Page 1

XIO2213A PCI Express to 1394b OHCI with 3-Port PHY
Data Manual
PRODUCTION DATA information is current as of publication date.
Products conform to specifications per the terms of the Texas
Instruments standard warranty. Production processing does not
necessarily include testing of all parameters.
Literature Number: SCPS183A
October 2007 – Revised March 2008
Page 2

XIO2213A PCI Express to 1394b OHCI with 3-Port PHY
SCPS183A – OCTOBER 2007 – REVISED MARCH 2008
www.ti.com
Contents
1 Introduction ....................................................................................................................... 13
1.1 XIO2213A Features ........................................................................................................ 13
2 Overview ........................................................................................................................... 14
2.1 Description .................................................................................................................. 14
2.2 Related Documents ........................................................................................................ 16
2.3 Trademarks ................................................................................................................. 16
2.4 Documents Conventions .................................................................................................. 16
2.5 Ordering Information ....................................................................................................... 17
2.6 Terminal Assignments ..................................................................................................... 17
2.7 Terminal Descriptions ...................................................................................................... 21
3 Feature/Protocol Descriptions .............................................................................................. 29
3.1 Power-Up/-Down Sequencing ............................................................................................ 29
3.1.1 Power-Up Sequence ............................................................................................ 30
3.1.2 Power-Down Sequence ......................................................................................... 31
3.2 XIO2213A Reset Features ................................................................................................ 31
3.3 PCI Express Interface ..................................................................................................... 32
3.3.1 External Reference Clock ...................................................................................... 32
3.3.2 Beacon and Wake ............................................................................................... 32
3.3.3 Initial Flow Control Credits ..................................................................................... 32
3.3.4 PCI Express Message Transactions .......................................................................... 33
3.4 PCI Interrupt Conversion to PCI Express Messages .................................................................. 34
3.5 Two-Wire Serial-Bus Interface ............................................................................................ 34
3.5.1 Serial-Bus Interface Implementation .......................................................................... 34
3.5.2 Serial-Bus Interface Protocol ................................................................................... 35
3.5.3 Serial-Bus EEPROM Application .............................................................................. 37
3.5.4 Accessing Serial-Bus Devices Through Softwaree ......................................................... 39
3.6 Advanced Error Reporting Registers .................................................................................... 40
3.7 Data Error Forwarding Capability ........................................................................................ 40
3.8 General-Purpose I/O Interfacee .......................................................................................... 40
3.9 Set Slot Power Limit Functionality ....................................................................................... 40
3.10 PCI Express and PCI Bus Power Management ........................................................................ 41
3.11 1394b OHCI Controller Functionality .................................................................................... 42
3.11.1 1394b OHCI Power Management ............................................................................. 42
3.11.2 1394b OHCI and V
3.11.3 1394b OHCI and Reset Options ............................................................................... 42
3.11.4 1394b OHCI PCI Bus Master .................................................................................. 42
3.11.5 1394b OHCI Subsystem Identification ........................................................................ 43
3.11.6 1394b OHCI PME Support ..................................................................................... 43
4 Classic PCI Configuration Space .......................................................................................... 44
4.1 Vendor ID Register ......................................................................................................... 45
4.2 Device ID Register ......................................................................................................... 45
4.3 Command Register ........................................................................................................ 45
4.4 Status Register ............................................................................................................. 47
4.5 Class Code and Revision ID Register ................................................................................... 48
4.6 Cache Line Size Register ................................................................................................. 48
4.7 Primary Latency Timer Register .......................................................................................... 48
4.8 Header Type Register ..................................................................................................... 49
4.9 BIST Register ............................................................................................................... 49
4.10 Device Control Base Address Register ................................................................................. 49
4.11 Scratchpad RAM Base Address .......................................................................................... 49
.......................................................................................... 42
AUX
Contents 2 Submit Documentation Feedback
Page 3

XIO2213A PCI Express to 1394b OHCI with 3-Port PHY
www.ti.com
4.12 Primary Bus Number Register ............................................................................................ 50
4.13 Secondary Bus Number Register ........................................................................................ 50
4.14 Subordinate Bus Number Register ...................................................................................... 50
4.15 Secondary Latency Timer Register ...................................................................................... 51
4.16 I/O Base Register .......................................................................................................... 52
4.17 I/O Limit Register ........................................................................................................... 52
4.18 Secondary Status Register ................................................................................................ 53
4.19 Memory Base Register .................................................................................................... 54
4.20 Memory Limit Register ..................................................................................................... 54
4.21 Prefetchable Memory Base Register .................................................................................... 54
4.22 Prefetchable Memory Limit Register ..................................................................................... 55
4.23 Prefetchable Base Upper 32 Bits Register .............................................................................. 55
4.24 Prefetchable Limit Upper 32 Bits Register .............................................................................. 55
4.25 I/O Base Upper 16 Bits Register ......................................................................................... 56
4.26 I/O Limit Upper 16 Bits Register .......................................................................................... 56
4.27 Capabilities Pointer Register .............................................................................................. 56
4.28 Interrupt Line Register ..................................................................................................... 57
4.29 Interrupt Pin Register ...................................................................................................... 57
4.30 Bridge Control Register .................................................................................................... 58
4.31 Capability ID Register ...................................................................................................... 60
4.32 Next Item Pointer Register ................................................................................................ 60
4.33 Power Management Capabilities Register .............................................................................. 60
4.34 Power Management Control/Status Register ........................................................................... 61
4.35 Power Management Bridge Support Extension Register ............................................................. 61
4.36 Power Management Data Register ...................................................................................... 62
4.37 MSI Capability ID Register ................................................................................................ 62
4.38 Next Item Pointer Register ................................................................................................ 62
4.39 MSI Message Control Register ........................................................................................... 63
4.40 MSI Message Lower Address Register ................................................................................. 63
4.41 MSI Message Upper Address Register ................................................................................. 64
4.42 MSI Message Data Register .............................................................................................. 64
4.43 Capability ID Register ...................................................................................................... 65
4.44 Next Item Pointer Register ............................................................................................... 65
4.45 Subsystem Vendor ID Register ........................................................................................... 65
4.46 Subsystem ID Register .................................................................................................... 65
4.47 PCI Express Capability ID Register ...................................................................................... 65
4.48 Next Item Pointer Register ................................................................................................ 66
4.49 PCI Express Capabilities Register ....................................................................................... 66
4.50 Device Capabilities Register .............................................................................................. 67
4.51 Device Control Register ................................................................................................... 68
4.52 Device Status Register .................................................................................................... 69
4.53 Link Capabilities Register ................................................................................................. 70
4.54 Link Control Register ...................................................................................................... 71
4.55 Link Status Register ........................................................................................................ 72
4.56 Serial-Bus Data Register .................................................................................................. 72
4.57 Serial-Bus Word Address Register ....................................................................................... 72
4.58 Serial-Bus Slave Address Register ..................................................................................... 73
4.59 Serial-Bus Control and Status Register ................................................................................. 73
4.60 GPIO Control Register ..................................................................................................... 75
4.61 GPIO Data Register ........................................................................................................ 76
4.62 Control and Diagnostic Register 0 ....................................................................................... 77
4.63 Control and Diagnostic Register 1 ....................................................................................... 78
4.64 PHY Control and Diagnostic Register 2 ................................................................................. 80
SCPS183A – OCTOBER 2007 – REVISED MARCH 2008
Contents 3
Page 4

XIO2213A PCI Express to 1394b OHCI with 3-Port PHY
SCPS183A – OCTOBER 2007 – REVISED MARCH 2008
4.65 Subsystem Access Register .............................................................................................. 80
4.66 General Control Register .................................................................................................. 81
4.67 TI Proprietary Register .................................................................................................... 83
4.68 TI Proprietary Register .................................................................................................... 83
4.69 TI Proprietary Register ..................................................................................................... 84
4.70 Arbiter Control Register ................................................................................................... 85
4.71 Arbiter Request Mask Registert .......................................................................................... 86
4.72 Arbiter Time-Out Status Register ........................................................................................ 86
4.73 TI Proprietary Register ..................................................................................................... 87
4.74 TI Proprietary Register .................................................................................................... 87
4.75 TI Proprietary Register ..................................................................................................... 87
5 PCI Express Extended Configuration Space .......................................................................... 89
5.1 Advanced Error Reporting Capability ID Register ..................................................................... 89
5.2 Next Capability Offset/Capability Version Register .................................................................... 89
5.3 Uncorrectable Error Status Register ..................................................................................... 91
5.4 Uncorrectable Error Mask Register ...................................................................................... 91
5.5 Uncorrectable Error Severity Register ................................................................................... 93
5.6 Correctable Error Status Register ........................................................................................ 94
5.7 Correctable Error Mask Register ......................................................................................... 95
5.8 Advanced Error Capabilities and Control Register ..................................................................... 96
5.9 Header Log Register ....................................................................................................... 96
5.10 Secondary Uncorrectable Error Status Register ....................................................................... 97
5.11 Secondary Uncorrectable Error Mask Register ........................................................................ 98
5.12 Secondary Uncorrectable Error Severity ................................................................................ 99
5.13 Secondary Error Capabilities and Control Register .................................................................. 100
5.14 Secondary Header Log Register ........................................................................................ 101
6 Memory-Mapped TI Proprietary Register Space .................................................................... 102
6.1 Device Control Map ID Register ........................................................................................ 102
6.2 Revision ID Register ...................................................................................................... 103
6.3 GPIO Control Register ................................................................................................... 103
6.4 GPIO Data Register ...................................................................................................... 104
6.5 Serial-Bus Data Register ................................................................................................ 105
6.6 Serial-Bus Word Address Register ..................................................................................... 105
6.7 Serial-Bus Slave Address Register .................................................................................... 105
6.8 Serial-Bus Control and Status Register ................................................................................ 105
7 1394 OHCI—PCI Configuration Space ................................................................................. 107
7.1 Vendor ID Register ....................................................................................................... 108
7.2 Device ID Register ........................................................................................................ 108
7.3 Command Register ....................................................................................................... 108
7.4 Status Register ............................................................................................................ 109
7.5 Class Code and Revision ID Register ................................................................................. 110
7.6 Cache Line Size and Latency Timer Register ........................................................................ 110
7.7 Header Type and BIST Register ........................................................................................ 111
7.8 OHCI Base Address Register ........................................................................................... 111
7.9 TI Extension Base Address Register ................................................................................... 112
7.10 CIS Base Address Register ............................................................................................. 113
7.11 CIS Pointer Register ...................................................................................................... 113
7.12 Subsystem Identification Register ...................................................................................... 113
7.13 Power Management Capabilities Pointer Register ................................................................... 114
7.14 Interrupt Line and Pin Register ......................................................................................... 114
7.15 MIN_GNT and MAX_LAT Register ..................................................................................... 114
7.16 OHCI Control Register ................................................................................................... 115
www.ti.com
Contents 4 Submit Documentation Feedback
Page 5

XIO2213A PCI Express to 1394b OHCI with 3-Port PHY
www.ti.com
7.17 Capability ID and Next Item Pointer Registers ....................................................................... 115
7.18 Power Management Capabilities Register ............................................................................ 116
7.19 Power Management Control and Status Register .................................................................... 116
7.20 Power Management Extension Registers ............................................................................. 117
7.21 PCI Miscellaneous Configuration Register ............................................................................ 118
7.22 Link Enhancement Control Register ................................................................................... 119
7.23 Subsystem Access Register ............................................................................................. 121
8 1394 OHCI Memory-Mapped Register Space ........................................................................ 122
8.1 OHCI Version Register ................................................................................................... 124
8.2 GUID ROM Register ..................................................................................................... 125
8.3 Asynchronous Transmit Retries Register .............................................................................. 126
8.4 CSR Data Register ...................................................................................................... 126
8.5 CSR Compare Register .................................................................................................. 127
8.6 CSR Control Register .................................................................................................... 127
8.7 Configuration ROM Header Register ................................................................................... 127
8.8 Bus Identification Register ............................................................................................... 128
8.9 Bus Options Register ..................................................................................................... 128
8.10 GUID High Register ...................................................................................................... 129
8.11 GUID Low Register ....................................................................................................... 130
8.12 Configuration ROM Mapping Register ................................................................................. 130
8.13 Posted Write Address Low Register ................................................................................... 130
8.14 Posted Write Address High Register ................................................................................... 131
8.15 Vendor ID Register ....................................................................................................... 131
8.16 Host Controller Control Register ........................................................................................ 131
8.17 Self-ID Buffer Pointer Register .......................................................................................... 133
8.18 Self-ID Count Register ................................................................................................... 133
8.19 Isochronous Receive Channel Mask High Register .................................................................. 134
8.20 Isochronous Receive Channel Mask Low Register .................................................................. 135
8.21 Interrupt Event Register .................................................................................................. 135
8.22 Interrupt Mask Register .................................................................................................. 137
8.23 Isochronous Transmit Interrupt Event Register ....................................................................... 139
8.24 Isochronous Transmit Interrupt Mask Register ....................................................................... 139
8.25 Isochronous Receive Interrupt Event Register ........................................................................ 140
8.26 Isochronous Receive Interrupt Mask Register ........................................................................ 140
8.27 Initial Bandwidth Available Register .................................................................................... 141
8.28 Initial Channels Available High Register ............................................................................... 141
8.29 Initial Channels Available Low Register ............................................................................... 142
8.30 Fairness Control Register ................................................................................................ 143
8.31 Link Control Register ..................................................................................................... 144
8.32 Node Identification Register ............................................................................................. 145
8.33 PHY Layer Control Register ............................................................................................. 146
8.34 Isochronous Cycle Timer Register ..................................................................................... 147
8.35 Asynchronous Request Filter High Register ......................................................................... 148
8.36 Asynchronous Request Filter Low Register ........................................................................... 150
8.37 Physical Request Filter High Register ................................................................................. 151
8.38 Physical Request Filter Low Register .................................................................................. 153
8.39 Physical Upper Bound Register (Optional Register) ................................................................. 153
8.40 Asynchronous Context Control Register ............................................................................... 154
8.41 Asynchronous Context Command Pointer Register .................................................................. 155
8.42 Isochronous Transmit Context Control Register ...................................................................... 156
8.43 Isochronous Transmit Context Command Pointer Register ......................................................... 157
8.44 Isochronous Receive Context Control Register ....................................................................... 157
8.45 Isochronous Receive Context Command Pointer Register ......................................................... 158
SCPS183A – OCTOBER 2007 – REVISED MARCH 2008
Contents 5
Page 6

XIO2213A PCI Express to 1394b OHCI with 3-Port PHY
SCPS183A – OCTOBER 2007 – REVISED MARCH 2008
8.46 Isochronous Receive Context Match Register ........................................................................ 159
9 1394 OHCI Memory-Mapped TI Extension Register Space ...................................................... 160
9.1 DV and MPEG2 Timestamp Enhancements .......................................................................... 160
9.2 Isochronous Receive Digital Video Enhancements .................................................................. 160
9.3 Isochronous Receive Digital Video Enhancements Register ....................................................... 161
9.4 Link Enhancement Register ............................................................................................. 162
9.5 Timestamp Offset Register .............................................................................................. 164
10 PHY Section .................................................................................................................... 165
10.1 PHY Section Register Configuration ................................................................................... 166
10.2 PHY Section Application Information ................................................................................... 172
10.2.1 Power Class Programming ................................................................................... 172
10.2.2 Power-Up Reset ................................................................................................ 172
10.2.3 Crystal Oscillator Selection ................................................................................... 172
10.2.4 Bus Reset ....................................................................................................... 173
11 Electrical Characteristics ................................................................................................... 175
11.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings ............................................................................................. 175
11.2 Recommended Operating Conditions .................................................................................. 175
11.3 PCI Express Differential Transmitter Output Ranges ................................................................ 175
11.4 PCI Express Differential Receiver Input Ranges ..................................................................... 177
11.5 PCI Express Differential Reference Clock Input Ranges ............................................................ 178
11.6 Electrical Characteristics Over Recommended Operating Conditions (3.3-V I/O) ............................... 178
11.7 Electrical Characteristics Over Recommended Operating Conditions (PHY Port Driver) ...................... 179
11.8 Switching Characteristics for PHY Port Driver ....................................................................... 179
11.9 Electrical Characteristics Over Recommended Operating Conditions PHY Port Receiver .................... 180
11.10 Jitter/Skew Characteristics for 1394a PHY Port Receiver ......................................................... 180
11.11 Operating, Timing, and Switching Characteristics of XI ............................................................ 180
11.12 Electrical Characteristics Over Recommended Operating Conditions (1394a Miscellaneous I/O) ........... 180
12 Glossary .......................................................................................................................... 181
13 Mechanical Data ............................................................................................................... 182
Important Notices ...................................................................................................................... 183
www.ti.com
Contents 6 Submit Documentation Feedback
Page 7

XIO2213A PCI Express to 1394b OHCI with 3-Port PHY
www.ti.com
SCPS183A – OCTOBER 2007 – REVISED MARCH 2008
List of Figures
3-1 XIO2213A Block Diagram ........................................................................................................ 29
3-2 Power-Up Sequence .............................................................................................................. 30
3-3 Power-Down Sequence .......................................................................................................... 31
3-4 PCI Express ASSERT_INTA Message ......................................................................................... 34
3-5 PCI Express DEASSERT_INTX Message ..................................................................................... 34
3-6 Serial EEPROM Application ..................................................................................................... 35
3-7 Serial-Bus Start/Stop Conditions and Bit Transfers .......................................................................... 35
3-8 Serial-Bus Protocol Acknowledge ............................................................................................... 36
3-9 Serial-Bus Protocol – Byte Write ................................................................................................ 36
3-10 Serial-Bus Protocol – Byte Read ................................................................................................ 37
3-11 Serial-Bus Protocol – Multibyte Read .......................................................................................... 37
11-1 Test Load Diagram .............................................................................................................. 179
List of Figures 7
Page 8

XIO2213A PCI Express to 1394b OHCI with 3-Port PHY
SCPS183A – OCTOBER 2007 – REVISED MARCH 2008
www.ti.com
List of Tables
2-1 XIO2213AZAY_12x12 Terminals Sorted Alphanumerically ................................................................. 18
2-2 XIO2213AZAY_12x12 Signals Sorted Alphanumerically .................................................................... 20
2-3 Power Supply Terminals ......................................................................................................... 23
2-4 Ground Terminals ................................................................................................................. 23
2-5 PCI Express Terminals ........................................................................................................... 24
2-6 Clock Terminals ................................................................................................................... 24
2-7 1394 Terminals .................................................................................................................... 24
2-8 Reserved Terminals .............................................................................................................. 27
2-9 Miscellaneous Terminals ......................................................................................................... 27
3-1 XIO2213A Reset Options ........................................................................................................ 31
3-2 Initial Flow Control Credit Advertisements ..................................................................................... 32
3-3 Messages Supported byf the Bridge ........................................................................................... 33
3-4 EEPROM Register Loading Map ................................................................................................ 37
3-5 Registers Used To Program Serial-Bus Devices ............................................................................. 39
3-6 Clocking In Low Power States ................................................................................................... 41
3-7 1394b OHCI Configuration Register Map ...................................................................................... 42
3-8 1394 OHCI Memory Command Options ....................................................................................... 43
4-1 Classic PCI Configuration Register Map ....................................................................................... 44
4-2 Command Register Description ................................................................................................. 46
4-3 Status Register Description ...................................................................................................... 47
4-4 Class Code and Revision ID Register Description ........................................................................... 48
4-5 Device Control Base Address Register Description .......................................................................... 49
4-6 Device Control Base Address Register Description .......................................................................... 50
4-7 I/O Base Register Description ................................................................................................... 52
4-8 I/O Limit Register Description ................................................................................................... 52
4-9 Secondary Status Register Description ........................................................................................ 53
4-10 Memory Base Register Description ............................................................................................. 54
4-11 Memory Limit Register Description ............................................................................................. 54
4-12 Prefetchable Memory Base Register Description ............................................................................. 54
4-13 Prefetchable Memory Limit Register Description ............................................................................. 55
4-14 Prefetchable Base Upper 32 Bits Register Description ...................................................................... 55
4-15 Prefetchable Limit Upper 32 Bits Register Description ....................................................................... 56
4-16 I/O Base Upper 16 Bits Register Description .................................................................................. 56
4-17 I/O Limit Upper 16 Bits Register Description .................................................................................. 56
4-18 Bridge Control Register Description ............................................................................................ 58
4-19 Power Management Capabilities Register Description ...................................................................... 60
4-20 Power Management Control/Status Register Description ................................................................... 61
4-21 PM Bridge Support Extension Register Description .......................................................................... 62
4-22 MSI Message Control Register Description ................................................................................... 63
List of Tables8 Submit Documentation Feedback
Page 9

XIO2213A PCI Express to 1394b OHCI with 3-Port PHY
www.ti.com
4-23 MSI Message Lower Address Register Description .......................................................................... 64
4-24 MSI Message Data Register Description ...................................................................................... 64
4-25 PCI Express Capabilities Register Description ................................................................................ 66
4-26 Device Capabilities Register Description ...................................................................................... 67
4-27 Device Control Register Description ............................................................................................ 68
4-28 Device Status Register Description ............................................................................................. 69
4-29 Link Capabilities Register Description .......................................................................................... 70
4-30 Link Control Register Description ............................................................................................... 71
4-31 Link Status Register Description ................................................................................................ 72
4-32 Serial-Bus Slave Address Register Descriptions ............................................................................. 73
4-33 Serial-Bus Control and Status Register Description .......................................................................... 73
4-34 GPIO Control Register Description ............................................................................................. 75
4-35 GPIO Data Register Description ................................................................................................ 76
4-36 Control and Diagnostic Register 0 Description ............................................................................... 77
4-37 Control and Diagnostic Register 1 Description ............................................................................... 78
4-38 Control and Diagnostic Register 2 Description ............................................................................... 80
4-39 Subsystem Access Register Description ....................................................................................... 81
4-40 General Control Register Description .......................................................................................... 81
4-41 Arbiter Control Register Description ............................................................................................ 85
4-42 Arbiter Request Mask Register Description ................................................................................... 86
4-43 Arbiter Time-Out Status Register Description ................................................................................. 86
5-1 PCI Express Extended Configuration Register Map .......................................................................... 89
5-2 Uncorrectable Error Status Register Description ............................................................................. 91
5-3 Uncorrectable Error Mask Register Description ............................................................................... 92
5-4 Uncorrectable Error Severity Register Description ........................................................................... 93
5-5 Correctable Error Status Register Description ................................................................................ 94
5-6 Correctable Error Mask Register Description ................................................................................. 95
5-7 Advanced Error Capabilities and Control Register Description ............................................................. 96
5-8 Secondary Uncorrectable Error Status Register Description ................................................................ 97
5-9 Secondary Uncorrectable Error Mask Register Description ................................................................. 98
5-10 Secondary Uncorrectable Error Severity Register Description ............................................................. 99
5-11 Secondary Error Capabilities and Control Register Description ........................................................... 100
5-12 Secondary Header Log Register Description ................................................................................ 101
6-1 Device Control Memory Window Register Map ............................................................................. 102
6-2 GPIO Control Register Description ............................................................................................ 103
6-3 GPIO Data Register Description ............................................................................................... 104
6-4 Serial-Bus Slave Address Register Descriptions ............................................................................ 105
6-5 Serial-Bus Control and Status Register Description ........................................................................ 106
7-1 1394 OHCI Configuration Register Map ...................................................................................... 107
7-2 Command Register Description ................................................................................................ 108
7-3 Status Register Description .................................................................................................... 109
SCPS183A – OCTOBER 2007 – REVISED MARCH 2008
List of Tables 9
Page 10

XIO2213A PCI Express to 1394b OHCI with 3-Port PHY
SCPS183A – OCTOBER 2007 – REVISED MARCH 2008
7-4 Class Code and Revision ID Register Description .......................................................................... 110
7-5 Latency Timer and Class Cache Line Size Register Description ......................................................... 111
7-6 Header Type and BIST Register Description ............................................................................... 111
7-7 OHCI Base Address Register Description .................................................................................... 112
7-8 TI Base Address Register Description ........................................................................................ 112
7-9 Subsystem Identification Register Description ............................................................................... 113
7-10 Interrupt Line and Pin Registers Description ................................................................................. 114
7-11 MIN_GNT and MAX_LAT Register Description ............................................................................. 115
7-12 OHCI Control Register Descriptioni ........................................................................................... 115
7-13 Capability ID and Next Item Pointer Registers Description ................................................................ 115
7-14 Interrupt Line and Pin Registers Description ................................................................................. 116
7-15 Power Management Control and Status Register Description ............................................................ 116
7-16 Power Management Extension Registers Description ...................................................................... 117
7-17 Miscellaneous Configuration Register ........................................................................................ 118
7-18 Link Enhancement Control Register Description ............................................................................ 120
7-19 Subsystem Access Register Description ..................................................................................... 121
8-1 OHCI Register Map ............................................................................................................. 122
8-2 OHCI Version Register Description ........................................................................................... 124
8-3 GUID ROM Register Description .............................................................................................. 125
8-4 Asynchronous Transmit Retries Register Description ...................................................................... 126
8-5 CSR Control Register Description ............................................................................................. 127
8-6 Configuration ROM Header Register Description ........................................................................... 128
8-7 Bus Options Register Description ............................................................................................. 128
8-8 Configuration ROM Mapping Register Description .......................................................................... 130
8-9 Posted Write Address Low Register Description ............................................................................ 131
8-10 Posted Write Address High Register Description ........................................................................... 131
8-11 Host Controller Control Register Description ................................................................................ 132
8-12 Self-ID Count Register Description ............................................................................................ 133
8-13 Isochronous Receive Channel Mask High Register Description .......................................................... 134
8-14 Isochronous Receive Channel Mask Low Register Description ........................................................... 135
8-15 Interrupt Event Register Description .......................................................................................... 135
8-16 Interrupt Mask Register Description ........................................................................................... 137
8-17 Isochronous Transmit Interrupt Event Register Description ............................................................... 139
8-18 Isochronous Receive Interrupt Event Register Description ................................................................ 140
8-19 Initial Bandwidth Available Register Description ............................................................................ 141
8-20 Initial Channels Available High Registr Description ......................................................................... 141
8-21 Initial Channels Available Low Register Description ........................................................................ 142
8-22 Fairness Control Registre Description ........................................................................................ 143
8-23 Link Control Register Description ............................................................................................. 144
8-24 Node Identification Register Description ...................................................................................... 145
8-25 PHY Control Register Description ............................................................................................. 146
www.ti.com
List of Tables10 Submit Documentation Feedback
Page 11

XIO2213A PCI Express to 1394b OHCI with 3-Port PHY
www.ti.com
8-26 Isochronous Cycle Timer Register Description .............................................................................. 147
8-27 Asynchronous Request Filter High Register Description ................................................................... 148
8-28 Asynchronous Request Filter Low Register Description ................................................................... 150
8-29 Physical Request Filter High Register Description .......................................................................... 151
8-30 Physical Request Filter Low Register Description .......................................................................... 153
8-31 Asynchronous Context Control Register Description ....................................................................... 154
8-32 Asynchronous Context Command Pointer Register Description ......................................................... 155
8-33 Isochronous Transmit Context Control Register Description .............................................................. 156
8-34 Isochronous Receive Context Control Register Description ............................................................... 157
8-35 Isochronous Receive Context Match Register Description ................................................................ 159
9-1 TI Extension Register Map ..................................................................................................... 160
9-2 Isochronous Receive Digital Video Enhancements Register Description ................................................ 161
9-3 Link Enhancement Register Description ...................................................................................... 162
9-4 Timestamp Offset Register Description ....................................................................................... 164
10-1 Base Register Description ...................................................................................................... 167
10-2 Base Register Field Description ............................................................................................... 167
10-3 Page-0 (Port Status) Register Description ................................................................................... 169
10-4 Page-0 (Port Status) Register Field Description ............................................................................. 169
10-5 Page 1 (Vendor ID) Register Configuration .................................................................................. 171
10-6 Page 1 (Vendor ID) Register Field Descriptions ............................................................................. 171
10-7 Page 7 (Vendor Dependant) Register Configuration ....................................................................... 171
10-8 Page 7 (Vendor Dependant) Register Field Descriptions .................................................................. 172
10-9 Register Description ............................................................................................................. 172
SCPS183A – OCTOBER 2007 – REVISED MARCH 2008
OHCI-Lynx is a trademark of Texas Instruments.
PCI Express is a trademark of PCI-SIG.
List of Tables 11
Page 12

XIO2213A PCI Express to 1394b OHCI with 3-Port PHY
SCPS183A – OCTOBER 2007 – REVISED MARCH 2008
www.ti.com
List of Tables12 Submit Documentation Feedback
Page 13

www.ti.com
1 Introduction
1.1 XIO2213A Features
• Full x1 PCI Express Throughput
• Fully Compliant with PCI Express Base
Specification, Revision 1.1
• Utilizes 100-MHz Differential PCI Express
Common Reference Clock or 125-MHz
Single-Ended Reference Clock
• Fully supports provisions of IEEE P1394b-2002
• Fully Compliant With Provisions of IEEE Std
1394-1995 for a High-Performance Serial Bus
and IEEE Std 1394a-2000
• Fully Compliant with 1394 Open Host
Controller Interface Specification, Revision 1.1
and Revision 1.2 draft
• Three IEEE Std 1394b Fully Compliant Cable
XIO2213A PCI Express to 1394b OHCI with 3-Port PHY
SCPS183A – OCTOBER 2007 – REVISED MARCH 2008
Ports at 100M Bits/s, 200M Bits/s, 400M Bits/s,
and 800M Bits/s
• Cable Ports Monitor Line Conditions for Active
Connection To Remote Node
• Cable Power Presence Monitoring
• EEPROM Configuration Support to Load the
Global Unique ID for the 1394 Fabric
• Support for D1, D2, D3
• Active State Link Power Management Saves
Power When Packet Activity on the PCI
Express™ Link is Idle, Using Both L0s and L1
States
• Eight 3.3-V, Multifunction, General-Purpose I/O
Terminals
hot
Please be aware that an important notice concerning availability, standard warranty, and use in critical applications of Texas
Instruments semiconductor products and disclaimers thereto appears at the end of this document.
OHCI-Lynx is a trademark of Texas Instruments.
PCI Express is a trademark of PCI-SIG.
PRODUCTION DATA information is current as of publication date.
Products conform to specifications per the terms of the Texas
Instruments standard warranty. Production processing does not
necessarily include testing of all parameters.
Copyright © 2007–2008, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Page 14

XIO2213A PCI Express to 1394b OHCI with 3-Port PHY
SCPS183A – OCTOBER 2007 – REVISED MARCH 2008
2 Overview
The Texas Instruments XIO2213A is a single-function PCI Express™ to PCI local bus translation bridge
where the PCI bus interface is internally connected to a 1394b open host controller link-layer controller
with a three-port 1394b PHY. When the XIO2213A is properly configured, this solution provides full PCI
Express and 1394b functionality and performance.
2.1 Description
The Texas Instruments XIO2213A is a PCI Express to PCI translation bridge where the PCI bus interface
is internally connected to a 1394b open host controller link-layer controller with a three-port 1394b PHY.
The PCI-Express to PCI translation bridge is fully compatible with the PCI Express to PCI/PCI-X Bridge
Specification, Revision 1.0. Also, the bridge supports the standard PCI-to-PCI bridge programming model.
The 1394b OHCI controller function is fully compatible with IEEE Standard 1394b and the latest 1394
Open Host Controller Interface (OHCI) Specification.
The XIO2213A simultaneously supports up to four posted write transactions, four non-posted transactions,
and four completion transactions pending in each direction at any time. Each posted write data queue and
completion data queue can store up to 8K bytes of data. The non-posted data queues can store up to 128
bytes of data.
The PCI Express interface supports a x1 link operating at full 250 MB/s packet throughput in each
direction simultaneously. Also, the bridge supports the advanced error reporting capability including ECRC
as defined in the PCI Express Base Specification, Revision 1.1. Supplemental firmware or software is
required to fully utilize both of these features.
www.ti.com
Robust pipeline architecture is implemented to minimize system latency. If parity errors are detected, then
packet poisoning is supported for both upstream and downstream operations.
The PCIe Power management (PM) features include active state link PM, PME mechanisms, and all
conventional PCI D-states. If the active state link PM is enabled, then the link automatically saves power
when idle using the L0s and L1 states. PM active state NAK, PM PME, and PME-to-ACK messages are
supported. The bridge is compliant with the latest PCI Bus Power Management Specification and provides
several low-power modes, which enable the host power system to further reduce power consumption
Eight general-purpose inputs and outputs (GPIOs), configured through accesses to the PCI Express
configuration space, allow for further system control and customization.
Deep FIFOs are provided to buffer 1394 data and accommodate large host bus latencies. The device
provides physical write posting and a highly tuned physical data path for SBP-2 performance. The device
is capable of transferring data between the PCI Express bus and the 1394 bus at 100M bits/s, 200M
bits/s, 400M bits/s, and 800M bits/s. The device provides three 1394 ports that have separate cable bias
(TPBIAS).
As required by the 1394 Open Host Controller Interface Specification, internal control registers are
memory-mapped and nonprefetchable. This configuration header is accessed through configuration cycles
specified by PCI Express, and it provides plug-and-play (PnP) compatibility.
The PHY-layer provides the digital and analog transceiver functions needed to implement a three-port
node in a cable-based 1394 network. Each cable port incorporates two differential line transceivers. The
transceivers include circuitry to monitor the line conditions as needed for determining connection status,
for initialization and arbitration, and for packet reception and transmission. An optional external 2-wire
serial EEPROM interface is provided to load the global unique ID for the 1394 fabric.
Overview 14 Submit Documentation Feedback
Page 15

