APPLICATION NOTE KingFisher instruments and Dynabeads magnetic beads
Automated immunoprecipitation with seamless
integration to protein analysis
Introduction
Immunoprecipitation (IP) is an
extensively used method in many
dierent research fields, aimed at
isolating a target antigen or its binding
partners for downstream analysis.
In its basic form, this complicated
and lengthy procedure is performed
manually. As protein–protein
complexes often involve transient and
weak interactions, it is critical to use
a workflow that oers rapid binding
kinetics and low nonspecific binding,
in combination with minimized manual
processes, to increase reproducibility
and allow rapid simultaneous
processing of several samples.
Here we present an automated IP
method with seamless integration to
protein analysis. IP was performed
using Invitrogen™ Dynabeads™
magnetic beads on the automated
Thermo Scientific™ KingFisher™ Duo
Prime, Flex, and Apex platforms.
Protein transfer and labeling were
automated using the Invitrogen™ iBlot™
2 Gel Transfer Device for dry blotting
and the Invitrogen™ iBind™ Western
Device (Figure 1).
Automated IP with downstream
integration to protein analysis ensures
high yield and reproducibility, and low
nonspecific binding with significant
reductions in total and hands-on time
compared to the manual protocol.
Manual
Replace
Sample preparation Immunoprecipitation Separation/transfer Immunolabeling
Cell lysis Dynabeads magnetic
beads and
KingFisher instrument
40 minutes
Automation
Bolt electrophoresis
and western blotting
and iBlot 2 system
using Bolt
™
gels
iBind western system,
SuperSignal substrate,
and iBright imaging system
Benefits of Dynabeads products:
• Proper ties:
– Monosized
– Nonporous
– Superparamagnetic
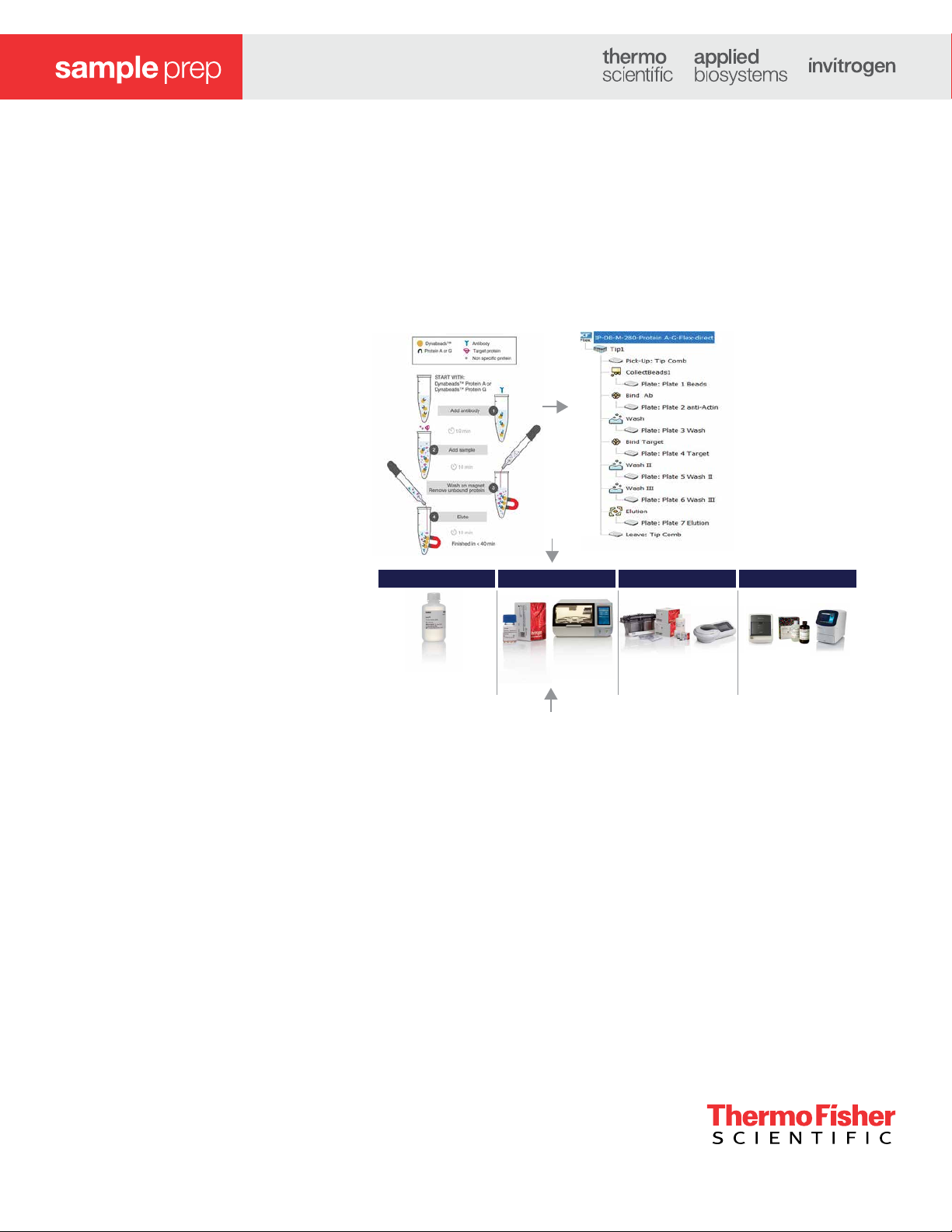
Figure 1. Automated protein capture and detection workflow—from cell lysis to
protein analysis.
