gateway to use a dedicated Network Time
Protocol (NTP) Server to synchronize its clock to. The following settings can be configured:
Timezone:
Choose your geographical timezone.
Summer Time:
Enable/disable time adjustment in regions where daylight saving is applicable.
Time Server 1..5:
Dedicated time server(s) for the Thomson Gateway to synchronize with.
Clear Auto-configuration to configure the Thomson Gateway time settings manually.
44
The following settings can be configured:
Date (dd-mm-yyyy):
Current date
Time (hh:mm:ss):
Current time
Timezone:
Geographical timezone
E-DOC-CTC-20090507-0002 v1.0
Page 51

6 Thomson Gateway GUI
Summer Time:
Enable/disable time adjustment in regions where applicable
Click Apply to apply and save your settings.
Setting up your Thomson Gateway
The Easy Setup wizard helps you to configure your Thomson Gateway Internet connection.
Proceed as follows:
1 In the Pick a task list, click Set up. The embedded Easy Setup wizard appears:
2 Click Next.
3 The following window invites you to select the appropriate service for your Internet connection:
In the Select a service list, select the service specifiied by your Serivce Provider and click Next to
continue.
4 Subsequent screens will guide you through the configuration setup of your Thomson Gateway. Follow
the instructions and enter the required information whenever needed. The requested information will
depend on the selected Service profile and should be provided by your Service Provider.
Click Next whenever requested.
E-DOC-CTC-20090507-0002 v1.0
45
Page 52

6 Thomson Gateway
5 Easy Setup will update the Thomson Gateway configuration according to the service profile.
6 As soon as the Easy Setup wizard completed the update of the Thomson Gateway configuration, the
following window appears:
GUI
46
Click Finish to close the Easy Setup wizard.
E-DOC-CTC-20090507-0002 v1.0
Page 53

6 Thomson Gateway GUI
Returning to Factory Default Settings
The Reset to Factory Defaults page allows you to return to the initial configuration of your Thomson
Gateway.
All changes you have made to the configuration will be deleted. If you want to save your current
configuration, see ”2.3 Backing Up/Restoring your Configuration” on page 16.
If you reset your Thomson Gateway to factory default settings, all wireless and broadband
connections may be disconnected permanently after reboot (other settings) or briefly interrupted
during the reboot.
Proceed as follows:
1 In the Pick a task list, click Return to Factory Default Settings.
2 The following page appears:
3 Click Yes, reset my Thomson Gateway.
Saving or Restoring Configuration
The Backup & Restore page allows you to:
Save your current configuration.
Restore a previously saved configuration.
For more information, see ”2.3 Backing Up/Restoring your Configuration” on page 16.
E-DOC-CTC-20090507-0002 v1.0
47
Page 54

6 Thomson Gateway
Firmware upgarde
This Firmware Upgrade page allows you to upgrade the Thomson Gateway with a firmware which is located
on your computer.
Proceed as follows:
1 In the Pick a task list, click Firmware Upgrade.
2 Click Browse. Browse to the firmware on your local computer and open it.
3 Click Apply. The Thomson Gateway upgrades your firmware.
GUI
48
E-DOC-CTC-20090507-0002 v1.0
Page 55

6 Thomson Gateway GUI
6.1.3 Event Logs
Introduction
The Event Logging page summarises the last events recorded on your Thomson Gateway.
The first entry is the most recent recorded event.
Recorded Events
The Recorded Events table gives you an overview of the last event logs that have been recorded since the
Thomson Gateway was turned on. You can perform the following actions:
Click Download to save the event logs to a location of your choice.
Click Clear to clear the event logs.
Click Refresh to refresh the Event Logging page.
E-DOC-CTC-20090507-0002 v1.0
49
Page 56

6 Thomson Gateway
6.2 Broadband Connection
The Broadband Connection page
The Broadband Connection page gives you a short status overview of the broadband connections and the
Internet service(s) configured on your Thomson Gateway.
GUI
Click:
View more to see more information on the corresponding broadband connection.
Connect/Disconnect to establish/terminate a dial-up connection.
The Broadband Connection menu
In the Broadband Connection menu, you can find the following items:
Click... To...
Broadband Connection View all information on the DSL connection configured on your Thomson
Gateway.
Internet Services View basic information on the Internet service(s) configured on your
Thomson Gateway.
Tas ks
On the Broadband Connection page you can carry out following tasks:
Checking connectivity to the Internet
50
E-DOC-CTC-20090507-0002 v1.0
Page 57

6.2.1 Broadband Connection
Overview
The DSL Connection Overview page displays basic DSL Link Information:
Uptime:
Time since the DSL link is up for this session.
DSL Type:
Type (modulation) of DSL line.
Bandwidth (Up/Down):
Available up- and downstream bandwidth in kilobits per second (kbps).
Data Transferred (Sent/Received):
Total amount of data sent and received during this session in kilobyte (kB).
6 Thomson Gateway GUI
Details
The DSL Connection Details page displays all DSL Link Information:
Besides the same information as on the Overview page, the following information is also displayed:
Output Power (Up/Down) in dBm
The Output Power in dBm (up and downstream direction).
Line Attenuation (Up/Down) in dB
The Line Attenuation in dB (up and downstream direction).
SN Margin (Up/Down)
The Signal to Noise (SN) margin in dB (up and downstream direction).
E-DOC-CTC-20090507-0002 v1.0
51
Page 58

