
Fast MicroSEQ™ 500 16S rDNA Identification
USER GUIDE
using:
Fast MicroSEQ™ 500 16S rDNA PCR Kit and
MicroSEQ™ 500 16S rDNA Sequencing Kit
Catalog Numbers 4370489 (PCR kit) and 4346480 (Sequencing kit)
Publication Number 4393007
Revision G
For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures.

Life Technologies Ltd | 7 Kingsland Grange | Woolston, Warrington WA1 4SR | United Kingdom
For descriptions of symbols on product labels or product documents, go to thermofisher.com/symbols-definition.
The information in this guide is subject to change without notice.
DISCLAIMER: TO THE EXTENT ALLOWED BY LAW, THERMO FISHER SCIENTIFIC INC. AND/OR ITS AFFILIATE(S) WILL NOT BE
LIABLE FOR SPECIAL, INCIDENTAL, INDIRECT, PUNITIVE, MULTIPLE, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES IN CONNECTION WITH OR
ARISING FROM THIS DOCUMENT, INCLUDING YOUR USE OF IT.
Revision history: Pub. No. 4393007
Revision Date Description
G 11 January 2021 Update for the launch of the MicroSEQ™ ID Software For SeqStudio™ Genetic Analyzer v1.0 (Cat. No.
F 31 August 2018 Update trademark, legal, and manufacturer information.
A49382).
Update the list of purification products in “Purify extension products” on page 13.
Important Licensing Information: These products may be covered by one or more Limited Use Label Licenses. By use of these
products, you accept the terms and conditions of all applicable Limited Use Label Licenses.
Trademarks: All trademarks are the property of Thermo Fisher Scientific and its subsidiaries unless otherwise specified.
©2021 Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc. All rights reserved.

Contents
■
Product Information .................................................................. 5
Product information ............................................................. 5
Instrument platforms ............................................................ 5
Contents and storage ............................................................ 6
Storage guidelines .......................................................... 6
Required materials not supplied ................................................... 6
■
Methods ............................................................................... 7
Workflow ....................................................................... 7
Collect and prepare samples ..................................................... 8
Important procedural guidelines .............................................. 8
Isolate genomic DNA from samples ........................................... 8
Dilute genomic DNA for PCR ................................................. 9
Amplify the 16S rDNA region ..................................................... 9
Important procedural guidelines .............................................. 9
Prepare the PCR reactions ................................................... 9
Perform the amplification run ................................................ 10
(Optional) Analyze PCR products ............................................ 11
Purify PCR products for cycle sequencing .................................... 11
Perform cycle sequencing ....................................................... 11
Important procedural guidelines ............................................. 12
Prepare cycle sequencing reactions .......................................... 12
Perform the cycle sequencing run ............................................ 12
Purify extension products ................................................... 13
Perform electrophoresis of extension products ..................................... 14
Important procedural guidelines ............................................. 14
Configure the instrument for electrophoresis .................................. 14
Prepare samples and perform electrophoresis ................................. 15
Troubleshooting ................................................................ 16
Frequently asked questions ..................................................... 17
Sensitivity and quantitation ................................................. 17
Sample preparation and storage ............................................. 18
Contamination ............................................................ 18
Overlapping sequences .................................................... 19
PCR product size .......................................................... 19
Fast MicroSEQ
™
500 16S rDNA Identification User Guide
3

Contents
■
■
■
Species libraries ........................................................... 19
Additional documentation ................................................... 20
APPENDIX A Ordering information .............................................. 21
APPENDIX B Additional supported instruments ................................ 23
Electrophoresis settings for additional supported instruments ....................... 23
APPENDIX C Supplemental procedures and guidelines ....................... 24
Good laboratory practices for PCR and RT-PCR ................................... 24
Seal the PCR plate ............................................................. 25
Seal the plate with strip caps ................................................ 25
Seal the plate with adhesive film ............................................. 26
Prevent evaporation during electrophoresis ........................................ 26
Prepare a diluted sample ................................................... 27
Dry-down, then resuspend the sample ....................................... 27
■
APPENDIX D Supplemental product information ............................... 29
MicroSEQ™ system overview .................................................... 29
About MicroSEQ™ ID software and MicroSEQ™ ID Software For SeqStudio
Genetic Analyzer ............................................................. 29
MicroSEQ™ ID proprietary libraries ........................................... 29
Custom libraries ........................................................... 30
MicroSEQ™ ID reports ...................................................... 30
About dye-labeled terminator chemistry .......................................... 33
■
APPENDIX E Safety ............................................................... 34
Chemical safety ................................................................ 35
Biological hazard safety ......................................................... 36
■
Documentation and support ....................................................... 37
Related documentation ......................................................... 37
Customer and technical support ................................................. 37
Limited product warranty ........................................................ 38
™
4
Fast MicroSEQ™ 500 16S rDNA Identification User Guide

