Page 1

WHITE PAPER Bigfoot Spectral Cell Sorter
Bigfoo t Spectral
Cell Sorter
A new approach to
cell sorter safety
Introduction
Cell sorting continues to be a powerful contributor in the
quest to improve human health, allowing researchers
to make timely advancements in drug and vaccine
development, as illustrated by the newly released SARSCoV-2 sorting protocols [1]. However, cell sorting is also
known to produce aerosols that can expose the operator
to both known and unknown pathogens. When cell sorters
are run at high pressures, they can produce aerosols
with high particulate content as well as extremely small
particles. Such particles, especially those smaller than
2μm, are prone to deposition in both the upper airway and
the alveolar spaces in the lungs, with potential to harm the
operator [2]. Thishazard necessitates protective barriers
and containment apparatus to be incorporated into the
cell sor t e r.
In the early 2000s, manufacturers sought to address
these concerns by adding aerosol management systems
(AMSs), which continuously evacuate the sorting chamber
to remove aerosols. In the same period, the first attempt
was made to fit a cell sorter into a Class II biosafety cabinet
(BSC). Though less than ideal, it served to protect the
sort sample and to some extent the operator. Current
International Society for Advancement of Cytometry
(ISAC) safety regulations require that all cell sorters now
be equipped with an AMS [2]. These standards also
state that most types of cell samples and lab spaces
necessitate the sorter to be enclosed in a BSC. Despite
these regulations, AMSs and BSCs are frequently marketed
as optional accessories when purchasing a sorter and,
as such, frequently fall victim to funding shortfalls.
Several newer sorters include an AMS integrated with a
standard BSC, but they continue to resemble an ad hoc
solution with manual operation of air-handling controls and
poor access for service manipulation, which can lead to
inconsistent results and an unsafe environment.
The referenced ISAC regulations require periodic testing
of AMS and BSC systems. While the recently developed
Cyclex-D air sampler and 1 µm Dragon Green fluorescent
microspheres AMS testing method is an improvement over
previous procedures, the process remains cumbersome
and not clearly defined for many sorters. The literature
describes the testing using only one manufacturer’s
cell sorter, and while general guidelines are included to
modify the procedure for other vendors’ equipment, such
modifications are not always clear-cut and frequently
require burdensome manual overrides and manipulations.
An instrument designed with a well-integrated AMS
and BSC will likely solve most if not all of these
common concerns.
Page 2
BSC and AMS design reinterpreted
The Invitrogen™ Bigfoot Spectral Cell Sorter is designed
with an integrated BSC and AMS. Sample-related
subsystems are segregated inside the BSC for optimal
safety, sanitation, and performance. Sealed optical
windows surround the nozzle, defining the barrier between
the inside and outside of the BSC. This separation allows
lasers, excitation optics, and scatter objective lenses to
remain outside the BSC yet close to the interrogation point,
which maintains the superior performance of a jet-in-air
sorter. All other systems, such as detection, electronics,
and fluidics, are also outside the containment area. This
allows better service access and temperature regulation as
compared to othersorters.
The Bigfoot Spectral Cell Sorter BSC system has been
verified to meet personnel and product protection