6 Thomson Gateway
Vendor ID (Local/Remote)
The Vendor ID of the equipment at the local (i.e. the Thomson Gateway) and remote (Central Office) side.
Loss of Link (Local/Remote)
The number of times "Loss of link" is occurred. This is an indication of how many times the link to the CO
is lost on the physical layer. This is displayed for both the local and remote side.
Error Seconds (Local/Remote)
The time in seconds (accumulated) of error indications occured on the line. This is displayed for both the
local and remote side.
FEC Errors (Up/Down)
The amount of Forward Error Correction (FEC) errors (up and downstream direction).
CRC Errors (Up/Down)
The amount of Cyclic Redundancy Check (CRC) errors (up and downstream direction).
HEC Errors (Up/Down)
The amount of Header Error Correction (HEC) errors (up and downstream direction).
GUI
52
E-DOC-CTC-20090507-0002 v1.0
Page 59

6 Thomson Gateway GUI
6.2.2 Internet Services
Introduction
The Internet Services page displays the following basic information on the Internet service(s) configured on
your Thomson Gateway:
Uptime
Data Transferred
Click View more on the corresponding service to view the Internet service settings of this Internet service.
Overview
The Internet Service Settings Overview page displays the following basic information:
Connection Information:
Uptime:
Displays the time since the Internet service is up for this session.
Data Transferred:
Displays the total amount of data sent and received during this session in kilobyte (kB).
TCP/IP Settings:
IP Address:
Displays the IP address of this Internet connection.
Default Gateway:
Displays the IP address of the remote peer of this Internet connection.
Primary DNS and Secondary DNS:
Displays the IP address of the primary and secondary DNS of this Internet connection.
E-DOC-CTC-20090507-0002 v1.0
53
Page 60

6 Thomson Gateway
Details
The Internet Service Settings Details page displays all information of this Internet service:
GUI
In addition to the information shown on the Overview page, the following fields are added:
Connection Settings:
PVC Info (VPI.VCI)
Typ e, either be “Bridge”, “PPPoE”, “PPPoA” and etc.
PPP Settings (only applicable for PPP connections):
Username and Password:
Displays the username and password of your Internet account.
Connection Mode:
Displays the PPP connection model, either be “Always-On”, “On-Demand” or “Manual”.
Connecting or disconnecting
If you configured a dial-up connection, you can establish/terminate the connection by clicking the Connect/
Disconnect button.
54
E-DOC-CTC-20090507-0002 v1.0
Page 61

6 Thomson Gateway GUI
Checking connectivity to the Internet
On the Connectivity Check page, you can check if your Internet connection is working correctly.
Proceed as follows:
1 In the Pick a task list, click Check connectivity to the Internet.
2 In the Internet Service to Check list, click the Internet service that you want to check (default setting =
Internet).
3 Click Check Connectivity. The following items are checked if applicable:
DSL line
ATM i n t e r f a c e
Ethernet interface
PPP connectivity
4 The Thomson Gateway lists the test results.
If a test is successful, you will get a green check mark. If a test fails you will get a red cross.
E-DOC-CTC-20090507-0002 v1.0
55
Page 62

6 Thomson Gateway
6.3 Toolbox
The Toolbox page
The Toolbox page gives you an overview of the available services and their current status. To go to the
corresponding Web page of a service, click the applicable service.
GUI
The Toolbox Menu
In the Too lb ox menu, you can find the following items:
Click... To...
Remote Access/Assistance Make your Thomson Gateway accessible for remote support (temporary or
permenant).
Game & Application
Sharing
Parental Control Block/allow access to specific Web sites.
Firewall Configure the Thomson Gateway Stateful Inspection Firewall.
Intrusion Detection View the intrusions you are protected against.
Dynamic DNS Assign a dynamic DNS host name to your broadband connection(s).
Dynamic Routing Allow the automation of static routing maintenance.
User Management Manage the users configured on your Thomson Gateway.
Share services and games that you run in your private network towards the
Internet.
56
E-DOC-CTC-20090507-0002 v1.0
Page 63

6 Thomson Gateway GUI
6.3.1 Remote Access/Assistance
Introduction
The Remote Access/Assistance page allows you to make your Thomson Gateway accessible for remote
support. Remote assistance implies one remote assistance session while remote access can be used for
multiple remote assistance sessions.
Before you can enable remote assistance, you must be connected to the Internet.
Enabling Remote Access/Assistance
Proceed as follows:
1 Complete and check the following parameters:
Mode:
Permanent Mode (Remote Access)
The remote session ends when the remote user ends the session or after restarting your
Thomson Gateway.
Temporary Mode (Remote Assistance)
The remote session will be automatically disabled, after 20 minutes of inactivity or on reboot.
URL
A remote user can access your Thomson Gateway via the specified URL.
User name and Password
This user name and password are needed to access your Thomson Gateway remotely. If desired, you
can change the automatically generated password in the Password text box.
2 Click Enable Remote Access/Assistance to pass your parameters to your technical support, in order for
them to be able to access your Thomson Gateway.
Once a remote authenticated session started, no other remote sessions can be started on the
Thomson Gateway.
It is now possible for a remote user to access your Thomson Gateway via the specified URL using the
provided user name and password.
You can replace the IP address in this URL by the dynamic DNS host name if you enabled and
configured dynamic DNS (+ link). For more information, see ”6.3.6 Dynamic DNS” on page 70.
Example: https://141.11.249.150:51003 can be replaced by https://dummy.dyndns.org:51003
E-DOC-CTC-20090507-0002 v1.0
57
Page 64