IMPORTANT! Before using this product, read and understand the information in the “Safety” appendix
in this document.
Product information
Product Information
The Applied Biosystems™ Fast MicroSEQ™ 500 16S rDNA PCR Kit and the Applied Biosystems
MicroSEQ™ 500 16S rDNA Sequencing Kit provide all of the reagents necessary for the amplification
and sequencing of the first 500 base pairs of the 16S ribosomal RNA gene (rDNA). The DNA sequence
of the unknown is deciphered by capillary electrophoresis on an Applied Biosystems™ Genetic Analyzer.
The FAST PCR technology used in the MicroSEQ™ PCR kits allows identification in 5 hours. MicroSEQ
ID software (3500/3500xL Genetic Analyzer) or MicroSEQ™ ID Software For SeqStudio™ Genetic
Analyzer compares the sequence to the validated MicroSEQ™ 16S rDNA 500 Library, then generates an
identification report. Variations found within the first 500 base pairs of the 16S region are sucient to
identify most bacteria to the species level.
Note: The MicroSEQ™ Full Gene 16S rDNA Identification is recommended if you need a full 16S rDNA
sequence to identify a bacterial species.
Instrument platforms
For optimum performance of the Fast MicroSEQ™ 500 16S rDNA Identification, use the:
•
Veriti™ 96‑Well Thermal Cycler
•
3500/3500xL Genetic Analyzer or SeqStudio™ Genetic Analyzer
For information on older instruments that can also be used, see Appendix B, “Additional supported
instruments”.
™
™
Fast MicroSEQ
™
500 16S rDNA Identification User Guide
5
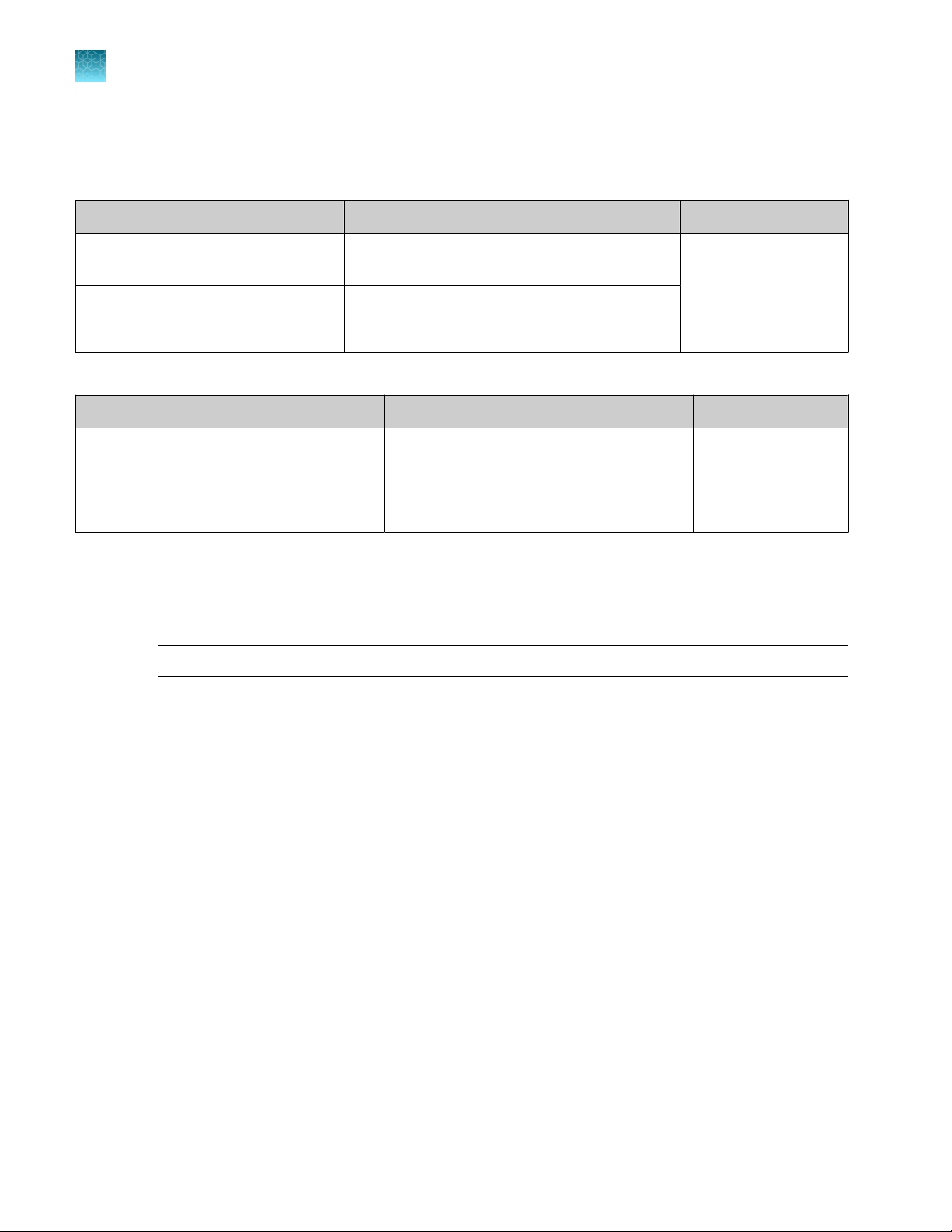
Product Information
Contents and storage
Contents and storage
Table 1 Fast MicroSEQ™ 500 16S rDNA PCR Kit (Cat. No. 4370489)
Contents Amount Storage
FAST MicroSEQ™ 500 16S PCR Master
Mix
Positive Control, E. coli, 1 ng/µL One tube sucient for 5 positive-control assays
Negative Control, water One tube sucient for 5 negative-control assays
Table 2 MicroSEQ™ 500 16S rDNA Sequencing Kit (Cat. No. 4346480)
Contents Amount Storage
MicroSEQ™ 500 16S Forward Sequence Mix Two tubes sucient for a total of 55
MicroSEQ™ 500 16S Reverse Sequence Mix Two tubes sucient for a total of 55
One tube sucient for 50 PCR amplifications On receipt:
reactions
reactions
Storage guidelines
•
Avoid excess freeze‐thaw cycles. Aliquot reagents in smaller amounts, if necessary.
•
Before each use of the kit, allow the frozen reagents to thaw at room temperature or on ice.
IMPORTANT! Do not heat the reagents.
•
Whenever possible, keep thawed reagents on ice during use.
•
Mix the reagents by gently vortexing the tubes. Centrifuge the tubes briefly to collect all liquid at
the bottom of the tube.
–25°C to –15°C
After first use:
2–8°C in a PCR clean
room
–25°C to –15°C
Required materials not supplied
Contact your local MicroSEQ™ ID representative for a list of additional materials and equipment
required.
6
Fast MicroSEQ™ 500 16S rDNA Identification User Guide
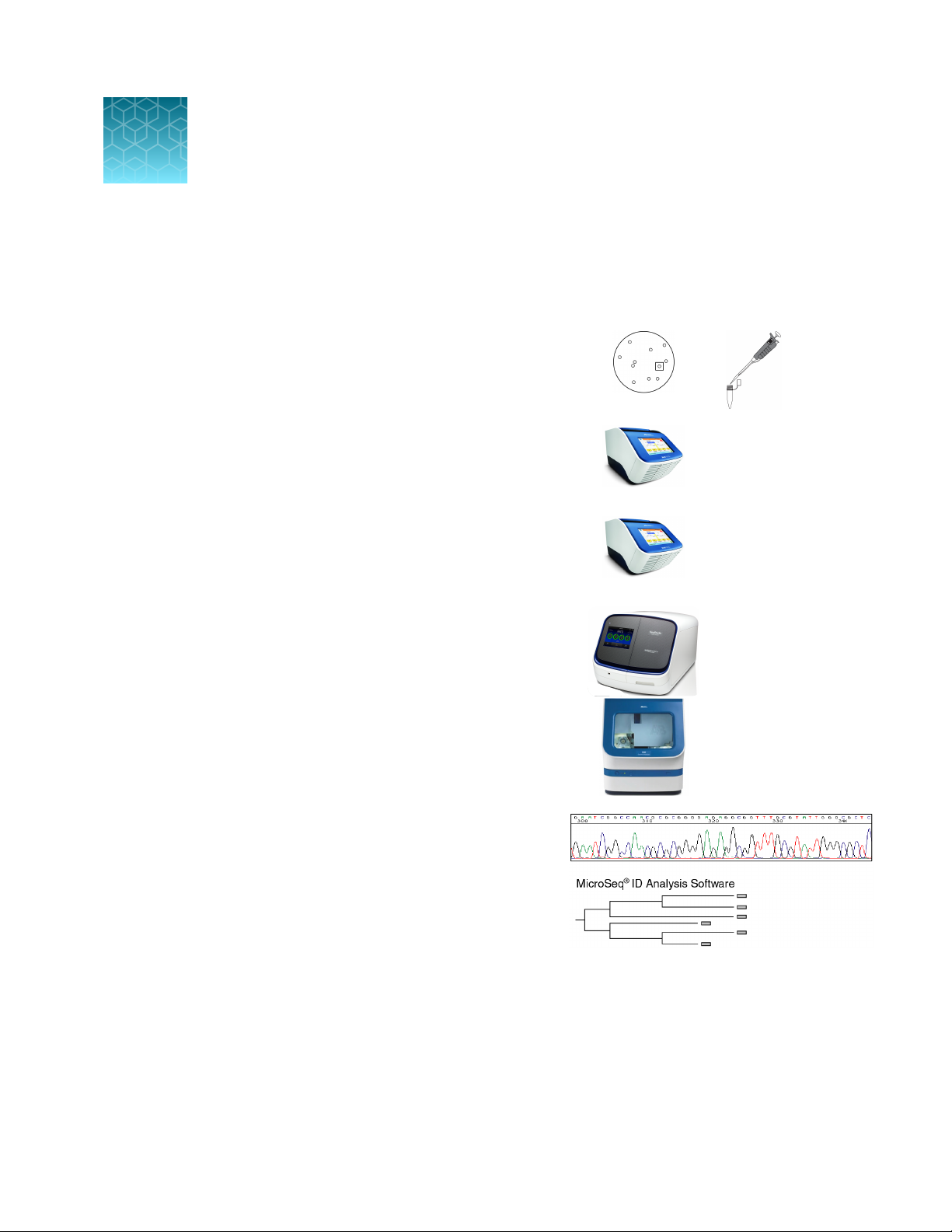
Workflow
Harvest bacterial colony, isolate DNA, then
Methods
Collect and prepare samples
dilute DNA for PCR
q
Amplify DNA
Prepare reactions, perform amplification, analyze PCR
products (optional), then purify PCR products
q
Perform cycle sequencing
Prepare reactions, perform cycle sequencing, then purify
extension products
q
Perform electrophoresis
Configure instrument, then prepare and run samples
q
Analyze data
Veriti™ 96‑Well
Thermal Cycler
Veriti™ 96‑Well
Thermal Cycler
SeqStudio™ Genetic
Analyzer or
3500/3500xL Genetic
Analyzer
Fast MicroSEQ™ 500 16S rDNA Identification User Guide
7
Methods
Collect and prepare samples
Collect and prepare samples
Important procedural guidelines
•
Review “Good laboratory practices for PCR and RT-PCR” on page 24.
•
When the isolated DNA (in PrepMan™ Ultra supernatant) is not in use, store it at −15 to −25°C .
Before use, thaw, then vortex and centrifuge the stored supernatant. Alternatively, cover and store
the supernatant at 4°C for up to 1 month.
Isolate genomic DNA from samples
Isolate bacterial genomic DNA from bacterial colonies using PrepMan™ Ultra Sample Preparation
Reagent. See the PrepMan™ Ultra Sample Preparation Reagent Protocol for additional information.
1.
Obtain the sample, then add PrepMan™ Ultra Sample Preparation Reagent:
If starting from a ...
Culture broth
Culture plate
IMPORTANT! The ideal colony size is 2–3 mm. For smaller colonies, decrease the amount of
PrepMan™ Ultra Sample Preparation Reagent to 50 μL from the 100 μL suggested in the protocol.
2.
Vortex the sample for 10 to 30 seconds.
3.
Heat the sample for 10 minutes at 100°C in a heat block, then cool the sample to room
temperature for 2 minutes.
Follow this procedure ...
1.
Pipet 1 mL of culture broth (containing less than 107 cfu/mL of bacteria) into a new
2-mL screw-cap microcentrifuge tube or any other microcentrifuge tube that can be
tightly closed.
2.
Centrifuge the sample for 2 minutes in a microcentrifuge at maximum speed. Aspirate
and discard the supernatant.
3.
Add 100 µL of PrepMan™ Ultra Sample Preparation Reagent, then close the cap tightly.
1.
Select a small sample amount (2–3 mm) from an isolated colony by using a 1 µL loop
or the straight end of a 1 µL loop.
2.
Suspend the cells in 100 µL of PrepMan™ Ultra Sample Preparation Reagent in a 2-mL
screw-cap microcentrifuge tube or any other microcentrifuge tube that can be tightly
closed.
4.
Centrifuge the sample for 2 minutes in a microcentrifuge at maximum speed.
5.
Transfer 50 µL of the supernatant into a new microcentrifuge tube.
8
Fast MicroSEQ™ 500 16S rDNA Identification User Guide