XIO2213A PCI Express to 1394b OHCI with 3-Port PHY
www.ti.com
The XIO2213A requires an external 98.304-MHz crystal oscillator to generate a reference clock. The
external clock drives an internal phase-locked loop (PLL), which generates the required reference signal.
This reference signal provides the clock signals that control transmission of the outbound encoded
information. The power-down (PD) function, when enabled by asserting the PD terminal high, stops
operation of the PLL. Data bits to be transmitted through the cable ports are latched internally, combined
serially, encoded, and transmitted at 98.304, 196.608, 393.216, 491.52, or 983.04 Mbps (referred to as
S100, S200, S400, S400B, or S800 speed, respectively) as the outbound information stream.
To ensure that the XIO2213A conforms to the IEEE Std 1394b-2002 standard, the BMODE terminal must
be asserted. The BMODE terminal does not select the cable-interface mode of operation. The BMODE
terminal selects the internal PHY section-LLC section interface mode of operation and affects the
arbitration modes on the cable. BMODE must be pulled high during normal operation.
Three package terminals are used as inputs to set the default value for three configuration status bits in
the self-ID packet. They can be pulled high through a 1-k Ω resistor or hardwired low as a function of the
equipment design. The PC0, PC1, and PC2 terminals indicate the default power class status for the node
(the need for power from the cable or the ability to supply power to the cable). The contender bit in the
PHY register set indicates that the node is a contender either for the isochronous resource manager (IRM)
or for the bus manager (BM). On the XIO2213A, this bit can only be set by a write to the PHY register set.
If a node is to be a contender for IRM or BM, the node software must set this bit in the PHY register set.
SCPS183A – OCTOBER 2007 – REVISED MARCH 2008
Submit Documentation Feedback Overview 15
Page 16

XIO2213A PCI Express to 1394b OHCI with 3-Port PHY
SCPS183A – OCTOBER 2007 – REVISED MARCH 2008
2.2 Related Documents
• PCI Express to PCI/PCI-X Bridge Specification, Revision 1.0
• PCI Express Base Specification, Revision 1.1
• PCI Express Card Electromechanical Specification, Revision 1.1
• PCI Local Bus Specification, Revision 2.3 and 3.0
• PCI-to-PCI Bridge Architecture Specification, Revision 1.1
• PCI Bus Power Management Interface Specification, Revision 1.1 or 1.2
• 1394 Open Host Controller Interface Specification Release 1.2
• IEEE Standard for a High Performance Serial Bus IEEE Std 1394-1995
• IEEE Standard for a High Performance Serial Bus—Amendment 1 IEEE Std 1394a-2000
• IEEE Standard for a High Performance Serial Bus—Amendment 2 IEEE Std 1394b-2002
• Express Card Standard, Release 1.0 and 1.1
• PCI Express Jitter and BER White Paper
• PCI Mobile Design Guide, Revision 1.1
2.3 Trademarks
• PCI Express is a trademark of PCI-SIG.
• OHCI-Lynx, and MicroStar BGA are trademarks of Texas Instruments.
• Other trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
www.ti.com
2.4 Documents Conventions
Throughout this data manual, several conventions are used to convey information. These conventions are
listed below:
1. To identify a binary number or field, a lower case b follows the numbers. For example: 000b is a 3-bit
binary field.
2. To identify a hexadecimal number or field, a lower case h follows the numbers. For example: 8AFh is a
12-bit hexadecimal field.
3. All other numbers that appear in this document that do not have either a b or h following the number
are assumed to be decimal format.
4. If the signal or terminal name has a bar above the name (for example, GRST), then this indicates the
logical NOT function. When asserted, this signal is a logic low, 0, or 0b.
5. Differential signal names end with P, N, +, or – designators. The P or + designators signify the positive
signal associated with the differential pair. The N or – designators signify the negative signal
associated with the differential pair.
6. RSVD indicates that the referenced item is reserved.
7. In Sections 4 through 6, the configuration space for the bridge is defined. For each register bit, the
software access method is identified in an access column. The legend for this access column includes
the following entries:
– r – read access by software
– u – updates by the bridge internal hardware
– w – write access by software
– c – clear an asserted bit with a write-back of 1b by software. Write of zero to the field has no effect
– s – the field may be set by a write of one. Write of zero to the field has no effect
– na – not accessible or not applicable
8. The XIO2213A consists of a PCI-Express to PCI translation bridge where the secondary PCI bus is
internally connected to a 1394b OHCI with a 3-port PHY. When describing functionality that is specific
to the PCI-Express to PCI translation bridge, the term bridge is used to reduce text. The term 1394b
OHCI is used to reduce text when describing the 1394b OHCI with 3-port PHY function.
Overview 16 Submit Documentation Feedback
Page 17

XIO2213A PCI Express to 1394b OHCI with 3-Port PHY
www.ti.com
9. LLC is used to refer to the 1394 link layer controller.
2.5 Ordering Information
ORDERING NAME VOLTAGE PACKAGE
NUMBER
XIO2213AZAY PCI-Express to PCI Translation 3.3-V and 1.5-V power terminals 167-terminal ZAY (Lead-Free) PBGA
Bridge with 1394b OHCI and
Three-Port PHY
2.6 Terminal Assignments
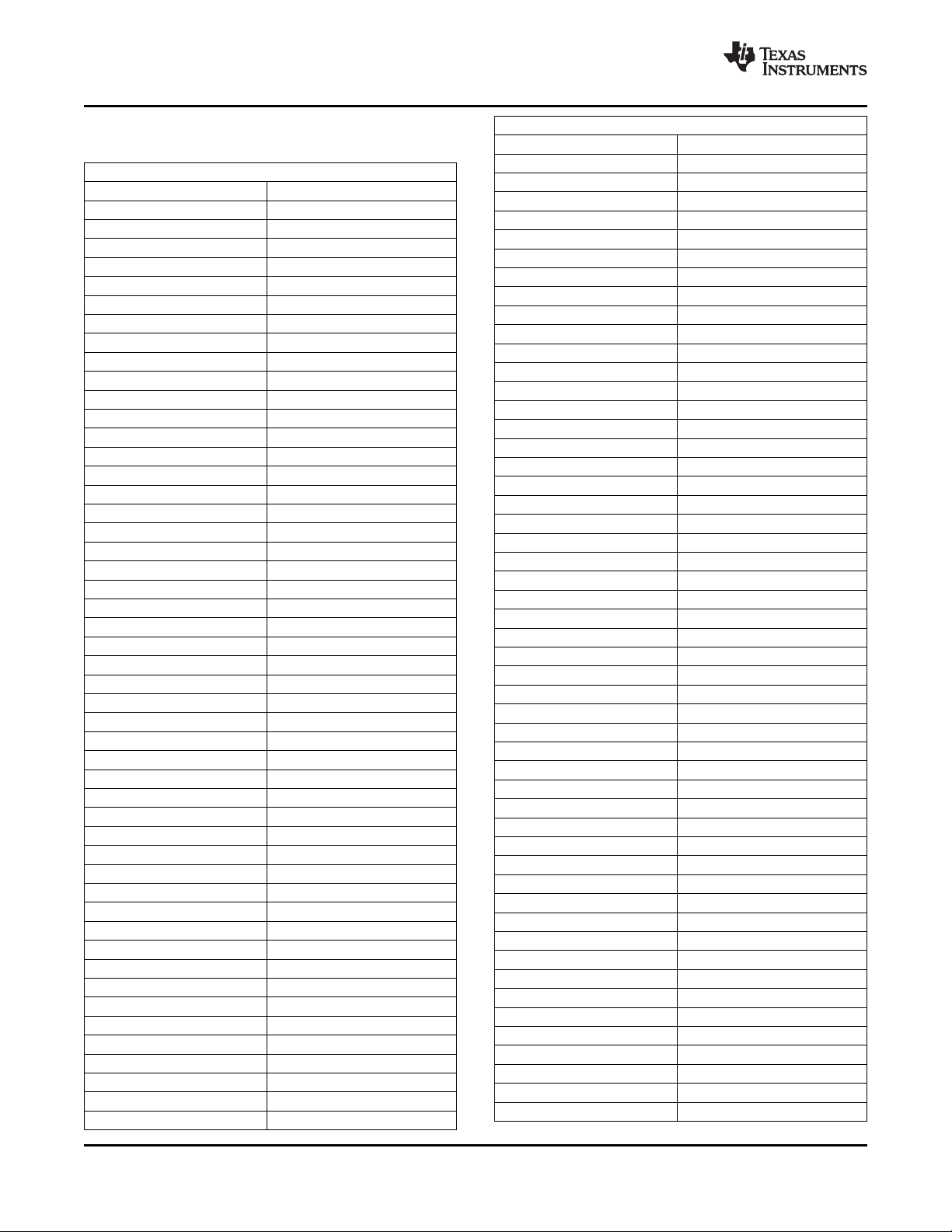
The XIO2213A is packaged in a 167-ball ZAY PBGA. For the ZAY BGATable 2-1 lists the terminals sorted
alphanumerically. Table 2-2 lists the signals in alphanumerical order.
SCPS183A – OCTOBER 2007 – REVISED MARCH 2008
Submit Documentation Feedback Overview 17
Page 18
XIO2213A PCI Express to 1394b OHCI with 3-Port PHY
SCPS183A – OCTOBER 2007 – REVISED MARCH 2008
www.ti.com
Table 2-1. XIO2213AZAY_12x12 Terminals Sorted
Alphanumerically
XIO2213A
BGA BALL # SIGNAL NAME
A01 REFCLK+
A02 CNA
A03 RXN
A04 RXP
A05 BMODE
A06 TESTW(VREG_PD)
A07 VSS
A08 TXN
A09 TXP
A10 VDDA_33
A11 PC2
A12 REF1_PCIE
A13 REF0_PCIE
A14 VSS
B01 REFCLKB02 TESTM
B03 PD
B04 PHY_RESET#
B05 VDDA_15
B06 VSSA
B07 VDDA_15
B08 VDD_15
B09 VDDA_15
B10 VDDA_15
B11 VDD_33_COMB
B12 VDD_33
B13 PERST#
B14 TPA2+
C01 LPS_L
C02 LPS_P
C03 VDDA_33
C04 VSSA_PCIE
C05 VSSA_PCIE
C06 VSSA_PCIE
C07 VSSA_PCIE
C08 DVDD_3.3
C09 DVDD_CORE
C10 VSSA
C11 VDD_33_COM_IO
C12 VDD_15_COMB
C13 GRST#
C14 TPA2D01 LKON/DS2_P
D02 PINT_L
D03 PINT_P
D12 RSVD
D13 RSVD
D14 TPB2+
E01 LINKON_L
XIO2213A
BGA BALL # SIGNAL NAME
E02 LREQ_P
E03 VDD_33
E06 GND
E07 GND
E08 PC1
E09 PC0
E10 AVDD_3.3
E12 RSVD
E13 TPBIAS2
E14 TPB2F01 PCLK_P
F02 LREQ_L
F03 DVDD_CORE
F05 VSSA
F06 GND
F07 GND
F08 GND
F09 GND
F10 AVDD_3.3
F12 RSVD
F13 RSVD
F14 TPA1+
G01 PCLK_L
G02 LCLK_L
G03 VDD_15
G05 GND
G06 GND
G07 GND
G08 GND
G09 GND
G10 VDD_33
G12 RSVD
G13 TPBIAS1
G14 TPA1H01 CTL0
H02 LCLK_P
H03 VDD_15
H05 GND
H06 GND
H07 GND
H08 GND
H09 GND
H10 VDD_33
H12 SDA
H13 REFCLK_SEL
H14 TPB1+
J01 CTL1
J02 D0
J03 DVDD_3.3
J05 GND
J06 GND
Overview 18 Submit Documentation Feedback
Page 19
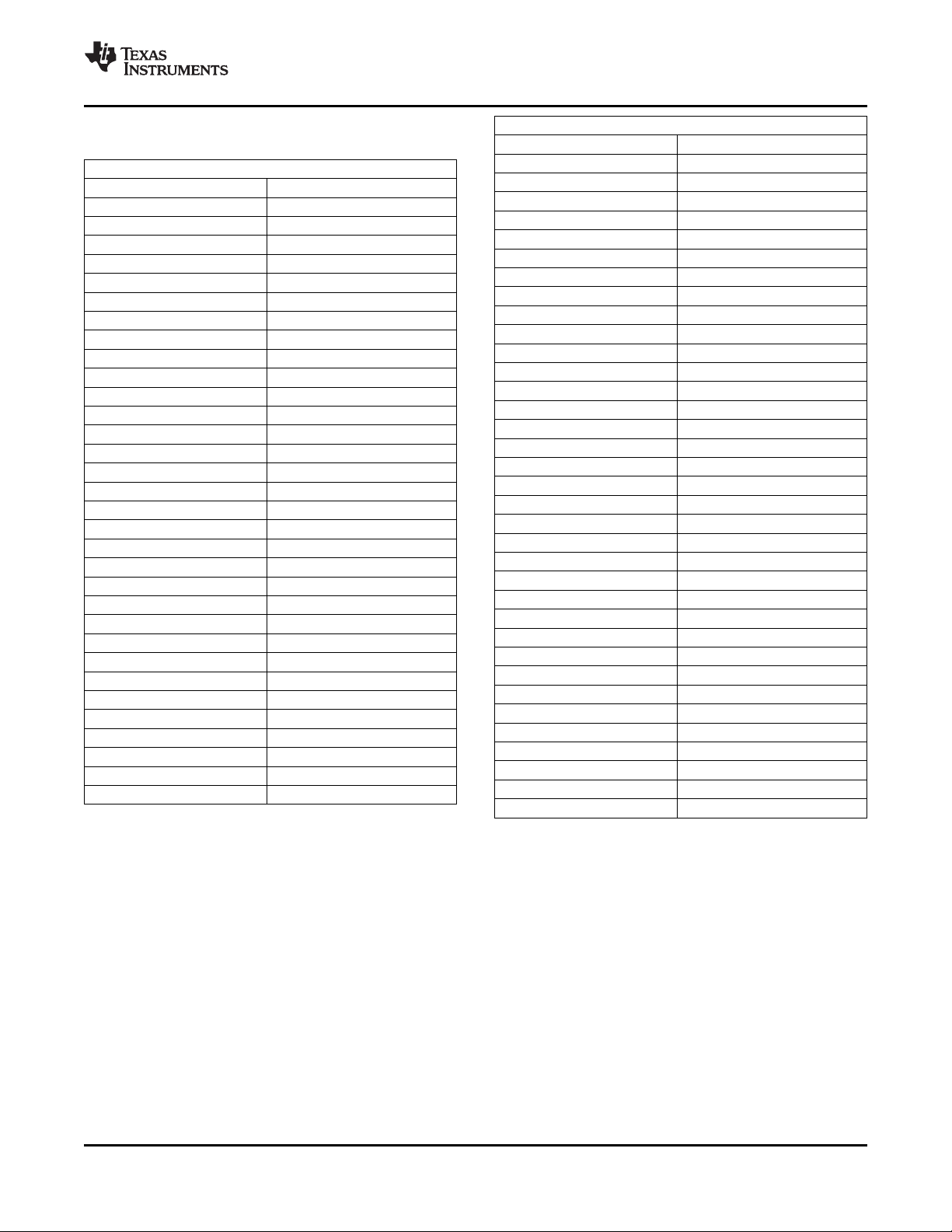
XIO2213A PCI Express to 1394b OHCI with 3-Port PHY
www.ti.com
SCPS183A – OCTOBER 2007 – REVISED MARCH 2008
Table 2-1. XIO2213AZAY_12x12 Terminals Sorted
Alphanumerically (continued)
XIO2213A
BGA BALL # SIGNAL NAME
J07 GND
J08 GND
J09 AVDD_3.3
J10 VDD_33
J12 CLKREQ#
J13 SCL
J14 TPB1K01 D2
K02 D1
K03 DVDD_3.3
K05 GND
K06 GND
K07 GND
K08 GND
K09 AVDD_3.3
K10 VDD_15
K12 RSVD
K13 TPBIAS0
K14 TPA0+
L01 D3
L02 D4
L03 D5
L12 RSVD
L13 RSVD
L14 TPA0M01 R1
M02 D6
M03 D7
M04 AVDD_3.3
M05 VDD_33
M06 VDD_15
M07 PLLVDD_CORE
XIO2213A
BGA BALL # SIGNAL NAME
M08 RSVD
M09 DVDD_CORE
M10 AVDD_3.3
M11 RSVD
M12 RSVD
M13 RSVD
M14 TPB0+
N01 R0
N02 GPIO1
N03 GPIO3
N04 GPIO4
N05 PLLGND
N06 GPIO7
N07 PLLVDD_3.3
N08 CYCLEOUT
N09 DS0
N10 RSVD
N11 RSVD
N12 RSVD
N13 RSVD
N14 TPB0P01 GPIO0
P02 GPIO2
P03 RSVD
P04 XI
P05 GPIO5
P06 GPIO6
P07 VDD_15
P08 OHCI_PME#
P09 DS1
P10 RSVD
P11 RSVD
P12 CPS
P13 SE
P14 SM
Submit Documentation Feedback Overview 19
Page 20
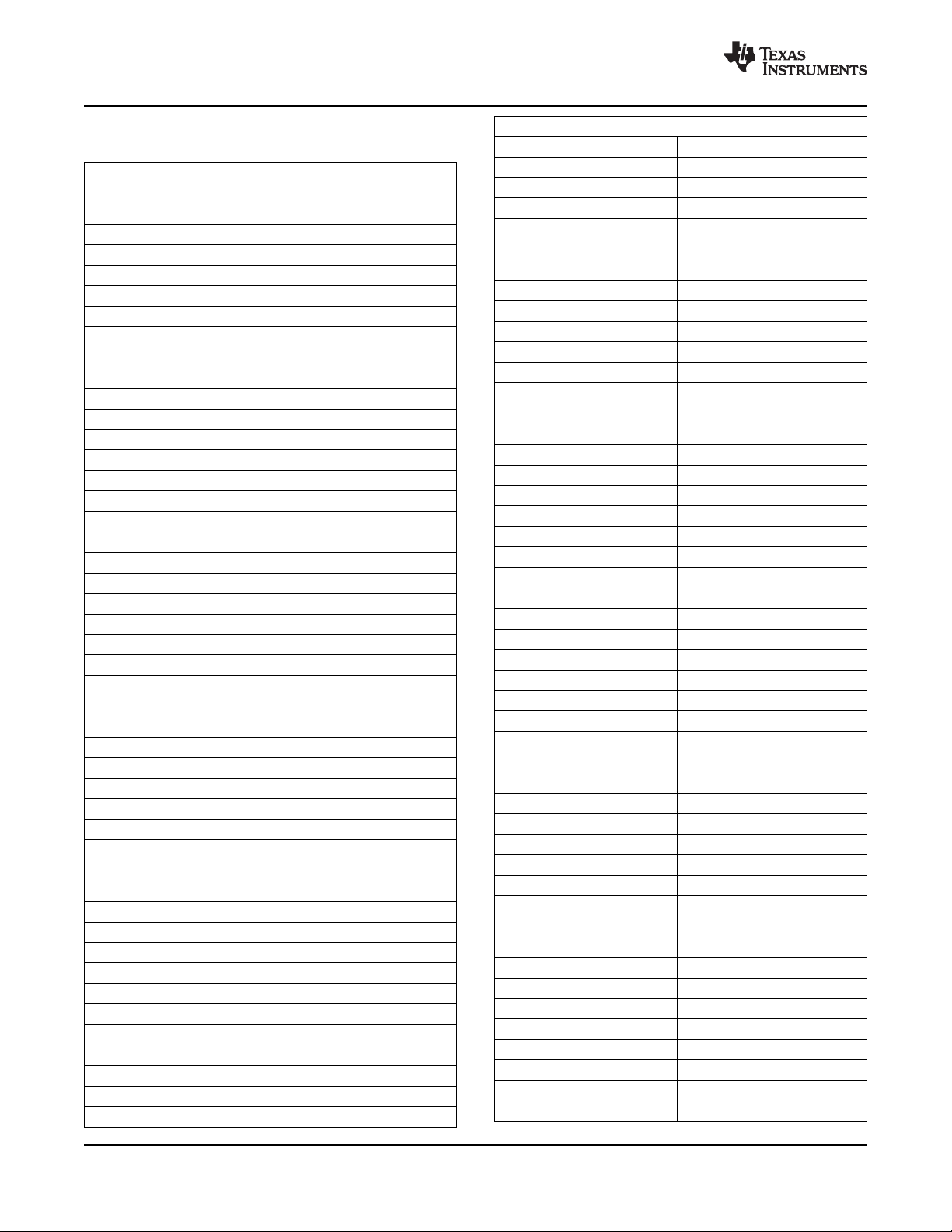
XIO2213A PCI Express to 1394b OHCI with 3-Port PHY
SCPS183A – OCTOBER 2007 – REVISED MARCH 2008
www.ti.com
Table 2-2. XIO2213AZAY_12x12 Signals Sorted
Alphanumerically
XIO2213A
BGA BALL # SIGNAL NAME
E10 AVDD_3.3
F10 AVDD_3.3
J09 AVDD_3.3
K09 AVDD_3.3
M10 AVDD_3.3
M04 AVDD_3.3
A05 BMODE
J12 CLKREQ#
A02 CNA
P12 CPS
H01 CTL0
J01 CTL1
N08 CYCLEOUT
J02 D0
K02 D1
K01 D2
L01 D3
L02 D4
L03 D5
M02 D6
M03 D7
N09 DS0
P09 DS1
C08 DVDD_3.3
J03 DVDD_3.3
K03 DVDD_3.3
C09 DVDD_CORE
F03 DVDD_CORE
M09 DVDD_CORE
E06 GND
E07 GND
F06 GND
F07 GND
F08 GND
F09 GND
G05 GND
G06 GND
G07 GND
G08 GND
G09 GND
H05 GND
H06 GND
H07 GND
H08 GND
H09 GND
XIO2213A
BGA BALL # SIGNAL NAME
J05 GND
J06 GND
J07 GND
J08 GND
K05 GND
K06 GND
K07 GND
K08 GND
P01 GPIO0
N02 GPIO1
P02 GPIO2
N03 GPIO3
N04 GPIO4
P05 GPIO5
P06 GPIO6
N06 GPIO7
C13 GRST#
G02 LCLK_L
H02 LCLK_P
E01 LINKON_L
D01 LKON/DS2_P
C01 LPS_L
C02 LPS_P
F02 LREQ_L
E02 LREQ_P
P08 OHCI_PME#
E09 PC0
E08 PC1
A11 PC2
G01 PCLK_L
F01 PCLK_P
B03 PD
B13 PERST#
D02 PINT_L
D03 PINT_P
N05 PLLGND
N07 PLLVDD_3.3
M07 PLLVDD_CORE
N01 R0
M01 R1
A13 REF0_PCIE
A12 REF1_PCIE
B01 REFCLKH13 REFCLK_SEL
A01 REFCLK+
B04 PHY_RESET#
G12 RSVD
Overview 20 Submit Documentation Feedback
Page 21
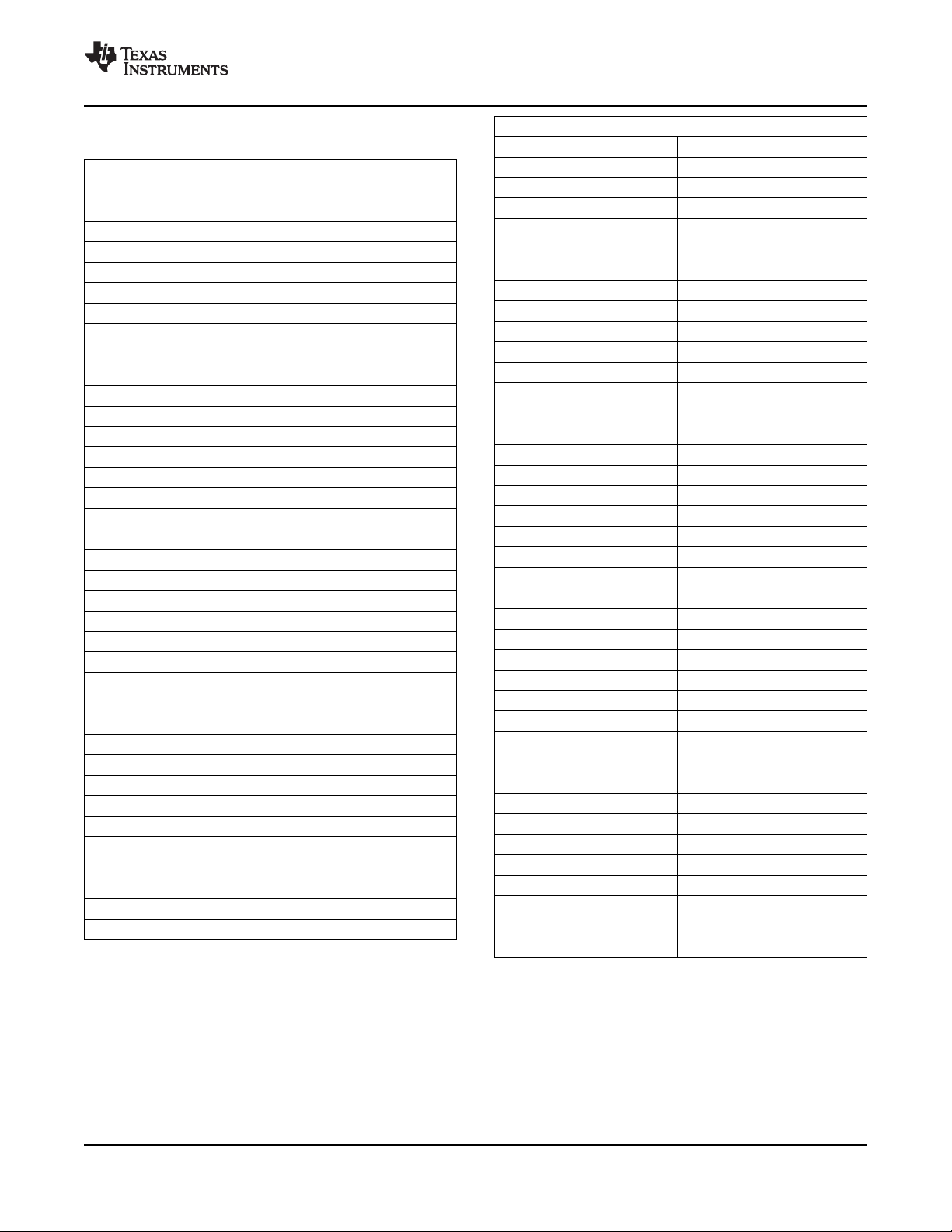
XIO2213A PCI Express to 1394b OHCI with 3-Port PHY
www.ti.com
SCPS183A – OCTOBER 2007 – REVISED MARCH 2008
Table 2-2. XIO2213AZAY_12x12 Signals Sorted
Alphanumerically (continued)
XIO2213A
BGA BALL # SIGNAL NAME
F13 RSVD
F12 RSVD
E12 RSVD
D12 RSVD
D13 RSVD
M08 RSVD
N10 RSVD
P10 RSVD
P11 RSVD
N11 RSVD
M11 RSVD
N12 RSVD
N13 RSVD
M12 RSVD
M13 RSVD
L13 RSVD
K12 RSVD
L12 RSVD
A03 RXN
A04 RXP
J13 SCL
H12 SDA
P13 SE
P14 SM
B02 TESTM
A06 TESTW(VREG_PD)
L14 TPA0K14 TPA0+
G14 TPA1F14 TPA1+
C14 TPA2B14 TPA2+
N14 TPB0M14 TPB0+
J14 TPB1H14 TPB1+
XIO2213A
BGA BALL # SIGNAL NAME
E14 TPB2D14 TPB2+
K13 TPBIAS0
G13 TPBIAS1
E13 TPBIAS2
A08 TXN
A09 TXP
G03 VDD_15
H03 VDD_15
K10 VDD_15
M06 VDD_15
B08 VDD_15
C12 VDD_15_COMB
E03 VDD_33
G10 VDD_33
H10 VDD_33
J10 VDD_33
M05 VDD_33
B12 VDD_33
C11 VDD_33_COM_IO
B11 VDD_33_COMB
B10 VDDA_15
B09 VDDA_15
B07 VDDA_15
B05 VDDA_15
C03 VDDA_33
A10 VDDA_33
P07 VDD_15
A14 VSS
A07 VSS
F05 VSSA
C10 VSSA
B06 VSSA
C04 VSSA_PCIE
C05 VSSA_PCIE
C06 VSSA_PCIE
C07 VSSA_PCIE
P04 XI
P03 RSVD
2.7 Terminal Descriptions
The following tables give a description of the terminals. These terminals are grouped in tables by
functionality. Each table includes the terminal name, terminal number, I/O type, and terminal description.
The following list describes the different input/output cell types that appear in the terminal description
tables:
• HS DIFF IN = High speed differential input
• HS DIFF OUT = High speed differential output
Submit Documentation Feedback Overview 21
Page 22