6 Thomson Gateway
Disabling Remote Access/Assistance
To disable remote access/assistance, click Disable Remote Access/Assistance.
GUI
58
E-DOC-CTC-20090507-0002 v1.0
Page 65

6 Thomson Gateway GUI
6.3.2 Game & Application Sharing
Overview
The Game & Application Sharing Overview page consists of the following sections:
Universal Plug and Play:
Displays Universal Plug and Play settings of your Thomson Gateway.
Assigned Games & Applications:
Displays an overview of all assigned Games & Applications. These are applications or games installed on
a specific local host on your network, for which the Thomson Gateway should accept inbound initiated
connections coming from the Internet.
For each game or application that has been assigned to a host, you can:
Click on its name to see its Game or Application Definition. For more information, see ” Game or
application definition” on page 63.
Click on the name of the assigned device to see more information about it. For more information, see
”6.4.1 Devices” on page 77.
Each game or application is only allowed to be assigned to one computer. The host should be
on default port.
E-DOC-CTC-20090507-0002 v1.0
59
Page 66

6 Thomson Gateway
Configure
The Game & Application Sharing Configure page consists of the following components:
GUI
Universal Plug and Play:
This section allows you to enable/disable UPnP on your Thomson Gateway.
UPnP provides NAT-Traversal: UPnP aware applications on a computer will automatically create HyperNAT entries on the Thomson Gateway for incoming traffic on the protocol ports this type of traffic needs.
As a consequence these applications are able to traverse the Thomson Gateway without the need for
extra and manual configuration.
To enable/disable UPnP, proceed as follows:
1 Select/clear the Use UPnP check box.
2 Click Apply.
UPnP is an architecture for transparent peer-to-peer connectivity of computers, intelligent
appliances, and (wireless) devices. It enables seamless operation of a wide range of games and
messaging applications.
Assigned Games & Applications:
This section allows you to:
Assign a game or application to a specific network device.
Proceed as follows:
1 In the Game or Application list, click the game or application that you want to assign.
2 In the Device list, click the device that you want to assign the game or application to.
3 Click Add.
Edit an existed assignment.
Proceed as follows:
1 Click Edit next to the game or application that you want to edit.
2 In the Device list, click the device that you want to assign the game or application to.
3 Click Apply.
Delete the assignment of the game or application to a local host, click Unassign next to the game or
application you want to unassign.
60
E-DOC-CTC-20090507-0002 v1.0
Page 67

6 Thomson Gateway GUI
Creating a new game or application
Proceed as follows:
1 In the Pick a task list, click Create a new game or application.
2 The New Game or Applications page appears:
3 In the Name box, type the name of the game or application.
4 Click:
Clone Existing Game or Application, if you want to start from the port mappings of an existing game
or application.
Manual Entry of Port Maps, if you want to configure the port mapping for this game or application
manually.
5 Click Next.
6 The Thomson Gateway creates the game or application sharing entry and guides you to the Game or
Application Definition Configure page to configure the port mappings for this game or application. For
more information, see ” Game or application definition” on page 63.
7 Enter each necessary port mapping in the Game or Application Definition section.
8 Click Add.
E-DOC-CTC-20090507-0002 v1.0
61
Page 68

6 Thomson Gateway
Defined games & applications
Proceed as follows:
1 In the Pick a task list, click Modify a game or application.
2 The Defined Games & Applications page appears:
GUI
62
This page gives you an overview of the games and applications defined on your Thomson Gateway. Each
game or application can be assigned to a device on your local network.
If you want to:
View the definition of a game or application, click on its name. For more information, see ” Game or
application definition”.
View information about a device assigned to a game or application, click on its name. For more
information, see ”6.4.1 Devices” on page 77.
Change the name or port mappings of a game or application, click the Edit link of the game or
application.
The Thomson Gateway guides you to the Game or Application Definition Configure page to
configure the name and/or port mappings for this game or application. For more information, see
” Game or application definition” on page 63.
Remove a game or application from your Thomson Gateway, click the Delete link of the game or
application.
E-DOC-CTC-20090507-0002 v1.0
Page 69

6 Thomson Gateway GUI
Game or application definition
On the Game or Application Definition Overview page, you can find an overview of the port mappings used
to allow this game or application to be initiated from the Internet.
A game or application definition consists of one or more TCP/UDP port ranges. Each incoming port range can
be translated into a different internal (local network) port range. Port ranges can be statically assigned to
devices or dynamically assigned using an outgoing trigger.
Consult the user guide or support pages of your game or application to know which ports are being
used by this application.
The Game or Application Definition Configure page allows you to:
Under Game or Application Name:
Change the name of the game or application, proceed as follows:
1 Fill in the New Name field.
2 Click Apply.
Under Game or Application Definition:
Add a port mapping, proceed as follows:
1 In the Protocol list, click the protocol the game or application uses. Any is the default value meaning
both UDP and TCP are used.
2 In the Port Range box, type the port range the game or application uses.
3 In the Translate To box, type the start port of the range to which the Thomson Gateway has to
translate the ports specified under Port Range. If you leave this box empty the same range is used as
for the Port Range.
E-DOC-CTC-20090507-0002 v1.0
The start port is mandatory. You can leave the end port blank when necessary. This
results in a port range equal to one port being the the start port number.
63
Page 70