Dilute genomic DNA for PCR
1.
Pipet 495 μL of nuclease‐free water into a 1.5‐mL microcentrifuge tube.
2.
Add 5 μL of the PrepMan™ Ultra supernatant to obtain a 1:100 dilution.
Note: For samples with low biomass, make a smaller dilution (for example, use 195 μL of
nuclease-free water to make a 1:40 dilution). The minimum recommended dilution for the
PrepMan™ Ultra supernatant is 1:10.
Note: If the PrepMan™ Ultra supernatant is colored (typically a shade of black or green), PCR
inhibition may occur. See “Troubleshooting” on page 16.
Amplify the 16S rDNA region
Important procedural guidelines
•
Select the appropriate tubes or 96‐well plates for your thermal cycler. See your instrument user
guide (available at thermofisher.com).
•
Using strip caps instead of 96-well adhesive plate covers may help reduce cross-contamination.
•
Before preparing the PCR reactions, review “Good laboratory practices for PCR and RT-PCR” on
page 24 and “Storage guidelines” on page 6 for sample and reagent handling instructions.
•
If necessary after performing PCR or purifying PCR products, cover and store the PCR products at
–15°C to –25°C until you are ready to use them.
Methods
Amplify the 16S rDNA region
Note: PCR products are stable for 6 months or longer at –15°C to –25°C.
Prepare the PCR reactions
1.
Vortex the diluted supernatant to mix the tube contents.
2.
Using the volumes that are shown in the table, prepare samples and controls in MicroAmp
reaction tubes or 96‐well plates.
Reaction type
Negative controls
Samples
Positive controls
Volume for one reaction
•
15 μL FAST PCR Master Mix
•
15 μL negative control (provided with kit)
•
15 μL FAST PCR Master Mix
•
15 μL of 1:100 dilution of PrepMan® Ultra supernatant
•
15 μL FAST PCR Master Mix
•
15 μL positive-control DNA (provided with kit)
™
Fast MicroSEQ™ 500 16S rDNA Identification User Guide
9
Methods
Amplify the 16S rDNA region
Note: To help avoid cross‐contamination, we recommend that you pipet components in the
following order: negative controls, samples, positive controls. If possible, leave empty cells
between dierent reaction types.
3.
Use strip caps and the capping tool, or adhesive film and the sealing tool, to cap the tubes or plate
(see “Seal the PCR plate” on page 25). Vortex, centrifuge briefly, then place the tubes or the plate
in the thermal cycler.
IMPORTANT! Apply significant downward pressure on the sealing tool in all steps to form a
complete seal.
Perform the amplification run
1.
Set the appropriate ramp mode for your thermal cycler:
•
Veriti™ 96‑Well Thermal Cycler—Default
Note: To use the default mode, select Browse/New Methods4New, then edit the thermal
cycling conditions. See the Veriti™ 96‑Well Thermal Cycler User Guide for details.
•
(3500/3500xL only) 9800 Fast Thermal Cycler—Fast (F96)
•
(3500/3500xL only) GeneAmp™ PCR System 9700—Maximum (Max)
2.
Set the thermal cycling conditions:
Initial step
HOLD CYCLE HOLD HOLD
95°C
10 seconds
3.
Set the reaction volume to 30 μL, then start the run.
4.
Before removing the caps or adhesive film, briefly centrifuge the tubes or plate.
Each of 30 cycles
Melt Anneal
95°C
0 seconds
15 seconds
64°C
Final extension Final step
72°C
1 minute
Note: Centrifuging helps avoid cross‐contamination from liquid remaining on the caps or plate
covers.
4°C
∞
10
Fast MicroSEQ™ 500 16S rDNA Identification User Guide

(Optional) Analyze PCR products
Analyze PCR products to confirm the presence of amplified DNA, or to estimate the PCR product yield.
The cycle-sequencing protocol works best with 5 to 20 ng of amplicon input.
1.
Load 5 μL of PCR product per lane on a 2% agarose gel separation (such as E‑Gel™ available from
thermofisher.com), or prepare your own gel.
2.
Use the Mass Standard Ladder to estimate the PCR product yield. In a positive control or sample,
a single fragment ranging from 460 to 560 bp in size should be detected on a gel. Actual fragment
size depends on the bacterial species. No product should be visible in a negative control reaction.
Methods
Perform cycle sequencing
IMPORTANT! If your samples show no PCR product, PCR inhibition is the most likely cause. See
“Troubleshooting” on page 16.
Purify PCR products for cycle sequencing
Remove unused dNTPs and primers from each PCR product with ExoSAP-IT™ Express PCR Product
Cleanup Reagent (Cat. No. 75001).
IMPORTANT!
product literature.
Follow the guidelines for the starting sample volume for cleanup as directed in the
Perform cycle sequencing
Cycle sequencing occurs when successive rounds of denaturation, primer annealing, and primer
extension in a thermal cycler result in the incorporation of dye terminators into extension products.
The products are then loaded into a genetic analyzer to determine the 16S rDNA sequence. For
additional information about cycle sequencing chemistries, refer to the DNA Sequencing by Capillary
Electrophoresis Chemistry Guide.
Fast MicroSEQ™ 500 16S rDNA Identification User Guide
11