XIO2213A PCI Express to 1394b OHCI with 3-Port PHY
SCPS183A – OCTOBER 2007 – REVISED MARCH 2008
• LV CMOS = 3.3-V low voltage CMOS input or output with 3.3-V clamp rail
• BIAS = Input/output terminals that generate a bias voltage to determine a driver's operating current
• Feed through = these terminals connect directly to macros within the part and not through an input or
output cell.
• PWR = Power terminal
• GND = Ground terminal
www.ti.com
22 Overview Submit Documentation Feedback
Page 23
XIO2213A PCI Express to 1394b OHCI with 3-Port PHY
www.ti.com
Table 2-3. Power Supply Terminals
SIGNAL BALL 12x12 I/O EXTERNAL DESCRIPTION
V
DD_15
V
DDA_15
V
DD_33
V
DD_33_AUX
V
DDA_33
DVDD_CORE C09 F03 M09 PWR Bypass Digital 1.95-V circuit power for the PHY. A combination of
PLLVDD_CORE M07 PWR Bypass PLL 1.95-V circuit power for the PHY. A combination of
DVDD_33 C08 J03 K03 PWR Bypass 3.3-V digital I/O power terminals for the PHY
AVDD_33 M04 E10 F10 J09 PWR Filter 3.3-V analog power terminals for the PHY
PLLVDD_33 N07 PWR Bypass PLL 3.3-V circuit power for the PHY. This supply terminal is
V
DD_15_COMB
V
DD_33_COMB
V
DD_33_COMBIO
ZAY TYPE PARTS
G03 H03 K10 PWR Bypass 1.5-V digital core power terminals for the link.
M06 B08 P07 capacitors
B10 B09 B07 PWR Filter 1.5-V analog power terminal for the link.
B05
E03 M05 J10 PWR Bypass 3.3-V digital I/O power terminals for the link
H10 G10 capacitors
B12 This terminal is connected to VSS through a pull-down resistor
since the XIO2213A does not support Auxiliary power
C03 A10 PWR Filter 3.3-V analog power terminals for the link. This supply terminal is
separated from the other power terminals internal to the device to
provide noise isolation.
capacitors high-frequency decoupling capacitors near each terminal is
suggested, such as paralleled 0.1- µ F and 0.001- µ F. An additional
1- µ F capacitor is required for voltage regulation. These supply
terminals are separated from the other power terminals internal to
the device to provide noise isolation.
capacitors high-frequency decoupling capacitors near each terminal is
suggested, such as paralleled 0.1- µ F and 0.001- µ F. An additional
1- µ F capacitor is required for voltage regulation, and the
PLLVDD_CORE terminals must be separate from the DVDD_CORE
terminals. These supply terminals are separated from the other
power terminals internal to the device to provide noise isolation.
capacitors
K09 M10
capacitors separated from the other power terminals internal to the device to
provide noise isolation. The PLLVDD_33 and V
be connected together with a low-dc-impedance connection on the
circuit board.
C12 PWR Bypass Internal 1.5-V main power output for external bypass capacitor
capacitors filtering.
Caution: Do not use this terminal to supply external power to other
devices.
B11 PWR Bypass Internal 3.3-V main power output for external bypass capacitor
capacitors filtering.
Caution: Do not use this terminal to supply external power to other
devices.
C11 PWR Bypass Internal 3.3-V IOpower output for external bypass capacitor filtering.
capacitors Caution: Do not use this terminal to supply external power to other
devices.
SCPS183A – OCTOBER 2007 – REVISED MARCH 2008
DDA_33
pins should
Table 2-4. Ground Terminals
SIGNAL BALL 12x12 ZAY I/O TYPE DESCRIPTION
V
SS
V
SSA
V
SSA_PCIE
PLLGND N05 GND PLL circuit ground. This terminal must be tied to the low-impedance
GND E06 E07 F06 F07 F08 GND Ground. These terminals must be tied together to the low-impedance
Submit Documentation Feedback Overview 23
A07 A14 GND Digital ground terminals for link
B06 C10 F05 GND Analog ground terminals for link
C04 C05 C06 C07 GND Analog ground terminals for PCI Express function
circuit-board ground plane.
F09 G05 G06 G07 G08 circuit-board ground plane.
G09 H05 H06 H07 H08
H09 J05 J06 J07 J08
K05 K06 K07 K08
Page 24
XIO2213A PCI Express to 1394b OHCI with 3-Port PHY
SCPS183A – OCTOBER 2007 – REVISED MARCH 2008
Table 2-5. PCI Express Terminals
SIGNAL BALL 12x12 I/O EXTERNAL DESCRIPTION
PERST B13 I — PCI Express reset input. The PERST signal identifies when the system power
REF0_PCIE A13 I/O External External reference resistor + and – terminals for setting TX driver current. An
REF1_PCIE A12 resistor external resistor is connected between terminals REF0_PCIE and REF1_PCIE.
RXP A04 DI — High-speed receive pair. RXP and RXN comprise the differential receive pair
RXN A03 for the single PCI Express lane supported.
TXP A09 DO Series High-speed transmit pair. TXP and TXN comprise the differential transmit pair
TXN A08 capacitors for the single PCI Express lane supported.
SIGNAL BALL 12x12 I/O EXTERNAL DESCRIPTION
REFCLK_SEL H13 I Pullup or Reference clock select. This terminal selects the reference clock input.
REFCLK+ A01 DI — Reference clock. REFCLK+ and REFCLK- comprise the differential input
REFCLK– B01 DI Capacitor to Reference clock. REFCLK+ and REFCLK– comprise the differential input
CLKREQ J12 O Clock Request. This terminal is used to support the clock request protocol.
XI P04 I Oscillator input. This terminal connects to a 98.304-MHz low-jitter external
ZAY TYPE PARTS
ZAY TYPE PARTS
is stable and generates an internal power-on reset.
Note: The PERST input buffer has hysteresis.
Table 2-6. Clock Terminals
pulldown
resistor
V
SS
single-ended system reference clock, attach a capacitor from REFCLK– to VSS.
mode
0 = 100-MHz differential common reference clock used
1 = 125-MHz single-ended reference clock used
pair for the 100-MHz system reference clock. For a single-ended, 125-MHz
system reference clock, use the REFCLK+ input.
for pair for the 100-MHz system reference clock. For a single-ended, 125-MHz
oscillator. XI is a 1.8-V CMOS input. Oscillator jitter must be 5-ps RMS or
better. If only 3.3-V oscillators can be acquired, great care must be taken to
not introduce significant jitter by the means used to level shift from 3.3 V to
1.8 V. If a resistor divider is used, a high-current oscillator and low-value
resistors must be used to minimize RC time constants.
www.ti.com
Table 2-7. 1394 Terminals
SIGNAL BALL 12x12 I/O DESCRIPTION
CNA A02 I/O Cable not active. This terminal is asserted high when there are no ports receiving incoming
CPS P12 I Cable power status input. This terminal is normally connected to cable power through a
DS0 N09 I Data-strobe-only mode for port 0. IEEE Std 1394a-2000-only port-0-enable programming
DS1 P09 I Data-strobe-only mode for port 1. IEEE Std 1394a-2000-only port-1-enable programming
PC0 E09 I Power class programming. On hardware reset, these inputs set the default value of the power
PC1 E08 class indicated during self-ID. Programming is done by tying the terminals high through a
PC2 A11 1-k Ω or smaller resistor or by tying directly to ground through a 1-k Ω or smaller resistor. Bus
Overview 24 Submit Documentation Feedback
ZAY TYPE
bias voltage. If it is not used, then this terminal should be left unconnected.
400-k Ω resistor. This circuit drives an internal comparator that detects the presence of cable
power. If CPS is not used to detect cable power, then this terminal must be connected to
V
.
SSA
terminal. On hardware reset, this terminal allows the user to select whether port 0 acts like an
IEEE Std 1394b-2002 bilingual port (terminal at logic 0) or as an IEEE Std 1394a-2000-only
port (terminal at logic 1). Programming is accomplished by tying the terminal low through a
1-k Ω or smaller resistor (to enable IEEE Std 1394b-2002 bilingual mode) or high through a
10-k Ω or smaller resistor (to enable IEEE Std 1394a-2000-only mode).
terminal. On hardware reset, this terminal allows the user to select whether port 1 acts like an
IEEE Std 1394b-2002 bilingual port (terminal at logic 0) or as an IEEE Std 1394a-2000-only
port (terminal at logic 1). Programming is accomplished by tying the terminal low through a
1-k Ω or smaller resistor (to enable IEEE Std 1394b-2002 bilingual mode) or high through a
10-k Ω or smaller resistor (to enable IEEE Std 1394a-2000-only mode).
holders are built into these terminals.
Page 25

XIO2213A PCI Express to 1394b OHCI with 3-Port PHY
www.ti.com
Table 2-7. 1394 Terminals (continued)
SIGNAL BALL 12x12 I/O DESCRIPTION
ZAY TYPE
R0 N01 I/O Current-setting resistor terminals. These terminals are connected to an external resistance to
R1 M01 set the internal operating currents and cable driver output currents. A resistance of 6.34 k Ω
± 1% is required to meet the IEEE Std 1394-1995 output voltage limits.
TPA0P K14 I/O Port 0 Twisted-pair cable A differential signal terminals. Board trace lengths from each pair of
TPA0N L14 positive and negative differential signal pins must be matched and as short as possible to the
TPB0P M14 external load resistors and to the cable connector. For an unused port, TPA+ and TPA– can
TPB0N N14 be left open.
TPA1P F14 I/O Port 1 Twisted-pair cable A differential signal terminals. Board trace lengths from each pair of
TPA1N G14 positive and negative differential signal pins must be matched and as short as possible to the
TPB1P H14 external load resistors and to the cable connector. For an unused port, TPA+ and TPA– can
TPB1N J14 be left open.
TPA2P B14 I/O Port 2 Twisted-pair cable A differential signal terminals. Board trace lengths from each pair of
TPA2N C14 positive and negative differential signal pins must be matched and as short as possible to the
TPB2P D14 external load resistors and to the cable connector. For an unused port, TPA+ and TPA– can
TPB2N E14 be left open.
TPBIAS0 K13 O Twisted-pair bias output. This provides the 1.86-V nominal bias voltage needed for proper
TPBIAS1 G13 operation of the twisted-pair cable drivers and receivers, and for signaling to the remote
TPBIAS2 E13 nodes that there is an active cable connection in IEEE Std 1394a-2000 mode. Each of these
terminals, except for an unused port, must be decoupled with a 1- µ F capacitor to ground. For
the unused port, this terminal can be left unconnected.
PCLK_L G01 I PHY-section clock. This terminal must be connected to the PCLK_P output of the PHY
section.
PCLK_P F01 O PHY-section clock. This terminal must be connected to the PCLK_L input of the LLC section.
LCLK_L G02 O LLC-section clock. This terminal must be connected to the LCLK_P input terminal of the PHY
section.
LCLK_P H02 I LLC-section clock. This terminal must be connected to the LCLK_L output terminal of the LLC
section.
LPS_L C01 O LLC-section power status. This terminal must be connected to the LPS_P input terminal of
the PHY section.
LPS_P C02 I Link power status. This terminal must be connected to the LPS_L ouput terminal of the LLC
section.
PINT_L D02 I PHY-section interrupt. The PHY section uses this signal to transfer status and interrupt
information serially to the LLC section. This terminal must be connected to the PINT_P output
of the PHY section.
PINT_P D03 O PHY-section interrupt. PINT_P is a serial input to the LLC section from the PHY section that
is used to transfer status, register, interrupt, and other information to the link. Information
encoded on PINT_P is synchronous to PCLK_P. This terminal must be connected to the
PINT_L input of the LLC section.
SCPS183A – OCTOBER 2007 – REVISED MARCH 2008
Submit Documentation Feedback Overview 25
Page 26

XIO2213A PCI Express to 1394b OHCI with 3-Port PHY
SCPS183A – OCTOBER 2007 – REVISED MARCH 2008
Table 2-7. 1394 Terminals (continued)
SIGNAL BALL 12x12 I/O DESCRIPTION
ZAY TYPE
LKON/DS2_P D01 I/O Link-on notification. If port is to operate in DS mode or is unused then it is necessary to pull
the terminal high through a 470- Ω or smaller resistor. This terminal must also be connected
to the LINKON_L input terminal of the LLC section via a 1-k Ω series resistor. A bus holder is
built into this terminal. If the port is to operate in bi-lingual mode then the terminal should be
tied low via a 1-k Ω resistor and directly connected to the link's LINKON_L pin with no series
termination. After hardware reset, this terminal is the link-on output, which notifies the LLC
section or other power-up logic to power up and become active. The link-on output is a
square-wave signal with a period of approximately 163 ns (eight PCLK cycles) when active.
The link-on output is otherwise driven low, except during hardware reset when it is high
impedance. The link-on output is activated if the LLC section is inactive (the LPS input
inactive or the LCtrl bit cleared) and when any of the following occurs:
a) The XIO2213A receives a link-on PHY packet addressed to this node.
b) The PEI (port-event interrupt) register bit is 1.
c) Any of the configuration-timeout interrupt (CTOI), cable-power-status interrupt (CPSI), or
state-time-out interrupt (STOI) register bits are 1 and the resuming-port interrupt enable
(RPIE) register bit also is 1.
d) The PHY is power cycled and the power class is 0 through 4.
Once activated, the link-on output is active until the LLC section becomes active (both the
LPS_L input active and the LCtrl bit set). The PHY section also deasserts the link-on output
when a bus reset occurs unless the link-on output is otherwise active because one of the
interrupt bits is set (that is, the link-on output is active due solely to the reception of a link-on
PHY packet) In the case of power cycling, the LKON signal must stop after 167 ms if the
previous conditions have not been met. NOTE: If an interrupt condition exists which
otherwise causes the link-on output to be activated if the LLC section were inactive, the
link-on output is activated when the LLC section subsequently becomes inactive.
LINKON_L E01 I/O Link-on notification. LINKON_L is an input to the LLC section from the PHY section that is
used to provide notification that a link-on packet has been received or an event, such as a
port connection, has occurred. This I/O only has meaning when LPS is disabled. This
includes the D0 (uninitialized), D2, and D3 power states. If LINKON_L becomes active in the
D0 (uninitialized), D2, or D3 power state, the XIO2213A device sets bit 15 (PME_STS) in the
power-management control and status register in the PCI configuration space at offset 48h.
This terminal must be connected to the LKON output terminal of the PHY section.
LREQ_L F02 O LLC-section request. The LLC section uses this output to initiate a service request to the
PHY section.This terminal must be connected to the LREQ_P input of the PHY section.
LREQ_P E02 I LLC-section request. LREQ_P is a serial input from the LLC section to the PHY section used
to request packet transmissions, read and write PHY section registers, and to indicate the
occurrence of certain link events that are relevant to the PHY section. Information encoded
on LREQ_P is synchronous to LCLK_P.This terminal must be connected to the LREQ_L
output of the LLC section.
PHY_RESET# B04 I Reset for the 1394 PHY logic
CTL1 J01 I/O Control. CTL[1:0] are bi-directional control bus signals that are used to indicate the phase of
CTL0 H01 operation of the PHY-link interface. Upon a reset of the interface, this bus is driven by the
PHY. When driven by the PHY, information on CTL[1:0] is synchronous to PCLK. When
driven by the link, information on CTL[1:0] is synchronous to LCLK. If not implemented, these
terminals should be left unconnected.
D0 J02 I/O Data. D[7:0] comprise a bi-directional data bus that is used to carry 1394 packet data, packet
D1 K02 speed, and grant type information between the PHY and the link. Upon a reset of the
D2 K01 interface, this bus is driven by the PHY. When driven by the PHY, information on D[7:0] is
D3 L01 synchronous to PCLK. When driven by the link, information on D[7:0] is synchronous to
D4 L02 LCLK. If not implemented, these terminals should be left unconnected.
D5 L03
D6 M02
D7 M03
www.ti.com
Overview 26 Submit Documentation Feedback
Page 27
XIO2213A PCI Express to 1394b OHCI with 3-Port PHY
www.ti.com
Table 2-8. Reserved Terminals
SIGNAL BALL 12x12 ZAY I/O TYPE DESCRIPTION
RSVD E12 F12 F13 K12 L12 I/O Reserved, do not connect to external signals.
L13 M11 M12 M13 N10
N11 N12 N13 P03 P10
P11
RSVD D12 D13 G12 M08 I Must be connected to VSS.
Table 2-9. Miscellaneous Terminals
SIGNAL BALL 12x12 ZAY I/O DESCRIPTION
TYPE
GPIO0 P01 I/O General-purpose I/O 0. This terminal functions as a GPIO controlled by bit 0 (GPIO0_DIR)
in the GPIO control register (see Section 4.60 ).
Note: This terminal has an internal active pullup resistor.
GPIO1 N02 I/O General-purpose I/O 1. This terminal functions as a GPIO controlled by bit 1 (GPIO1_DIR)
in the GPIO control register (see Section 4.60 ).
Note: This terminal has an internal active pullup resistor.
GPIO2 P02 I/O General-purpose I/O 2. This terminal functions as a GPIO controlled by bit 2 (GPIO2_DIR)
in the GPIO control register (see Section 4.60 ).
Note: This terminal has an internal active pullup resistor.
GPIO3 N03 I/O General-purpose I/O 3. This terminal functions as a GPIO controlled by bit 3 (GPIO3_DIR)
in the GPIO control register (see Section 4.60 ).
Note: This terminal has an internal active pullup resistor.
GPIO4 N04 I/O General-purpose I/O 4. This terminal functions as a GPIO controlled by bit 4 (GPIO4_DIR)
in the GPIO control register (see Section 4.60 ).
Note: This terminal has an internal active pullup resistor.
GPIO5 P05 I/O General-purpose I/O 5. This terminal functions as a GPIO controlled by bit 5 (GPIO5_DIR)
in the GPIO control register (see Section 4.60 ).
Note: This terminal has an internal active pullup resistor.
GPIO6 P06 I/O General-purpose I/O 6. This terminal functions as a GPIO controlled by bit 6 (GPIO6_DIR)
in the GPIO control register (see Section 4.60 ).
Note: This terminal has an internal active pullup resistor.
GPIO7 N06 I/O General-purpose I/O 7. This terminal functions as a GPIO controlled by bit 7 (GPIO7_DIR)
in the GPIO control register (see Section 4.60 ).
Note: This terminal has an internal active pullup resistor.
OHCI_PME# P08 O The Power Management Event signal is an optional signal that can be used by a device to
request a change in the device or system power state. This signal must be enabled by
software.
CYCLEOUT N08 O This terminal provides an 8-kHz cycle timer synchronization signal. If not implemented, this
terminal should be left unconnected.
PD B03 I Power down. A high on this terminal turns off all internal circuitry, except the cable-active
monitor circuits that control the CNA output. Asserting PD high also activates an internal
pulldown to force a reset of the internal control logic. If PD is not used, then this terminal
must be connected to VSS.
GRST C13 I Global power reset. This reset brings all of the XIO2213A internal link registers to their
default states. This should be a one time power on reset. This terminal has hysteresis and
an integrated pull up resistor
SCL J13 I/O Serial-bus clock. This pin is used as Serial Bus Clock when a pull-up is detected on SDA
or when the SBDETECT bit is set in the Serial Bus Control and Status Register.
Note: This terminal has an internal active pullup resistor.
SDA H12 I/O Serial-bus data. This pin is used as Serial Bus Data when a pull-up is detected on SDA or
when the SBDETECT bit is set in the Serial Bus Control and Status Register.
Note: In serial-bus mode, an external pullup resistor is required to prevent the SDA signal
from floating.
SCPS183A – OCTOBER 2007 – REVISED MARCH 2008
Submit Documentation Feedback Overview 27
Page 28

XIO2213A PCI Express to 1394b OHCI with 3-Port PHY
SCPS183A – OCTOBER 2007 – REVISED MARCH 2008
Table 2-9. Miscellaneous Terminals (continued)
SIGNAL BALL 12x12 ZAY I/O DESCRIPTION
TYPE
BMODE A05 I Beta mode. This terminal determines the PHY section-LLC section interface connection
protocol. When logic-high (asserted), the PHY section-LLC section interface complies with
the IEEE Std 1394b-2002 revision 1.33 Beta interface. When logic low (deasserted), the
PHY section-LLC section interface complies with the legacy IEEE Std 1394a-2000
standard. This terminal must be pulled high with a 1-k Ω resistor during normal operation.
TESTM B02 I Test control. This input is used in the manufacturing test of the XIO2213A. For normal use,
this terminal must be pulled high through a 1-k Ω resistor to VDD.
TESTW A06 I Test control. This input is used in the manufacturing test of the XIO2213A. For normal use,
this terminal must be pulled high through a 1-k Ω resistor to VDD.
SE P13 I Test control. This input is used in the manufacturing test of the XIO2213A. For normal use,
this terminal must be pulled low either through a 1-k Ω resistor to GND or directly to GND.
SM P14 I Test control. This input is used in the manufacturing test of the XIO2213A. For normal use,
this terminal must be pulled low either through a 1-k Ω resistor to GND or directly to GND.
www.ti.com
28 Overview Submit Documentation Feedback
Page 29
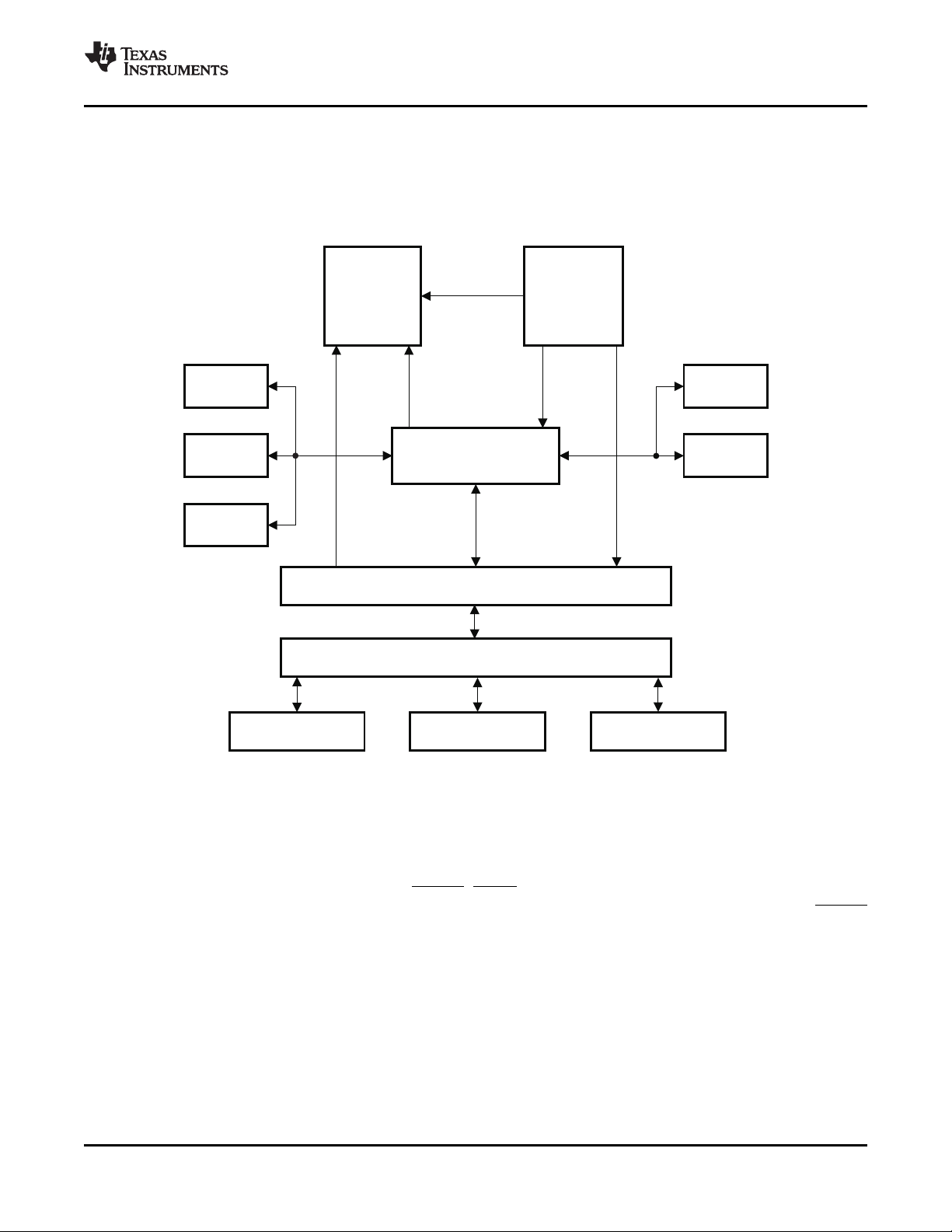
PCIExpress
Transmitter
PCIExpress
Receiver
PCIBusInterface
Configurationand
MemoryRegister
GPIO
Serial
EEPROM
Reset
Controller
Clock
Generator
Power
Mgmt
1394bOHCIwith3-PortPHY
1394CablePort 1394CablePort 1394CablePort
www.ti.com
3 Feature/Protocol Descriptions
This chapter provides a high-level overview of all significant device features. Figure 3-1 shows a simplified
block diagram of the basic architecture of the PCI-Express to PCI Bridge with 1394b OHCI and three-port
PHY. The top of the diagram is the PCI Express interface and the 1394b OHCI with three-port PHY is
located at the bottom of the diagram.
XIO2213A PCI Express to 1394b OHCI with 3-Port PHY
SCPS183A – OCTOBER 2007 – REVISED MARCH 2008
Figure 3-1. XIO2213A Block Diagram
3.1 Power-Up/-Down Sequencing
The bridge contains both 1.5-V and 3.3-V power terminals. The following power-up and power-down
sequences describe how power is applied to these terminals.
In addition, the bridge has three resets: PERST, GRST and an internal power-on reset. These resets are
fully described in Section 3.2 . The following power-up and power-down sequences describe how PERST
is applied to the bridge.
The application of the PCI Express reference clock (REFCLK) is important to the power-up/-down
sequence and is included in the following power-up and power-down descriptions.
Submit Documentation Feedback Feature/Protocol Descriptions 29
Page 30
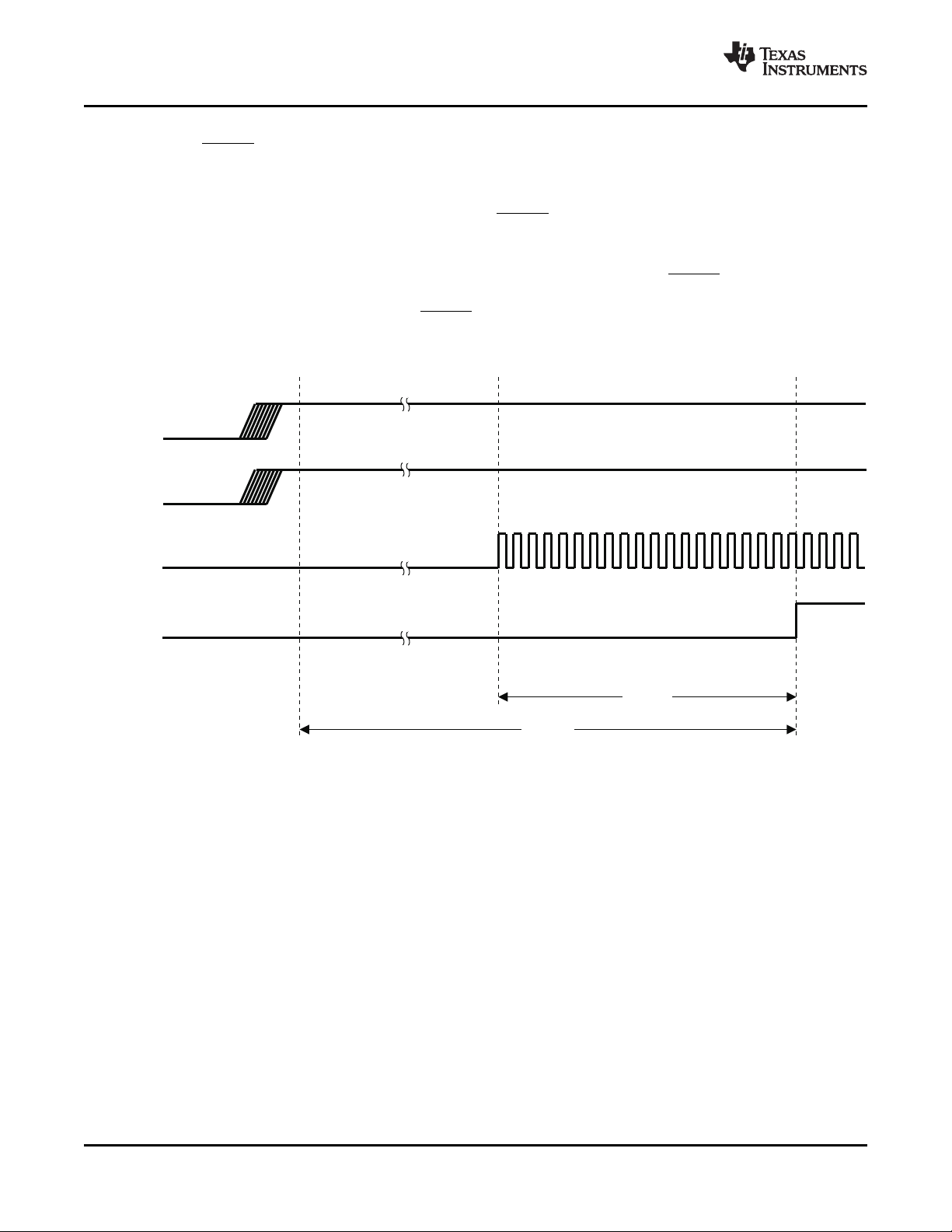
VDD_15and
VDDA_15
VDD_33and
VDDA_33
REFCLK
PERST
100ms
100 ms
XIO2213A PCI Express to 1394b OHCI with 3-Port PHY
SCPS183A – OCTOBER 2007 – REVISED MARCH 2008
3.1.1 Power-Up Sequence
1. Assert PERST to the device.
2. Apply 1.5-V and 3.3-V voltages.
3. Apply a stable PCI Express reference clock.
4. To meet PCI Express specification requirements, PERST cannot be deasserted until the following two
delay requirements are satisfied:
– Wait a minimum of 100 µ s after applying a stable PCI Express reference clock. The 100- µ s limit
satisfies the requirement for stable device clocks by the deassertion of PERST.
– Wait a minimum of 100 ms after applying power. The 100-ms limit satisfies the requirement for
stable power by the deassertion of PERST.
See the power-up sequencing diagram in Figure 3-2 .
www.ti.com
Figure 3-2. Power-Up Sequence
Feature/Protocol Descriptions30 Submit Documentation Feedback
Page 31

VDD_15and
VDDA_15
VDD_33and
VDDA_33
REFCLK
PERST
www.ti.com
3.1.2 Power-Down Sequence
1. Assert PERST to the device.
2. Remove the reference clock.
3. Remove 3.3-V and 1.5-V voltages.
See the power-down sequencing diagram in Figure 3-3 . If the VDD_33_AUX terminal is to remain
powered after a system shutdown, then the bridge power-down sequence is exactly the same as shown in
Figure 3-3 .
XIO2213A PCI Express to 1394b OHCI with 3-Port PHY
SCPS183A – OCTOBER 2007 – REVISED MARCH 2008
Figure 3-3. Power-Down Sequence
3.2 XIO2213A Reset Features
There are five XIO2213A reset options that include internally-generated power-on reset, resets generated
by asserting input terminals, and software-initiated resets that are controlled by sending a PCI Express hot
reset or setting a configuration register bit. Table 3-1 identifies these reset sources and describes how the
XIO2213A responds to each reset.
Table 3-1. XIO2213A Reset Options
RESET XIO2213A FEATURE RESET RESPONSE
OPTION
XIO2213A During a power-on cycle, the XIO2213A asserts an internal When the internal power-on reset is asserted, all control
internally- reset and monitors the V
generated this terminal reaches 90% of the nominal input voltage management state machines are initialized to their default
power-on reset specification, power is considered stable. After stable power, state.
the XIO2213A monitors the PCI Express reference clock In addition, the XIO2213A asserts the internal PCI bus
(REFCLK) and waits 10 µ s after active clocks are detected. reset.
Then, internal power-on reset is deasserted.
PCI Express This XIO2213A input terminal is used by an upstream PCI When PERST is asserted low, all control register bits that
reset input Express device to generate a PCI Express reset and to are not sticky are reset. Within the configuration register
PERST (B12) signal a system power good condition. maps, the sticky bits are indicated by the I symbol. Also, all
When PERST is asserted low, the XIO2213A generates an
internal PCI Express reset as defined in the PCI Express
specification.
When PERST transitions from low to high, a system power In addition, the XIO2213A asserts the internal PCI bus
good condition is assumed by the XIO2213A. reset.
Note: The system must assert PERST before power is When the rising edge of PERST occurs, the XIO2213A
removed, before REFCLK is removed or before REFCLK samples the state of all static control inputs and latches
becomes unstable. the information internally. If an external serial EEPROM is
DD_15_COMB
(B11) terminal. When registers, state machines, sticky register bits, and power
state machines that are not associated with sticky
functionality are reset.
detected, then a download cycle is initiated. Also, the
process to configure and initialize the PCI Express link is
started. The XIO2213A starts link training within 80 ms
after PERST is deasserted.
Submit Documentation Feedback Feature/Protocol Descriptions 31
Page 32

XIO2213A PCI Express to 1394b OHCI with 3-Port PHY
SCPS183A – OCTOBER 2007 – REVISED MARCH 2008
Table 3-1. XIO2213A Reset Options (continued)
RESET XIO2213A FEATURE RESET RESPONSE
OPTION
PCI Express The XIO2213A responds to a training control hot reset In the DL_DOWN state, all remaining configuration register
training control received on the PCI Express interface. After a training bits and state machines are reset. All remaining bits
hot reset control hot reset, the PCI Express interface enters the exclude sticky bits and EEPROM loadable bits. All
DL_DOWN state. remaining state machines exclude sticky functionality and
EEPROM functionality.
Within the configuration register maps, the sticky bits are
indicated by the I symbol and the EEPROM loadable bits
are indicated by the † symbol.
In addition, the XIO2213A asserts the internal PCI bus
reset.
PCI bus reset System software has the ability to assert and deassert the When bit 6 (SRST) in the XIO2213A control register at
PCI bus reset on the secondary PCI bus interface. offset 3Eh (see Section 4.30 ) is asserted, the XIO2213A
asserts the internal PCI bus reset. A 0b in the SRST bit
deasserts the PCI bus reset.
3.3 PCI Express Interface
3.3.1 External Reference Clock
The XIO2213A requires either a differential, 100-MHz common clock reference or a single-ended,
125-MHz clock reference. The selected clock reference must meet all PCI Express Electrical Specification
requirements for frequency tolerance, spread spectrum clocking, and signal electrical characteristics.
www.ti.com
If the REFCLK_SEL input is connected to V
expected by the XIO2213A. If the REFCLK_SEL terminal is connected to V
125-MHz clock reference is expected by the XIO2213A.
When the single-ended, 125-MHz clock reference option is enabled, the single-ended clock signal is
connected to the REFCLK+ terminal. The REFCLK– terminal is connected to one side of an external
capacitor with the other side of the capacitor connected to V
When using a single-ended reference clock, care must be taken to ensure interoperability from a system
jitter standpoint. The PCI Express Base Specification does not ensure interoperability when using a
differential reference clock commonly used in PC applications along with a single-ended clock in a
noncommon clock architecture. System jitter budgets will have to be verified to ensure interoperability.
See the PCI Express Jitter and BER White Paper from the PCI-SIG.
3.3.2 Beacon and Wake
Since the 1394b OHCI function in XIO2213A does not support PME# from D3cold, it is not necessary for
the PCI Express to PCI Bridge portion of the design to support Beacon generation or WAKE# signaling.
As a result, the XIO2213A does not implement VAUX power support.
3.3.3 Initial Flow Control Credits
The bridge flow control credits are initialized using the rules defined in the PCI Express Base
Specification. Table 3-2 identifies the initial flow control credit advertisement for the bridge.
, then a differential, 100-MHz common clock reference is
SS
.
SS
Table 3-2. Initial Flow Control Credit Advertisements
CREDIT TYPE INITIAL ADVERTISEMENT
Posted request headers (PH) 8
Posted request data (PD) 128
Nonposted header (NPH) 4
Nonposted data (NPD) 4
Completion header (CPLH) 0 (infinite)
Completion data (CPLD) 0 (infinite)
, then a single-ended,
DD_33
Feature/Protocol Descriptions32 Submit Documentation Feedback
Page 33