6 Thomson Gateway
4 If you want to make a dynamic translation rule (optional) you must specify a Trigger Protocol and
Trigger Port.
As soon as the Thomson Gateway receives outgoing traffic on this trigger port, it will
activate this translation rule. The mapping will be added dynamically in an internal
table of the device and will exist only for the lifetime of this connection.
5 Click Add.
Edit a port mapping, proceed as follows:
1 Click Edit on the port mapping you want to edit.
2 Make the necessary changes.
3 Click Apply/Add.
Remove a port mapping:
Click Delete on the port mapping you want to remove.
It is not possible to edit/delete the game or application that has been assigned to a computer.
Always make sure that the assigned IP address is unique in the network.
GUI
64
E-DOC-CTC-20090507-0002 v1.0
Page 71

6 Thomson Gateway GUI
6.3.3 Parental Control
Introduction
Parental Control can be done:
Based on the Web site’s address (URL), also known as address-based filtering.
Overview
The Overview page displays the current parental control settings.
The status of Address Based Filter, being enabled (Yes ) or disabled (No).
What action has to be carried out for unknown sites in case address based filtering is enabled:
Those sites are either Allowed or Blocked.
An overview of all of the address based filtering rules in case address based filtering is enabled.
The table informs whether a specific web site is Allowed or Blocked .
Configure
On the Configure page, you can restrict access to specific pages based on their URL.
You are allowed to:
Enable/disable Address Based Filtering, proceed as follows:
E-DOC-CTC-20090507-0002 v1.0
65
Page 72

6 Thomson Gateway
1 Select/clear the Use Address Based Filter check box.
2 Click Apply.
If your administrator account is configured as default user, make sure you configure a
password for this account or change the default user. Otherwise any user on your local network
can browse to your Thomson Gateway to disable your filtering rules.
For more information, see also ”6.3.8 User Management” on page 73 and ” Adding a new
user” on page 75.
Add Address Based Filtering rules:
Before you can perform the following actions, make sure that Address Based Filtering is enabled.
Block all Web sites and allow some Web sites, proceed as follows:
1 In the Action for unknown sites list, select Block.
2 Click Apply.
3 In the Web Site text box type the URL of the Web site you want to allow.
4 In the Action list, select Allow.
5 Click Add.
6 Repeat steps 3 to 5 for every URL you want to allow.
Allow all Web sites and block some Web sites, proceed as follows:
1 In the Action for unknown sites list, select Allow.
2 Click Apply.
3 In the Web Site text box type the URL of the Web site you want to block.
4 In the Action list, select Block.
5 Click Add.
6 Repeat steps 3 to 5 for every URL you want to block.
Edit or delete Address Based Filtering rules:
To delete or edit a address based filtering rule, click respectively Edit or Delete after the rule you want to
edit or delete.
GUI
66
E-DOC-CTC-20090507-0002 v1.0
Page 73

6 Thomson Gateway GUI
6.3.4 Firewall
Introduction
The firewall allows you to secure traffic from, through and to the Thomson Gateway. There are different
security levels, depending on the degree of security you need.
Overview
The Overview page summarizes the overall security policy configured on your Thomson Gateway.
To view the details of the active security level, click Details... . For more information, see ” Security level
settings” on page 68.
Configure
On the Configure page, you can select one of the predefined security levels of the Thomson Gateway.
To activate a firewall security level, proceed as follows:
1 In the Security Level list, select a security level.
2 Click Apply.
E-DOC-CTC-20090507-0002 v1.0
67
Page 74

6 Thomson Gateway
Security Levels
Following describes all of the predefined security levels:
BlockAll:
All traffic from and to the Internet is blocked. Game and Application Sharing is not allowed by the
firewall.
Although BlockAll should block all connections, some mandatory types of traffic such as
DNS will still be relayed between LAN and WAN by the Thomson Gateway.
Standard:
All outgoing connections are allowed. All incoming connections are blocked, except for inbound
connections assigned to a local host via Game and Application Sharing.
Disabled: (This is the default firewall level)
All in- and outgoing traffic is allowed to pass through your Thomson Gateway, including Game and
Application Sharing.
The firewall levels only have impact on traffic passing through your Thomson Gateway. This
means that the handling of traffic directly appointed from and to Thomson Gateway is independent
of the selected firewall level. The Thomson Gateway itself is always protected, even if you disable
the firewall.
GUI
Protocol checks will be performed on all accepted connections, irrespective of the chosen level.
It is not possible to deactivate the firewall completely via the GUI.
Security level settings
The Security Level Settings page displays the overview of the different firewall rules of the active security
level.
Under Firewall Settings, you can find following details:
The status of the firewall rule: either enabled or disabled.
The Name of the rule.
The Action that is applied on the traffic when the rule is valid.
Traffic blocked is indicated with a red cross, while traffic allowed with a green check mark.
The Source and Destination interface or IP address (range) to which the rule applies.
The protocol or Thomson Gateway Service (Any/ftp/dns...) for which the rule applies.
The number of Hits (number of times that the rule was applied to traffic).
68
E-DOC-CTC-20090507-0002 v1.0
Page 75

6 Thomson Gateway GUI
6.3.5 Intrusion Detection
Introduction
Your Thomson Gateway protects your network against malicious intrusions. The Intrusion Detection page
shows you the intrusions you are protected against.
Enabling Intrusion Detection
Proceed as follows:
1 Under Firewall Options, select the check box(es) of the Intrusion Name(s) you want to block.
2 Click Apply.
E-DOC-CTC-20090507-0002 v1.0
69
Page 76