Methods
Perform cycle sequencing
Important procedural guidelines
•
Select the appropriate tubes or 96‐well plates for your thermal cycler. See your instrument user
guide (available at thermofisher.com).
•
Using strip caps instead of 96‐well adhesive plate covers may help reduce cross-contamination.
•
If you are using a CentriSep™ Spin Column to purify extension products (see “Purifying Extension
Products” on page 15), hydrate the column with highly purified (nuclease free) water during the
cycle sequencing run.
•
If necessary, cover and store the unused portions of the purified PCR products at –15°C to –25°C
until you are ready to use them.
Note: PCR products are stable for 6 months or longer at –15°C to –25°C.
•
If necessary, cover and store the extension products at 4°C overnight or at –15°C to –25°C for up
to 1 week before purifying them.
Prepare cycle sequencing reactions
1.
Before you remove the tube or plate caps, briefly centrifuge the purified PCR products.
Note: Centrifuging helps avoid cross‐contamination from liquid remaining on the caps or plate
covers.
2.
In reaction tubes or a 96‐well plate, prepare separate forward‐ and reverse-sequencing reactions
for each PCR product and control:
•
Forward‐sequencing reaction—Combine 7 μL of purified PCR product or control with 13 μL
forward sequence mix.
•
Reverse‐sequencing reaction—Combine 7 μL of purified PCR product or control with 13 μL
reverse sequence mix.
Note: To help avoid cross‐contamination, pipet components in the following order: negative
controls, samples, positive controls.
Perform the cycle sequencing run
1.
Cap the tubes or the plate, then place the tubes or the plate in the thermal cycler.
2.
Set the appropriate ramp mode for your thermal cycler:
•
Veriti™ 96‑Well Thermal Cycler—Default
•
(3500/3500xL only) 9800 Fast Thermal Cycler—Fast (F96)
•
(3500/3500xL only) GeneAmp™ PCR System 9700—Maximum (Max)
12
Fast MicroSEQ™ 500 16S rDNA Identification User Guide

3.
Set the thermal cycling conditions:
Methods
Perform cycle sequencing
Initial step
HOLD CYCLE HOLD
96°C
1 minute
4.
Set the reaction volume to 20 μL, then start the run.
5.
Before removing the tube or plate caps, briefly centrifuge the extension products.
Note: Centrifuging helps avoid cross‐contamination from liquid remaining on the caps or plate
covers.
Purify extension products
After cycle sequencing, use one of the following products to remove excess dye terminators,
non‑incorporated nucleotides, and primers from the extension products. Select an appropriate
purification product depending on whether you performed cycle sequencing in tubes or a plate. Follow
the guidelines and procedures that are supplied with the kits.
For cycle sequencing
in ...
Each of 25 cycles
Melt Anneal Extend
96°C
10 seconds
50°C
5 seconds
Purify using ...
60°C 1 minute
15 seconds
Final step
4°C
∞
[1]
8-strips kit
96-well plates
[1]
Contact your local MicroSEQ™ ID representative for additional options.
•
MicroSEQ™ ID Purification Combo Kit v2.0 8-strips Kit (includes ExoSAPIT™ Express PCR Product Cleanup Reagent) , Cat. No. A35854
or
•
MicroSEQ™ ID Ultra Sequencing 8-strips Kit, Cat. No. A33246
•
MicroSEQ™ ID Purification Combo Kit v2.0 (includes ExoSAP-IT™ Express
PCR Product Cleanup Reagent) , Cat. No. A35852
or
•
MicroSEQ™ ID Ultra Sequencing Cleanup Plates Kit, Cat. No. A33245
Fast MicroSEQ™ 500 16S rDNA Identification User Guide
13

Methods
Perform electrophoresis of extension products
Perform electrophoresis of extension products
Important procedural guidelines
•
(3500/3500xL) Use the 50‐cm capillary array length. See the 3500/3500xL Genetic Analyzer User
Guide (Pub. No. 100079380) for more information.
•
If you are not using a SeqStudio™ Genetic Analyzer or 3500/3500xL Genetic Analyzer, select the
appropriate parameter settings from the table in “Electrophoresis settings for additional supported
instruments” on page 23.
•
Cover and store any unused purified extension products at 4°C overnight or at –15°C to –25°C for
up to 1 week.
Configure the instrument for electrophoresis
1.
Configure your data collection software according to the platform being used:
•
SeqStudio™ Genetic Analyzer—Use MicroSEQ™ ID Software For SeqStudio™ Genetic Analyzer
v1.0
•
Applied Biosystems™ 3500 Series Genetic Analyzers—Use MicroSEQ™ ID Analysis Software
v3.0 (or later)
Note: See “Additional documentation” on page 20 for a list of MicroSEQ™ ID documentation.
2.
Configure the instrument as described in the following table:
Instrument
SeqStudio
3500/3500xL
1.
Create a run in the MicroSEQ™ ID Software For SeqStudio™ Genetic Analyzer
by clicking Create MicroSEQ ID Run or Open MicroSEQ ID Template on the
home screen.
2.
Export the plate to the network drive.
3.
Import the plate to the SeqStudio™ Genetic Analyzer.
1.
Create a run in the MicroSEQ™ ID software v3.0 (or later) by clicking Create
MicroSEQ ID Run or Open MicroSEQ ID Template on the home screen.
2.
Save the run.
Procedure
14
Fast MicroSEQ™ 500 16S rDNA Identification User Guide

Prepare samples and perform electrophoresis
Methods
Perform electrophoresis of extension products
IMPORTANT! If the electrophoresis run time is longer than 12 hours on the SeqStudio
™
Genetic
Analyzer or 48 hours on the 3500/3500xL Genetic Analyzer (for example, if you are injecting more than
48 wells on the SeqStudio™ Genetic Analyzer or more than 192 wells on the 3500/3500xL Genetic
Analyzer), see “Prevent evaporation during electrophoresis” on page 26.
1.
Before removing the tube caps or plate cover, briefly centrifuge the extension products.
2.
Prepare reactions using a 1:1 ratio of purified extension product and formamide:
a.
In a 96-well plate, pipette 10 µL Hi‑Di™ Formamide into each well to which you add purified
extension products or controls.
b.
Pipette 10 µL Hi‑Di™ Formamide into each blank well that is injected together with the
samples.
c.
Add 10 µL of purified extension product or control to each well filled in step 2a, then mix by
pipetting up and down.
Note: Dilution in Hi‑Di™ Formamide normalizes the signal strength of the sequencing reaction and
stabilizes extension products. If after a 1:1 dilution you do not detect a sequencing ladder due to a
low signal, run 15 µL of each sample without diluting.
3.
Cover the plate, centrifuge, then load the plate into your instrument. Start the run.
Note: Centrifuging removes bubbles from the bottom of the wells.
4.
When the run is complete, review the data using the MicroSEQ™ ID software (3500/3500xL) or
MicroSEQ™ ID Software For SeqStudio™ Genetic Analyzer.
Fast MicroSEQ™ 500 16S rDNA Identification User Guide
15