XIO2213A PCI Express to 1394b OHCI with 3-Port PHY
www.ti.com
3.3.4 PCI Express Message Transactions
PCI Express messages are both initiated and received by the bridge. Table 3-3 outlines message support
within the bridge.
Table 3-3. Messages Supported byf the Bridge
MESSAGE SUPPORTED BRIDGE ACTION
Assert_INTx Yes Transmitted upstream
Deassert_INTx Yes Transmitted upstream
PM_Active_State_Nak Yes Received and processed
PM_PME Yes Transmitted upstream
PME_Turn_Off Yes Received and processed
PME_TO_Ack Yes Transmitted upstream
ERR_COR Yes Transmitted upstream
ERR_NONFATAL Yes Transmitted upstream
ERR_FATAL Yes Transmitted upstream
Set_Slot_Power_Limit Yes Received and processed
Unlock No Discarded
Hot plug messages No Discarded
Advanced switching messages No Discarded
Vendor defined type 0 No Unsupported request
Vendor defined type 1 No Discarded
SCPS183A – OCTOBER 2007 – REVISED MARCH 2008
All supported message transactions are processed per the PCI Express Base Specification.
Submit Documentation Feedback Feature/Protocol Descriptions 33
Page 34

R
+0
+1 +2
+3
01
23
4567
0
12
3
4
5
6
77
6
5
4
3
2 1
0
7
6
5
4
3
2 1
0
Type
Fmt
0
1
1
0
1
0
0
R
TC
Reserved
ReservedID
0
0
0
Reserved
Tag
R
Length
Code
Attr
00
00
00
0
0
0
0
00
00
01
0
0
E
T
P
D
0
0
Byte0>
Byte4>
Byte8>
Byte12>
R
+0
+1 +2
+3
01
23
4567
0
12
3
4
5
6
77
6
5
4
3
2 1
0
7
6
5
4
3
2 1
0
Type
Fmt
0
1
1
0
1
0
0
R
TC
Reserved
ReservedID
0
0
0
Reserved
Tag
R
Length
Code
Attr
00
00
00
0
0
0
0
00
10
01
0
0
E
T
P
D
0
0
Byte0>
Byte4>
Byte8>
Byte12>
XIO2213A PCI Express to 1394b OHCI with 3-Port PHY
SCPS183A – OCTOBER 2007 – REVISED MARCH 2008
3.4 PCI Interrupt Conversion to PCI Express Messages
The bridge converts interrupts from the PCI bus sideband interrupt signals to PCI Express interrupt
messages. Since the 1394a OHCI only generates INTA interrupts, only PCI Express INTA messages are
generated by the bridge.
PCI Express Assert_INTA messages are generated when the 1394a OHCI signals an INTA interrupt. The
requester ID portion of the Assert_INTA message uses the value stored in the primary bus number
register (see Section 4.12 ) as the bus number, 0 as the device number, and 0 as the function number.
The tag field for each Assert_INTA message is 00h.
PCI Express Deassert_INTA messages are generated when the 1394a OHCI deasserts the INTA
interrupt. The requester ID portion of the Deassert_INTA message uses the value stored in the primary
bus number register as the bus number, 0 as the device number, and 0 as the function number. The Tag
field for each Deassert_INTA message is 00h.
Figure 3-4 and Figure 3-5 illustrate the format for both the assert and deassert INTA messages.
www.ti.com
3.5 Two-Wire Serial-Bus Interface
The bridge provides a two-wire serial-bus interface to load subsystem identification information and
specific register defaults from an external EEPROM. The serial-bus interface signals are SCL and SDA.
3.5.1 Serial-Bus Interface Implementation
To enable the serial-bus interface, a pullup resistor must be implemented on the SDA signal. At the rising
edge of PERST or GRST, whichever occurs later in time, the SDA terminal is checked for a pullup
resistor. If one is detected, then bit 3 (SBDETECT) in the serial-bus control and status register (see
Section 4.59 ) is set. Software may disable the serial-bus interface at any time by writing a 0b to the
SBDETECT bit. If no external EEPROM is required, then the serial-bus interface is permanently disabled
by attaching a pulldown resistor to the SDA signal.
The bridge implements a two-terminal serial interface with one clock signal (SCL) and one data signal
Feature/Protocol Descriptions34 Submit Documentation Feedback
Figure 3-4. PCI Express ASSERT_INTA Message
Figure 3-5. PCI Express DEASSERT_INTX Message
Page 35
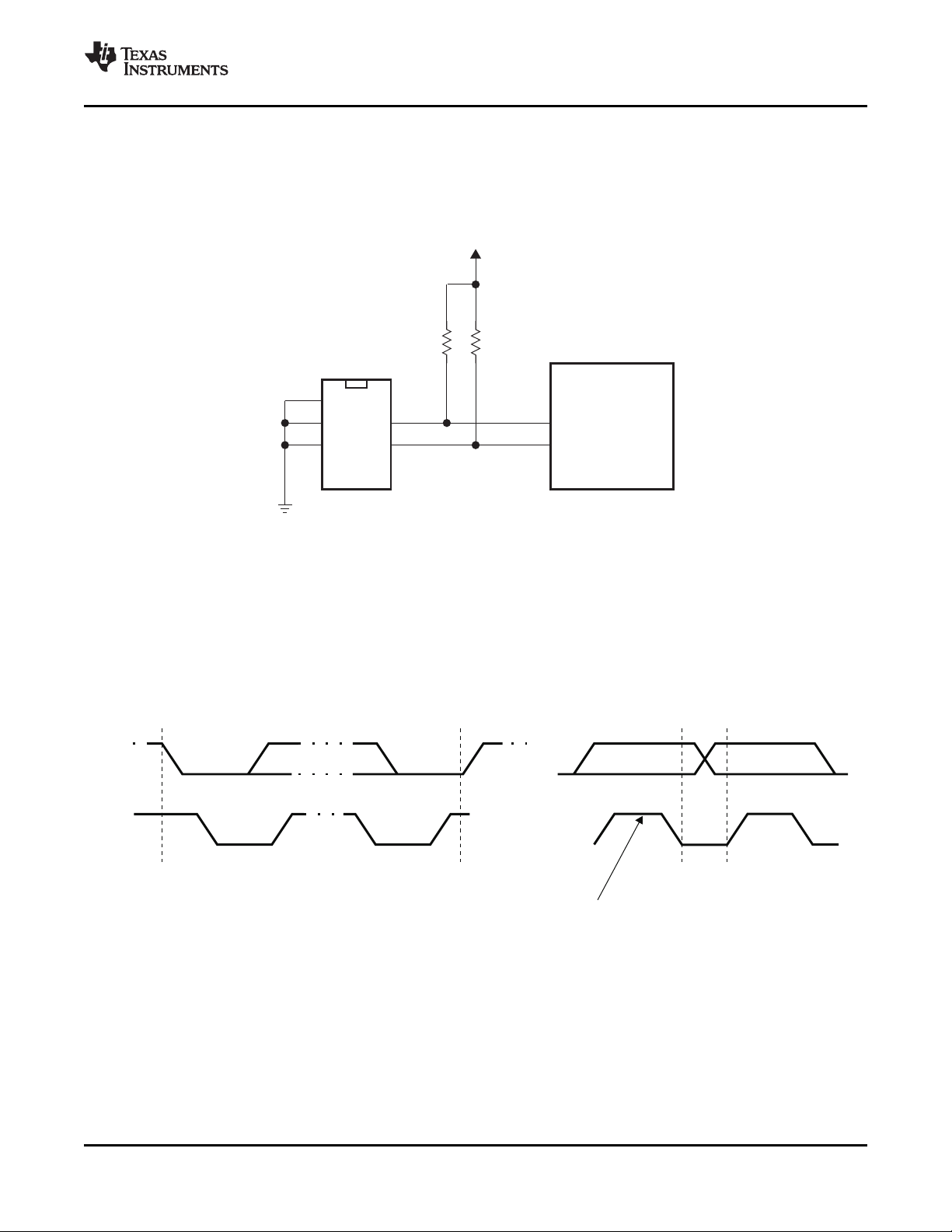
SCL
SDA
VDD_33
A0
A1
A2
SCL
SDA
XIO2213A
Serial
EEPROM
SDA
SCL
Start
Condition
Stop
Condition
Changeof
Data Allowed
DataLineStable,
DataValid
XIO2213A PCI Express to 1394b OHCI with 3-Port PHY
www.ti.com
(SDA). The SCL signal is a unidirectional output from the bridge and the SDA signal is bidirectional. Both
are open-drain signals and require pullup resistors. The bridge is a bus master device and drives SCL at
approximately 60 kHz during data transfers and places SCL in a high-impedance state (0 frequency)
during bus idle states. The serial EEPROM is a bus slave device and must acknowledge a slave address
equal to A0h. Figure 3-6 illustrates an example application implementing the two-wire serial bus.
SCPS183A – OCTOBER 2007 – REVISED MARCH 2008
3.5.2 Serial-Bus Interface Protocol
All data transfers are initiated by the serial-bus master. The beginning of a data transfer is indicated by a
start condition, which is signaled when the SDA line transitions to the low state while SCL is in the high
state, as illustrated in Figure 3-7 . The end of a requested data transfer is indicated by a stop condition,
which is signaled by a low-to-high transition of SDA while SCL is in the high state, as shown in Figure 3-7 .
Data on SDA must remain stable during the high state of the SCL signal, as changes on the SDA signal
during the high state of SCL are interpreted as control signals, that is, a start or stop condition.
Figure 3-6. Serial EEPROM Application
Figure 3-7. Serial-Bus Start/Stop Conditions and Bit Transfers
Data is transferred serially in 8-bit bytes. During a data transfer operation, the exact number of bytes that
are transmitted is unlimited. However, each byte must be followed by an acknowledge bit to continue the
data transfer operation. An acknowledge (ACK) is indicated by the data byte receiver pulling the SDA
signal low, so that it remains low during the high state of the SCL signal. Figure 3-8 illustrates the
acknowledge protocol.
Submit Documentation Feedback Feature/Protocol Descriptions 35
Page 36

SCL From
Master
1 2
3
7
8 9
SDA Output
ByTransmitter
SDA Output
ByReceiver
S
b6
b4
b5
b3
b2 b1
b0 0
b7
b6
b5
b4
b3
b2 b1
b0
A A
Slave Address
Word Address
R/W
S/P =Start/StopCondition
A =Slave Acknowledgement
b7
b6
b4
b5
b3
b2 b1
b0
A P
DataByte
XIO2213A PCI Express to 1394b OHCI with 3-Port PHY
SCPS183A – OCTOBER 2007 – REVISED MARCH 2008
Figure 3-8. Serial-Bus Protocol Acknowledge
The bridge performs three basic serial-bus operations: single byte reads, single byte writes, and multibyte
reads. The single byte operations occur under software control. The multibyte read operations are
performed by the serial EEPROM initialization circuitry immediately after a PCI Express reset. See
Section 3.5.3 , Serial-Bus EEPROM Application, for details on how the bridge automatically loads the
subsystem identification and other register defaults from the serial-bus EEPROM.
Figure 3-9 illustrates a single byte write. The bridge issues a start condition and sends the 7-bit slave
device address and the R/W command bit is equal to 0b. A 0b in the R/W command bit indicates that the
data transfer is a write. The slave device acknowledges if it recognizes the slave address. If no
acknowledgment is received by the bridge, then bit 1 (SB_ERR) is set in the serial-bus control and status
register (PCI offset B3h, see Section 4.59 ). Next, the EEPROM word address is sent by the bridge, and
another slave acknowledgment is expected. Then the bridge delivers the data byte MSB first and expects
a final acknowledgment before issuing the stop condition.
www.ti.com
Figure 3-10 illustrates a single byte read. The bridge issues a start condition and sends the 7-bit slave
device address and the R/ W command bit is equal to 0b (write). The slave device acknowledges if it
recognizes the slave address. Next, the EEPROM word address is sent by the bridge, and another slave
acknowledgment is expected. Then, the bridge issues a restart condition followed by the 7-bit slave
address and the R/ W command bit is equal to 1b (read). Once again, the slave device responds with an
acknowledge. Next, the slave device sends the 8-bit data byte, MSB first. Since this is a 1-byte read, the
bridge responds with no acknowledge (logic high) indicating the last data byte. Finally, the bridge issues a
stop condition.
Feature/Protocol Descriptions36 Submit Documentation Feedback
Figure 3-9. Serial-Bus Protocol – Byte Write
Page 37
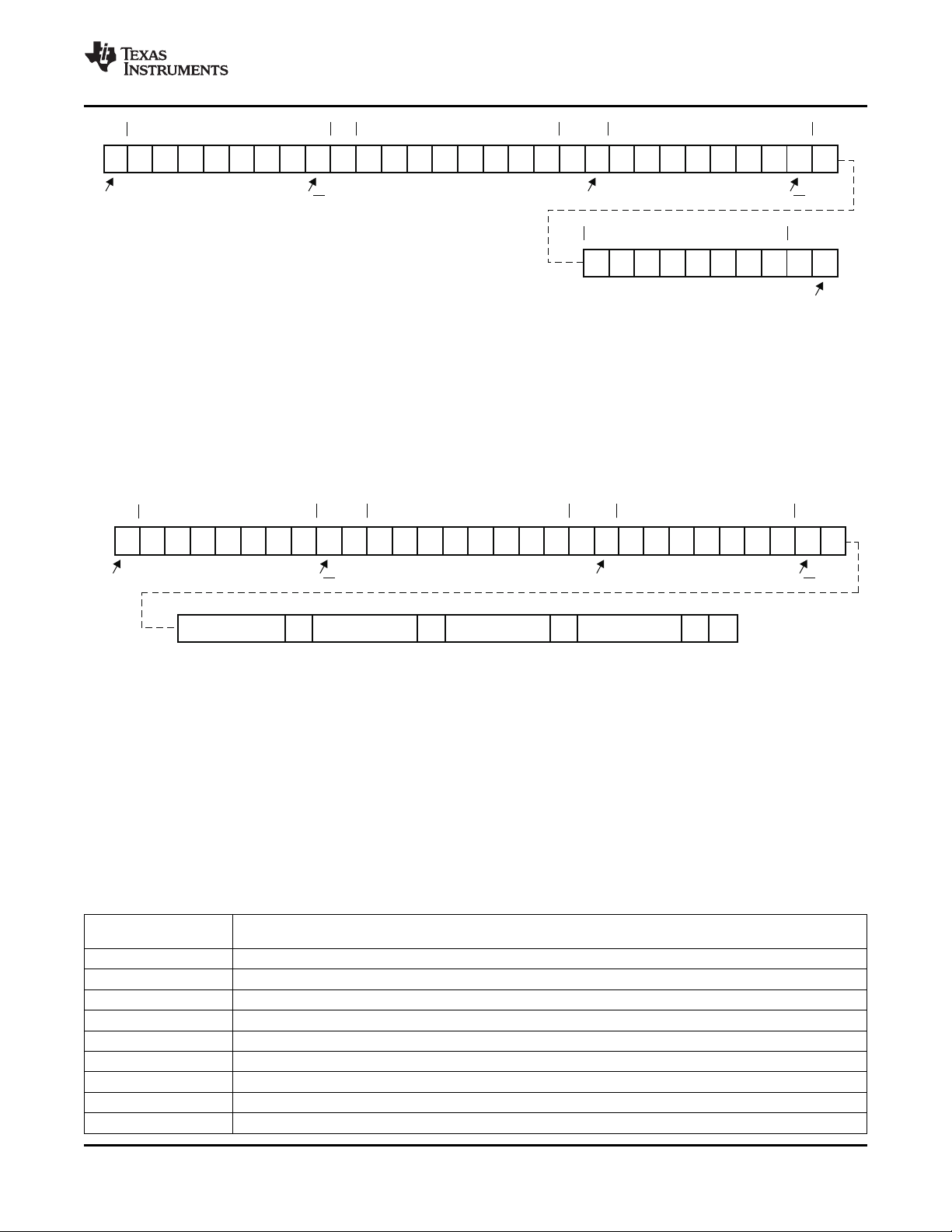
S
b6
b4
b5
b3
b2
b1
b0 0
b7
b6
b5
b4
b3
b2
b1
b0
A
A
Slave Address
Word Address
R/W
S
b6
b4
b5
b3
b2 b1
b0
1
A
Slave Address
S/P =Start/StopCondition
M=Master Acknowledgement
b7
b6
b4
b5
b3
b2
b1
b0
M P
DataByte
Start
Restart
R/W
A =Slave Acknowledgement
Stop
S
1 1
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
A A
Slave Address
Word Address
R/W
DataByte1 DataByte2 DataByte3
M
P
M
M
M=Master Acknowledgement
S/P =Start/StopCondition
A =Slave Acknowledgement
DataByte0
M
S
1 1
0 0 0 0 0
1
A
Restart
R/W
Slave Address
Start
XIO2213A PCI Express to 1394b OHCI with 3-Port PHY
www.ti.com
Figure 3-10. Serial-Bus Protocol – Byte Read
Figure 3-11 illustrates the serial interface protocol during a multi-byte serial EEPROM download. The
serial-bus protocol starts exactly the same as a 1-byte read. The only difference is that multiple data bytes
are transferred. The number of transferred data bytes is controlled by the bridge master. After each data
byte, the bridge master issues acknowledge (logic low) if more data bytes are requested. The transfer
ends after a bridge master no acknowledge (logic high) followed by a stop condition.
SCPS183A – OCTOBER 2007 – REVISED MARCH 2008
Figure 3-11. Serial-Bus Protocol – Multibyte Read
Bit 7 (PROT_SEL) in the serial-bus control and status register changes the serial-bus protocol. Each of
the three previous serial-bus protocol figures illustrates the PROT_SEL bit default (logic low). When this
control bit is asserted, the word address and corresponding acknowledge are removed from the serial-bus
protocol. This feature allows the system designer a second serial-bus protocol option when selecting
external EEPROM devices.
3.5.3 Serial-Bus EEPROM Application
The registers and corresponding bits that are loaded through the EEPROM are provided in Table 3-4 .
Table 3-4. EEPROM Register Loading Map
SERIAL EEPROM BYTE DESCRIPTION
WORD ADDRESS
00h PCI-Express to PCI bridge function indicator (00h)
01h Number of bytes to download (1Eh)s
02h PCI 84h, subsystem vendor ID, byte 0
Submit Documentation Feedback Feature/Protocol Descriptions 37
03h PCI 85h, subsystem vendor ID, byte 1
04h PCI 86h, subsystem ID, byte 0s
05h PCI 87h, subsystem ID, byte 1s
06h PCI D4h, general control, byte 0
07h PCI D5h, general control, byte 1
08h PCI D6h, general control, byte 2
Page 38

XIO2213A PCI Express to 1394b OHCI with 3-Port PHY
SCPS183A – OCTOBER 2007 – REVISED MARCH 2008
Table 3-4. EEPROM Register Loading Map (continued)
SERIAL EEPROM BYTE DESCRIPTION
WORD ADDRESS
09h PCI D7h, general control, byte 3
0Ah TI Proprietary register load 00h (PCI D8h)
0Bh TI Proprietary register load 00h (PCI D9h)
0Ch Reserved—no bits loaded 00h (PCI DAh)
0Dh PCI DCh, arbiter control
0Eh PCI DDh, arbiter request mask
0Fh PCI C0h, TL control and diagnostic register, byte 0
10h PCI C0h, TL control and diagnostic register, byte 1
11h PCI C0h, TL control and diagnostic register, byte 2
12h PCI C0h, TL control and diagnostic register, byte 3
13h PCI C4h, DLL control and diagnostic register, byte 0
14h PCI C5h, DLL control and diagnostic register, byte 1
15h PCI C6h, DLL control and diagnostic register, byte 2
16h PCI C7h, DLL control and diagnostic register, byte 3
17h PCI C8h, PHY control and diagnostic register, byte 0
18h PCI C9h, PHY control and diagnostic register, byte 1
19h PCI CAh, PHY control and diagnostic register, byte 2
1Ah PCI CBh, PHY control and diagnostic register, byte 3
1Bh Reserved—no bits loaded 00h (PCI CEh)
1Ch Reserved—no bits loaded 00h (PCI CFh)
1Dh TI Proprietary register load 00h (PCI E0h)
1Eh TI Proprietary register load 00h (PCI E2h)
1Fh TI Proprietary register load 00h (PCI E3h)
20h 1394 OHCI function indicator (01h)
21h Number of bytes (18h)
22h PCI 3Fh, maximum latency, bits 7-4 PCI 3Eh, minimum grant, bits 3-0
23h PCI 2Ch, subsystem vendor ID, byte 0
24h PCI 2Dh, subsystem vendor ID, byte 1
25h PCI 2Eh, subsystem ID, byte 0
26h PCI 2Fh, subsystem ID, byte 1
[7] [6] [5:3] [2] [1] [0]
27h Link_Enh HC Control Program RSVD Link_Enh bit 2 Link_Enh RSVD
enab_unfair Phy Enable enab_accel
28h Mini-ROM Address, this byte indicates the MINI ROM offset into the EEPROM
29h OHCI 24h, GUIDHi, byte 0
2Ah OHCI 25h, GUIDHi, byte 1
2Bh OHCI 26h, GUIDHi, byte 2
2Ch OHCI 27h, GUIDHi, byte 3
2Dh OHCI 28h, GUIDLo, byte 0
2Eh OHCI 29h, GUIDLo, byte 1
2Fh OHCI 2Ah, GUIDLo, byte 2
30h OHCI 2Bh, GUIDLo, byte 3
31h Reserved – No bits loaded
32h PCI F5h, Link_Enh, byte 1, bits 7, 6, 5, 4
33h PCI F0h, PCI miscellaneous, byte 0, bits 7, 4, 2, 1, 0
34h PCI F1h, PCI miscellaneous, byte 1, bits 1, 0
www.ti.com
00h = No MINI ROM
01h to FFh = MINI ROM offset
Feature/Protocol Descriptions38 Submit Documentation Feedback
Page 39

www.ti.com
Table 3-4. EEPROM Register Loading Map (continued)
SERIAL EEPROM BYTE DESCRIPTION
WORD ADDRESS
35h Reserved – No bits loaded
36h Reserved – No bits loaded
37h Reserved – No bits loaded
38h Reserved – No bits loaded
39h Reserved – Multifuntion Select Register
3Ah End-of-list indicator (80h)
This format must be explicitly followed for the bridge to correctly load initialization values from a serial
EEPROM. All byte locations must be considered when programming the EEPROM.
The serial EEPROM is addressed by the bridge at slave address 1010 000b. This slave address is
internally hardwired and cannot be changed by the system designer. Therefore, all three hardware
address bits for the EEPROM are tied to VSS to achieve this address. The serial EEPROM in the sample
application circuit (Figure 3-6 ) assumes the 1010b high-address nibble. The lower three address bits are
terminal inputs to the chip, and the sample application shows these terminal inputs tied to V
During an EEPROM download operation, bit 4 (ROMBUSY) in the serial-bus control and status register is
asserted. After the download is finished, bit 0 (ROM_ERR) in the serial-bus control and status register
may be monitored to verify a successful download.
XIO2213A PCI Express to 1394b OHCI with 3-Port PHY
SCPS183A – OCTOBER 2007 – REVISED MARCH 2008
SS
.
3.5.4 Accessing Serial-Bus Devices Through Softwaree
The bridge provides a programming mechanism to control serial-bus devices through system software.
The programming is accomplished through a doubleword of PCI configuration space at offset B0h.
Table 3-5 lists the registers that program a serial-bus device through software.
Table 3-5. Registers Used To Program Serial-Bus Devices
PCI OFFSET REGISTER NAME DESCRIPTION
B0h Serial-bus data (see Contains the data byte to send on write commands or the received data byte on read
B1h Serial-bus word address The content of this register is sent as the word address on byte writes or reads. This register is
B2h Serial-bus slave address Write transactions to this register initiate a serial-bus transaction. The slave device address and
B3h Serial-bus control and Serial interface enable, busy, and error status are communicated through this register. In
Section 4.56 ) commands.
(see Section 4.57 ) not used in the quick command protocol. Bit 7 (PROT_SEL) in the serial-bus control and status
register (offset B3h, see Section 4.59 ) is set to 1b to enable the slave address to be sent.
(see Section 4.58 ) the R/ W command selector are programmed through this register.
status (see Section 4.59 ) addition, the protocol-select bit (PROT_SEL) and serial-bus test bit (SBTEST) are programmed
through this register.
To access the serial EEPROM through the software interface, the following steps are performed:
1. The control and status byte is read to verify the EEPROM interface is enabled (SBDETECT asserted)
and not busy (REQBUSY and ROMBUSY deasserted).
2. The serial-bus word address is loaded. If the access is a write, then the data byte is also loaded.
3. The serial-bus slave address and R/W command selector byte is written.
4. REQBUSY is monitored until this bit is deasserted.
5. SB_ERR is checked to verify that the serial-bus operation completed without error. If the operation is a
read, then the serial-bus data byte is now valid.
Submit Documentation Feedback Feature/Protocol Descriptions 39
Page 40

XIO2213A PCI Express to 1394b OHCI with 3-Port PHY
SCPS183A – OCTOBER 2007 – REVISED MARCH 2008
3.6 Advanced Error Reporting Registers
In the extended PCI Express configuration space, the bridge supports the advanced error reporting
capabilities structure. For the PCI Express interface, both correctable and uncorrectable error statuses are
provided. For the PCI bus interface, secondary uncorrectable error status is provided. All uncorrectable
status bits have corresponding mask and severity control bits. For correctable status bits, only mask bits
are provided.
Both the primary and secondary interfaces include first error pointer and header log registers. When the
first error is detected, the corresponding bit position within the uncorrectable status register is loaded into
the first error pointer register. Likewise, the header information associated with the first failing transaction
is loaded into the header log. To reset this first error control logic, the corresponding status bit in the
uncorrectable status register is cleared by a writeback of 1b.
For systems that require high data reliability, ECRC is fully supported on the PCI Express interface. The
primary side advanced error capabilities and control register has both ECRC generation and checking
enable control bits. When the checking bit is asserted, all received TLPs are checked for a valid ECRC
field. If the generation bit is asserted, then all transmitted TLPs contain a valid ECRC field.
3.7 Data Error Forwarding Capability
The bridge supports the transfer of data errors in both directions.
If a downstream PCI Express transaction with a data payload is received that targets the internal PCI bus
and the EP bit is set indicating poisoned data, then the bridge must ensure that this information is
transferred to the PCI bus. To do this, the bridge forces a parity error on each PCI bus data phase by
inverting the parity bit calculated for each double-word of data.
www.ti.com
If the bridge is the target of a PCI transaction that is forwarded to the PCI Express interface and a data
parity error is detected, then this information is passed to the PCI Express interface. To do this, the bridge
sets the EP bit in the upstream PCI Express header.
3.8 General-Purpose I/O Interfacee
Up to eight general-purpose input/output (GPIO) terminals are provided for system customization. These
GPIO terminals are 3.3-V tolerant.
The exact number of GPIO terminals varies based on implementing the clock run, power override, and
serial EEPROM interface features. These features share four of the eight GPIO terminals. When any of
the three shared functions are enabled, the associated GPIO terminal is disabled.
All eight GPIO terminals are individually configurable as either inputs or outputs by writing the
corresponding bit in the GPIO control register at offset B4h. A GPIO data register at offset B6h exists to
either read the logic state of each GPIO input or to set the logic state of each GPIO output. The power-up
default state for the GPIO control register is input mode.
3.9 Set Slot Power Limit Functionality
The PCI Express Specification provides a method for devices to limit internal functionality and save power
based on the value programmed into the captured slot power limit scale (CSPLS) and capture slot power
limit value (CSPLV) fields of the PCI Express device capabilities register at offset 94h. See Section 4.50 ,
Device Capabilities Register, for details. The bridge writes these fields when a set slot power limit
message is received on the PCI Express interface.
After the deassertion of PERST, the XIO2213A compares the information within the CSPLS and CSPLV
fields of the device capabilities register to the minimum power scale (MIN_POWER_SCALE) and minimum
power value (MIN_POWER_VALUE) fields in the general control register at offset D4h. See Section 4.66 ,
General Control Register, for details. If the CSPLS and CSPLV fields are less than the
MIN_POWER_SCALE and MIN_POWER_VALUE fields, respectively, then the bridge takes the
appropriate action that is defined below.
Feature/Protocol Descriptions40 Submit Documentation Feedback
Page 41

www.ti.com
The power usage action is programmable within the bridge. The general control register includes a 3-bit
POWER_OVRD field. This field is programmable to the following two options:
1. Ignore slot power limit fields
2. Respond with unsupported request to all transactions except type 0/1 configuration transactions and
set slot power limit messages
3.10 PCI Express and PCI Bus Power Management
The bridge supports both software-directed power management and active state power management
through standard PCI configuration space. Software-directed registers are located in the power
management capabilities structure located at offset 50h. Active state power management control registers
are located in the PCI Express capabilities structure located at offset 90h.
During software-directed power management state changes, the bridge initiates link state transitions to L1
or L2/L3 after a configuration write transaction places the device in a low power state. The power
management state machine is also responsible for gating internal clocks based on the power state.
Table 3-6 identifies the relationship between the D-states and bridge clock operation.
PCI express reference clock input (REFCLK) On On On On/Off
Internal PCI bus clock to bridge function On Off Off Off
Internal PCI bus clock to 1394b OHCI function On On On On/Off
XIO2213A PCI Express to 1394b OHCI with 3-Port PHY
SCPS183A – OCTOBER 2007 – REVISED MARCH 2008
Table 3-6. Clocking In Low Power States
CLOCK SOURCE D0/L0 D1/L1 D2/L1 D3/L2/L3
The link power management (LPM) state machine manages active state power by monitoring the PCI
Express transaction activity. If no transactions are pending and the transmitter has been idle for at least
the minimum time required by the PCI Express Specification, then the LPM state machine transitions the
link to either the L0s or L1 state. By reading the bridge’s L0s and L1 exit latency in the link capabilities
register, the system software may make an informed decision relating to system performance versus
power savings. The ASLPMC field in the link control register provides an L0s only option, L1 only option,
or both L0s and L1 option.
Finally, the bridge generates the PM_Active_State_Nak Message if a PM_Active_State_Request_L1
DLLP is received on the PCI Express interface and the link cannot be transitioned to L1.
Submit Documentation Feedback Feature/Protocol Descriptions 41
Page 42