6 Thomson Gateway
6.3.6 Dynamic DNS
Overview
The Dynamic DNS Service Overview page displays the configuration of dynamic DNS.
Under Configuration, the following items are displayed:
Use DynDNS:
Informs whether the service is enabled (Yes ) or not (No).
Internet Service:
Informs the Interface on which the dynamic DNS service is enabled.
User name:
The user name you are registered with at the dynamic DNS service provider.
Password:
The password you are registered with at the dynamic DNS service provider.
Dynamic DNS service:
The dynamic DNS service that is active.
Host(s):
The hostname(s) which will be redirected to you current IP address (and informs their update status).
GUI
70
E-DOC-CTC-20090507-0002 v1.0
Page 77

6 Thomson Gateway GUI
Configure
On the Dynamic DNS Service Configure page, you can assign a dynamic DNS host name to an Internet
connection.
Before you start configuring the dynamic DNS service, you have to create an account at a dynamic
DNS service provider of your choice, for example:
www.dyndns.com
www.no-ip.com
www.dtdns.com
A dynamic DNS service provided by your ISP.
To configure the dynamic DNS service, proceed as follows:
1 Select the Enabled check box.
2 Type the Username and Password of your dynamic DNS service account.
3 In the Service list, click your dynamic DNS service provider.
4 In the Host text box, type the host name you want to assign to this interface (for example Thomson
Gateway.dyndns.org), as registered at the dynamic DNS service provider.
5 Click Apply.
E-DOC-CTC-20090507-0002 v1.0
71
Page 78

6 Thomson Gateway
6.3.7 Dynamic Routing
Introduction
Dynamic Routing can be used to cache routes learned by routing protocols, thus allowing the automation of
static routing maintenance. The Thomson Gateway, using the RIP (Routing Information Protocol) protocol,
determines the network packet's route based on the fewest number of hops between the source and the
destination. In this case, you can allow the Thomson Gateway to automatically adjust its ranking to physical
changes in the network layout.
GUI
Enabling Dynamic Routing
Proceed as follows:
1 Choose the following parameters:
Working Mode:
Choose the function mode of the Thomson Gateway: working as either a Router or a Gateway.
Listen Mode:
Enable this mode to allow RIP server to receive routing information and updating the routing
information. You can choose among the three types of Routing Information Protocol: RIP1, RIP2 or
Both(RIP1+RIP2).
Supply Mode:
Enable this mode to allow RIP server to send routing information and updating the routing
information. You can choose among the three types of Routing Information Protocol: RIP1, RIP2 or
Both(RIP1+RIP2).
2 Click Apply.
72
E-DOC-CTC-20090507-0002 v1.0
Page 79

6 Thomson Gateway GUI
6.3.8 User Management
Introduction
The User Management page gives you an overview of the currently configured users and their privileges.
On this page, you can:
Change password:
Click Change Password to change the password of the selected user account. For more information, see
” Changing the password”.
Edit a user.
Click Edit to change a user account. For more information, see ” Editing a user”.
Add a user.
Click Add User to create a new user account. For more information, see ” Adding a new user”.
Delete a user.
Click Delete to remove a user.
User Types
The table below shows the different types of users and their privileges:
User Type Privileges
Administrator This user can perform any service via any access channel from LAN or Local origin
only.
Poweruser This user has read access to the GUI (Service/overview pages) via HTTP or HTTPS
access channel from LAN origin only.
User This user has read access to the limited GUI (Overview pages/part of the services in
Toolbox) via HTTP or HTTPS access channel from LAN origin only.
E-DOC-CTC-20090507-0002 v1.0
73
Page 80

6 Thomson Gateway
Changing the password
Proceed as follows:
1 Click Change Password after the user you want to edit on the User management page, the Change
Password page appears:
2 Fill in the Old Password box with the current password of the user account your are currently logged on
with.
By default no password is defined. In this case, leave the Old Password box blank.
GUI
3 Fill in the New Password and Confirm New Password boxes with the desired new password for the user
account your are currently logged on with.
You can configure an account with a blank password by leaving the New Password and
Confirm New Password boxes blank.
4 Click Change Password to confirm.
Editing a user
Proceed as follows:
1 Click Edit after the user you want to edit on the User management page, the following page appears:
74
2 Edit the user name in the User Name textbox.
3 Select the administration right from the User privilege dropdown list.
4 Click Apply.
E-DOC-CTC-20090507-0002 v1.0
Page 81

6 Thomson Gateway GUI
Adding a new user
Proceed as follows:
You can only add users with less than or equal administration rights as yourself.
1 On the User Management page, click Add User, the following page appears:
2 In the Login Account table, you can configure:
The Name of the new user.
The User Privileges of the new user.
3 Click Apply to confirm.
Switching to another user
Proceed as follows:
1 In the Pick a task list, click Switch to another user.
A pop-up window appears:
2 Fill in the user name of the user account you want to switch to and its corresponding password.
3 Click OK.
E-DOC-CTC-20090507-0002 v1.0
75
Page 82

6 Thomson Gateway
6.4 Home Network
The Home Network page
The Home Network page summarises your Thomson Gateway network configuration (all interfaces and
detected devices).
GUI
You can find an overview of the following interfaces:
Wireless (only in case of a WLAN)
Ethernet
The detected devices and interfaces are indicated with a corresponding icon.
The Home Network menu
In the Home Network menu, you can find the following items:
Click... To...
Devices View/configure the devices detected on your local network.
Interfaces View/configure the interfaces that are available on your Thomson Gateway.
76
E-DOC-CTC-20090507-0002 v1.0
Page 83