Methods
Troubleshooting
Troubleshooting
Observation Possible cause Recommended action
No PCR product •
Signal is too high
Too much amplicon in the
sequencing reaction
No biomass
or
•
Fungal sample
or
•
PCR inhibition
or
•
Cells were not disrupted by
the PrepMan™ Ultra method
or
•
Incorrect dilution
1.
If no PCR product is seen, use more
bacterial cells.
2.
If the problem persists, the isolate you are
trying to identify may be fungi. Amplify the
sample with the Fast MicroSEQ™ D2 LSU
rDNA Fungal PCR Kit (Cat. no. 4396787).
3.
If the problem persists, make one or
more new dilutions of the PrepMan
Ultra supernatant, then run several PCR
reactions of each dilution to increase your
chance of obtaining a PCR product of
the correct size. If the PrepMan™ Ultra
supernatant is:
•
Clear–Make smaller dilutions (1:40 or
1:10) of the original PrepMan™ Ultra
supernatant.
•
Colored (typically a shade of black or
green)– Make the following dilutions:
–
Smaller dilutions (1:40 or 1:10)
of the original PrepMan™ Ultra
supernatant.
–
A 1:1000 dilution of the original
PrepMan™ Ultra supernatant.
4.
If you do not obtain a PCR product from
any of the diluted samples, try one of the
following solutions:
•
Use a DNA extraction kit to isolate
pure DNA.
or
•
Use the bead-beating method to
isolate fungal genomic DNA or
bacterial genomic DNA.
Dilute the purified extension product with Hi‑Di
Formamide, then perform a new run.
™
™
16
If you ran purified extension product that was:
•
Not diluted—Dilute the purified extension
product at a ratio of 1:1.
•
Diluted at a 1:1 ratio—Dilute the purified
extension product at a 1:10 ratio.
•
Diluted at a 1:10 ratio—Dilute the purified
extension product at a 1:40 ratio.
See “Prevent evaporation during
electrophoresis” on page 26.
Fast MicroSEQ™ 500 16S rDNA Identification User Guide

Methods
Frequently asked questions
Observation Possible cause Recommended action
Absence of signal/blank
electropherogram
The sequence is short and/or
the first part of the sequence is
very bright and o-scale and the
remainder has very low intensity
Both results and raw data show
occasional high spikes for all
four dye colors
Large regions of overlapping
sequence or cannot call bases
for large regions of sequence
Small regions of overlapping
sequence
Sample evaporation See “Prevent evaporation during
electrophoresis” on page 26.
•
High starting amount of
DNA
or
•
Too much DNA template in
the sequencing reaction
Bubbles in the capillary Check the instrument maintenance and
•
Pipetting more than one
template per well
or
•
DNA sample is
contaminated (that is, the
DNA is derived from
more than one species of
bacteria)
or
•
The organism has multiple
copies of the rDNA gene,
and some copies have
insertions or deletions
In bacterial species with multiple
copies of the rRNA gene,
the gene can be polymorphic,
resulting in overlap of up to 1%
of the sequence
1.
Decrease the amount of bacterial cell
material using one of the following
methods:
•
Use a smaller colony or pellet.
•
Further dilute the PrepMan™ Ultra
supernatant.
2.
If the problem persists, estimate the PCR
product yield on agarose gel and use
5–20 ng of amplicon for sequencing
as described in “(Optional) Analyze PCR
products” on page 11.
troubleshooting guides.
1.
Prepare new reactions, then repeat
electrophoresis.
2.
If the problem persists, sub-culture the
organism to pure culture, then repeat
identification.
3.
If the problem persists, clone the PCR
product (using a kit such as the TOPO
PCR Cloning Kit) before performing
sequencing.
No action needed.
™
Frequently asked questions
Sensitivity and quantitation
What is the sensitivity of the Fast MicroSEQ™ 500 16S rDNA Identification?
As long as you start from a visible colony or cell pellet, MicroSEQ™ kits will work.
Fast MicroSEQ™ 500 16S rDNA Identification User Guide
17

Methods
Frequently asked questions
Can I use the Fast MicroSEQ™ 500 16S rDNA Identification to quantify fungi or
yeast?
No. The PCR is an endpoint assay.
Sample preparation and storage
Which kits should I use to identify yeast samples?
Use the Fast MicroSEQ™ D2 rDNA Fungal Identification or the MicroSEQ™ D2 rDNA Fungal Identification
to sequence and identify yeast samples.
What is the best way to prepare yeast samples?
Prepare yeast samples using the PrepMan™ Ultra Sample Preparation Reagent or bead-beating method,
just as you would prepare bacterial samples. Extra dilutions of the fungal DNA supernatant are
sometimes necessary.
Are there alternative methods for preparing genomic DNA?
If the PrepMan™ Ultra Sample Preparation Reagent method does not successfully disrupt cells, you can
use the bead‐beating method to isolate genomic DNA.
Alternatively, you can use a DNA extraction kit (available from various vendors) to isolate pure DNA.
Can I use less PrepMan™ Ultra Sample Preparation Reagent if I start with a smaller colony?
Yes. The ideal colony size is 2–3 mm. For smaller colonies, you can decrease the amount of PrepMan
Ultra Sample Preparation Reagent to 50 μL from the suggested 100 μL in the PrepMan™ Ultra Sample
Preparation Reagent Protocol.
Can I enrich my genomic DNA by using less PrepMan™ Ultra Sample Preparation Reagent?
Yes. However, be careful not to overload the PCR mix. Enriched samples tend to have more cellular and
other debris, which can interfere with PCR.
At what temperature should I store my PrepMan™ Ultra-isolated DNA?
Store isolated DNA at –15 to –25°C. (Alternatively, you can safely keep it overnight at room temperature
or at 4°C.)
Contamination
™
18
How can I tell if my sequence is representative of a single species?
The DNA sequence from a single species should be distinct (easy to call base pairs), without significant
regions of overlapping sequence.
Fast MicroSEQ™ 500 16S rDNA Identification User Guide

If my initial DNA sample is contaminated (that is, it comes from multiple species), how can I sequence my PCR product?
Clone the PCR product using a kit such as the TOPO™ TA Cloning™ Kit (Cat. no. K4575‑J10) .
Overlapping sequences
My sequence has large regions of overlap (>5% mixed bases). What does this
mean?
See Troubleshooting, “Large regions of overlapping sequence or cannot call bases for large regions of
sequence” on page 17.
My sequence has small regions (less than or equal to 1% of overlap). What does this mean?
See Troubleshooting, “Small regions of overlapping sequence” on page 17.
PCR product size
Methods
Frequently asked questions
Can I always expect the same size PCR product for all species?
PCR products can vary from the expected product size, depending on the species.
Expected product sizes for the:
•
MicroSEQ™ Fungal Kits – 1 band at 300–500 bp
•
MicroSEQ™ 500 Kits – 1 band at 460–560 bp
•
MicroSEQ™ Full Gene Kit – 1 band at 460–560 bp and 2 bands at 700–800 bp
Can I increase the number of cycles to increase the PCR yield?
Yes, but doing so can cause additional background signal from the negative control.
Species libraries
How are species in the MicroSEQ™ libraries validated?
Please contact your local MicroSEQ™ representative to obtain a copy of the MicroSEQ™ ID Library
Validation Statement for additional information.
Where does Thermo Fisher Scientific obtain the strains used to determine the
reference sequencing in the MicroSEQ™ libraries?
The strains are derived from major culture collections such as the American Type Culture Collection
(ATCC) and the Deutsche Sammlung von Mikroorganismen und Zellkulturen GmbH (DSMZ) (German
Collection of Microorganisms and Cell Cultures).
Fast MicroSEQ™ 500 16S rDNA Identification User Guide
19