XIO2213A PCI Express to 1394b OHCI with 3-Port PHY
SCPS183A – OCTOBER 2007 – REVISED MARCH 2008
3.11 1394b OHCI Controller Functionality
3.11.1 1394b OHCI Power Management
The 1394b OHCI controller complies with the PCI Bus Power Management Interface Specification. The
controller supports the D0 (uninitialized), D0 (active), D1, D2, and D3 power states as defined by the
power management definition in the 1394 Open Host Controller Interface Specification, Appendix A4.
Table 3-7 identifies the supported power management registers within the 1394 OHCI configuration
register map.
Table 3-7. 1394b OHCI Configuration Register Map
REGISTER NAME OFFSET
Power management capabilities Next item pointer Capability ID 44h
PM data Power management control/status register bridge support extensions Power management control/status (CSR) 48h
www.ti.com
3.11.2 1394b OHCI and V
The 1394b OHCI function within the XIO2213A is powered by V
power management state, V
This implies that the 1394b OHCI function does not implement sticky bits and needs to be initialized after
a D3
power management state. An external serial EEPROM interface is available to initialize critical
cold
configuration register bits. The EEPROM download is triggered by the deassertion of the PERST input.
Otherwise, the BIOS will need to initialize the 1394b OHCI function.
3.11.3 1394b OHCI and Reset Options
The 1394b OHCI function is completely reset by the internal power-on reset feature, by the GRST input, or
by the PCI Express reset (PERST) input. This includes all EEPROM loadable bits, power management
functions, and all remaining configuration register bits and logic.
A PCI Express training control hot reset or the PCI bus configuration register reset bit (SRST) excludes
the EEPROM loadable bits, power management functions, and 1394 PHY. All remaining configuration
registers and logic are reset.
If the OHCI controller is in the power management D2 or D3 state or if the OHCI configuration register
reset bit (SoftReset) is set, the OHCI controller DMA logic and link logic is reset.
Finally, if the OHCI configuration register PHY reset bit (ISBR) is set, the 1394 PHY logic is reset.
3.11.4 1394b OHCI PCI Bus Master
As a bus master, the 1394 OHCI function supports the memory commands specified in Table 3-8 . The
commands include memory read, memory read line, memory read multiple, memory write, and memory
write and invalidate.
AUX
only. Therefore, during the D3
cold
is not supplied to the 1394b OHCI function.
AUX
DD_MAIN
The read command usage for read transactions of greater than two data phases are determined by the
selection in bits 9:8 (MR_ENHANCE field) of the PCI miscellaneous configuration register at offset F0h
(see Section 7.21 ). For read transactions of one or two data phases, a memory read command is used.
The write command usage is determined by the MWI_ENB bit 4 of the command configuration register at
offset 04h (see Section 4.3 ). If bit 4 is asserted and a memory write starts on a cache boundary with a
length greater than one cache line, then memory write and invalidate commands are used. Otherwise,
memory write commands are used.
42 Feature/Protocol Descriptions Submit Documentation Feedback
Page 43

www.ti.com
3.11.5 1394b OHCI Subsystem Identification
The subsystem identification register at offset 2Ch is used for system and option card identification
purposes. This register can be initialized from the serial EEPROM or programmed via the subsystem
access register at offset F8h in the 1394a OHCI PCI configuration space (see Section 7.23 ).
Write access to the subsystem access register updates the subsystem identification registers identically to
OHCI-Lynx™. The contents of the subsystem access register are aliased to the subsystem vendor ID and
subsystem ID registers at PCI offsets 2Ch and 2Eh, respectively. The subsystem ID value written to this
register may also be read back from this register.
3.11.6 1394b OHCI PME Support
Since the 1394b OHCI controller is not connected to VAUX, PME generation is disabled for D3cold power
management states.
XIO2213A PCI Express to 1394b OHCI with 3-Port PHY
SCPS183A – OCTOBER 2007 – REVISED MARCH 2008
Table 3-8. 1394 OHCI Memory Command Options
PCI COMMAND OHCI MASTER FUNCTION
C/ BE3–C/ BE0
Memory read 0110 DMA read from memory
Memory write 0111 DMA write to memory
Memory read multiple 1100 DMA read from memory
Memory read line 1110 DMA read from memory
Memory write and invalidate 1111 DMA write to memory
Submit Documentation Feedback Feature/Protocol Descriptions 43
Page 44

XIO2213A PCI Express to 1394b OHCI with 3-Port PHY
SCPS183A – OCTOBER 2007 – REVISED MARCH 2008
4 Classic PCI Configuration Space
The programming model of the XIO2213A PCI-Express to PCI bridge is compliant to the classic
PCI-to-PCI bridge programming model. The PCI configuration map uses the type 1 PCI bridge header.
All bits marked with a are sticky bits and are reset by a global reset ( GRST) or the internally-generated
power-on reset. All bits marked with a I are reset by a PCI Express reset ( PERST), a GRST, or the
internally-generated power-on reset. The remaining register bits are reset by a PCI Express hot reset,
PERST, GRST, or the internally-generated power-on reset.
Table 4-1. Classic PCI Configuration Register Map
REGISTER NAME OFFSET
Device ID Vendor ID 000h
Status Command 004h
Class code Revision ID 008h
BIST Header type Latency timer Cache line size 00Ch
Device contol base address 010h
Scratchpad RAM base address 014h
Secondary latency timer Subordinate bus number Secondary bus number Primary bus number 018h
Secondary status I/O limit I/O base 01Ch
Memory limit Memory base 020h
Prefetchable memory limit Prefetchable memory base 024h
Prefetchable base upper 32 bits 028h
Prefetchable limit upper 32 bits 02Ch
I/O limit upper 16 bits I/O base upper 16 bits 030h
Reserved Capabilities pointer 034h
Reserved 038h
Bridge control Interrupt pin Interrupt line 03Ch
Reserved 040h-04Ch
Power management capabilities Next item pointer PM capability ID 050h
PM data PMCSR_BSE Power management CSR 054h
Reserved 058h-05Ch
MSI message control Next item pointer MSI CAP ID 060h
MSI message address 064h
MSI upper message address 068h
Reserved MSI message data 06Ch
Reserved 070h-07Ch
Reserved Next item pointer SSID/SSVID capability ID 080h
Subsystem ID
PCI Express capabilities register Next item pointer PCI Express capability ID 090h
Device status Device control 098h
Link status Link control 0A0h
Serial-bus control and Serial-bus slave address
(1)
status
GPIO data
(1)
(1)
Subsystem vendor ID
Reserved 088h-08Ch
Device capabilities 094h
Link capabilities 09Ch
Reserved 0A4h-0ACh
(1)
Serial-bus word address
Reserved 0B8h-0BCh
(1)
GPIO control
(1)
Serial-bus data
(1)
www.ti.com
084h
(1)
0B0h
0B4h
(1) One or more bits in this register are reset by a PCI Express reset ( PERST), a GRST, or the internally-generated power-on reset.
Classic PCI Configuration Space44 Submit Documentation Feedback
Page 45

XIO2213A PCI Express to 1394b OHCI with 3-Port PHY
www.ti.com
Table 4-1. Classic PCI Configuration Register Map (continued)
REGISTER NAME OFFSET
Control and diagnostic register 0
Control and diagnostic register 1
Control and diagnostic register 2
Reserved 0CCh
Subsystem access
General control
Reserved TI proprietary
Reserved Arbiter time-out status Arbiter request mask
TI proprietary
Reserved TI proprietary 0E4h
(1)
(1)
Reserved 0E8h-0FCh
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
TI proprietary
Reserved TI proprietary
4.1 Vendor ID Register
This 16-bit read-only register contains the value 104Ch, which is the vendor ID assigned to Texas
Instruments.,
PCI register offset: 00h
Register type: Read-only
Default value: 104Ch
BIT NUMBER 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
RESET STATE 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 1 1 0 0
SCPS183A – OCTOBER 2007 – REVISED MARCH 2008
(1)
(1)
TI proprietary
Arbiter control
(1)
(1)
(1)
0C0h
0C4h
0C8h
0D0h
0D4h
0D8h
0DCh
0E0h
4.2 Device ID Register
This 16-bit read-only register contains the value 823Eh, which is the device ID assigned by TI for the
bridge.,
PCI register offset: 02h
Register type: Read-only
Default value: 823Eh
BIT NUMBER 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
RESET STATE 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 1 1 0 0 0 1
4.3 Command Register
The command register controls how the bridge behaves on the PCI Express interface. See Table 4-2 for a
complete description of the register contents.
PCI register offset: 04h
Register type: Read-only, Read/Write
Default value: 0000h
BIT NUMBER 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
RESET STATE 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Submit Documentation Feedback Classic PCI Configuration Space 45
Page 46

XIO2213A PCI Express to 1394b OHCI with 3-Port PHY
SCPS183A – OCTOBER 2007 – REVISED MARCH 2008
Table 4-2. Command Register Description
BIT FIELD NAME ACCESS DESCRIPTION
15:11 RSVD R Reserved. Returns 00000b when read.
10 INT_DISABLE R
9 FBB_ENB R
8 SERR_ENB RW
7 STEP_ENB R
6 PERR_ENB RW
5 VGA_ENB R
4 MWI_ENB RW
3 SPECIAL R
2 MASTER_ENB RW
1 MEMORY_ENB RW
0 IO_ENB RW
INTx disable. This bit enables device specific interrupts. Since the bridge does not
generate any internal interrupts, this bit is read-only 0b.
Fast back-to-back enable. The bridge does not generate fast back-to-back transactions;
therefore, this bit returns 0b when read.
SERR enable bit. When this bit is set, the bridge can signal fatal and nonfatal errors on the
PCI Express interface on behalf of SERR assertions detected on the PCI bus.
0 = Disable the reporting of nonfatal errors and fatal errors (default)
1 = Enable the reporting of nonfatal errors and fatal errors
Address/data stepping control. The bridge does not support address/data stepping, and
this bit is hardwired to 0b.
Controls the setting of bit 8 (DATAPAR) in the status register (offset 06h, see Section 4.4 )
in response to a received poisoned TLP from PCI Express. A received poisoned TLP is
forwarded with bad parity to conventional PCI regardless of the setting of this bit.
0 = Disables the setting of the master data parity error bit (default)
1 = Enables the setting of the master data parity error bit
VGA palette snoop enable. The bridge does not support VGA palette snooping; therefore,
this bit returns 0b when read.
Memory write and invalidate enable. When this bit is set, the bridge translates PCI
Express memory write requests into memory write and invalidate transactions on the PCI
interface.
0 = Disable the promotion to memory write and invalidate (default)
1 = Enable the promotion to memory write and invalidate
Special cycle enable. The bridge does not respond to special cycle transactions; therefore,
this bit returns 0b when read.
Bus master enable. When this bit is set, the bridge is enabled to initiate transactions on
the PCI Express interface.
0 = PCI Express interface cannot initiate transactions. The bridge must disable the
response to memory and I/O transactions on the PCI interface (default).
1 = PCI Express interface can initiate transactions. The bridge can forward memory
and I/O transactions from PCI secondary interface to the PCI Express interface.
Memory space enable. Setting this bit enables the bridge to respond to memory
transactions on the PCI Express interface.
0 = PCI Express receiver cannot process downstream memory transactions and must
respond with an unsupported request (default)
1 = PCI Express receiver can process downstream memory transactions. The bridge
can forward memory transactions to the PCI interface.
I/O space enable. Setting this bit enables the bridge to respond to I/O transactions on the
PCI Express interface.
0 = PCI Express receiver cannot process downstream I/O transactions and must
respond with an unsupported request (default)
1 = PCI Express receiver can process downstream I/O transactions. The bridge can
forward I/O transactions to the PCI interface.
www.ti.com
Classic PCI Configuration Space46 Submit Documentation Feedback
Page 47

XIO2213A PCI Express to 1394b OHCI with 3-Port PHY
www.ti.com
4.4 Status Register
The status register provides information about the PCI Express interface to the system. See Table 4-3 for
a complete description of the register contents.
PCI register offset: 06h
Register type: Read-only, Read/Clear
Default value: 0010h
BIT NUMBER 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
RESET STATE 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0
Table 4-3. Status Register Description
BIT FIELD NAME ACCESS DESCRIPTION
Detected parity error. This bit is set when the PCI Express interface receives a poisoned
TLP. This bit is set regardless of the state of bit 6 (PERR_ENB) in the command register
15 PAR_ERR RCU
14 SYS_ERR RCU
13 MABORT RCU
12 TABORT_REC RCUT
11 TABORT_SIG RCUT
10:9 PCI_SPEED R DEVSEL timing. These bits are read-only 00b, because they do not apply to PCI Express.
8 DATAPAR RCU
7 FBB_CAP R
6 RSVD R Reserved. Returns 0b when read.
5 66MHZ R
4 CAPLIST R
3 INT_STATUS R
2:0 RSVD R Reserved. Returns 000b when read.
(offset 04h, see Section 4.3 ).
0 = No parity error detected
1 = Parity error detectedr
Signaled system error. This bit is set when the bridge sends an ERR_FATAL or
ERR_NONFATAL message and bit 8 (SERR_ENB) in the command register (offset 04h,
see Section 4.3 ) is set.
0 = No error signaled
1 = ERR_FATAL or ERR_NONFATAL signaled
Received master abort. This bit is set when the PCI Express interface of the bridge
receives a completion-with-unsupported-request status.
0 = Unsupported request not received on the PCI Express interface
1 = Unsupported request received on the PCI Express interface
Received target abort. This bit is set when the PCI Express interface of the bridge receives
a completion-with-completer-abort status.
0 = Completer abort not received on the PCI Express interface
1 = Completer abort received on the PCI Express interface
Signaled target abort. This bit is set when the PCI Express interface completes a request
with completer abort status.
0 = Completer abort not signaled on the PCI Express interface
1 = Completer abort signaled on the PCI Express interface
Master data parity error. This bit is set if bit 6 (PERR_ENB) in the command register (offset
04h, see Section 4.3 ) is set and the bridge receives a completion with data marked as
poisoned on the PCI Express interface or poisons a write request received on the PCI
Express interface.
0 = No uncorrectable data error detected on the primary interface
1 = Uncorrectable data error detected on the primary interface
Fast back-to-back capable. This bit does not have a meaningful context for a PCI Express
device and is hardwired to 0b.
66-MHz capable. This bit does not have a meaningful context for a PCI Express device and
is hardwired to 0b.
Capabilities list. This bit returns 1b when read, indicating that the bridge supports additional
PCI capabilities.
Interrupt status. This bit reflects the interrupt status of the function. This bit is read-only 0b
since the bridge does not generate any interrupts internally.
SCPS183A – OCTOBER 2007 – REVISED MARCH 2008
Submit Documentation Feedback Classic PCI Configuration Space 47
Page 48

XIO2213A PCI Express to 1394b OHCI with 3-Port PHY
SCPS183A – OCTOBER 2007 – REVISED MARCH 2008
4.5 Class Code and Revision ID Register
This read-only register categorizes the base class, subclass, and programming interface of the bridge. The
base class is 06h, identifying the device as a bridge. The subclass is 04h, identifying the function as a
PCI-to-PCI bridge, and the programming interface is 00h. Furthermore, the TI device revision is indicated
in the lower byte (00h). See Table 4-4 for a complete description of the register contents.
PCI register offset: 08h
Register type: Read-only
Default value: 0604 0001h
BIT NUMBER 31 30 29 28 27 26 25 24 23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16
RESET STATE 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0
BIT NUMBER 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
RESET STATE 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1
Table 4-4. Class Code and Revision ID Register Description
BIT FIELD NAME ACCESS DESCRIPTION
31:24 BASECLASS R Base class. This field returns 06h when read, which classifies the function as a bridge device.
23:16 SUBCLASS R Subclass. This field returns 04h when read, which classifies the function as a PCI-to-PCI bridge.
15:8 PGMIF R Programming interface. This field returns 00h when read.
7:0 CHIPREV R Silicon revision. This field returns the silicon revision of the function.
www.ti.com
4.6 Cache Line Size Register
If the EN_CACHE_LINE_CHECK bit in the TL Control and Diagnostic Register is ‘0’, then CheetahExpress shall use side-band signals from the 1394b OHCI core to determine how much data to fetch when
handling delayed read transactions. In this case, the Cache Line Size Register shall have no effect on the
design and shall essentially be a read/write scratch pad register. If the EN_CACHE_LINE_CHECK bit is
‘1’, then the Cache Line Size Register is used by the bridge to determine how much data to pre-fetch
when handling delayed read transactions. In this case, the value in this register must be programmed to a
power of 2, and any value greater than 32 DWORDs will be treated as 32 DWORDs.
PCI register offset: 0Ch
Register type: Read/Write
Default value: 00h
BIT NUMBER 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
RESET STATE 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
4.7 Primary Latency Timer Register
This read-only register has no meaningful context for a PCI Express device and returns 00h when read.
PCI register offset: 0Dh
Register type: Read only
Default value: 00h
BIT NUMBER 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
RESET STATE 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
48 Classic PCI Configuration Space Submit Documentation Feedback
Page 49

www.ti.com
4.8 Header Type Register
This read-only register indicates that this function has a type one PCI header. Bit 7 of this register is 0b
indicating that the bridge is a single-function device.
PCI register offset: 0Eh
Register type: Read only
Default value: 01h
BIT NUMBER 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
RESET STATE 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1
4.9 BIST Register
Since the bridge does not support a built-in self test (BIST), this read-only register returns the value of 00h
when read.
PCI register offset: 0Fh
Register type: Read only
Default value: 00h
BIT NUMBER 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
RESET STATE 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
XIO2213A PCI Express to 1394b OHCI with 3-Port PHY
SCPS183A – OCTOBER 2007 – REVISED MARCH 2008
4.10 Device Control Base Address Register
This read/write register programs the memory base address that accesses the device control registers.
See Table 4-5 for a complete description of the register contents.
PCI register offset: 10h
Register type: Read-only, Read/Write
Default value: 0000 0000h
BIT NUMBER 31 30 29 28 27 26 25 24 23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16
RESET STATE 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
BIT NUMBER 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
RESET STATE 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Table 4-5. Device Control Base Address Register Description
BIT FIELD NAME ACCESS DESCRIPTION
31:12 ADDRESS R or RW Memory Address. The memory address field for XIO2213A uses 20 read/write bits indicating
11:4 RSVD R Reserved. These bits are read-only and return 00h when read.
3 PRE_FETCH R Prefetchable. This bit is read-only 0b indicating that this memory window is not prefetchable.
2:1 MEM_TYPE R Memory type. This field is read-only 00b indicating that this window can be located anywhere
0 MEM_IND R Memory space indicator. This field returns 0b indicating that memory space is used.
that 4096 bytes of memory space are required. While less than this is actually used, typical
systems will allocate this space on a 4K boundary. If the BAR0_EN bit (bit 5 at C8h) is ‘0’,
then these bits are read-only and return zeros when read. If the BAR0_EN bit is ‘1’, then
these bits are read/write.
in the 32-bit address space.
4.11 Scratchpad RAM Base Address
This register is used to program the memory address used to access the embedded scratchpad RAM.
PCI register offset: 14h
Register type: Read-only, Read/Write
Submit Documentation Feedback Classic PCI Configuration Space 49
Page 50

XIO2213A PCI Express to 1394b OHCI with 3-Port PHY
SCPS183A – OCTOBER 2007 – REVISED MARCH 2008
Default value: 0000 0000h
BIT NUMBER 31 30 29 28 27 26 25 24 23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16
RESET STATE 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
BIT NUMBER 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
RESET STATE 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Table 4-6. Device Control Base Address Register Description
BIT FIELD NAME ACCESS DESCRIPTION
31:12 ADDRESS R or RW Memory Address. The memory address field for XIO2213A uses 20 read/write bits indicating
that 4096 bytes of memory space are required. If the BAR1_EN bit (bit 6 at C8h) is ‘0’, then
these bits are read-only and return zeros when read. If the BAR1_EN bit is ‘1’, then these
bits are read/write.
11:4 RSVD R Reserved. These bits are read-only and return 00h when read.
3 PRE_FETCH R Prefetchable. This bit is read-only 0b indicating that this memory window is not prefetchable.
2:1 MEM_TYPE R Memory type. This field is read-only 00b indicating that this window can be located anywhere
in the 32-bit address space.
0 MEM_IND R Memory space indicator. This field returns 0b indicating that memory space is used.
4.12 Primary Bus Number Register
This read/write register specifies the bus number of the PCI bus segment that the PCI Express interface is
connected to.
www.ti.com
PCI register offset: 18h
Register type: Read/Write
Default value: 00h
BIT NUMBER 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
RESET STATE 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
4.13 Secondary Bus Number Register
This read/write register specifies the bus number of the PCI bus segment that the PCI interface is
connected to. The bridge uses this register to determine how to respond to a type 1 configuration
transaction.
PCI register offset: 19h
Register type: Read/Write
Default value: 00h
BIT NUMBER 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
RESET STATE 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
4.14 Subordinate Bus Number Register
This read/write register specifies the bus number of the highest number PCI bus segment that is
downstream of the bridge. Since the PCI bus is internal and only connects to the 1394a OHCI, this
register must always be equal to the secondary bus number register (offset 19h, see Section 4.13 ). The
bridge uses this register to determine how to respond to a type 1 configuration transaction.
PCI register offset: 1Ah
Register type: Read/Write
Default value: 00h
Classic PCI Configuration Space50 Submit Documentation Feedback
Page 51

www.ti.com
BIT NUMBER 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
RESET STATE 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
4.15 Secondary Latency Timer Register
This read/write register specifies the secondary bus latency timer for the bridge, in units of PCI clock
cycles.
PCI register offset: 1Bh
Register type: Read/Write
Default value: 00h
BIT NUMBER 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
RESET STATE 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
XIO2213A PCI Express to 1394b OHCI with 3-Port PHY
SCPS183A – OCTOBER 2007 – REVISED MARCH 2008
Submit Documentation Feedback Classic PCI Configuration Space 51
Page 52
XIO2213A PCI Express to 1394b OHCI with 3-Port PHY
SCPS183A – OCTOBER 2007 – REVISED MARCH 2008
4.16 I/O Base Register
This read/write register specifies the lower limit of the I/O addresses that the bridge forwards downstream.
See Table 4-7 for a complete description of the register contents.
PCI register offset: 1Ch
Register type: Read-only, Read/Write
Default value: 01h
BIT NUMBER 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
RESET STATE 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1
Table 4-7. I/O Base Register Description
BIT FIELD NAME ACCESS DESCRIPTION
I/O base. Defines the bottom address of the I/O address range that determines when to forward I/O
transactions from one interface to the other. These bits correspond to address bits [15:12] in the I/O
7:4 IOBASE RW address. The lower 12 bits are assumed to be 000h. The 16 bits corresponding to address bits
[31:16] of the I/O address are defined in the I/O base upper 16 bits register (offset 30h, see
Section 4.25 ).
3:0 IOTYPE R I/O type. This field is read-only 1h indicating that the bridge supports 32-bit I/O addressing.
4.17 I/O Limit Register
This read/write register specifies the upper limit of the I/O addresses that the bridge forwards downstream.
See Table 4-8 for a complete description of the register contents.
www.ti.com
PCI register offset: 1Dh
Register type: Read-only, Read/Write
Default value: 01h
BIT NUMBER 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
RESET STATE 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1
Table 4-8. I/O Limit Register Description
BIT FIELD NAME ACCESS DESCRIPTION
I/O limit. Defines the top address of the I/O address range that determines when to forward I/O
7:4 IOLIMIT RW address. The lower 12 bits are assumed to be FFFh. The 16 bits corresponding to address bits
3:0 IOTYPE R I/O type. This field is read-only 1h indicating that the bridge supports 32-bit I/O addressing.
transactions from one interface to the other. These bits correspond to address bits [15:12] in the I/O
[31:16] of the I/O address are defined in the I/O limit upper 16 bits register (offset 32h, see
Section 4.26 ).
Classic PCI Configuration Space52 Submit Documentation Feedback
Page 53

XIO2213A PCI Express to 1394b OHCI with 3-Port PHY
www.ti.com
4.18 Secondary Status Register
The secondary status register provides information about the PCI bus interface. See Table 4-9 for a
complete description of the register contents.
PCI register offset: 1Eh
Register type: Read-only, Read/Clear
Default value: 02X0h
BIT NUMBER 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
RESET STATE 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 x 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Table 4-9. Secondary Status Register Description
BIT FIELD NAME ACCESS DESCRIPTION
Detected parity error. This bit reports the detection of an uncorrectable address, attribute, or data
error by the bridge on its internal PCI bus secondary interface. This bit must be set when any of the
following three conditions are true:
• The bridge detects an uncorrectable address or attribute error as a potential target.
• The bridge detects an uncorrectable data error when it is the target of a write transaction.
15 PAR_ERR RCU • The bridge detects an uncorrectable data error when it is the master of a read transaction
14 SYS_ERR RCU
13 MABORT RCU
12 TABORT_REC RCU
11 TABORT_SIG RCU
10:9 PCI_SPEED R DEVSEL timing. These bits are 01b indicating that this is a medium speed decoding device.
8 DATAPAR RCU
7 FBB_CAP R
6 RSVD R Reserved. Returns 0b when read.
5 66MHZ R
4:0 RSVD R Reserved. Returns 00000b when read.
(immediate read data).
The bit is set irrespective of the state of bit 0 (PERR_EN) in the bridge control register at offset 3Eh
(see Section 4.30 ).
0 = Uncorrectable address, attribute, or data error not detected on secondary interface
1 = Uncorrectable address, attribute, or data error detected on secondary interface
Received system error. This bit is set when the bridge detects an SERR assertion.
0 = No error asserted on the PCI interface
1 = SERR asserted on the PCI interface
Received master abort. This bit is set when the PCI interface of the bridge reports the detection of a
master abort termination by the bridge when it is the master of a transaction on its secondary
interface.
0 = Master abort not received on the PCI interface
1 = Master abort received on the PCI interface
Received target abort. This bit is set when the PCI interface of the bridge receives a target abort.
0 = Target abort not received on the PCI interface
1 = Target abort received on the PCI interface
Signaled target abort. This bit reports the signaling of a target abort termination by the bridge when it
responds as the target of a transaction on its secondary interface.
0 = Target abort not signaled on the PCI interface
1 = Target abort signaled on the PCI interface
Master data parity error. This bit is set if the bridge is the bus master of the transaction on the PCI
bus, bit 0 (PERR_EN) in the bridge control register (offset 3Eh see Section 4.30 ) is set, and the
bridge either asserts PERR on a read transaction or detects PERR asserted on a write transaction.
0 = No data parity error detected on the PCI interface
1 = Data parity error detected on the PCI interfacee
Fast back-to-back capable. This bit returns a 1b when read indicating that the secondary PCI
interface of bridge supports fast back-to-back transactions.
66-MHz capable. The bridge operates at a PCI bus CLK frequency of 66 MHz; therefore, this bit
always returns a 1b.
SCPS183A – OCTOBER 2007 – REVISED MARCH 2008
Submit Documentation Feedback Classic PCI Configuration Space 53
Page 54

XIO2213A PCI Express to 1394b OHCI with 3-Port PHY
SCPS183A – OCTOBER 2007 – REVISED MARCH 2008
4.19 Memory Base Register
This read/write register specifies the lower limit of the memory addresses that the bridge forwards
downstream. See Table 4-10 for a complete description of the register contents.
PCI register offset: 20h
Register type: Read-only, Read/Write
Default value: 0000h
BIT NUMBER 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
RESET STATE 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Table 4-10. Memory Base Register Description
BIT FIELD NAME ACCESS DESCRIPTION
Memory base. Defines the lowest address of the memory address range that determines when to
15:4 MEMBASE RW forward memory transactions from one interface to the other. These bits correspond to address bits
[31:20] in the memory address. The lower 20 bits are assumed to be 00000h.
3:0 RSVD R Reserved. Returns 0h when read.
4.20 Memory Limit Register
This read/write register specifies the upper limit of the memory addresses that the bridge forwards
downstream. See Table 4-11 for a complete description of the register contents.
www.ti.com
PCI register offset: 22h
Register type: Read-only, Read/Write
Default value: 0000h
BIT NUMBER 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
RESET STATE 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Table 4-11. Memory Limit Register Description
BIT FIELD NAME ACCESS DESCRIPTION
15:4 MEMLIMIT RW forward memory transactions from one interface to the other. These bits correspond to address bits
3:0 RSVD R Reserved. Returns 0h when read.
Memory limit. Defines the highest address of the memory address range that determines when to
[31:20] in the memory address. The lower 20 bits are assumed to be FFFFFh.
4.21 Prefetchable Memory Base Register
This read/write register specifies the lower limit of the prefetchable memory addresses that the bridge
forwards downstream. See Table 4-12 for a complete description of the register contents.
PCI register offset: 24h
Register type: Read-only, Read/Write
Default value: 0001h
BIT NUMBER 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
RESET STATE 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1
Table 4-12. Prefetchable Memory Base Register Description
BIT FIELD NAME ACCESS DESCRIPTION
Prefetchable memory base. Defines the lowest address of the prefetchable memory address range
15:4 PREBASE RW correspond to address bits [31:20] in the memory address. The lower 20 bits are assumed to be
Classic PCI Configuration Space54 Submit Documentation Feedback
that determines when to forward memory transactions from one interface to the other. These bits
00000h. The prefetchable base upper 32 bits register (offset 28h, see Section 4.23 ) specifies the bit
[63:32] of the 64-bit prefetchable memory address.
Page 55

XIO2213A PCI Express to 1394b OHCI with 3-Port PHY
www.ti.com
Table 4-12. Prefetchable Memory Base Register Description (continued)
BIT FIELD NAME ACCESS DESCRIPTION
3:0 64BIT 64-bit memory indicator. These read-only bits indicate that 64-bit addressing is supported for this
R
memory window.
4.22 Prefetchable Memory Limit Register
This read/write register specifies the upper limit of the prefetchable memory addresses that the bridge
forwards downstream. See Table 4-13 for a complete description of the register contents.
PCI register offset: 26h
Register type: Read-only, Read/Write
Default value: 0001h
BIT NUMBER 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
RESET STATE 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1
Table 4-13. Prefetchable Memory Limit Register Description
BIT FIELD NAME ACCESS DESCRIPTION
Prefetchable memory limit. Defines the highest address of the prefetchable memory address range
15:4 PRELIMIT RW correspond to address bits [31:20] in the memory address. The lower 20 bits are assumed to be
3:0 64BIT 64-bit memory indicator. These read-only bits indicate that 64-bit addressing is supported for this
that determines when to forward memory transactions from one interface to the other. These bits
FFFFFh. The prefetchable limit upper 32 bits register (offset 2Ch, see Section 4.24 ) specifies the bit
[63:32] of the 64-bit prefetchable memory address.
R
memory window.
SCPS183A – OCTOBER 2007 – REVISED MARCH 2008
4.23 Prefetchable Base Upper 32 Bits Register
This read/write register specifies the upper 32 bits of the prefetchable memory base register. See
Table 4-14 for a complete description of the register contents.
PCI register offset: 28h
Register type: Read/Write
Default value: 0000 0000h
BIT NUMBER 31 30 29 28 27 26 25 24 23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16
RESET STATE 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
BIT NUMBER 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
RESET STATE 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Table 4-14. Prefetchable Base Upper 32 Bits Register Description
BIT FIELD NAME ACCESS DESCRIPTION
31:0 PREBASE RW prefetchable memory address range that determines when to forward memory transactions
Prefetchable memory base upper 32 bits. Defines the upper 32 bits of the lowest address of the
downstream.
4.24 Prefetchable Limit Upper 32 Bits Register
This read/write register specifies the upper 32 bits of the prefetchable memory limit register. See
Table 4-15 for a complete description of the register contents.
PCI register offset: 2Ch
Register type: Read/Write
Default value: 0000 0000h
Submit Documentation Feedback Classic PCI Configuration Space 55
Page 56

XIO2213A PCI Express to 1394b OHCI with 3-Port PHY
SCPS183A – OCTOBER 2007 – REVISED MARCH 2008
BIT NUMBER 31 30 29 28 27 26 25 24 23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16
RESET STATE 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
BIT NUMBER 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
RESET STATE 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Table 4-15. Prefetchable Limit Upper 32 Bits Register Description
BIT FIELD NAME ACCESS DESCRIPTION
Prefetchable memory limit upper 32 bits. Defines the upper 32 bits of the highest address of the
31:0 PRELIMIT RW prefetchable memory address range that determines when to forward memory transactions
downstream.
4.25 I/O Base Upper 16 Bits Register
This read/write register specifies the upper 16 bits of the I/O base register. See Table 4-16 for a complete
description of the register contents.
PCI register offset: 30h
Register type: Read/Write
Default value: 0000h
BIT NUMBER 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
RESET STATE 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
www.ti.com
Table 4-16. I/O Base Upper 16 Bits Register Description
BIT FIELD NAME ACCESS DESCRIPTION
15:0 IOBASE RW that determines when to forward I/O transactions downstream. These bits correspond to address
I/O base upper 16 bits. Defines the upper 16 bits of the lowest address of the I/O address range
bits [31:20] in the I/O address. The lower 20 bits are assumed to be 00000h.
4.26 I/O Limit Upper 16 Bits Register
This read/write register specifies the upper 16 bits of the I/O limit register. See Table 4-17 for a complete
description of the register contents.
PCI register offset: 32h
Register type: Read/Write
Default value: 0000h
BIT NUMBER 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
RESET STATE 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Table 4-17. I/O Limit Upper 16 Bits Register Description
BIT FIELD NAME ACCESS DESCRIPTION
15:0 IOLIMIT RW determines when to forward I/O transactions downstream. These bits correspond to address bits
I/O limit upper 16 bits. Defines the upper 16 bits of the top address of the I/O address range that
[31:20] in the I/O address. The lower 20 bits are assumed to be FFFFFh.
4.27 Capabilities Pointer Register
This read-only register provides a pointer into the PCI configuration header where the PCI power
management block resides. Since the PCI power management registers begin at 50h, this register is
hardwired to 50h.
PCI register offset: 34h
Register type: Read-only
Classic PCI Configuration Space56 Submit Documentation Feedback
Page 57

www.ti.com
Default value: 50h
BIT NUMBER 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
RESET STATE 0 1 0 1 0 0 0 0
4.28 Interrupt Line Register
This read/write register is programmed by the system and indicates to the software which interrupt line the
bridge has assigned to it. The default value of this register is FFh, indicating that an interrupt line has not
yet been assigned to the function. Since the bridge does not generate interrupts internally, this register is
a scratch pad register.
PCI register offset: 3Ch
Register type: Read/Write
Default value: FFh
BIT NUMBER 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
RESET STATE 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
4.29 Interrupt Pin Register
The interrupt pin register is read-only 00h indicating that the bridge does not generate internal interrupts.
While the bridge does not generate internal interrupts, it does forward interrupts from the secondary
interface to the primary interface.
XIO2213A PCI Express to 1394b OHCI with 3-Port PHY
SCPS183A – OCTOBER 2007 – REVISED MARCH 2008
PCI register offset: 3Dh
Register type: Read-only
Default value: 00h
BIT NUMBER 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
RESET STATE 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Submit Documentation Feedback Classic PCI Configuration Space 57
Page 58