standards for a Class II Type A2 biosafety cabinet per the
National Sanitation Foundation (NSF) International Standard
49, Section 3.8.2.3. Specifically, this means the BSC:
deliver uniform downflow air, and the remaining filtered air
is exhausted to the laboratory environment, or through an
external exhaust system connected to the optional cabinet
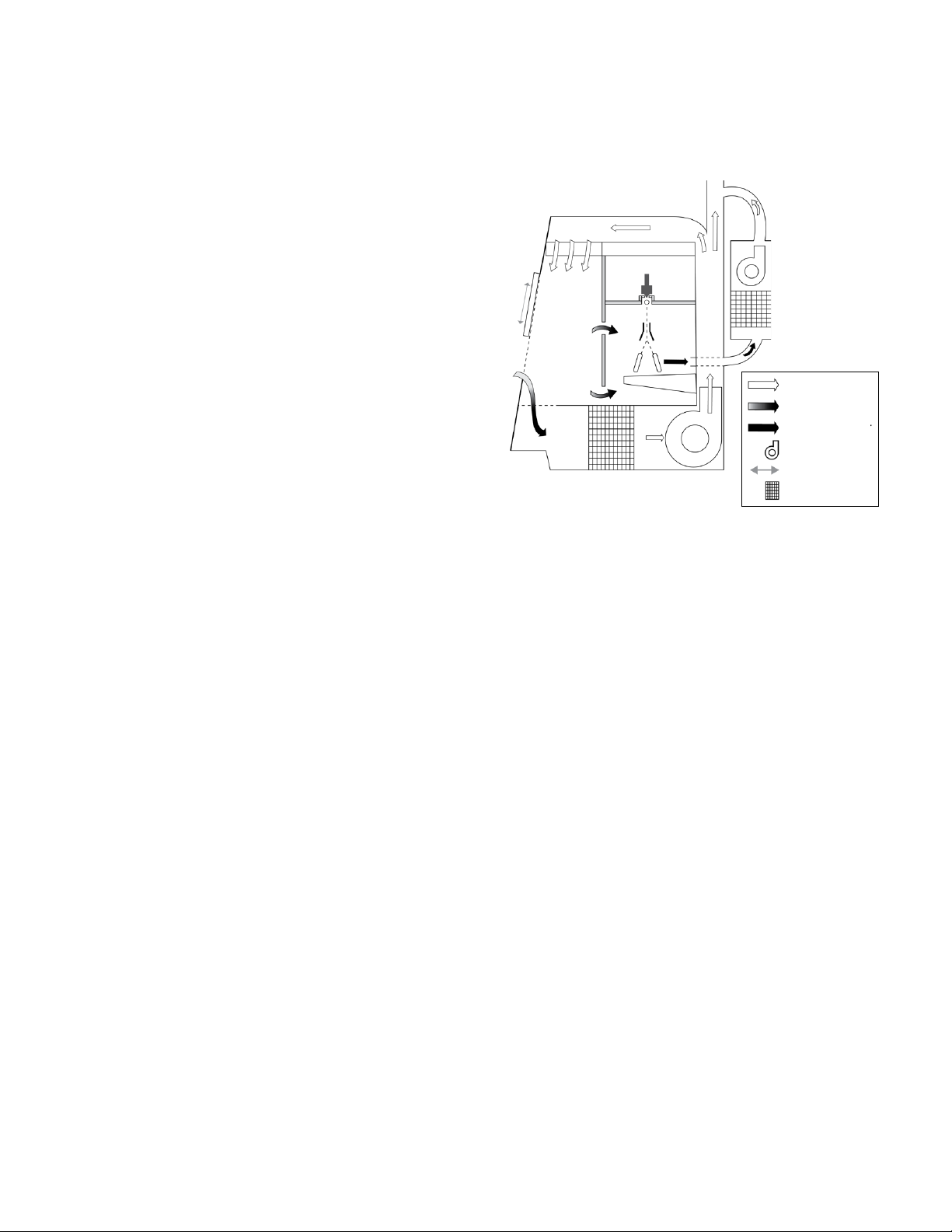
canopy connection (Figure 1).
HEPA-filtered air
Mixed air
Contaminated air
Fan
Adjustable sash
HEPA filter
• Maintains an average air velocity of 100 ft/min through
the work access opening
• Provides high-eciency particulate air (HEPA)–filtered
downflow air that is a mixed with the downflow and
inflow air
• Exhausts HEPA-filtered air into either the laboratory or,
via an optional canopy connection, through an external
exhaust system
• Holds all biologically contaminated ducts and plenums
under negative pressure
The AMS and BSC portions of the system can be operated,
and are monitored, independently. The system houses two
independent exhaust fans and two independent HEPA
filters; one fan and filter for the AMS, and one fan and
filter for the BSC. Pressure sensors independently monitor
containment in both the AMS and the BSC for redundant
biosafety containment.
Aerosols in the segregated sort chamber are entrained
in air that is ducted to a HEPA filter in the AMS. The door
to access the sort chamber is inside the greater BSC. In
the unlikely event hazardous aerosols leak out of the sort
chamber, the greater BSC oers a secondary biosafety
system to capture aerosols. As with all Class II Type A2
cabinets, a portion of the filtered air is recirculated to
Figure 1. Airflow diagram.
Recirculated and exhausted air is HEPA filtered to remove
99.97% of particles greater than 0.3 μm. Inflow air velocity
is regulated to a minimum of 100 ft/min through the work
access opening. During a sort, the AMS continuously
draws air from the sort chamber and through a HEPA
filter. If a clog is detected, software notifies the operator;
stops the sort, sample, and sheath; and automatically
increases the speed of the AMS fan to quickly purge
the sort chamber of aerosols prior to allowing the user
access to the aected area. All the while, the BSC portion
of the system continues operating independently to
maintaincontainment.
In contrast to standard BSCs, the Bigfoot Spectral
Cell Sorter’s integrated BSC filters the air before a
fan pressurizes it for recirculation or exhaust. Uniform
downflow air is established with a low-profile, three-stage
diuser. Therefore, all ducts under positive pressure
contain only filtered air, reducing the risk of leaks containing
aerosols. The fans and sensitive HEPA filters are located
below the work surfaces and to the rear of the instrument.
Thus, HEPA filters are protected from inadvertent damage
during daily operation, noise is kept to a minimum, and
vibrations are isolated from the optical path, which helps
to maintain the superior optical stability of the Bigfoot
Spectral Cell Sorter.
Page 3

User experience innovation
In addition to the eort invested in technical ingenuity,
significant resources were also devoted to user experience
innovations. Inside the laminar airflow barrier there is ample
deck space for sample racks and plates, as well as access
to a built-in sample vortex mixer, tube rack, and biohazard
bag. This makes it possible for the operator to complete
common tasks without breaching the safety barrier multiple
times during the normal workflow (Figure 2). Interior work
surfaces are made with nonporous, durable 304 stainless
steel for easy cleaning.