Methods
Frequently asked questions
What is the dierence between the libraries for the MicroSEQ™ Full Gene kit and the
MicroSEQ™ 500 kits?
The sequences in the library for the MicroSEQ™ 500 kits are ~500 bp, which is the expected size of the
PCR products for this kit. The sequences in the library for the MicroSEQ™ Full Gene kit are ~1440 bp,
the maximum sequence length that the kit allows you to determine.
Additional documentation
Where can I find additional information about MicroSEQ™ ID software or
MicroSEQ™ ID Software For SeqStudio™ Genetic Analyzer?
Refer to the following documentation for MicroSEQ™ ID software (3500/3500xL):
•
MicroSEQ™ ID Analysis Software Quick Reference Card
•
MicroSEQ™ ID Analysis Software Getting Started Guide
•
MicroSEQ™ ID Analysis Software Online Help
Refer to the following documentation for MicroSEQ™ ID Software For SeqStudio™ Genetic Analyzer:
•
MicroSEQ™ ID Software For SeqStudio™ Genetic Analyzer v1.0 Quick Reference
•
MicroSEQ™ ID Software For SeqStudio™ Genetic Analyzer v1.0 User Guide
Note: For additional documentation, see “Customer and technical support” on page 37.
20
Fast MicroSEQ™ 500 16S rDNA Identification User Guide

A
The following products are available at thermofisher.com.
Product Description Cat. No.
Ordering information
Fast MicroSEQ™ D2 LSU
rDNA Fungal PCR Kit
MicroSEQ™ D2 rDNA Fungal
PCR Kit
MicroSEQ™ D2 rDNA Fungal
Sequencing Kit
Fast MicroSEQ™ 500 16S
rDNA PCR Kit
MicroSEQ™ 500 16S rDNA
PCR Kit
MicroSEQ™ 500 16S rDNA
Sequencing Kit
This kit is the PCR component of the FAST MicroSEQ™ Fungal
Identification System containing enough reagents for 50 PCR
amplifications of fungal DNA unknowns. The sequencing
component of the kit is required for species identification.
This kit is the PCR component of the MicroSEQ™ Fungal
Identification System containing enough reagents for 50 PCR
amplifications of fungal DNA unknowns. The sequencing
component of the kit is required for species identification.
This kit is the sequencing component of the MicroSEQ
Fungal Identification System, which provides an easy-to-use
DNA sequence-based method to identify most fungi. It
includes the primers needed to sequence the PCR products
generated using the PCR component.
This kit is the PCR component of the MicroSEQ™ Bacterial
Identification System containing enough reagents for 50 PCR
amplifications of bacterial DNA unknowns. The sequencing
component of the kit is required for species identification.
This kit is the PCR component of the MicroSEQ™ Bacterial
Identification System containing enough reagents for 50 PCR
amplifications of bacterial DNA unknowns. The sequencing
component of the kit is required for species identification.
This kit is the sequencing component of the MicroSEQ
Bacterial Identification System, which provides an easy-to-use
DNA sequence-based method to identify most bacteria. It
includes the primers needed to sequence the PCR products
generated using the PCR component. There are enough
reagents for 55 sequencing reactions.
™
™
4382397
4349153
4347481
4370489
4348228
4346480
MicroSEQ™ Full Gene 16S
rDNA PCR Kit
Fast MicroSEQ™ 500 16S rDNA Identification User Guide
This kit is the PCR component of the MicroSEQ™ Bacterial
Identification System containing enough reagents for 50 PCR
amplifications of bacterial DNA unknowns. The sequencing
component of the kit is required for species identification.
4349155
21

Appendix A Ordering information
A
Frequently asked questions
(continued)
Product Description Cat. No.
MicroSEQ™ Full Gene 16S
rDNA Sequencing Kit
This kit is the sequencing component of the MicroSEQ
Bacterial Identification System, which provides an easy-to-use
DNA sequence-based method to identify most bacteria. It
includes the primers needed to sequence the PCR products
generated using the PCR component. There are enough
reagents for 55 sequencing reactions.
™
4347484
PrepMan™ Ultra Sample
Preparation Reagent
MicroSEQ™ ID
Analysis Software
(3500/3500xL Genetic
Analyzer)
MicroSEQ™ ID Software For
SeqStudio™ Genetic Analyzer
PrepMan™ Ultra Sample Preparation Reagent was developed
for the rapid preparation of DNA template from Gram-negative
food-borne pathogens for use in PCR amplification reactions.
These samples often have high lipid content that can inhibit
PCR amplification of the template. Using a simple boil and
spin protocol, PrepMan™ Ultra Sample Preparation Reagent
eciently inactivates PCR inhibitors, significantly reducing the
need to repeat the template preparation step.
This easy-to-use software enables you to identify and classify
unidentified bacterial or fungal sequences by comparing them
to a validated microbial library.
4318930
Contact your local
MicroSEQ™ ID
representative
22
Fast MicroSEQ™ 500 16S rDNA Identification User Guide

Additional supported instruments
B
To take advantage of the reduced amplification and sequencing times allowed by the FAST PCR
chemistry, we recommend that you use the Applied Biosystems™ Veriti™ 96‑Well Thermal Cycler and
the Applied Biosystems™ 3500/3500xL Genetic Analyzer or SeqStudio™ Genetic Analyzer with the
MicroSEQ™ kits.
However, the MicroSEQ™ kits can also be used with:
•
Applied Biosystems™ GeneAmp™ PCR System 9700 thermal cycler
Note: The FAST MicroSEQ™ PCR chemistry reduces amplification time when used on the
GeneAmp™ PCR System 9700 in Maximum ramp mode, but the time is further reduced when
the FAST chemistry is used with the recommended thermal cycler.
Note: An amplification run using a GeneAmp™ PCR System 9700 can take up to 20 minutes longer
than a run using the Veriti™ 96‑Well Thermal Cycler or 9800 Fast Thermal Cycler.
•
Applied Biosystems™ 9800 Fast Thermal Cycler
•
Applied Biosystems™ 3730 and 3730xl DNA Analyzers
Electrophoresis settings for additional supported instruments
Instrument
Applied Biosystems™ 3730
and 3730xl DNA Analyzers
Filter Set Run Module Base-caller
E StdSeq50_POP7 KB.bcp KB_3730_POP7_BDT
DyeSet/Primer (Mobility
v1.mob
File)
Fast MicroSEQ™ 500 16S rDNA Identification User Guide
23

Supplemental procedures and
C
guidelines
Good laboratory practices for PCR and RT-PCR
•
Wear clean gloves and a clean lab coat.
–
Do not wear the same gloves and lab coat that you have previously used when handling
amplified products or preparing samples.
•
Change gloves if you suspect that they are contaminated.
•
Maintain separate areas and dedicated equipment and supplies for:
–
Sample preparation and reaction setup.
–
Amplification and analysis of products.
•
Do not bring amplified products into the reaction setup area.
•
Open and close all sample tubes carefully. Avoid splashing or spraying samples.
•
Keep reactions and components capped as much as possible.
•
Use a positive-displacement pipettor or aerosol‑resistant barrier pipette tips.
•
Clean lab benches and equipment periodically with 10% bleach solution or DNA decontamination
solution.
24
Fast MicroSEQ™ 500 16S rDNA Identification User Guide

Seal the PCR plate
Seal the plate with strip caps
IMPORTANT! Apply significant downward pressure on the sealing tool in all steps to form a complete
seal.
Note: Use of strip caps instead of 96‐well adhesive plate covers may help reduce cross-contamination.
To use the rolling capping tool:
•
Roll the capping tool across all strips of caps on the short edge,
then the long edge of the tray.
•
Roll the capping tool around all outer rows of strips of caps.
To use the rocking capping tool:
•
Slip your fingers through the handle with the holes in the tool
facing down.
•
Place the holes in the tool over the first eight caps in a row.
•
Rock the tool back and forth a few times to seal the caps.
•
Repeat for the remaining caps in the row, then for all remaining
rows.
Appendix C Supplemental procedures and guidelines
Seal the PCR plate
C
Fast MicroSEQ™ 500 16S rDNA Identification User Guide
25