XIO2213A PCI Express to 1394b OHCI with 3-Port PHY
SCPS183A – OCTOBER 2007 – REVISED MARCH 2008
4.30 Bridge Control Register
The bridge control register provides extensions to the command register that are specific to a bridge. See
Table 4-18 for a complete description of the register contents.
PCI register offset: 3Eh
Register type: Read-only, Read/Write, Read/Clear
Default value: 0000h
BIT NUMBER 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
RESET STATE 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Table 4-18. Bridge Control Register Description
BIT FIELD NAME ACCESS DESCRIPTION
15:12 RSVD R Reserved. Returns 0h when read.
11 DTSERR RW Discard timer SERR enable. Applies only in conventional PCI mode. This bit enables the
bridge to generate either an ERR_NONFATAL (by default) or ERR_FATAL transaction on
the primary interface when the secondary discard timer expires and a delayed transaction
is discarded from a queue in the bridge. The severity is selectable only if advanced error
reporting is supported.
0 = Do not generate ERR_NONFATAL or ERR_FATAL on the primary interface as a
result of the expiration of the secondary discard timer. Note that an error message
can still be sent if advanced error reporting is supported and bit 10
(DISCARD_TIMER_MASK) in the secondary uncorrectable error mask register
(offset 130h, see Section 5.11 ) is clear (default).
1 = Generate ERR_NONFATAL or ERR_FATAL on the primary interface if the
secondary discard timer expires and a delayed transaction is discarded from a
queue in the bridges.
10 DTSTATUS RCU Discard timer status. This bit indicates if a discard timer expires and a delayed transaction
is discarded.
0 = No discard timer error
1 = Discard timer error
9 SEC_DT RW Selects the number of PCI clocks that the bridge waits for the 1394a OHCI
master on the secondary interface to repeat a delayed transaction request. The
counter starts once the delayed completion (the completion of the delayed
transaction on the primary interface) has reached the head of the downstream
queue of the bridge (i.e., all ordering requirements have been satisfied and the
bridge is ready to complete the delayed transaction with the initiating master on the
secondary bus). If the master does not repeat the transaction before the counter
expires, then the bridge deletes the delayed transaction from its queue and sets
the discard timer status bit.
0 = The secondary discard timer counts 215PCI clock cycles (default)
1 = The secondary discard timer counts 210PCI clock cycles
8 PRI_DEC R Primary discard timer. This bit has no meaning in PCI Express and is hardwired to 0b.
7 FBB_EN RW Fast back-to-back enable. This bit allows software to enable fast back-to-back
transactions on the secondary PCI interface.
0 = Fast back-to-back transactions are disabled (default)
1 = Secondary interface fast back-to-back transactions are enabled
6 SRST RW Secondary bus reset. This bit is set when software wishes to reset all devices
downstream of the bridge. Setting this bit causes the PRST signal on the secondary
interface to be asserted.
0 = Secondary interface is not in reset state (default)
1 = Secondary interface is in the reset state
www.ti.com
Classic PCI Configuration Space58 Submit Documentation Feedback
Page 59

XIO2213A PCI Express to 1394b OHCI with 3-Port PHY
www.ti.com
Table 4-18. Bridge Control Register Description (continued)
BIT FIELD NAME ACCESS DESCRIPTION
5 MAM RW Master abort mode. This bit controls the behavior of the bridge when it receives a master
abort or an unsupported request.
0 = Do not report master aborts. Returns FFFF FFFFh on reads and discard data on
writes (default)
1 = Respond with an unsupported request on PCI Express when a master abort is
received on PCI. Respond with target abort on PCI when an unsupported request
completion on PCI Express is received. This bit also enables error signaling on
master abort conditions on posted writes.
4 VGA16 RW VGA 16-bit decode. This bit enables the bridge to provide full 16-bit decoding for VGA I/O
addresses. This bit only has meaning if the VGA enable bit is set.
0 = Ignore address bits [15:10] when decoding VGA I/O addresses (default)
1 = Decode address bits [15:10] when decoding VGA I/O addresses
3 VGA RW VGA enable. This bit modifies the response by the bridge to VGA compatible addresses.
If this bit is set, then the bridge decodes and forwards the following accesses on the
primary interface to the secondary interface (and, conversely, block the forwarding of
these addresses from the secondary to primary interface):
• Memory accesses in the range 000A 0000h to 000B FFFFh
• I/O addresses in the first 64 KB of the I/O address space (address bits [31:16] are
0000h) and where address bits [9:0] are in the range of 3B0h to 3BBh or 3C0h to
3DFh (inclusive of ISA address aliases – address bits [15:10] may possess any
value and are not used in the decoding)
If this bit is set, then forwarding of VGA addresses is independent of the value of bit 2
(ISA), the I/O address and memory address ranges defined by the I/O base and limit
registers, the memory base and limit registers, and the prefetchable memory base and
limit registers of the bridge. The forwarding of VGA addresses is qualified by bits 0
(IO_ENB) and 1 (MEMORY_ENB) in the command register (offset 04h, see Section 4.3 ).
0 = Do not forward VGA compatible memory and I/O addresses from the primary to
secondary interface (addresses defined above) unless they are enabled for
forwarding by the defined I/O and memory address ranges (default).
1 = Forward VGA compatible memory and I/O addresses (addresses defined above)
from the primary interface to the secondary interface (if the I/O enable and memory
enable bits are set) independent of the I/O and memory address ranges and
independent of the ISA enable bit.
2 ISA RW ISA enable. This bit modifies the response by the bridge to ISA I/O addresses. This
applies only to I/O addresses that are enabled by the I/O base and I/O limit registers and
are in the first 64 KB of PCI I/O address space (0000 0000h to 0000 FFFFh). If this bit is
set, then the bridge blocks any forwarding from primary to secondary of I/O transactions
addressing the last 768 bytes in each 1-KB block. In the opposite direction (secondary to
primary), I/O transactions are forwarded if they address the last 768 bytes in each 1K
block.
0 = Forward downstream all I/O addresses in the address range defined by the I/O
base and I/O limit registers (default)
1 = Forward upstream ISA I/O addresses in the address range defined by the I/O base
and I/O limit registers that are in the first 64 KB of PCI I/O address space (top 768
bytes of each 1-KB block)
1 SERR_EN RW SERR enable. This bit controls forwarding of system error events from the secondary
interface to the primary interface. The bridge forwards system error events when:
• This bit is set
• Bit 8 (SERR_ENB) in the command register (offset 04h, see Section 4.3 ) is set
• SERR is asserted on the secondary interface
0 = Disable the forwarding of system error events (default)
1 = Enable the forwarding of system error events
SCPS183A – OCTOBER 2007 – REVISED MARCH 2008
Submit Documentation Feedback Classic PCI Configuration Space 59
Page 60

XIO2213A PCI Express to 1394b OHCI with 3-Port PHY
SCPS183A – OCTOBER 2007 – REVISED MARCH 2008
Table 4-18. Bridge Control Register Description (continued)
BIT FIELD NAME ACCESS DESCRIPTION
0 PERR_EN RW Parity error response enable. Controls the bridge's response to data, uncorrectable
address, and attribute errors on the secondary interface. Also, the bridge always forwards
data with poisoning, from conventional PCI to PCI Express on an uncorrectable
conventional PCI data error, regardless of the setting of this bit.
0 = Ignore uncorrectable address, attribute, and data errors on the secondary interface
(default)
1 = Enable uncorrectable address, attribute, and data error detection and reporting on
the secondary interface
4.31 Capability ID Register
This read-only register identifies the linked list item as the register for PCI power management. The
register returns 01h when read.
PCI register offset: 50h
Register type: Read-only
Default value: 01h
BIT NUMBER 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
RESET STATE 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1
www.ti.com
4.32 Next Item Pointer Register
The contents of this read-only register indicate the next item in the linked list of capabilities for the bridge.
This register reads 80h pointing to the Subsystem ID capabilities registers.
PCI register offset: 51h
Register type: Read-only
Default value: 60h
BIT NUMBER 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
RESET STATE 0 1 1 0 0 0 0 0
4.33 Power Management Capabilities Register
This read-only register indicates the capabilities of the bridge related to PCI power management. See
Table 4-19 for a complete description of the register contents.
PCI register offset: 52h
Register type: Read-only
Default value: 0603h
BIT NUMBER 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
RESET STATE 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1
Table 4-19. Power Management Capabilities Register Description
BIT FIELD NAME ACCESS DESCRIPTION
15:11 PME_SUPPORT R PME support. This 5-bit field indicates the power states from which the bridge may assert
10 D2_SUPPORT R This bit returns a 1b when read, indicating that the function supports the D2 device power
9 D1_SUPPORT R This bit returns a 1b when read, indicating that the function supports the D1 device power
8:6 AUX_CURRENT R 3.3 V
PME. Because the bridge never generates a PME except on a behalf of a secondary
device, this field is read-only and returns 00000b.
state.
state.
auxiliary current requirements. This field returns 000b since the bridge does not
AUX
generate PME from D3
.
cold
Classic PCI Configuration Space60 Submit Documentation Feedback
Page 61

XIO2213A PCI Express to 1394b OHCI with 3-Port PHY
www.ti.com
Table 4-19. Power Management Capabilities Register Description (continued)
BIT FIELD NAME ACCESS DESCRIPTION
5 DSI R Device specific initialization. This bit returns 0b when read, indicating that the bridge does
4 RSVD R Reserved. Returns 0b when read.
3 PME_CLK R PME clock. This bit returns 0b indicating that the PCI clock is not needed to generate PME.
2:0 PM_VERSION R Power management version. If bit 26 (PCI_PM_VERSION_CTRL) in the general control
not require special initialization beyond the standard PCI configuration header before a
generic class driver is able to use it.
register (offset D4h, see Section 4.66 ) is 0b, then this field returns 010b indicating revision
1.1 compatibility. If PCI_PM_VERSION_CTRL is 1b, then this field returns 011b indicating
revision 1.2 compatibility.
4.34 Power Management Control/Status Register
This register determines and changes the current power state of the bridge. No internal reset is generated
when transitioning from the D3
register contents.
PCI register offset: 54h
Register type: Read-only, Read/Write
Default value: 0008h
BIT NUMBER 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
RESET STATE 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0
state to the D0 state. See Table 4-20 for a complete description of the
hot
SCPS183A – OCTOBER 2007 – REVISED MARCH 2008
Table 4-20. Power Management Control/Status Register Description
BIT FIELD NAME ACCESS DESCRIPTION
15 PME_STAT R PME status. This bit is read-only and returns 0b when read.
14:13 DATA_SCALE R Data scale. This 2-bit field returns 00b when read since the bridge does not use the data
12:9 DATA_SEL R Data select. This 4-bit field returns 0h when read since the bridge does not use the data
8 PME_EN RW PME enable. This bit has no function and acts as scratchpad space. The default value for
7:4 RSVD R Reserved. Returns 0h when read.
3 NO_SOFT_RESET R No soft reset. If bit 26 (PCI_PM_VERSION_CTRL) in the general control register (offset
2 RSVD R Reserved. Returns 0b when read.
1:0 PWR_STATE RW Power state. This 2-bit field determines the current power state of the function and sets the
register.
register.
this bit is 0b.
D4h, see Section 4.66 ) is 0b, then this bit returns 0b for compatibility with version 1.1 of the
PCI Power Management Specification. If PCI_PM_VERSION_CTRL is 1b, then this bit
returns 1b indicating that no internal reset is generated and the device retains its
configuration context when transitioning from the D3
function into a new power state. This field is encoded as follows:
00 = D0 (default)
01 = D1
10 = D2
11 = D3
hot
state to the D0 state.
hot
4.35 Power Management Bridge Support Extension Register
This read-only register indicates to host software what the state of the secondary bus will be when the
bridge is placed in D3. See Table 4-21 for a complete description of the register contents.
PCI register offset: 56h
Register type: Read-only
Default value: 40h
Submit Documentation Feedback Classic PCI Configuration Space 61
Page 62

XIO2213A PCI Express to 1394b OHCI with 3-Port PHY
SCPS183A – OCTOBER 2007 – REVISED MARCH 2008
BIT NUMBER 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
RESET STATE 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0
Table 4-21. PM Bridge Support Extension Register Description
BIT FIELD NAME ACCESS DESCRIPTION
7 BPCC R Bus power/clock control enable. This bit indicates to the host software if the bus secondary
clocks are stopped when the bridge is placed in D3. The state of the BPCC bit is
controlled by bit 11 (BPCC_E) in the general control register (offset D4h, see
Section 4.66 ).
0 = The secondary bus clocks are not stopped in D3
1 = The secondary bus clocks are stopped in D3
6 BSTATE R B2/B3 support. This bit is read-only 1b indicating that the bus state in D3 is B2.
5:0 RSVD R Reserved. Returns 00 0000b when read.
4.36 Power Management Data Register
The read-only register is not applicable to the bridge and returns 00h when read.
PCI register offset: 57h
Register type: Read-only
Default value: 00h
BIT NUMBER 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
RESET STATE 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
www.ti.com
4.37 MSI Capability ID Register
This read-only register identifies the linked list item as the register for message signaled interrupts
capabilities. The register returns 05h when read.
PCI register offset: 60h
Register type: Read-only
Default value: 05h
BIT NUMBER 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
RESET STATE 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 1
4.38 Next Item Pointer Register
The contents of this read-only register indicate the next item in the linked list of capabilities for the bridge.
This register reads 80h pointing to the subsystem ID capabilities registers.
PCI register offset: 61h
Register type: Read-only
Default value: 80h
BIT NUMBER 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
RESET STATE 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
62 Classic PCI Configuration Space Submit Documentation Feedback
Page 63

XIO2213A PCI Express to 1394b OHCI with 3-Port PHY
www.ti.com
4.39 MSI Message Control Register
This register controls the sending of MSI messages. See Table 4-22 for a complete description of the
register contents.
PCI register offset: 62h
Register type: Read-only, Read/Write
Default value: 0088h
BIT NUMBER 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
RESET STATE 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 1 0 0 0
Table 4-22. MSI Message Control Register Description
BIT FIELD NAME ACCESS DESCRIPTION
15:8 RSVD R Reserved. Returns 00h when read.
7 64CAP R 64-bit message capability. This bit is read-only 1b indicating that the bridge supports 64-bit
MSI message addressing.
6:4 MM_EN RW Multiple message enable. This bit indicates the number of distinct messages that the
bridge is allowed to generate.
000 = 1 message (default)
001 = 2 messages
010 = 4 messages
011 = 8 messages
100 = 16 messages
101 = Reserved
110 = Reserved
111 = Reserved
3:1 MM_CAP R Multiple message capabilities. This field indicates the number of distinct messages that
bridge is capable of generating. This field is read-only 100b indicating that the bridge can
signal 1 interrupt for each IRQ supported on the serial IRQ stream up to a maximum of 16
unique interrupts.
0 MSI_EN RW MSI enable. This bit enables MSI interrupt signaling. MSI signaling must be enabled by
software for the bridge to signal that a serial IRQ has been detected.
0 = MSI signaling is prohibited (default)
1 = MSI signaling is enabled
SCPS183A – OCTOBER 2007 – REVISED MARCH 2008
NOTE
Enabling MSI messaging in the XIO2213A has no effect.
4.40 MSI Message Lower Address Register
This register contains the lower 32 bits of the address that a MSI message writes to when a serial IRQ is
detected. See Table 4-23 for a complete description of the register contents.
PCI register offset: 64h
Register type: Read-only, Read/Write
Default value: 0000 0000h
BIT NUMBER 31 30 29 28 27 26 25 24 23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16
RESET STATE 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
BIT NUMBER 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
RESET STATE 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Submit Documentation Feedback Classic PCI Configuration Space 63
Page 64

XIO2213A PCI Express to 1394b OHCI with 3-Port PHY
SCPS183A – OCTOBER 2007 – REVISED MARCH 2008
Table 4-23. MSI Message Lower Address Register Description
BIT FIELD NAME ACCESS DESCRIPTION
31:2 ADDRESS RW System specified message address
1:0 RSVD R Reserved. Returns 00b when read.
NOTE
Enabling MSI messaging in the XIO2213A has no effect.
4.41 MSI Message Upper Address Register
This register contains the upper 32 bits of the address that a MSI message writes to when a serial IRQ is
detected. If this register contains 0000 0000h, then 32-bit addressing is used; otherwise, 64-bit addressing
is used.
PCI register offset: 68h
Register type: Read/Write
Default value: 0000 0000h
BIT NUMBER 31 30 29 28 27 26 25 24 23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16
RESET STATE 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
BIT NUMBER 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
RESET STATE 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
www.ti.com
NOTE
Enabling MSI messaging in the XIO2213A has no effect.
4.42 MSI Message Data Register
This register contains the data that software programmed the bridge to send when it send a MSI message.
See Table 4-24 for a complete description of the register contents.
PCI register offset: 6Ch
Register type: Read/Write
Default value: 0000h
BIT NUMBER 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
RESET STATE 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Table 4-24. MSI Message Data Register Description
BIT FIELD NAME ACCESS DESCRIPTION
15:4 MSG RW System specific message. This field contains the portion of the message that the bridge
3:0 MSG_NUM RW Message number. This portion of the message field may be modified to contain the
forwards unmodified.
message number is multiple messages are enable. The number of bits that are modifiable
depends on the number of messages enabled in the message control register.
1 message = No message data bits can be modified (default)
2 messages = Bit 0 can be modified
4 messages = Bits 1:0 can be modified
8 messages = Bits 2:0 can be modified
16 messages = Bits 3:0 can be modified
Classic PCI Configuration Space64 Submit Documentation Feedback
Page 65

www.ti.com
Enabling MSI messaging in the XIO2213A has no effect.
4.43 Capability ID Register
This read-only register identifies the linked list item as the register for subsystem ID and subsystem
vendor ID capabilities. The register returns 0Dh when read.
PCI register offset: 80h
Register type: Read-only
Default value: 0Dh
BIT NUMBER 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
RESET STATE 0 0 0 0 1 1 0 1
4.44 Next Item Pointer Register
The contents of this read-only register indicate the next item in the linked list of capabilities for the bridge.
This register reads 90h pointing to the PCI Express capabilities registers.
PCI register offset: 81h
Register type: Read-only
Default value: 90h
BIT NUMBER 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
RESET STATE 1 0 0 1 0 0 0 0
XIO2213A PCI Express to 1394b OHCI with 3-Port PHY
SCPS183A – OCTOBER 2007 – REVISED MARCH 2008
NOTE
4.45 Subsystem Vendor ID Register
This register, used for system and option card identification purposes, may be required for certain
operating systems. This read-only register is initialized through the EEPROM and can be written through
the subsystem alias register. This register shall only be reset by a Fundamental Reset (FRST#).
PCI register offset: 84h
Register type: Read-only
Default value: 0000h
BIT NUMBER 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
RESET STATE 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
4.46 Subsystem ID Register
This register, used for system and option card identification purposes, may be required for certain
operating systems. This read-only register is initialized through the EEPROM and can be written through
the subsystem alias register. This register shall only be reset by a Fundamental Reset (FRST#).
PCI register offset: 86h
Register type: Read-only
Default value: 0000h
BIT NUMBER 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
RESET STATE 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
4.47 PCI Express Capability ID Register
This read-only register identifies the linked list item as the register for PCI Express capabilities. The
register returns 10h when read.
Submit Documentation Feedback Classic PCI Configuration Space 65
Page 66

XIO2213A PCI Express to 1394b OHCI with 3-Port PHY
SCPS183A – OCTOBER 2007 – REVISED MARCH 2008
PCI register offset: 90h
Register type: Read-only
Default value: 10h
BIT NUMBER 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
RESET STATE 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0
4.48 Next Item Pointer Register
The contents of this read-only register indicate the next item in the linked list of capabilities for the bridge.
This register reads 00h indicating no additional capabilities are supported.
PCI register offset: 91h
Register type: Read-only
Default value: 00h
BIT NUMBER 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
RESET STATE 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
4.49 PCI Express Capabilities Register
This read-only register indicates the capabilities of the bridge related to PCI Express. See Table 4-25 for a
complete description of the register contents.
www.ti.com
PCI register offset: 92h
Register type: Read-only
Default value: 0071h
BIT NUMBER 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
RESET STATE 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 0 0 0 1
Table 4-25. PCI Express Capabilities Register Description
BIT FIELD NAME ACCESS DESCRIPTION
15:9 RSVD R Reserved. Returns 000 0000b when read.
8 SLOT R Slot implemented. This bit is not valid for the bridge and is read-only 0b.
7:4 DEV_TYPE R Device/port type. This read-only field returns 0111b indicating that the device is a PCI
3:0 VERSION R Capability version. This field returns 1h indicating revision 1 of the PCI Express capability.
Express-to-PCI bridge.
Classic PCI Configuration Space66 Submit Documentation Feedback
Page 67

XIO2213A PCI Express to 1394b OHCI with 3-Port PHY
www.ti.com
4.50 Device Capabilities Register
The device capabilities register indicates the device specific capabilities of the bridge. See Table 4-26 for
a complete description of the register contents.
PCI register offset: 94h
Register type: Read-only
Default value: 0000 8002
BIT NUMBER 31 30 29 28 27 26 25 24 23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16
RESET STATE 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
BIT NUMBER 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
RESET STATE 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0
Table 4-26. Device Capabilities Register Description
BIT FIELD NAME ACCESS DESCRIPTION
31:28 RSVD R Reserved. Returns 0h when read.
27:26 CSPLS RU Captured slot power limit scale. The value in this field is programmed by the host by issuing a
Set_Slot_Power_Limit message. When a Set_Slot_Power_Limit message is received, bits 9:8
are written to this field. The value in this field specifies the scale used for the slot power limit.
00 = 1.0x
01 = 0.1x
10 = 0.01x
11 = 0.001x1
25:18 CSPLV RU Captured slot power limit value. The value in this field is programmed by the host by issuing a
Set_Slot_Power_Limit message. When a Set_Slot_Power_Limit message is received, bits 7:0
are written to this field. The value in this field in combination with the slot power limit scale value
(bits 27:26) specifies the upper limit of power supplied to the slot. The power limit is calculated
by multiplying the value in this field by the value in the slot power limit scale field.
17:16 RSVD R Reserved. Return 000b when read.
15 RBER R Role Based Error Reporting. This bit is hardwired to 1 indicating that the XIO2213A supports
Role Based Error Reporting
14 PIP R Power indicator present. This bit is hardwired to 0b indicating that a power indicator is not
implemented.
13 AIP R Attention indicator present. This bit is hardwired to 0b indicating that an attention indicator is not
implemented.
12 ABP R Attention button present. This bit is hardwired to 0b indicating that an attention button is not
implemented.
11:9 EP_L1_LAT RU Endpoint L1 acceptable latency. This field indicates the maximum acceptable latency for a
transition from L1 to L0 state. This field can be programmed by writing to the L1_LATENCY
field (bits 15:13) in the general control register (offset D4h, see Section 4.66 ). The default value
for this field is 000b which indicates a range less than 1 µ s. This field cannot be programmed to
be less than the latency for the PHY to exit the L1 state.
8:6 EP_L0S_LAT RU Endpoint L0s acceptable latency. This field indicates the maximum acceptable latency for a
transition from L0s to L0 state. This field can be programmed by writing to the L0s_LATENCY
field (bits 18:16) in the general control register (offset D4h, see Section 4.66 ). The default value
for this field is 000b which indicates a range less than 1 µ s. This field cannot be programmed to
be less than the latency for the PHY to exit the L0s state.
5 ETFS R Extended tag field supported. This field indicates the size of the tag field not supported.
4:3 PFS R Phantom functions supported. This field is read-only 00b indicating that function numbers are
not used for phantom functions.
2:0 MPSS R Maximum payload size supported. This field indicates the maximum payload size that the
device can support for TLPs. This field is encoded as 010b indicating the maximum payload
size for a TLP is 512 bytes.
SCPS183A – OCTOBER 2007 – REVISED MARCH 2008
Submit Documentation Feedback Classic PCI Configuration Space 67
Page 68

XIO2213A PCI Express to 1394b OHCI with 3-Port PHY
SCPS183A – OCTOBER 2007 – REVISED MARCH 2008
4.51 Device Control Register
The device control register controls PCI Express device specific meters. See Table 4-27 for a complete
description of the register contents.
PCI register offset: 98h
Register type: Read-only, Read/Write
Default value: 2800h
BIT NUMBER 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
RESET STATE 0 0 1 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Table 4-27. Device Control Register Description
BIT FIELD NAME ACCESS DESCRIPTION
15 CFG_RTRY_ENB RW Configuration retry status enable. When this read/write bit is set to 1b, the bridge returns a
completion with completion retry status on PCI Express if a configuration transaction
forwarded to the secondary interface did not complete within the implementation specific
time-out period. When this bit is set to 0b, the bridge does not generate completions with
completion retry status on behalf of configuration transactions. The default value of this bit is
0b.
14:12 MRRS RW Maximum read request size. This field is programmed by host software to set the maximum
size of a read request that the bridge can generate. The bridge uses this field in conjunction
with the cache line size register (offset 0Ch, see Section 7.6 ) to determine how much data to
fetch on a read request. This field is encoded as:
000 = 128B
001 = 256B
010 = 512B (default)
011 = 1024B
100 = 2048B
101 = 4096B
110 = Reserved
111 = Reserved
11 ENS RW Enable no snoop. Controls the setting of the no snoop flag within the TLP header for upstream
memory transactions mapped to any traffic class mapped to a virtual channel (VC) other than
VC0 through the upstream decode windows.
0 = No snoop field is 0b
1 = No snoop field is 1b (default)
10 APPE RW Auxiliary power PM enable. This bit has no effect in the bridge.
0 = AUX power is disabled (default)
1 = AUX power is enabled
9 PFE R Phantom function enable. Since the bridge does not support phantom functions, this bit is
read-only 0b.
8 ETFE R Extended tag field enable. Since the bridge does not support extended tags, this bit is
read-only 0b.
7:5 MPS RW Maximum payload size. This field is programmed by host software to set the maximum size of
posted writes or read completions that the bridge can initiate. This field is encoded as:
000 = 128B (default)
001 = 256B
010 = 512B
011 = 1024B
100 = 2048B
101 = 4096B
110 = Reserved
111 = Reserved
4 ERO R Enable relaxed ordering. Since the bridge does not support relaxed ordering, this bit is
read-only 0b.
3 URRE RW Unsupported request reporting enable. If this bit is set, then the bridge sends an
ERR_NONFATAL message to the root complex when an unsupported request is received.
0 = Do not report unsupported requests to the root complex (default)
1 = Report unsupported requests to the root complexd
www.ti.com
Classic PCI Configuration Space68 Submit Documentation Feedback
Page 69

XIO2213A PCI Express to 1394b OHCI with 3-Port PHY
www.ti.com
Table 4-27. Device Control Register Description (continued)
BIT FIELD NAME ACCESS DESCRIPTION
2 FERE RW Fatal error reporting enable. If this bit is set, then the bridge is enabled to send ERR_FATAL
messages to the root complex when a system error event occurs.
0 = Do not report fatal errors to the root complex (default)
1 = Report fatal errors to the root complexd
1 NFERE RW Nonfatal error reporting enable. If this bit is set, then the bridge is enabled to send
ERR_NONFATAL messages to the root complex when a system error event occurs.
0 = Do not report nonfatal errors to the root complex (default)
1 = Report nonfatal errors to the root complexd
0 CERE RW Correctable error reporting enable. If this bit is set, then the bridge is enabled to send
ERR_COR messages to the root complex when a system error event occurs.
0 = Do not report correctable errors to the root complex (default)
1 = Report correctable errors to the root complex.
4.52 Device Status Register
The device status register provides PCI Express device specific information to the system. See Table 4-28
for a complete description of the register contents.
PCI register offset: 9Ah
Register type: Read-only
Default value: 0000h
BIT NUMBER 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
RESET STATE 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
SCPS183A – OCTOBER 2007 – REVISED MARCH 2008
Table 4-28. Device Status Register Description
BIT FIELD NAME ACCESS DESCRIPTION
15:6 RSVD R Reserved. Returns 00 0000 0000b when read.
5 PEND RU Transaction pending. This bit is set when the bridge has issued a nonposted transaction that has
4 APD RU AUX power detected. This bit indicates that AUX power is present.
3 URD RCU Unsupported request detected. This bit is set by the bridge when an unsupported request is
2 FED RCU Fatal error detected. This bit is set by the bridge when a fatal error is detected.
1 NFED RCU Nonfatal error detected. This bit is set by the bridge when a nonfatal error is detected.
0 CED RCU Correctable error detected. This bit is set by the bridge when a correctable error is detected.
not been completed.
0 = No AUX power detected
1 = AUX power detectedd
received.
Submit Documentation Feedback Classic PCI Configuration Space 69
Page 70

XIO2213A PCI Express to 1394b OHCI with 3-Port PHY
SCPS183A – OCTOBER 2007 – REVISED MARCH 2008
4.53 Link Capabilities Register
The link capabilities register indicates the link specific capabilities of the bridge. See Table 4-29 for a
complete description of the register contents.
PCI register offset: 9Ch
Register type: Read-only
Default value: 0006 XC11h
BIT NUMBER 31 30 29 28 27 26 25 24 23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16
RESET STATE 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 0
BIT NUMBER 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
RESET STATE 0 x x x 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 1
Table 4-29. Link Capabilities Register Description
BIT FIELD NAME ACCESS DESCRIPTION
31:24 PORT_NUM R Port number. This field indicates port number for the PCI Express link. This field is read-only
00h indicating that the link is associated with port 0.
23:19 RSVD R Reserved. Return 00 0000b when read.
18 CLK_PM R Clock Power Management. This bit is hardwired to 1 to indicate that XIO2213A supports Clock
Power Management through CLKREQ protocol.
17:15 L1_LATENCY R L1 exit latency. This field indicates the time that it takes to transition from the L1 state to the L0
state. Bit 6 (CCC) in the link control register (offset A0h, see Section 4.54 ) equals 1b for a
common clock and equals 0b for an asynchronous clock.
For a common reference clock, the value of this field is determined by bits 20:18
(L1_EXIT_LAT_ASYNC) of the control and diagnostic register 1 (offset C4h, see Section 4.63 ).
For an asynchronous reference clock, the value of this field is determined by bits 17:15
(L1_EXIT_LAT_COMMON) of the control and diagnostic register 1 (offset C4h, see
Section 4.63 ).
14:12 L0S_LATENCY R L0s exit latency. This field indicates the time that it takes to transition from the L0s state to the
L0 state. Bit 6 (CCC) in the link control register (offset A0h, see Section 4.54 ) equals 1b for a
common clock and equals 0b for an asynchronous clock.
For a common reference clock, the value of 011b indicates that the L1 exit latency falls between
256 ns to less than 512 ns.
For an asynchronous reference clock, the value of 100b indicates that the L1 exit latency falls
between 512 ns to less than 1 µ s.
11:10 ASLPMS R Active state link PM support. This field indicates the level of active state power management
that the bridge supports. The value 11b indicates support for both L0s and L1 through active
state power management.
9:4 MLW R Maximum link width. This field is encoded 00 0001b to indicate that the bridge only supports a
1x PCI Express link.
3:0 MLS R Maximum link speed. This field is encoded 1h to indicate that the bridge supports a maximum
link speed of 2.5 Gb/s.
www.ti.com
Classic PCI Configuration Space70 Submit Documentation Feedback
Page 71