6 Thomson Gateway GUI
6.4.1 Devices
Overview
The Local Network Devices Overview page summarises all devices that are connected to the Thomson
Gateway network.
Click on a device name to get more information on a specific device.
The first detected device in the list is the Thomson Gateway itself.
Previously connected devices that are currently not connected are displayed with a blue
background.
Device settings
The Device Settings page displays the following parameters:
Under Information:
Status:
Displays whether the device is currently connected to the Thomson Gateway network or not.
Typ e:
Displays the device type (default: generic device).
Connected To:
Displays the interface to which the device is currently connected.
Under Addressing:
E-DOC-CTC-20090507-0002 v1.0
77
Page 84

6 Thomson Gateway
Physical Address:
Displays the MAC address of the device.
IP Address Assignment:
Displays whether the device is using a static or dynamic IP address.
IP Address:
Displays the IP address of the device.
DHCP Lease Time (if applicable):
Displays the time for which the client can use this IP address.
Under Connection Sharing:
You can view the games or services that are currently assigned to this device. Click the name of the game
or service to view the used port mappings (For more information, see ” Game or application definition”
on page 63).
GUI
Assigning the public IP address of a connection to a device
You can assign the public IP address of your Internet Connection(s) to a specific device on your local network.
You might want to do this if:
You encounter issues with some applications through the Network Address Translation engine of your
Thomson Gateway.
This device is running server applications (Web server, ...) and you want it to be accessible from the
Internet.
You can also achieve this by creating a port mapping for the specified server, as described in
”6.3.2 Game & Application Sharing” on page 59.
This device has to be considered as the unique access point to your local network (DMZ).
Be aware that the device to which you assign the public IP address will lose all security offered by
the Thomson Gateway.
Proceed as follows:
1 In the Pick a task list, click Assign the public IP address of a connection to a device.
2 Click the Edit link of your Internet connection.
3 In the Device list, select the device you want to assign the public address to and click Apply.
4 Release and renew the IP address of the device.
78
E-DOC-CTC-20090507-0002 v1.0
Page 85

6 Thomson Gateway GUI
6.4.2 Interfaces
Introduction
The Interfaces page gives you an overview of the interfaces available on your Thomson Gateway.
Viewing and configuring LAN interface
If you want to know more about the network settings of the LAN interface, click on LocalNetwork. For
more information, see ” Interface Settings” on page 79.
Viewing and configuring Wireless Access Point
To view and configure your wireless access point under LocalNetwork, click your wireless access point.
The wireless Access Point has the following format: “WLAN: “ + Network Name (or SSID)”, for
example “WLAN: Thomson1ABC23”.
For more information, see ” Wireless Access Point Settings” on page 81.
Interface Settings
The Interface settings Overview page gives you an overview of the current settings of the interface:
Under Lan IP:
IP Address:
Displays the IP addresses configured on the interface.
IP Subnet Mask:
Displays the subnet mask of the DHCP server’s address pool.
E-DOC-CTC-20090507-0002 v1.0
79
Page 86

6 Thomson Gateway
Host Name:
Displays the host name for the local network.
Domain Name:
Displays the domain name you specified.
DHCP Server:
Indicates the DHCP server is enabled (Yes ) or disabled (No).
Under DHCP Server Parameters:
Address Pool Start IP:
The start IP address of the DHCP server’s address pool.
Address Pool End IP:
The end IP address of the DHCP server’s address pool.
Lease Time:
The time for which the DHCP client is allowed to use the assigned IP address.
Always give same address to DHCP clients:
If you enabled this, the lease time will be automatically set to Infinite.
The Interface settings Configure page allows you to:
GUI
80
Under LAN IP :
Typ e t he IP Address of your choice (for example 10.0.0.138) in the text box.
Specify the Host Name and Domain Name in the text box.
Select/clear the DHCP Server check box to enable/disable DHCP Server on the interface.
Under DHCP Server Parameters:
Typ e t he Address Pool Start/End IP of your choice in the text boxes.
Specify a Lease Time in the text boxes.
Select the Always give same address to DHCP clients check box if you want to make sure that a DHCP
client always gets the same DHCP lease IP address..
Click Apply to save these settings.
E-DOC-CTC-20090507-0002 v1.0
Page 87

6 Thomson Gateway GUI
Wireless Access Point Settings
The Wireless Access Point Overview page displays basic configuration information.
Under Configuration:
Interface Enabled:
Indicates whether the wireless interface is enabled (Yes ) or disabled (No).
Physical Address:
Displays the MAC address of your Thomson Gateway’s wireless access point interface.
Network Name (SSID):
Displays the Network Name or the SSID of your wireless network.
Interface Type:
Displays one of the following interface types (supported interface types depend on Thomson
Gateway variant):
802.11b/g
802.11b/g/n
BandWidth:
The maximum available bandwidth in both up- and downstream direction.
Actual Speed:
Displays the current maximum transmission speed.
Band
Displays the band in which your Wireless Access Point operates.
Under Security:
Security Mode:
Displays the encryption method used by your wireless network.
E-DOC-CTC-20090507-0002 v1.0
81
Page 88