Lab personnel in biohazardous environments must
work eciently and make use of techniques that reduce
interactions with hazards in order to maximize safety. The
Bigfoot Spectral Cell Sorter includes four major innovations
to help operators limit hazardous contact:
• The sample loader holds multiple controls or samples,
which reduces the need for the operator to enter and
exit the BSC continuously for sample loading
Figure 3. The sort collector accommodates numerous sort tubes.
• The sort collection rack accommodates numerous sort
tubes to collect multiple sorts from dierent runs or
one long run, which reduces the need for the operator
to enter and exit the BSC to unload sorted samples
(Figure 3)
• Plates can be sorted in less than 20 sec; therefore,
the time the operator interacts with the biohazardous
environment is reduced
• The internal control panel limits the need for the
operator to reach in and out of the BSC to operate
the system (Figure 4)
Figure 4. The internal control panel limits the need for the operator to
reach in and out of the BSC.
Figure 2. Adjustable sash in the up position for sampleaccess.
Page 4

Low noise
Due to the integrated design, the Bigfoot Spectral Cell
Sorter is far more compact compared to other models
currently available. The smaller containment area and
thoughtful fan placement have resulted in a system that
produces less noise during operation. Therefore, the
Bigfoot Spectral Cell Sorter can be more comfortably
housed near other laboratory instrumentation and
operators, which is a valuable consideration for spacelimited facilities. Furthermore, by minimizing materials
use, integrated containment reduces the overall cost of
the system so that safety is not compromised due to
limitedfunding.
Conclusion
We have reinterpreted BSC design by enclosing only
potentially pathogen-exposed components and leaving
the rest of the instrument accessible to operators and
service personnel. The recent SARS-CoV-2 crisis has
focused global attention on the importance of biosafety,
which should prompt scientific laboratories to reevaluate
existing biosafety measures, reinforce old procedures,
and implement improvements. Biosafety is increasingly
critical in sorting facilities and is mandated as a condition
of obtaining some grants and funding [4]. The softwareguided containment testing protocol simplifies and
streamlines mandated safety assessments. The Bigfoot
Spectral Cell Sorter provides containment and operator
protections that meet the need for modern cell sorter safety
without sacrificing performance or laboratory space.
Persistent containment
Unlike traditional biosafety cabinets applied to flow
cytometry applications, the sliding sash on the Bigfoot
Spectral Cell Sorter allows improved operator access to
the instrument while still maintaining aerosol containment.
When the sash is in the up position, the operator has safe
access to the sample area (similar to traditional cabinets).
Uniquely, when interaction with the nozzle is necessary, the
operator slides the sash down to access a BSC-contained
upper opening for ergonomic interaction. Upon opening
the nozzle door, the nozzle automatically moves forward
where it can be easily cleaned or changed (Figure 5).
The BSC maintains personnel safety protections for total
system operation regardless of the sash position.
Seamless laboratory integration
The previously referenced ISAC standard was used to
develop an integrated airflow-and-containment software
wizard that guides personnel through the recommended
protocols for periodic AMS testing and yearly BSC
certification. This integrated software has been developed
specifically to run the instrument and the BSC together,
which helps the operator seamlessly follow all biosafety
precautions while running the Bigfoot Spectral Cell Sorter.
Figure 5. Adjustable sash in the down position for nozzleaccess.
References
1. Perfet to, Stephen P. and Ben Fontes. New SARS-CoV-2 Sorting Protocols Released.
ISAC, 26 March 2020, https://isac-net.org/news/497501/NEW-SARS-CoV-2SORTING-PROTOCOLS-RELEASED.htm.
2. Holmes K, Fontes B, Hogarth P, Kunz R, Monard S, Pletcher C, Wadley R, Schmid I,
Perfetto S. International Society for the Advancement of Cytometr y Cell Sorter Biosafety
Standards Cytometry A. May;85(5):434–53. doi: 10.1002/cyto.a.2245 4. Epub 2014
Mar 13. PubMed PMID: 24634405; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC4117398.
3. The NFS Joint Committee on Biosafety Cabinetry. NSF/ANSI 49 - 2018 Biosafety
Cabinetry: Design, Construction, Performance, and Field Certification. NSF
International/American Standards Institute 2019;3.8.2:5–6.
4. Oce of Biotechnology Activities.NIH Guidelines for Research Involving Recombinant
and Synthetic Nucleic Acid Molecules.O ce of Biotechnology Activities;
2013. [Online: the most current version can be found athttp://osp.od.nih.gov/
oce-biotechnology-activities/biosafety/nih-guidelines.]
Find out more at thermofisher.com/bigfoot
For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures. © 20 21 Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc. All right s reserved. All trademarks
are the property of Thermo Fisher Scientific and its subsidiaries unless otherwise specified. COL014843 0321
 Loading...
Loading...