XIO2213A PCI Express to 1394b OHCI with 3-Port PHY
www.ti.com
4.54 Link Control Register
The link control register controls link specific behavior. See Table 4-30 for a complete description of the
register contents.
PCI register offset: A0h
Register type: Read-only, Read/Write
Default value: 0000h
BIT NUMBER 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
RESET STATE 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Table 4-30. Link Control Register Description
BIT FIELD NAME ACCESS DESCRIPTION
15:9 RSVD RW Reserved. Returns 00h when read.
8 CPM_EN RW Clock Power Management Enable. This bit is used to enable XIO2213A to use CLKREQ
for clock power management
0 = Clock Power Management is disabled and XIO2213A shall hold the CLKREQ
signal low
1 = Clock Power Management is enabled and XIO2213A is permitted to use the
CLKREQ signal to allow the REFCLK input to be stopped
7 ES RW Extended synch. This bit forces the bridge to extend the transmission of FTS ordered sets
and an extra TS2 when exiting from L1 prior to entering to L0.
0 = Normal synch (default)
1 = Extended synch
6 CCC RW Common clock configuration. When this bit is set, it indicates that the bridge and the
device at the opposite end of the link are operating with a common clock source. A value
of 0b indicates that the bridge and the device at the opposite end of the link are operating
with se te reference clock sources. The bridge uses this common clock configuration
information to report the correct L0s and L1 exit latencies.
0 = Reference clock is asynchronous (default)
1 = Reference clock is common
5 RL R Retrain link. This bit has no function and is read-only 0b.
4 LD R Link disable. This bit has no function and is read-only 0b.
3 RCB RW Read completion boundary. This bit is an indication of the RCB of the root complex. The
state of this bit has no affect on the bridge, since the RCB of the bridge is fixed at 128
bytes.
0 = 64 bytes (default)
1 = 128 bytes
2 RSVD R Reserved. Returns 0b when read.
1:0 ASLPMC RW Active state link PM control. This field enables and disables the active state PM.
00 = Active state PM disabled (default)
01 = L0s entry enabled
10 = L1 entry enabled
11 = L0s and L1 entry enabled
SCPS183A – OCTOBER 2007 – REVISED MARCH 2008
Submit Documentation Feedback Classic PCI Configuration Space 71
Page 72
XIO2213A PCI Express to 1394b OHCI with 3-Port PHY
SCPS183A – OCTOBER 2007 – REVISED MARCH 2008
4.55 Link Status Register
The link status register indicates the current state of the PCI Express link. See Table 4-31 for a complete
description of the register contents.
PCI register offset: A2h
Register type: Read-only
Default value: X011h
BIT NUMBER 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
RESET STATE 0 0 0 x 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 1
Table 4-31. Link Status Register Description
BIT FIELD NAME ACCESS DESCRIPTION
15:13 RSVD R Reserved. Returns 000b when read.
12 SCC R Slot clock configuration. This bit indicates that the bridge uses the same physical reference
clock that the platform provides on the connector. If the bridge uses an independent clock
irrespective of the presence of a reference on the connector, then this bit must be cleared.
0 = Independent 125-MHz reference clock is used
1 = Common 100-MHz reference clock is used
11 LT R Link training. This bit has no function and is read-only 0b.
10 TE R Retrain link. This bit has no function and is read-only 0b.
9:4 NLW R Negotiated link width. This field is read-only 00 0001b indicating the lane width is 1x.
3:0 LS R Link speed. This field is read-only 1h indicating the link speed is 2.5 Gb/s.
www.ti.com
4.56 Serial-Bus Data Register
The serial-bus data register reads and writes data on the serial-bus interface. Write data is loaded into this
register prior to writing the serial-bus slave address register (offset B2h, see Section 4.58 ) that initiates the
bus cycle. When reading data from the serial bus, this register contains the data read after bit 5
(REQBUSY) of the serial-bus control and status register (offset B3h, see Section 4.59 ) is cleared. This
register shall only be reset by a Fundamental Reset ( FRST).
PCI register offset: B0h
Register type: Read/Write
Default value: 00h
BIT NUMBER 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
RESET STATE 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
4.57 Serial-Bus Word Address Register
The value written to the serial-bus word address register represents the word address of the byte being
read from or written to the serial-bus device. The word address is loaded into this register prior to writing
the serial-bus slave address register (offset B2h, see Section 4.58 ) that initiates the bus cycle. This
register shall only be reset by a Fundamental Reset ( FRST).
PCI register offset: B1h
Register type: Read/Write
Default value: 00h
BIT NUMBER 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
RESET STATE 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
72 Classic PCI Configuration Space Submit Documentation Feedback
Page 73

www.ti.com
4.58 Serial-Bus Slave Address Register
The serial-bus slave address register indicates the slave address of the device being targeted by the
serial-bus cycle. This register also indicates if the cycle is a read or a write cycle. Writing to this register
initiates the cycle on the serial interface. See Table 4-32 for a complete description of the register
contents.
PCI register offset: B2h
Register type: Read/Write
Default value: 00h
BIT NUMBER 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
RESET STATE 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Table 4-32. Serial-Bus Slave Address Register Descriptions
BIT FIELD NAME ACCESS DESCRIPTION
(1)
7:1
(1) This register shall only be reset by a Fundamental Reset ( FRST).
SLAVE_ADDR RW Serial-bus slave address. This 7-bit field is the slave address for a serial-bus read or write
(1)
0
RW_CMD RW Read/write command. This bit determines if the serial-bus cycle is a read or a write cycle.
transaction. The default value for this field is 000 0000b.
0 = A single byte write is requested (default).
1 = A single byte read is requested.
XIO2213A PCI Express to 1394b OHCI with 3-Port PHY
SCPS183A – OCTOBER 2007 – REVISED MARCH 2008
4.59 Serial-Bus Control and Status Register
The serial-bus control and status register controls the behavior of the serial-bus interface. This register
also provides status information about the state of the serial bus. See Table 4-33 for a complete
description of the register contents.
PCI register offset: B3h
Register type: Read-only, Read/Write, Read/Clear
Default value: 00h
BIT NUMBER 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
RESET STATE 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Table 4-33. Serial-Bus Control and Status Register Description
BIT FIELD NAME ACCESS DESCRIPTION
(1)
7
PROT_SEL RW Protocol select. This bit selects the serial-bus address mode used.
0 = Slave address and word address are sent on the serial-bus (default)
1 = Only the slave address is sent on the serial-bus
6 RSVD R Reserved. Returns 0b when read.
(1)
5
REQBUSY RU Requested serial-bus access busy. This bit is set when a software-initiated serial-bus cycle
(1)
4
ROMBUSY RU Serial EEPROM access busy. This bit is set when the serial EEPROM circuitry in the bridge
(1) This register shall only be reset by a Fundamental Reset ( FRST).
is in progress.
0 = No serial-bus cycle
1 = Serial-bus cycle in progress
is downloading register defaults from a serial EEPROM.
0 = No EEPROM activity
1 = EEPROM download in progress
Submit Documentation Feedback Classic PCI Configuration Space 73
Page 74

XIO2213A PCI Express to 1394b OHCI with 3-Port PHY
SCPS183A – OCTOBER 2007 – REVISED MARCH 2008
Table 4-33. Serial-Bus Control and Status Register Description (continued)
BIT FIELD NAME ACCESS DESCRIPTION
(1)
3
SBDETECT RWU Serial EEPROM access busy. This bit is set when the serial EEPROM circuitry in the bridge
(1)
2
SBTEST RW Serial-bus test. This bit is used for internal test purposes. This bit controls the clock source
(1)
1
SB_ERR RCU Serial-bus error. This bit is set when an error occurs during a software-initiated serial-bus
(1)
0
ROM_ERR RCU Serial EEPROM load error. This bit is set when an error occurs while downloading registers
is downloading register defaults from a serial EEPROM.
Note: A serial EEPROM is only detected once following PERST.
0 = No EEPROM present, EEPROM load process does not happen. GPIO4//SCL and
GPIO5//SDA terminals are configured as GPIO signals.
1 = EEPROM present, EEPROM load process takes place. GPIO4//SCL and
GPIO5//SDA terminals are configured as serial-bus signals.
for the serial interface clock.
0 = Serial-bus clock at normal operating frequency ~ 60 kHz (default)
1 = Serial-bus clock frequency increased for test purposes ~ 4 MHz
cycle.
0 = No error
1 = Serial-bus error
from serial EEPROM.
0 = No error
1 = EEPROM load error
www.ti.com
Classic PCI Configuration Space74 Submit Documentation Feedback
Page 75

XIO2213A PCI Express to 1394b OHCI with 3-Port PHY
www.ti.com
4.60 GPIO Control Register
This register controls the direction of the eight GPIO terminals. This register has no effect on the behavior
of GPIO terminals that are enabled to perform secondary functions. The secondary functions share GPIO4
(SCL) and GPIO5 (SDA). See Table 4-34 for a complete description of the register contents.
PCI register offset: B4h
Register type: Read-only, Read/Write
Default value: 0000h
BIT NUMBER 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
RESET STATE 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Table 4-34. GPIO Control Register Description
BIT FIELD NAME ACCESS DESCRIPTION
15:8 RSVD R Reserved. Return 00h when read.
(1)
7
GPIO7_DIR RW GPIO 7 data direction. This bit selects whether GPIO7 is in input or output mode.
0 = Input (default)
1 = Output
(1)
6
GPIO6_DIR RW GPIO 6 data direction. This bit selects whether GPIO6 is in input or output mode.
0 = Input (default)
1 = Output
(1)
5
GPIO5_DIR RW GPIO 5 data direction. This bit selects whether GPIO5 is in input or output mode.
0 = Input (default)
1 = Output
(1)
4
GPIO4_DIR RW GPIO 4 data direction. This bit selects whether GPIO4 is in input or output mode.
0 = Input (default)
1 = Output
(1)
3
GPIO3_DIR RW GPIO 3 data direction. This bit selects whether GPIO3 is in input or output mode.
0 = Input (default)
1 = Output
(1)
2
GPIO2_DIR RW GPIO 2 data direction. This bit selects whether GPIO2 is in input or output mode.
0 = Input (default)
1 = Output
(1)
1
GPIO1_DIR RW GPIO 1 data direction. This bit selects whether GPIO1 is in input or output mode.
0 = Input (default)
1 = Output
(1)
0
GPIO0_DIR RW GPIO 0 data direction. This bit selects whether GPIO0 is in input or output mode.
0 = Input (default)
1 = Output
(1) This register shall only be reset by a Fundamental Reset ( FRST).
SCPS183A – OCTOBER 2007 – REVISED MARCH 2008
Submit Documentation Feedback Classic PCI Configuration Space 75
Page 76

XIO2213A PCI Express to 1394b OHCI with 3-Port PHY
SCPS183A – OCTOBER 2007 – REVISED MARCH 2008
4.61 GPIO Data Register
This register reads the state of the input mode GPIO terminals and changes the state of the output mode
GPIO terminals. Writing to a bit that is in input mode or is enabled for a secondary function is ignored. The
secondary functions share GPIO4 (SCL) and GPIO5 (SDA). The default value at power up depends on
the state of the GPIO terminals as they default to general-purpose inputs. See Table 4-35 for a complete
description of the register contents.
PCI register offset: B6h
Register type: Read-only, Read/Write
Default value: 00XXh
BIT NUMBER 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
RESET STATE 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 x x x x x x x x
Table 4-35. GPIO Data Register Description
BIT FIELD NAME ACCESS DESCRIPTION
15:8 RSVD R Reserved
(1)
7
GPIO7_DATA RW GPIO 7 data. This bit reads the state of GPIO7 when in input mode or changes the state of
(1)
6
GPIO6_DATA RW GPIO 6 data. This bit reads the state of GPIO6 when in input mode or changes the state of
(1)
5
GPIO5_DATA RW GPIO 5 data. This bit reads the state of GPIO5 when in input mode or changes the state of
(1)
4
GPIO4_DATA RW GPIO 4 data. This bit reads the state of GPIO4 when in input mode or changes the state of
(1)
3
GPIO3_DATA RW GPIO 3 data. This bit reads the state of GPIO3 when in input mode or changes the state of
(1)
2
GPIO2_DATA RW GPIO 2 data. This bit reads the state of GPIO2 when in input mode or changes the state of
(1)
1
GPIO1_DATA RW GPIO 1 data. This bit reads the state of GPIO1 when in input mode or changes the state of
(1)
0
GPIO0_DATA RW GPIO 0 data. This bit reads the state of GPIO0 when in input mode or changes the state of
(1) This register shall only be reset by a Fundamental Reset ( FRST).
GPIO7 when in output mode.
GPIO6 when in output mode.
GPIO5 when in output mode.
GPIO4 when in output mode.
GPIO3 when in output mode.
GPIO2 when in output mode.
GPIO1 when in output mode.
GPIO0 when in output mode.
www.ti.com
Classic PCI Configuration Space76 Submit Documentation Feedback
Page 77

XIO2213A PCI Express to 1394b OHCI with 3-Port PHY
www.ti.com
4.62 Control and Diagnostic Register 0
The contents of this register are used for monitoring status and controlling behavior of the bridge. See
Table 4-36 for a complete description of the register contents. It is recommended that all values within this
register be left at the default value. Improperly programming fields in this register may cause
interoperability or other problems.
PCI register offset: C0h
Register type: Read/Write
Default value: 0000 0000h
BIT NUMBER 31 30 29 28 27 26 25 24 23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16
RESET STATE 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
BIT NUMBER 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
RESET STATE 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Table 4-36. Control and Diagnostic Register 0 Description
BIT FIELD NAME S DESCRIPTION
(1)
31:24
23:19
15:14
13:12 RSVD R Reserved. Returns 00b when read.
(1) This register shall only be reset by a Fundamental Reset ( FRST).
PRI_BUS_NUM R This field contains the captured primary bus number.
(1)
PRI_DEVICE_ NUM R This field contains the captured primary device number.
18 ALT_ERROR_REP RW Alternate Error Reporting. This bit controls the method that the XIO2213A uses for error
17 DIS_BRIDGE_PME RW Disable Bridge PME# input
16 DIS_OHCI_PME RW Disable OHCI_PME# pin
(1)
FIFO_SIZE RW FIFO size. This field contains the maximum size (in DW) of the FIFO.
11 ALLOW_CFG_ANY_FN RW Allow Config Access to any Functin. When this bit is set, the bridge shall respond to config
10 RETURN_PW_CREDIT RW Return PW Packet Credits. When this bit is set, the bridge shall return all the PW packet
S credits.
9 RSVD R Reserved. Returns 0b when read.
8 RETURN_CPL_CREDIT RW Return Completion Credits. When this bit is set, the bridge shall return all completion
S credits immediately.
7 EN_CACHE_LINE_CHE RW Enable Cache Line Check.
CK
ACCES
reporting.
0 = Advisory Non-Fatal Error reporting supported (default)
1 = Advisory Non-Fatal Error reporting not supported
0 = The PME# input signal to the bridge is enabled and connected to the PME# signal
from the 1394 OHCI function (default)
1 = The PME# input signal to the bridge is disabled
0 = OHCI_PME# pin is enabled and connected to the PME# signal from the 1394
OHCI function (default)
1 = OHCI_PME# pin is disabled
accesses to any function number.
0 = The bridge shall use side band signals to determine the transaction size (default)
1 = The bridge shall use the Cache Line Size Register to determine the transaction
size
SCPS183A – OCTOBER 2007 – REVISED MARCH 2008
Submit Documentation Feedback Classic PCI Configuration Space 77
Page 78

XIO2213A PCI Express to 1394b OHCI with 3-Port PHY
SCPS183A – OCTOBER 2007 – REVISED MARCH 2008
Table 4-36. Control and Diagnostic Register 0 Description (continued)
BIT FIELD NAME S DESCRIPTION
(1)
6
PREFETCH_4X RW Prefetch 4X enable.
(1)
5:4
UP_REQ_BUF _VALUE RW PCI upstream req-res buffer threshold value. The value in this field controls the buffer
(1)
3
UP_REQ_BUF _CTRL RW PCI upstream req-res buffer threshold control. This bit enables the PCI upstream req-res
(1)
2
CFG_ACCESS RW Configuration access to memory-mapped registers. When this bit is set, the bridge allows
_MEM_REG configuration access to memory-mapped configuration registers.
(1)
1
RSVD RW Reserved. Bit 1 defaults to 0b. If this register is programmed via EEPROM or another
0 RSVD R Reserved. Returns 0b when read.
ACCES
0 = The bridge will prefetch up to 2 cache lines, as defined in the cache line size
register (offset 0Ch, see Section 7.6 ) for upstream memory read multiple (MRM)
transactions (default)
1 = The bridge device will prefetch up to 4 cache lines, as defined in the cache line
size register (offset 0Ch, see Section 7.6 ) for upstream memory read multiple
(MRM) transactions.
Note1: When this bit is set and the FORCE_MRM bit in the General Control Register is set,
then both upstream memory read multiple transactions and upstream memory transactions
will prefetch up to 4 cache lines.
Note2: When the READ_PREFETCH_DIS bit in the General Control Register is set, this bit
shall have no effect and only one DWORD shall be fetched on a burst read.
This bit shall only affect the XIO2213A design when the EN_CACHE_LINE_CHECK bit is
set.
space that must be available for the device to accept a PCI bus transaction. If the cache
line size is not valid, then the device will use 8 DW for calculating the threshold value.
00 = 1 Cacheline + 4 DW (default)
01 = 1 Cacheline + 8 DW
10 = 1 Cacheline + 12 DW
11 = 2 Cachelines + 4 DW
buffer threshold control mode of the bridge.
0 = PCI upstream req-res buffer threshold control mode disabled (default)
1 = PCI upstream req-res buffer threshold control mode enabled
mechanism, the value written into this field must be 0b.
www.ti.com
4.63 Control and Diagnostic Register 1
The contents of this register are used for monitoring status and controlling behavior of the bridge. See
Table 4-37 for a complete description of the register contents. It is recommended that all values within this
register be left at the default value. Improperly programming fields in this register may cause
interoperability or other problems.
PCI register offset: C4h
Register type: Read/Write
Default value: 0012 0108h
BIT NUMBER 31 30 29 28 27 26 25 24 23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16
RESET STATE 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 1 0
BIT NUMBER 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
RESET STATE 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0
Table 4-37. Control and Diagnostic Register 1 Description
BIT FIELD NAME ACCESS DESCRIPTION
32:21 RSVD R Reserved. Returns 000h when read.
(1)
20:18
(1) This register shall only be reset by a Fundamental Reset ( FRST).
L1_EXIT_LAT_ RW L1 exit latency for asynchronous clock. When bit 6 (CCC) of the link control register (offset
ASYNC A0h, see Section 4.54 ) is set, the value in this field is mirrored in bits 17:15 (L1_LATENCY)
field in the link capabilities register (offset 9Ch, see Section 4.53 ). This field defaults to 100b.
Classic PCI Configuration Space78 Submit Documentation Feedback
Page 79

www.ti.com
Table 4-37. Control and Diagnostic Register 1 Description (continued)
BIT FIELD NAME ACCESS DESCRIPTION
(1)
17:15
14:11
10
9:6
5:2
1:0
L1_EXIT_LAT_ RW L1 exit latency for common clock. When bit 6 (CCC) of the link control register (offset A0h, see
COMMON Section 4.54 ) is clear, the value in this field is mirrored in bits 17:15 (L1_LATENCY) field in the
link capabilities register (offset 9Ch, see Section 4.53 ). This field defaults to 100b.
(1)
RSVD RW Reserved. Bits 14:11 default to 0000b. If this register is programmed via EEPROM or another
mechanism, the value written into this field must be 0000b.
(1)
SBUS_RESET RW Secondary bus reset bit mask. When this bit is set, the bridge masks the reset caused by bit 6
_MASK (SRST) of the bridge control register (offset 3Eh, see Section 4.30 ). This bit defaults to 0b.
(1)
L1ASPM_ TIMER RW L1ASPM entry timer. This field specifies the value (in 512-ns ticks) of the L1ASPM entry timer.
This field defaults to 0100b.
(1)
L0s_TIMER RW L0s entry timer. This field specifies the value (in 62.5-MHz clock ticks) of the L0s entry timer.
This field defaults to 0010b.
(1)
RSVD RW Reserved. Bits 1:0 default to 00b. If this register is programmed via EEPROM or another
mechanism, then the value written into this field must be 00b.
XIO2213A PCI Express to 1394b OHCI with 3-Port PHY
SCPS183A – OCTOBER 2007 – REVISED MARCH 2008
Submit Documentation Feedback Classic PCI Configuration Space 79
Page 80

XIO2213A PCI Express to 1394b OHCI with 3-Port PHY
SCPS183A – OCTOBER 2007 – REVISED MARCH 2008
4.64 PHY Control and Diagnostic Register 2
The contents of this register are used for monitoring status and controlling behavior of the physical layer
macro for diagnostic purposes. See Table 4-38 for a complete description of the register contents. It is
recommended that all values within this register be left at the default value. Improperly programming fields
in this register may cause interoperability or other problems.
PCI register offset: C8h
Register type: Read/Write
Default value: 3214 2000h
BIT NUMBER 31 30 29 28 27 26 25 24 23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16
RESET STATE 0 0 1 1 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 0
BIT NUMBER 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
RESET STATE 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Table 4-38. Control and Diagnostic Register 2 Description
BIT FIELD NAME ACCESS DESCRIPTION
(1)
31:24
23:16
15:13 PHY_REV R PHY revision number
12:8
(1) This register shall only be reset by a Fundamental Reset ( FRST).
N_FTS_ RW N_FTS for asynchronous clock. When bit 6 (CCC) of the link control register (offset A0h, see
ASYNC_CLK Section 4.54 ) is clear, the value in this field is the number of FTS that are sent on a transition from
(1)
N_FTS_ RW N_FTS for common clock. When bit 6 (CCC) of the link control register (offset A0h, see Section 4.54 )
COMMON_ is set, the value in this field is the number of FTS that are sent on a transition from L0s to L0. This
CLK field defaults to 14h.
(1)
LINK_NUM RW Link number
7 EN_L2_PWR_ RW Enable L2 Power Savings
SAVE
6 BAR1_EN RW BAR 1 Enable.
5 BAR0_EN RW BAR01 Enable.
4 REQ_RECOV RW REQ_RECOVERY to LTSSM
ERY
3 REQ_RECON RW REQ_RECONFIGURE to LTSSM
FIG
2 REQ_HOT_R RW REQ_HOT_RESET to LTSSM
ESET
1 REQ_DIS_SC RW REQ_DISABLE_SCRAMBLER to LTSSM
RAMBLER
0 REQ_LOOPB RW REQ_LOOPBACK to LTSSM
ACK
L0s to L0. This field shall default to 32h.
0= Power savings not enabled when in L2
1= Power savings enabled when in L2.
0 = BAR at offset 14h is disabled (default)
1 = BAR at offset 14h is enabled
0 = BAR at offset 10h is disabled (default)
1 = BAR at offset 10h is enabled
www.ti.com
4.65 Subsystem Access Register
The contents of this read/write register are aliased to the subsystem vendor ID and subsystem ID registers
at PCI offsets 84h and 86h. See Table 4-39 for a complete description of the register contents.
PCI register offset: D0h
Register type: Read/Write
Default value: 0000 0000h
Classic PCI Configuration Space80 Submit Documentation Feedback
Page 81

XIO2213A PCI Express to 1394b OHCI with 3-Port PHY
www.ti.com
BIT NUMBER 31 30 29 28 27 26 25 24 23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16
RESET STATE 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
BIT NUMBER 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
RESET STATE 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Table 4-39. Subsystem Access Register Description
BIT FIELD NAME ACCESS DESCRIPTION
(1)
31:16
15:0
(1) This register shall only be reset by a Fundamental Reset ( FRST).
SubsystemID RW Subsystem ID. The value written to this field is aliased to the subsystem ID register at PCI
(1)
SubsystemVendorID RW Subsystem vendor ID. The value written to this field is aliased to the subsystem vendor ID
offset 86h (see Section 4.46 ).
register at PCI offset 84h (seeSection 4.45 ).
4.66 General Control Register
This read/write register controls various functions of the bridge. See Table 4-40 for a complete description
of the register contents.
PCI register offset: D4h
Register type: Read-only, Read/Write
Default value: 8600 025Fh
BIT NUMBER 31 30 29 28 27 26 25 24 23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16
RESET STATE 1 0 0 0 0 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
SCPS183A – OCTOBER 2007 – REVISED MARCH 2008
BIT NUMBER 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
RESET STATE 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 1 1 1 1 1
Table 4-40. General Control Register Description
BIT FIELD NAME ACCESS DESCRIPTION
(1)
31:30
29:28 ASPM_CTRL_DE RW Active State Power Management Control Default Override. These bits are used to determine the
27
26
CFG_RETRY RW Configuration retry counter. Configures the amount of time that a configuration request must be
_CNTR retried on the secondary PCI bus before it may be completed with configuration retry status on
F_OVRD power up default for bits 1:0 of the Link Control Register in the PCI Express Capability Structure.
(1)
LOW_POWER RW Low-power enable. When this bit is set, the half-ampitude, no preemphasis mode for the PCI
_EN Express TX drivers is enabled. The default for this bit is 0b.
(1)
PCI_PM_ RW PCI power management version control. This bit controls the value reported in bits 2:0
VERSION_ CTRL (PM_VERSION) in the power management capabilities register (offset 52h, see Section 4.33 ). It
the PCI Express side.
00 = 25 µ s
01 = 1 ms
10 = 25 ms (default)
11 = 50 ms
00 = Power on default indicates that the active state power management is disable (00b)
01 = (default)
10 = Power on default indicates that the active state power management is enabled for L0s
11 = (01b)
Power on default indicates that the active state power management is enabled for L1s
(10b)
Power on default indicates that the active state power management is enabled for L0s
and L1s (11b)
also controls the value of bit 3 (NO_SOFT_RESET) in the power management control/status
register (offset 54h, see Section 4.34 ).
0 = Version fields reports 010b and NO_SOFT_RESET reports 0b for Power
Management 1.1 compliance
1 = Version fields reports 011b and NO_SOFT_RESET reports 1b for Power
Management 1.2 compliance (default)
(1) This register shall only be reset by a Fundamental Reset ( FRST).
Submit Documentation Feedback Classic PCI Configuration Space 81
Page 82

XIO2213A PCI Express to 1394b OHCI with 3-Port PHY
SCPS183A – OCTOBER 2007 – REVISED MARCH 2008
Table 4-40. General Control Register Description (continued)
BIT FIELD NAME ACCESS DESCRIPTION
(1)
25
24
23
22:20
19
18:16
15:13
STRICT_ RW Strict Priority Enable. When this bit is 0, the default LOW_PRIORITY_COUNT will be ‘001’. When
PRIORITY_EN this bit is 1, the default LOW_PRIORITY_COUNT will be ‘000’. This default value for this bit is ‘1’.
When this bit is set and the LOW-PRIORITY_COUNT is ‘000’ meaning that Strict Priority VC
arbitration is used and the extended virtual channel ALWAYS receives priority over VC0 at the
PCI Express port.
0 = The default LOW_PRIORITY_COUNT is 001b
1 = The default LOW_PRIORITY_COUNT is 000b (default)
(1)
FORCE_MRM RW Force memory read multiple
0 = Memory read multiple transactions are disabled (default).
1 = All upstream memory read transactions initiated on the PCI bus are treated as though
they are Memory Read Multiple transactions in which pre-fetching is supported for the
transaction. This bit shall only affect the XIO2213A design when the
EN_CACHE_LINE_CHECK bit in the TL Control and Diagnostic Register is set.
(1)
CPM_EN_ RW Clock Power Management Enable Default Override. This bit is used to determine the power up
DEF_OVRD default for bit 8 of the Link Control Register in the PCI Express Capability Structure
0 = Power-on default indicates that clock power management is disabled (00b) (default)
1 = Power-on default indicates that clock power management is enabled for L0s and L1
(11b)
(1)
POWER_ OVRD RW Power override. This bit field determines how the bridge responds when the slot power limit is
less than the amount of power required by the bridge and the devices behind the bridge. This
field shall be hardwired to 000b since XIO2213A does not support slot power limit functionality.
000 = Ignore slot power limit (default).
001 = Assert the PWR_OVRD terminal.
010 = Disable secondary clocks selected by the clock mask register.
011 = Disable secondary clocks selected by the clock mask register and assert the
PWR_OVRD terminal.
100 = Respond with unsupported request to all transactions except for configuration
transactions (type 0 or type 1) and set slot power limit messages.
101, 110, 111 = Reserved
(1)
READ_ RW Read prefetch disable. This bit controls the prefetch functionality on PCI memory read
PREFETCH_ DIS transactions.
0 = Prefetch to the next cache line boundary on a burst read (default)
1 = Fetch only a single DWORD on a burst read
Note: When this bit is set, the PREFETCH_4X bit in the TL Control and Diagnostic Register shall
have no effect on the design. This bit shall only affect the XIO2213A when the
EN_CACHE_LINE_CHECK bit in the TL Control and Diagnostic Register is set.
(1)
L0s_LATENCY RW L0s maximum exit latency. This field programs the maximum acceptable latency when exiting the
L0s state. This sets bits 8:6 (EP_L0S_LAT) in the device capabilities register (offset 94h, see
Section 4.50 ).
000 = Less than 64 ns (default)
001 = 64 ns up to less than 128 ns
010 = 128 ns up to less than 256 ns
011 = 256 ns up to less than 512 ns
100 = 512 ns up to less than 1 µ s
101 = 1 µ s up to less than 2 µ s
110 = 2 µ s to 4 µ s
111 = More than 4 µ s
(1)
L1_LATENCY RW L1 maximum exit latency. This field programs the maximum acceptable latency when exiting the
L1 state. This sets bits 11:9 (EP_L1_LAT) in the device capabilities register (offset 94h, see
Section 4.50 ).
000 = Less than 1 µ s (default)
001 = 1 µ s up to less than 2 µ s
010 = 2 µ s up to less than 4 µ s
011 = 4 µ s up to less than 8 µ s
100 = 8 µ s up to less than 16 µ s
101 = 6 µ s up to less than 32 µ s
110 = 32 µ s to 64 µ s
111 = More than 64 µ s
www.ti.com
Classic PCI Configuration Space82 Submit Documentation Feedback
Page 83

XIO2213A PCI Express to 1394b OHCI with 3-Port PHY
www.ti.com
Table 4-40. General Control Register Description (continued)
BIT FIELD NAME ACCESS DESCRIPTION
(1)
12
9:8
7:0
VC_CAP_EN R VC capability structure enable. This bit enables the VC capability structure by changing the next
11 BPCC_E RW Bus power clock control enable. This bit controls whether the secondary bus PCI clocks are
10 BEACON_ RW Beacon enable. This bit controls the mechanism for waking up the physical PCI Express link
ENABLE when in L2.
(1)
MIN_POWER_ RW Minimum power scale. This value is programmed to indicate the scale of bits 7:0
SCALE (MIN_POWER_VALUE).
(1)
MIN_POWER_ RW Minimum power value. This value is programmed to indicate the minimum power requirements.
VALUE This value is multiplied by the minimum power scale field (bits 9:8) to determine the minimum
offset field of the advanced error reporting capability register at offset 102h. This bit is a read only
0b indicating that the VC Capability structure is permanently disabled.
0 = VC capability structure disabled (offset field = 000h)
1 = VC capability structure enabled (offset field = 150h)
stopped when the XIO2213A is placed in the D3 state. It is assumed that if the secondary bus
clocks are required to be active, that a reference clock continues to be provided on the PCI
Express interface.
0 = Secondary bus clocks are not stopped in D3 (default)
1 = Secondary bus clocks are stopped on D3
0 = WAKE mechanism is used exclusively. Beacon is not used (default)
1 = Beacon and WAKE mechanisms are used
00 = 1.0x
01 = 0.1x
10 = 0.01x (default)
11 = 0.001x
power requirements for the bridge. The default is 5Fh, indicating that XIO2213A requires 0.95 W
of power. This field can be reprogrammed through an EEPROM or the system BIOS.
SCPS183A – OCTOBER 2007 – REVISED MARCH 2008
4.67 TI Proprietary Register
This read/write TI proprietary register is located at offset D8h and controls TI proprietary functions. This
register must not be changed from the specified default state. This register shall only be reset by a
Fundamental Reset ( FRST).
PCI register offset: D8h
Register type: Read-only, Read/Write
Default value: 00h
BIT NUMBER 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
RESET STATE 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
4.68 TI Proprietary Register
This read/write TI proprietary register is located at offset D9h and controls TI proprietary functions. This
register must not be changed from the specified default state. This register shall only be reset by a
Fundamental Reset ( FRST).
PCI register offset: D9h
Register type: Read-only, Read/Write
Default value: 00h
BIT NUMBER 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
RESET STATE 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Submit Documentation Feedback Classic PCI Configuration Space 83
Page 84