6 Thomson Gateway
The Wireless Access Point Details page displays all of the available configuration information.
Besides the same information as on the Overview page, the following fields are available:
Under Configuration:
Channel Selection:
Displays whether you select a fixed channel yourself (Manual)or the Thomson Gateway selects a
channel for you (Auto).
Region:
Displays your regulatory region.
Channel:
Displays the channel that is currently used by the Access Point (AP).
Extension Channel:
Displays the secondary channel that is used to send and receive data.
Under Wireless Security:
Broadcast Network Name:
Indicates whether your Network Name is broadcasted or not.
GUI
82
E-DOC-CTC-20090507-0002 v1.0
Page 89

6 Thomson Gateway GUI
On the Wireless Access Point Configure page, you can change the configuration details displayed on the
Details page.
Under Configuration:
Interface Enabled:
To enable the wireless access point, select the check box.
Physical Address:
The physical address or MAC address of the wireless access point (your Thomson Gateway) is static and
can not be configured.
Network Name (SSID):
The network name or SSID of your wireless LAN is by default the SSID of your Thomson Gateway as
mentioned on a label. You can change the name of the SSID by typing a new name in the text box.
Interface Type:
The interface type is the specific wireless standard that must be applied in your wireless LAN. This can
either be (supported interface types depend on Thomson Gateway variant):
802.11b/g
Only stations that are configured in 802.11b or 802.11g mode can associate.
802.11b/g/n
All stations that are configured in 802.11b or in 802.11g or in 802.11n mode can associate.
BandWidth:
The maximum available bandwidth in both up- and downstream direction.
Actual Speed:
Displays the current maximum transmission speed and is not configurable.
Band:
Displays the band in which your Wireless Access Point operates and is not configurable.
Channel Selection:
The channel selection allows you to set the channel selection to Automatic (the Thomson Gateway
selects the channel) or you can set is to Manual. When set to Manual, you can select the channel yourself.
E-DOC-CTC-20090507-0002 v1.0
83
Page 90

6 Thomson Gateway
Region:
Displays your regulatory region and is not configurable.
You may only use the Thomson Gateway in the regulatory region mentioned.
Channel:
Displays the channel that is currently used by the Access Point.
When the Channel Selection is set to Automatic this parameter is not configurable.
When the Channel Selection is set to Manual, you can select the channel.
Extension Channel:
Displays the secondary channel that is used to send and receive data.
Under Security:
Broadcast Network Name:
By default the Thomson Gateway broadcasts its network name, allowing you to easily recognize your
wireless network in the list of available networks. Once you have configured your wireless clients, you
can disable this feature by clearing this check box.
Encryption:
Allows you to select an encryption method for your wireless network. The following encryption methods
are supported by the Thomson Gateway:
Disabled:
No encryption level is used.
GUI
It is not recommended to use no encryption level for your wireless network!
WEP Encryption:
To enable WEP encryption, proceed as follows:
1 Select Use WEP Encryption
2 In the WEP Key Length list, click the desired data security level (either 64 bit or 128 bit).
3 In the WEP Encryption key box, type a Network key of your choice. In case of:
64 bit:
The 40-bit Network key must consist of 5 alphanumeric characters or 10 hexadecimal digits.
128 bit:
The 104-bit Network key consists of 13 alphanumeric characters or 26 hexadecimal digits.
4 Click Apply to immediately apply your changes.
5 Configure your wireless client(s) with the same settings.
If your wireless client(s) support(s) WPA-PSK we recommend you to use WPA-PSK,
because WEP encryption has been proven to have some security issues.
WPA-PSK Encryption:
To enable WPA-PSK encryption, proceed as follows:
1 Select Use WPA-PSK Encryption.
2 In the WPA-PSK Encryption Key box, type a pass phrase (also known as Pre-shared key) of your
choice. The pass phrase must consist of 8 to 63 ASCII characters or 64 hexadecimal digits.
84
E-DOC-CTC-20090507-0002 v1.0
Page 91

6 Thomson Gateway GUI
3 In the WPA-PSK Version list, click the desired WPA-PSK version.
WPA2:
WPA2 is the most secure version, but not all wireless clients already support it. Before you select
this version, make sure all of your wireless clients support it.
WPA+WPA2:
If not all of your wireless clients support WPA2 or you are not sure if they support WPA2, we
recommend you to choose WPA+WPA2. Wireless clients that support WPA2 will use WPA2, the
others will use WPA.
WPA:
If none of your wireless clients support WPA2 choose this option.
4 Click Apply to immediately apply your changes.
5 Configure your wireless client(s) with the same settings.
The default WEP key and the default WPA-PSK key are printed on the Thomson Gateway
bottom label.
Before configuring the Thomson Gateway encryption, make sure you know which
encryption methods are supported by your wireless client.
E-DOC-CTC-20090507-0002 v1.0
85
Page 92

6 Thomson Gateway
GUI
86
E-DOC-CTC-20090507-0002 v1.0
Page 93

7 Troubleshooting
7 Troubleshooting
Introduction
This chapter suggests solutions for problems you may encounter while installing or configuring your
Thomson Gateway.
If the suggestions do not resolve the problem, look at the support pages on http://www.thomson.net
contact your service provider.
Topics
This chapter describes the following topics:
Topi c Page
General Thomson Gateway Troubleshooting 88
Reset to Factory Defaults 91
or
E-DOC-CTC-20090507-0002 v1.0
87
Page 94