Appendix C
C
Prevent evaporation during electrophoresis
Supplemental procedures and guidelines
Seal the plate with adhesive film
IMPORTANT! Apply significant downward pressure on the applicator to completely seal the wells.
Pressure is required to activate the adhesive on the optical cover.
1.
Place an optical adhesive cover on the plate, then rub the flat
edge of the applicator back and forth along the long edge of the
plate.
2.
Rub the flat edge of the applicator back and forth along the short
edge of the plate.
3.
Rub the edge of the applicator horizontally and vertically between
all wells.
4.
Rub the edge of the applicator around all outside edges of the
plate using small back and forth motions to completely seal
around the outside wells.
5.
Vortex the plate on the low setting for 5 seconds. If you see
liquid on the well sidewalls, spin down the plate at 2000 × g for
20 seconds using a centrifuge with a plate adapter.
IMPORTANT! Make sure reagents are in the bottom of the
wells.
Prevent evaporation during electrophoresis
We recommend that you use Hi‑Di™ Formamide to prevent sample evaporation during long
electrophoresis runs. If your run time is:
•
24 hours or less, addition of formamide is not necessary
•
Between 24 and 48 hours, see “Prepare a diluted sample” on page 27
•
Longer than 48 hours, see “Dry-down, then resuspend the sample” on page 27
26
Fast MicroSEQ™ 500 16S rDNA Identification User Guide

Prepare a diluted sample
1.
Prepare reactions using a 1:1 ratio of purified extension product and formamide:
a.
In a 96‐well plate, pipette 10 μL of Hi‑Di™ Formamide into each well to which you will add
purified extension products or controls.
b.
Pipette 10 μL of Hi‑Di™ Formamide into each blank well that will be injected together with the
samples.
c.
Add 10 μL of purified extension product or control to each well filled in step 1a, then mix by
pipetting up and down.
Note: If after a 1:1 dilution you do not detect a sequencing ladder due to a low signal, rerun the
sample without diluting.
2.
Centrifuge the plate, load the plate into your instrument, then start the run.
Note: Centrifuging removes bubbles from the bottom of the wells.
Appendix C
Supplemental procedures and guidelines
Prevent evaporation during electrophoresis
C
Note: See “Configure the instrument for electrophoresis” on page 14 for details.
3.
Cover and store the unused portion of the purified extension products overnight at 4°C or for up to
1 week at –15°C to –25°C.
When the run is complete, review the data using the MicroSEQ™ ID software or MicroSEQ™ ID Software
For SeqStudio™ Genetic Analyzer.
Dry-down, then resuspend the sample
1.
Centrifuge the tubes or plate containing the purified extension products in a speed vac.
Note: Centrifuge time and speed depend on the number of samples and the type of speed vac
used. Typical times range from 30–60 minutes.
IMPORTANT! Do not over‐dry the DNA pellet, and do not use heat to dry the pellet.
2.
Resuspend the DNA in 15 μL of Hi‑Di™ Formamide.
Note: Formamide disrupts hydrogen bonds in double‐stranded DNA, inhibiting secondary
structure and DNA conglomeration, and resulting in cleaner and more consistent electrophoresis
runs.
3.
Centrifuge the plate, load the plate into your instrument, then start the run.
Note: Centrifuging removes bubbles from the bottom of the wells.
Note: See “Configure the instrument for electrophoresis” on page 14 for details.
Fast MicroSEQ™ 500 16S rDNA Identification User Guide
27

Appendix C Supplemental procedures and guidelines
C
Prevent evaporation during electrophoresis
When the run is complete, review the data using the MicroSEQ™ ID software or MicroSEQ™ ID Software
For SeqStudio™ Genetic Analyzer.
28
Fast MicroSEQ™ 500 16S rDNA Identification User Guide

Supplemental product information
D
MicroSEQ™ system overview
The MicroSEQ™ Microbial Identification System combines all of the instruments, reagents, sequence
libraries, and software required for automated microbial identification using DNA sequencing.
The MicroSEQ™ system is easy to use and suitable for the routine identification of all bacterial
and fungal isolates, including organisms that are dicult to grow, non‐viable, or unidentifiable using
phenotypic methods. The MicroSEQ™ system identifies bacterial and fungal isolates from a small
sample of pure culture without preliminary testing or growth on selective media.
About MicroSEQ™ ID software and MicroSEQ™ ID Software For SeqStudio™ Genetic Analyzer
The software analyzes sequences obtained with any of the MicroSEQ™ Microbial Identification Kits.
The software assembles the 16S region rDNA sequence for the unknown, then compares the
sequence with known reference 16S region rDNA sequences. For the Fast MicroSEQ™ 500 16S rDNA
Identification, data is compared to the MicroSEQ™ ID 16S rDNA 500 Library. Based on the comparison,
the software provides a potential ID for the unknown bacterial species.
With the software, you can perform:
•
Basecalling with assignment of quality values
•
Clear‐range determination, which lets you exclude data near sequence ends (typically poor‐quality
data) from analysis
•
Assembly and alignment of sequences to generate a high‐quality consensus sequence
•
Comparison of the consensus sequence to the MicroSEQ™ ID proprietary libraries to generate a list
of the closest matches, including percentage match scores
•
Exports of projects and consensus sequences to facilitate data‐sharing between collaborators
The software also has features that assist with 21 CFR Part 11 compliance requirements.
For more information, see “Related documentation” on page 37.
MicroSEQ
MicroSEQ™ ID library sequences are carefully validated. Polymorphic positions are taken into account
and included in library species.
™
ID proprietary libraries
Fast MicroSEQ™ 500 16S rDNA Identification User Guide
29

Appendix D Supplemental product information
D
About MicroSEQ™ ID software and MicroSEQ™ ID Software For SeqStudio™ Genetic Analyzer
Custom libraries
MicroSEQ™ ID Analysis Software allows you to create custom libraries using data generated by the
MicroSEQ™ ID software, or using sequences from public databases. Custom libraries are easy to import
and export, making information sharing convenient.
During the analysis process, you can search proprietary and custom libraries simultaneously to
determine 3–20 closest matches to the sequence of your unknown bacterial species.
MicroSEQ™ ID reports
MicroSEQ™ ID Analysis Software generates four detailed reports:
•
Analysis QC Report – Allows you to quickly scan the unknowns in a project to gather information
about the samples, including the top percent identity match and specimen score to measure data
quality. See Figure 1.
•
Library Search Report – Provides more detailed information about the libraries that were
searched, including a list of all the top matches and the total number of bases searched. See
Figure 2.
•
Audit Trail Report – Tracks changes made to projects after analysis.
•
Electronic Signature History Report – Provides a summary of the electronic signatures used in a
project.
All reports can be generated on project and specimen levels. In addition, the software allows you to
create custom reports. For information, see “Related documentation” on page 37.
30
Fast MicroSEQ™ 500 16S rDNA Identification User Guide

Appendix D Supplemental product information
About MicroSEQ™ ID software and MicroSEQ™ ID Software For SeqStudio™ Genetic Analyzer
D
Figure 1 Example Analysis QC Report
Fast MicroSEQ™ 500 16S rDNA Identification User Guide
31

Appendix D
D
About MicroSEQ™ ID software and MicroSEQ™ ID Software For SeqStudio™ Genetic Analyzer
Supplemental product information
32
Figure 2 Example Library Search Report
Fast MicroSEQ™ 500 16S rDNA Identification User Guide