XIO2213A PCI Express to 1394b OHCI with 3-Port PHY
SCPS183A – OCTOBER 2007 – REVISED MARCH 2008
4.69 TI Proprietary Register
This read-only TI proprietary register is located at offset DAh and controls TI proprietary functions. This
register must not be changed from the specified default state. This register shall only be reset by a
Fundamental Reset ( FRST).
PCI register offset: DAh
Register type: Read-only
Default value: 00h
BIT NUMBER 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
RESET STATE 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
www.ti.com
84 Classic PCI Configuration Space Submit Documentation Feedback
Page 85

www.ti.com
4.70 Arbiter Control Register
The arbiter control register controls the device's internal arbiter. The arbitration scheme used is a
two-tier rotational arbitration. The device is the only secondary bus master that defaults to the higher
priority arbitration tier. See Table 4-41 for a complete description of the register contents.
PCI register offset: DCh
Register type: Read/Write
Default value: 40h
BIT NUMBER 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
RESET STATE 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0
Table 4-41. Arbiter Control Register Description
BIT FIELD NAME ACCESS DESCRIPTION
(1)
7
PARK RW Bus parking mode. This bit determines where the internal arbiter parks the secondary bus.
(1)
6
BRIDGE_TIER_SEL RW Bridge tier select. This bit determines in which tier the bridge is placed in the arbitration
(1)
5:1
(1) This register shall only be reset by a Fundamental Reset ( FRST).
RSVD RW Reserved. These bits are reserved and must not be changed from their default value of
(1)
0
TIER_SEL0 RW GNT0 Tier Select. This bit determines in which tier GNT0 is placed in the arbitration
When this bit is set, the arbiter parks the secondary bus on the bridge. When this bit is
cleared, the arbiter parks the bus on the last device mastering the secondary bus.
0 = Park the secondary bus on the last secondary bus master (default)
1 = Park the secondary bus on the bridge
scheme.
0 = 0Lowest priority tier
1 = Highest priority tier (default)
00000b.
scheme
0 = Lowest priority tier (default)
1 = Highest priority tier
XIO2213A PCI Express to 1394b OHCI with 3-Port PHY
SCPS183A – OCTOBER 2007 – REVISED MARCH 2008
Submit Documentation Feedback Classic PCI Configuration Space 85
Page 86

XIO2213A PCI Express to 1394b OHCI with 3-Port PHY
SCPS183A – OCTOBER 2007 – REVISED MARCH 2008
4.71 Arbiter Request Mask Registert
The arbiter request mask register enables and disables support for requests from specific masters on the
secondary bus. The arbiter request mask register also controls if a request input is automatically masked
on an arbiter time-out. See Table 4-42 for a complete description of the register contents.
PCI register offset: DDh
Register type: Read/Write
Default value: 00h
BIT NUMBER 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
RESET STATE 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Table 4-42. Arbiter Request Mask Register Description
BIT FIELD NAME ACCESS DESCRIPTION
(1)
7
ARB_TIMEOUT RW Arbiter time-out. This bit enables the arbiter time-out feature. The arbiter time-out is
(1)
6
AUTO_MASK RW Automatic request mask. This bit enables automatic request masking when an arbiter
(1)
5:1
(1) This register shall only be reset by a Fundamental Reset ( FRST).
RSVD RW Reserved. These bits are reserved and must not be changed from their default value of
(1)
0
REQ0_MASK RW Request 0 (REQ0) Mask. Setting this bit forces the internal arbiter to ignore requests
defined as the number of PCI clocks after the PCI bus has gone idle for a device to assert
FRAME before the arbiter assumes the device will not respond.
0 = Arbiter time disabled (default)
1 = Arbiter time-out set to 16 PCI clocks
time-out occurs.
0 = Automatic request masking disabled (default)
1 = Automatic request masking enabled
00000b.
signal on request input 0.
0 = Use 1394a OHCI request (default)
1 = Ignore 1394a OHCI request
www.ti.com
4.72 Arbiter Time-Out Status Register
The arbiter time-out status register contains the status of each request (request 5–0) time-out. The
time-out status bit for the respective request is set if the device did not assert FRAME after the arbiter
time-out value. See Table 4-43 for a complete description of the register contents.
PCI register offset: DEh
Register type: Read/Clear
Default value: 00h
BIT NUMBER 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
RESET STATE 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Table 4-43. Arbiter Time-Out Status Register Description
BIT FIELD NAME ACCESS DESCRIPTION
7:6 RSVD R Reserved. Returns 00b when read.
5 REQ5_TO RCU Request 5 Time Out Status
0 = No time-out
1 = Time-out has occurred
4 REQ4_TO RCU Request 4 Time Out Status
0 = No time-out
1 = Time-out has occurred
Classic PCI Configuration Space86 Submit Documentation Feedback
Page 87

www.ti.com
Table 4-43. Arbiter Time-Out Status Register Description (continued)
BIT FIELD NAME ACCESS DESCRIPTION
3 REQ3_TO RCU Request 3 Time Out Status
0 = No time-out
1 = Time-out has occurred
2 REQ2_TO RCU Request 2 Time Out Status
0 = No time-out
1 = Time-out has occurred
1 REQ1_TO RCU Request 1Time Out Status
0 = No time-out
1 = Time-out has occurred
0 REQ0_TO RCU Request 0 Time Out Status
0 = No time-out
1 = Time-out has occurred
4.73 TI Proprietary Register
This read/write TI proprietary register is located at offset E0h and controls TI proprietary functions. This
register must not be changed from the specified default state. This register shall only be reset by a
Fundamental Reset ( FRST).
PCI register offset: E0h
Register type: Read-only, Read/Write
Default value: 00h
BIT NUMBER 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
RESET STATE 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
XIO2213A PCI Express to 1394b OHCI with 3-Port PHY
SCPS183A – OCTOBER 2007 – REVISED MARCH 2008
4.74 TI Proprietary Register
This read/write TI proprietary register is located at offset E2h and controls TI proprietary functions. This
register must not be changed from the specified default state. This register shall only be reset by a
Fundamental Reset ( FRST).
PCI register offset: E2h
Register type: Read/Write
Default value: 0000h
BIT NUMBER 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
RESET STATE 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
4.75 TI Proprietary Register
This read/clear TI proprietary register is located at offset E4h and controls TI proprietary functions. This
register must not be changed from the specified default state.
PCI register offset: E4h
Register type: Read/Clear
Default value: 0000h
BIT NUMBER 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
RESET STATE 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Submit Documentation Feedback Classic PCI Configuration Space 87
Page 88

XIO2213A PCI Express to 1394b OHCI with 3-Port PHY
SCPS183A – OCTOBER 2007 – REVISED MARCH 2008
www.ti.com
Classic PCI Configuration Space88 Submit Documentation Feedback
Page 89

www.ti.com
5 PCI Express Extended Configuration Space
The programming model of the PCI Express extended configuration space is compliant to the PCI Express
Base Specification and the PCI Express to PCI/PCI-X Bridge Specification programming models. The PCI
Express extended configuration map uses the PCI Express advanced error reporting capability and PCI
Express virtual channel (VC) capability headers.
All bits marked with a I are sticky bits and are reset by a global reset ( GRST) or the internally-generated
power-on reset. All bits marked with a I are reset by a PCI Express reset ( PERST), a GRST, or the
internally-generated power-on reset. The remaining register bits are reset by a PCI Express hot reset,
PERST, GRST, or the internally-generated power-on reset.
Table 5-1. PCI Express Extended Configuration Register Map
REGISTER NAME OFFSET
Next capability offset / capability version PCI Express advanced error reporting capabilities ID 100h
Uncorrectable error status register
Uncorrectable error mask register
Uncorrectable error severity register
Correctable error status register
Correctable error mask
Advanced error capabilities and control
Header log register
Header log register
Header log register
Header log register
Secondary uncorrectable error status
Secondary uncorrectable error mask
Secondary uncorrectable error severity register
Secondary error capabilities and control register
Secondary header log register
Secondary header log register
Secondary header log register
Secondary header log register
Reserved 14Ch – FFCh
(1) This register shall only be reset by a Fundamental Reset ( FRST).
XIO2213A PCI Express to 1394b OHCI with 3-Port PHY
SCPS183A – OCTOBER 2007 – REVISED MARCH 2008
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
104h
108h
10Ch
110h
114h
118h
11Ch
120h
124h
128h
12Ch
130h
134h
138h
13Ch
140h
144h
148h
5.1 Advanced Error Reporting Capability ID Register
This read-only register identifies the linked list item as the register for PCI Express advanced error
reporting capabilities. The register returns 0001h when read.
PCI Express extended register offset: 100h
Register type: Read-only
Default value: 0001h
BIT NUMBER 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
RESET STATE 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1
5.2 Next Capability Offset/Capability Version Register
This read-only register identifies the next location in the PCI Express extended capabilities link list. The
upper 12 bits in this register shall be 000h, indicating that the Advanced Error Reporting Capability is the
last capability in the linked list. The least significant four bits identify the revision of the current capability
block as 1h.
Submit Documentation Feedback PCI Express Extended Configuration Space 89
Page 90

XIO2213A PCI Express to 1394b OHCI with 3-Port PHY
SCPS183A – OCTOBER 2007 – REVISED MARCH 2008
PCI Express extended register offset: 102h
Register type: Read-only
Default value: 0001h
BIT NUMBER 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
RESET STATE 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1
www.ti.com
90 PCI Express Extended Configuration Space Submit Documentation Feedback
Page 91

XIO2213A PCI Express to 1394b OHCI with 3-Port PHY
www.ti.com
5.3 Uncorrectable Error Status Register
The uncorrectable error status register reports the status of individual errors as they occur on the primary
PCI Express interface. Software may only clear these bits by writing a 1b to the desired location. See
Table 5-2 for a complete description of the register contents.
PCI Express extended register offset: 104h
Register type: Read-only, Read/Clear
Default value: 0000h
BIT NUMBER 31 30 29 28 27 26 25 24 23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16
RESET STATE 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
BIT NUMBER 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
RESET STATE 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Table 5-2. Uncorrectable Error Status Register Description
BIT FIELD NAME ACCESS DESCRIPTION
31:21 RSVD R Reserved. Returns 000 0000 0000b when read.
(1)
20
19
18
17
16
15
14
13
12
11:5 RSVD R Reserved. Returns 000 0000b when read.
(1) This register shall only be reset by a Fundamental Reset ( FRST).
UR_ERROR RCU Unsupported request error. This bit is asserted when an unsupported request is received.
(1)
ECRC_ERROR RCU Extended CRC error. This bit is asserted when an extended CRC error is detected.
(1)
MAL_TLP RCU Malformed TLP. This bit is asserted when a malformed TLP is detected.
(1)
RX_OVERFLOW RCU Receiver overflow. This bit is asserted when the flow control logic detects that the
(1)
UNXP_CPL RCU Unexpected completion. This bit is asserted when a completion packet is received that
(1)
CPL_ABORT RCU Completer abort. This bit is asserted when the bridge signals a completer abort.
(1)
CPL_TIMEOUT RCU Completion time-out. This bit is asserted when no completion has been received for an
(1)
FC_ERROR RCU Flow control error. This bit is asserted when a flow control protocol error is detected either
(1)
PSN_TLP RCU Poisoned TLP. This bit is asserted when a poisoned TLP is received.
(1)
4
DLL_ERROR RCU Data link protocol error. This bit is asserted if a data link layer protocol error is detected.
3:0 RSVD R Reserved. Returns 0h when read.
transmitting device has illegally exceeded the number of credits that were issued.
does not correspond to an issued request.
issued request before the time-out period.
during initialization or during normal operation.
SCPS183A – OCTOBER 2007 – REVISED MARCH 2008
5.4 Uncorrectable Error Mask Register
The uncorrectable error mask register controls the reporting of individual errors as they occur. When a
mask bit is set to 1b, the corresponding error status bit is not set, PCI Express error messages are
blocked, the header log is not loaded, and the first error pointer is not updated. See Table 5-3 for a
complete description of the register contents.
PCI Express extended register offset: 108h
Register type: Read-only, Read/Write
Default value: 0000h
BIT NUMBER 31 30 29 28 27 26 25 24 23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16
RESET STATE 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
BIT NUMBER 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
RESET STATE 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Submit Documentation Feedback PCI Express Extended Configuration Space 91
Page 92

XIO2213A PCI Express to 1394b OHCI with 3-Port PHY
SCPS183A – OCTOBER 2007 – REVISED MARCH 2008
Table 5-3. Uncorrectable Error Mask Register Description
BIT FIELD NAME ACCESS DESCRIPTION
31:21 RSVD R Reserved. Returns 000 0000 0000b when read.
(1)
20
19
18
17
16
15
14
13
12
11:5 RSVD R Reserved. Returns 000 0000b when read.
(1) This register shall only be reset by a Fundamental Reset ( FRST).
UR_ERROR_MASK RW Unsupported request error mask
0 = Error condition is unmasked (default)
1 = Error condition is masked
(1)
ECRC_ERROR_MASK RW Extended CRC error mask
0 = Error condition is unmasked (default)
1 = Error condition is masked
(1)
MAL_TLP_MASK RW Malformed TLP mask
0 = Error condition is unmasked (default)
1 = Error condition is masked
(1)
RX_OVERFLOW_MASK RW Receiver overflow mask
0 = Error condition is unmasked (default)
1 = Error condition is masked
(1)
UNXP_CPL_MASK RW Unexpected completion mask
0 = Error condition is unmasked (default)
1 = Error condition is masked
(1)
CPL_ABORT_MASK RW Completer abort mask
0 = Error condition is unmasked (default)
1 = Error condition is masked
(1)
CPL_TIMEOUT_MASK RW Completion time-out mask
0 = Error condition is unmasked (default)
1 = Error condition is masked
(1)
FC_ERROR_MASK RW Flow control error mask
0 = Error condition is unmasked (default)
1 = Error condition is masked
(1)
PSN_TLP_MASK RW Poisoned TLP mask
0 = Error condition is unmasked (default)
1 = Error condition is masked
(1)
4
DLL_ERROR_MASK RW Data link protocol error mask
0 = Error condition is unmasked (default)
1 = Error condition is masked
3:0 RSVD R Reserved. Returns 0h when read.
www.ti.com
PCI Express Extended Configuration Space92 Submit Documentation Feedback
Page 93

XIO2213A PCI Express to 1394b OHCI with 3-Port PHY
www.ti.com
5.5 Uncorrectable Error Severity Register
The uncorrectable error severity register controls the reporting of individual errors as ERR_FATAL or
ERR_NONFATAL. When a bit is set, the corresponding error condition is identified as fatal. When a bit is
cleared, the corresponding error condition is identified as nonfatal. See Table 5-4 for a complete
description of the register contents.
PCI Express extended register offset: 10Ch
Register type: Read-only, Read/Write
Default value: 0006 2011h
BIT NUMBER 31 30 29 28 27 26 25 24 23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16
RESET STATE 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 0
BIT NUMBER 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
RESET STATE 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 0 0 0 1
Table 5-4. Uncorrectable Error Severity Register Description
BIT FIELD NAME ACCESS DESCRIPTION
31:21 RSVD R Reserved. Returns 000 0000 0000b when read.
(1)
20
UR_ERROR_SEVRO RW Unsupported request error severity
0 = Error condition is signaled using ERR_NONFATAL
1 = Error condition is signaled using ERR_FATAL
(1)
19
ECRC_ERROR_SEVRR RW Extended CRC error severity
0 = Error condition is signaled using ERR_NONFATAL
1 = Error condition is signaled using ERR_FATAL
(1)
18
MAL_TLP_SEVR RW Malformed TLP severity
0 = Error condition is signaled using ERR_NONFATAL
1 = Error condition is signaled using ERR_FATAL
(1)
17
RX_OVERFLOW_SEVR RW Receiver overflow severity
0 = Error condition is signaled using ERR_NONFATAL
1 = Error condition is signaled using ERR_FATAL
(1)
16
UNXP_CPL_SEVRP RW Unexpected completion severity
0 = Error condition is signaled using ERR_NONFATAL
1 = Error condition is signaled using ERR_FATAL
(1)
15
CPL_ABORT_SEVR RW Completer abort severity
0 = Error condition is signaled using ERR_NONFATAL
1 = Error condition is signaled using ERR_FATAL
(1)
14
CPL_TIMEOUT_SEVR RW Completion time-out severit
0 = Error condition is signaled using ERR_NONFATAL
1 = Error condition is signaled using ERR_FATAL
(1)
13
FC_ERROR_SEVR RW Flow control error severity
0 = Error condition is signaled using ERR_NONFATAL
1 = Error condition is signaled using ERR_FATAL
(1)
12
PSN_TLP_SEVR RW Poisoned TLP severity
0 = Error condition is signaled using ERR_NONFATAL
1 = Error condition is signaled using ERR_FATAL
11:6 RSVD R Reserved. Returns 000 000b when read.
5 RSVD R Reserved. Returns 1h when read
(1)
4
DLL_ERROR_SEVR RW Data link protocol error severity
0 = Error condition is signaled using ERR_NONFATAL
1 = Error condition is signaled using ERR_FATAL
3:1 RSVD R Reserved. Retirms 000b wjem read/
0 RSVD R Reserved. Returns 1h when read.
(1) This register shall only be reset by a Fundamental Reset ( FRST).
SCPS183A – OCTOBER 2007 – REVISED MARCH 2008
Submit Documentation Feedback PCI Express Extended Configuration Space 93
Page 94

XIO2213A PCI Express to 1394b OHCI with 3-Port PHY
SCPS183A – OCTOBER 2007 – REVISED MARCH 2008
5.6 Correctable Error Status Register
The correctable error status register reports the status of individual errors as they occur. Software may
only clear these bits by writing a 1b to the desired location. See Table 5-5 for a complete description of
the register contents.t
PCI Express extended register offset: 110h
Register type: Read-only, Read/Clear
Default value: 0000 0000h
BIT NUMBER 31 30 29 28 27 26 25 24 23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16
RESET STATE 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
BIT NUMBER 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
RESET STATE 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Table 5-5. Correctable Error Status Register Description
BIT FIELD NAME ACCESS DESCRIPTION
31:14 RSVD R Reserved. Returns 000 0000 0000 0000 0000b when read.
13 ANFES RCU Advisory Non-Fatal Error Status. This bit is asserted when an Advisor Non-Fatal Error has
(1)
12
(1) This register shall only be reset by a Fundamental Reset ( FRST).
REPLAY_TMOUT RCU Replay timer time-out. This bit is asserted when the replay timer expires for a pending request
11:9 RSVD R Reserved. Returns 000b when read.
(1)
8
REPLAY_ROLL RCU REPLAY_NUM rollover. This bit is asserted when the replay counter rolls over after a pending
(1)
7
BAD_DLLP RCU Bad DLLP error. This bit is asserted when an 8b/10b error was detected by the PHY during
(1)
6
BAD_TLP RCU Bad TLP error. This bit is asserted when an 8b/10b error was detected by the PHY during the
5:1 RSVD R Reserved. Returns 00000b when read.
(1)
0
RX_ERROR RCU Receiver error. This bit is asserted when an 8b/10b error is detected by the PHY at any time.
been reported.
or completion that has not been acknowledged.
request or completion has not been acknowledged.
the reception of a DLLP.
reception of a TLP.
www.ti.com
PCI Express Extended Configuration Space94 Submit Documentation Feedback
Page 95

XIO2213A PCI Express to 1394b OHCI with 3-Port PHY
www.ti.com
5.7 Correctable Error Mask Register
The correctable error mask register controls the reporting of individual errors as they occur. When a mask
bit is set to 1b, the corresponding error status bit is not set, PCI Express error messages are blocked, the
header log is not loaded, and the first error pointer is not updated. See Table 5-6 for a complete
description of the register contents.
PCI Express extended register offset: 114h
Register type: Read-only, Read/Write
Default value: 0000 2000h
BIT NUMBER 31 30 29 28 27 26 25 24 23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16
RESET STATE 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
BIT NUMBER 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
RESET STATE 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Table 5-6. Correctable Error Mask Register Description
BIT FIELD NAME ACCESS DESCRIPTION
31:14 RSVD R Reserved. Returns 000 0000 0000 0000 0000b when read.
13 ANFEM RW Advisory Non-Fatal Error Mask.
0 = Error condition is unmasked
1 = Error condition is masked (default)
(1)
12
REPLAY_TMOUT_MAS RW Replay timer time-out mask.
K
11:9 RSVD R Reserved. Returns 000b when read.
(1)
8 †
REPLAY_ROLL_MASK RW REPLAY_NUM rollover mask.
(1)
7
BAD_DLLP_MASK RW Bad DLLP error mask.
(1)
6
BAD_TLP_MASK RW Bad TLP error mask.
5:1 RSVD R Reserved. Returns 00000b when read.
(1)
0
RX_ERROR_MASK RW Receiver error mask.
(1) This register shall only be reset by a Fundamental Reset ( FRST).
0 = Error condition is unmasked (default)
1 = Error condition is masked
0 = Error condition is unmasked (default)
1 = Error condition is masked
0 = Error condition is unmasked (default)
1 = Error condition is masked
0 = Error condition is unmasked (default)
1 = Error condition is masked
0 = Error condition is unmasked (default)
1 = Error condition is masked
SCPS183A – OCTOBER 2007 – REVISED MARCH 2008
Submit Documentation Feedback PCI Express Extended Configuration Space 95
Page 96

XIO2213A PCI Express to 1394b OHCI with 3-Port PHY
SCPS183A – OCTOBER 2007 – REVISED MARCH 2008
5.8 Advanced Error Capabilities and Control Register
The advanced error capabilities and control register allows the system to monitor and control the
advanced error reporting capabilities. See Table 5-7 for a complete description of the register contents.
PCI Express extended register 118h
offset:
Register type: Read-only, Read/Write
Default value: 0000 00A0h
BIT NUMBER 31 30 29 28 27 26 25 24 23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16
RESET STATE 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
BIT NUMBER 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
RESET STATE 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 0 0 0 0
Table 5-7. Advanced Error Capabilities and Control Register Description
BIT FIELD NAME ACCESS DESCRIPTION
31:9 RSVD R Reserved. Returns 000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000b when read.
(1)
8
ECRC_CHK_EN RW Extended CRC check enable
0 = Extended CRC checking is disabled
1 = Extended CRC checking is enabled
7 ECRC_CHK_CAPABLE R Extended CRC check capable. This read-only bit returns a value of 1b indicating that the
(1)
6
ECRC_GEN_EN RW Extended CRC generation enable
5 ECRC_GEN_CAPABLE R Extended CRC generation capable. This read-only bit returns a value of 1b indicating
(1)
4:0
(1) This register shall only be reset by a Fundamental Reset ( FRST).
FIRST_ERR RU First error pointer. This 5-bit value reflects the bit position within the uncorrectable error
bridge is capable of checking extended CRC information.
0 = Extended CRC generation is disabled
1 = Extended CRC generation is enabled
that the bridge is capable of generating extended CRC information.
status register (offset 104h, see Section 5.3 ) corresponding to the class of the first error
condition that was detected.
www.ti.com
5.9 Header Log Register
The header log register stores the TLP header for the packet that lead to the most recently detected error
condition. Offset 11Ch contains the first DWORD. Offset 128h contains the last DWORD (in the case of a
4DW TLP header). Each DWORD is stored with the least significant byte representing the earliest
transmitted. This register shall only be reset by a Fundamental Reset ( FRST).
PCI Express extended register offset: 11Ch, 120h, 124h, and 128h
Register type: Read-only
Default value: 0000 0000h
BIT NUMBER 31 30 29 28 27 26 25 24 23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16
RESET STATE 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
BIT NUMBER 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
RESET STATE 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
PCI Express Extended Configuration Space96 Submit Documentation Feedback
Page 97

XIO2213A PCI Express to 1394b OHCI with 3-Port PHY
www.ti.com
5.10 Secondary Uncorrectable Error Status Register
The secondary uncorrectable error status register reports the status of individual PCI bus errors as they
occur. Software may only clear these bits by writing a 1b to the desired location. See Table 5-8 for a
complete description of the register contents.
PCI Express extended register offset: 12Ch
Register type: Read-only, Read/Clear
Default value: 0000 0000h
BIT NUMBER 31 30 29 28 27 26 25 24 23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16
RESET STATE 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
BIT NUMBER 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
RESET STATE 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Table 5-8. Secondary Uncorrectable Error Status Register Description
BIT FIELD NAME ACCESS DESCRIPTION
31:13 RSVD R Reserved. Returns 000 0000 0000 0000 0000b when read.
(1)
12
11
10
(1) This register shall only be reset by a Fundamental Reset ( FRST).
SERR_DETECT RCU SERR assertion detected. This bit is asserted when the bridge detects the assertion of
(1)
PERR_DETECT RCU PERR assertion detected. This bit is asserted when the bridge detects the assertion of
(1)
DISCARD_TIMER RCU Delayed transaction discard timer expired. This bit is asserted when the discard timer
(1)
9
UNCOR_ADDR RCU Uncorrectable address error. This bit is asserted when the bridge detects a parity error
8 RSVD R Reserved. Returns 0b when read.
(1)
7
UNCOR_DATA RCU Uncorrectable data error. This bit is asserted when the bridge detects a parity error during
6:4 RSVD R Reserved. Returns 000b when read.
(1)
3
MASTER_ABORT RCU Received master abort. This bit is asserted when the bridge receives a master abort on
(1)
2
TARGET_ABORT RCU Received target abort. This bit is asserted when the bridge receives a target abort on the
1:0 RSVD R Reserved. Returns 00b when read.
SERR on the secondary bus.
PERR on the secondary bus.
expires for a pending delayed transaction that was initiated on the secondary bus.
during the address phase of an upstream transaction.
a data phase of an upstream write transaction, or when the bridge detects the assertion of
PERR when forwarding read completion data to a PCI device.
the PCI interface.
PCI interface.
SCPS183A – OCTOBER 2007 – REVISED MARCH 2008
Submit Documentation Feedback PCI Express Extended Configuration Space 97
Page 98

XIO2213A PCI Express to 1394b OHCI with 3-Port PHY
SCPS183A – OCTOBER 2007 – REVISED MARCH 2008
5.11 Secondary Uncorrectable Error Mask Register
The secondary uncorrectable error mask register controls the reporting of individual errors as they occur.
When a mask bit is set to 1b, the corresponding error status bit is not set, PCI Express error messages
are blocked, the header log is not loaded, and the first error pointer is not updated. See Table 5-9 for a
complete description of the register contents.
PCI Express extended register offset: 130h
Register type: Read-only, Read/Write
Default value: 0000 17A8h
BIT NUMBER 31 30 29 28 27 26 25 24 23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16
RESET STATE 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
BIT NUMBER 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
RESET STATE 0 0 0 1 0 1 1 1 1 0 1 0 1 0 0 0
Table 5-9. Secondary Uncorrectable Error Mask Register Description
BIT FIELD NAME ACCESS DESCRIPTION
31:14 RSVD R Reserved. Returns 00 0000 0000 0000 0000b when read.
(1)
13
BRIDGE_ERROR_MASK RW Internal bridge error. This mask bit is associated with a PCI-X error and has no effect
(1)
12
SERR_DETECT_MASK RW SERR assertion detected
(1)
11
PERR_DETECT_MASK RW PERR assertion detectedi
(1)
10
DISCARD_TIMER_MASK RW Delayed transaction discard timer expired
(1)
9
UNCOR_ADDR_MASK RW Uncorrectable address error
(1)
8
ATTR_ERROR_MASK RW Uncorrectable attribute error. This mask bit is associated with a PCI-X error and has
(1)
7
UNCOR_DATA_MASK RW Uncorrectable data error
(1)
6
SC_MSG_DATA_MASK RW Uncorrectable split completion message data error. This mask bit is associated with a
(1)
5
SC_ERROR_MASK RW Unexpected split completion error. This mask bit is associated with a PCI-X error and
4 RSVD R Reserved. Returns 0b when read.
(1)
3
MASTER_ABORT_MASK RW Received master abort
(1)
2
TARGET_ABORT_MASK RW Received target abort
(1)
1
SC_MSTR_ABORT_MASK RW Master abort on split completion. This mask bit is associated with a PCI-X error and
0 RSVD R Reserved. Returns 0b when read.
(1) This register shall only be reset by a Fundamental Reset ( FRST).
on the bridge.
0 = Error condition is unmasked
1 = Error condition is masked (default)
0 = Error condition is unmasked
1 = Error condition is masked (default)
0 = Error condition is unmasked
1 = Error condition is masked (default)
0 = Error condition is unmasked
1 = Error condition is masked (default)
no effect on the bridge.
0 = Error condition is unmasked
1 = Error condition is masked (default)
PCI-X error and has no effect on the bridge.
has no effect on the bridge.
0 = Error condition is unmasked
1 = Error condition is masked (default)
0 = Error condition is unmasked
1 = Error condition is masked (default)
has no effect on the bridge.
www.ti.com
PCI Express Extended Configuration Space98 Submit Documentation Feedback
Page 99

XIO2213A PCI Express to 1394b OHCI with 3-Port PHY
www.ti.com
5.12 Secondary Uncorrectable Error Severity
The uncorrectable error severity register controls the reporting of individual errors as ERR_FATAL or
ERR_NONFATAL. When a bit is set, the corresponding error condition is identified as fatal. When a bit is
cleared, the corresponding error condition is identified as nonfatal. See Table 5-10 for a complete
description of the register contents.
PCI Express extended register offset: 134h
Register type: Read-only, Read/Write
Default value: 0000 1340h
BIT NUMBER 31 30 29 28 27 26 25 24 23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16
RESET STATE 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
BIT NUMBER 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
RESET STATE 0 0 0 1 0 0 1 1 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0
Table 5-10. Secondary Uncorrectable Error Severity Register Description
BIT FIELD NAME ACCESS DESCRIPTION
31:14 RSVD R Reserved. Returns 00 0000 0000 0000 0000b when read.
(1)
13
BRIDGE_ERROR_SEVR RW Internal bridge error. This severity bit is associated with a PCI-X error and has no effect
(1)
12
SERR_DETECT_SEVR RW SERR assertion detected
(1)
11
PERR_DETECT_SEVR RW PERR assertion detected
(1)
10
DISCARD_TIMER_SEVR RW Delayed transaction discard timer expired
(1)
9
UNCOR_ADDR_SEVR RW Uncorrectable address error
(1)
8
ATTR_ERROR_SEVR RW Uncorrectable attribute error. This severity bit is associated with a PCI-X error and has
(1)
7
UNCOR_DATA_SEVR RW Uncorrectable data error
(1)
6
SC_MSG_DATA_SEVR RW Uncorrectable split completion message data error. This severity bit is associated with
(1)
5
SC_ERROR_SEVR RW Unexpected split completion error. This severity bit is associated with a PCI-X error and
4 RSVD R Reserved. Returns 0b when read.
(1)
3
MASTER_ABORT_SEVR RW Received master abort
(1)
2
TARGET_ABORT_SEVR RW Received target aborta
(1)
1
SC_MSTR_ABORT_SEVR RW Master abort on split completion. This severity bit is associated with a PCI-X error and
0 RSVD R Reserved. Returns 0b when read.
(1) This register shall only be reset by a Fundamental Reset ( FRST).
on the bridge.
0 = Error condition is signaled using ERR_NONFATAL
1 = Error condition is signaled using ERR_FATAL (default)
0 = Error condition is signaled using ERR_NONFATAL (default)
1 = Error condition is signaled using ERR_FATAL
0 = Error condition is signaled using ERR_NONFATAL (default)
1 = Error condition is signaled using ERR_FATAL
0 = Error condition is signaled using ERR_NONFATAL
1 = Error condition is signaled using ERR_FATAL (default)
no effect on the bridge.
0 = Error condition is signaled using ERR_NONFATAL (default)
1 = Error condition is signaled using ERR_FATAL
a PCI-X error and has no effect on the bridge.
has no effect on the bridge.
0 = Error condition is signaled using ERR_NONFATAL (default)
1 = Error condition is signaled using ERR_FATAL
0 = Error condition is signaled using ERR_NONFATAL (default)
1 = Error condition is signaled using ERR_FATAL
has no effect on the bridge.
SCPS183A – OCTOBER 2007 – REVISED MARCH 2008
Submit Documentation Feedback PCI Express Extended Configuration Space 99
Page 100

XIO2213A PCI Express to 1394b OHCI with 3-Port PHY
SCPS183A – OCTOBER 2007 – REVISED MARCH 2008
5.13 Secondary Error Capabilities and Control Register
The secondary error capabilities and control register allows the system to monitor and control the
secondary advanced error reporting capabilities. See Table 5-11 for a complete description of the register
contents.
PCI Express extended register offset: 138h
Register type: Read-only
Default value: 0000 0000h
BIT NUMBER 31 30 29 28 27 26 25 24 23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16
RESET STATE 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
BIT NUMBER 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
RESET STATE 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Table 5-11. Secondary Error Capabilities and Control Register Description
BIT FIELD NAME ACCESS DESCRIPTION
31:5 RSVD R Reserved. Return 000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000b when read.
(1)
4:0
(1) This register shall only be reset by a Fundamental Reset ( FRST).
SEC_FIRST_ERR RU First error pointer. This 5-bit value reflects the bit position within the secondary
uncorrectable error status register (offset12Ch, see Section 5.10 ) corresponding to the
class of the first error condition that was detected.
www.ti.com
PCI Express Extended Configuration Space100 Submit Documentation Feedback
 Loading...
Loading...