7 Troubleshooting
7.1 General Thomson Gateway Troubleshooting
None of the lights light up (Thomson Gateway does not work)
Make sure that:
The Thomson Gateway is plugged into a power socket outlet.
You are using the correct power supply for your Thomson Gateway device.
The power requirements for your Thomson Gateway are clearly indicated on the identification
label on the bottom of the Thomson Gateway. Only use the power adaptor supplied with your
Thomson Gateway.
The Thomson Gateway is turned on via the push button or rocker switch on the back panel.
The Broadband LED does not light up
Make sure that:
The DSL cable is correctly connected. For more information, see “1.2 Installing your Thomson Gateway“.
The DSL service is enabled on your telephone line. For more information, contact your Internet Service
Provider.
The Internet LED does not light up
Make sure that your user name and password are correct.
Proceed as follows:
1 Browse to the Thomson Gateway GUI.
2 On the Broadband menu, click Internet Services.
3 Under Internet, click View More.
4 Check your user name and password.
5 If your password was not correct, re-enter your password.
6 Click Connect.
Thomson Gateway unreachable
If your Thomson Gateway cannot be reached due to misconfiguration, you might consider a hardware reset
to factory defaults as described in “7.2 Reset to Factory Defaults“ on page 91.
Poor Thomson Gateway performance
Make sure that the Thomson Gateway is installed and configured as instructed in “1 Installation“ on page 3
or as instructed by the Service Provider.
88
E-DOC-CTC-20090507-0002 v1.0
Page 95

7 Troubleshooting
7.1.1 Wired Connection Troubleshooting
Ethernet LED does not light up
Make sure that:
The Ethernet cable is securely connected to the Ethernet port on your Thomson Gateway and your
computer.
You are using the correct cable type for your Ethernet equipment, that is at least UTP CAT5 with RJ-45
connectors.
E-DOC-CTC-20090507-0002 v1.0
89
Page 96

7 Troubleshooting
7.1.2 Wireless Connection Troubleshooting
No Wireless Connectivity
Make sure that:
Both the wireless client adapter and the Thomson Gateway are allowed to connect through wireless
channels as defined for local regulatory domain.
The wireless client is configured for the correct wireless settings (SSID, security settings).
Check the signal strength, indicated by the wireless client manager. If the signal is low, try repositioning
the Thomson Gateway or directing the Thomson Gateway’s antenna(s) for optimal performance.
Make sure that the wireless client adapter is enabled (message like “radio on”).
Poor Wireless Connectivity or Range
Try the following:
Change the wireless channel.
Make sure both the wireless client adapter and the Thomson Gateway are allowed to connect through
wireless channels as defined for local regulatory domain.
Check the location of the Thomson Gateway in the building.
Check the signal strength, indicated by the wireless client manager. If the signal is low, try to place the
Thomson Gateway or to direct the Thomson Gateway’s antenna(s) for optimal performance.
Use WPA(2)-PSK as encryption.
For more information, see “3.3 Securing Your Wireless Connection“ on page 21.
Change the wireless channel
Proceed as follows:
1 Browse to the Thomson Gateway GUI.
2 On the left menu, click Home Network.
3 Under Wireless, click your access point.
Your access point will be listed in the following format: “WLAN:<Network Name> (<Actual
Speed>)”. For example, WLAN: Thomson83C7C7 (54Mbps).
4 The Wireless Access Point page appears.
5 In the Location bar, click Configure.
6 Under Configuration, select the channel of your choice in the Channel Selection list.
7 Click Apply.
Can not connect via WPS
If you are having trouble connecting your wireless client via WPS, try to configure it manually. For more
information, see “3.2 Connecting Your Wireless Client without WPS“ on page 20.
90
E-DOC-CTC-20090507-0002 v1.0
Page 97

7 Troubleshooting
7.2 Reset to Factory Defaults
Resetting your Thomson Gateway
If at some point you can no longer connect to the Thomson Gateway or you want to make a fresh install, it
may be useful to perform a reset to factory defaults.
Warning
A reset to factory default settings deletes all configuration changes you made. Therefore, after the reset, a
reconfiguration of your Thomson Gateway may be needed.
Also your WLAN clients may have to be re-associated, as described in “3 Wireless Access“ on page 17.
Methods
You can choose between:
Software Reset
Hardware Reset
Software Reset
Proceed as follows:
1 Browse to the Thomson Gateway GUI.
2 On the Thomson Gateway menu, click Configuration.
3 In the Pick a task list, click Reset my Thomson Gateway to default settings.
4 The Thomson Gateway restores the initial configuration and restarts.
5 The Thomson Gateway returns to the Thomson Gateway home page (unless the IP address of your
computer is not in the same subnet as the default IP address of the Thomson Gateway, being
192.168.1.254
).
E-DOC-CTC-20090507-0002 v1.0
91
Page 98

7 Troubleshooting
Hardware Reset
Proceed as follows:
1 Make sure the Thomson Gateway is turned on.
2 Use a pen or an unfolded paper clip to push the recessed Reset button. Push it until the Power LED lights
red - this will take about 7 seconds.
3 Release the Reset button.
4 The Thomson Gateway restarts.
92
E-DOC-CTC-20090507-0002 v1.0
Page 99

Page 100

THOMSON Telecom Belgium
Prins Boudewijnlaan 47
2650 Edegem
www.thomson-broadband.com
© THOMSON 2009. All rights reserved.
E-DOC-CTC-20090507-0002 v1.0.
 Loading...
Loading...