Appendix D Supplemental product information
About dye-labeled terminator chemistry
The MicroSEQ™ 500 16S rDNA Sequencing Kit uses BigDye™ Terminator v1.1 chemistry. Forward and
Reverse Sequence Mixes contain sequence‐terminating 3′‐dideoxynucleotide triphosphates (ddNTPs).
Each of the four ddNTPs is tagged with a dierent fluorescent dye. When the ddNTPs are incorporated
into extension products during cycle sequencing, the extension products are simultaneously terminated
and labeled with the dye that corresponds to the incorporated base, as shown in the following figure.
Figure 3 BigDye™ Terminator v1.1 chemistry
For more information about dye‐labeled terminators and other sequencing chemistries, refer to the DNA
Sequencing by Capillary Electrophoresis Chemistry Guide. See “Related documentation” on page 37.
About dye-labeled terminator chemistry
D
Fast MicroSEQ™ 500 16S rDNA Identification User Guide
33

E
WARNING! GENERAL SAFETY. Using this product in a manner not specified in the user
documentation may result in personal injury or damage to the instrument or device. Ensure that
anyone using this product has received instructions in general safety practices for laboratories and
the safety information provided in this document.
Before using an instrument or device, read and understand the safety information provided in the
·
user documentation provided by the manufacturer of the instrument or device.
Before handling chemicals, read and understand all applicable Safety Data Sheets (SDSs) and use
·
appropriate personal protective equipment (gloves, gowns, eye protection, and so on). To obtain
SDSs, see the “Documentation and Support” section in this document.
Safety
34
Fast MicroSEQ™ 500 16S rDNA Identification User Guide

Chemical safety
WARNING! GENERAL CHEMICAL HANDLING. To minimize hazards, ensure laboratory personnel
read and practice the general safety guidelines for chemical usage, storage, and waste provided
below. Consult the relevant SDS for specific precautions and instructions:
Read and understand the Safety Data Sheets (SDSs) provided by the chemical manufacturer
·
before you store, handle, or work with any chemicals or hazardous materials. To obtain SDSs, see
the "Documentation and Support" section in this document.
Minimize contact with chemicals. Wear appropriate personal protective equipment when handling
·
chemicals (for example, safety glasses, gloves, or protective clothing).
Minimize the inhalation of chemicals. Do not leave chemical containers open. Use only with
·
sucient ventilation (for example, fume hood).
Check regularly for chemical leaks or spills. If a leak or spill occurs, follow the manufacturer
·
cleanup procedures as recommended in the SDS.
Handle chemical wastes in a fume hood.
·
Ensure use of primary and secondary waste containers. (A primary waste container holds the
·
immediate waste. A secondary container contains spills or leaks from the primary container.
Both containers must be compatible with the waste material and meet federal, state, and local
requirements for container storage.)
After emptying a waste container, seal it with the cap provided.
·
Characterize (by analysis if needed) the waste generated by the particular applications, reagents,
·
and substrates used in your laboratory.
Ensure that the waste is stored, transferred, transported, and disposed of according to all local,
·
state/provincial, and/or national regulations.
IMPORTANT! Radioactive or biohazardous materials may require special handling, and disposal
·
limitations may apply.
Appendix E Safety
Chemical safety
E
WARNING! HAZARDOUS WASTE (from instruments). Waste produced by the instrument is
potentially hazardous. Follow the guidelines noted in the preceding General Chemical Handling
warning.
WARNING! 4L Reagent and Waste Bottle Safety. Four-liter reagent and waste bottles can crack
and leak. Each 4-liter bottle should be secured in a low-density polyethylene safety container with the
cover fastened and the handles locked in the upright position.
Fast MicroSEQ™ 500 16S rDNA Identification User Guide
35

Appendix E Safety
E
Biological hazard safety
Biological hazard safety
WARNING! Potential Biohazard. Depending on the samples used on this instrument, the surface
may be considered a biohazard. Use appropriate decontamination methods when working with
biohazards.
WARNING! BIOHAZARD. Biological samples such as tissues, body fluids, infectious agents,
and blood of humans and other animals have the potential to transmit infectious diseases.
Conduct all work in properly equipped facilities with the appropriate safety equipment (for example,
physical containment devices). Safety equipment can also include items for personal protection,
such as gloves, coats, gowns, shoe covers, boots, respirators, face shields, safety glasses, or
goggles. Individuals should be trained according to applicable regulatory and company/ institution
requirements before working with potentially biohazardous materials. Follow all applicable local,
state/provincial, and/or national regulations. The following references provide general guidelines when
handling biological samples in laboratory environment.
U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Biosafety in Microbiological and Biomedical
·
Laboratories (BMBL), 5th Edition, HHS Publication No. (CDC) 21-1112, Revised December 2009;
found at:
https://www.cdc.gov/labs/pdf/CDC-BiosafetymicrobiologicalBiomedicalLaboratories-2009P.pdf
World Health Organization, Laboratory Biosafety Manual, 3rd Edition,
·
WHO/CDS/CSR/LYO/2004.11; found at:
www.who.int/csr/resources/publications/biosafety/Biosafety7.pdf
36
Fast MicroSEQ™ 500 16S rDNA Identification User Guide

Documentation and support
Related documentation
The following related documents are available at thermofisher.com/support:
Document Publication number
Fast MicroSEQ™ 500 16S rDNA Identification Quick Reference 4393012
PrepMan™ Ultra Sample Preparation Reagent Protocol 4367554
Veriti™ Thermal Cycler User Guide 4375799
DNA Sequencing by Capillary Electrophoresis Chemistry Guide 4305080
3500/3500xL Genetic Analyzer
MicroSEQ™ ID Microbial Identification Software Version 3.0 Getting Started
Guide
MicroSEQ™ ID Microbial Identification Software Version 3.0 Quick Reference
Card
MicroSEQ™ ID Analysis Software v2.2 Getting Started Guide 4445126
MicroSEQ™ ID Analysis Software v2.2 Quick Reference Card 4445420
SeqStudio™ Genetic Analyzer
MicroSEQ™ ID Software For SeqStudio™ Genetic Analyzer v1.0 User Guide MAN0019554
MicroSEQ™ ID Software For SeqStudio™ Genetic Analyzer v1.0 Quick Reference MAN0019555
Note: For additional documentation, see “Customer and technical support” on page 37.
Customer and technical support
Visit thermofisher.com/support for the latest service and support information.
•
Worldwide contact telephone numbers
•
Product support information
–
Product FAQs
–
Software, patches, and updates
–
Training for many applications and instruments
•
Order and web support
4465137
4465103
Fast MicroSEQ
™
500 16S rDNA Identification User Guide
37

Documentation and support
Limited product warranty
•
Product documentation
–
User guides, manuals, and protocols
–
Certificates of Analysis
–
Safety Data Sheets (SDSs; also known as MSDSs)
Note: For SDSs for reagents and chemicals from other manufacturers, contact the
manufacturer.
Limited product warranty
Life Technologies Corporation and/or its aliate(s) warrant their products as set forth in the
Life Technologies' General Terms and Conditions of Sale at www.thermofisher.com/us/en/home/
global/terms-and-conditions.html. If you have any questions, please contact Life Technologies at
www.thermofisher.com/support.
38
Fast MicroSEQ™ 500 16S rDNA Identification User Guide


1a Fast MicroSEQ 500 16S rDNA Identification Kit_UG_4393007-v12-GUID-81D5C552-8D10-4E53-8909FACD88D28465-2021/01/12 00:30:49 en
00:32:04.765Z
thermofisher.com/support | thermofisher.com/askaquestion
thermofisher.com
11 January 2021
 Loading...
Loading...