Performing IP and downstream protein
analysis is a time-consuming and
labor-intensive process that can take
up to 2–3 days before results can be
evaluated. With this seamless IP and
• Low nonspecific binding
• High reproducibility
• Low antibody consumption
• Fast binding kinetics
The time is reduced by 1 hour when
performing an automated blotting
procedure, and finally the time can be
reduced to 1 day when performing an
automated immunolabeling procedure.
• IP critical factors
– Washing steps
– Mixing (washing)
– Elution volume
protein analysis workflow, it is now
possible to evaluate the results in less
than a day—all with minimal hands-on
activities. The automated IP workflow
provides a 20 minute reduction in
time, compared to a manual workflow.

Immunoprecipitation—reduced
hands-on time
The manual IP protocol starts with
addition of the primary antibody to
the Dynabeads magnetic beads,
followed by a 10 min incubation step.
Unbound antibodies are washed
o; the functionalized Dynabeads
beads are then incubated with the
sample containing the target of
interest. Several washes are included
to reduce the nonspecific binding,
and finally the target is eluted. A
considerable number of hands-on
manipulations are required when
performing IP manually. These
procedures are tedious and errorprone, compared to quick up-front
setup followed by automated IP on the
KingFisher platform. To estimate the
hands-on time saved by automated
vs. manual IP, a stop-watch analysis
was performed when handling 24
samples at a time (Table 1). Handson activities for the manual protocol
included adding the beads to a tube,
washing the beads after antibody
binding, and three washes after
target capture. Hands-on activities
for the automated approach only
included loading plates with the
beads, reagents, and samples
according to the protocol. The results
demonstrated a significant reduction
in hands-on time—for processing
24 samples, automated IP saved 22
minutes (63%) compared to manual
IP. Importantly, in the automated
approach, the hands-on time was
solely limited to the initial phase of the
workflow, while manual IP required the
presence of the operator throughout
the entire protocol.
Western blotting and
immunolabeling—reduced
protocol time
Proteins separated by electrophoresis
are often transferred to a membrane
(nitrocellulose, PVDF) by “wet
transfer”, which involves multiple
manual procedures and requires
preparation of several reagents
and buers. The blotting takes
up to 60 min to complete. For the
automated approach using the
iBlot 2 Gel Transfer Device, where
preparation of reagents, buers,
and stacking gel is not required,
approximately 50 min were saved
on the transfer process compared
to wet transfer (Table 1). Even more
time is saved when the labeling
process is automated using the iBind
Western Device. Immunolabeling
of the blot usually includes several
manual steps—blocking, washing,
and labeling, where extended labeling
times (e.g., overnight) are frequently
used. Limiting the hands-on activities
to preparation of reagents required for
all the steps in the labeling protocol,
and using the iBind device for labeling,
saves a significant amount of time
( Ta b le 1).
Table 1. Comparison of hands-on time using a manual vs. automated approach for protein capture and detection, for 24 samples.
Hands-on time for 24 samples—manual vs. automated IP
Protocol steps Manual Automated
Add antibody to Dynabeads beads 11 m i n
Incubate antibody–beads complex 10 min (incubation)
Wash 1 6 min
Capture target 10 min (incubation)
Wash 2
18 m inWash 3
Wash 4
Elute target 10 min (incubation)
Total hands-on time 35 min 13 min
Western blotting
Manual (1 blot) Automated (1 blot)
Running time 60 min 7 min
Immunolabeling
Manual (1 blot) Automated (1 blot)
Running time 2 days <7 hr
13 min (plate loading)
 Loading...
Loading...